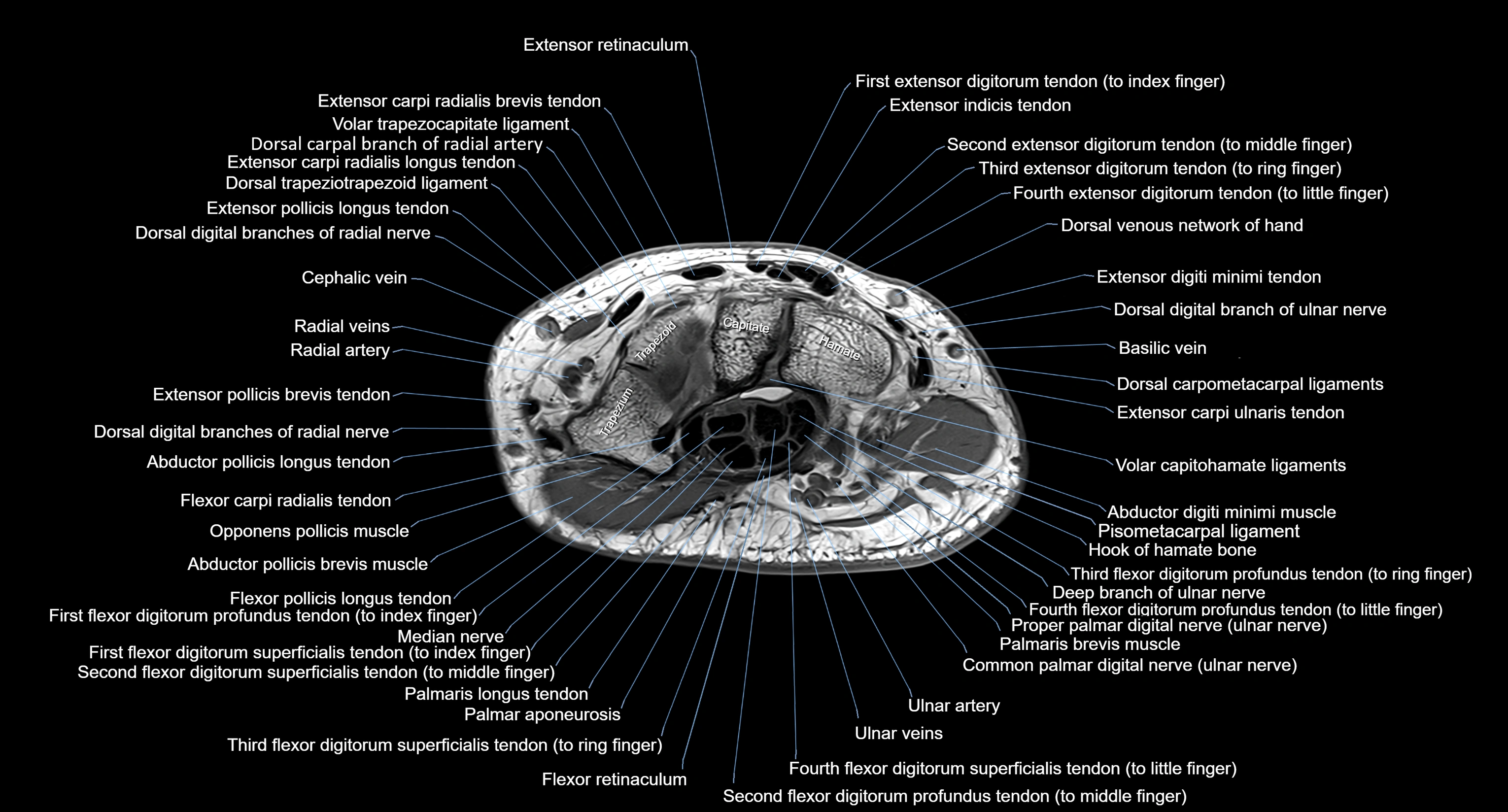
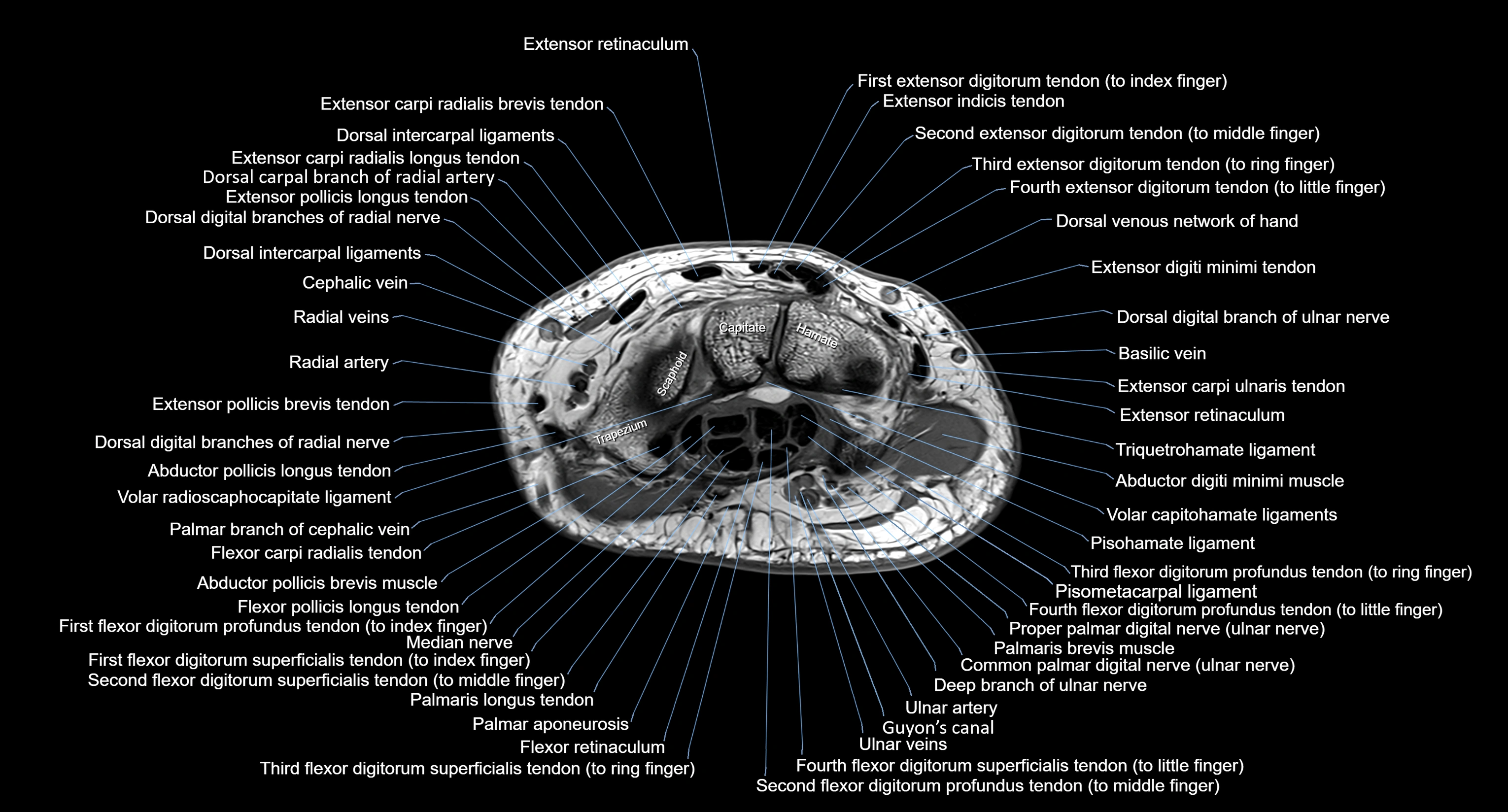
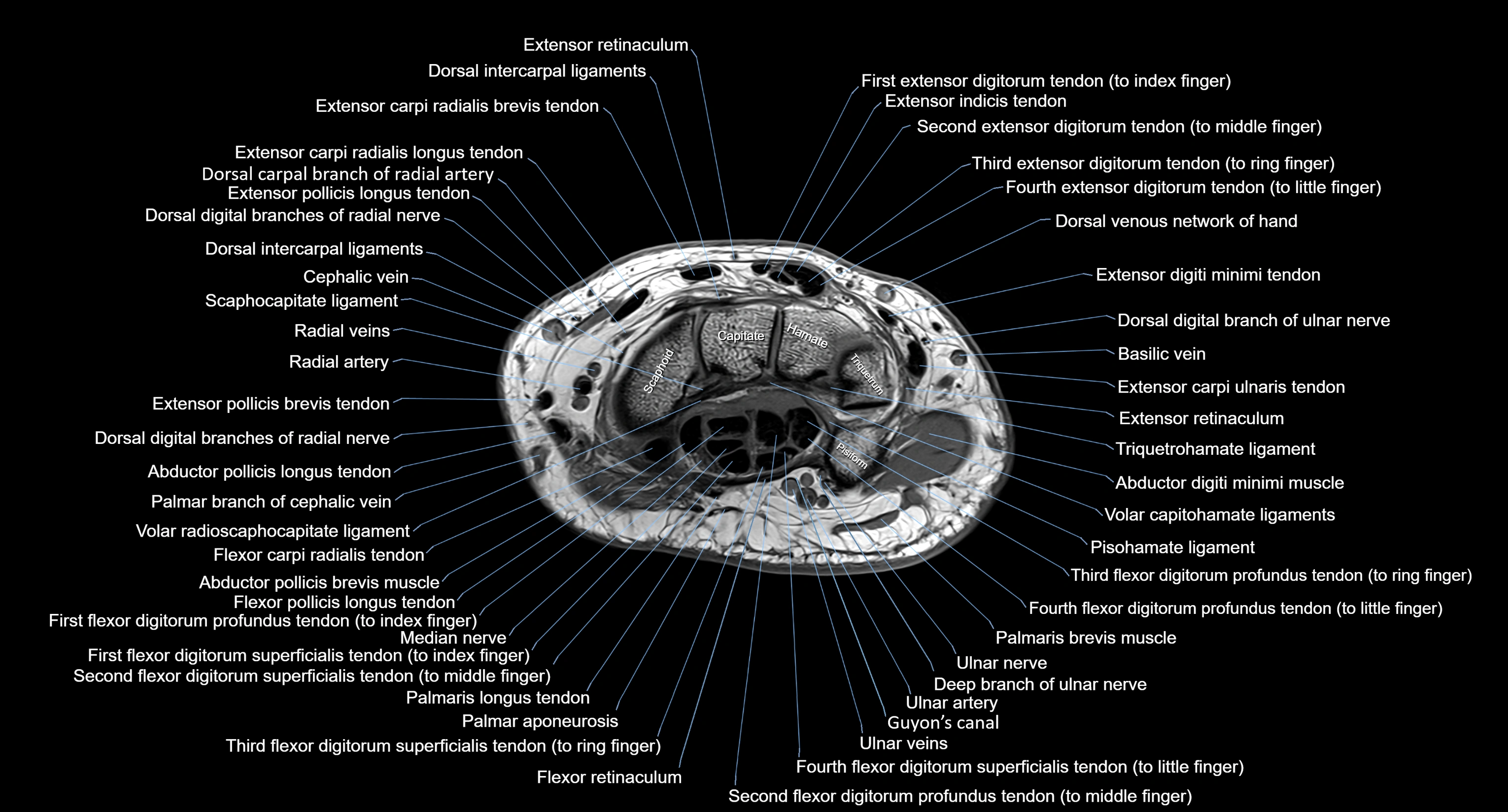
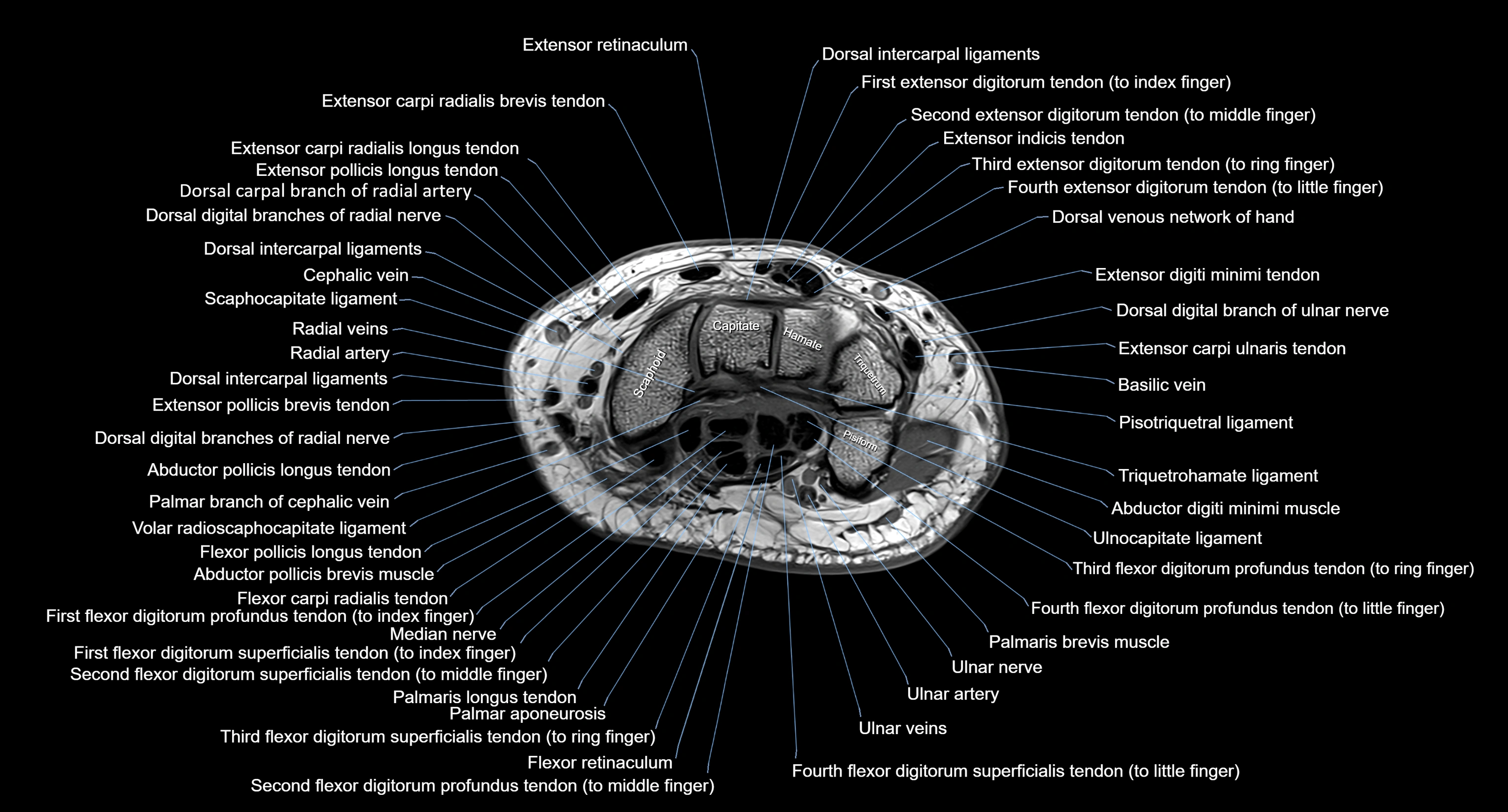
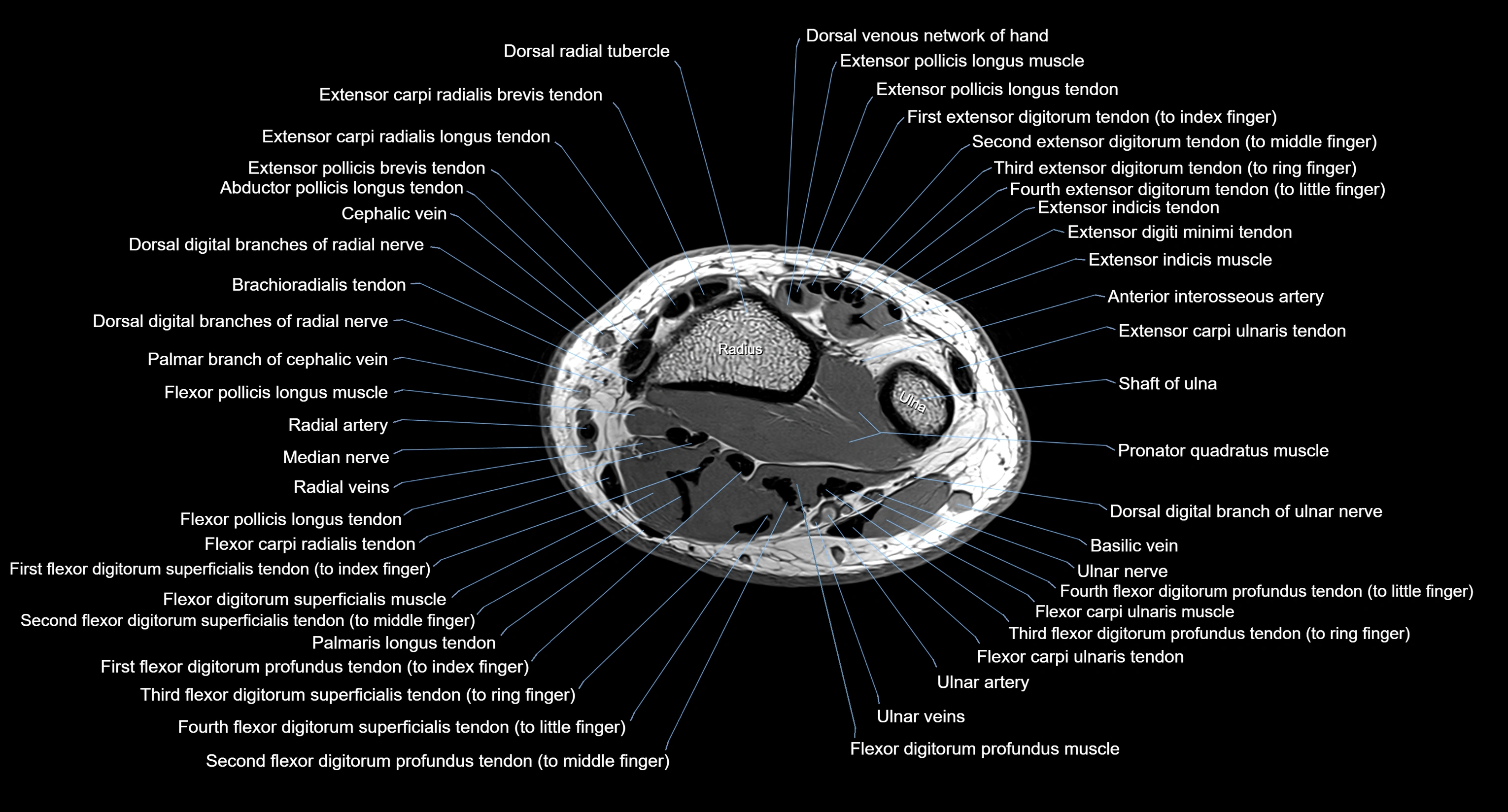
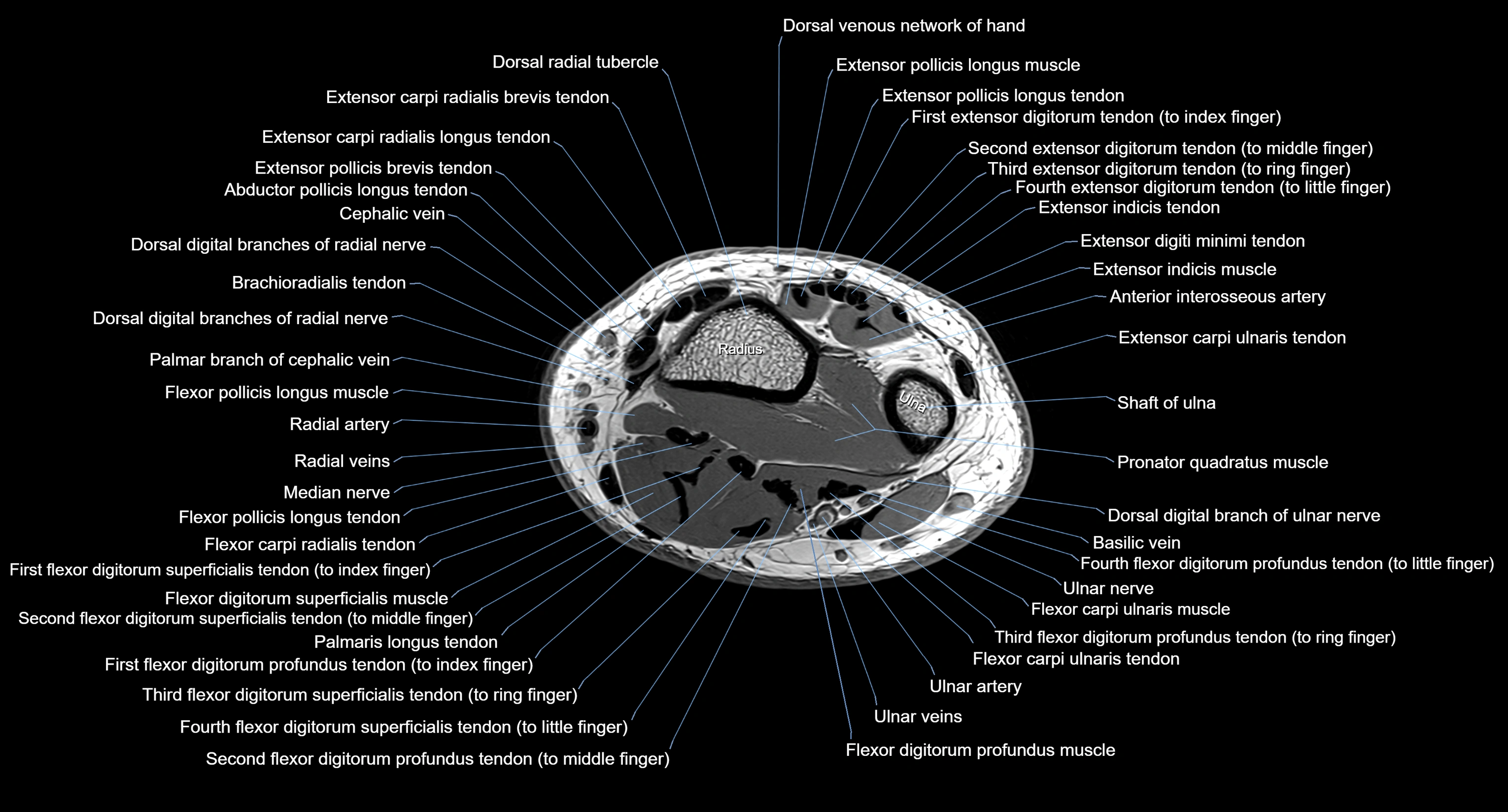
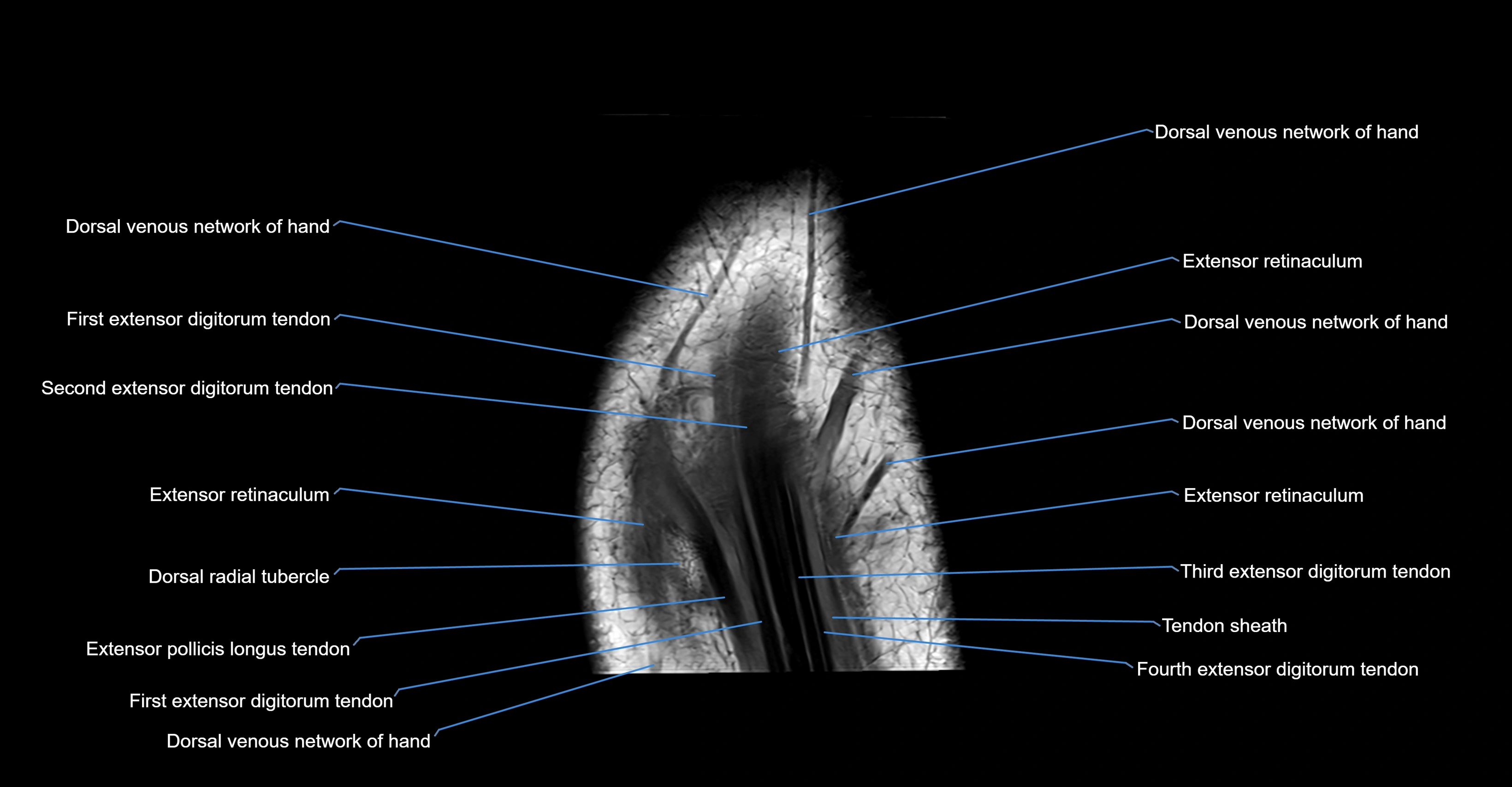
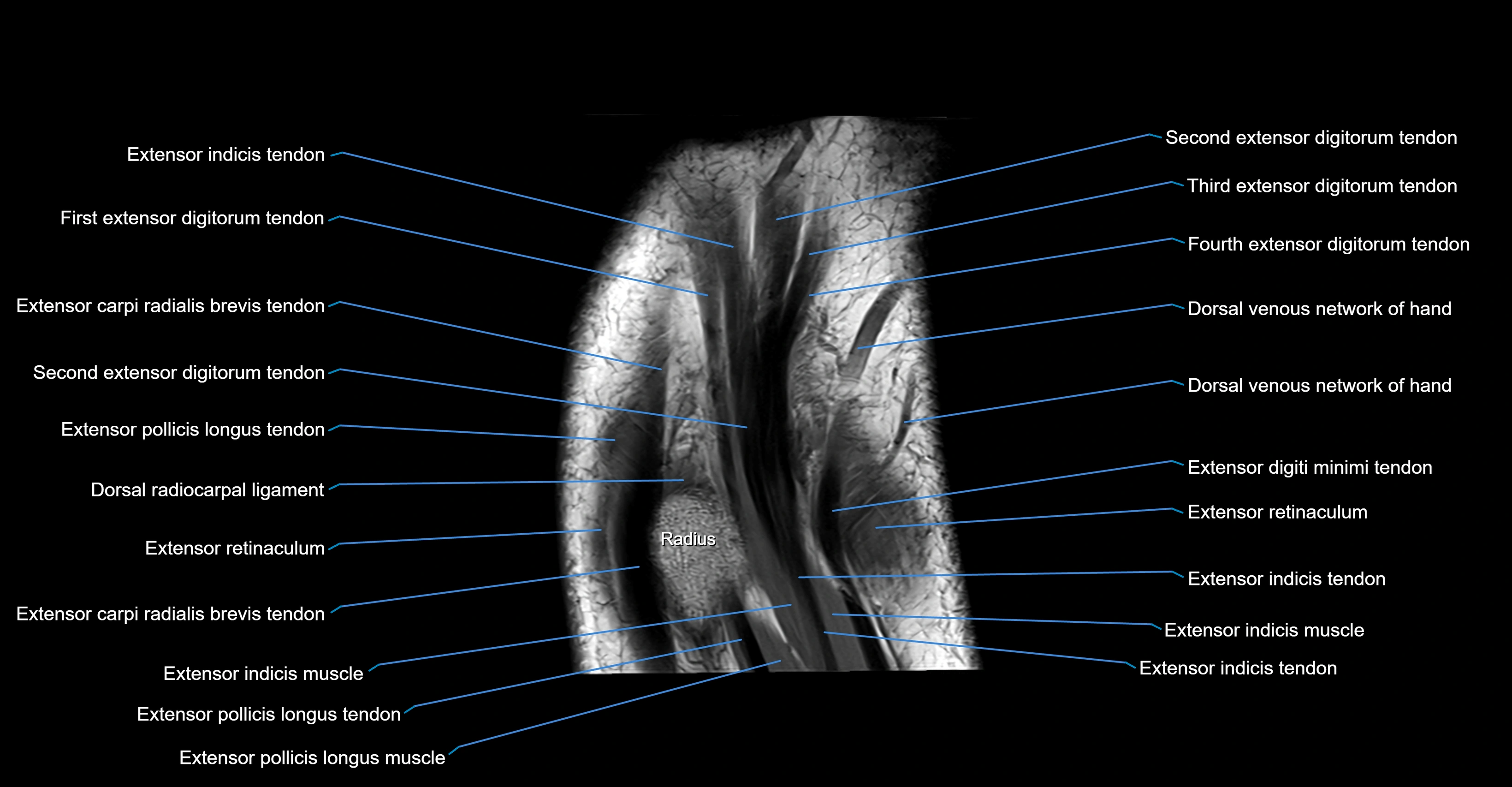
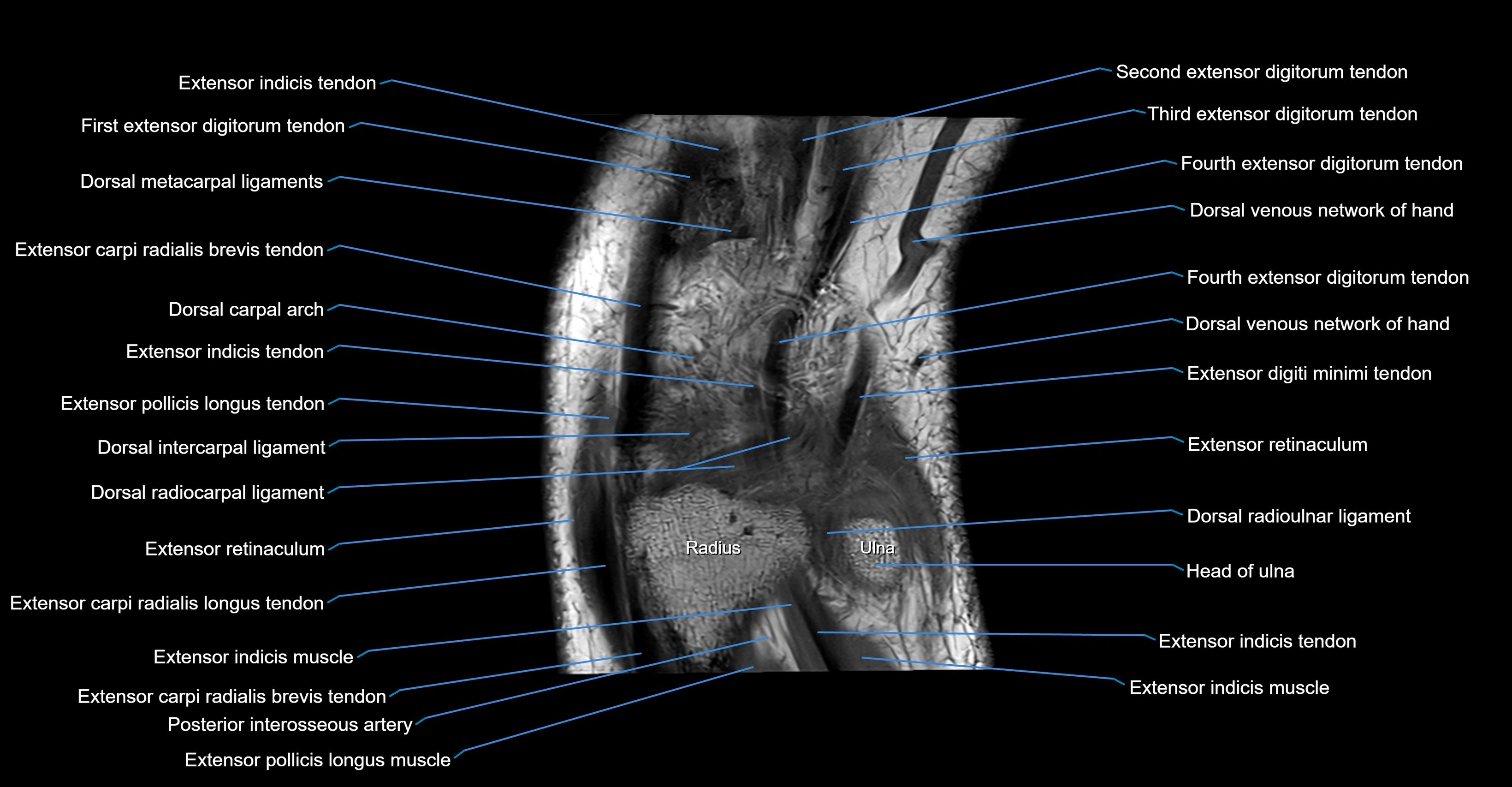
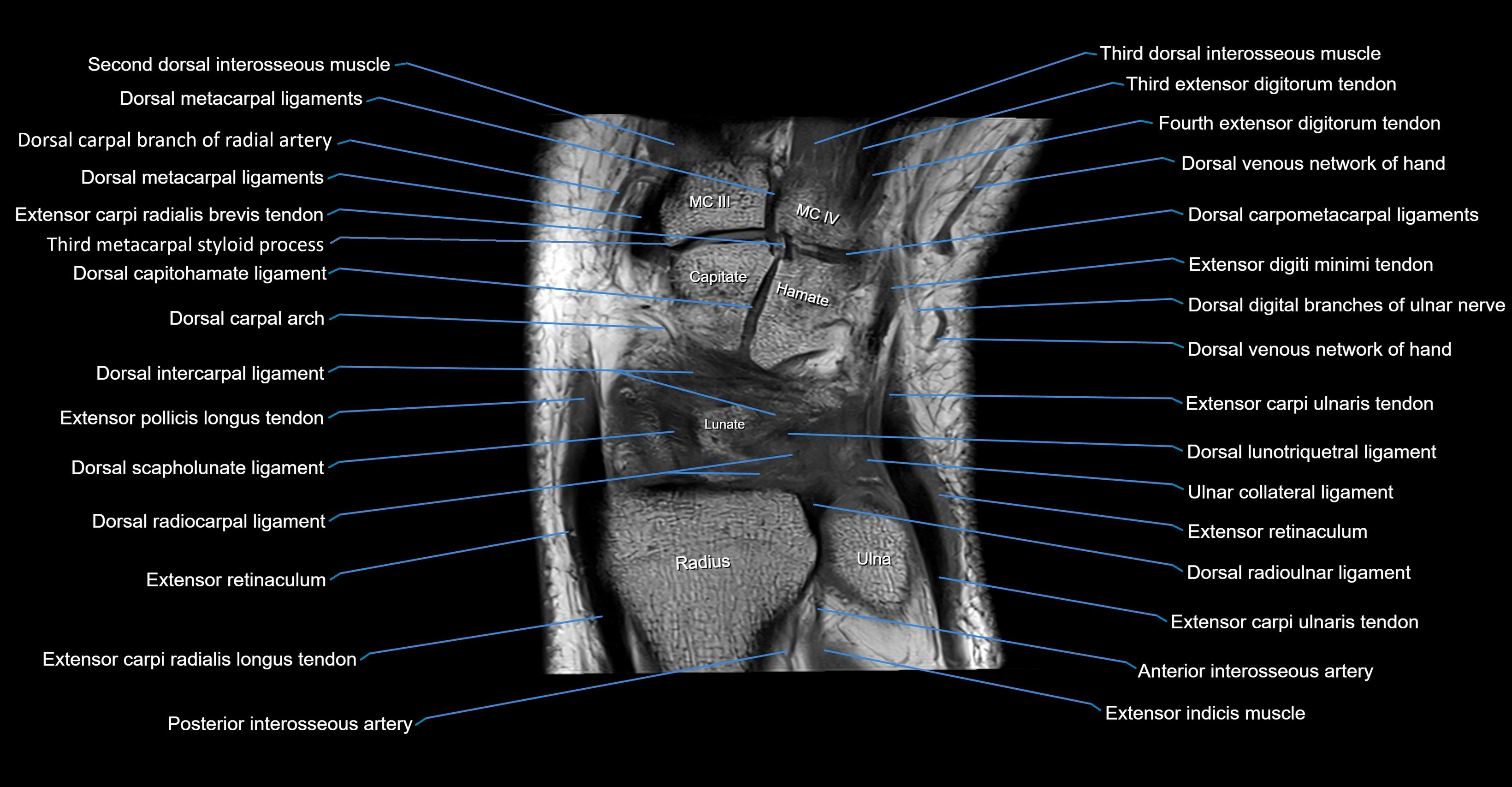
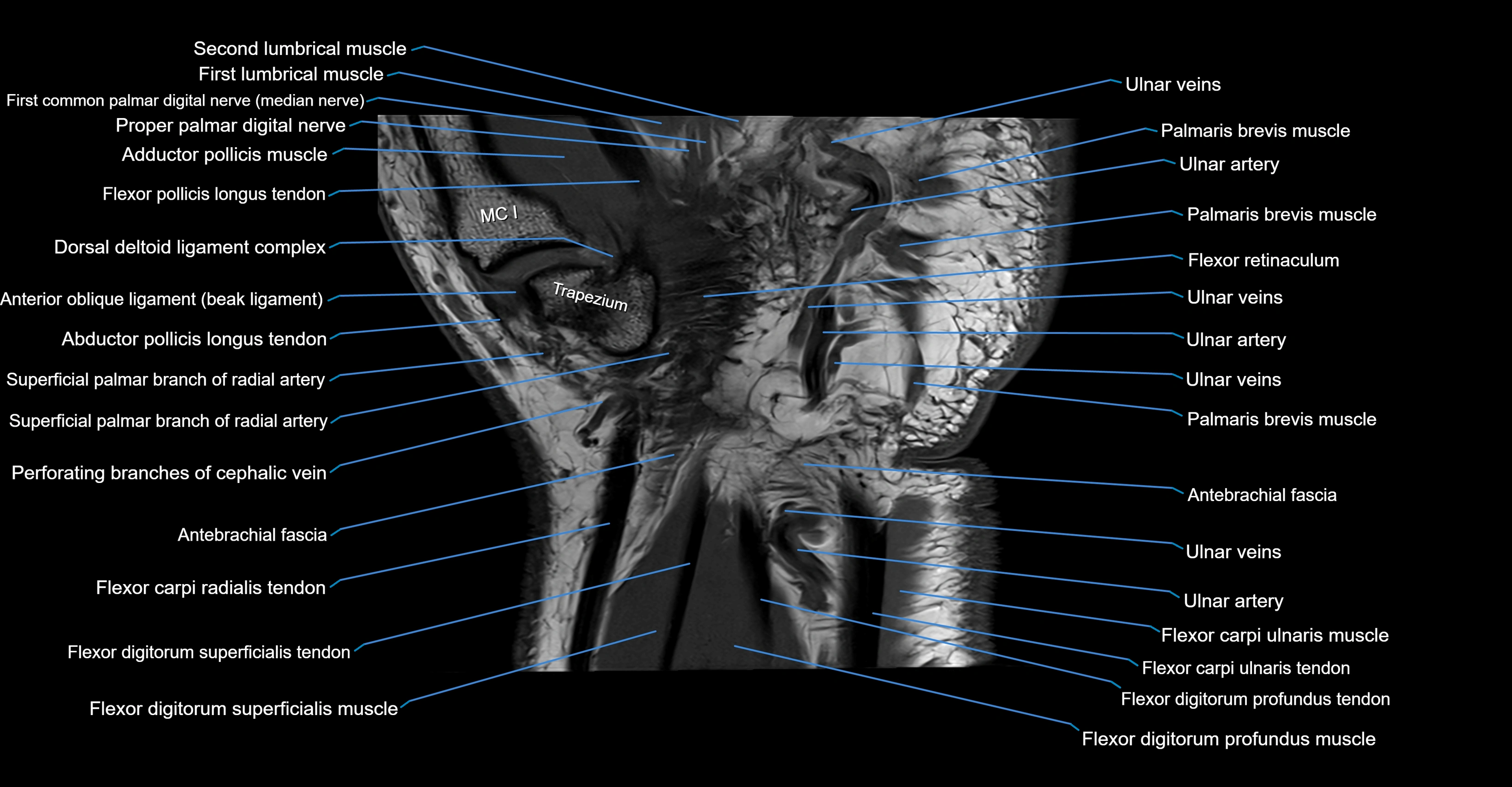
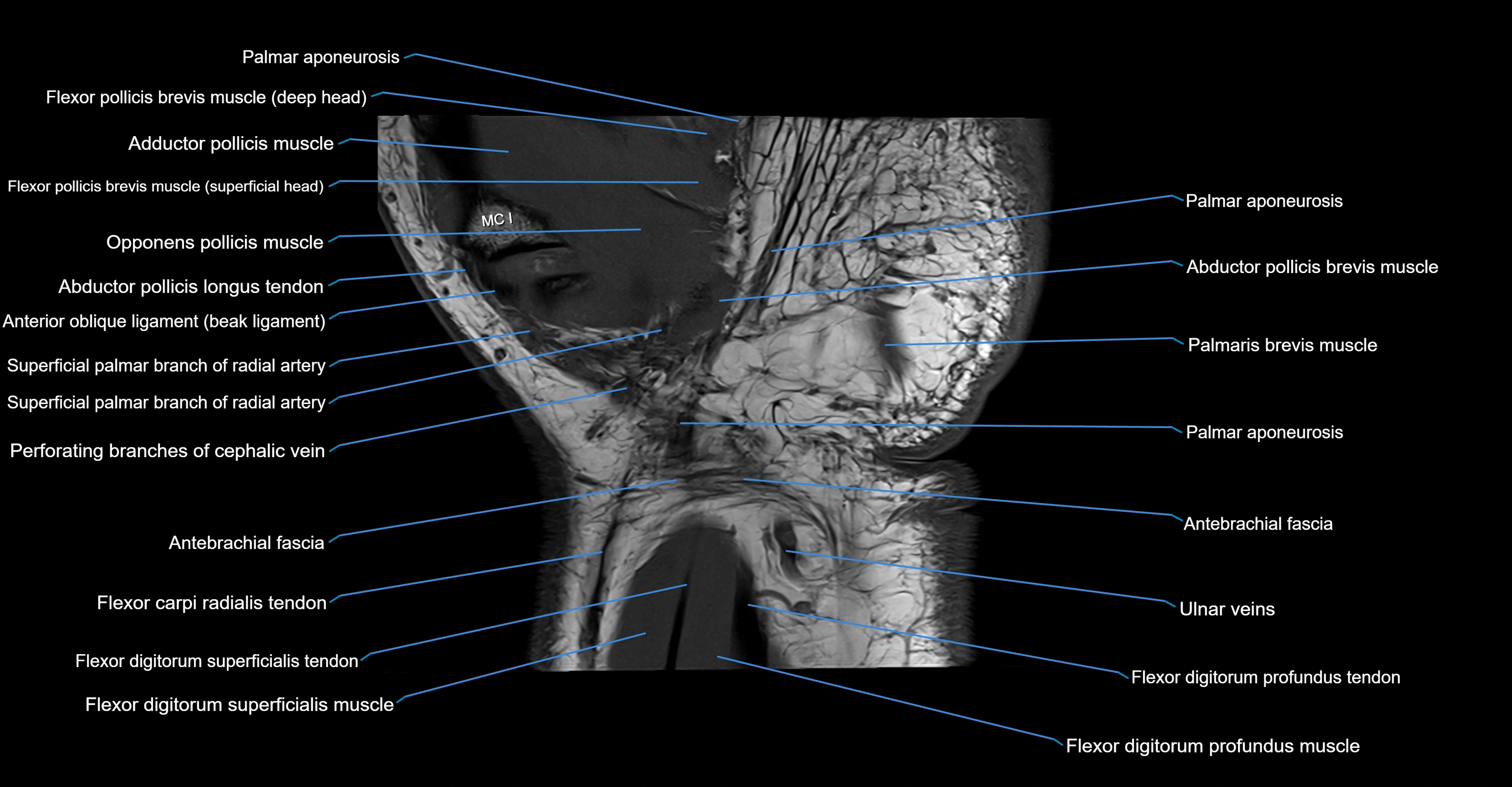
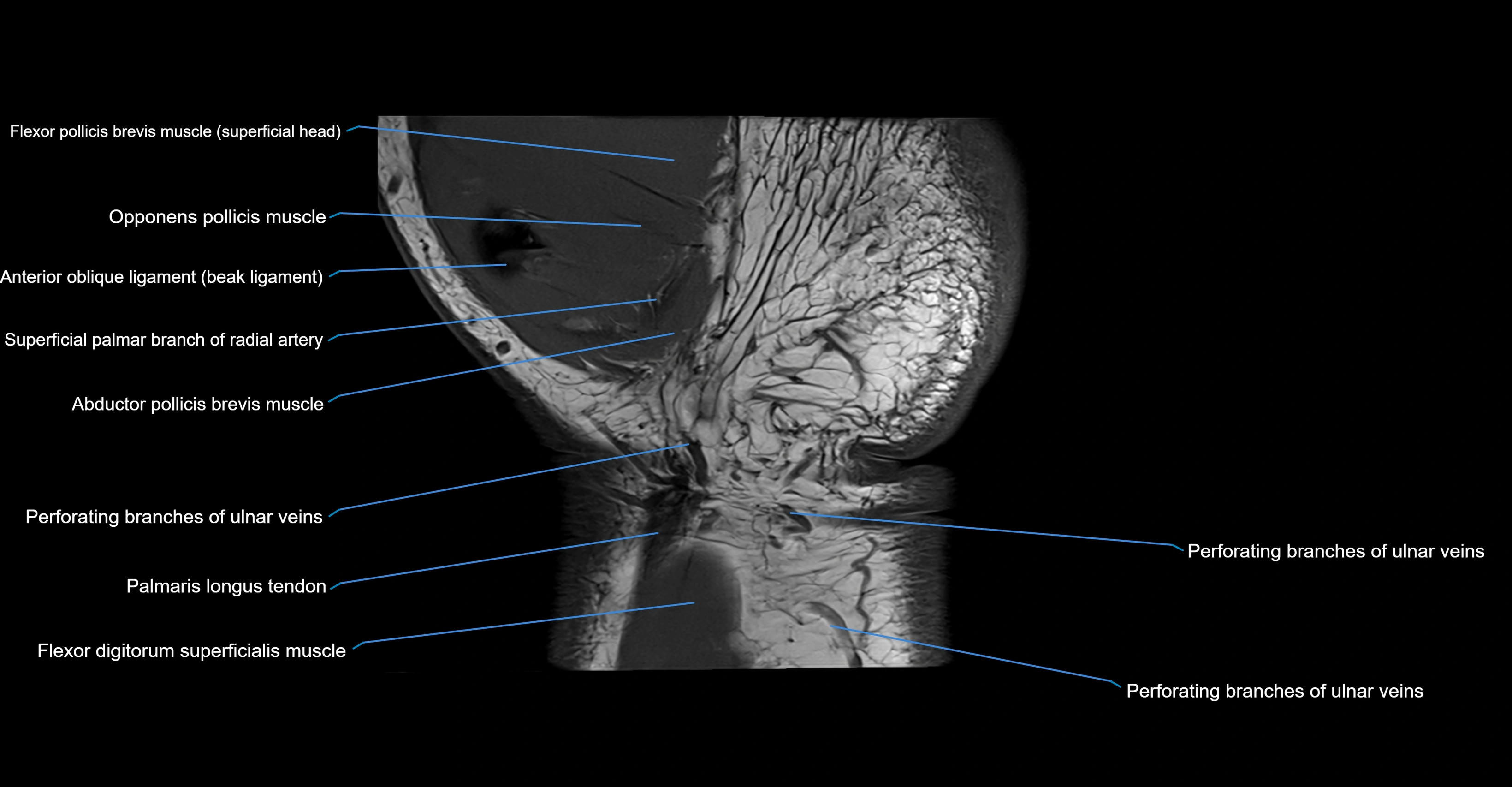
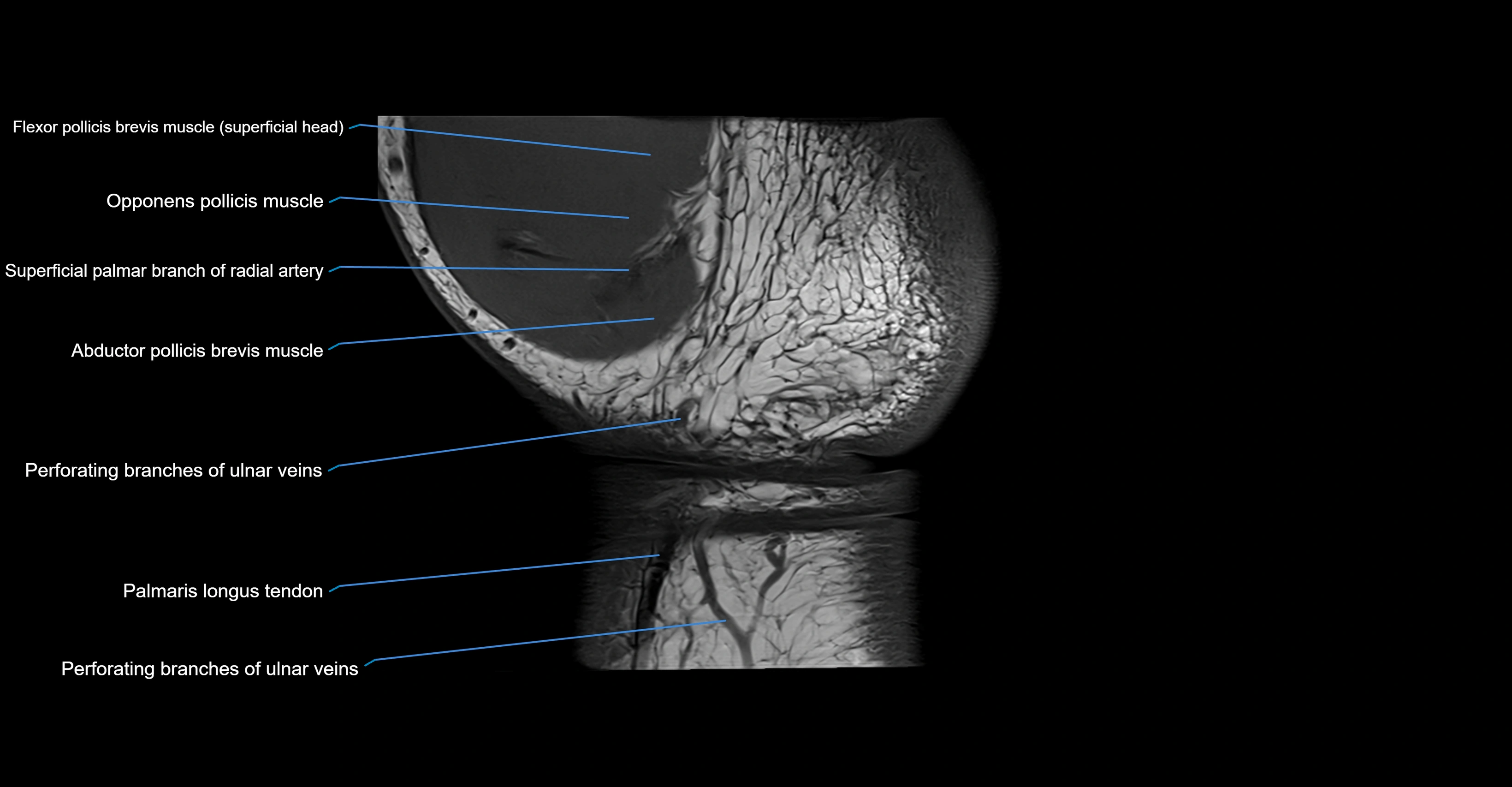
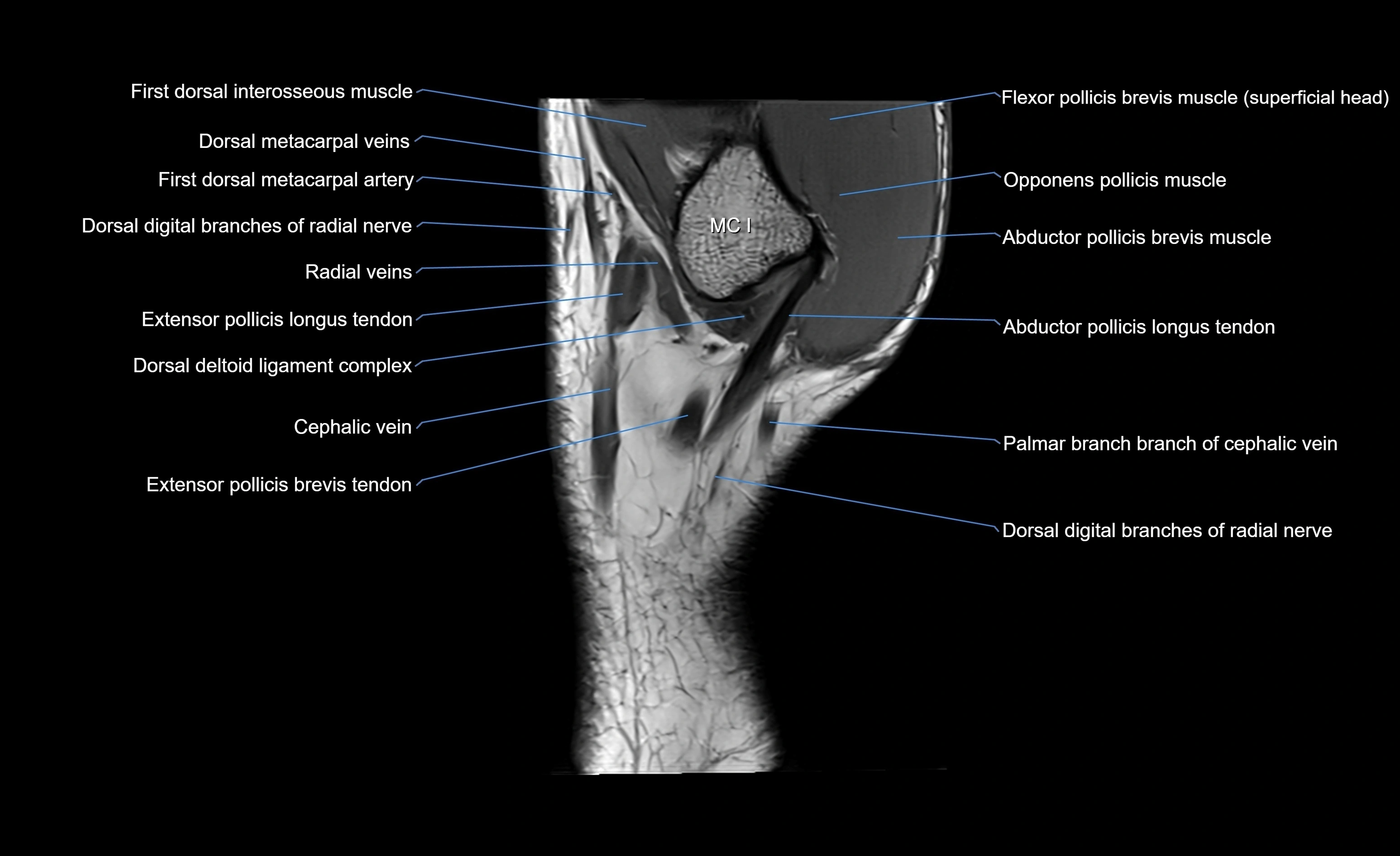
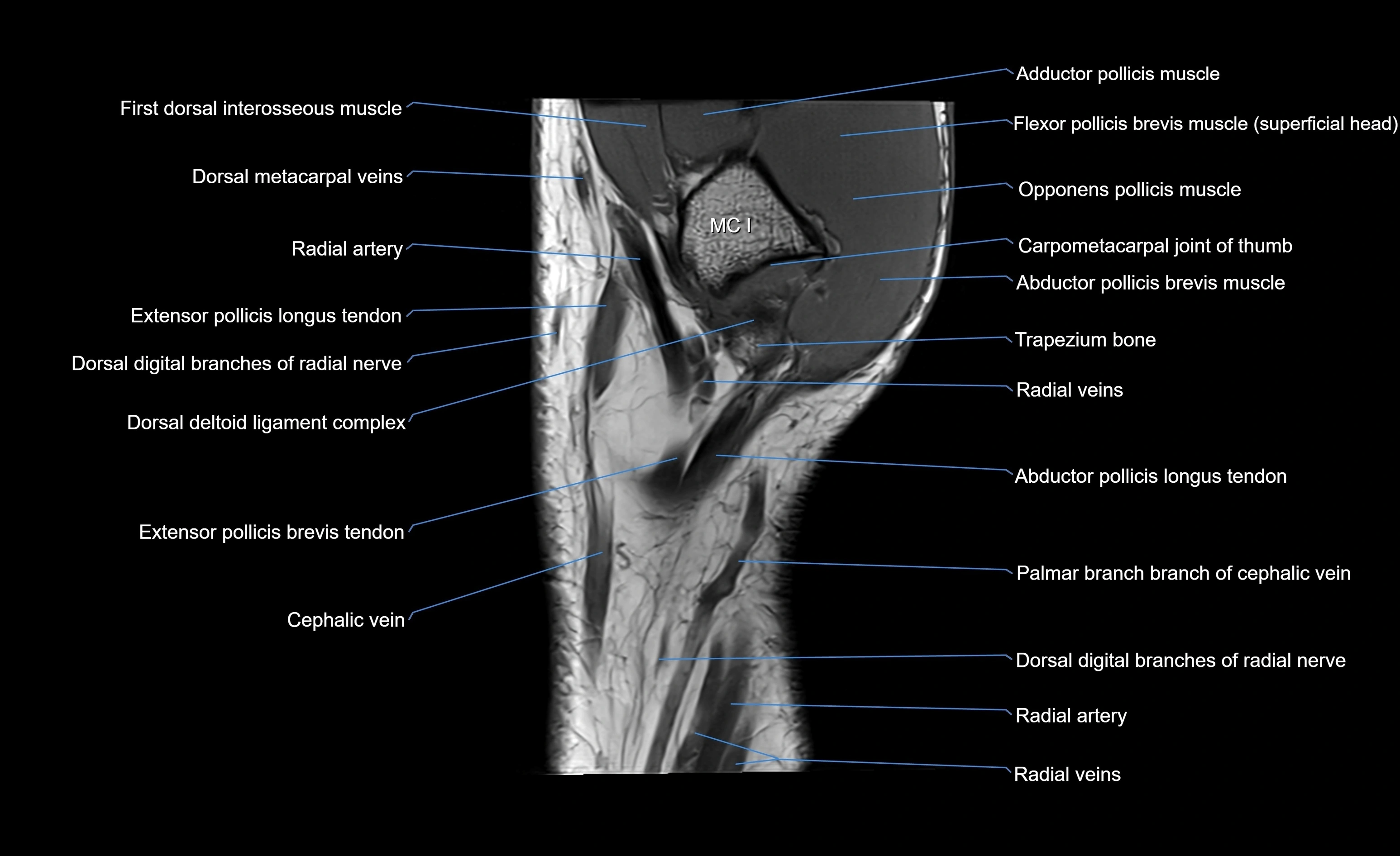
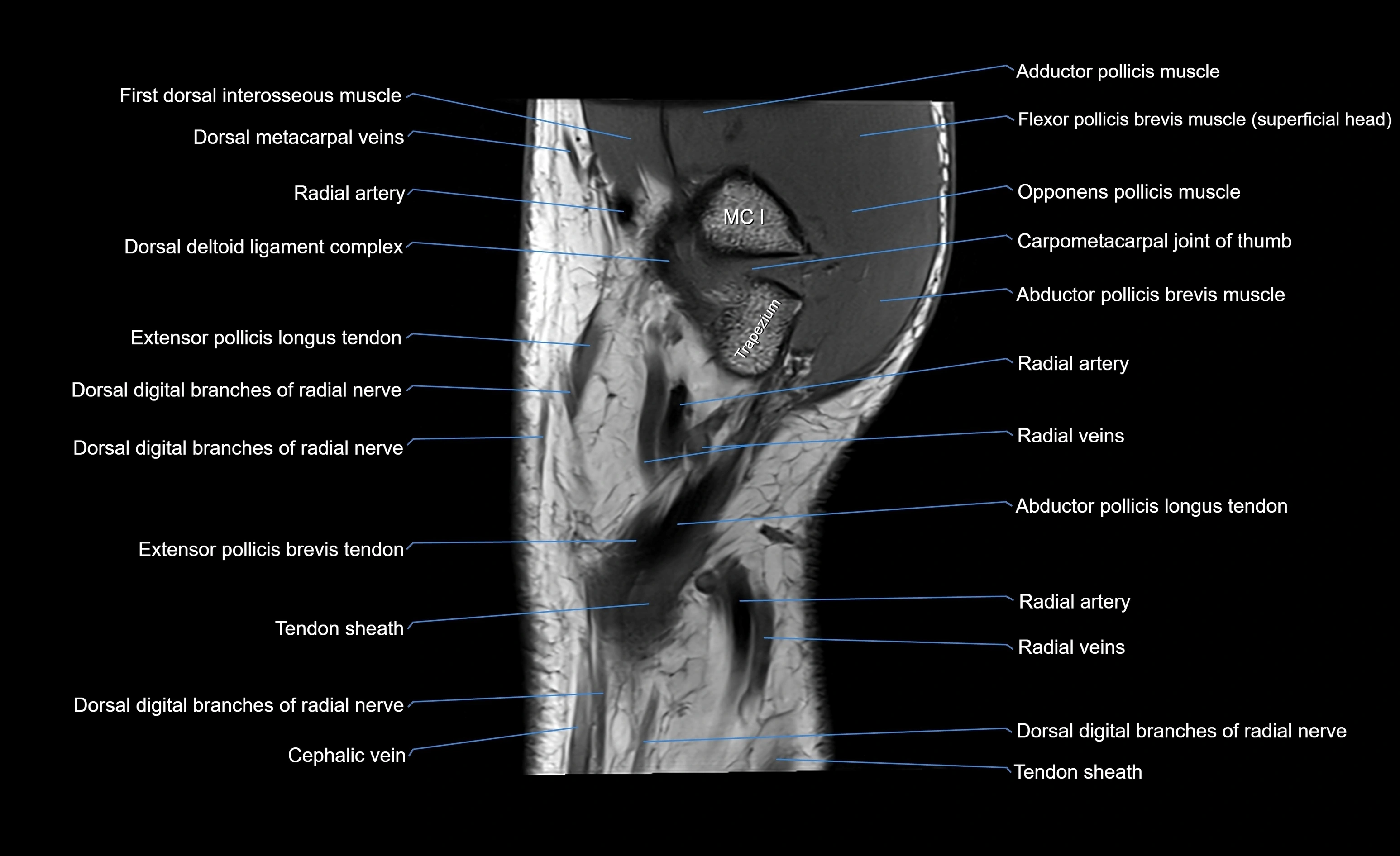
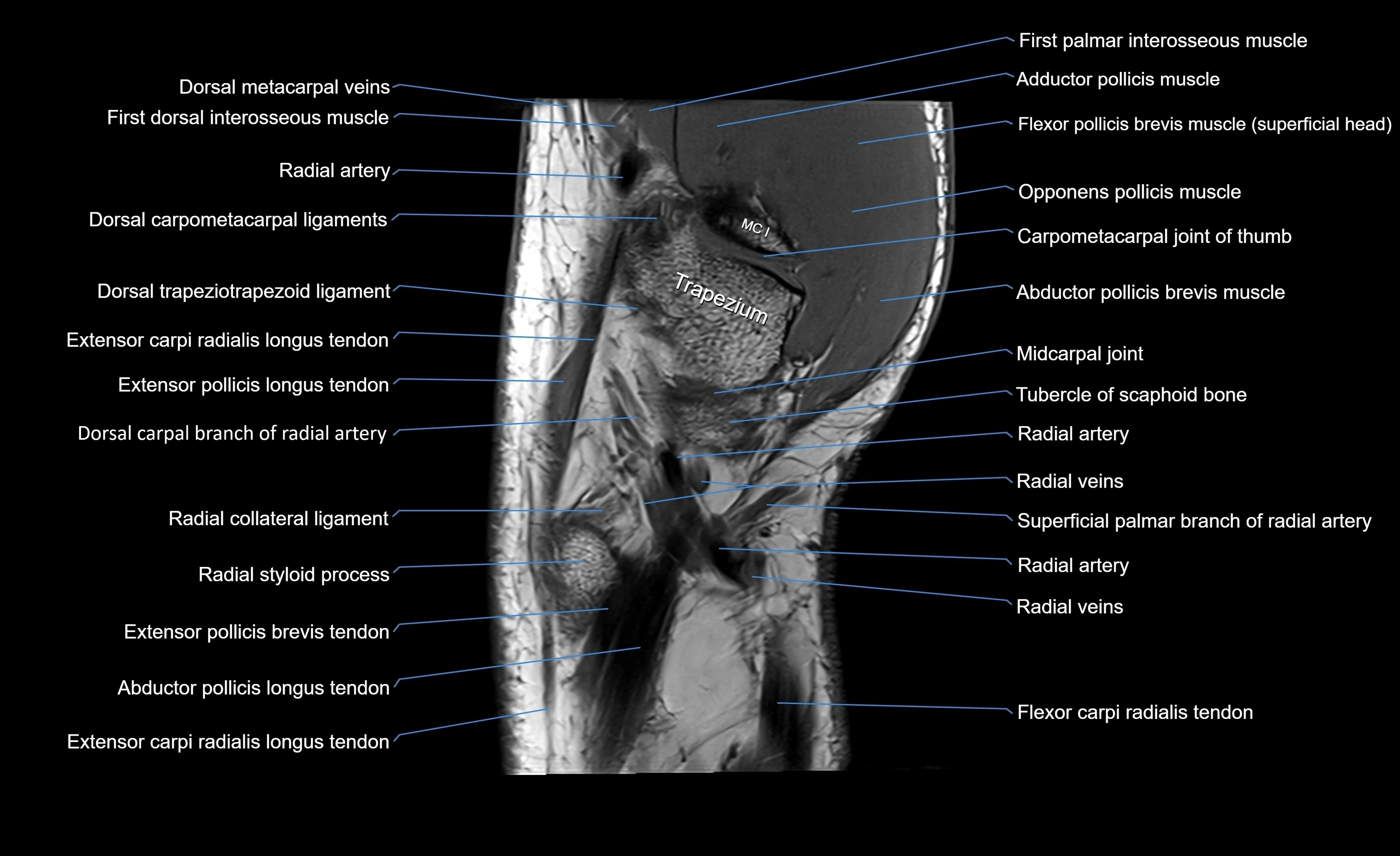
Topic
- Abductor digiti minimi muscle (hand)
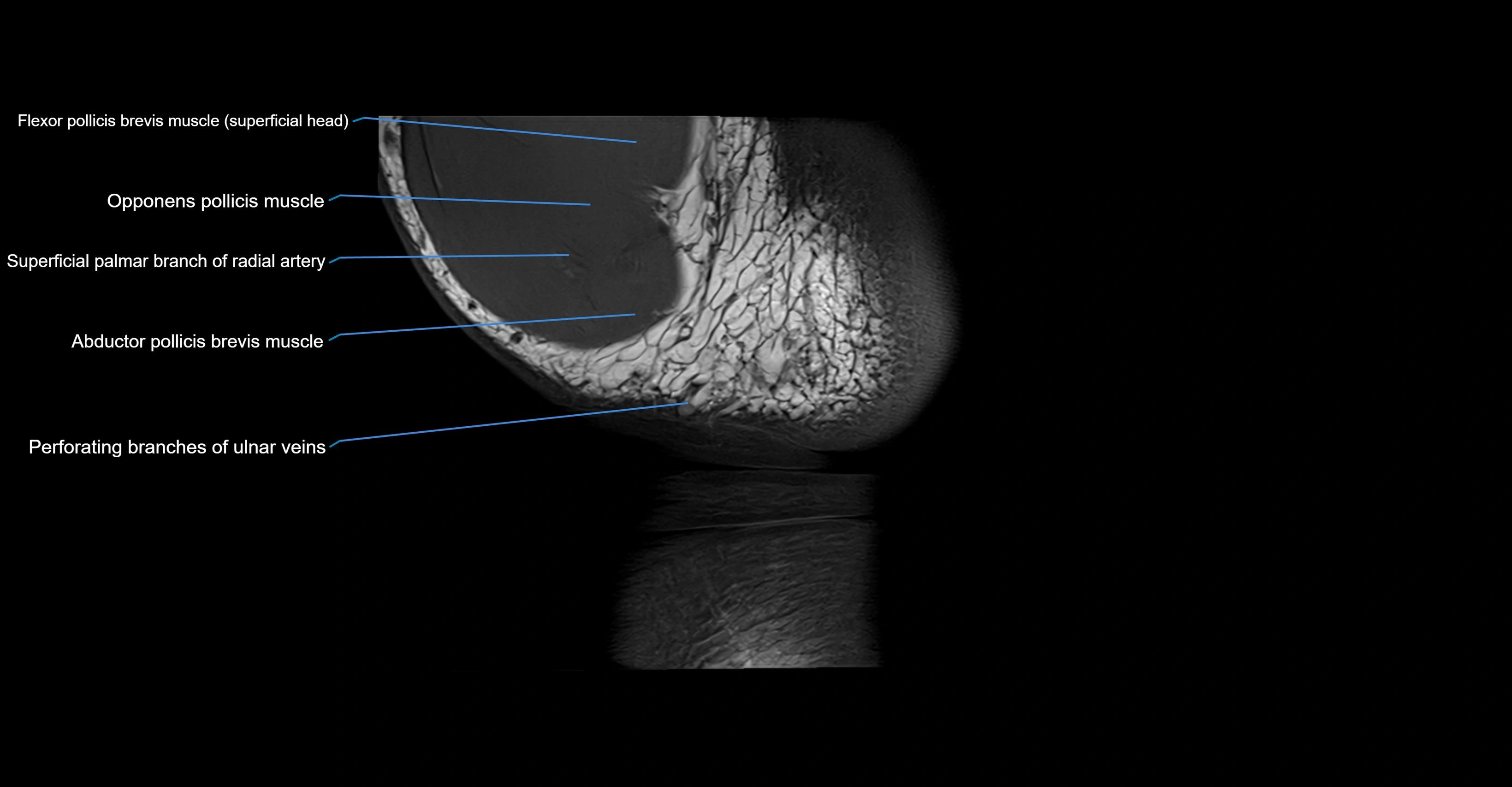
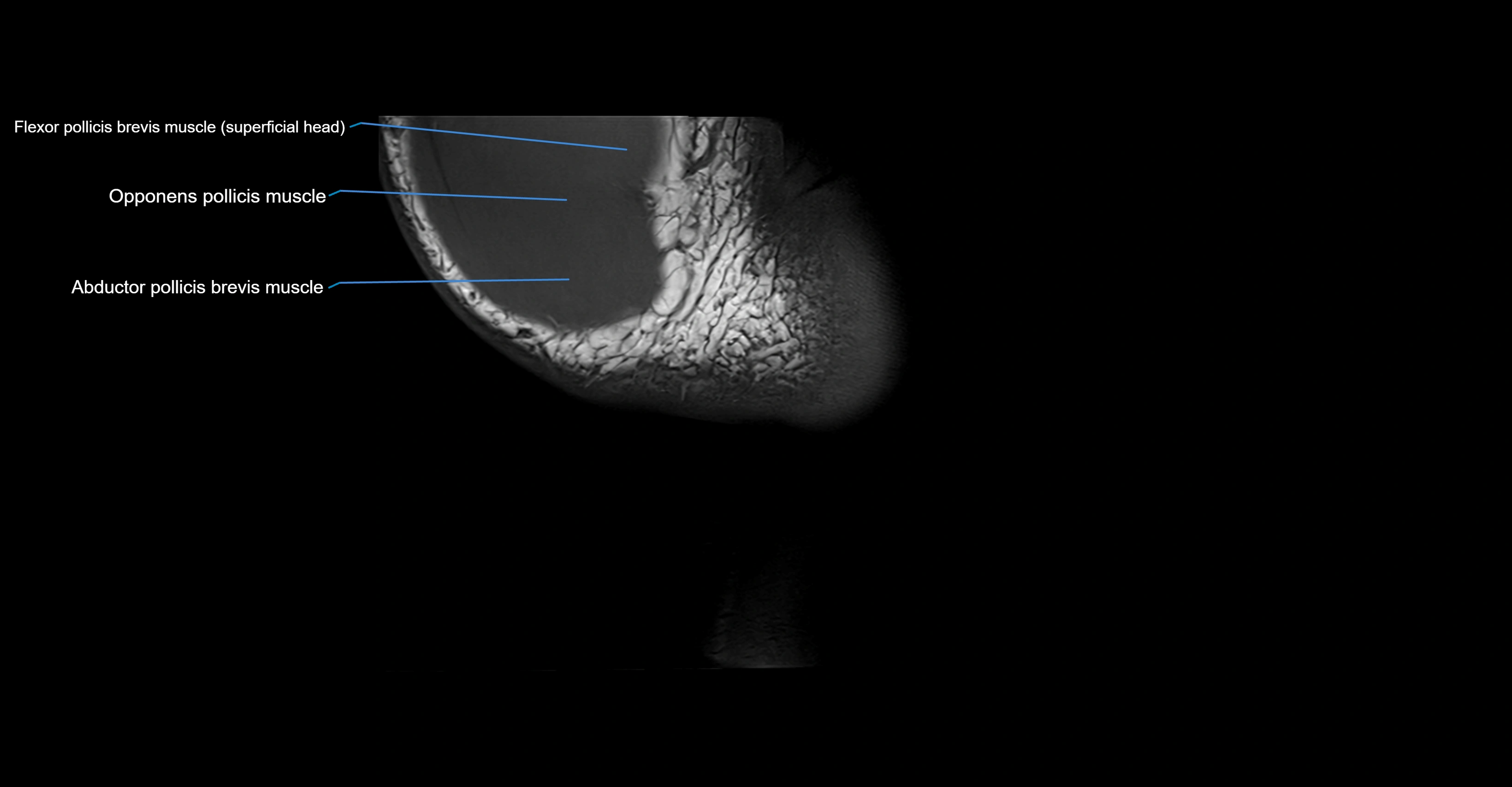
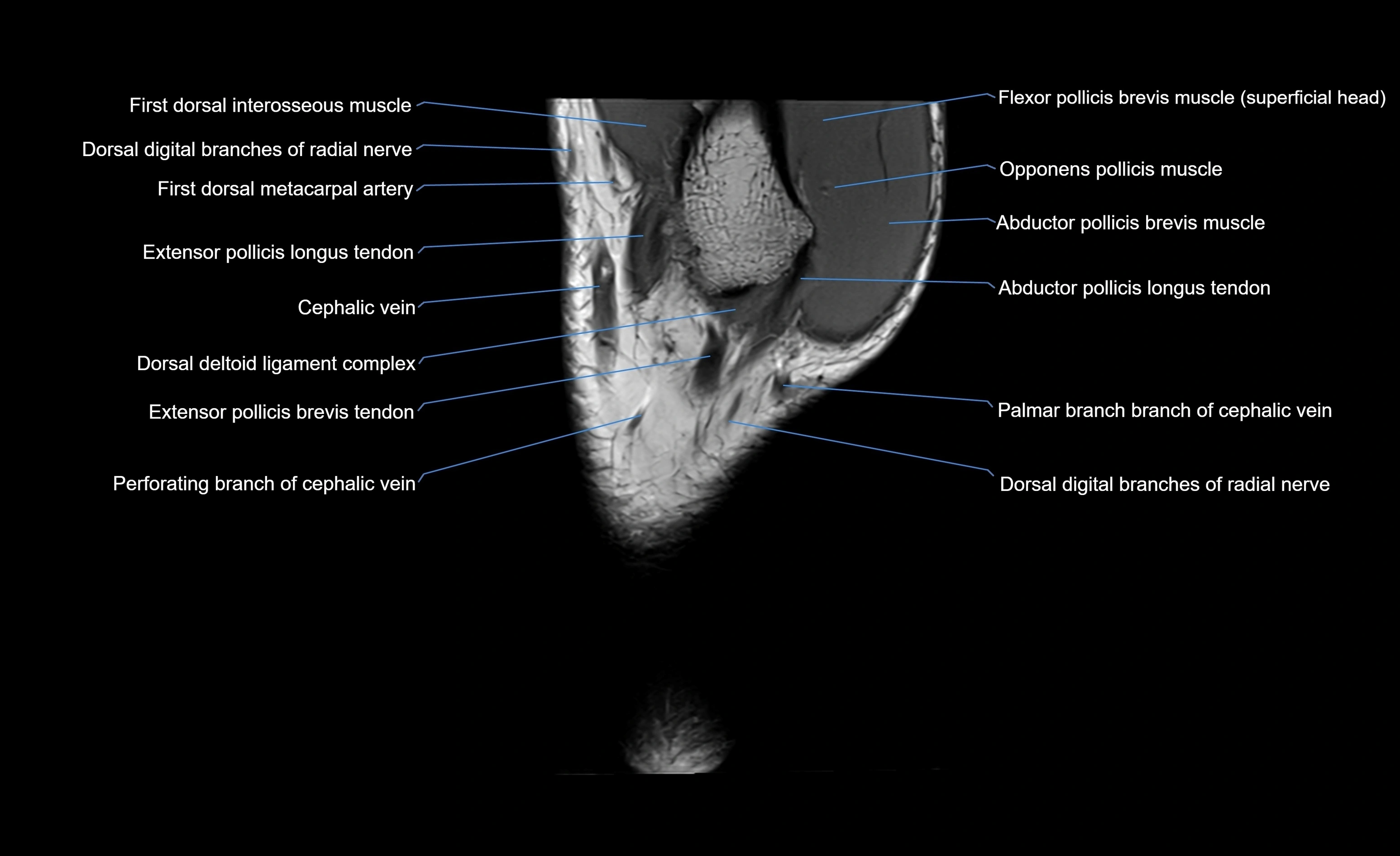
- Abductor pollicis brevis muscle
- Abductor pollicis longus muscle
- Abductor pollicis longus tendon
- Accessory cephalic vein
- Adductor pollicis muscle
- Adductor pollicis muscle (Oblique head)
- Adductor pollicis muscle (Transverse head)
- Anconeus muscle
- Anterior interosseous artery
- Anterior interosseous veins
- Anterior oblique ligament (beak ligament)
- Articularis cubiti muscle
- Base of metacarpal bone
- Base of proximal phalanx
- Base of the phalanx (hand)
- Basilic vein
- Body of metacarpal bone
- Body of proximal phalanx
- Body of the phalanx (hand)
- Body of ulna
- Brachialis muscle
- Brachioradialis muscle
- Brachioradialis tendon
- Capitate
- Capitohamate ligament
- Capitotrapezoid ligament (Trapezocapitate ligament)
- Carpal articular surface
- Carpal bones
- Carpal tunnel region
- Carpometacarpal joint of thumb
- Carpometacarpal joints
- Cephalic vein of forearm
- Common palmar digital branch of ulnar nerve
- Common palmar digital nerves of median nerve
- Deep branch of ulnar nerve
- Deep palmar arch
- Deep venous palmar arch
- Distal radioulnar joint
- Dorsal capitohamate ligament
- Dorsal capitotrapezoid ligament (Trapezocapitate ligament)
- Dorsal carpal branch of radial artery
- Dorsal deltoid ligament
- Dorsal digital branch of ulnar nerve
- Dorsal digital branches of radial nerve
- Dorsal intercarpal ligaments
- Dorsal interosseous muscle of hand
- Dorsal lunotriquetral ligament
- Dorsal radial tubercle (Lister’s tubercle)
- Dorsal radiocarpal ligament
- Dorsal radioulnar ligament
- Dorsal scapholunate ligament
- Dorsal trapeziotrapezoid ligament
- Dorsal ulnolunate ligament
- Dorsal venous network of hand
- Extensor carpi radialis brevis muscle
- Extensor carpi radialis brevis tendon
- Extensor carpi radialis longus muscle
- Extensor carpi radialis longus tendon
- Extensor carpi ulnaris muscle
- Extensor carpi ulnaris muscle (Humeral Head)
- Extensor carpi ulnaris tendon
- Extensor digiti minimi muscle
- Extensor digiti minimi tendon
- Extensor digitorum muscle
- Extensor digitorum tendons
- Extensor indicis muscle
- Extensor indicis tendon
- Extensor pollicis brevis muscle
- Extensor pollicis brevis tendon
- Extensor pollicis longus muscle
- Extensor pollicis longus tendon
- Extensor retinaculum of wrist
- Fifth metacarpal bone (metacarpal V)
- First dorsal interosseous muscle of hand
- First extensor digitorum tendon (Extensor digitorum tendon to index finger)
- First flexor digitorum profundus tendon
- First flexor digitorum superficialis tendon
- First lumbrical muscle of hand
- First metacarpal bone (metacarpal I)
- First plantar interosseous muscle of hand
- Flexor carpi radialis muscle
- Flexor carpi radialis tendon
- Flexor carpi ulnaris (ulnar head)
- Flexor carpi ulnaris muscle
- Flexor carpi ulnaris muscle (humeral head)
- Flexor carpi ulnaris tendon
- Flexor digiti minimi brevis muscle (hand)
- Flexor digitorum profundus muscle
- Flexor digitorum profundus tendons
- Flexor digitorum superficialis muscle
- Flexor digitorum superficialis muscle (humeroulnar head)
- Flexor digitorum superficialis muscle (radial head)
- Flexor digitorum superficialis tendons
- Flexor pollicis brevis muscle
- Flexor pollicis brevis muscle (Deep head)
- Flexor pollicis brevis muscle (Superficial head)
- Flexor pollicis longus muscle
- Flexor pollicis longus tendon
- Flexor retinaculum of wrist
- Fourth dorsal interosseous muscle of hand
- Fourth extensor digitorum tendon (Extensor digitorum tendon to little finger)
- Fourth flexor digitorum profundus tendon
- Fourth flexor digitorum superficialis tendon
- Fourth lumbrical muscle of hand
- Fourth metacarpal bone (metacarpal IV)
- Guyon’s canal
- Hamate
- Head of metacarpal bone
- Head of the phalanx (hand)
- Head of ulna
- Hook of hamate bone
- Intermetacarpal joints
- Interosseous border
- Interosseous scapholunate ligament
- Long radiolunate ligament
- Lunate
- Median nerve
- Metacarpal bones
- Metacarpophalangeal joint of thumb
- Metacarpophalangeal joints
- Midcarpal joint
- Opponens digiti minimi muscle (hand)
- Opponens pollicis muscle
- Palmar aponeurosis
- Palmar branch of cephalic vein
- Palmar capitotrapezoid ligament (Trapezocapitate ligament)
- Palmar interosseous muscles of hand
- Palmar trapeziotrapezoid ligament
- Palmaris brevis muscle
- Palmaris longus muscle
- Palmaris longus tendon
- Perforating branches of ulnar veins
- Phalanx bone (hand)
- Pisiform
- Pisohamate ligament
- Pisometacarpal ligament
- Posterior interosseous artery
- Posterior interosseous veins
- Princeps pollicis artery
- Pronator quadratus muscle
- Pronator teres muscle
- Pronator teres muscle (humeral head)
- Pronator teres muscle (ulnar head)
- Proper palmar digital nerves
- Proximal phalanx of hand
- Radial artery
- Radial collateral ligament of wrist
- Radial nerve
- Radial nerve (deep branch)
- Radial nerve (superficial branch)
- Radial sesamoid bone of thumb
- Radial styloid process
- Radial veins
- Radialis indicis artery
- Radiocarpal joint (wrist joint)
- Radius
- Scaphoid
- Second dorsal interosseous muscle of hand
- Second dorsal interosseous of hand
- Second extensor digitorum tendon (Extensor digitorum tendon to middle finger)
- Second flexor digitorum profundus tendon
- Second flexor digitorum superficialis tendon
- Second lumbrical muscle of hand
- Second metacarpal bone (metacarpal II)
- Second plantar interosseous muscle of hand
- Short radiolunate ligament
- Superficial palmar arch
- Supinator muscle
- Third dorsal interosseous muscle of hand
- Third extensor digitorum tendon (Extensor digitorum tendon to ring finger)
- Third flexor digitorum profundus tendon
- Third flexor digitorum superficialis tendon
- Third lumbrical muscle of hand
- Third metacarpal bone (metacarpal III)
- Third metacarpal styloid process
- Third plantar interosseous muscle of hand
- Trapeziotrapezoid ligament
- Trapezium
- Trapezoid
- Triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC )
- Triangular fibrocartilage disc
- Triquetrum
- Tubercle of scaphoid
- Tubercle of the scaphoid bone
- Tubercle of trapezium bone
- Ulna
- Ulnar artery
- Ulnar collateral ligament of wrist
- Ulnar nerve
- Ulnar sesamoid bone of thumb
- Ulnar styloid process
- Ulnar veins
- Ulnocapitate ligament
- Ulnocarpal ligaments
- Ulnotriquetral ligament
- Volar capitohamate ligament
- Volar lunotriquetral ligament
- Volar radioscaphocapitate ligament
- Volar radioulnar ligament
- Volar scapholunate ligament
- Volar ulnolunate ligament
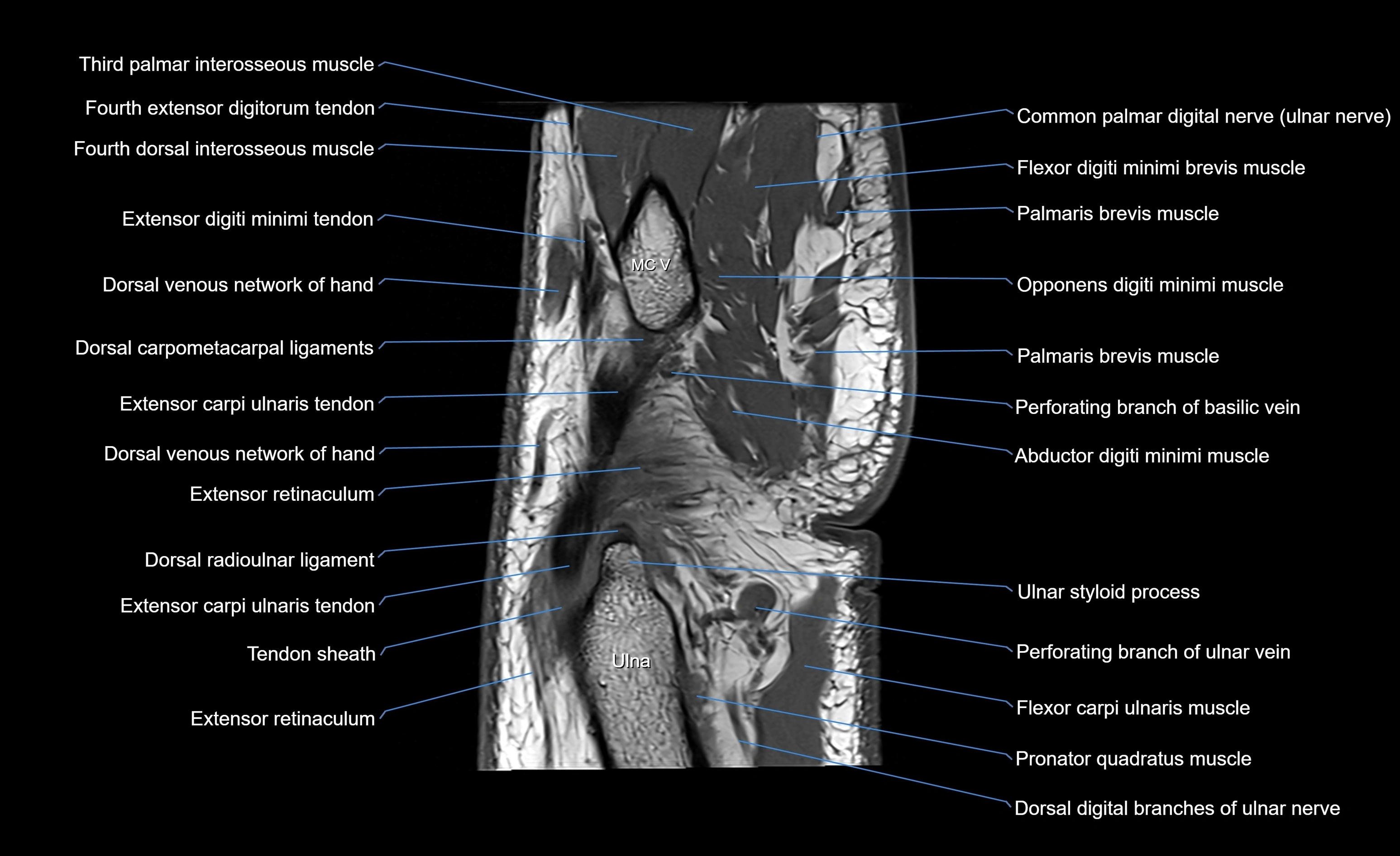
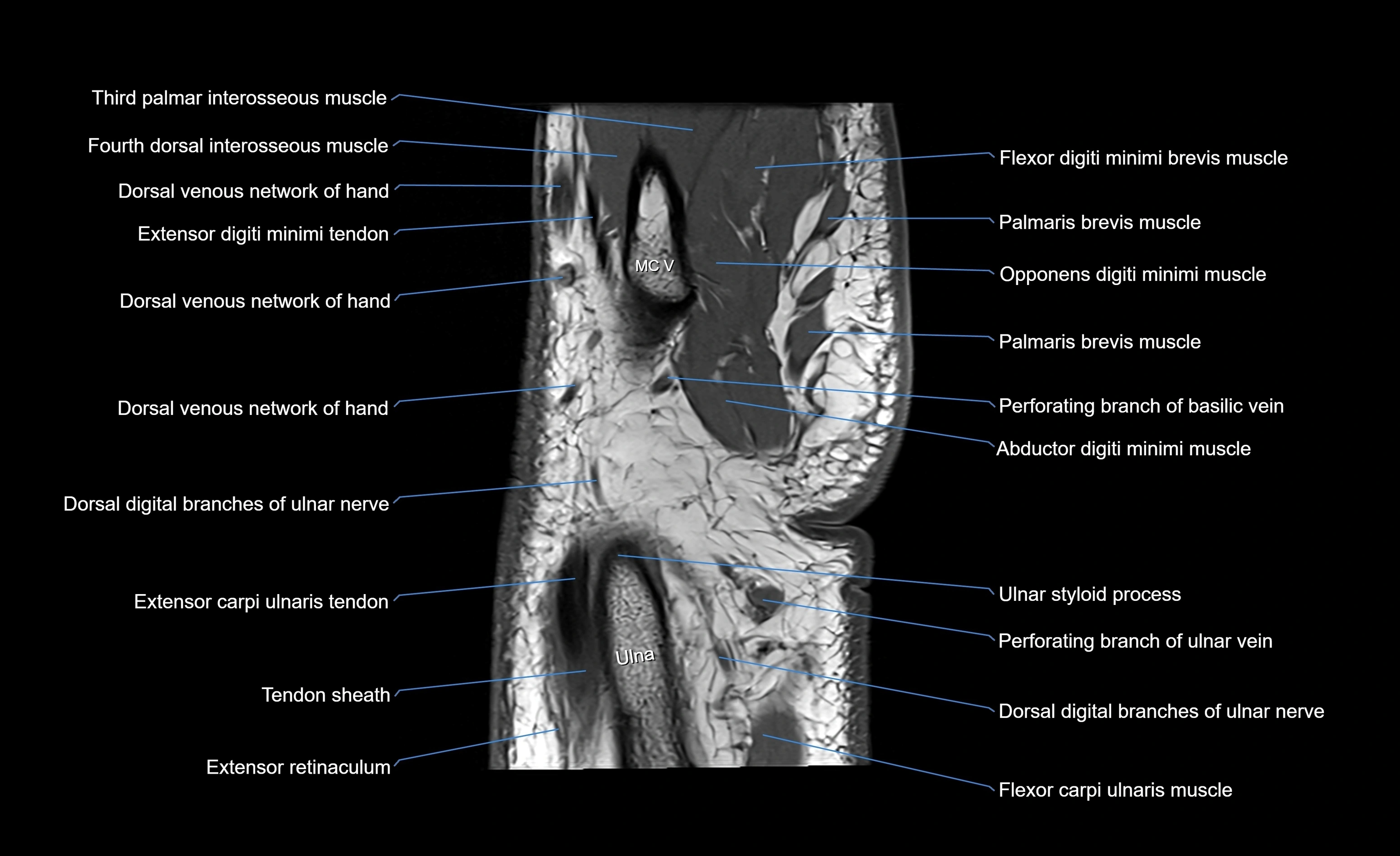
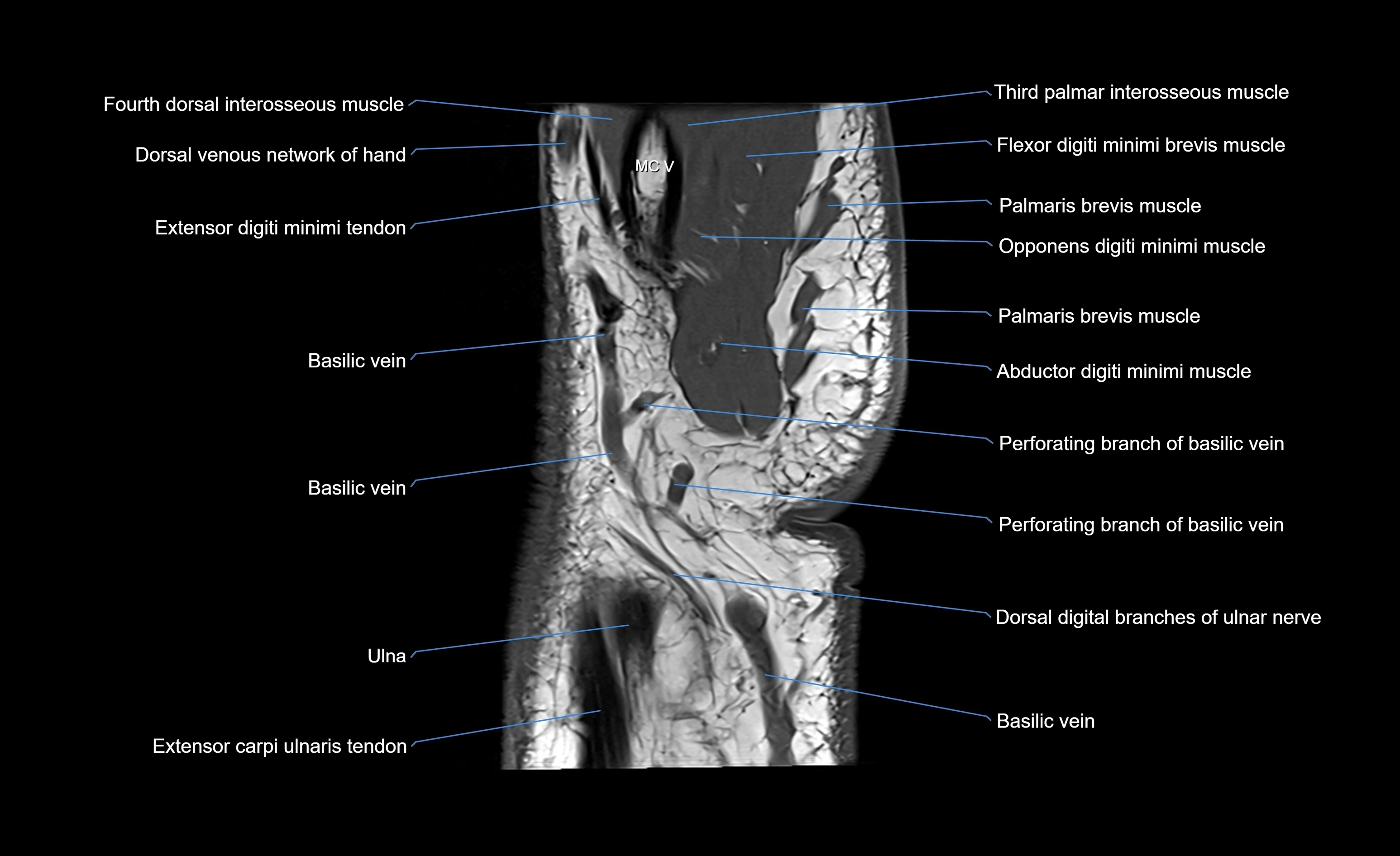
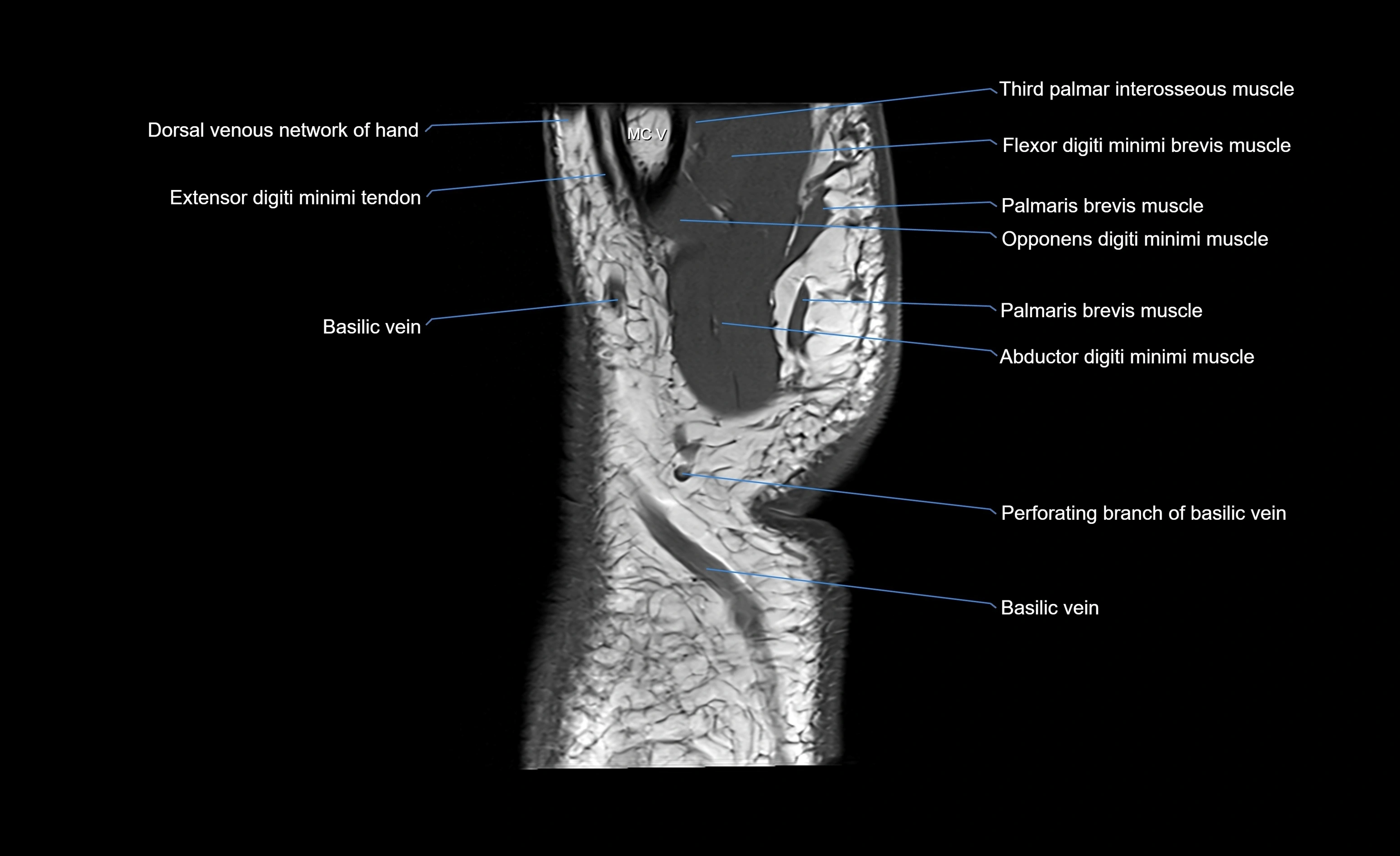
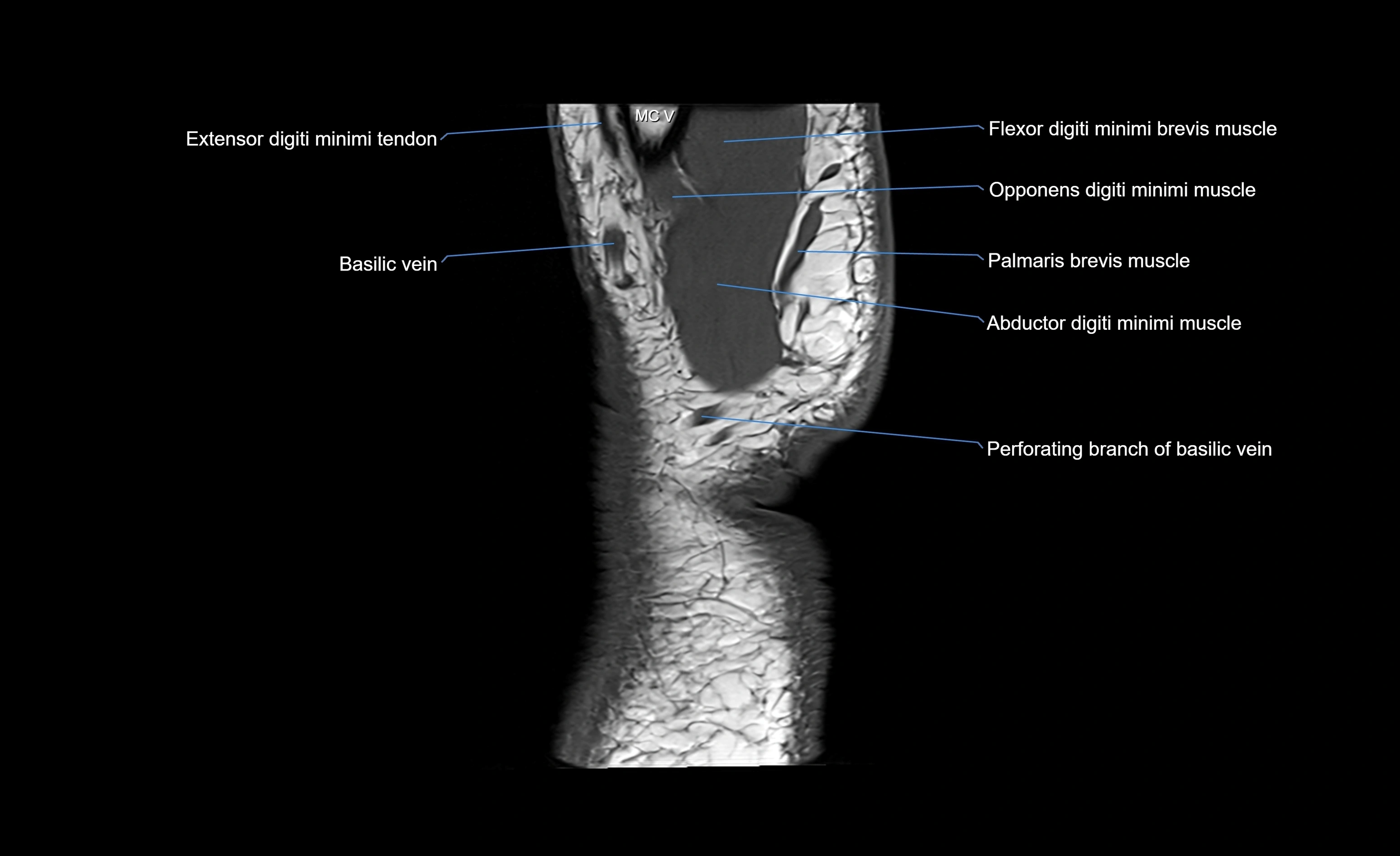
The abductor digiti minimi (ADM) is a superficial muscle located along the ulnar border of the palm in the hypothenar eminence of the hand. It is the most medial of the hypothenar muscles and lies superficial to the flexor digiti minimi brevis and opponens digiti minimi. The ADM plays a key role in abducting the little finger (fifth digit) away from the ring finger and contributes to grip and hand stability. It also assists in flexion of the metacarpophalangeal joint and extension of the interphalangeal joints through its connection with the extensor expansion.
Synonyms
-
Abductor of the little finger
-
Abductor minimi digiti
-
Abductor digiti quinti
Origin, Course, and Insertion
Origin: From the pisiform bone, the pisohamate ligament, and the tendon of the flexor carpi ulnaris.
Course: Muscle fibers run distally along the ulnar side of the hand, forming a flat tendon near the base of the little finger.
Insertion: Ulnar side of the base of the proximal phalanx of the fifth digit and the extensor expansion of the same finger.
Tendon Attachments
-
The tendon passes along the medial side of the fifth metacarpal and inserts into both the base of the proximal phalanx and dorsal digital expansion.
-
It may send a slip to the extensor digiti minimi tendon, facilitating combined extension and abduction.
Relations
Superficial: Palmar fascia and skin of the hypothenar eminence
Deep: Flexor digiti minimi brevis and opponens digiti minimi
Medially: Ulnar border of the hand
Laterally: Flexor tendons of the little finger
Proximally: Pisiform and ulnar artery and nerve branches
Distally: Proximal phalanx and extensor expansion of the little finger
Nerve Supply
Deep branch of the ulnar nerve (C8, T1)
Arterial Supply
Ulnar artery, via its deep palmar branch and ulnar digital artery to the little finger
Function
-
Abduction: Moves the little finger away from the ring finger at the metacarpophalangeal joint.
-
Flexion: Assists in flexing the proximal phalanx of the fifth digit.
-
Extension: Through the extensor expansion, aids in extending the distal phalanges.
-
Grip assistance: Contributes to hypothenar support and cupping of the hand during grasp.
-
Stabilization: Maintains the ulnar border of the palm during object manipulation.
Clinical Significance
-
Ulnar nerve injury: Paralysis or weakness of ADM leads to loss of little finger abduction and atrophy of the hypothenar eminence.
-
Muscle hypertrophy or fibrotic bands: May compress the ulnar nerve in Guyon’s canal.
-
Tendon tears or strain: Rare but can occur in repetitive hand use or trauma.
-
Surgical relevance: Important landmark in ulnar nerve decompression and hypothenar flap surgeries.
-
Imaging importance: MRI evaluates ADM for denervation changes, trauma, and space-occupying lesions in the hypothenar region.
MRI Appearance
T1-weighted images:
-
Normal muscle: intermediate signal intensity with distinct fascicular pattern.
-
Tendon: low signal (dark) extending to proximal phalanx of the little finger.
-
Fatty tissue of hypothenar region: bright, providing contrast with muscle.
-
Chronic denervation: increased intramuscular fat causing hyperintense signal.
T2-weighted images:
-
Normal muscle: intermediate-to-dark signal, slightly darker than on T1.
-
Tendon: uniformly dark.
-
Pathology: edema or inflammation produces bright hyperintense signal in acute injury or myositis.
STIR:
-
Normal muscle: intermediate-to-dark signal.
-
Pathology: bright hyperintense signal indicating edema, strain, or nerve-related denervation changes.
Proton Density Fat-Saturated (PD FS):
-
Normal ADM: intermediate-to-dark signal with smooth margins.
-
Muscle strain or tendinitis: bright focal hyperintensity within or around tendon.
-
Excellent for identifying subtle peritendinous edema or fascial inflammation.
T1 Fat-Sat Post-Contrast:
-
Normal muscle: mild homogeneous enhancement.
-
Active inflammation or tear: focal enhancement at musculotendinous junction.
-
Denervation or chronic fibrosis: little to no enhancement with volume loss and fatty infiltration.
CT Appearance
Non-Contrast CT:
-
Muscle: soft-tissue density, well defined in the hypothenar region.
-
Tendon: linear low-density structure extending to the base of the little finger.
-
Calcification or chronic scarring may appear as localized high-density foci.
-
Useful for assessing bony attachment sites at the pisiform and proximal phalanx.
Post-Contrast CT (standard):
-
Normal muscle: homogeneous mild enhancement.
-
Inflamed or injured muscle: increased enhancement and surrounding soft-tissue edema.
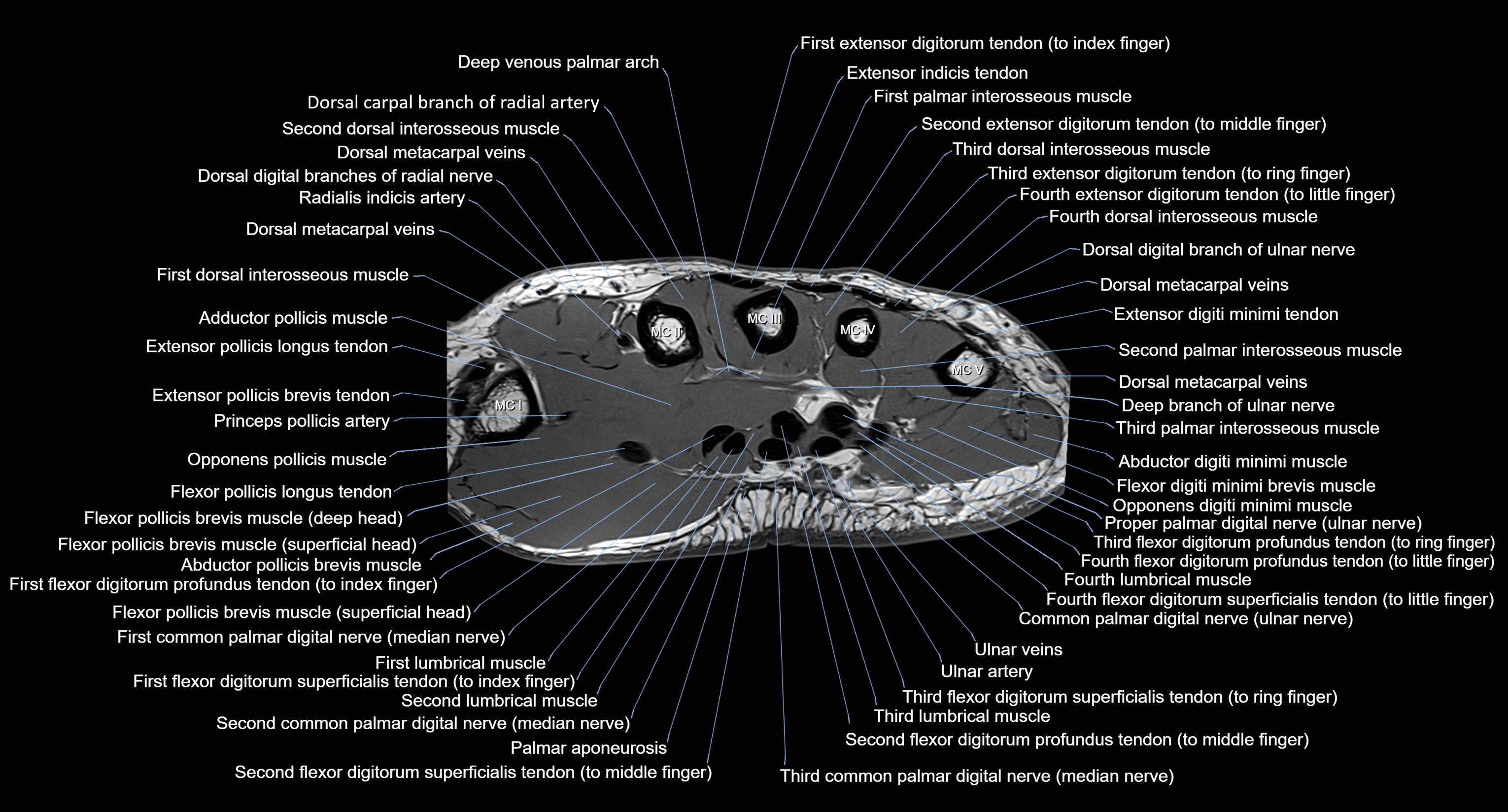
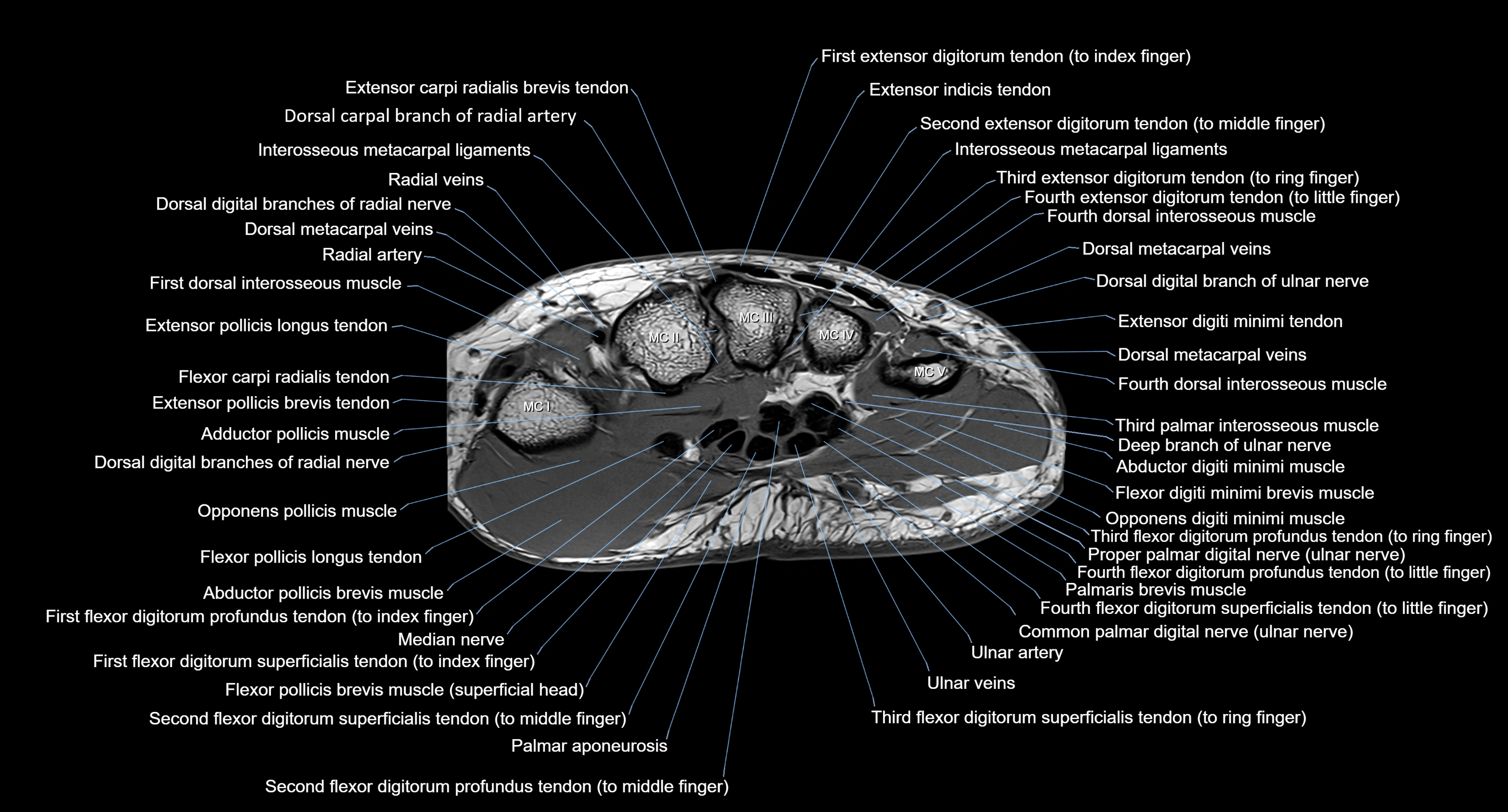
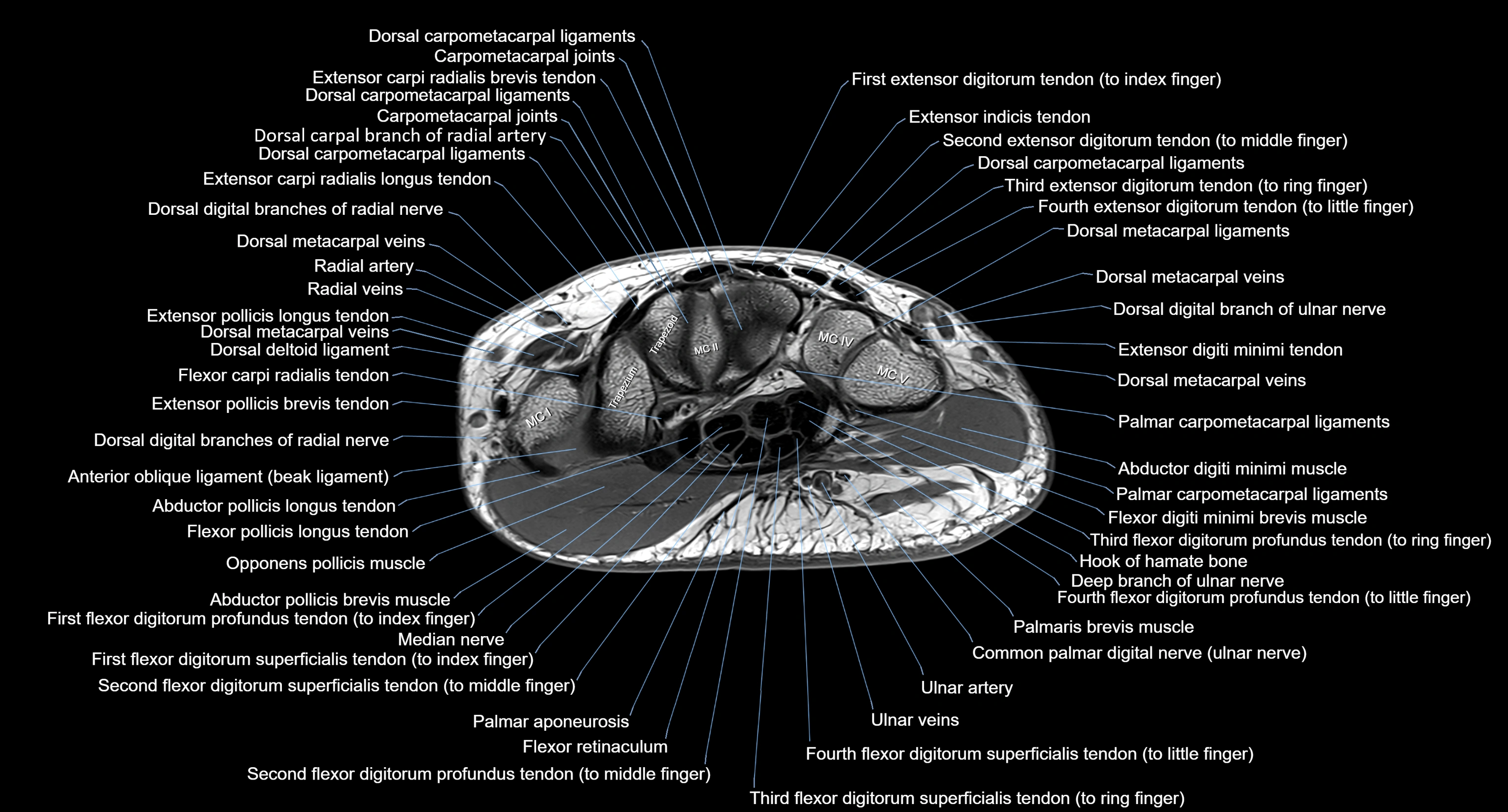
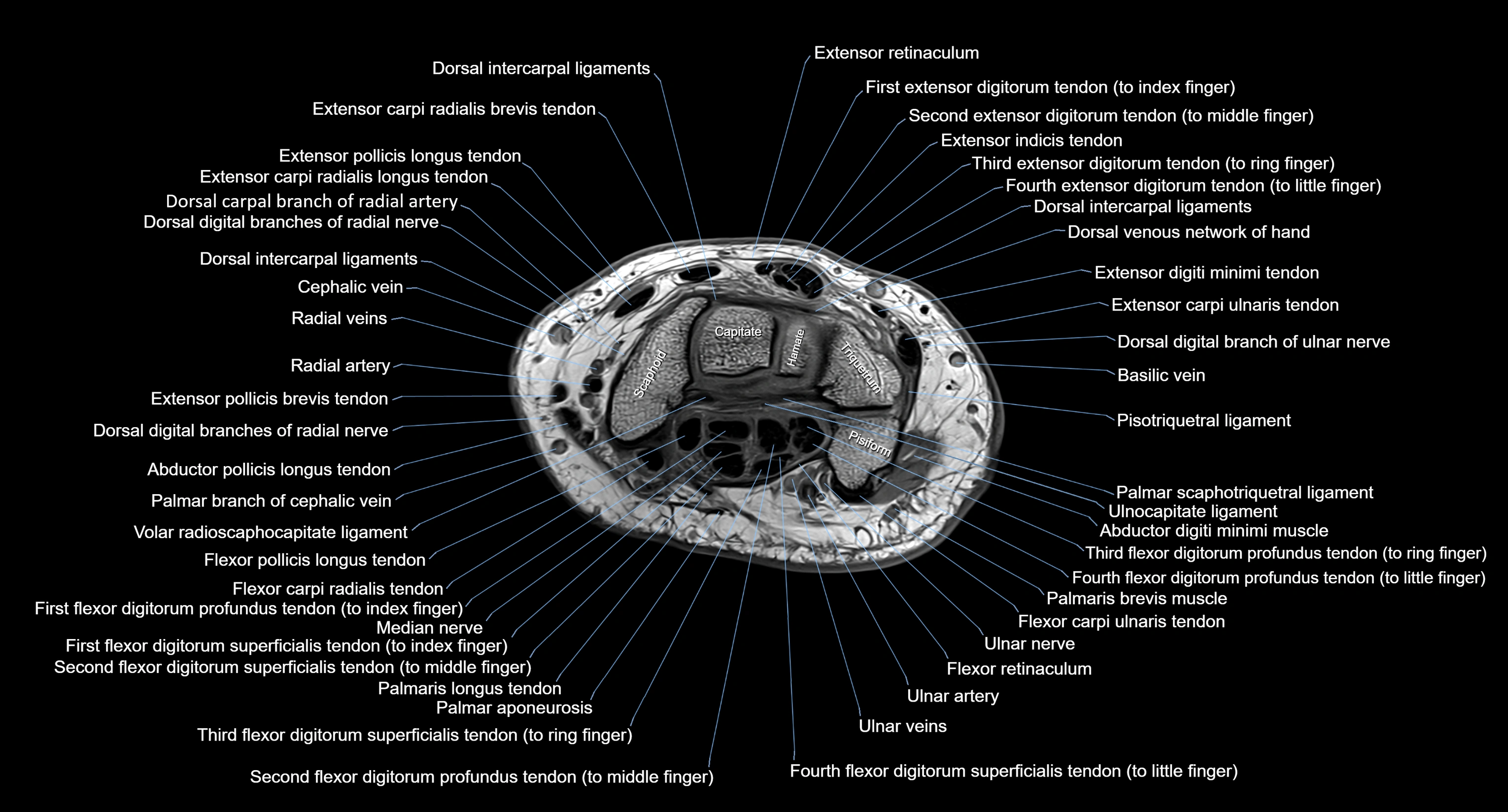
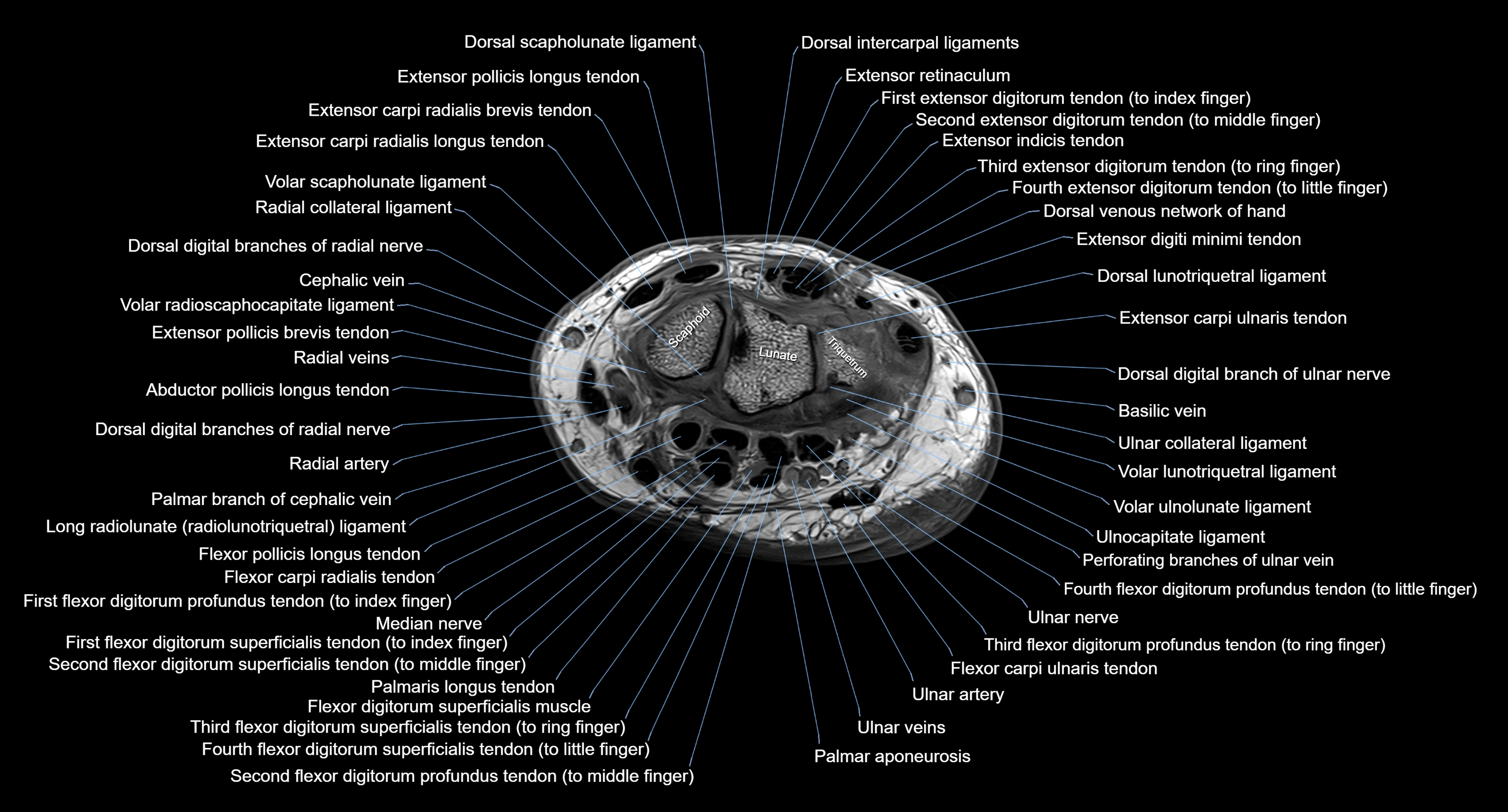
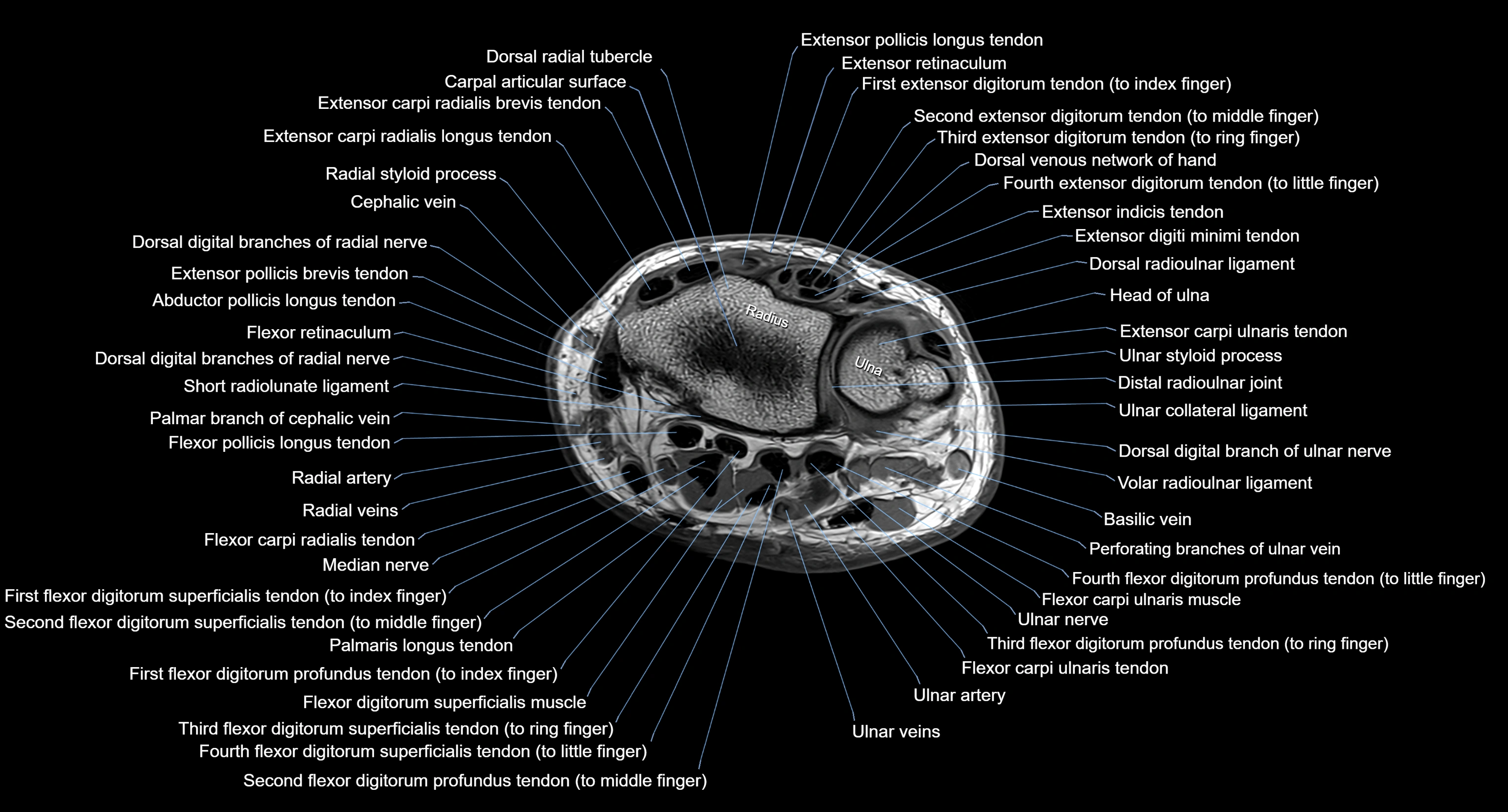
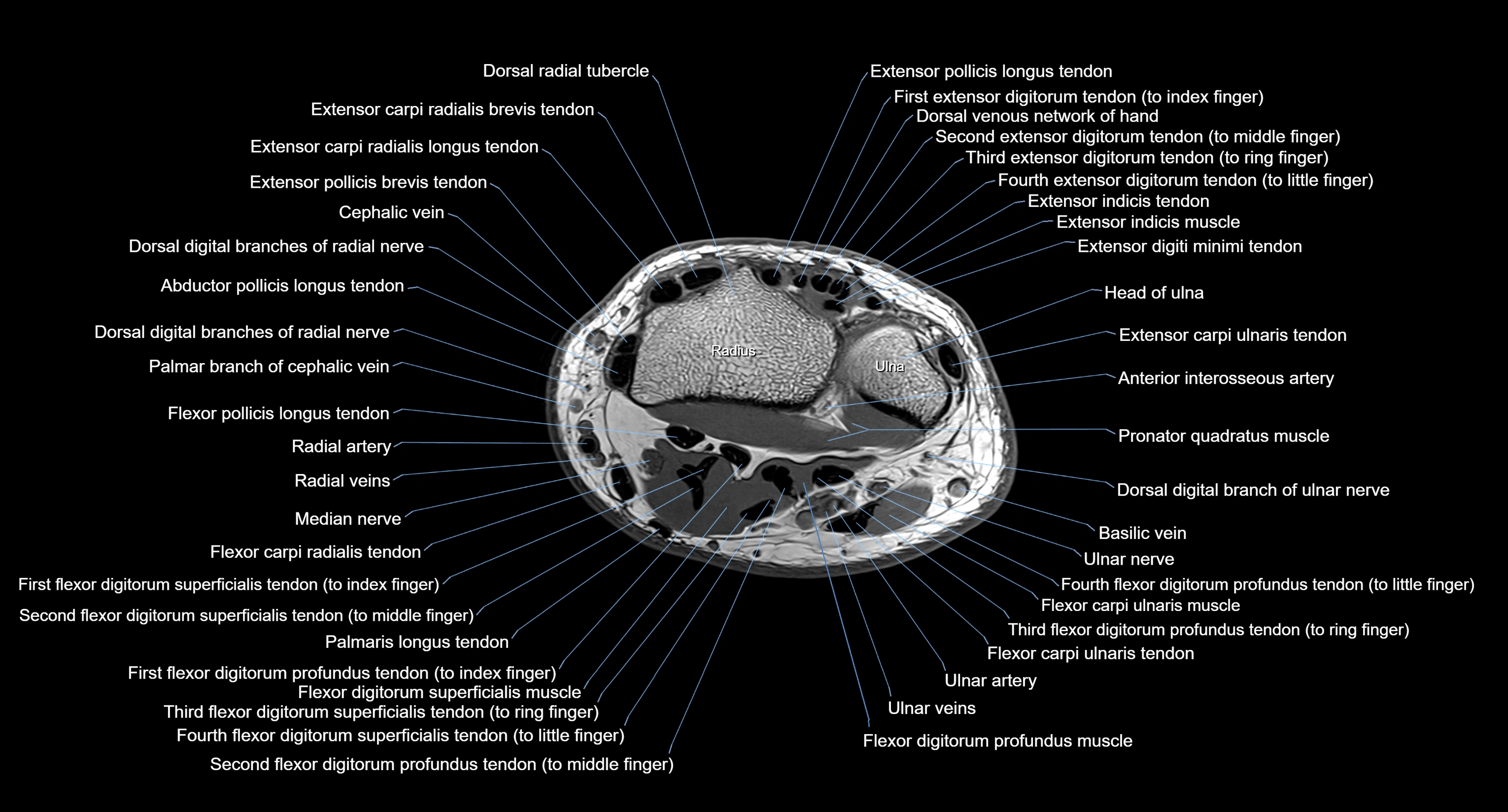
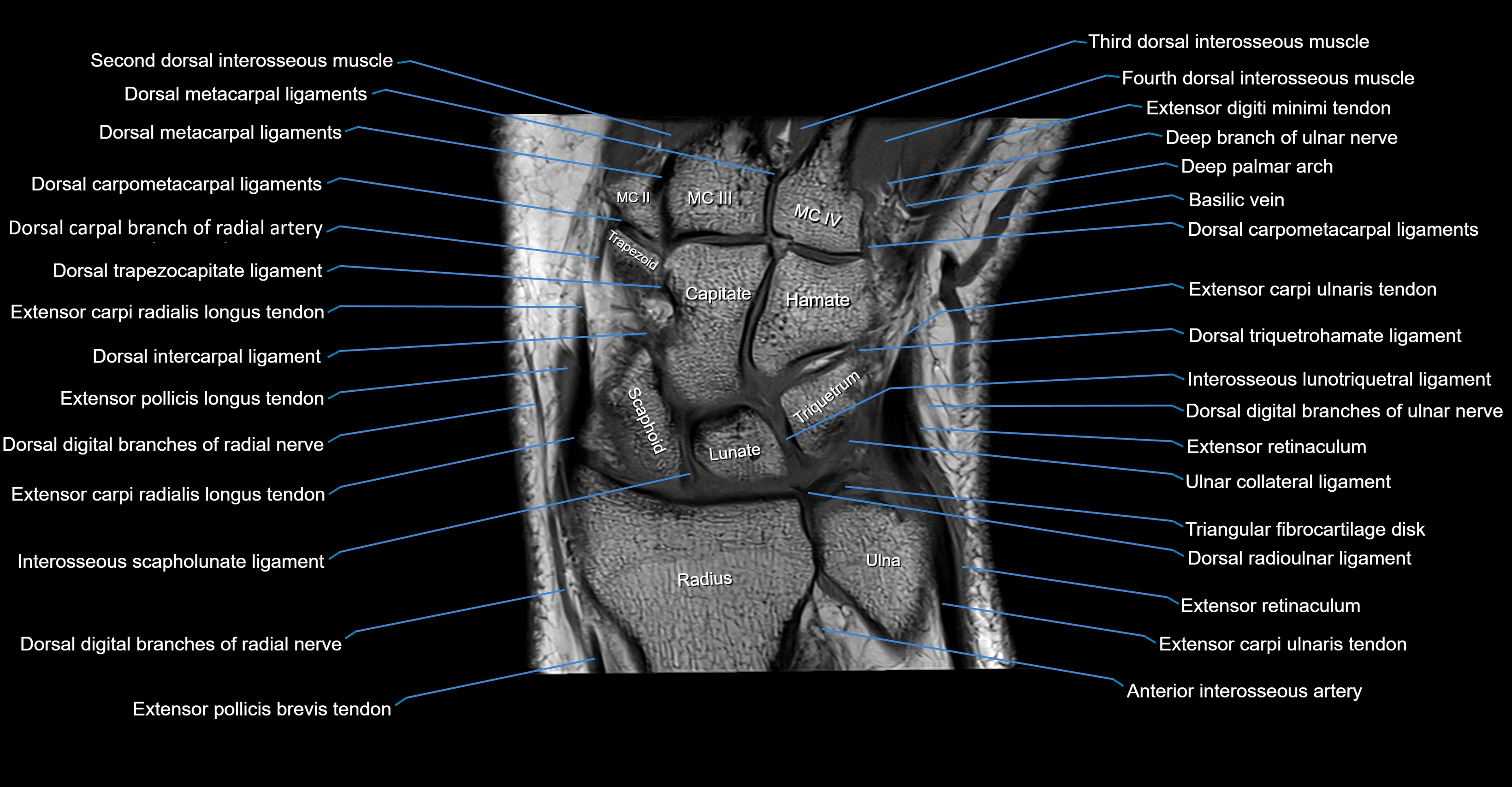
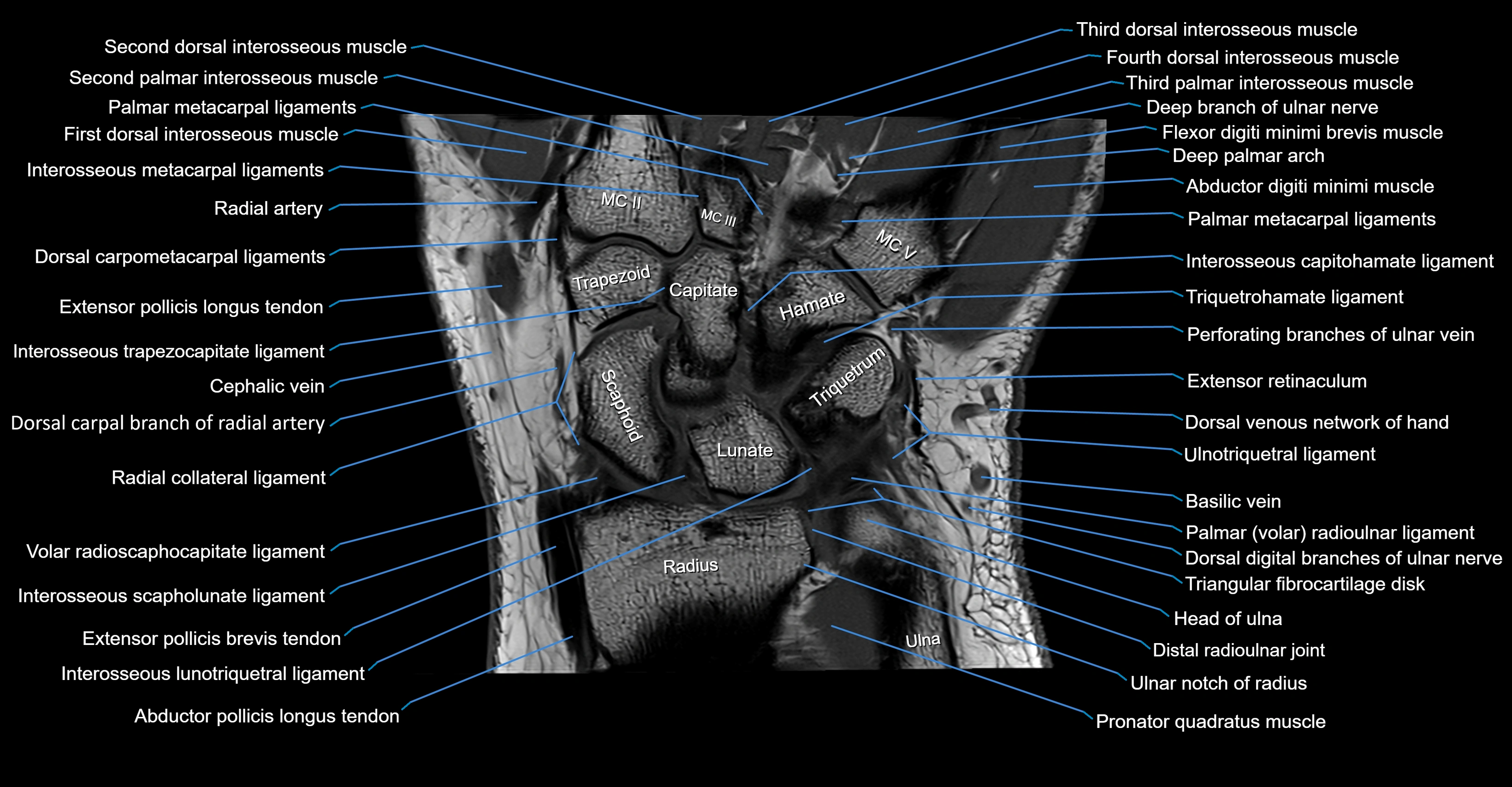
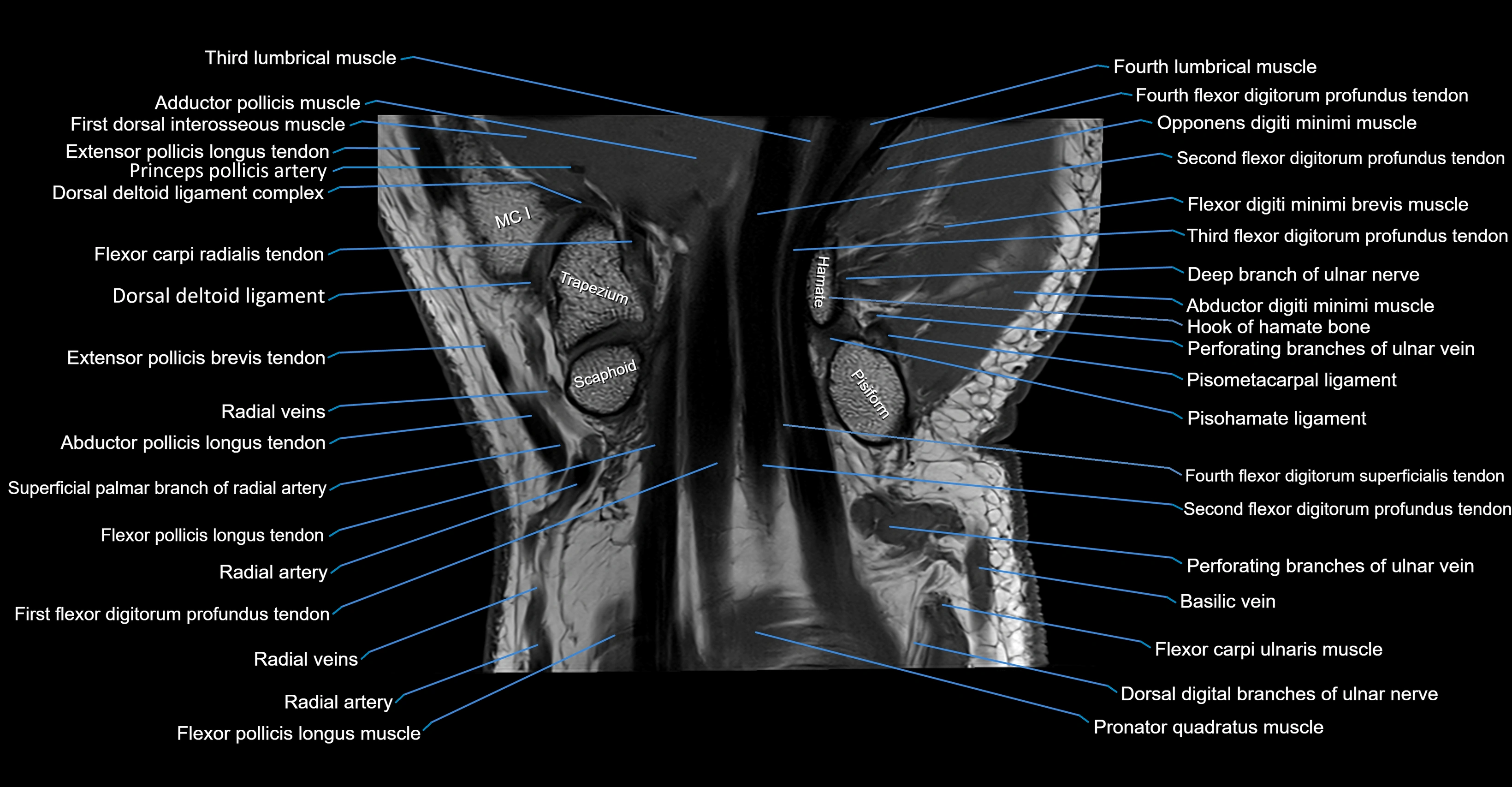
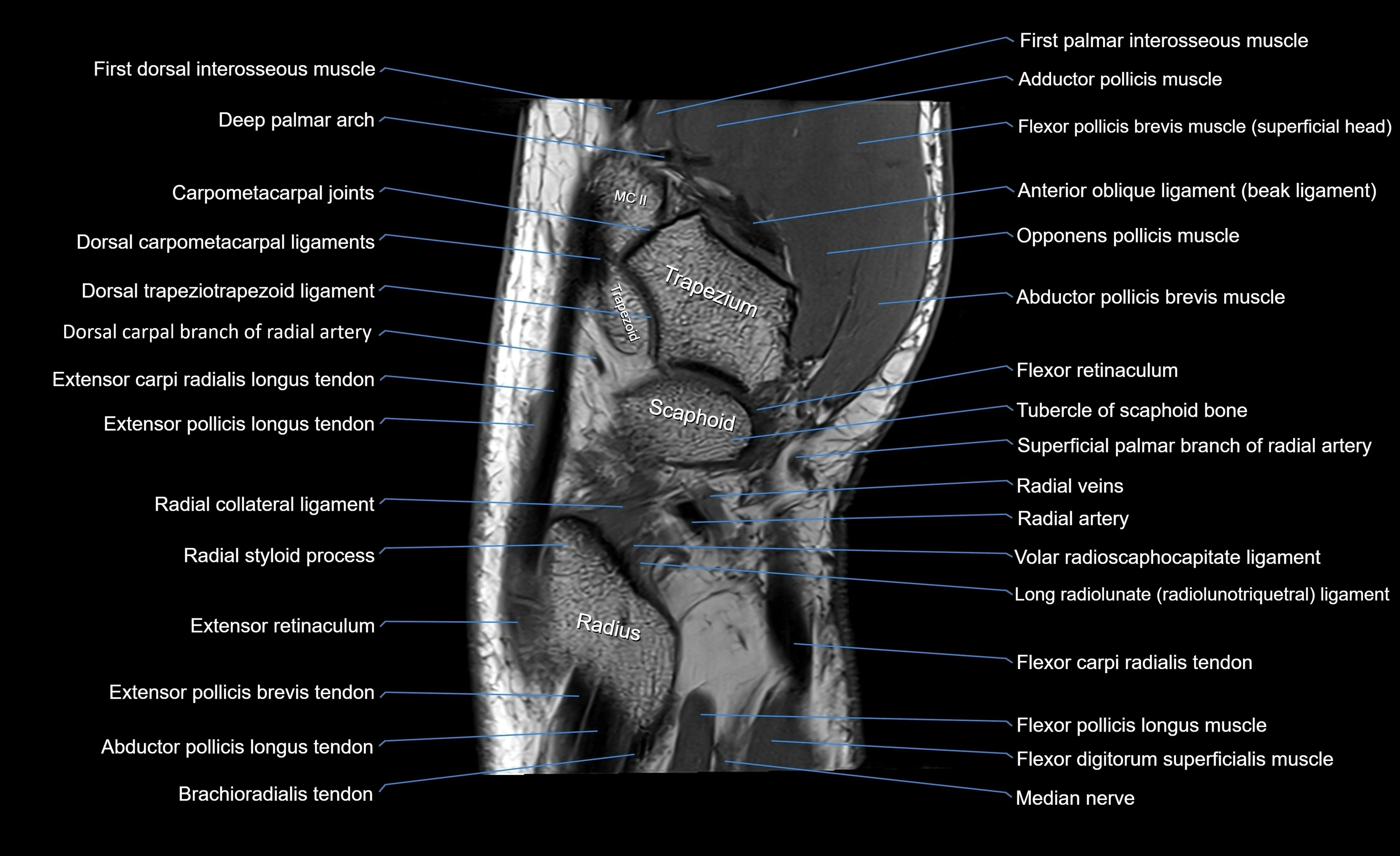
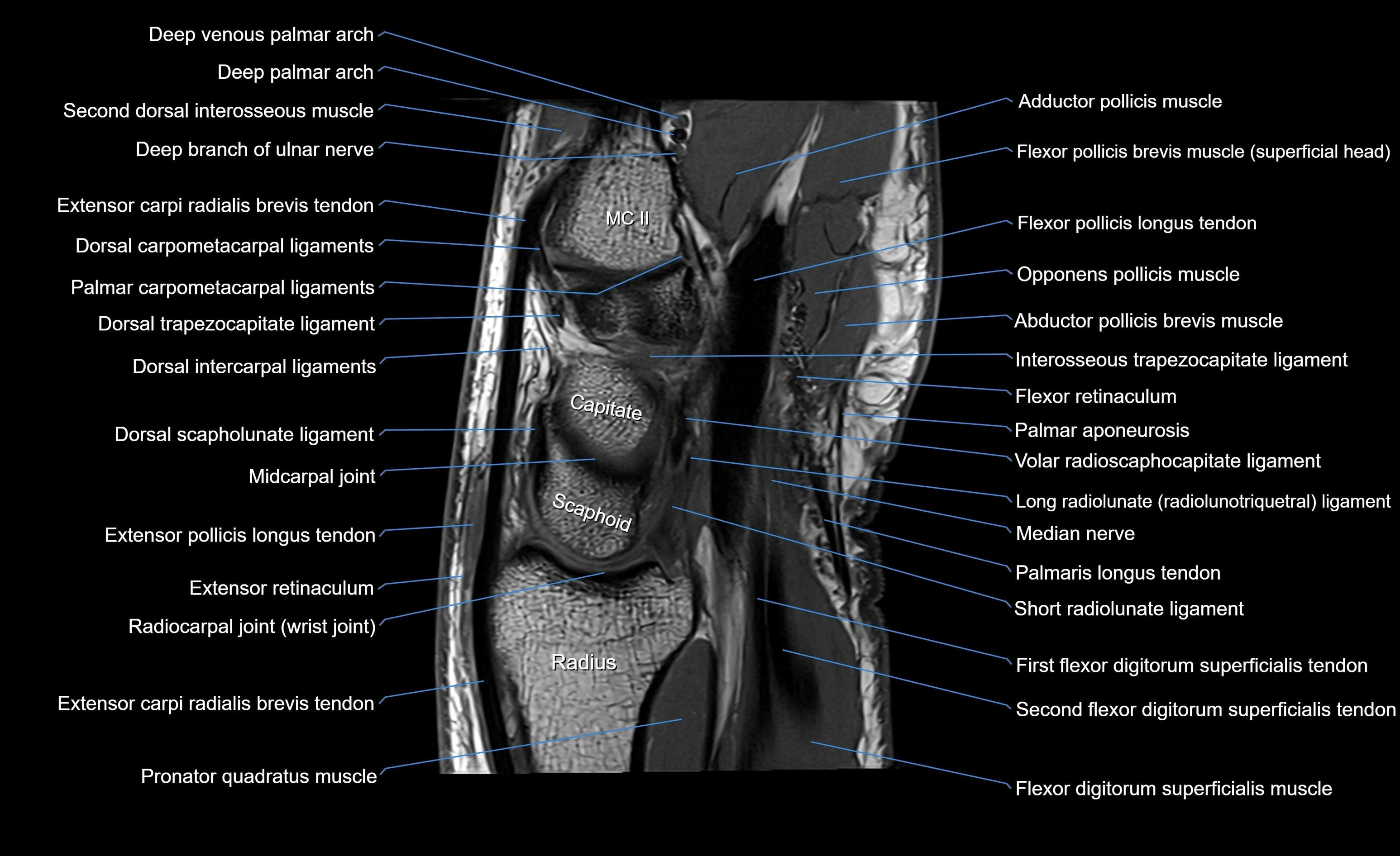
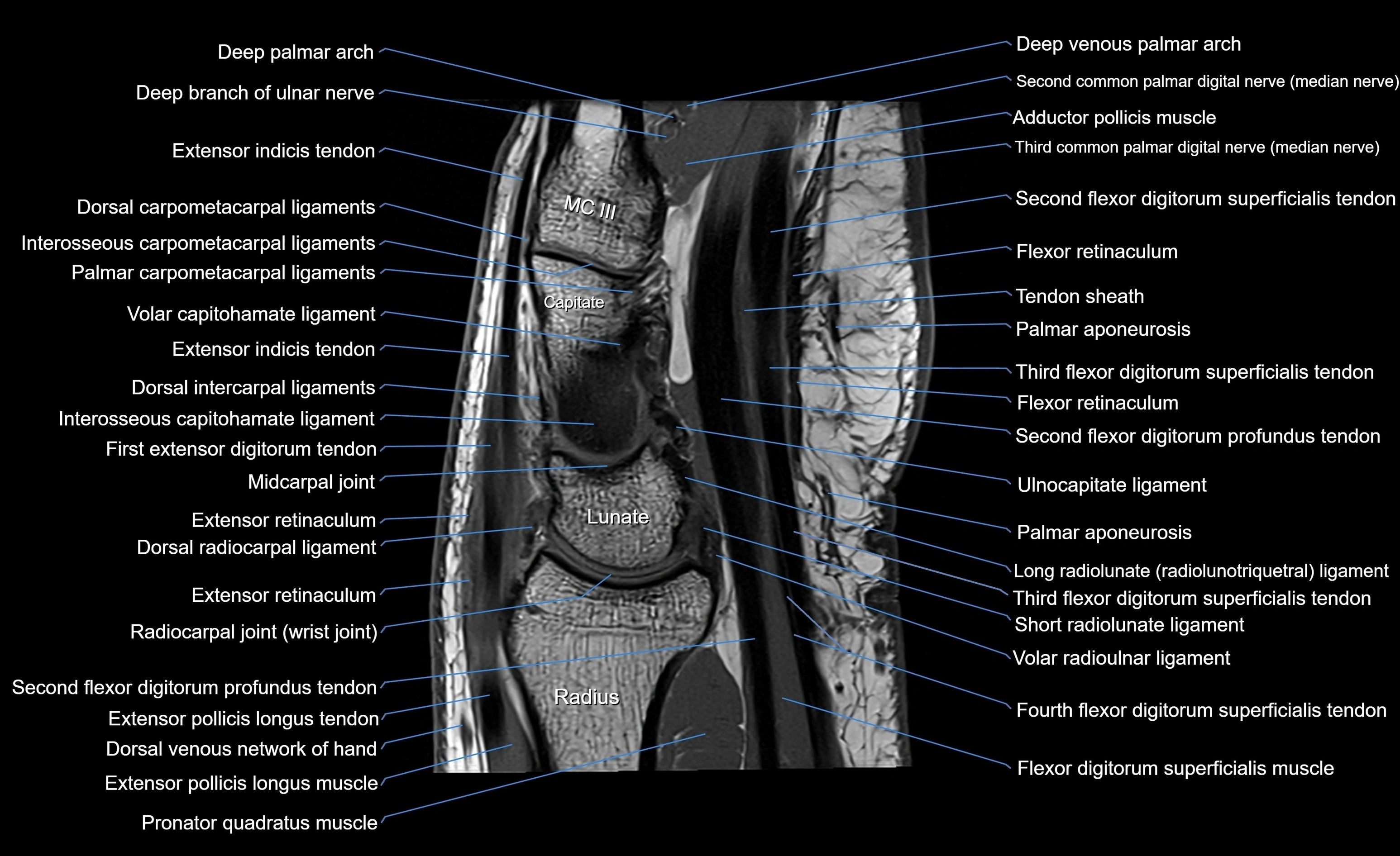
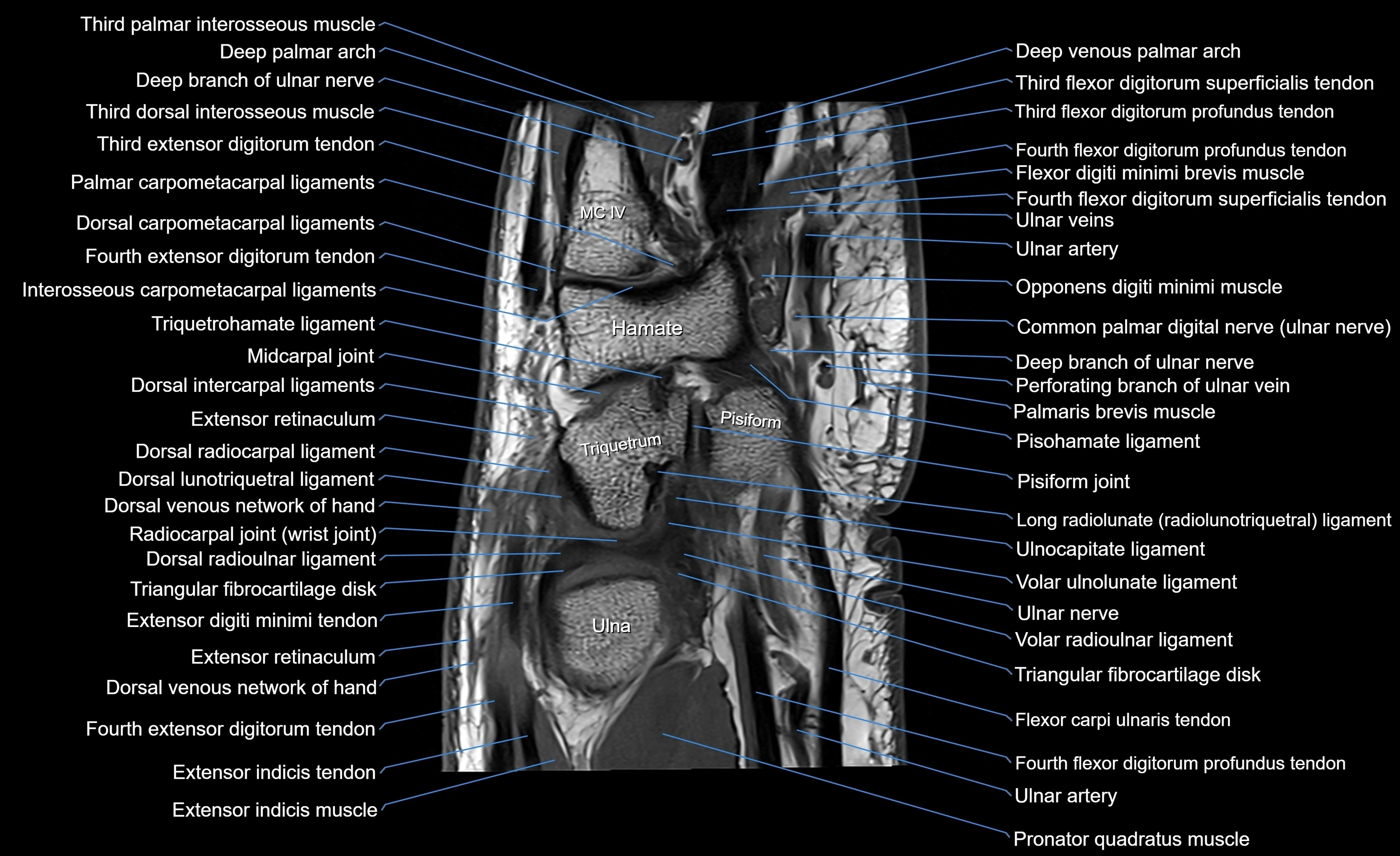
MRI image

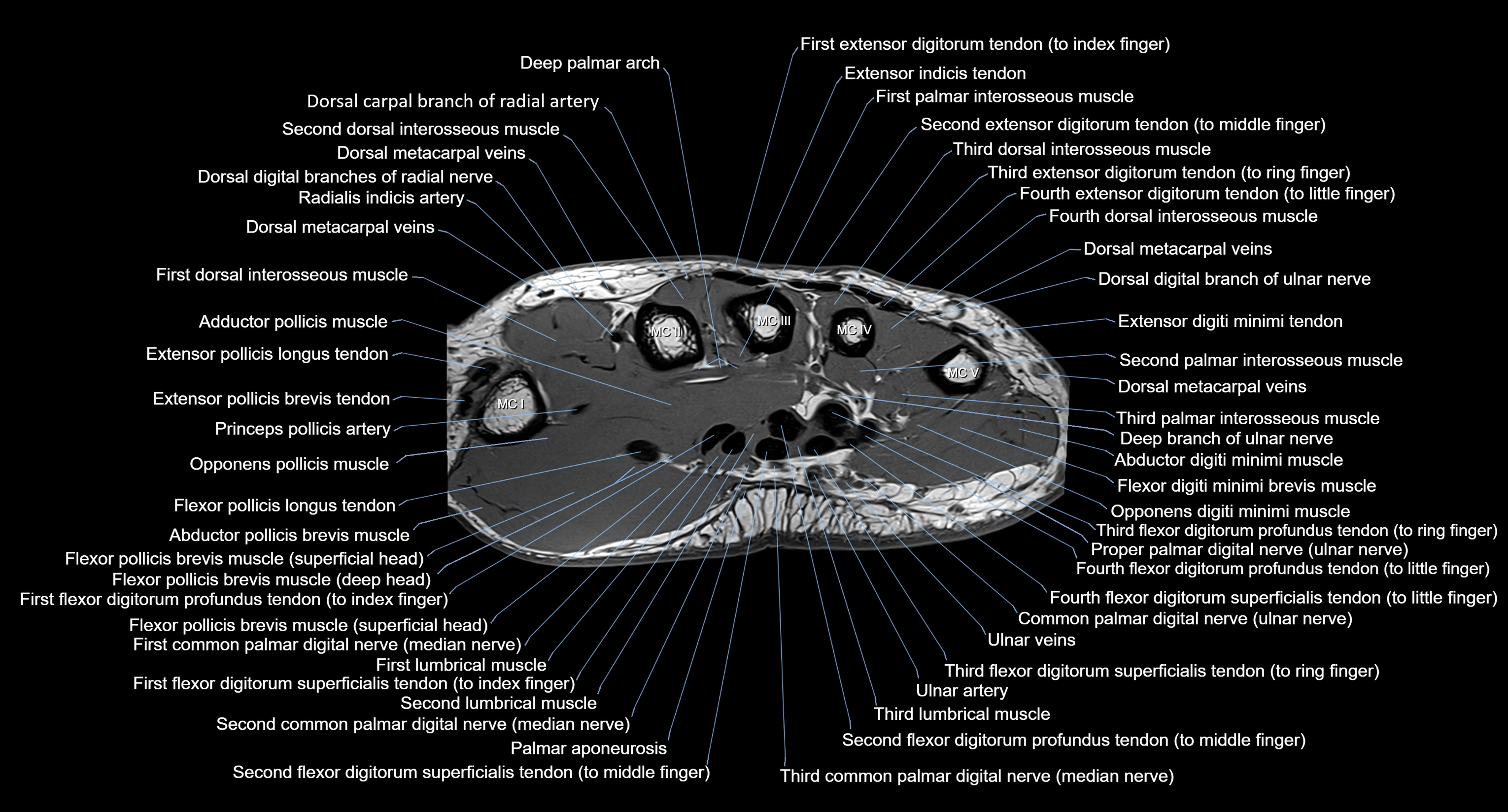
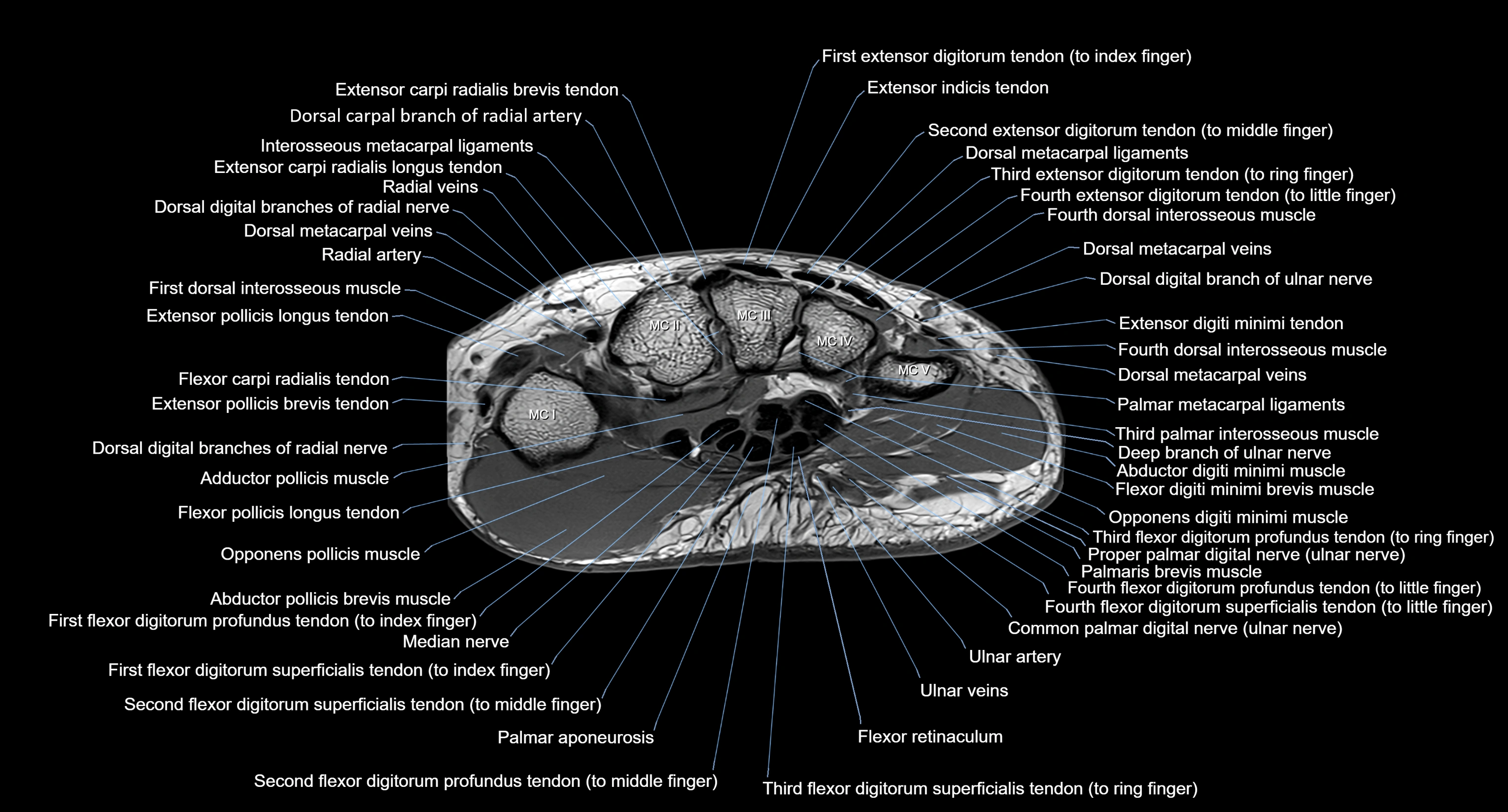
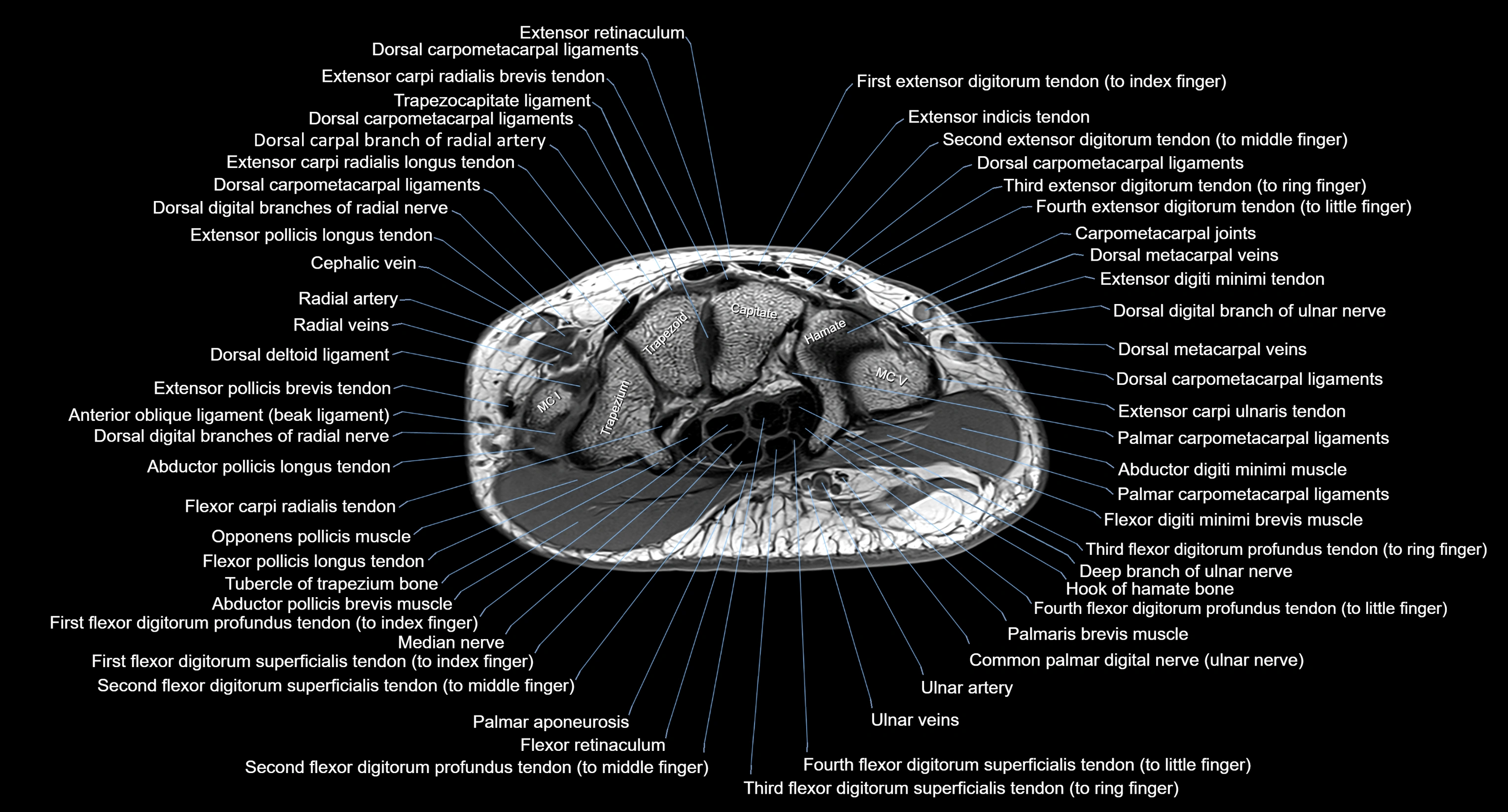
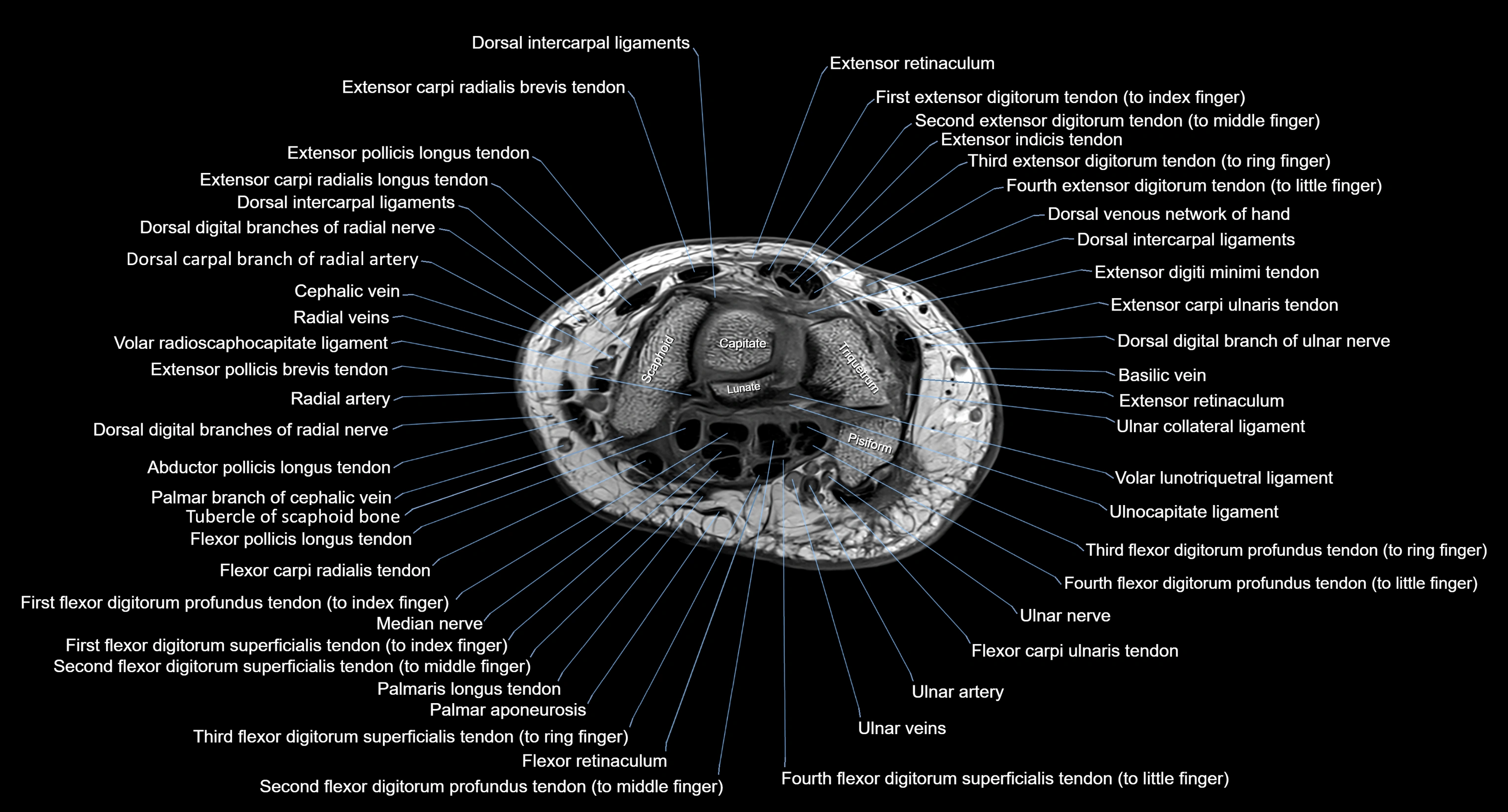
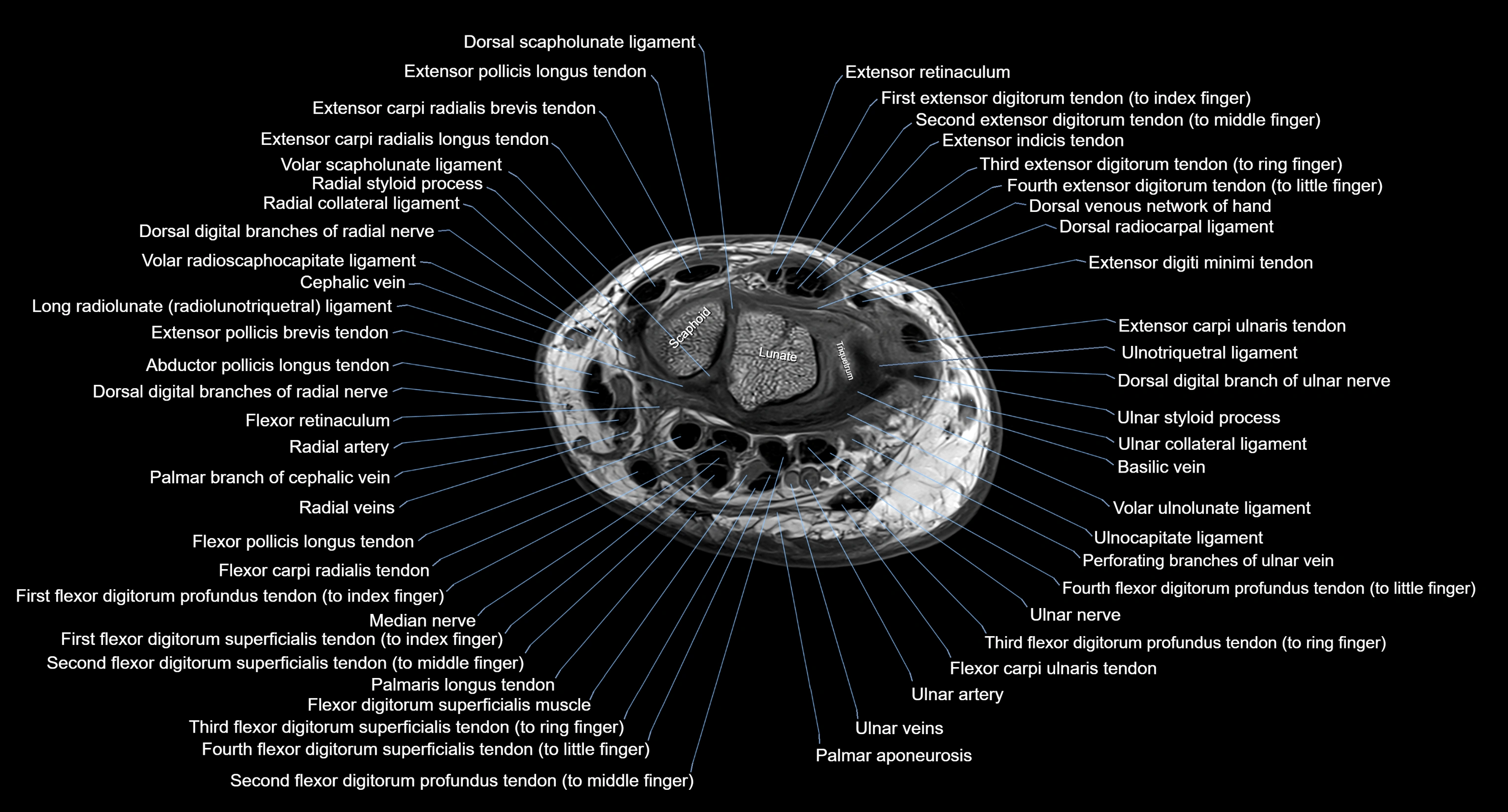
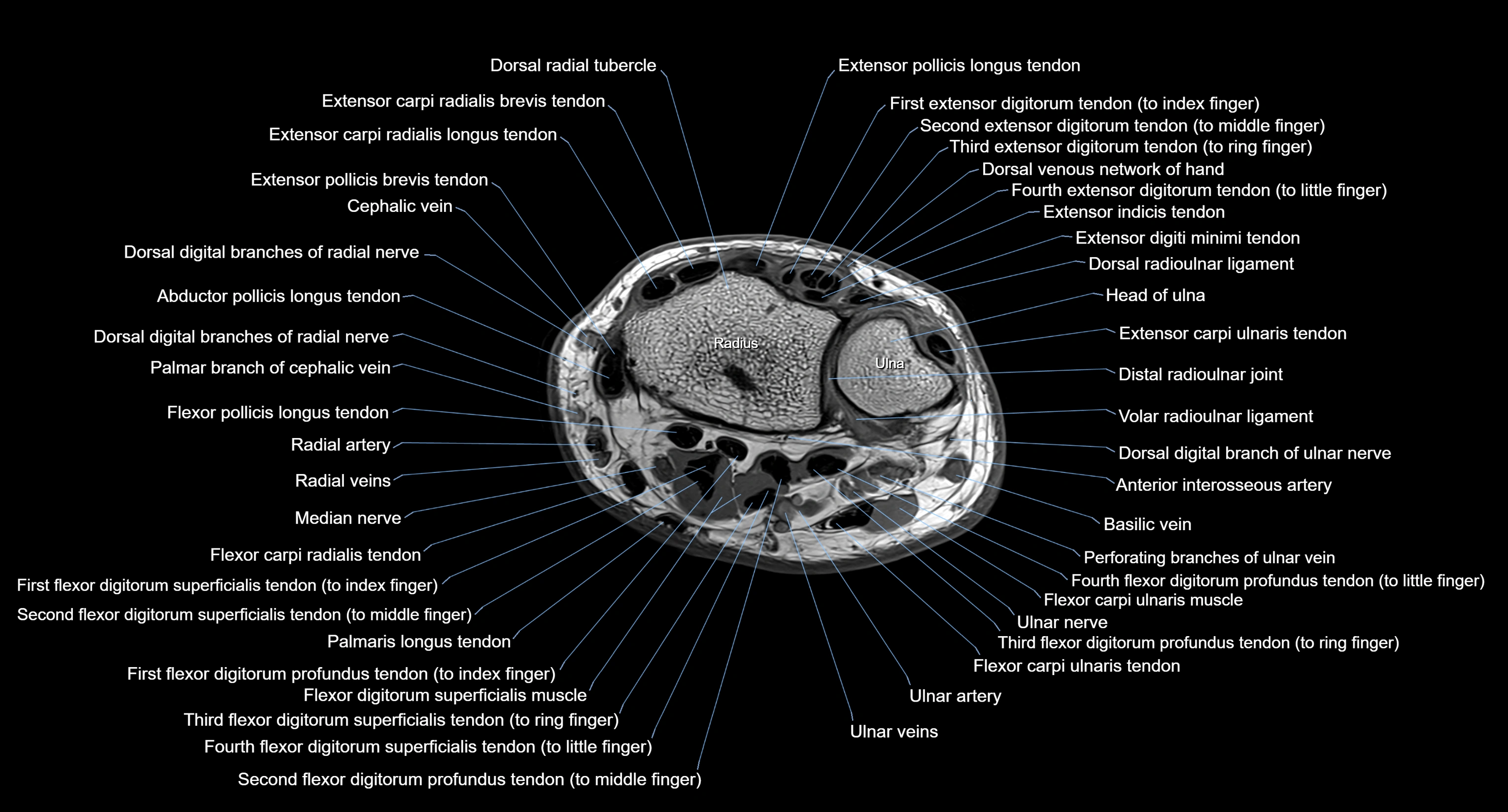
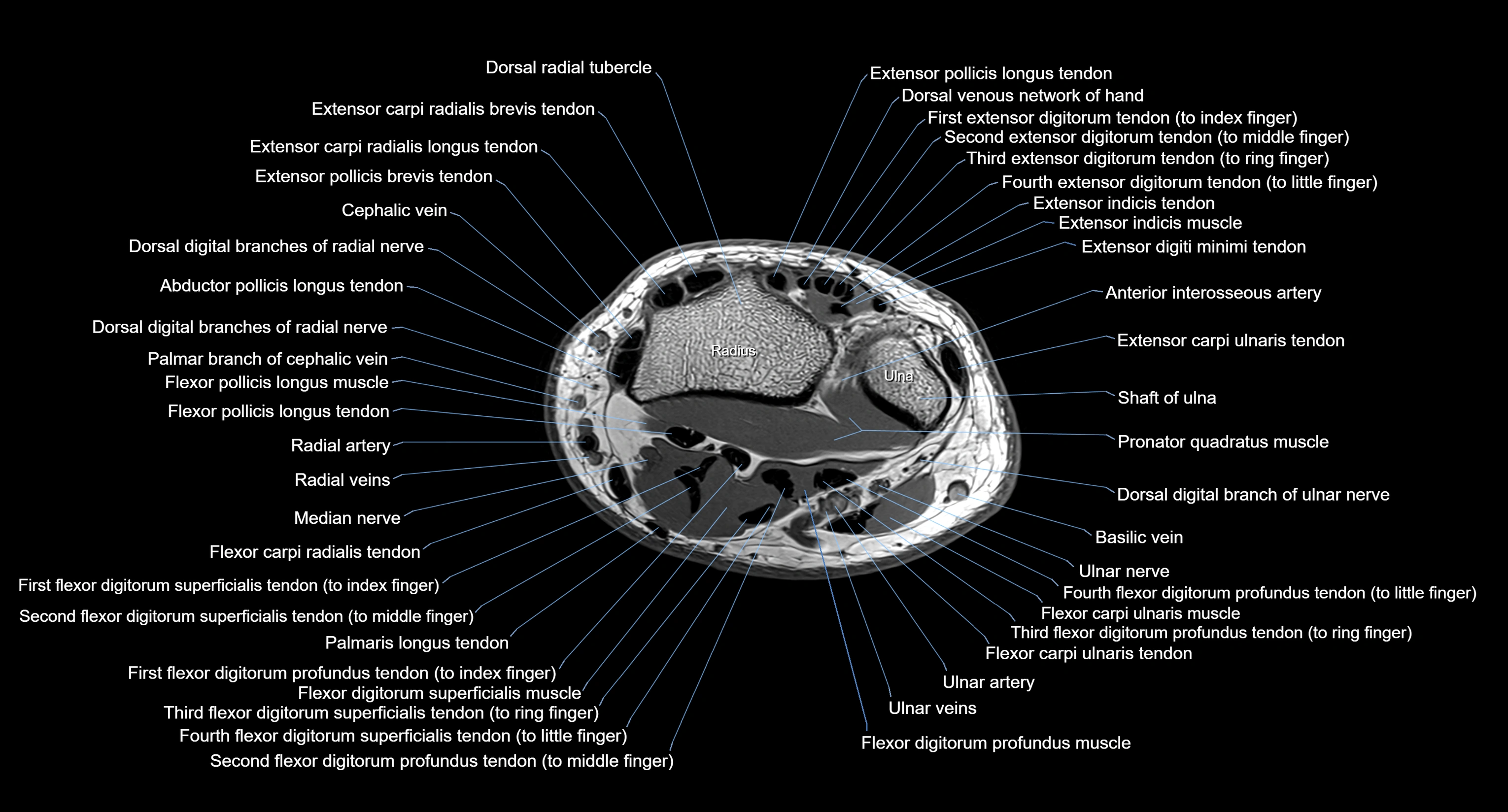
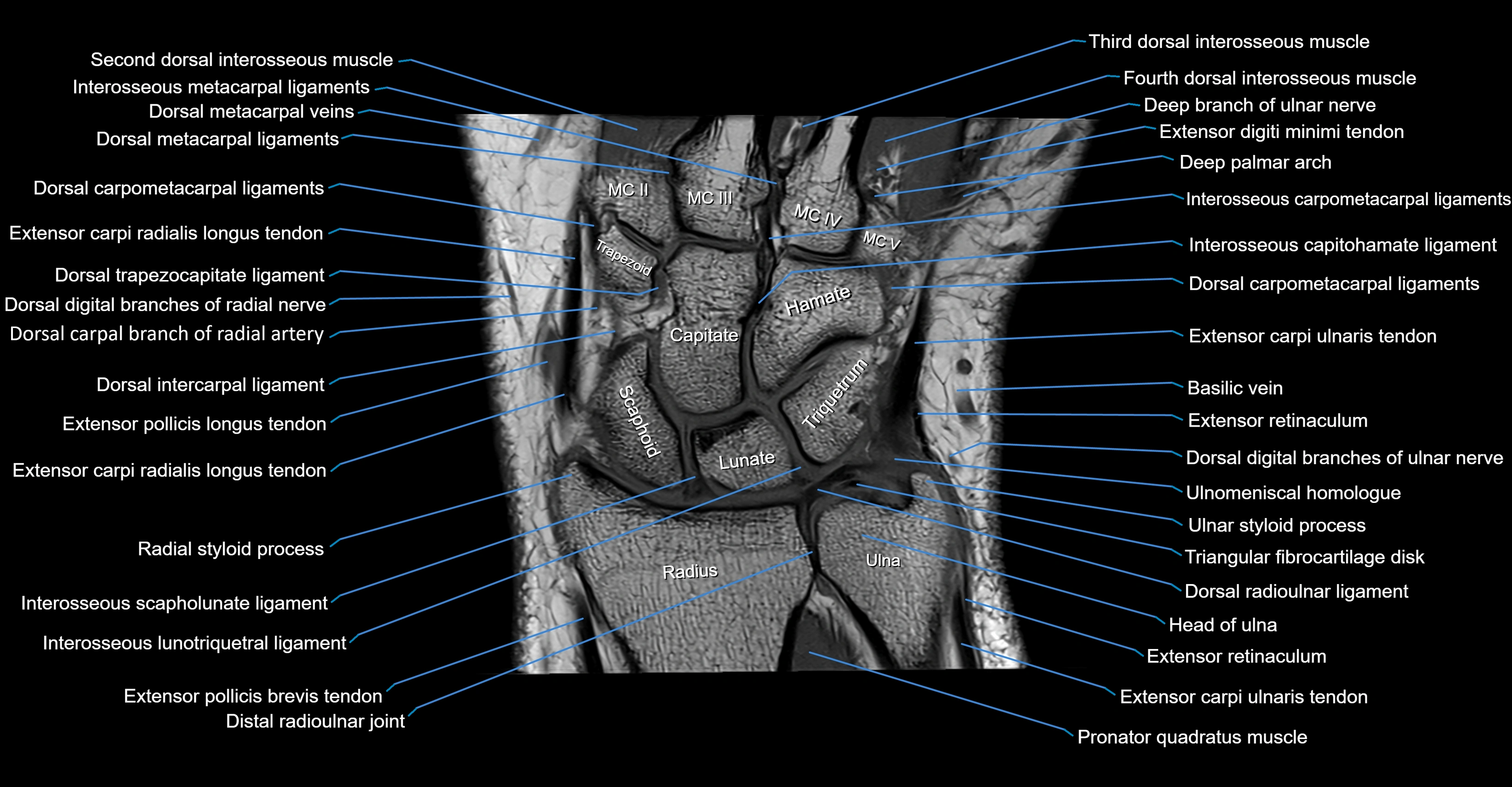
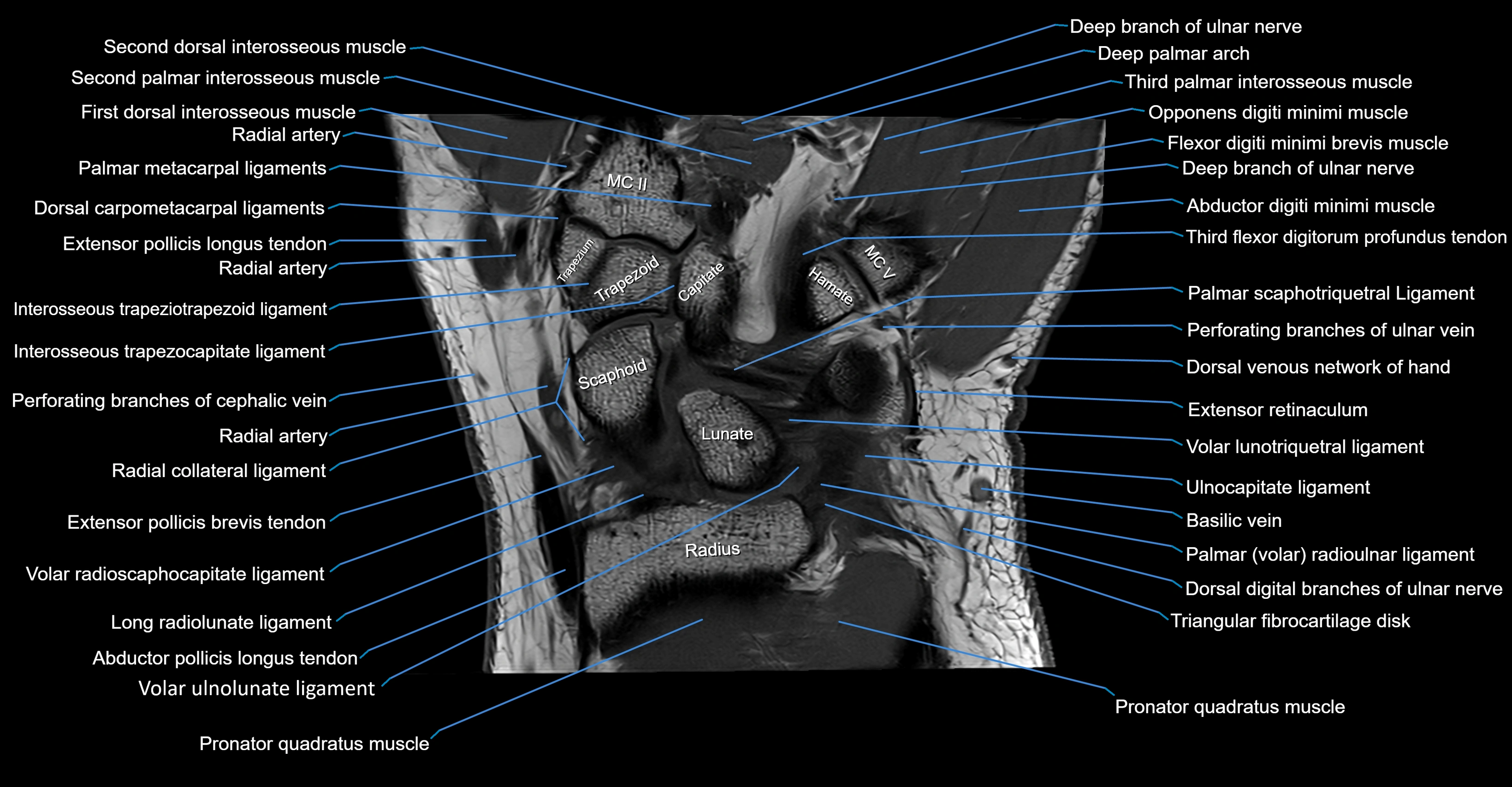
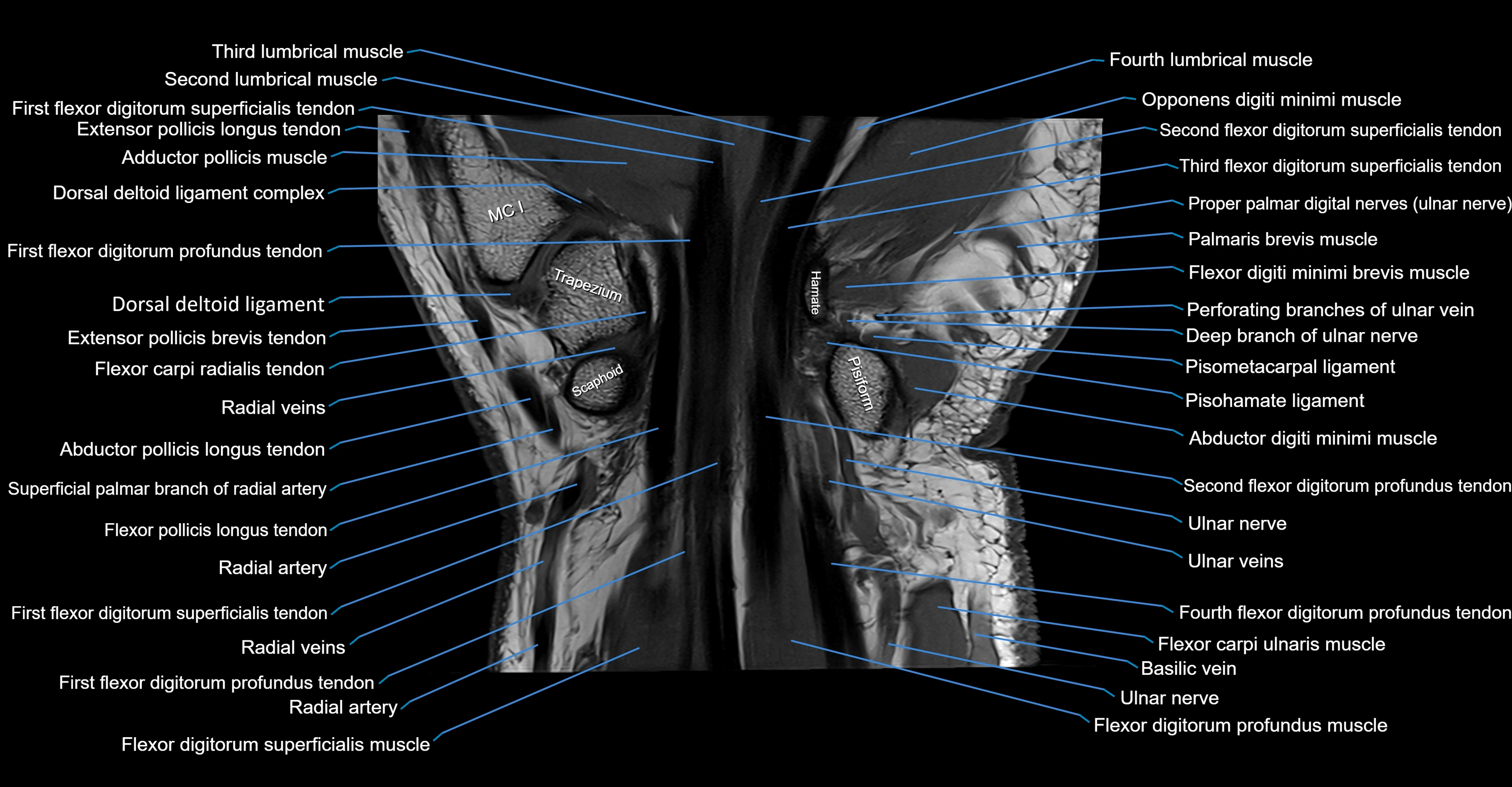
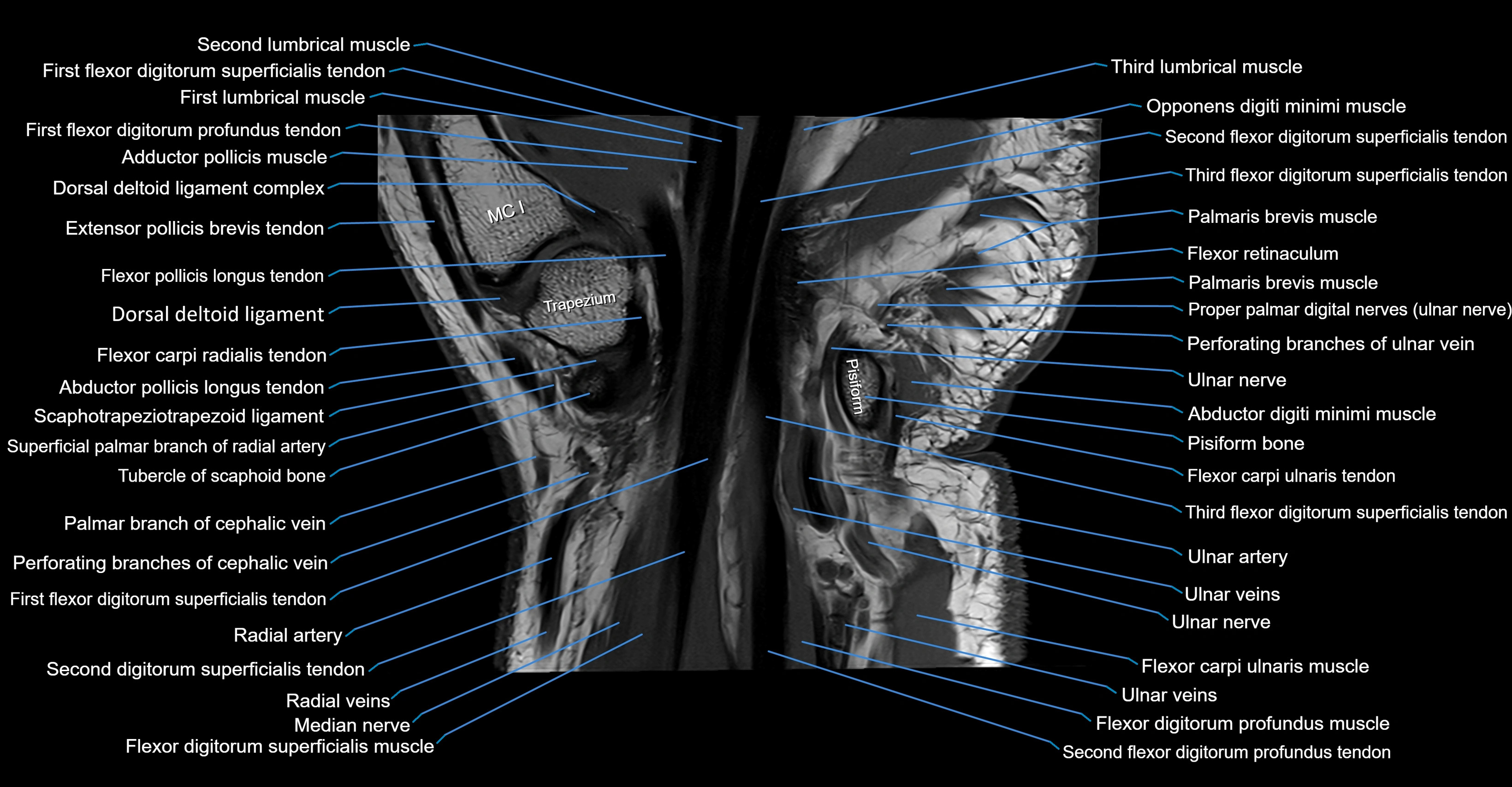
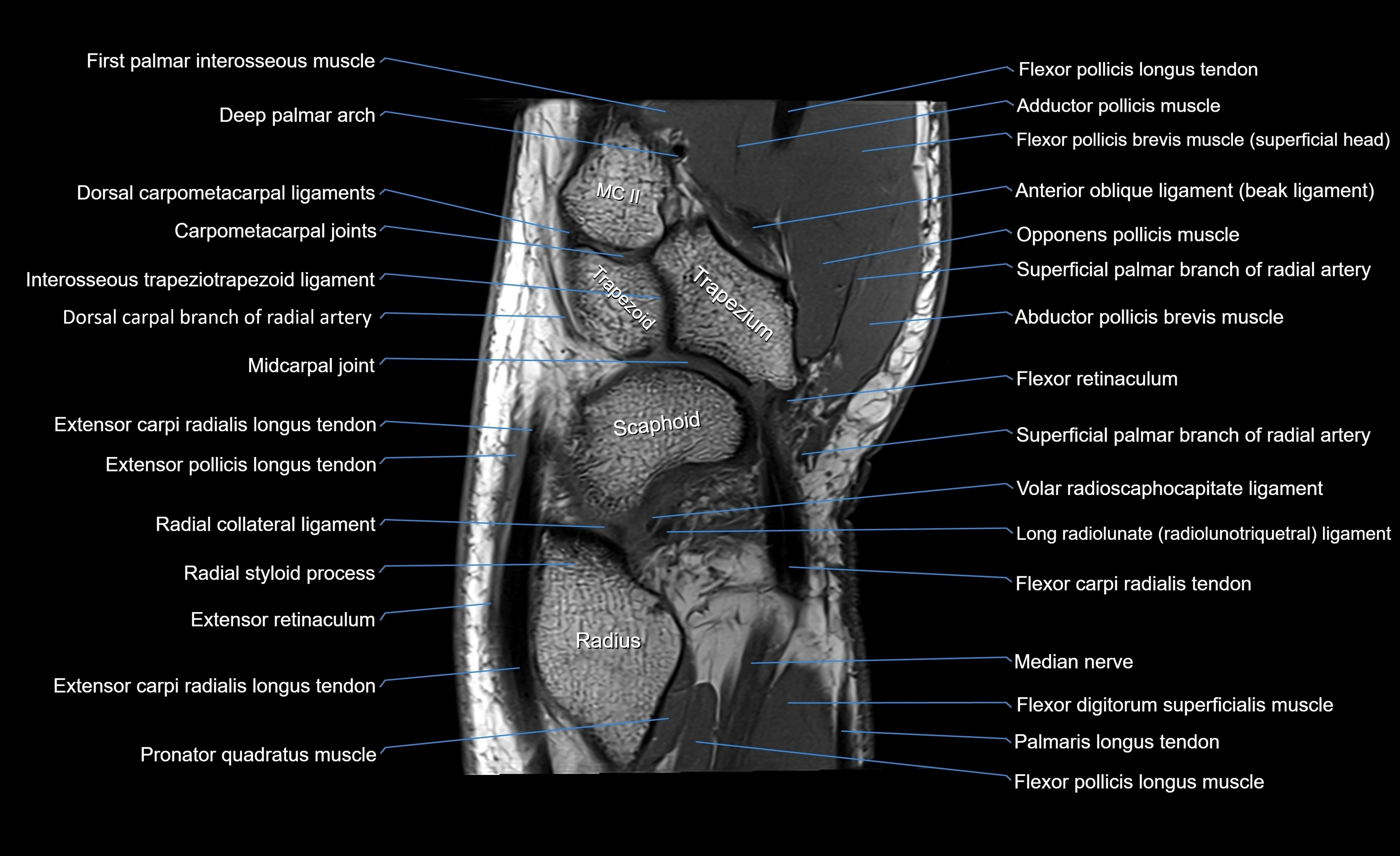
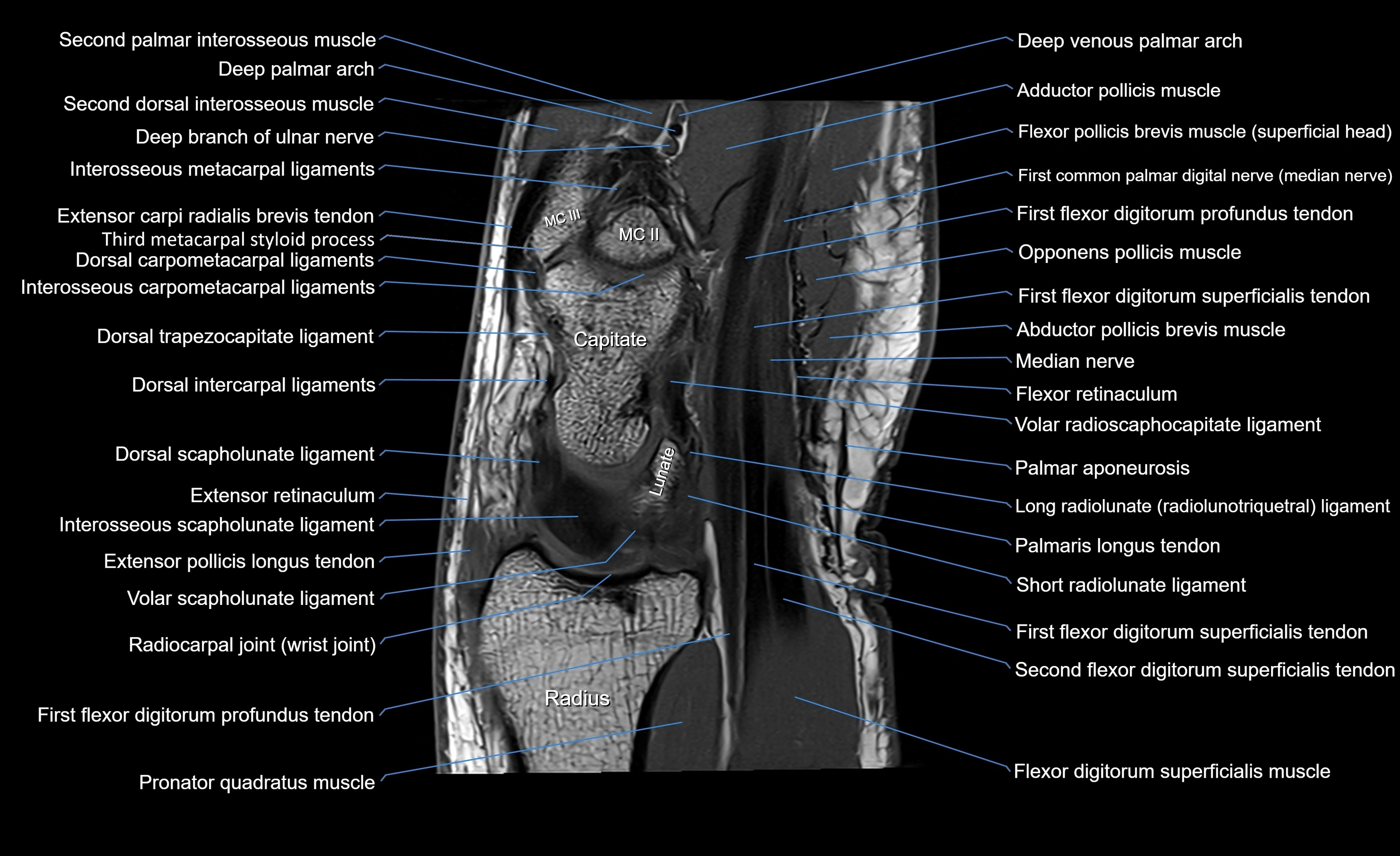
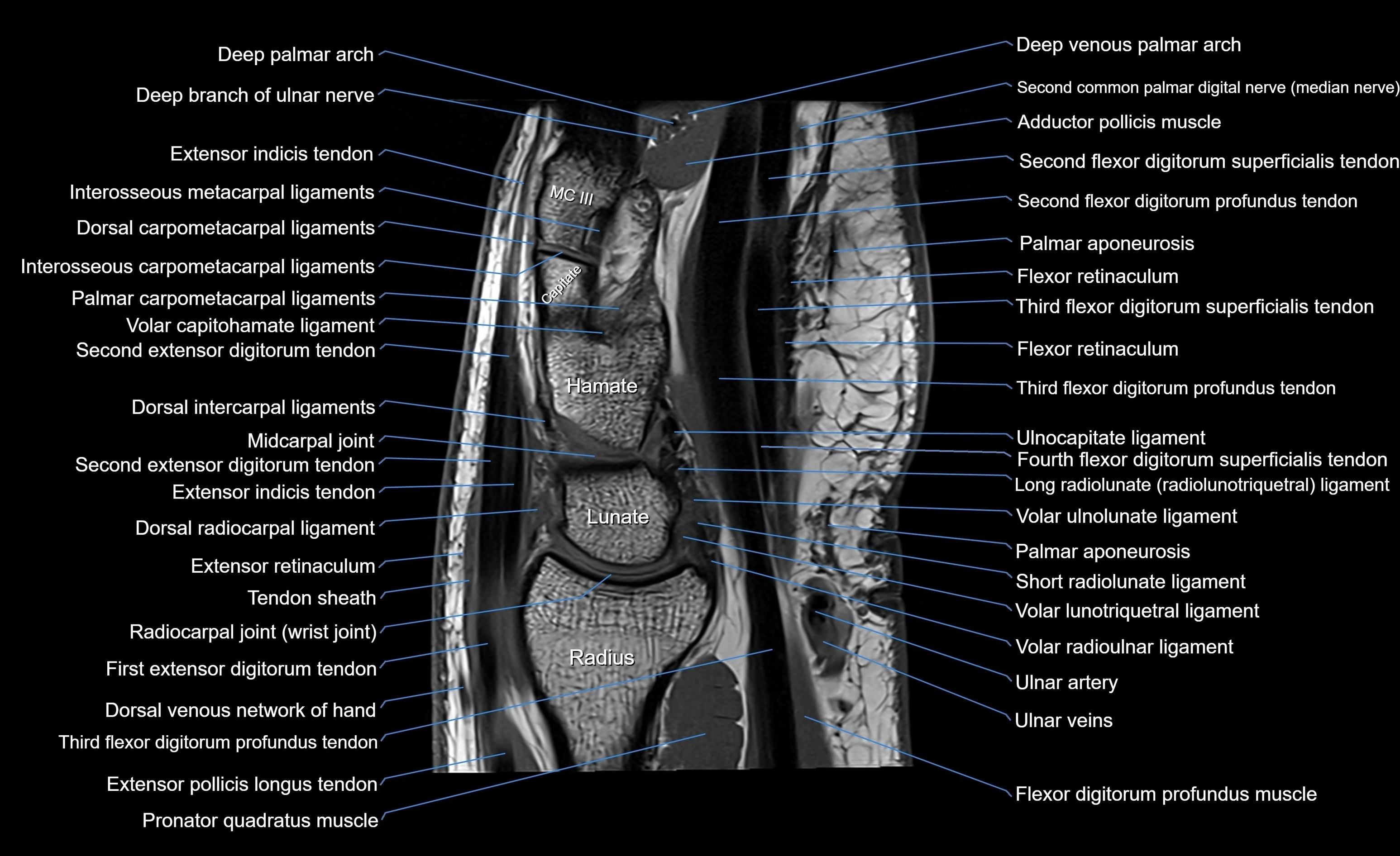
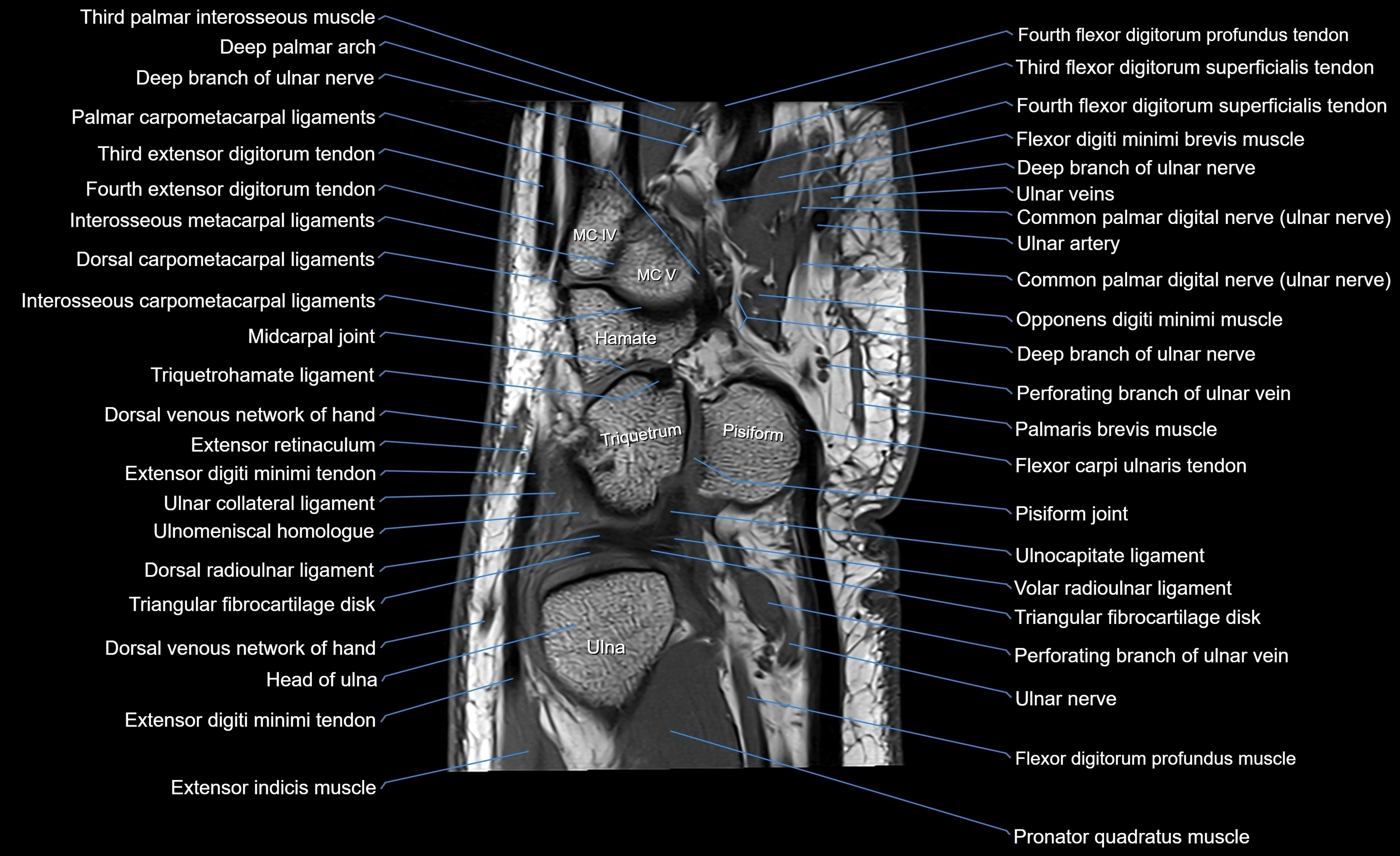
MRI image

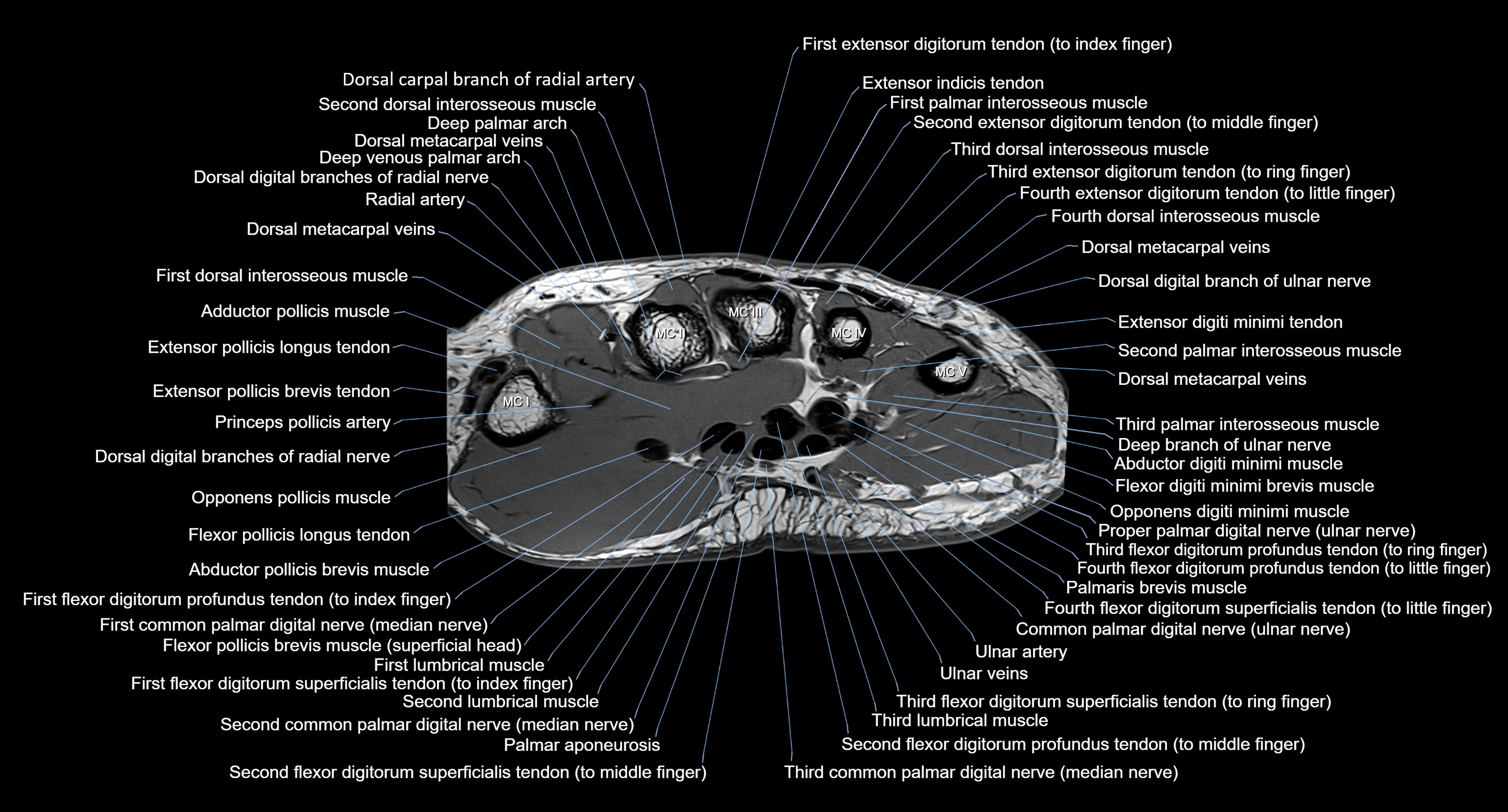
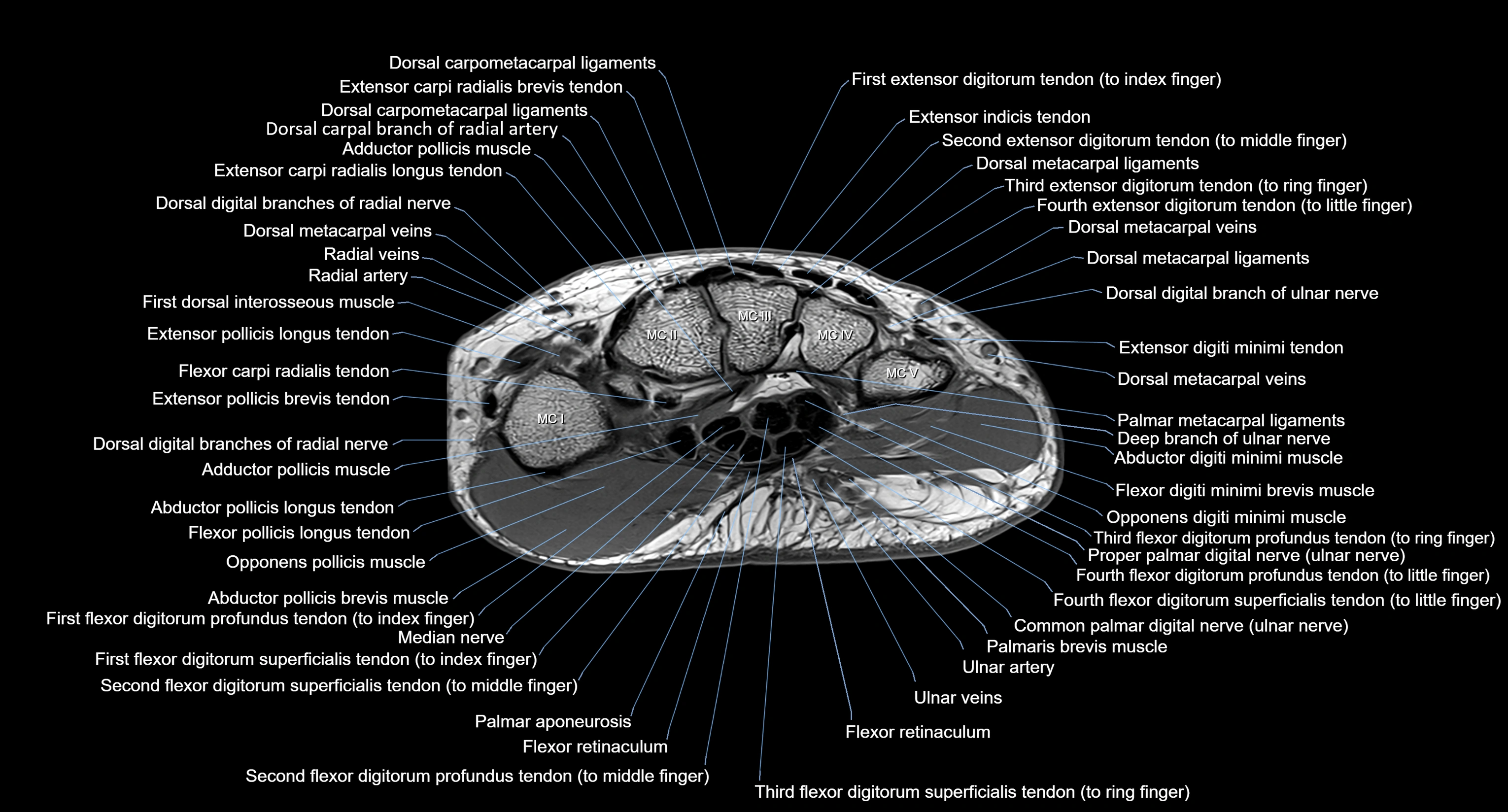
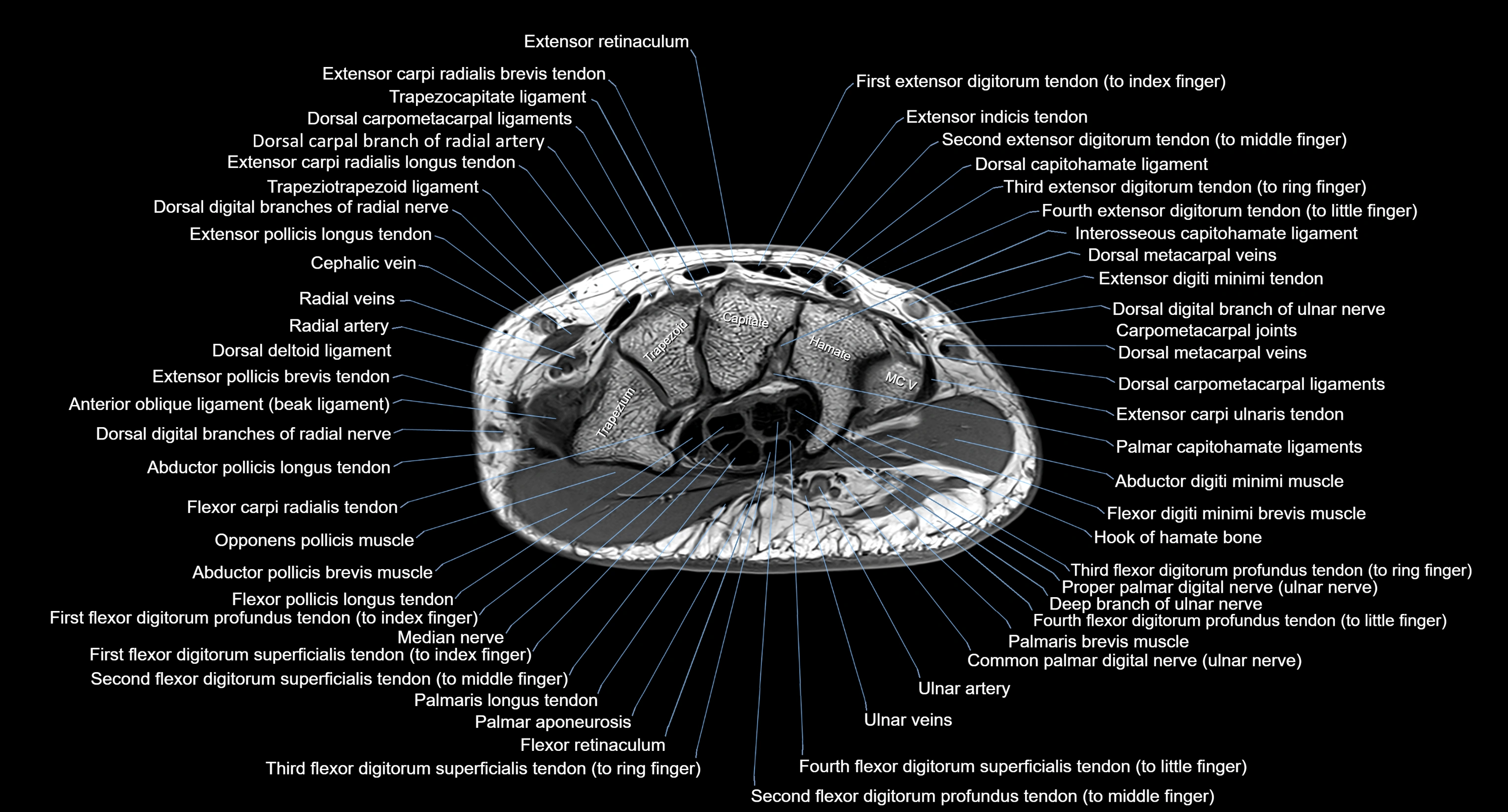
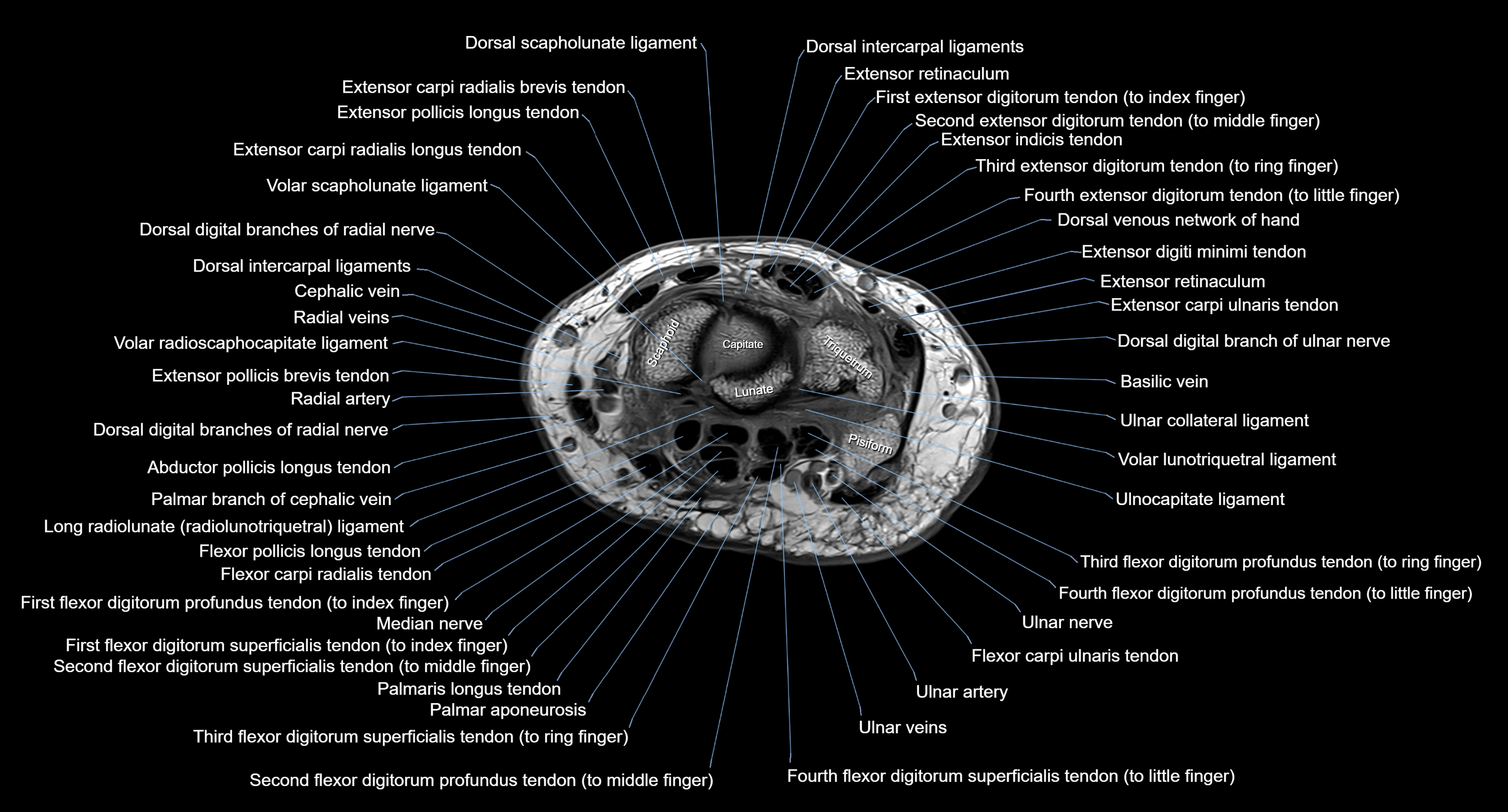
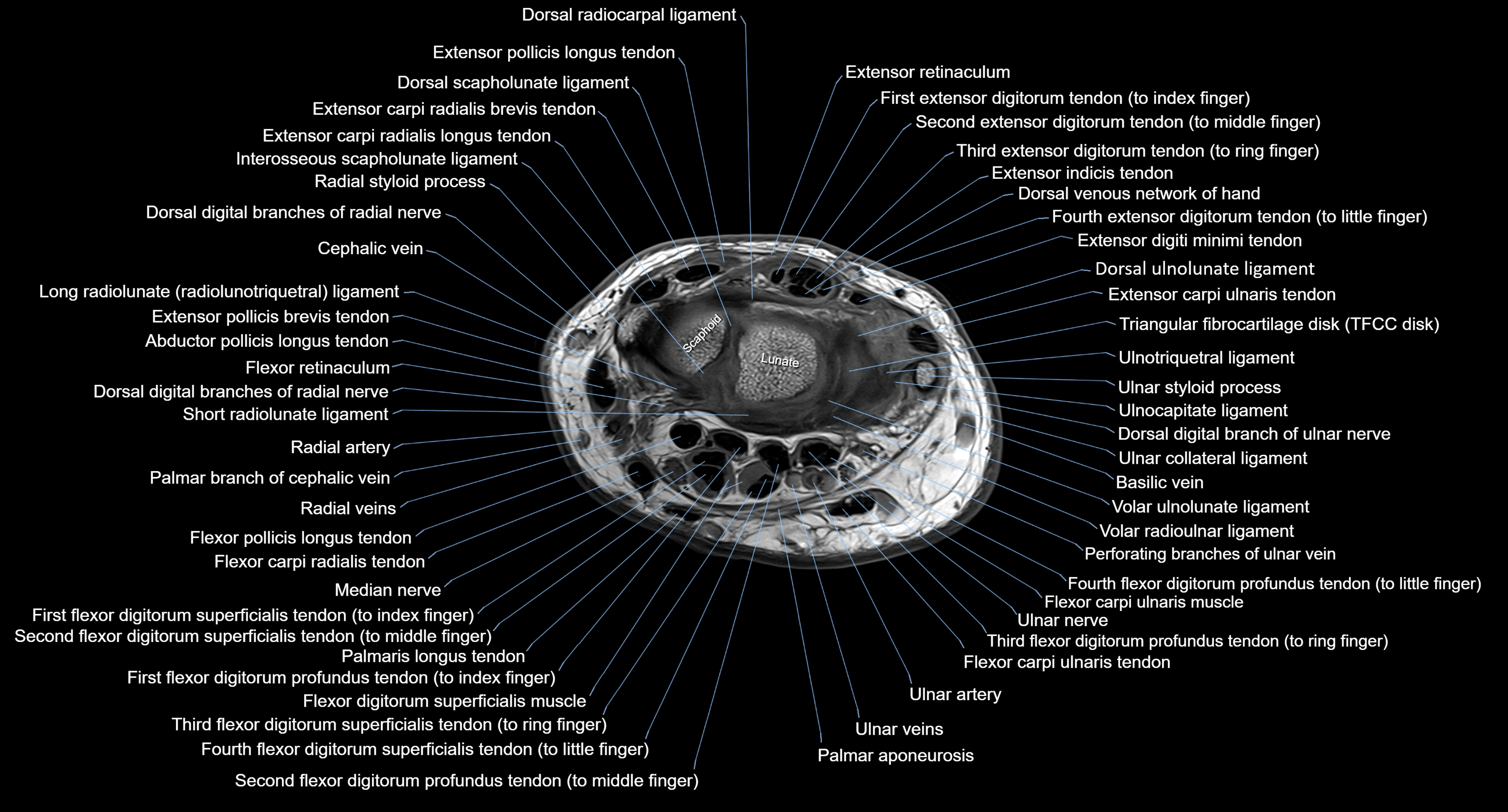
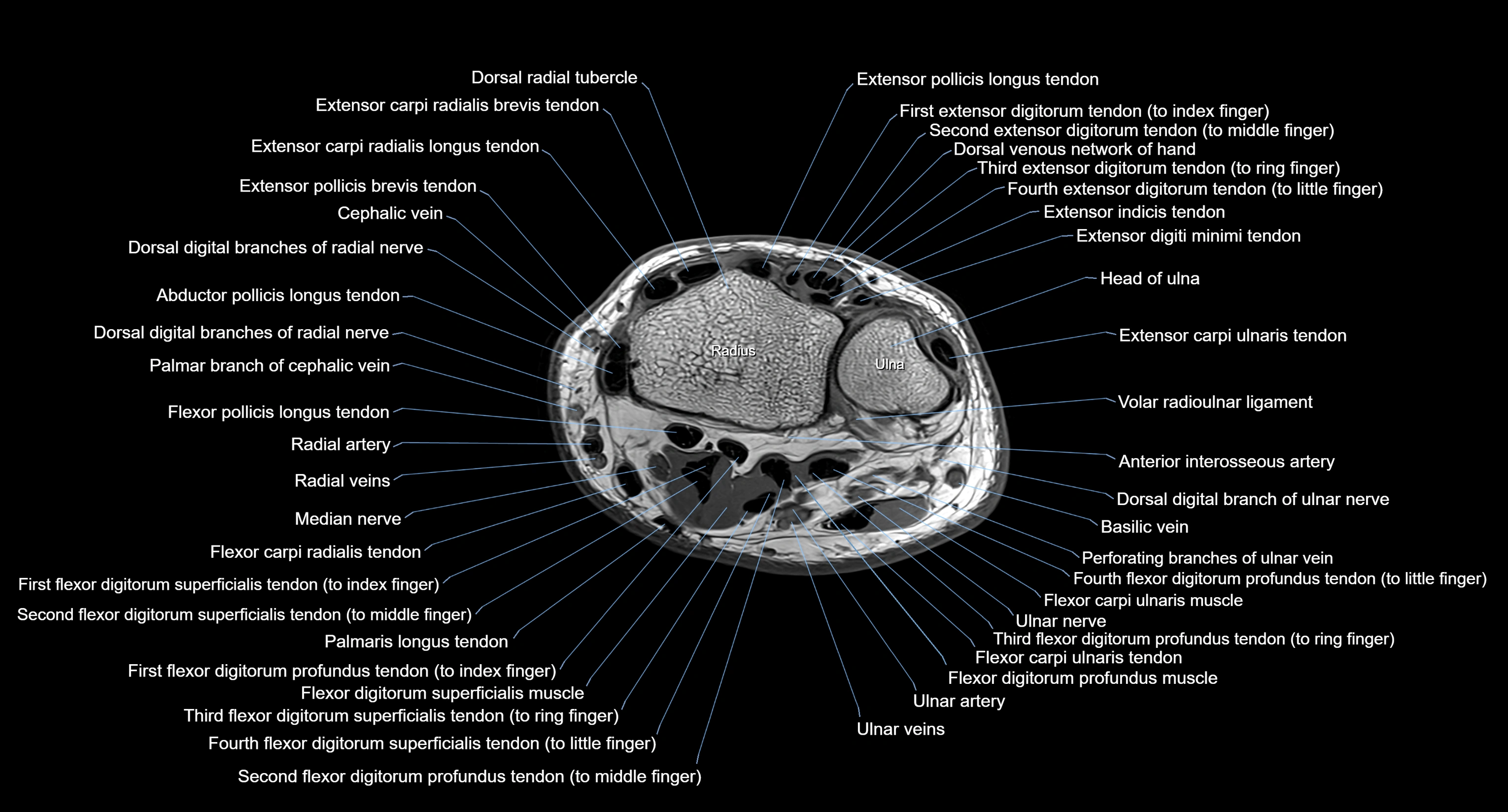
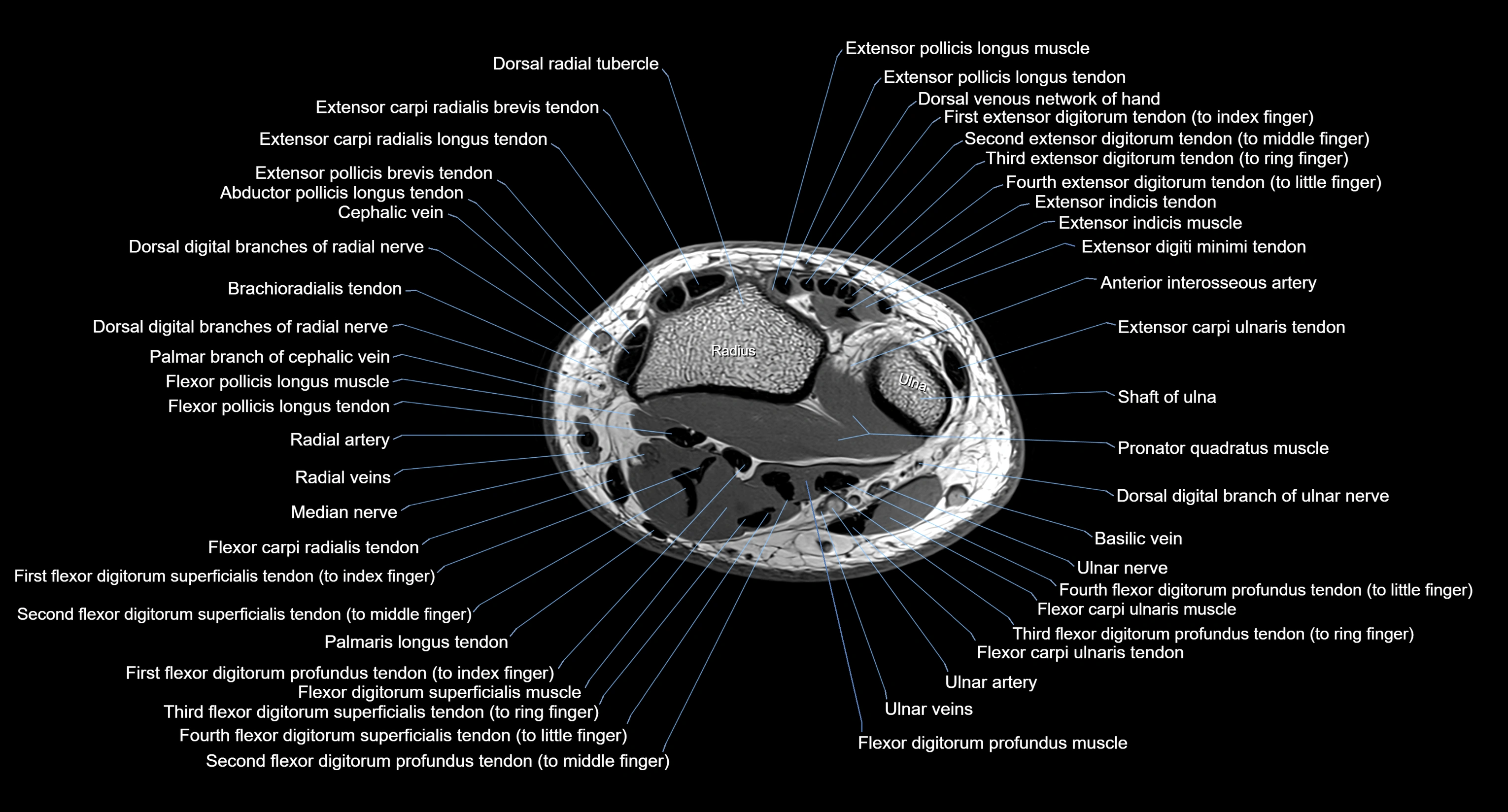
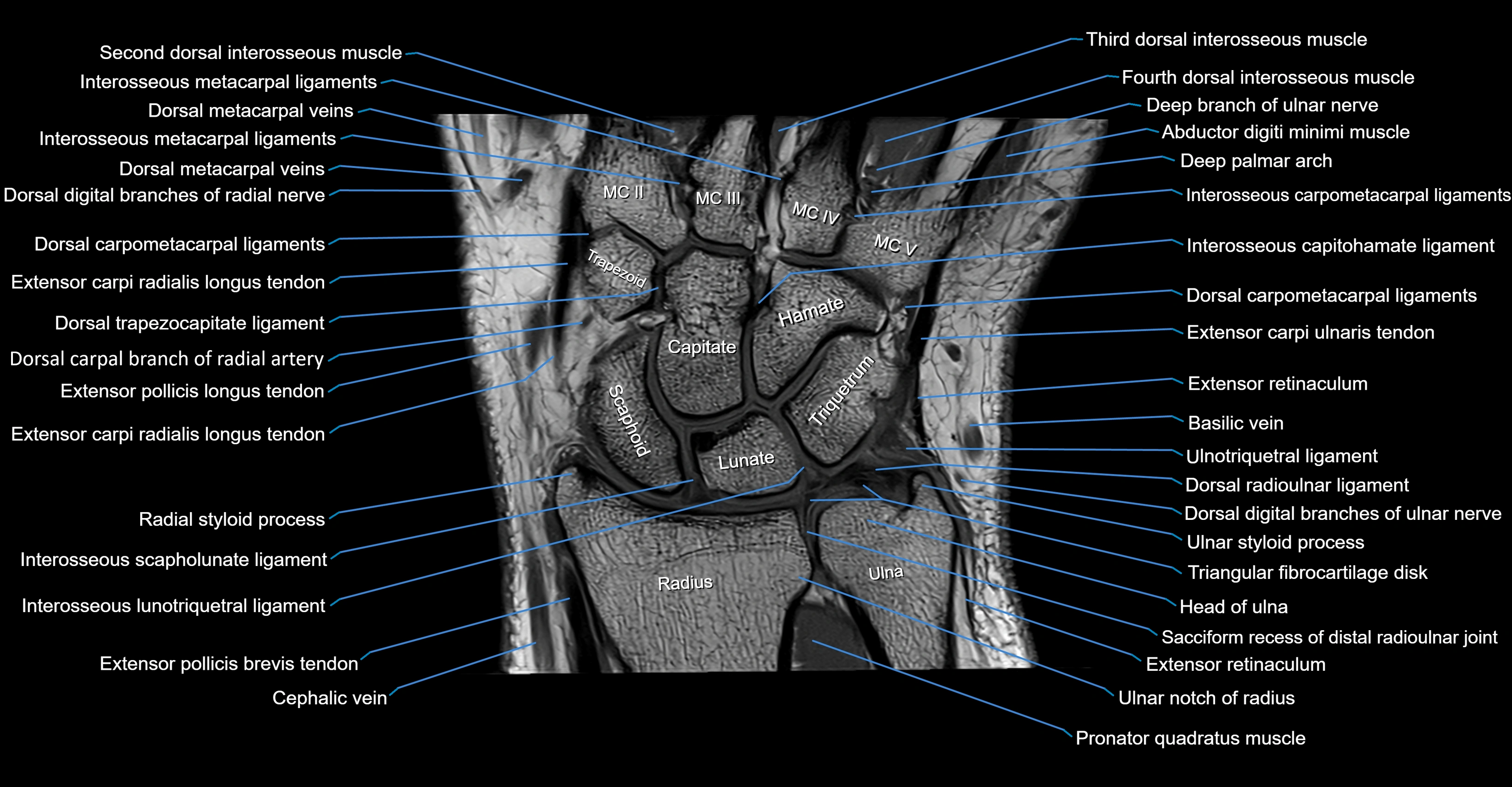
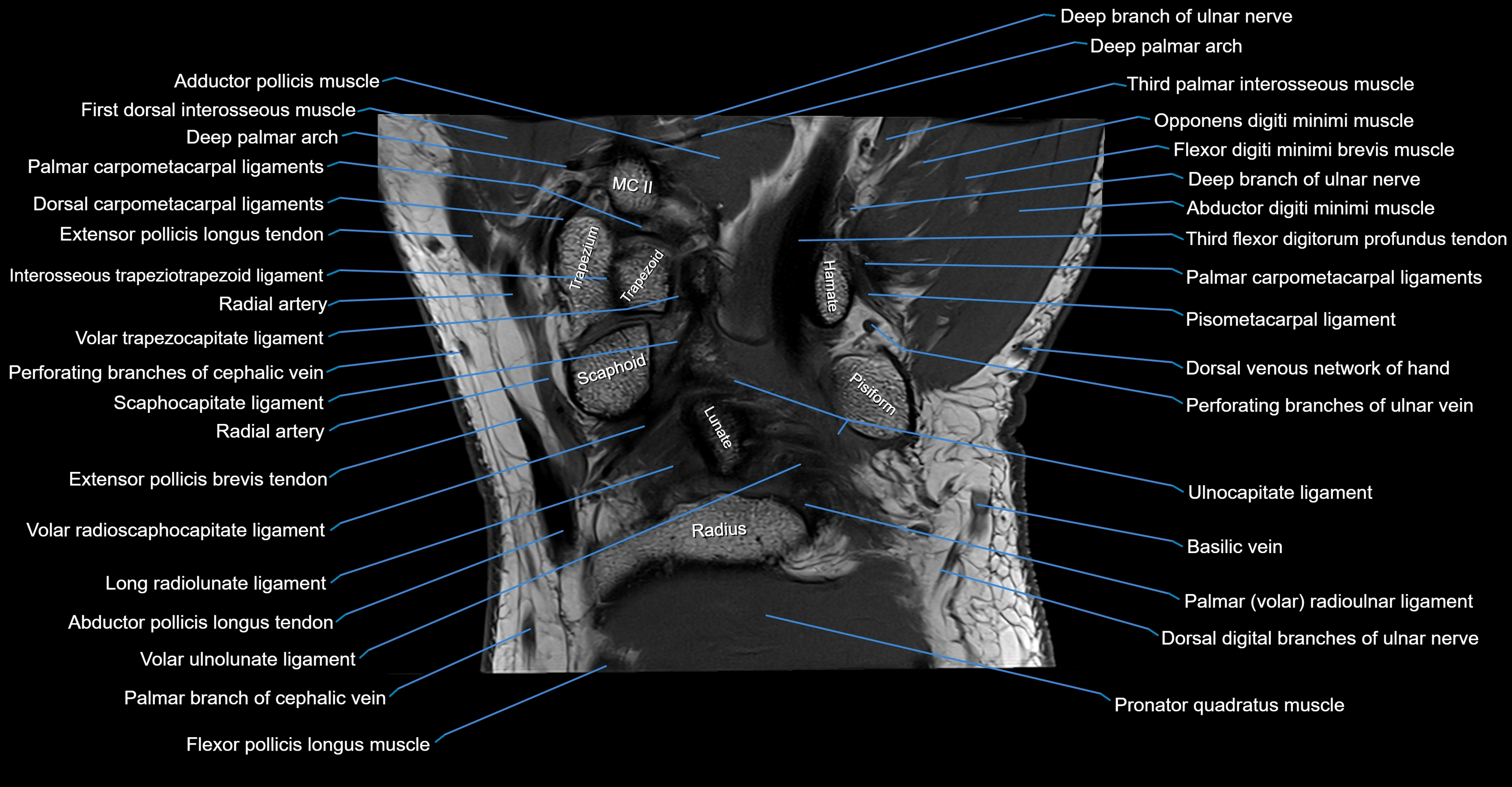
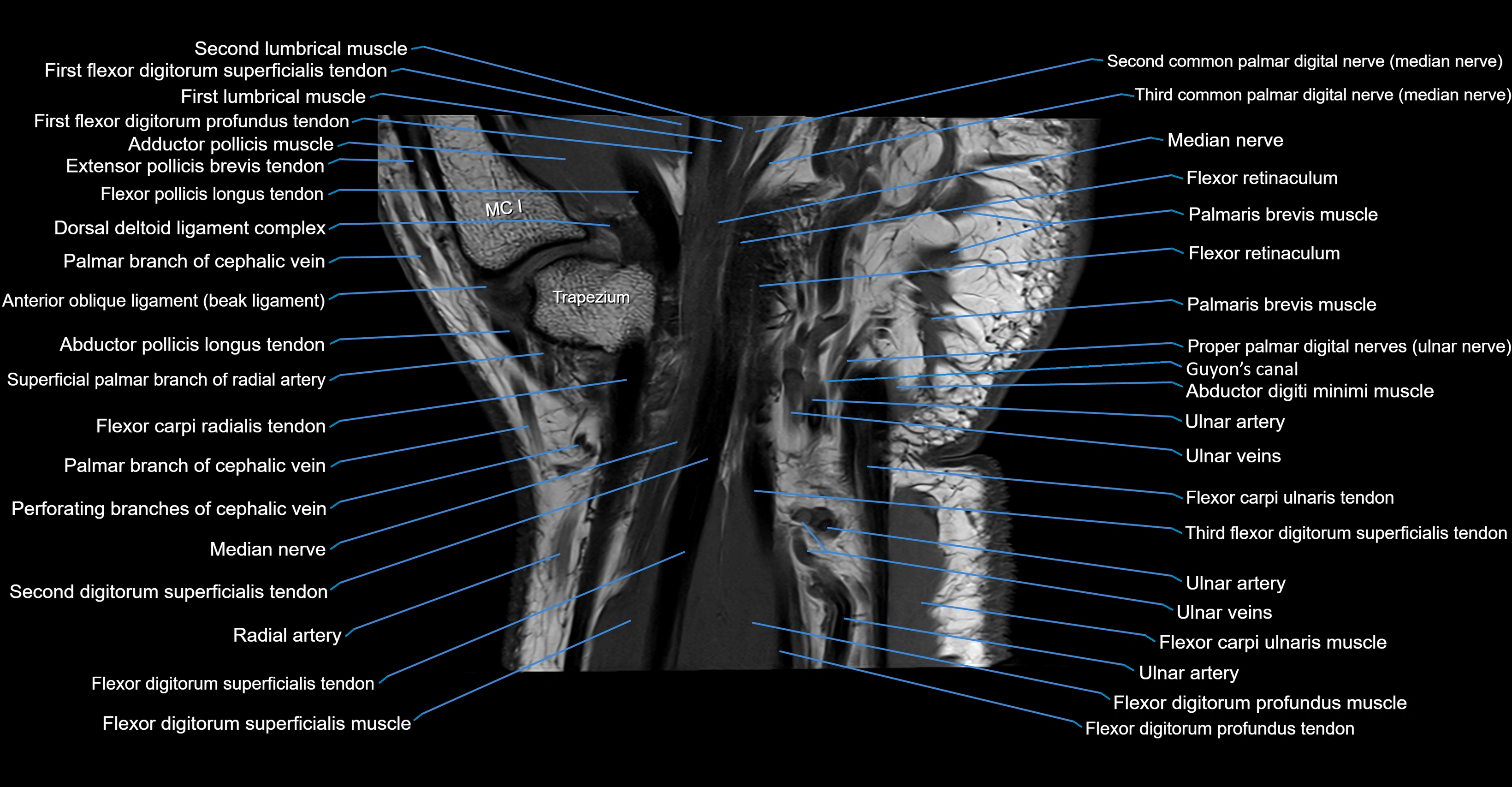
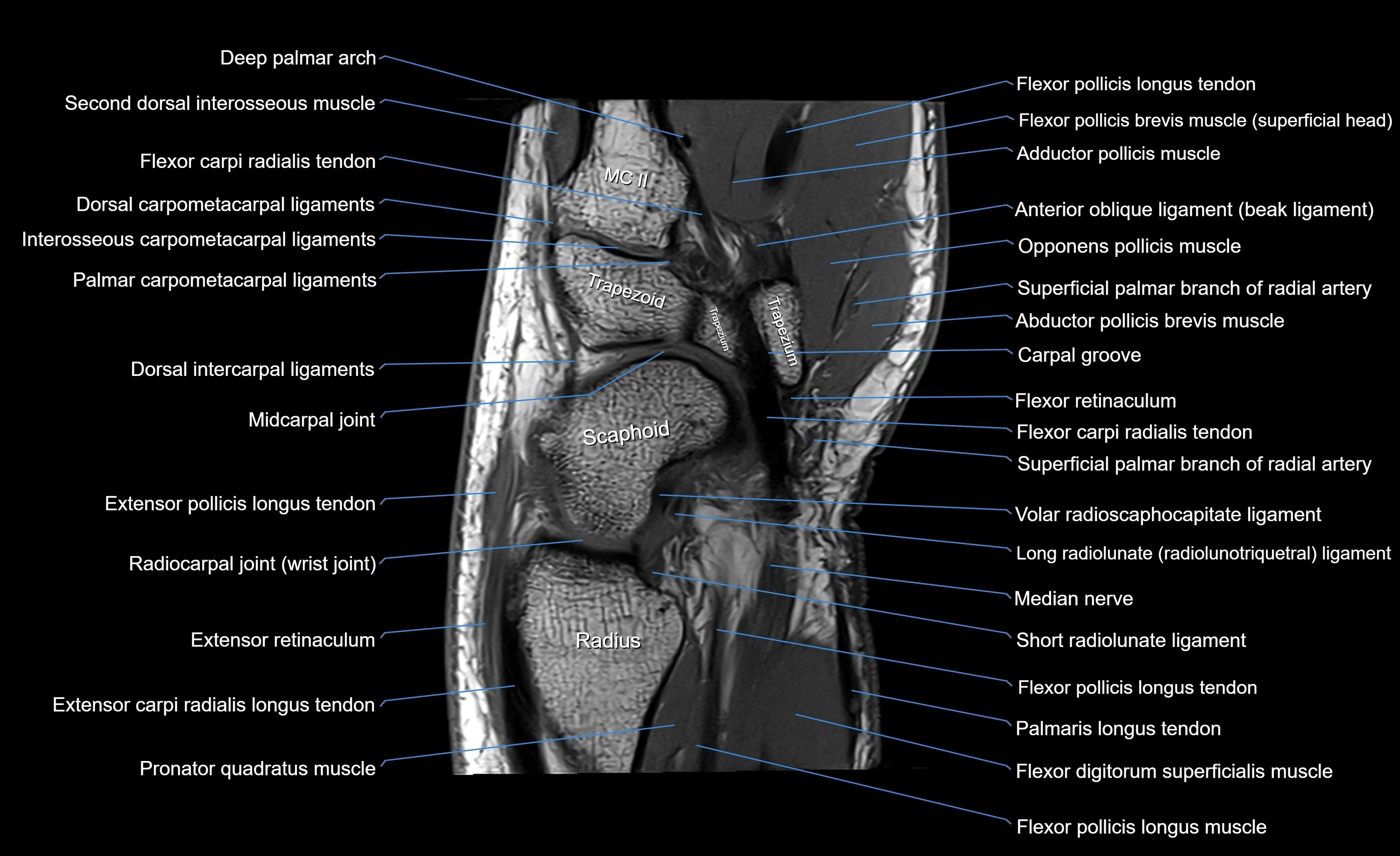
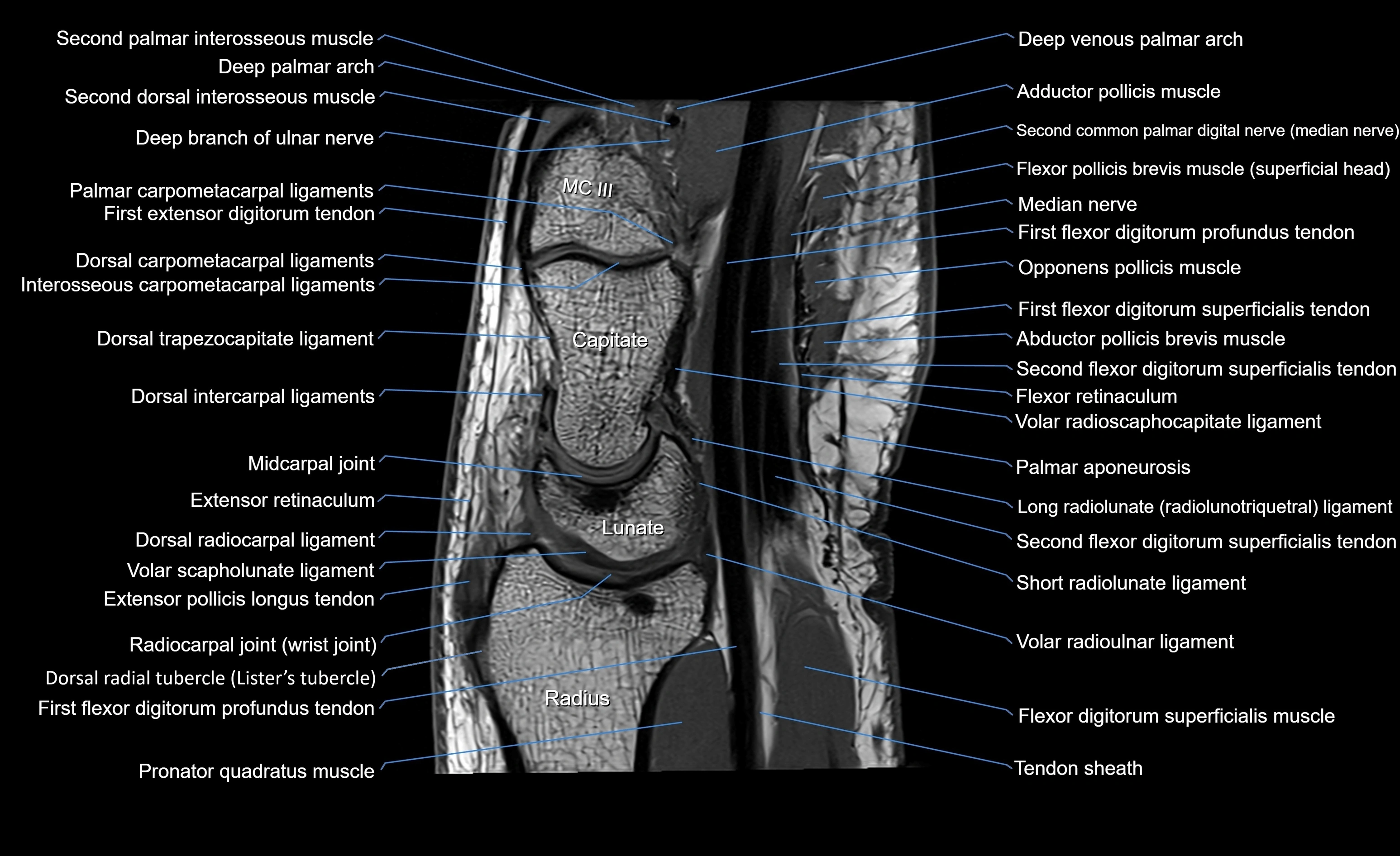
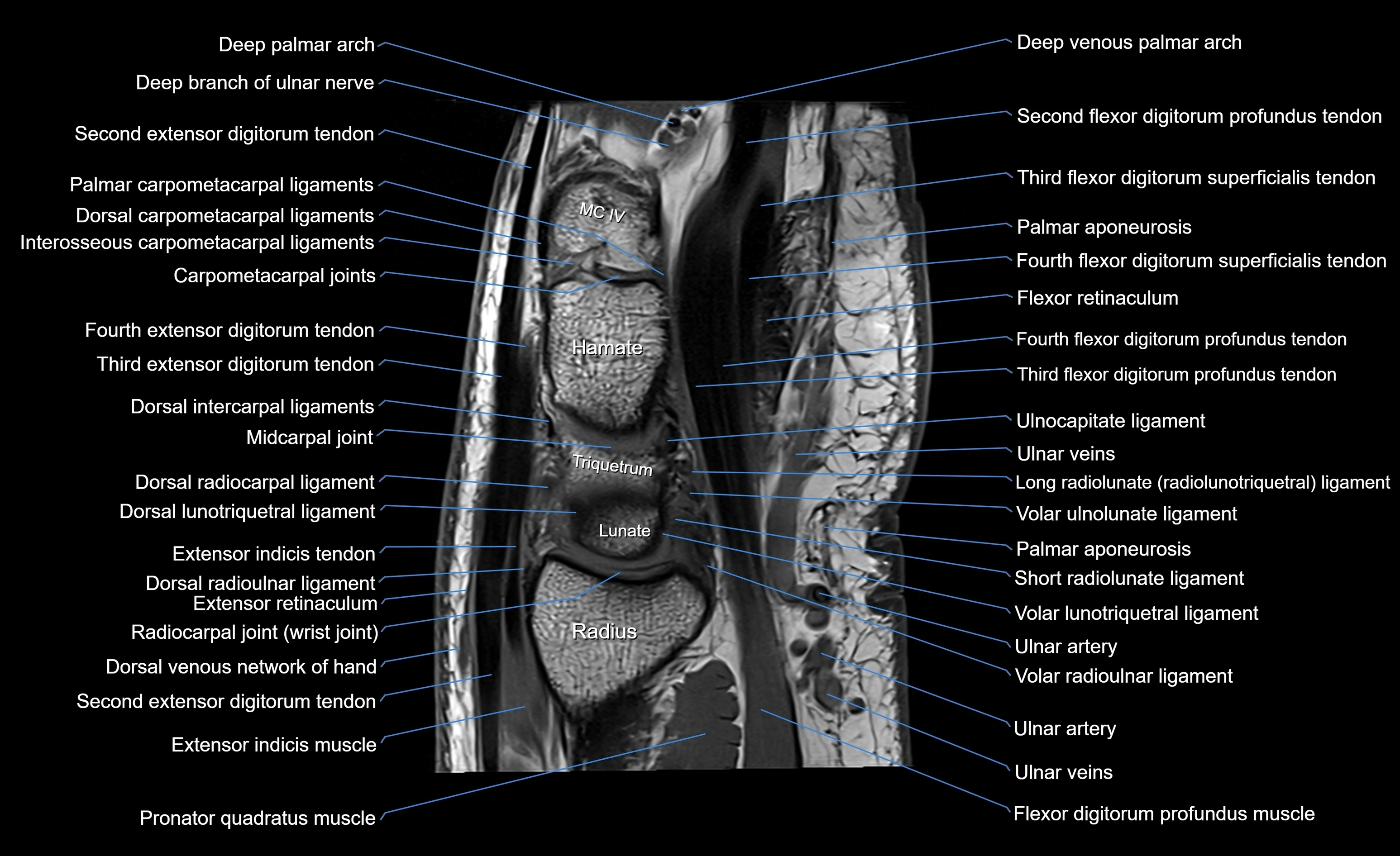
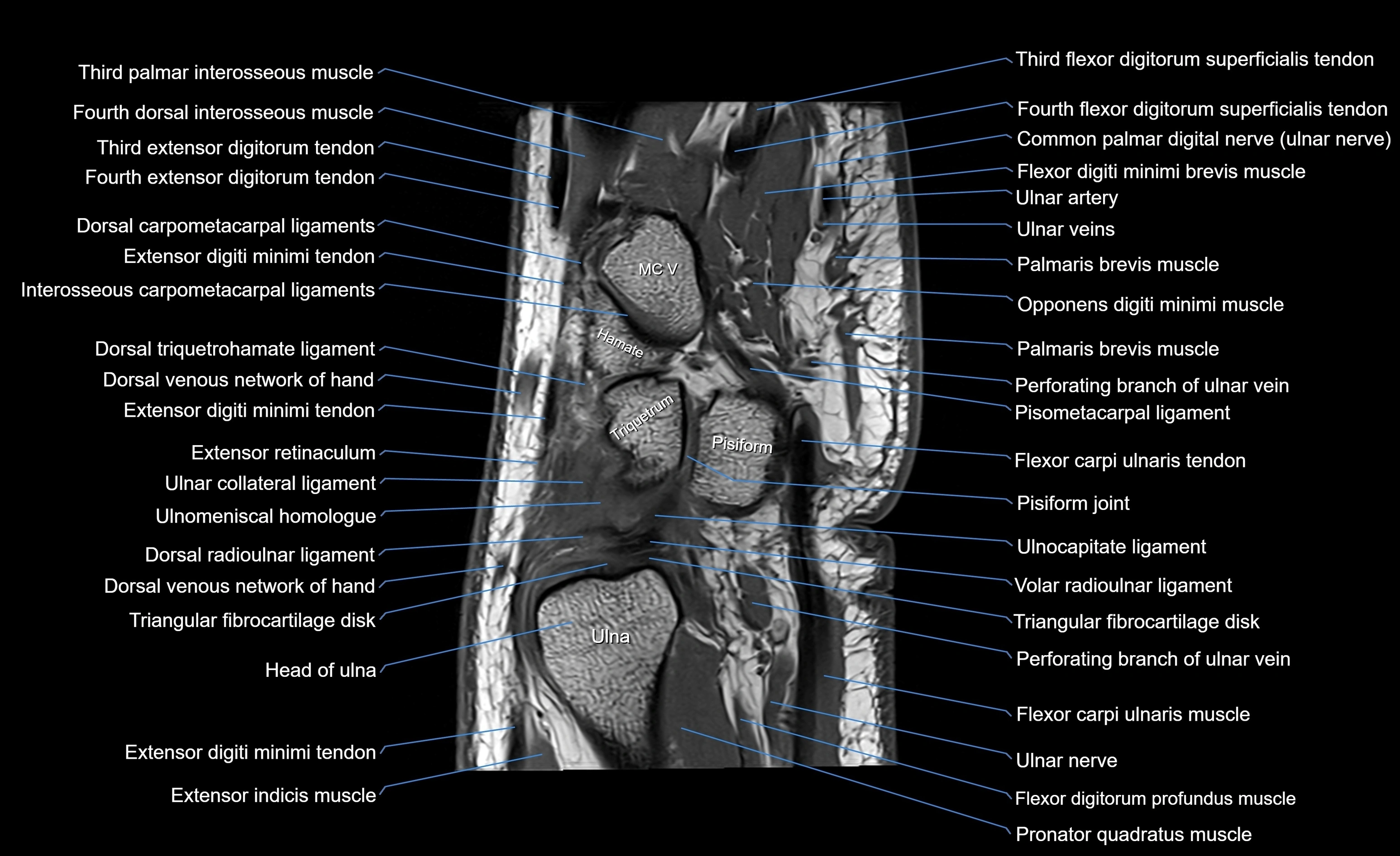
MRI image

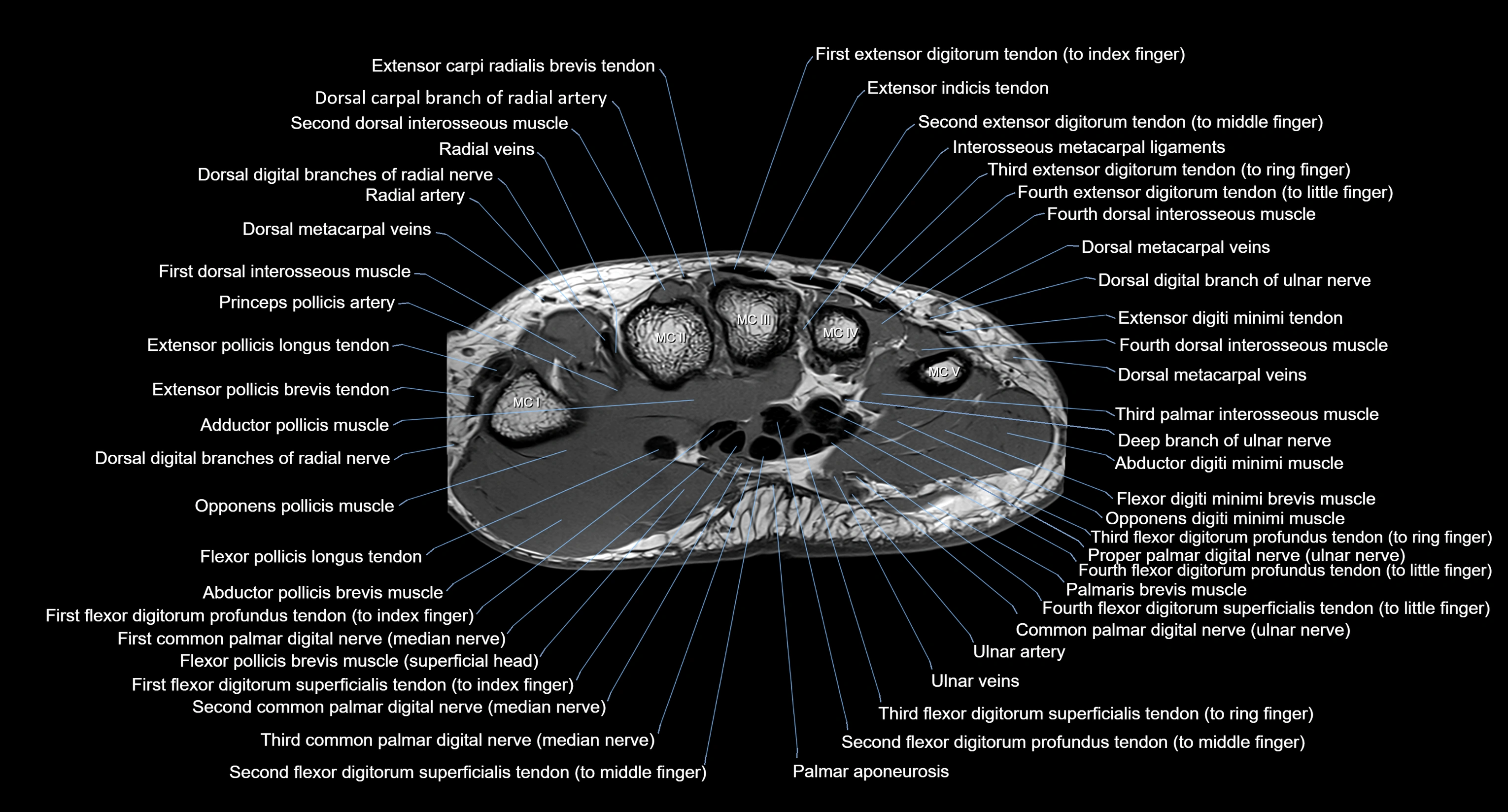
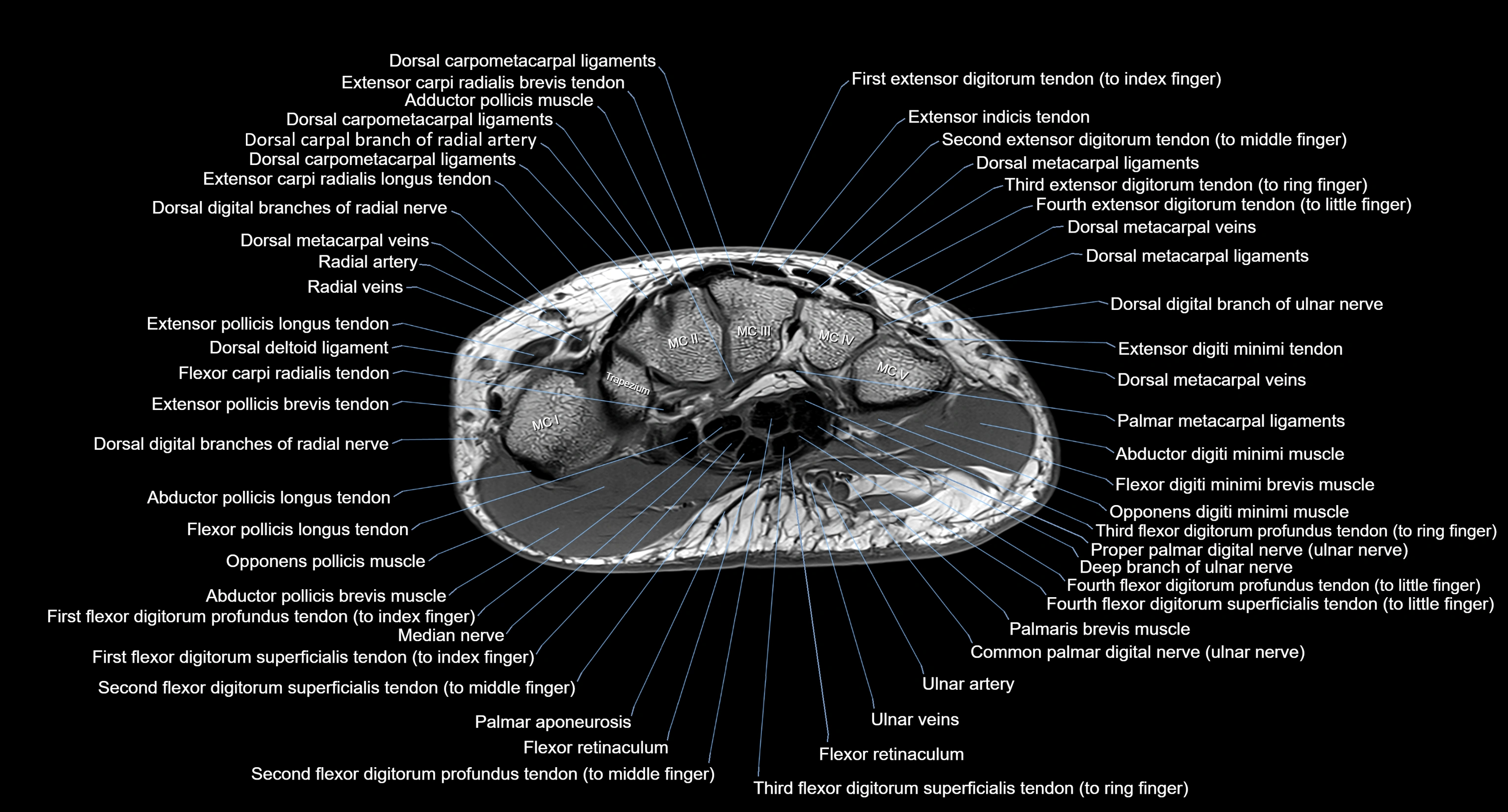
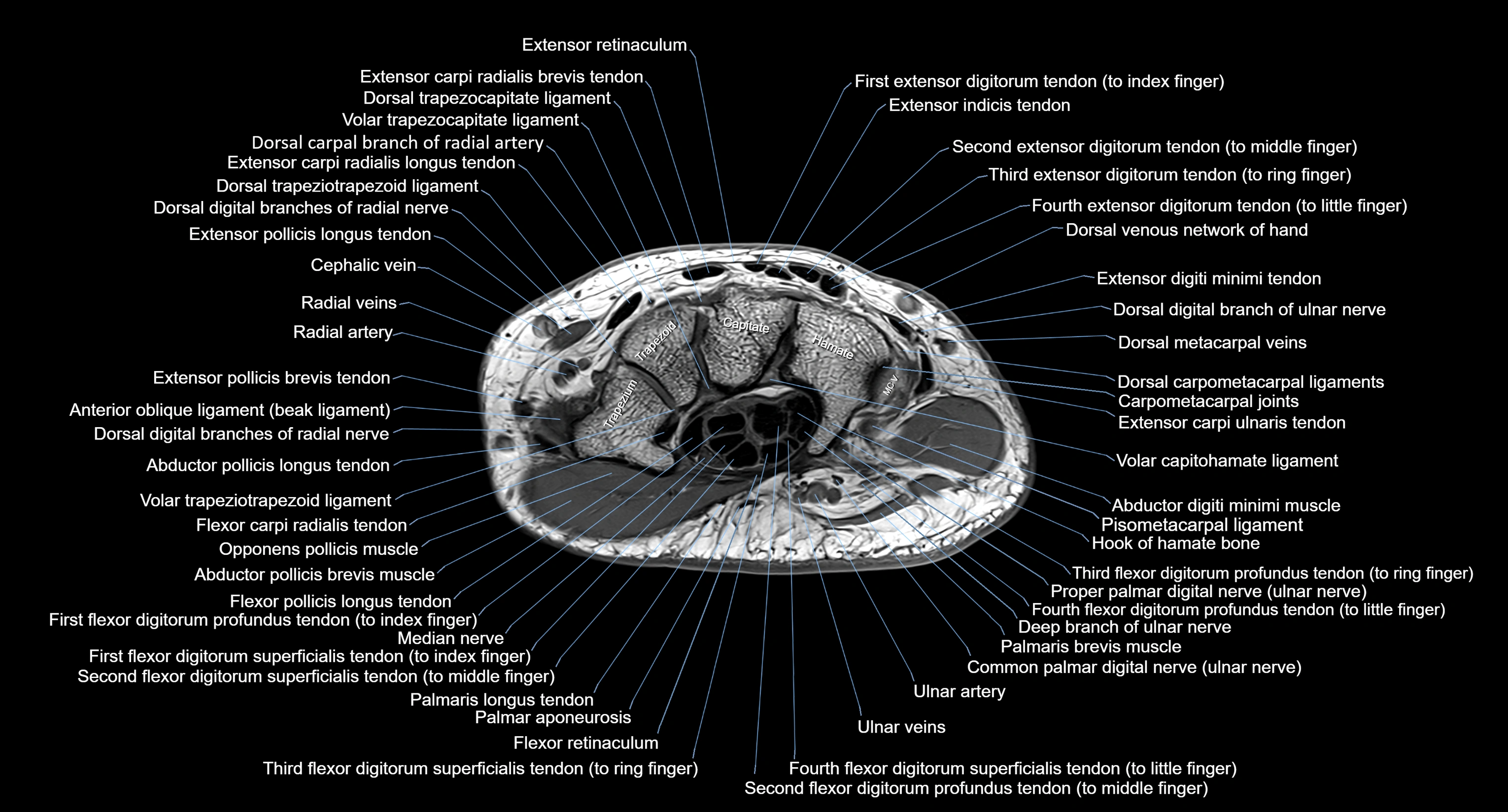
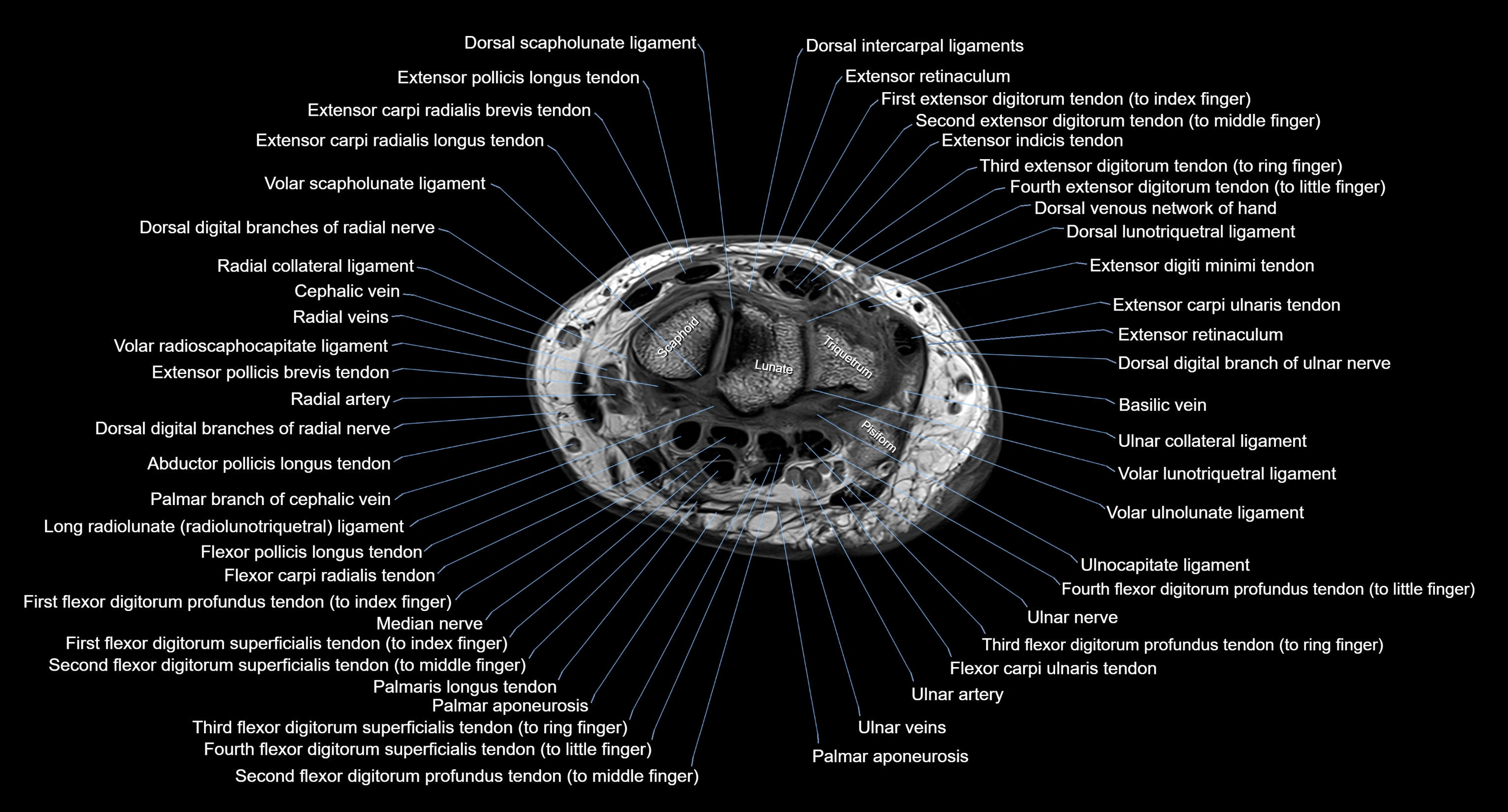
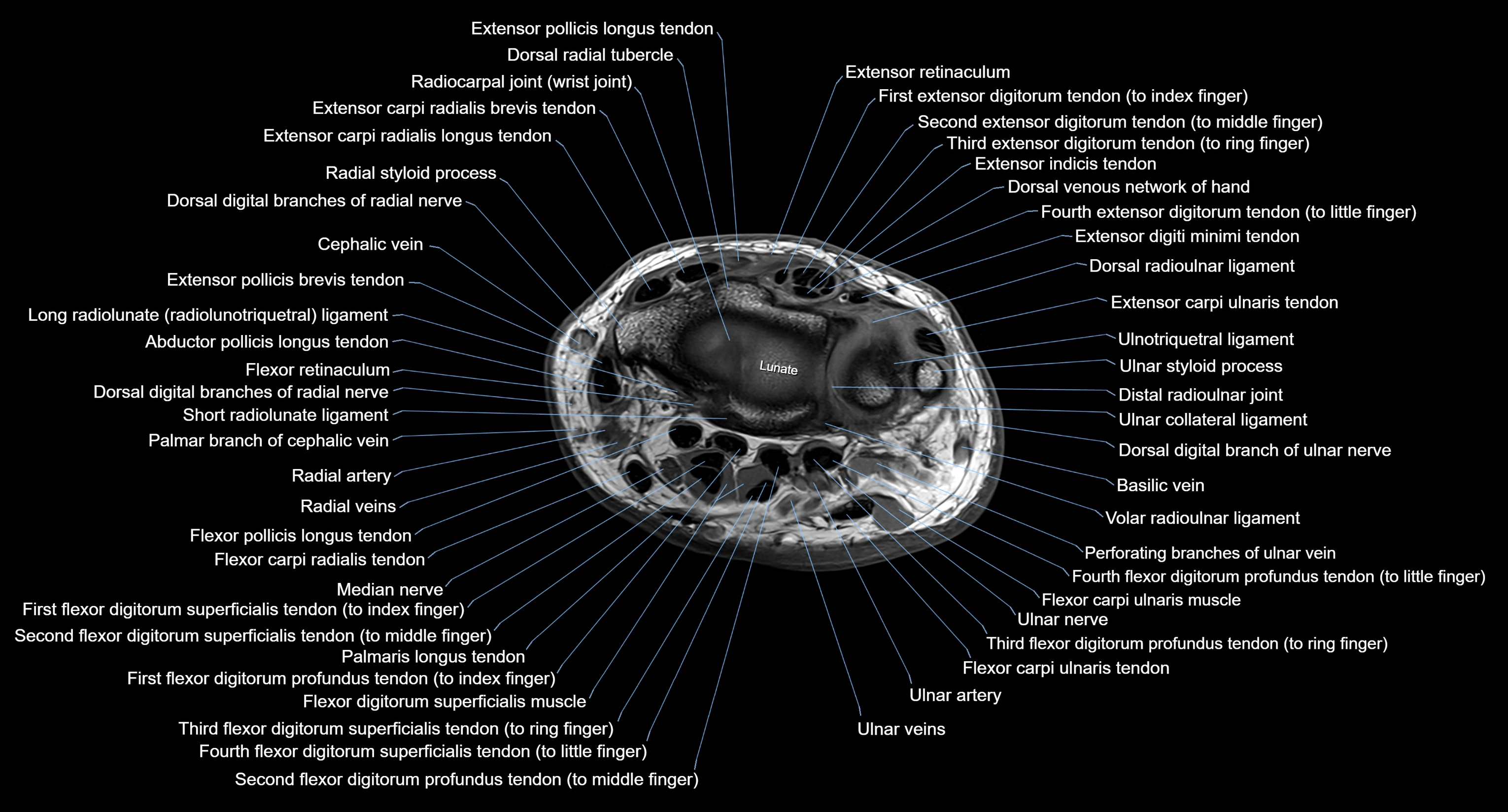
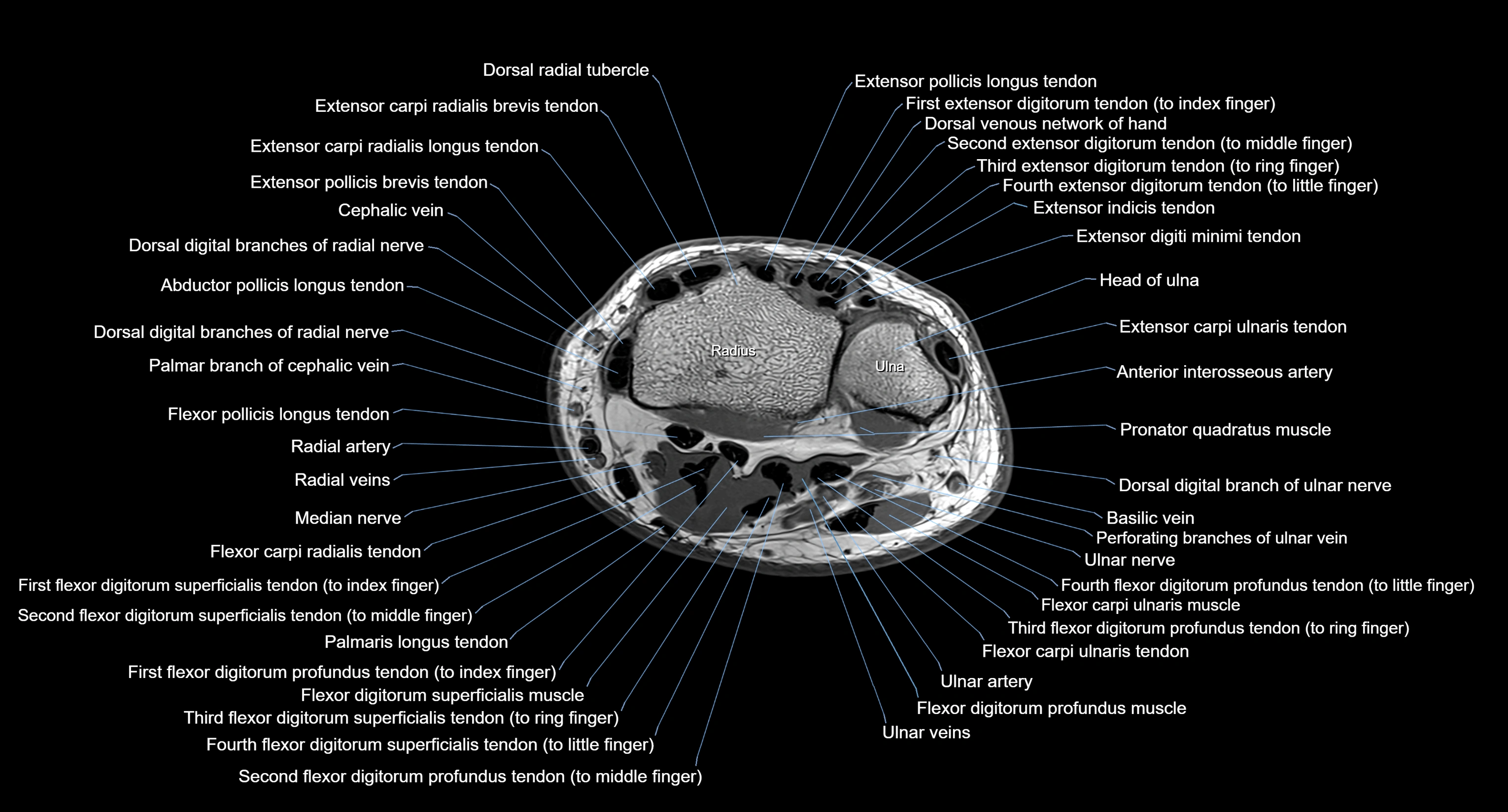
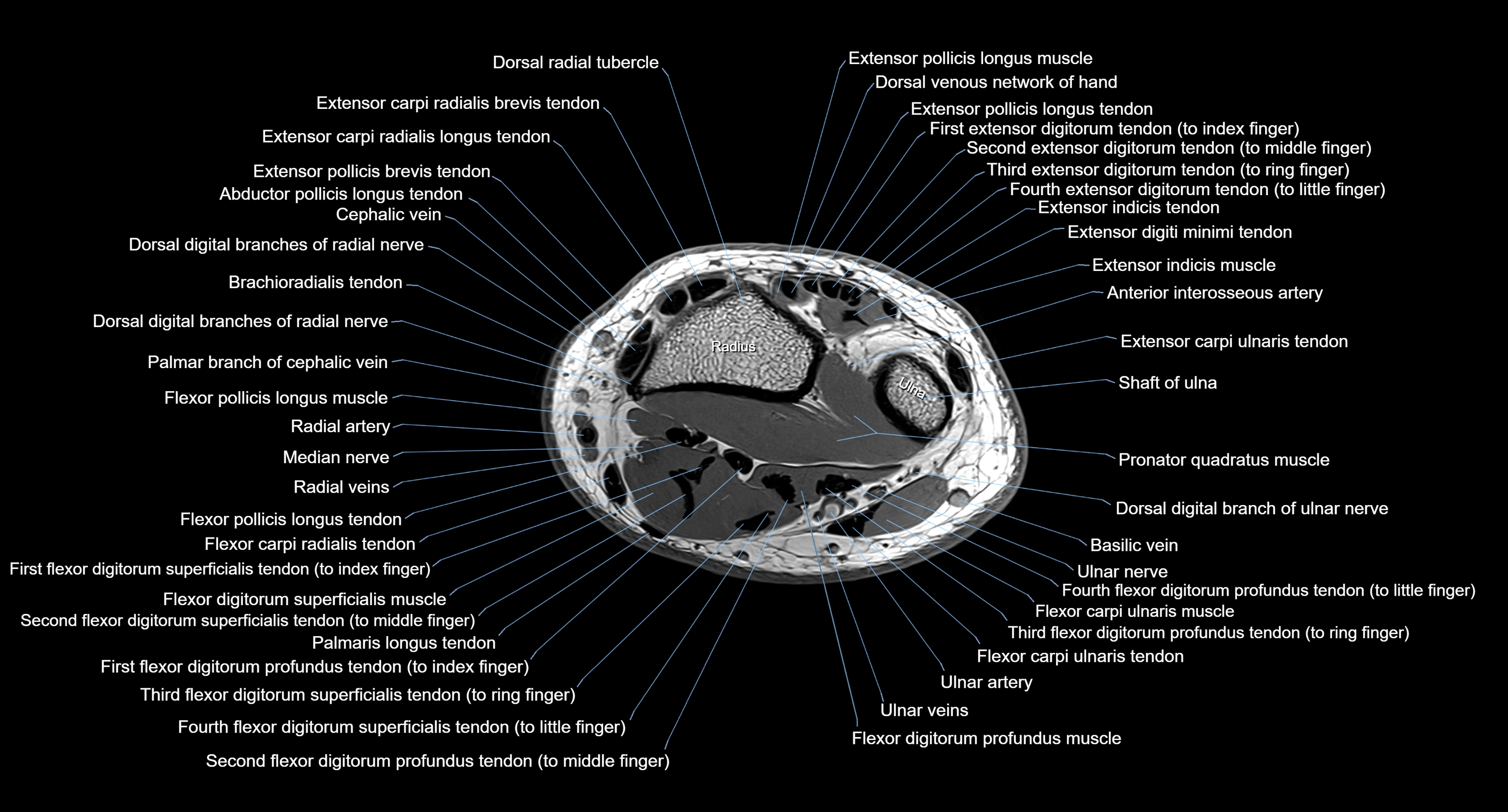
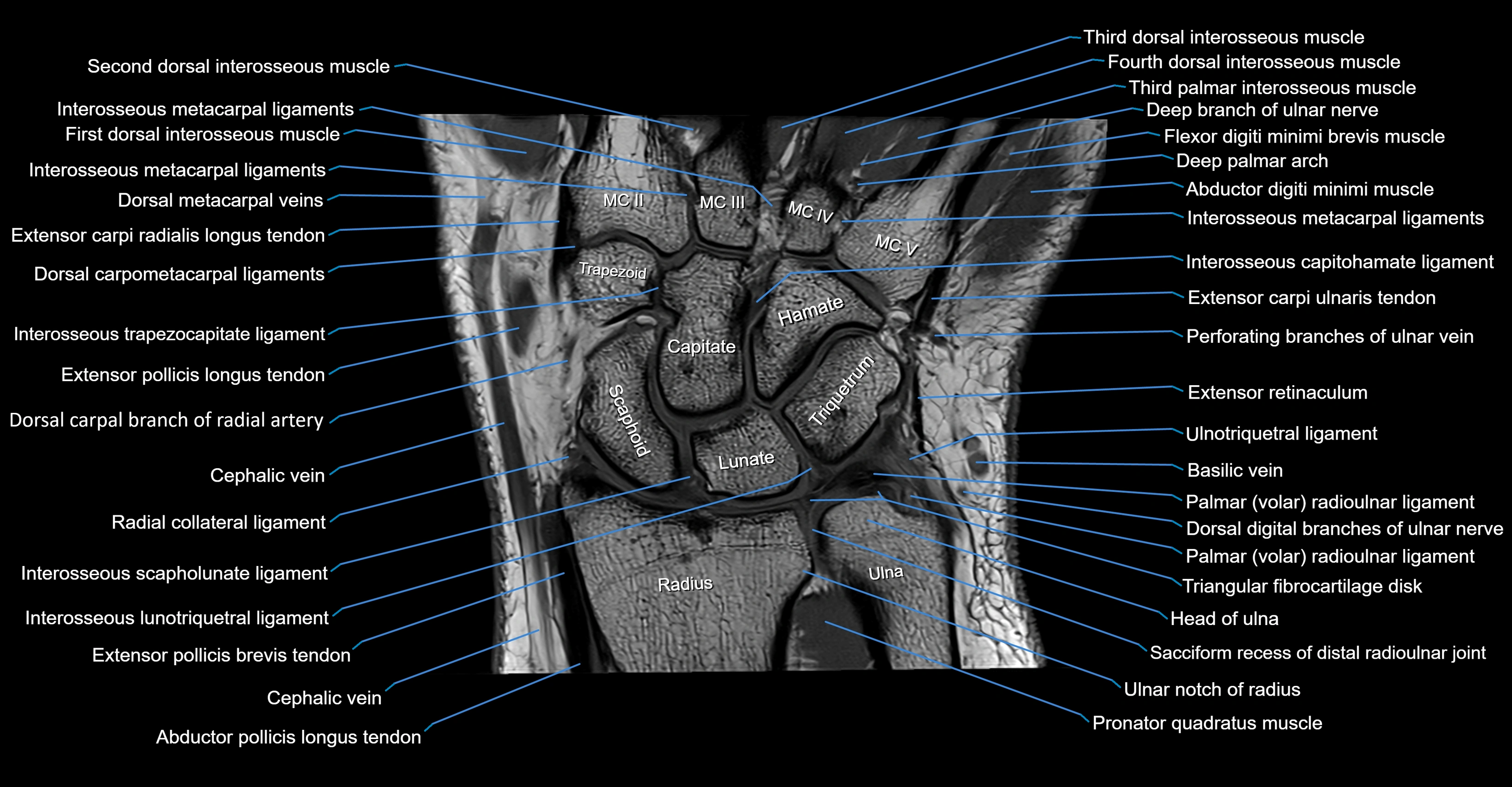
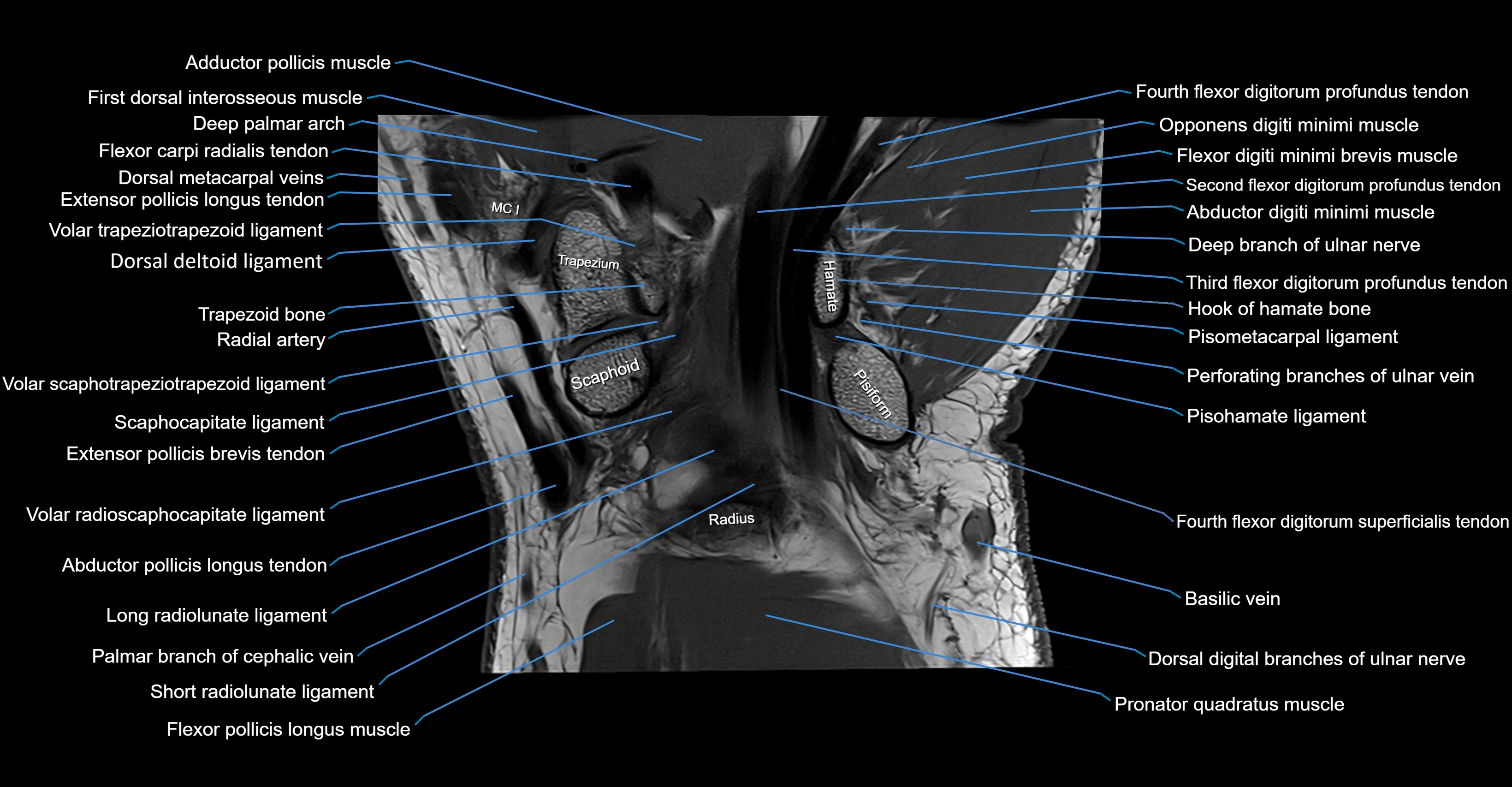
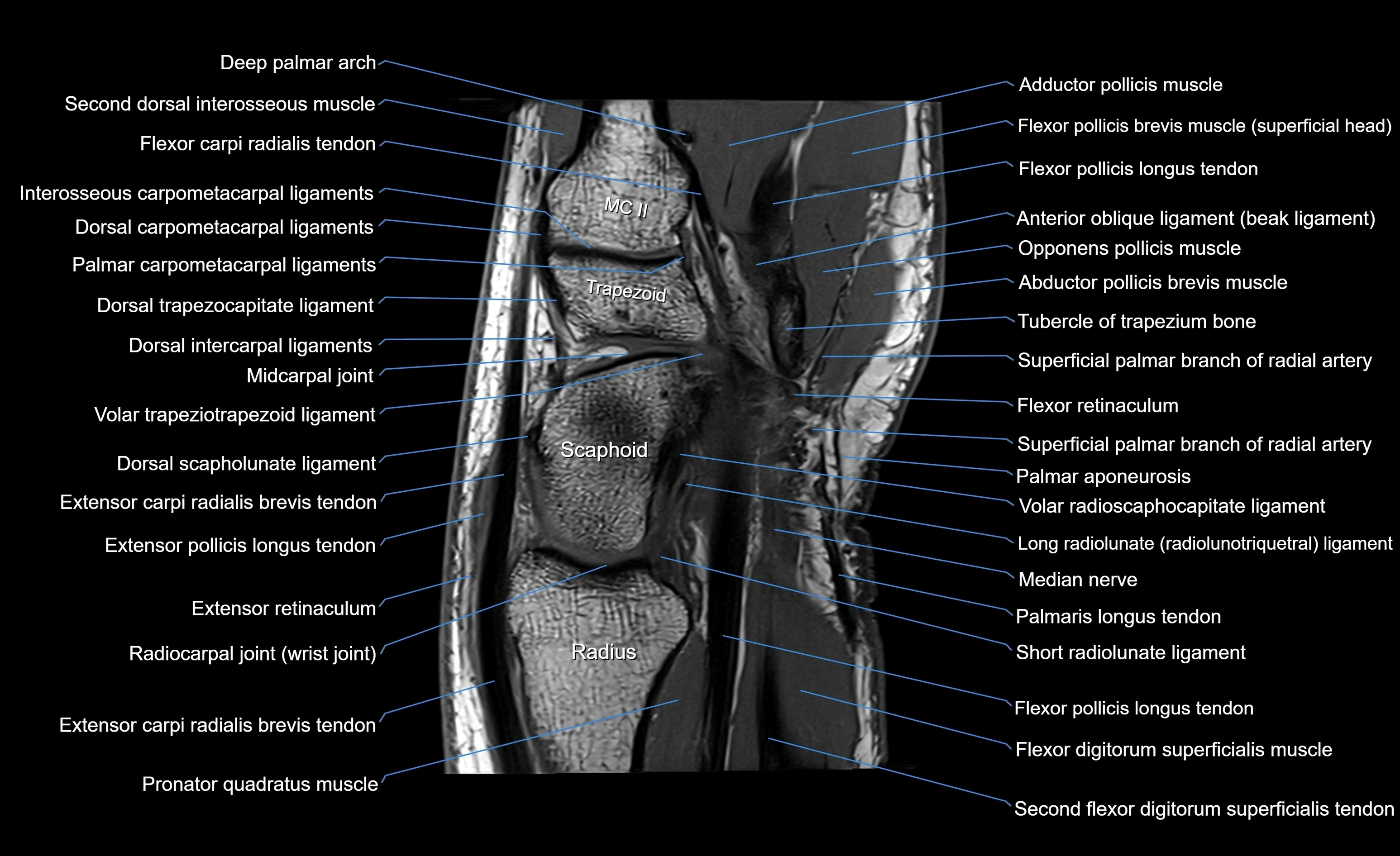
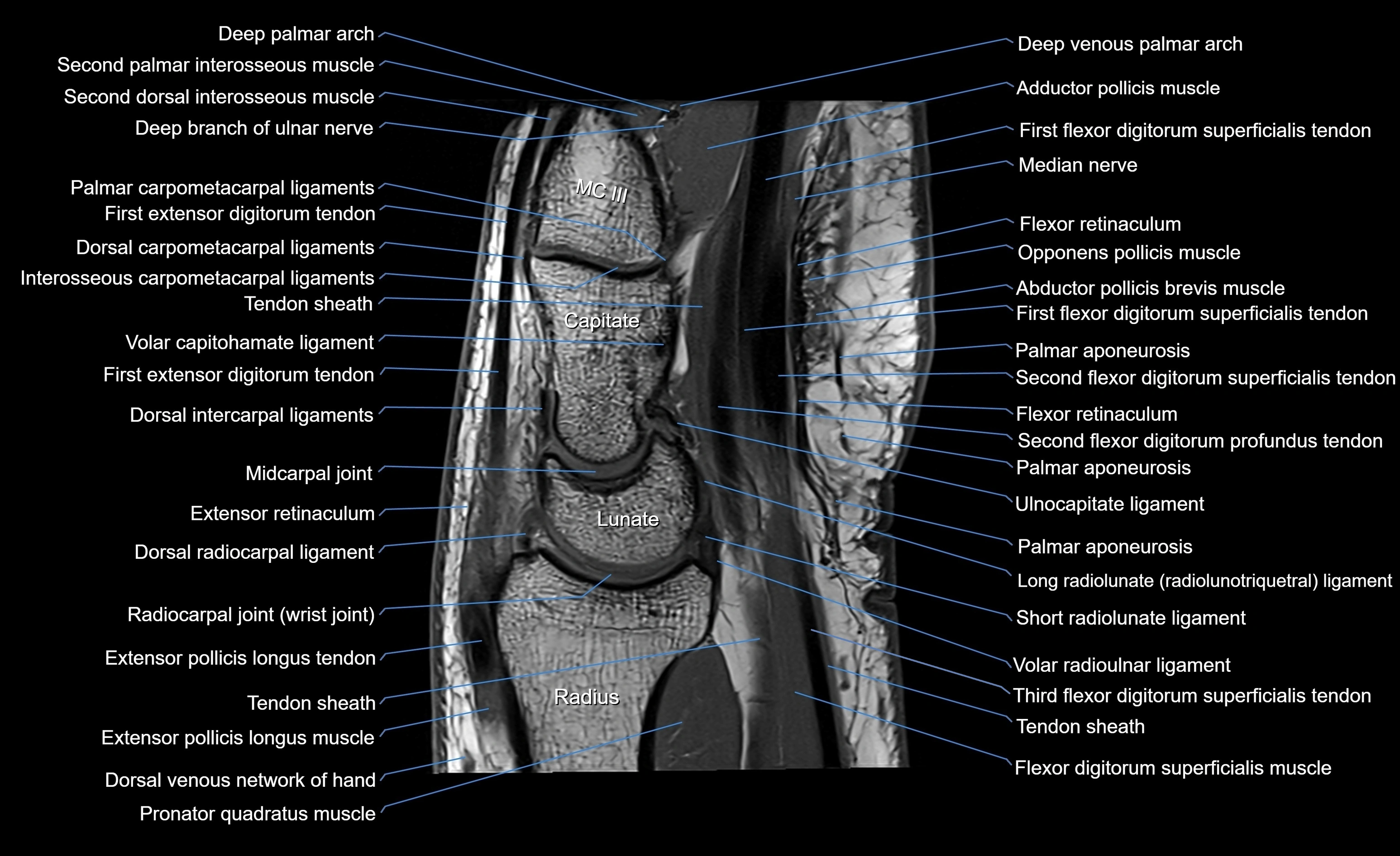
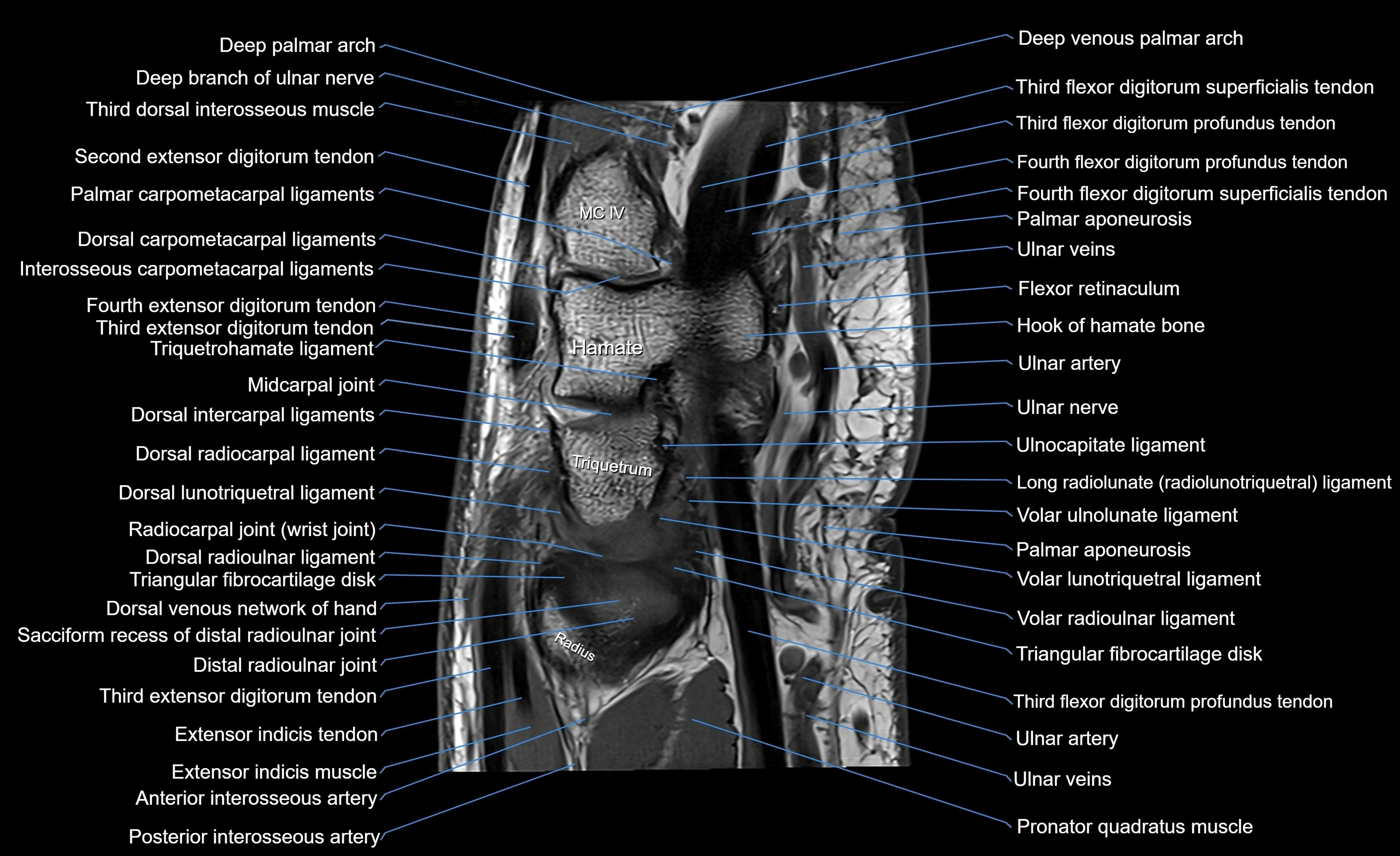
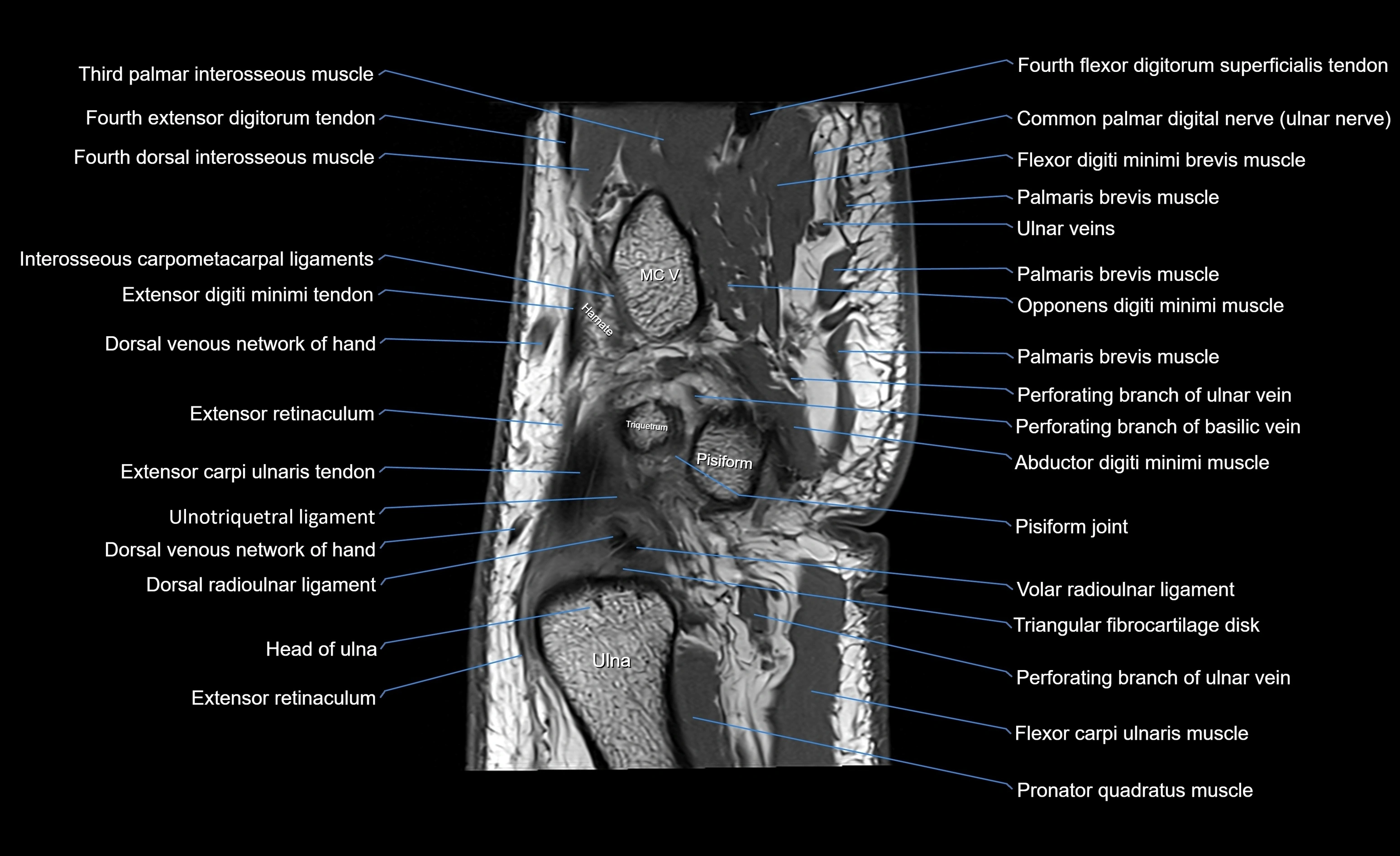
CT image