Topic
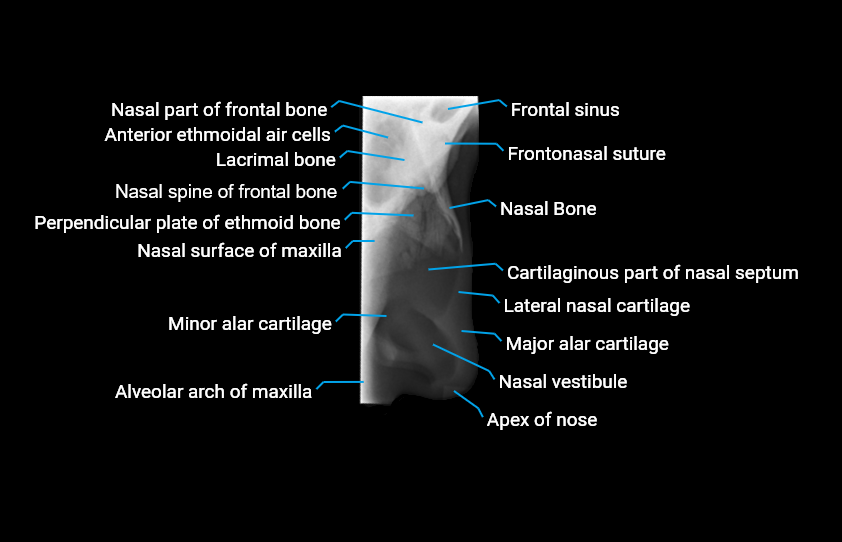
The alveolar arch of the maxilla is the curved, horseshoe-shaped bony structure forming the inferior portion of the maxilla. It contains the alveoli (tooth sockets) for the maxillary teeth and plays a central role in dental anatomy, occlusion, facial contour, and maxillofacial imaging.
The alveolar arch is dynamic, undergoing structural changes with tooth eruption, loss, and age, and is a key region assessed in dentistry, orthodontics, implant planning, trauma evaluation, and head and neck imaging.
Synonyms
-
Maxillary alveolar arch
-
Alveolar process of maxilla
-
Maxillary dental arch
Location
-
Forms the inferior margin of the maxilla
-
Extends bilaterally from the maxillary tuberosity on each side
-
Curves anteriorly to form the upper dental arch
-
Located inferior to the maxillary sinus
-
Superior to the oral cavity
-
Anterior to the hard palate
Anatomical components
-
Alveolar process:
-
Vertical bony ridge of the maxilla
-
-
Dental alveoli:
-
Sockets for incisors, canines, premolars, and molars
-
-
Interalveolar septa:
-
Bone between adjacent tooth sockets
-
-
Interradicular septa:
-
Bone between roots of multirooted teeth
-
-
Alveolar crest:
-
Superior margin of the alveolar bone between teeth
-
Relations
Superiorly:
-
Maxillary sinus floor
-
Body of the maxilla
Inferiorly:
-
Oral cavity
-
Gingiva and maxillary teeth
Anteriorly:
-
Anterior nasal spine (near midline)
-
Upper lip soft tissues
Posteriorly:
-
Maxillary tuberosity
-
Pterygopalatine region (posterior relation)
Medially:
-
Hard palate
-
Nasal cavity (via palatal process)
Laterally:
-
Buccal cortex of the maxilla
-
Buccal soft tissues
Developmental anatomy
-
Develops in association with tooth eruption
-
Alveolar height increases during mixed and permanent dentition
-
Tooth loss leads to alveolar resorption, most pronounced in the vertical dimension
-
Degree of pneumatization of maxillary sinus influences alveolar bone thickness
X-ray appearance
Dental and skull radiographs (periapical / panoramic / occlusal views):
-
Alveolar arch: Curved radiopaque bony ridge
-
Dental sockets: Radiolucent spaces surrounded by radiopaque lamina dura
-
Alveolar crest: Thin radiopaque line between teeth
-
Relationship to teeth: Clearly delineated tooth roots within alveoli
CT appearance
Non-contrast CT:
-
Cortical bone: Hyperdense buccal and palatal cortices
-
Cancellous bone: Lower-density trabecular pattern
-
Dental alveoli: Well-defined socket contours
-
Maxillary sinus floor: Closely related to posterior alveolar arch
Post-contrast CT:
-
Alveolar bone: No intrinsic enhancement
MRI appearance
T1-weighted images:
-
Cortical bone: Low signal intensity
-
Cancellous marrow: Intermediate to high signal depending on fatty content
-
Teeth: Signal void structures
-
Adjacent soft tissues: Normal gingiva and oral mucosa signal
T2-weighted images:
-
Cortical bone and teeth: Low signal
-
Marrow: Intermediate signal
CT VRT 3D image

X-Ray image