Topic
- Abdominal part of esophagus
- Accessory hepatic vein
- Accessory pancreatic duct
- Accessory process of vertebrae
- Acetabular margin (Acetabular rim)
- Acetabulum
- Adrenal gland
- Ala of ilium (wing of ilium)
- Ala of sacrum
- Annular epiphysis
- Anterior branch of right hepatic duct
- Anterior cecal artery
- Anterior inferior iliac spine
- Anterior sacral foramina
- Anterior superior iliac spine
- Appendicular artery
- Ascending colon
- Ascending mesocolon
- Axilla
- Axillary artery
- Bile duct serving liver segment I
- Bile duct serving liver segment II
- Bile duct serving liver segment III
- Bile duct serving liver segment IVa
- Bile duct serving liver segment IVb
- Bile duct serving liver segment V
- Bile duct serving liver segment VI
- Bile duct serving liver segment VII
- Bile duct serving liver segment VIII
- Body of gallbladder
- Body of ilium
- Body of ischium
- Body of pancreas
- Body of pubis
- Body of vertebra
- Cardia of stomach
- Caudate lobe of liver
- Cecum
- Co (Coccyx)
- Coccyx
- Common hepatic duct
- Costal part of diaphragm
- Costochondral joints
- Costotransverse joint
- Costotransverse joint of twelfth rib
- Costovertebral joint
- Costovertebral joint of twelfth rib
- Costoxiphoid ligaments
- Crura of diaphragm
- Crural part of diaphragm
- Cystic artery
- Cystic duct
- Descending colon
- Descending mesocolon
- Diaphragm
- Distal left anterior descending artery (dLAD)
- Duodenal bulb
- Duodenum – Ascending part (D4)
- Duodenum – Descending part (D2)
- Duodenum – Horizontal part (D3)
- Duodenum – Superior part (D1)
- External oblique muscle
- Fovea for ligament of head of femur
- Fundus of gallbladder
- Gastric bubble
- Gluteus maximus muscle
- Gluteus medius muscle
- Gluteus minimus muscle
- Great pancreatic vein
- Greater trochanter
- Head of femur
- Head of pancreas
- Head of twelfth rib
- Heart
- Hepatic portal vein
- Hepatopancreatic ampulla (ampulla of Vater)
- Hip joint
- Ileal arteries
- Ileocaecal valve (ileocecal junction)
- Ileocolic artery
- Ileocolic artery colic branches
- Ileocolic artery ileal branches
- Ileum
- Iliac bone
- Iliac crest
- Iliac fossa
- Iliac tubercle
- Iliac tuberosity
- Inferior articular process of vertebra
- Inferior phrenic artery
- Inferior phrenic vein
- Inferior pubic ramus
- Inferior vena cava
- Interlobar arteries of kidney
- Intermediate hepatic vein
- Internal oblique muscle
- Internal thoracic veins
- Intertrochanteric crest
- Intervertebral disc space
- Intervertebral foramen
- Ischial spine
- Ischial tuberosity
- Jejunum
- L (Lumbar spine)
- L1–L2 Intervertebral Disc
- L2–L3 Intervertebral Disc
- L3–L4 Intervertebral Disc
- L4–L5 Intervertebral Disc
- L5–S1 Intervertebral disc
- Lamina of vertebra
- Lateral branch of left hepatic duct
- Left atrium
- Left auricle
- Left branch of hepatic portal vein
- Left colic flexure (splenic flexure)
- Left common carotid artery
- Left crus of diaphragm
- Left gastro-omental (gastroepiploic) vein
- Left hemidiaphragm
- Left hepatic duct
- Left hepatic vein
- Left internal thoracic artery
- Left internal thoracic veins
- Left kidney
- Left lumbar part of diaphragm
- Left paracolic gutter
- Left renal artery
- Left renal vein
- Left ureter
- Left ventricle
- Lesser curvature lymph nodes
- Linea alba
- Liver
- Liver Segment I – Caudate lobe
- Liver Segment II – Left lateral superior segment
- Liver Segment III – Left lateral inferior segment
- Liver Segment IVa – Left medial superior segment
- Liver Segment IVb – Left medial inferior segment
- Liver Segment V – Right anteroinferior segment
- Liver Segment VI – Right posteroinferior segment
- Liver Segment VII – Right posterosuperior segment
- Liver Segment VIII – Right anterosuperior segment
- Lumbar triangle
- Lumbosacral joint
- Mammillary process of vertebra
- Marginal artery of Drummond
- Median sacral crest
- Middle colic artery
- Neck of femur
- Neck of gallbladder
- Neck of pancreas
- Obturator foramen
- Omental branches of gastro-omental (gastroepiploic) artery
- Pancreatic duct
- Paraesophageal lymph nodes
- Parietal peritoneum
- Pedicle of vertebra
- Penis
- Pericardium
- Pleura
- Portal vein branch to liver segment I
- Portal vein branch to liver segment II
- Portal vein branch to liver segment III
- Portal vein branch to liver segment IV
- Portal vein branch to liver segment V
- Portal vein branch to liver segment VI
- Portal vein branch to liver segment VII
- Portal vein branch to liver segment VIII
- Posterior branch of right hepatic duct
- Posterior inferior iliac spine
- Posterior sacral foramina
- Posterior superior iliac spine
- Prepericardial lymph nodes
- Preperitoneal space
- Psoas major muscle
- Pubic symphysis
- Pubic tubercle
- Pulmonary trunk
- Quadrate lobe of liver
- Ramus of ischium
- Rectum
- Rectus abdominis muscle
- Renal capsule
- Renal fascia
- Renal medulla
- Renal pyramids
- Ribs
- Right atrium
- Right branch of hepatic portal vein
- Right colic artery
- Right colic flexure (hepatic flexure)
- Right crus of diaphragm
- Right gastric artery
- Right gastric vein CT axial image
- Right hemidiaphragm
- Right hepatic duct
- Right hepatic vein
- Right internal thoracic artery
- Right internal thoracic veins
- Right kidney
- Right lumbar part of diaphragm
- Right ovarian vein
- Right paracolic gutter
- Right posterior descending coronary artery (Right PDA)
- Right renal artery
- Right renal vein
- Right ureter
- Right ventricle
- S (Sacral spine)
- Sacral canal
- Sacrococcygeal joint
- Sacroiliac joint
- Sacrum
- Short gastric arteries
- Short gastric veins
- Sigmoid colon
- Sigmoid veins
- Small intestine
- Spinous process of vertebra
- Spleen
- Splenic branches of splenic artery
- Splenic vein
- Sternal end of the clavicle
- Sternocostal joint
- Sternocostal synchondrosis of first rib
- Stomach
- Superior articular process of sacrum
- Superior articular process of vertebra
- Superior diaphragmatic lymph nodes
- Superior epigastric artery
- Superior mesenteric artery (SMA)
- Superior mesenteric lymph nodes
- Superior mesenteric vein (SMV)
- Superior phrenic artery
- Superior pubic ramus
- Superior rectal artery
- Superior rectal vein
- T (Thoracic spine)
- T12–L1 Intervertebral Disc
- Tail of pancreas
- Terminal ileum
- Thoracic aorta
- Thoracolumbar fascia (anterior layer)
- Thoracolumbar fascia (middle layer)
- Thoracolumbar fascia (posterior layer)
- Transverse abdominal muscle
- Transverse colon
- Transverse mesocolon
- Transverse process of vertebra
- Transverse processes
- Transversus abdominis muscle
- Transversus thoracis muscle
- Trochanteric fossa
- Uncinate process of pancreas
- Ureteropelvic junction
- Ureters
- Urinary bladder
- Vasa recta (kidney)
- Ventral exiting nerve root
- Ventral traversing nerve root
- Vertebrae
- Zygapophyseal joint
- kidney cortex (renal cortex)
- kidneys
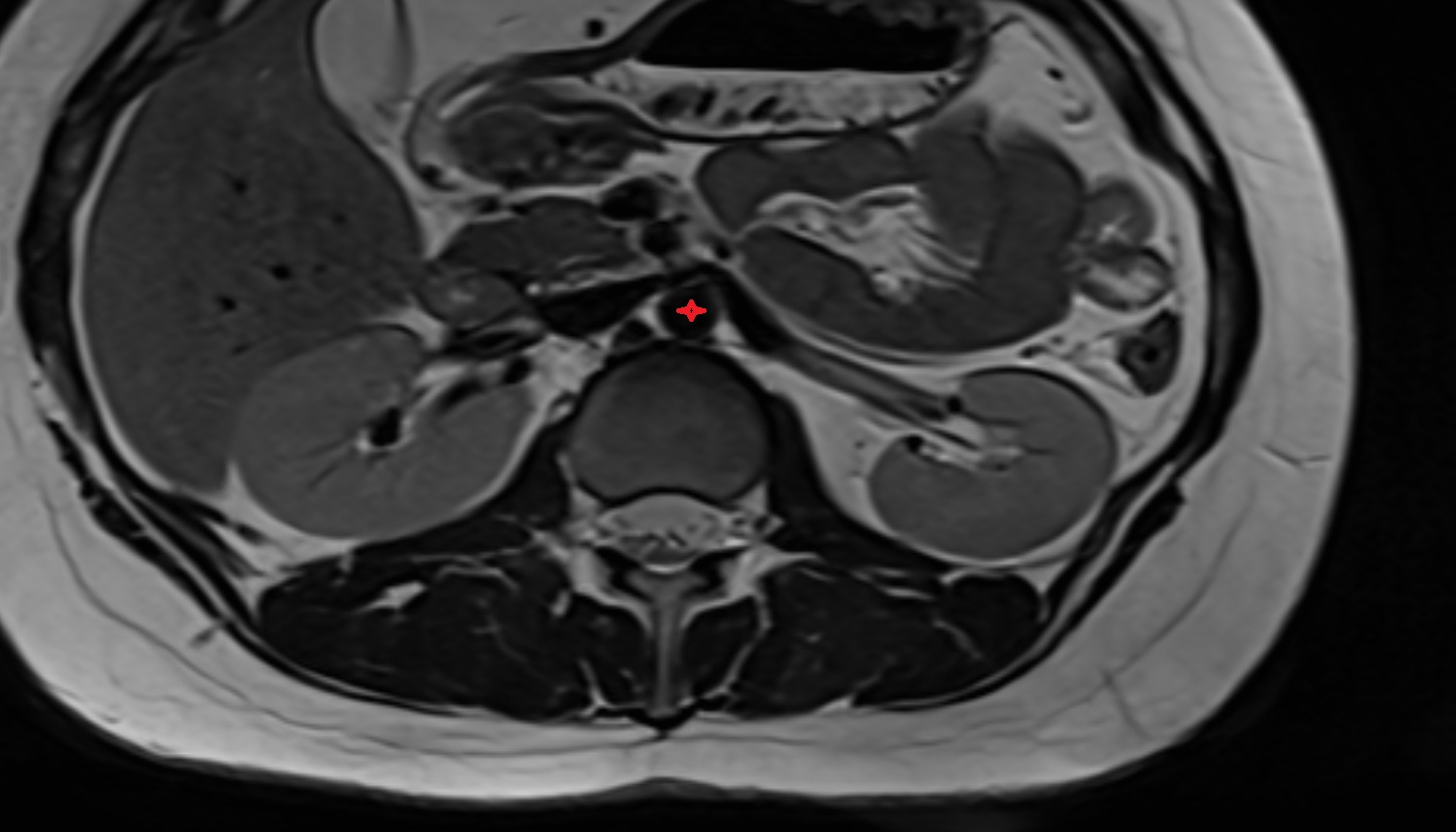
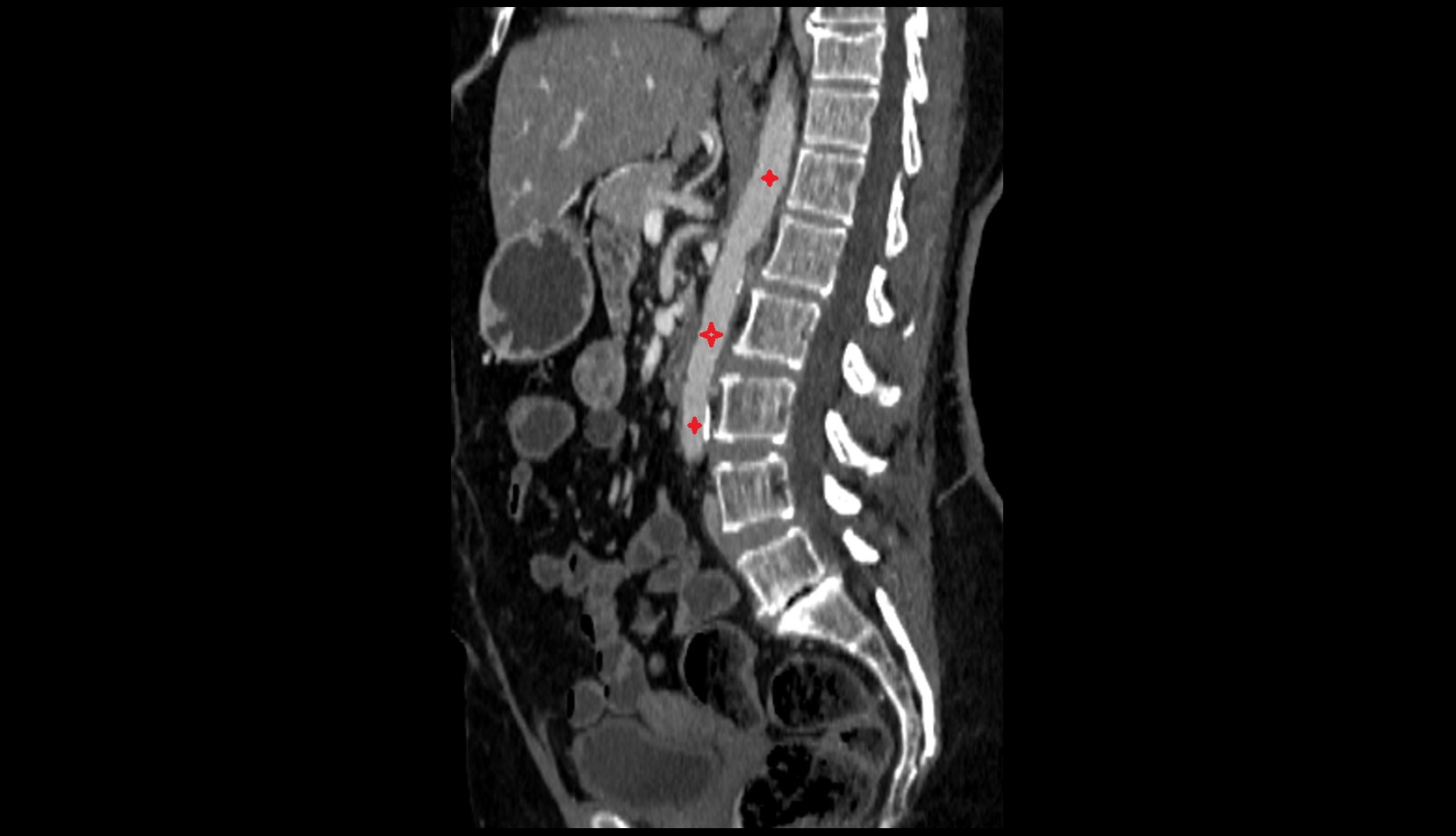
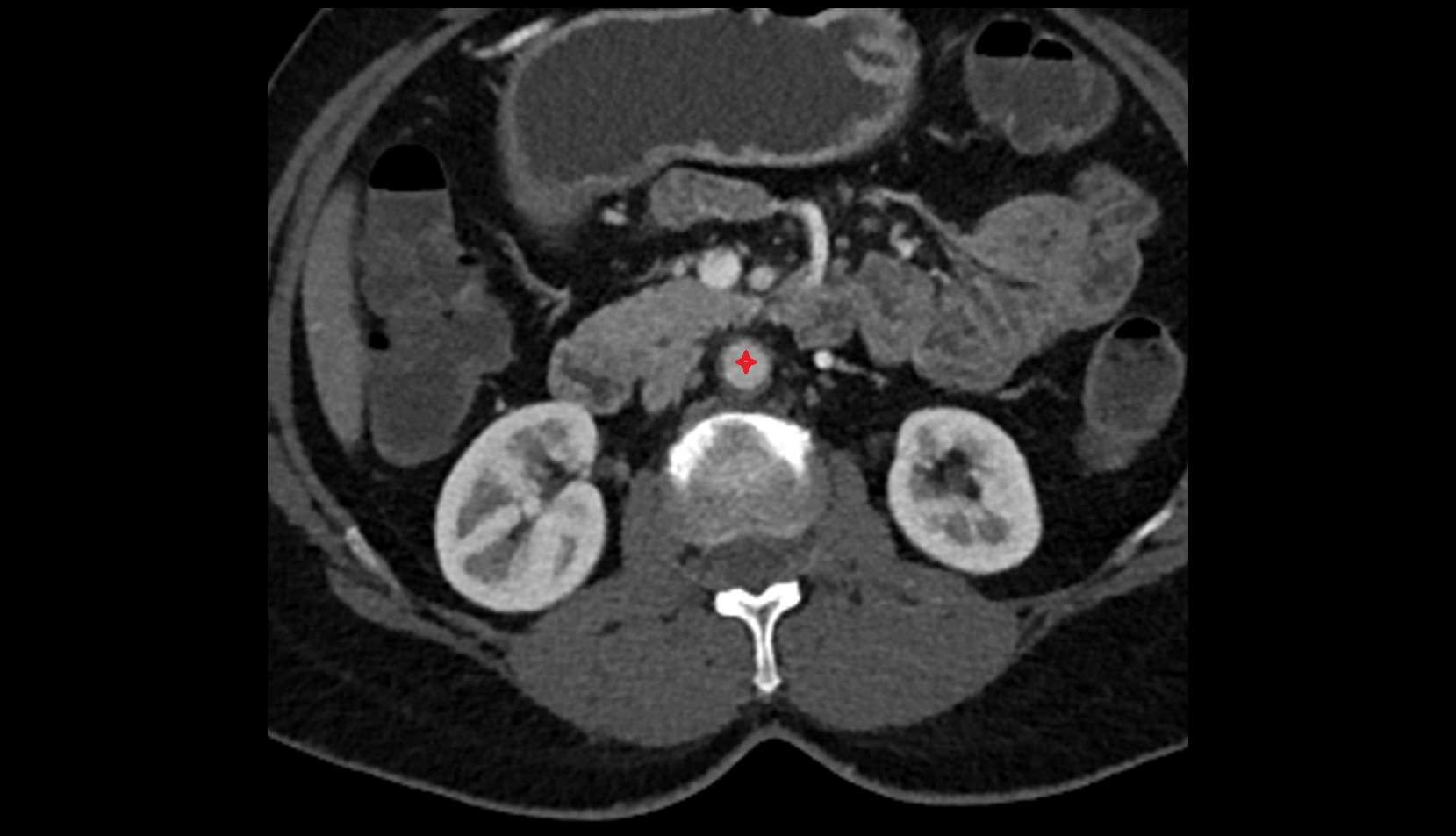
The abdominal part of the esophagus is the short terminal segment of the esophagus, approximately 1–2 cm in length, located between the esophageal hiatus of the diaphragm and the cardial orifice of the stomach. It lies in the left upper abdomen, anterior to the left crus of the diaphragm, and continues into the stomach at the gastroesophageal junction.
This segment is enclosed by the phrenoesophageal ligament, which anchors it at the diaphragm. The abdominal esophagus is of great clinical importance as it contains the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) region, which regulates the passage of food into the stomach and prevents reflux. Weakness in this area leads to conditions such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and hiatal hernia.
Synonyms
-
Distal esophagus
-
Abdominal esophageal segment
-
Gastroesophageal segment
Function
-
Serves as the terminal conduit for food and liquid into the stomach
-
Houses the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), preventing gastric reflux
-
Coordinates with diaphragmatic crura to maintain anti-reflux barrier
-
Plays a role in swallowing and gastric emptying mechanics
Nerve Supply
-
Parasympathetic: Esophageal plexus formed by the vagal trunks
-
Sympathetic: Greater splanchnic nerves via the celiac plexus
-
Provides autonomic innervation for peristalsis and sphincter control
Arterial Supply
-
Primarily from the left gastric artery (branch of celiac trunk)
-
Small contributions from the left inferior phrenic artery
Venous Drainage
-
Drains into the left gastric vein, which communicates with the portal vein
-
Forms part of the porto-systemic anastomosis with the azygos system, a site prone to esophageal varices in portal hypertension
MRI Appearance
T1-weighted images:
-
Esophageal wall appears as intermediate signal intensity with clear distinction from adjacent fat
-
Lumen may show variable signal depending on swallowed contents
T2-weighted images:
-
Wall appears intermediate to low signal, lumen shows bright hyperintense fluid if distended
-
Useful for detecting edema, inflammation, or masses
STIR:
-
Suppresses fat, making the esophageal wall and surrounding pathology stand out
-
Highlights edema, tumor infiltration, or peri-esophageal inflammation
T1 Fat-Saturated (Pre-contrast):
-
Wall shows intermediate signal, standing out against suppressed fat of mediastinum and upper abdomen
T1 Fat-Saturated Post-Contrast (Gadolinium):
-
Normal wall shows thin, uniform enhancement
-
Pathologies (esophagitis, tumors) show thickened, heterogeneous enhancement
-
Detects early neoplasia, inflammation, and perfusion defects
MRI Non-Contrast 3D Imaging:
-
Provides 3D reconstruction of the distal esophagus and gastroesophageal junction
-
Useful for pre-surgical mapping of tumors, hiatal hernias, and reflux disease
CT Appearance
CT Pre-Contrast:
-
Esophagus seen as a soft-tissue tubular structure just below the diaphragm
-
Distended lumen may contain air or fluid, useful in detecting obstruction
CT Post-Contrast:
-
Esophageal wall enhances moderately and uniformly
-
Thickening, irregularity, or heterogeneous enhancement suggests malignancy, esophagitis, or varices
-
Useful for staging of distal esophageal cancer and hiatal hernia assessment
CT images

CT images

CT images

MRI image