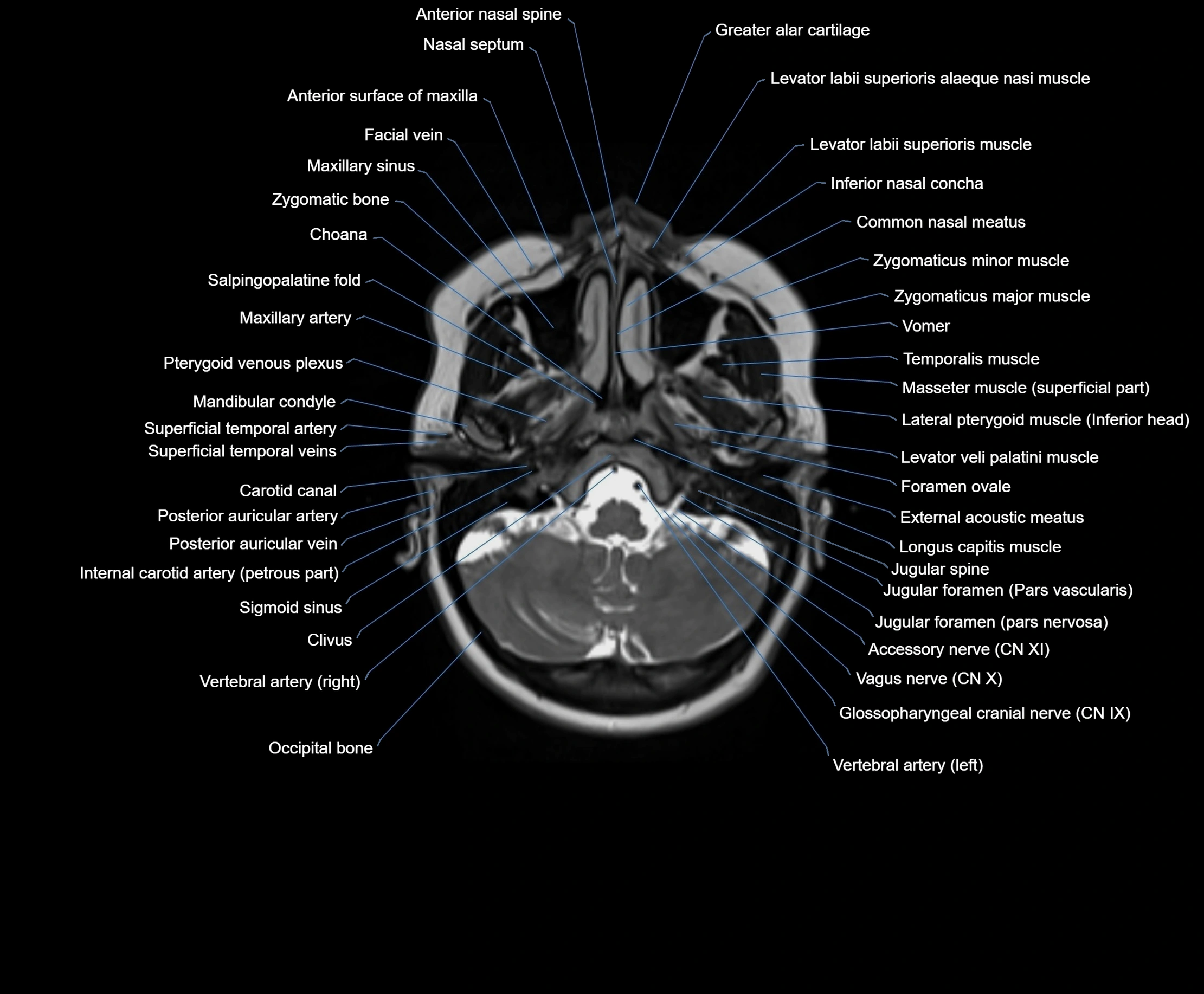
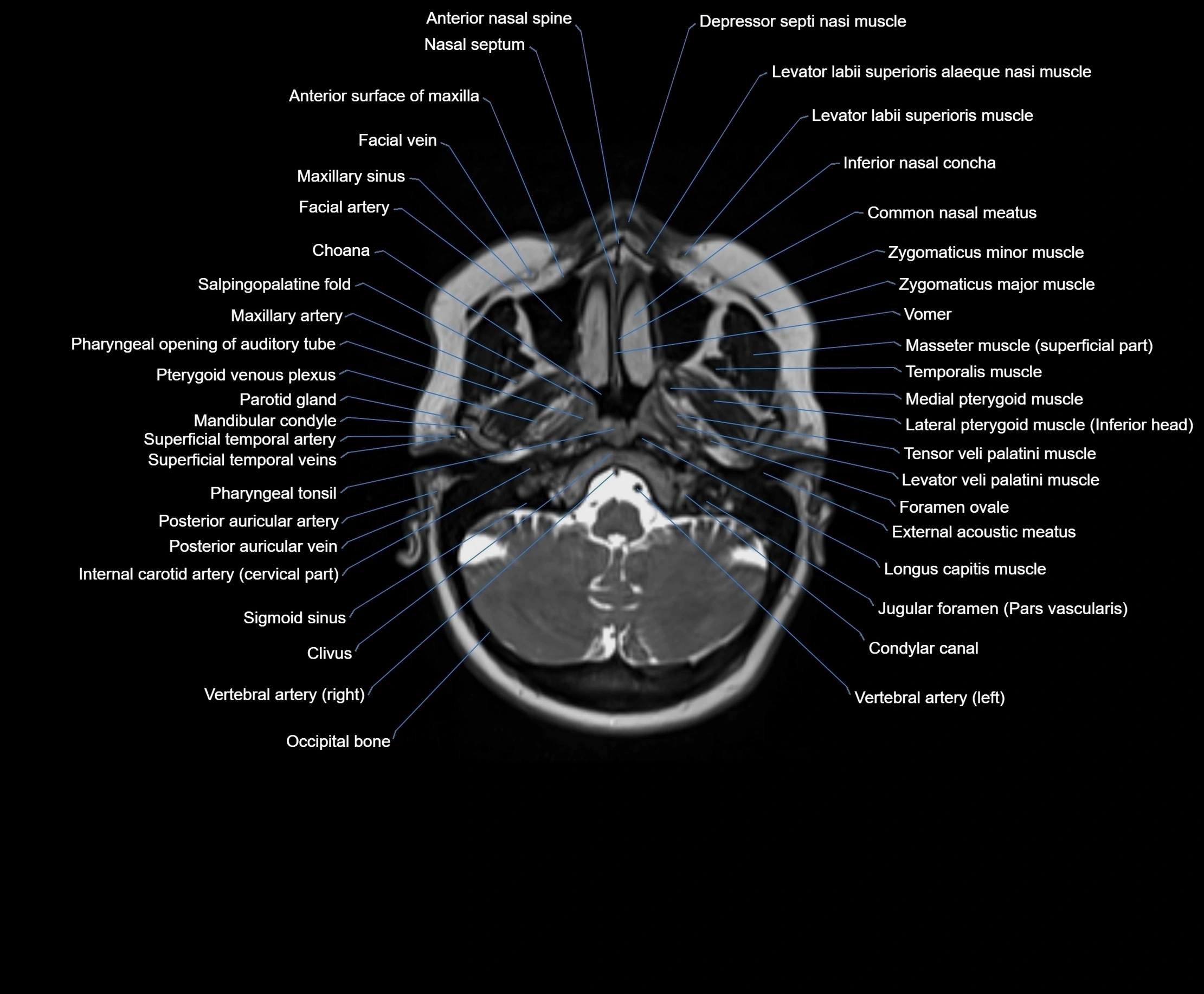
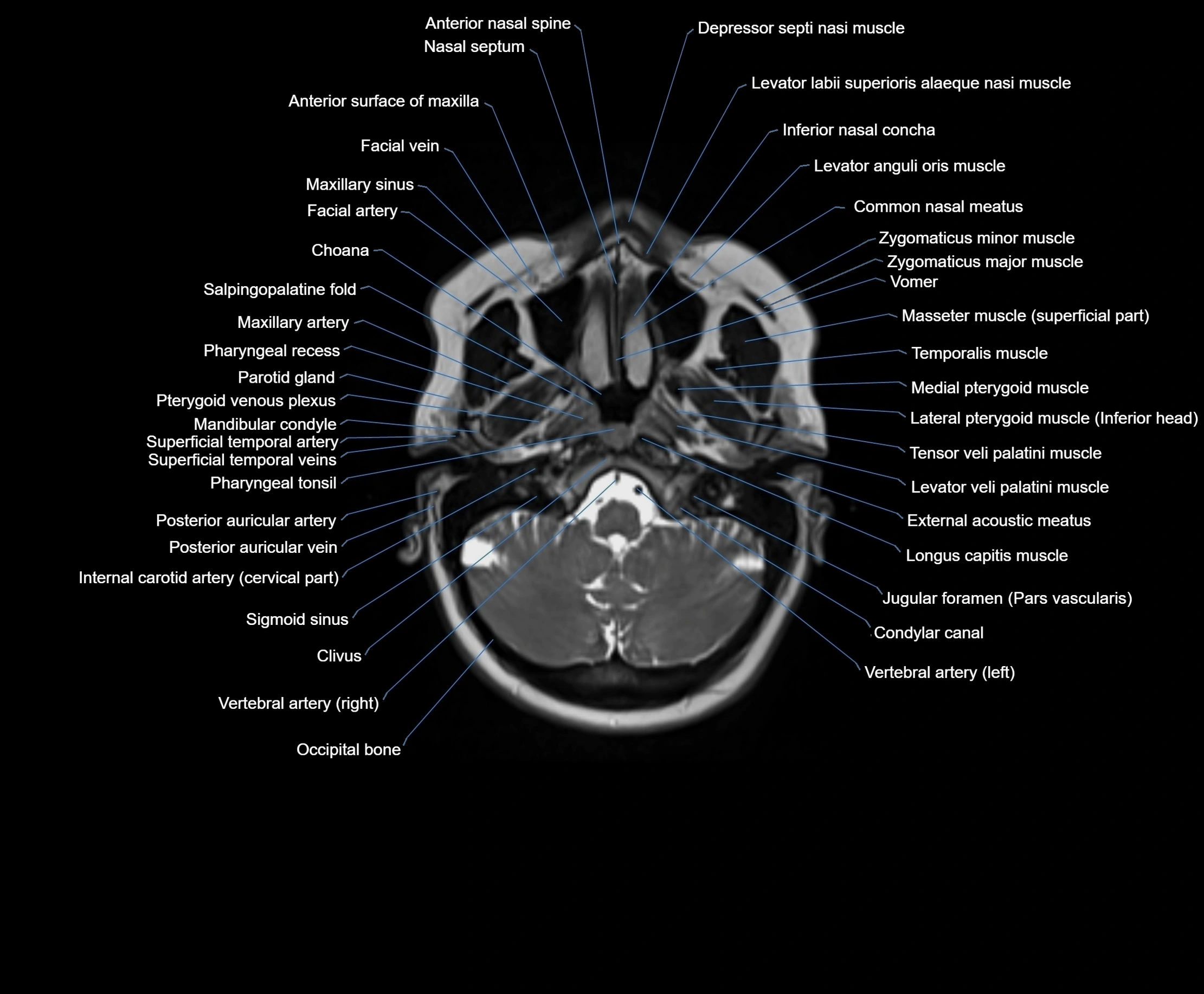
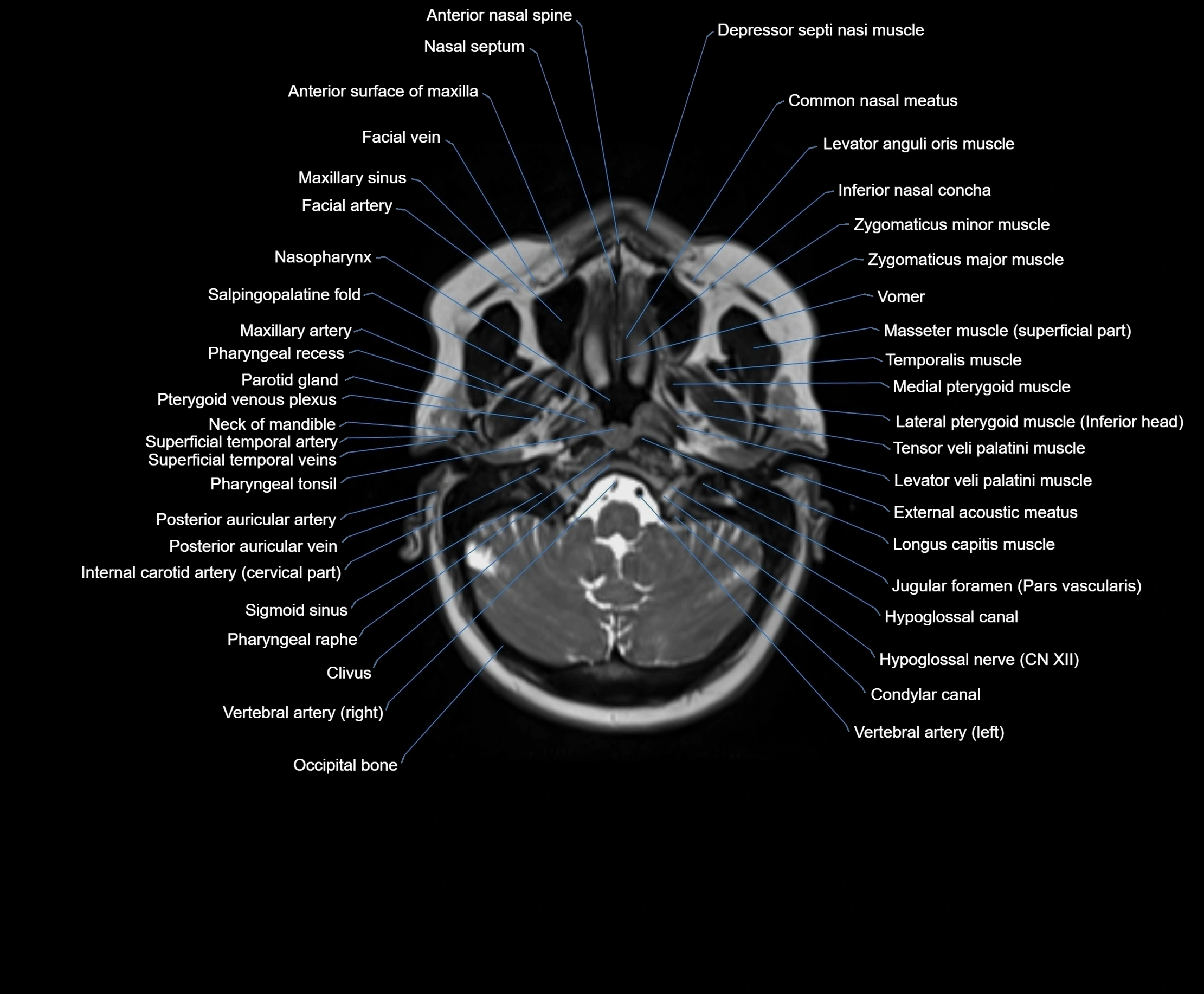
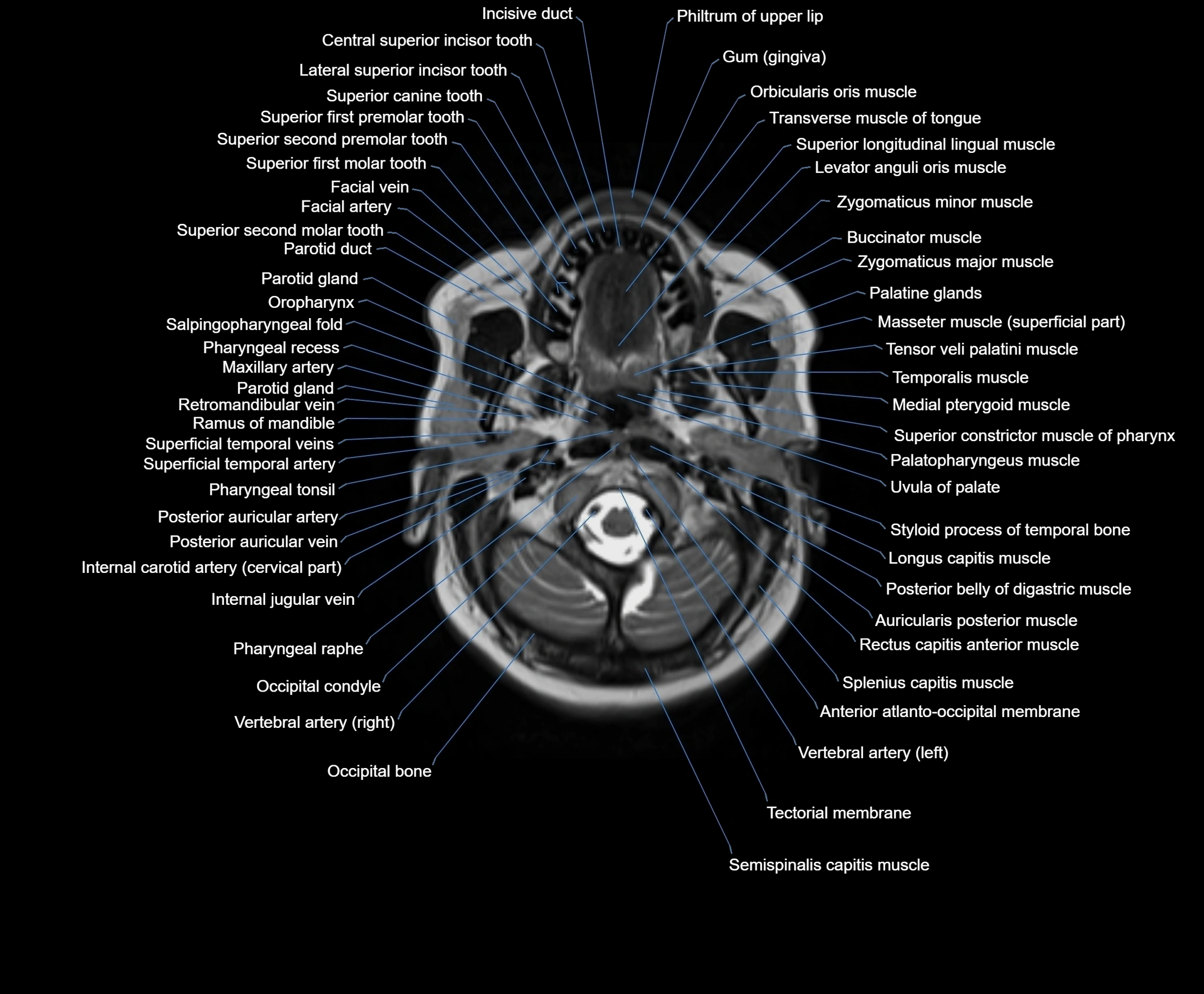
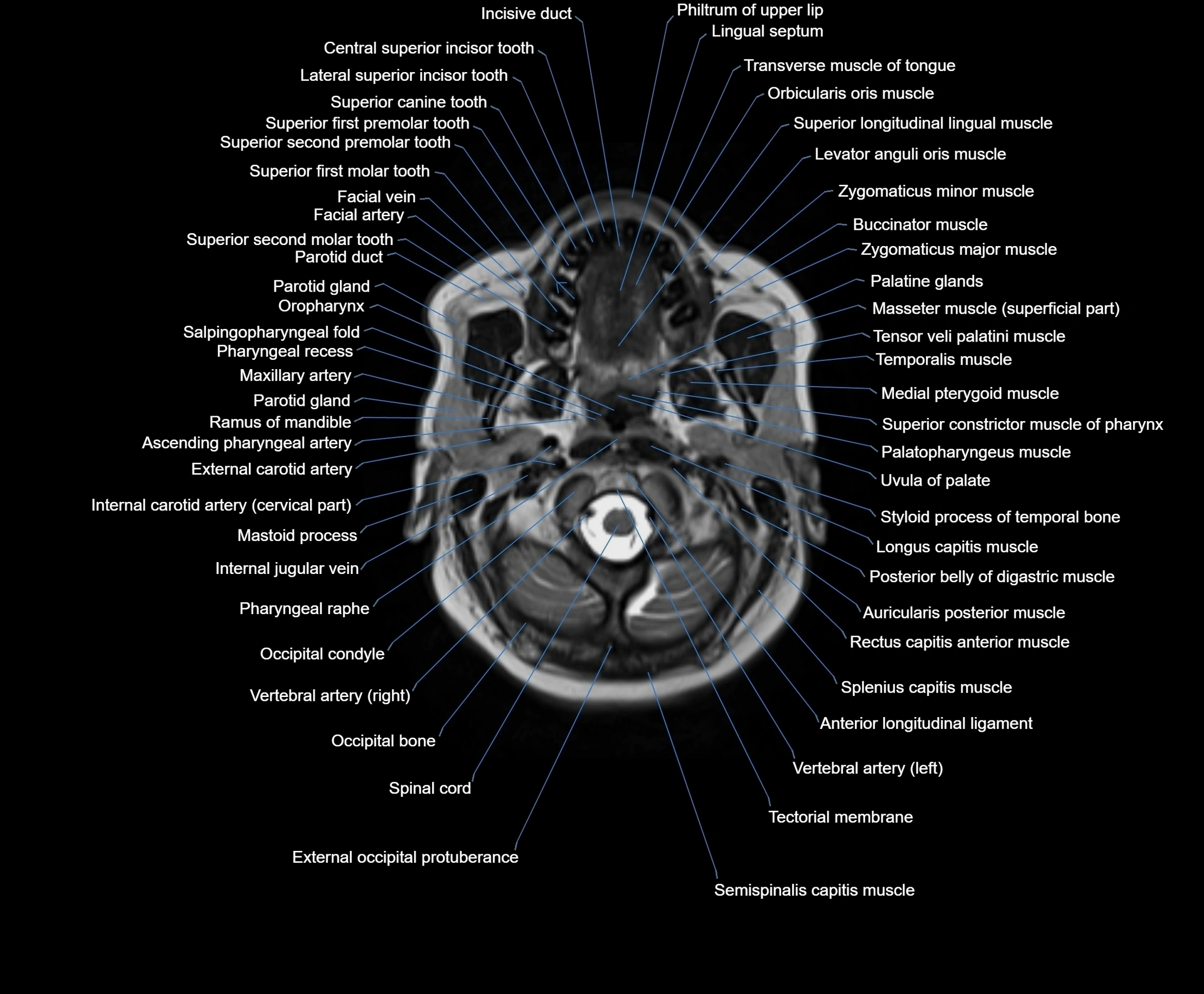
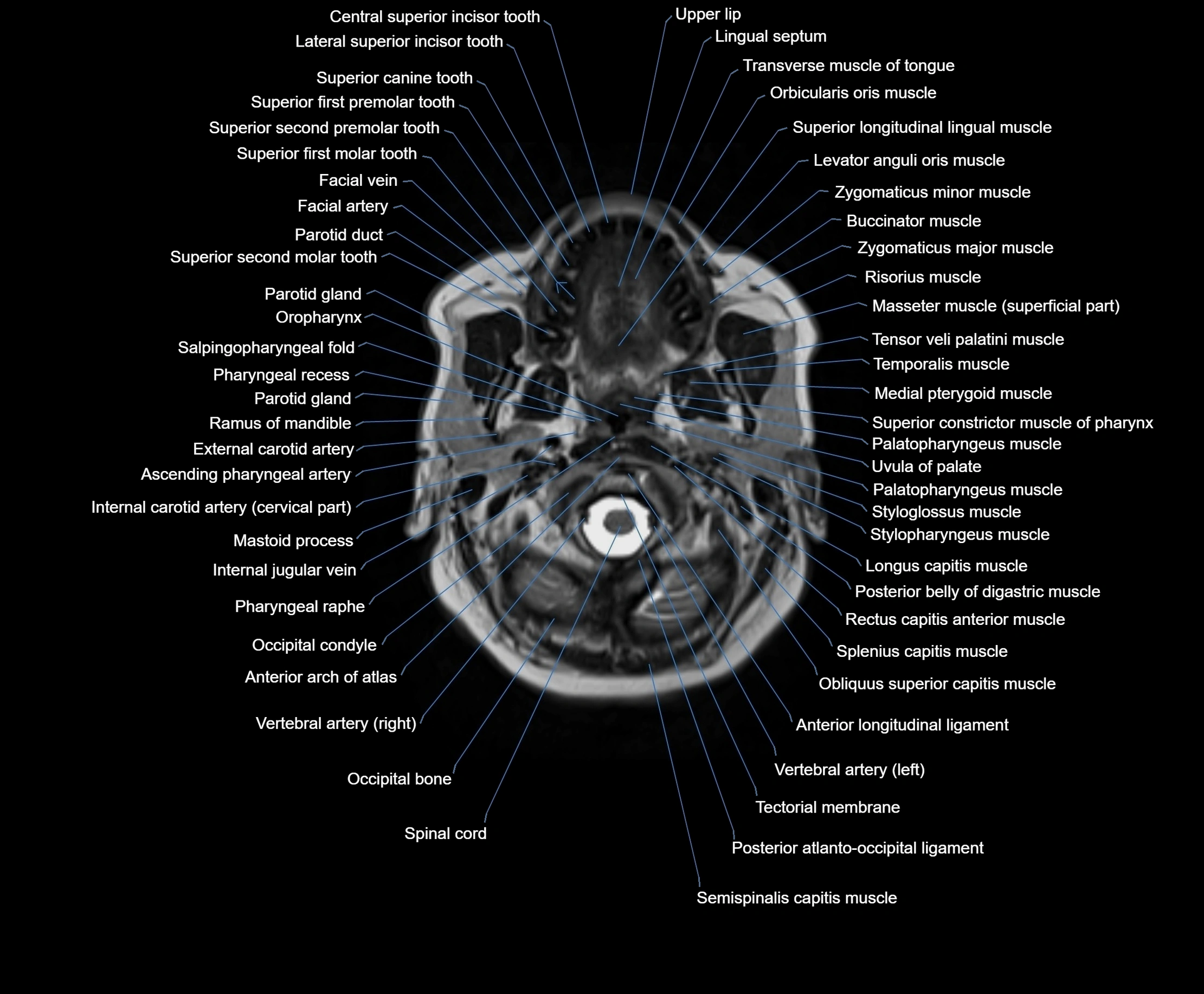
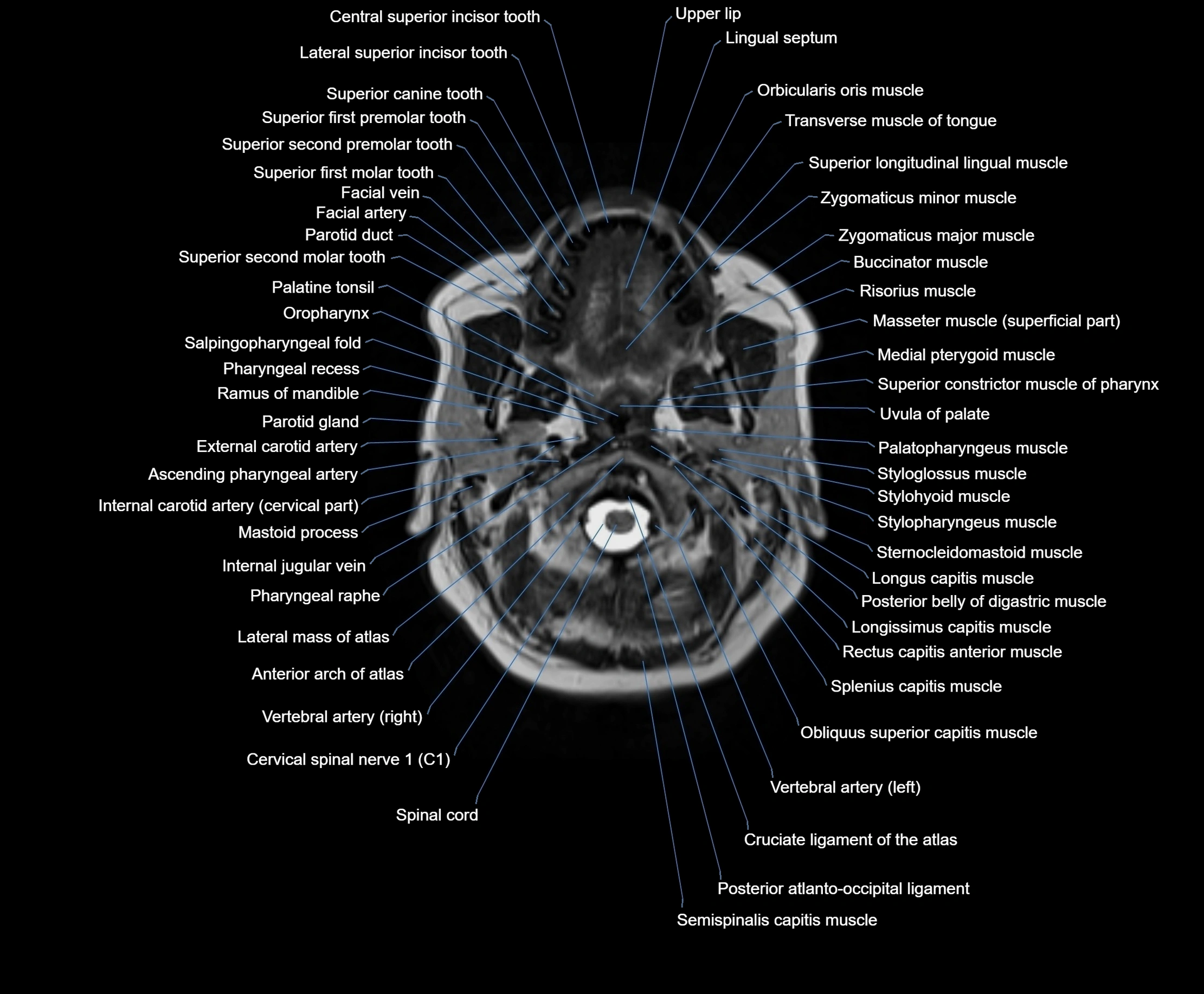
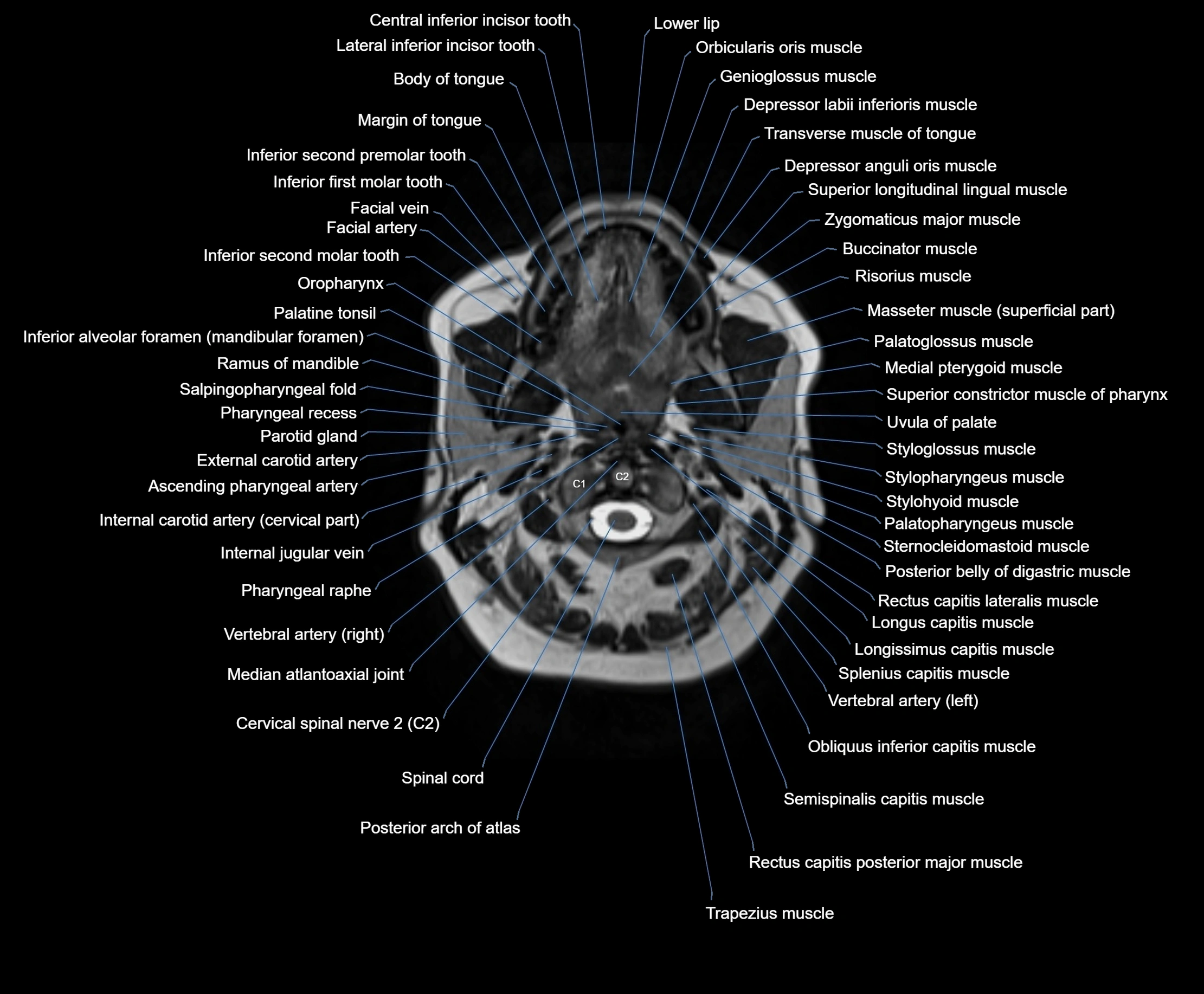
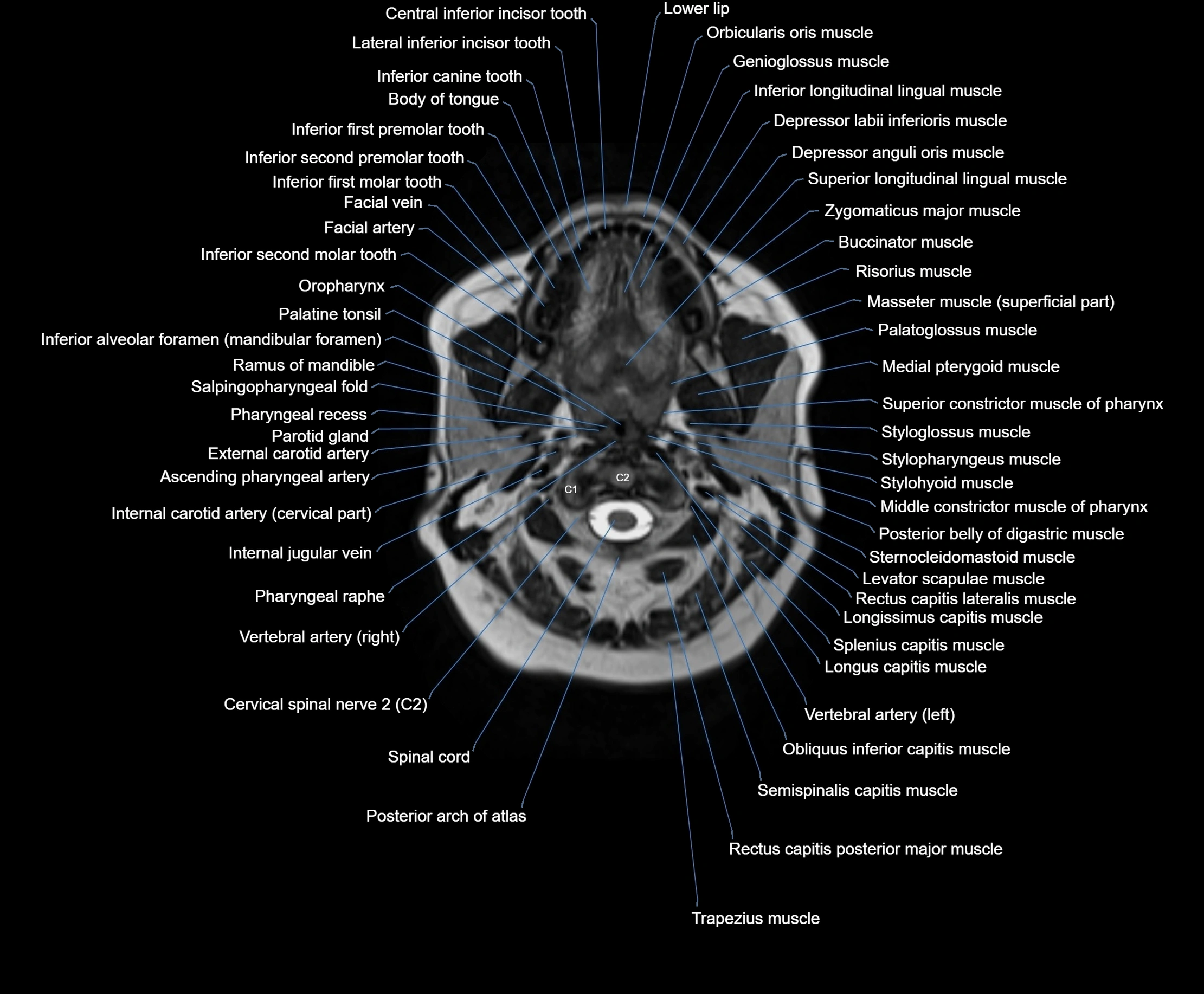
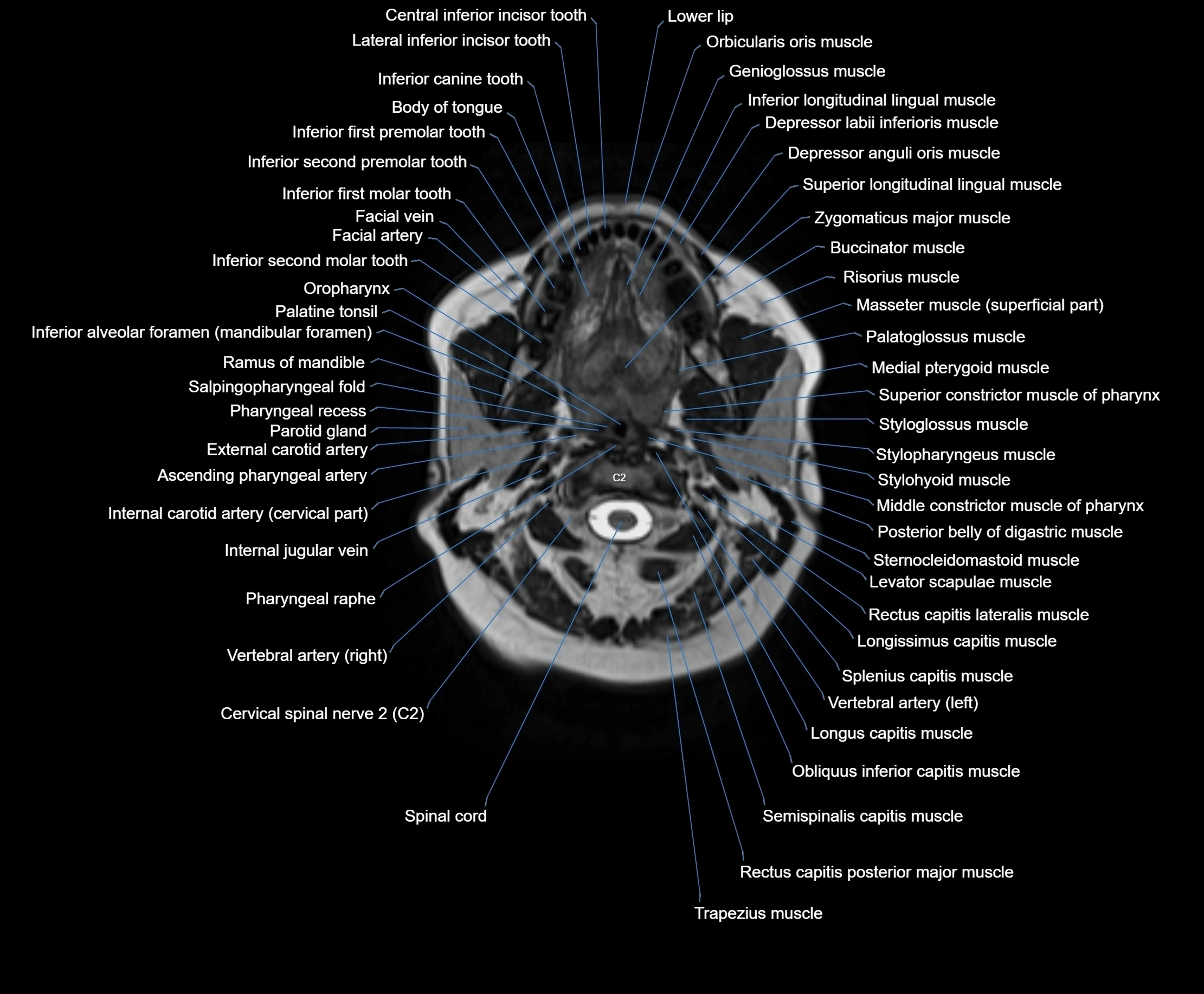
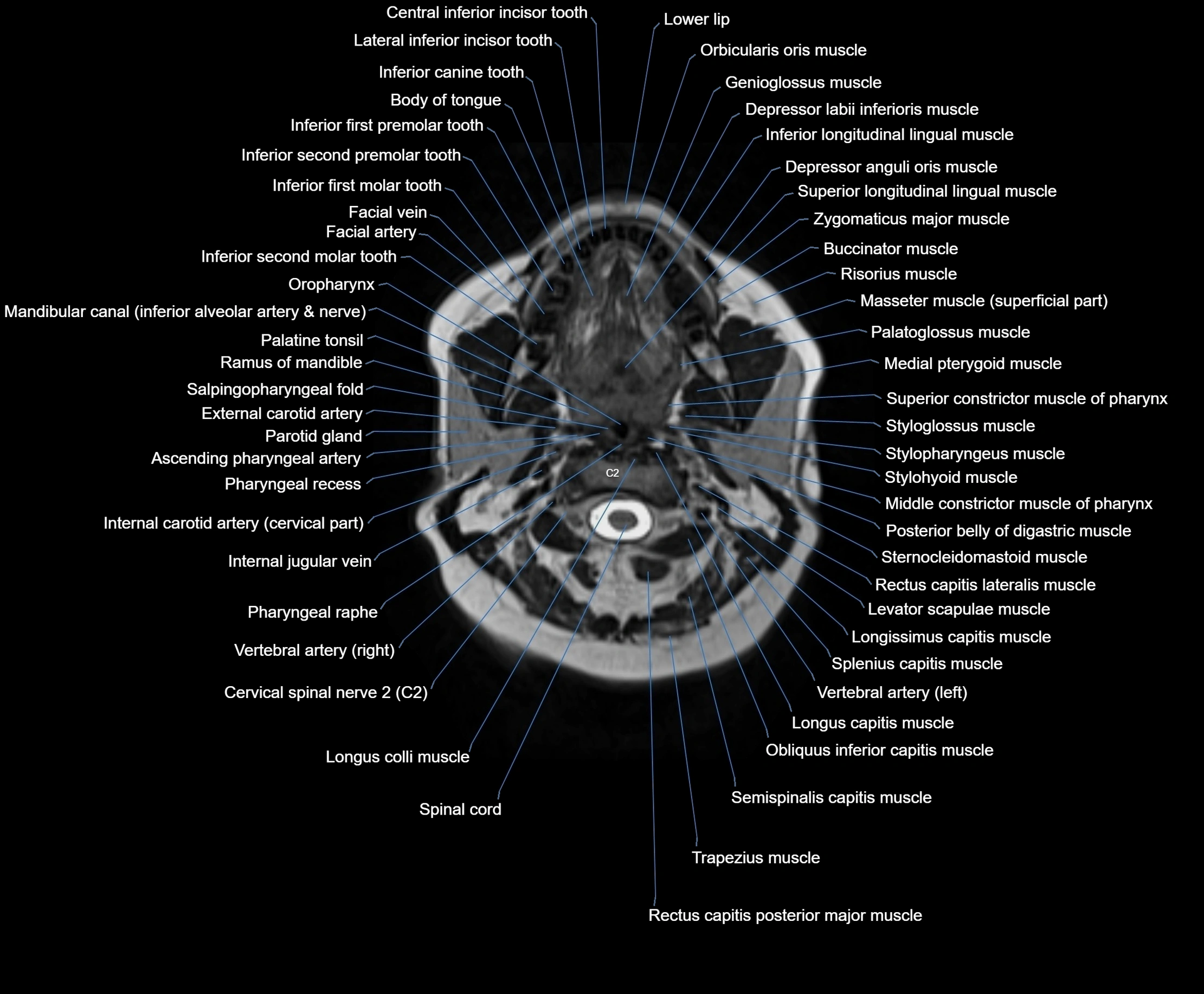
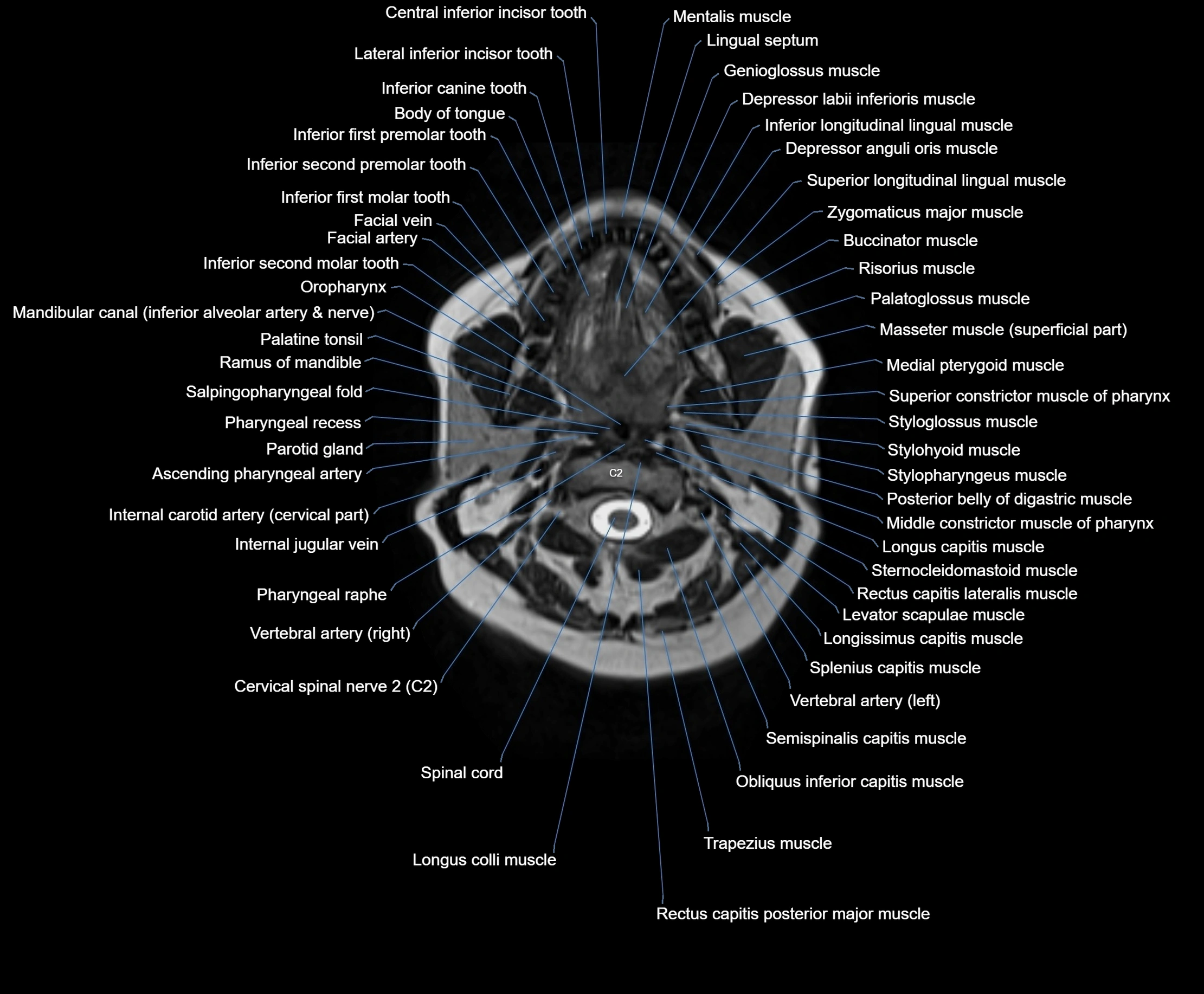
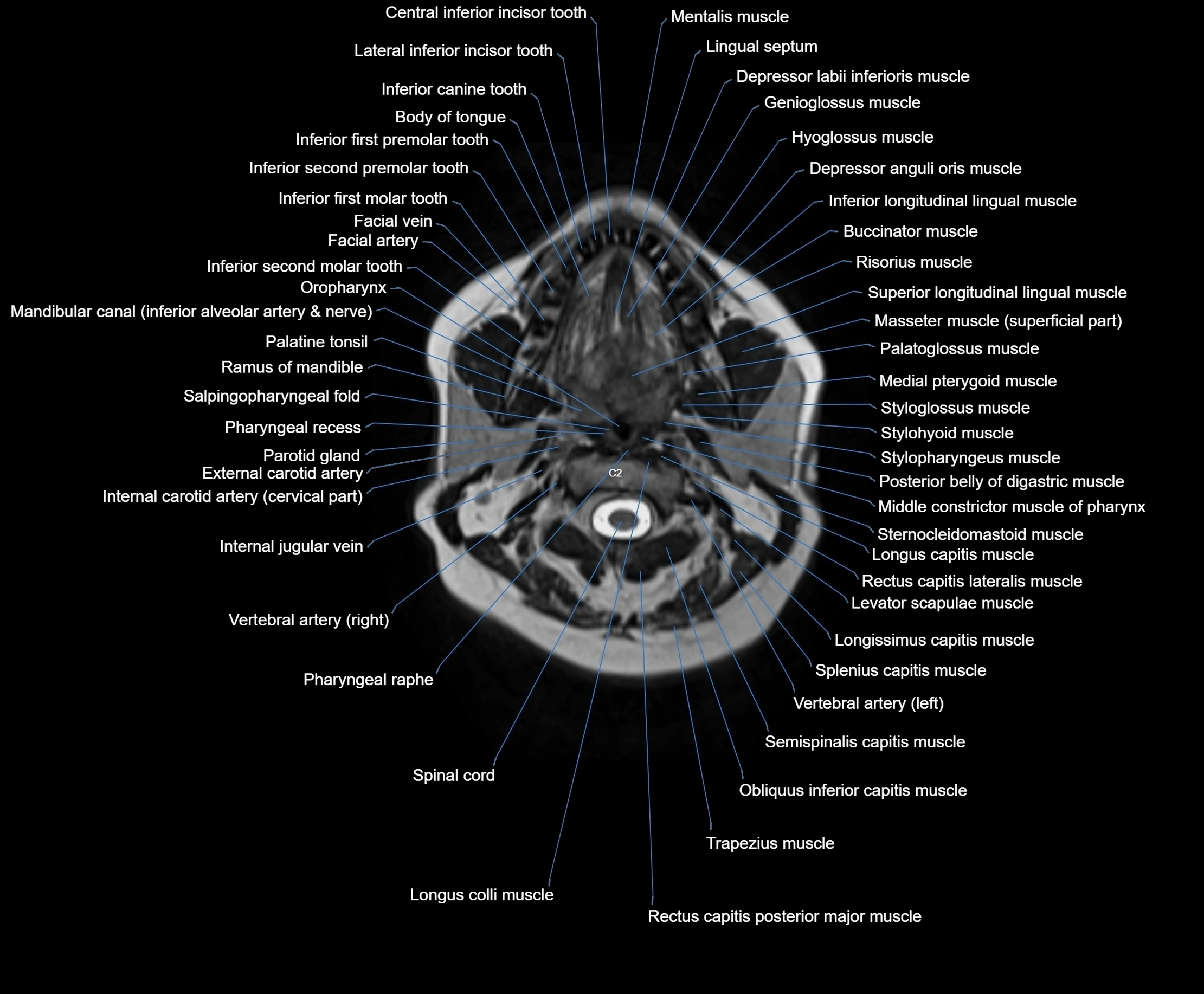
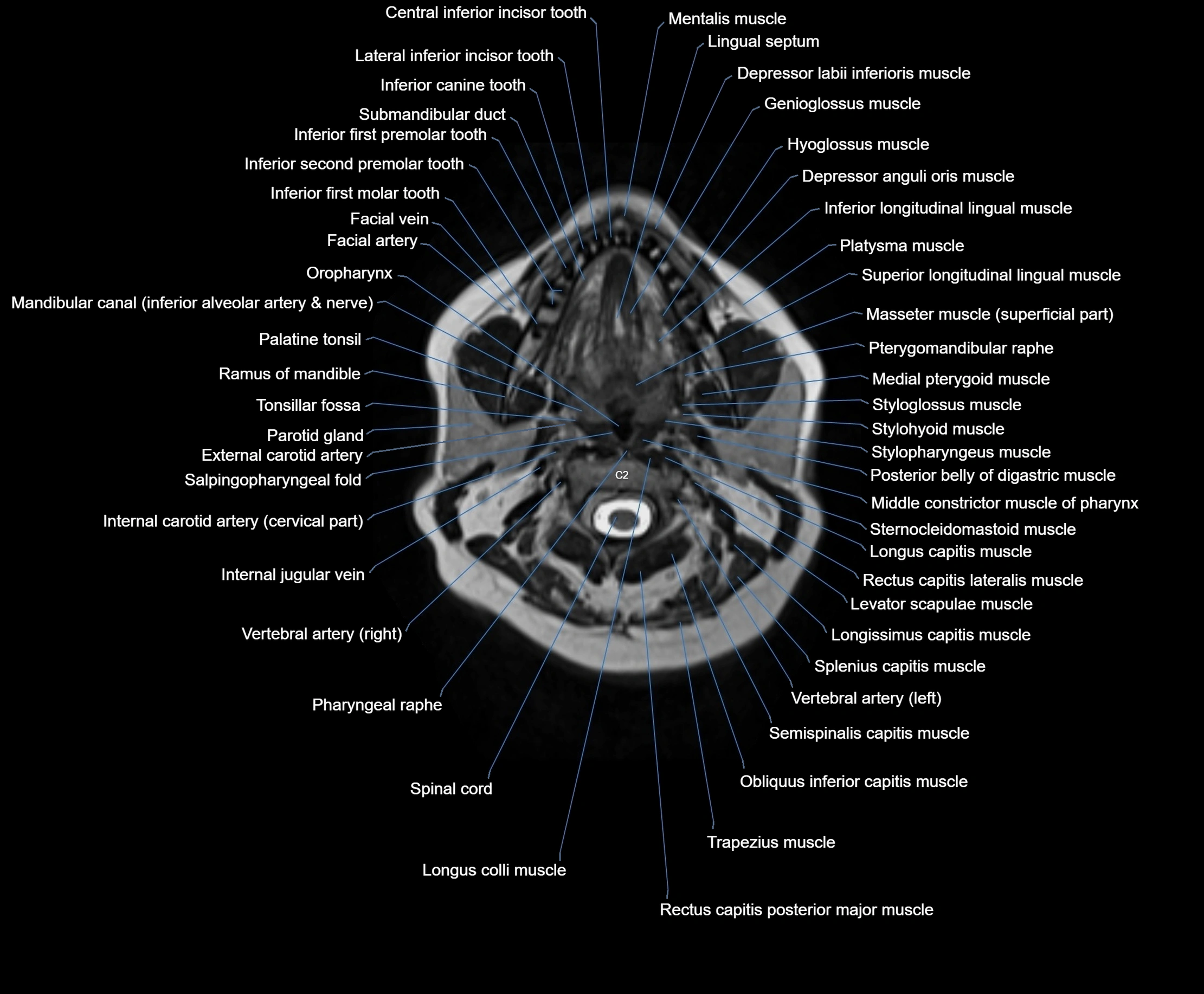
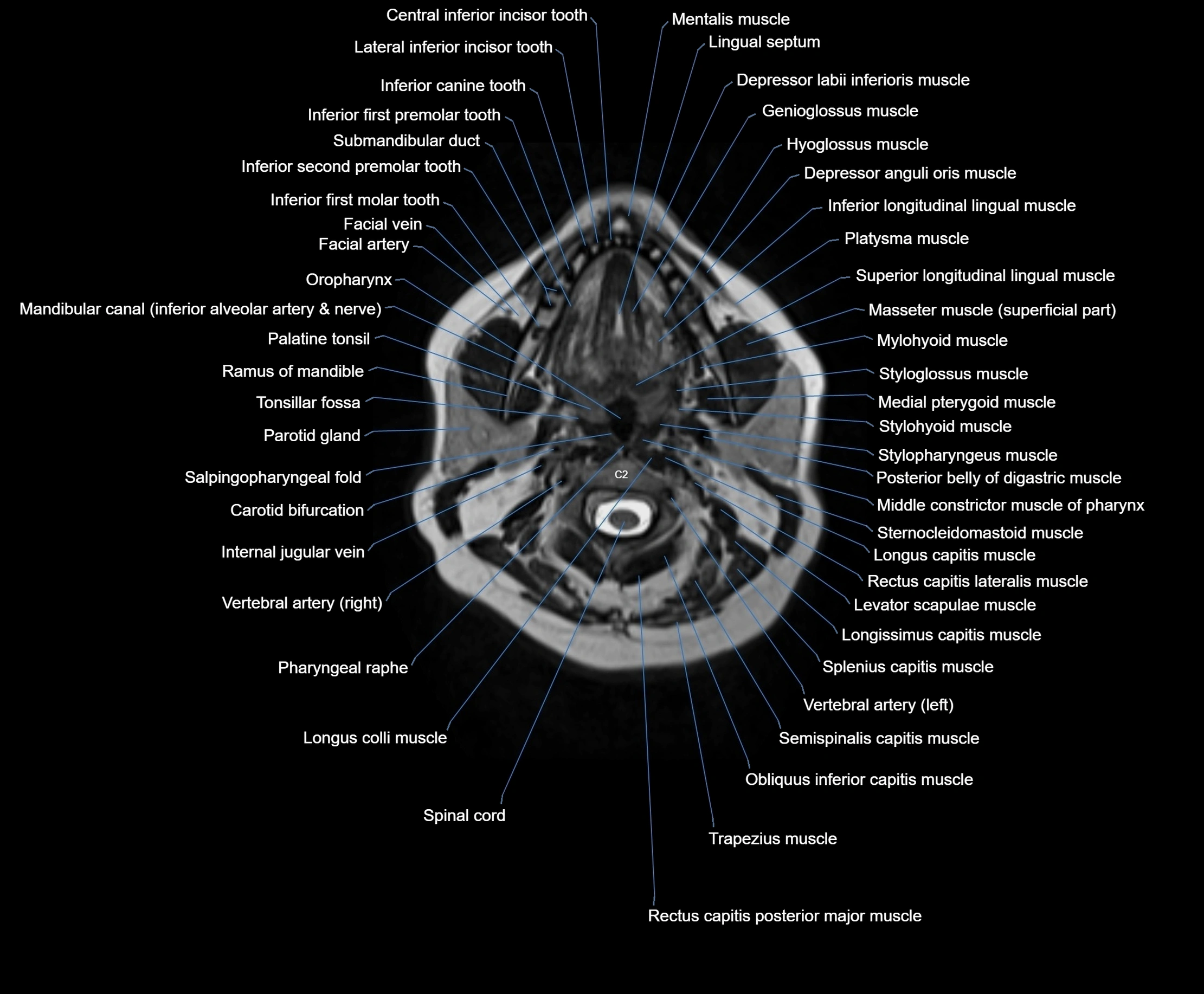
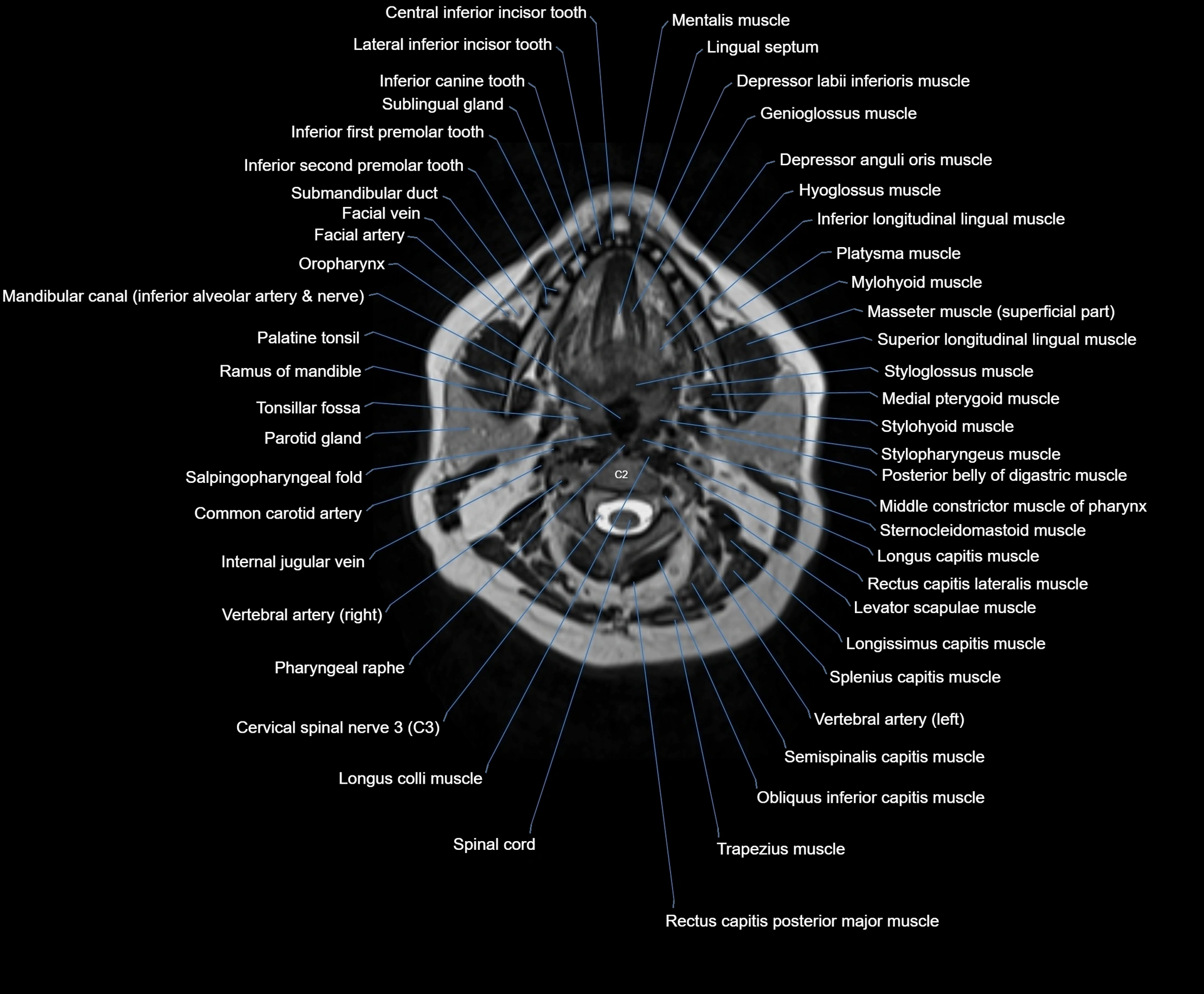
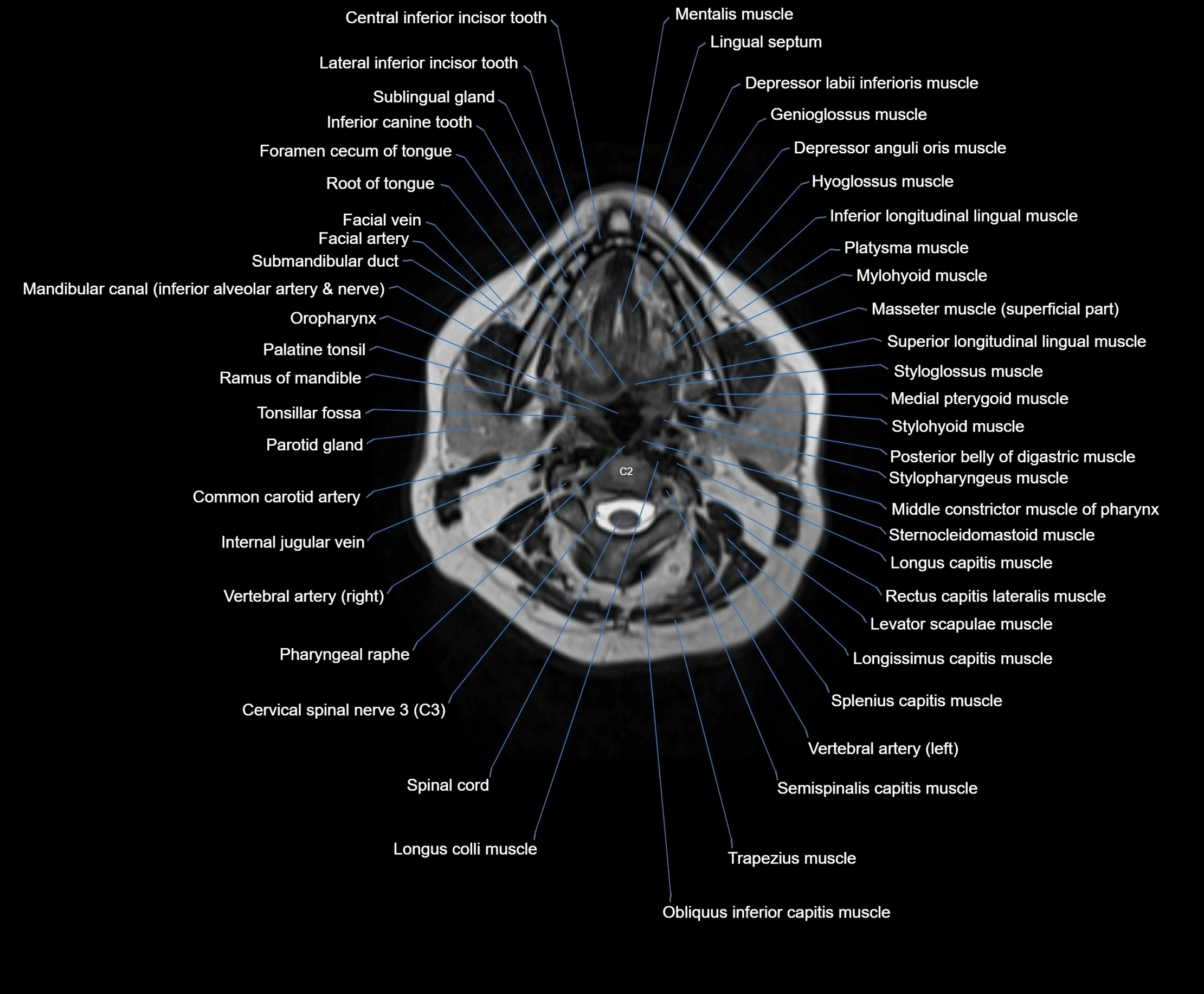
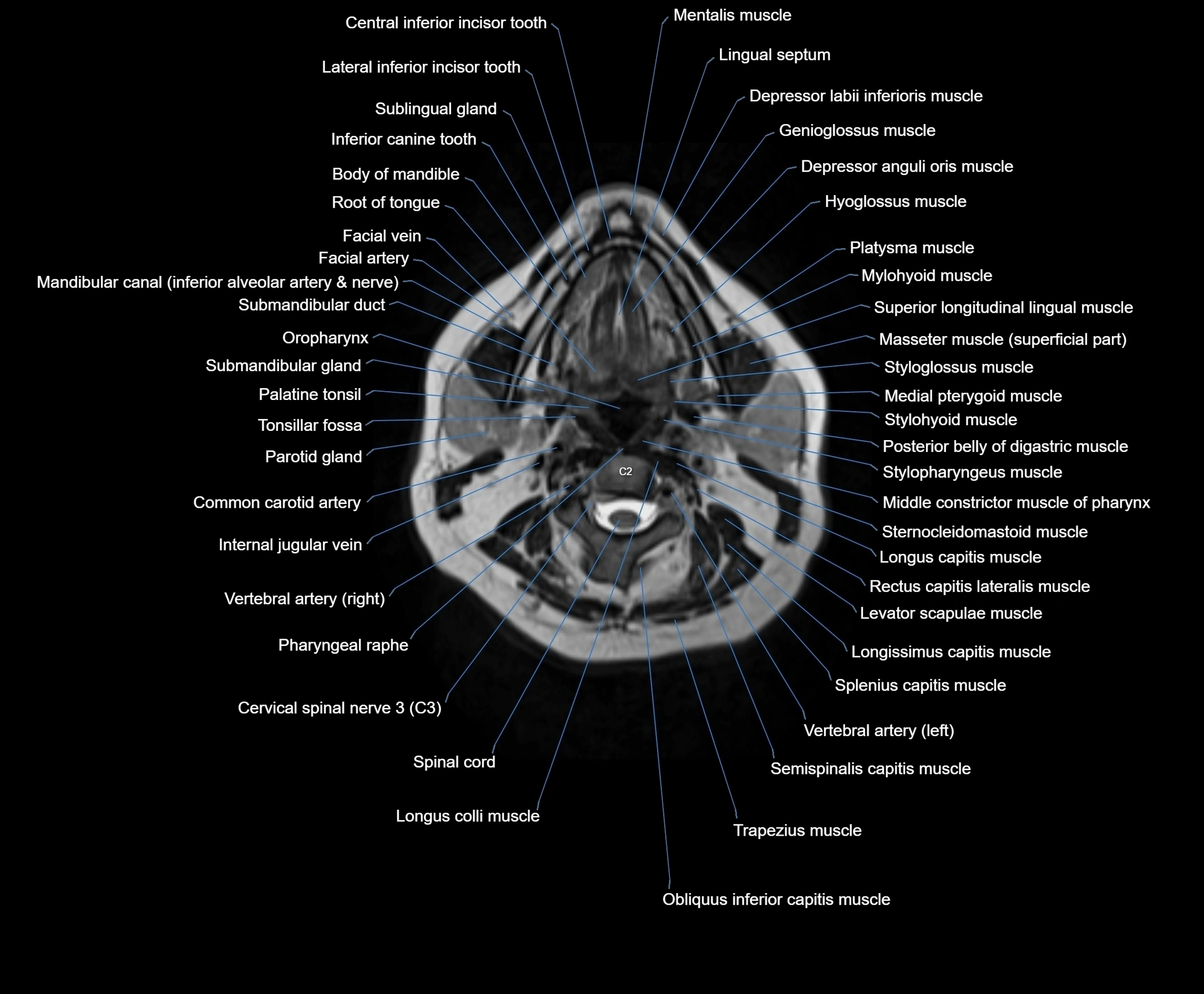
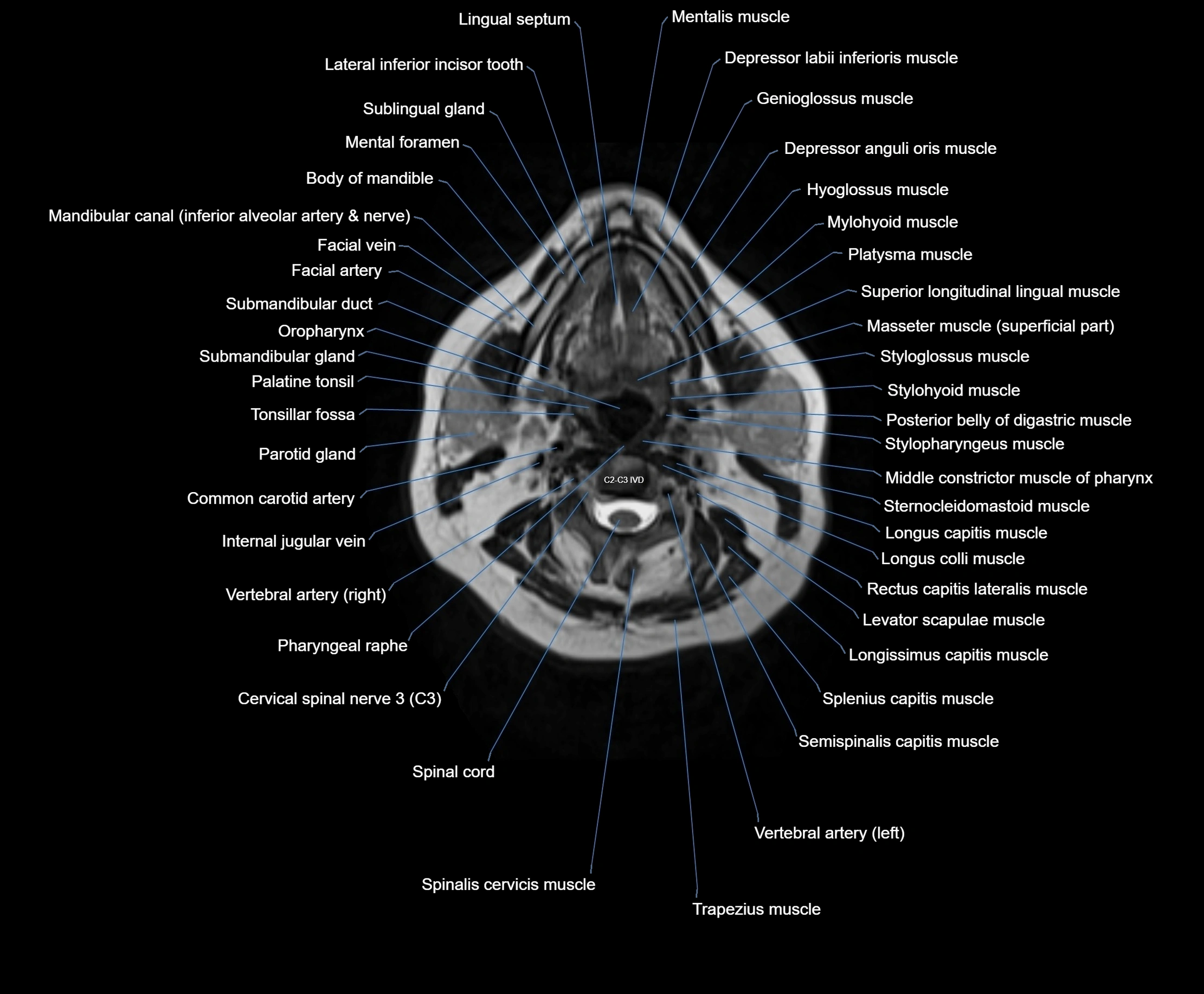
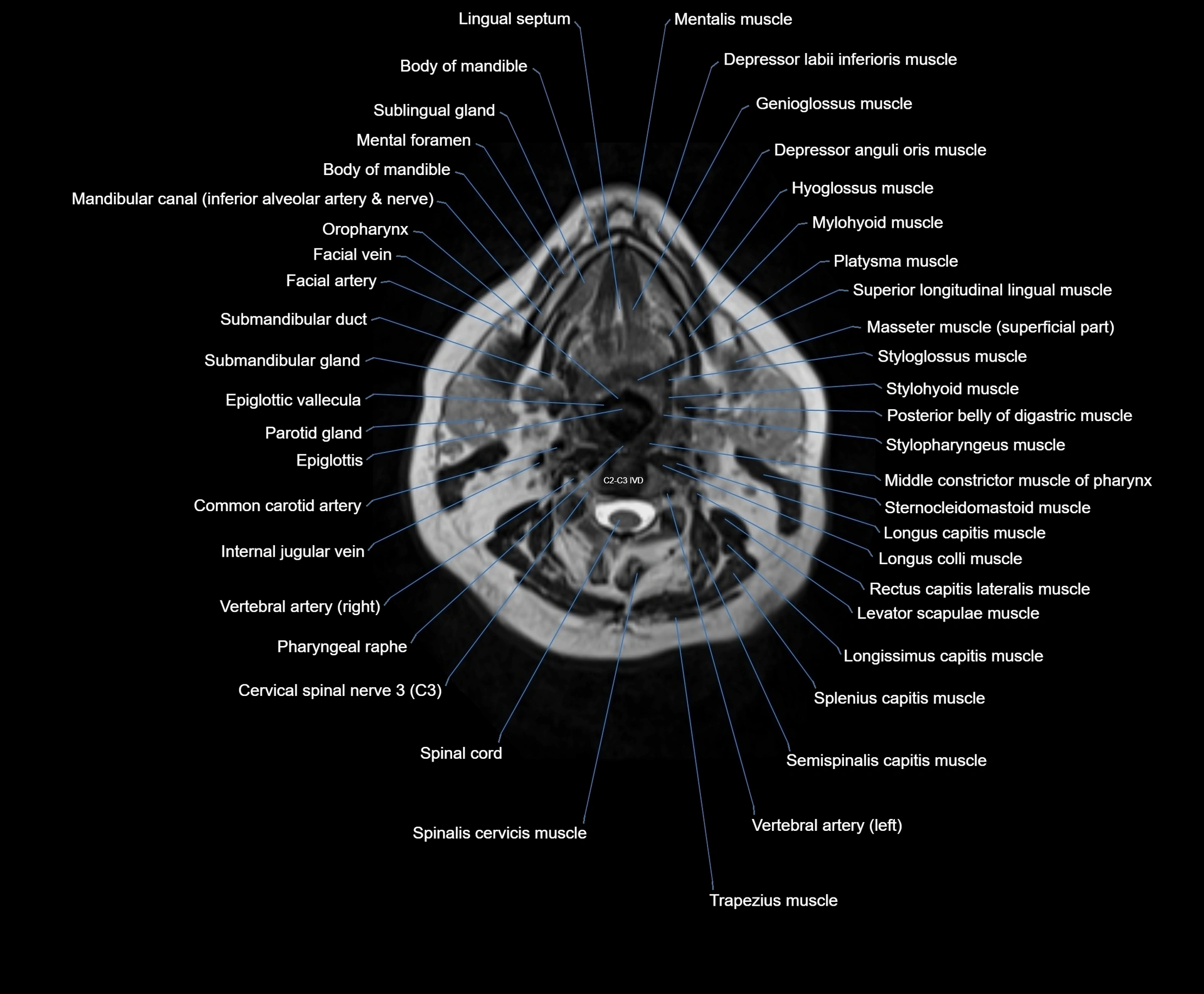
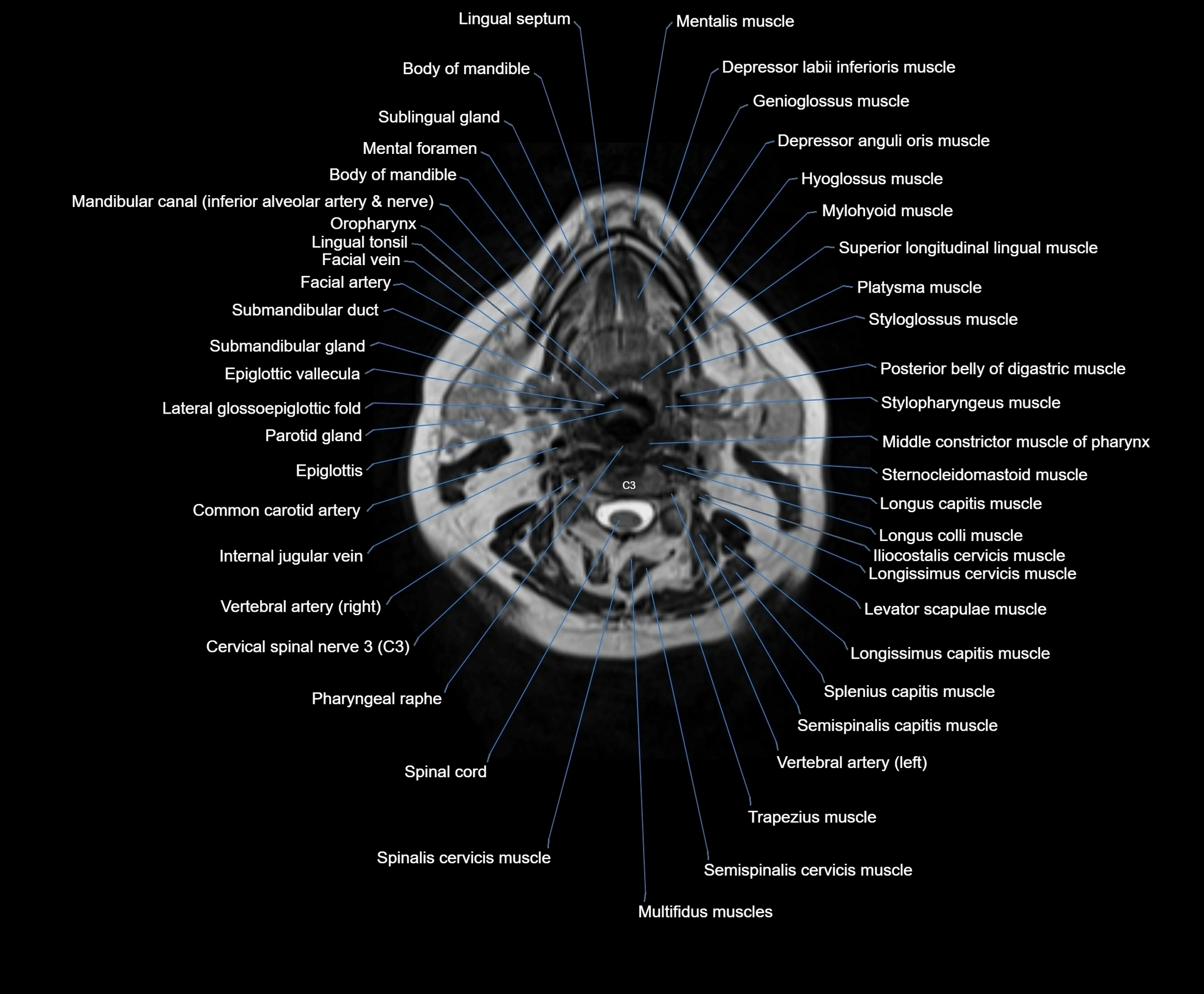
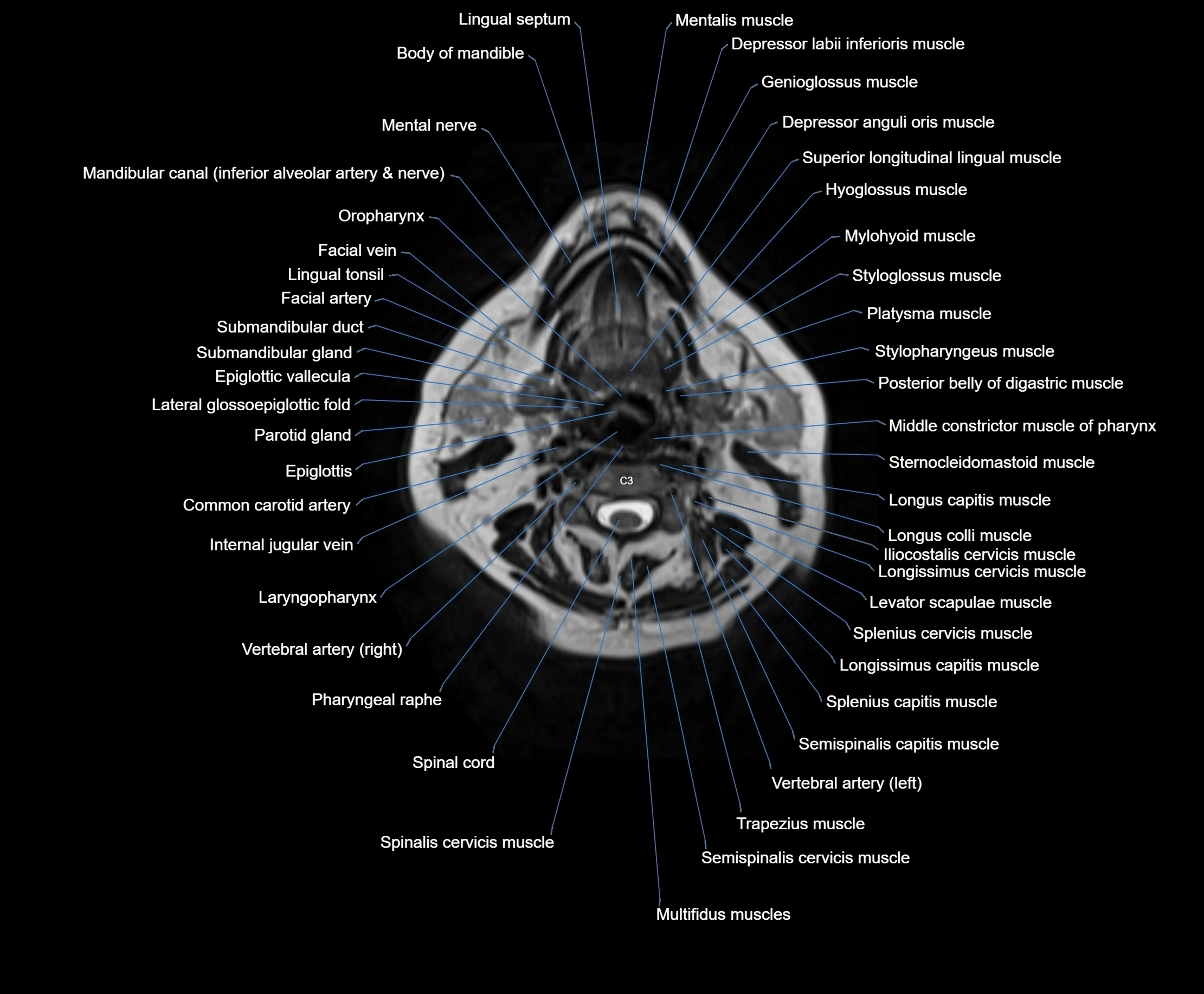
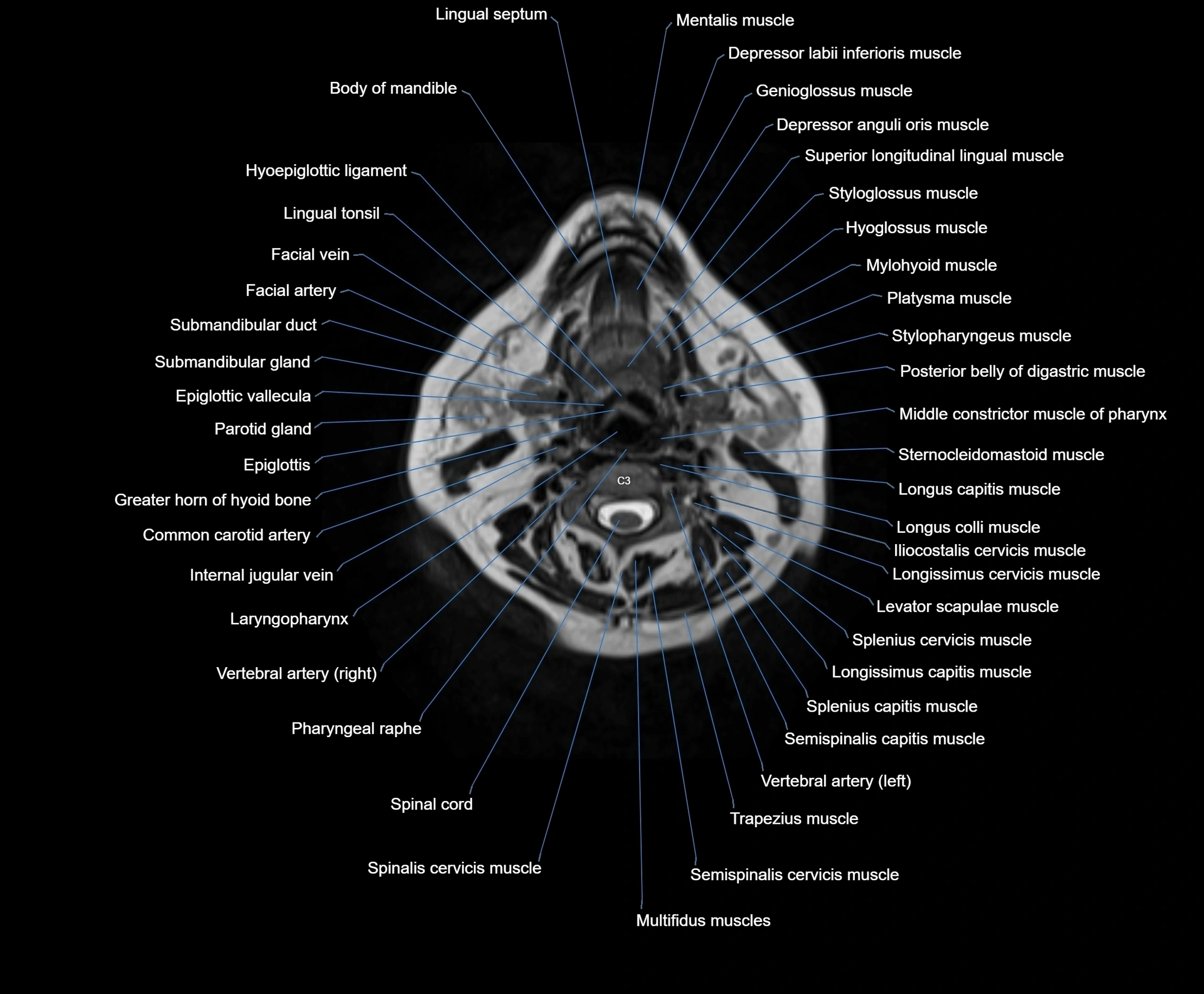
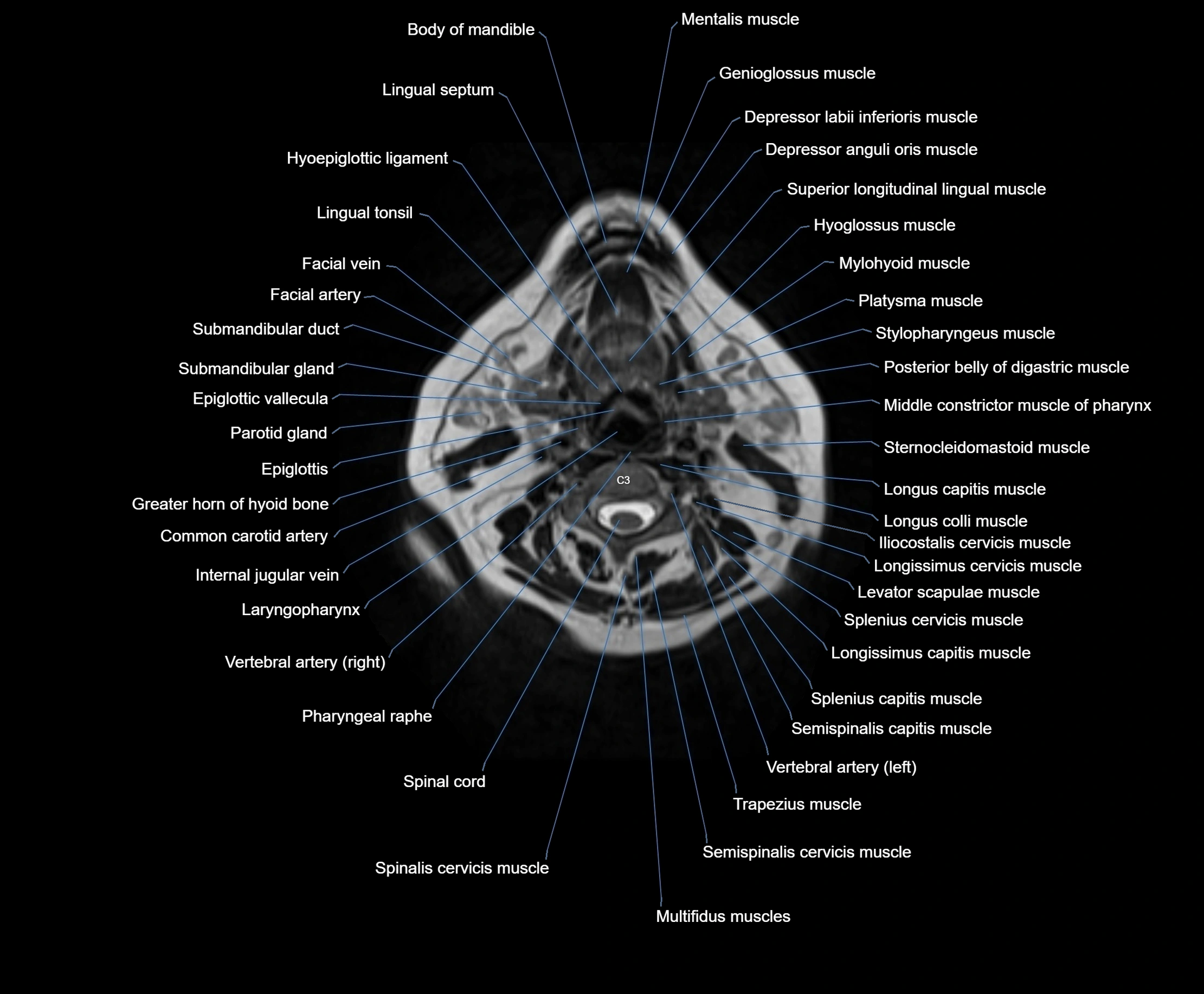
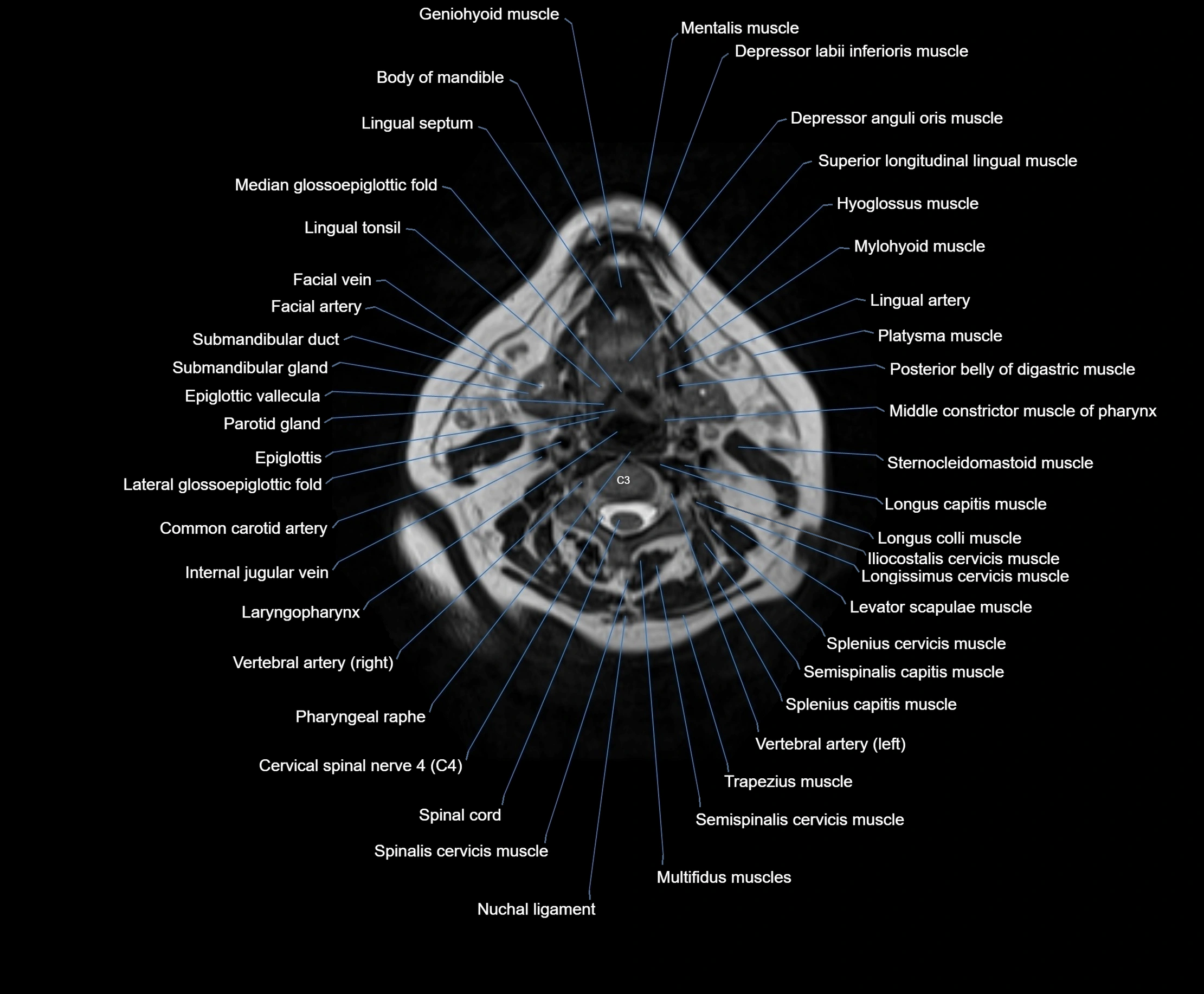
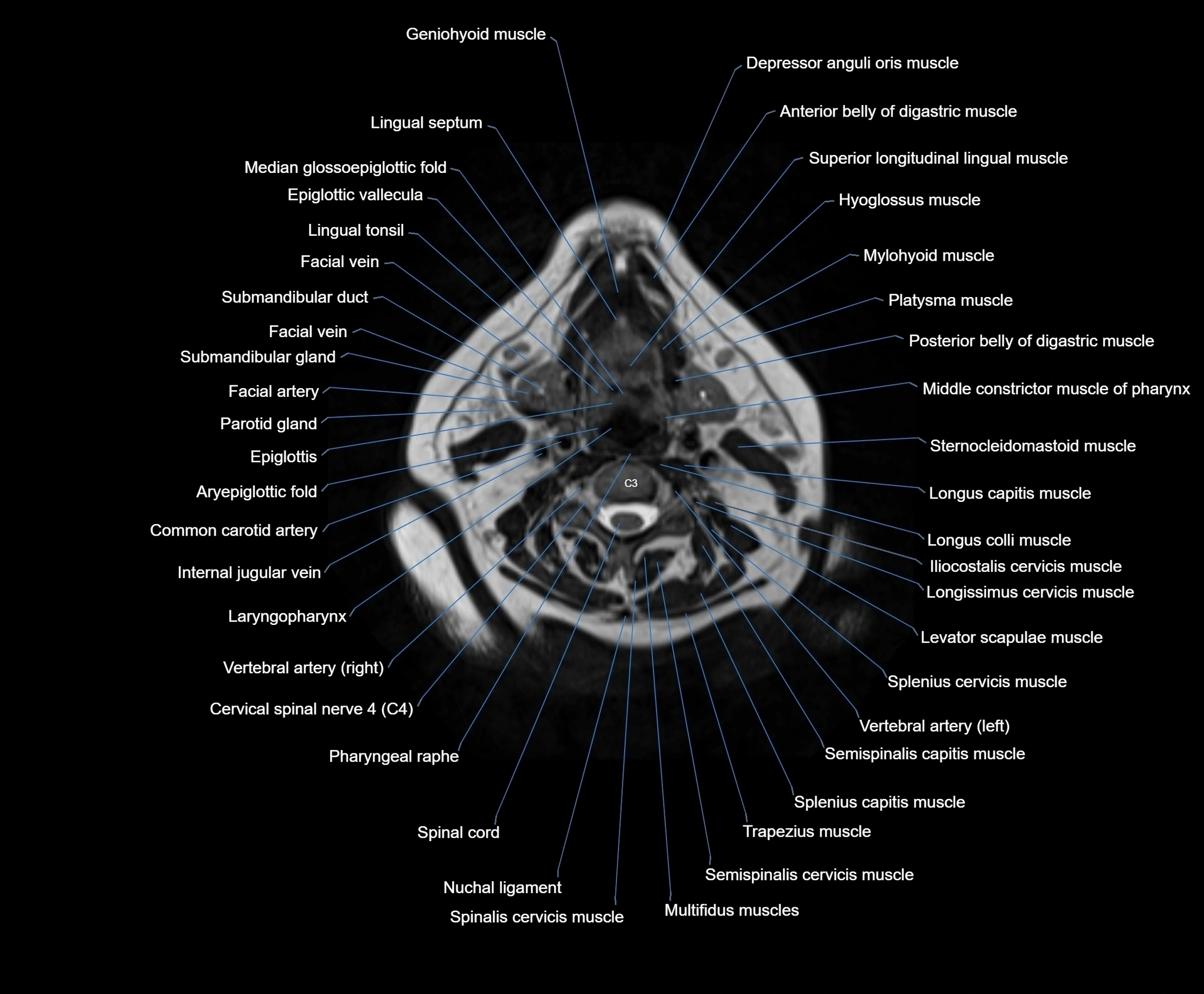
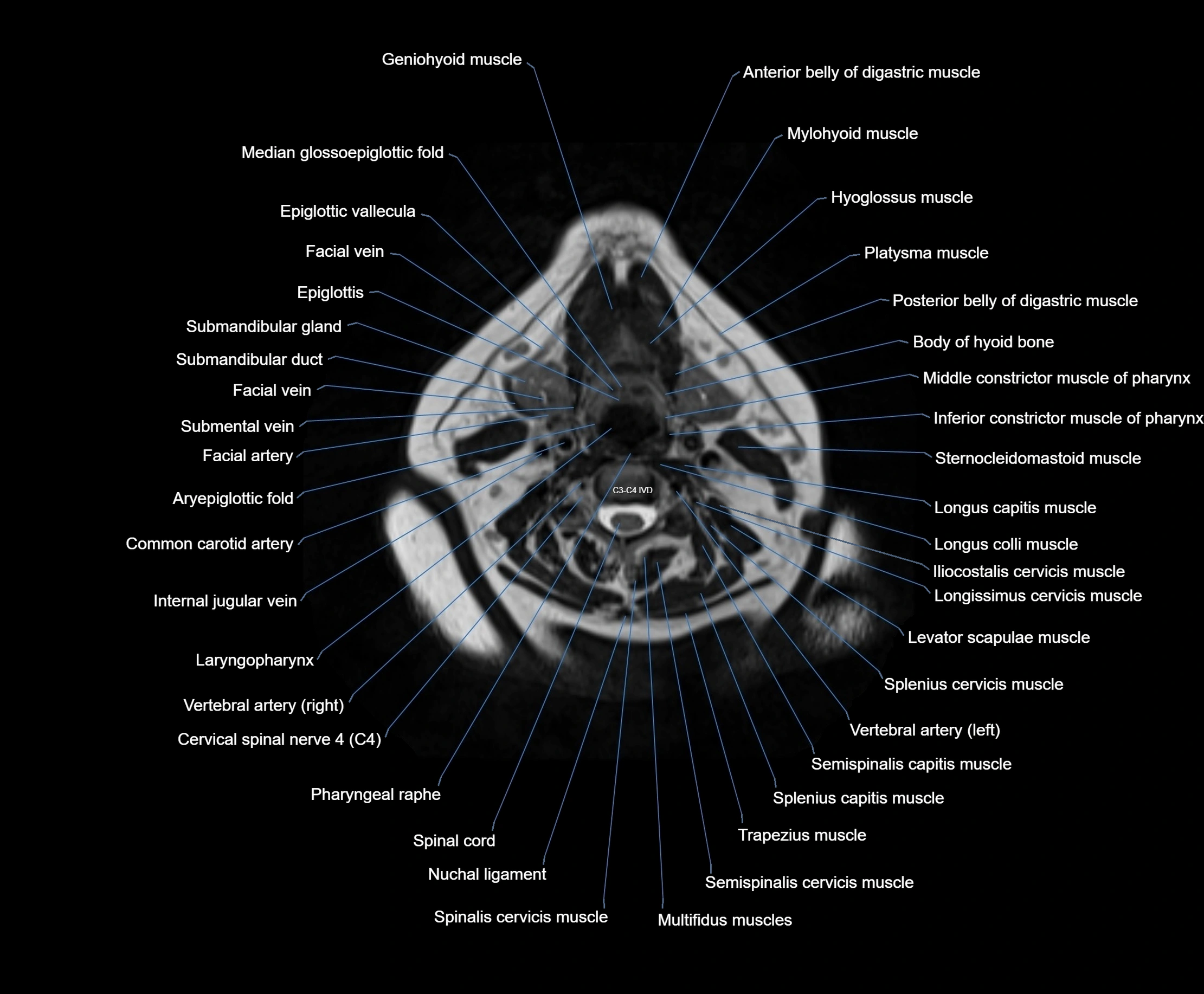
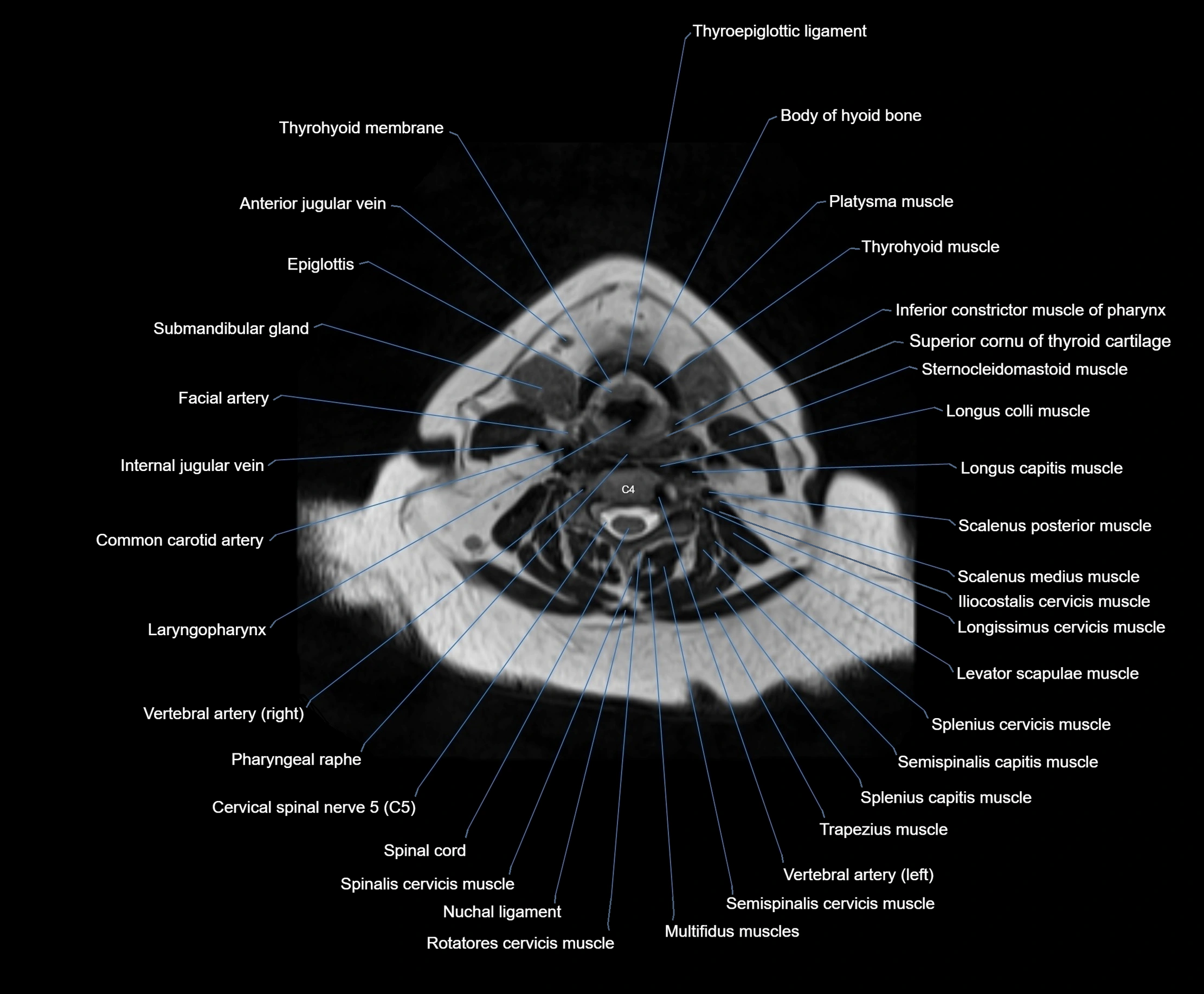
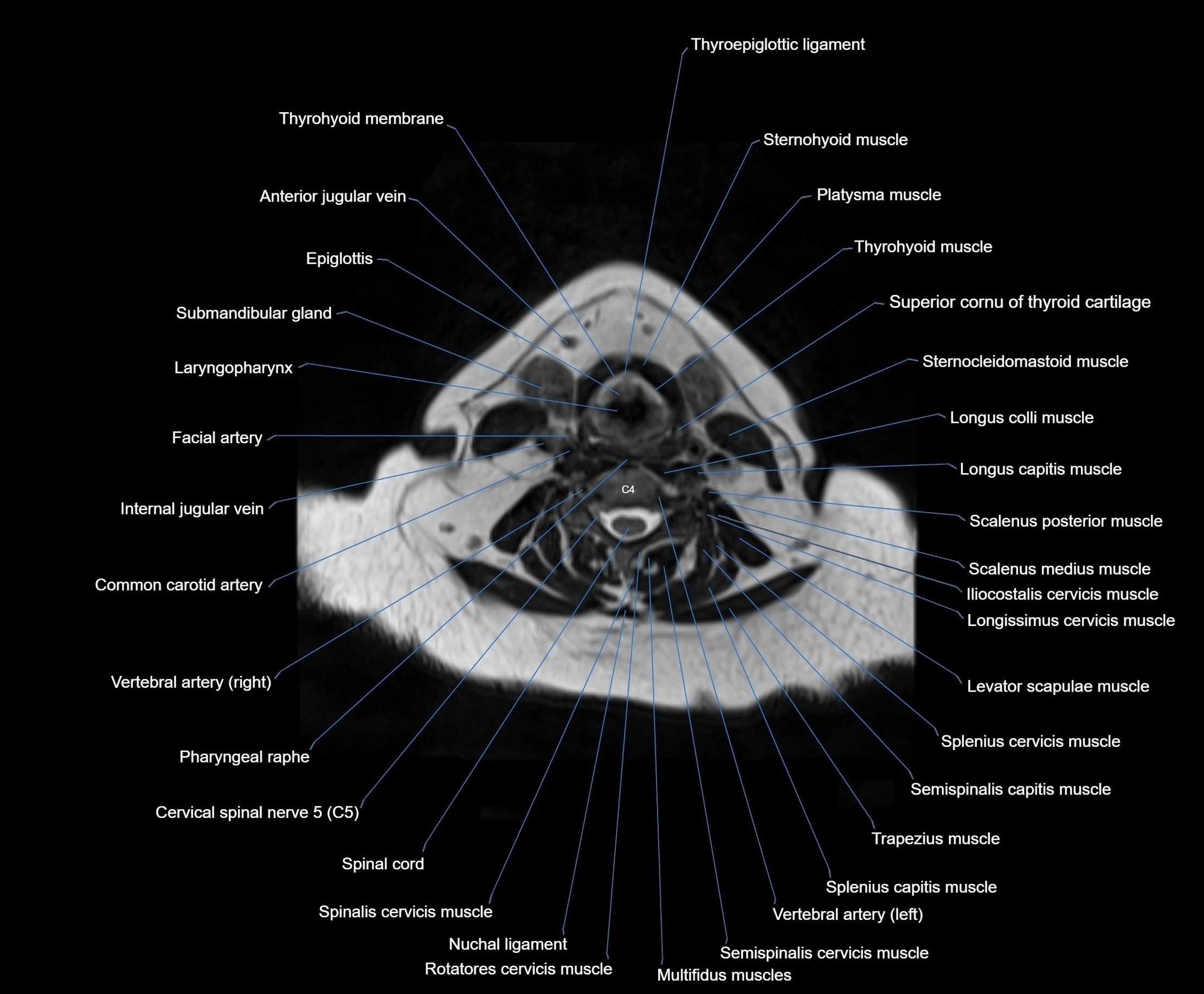
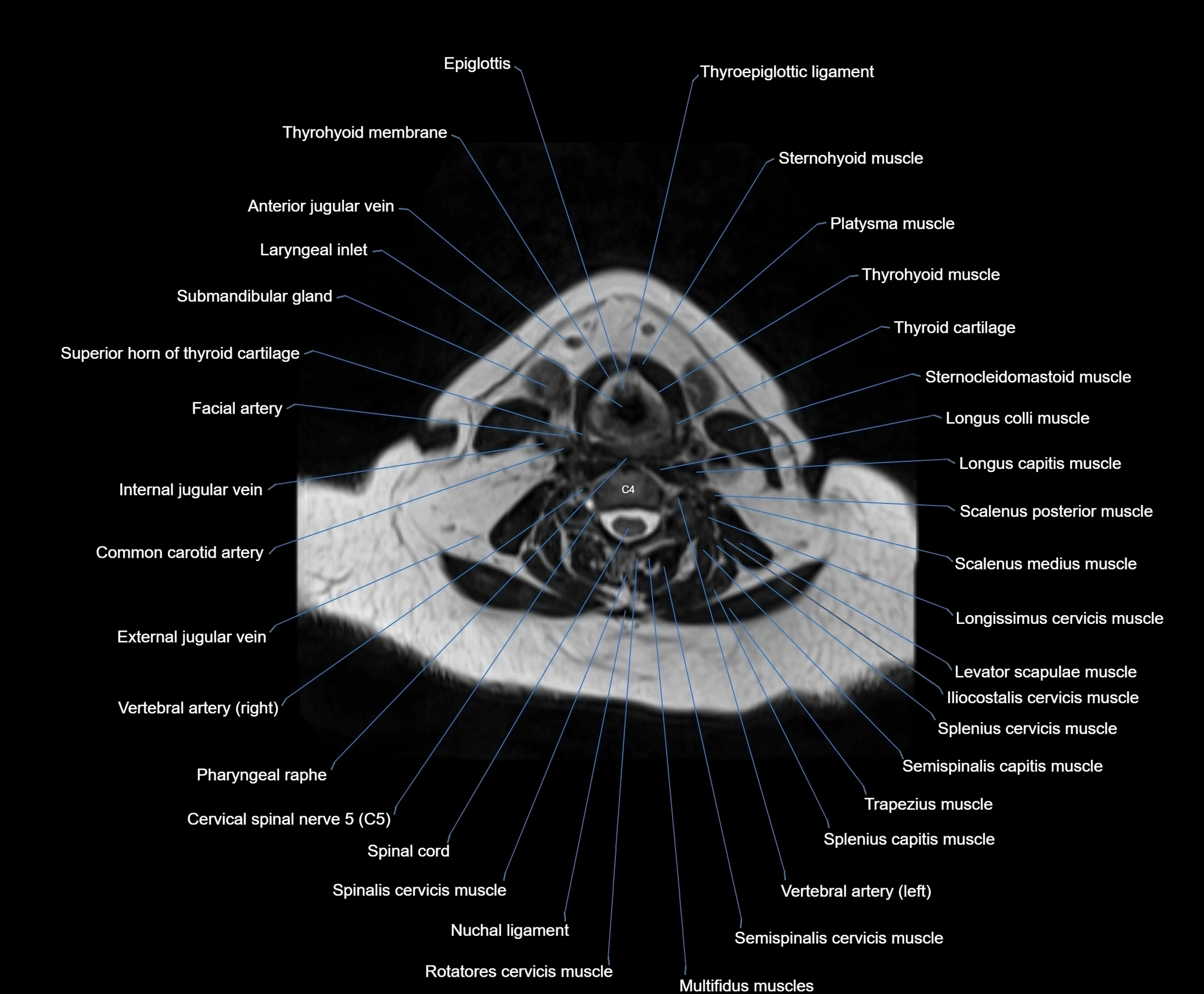
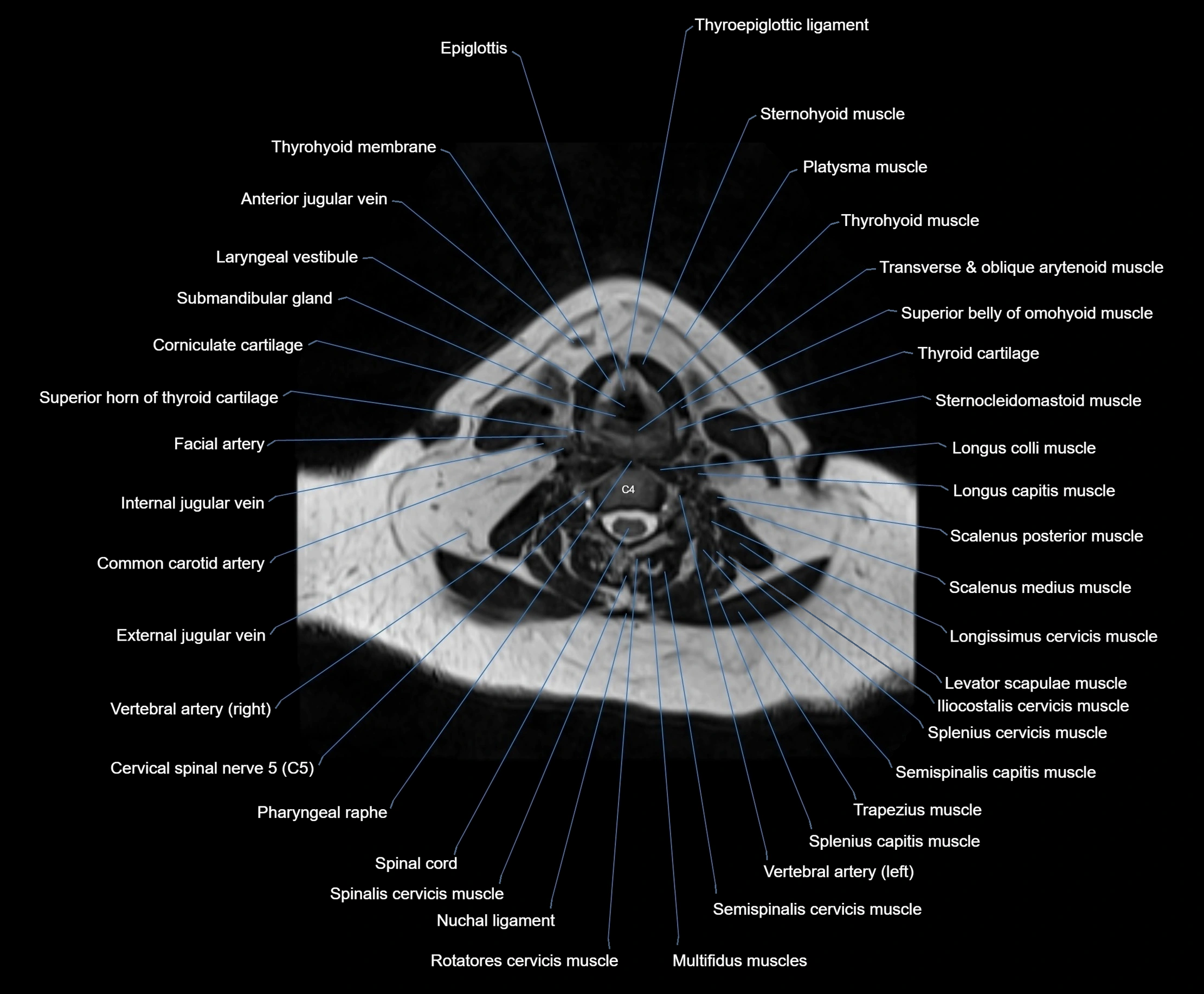
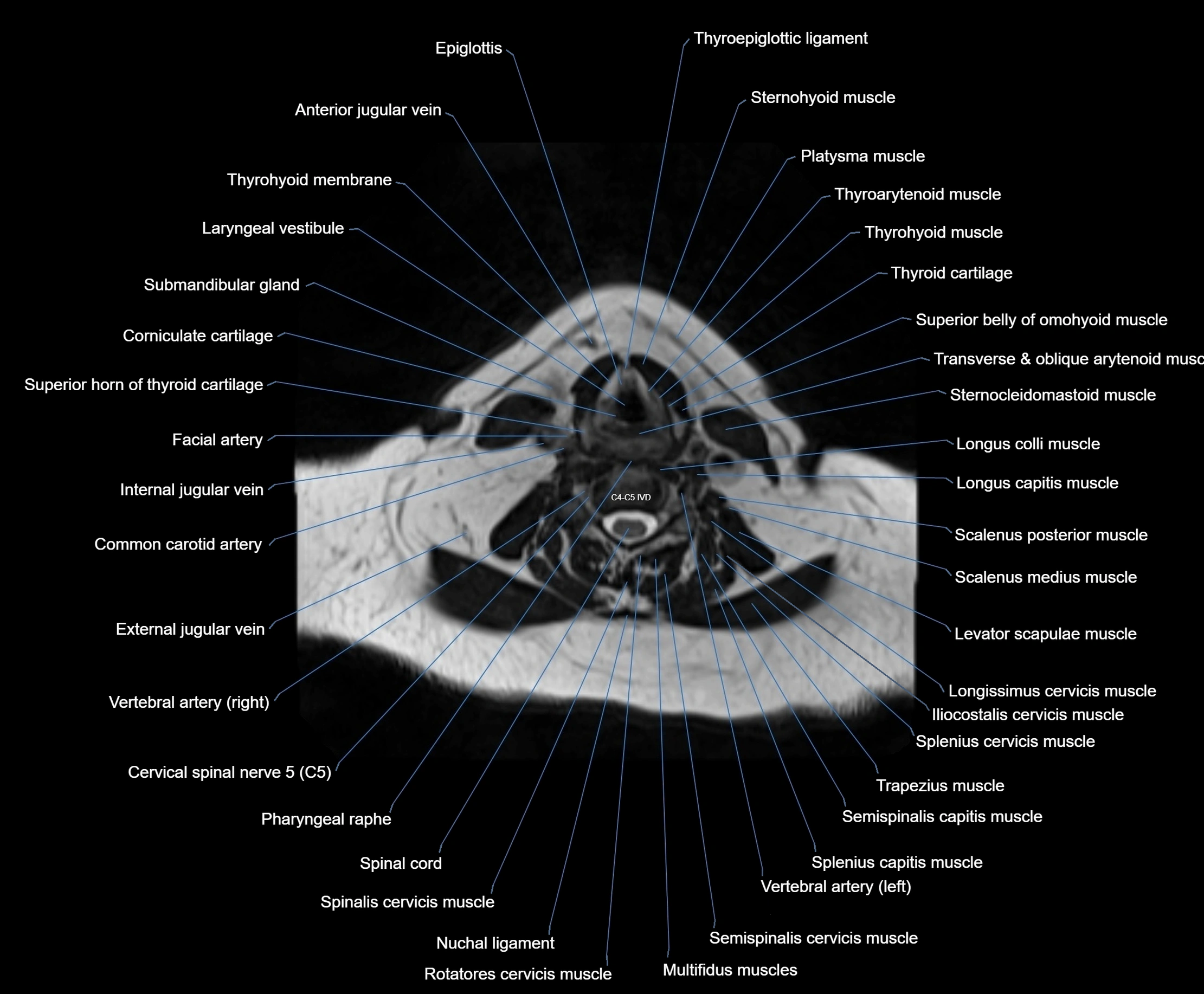
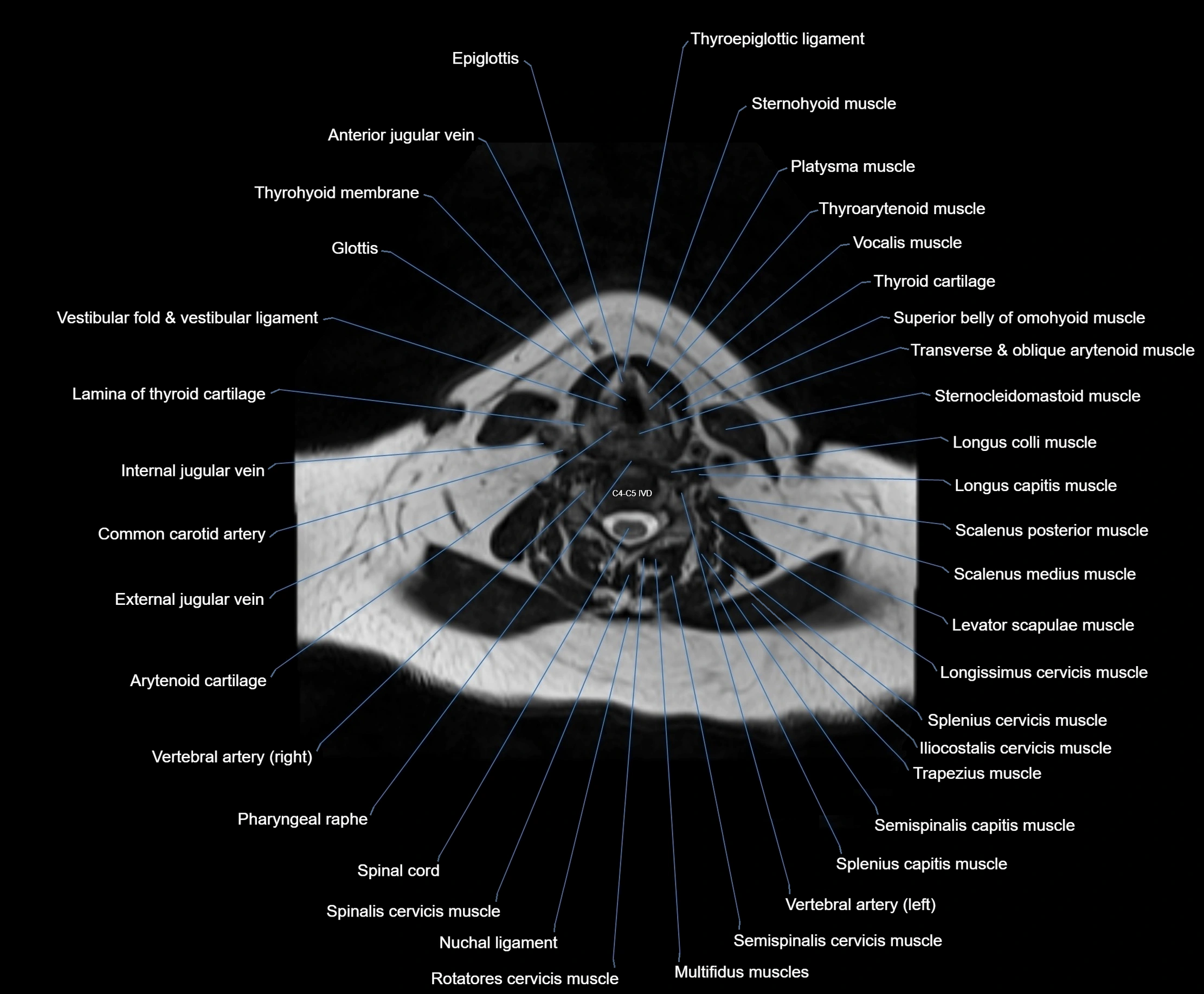
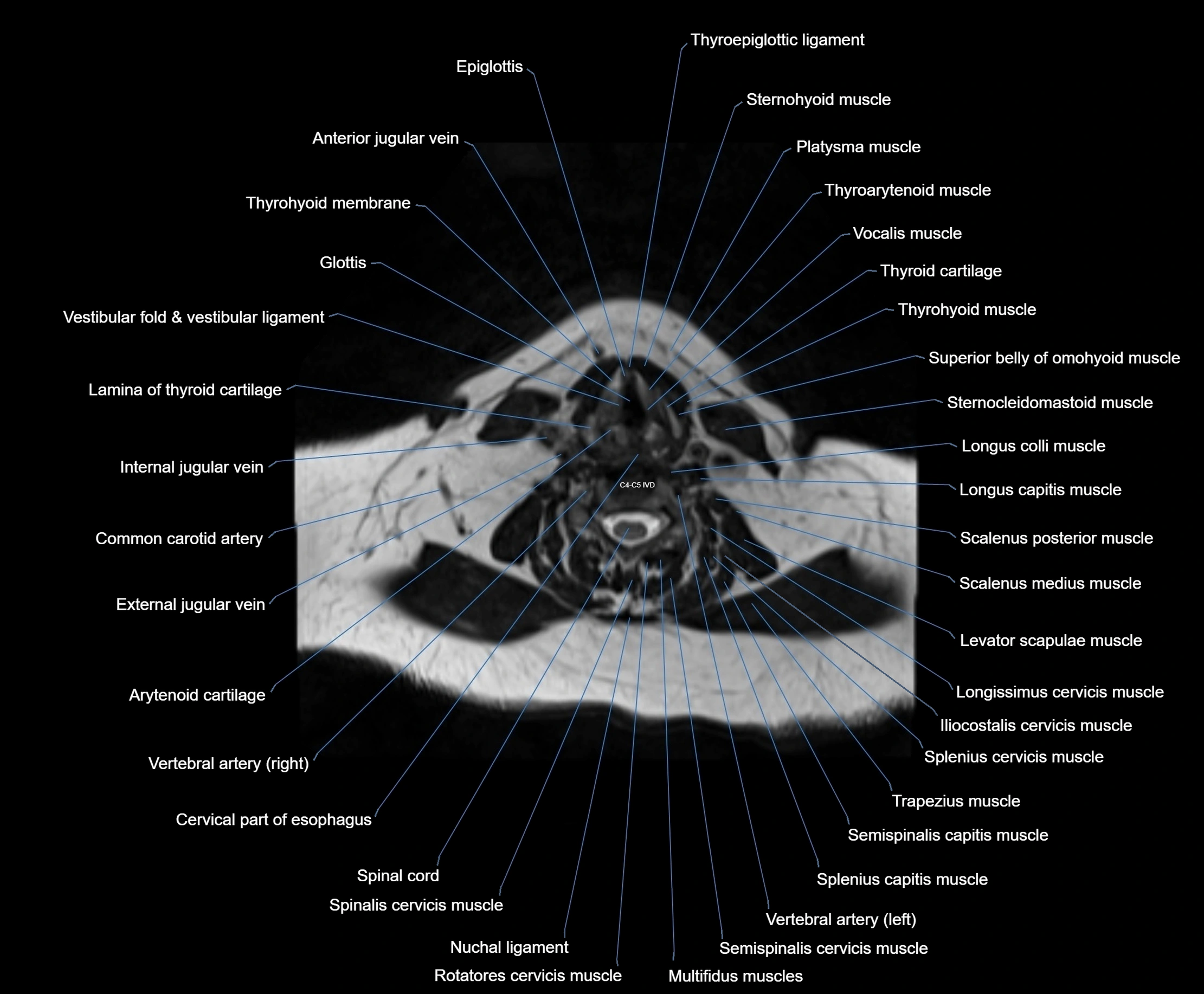
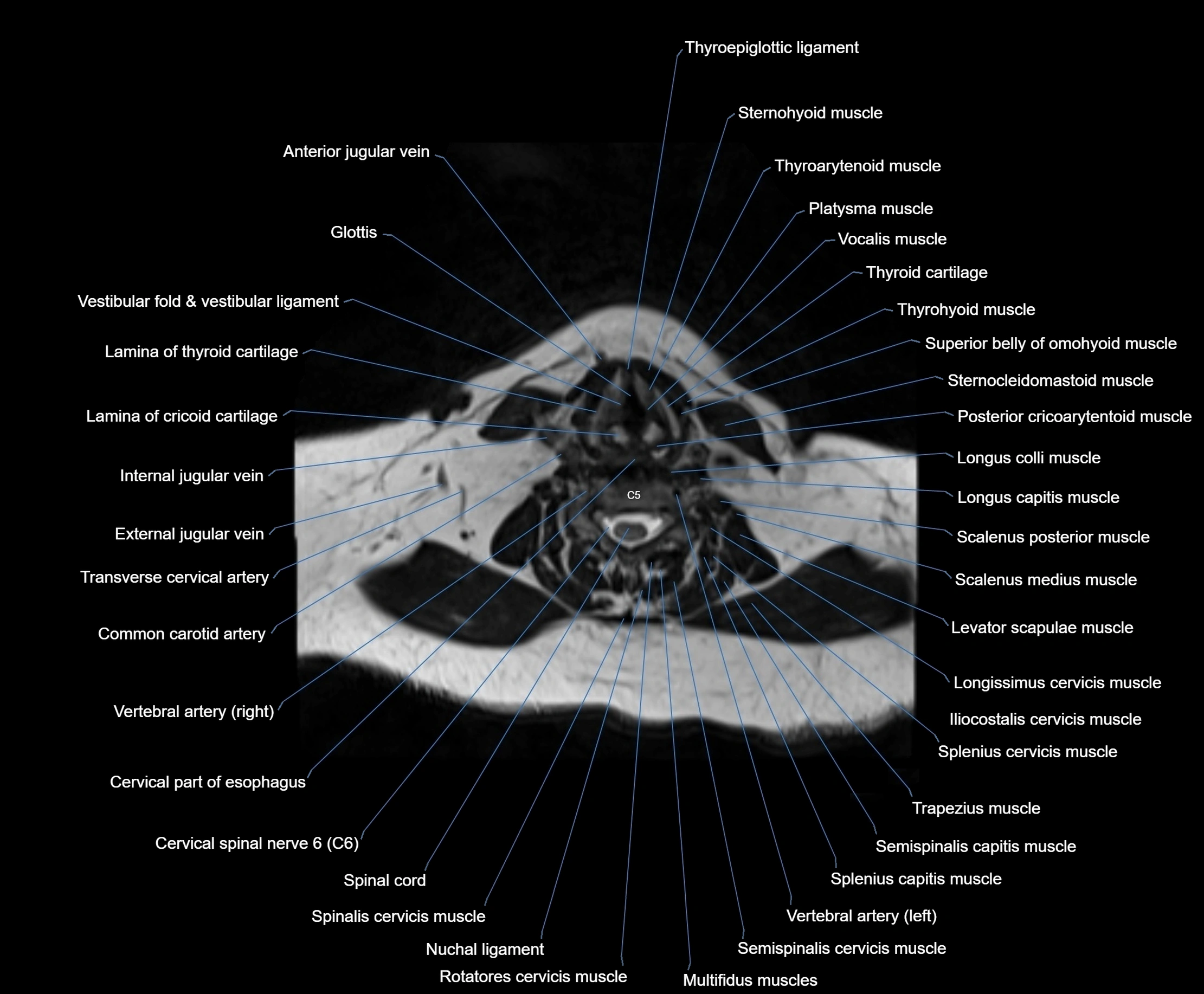
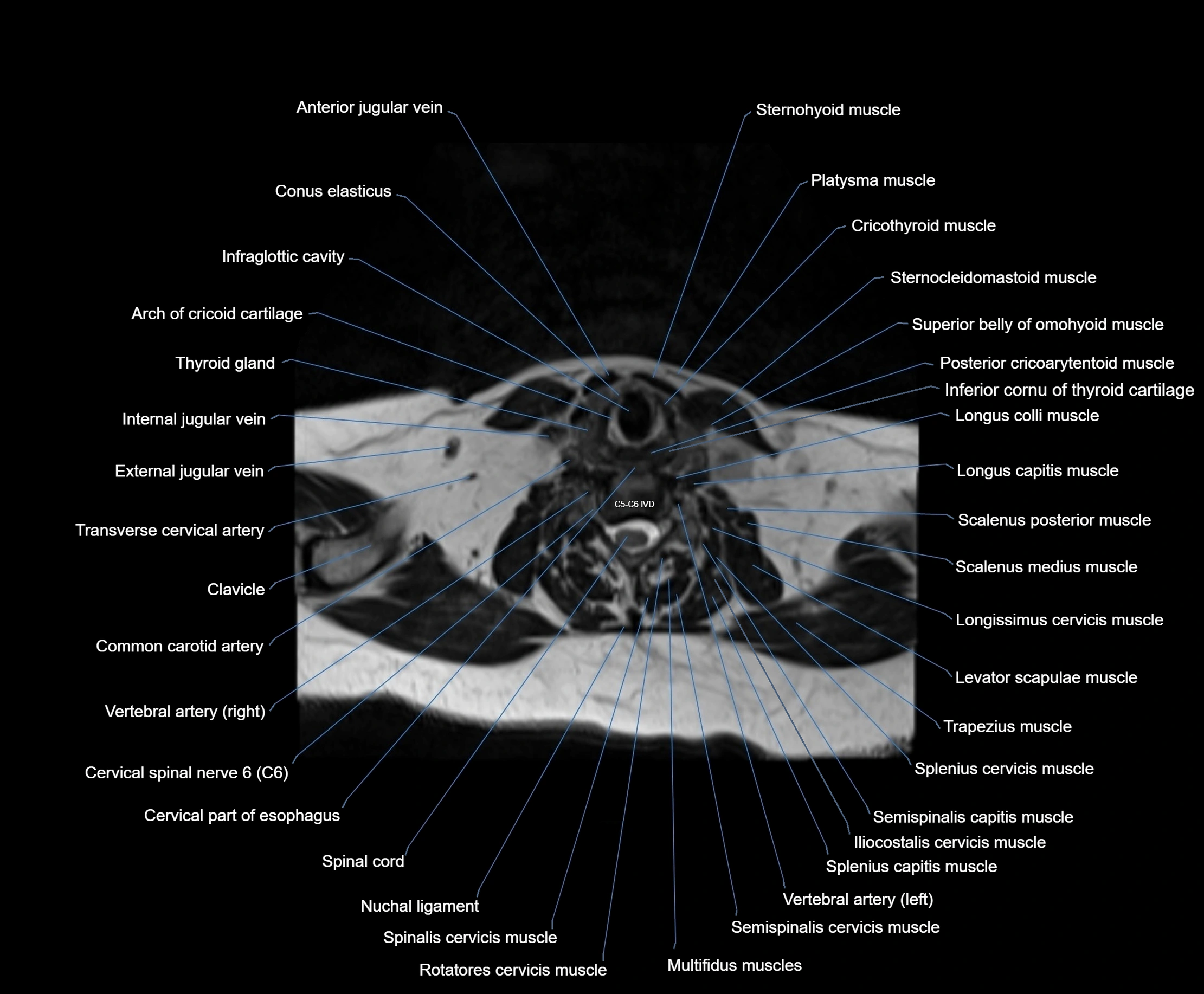
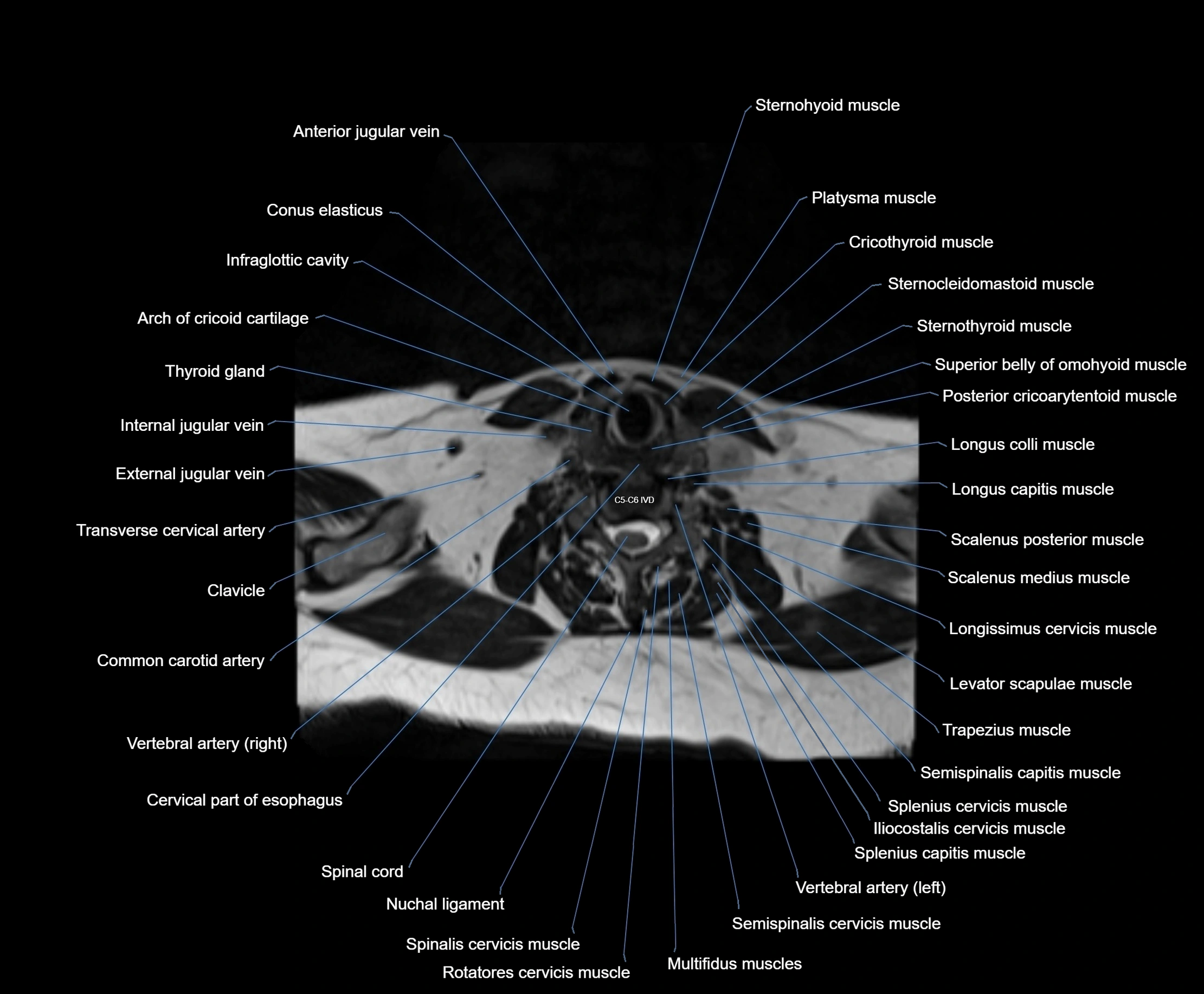
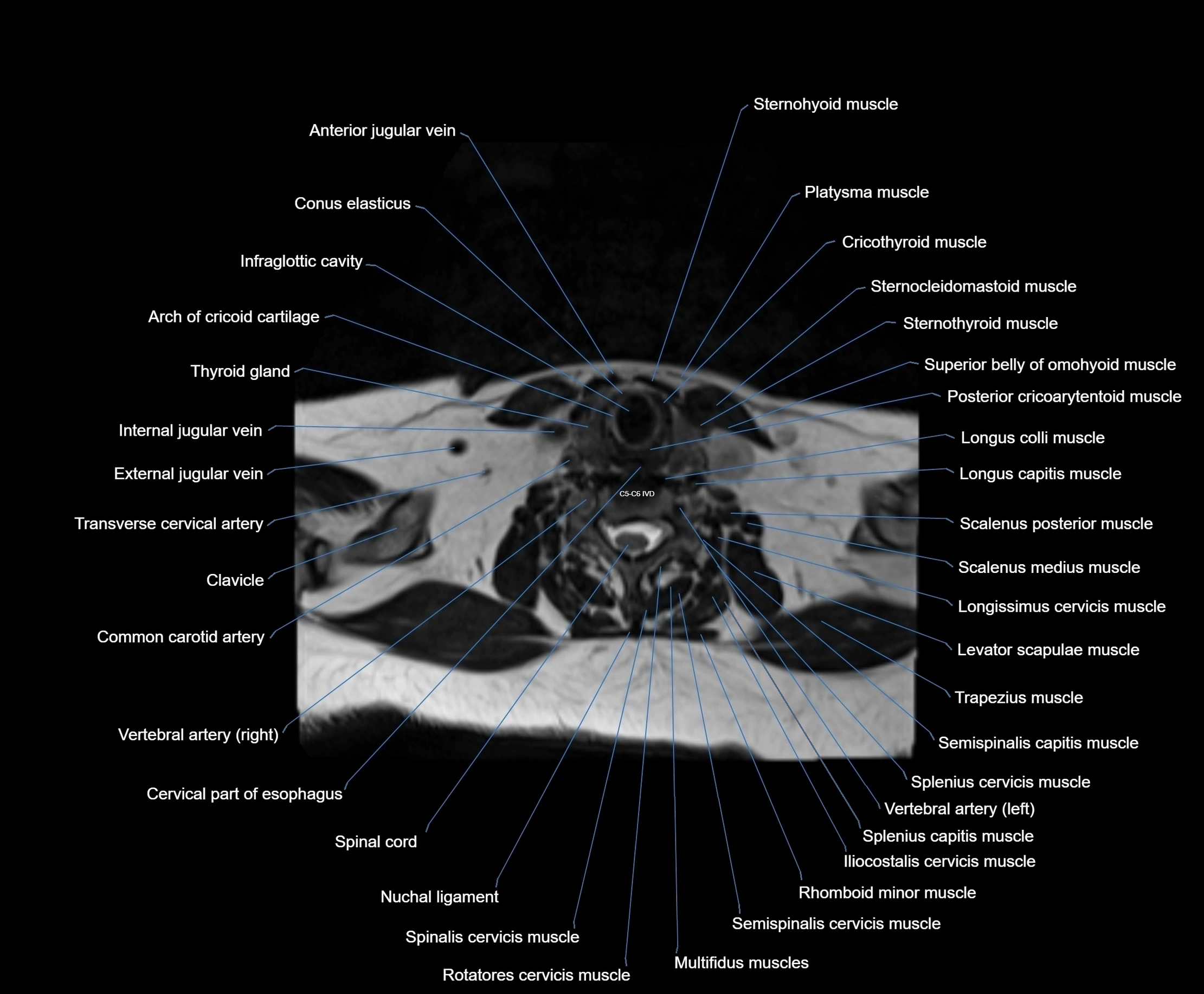
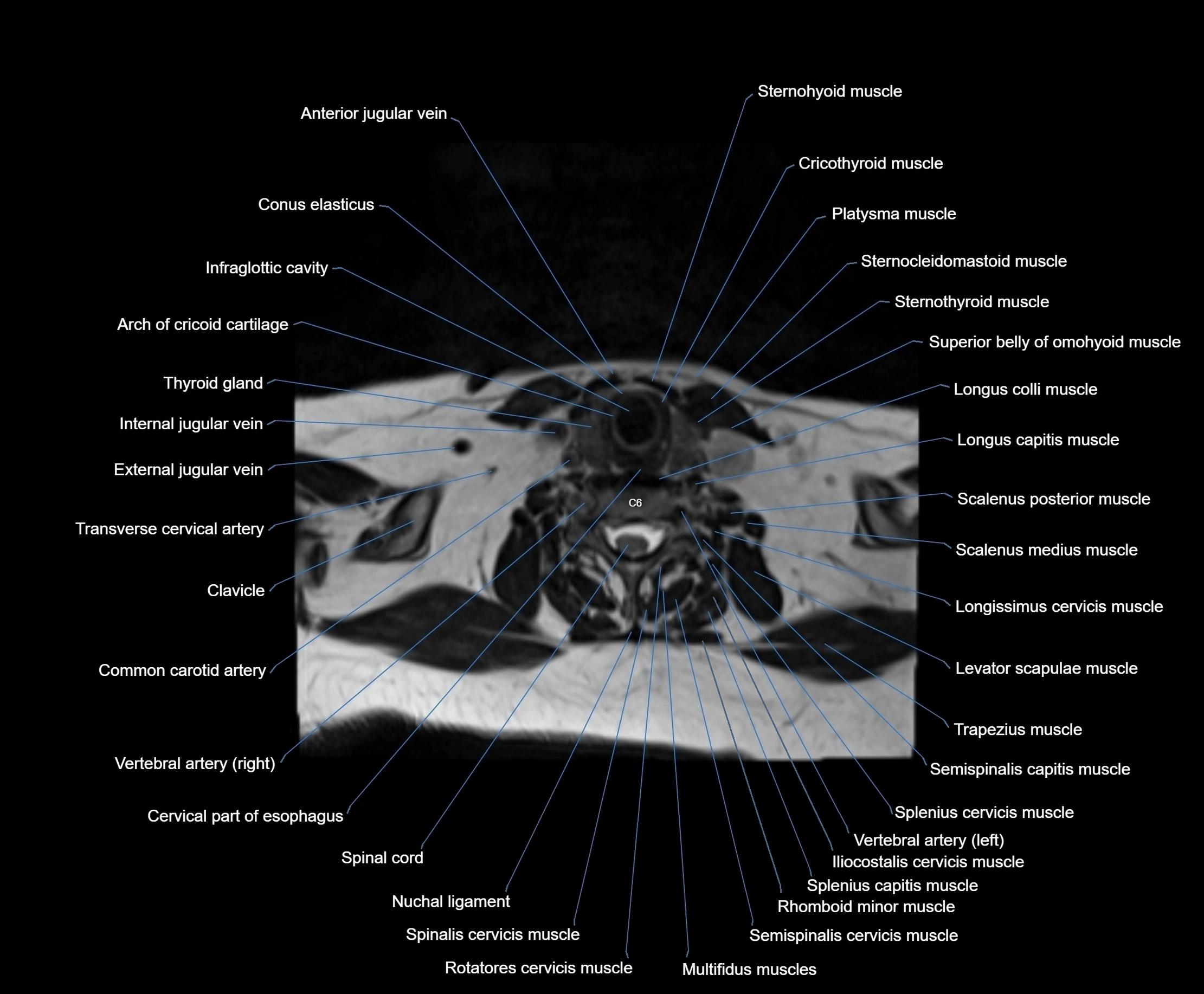
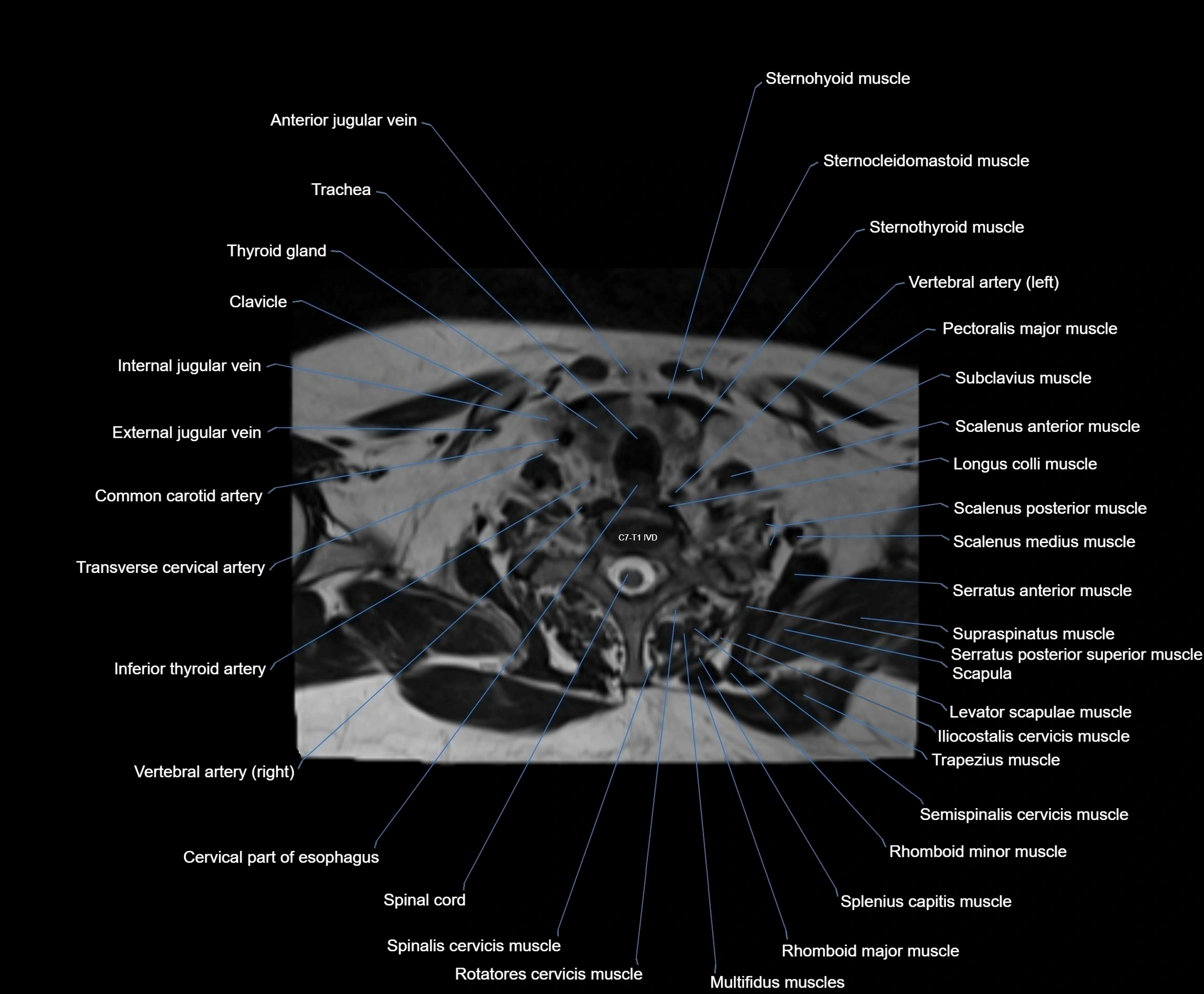
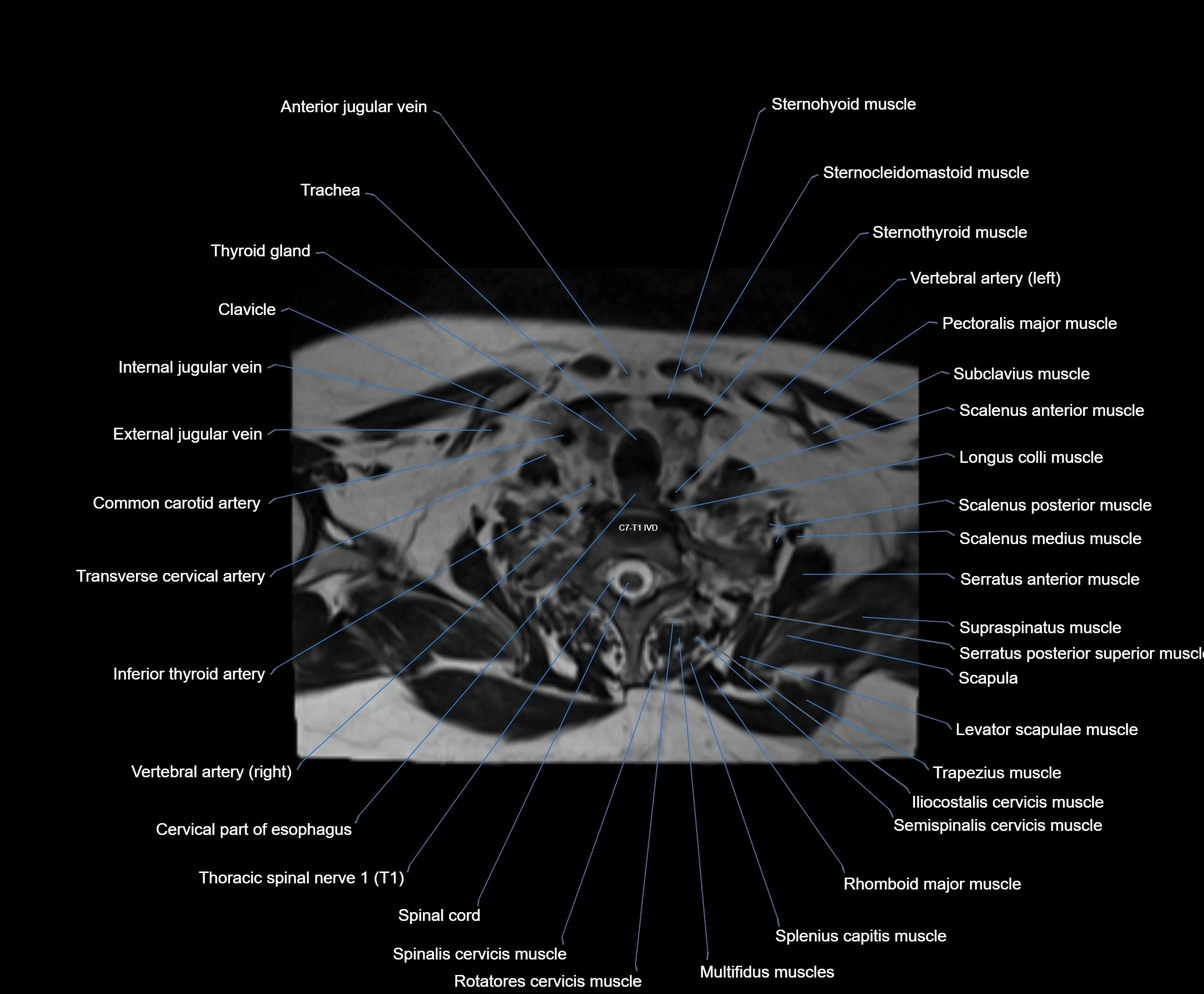
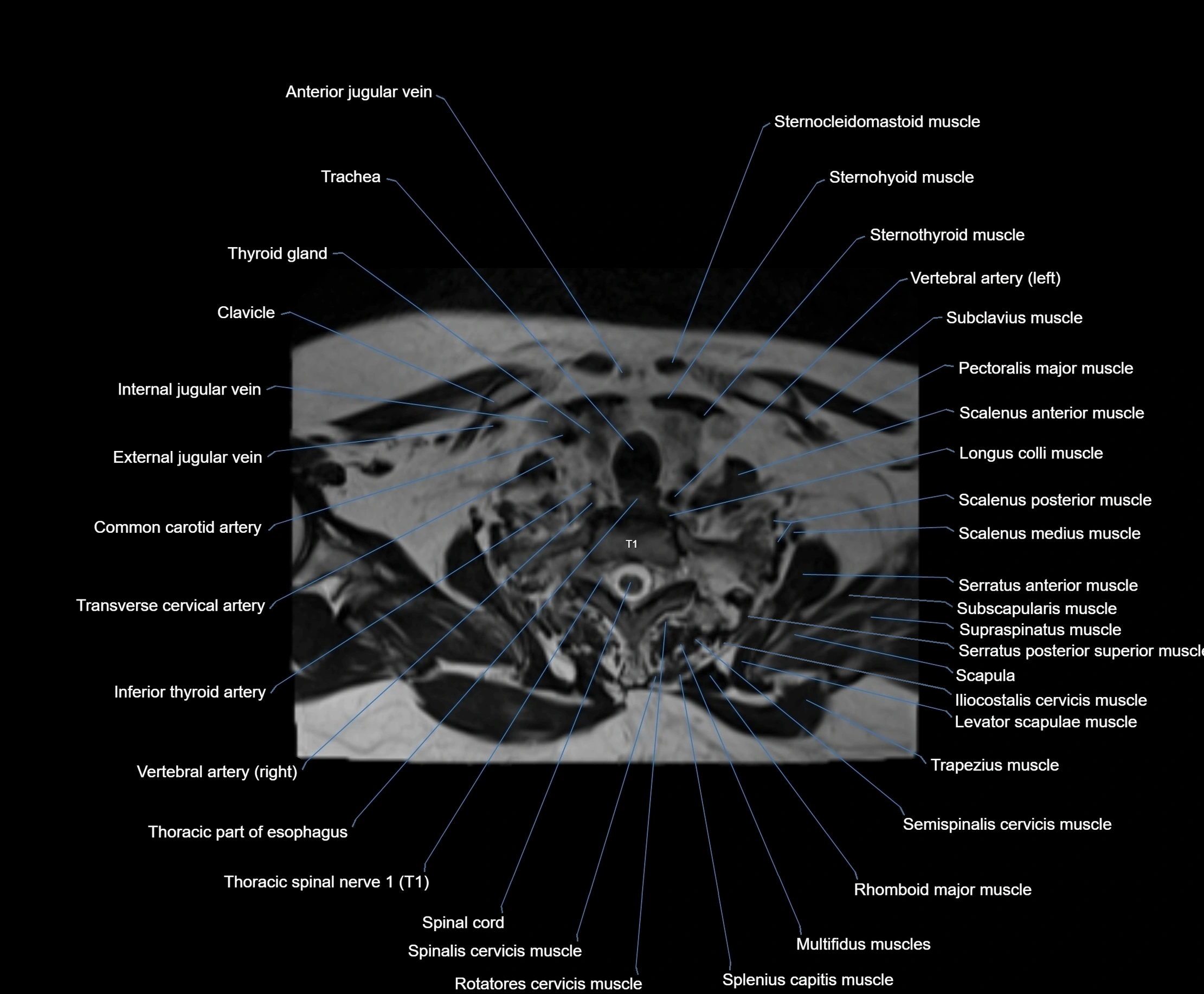
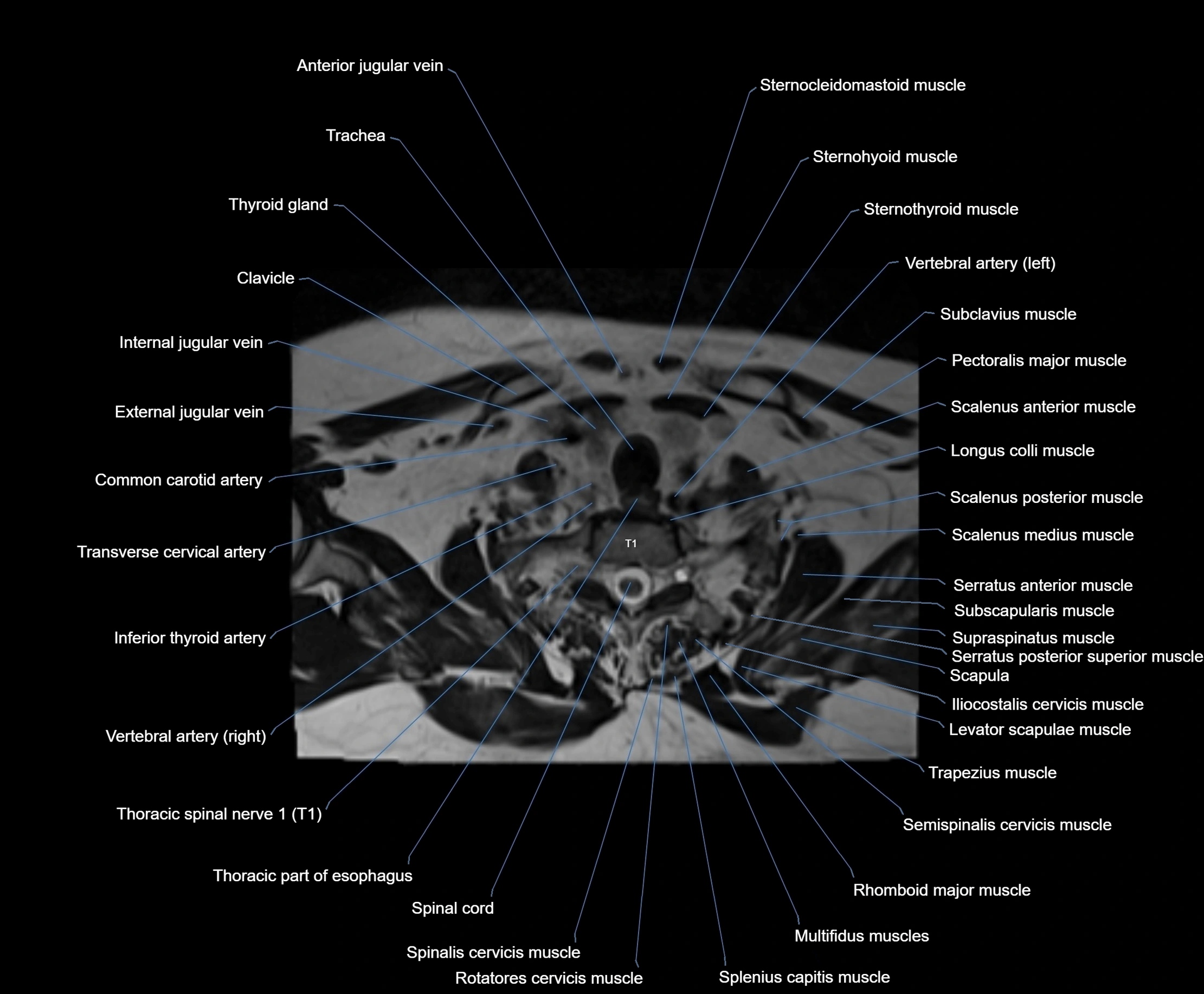
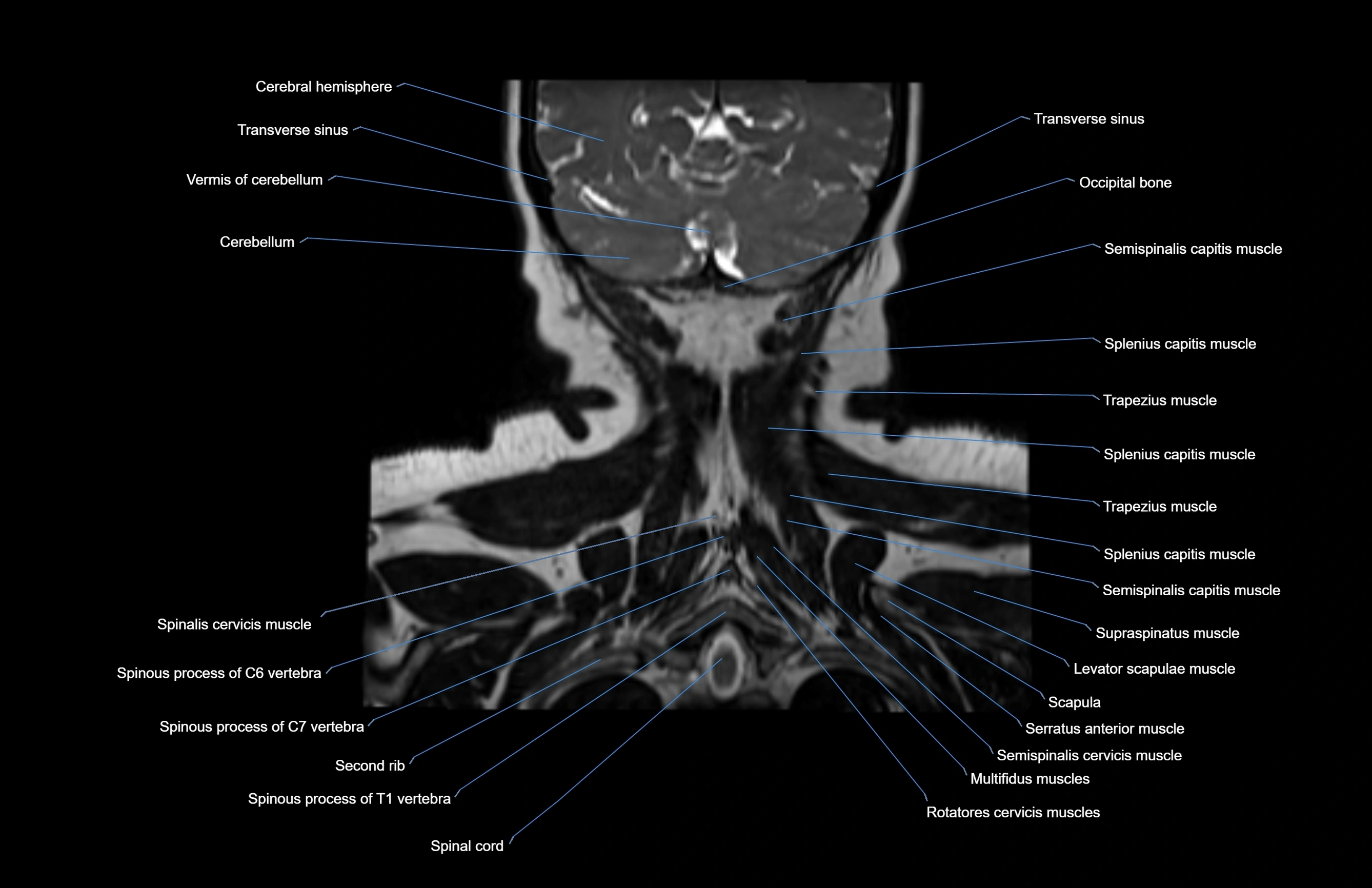
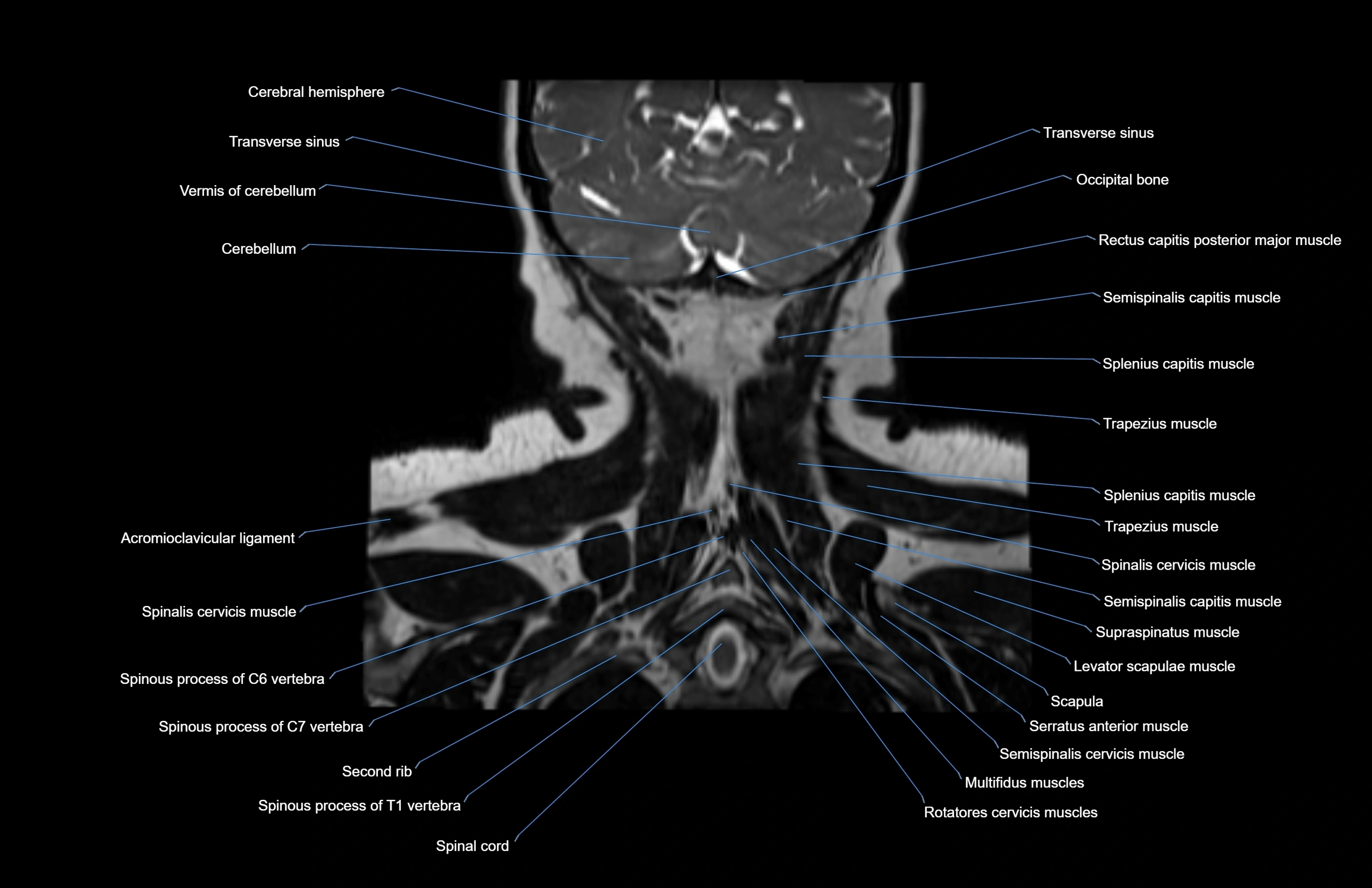
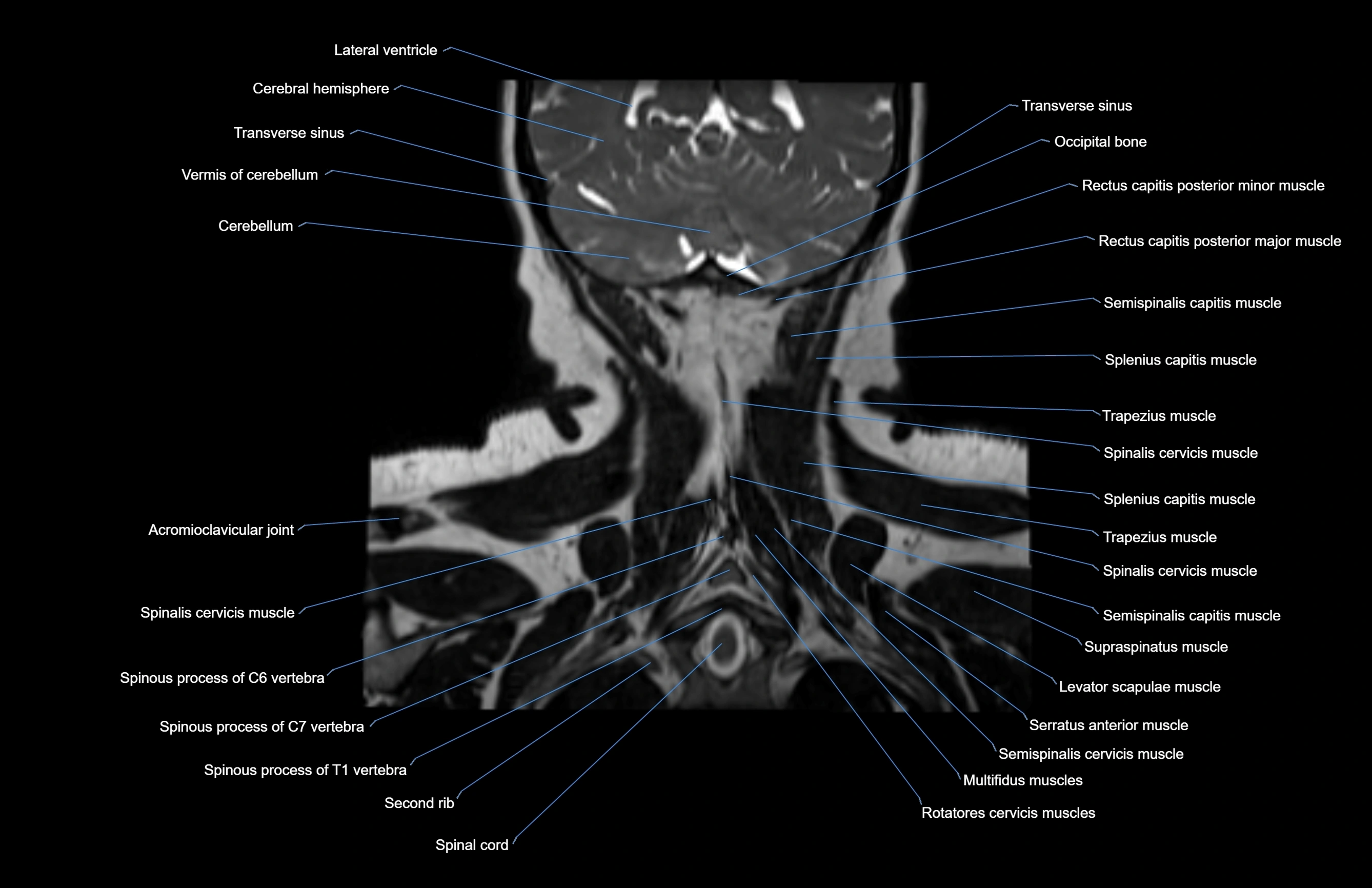
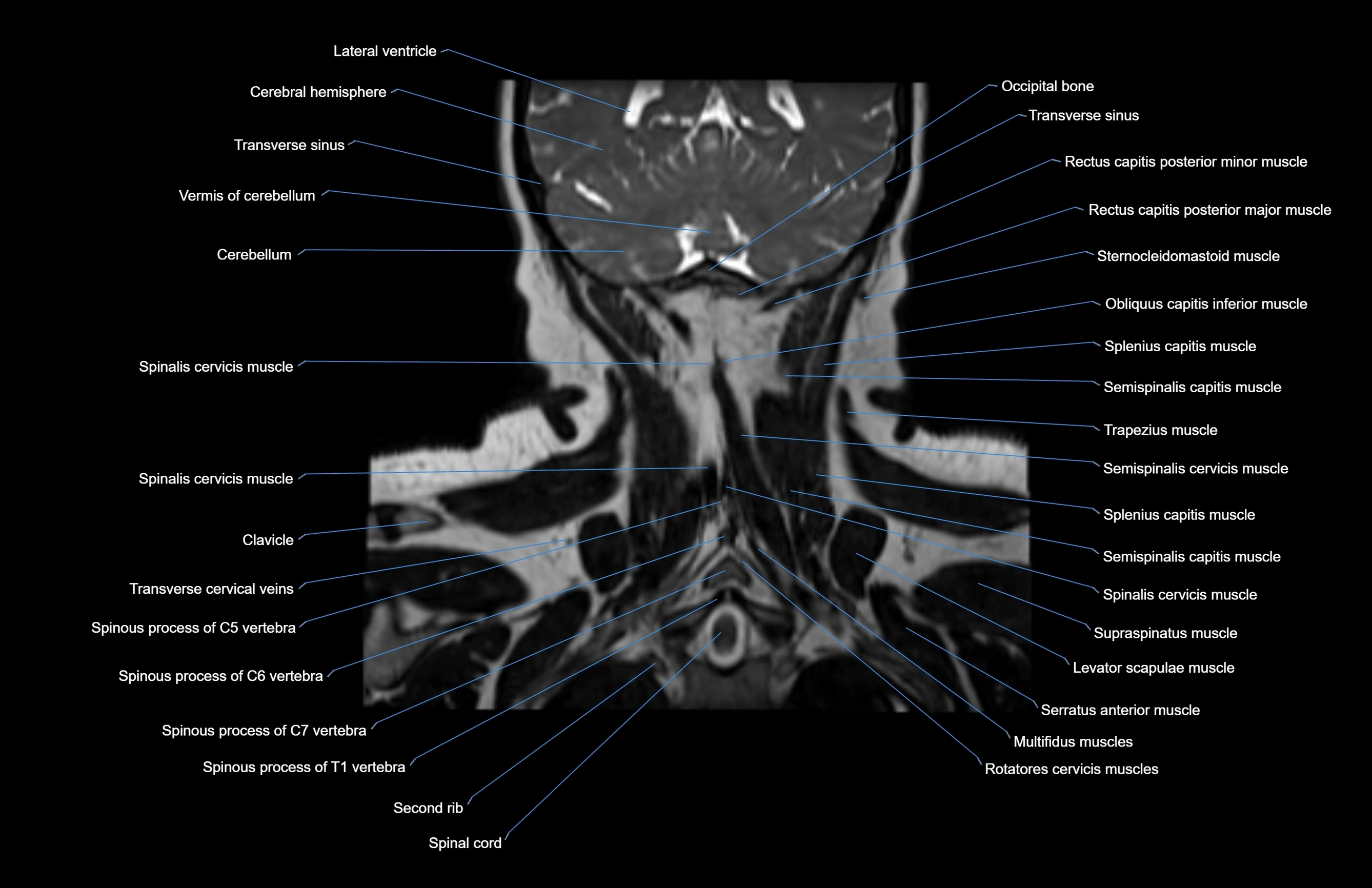
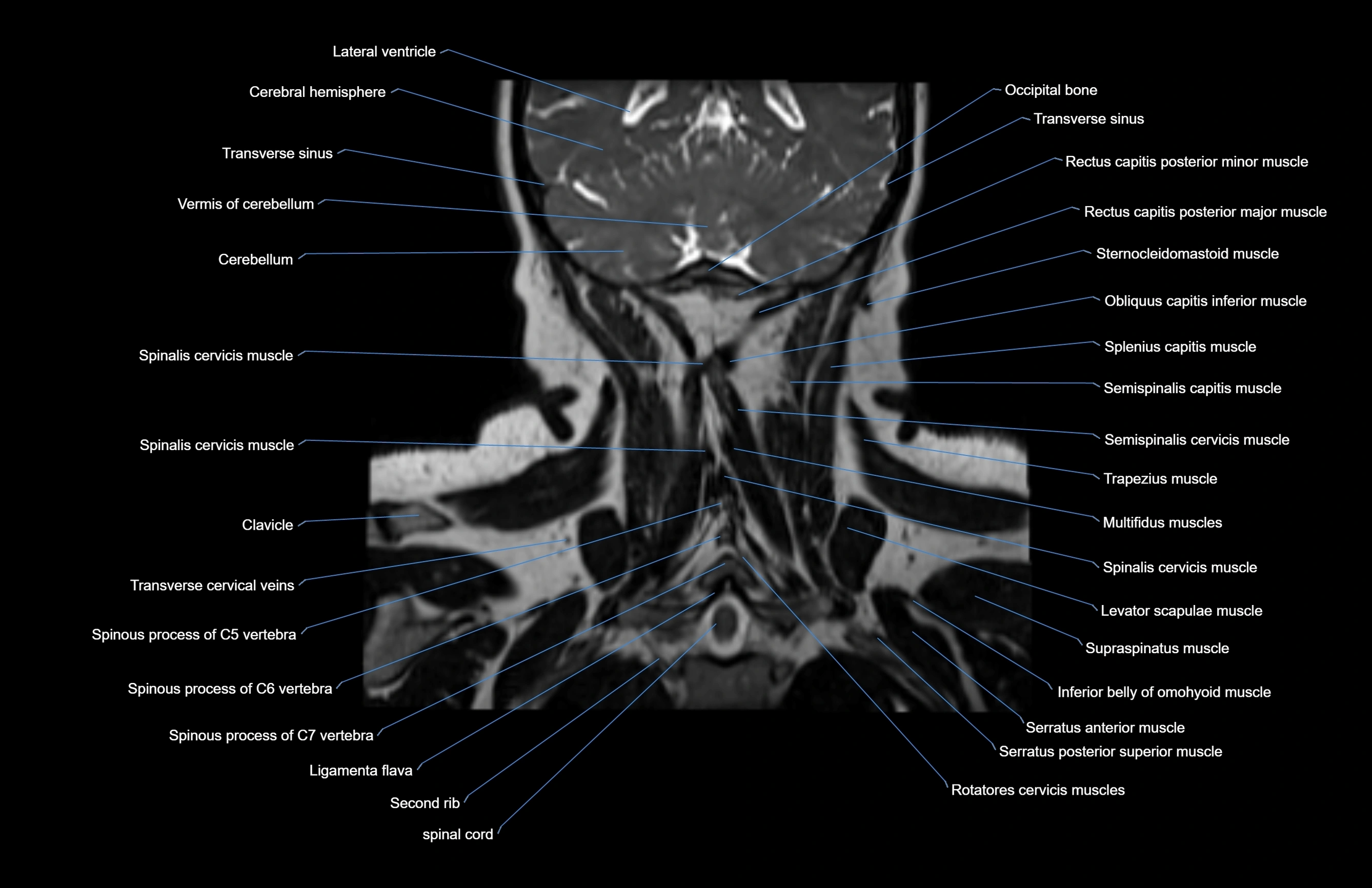
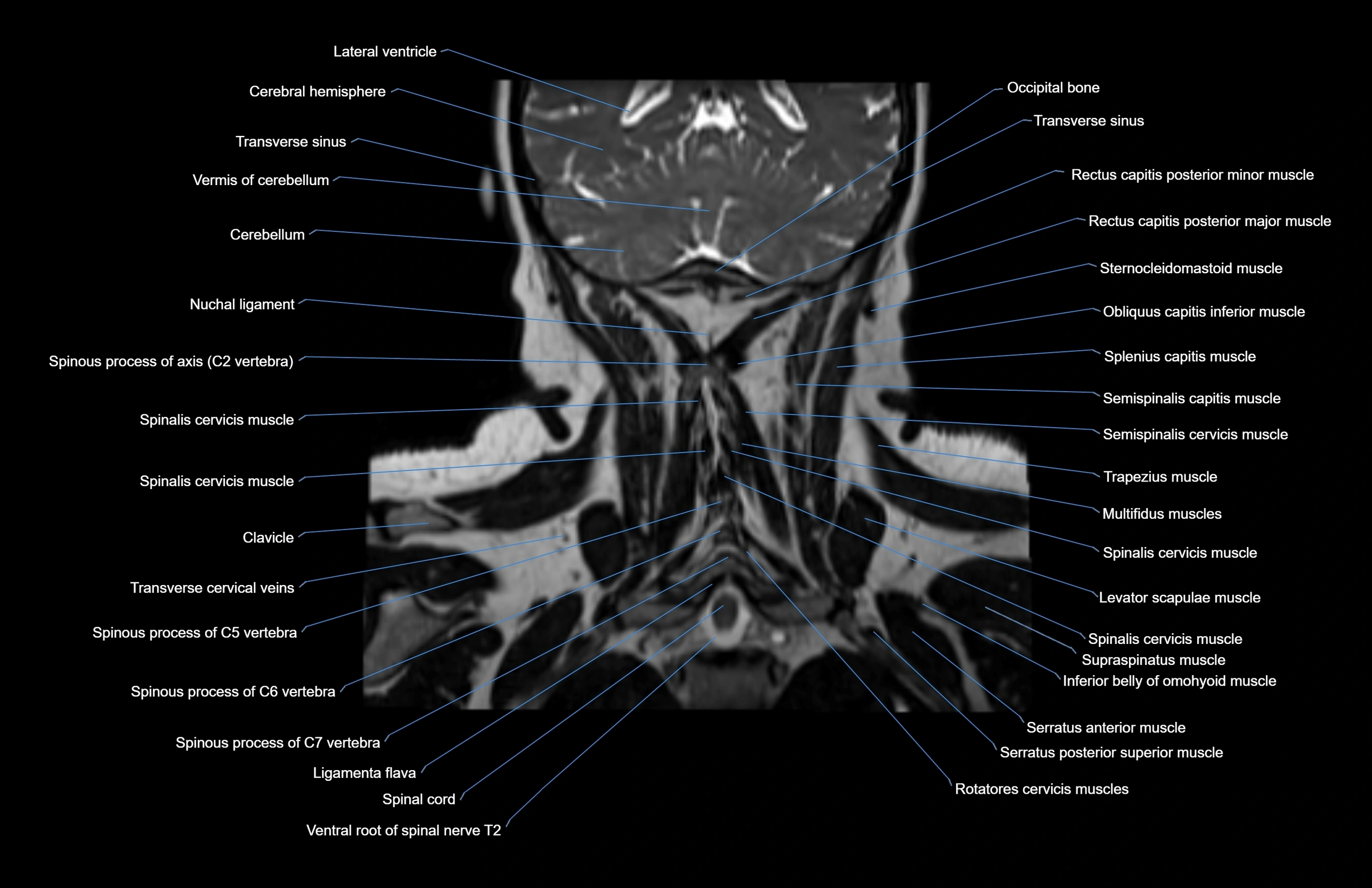
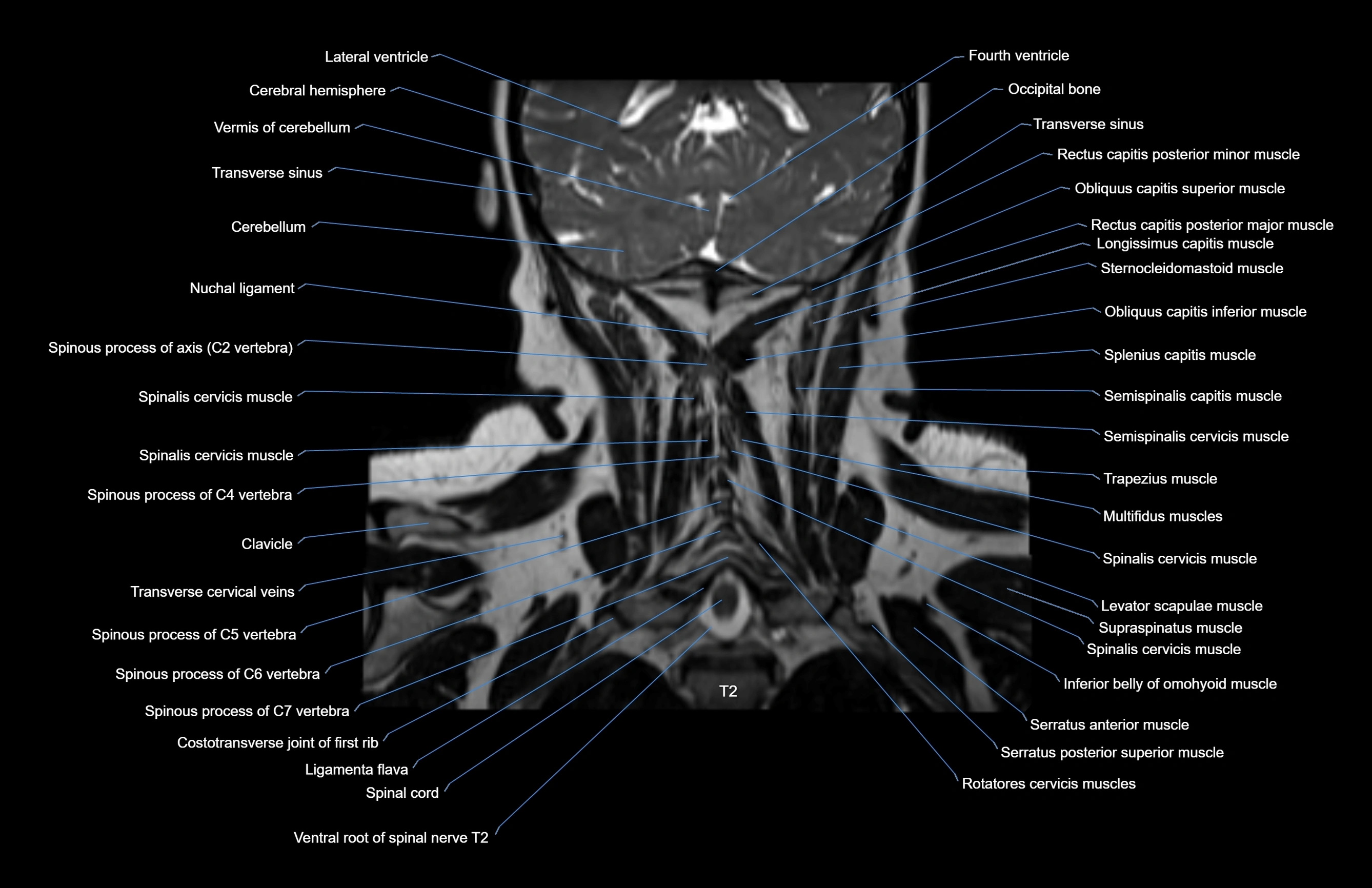
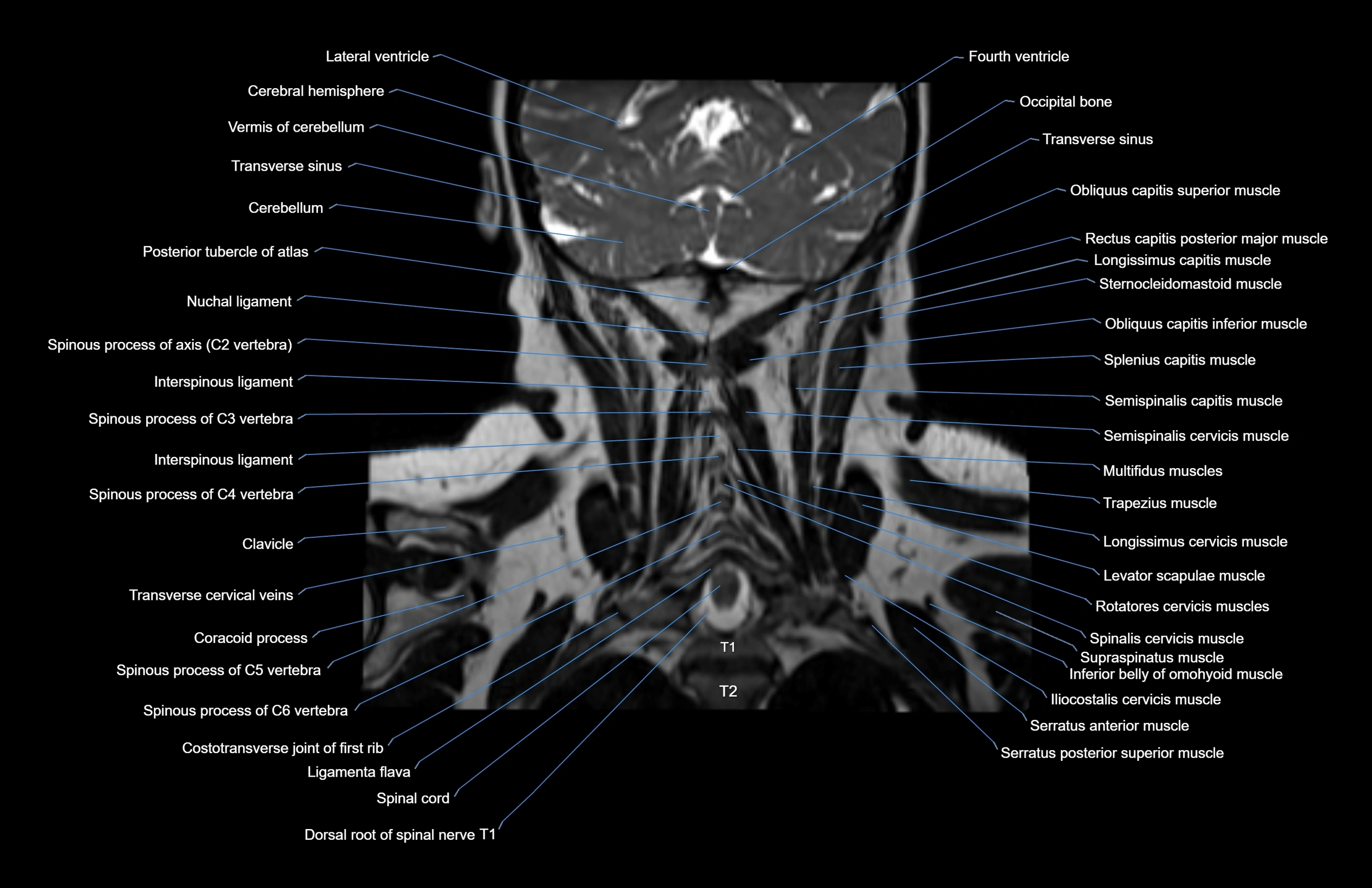
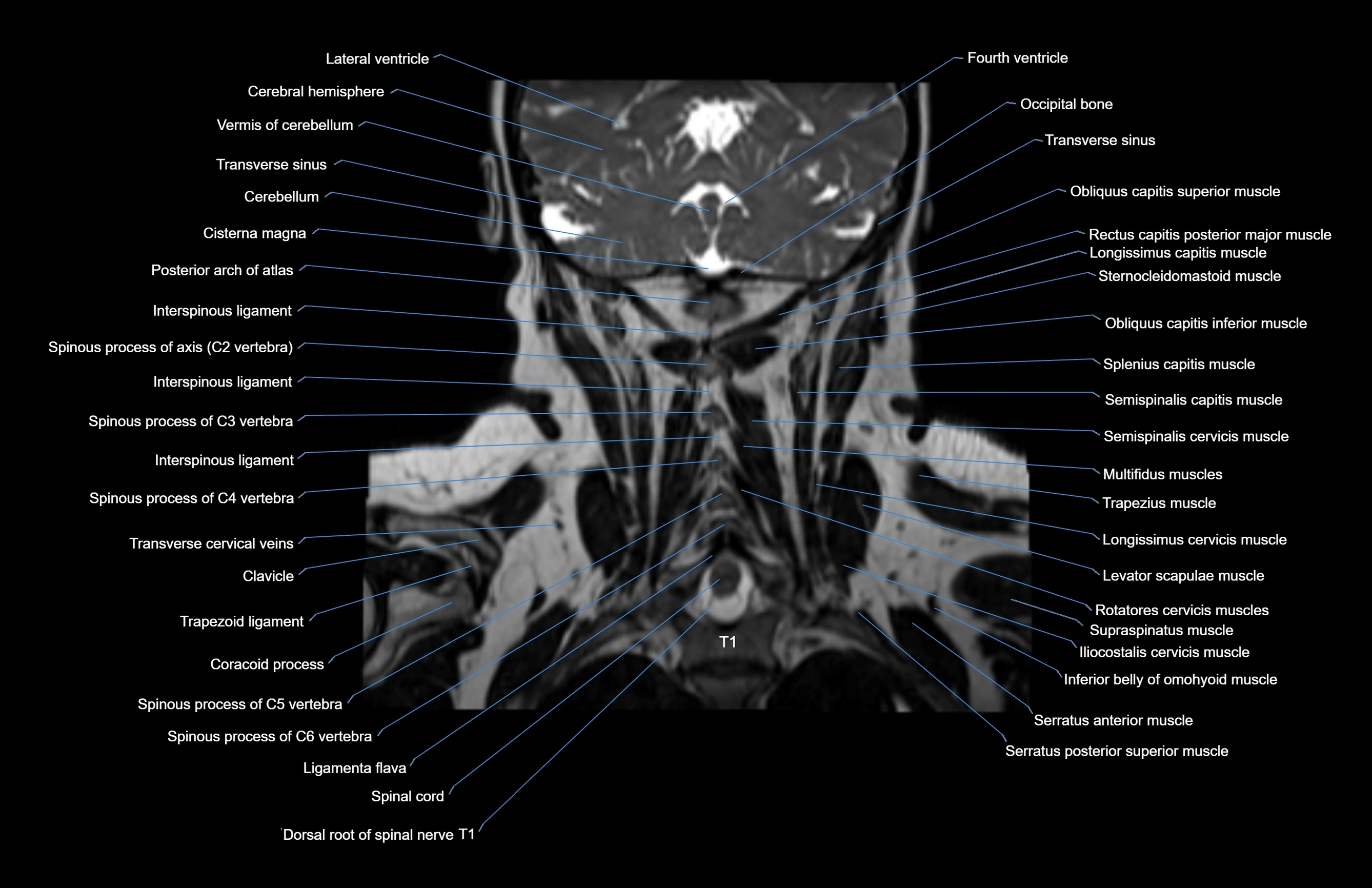
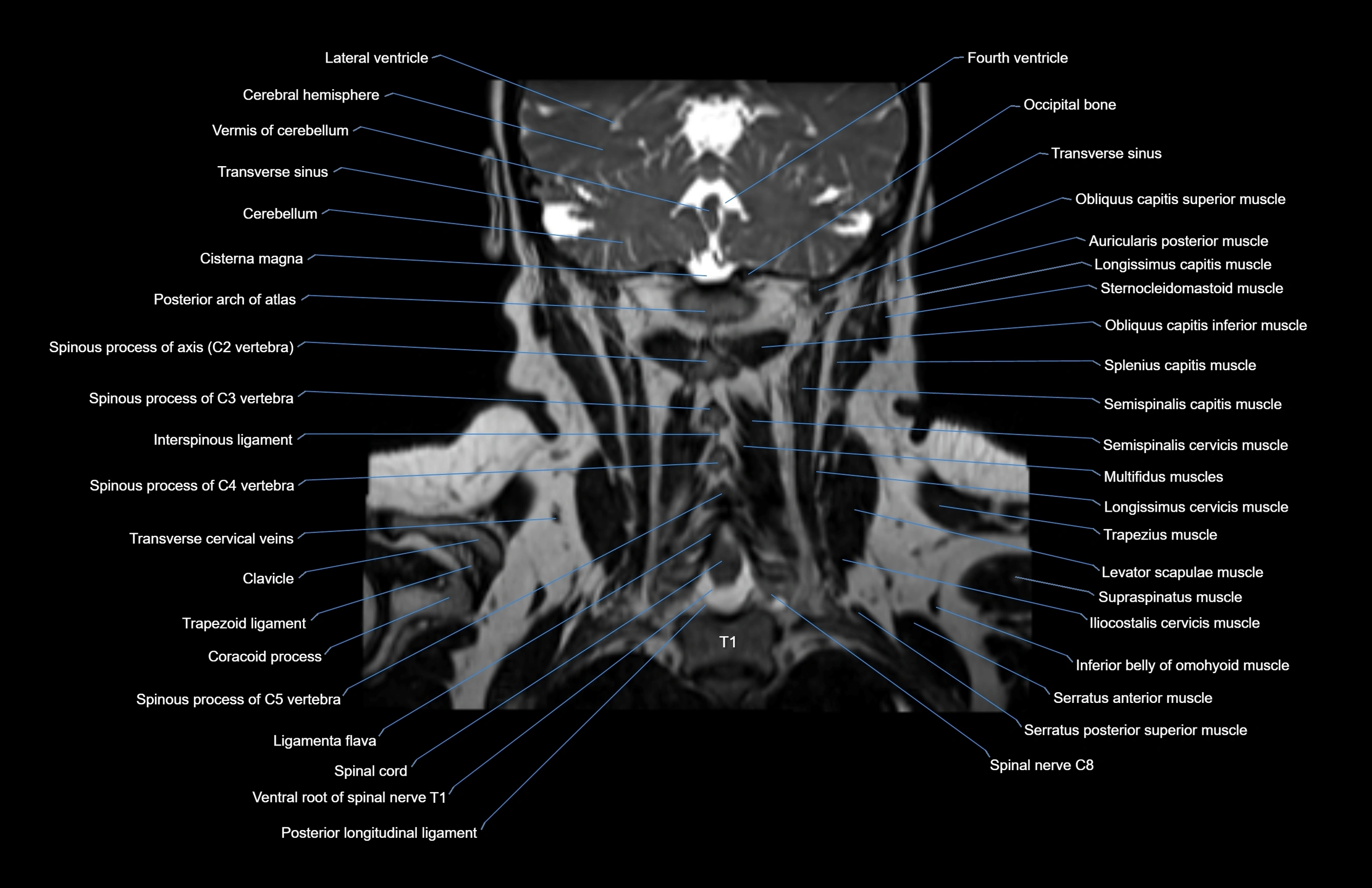
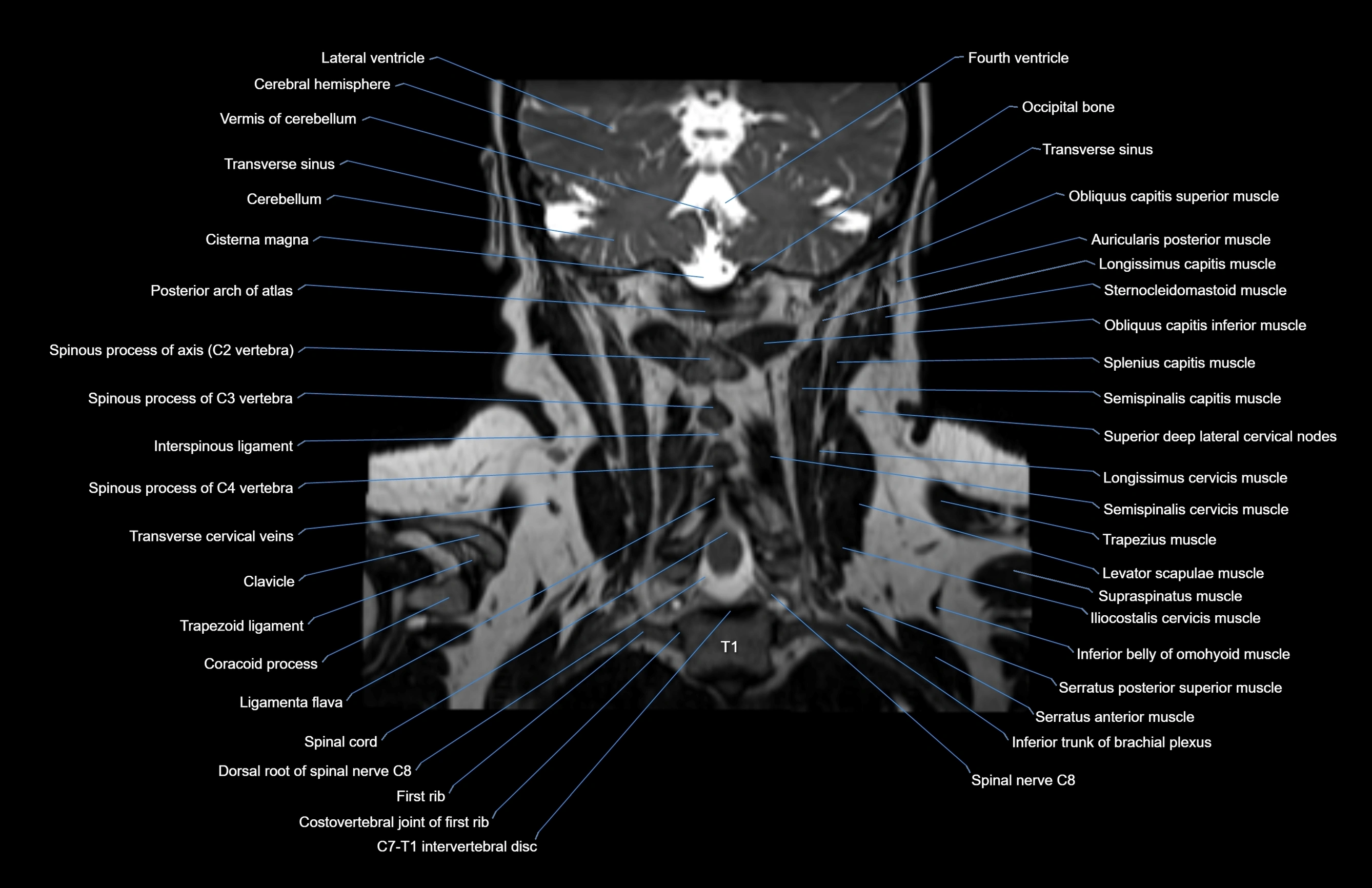
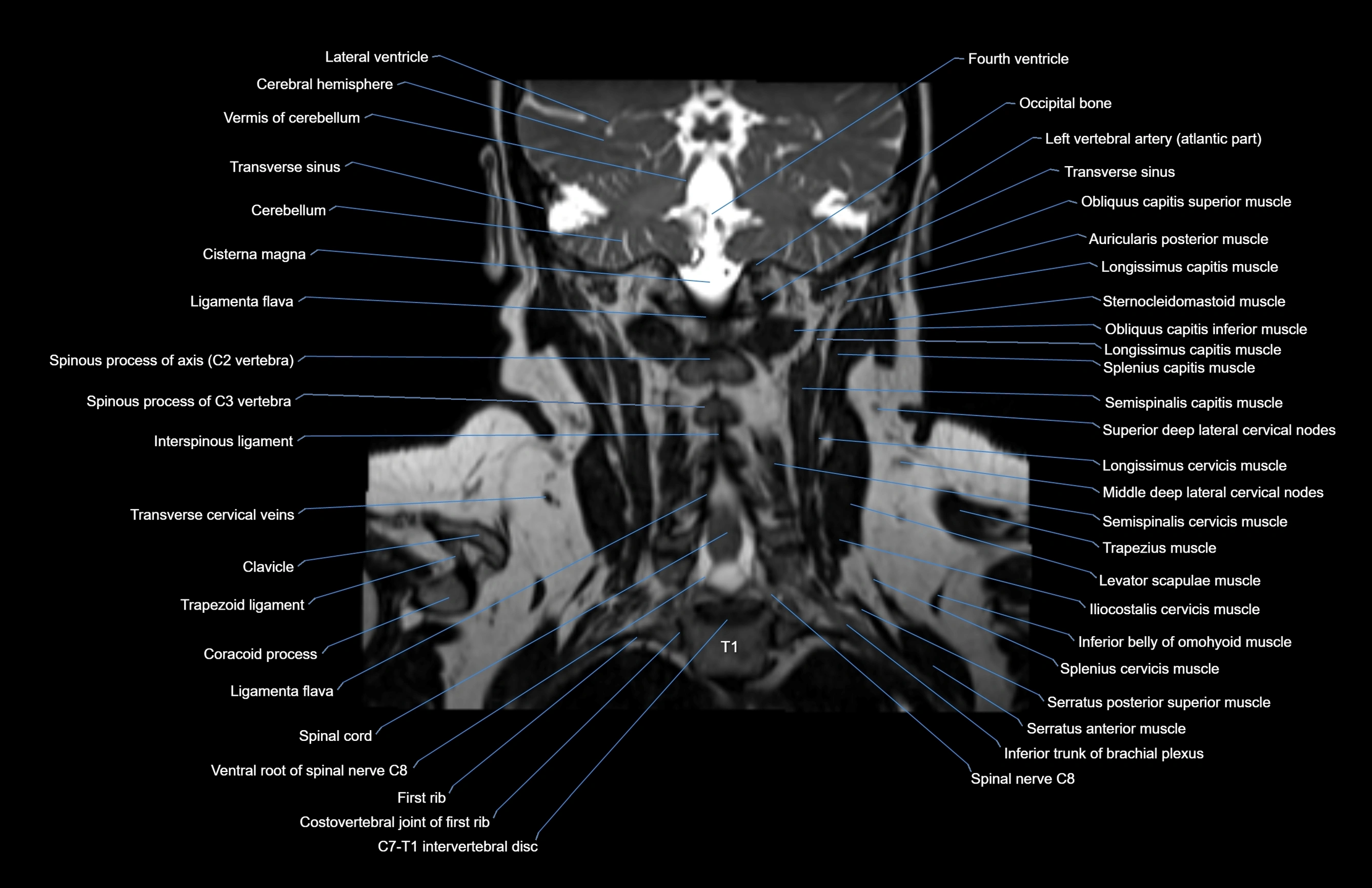
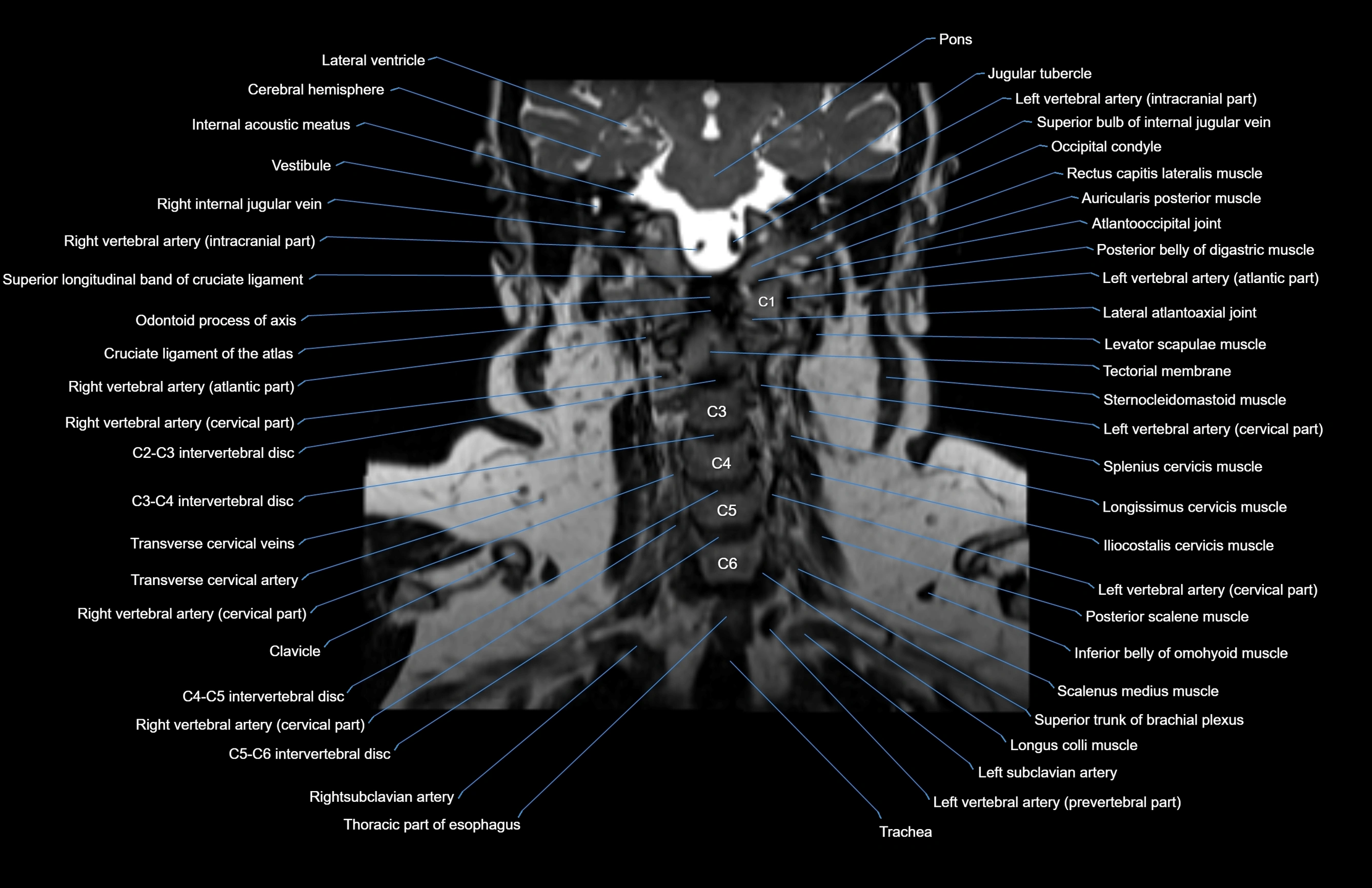
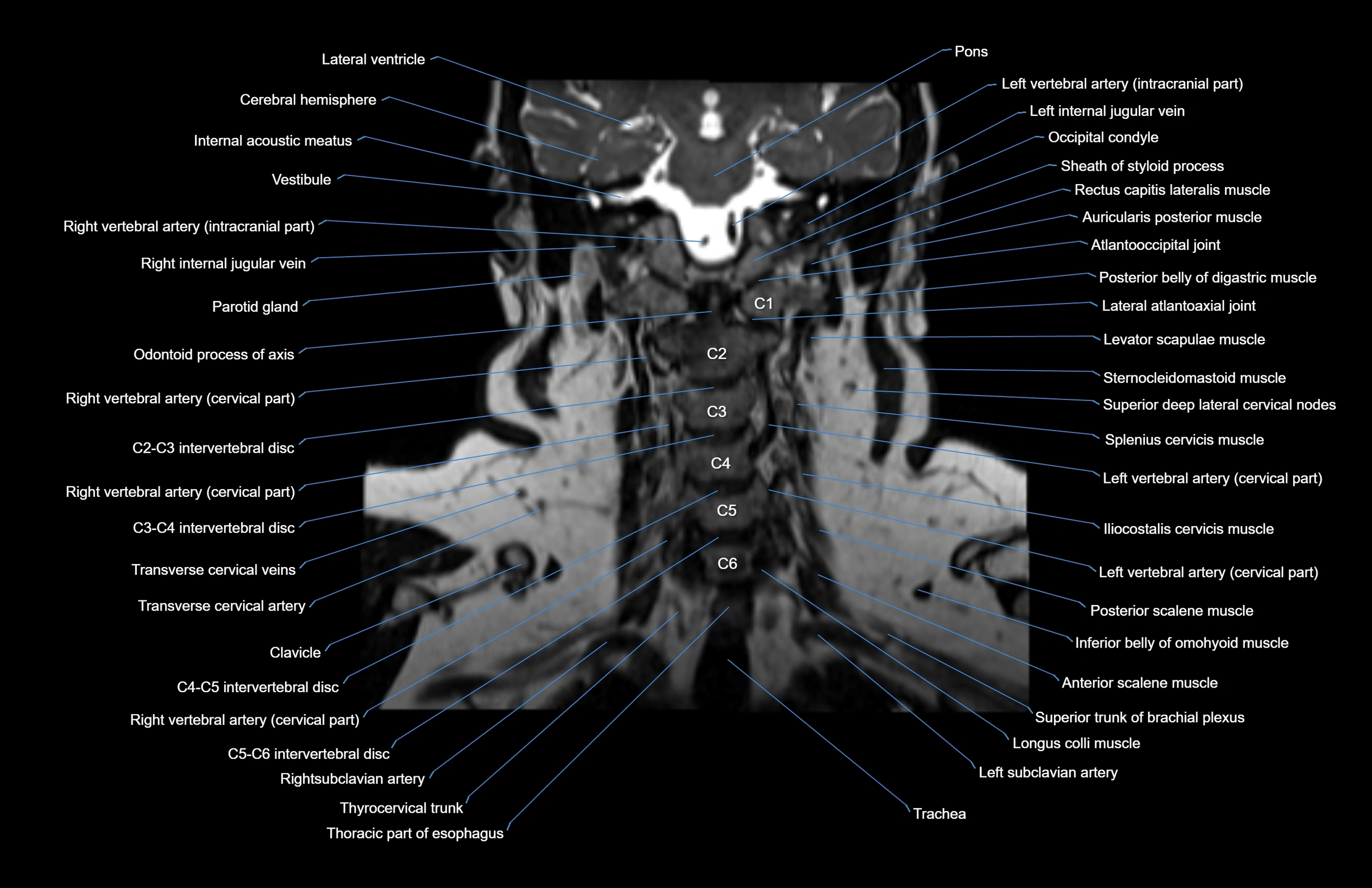
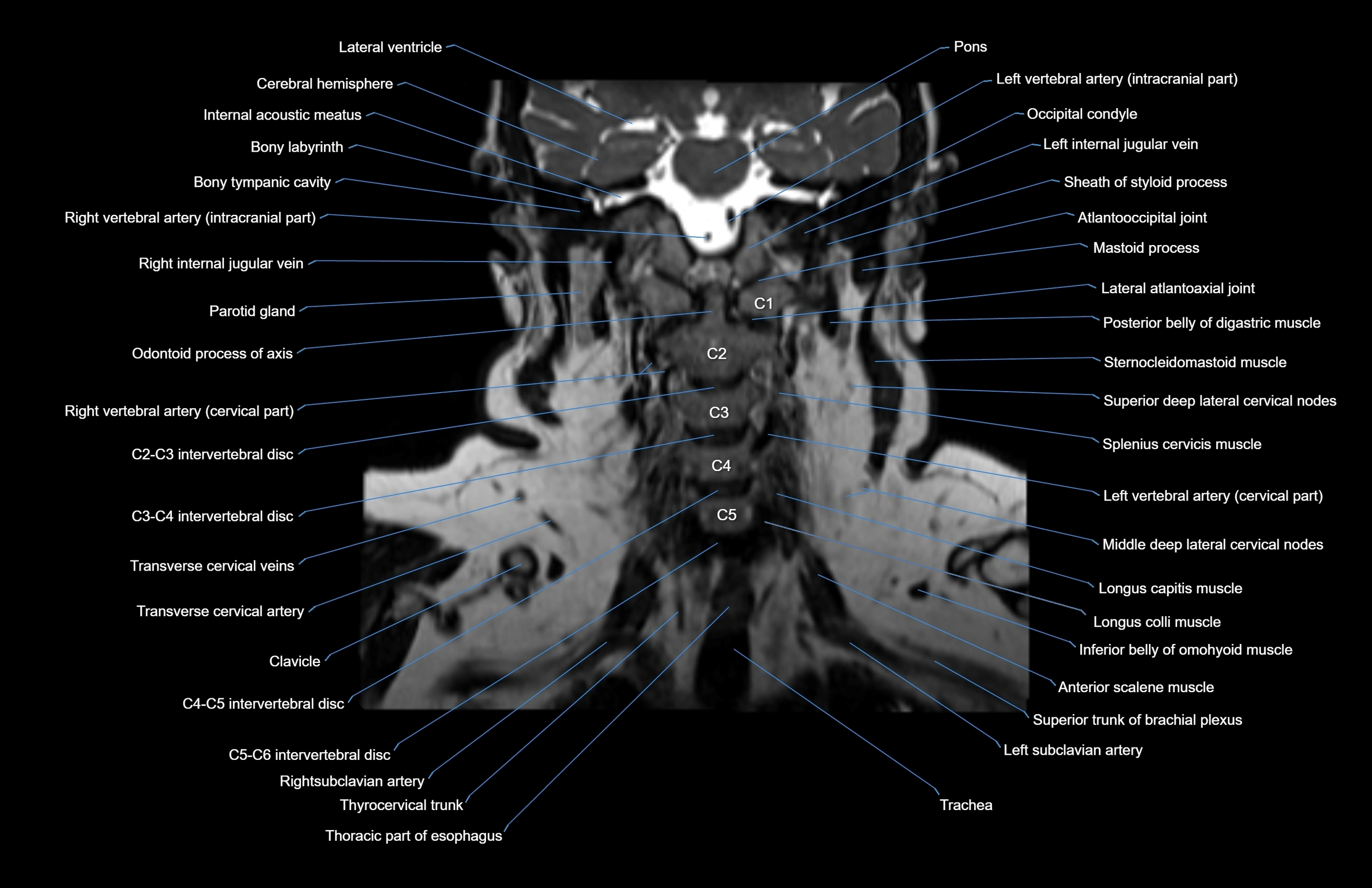
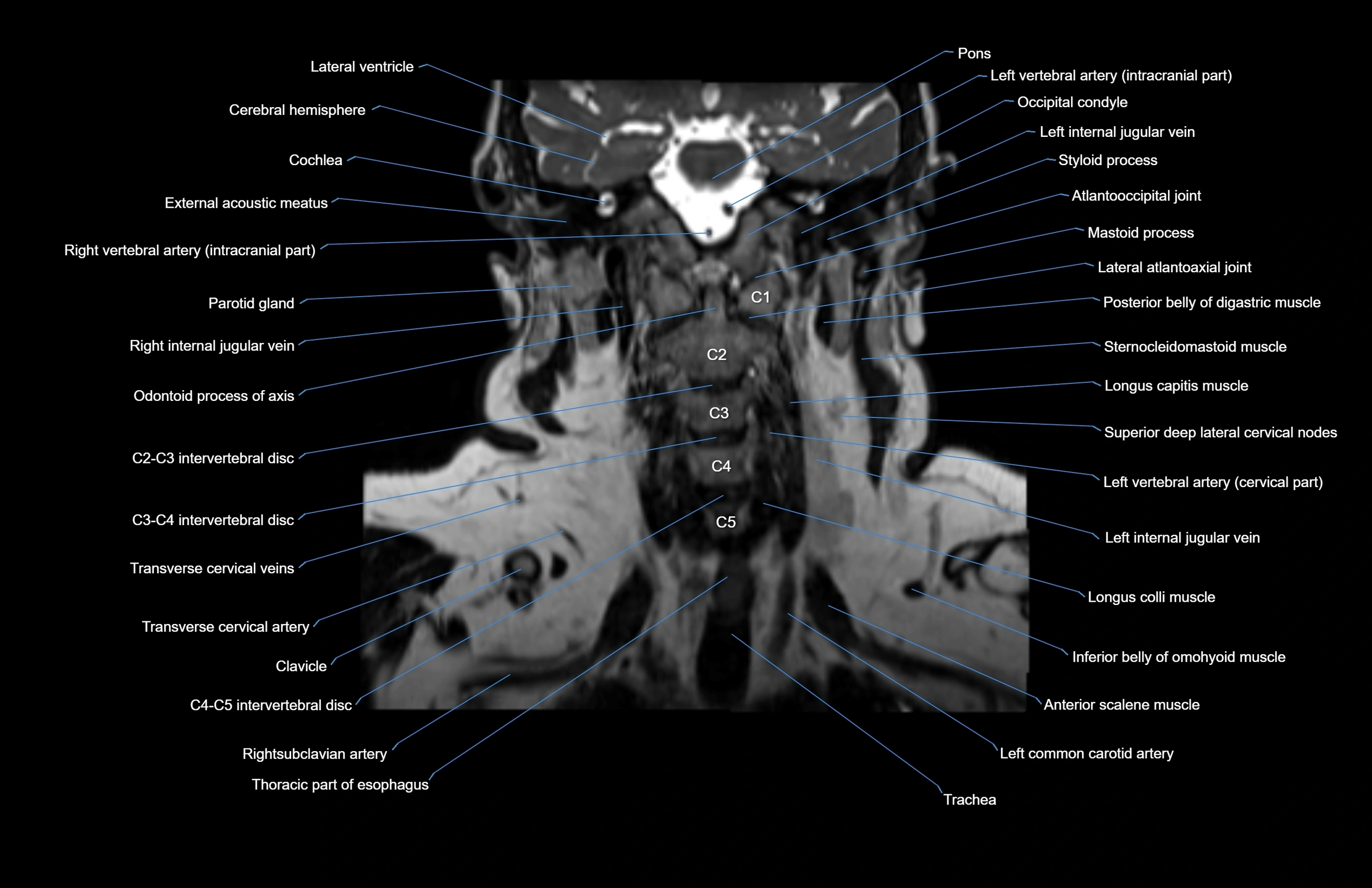
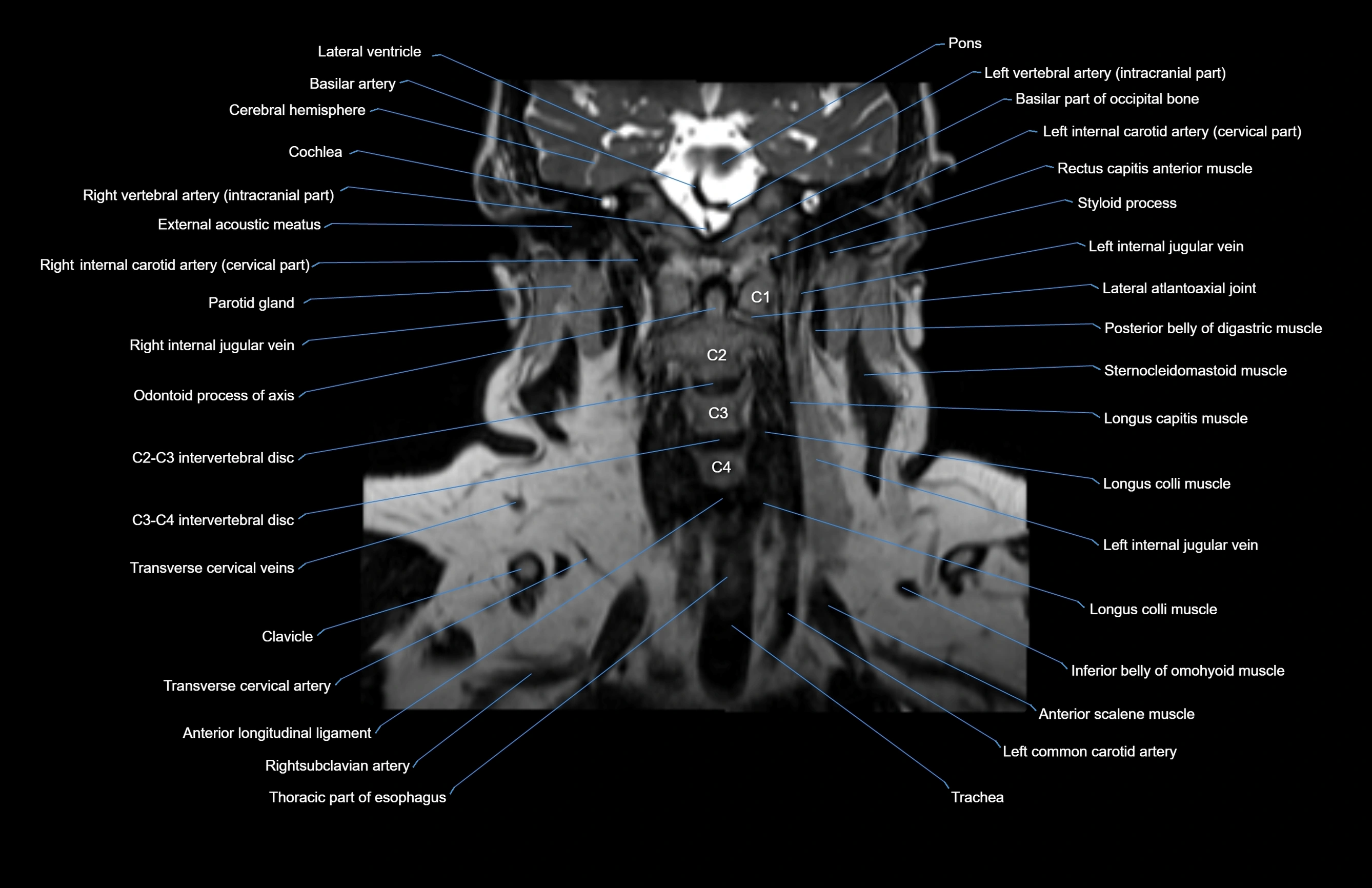
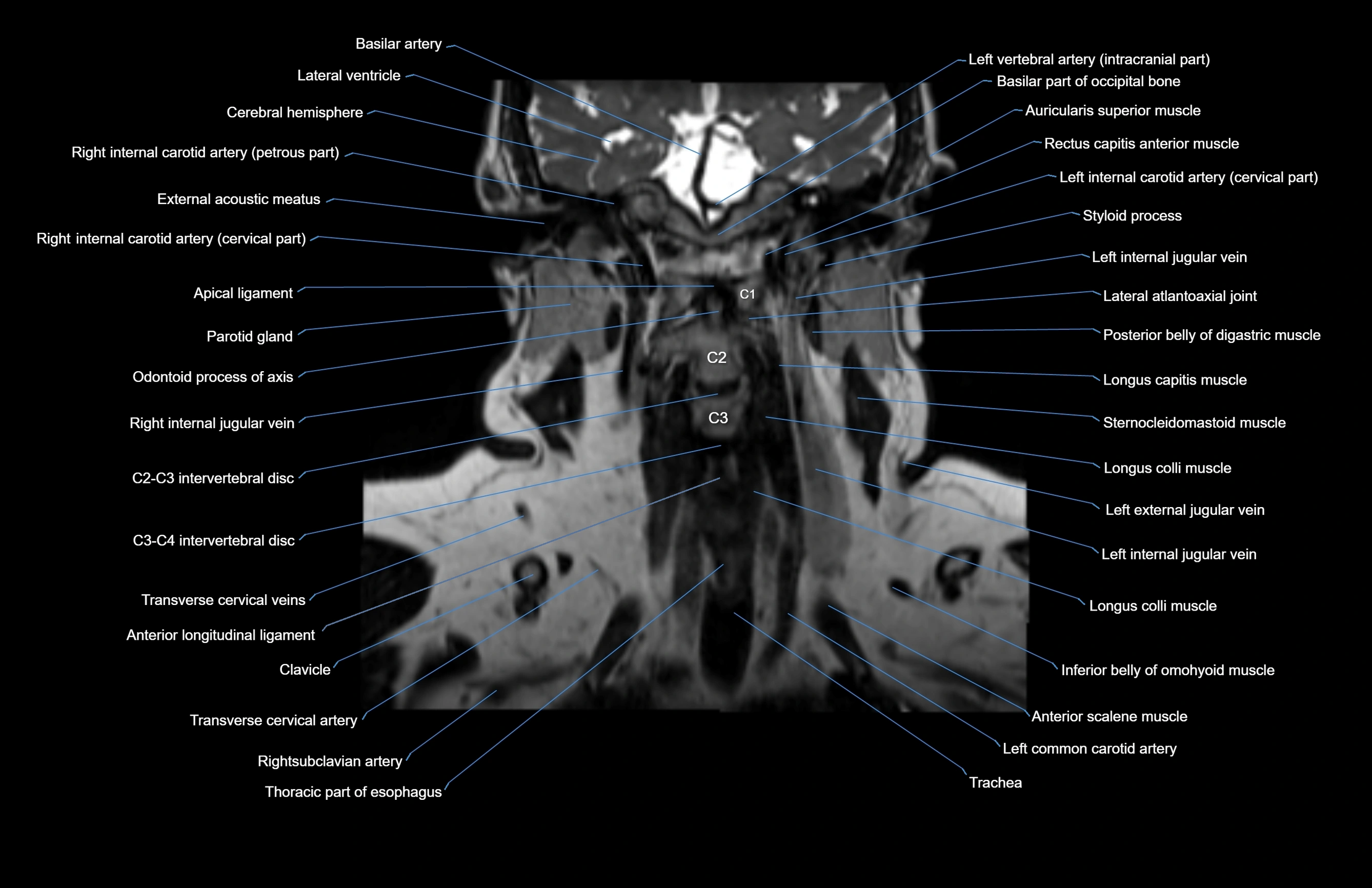
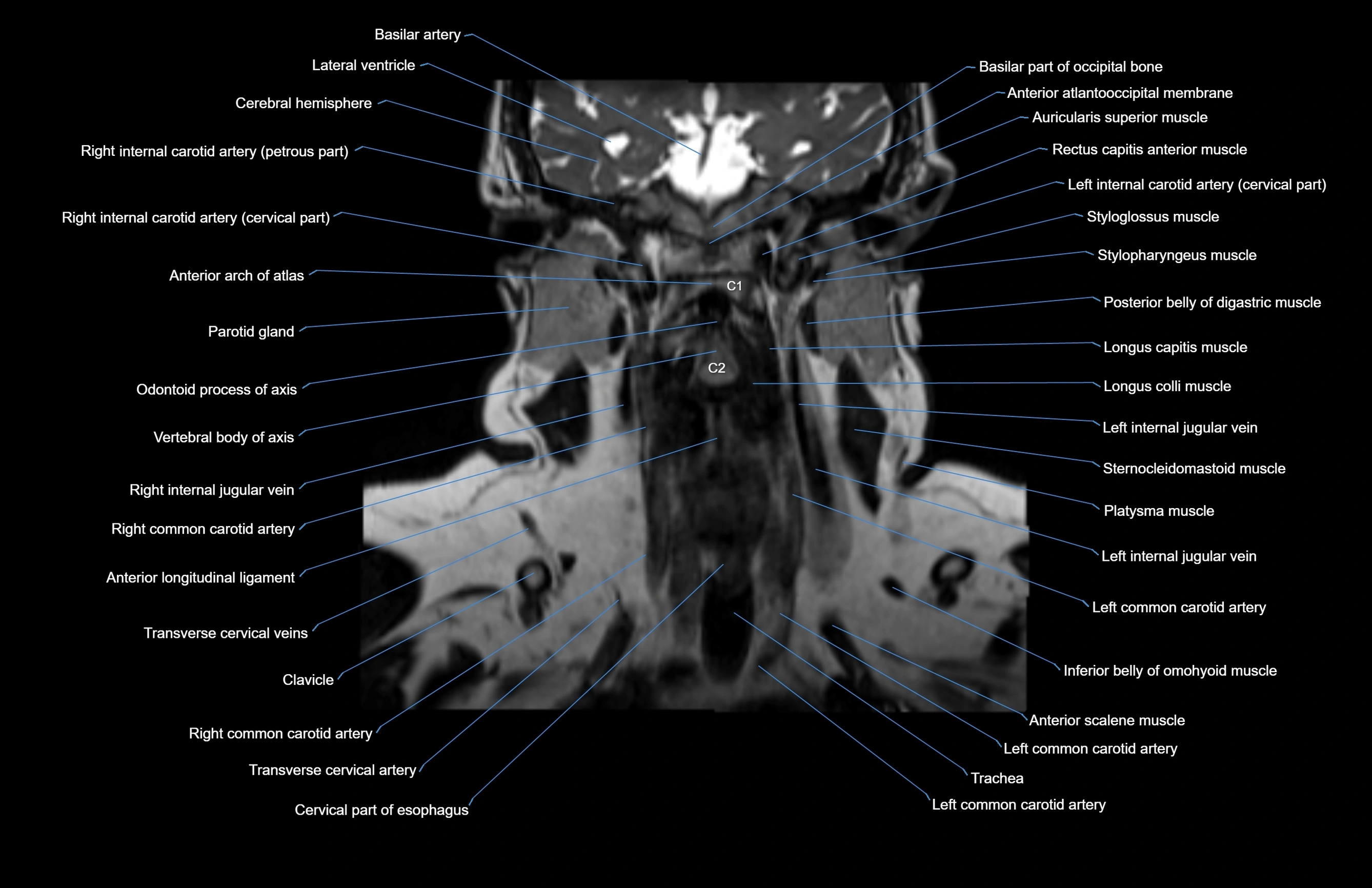
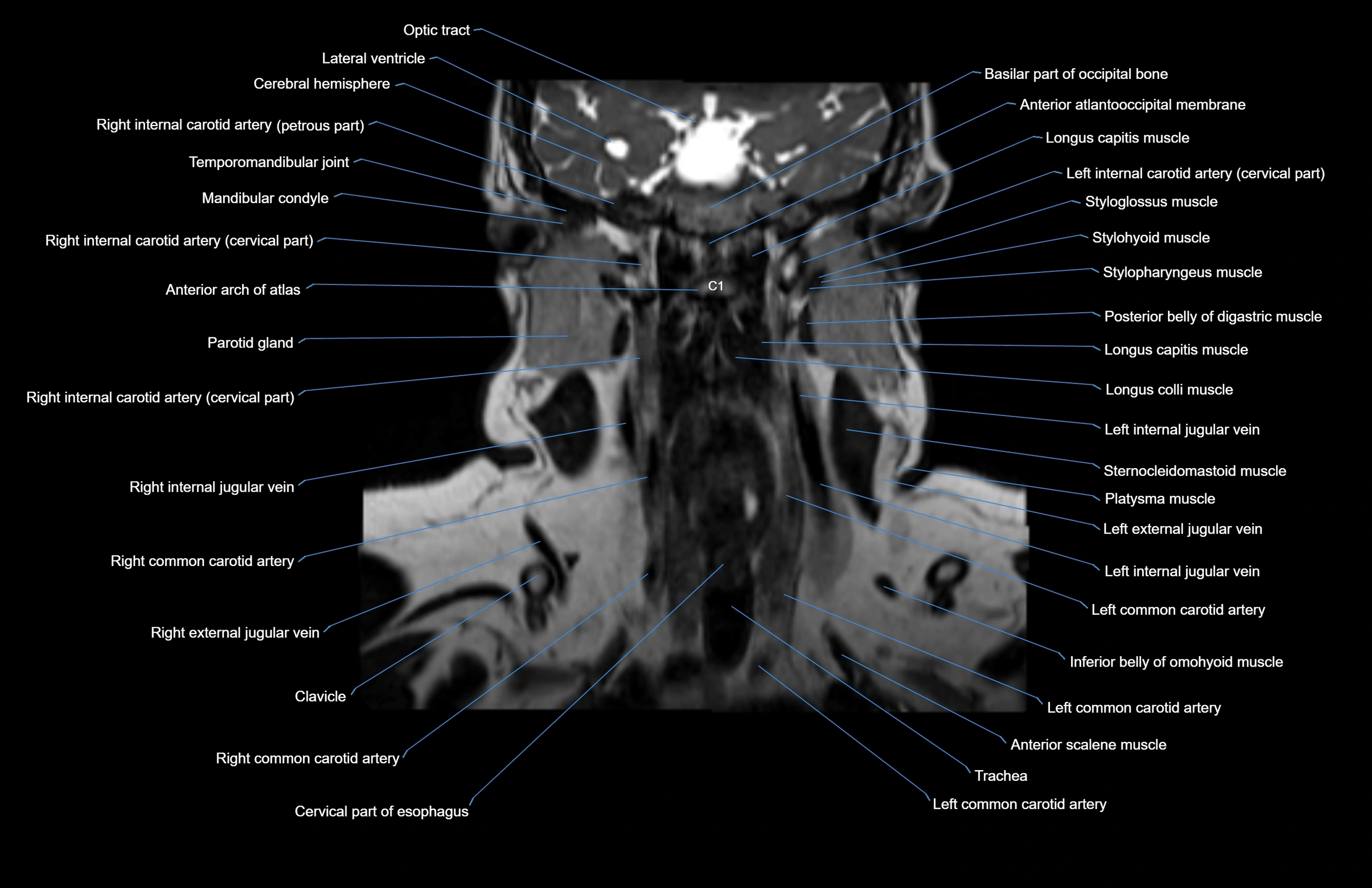
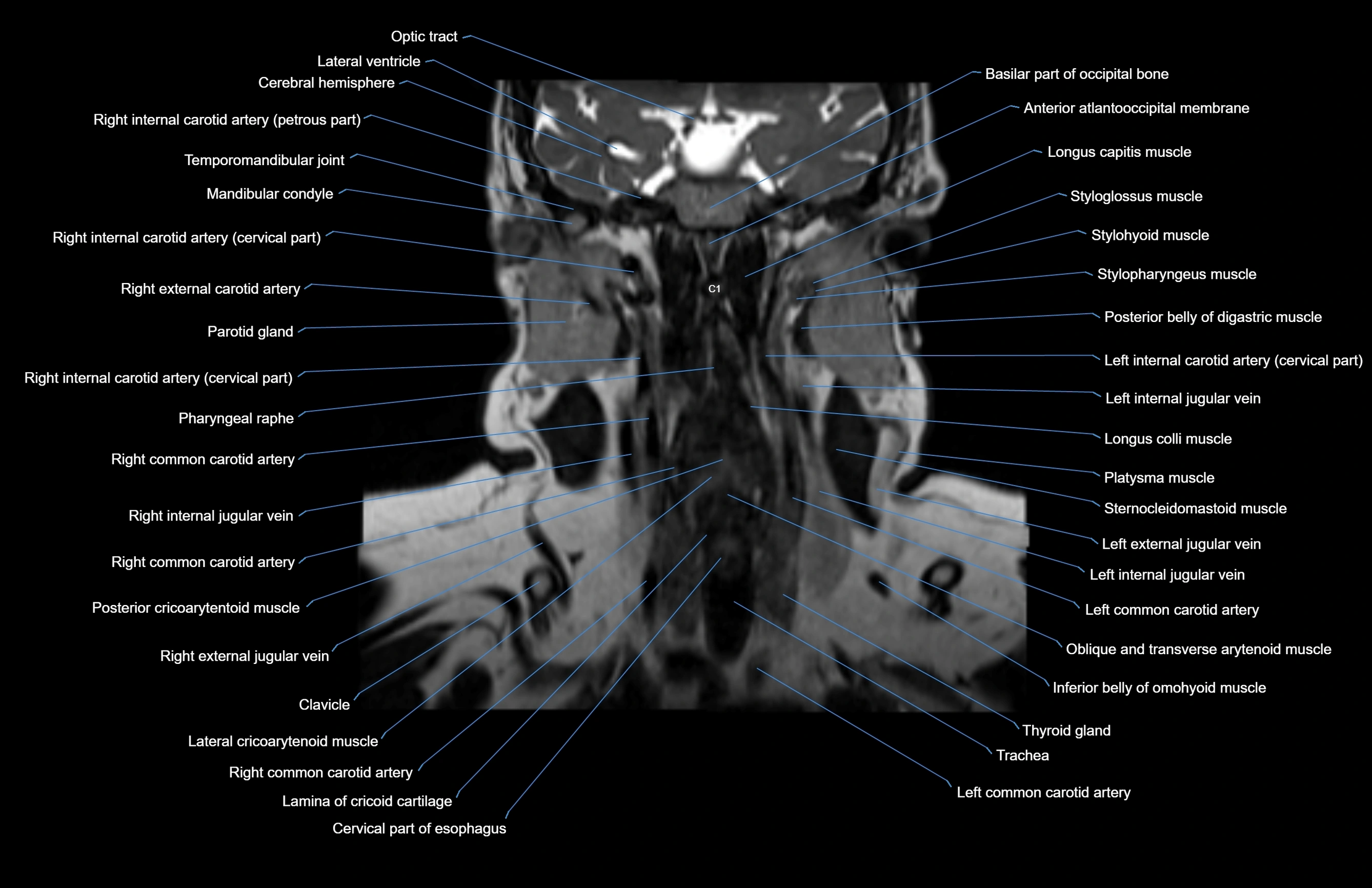
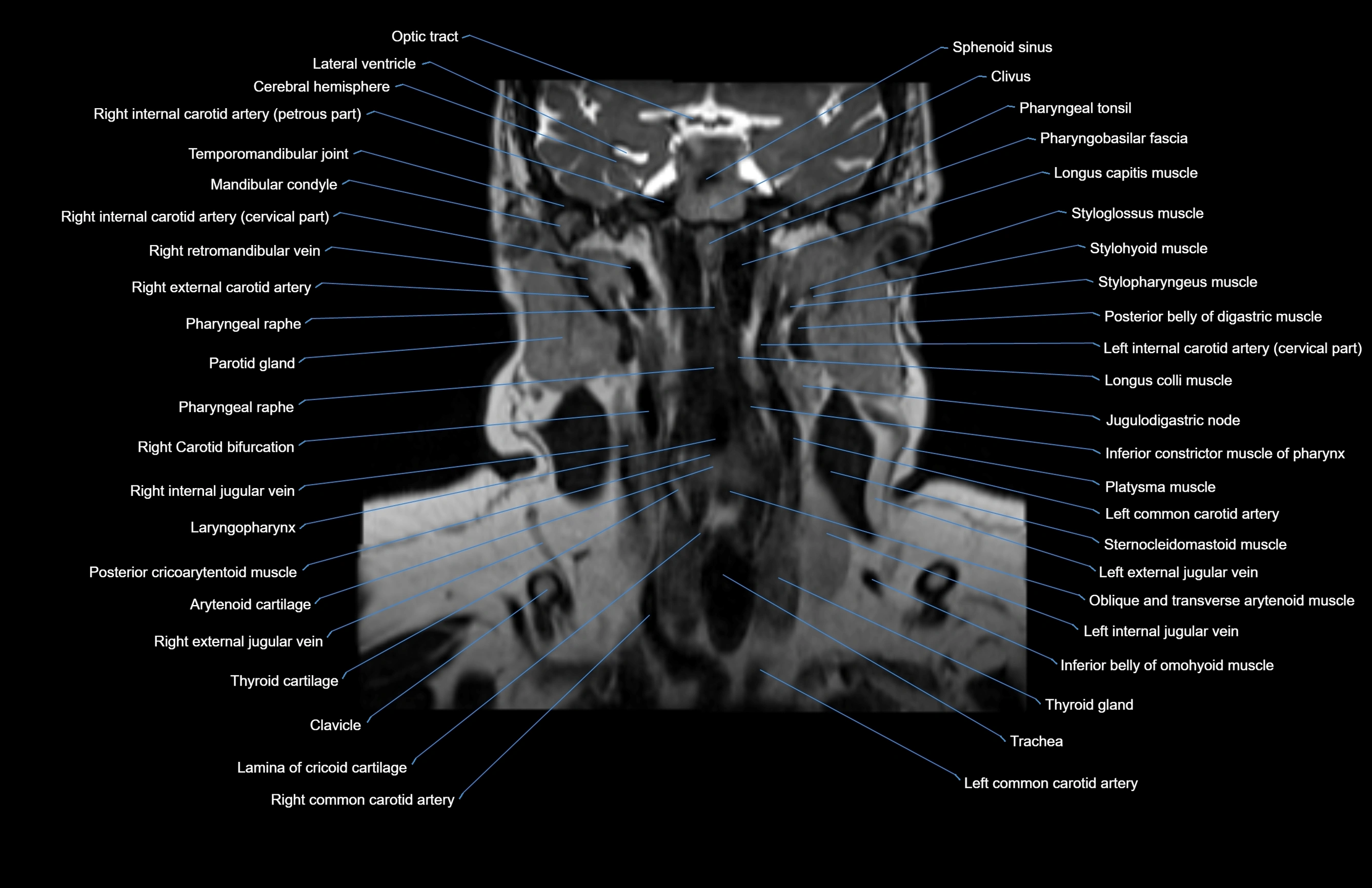
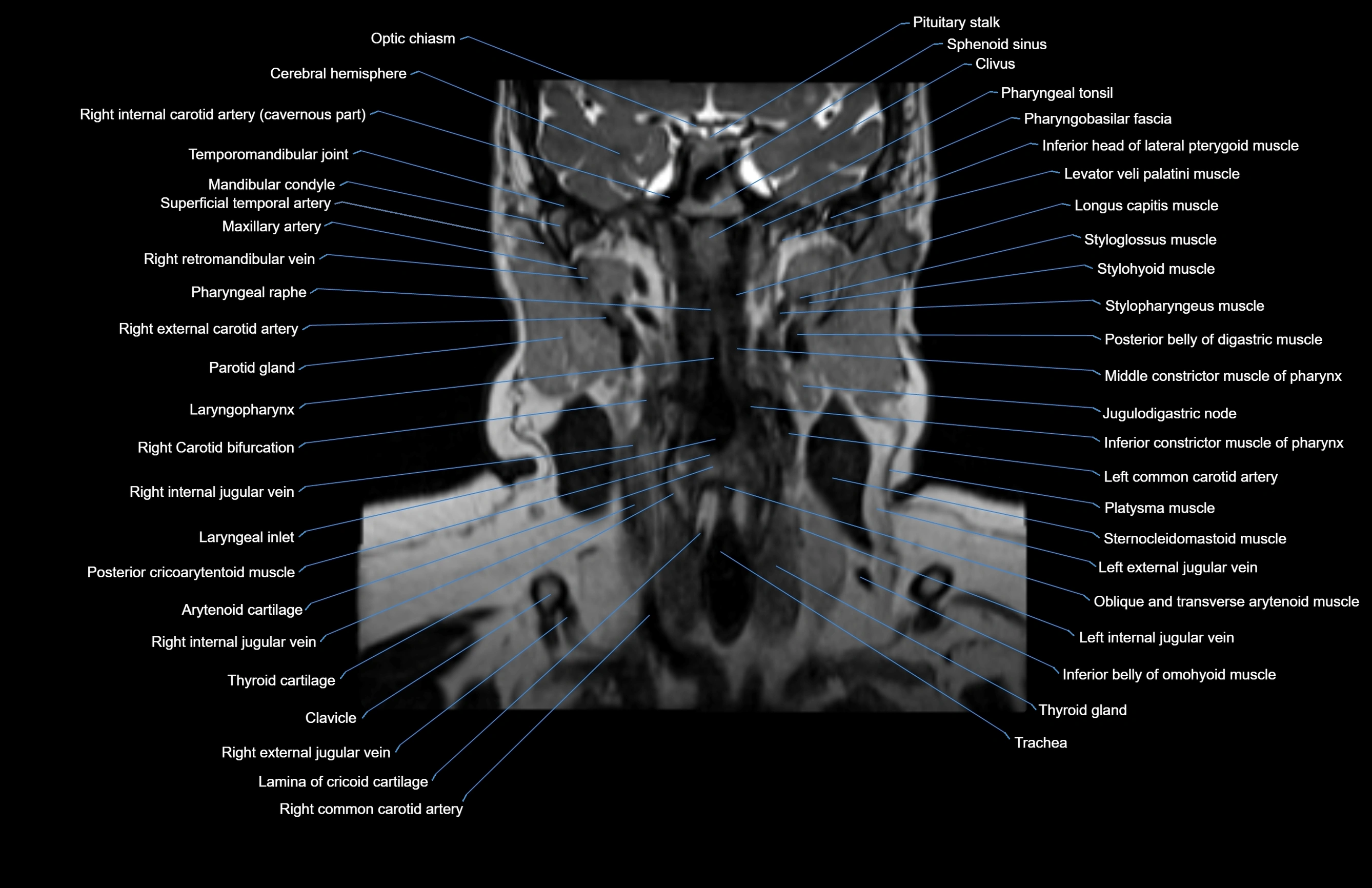
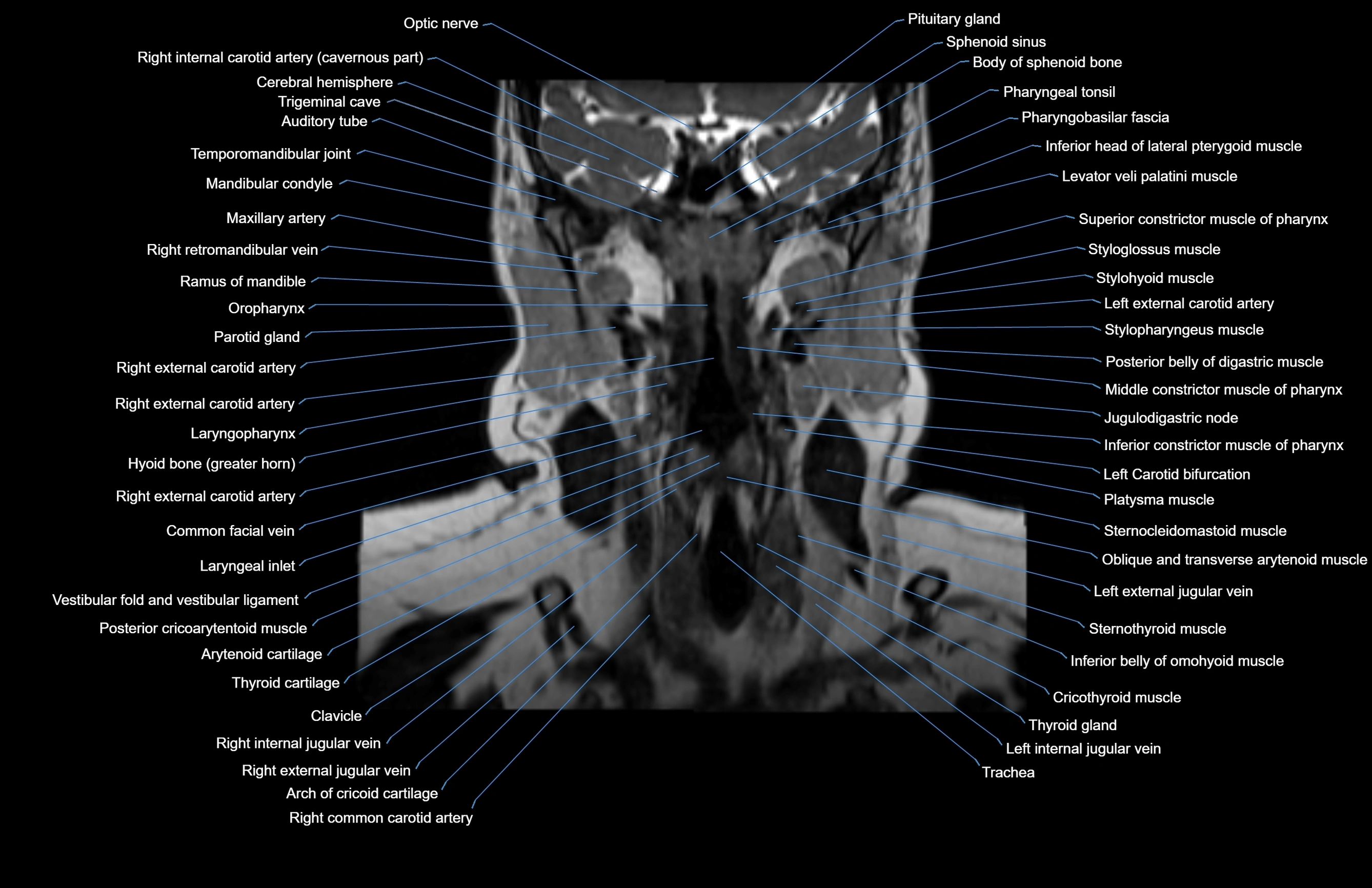
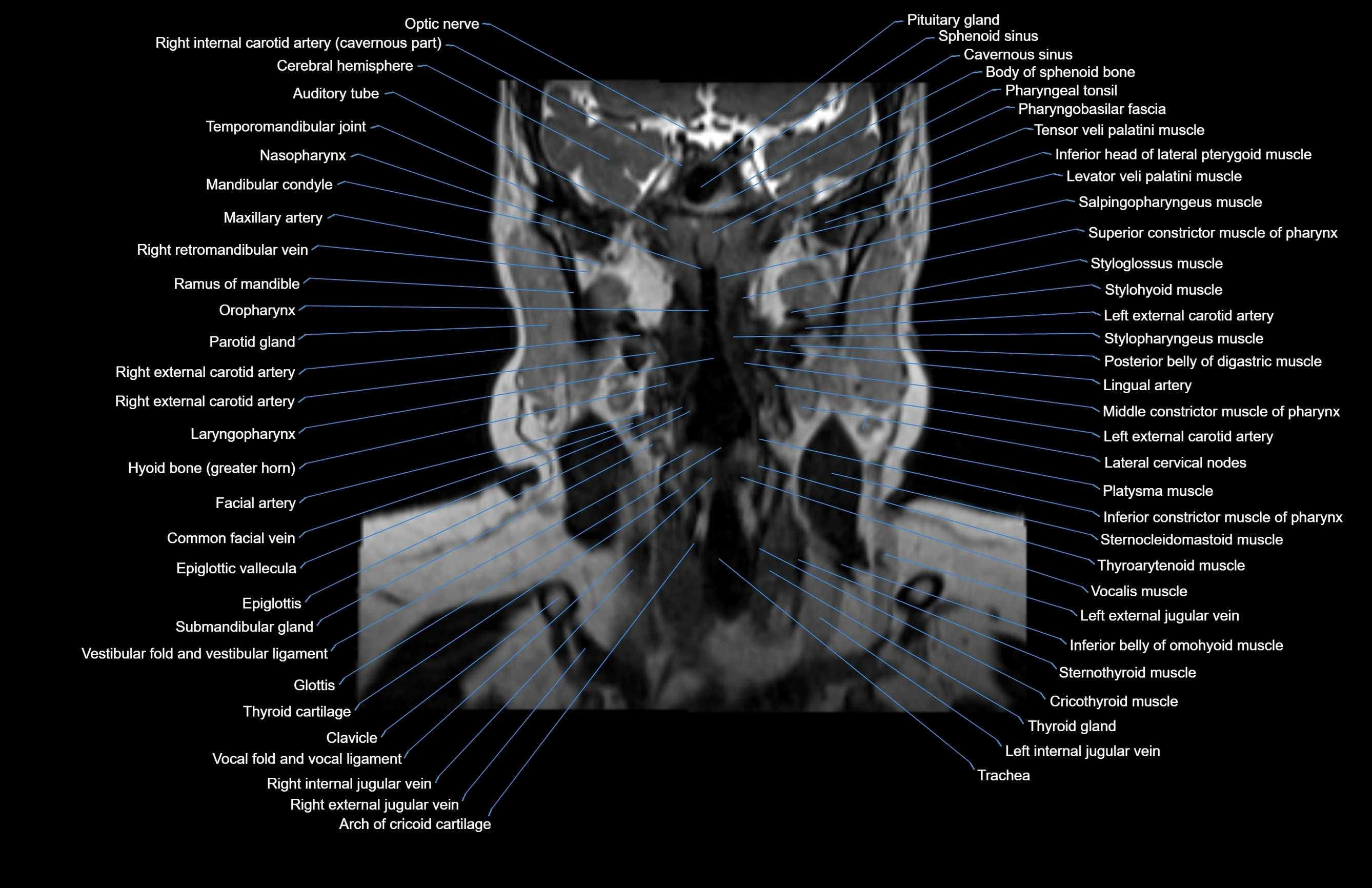
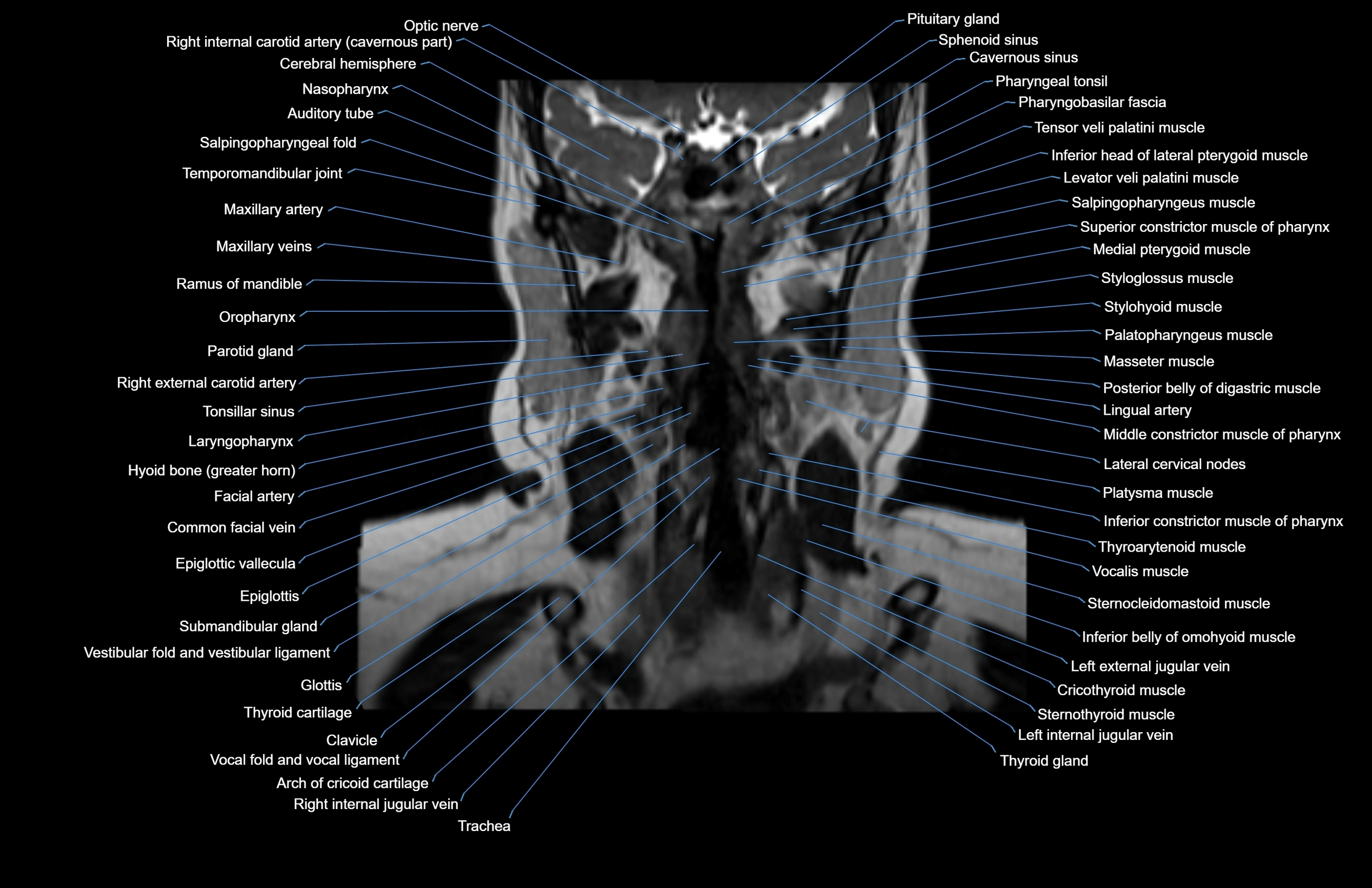
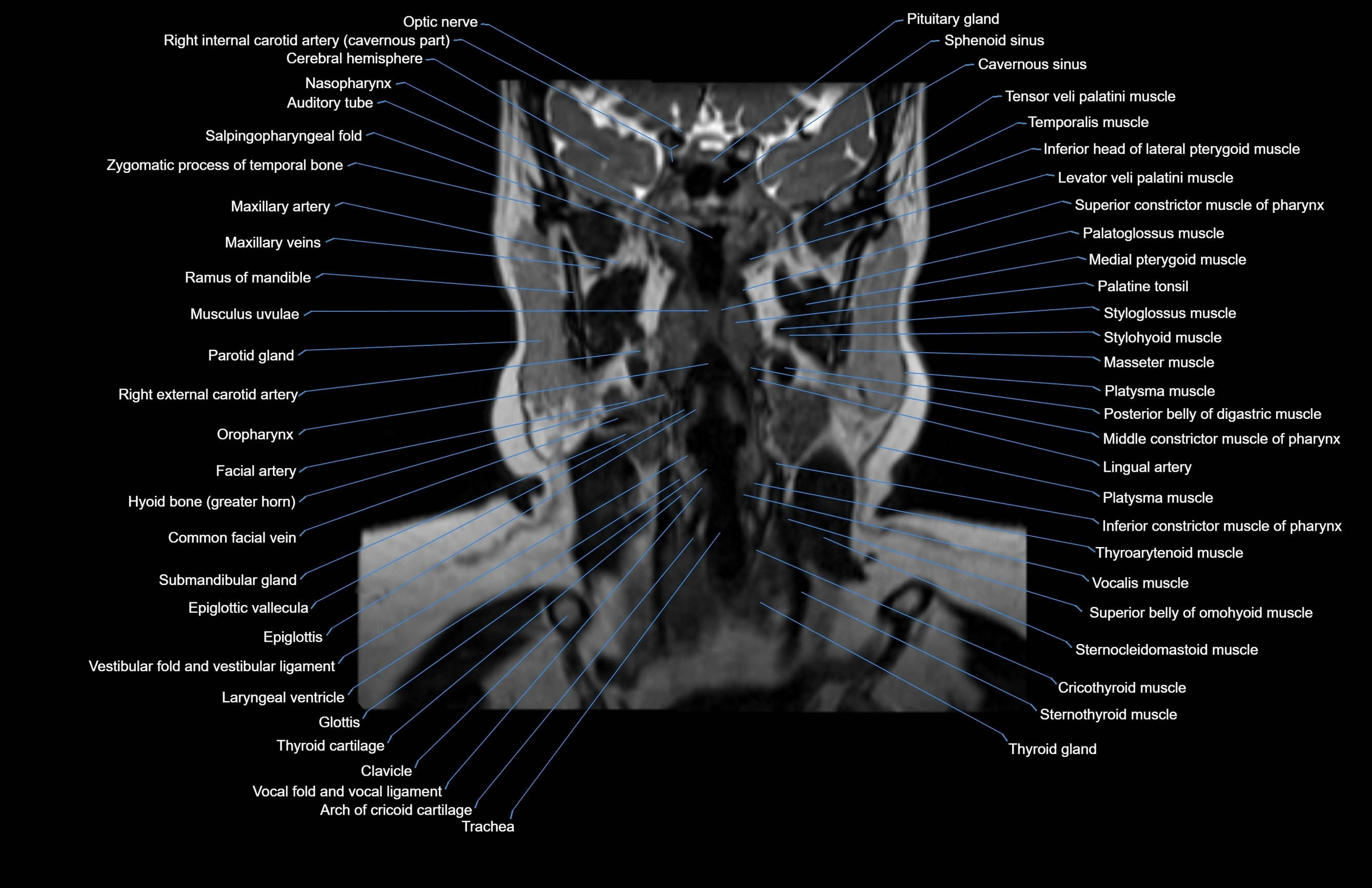
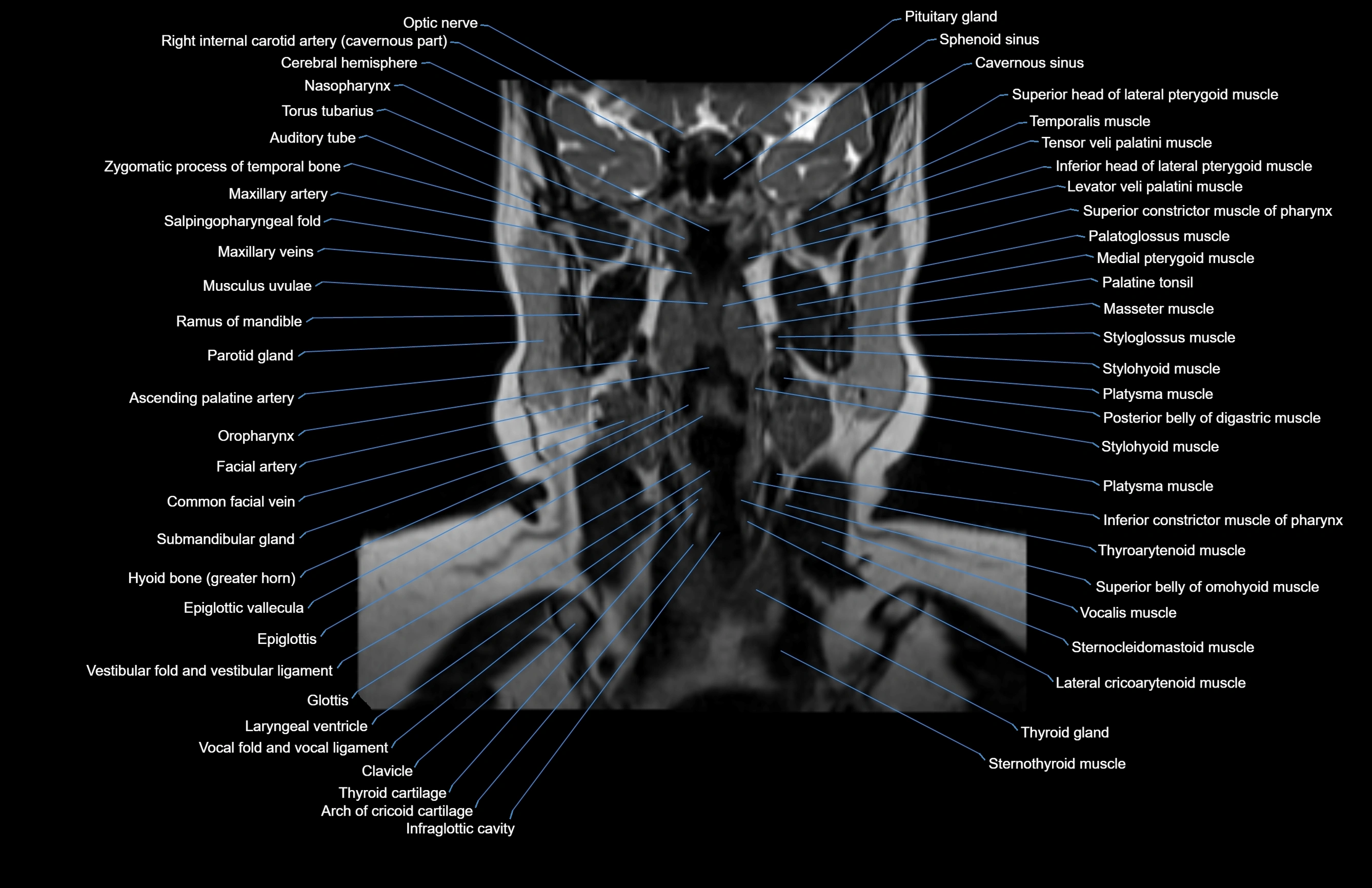
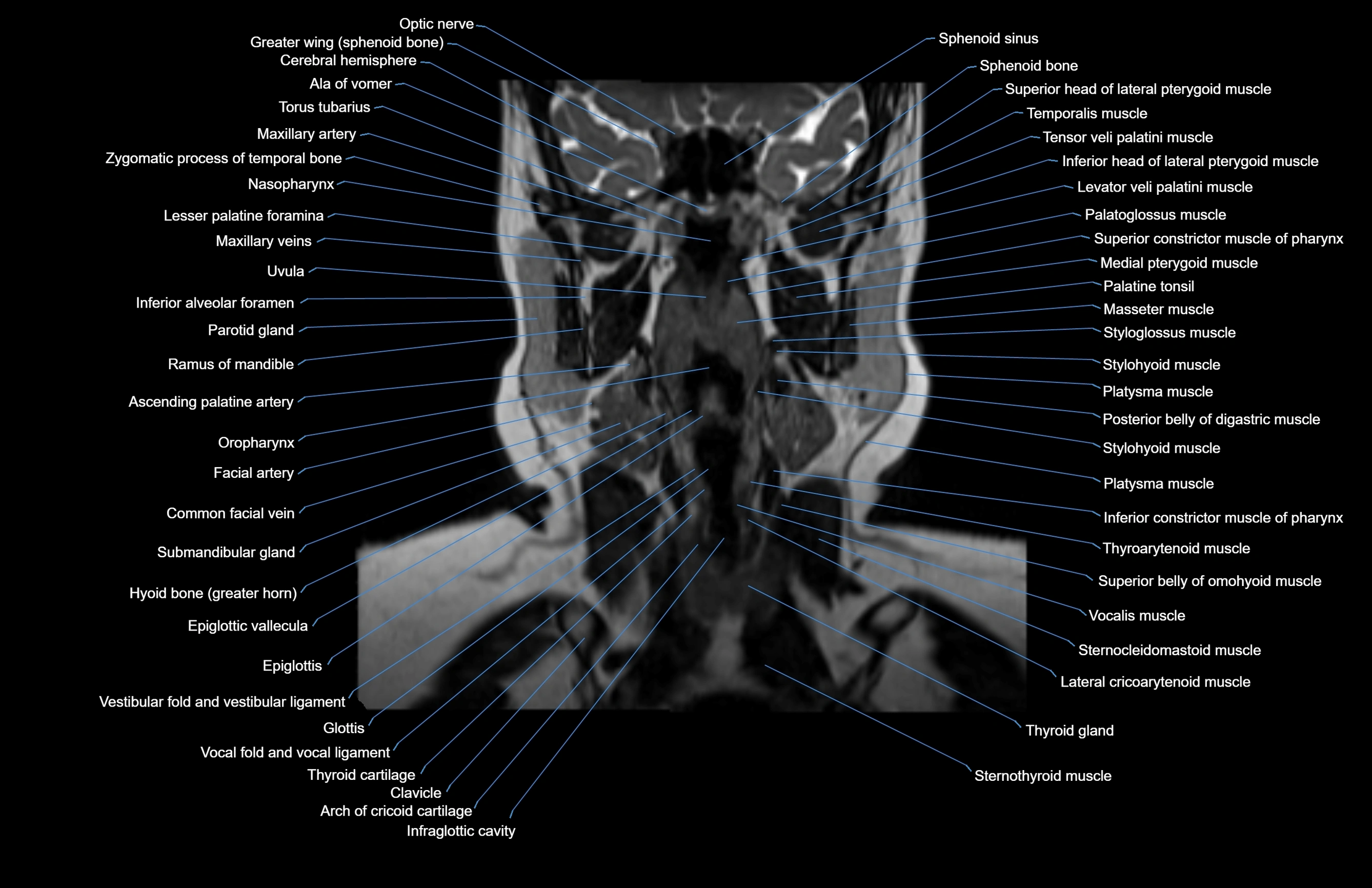
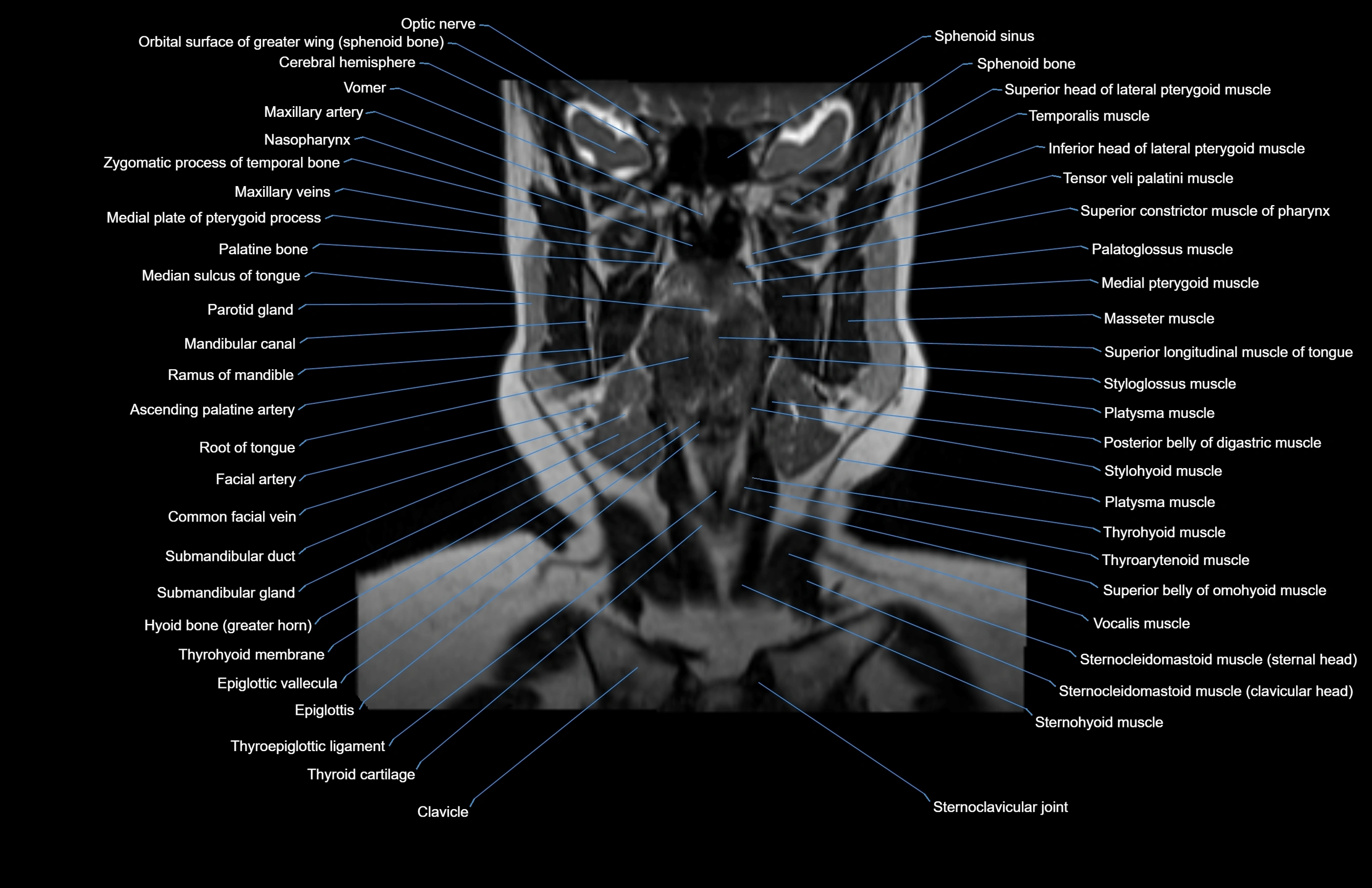
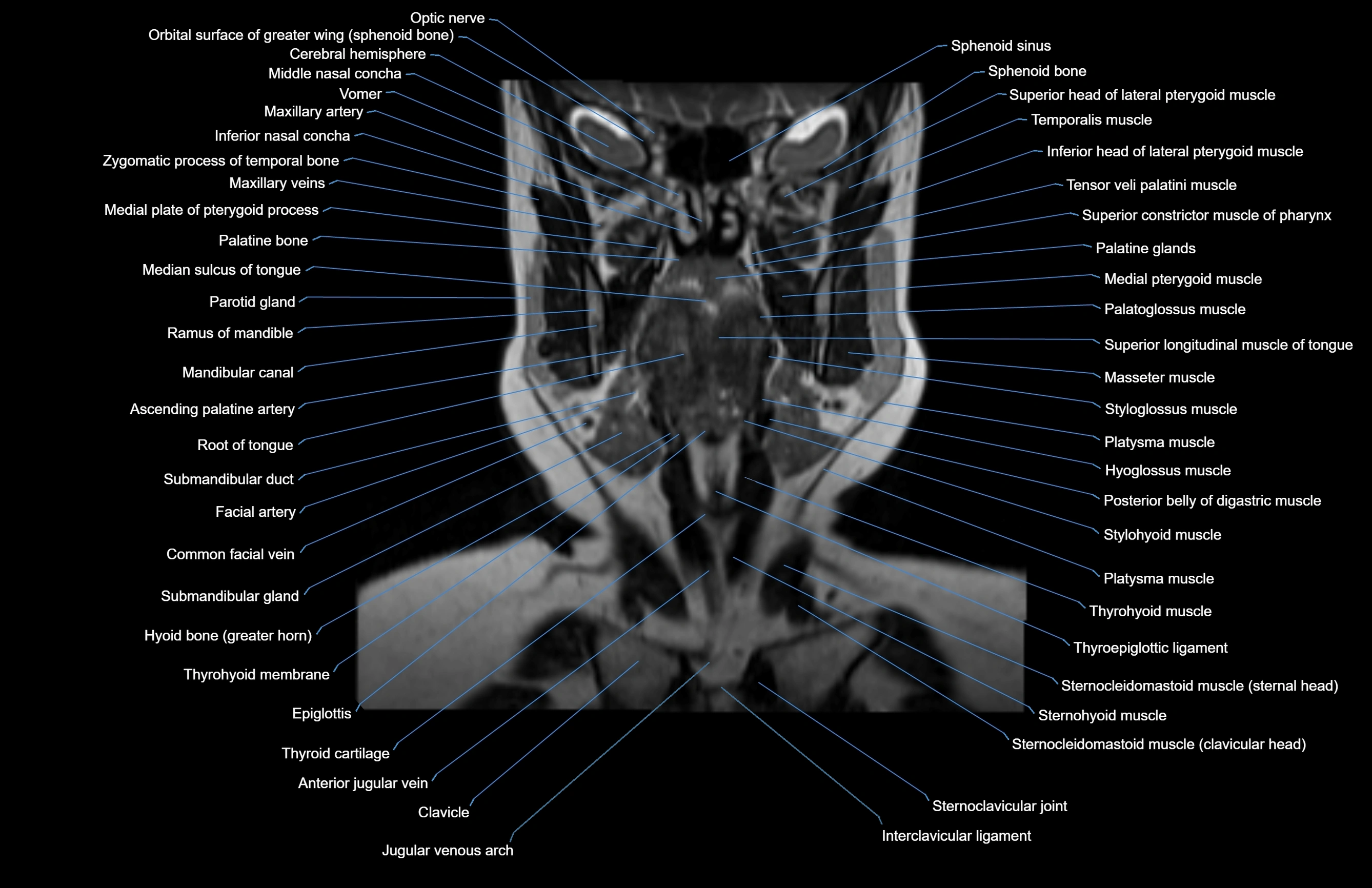
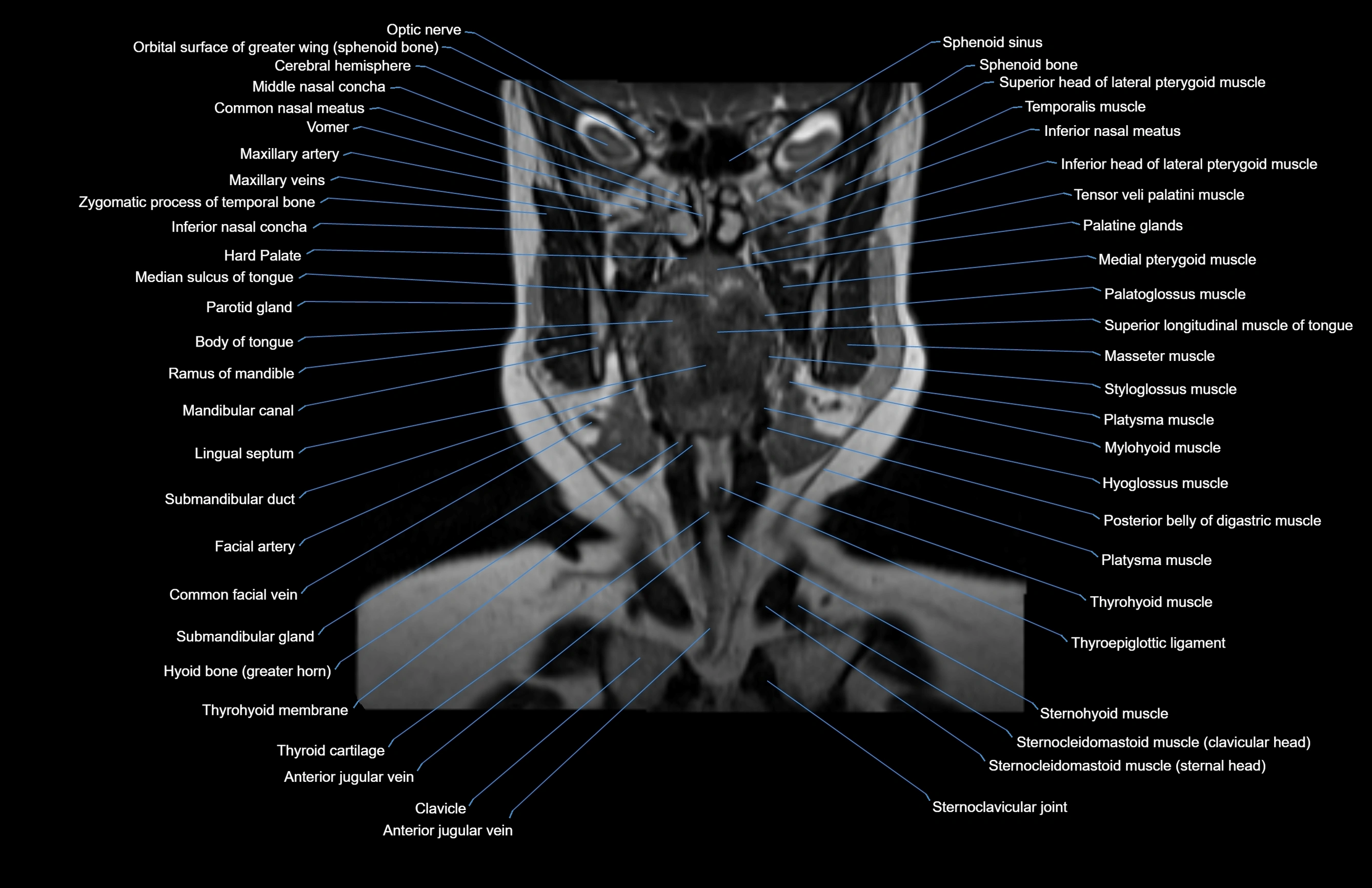
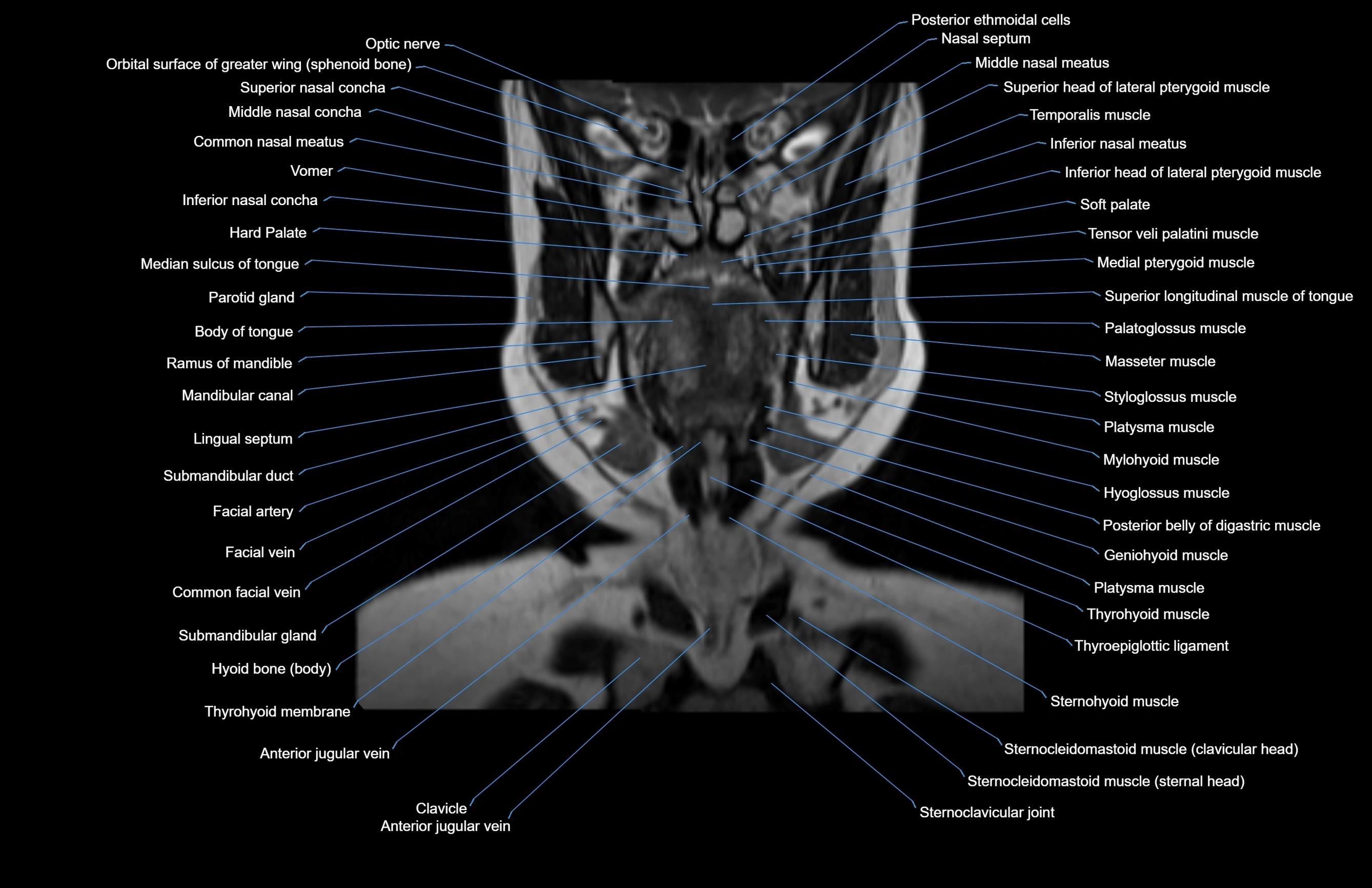
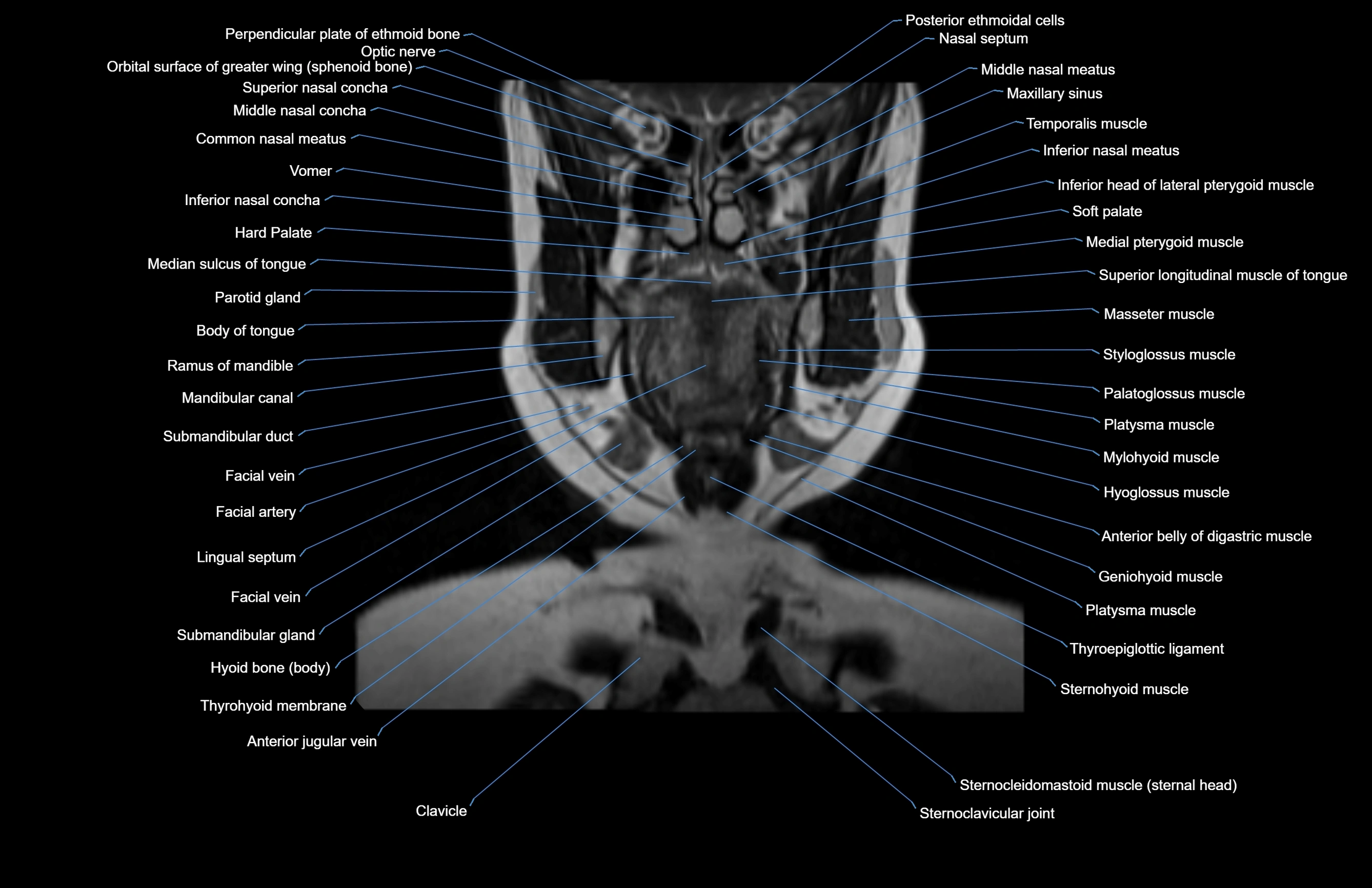
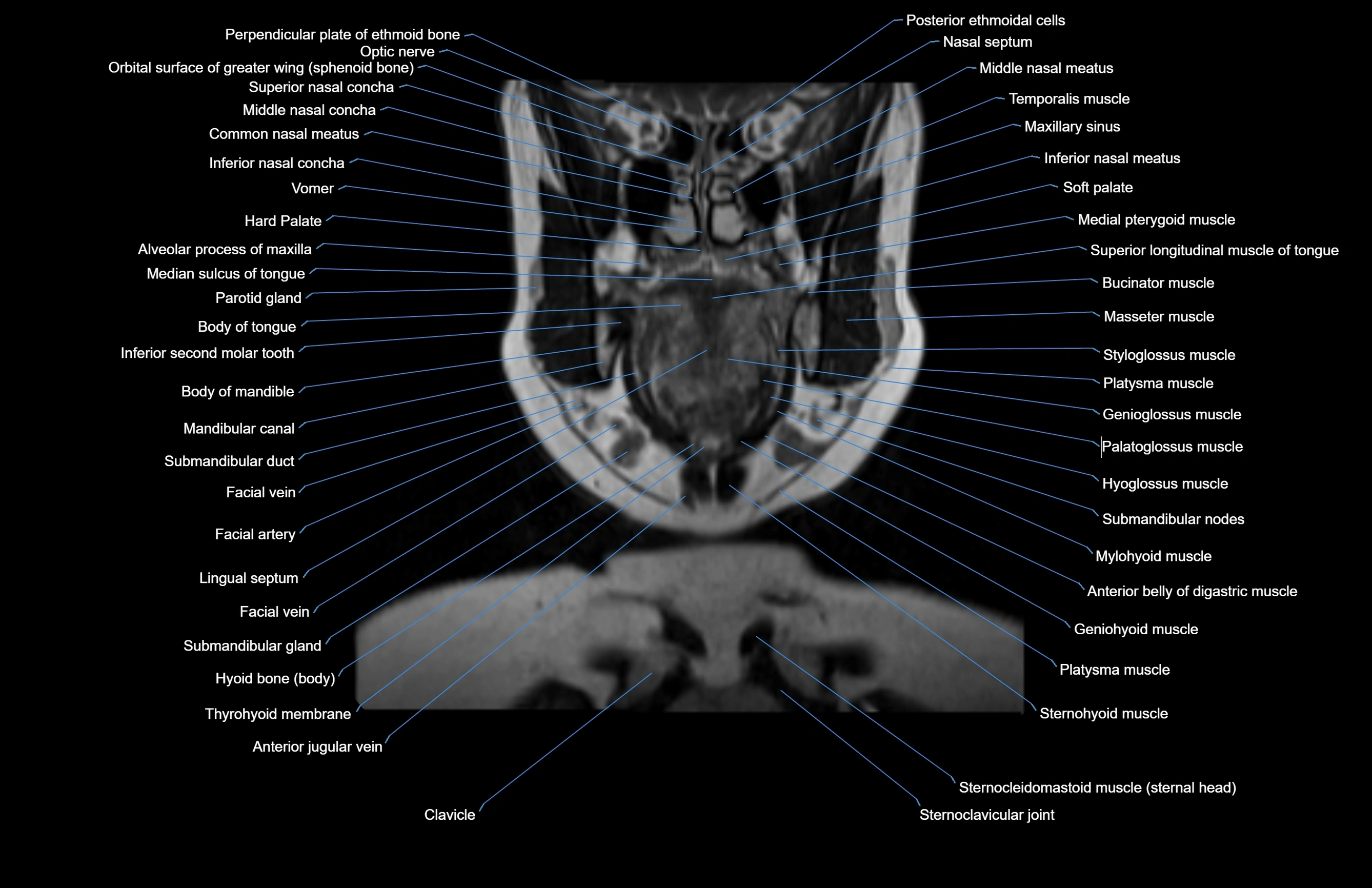
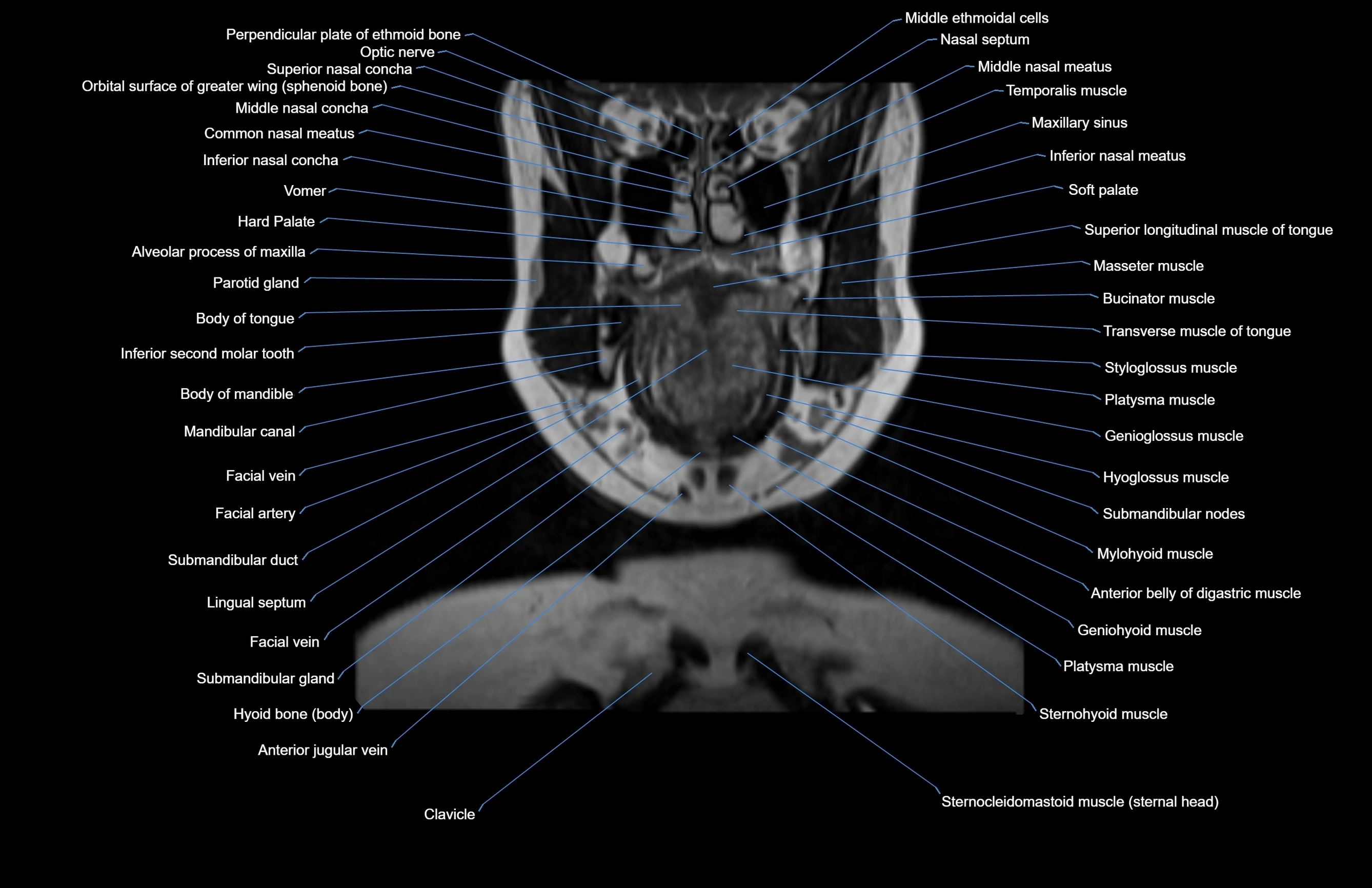
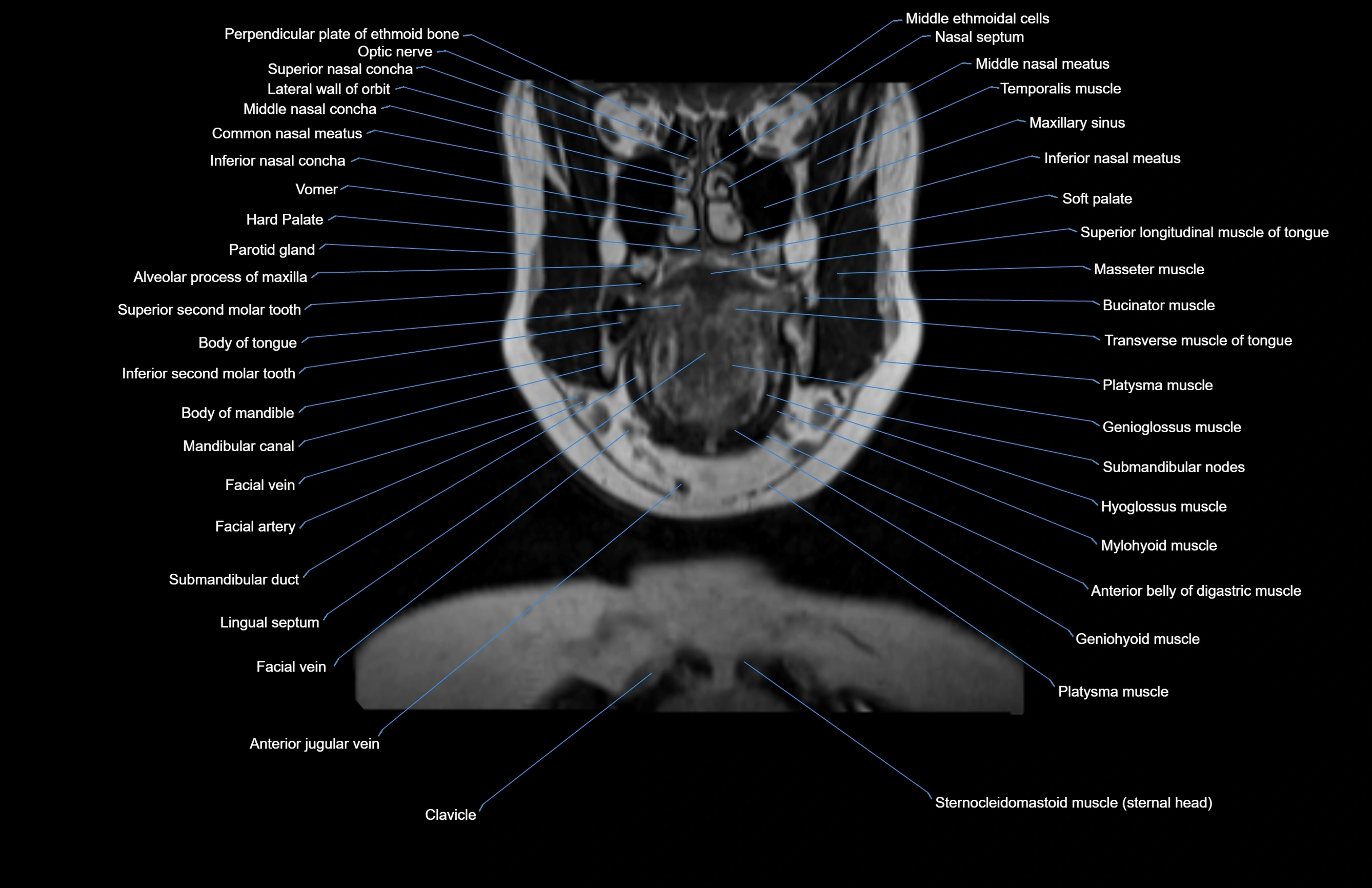
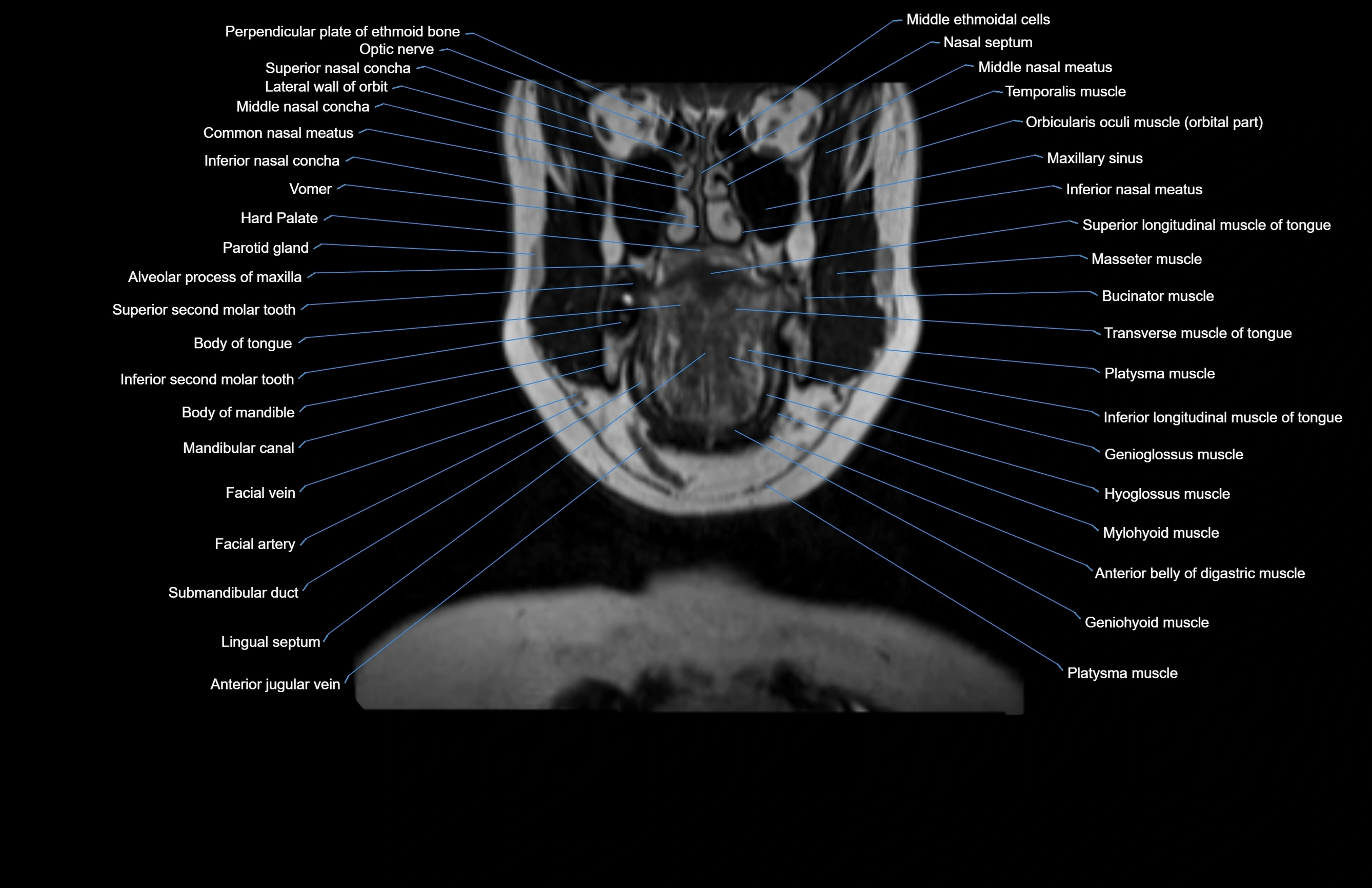
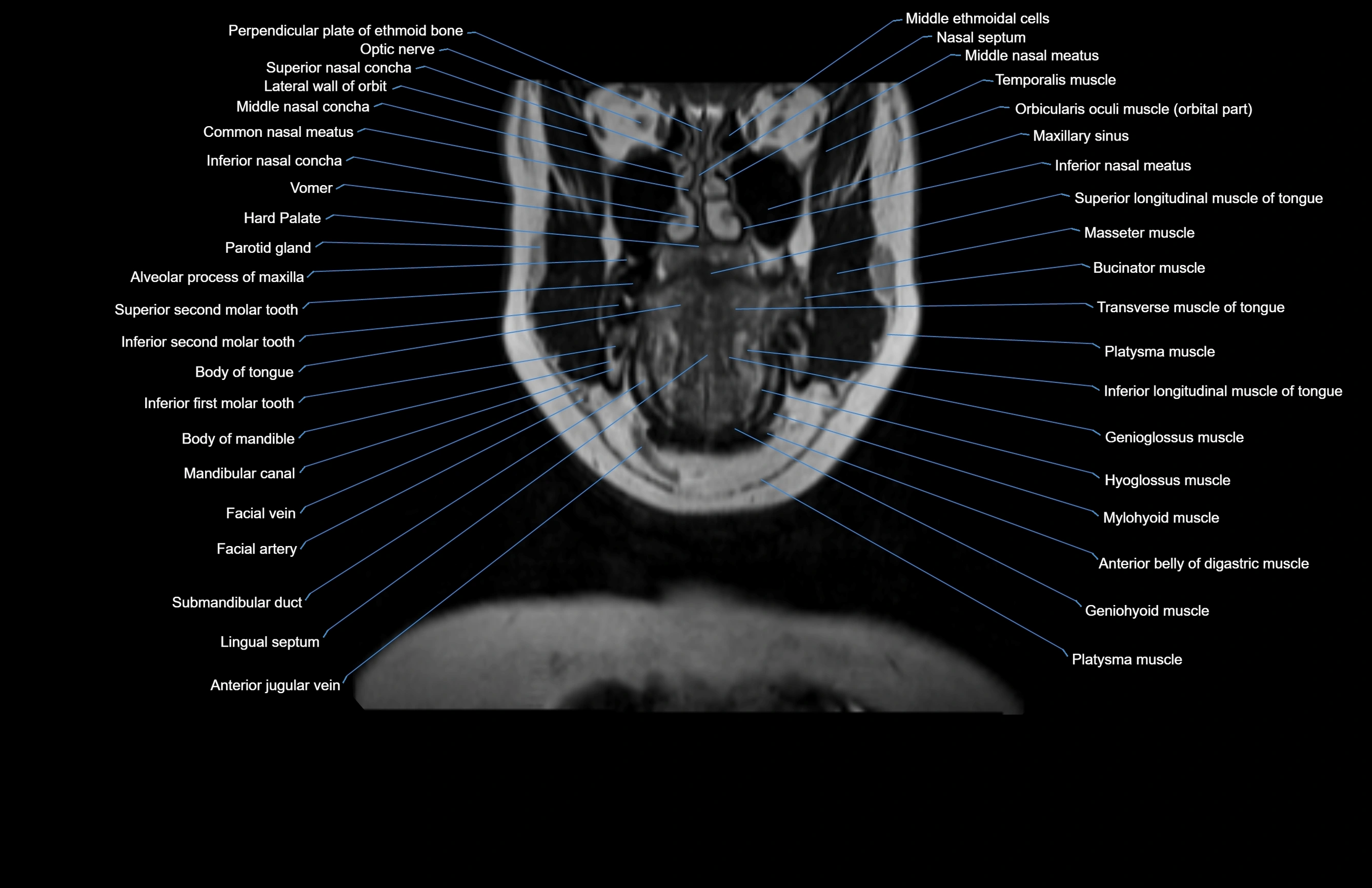
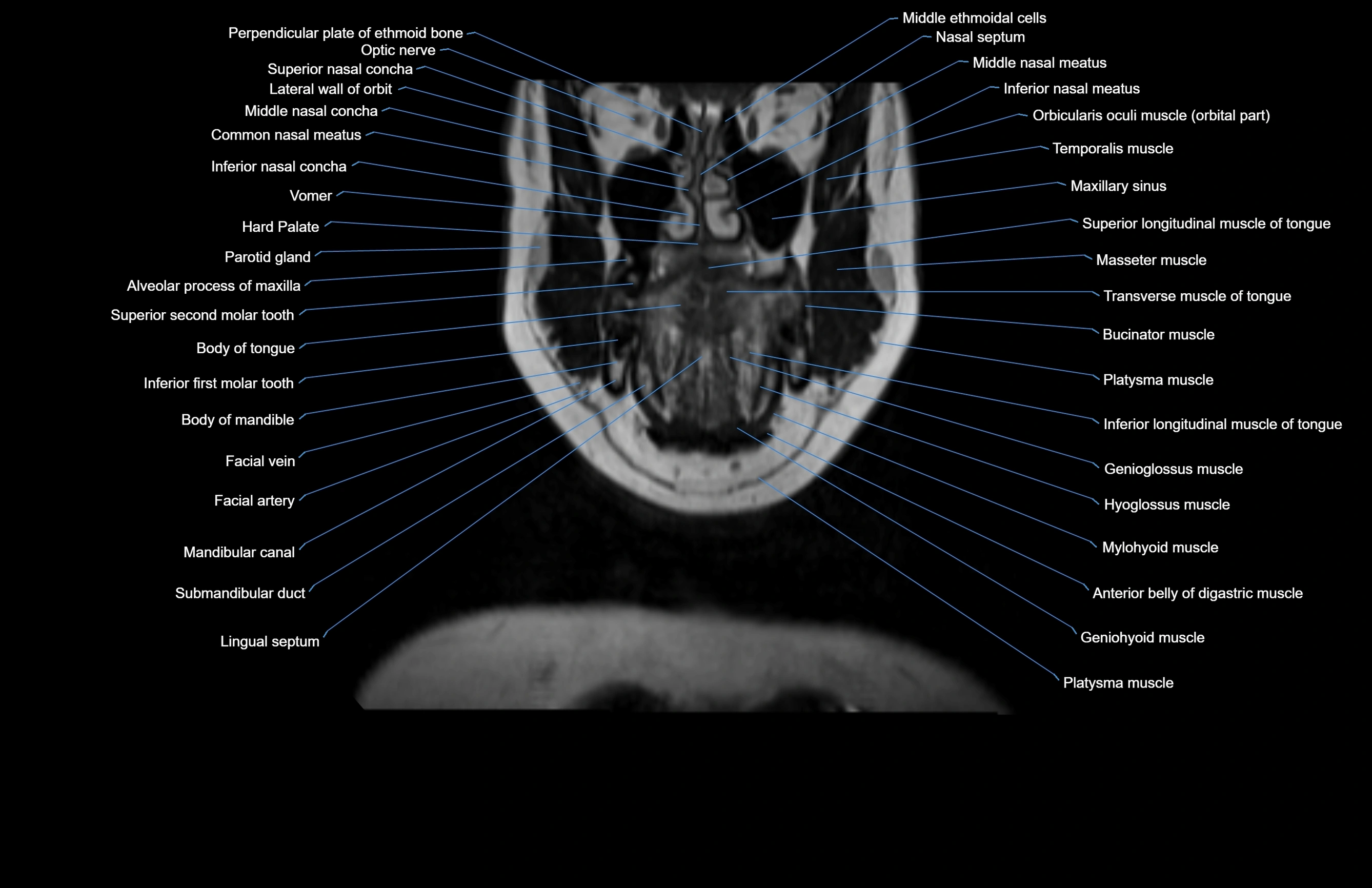
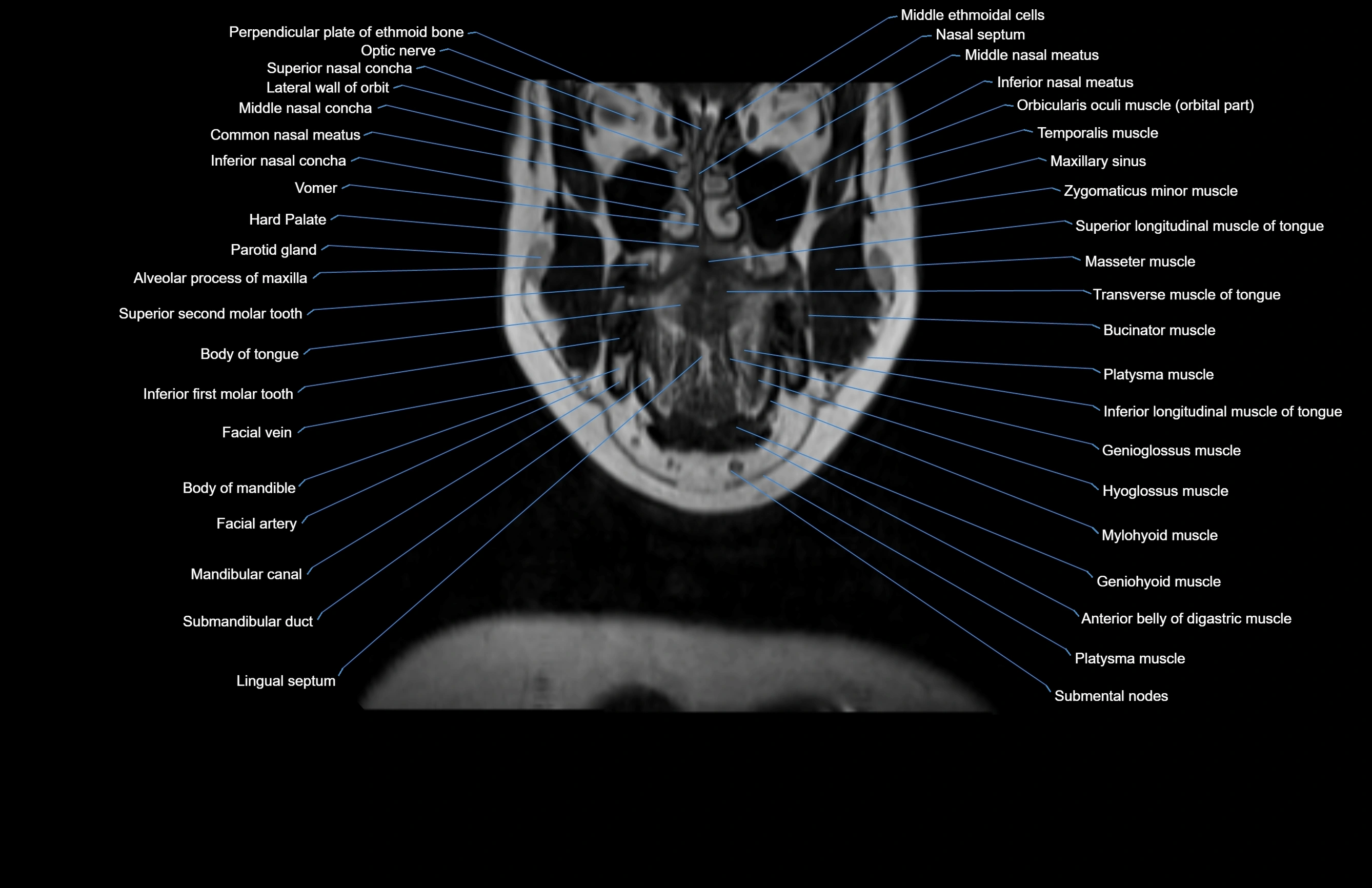
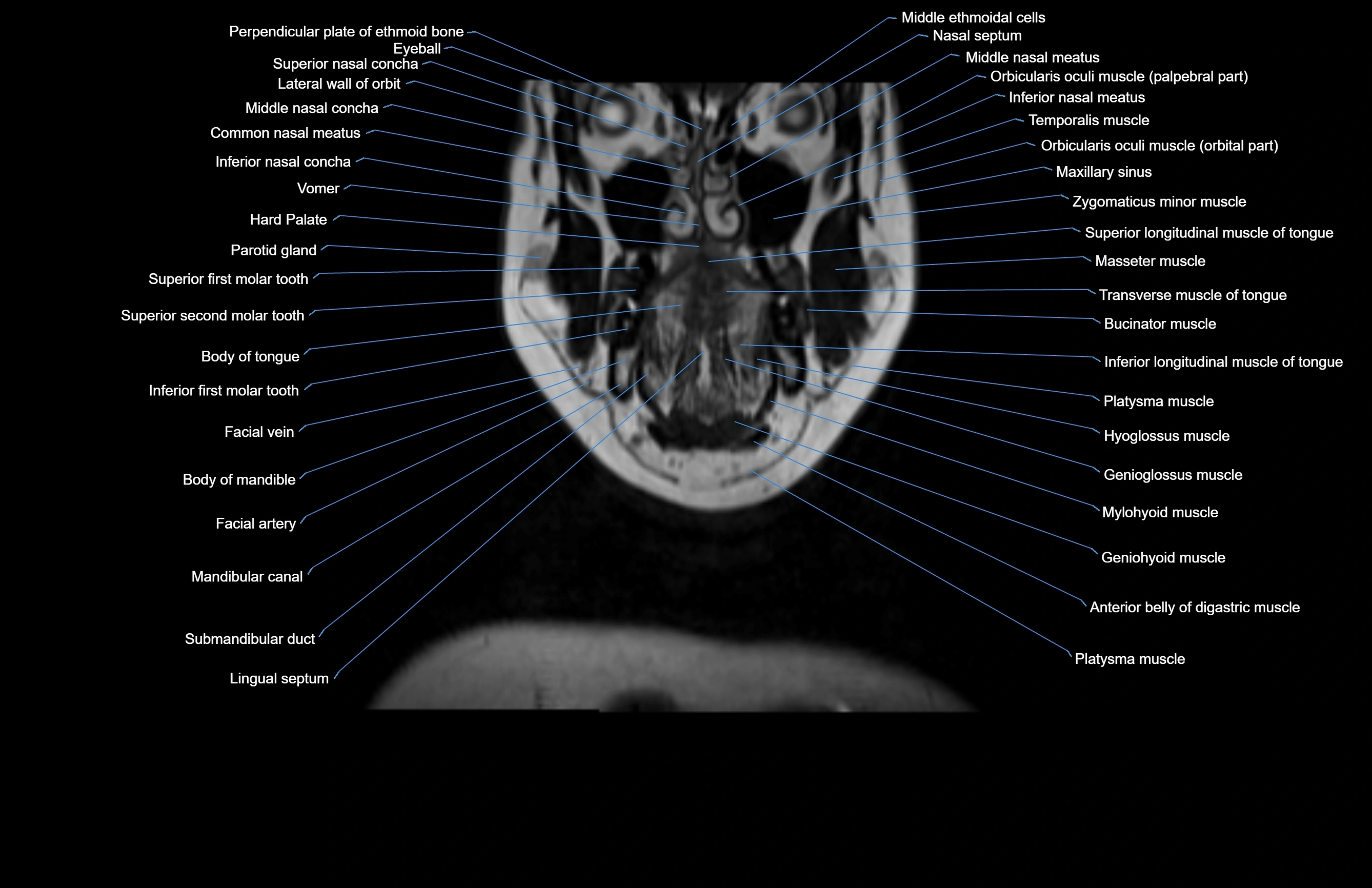
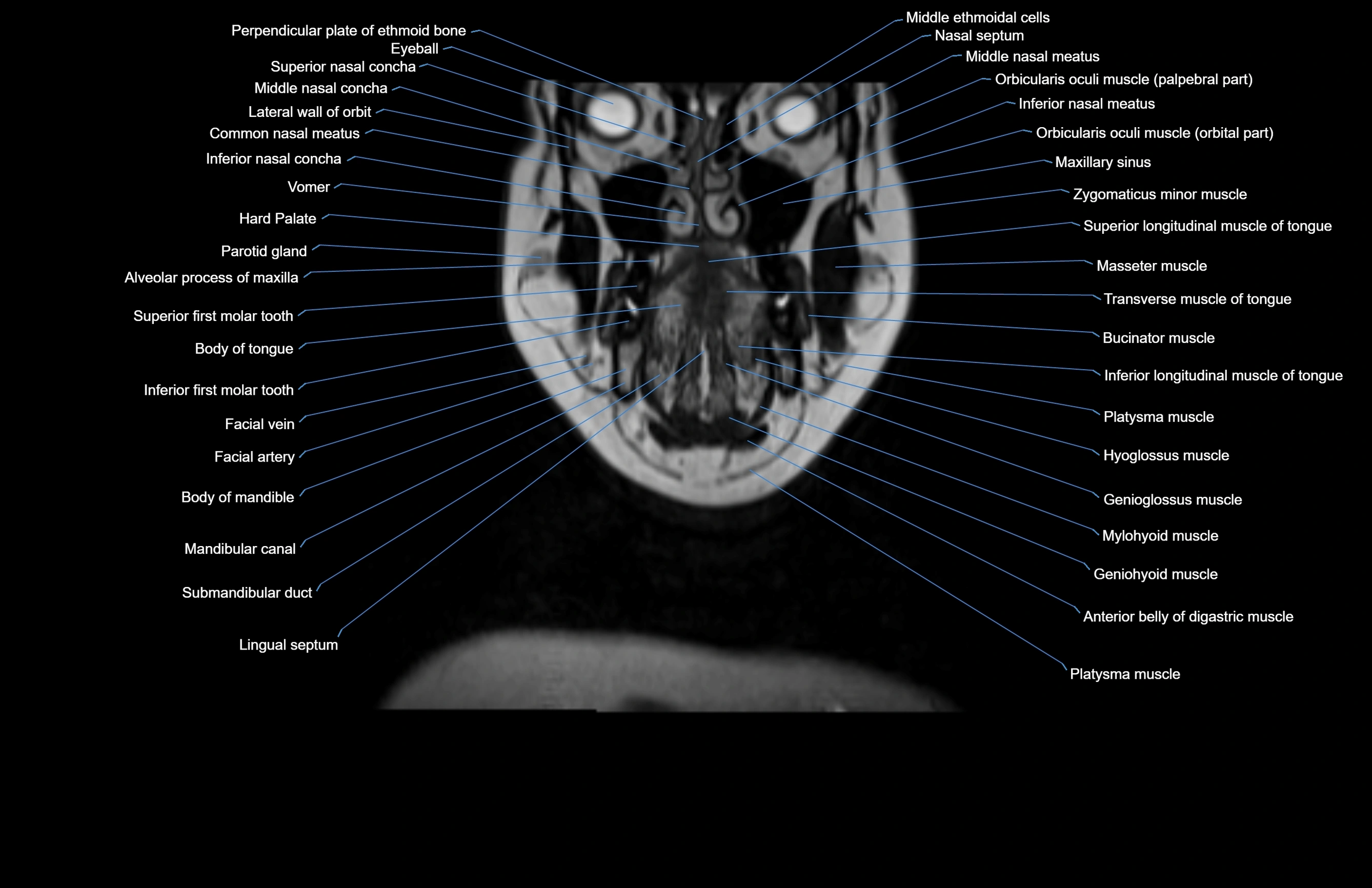
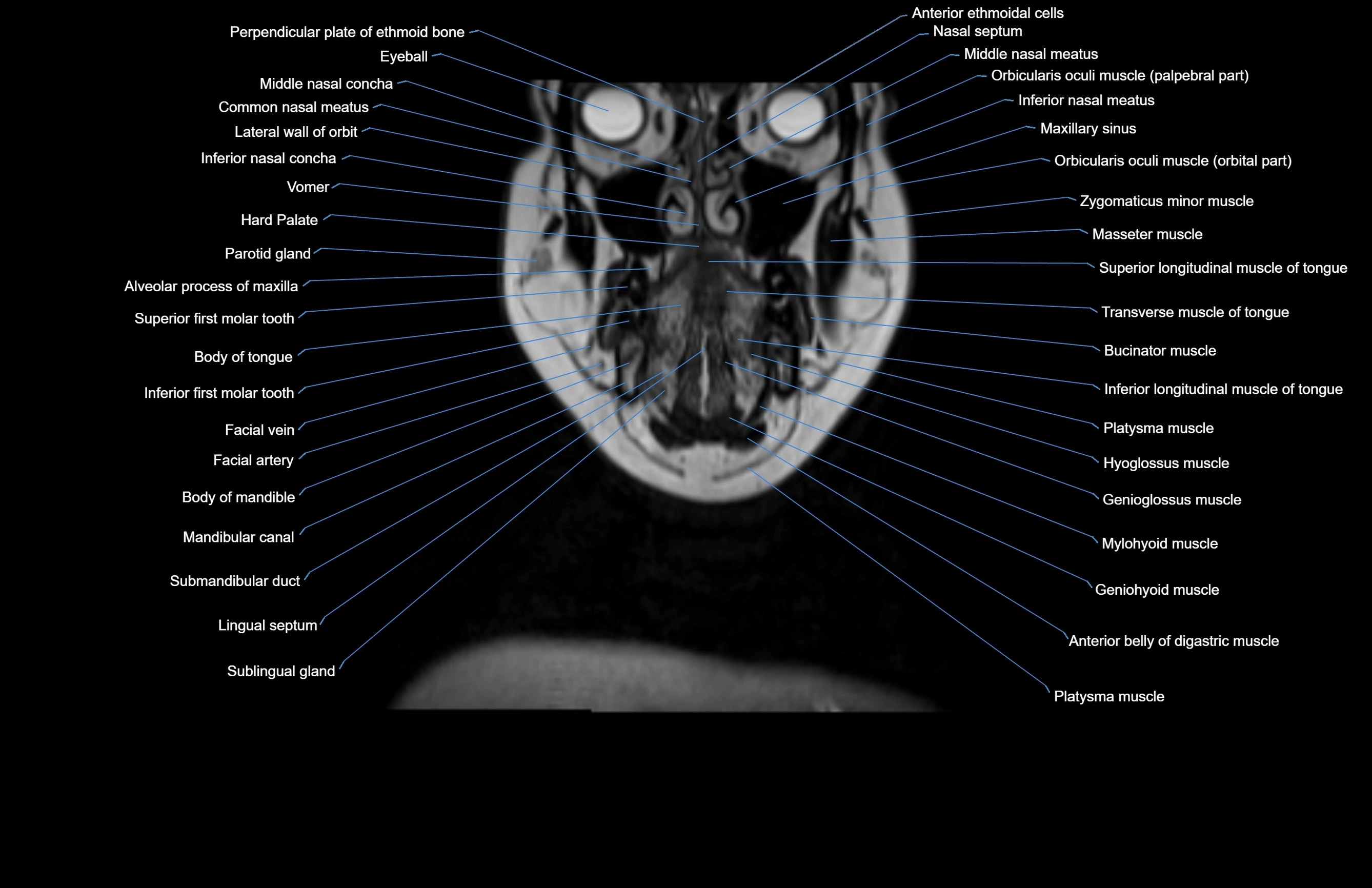
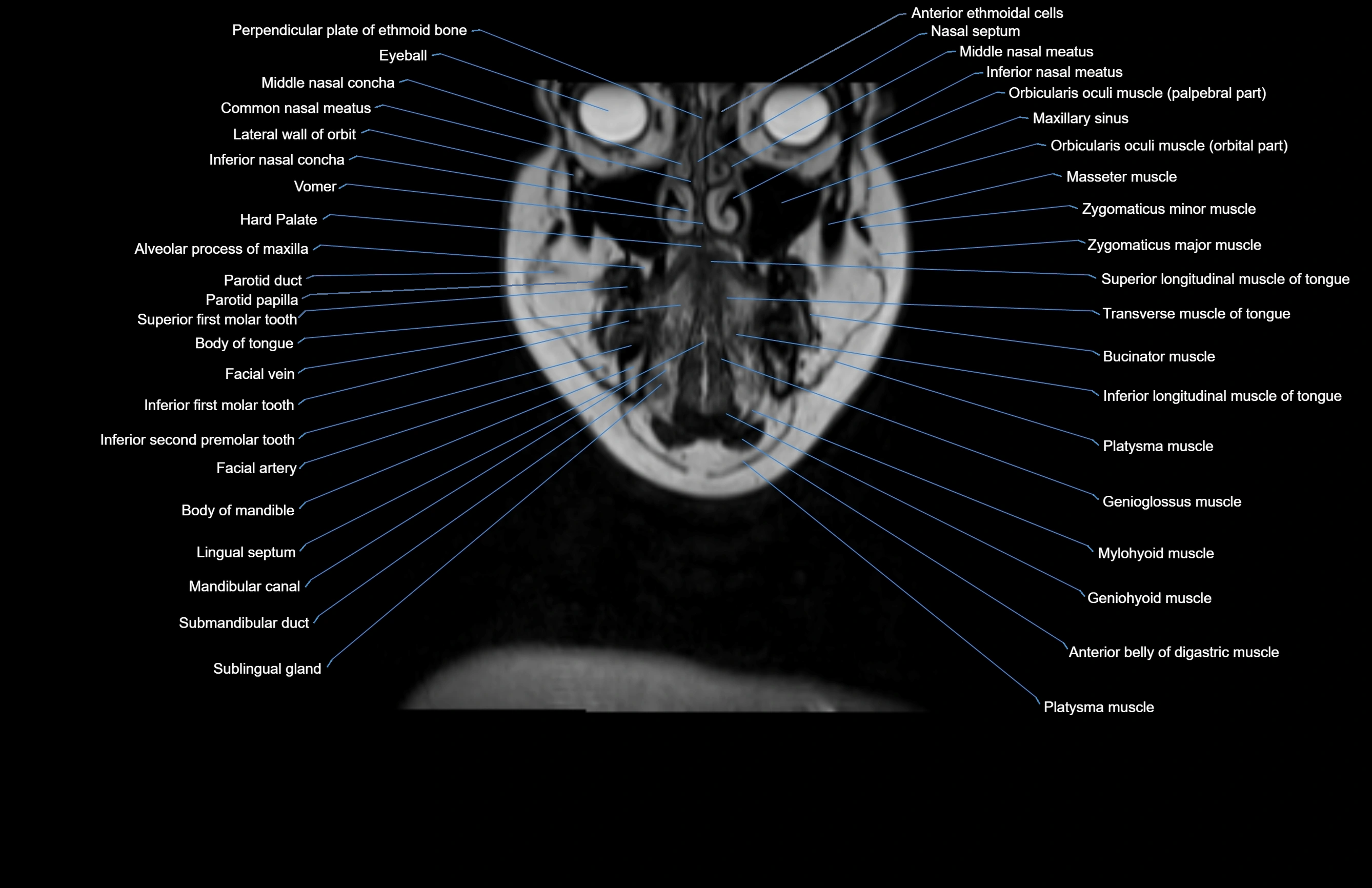
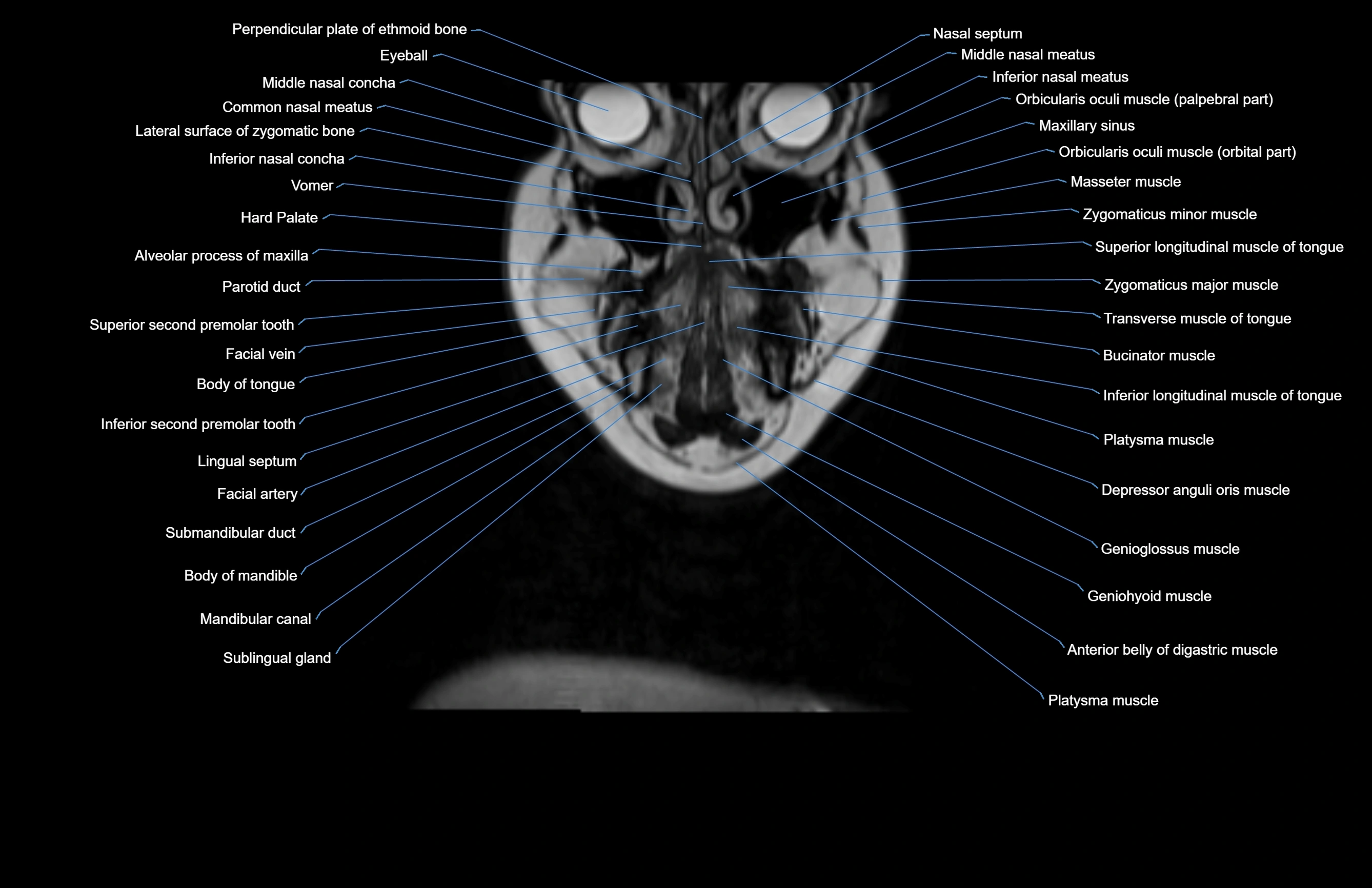
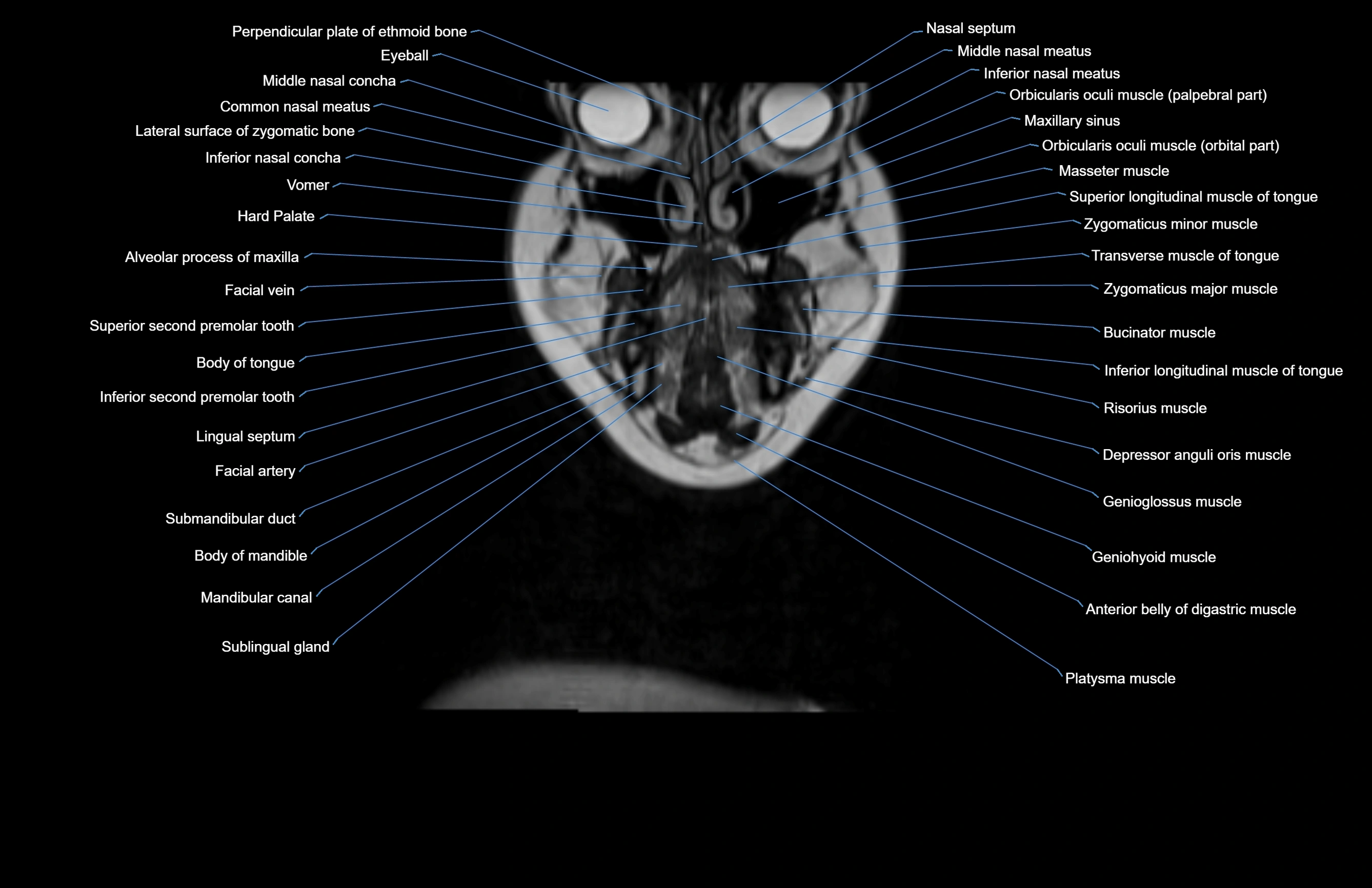
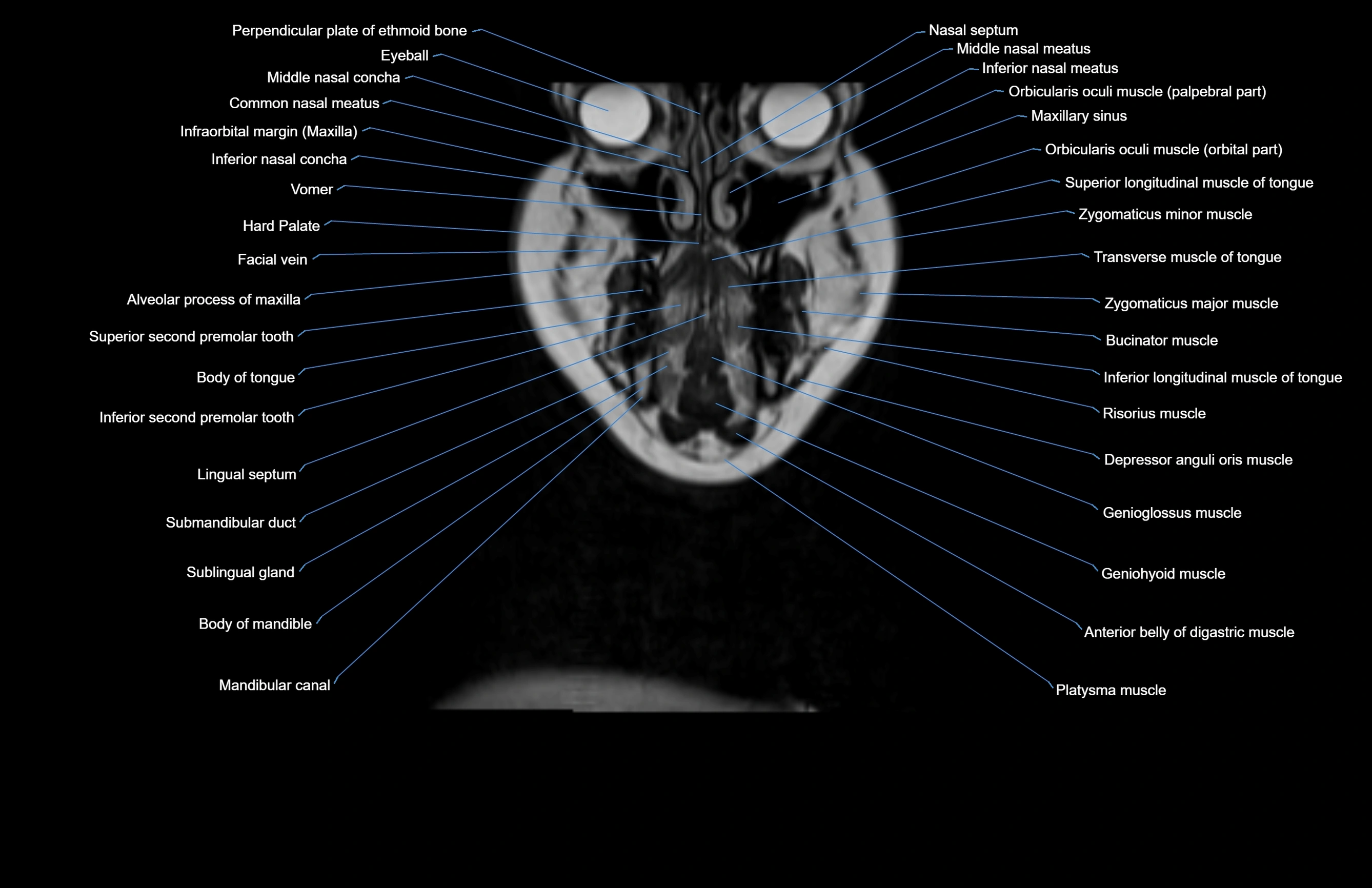
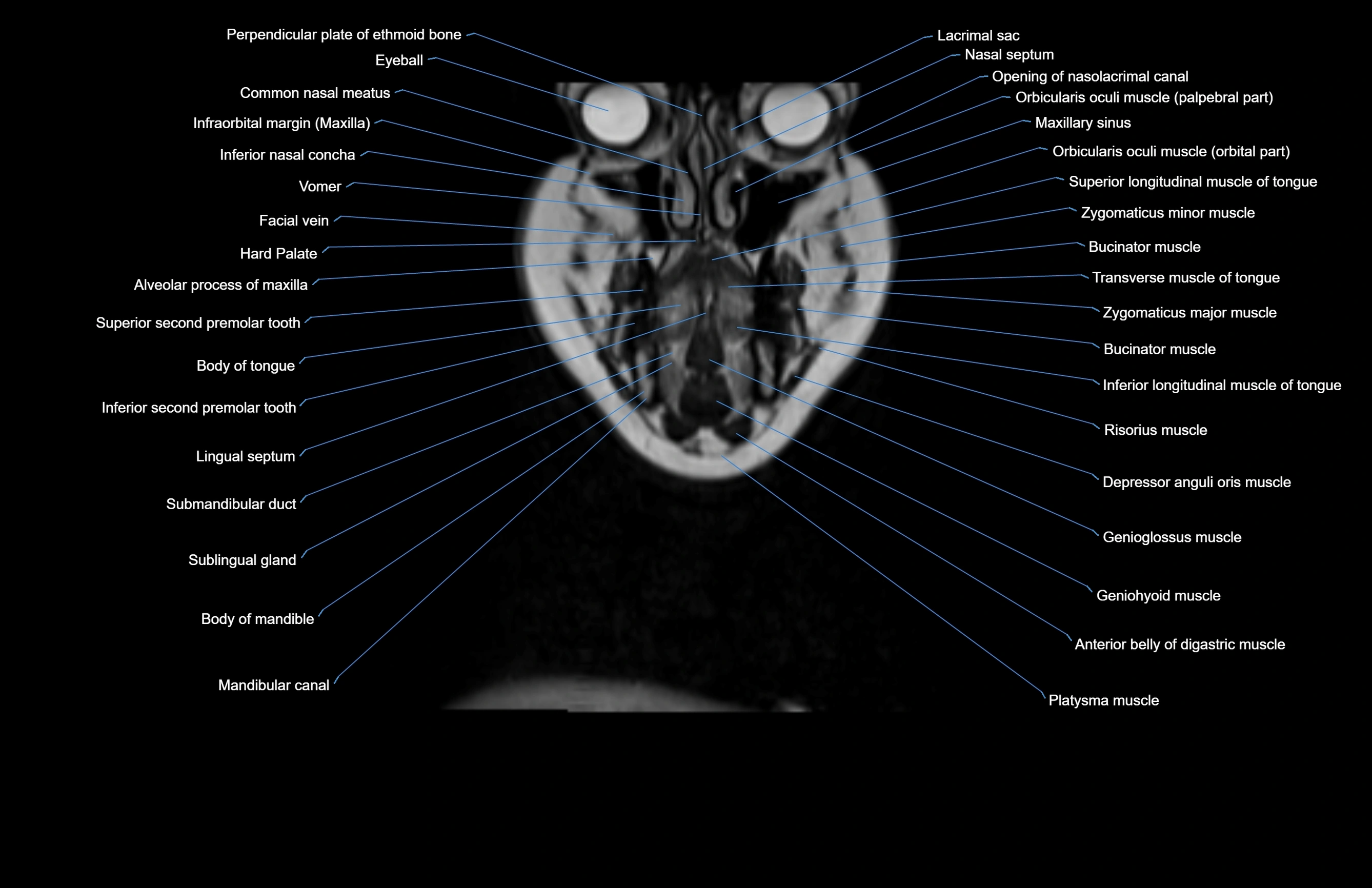
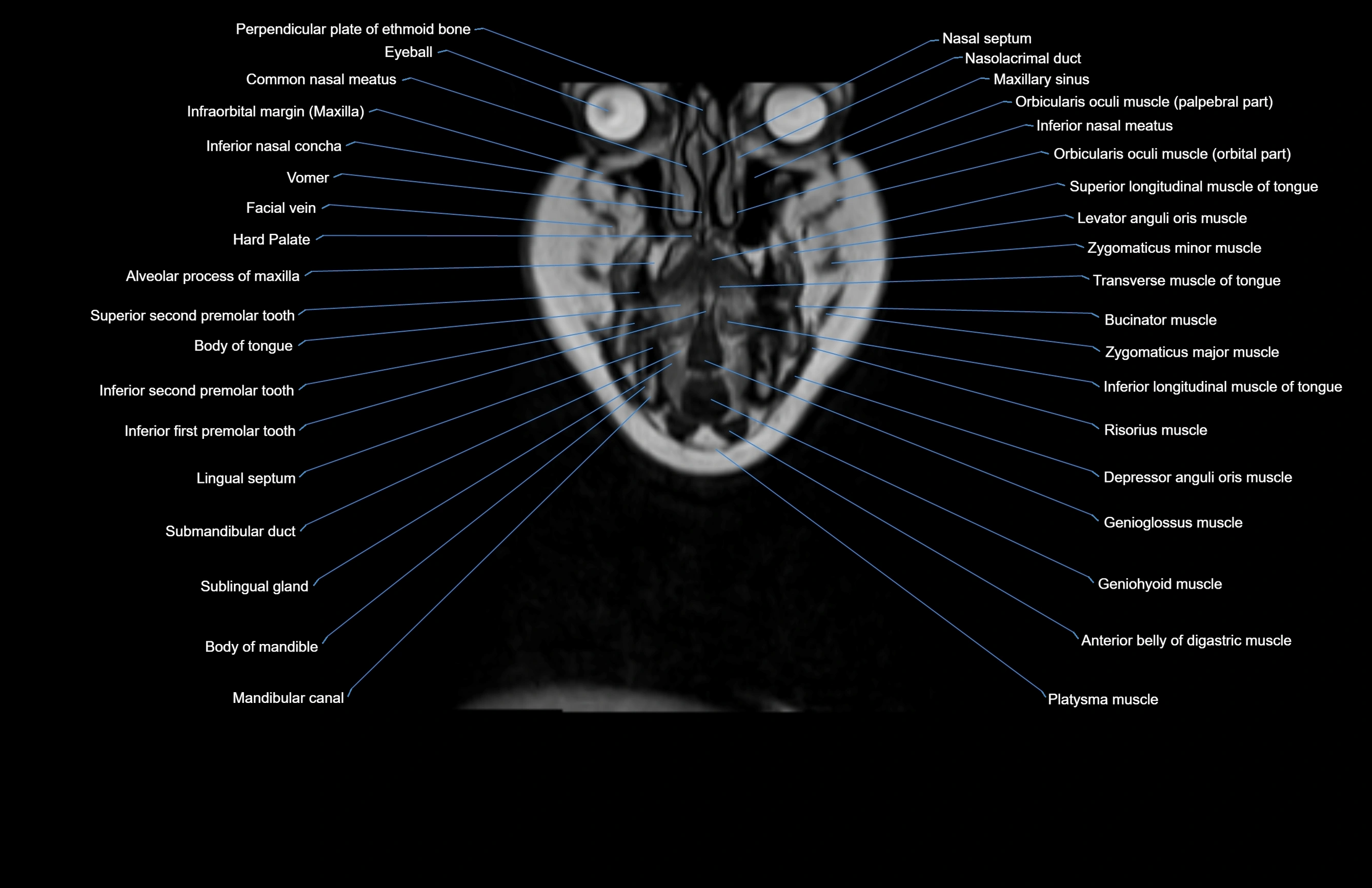
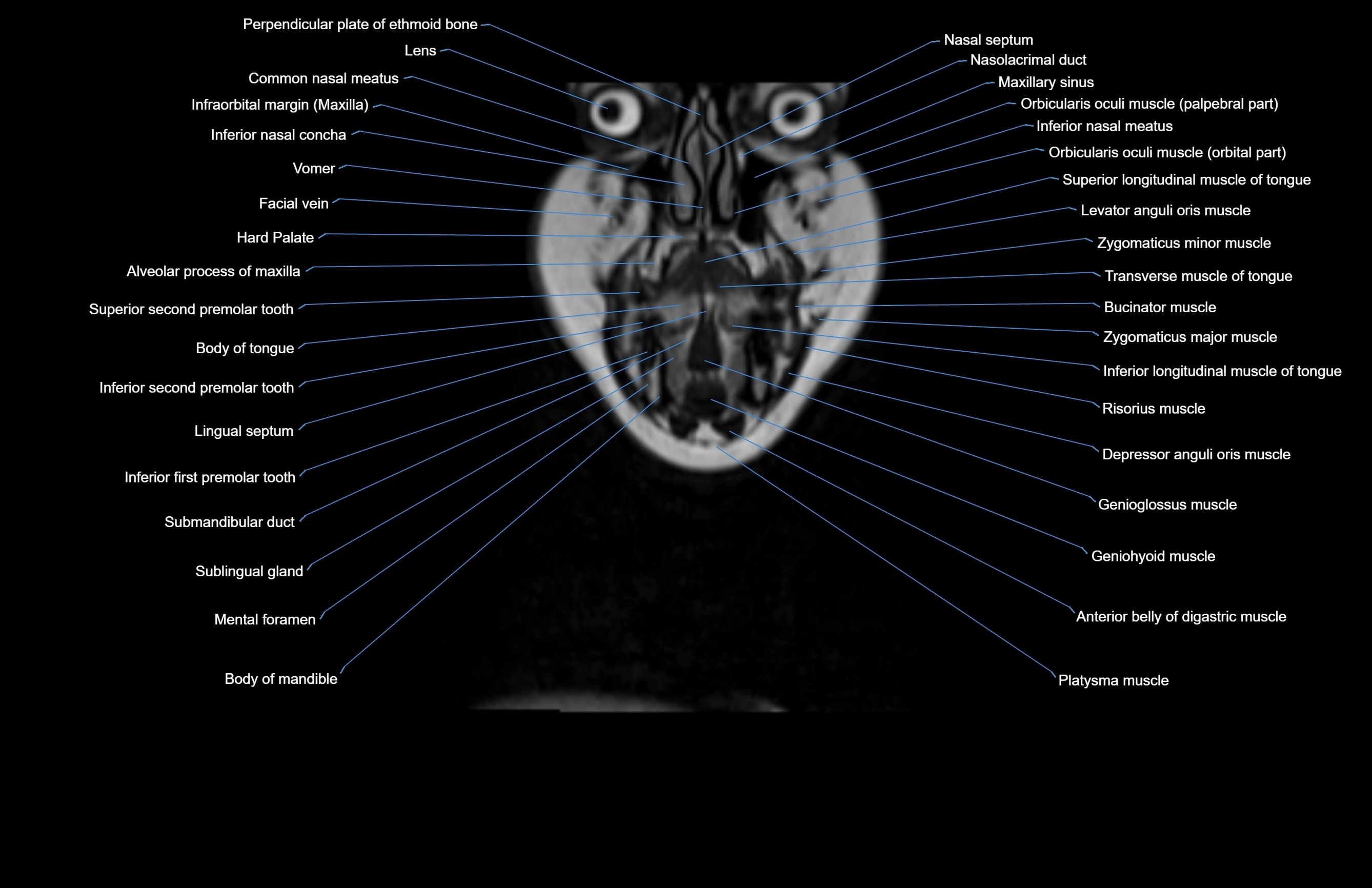
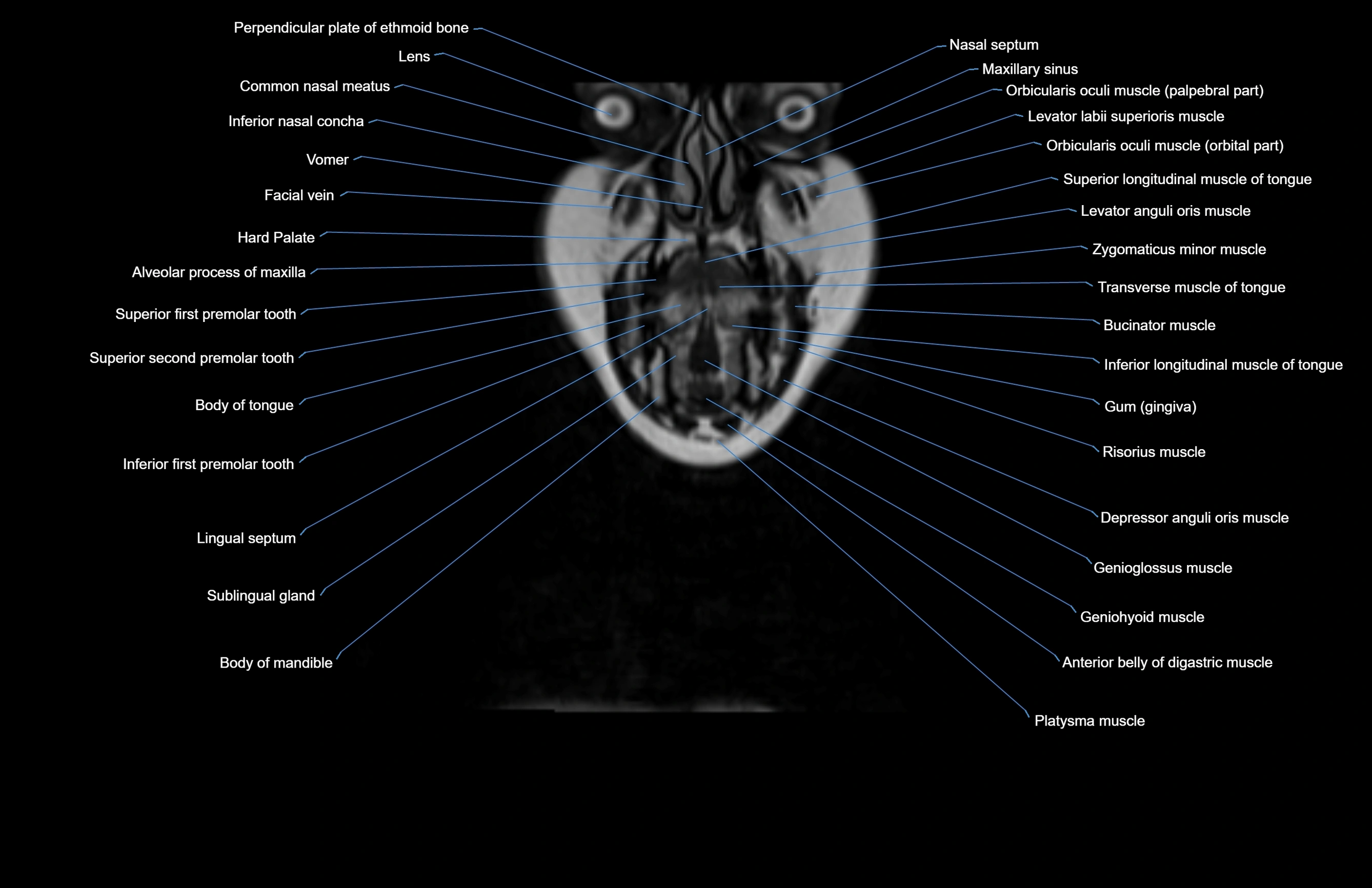
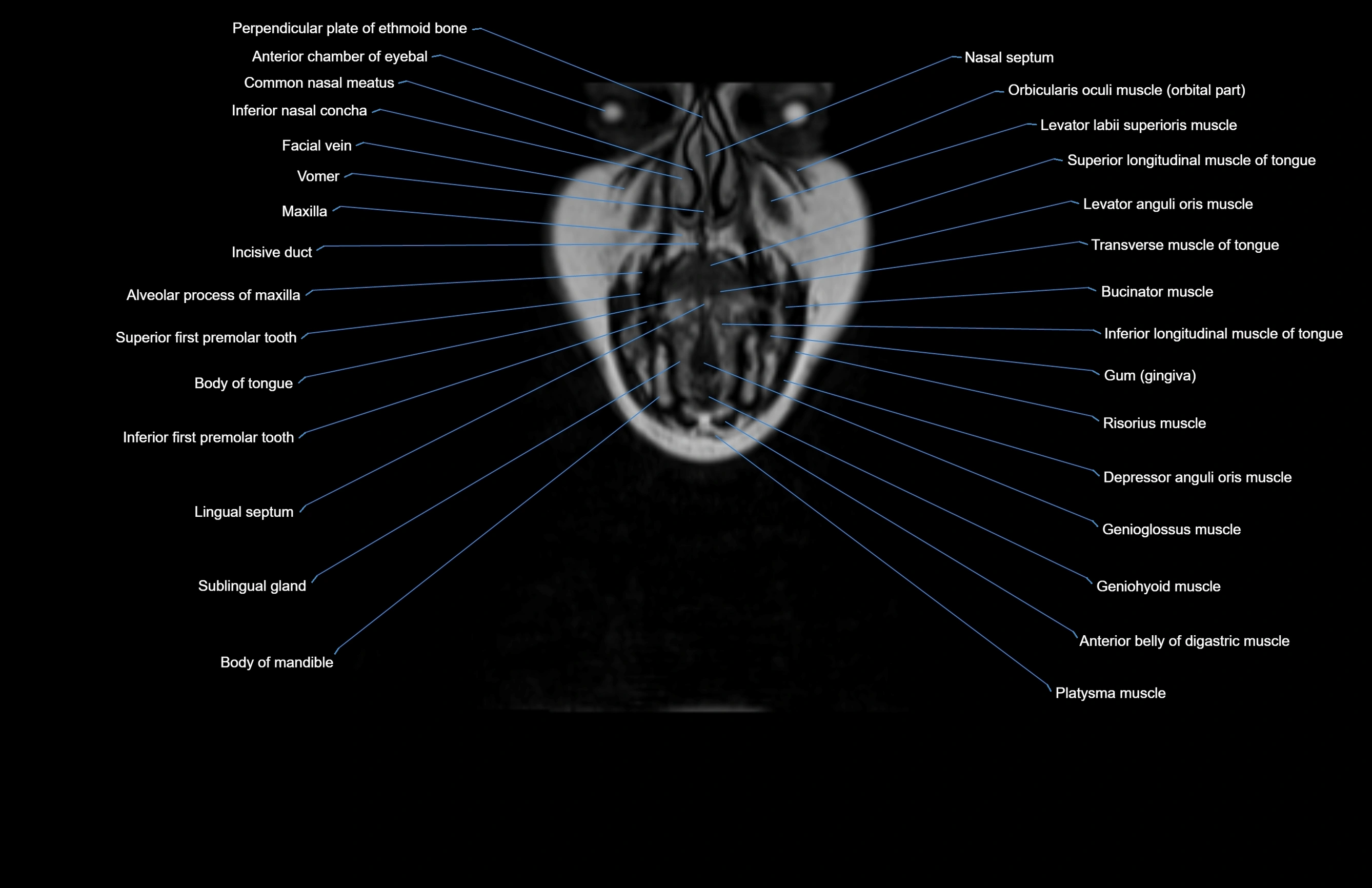
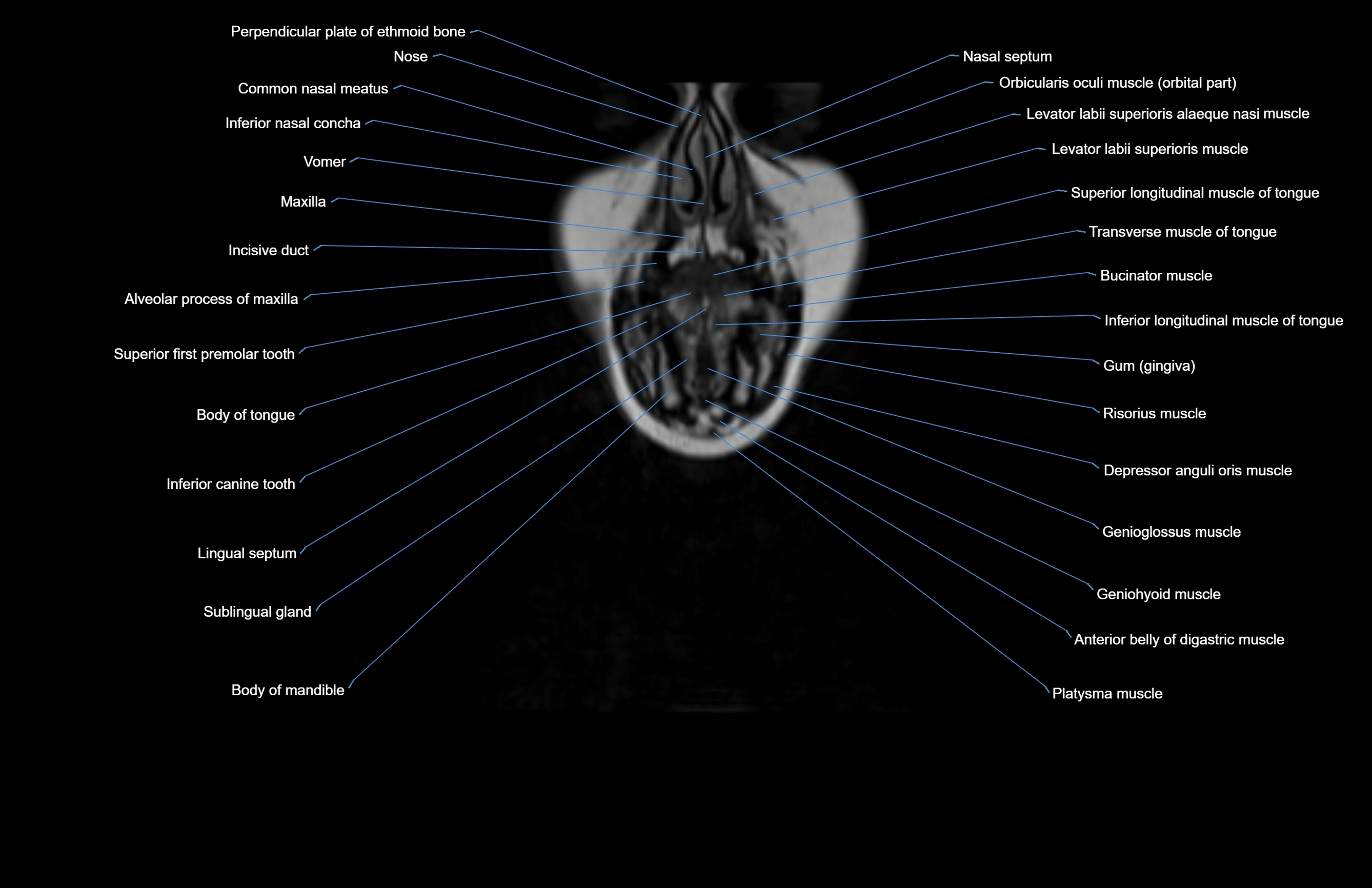
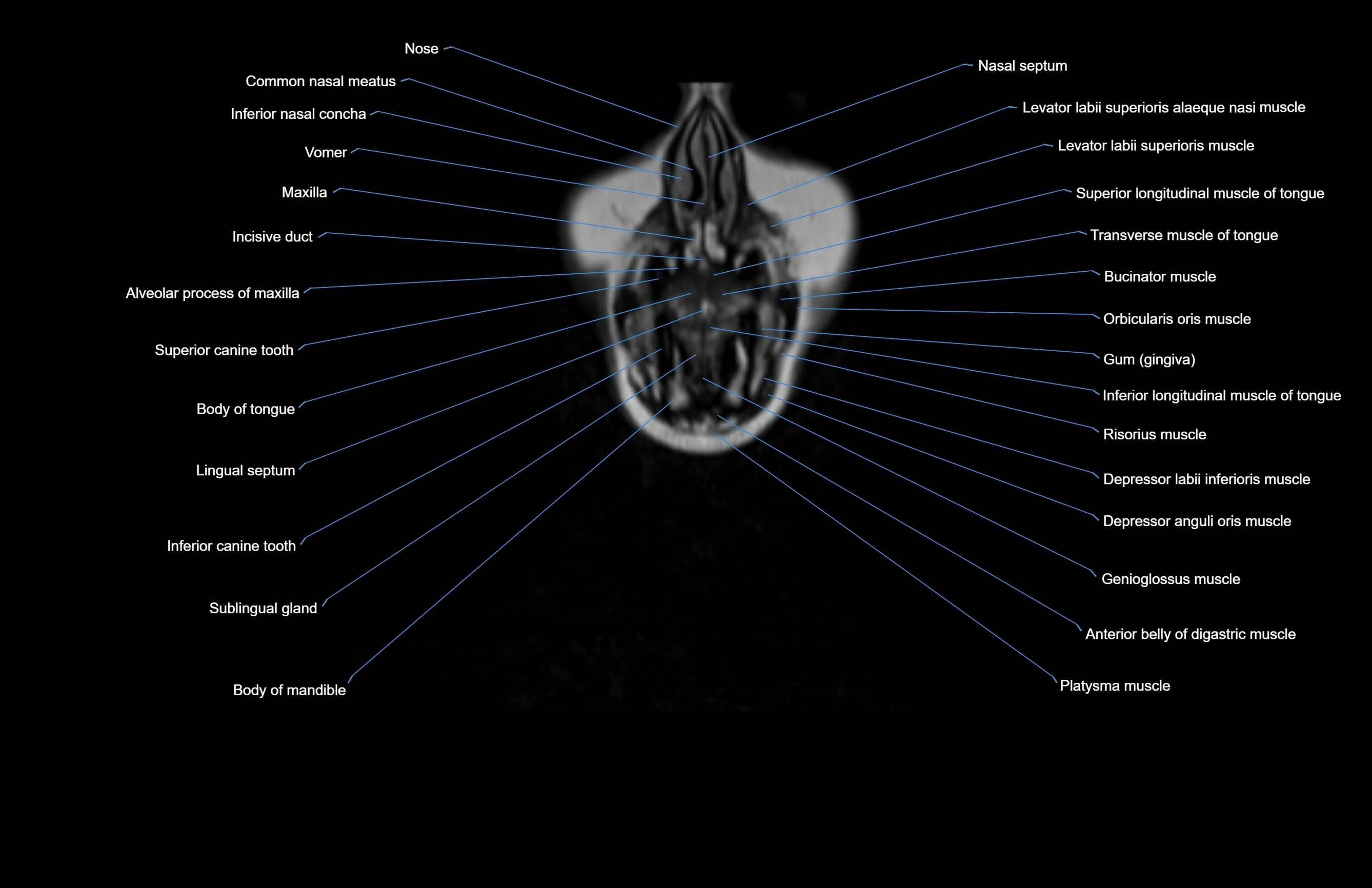
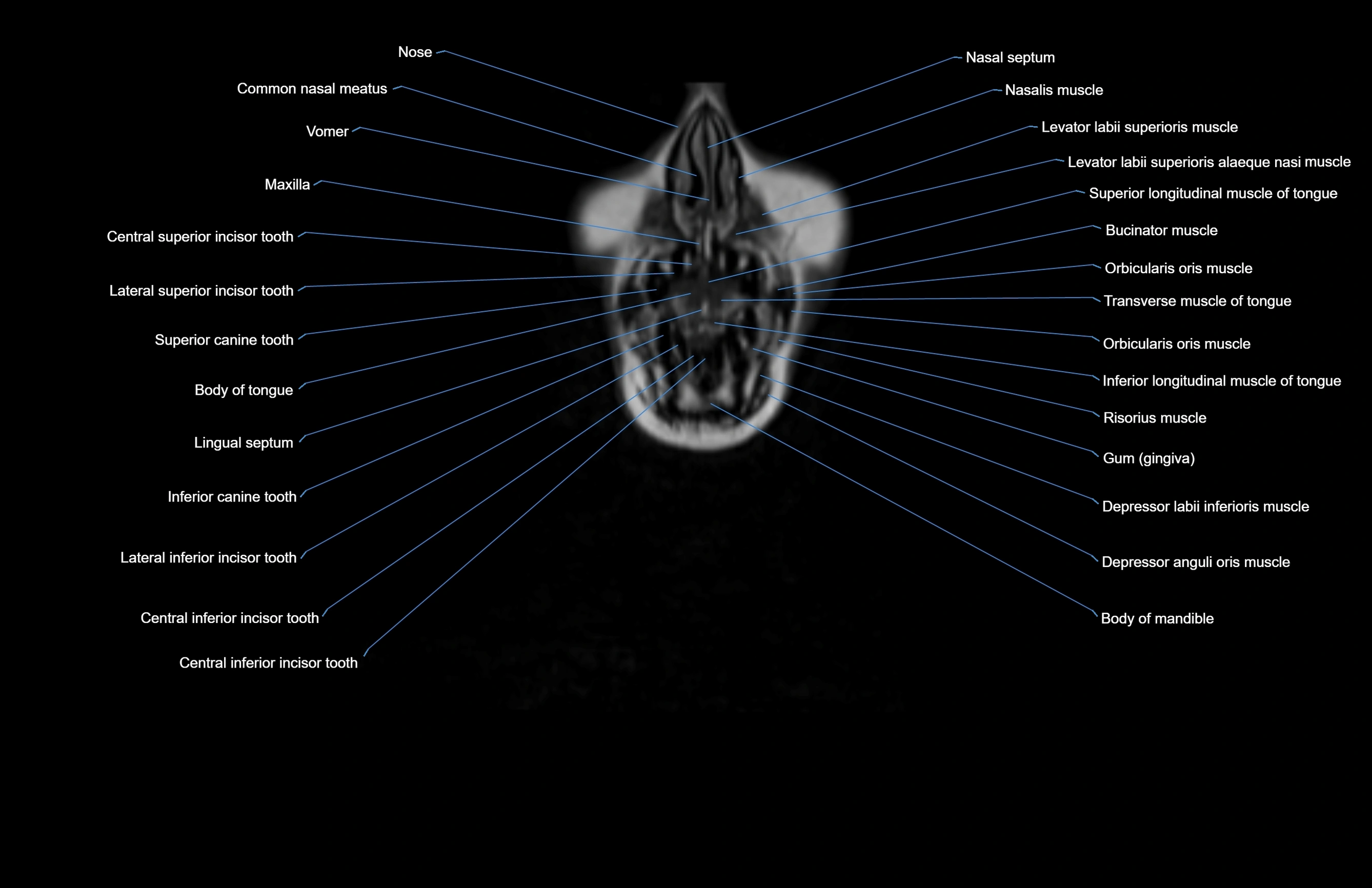
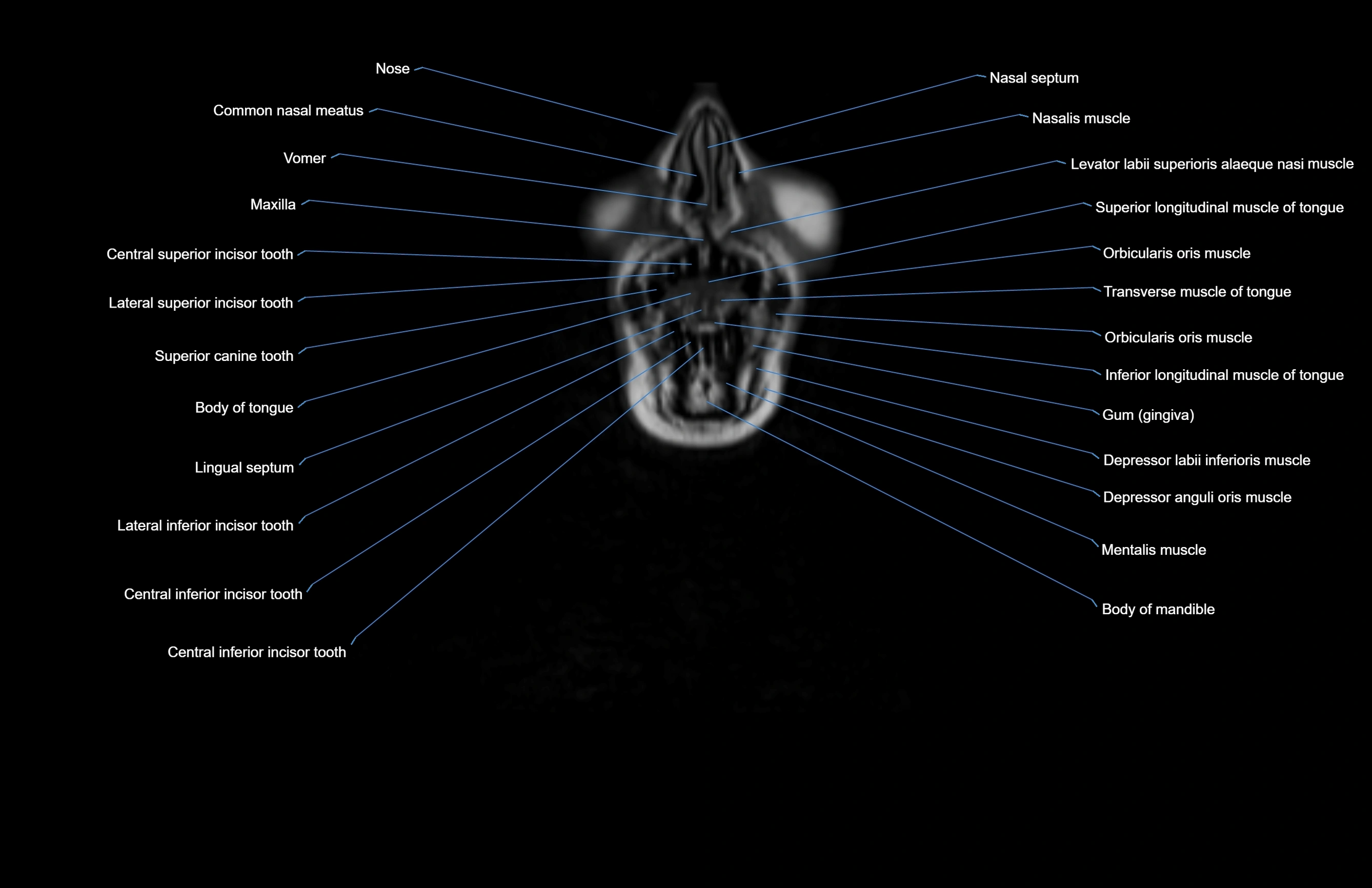
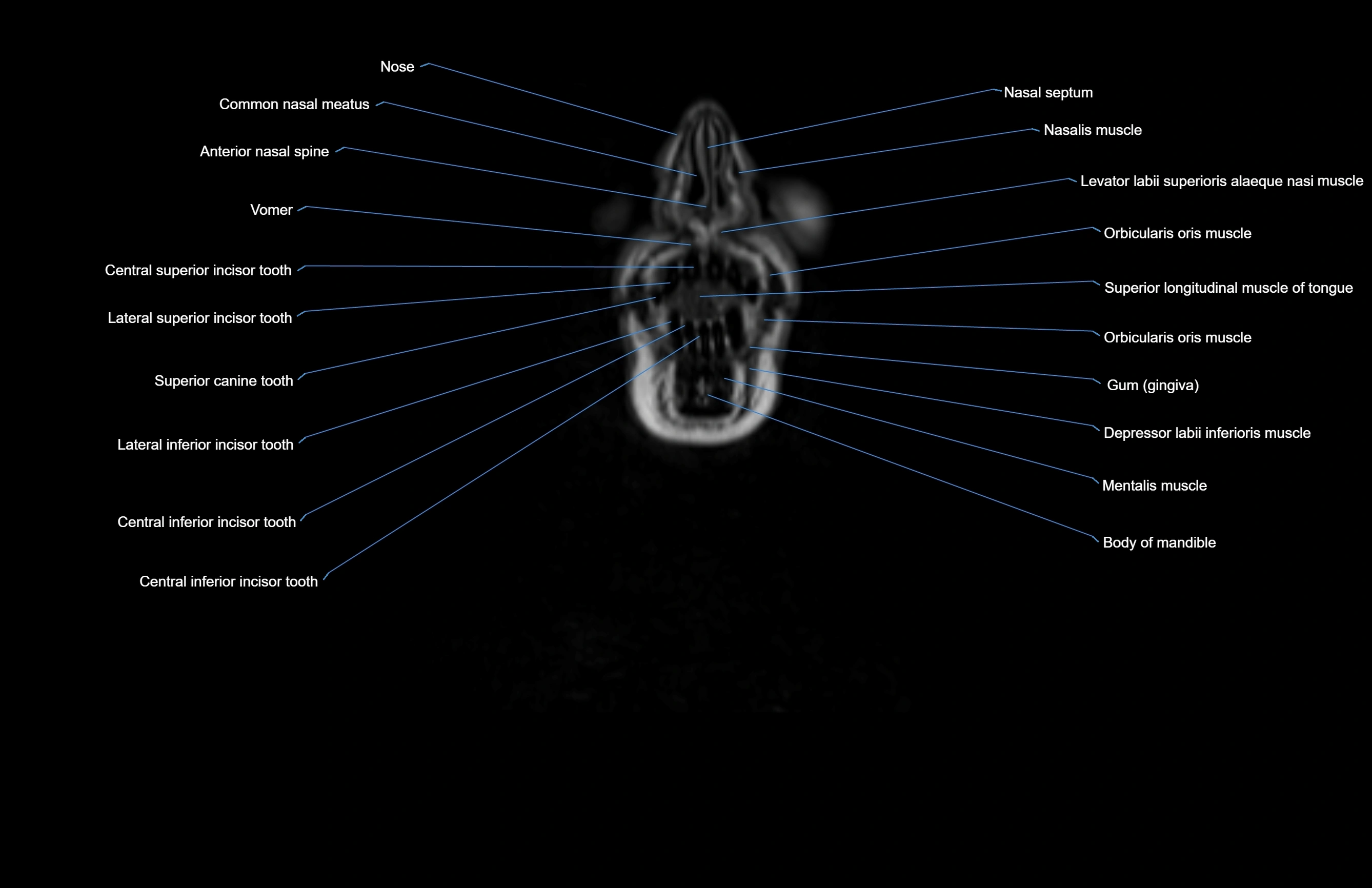
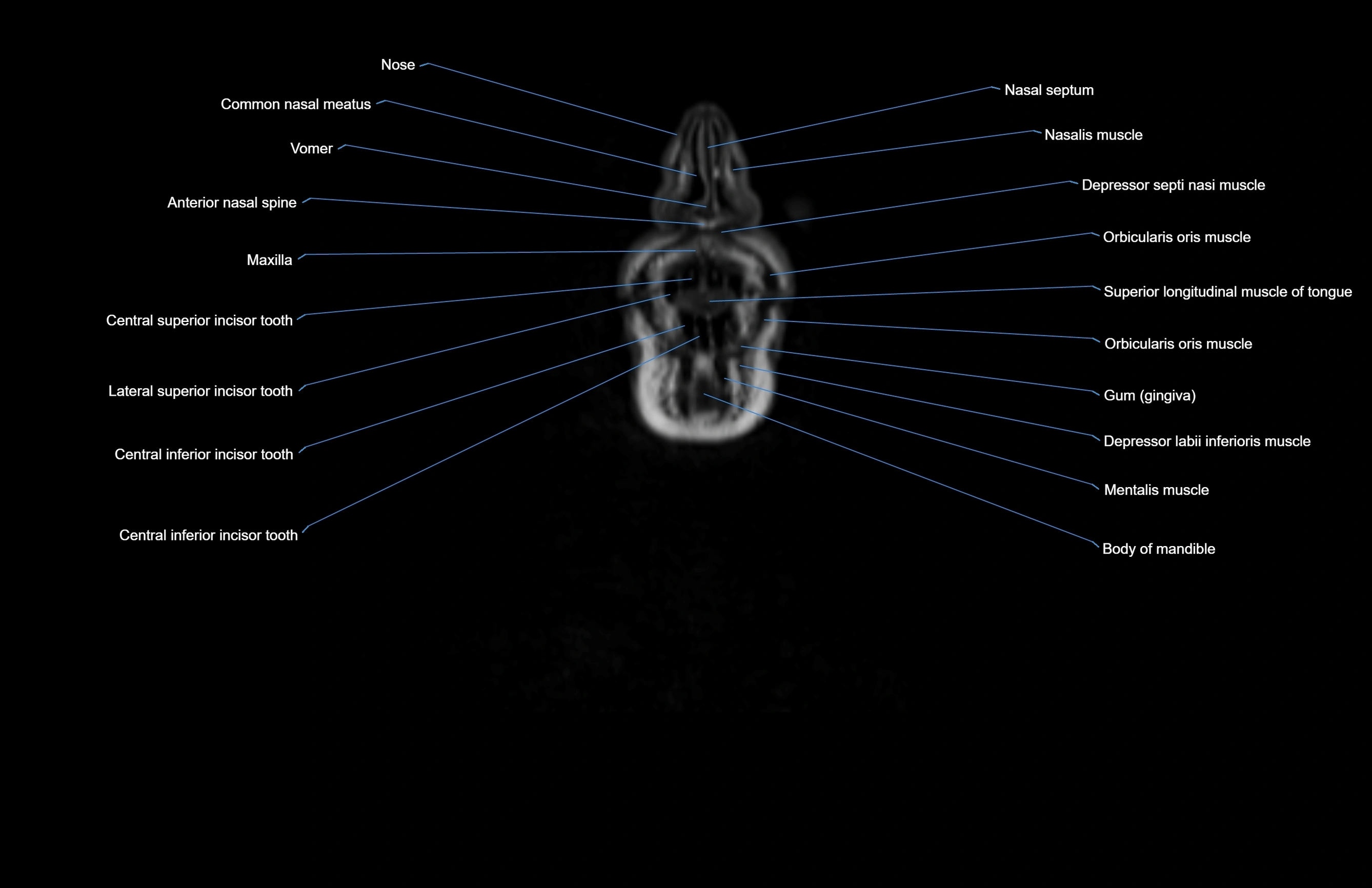
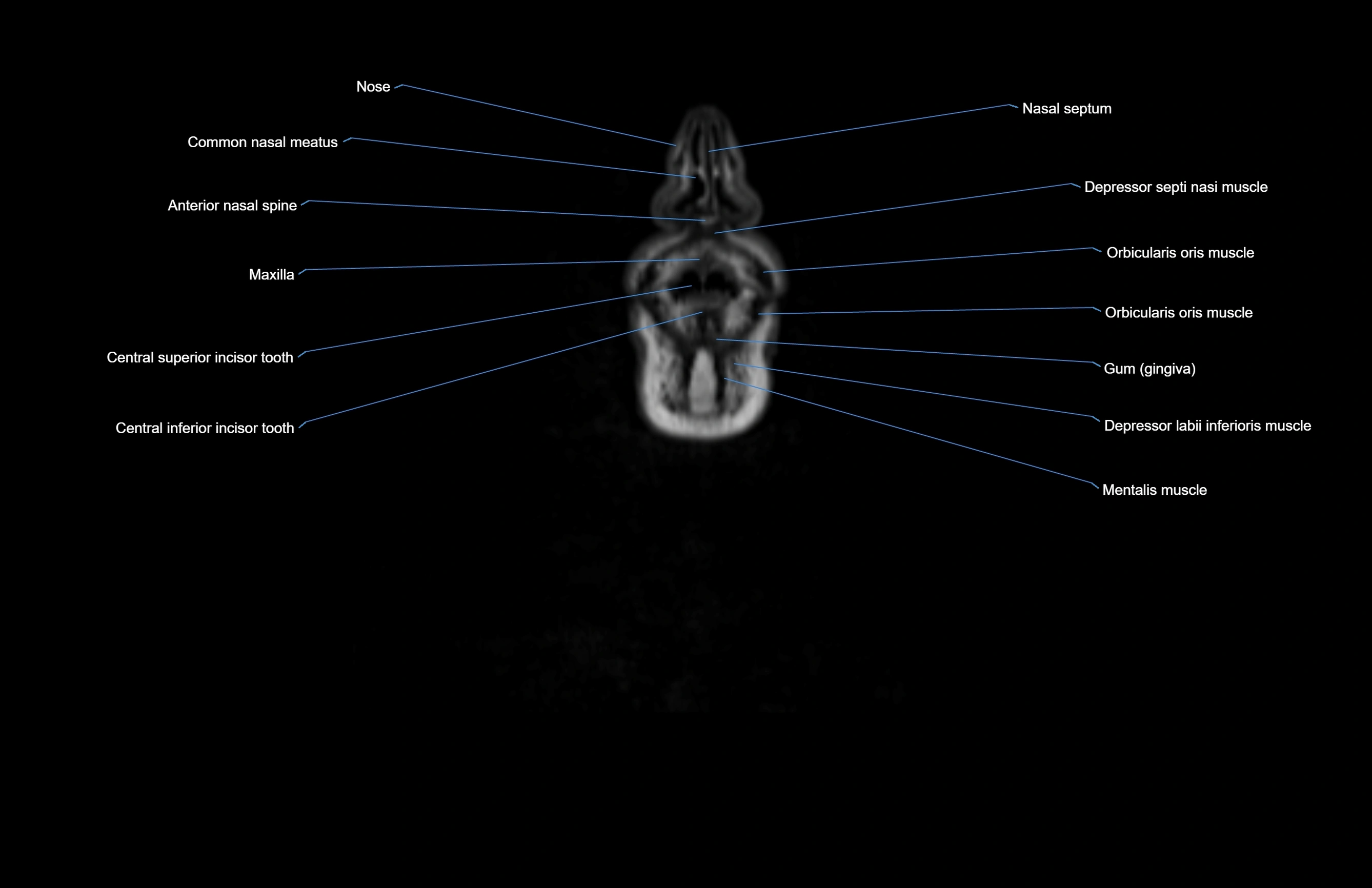
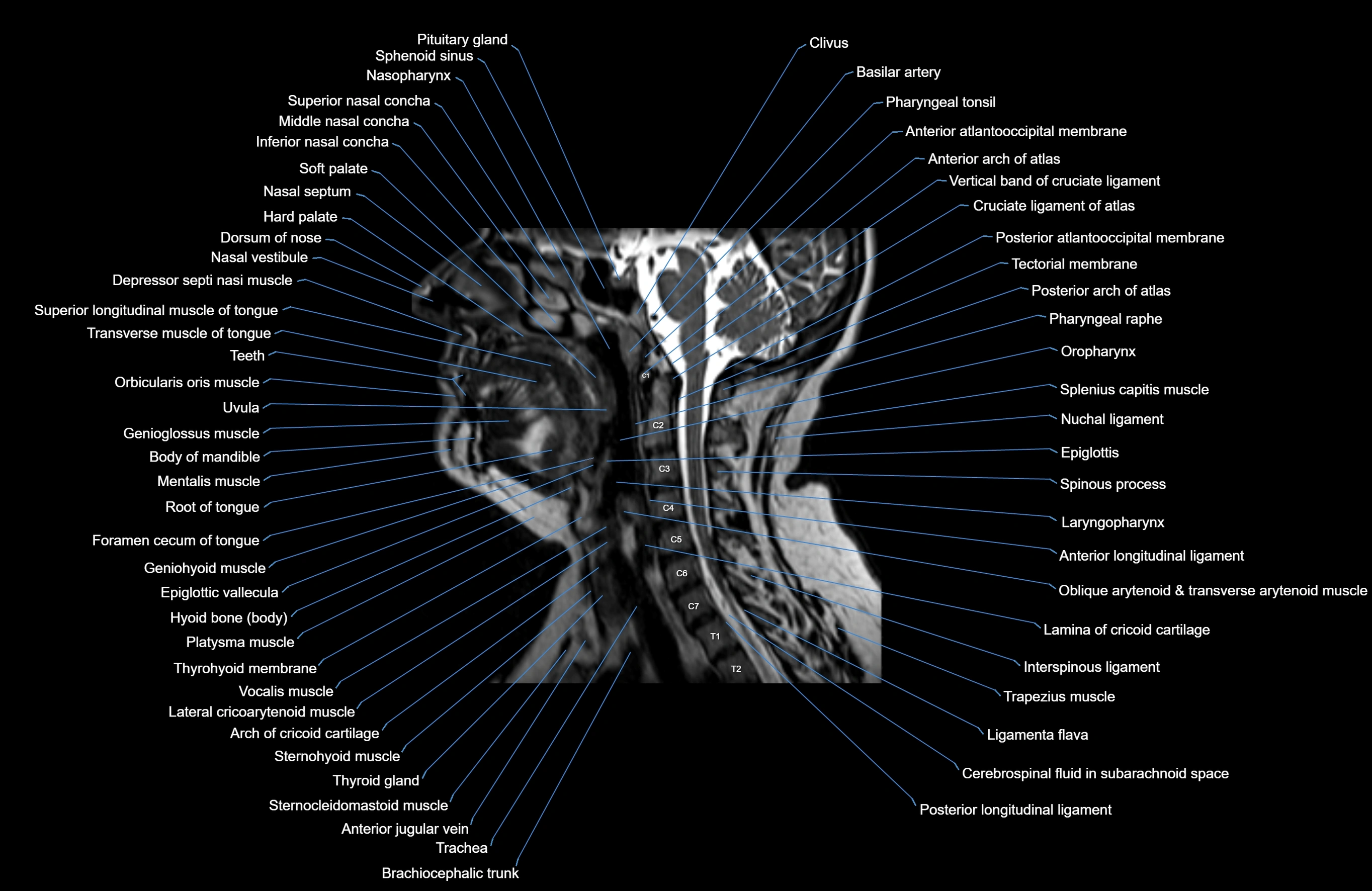
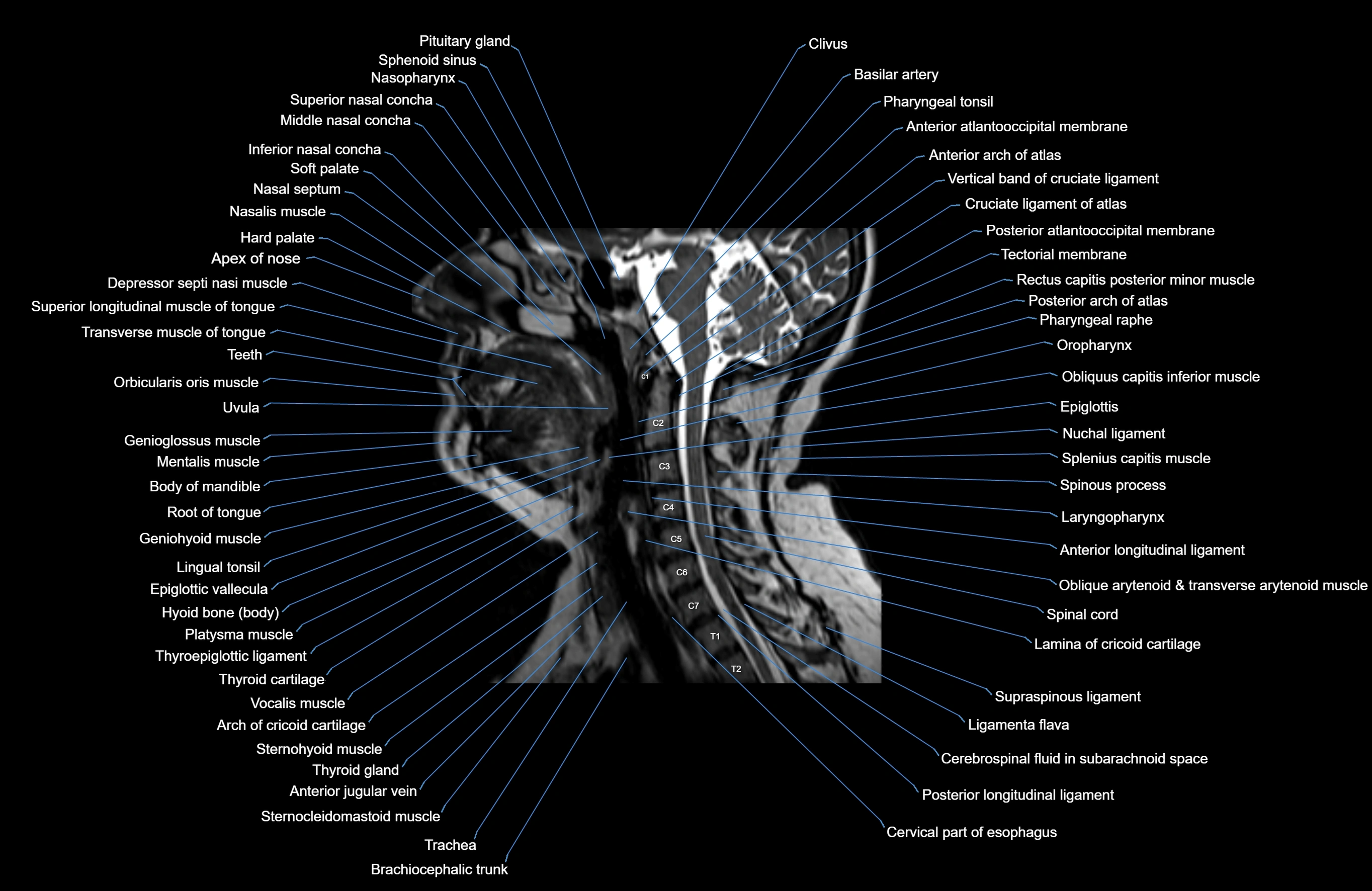
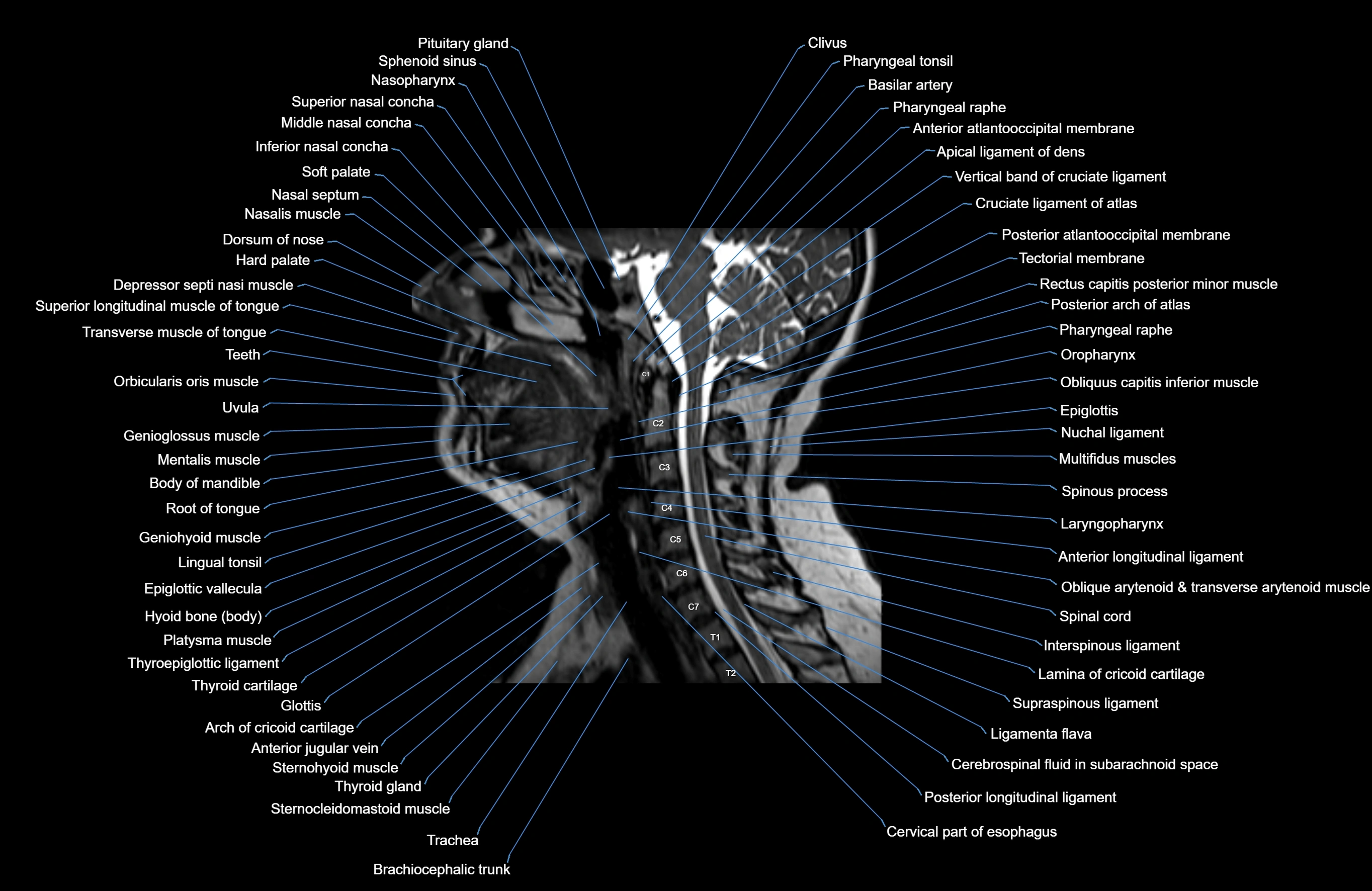
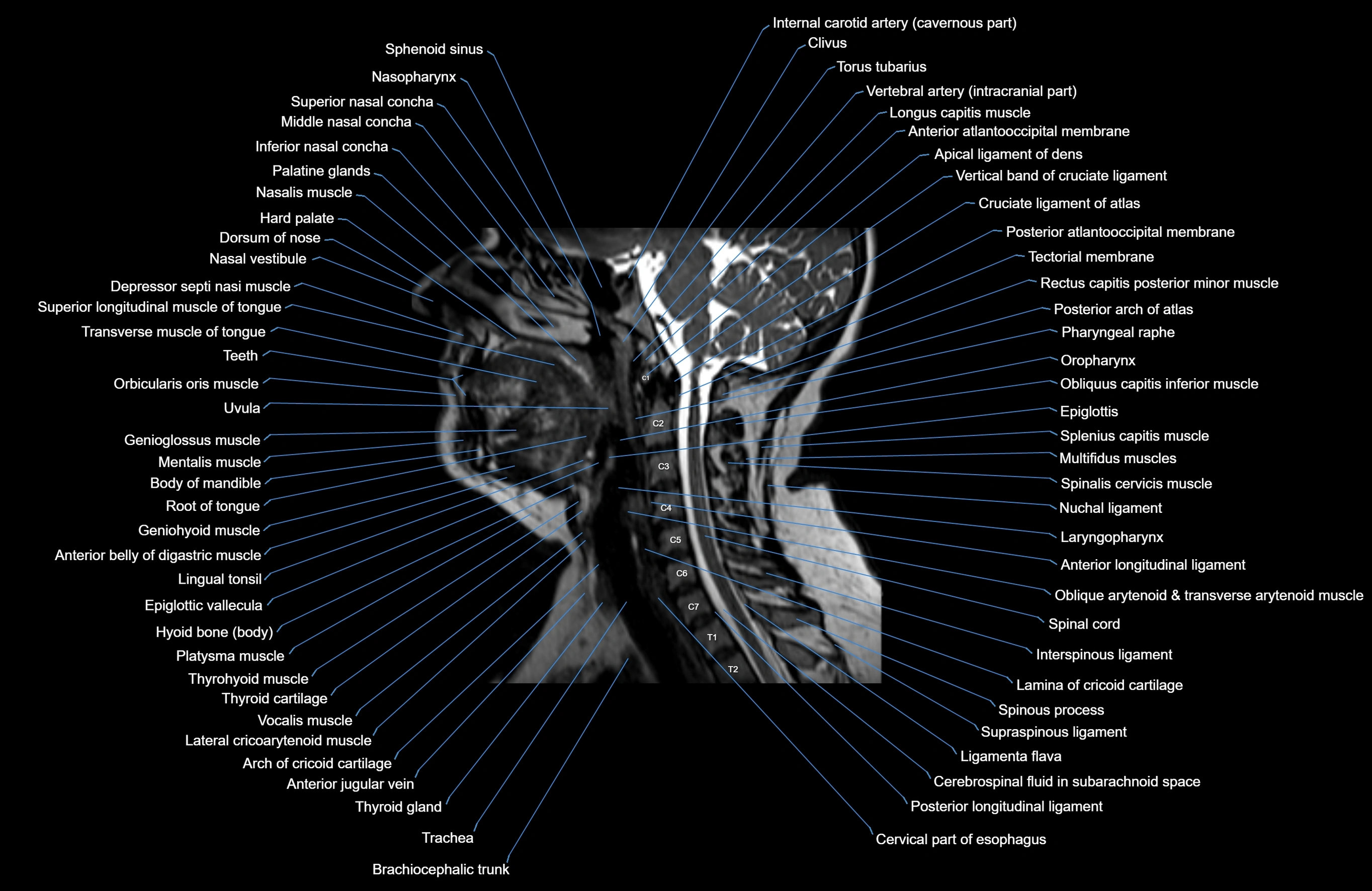
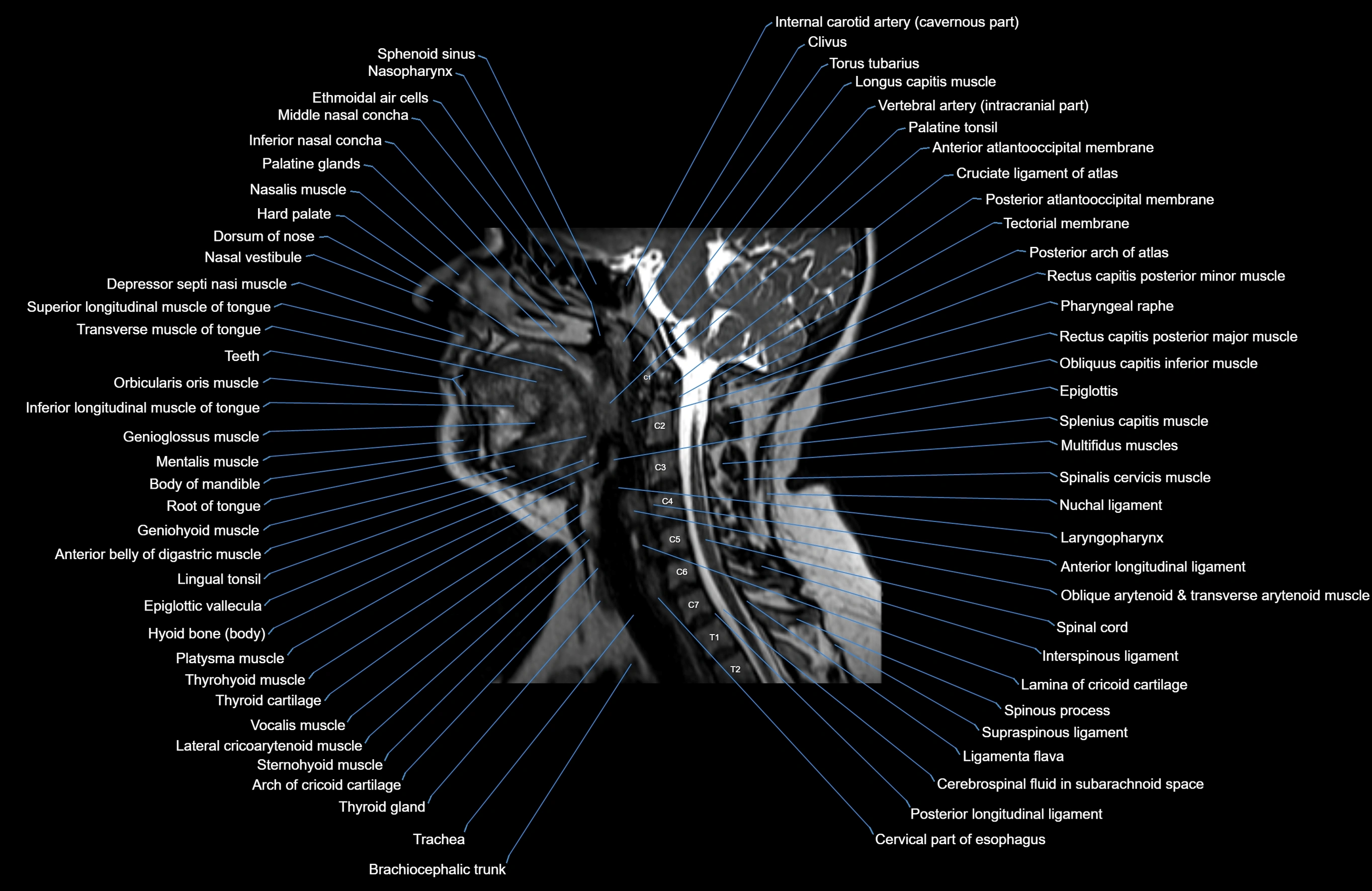
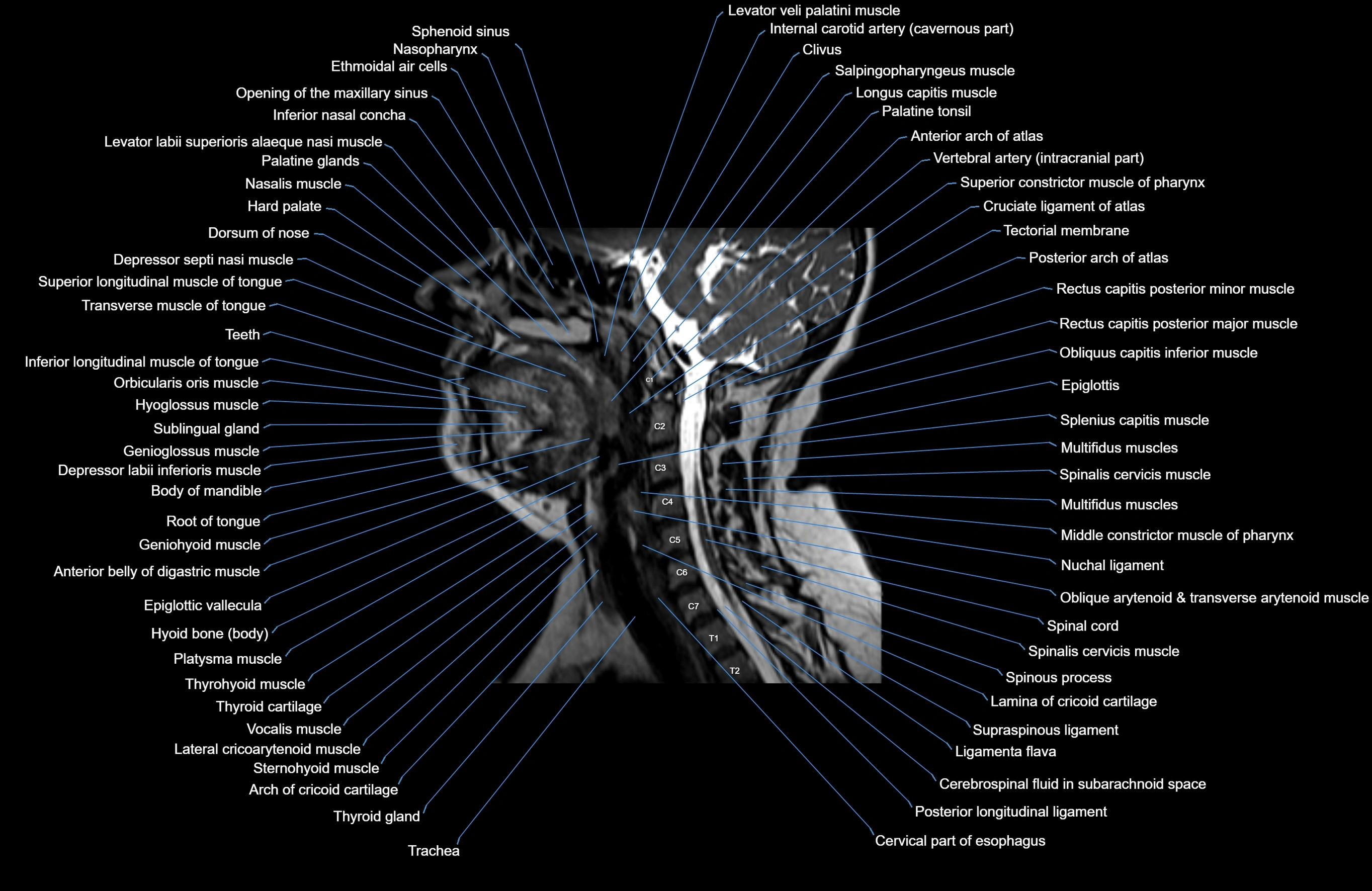
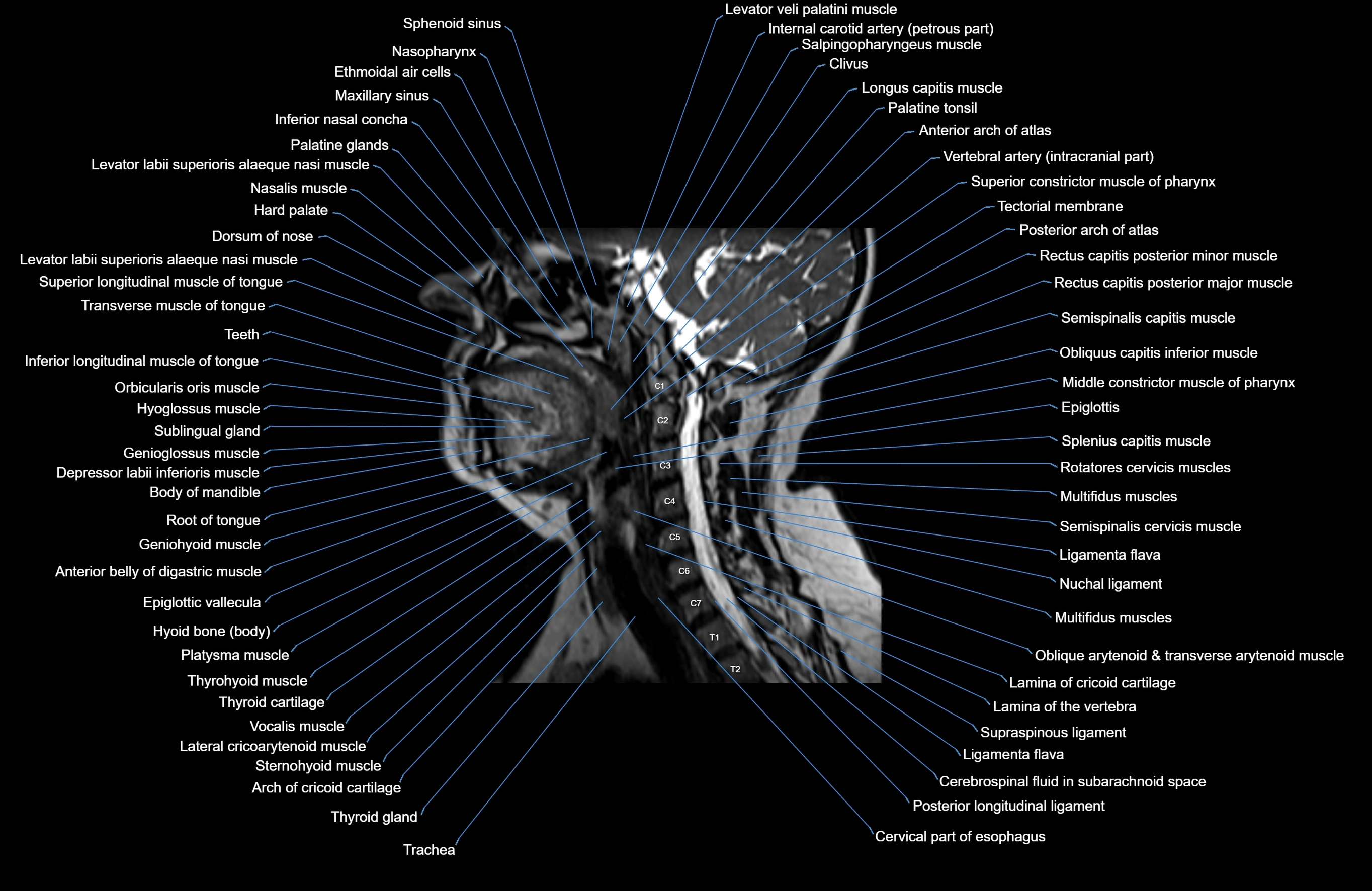
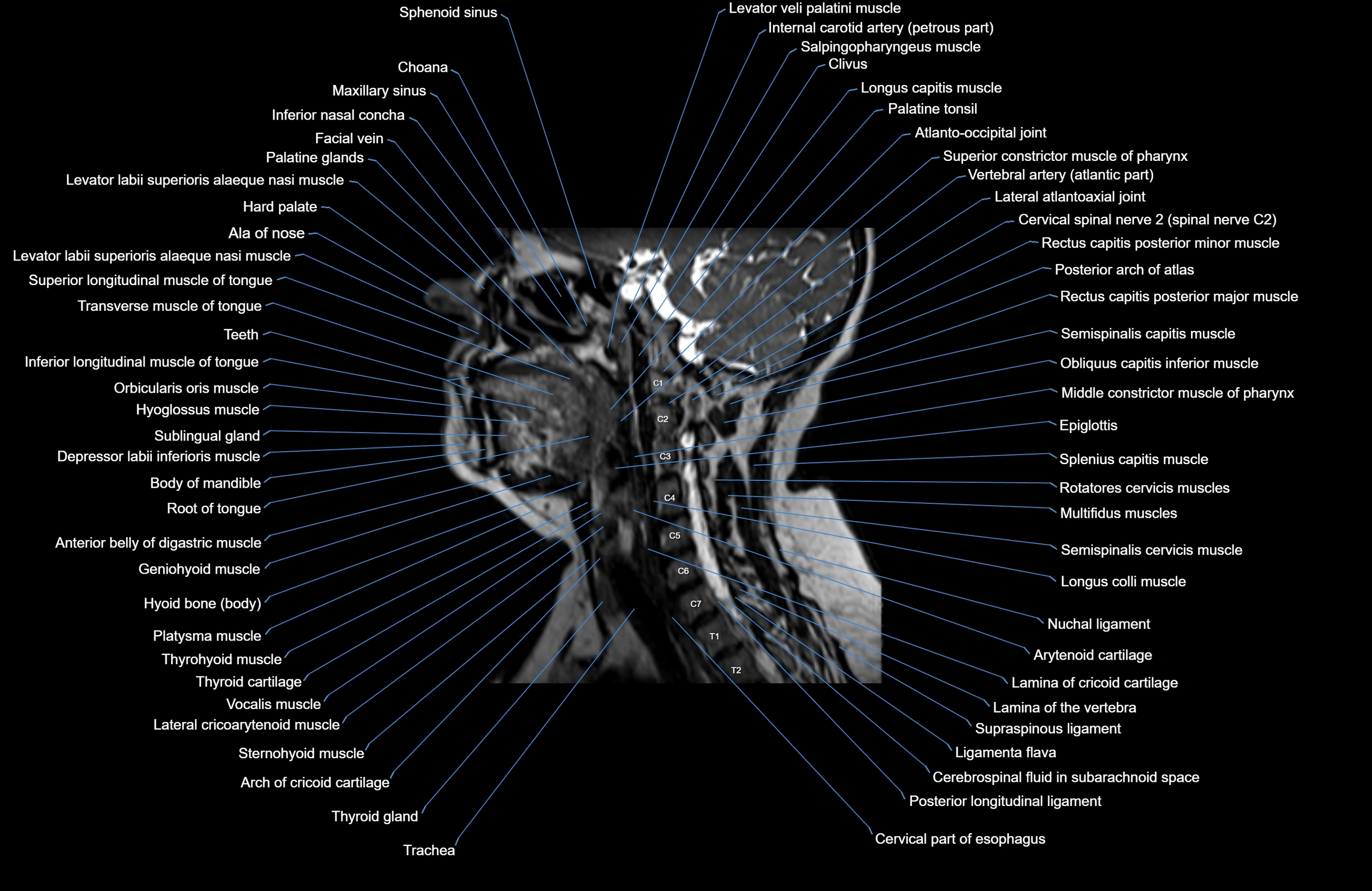
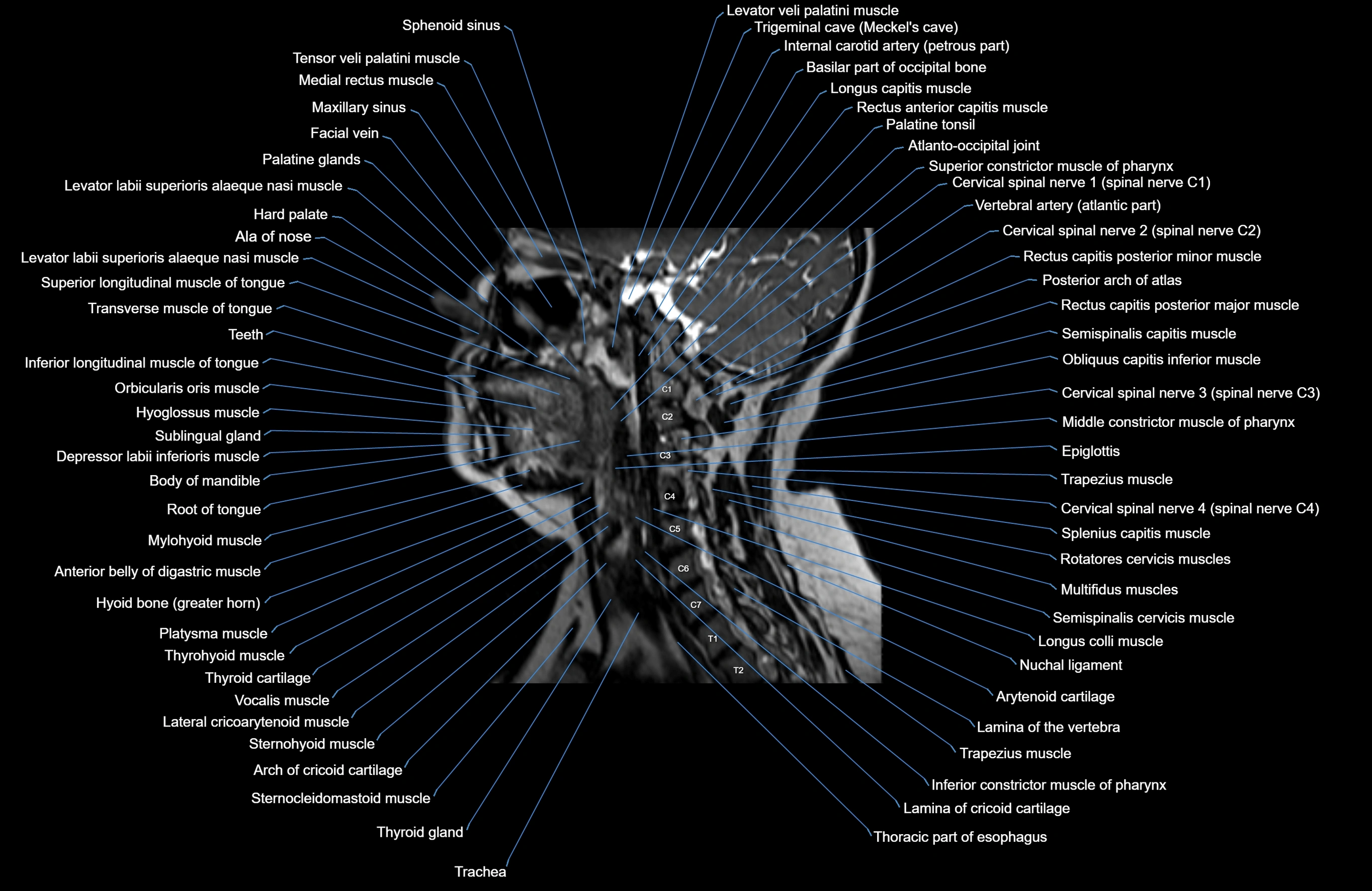
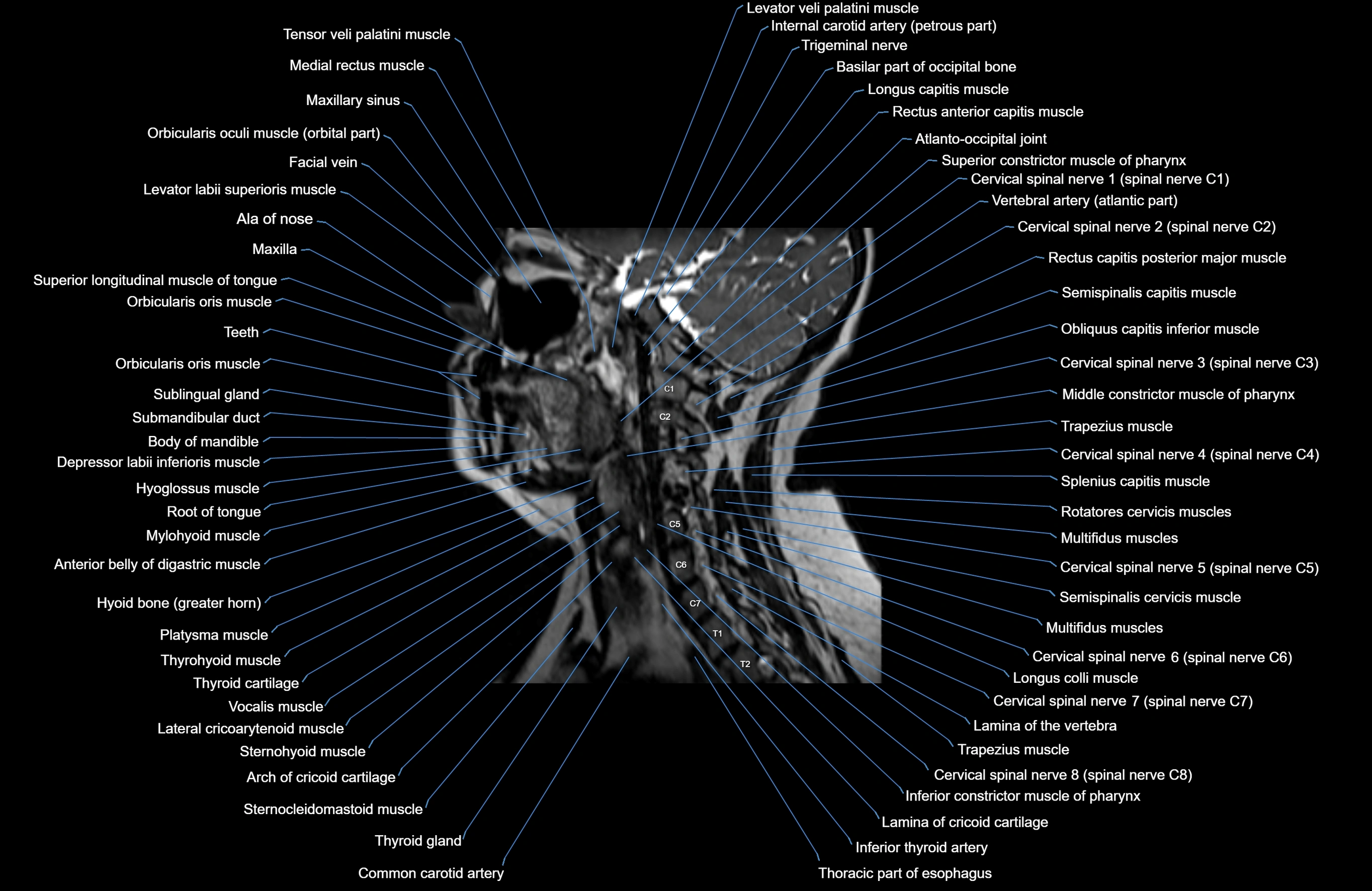
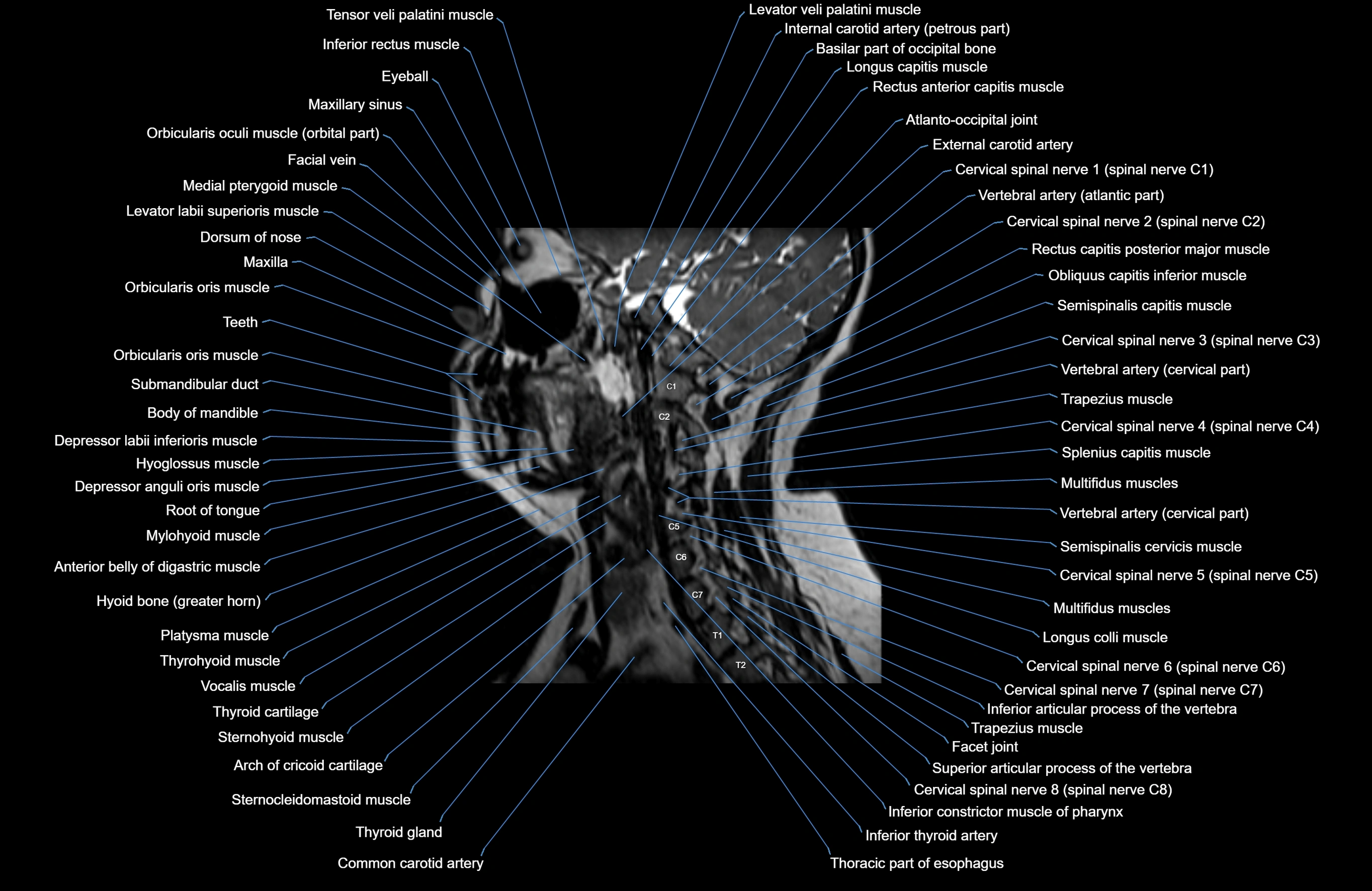
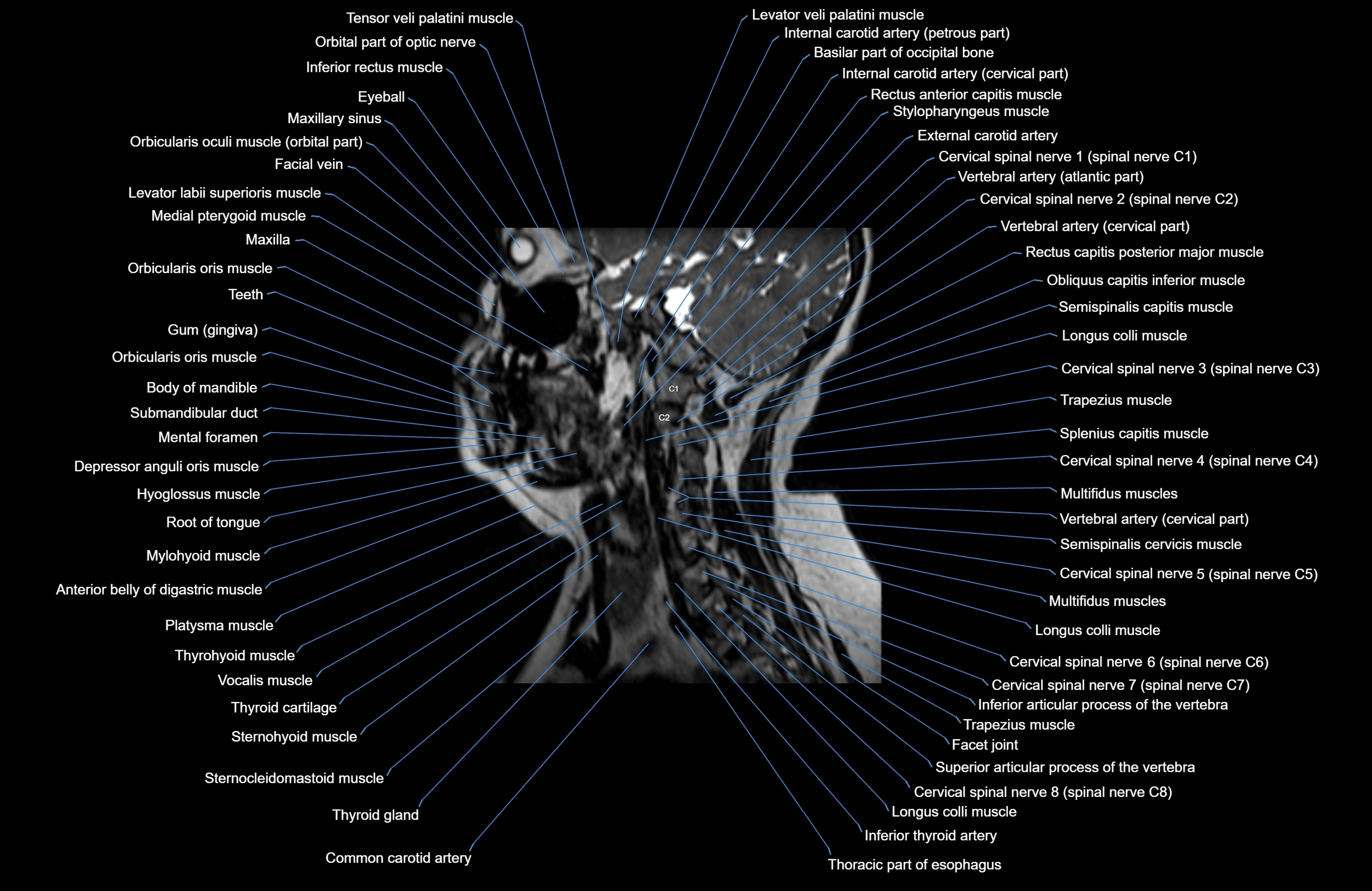
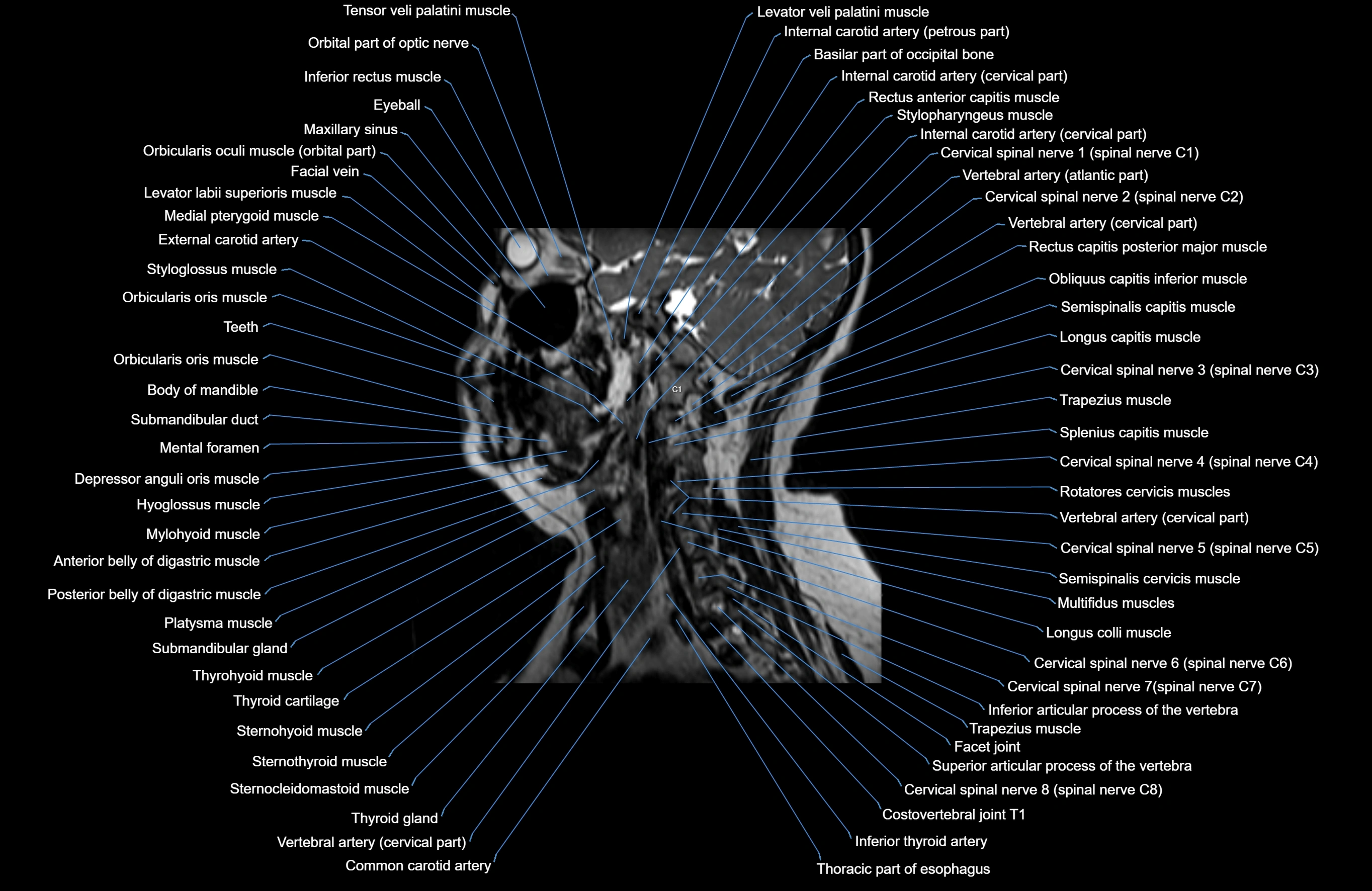
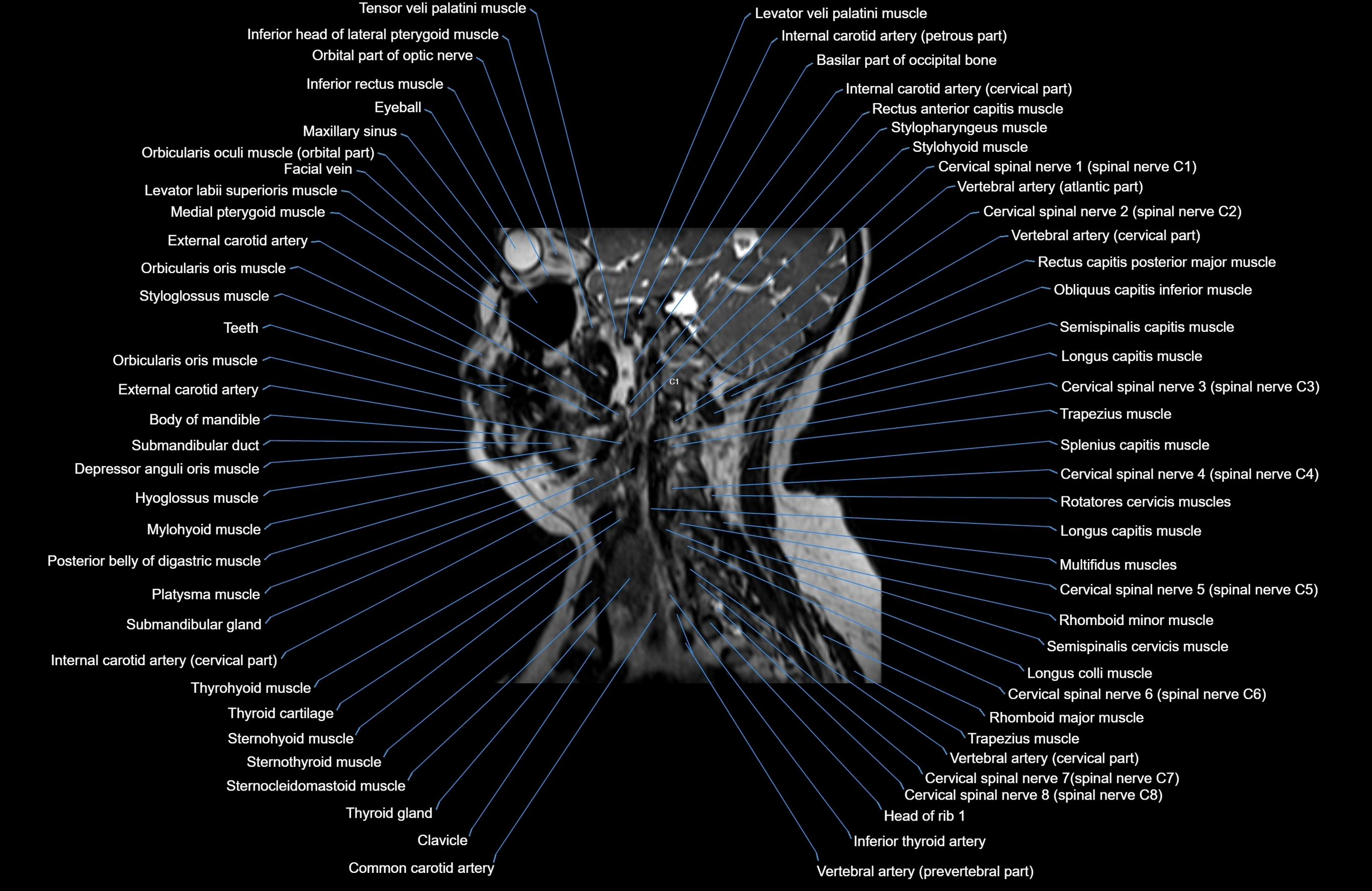
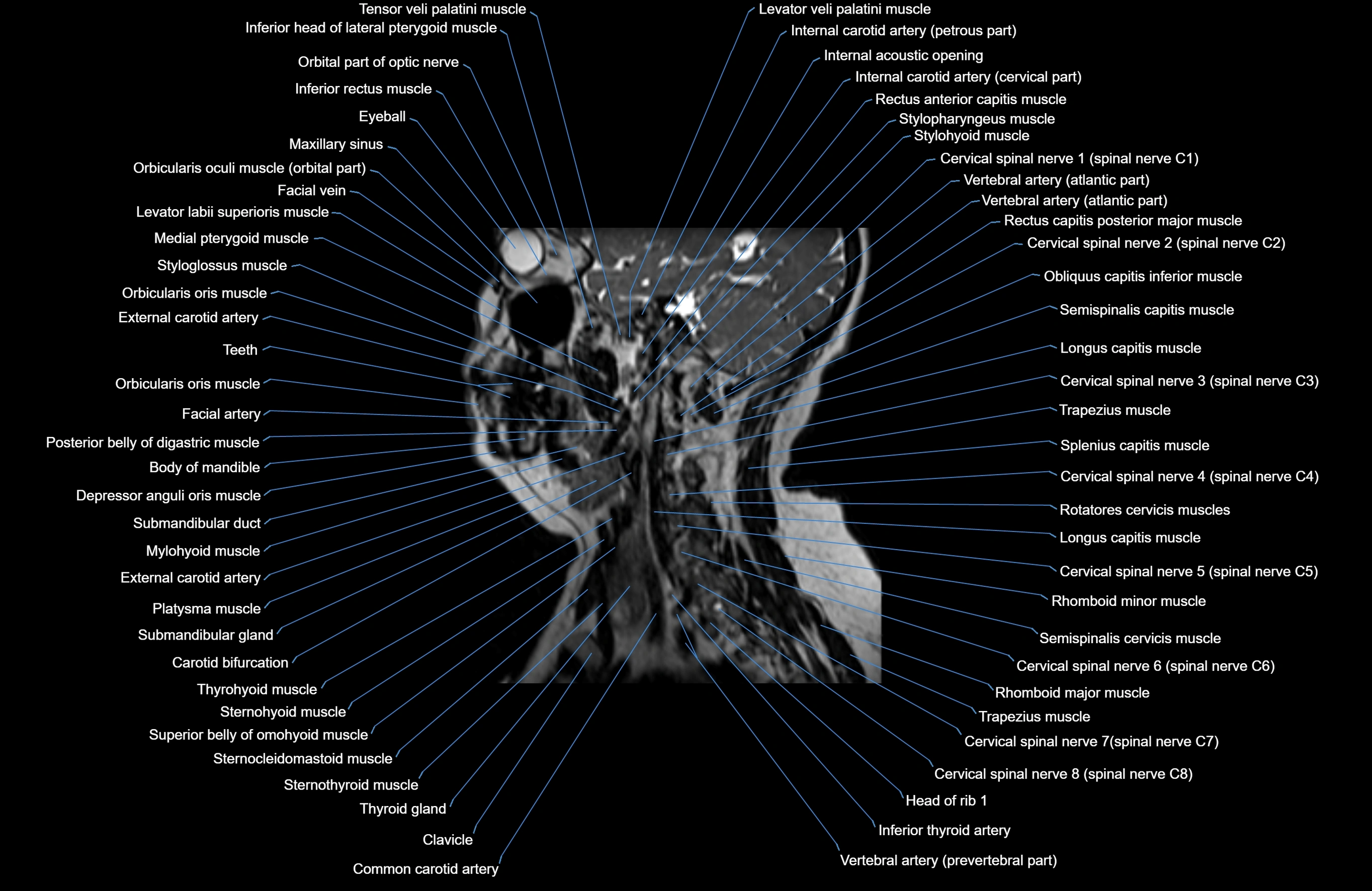
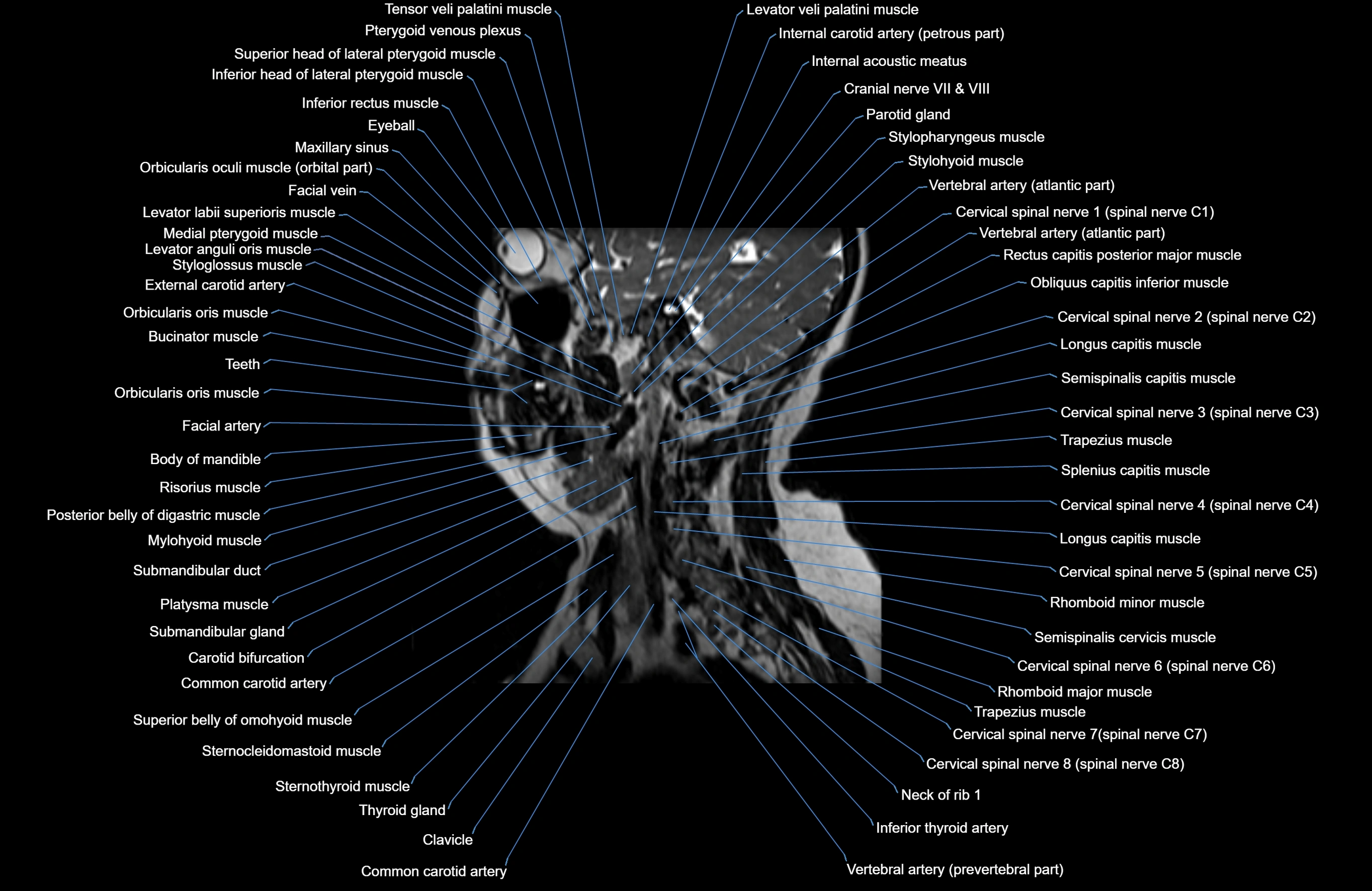
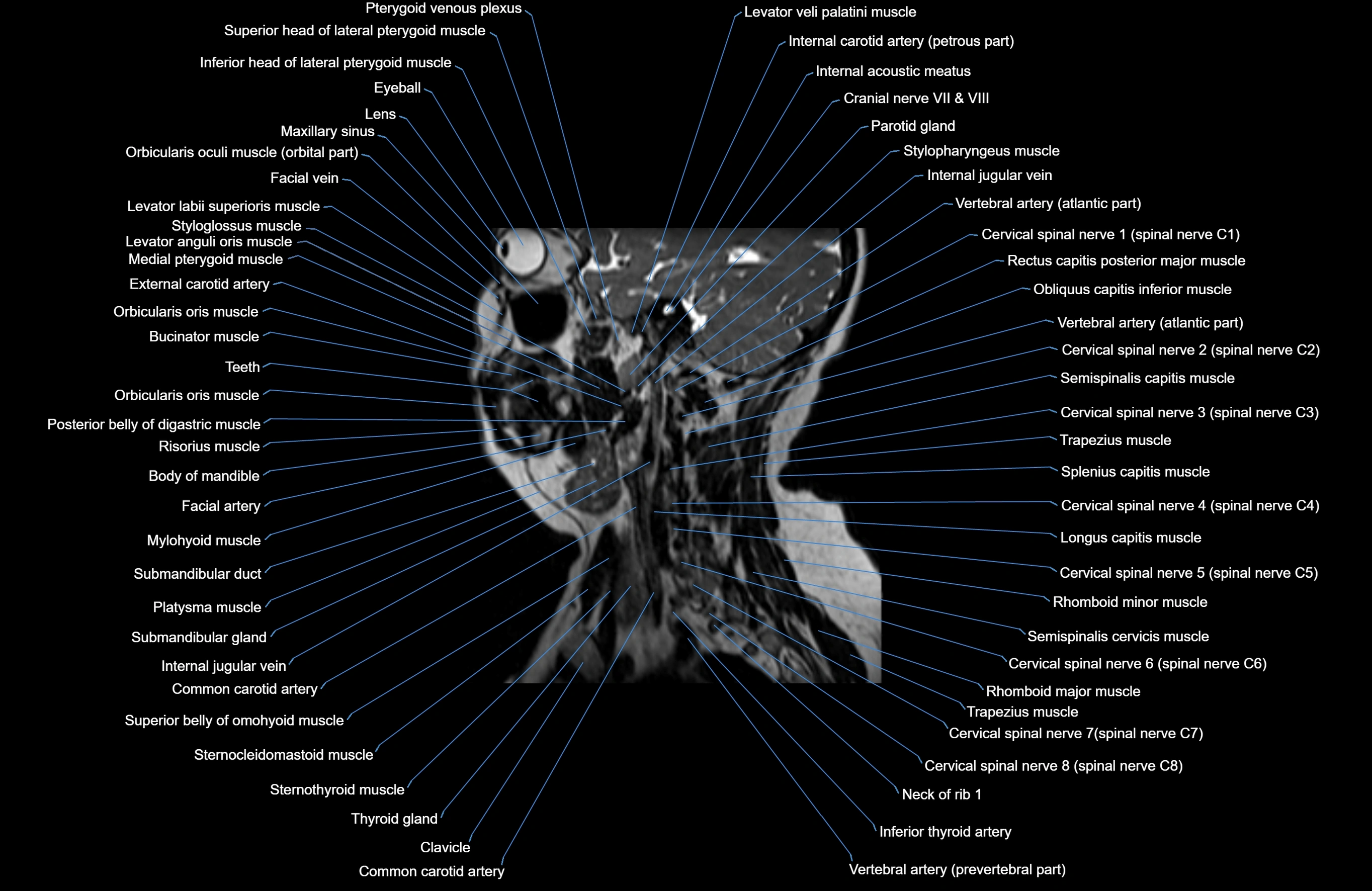
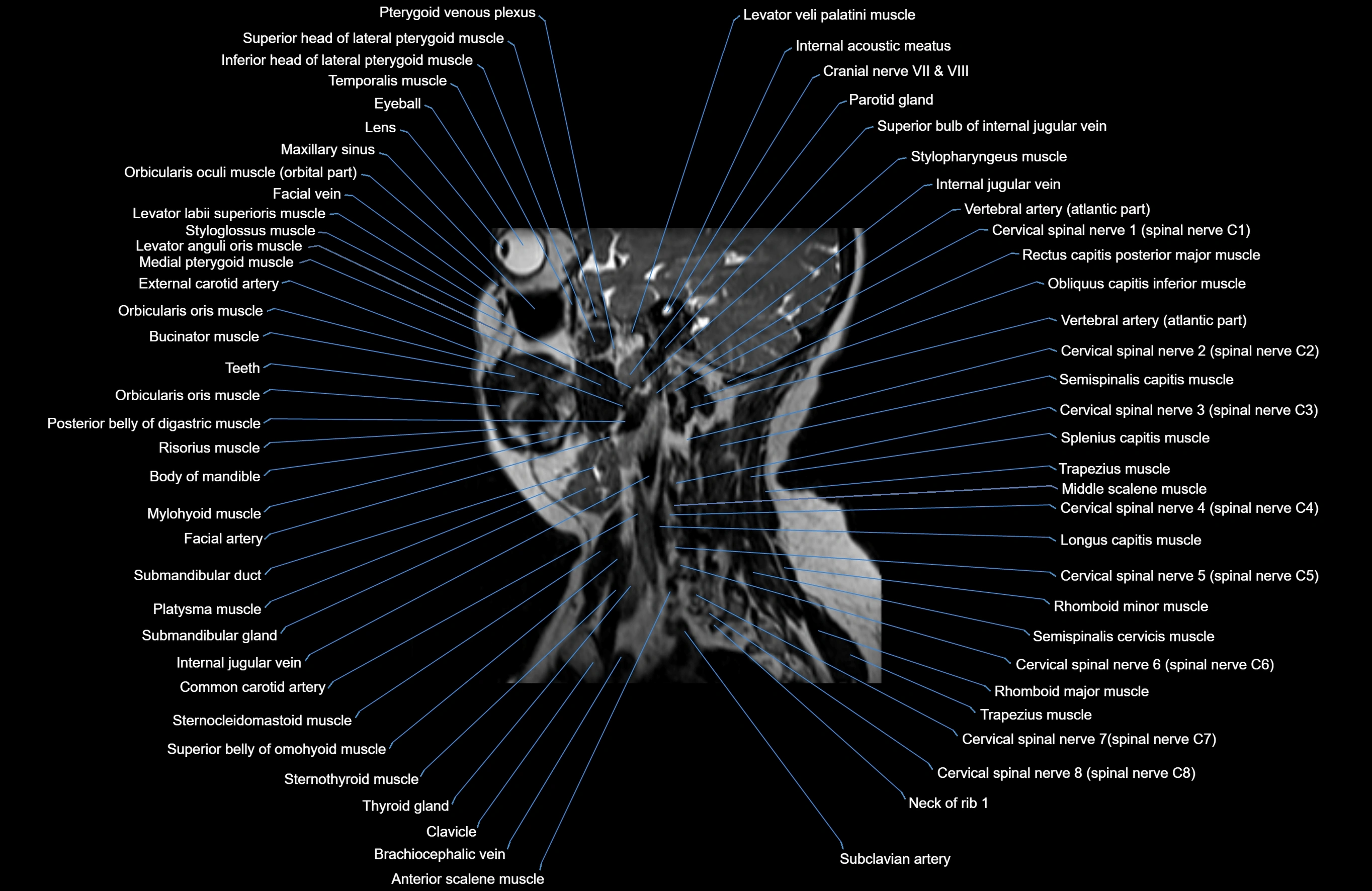
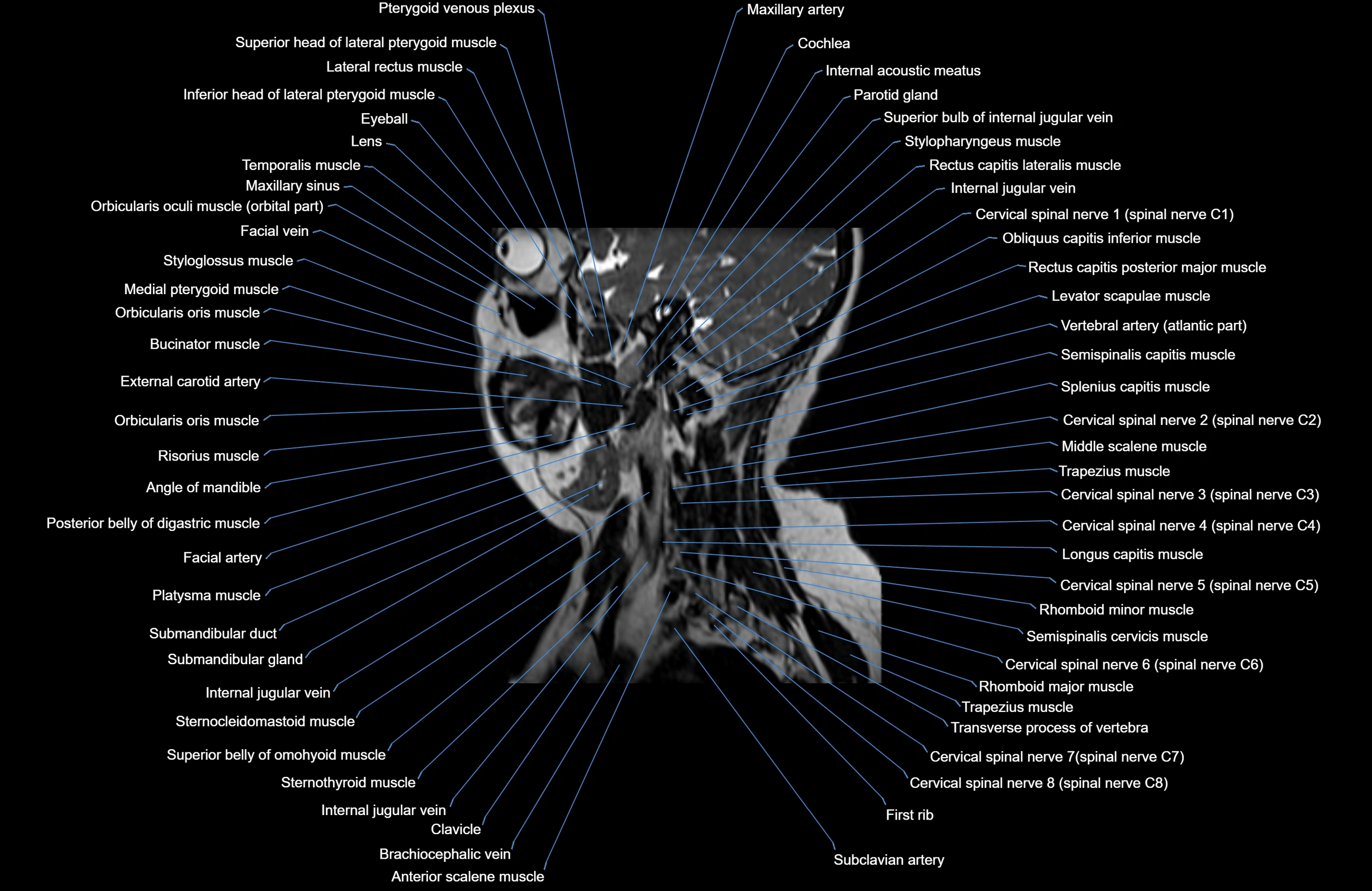
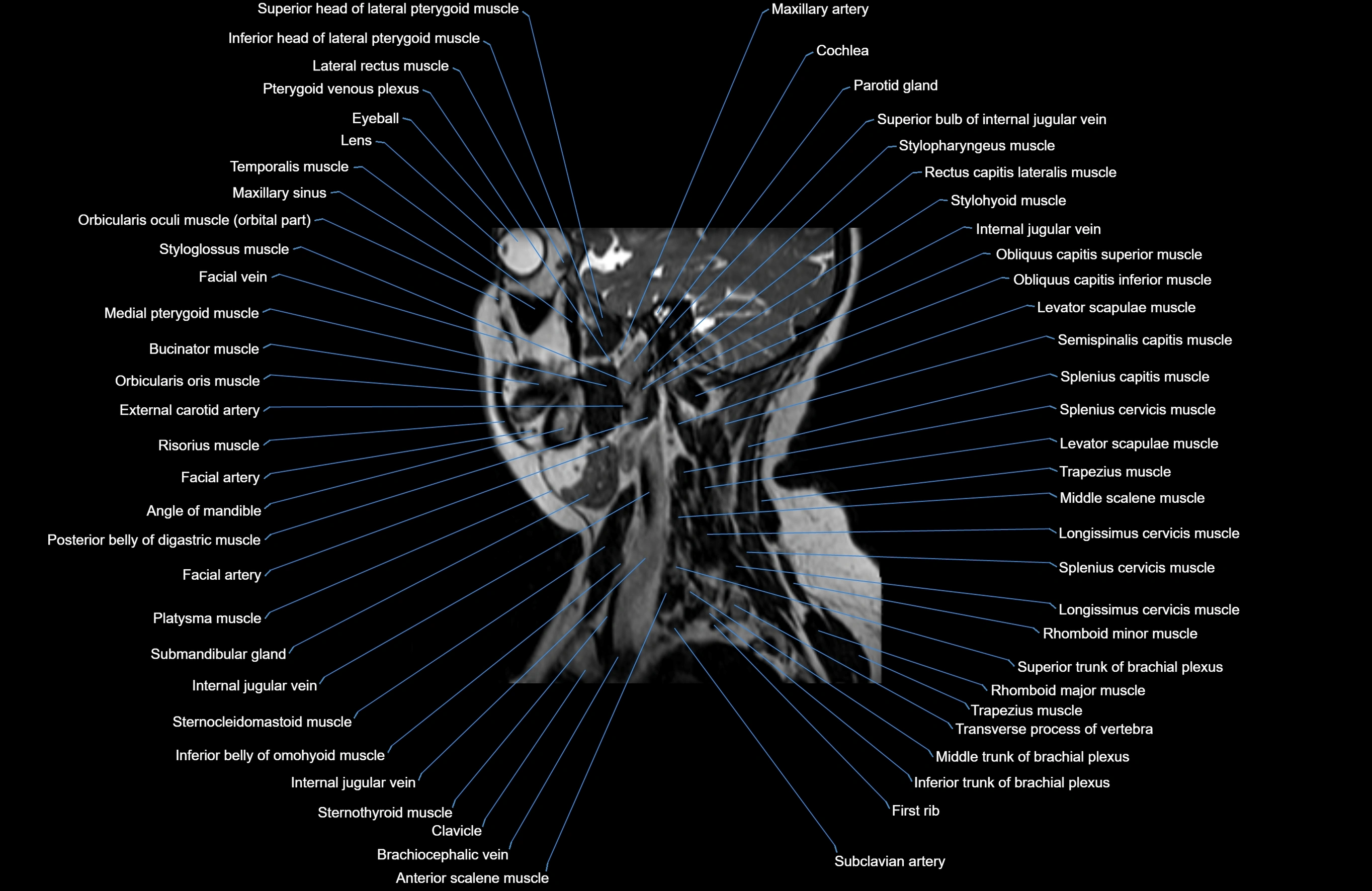
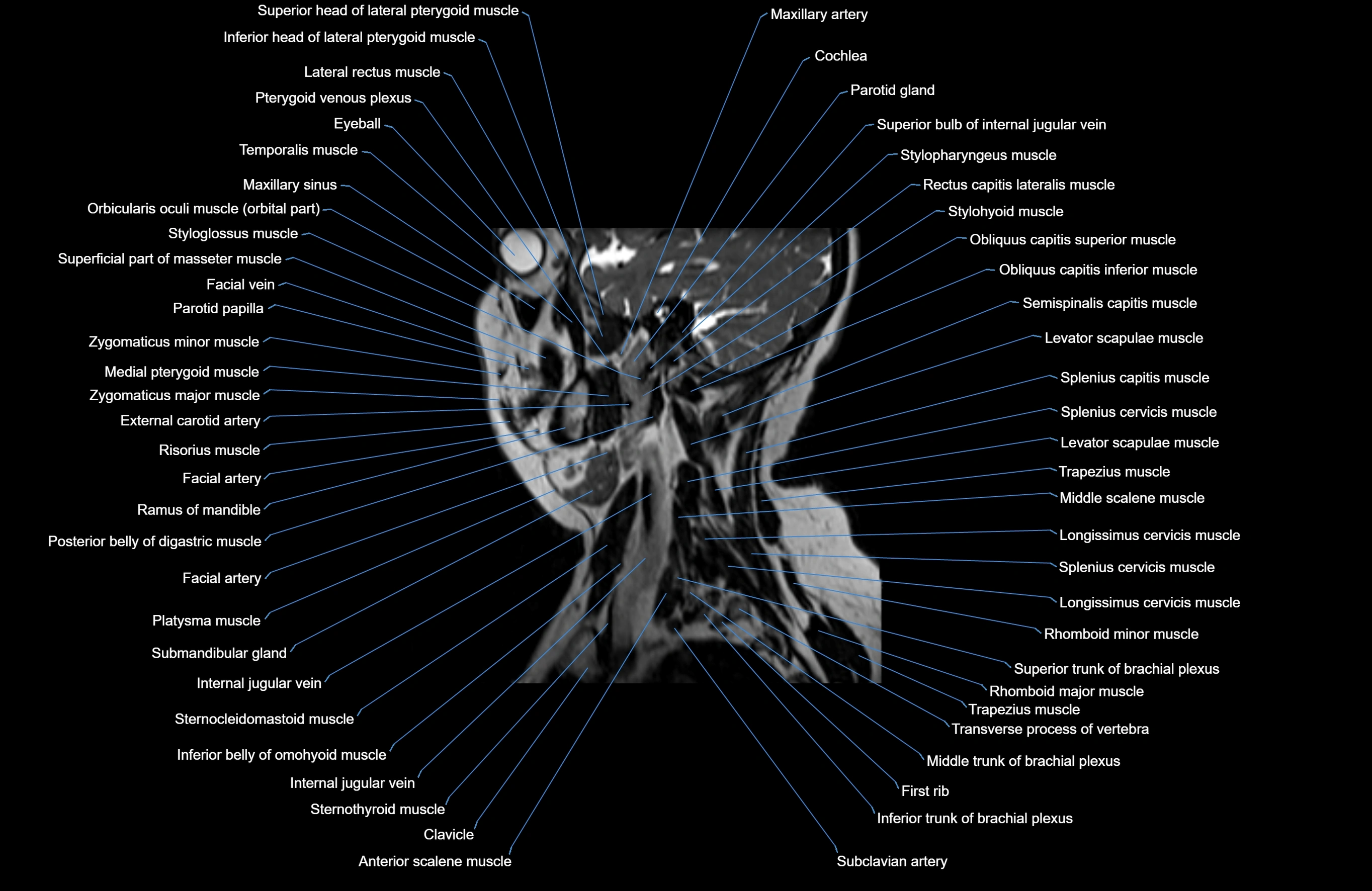
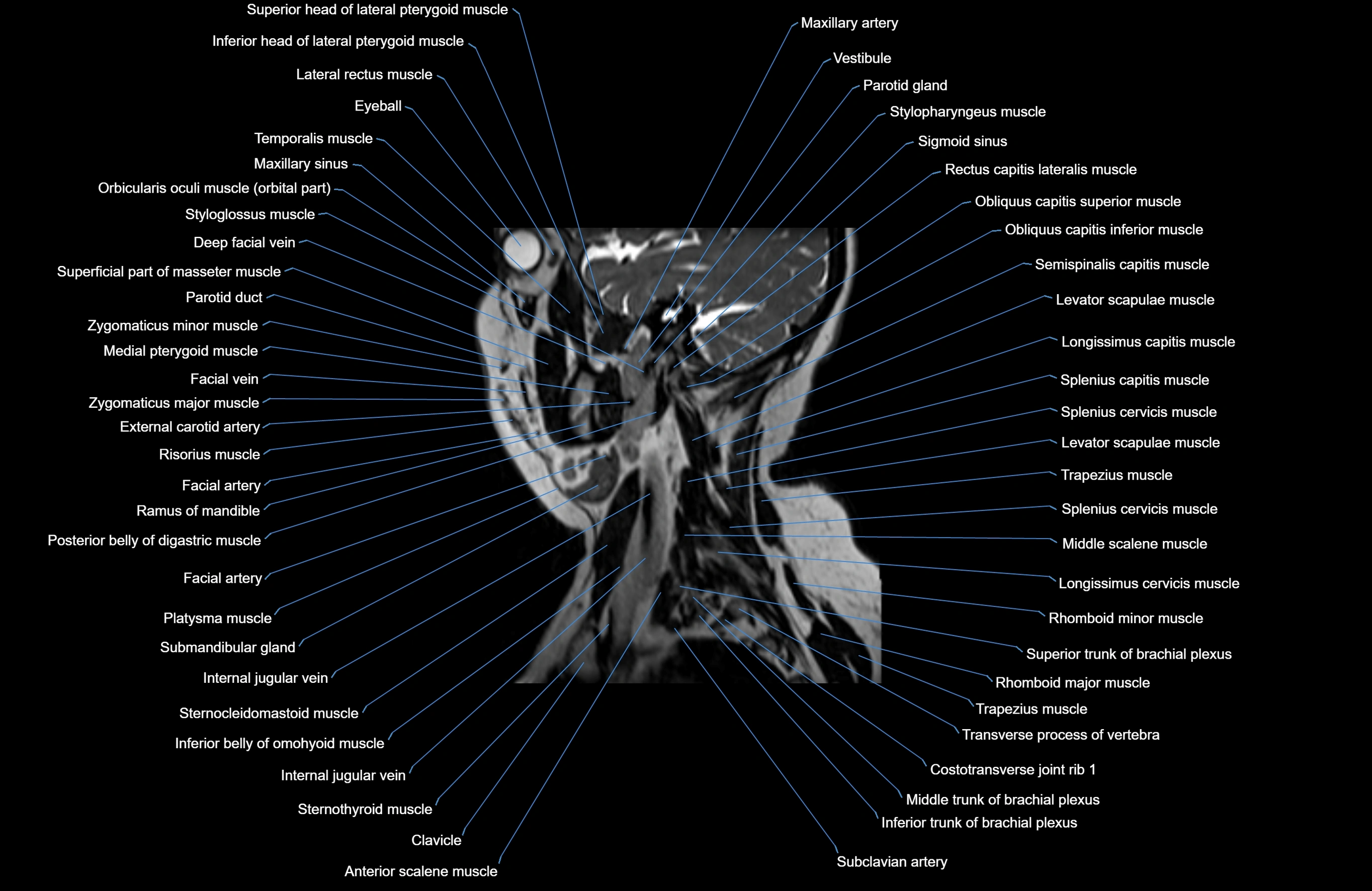
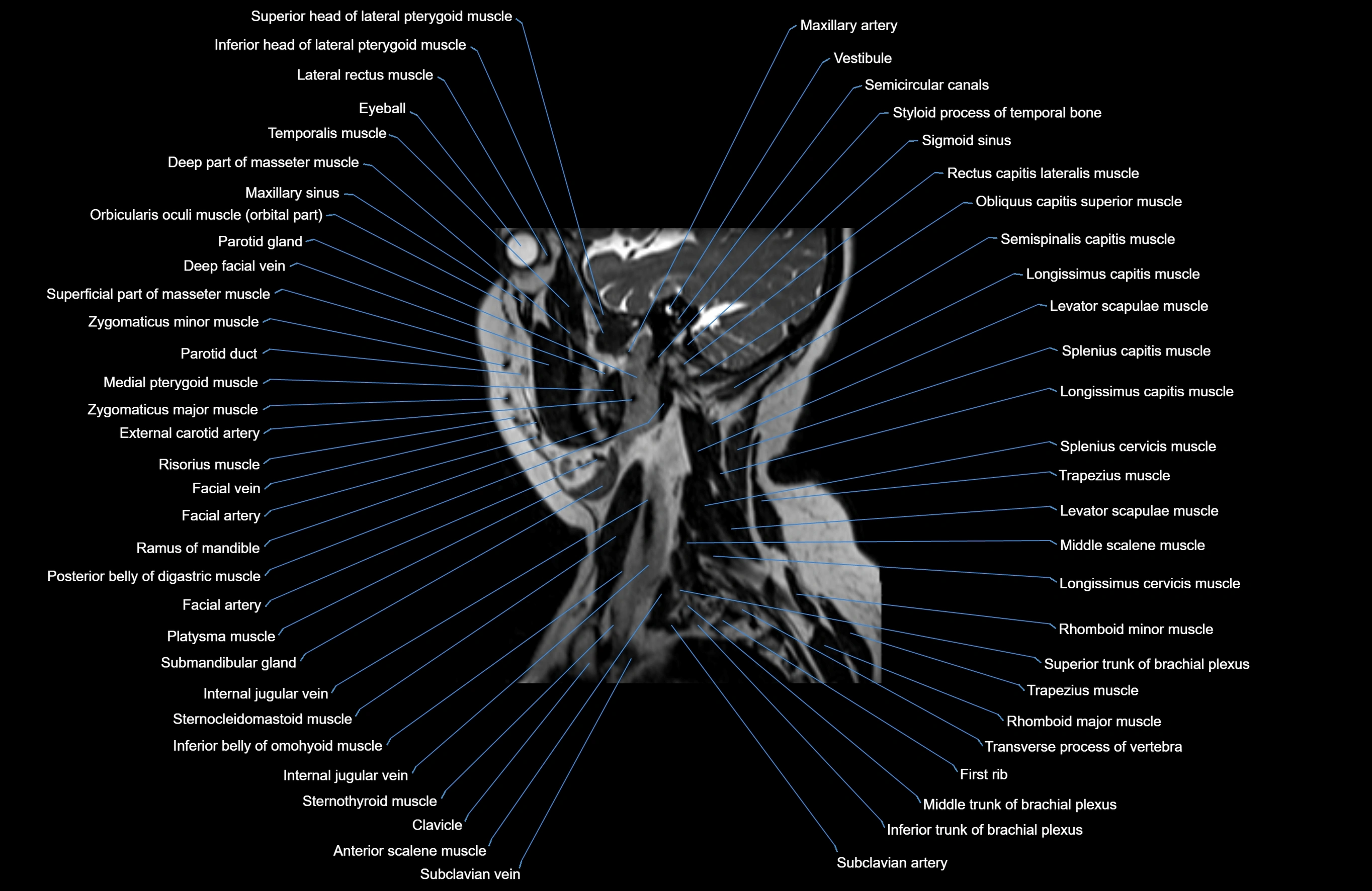
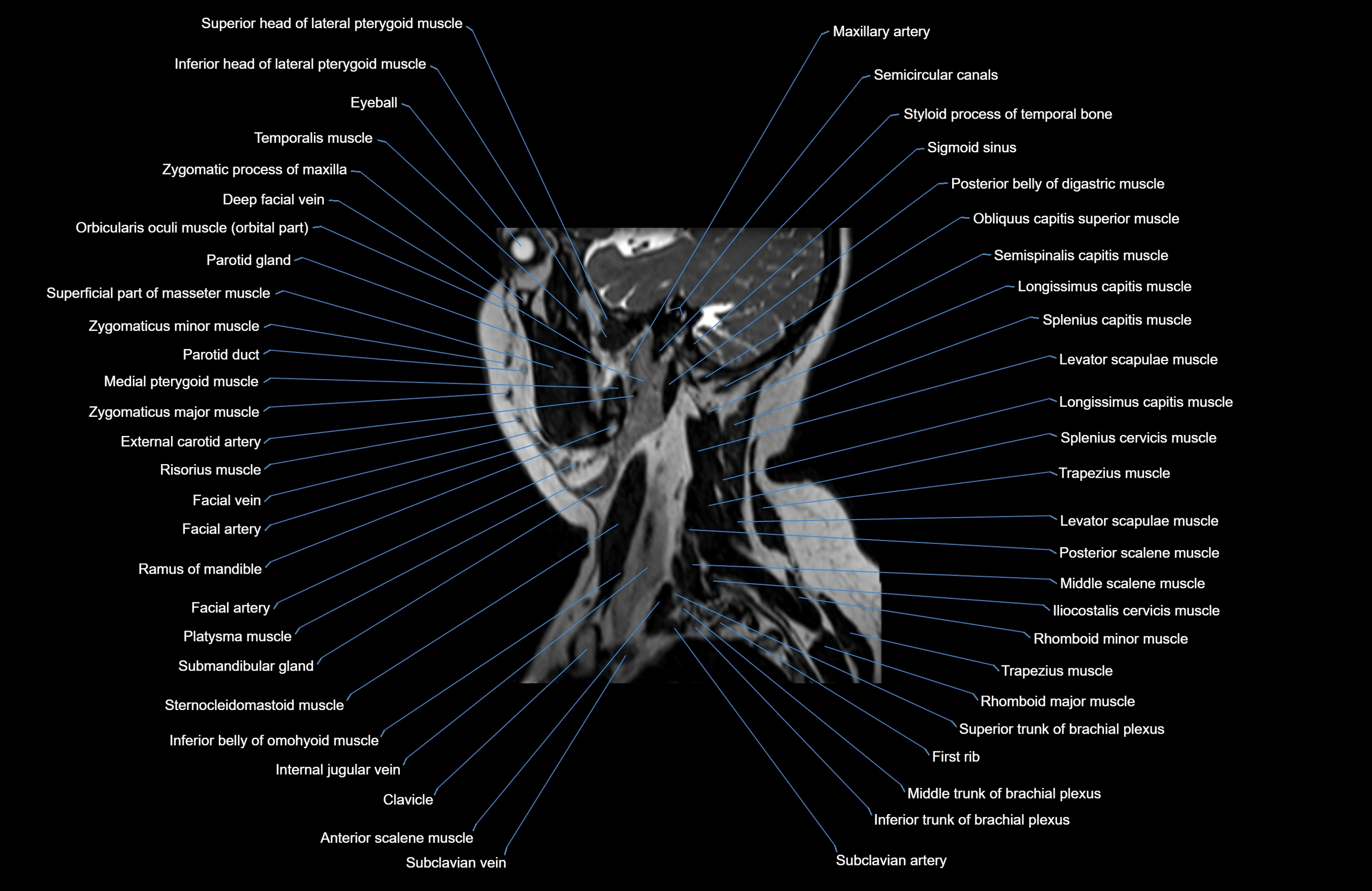
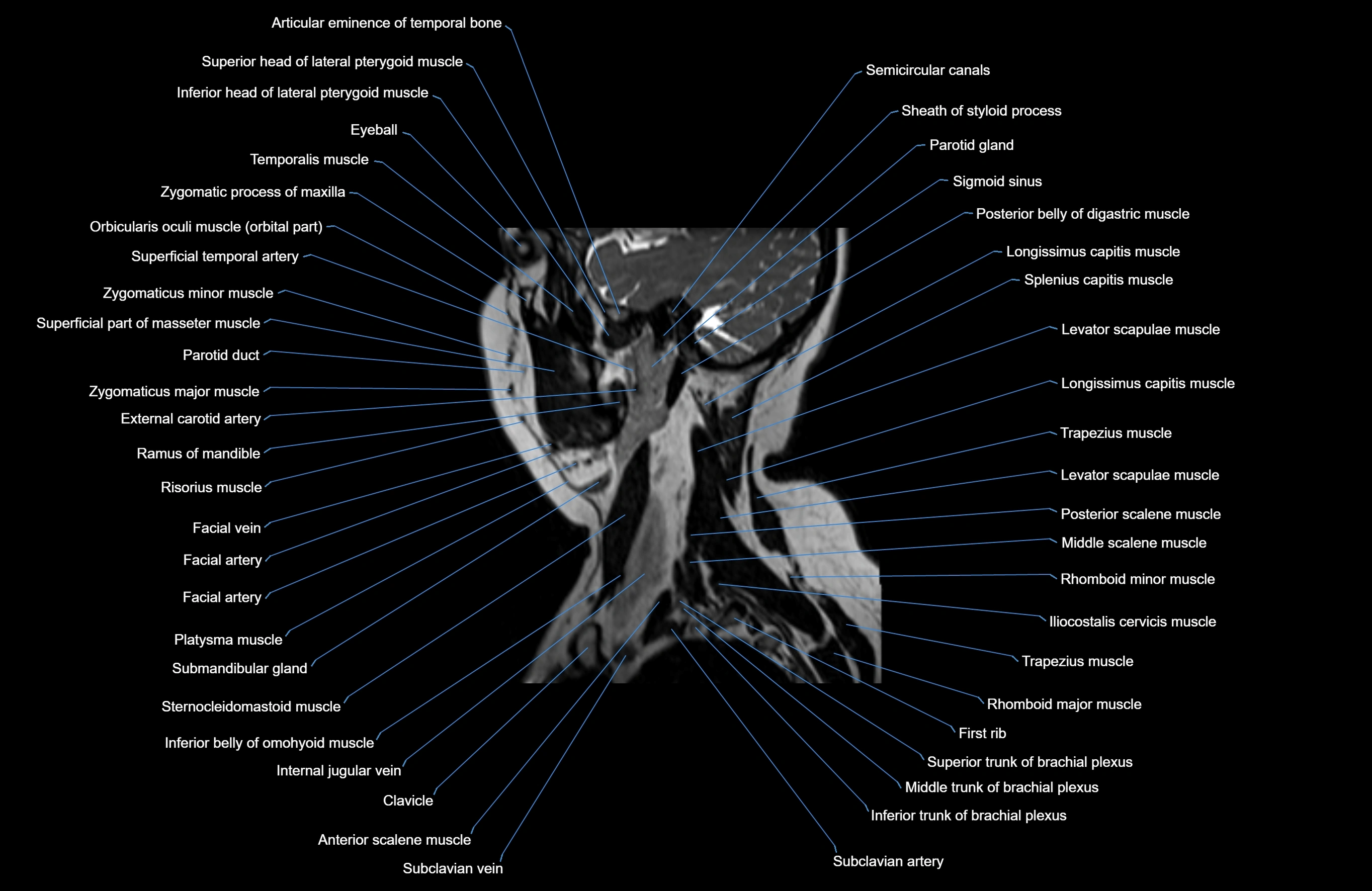
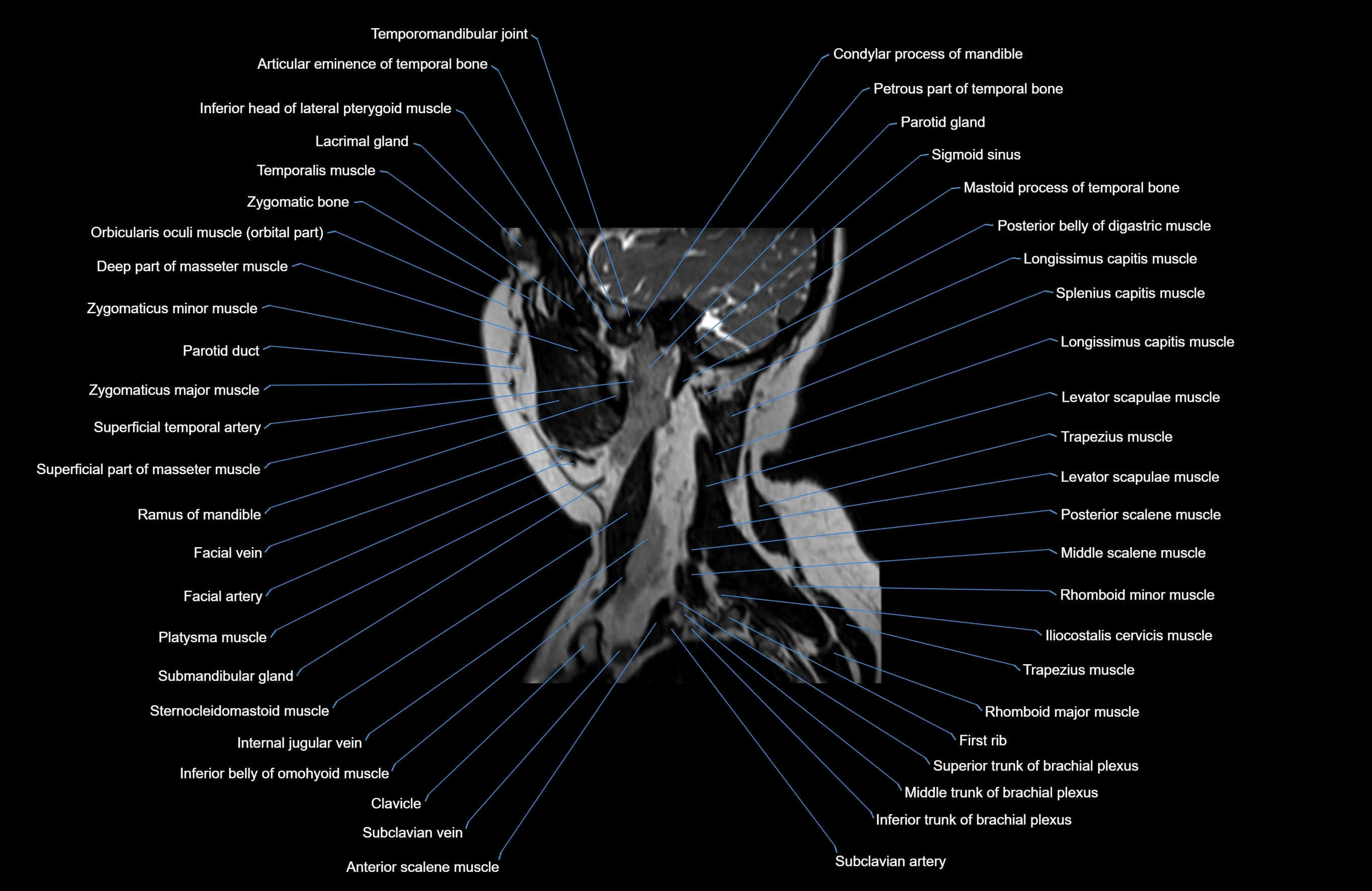
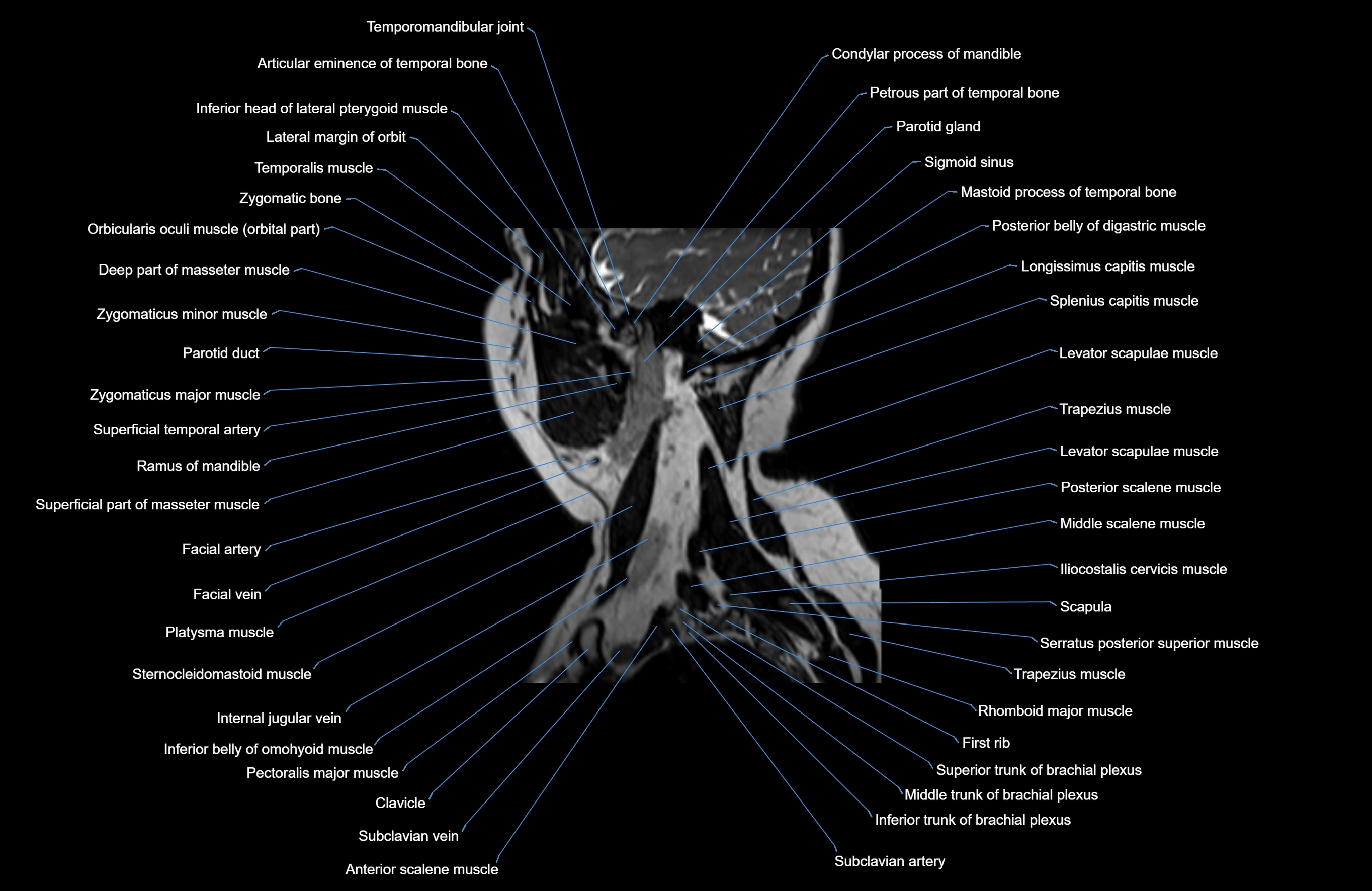
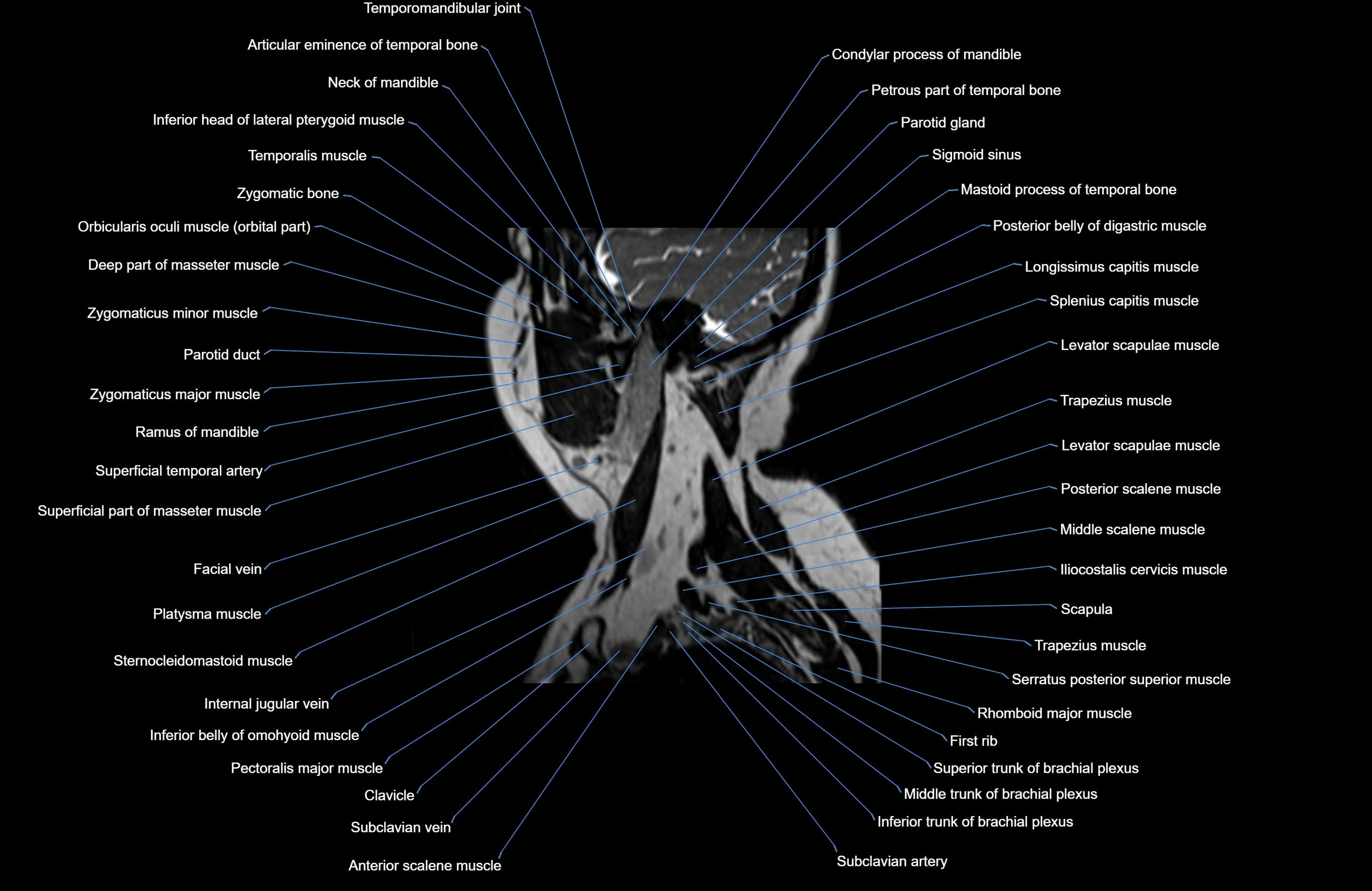
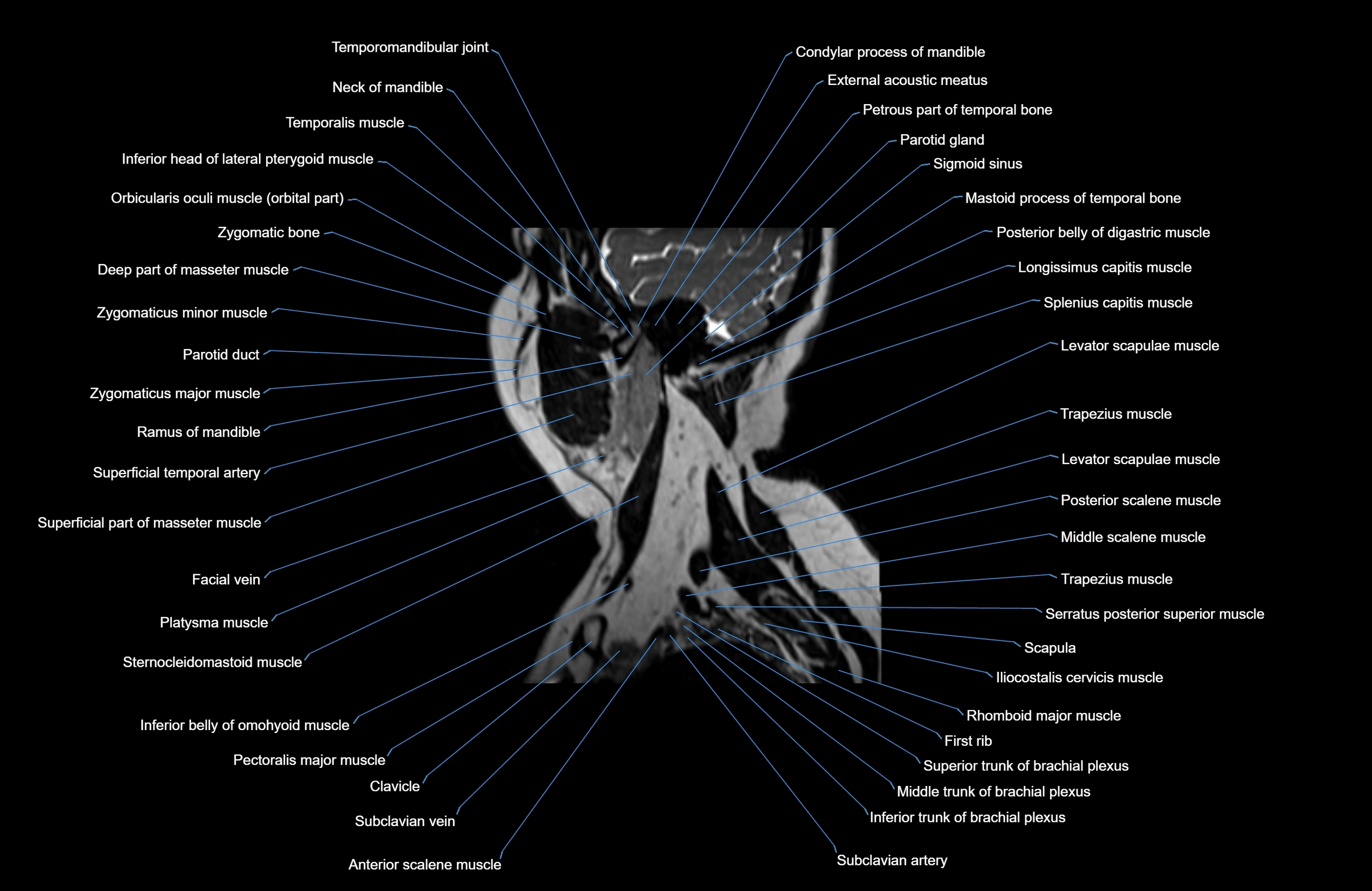
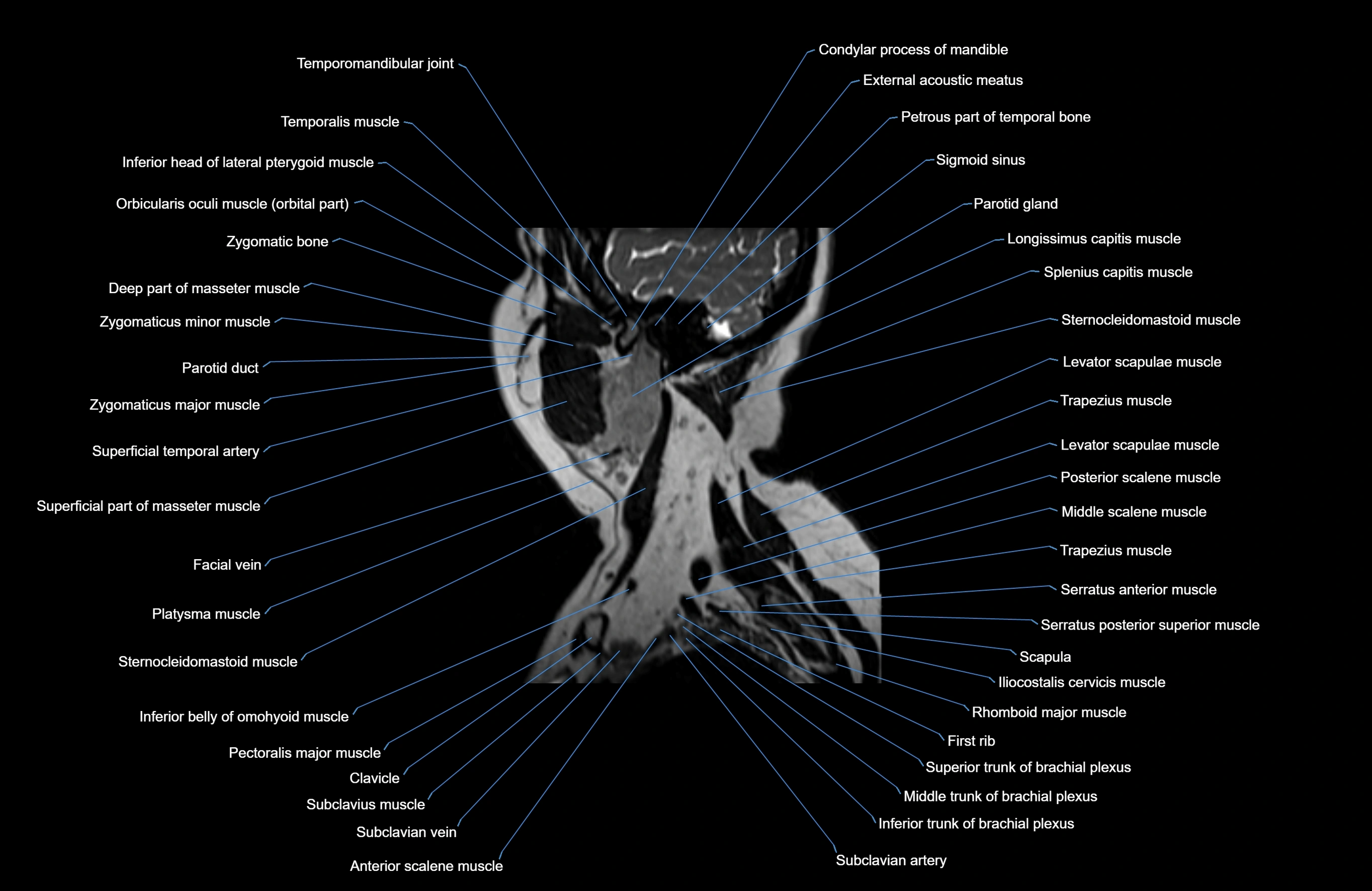
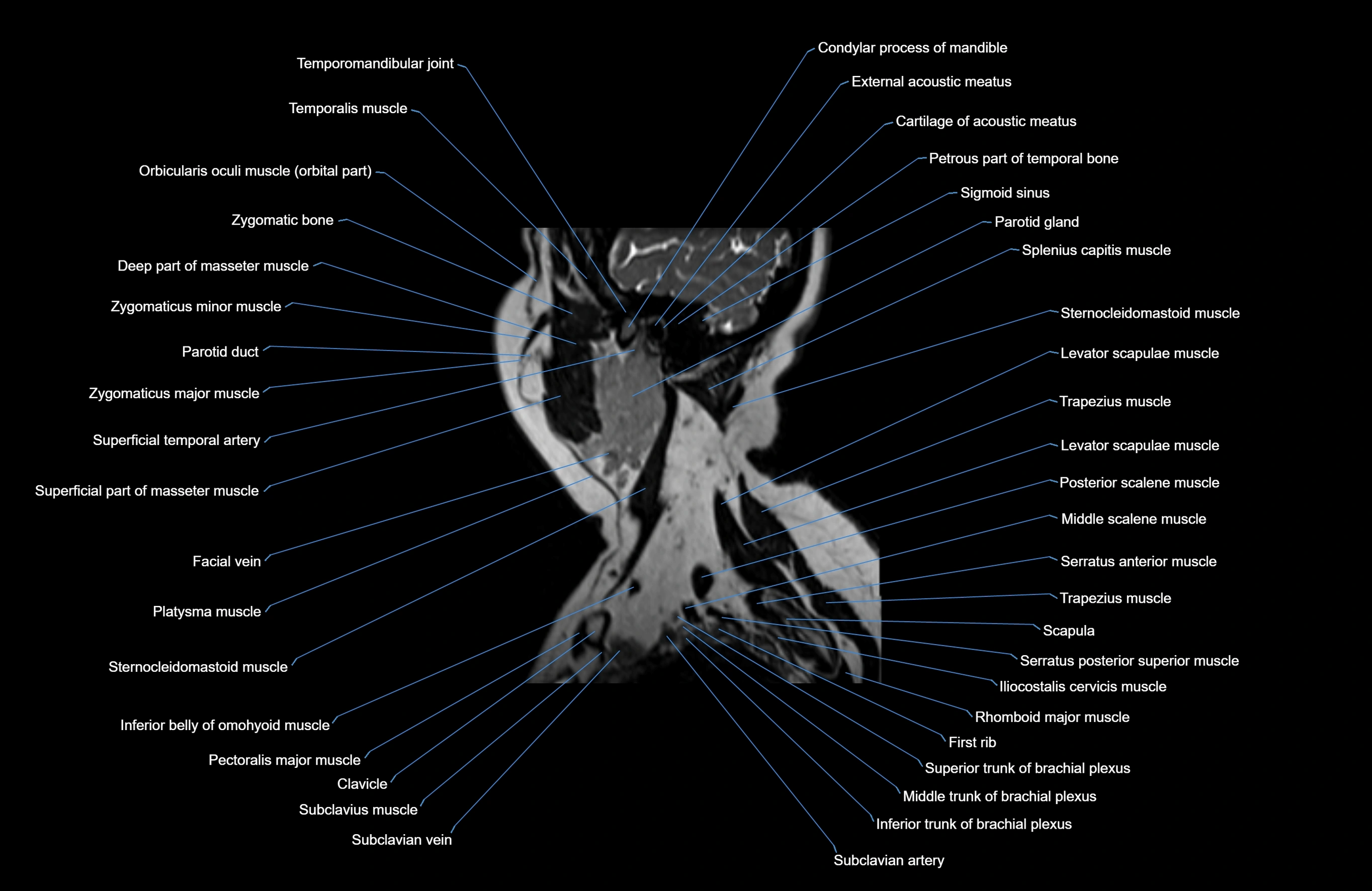
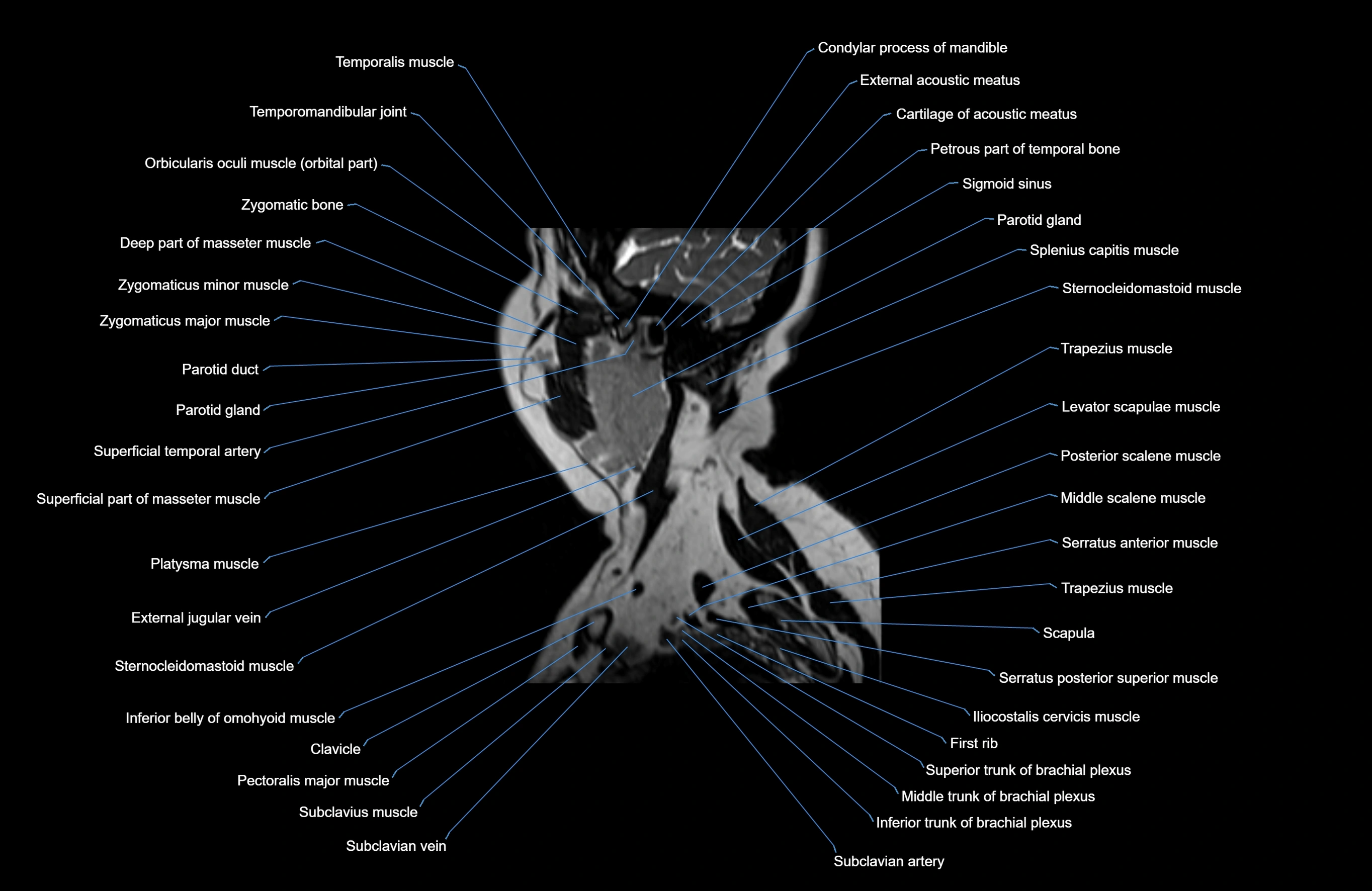
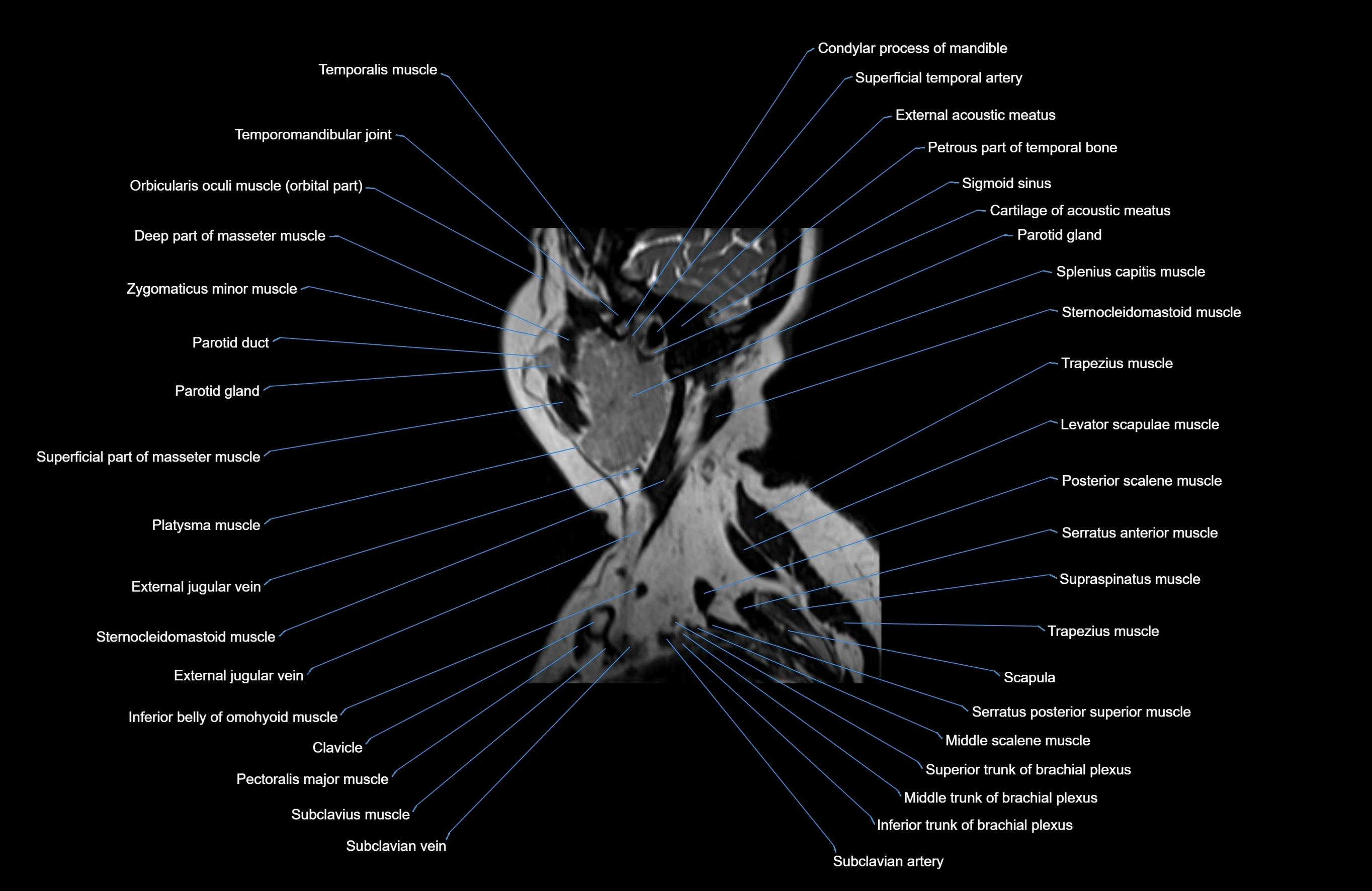
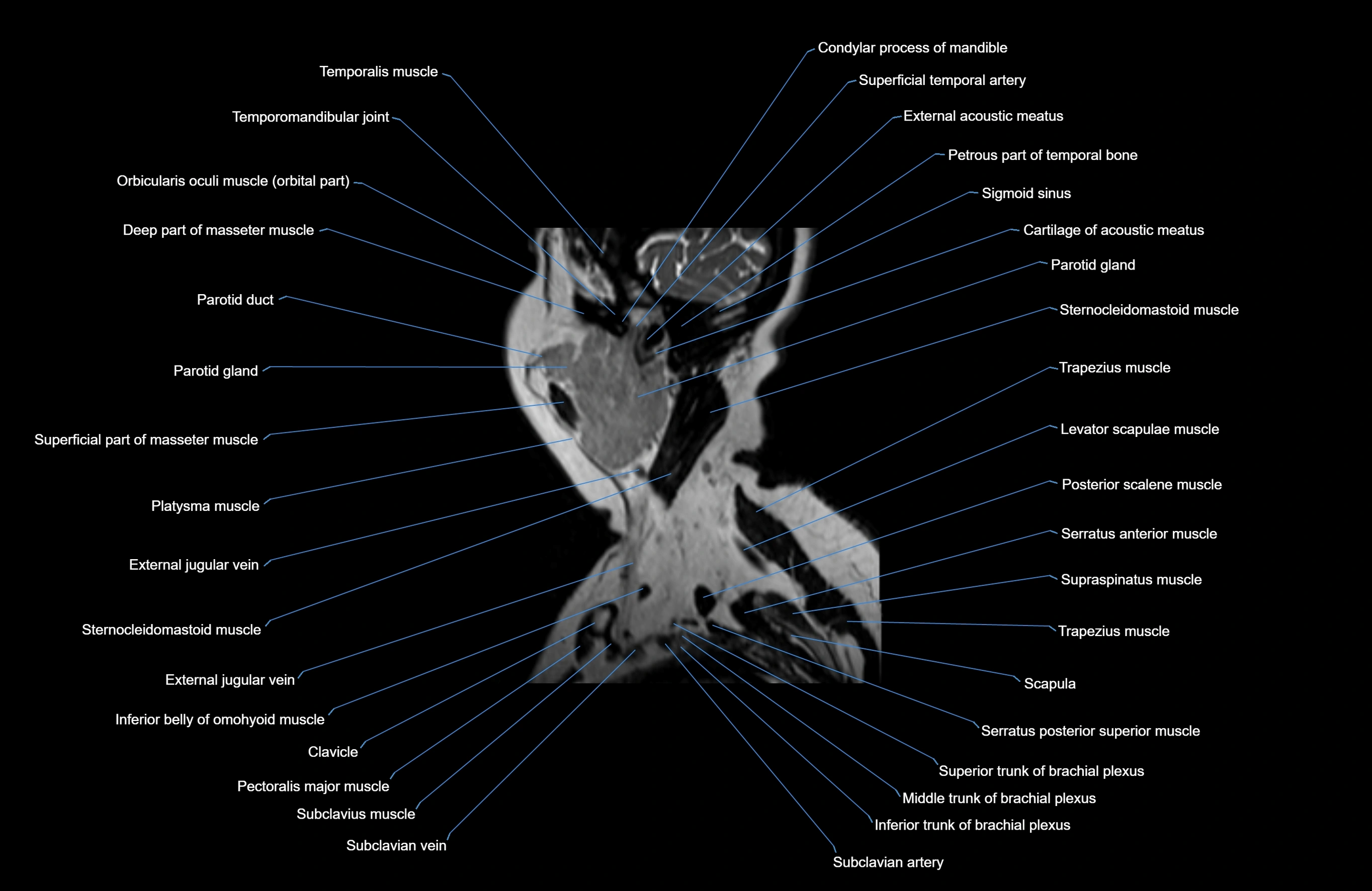
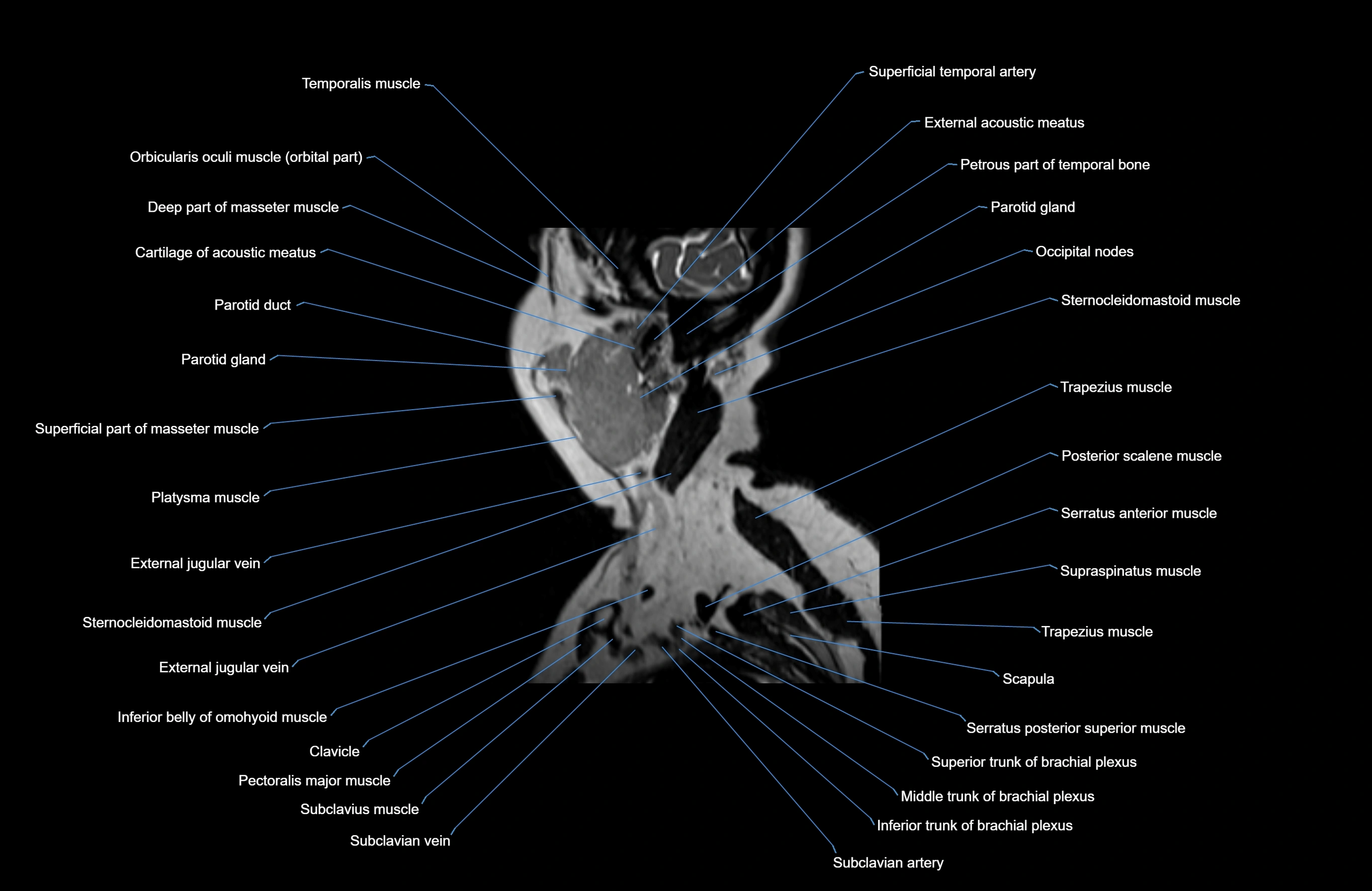
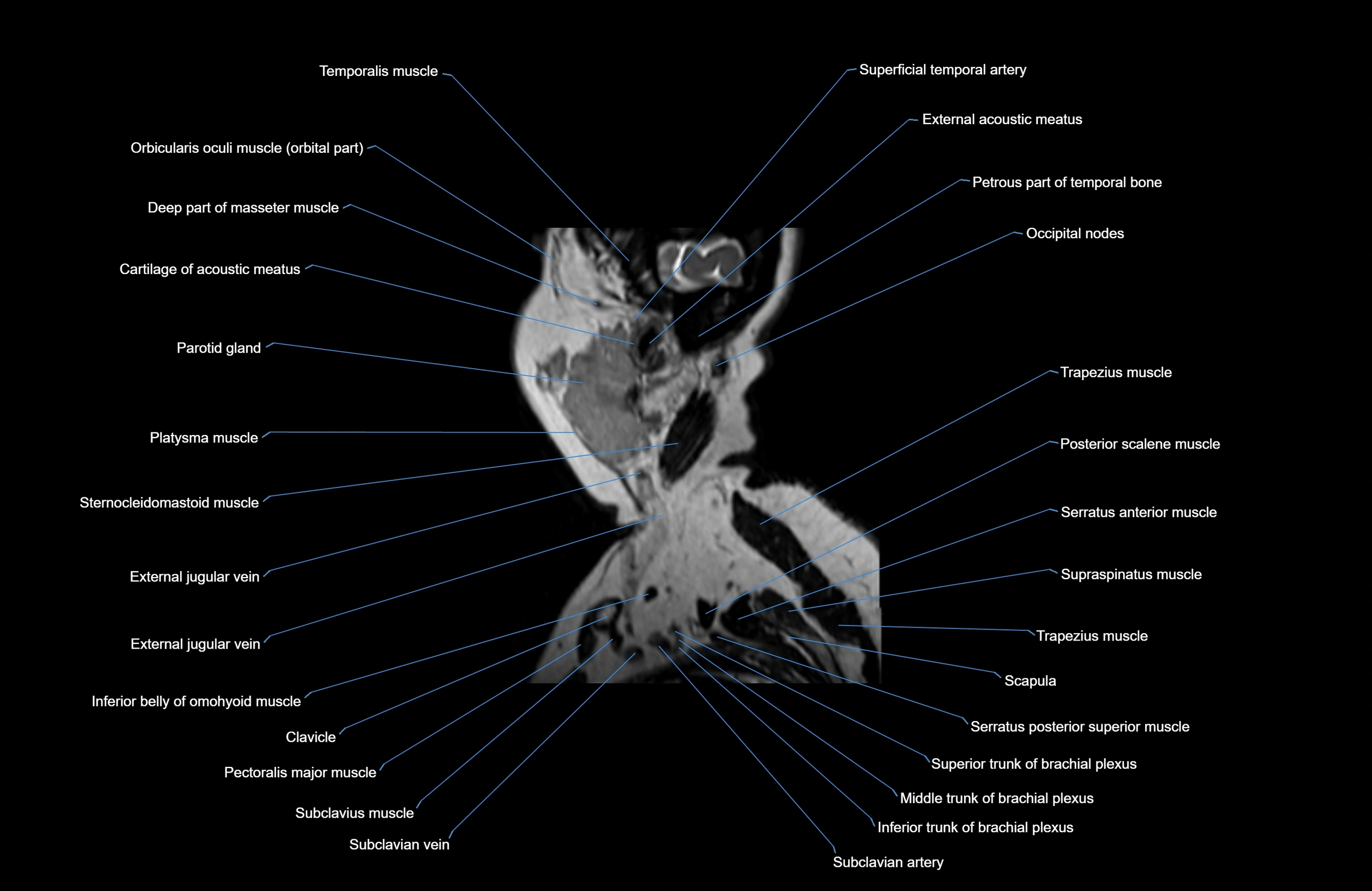
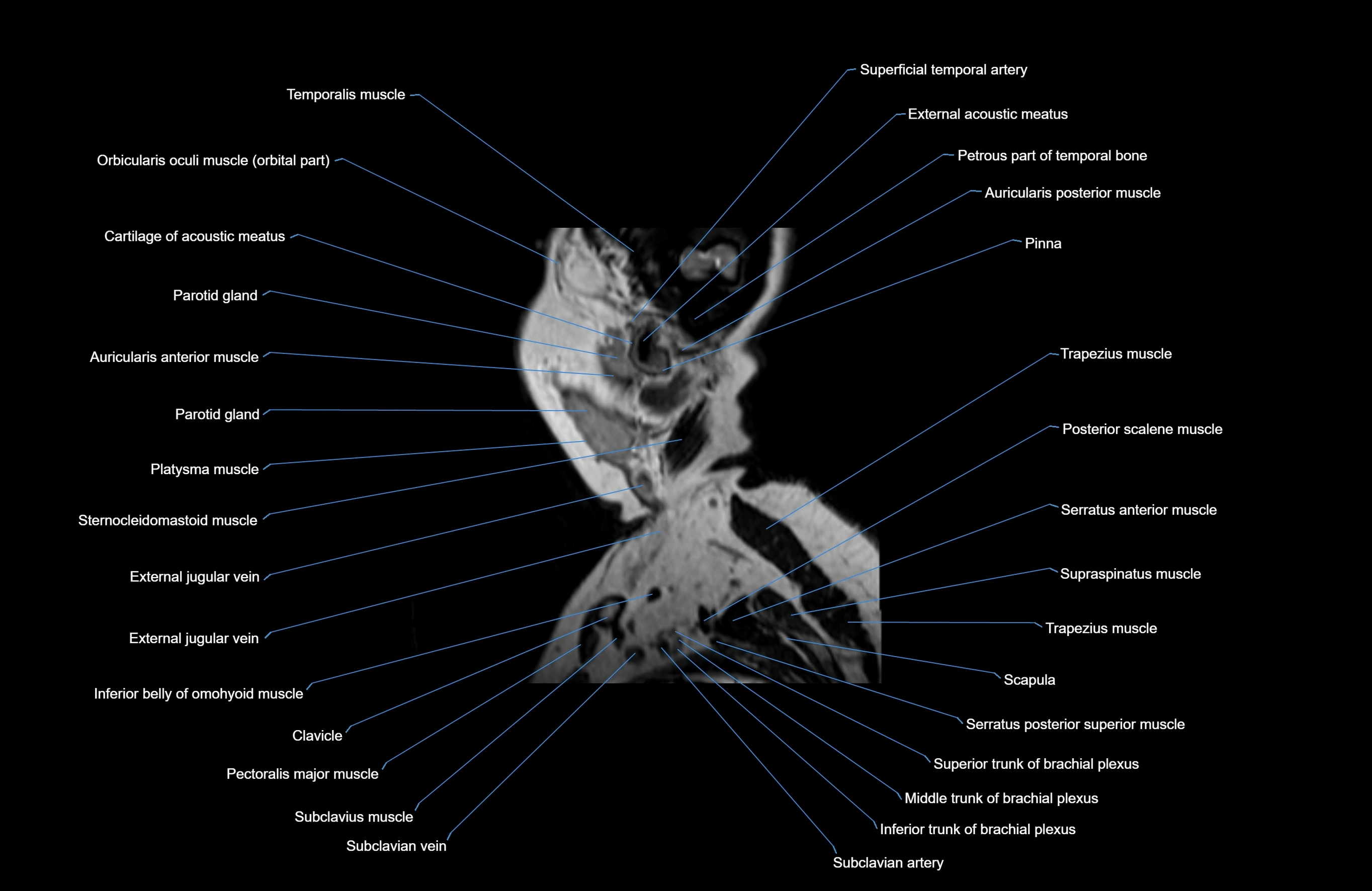
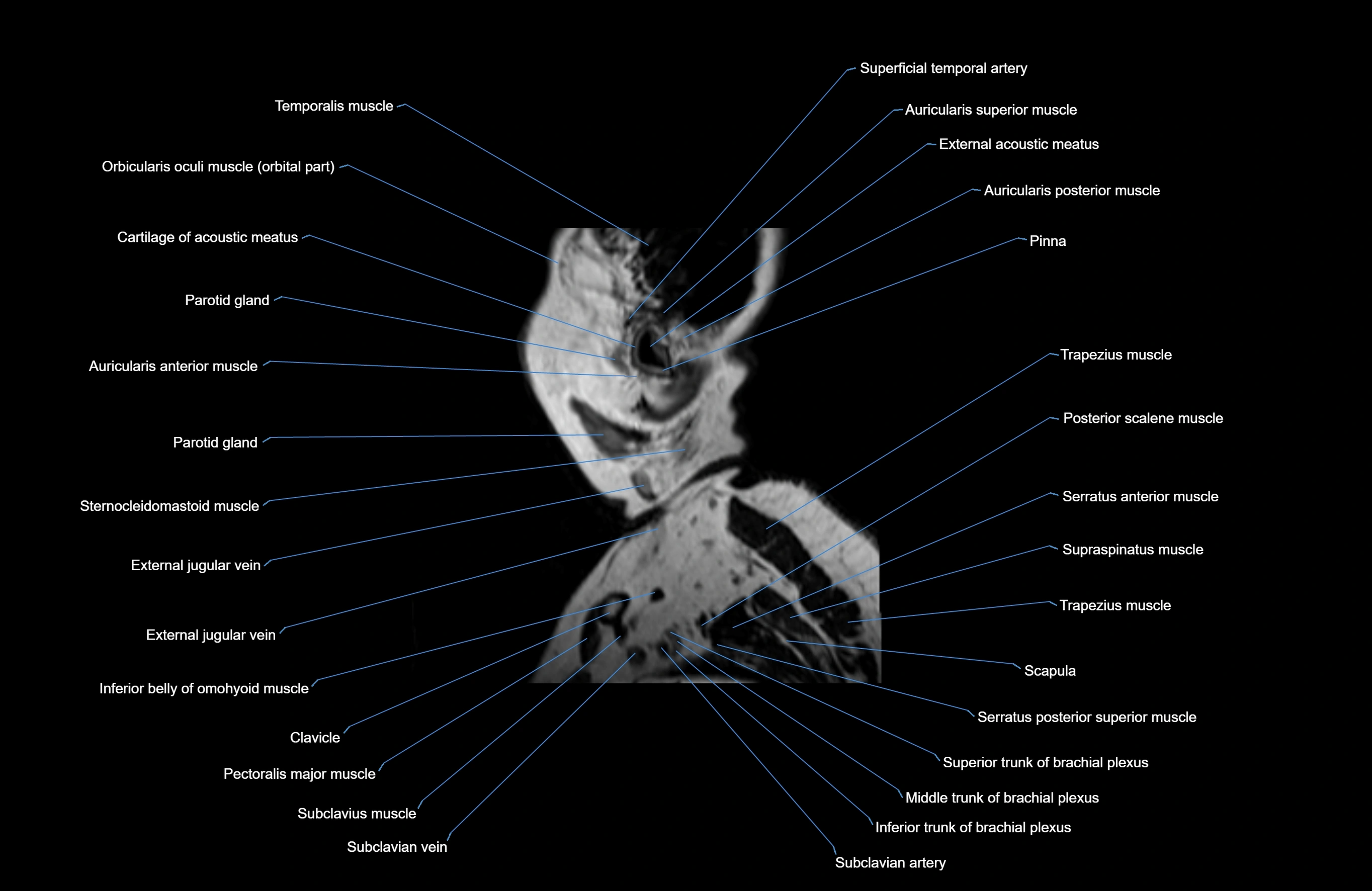
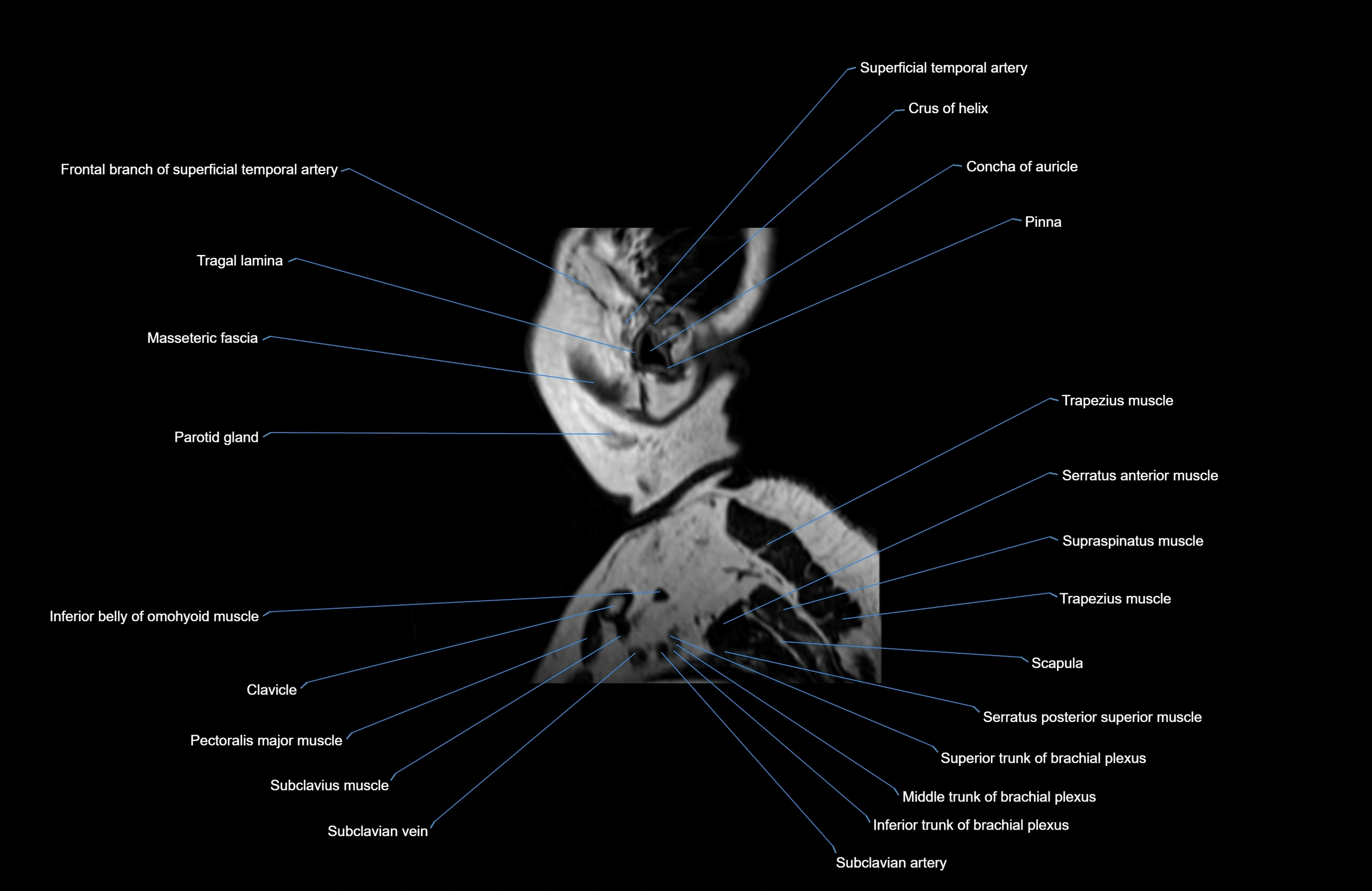
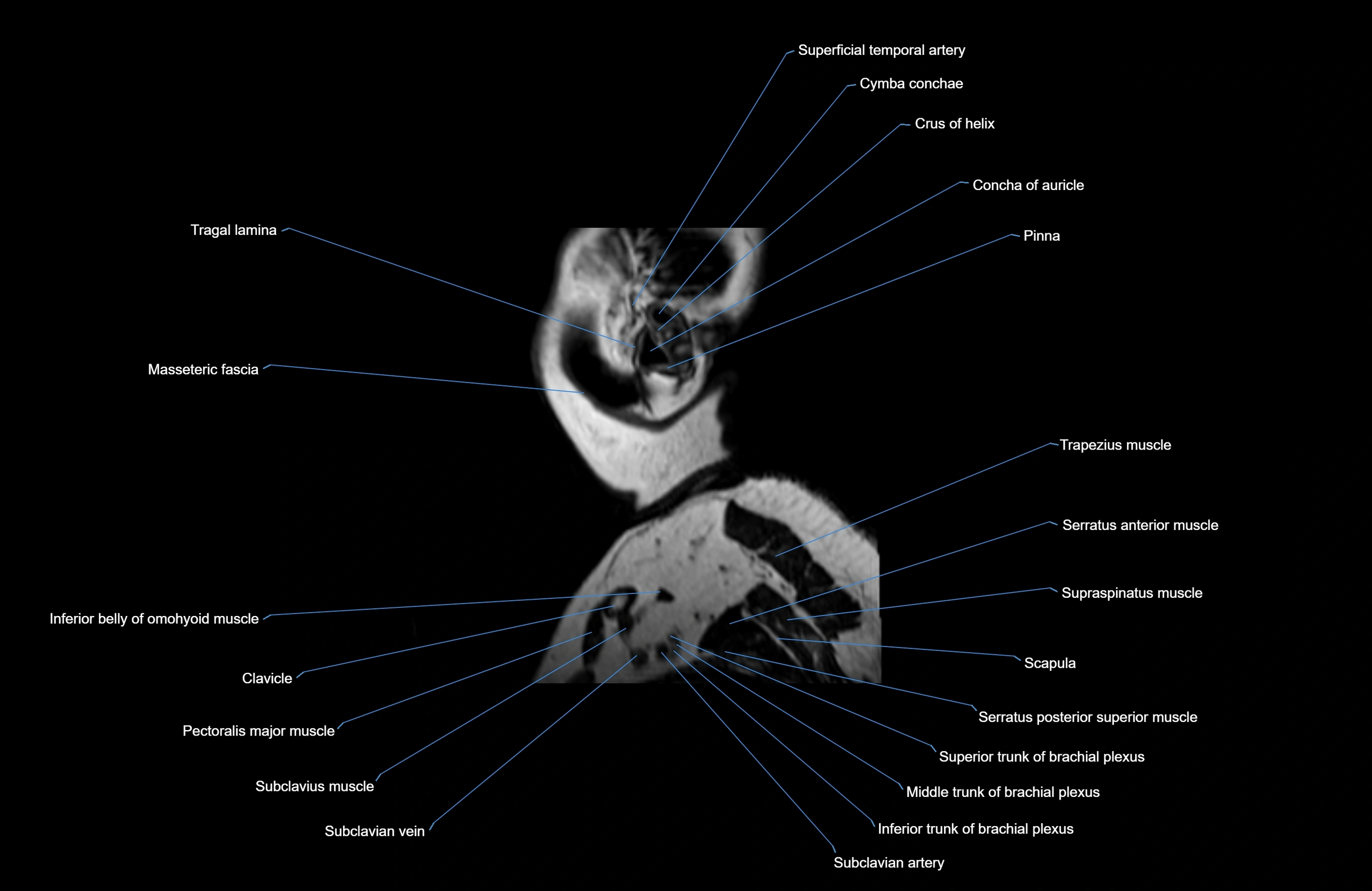
Topic
- Abducens nerve (Cranial nerve VI)
- Abducens nerve (orbital part )
- Accessory Nerve (Cranial nerve XI)
- Accessory lymph nodes
- Alar ligament
- Alveolar arch of maxilla
- Alveolar process of maxilla
- Alveolar ridge
- Angle of mandible
- Anterior Band of Articular Disc TMJ
- Anterior arch of atlas
- Anterior atlanto-occipital membrane
- Anterior atlantooccipital membrane
- Anterior belly of digastric muscle
- Anterior chamber of eyeball
- Anterior cochlear nucleus
- Anterior ethmoidal air cells
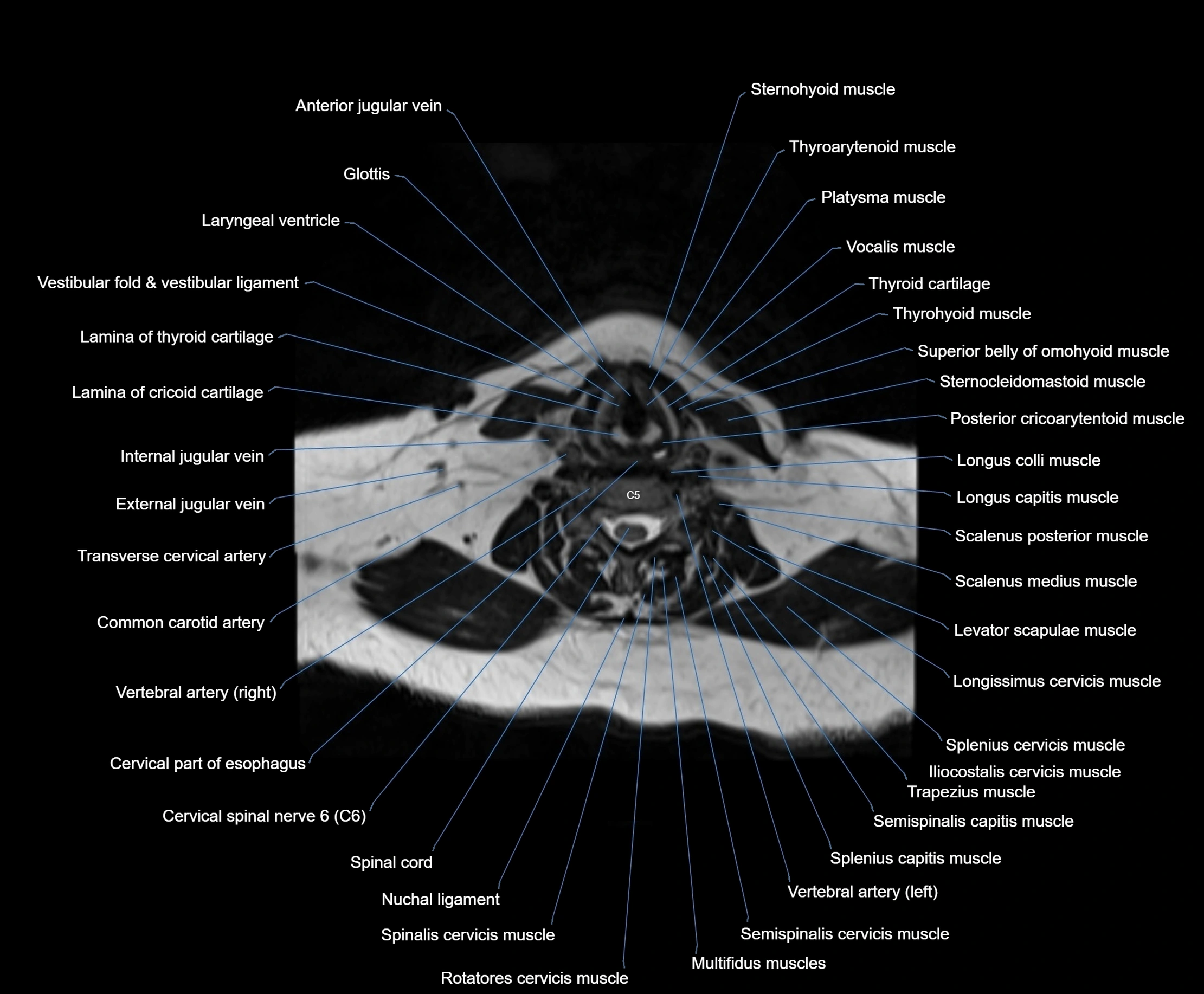
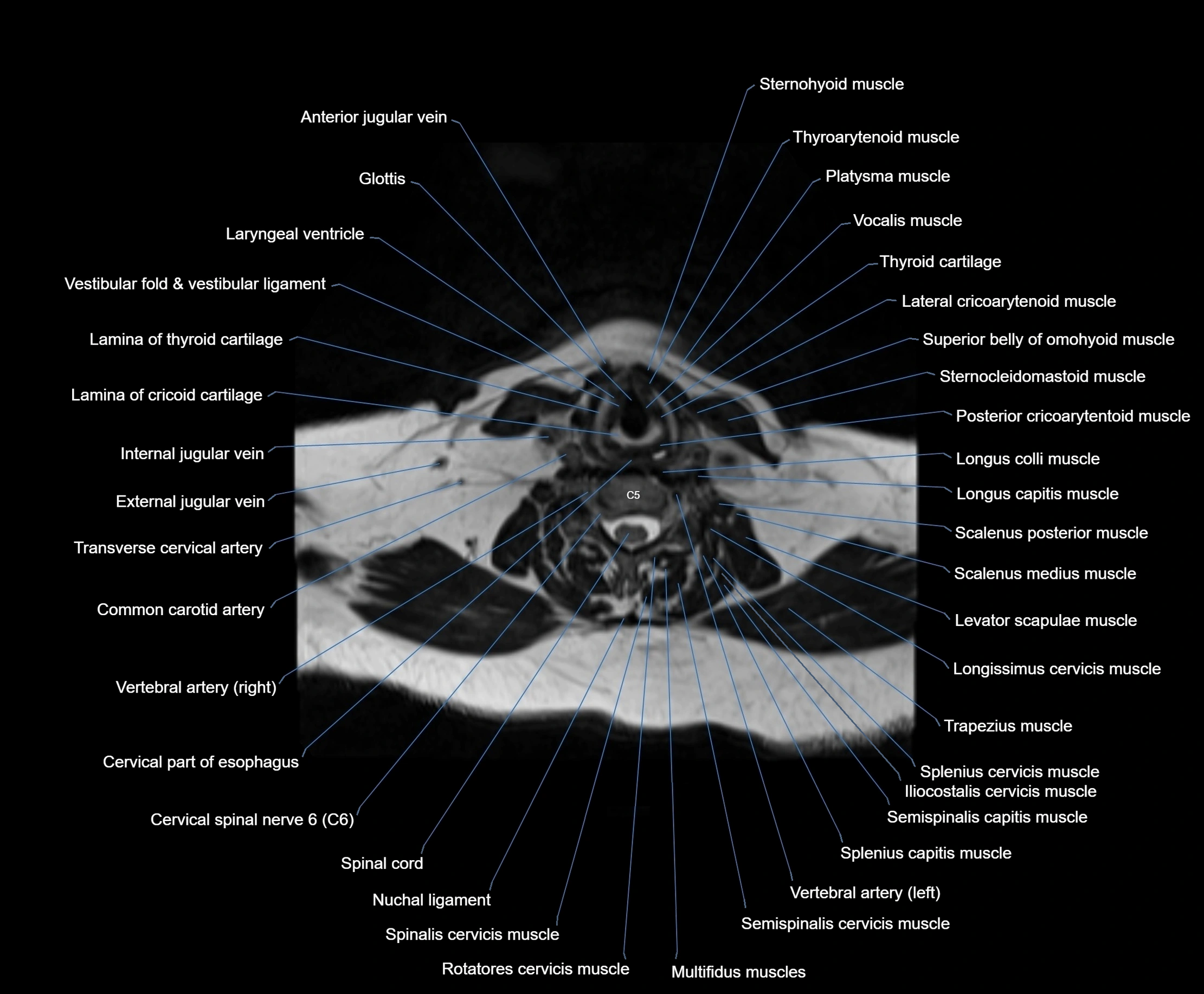
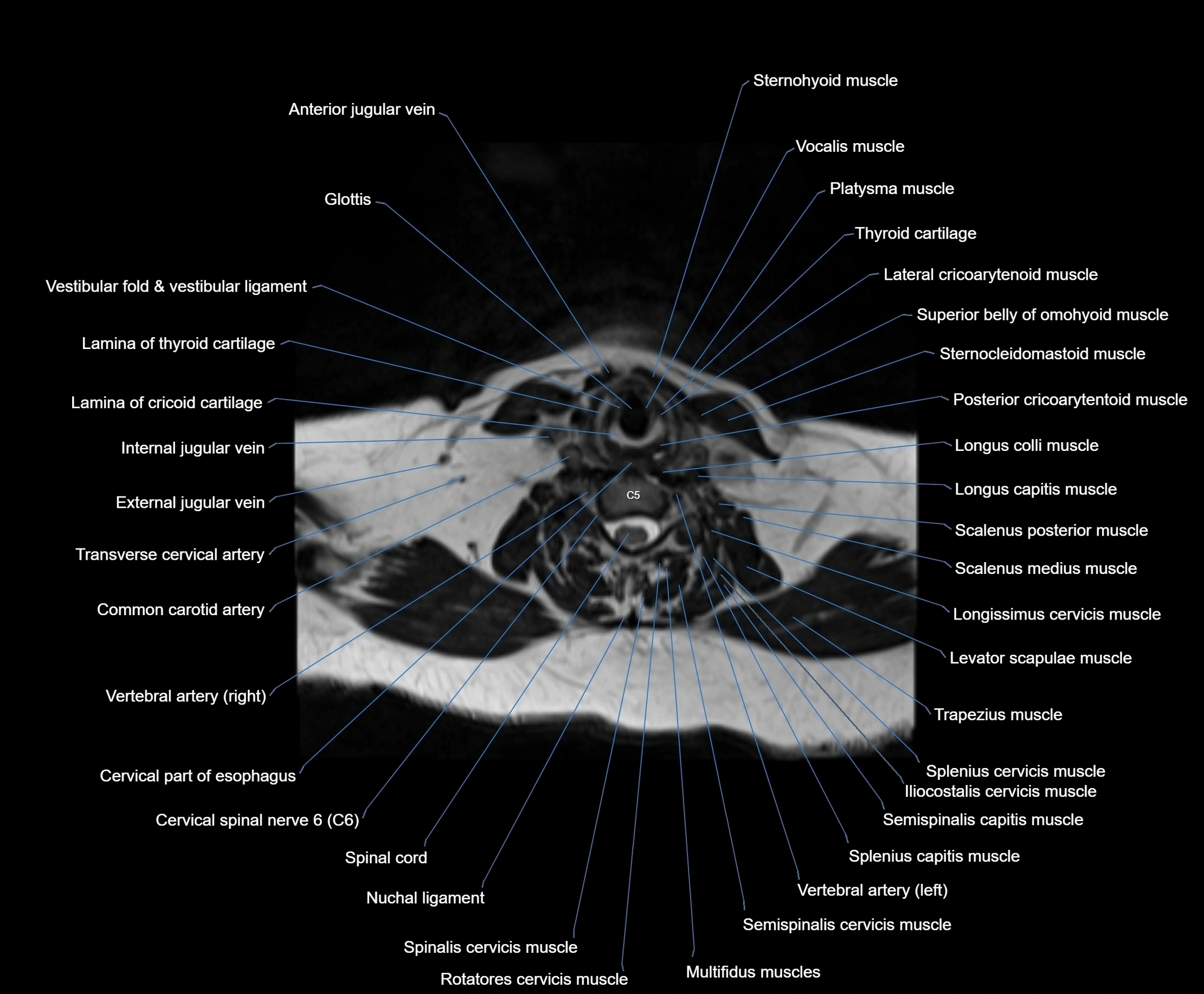
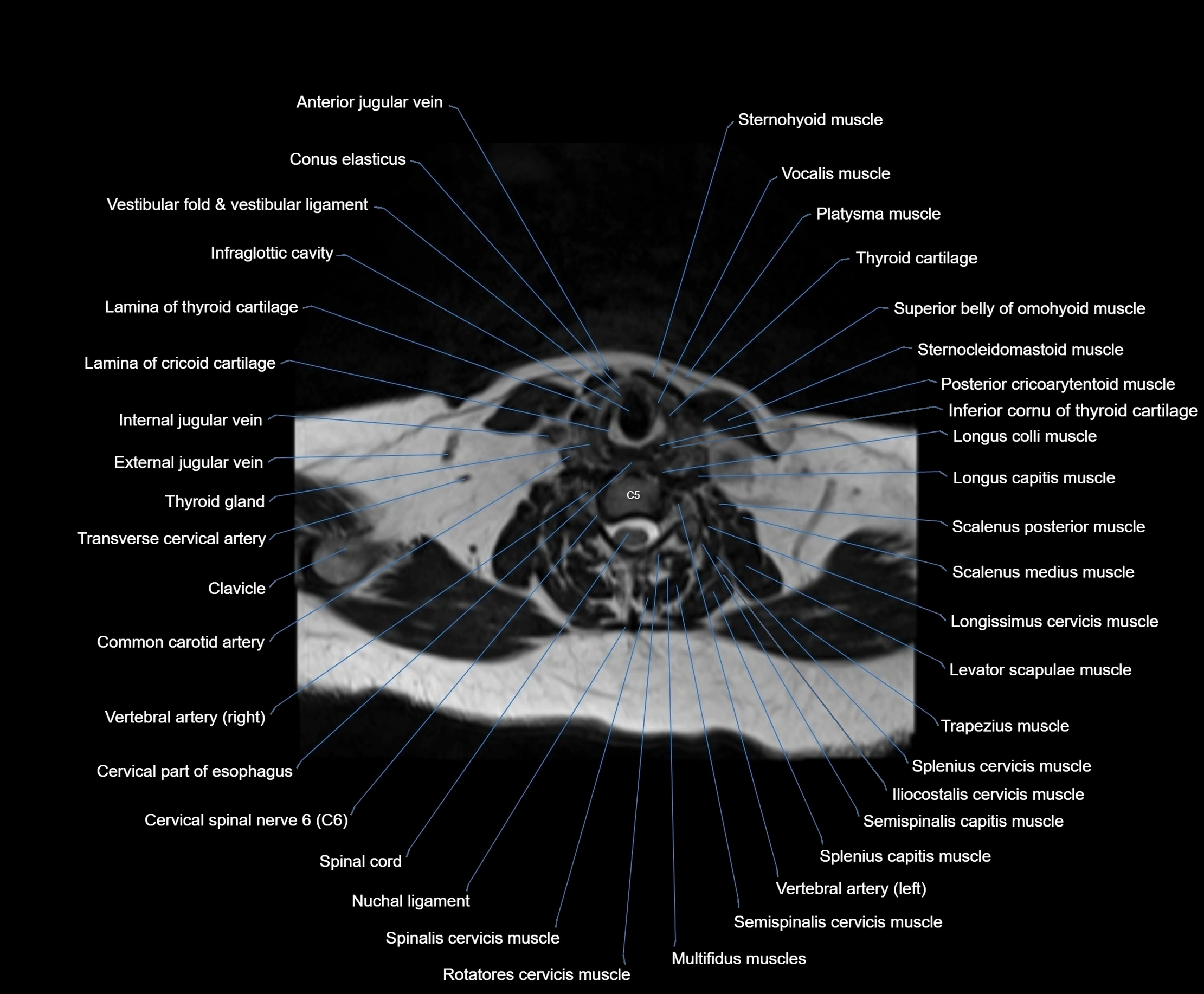
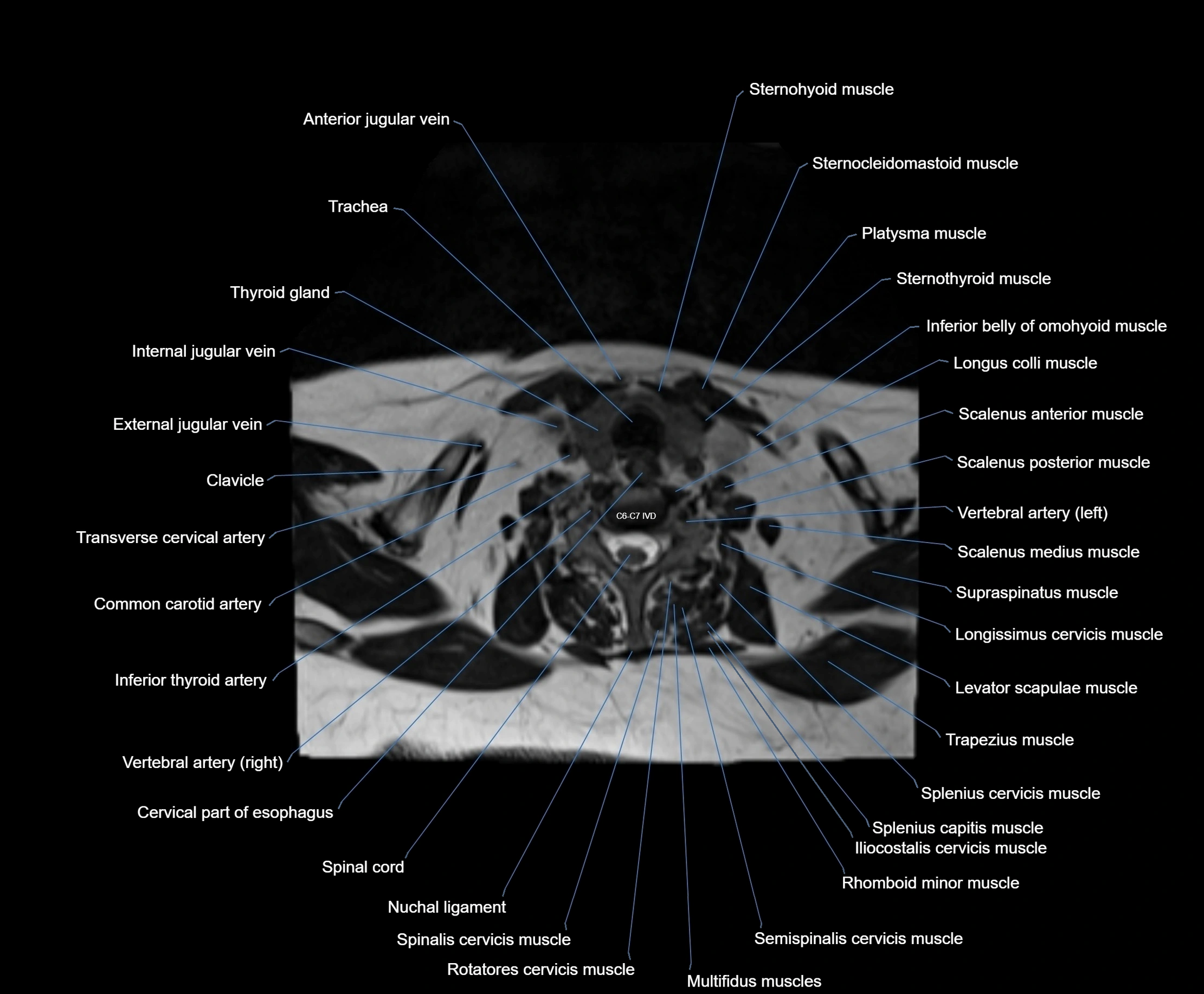
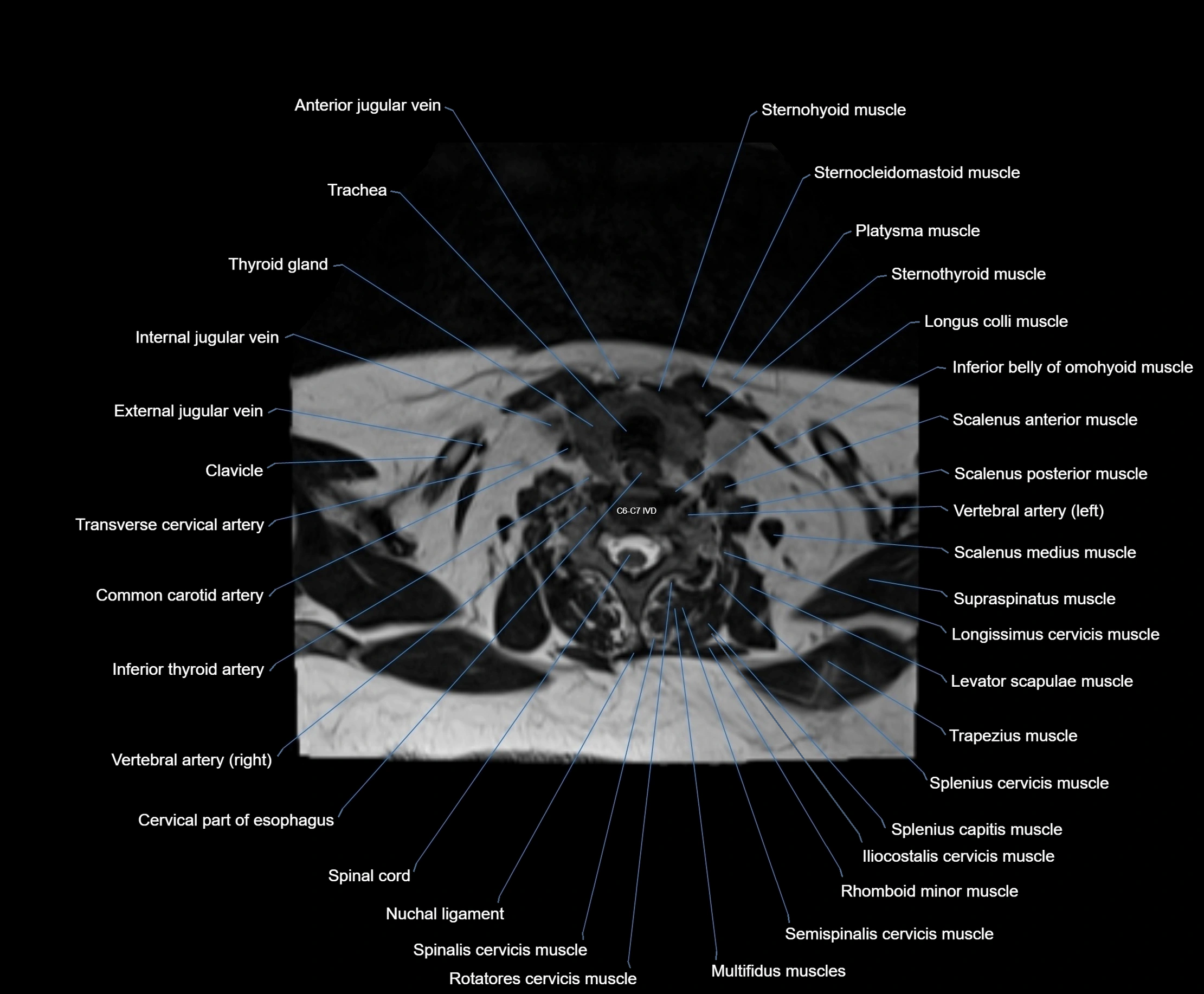
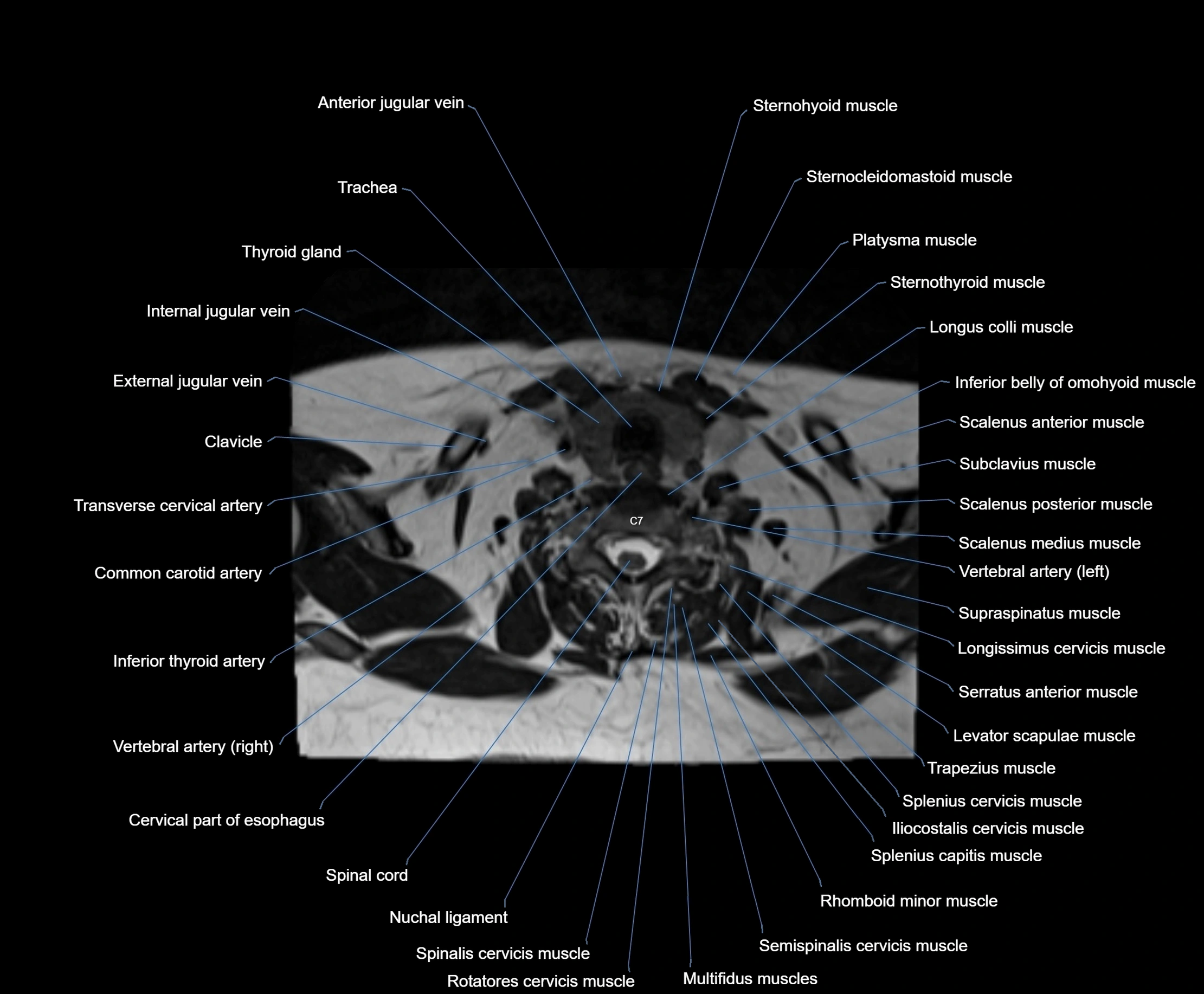
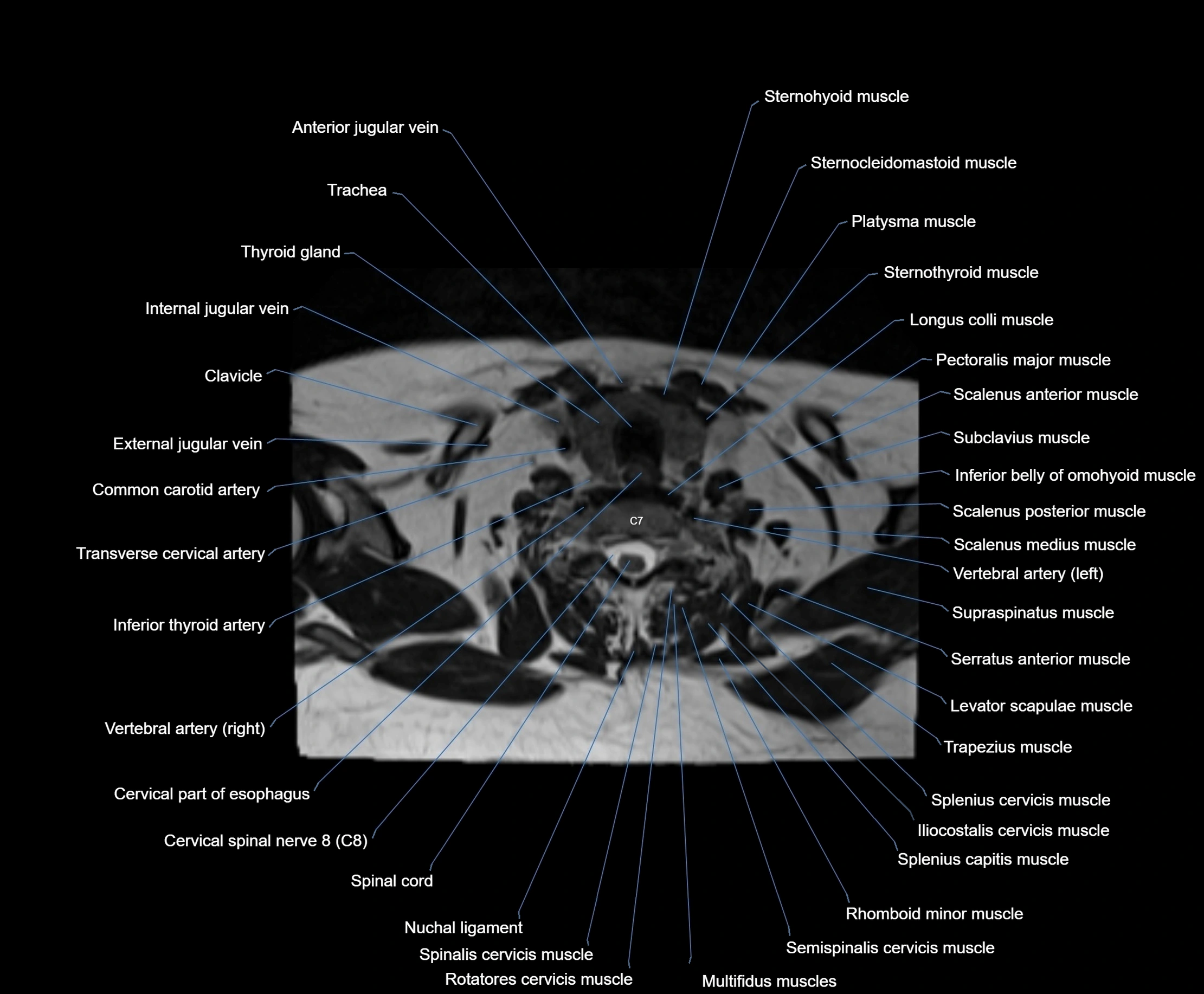
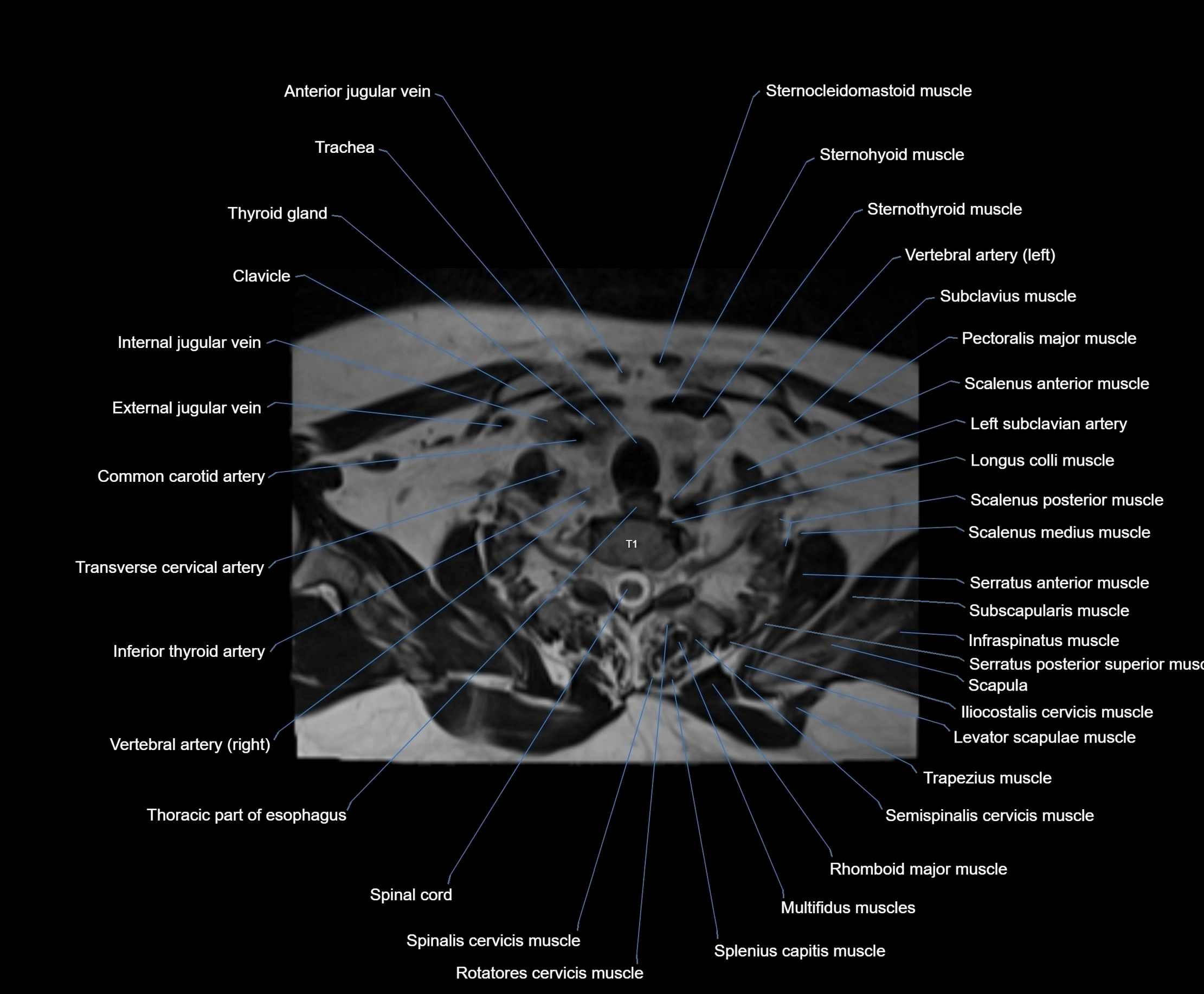
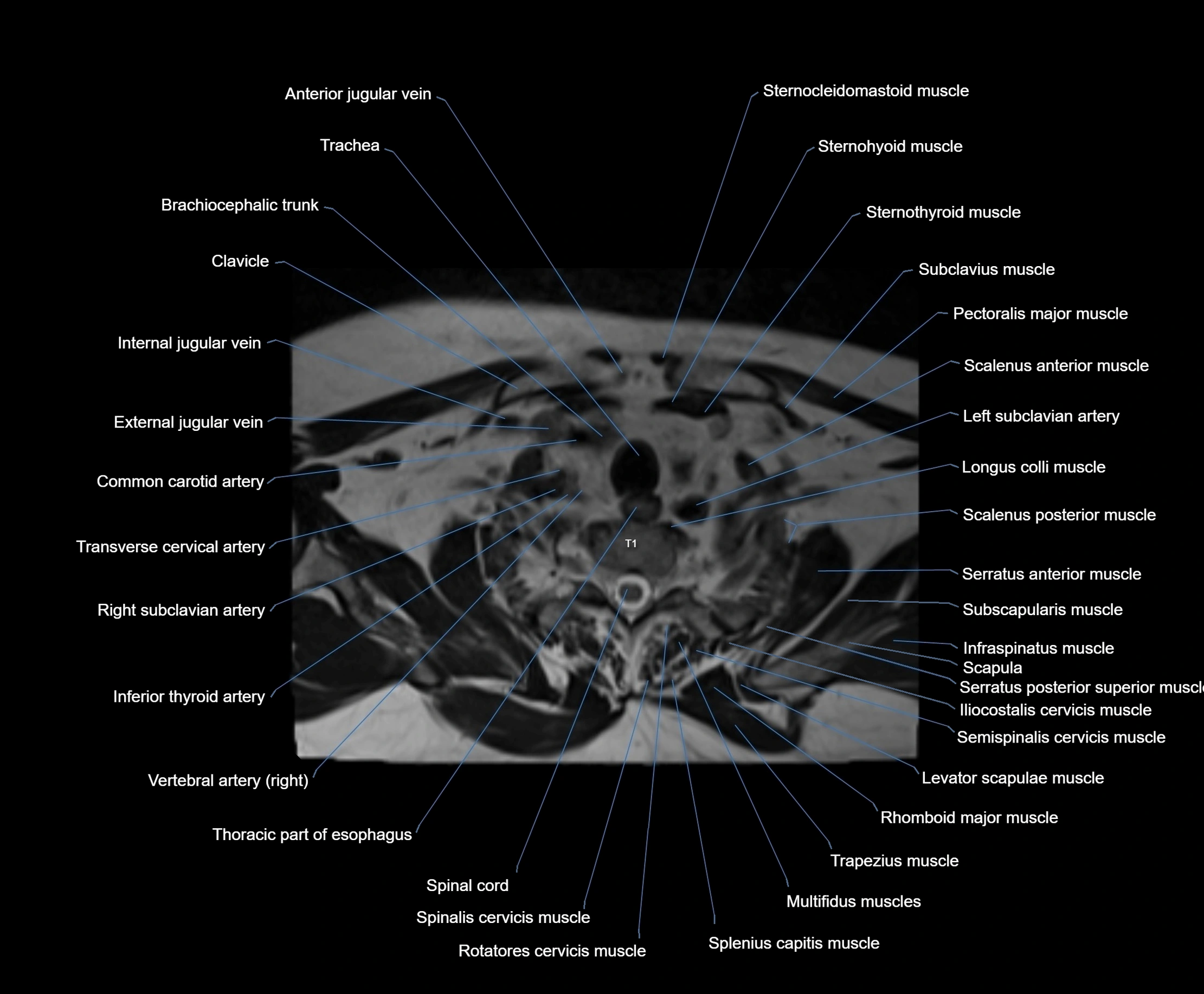
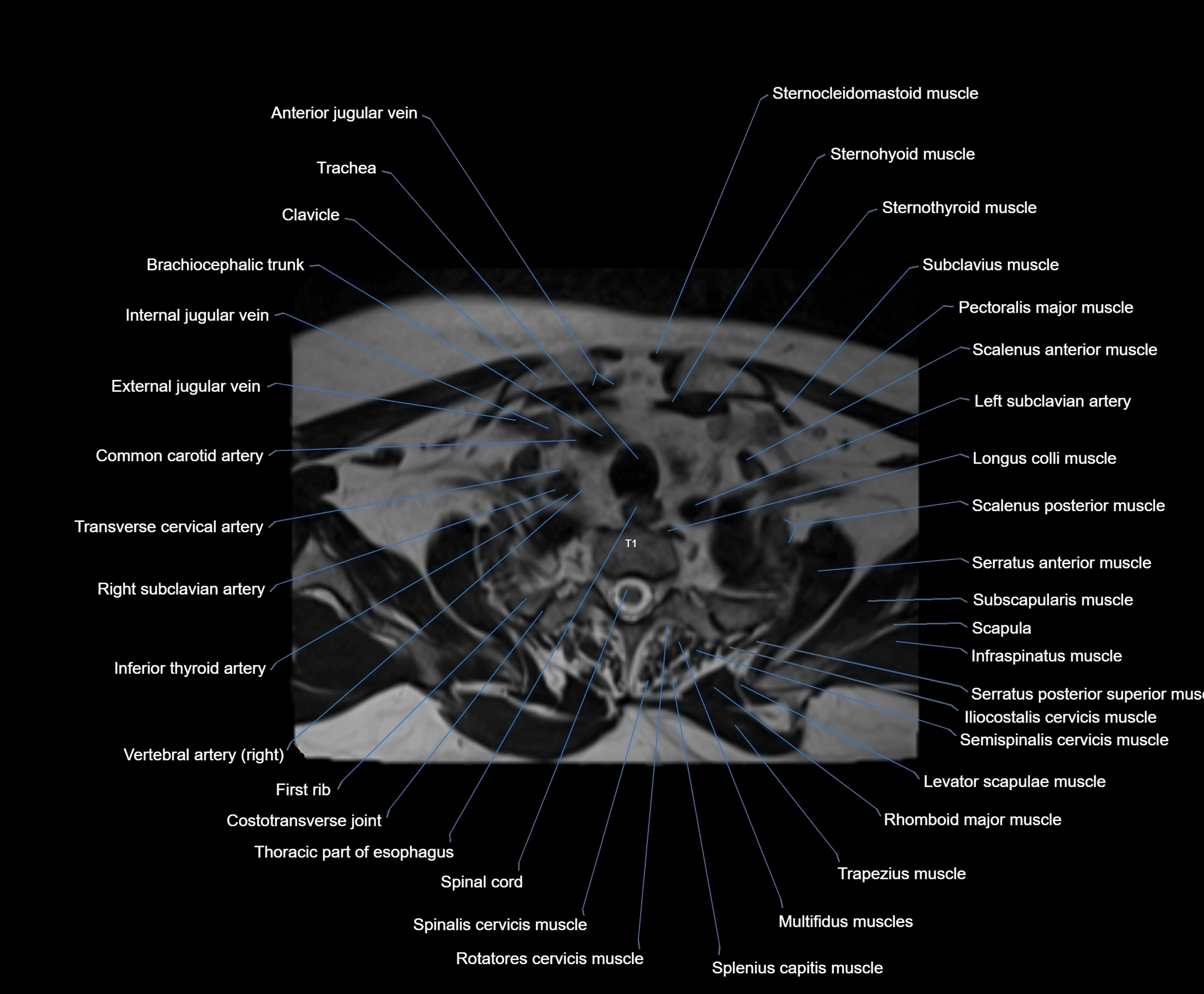
- Anterior jugular vein
- Anterior longitudinal ligament
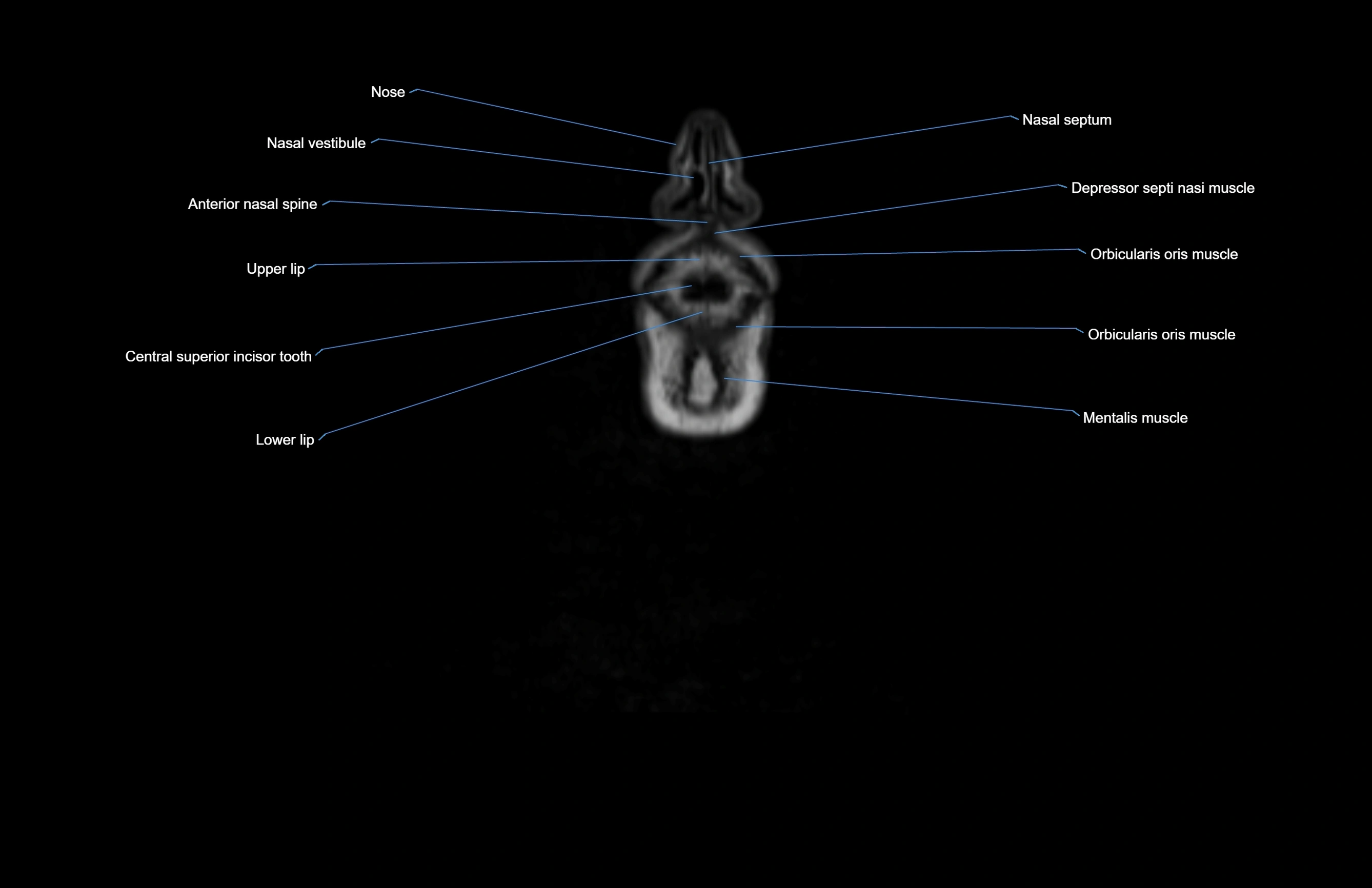
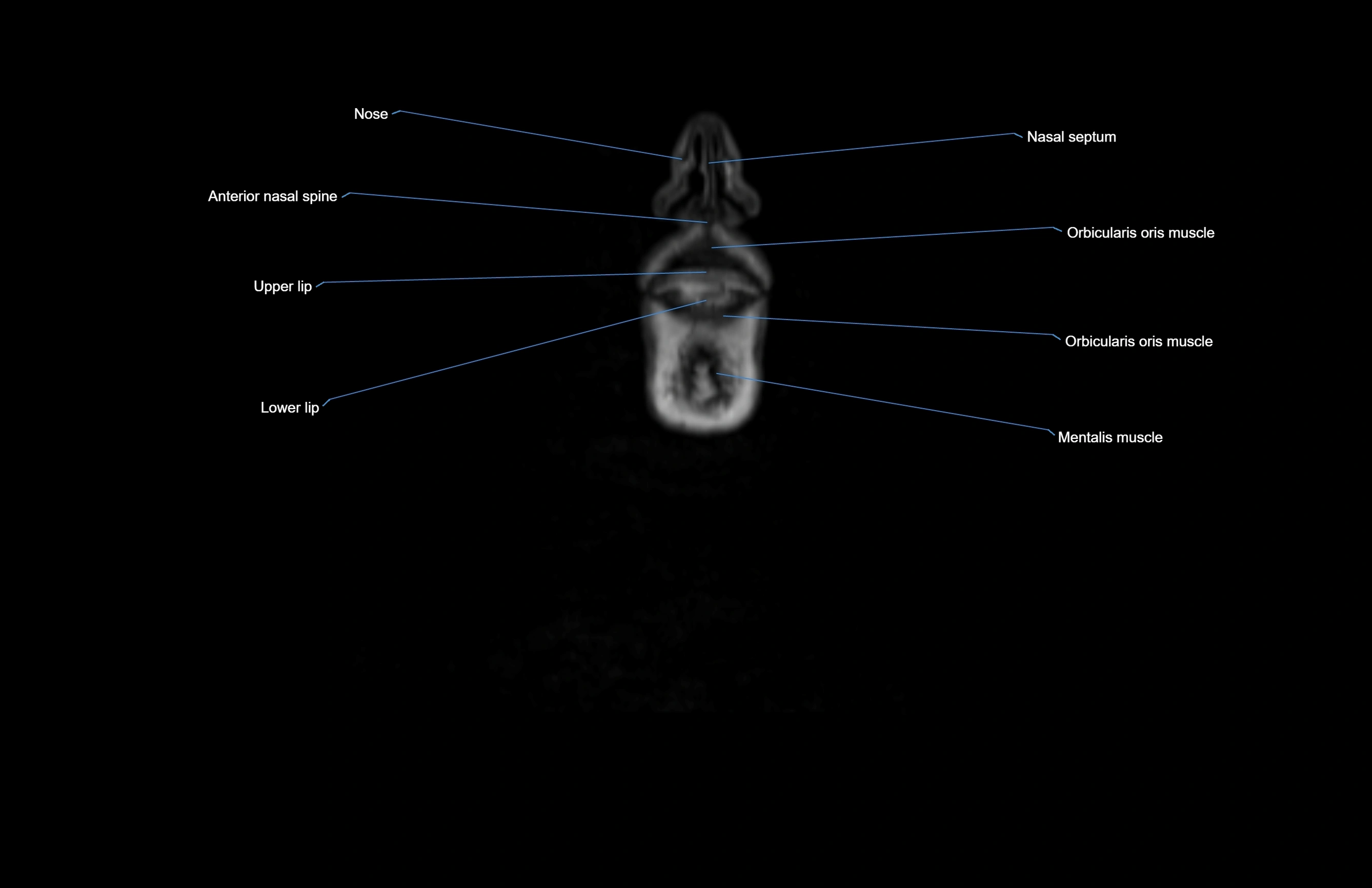
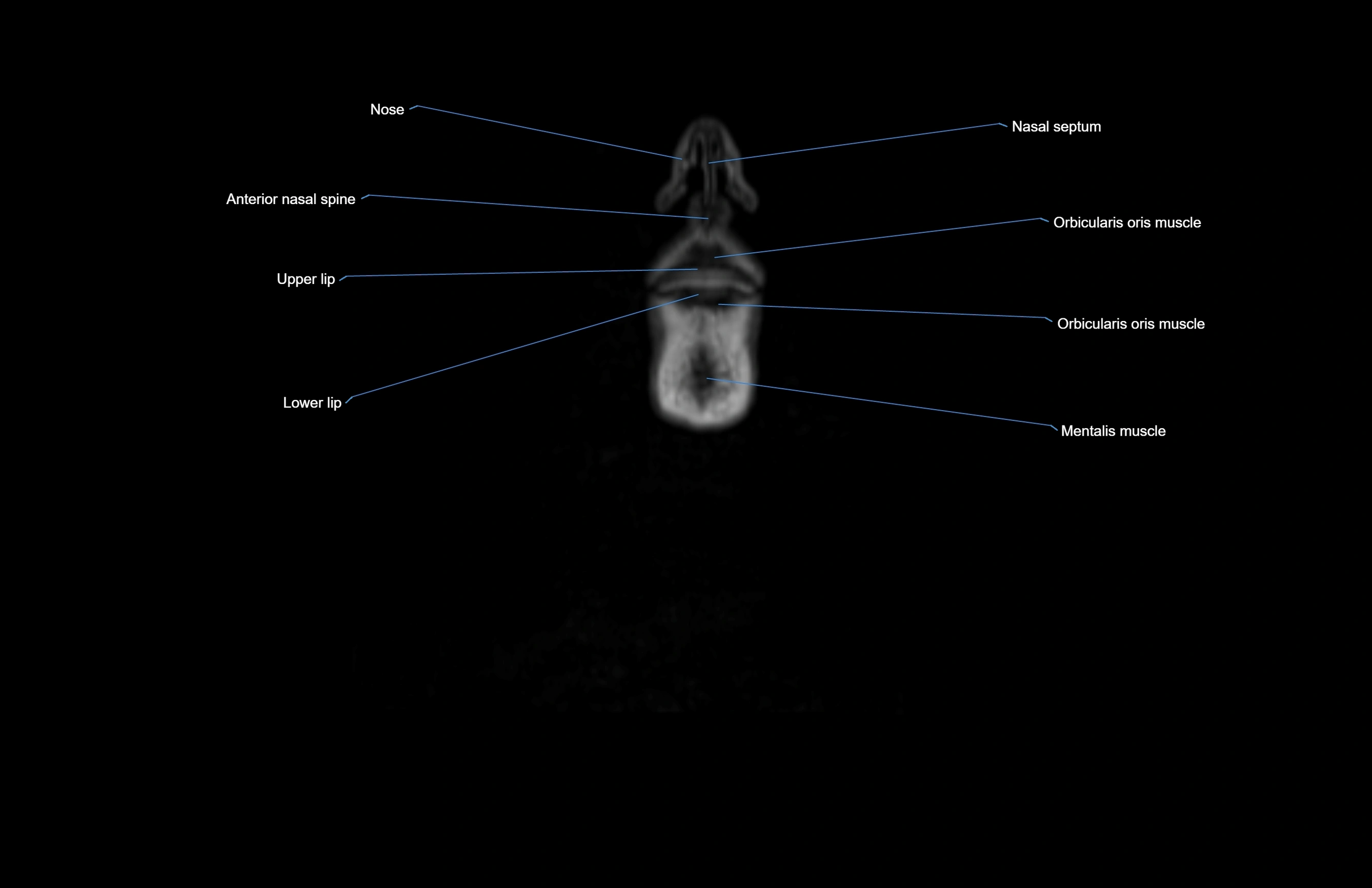
- Anterior nasal spine
- Anterior quadrangular lobule
- Anterior superior alveolar nerve
- Anterior tubercle of atlas
- Anulus fibrosus of intervertebral disc
- Apex of nose
- Arbor Vitae (Cerebellar White Matter)
- Arch of cricoid cartilage
- Articular capsule of temporomandibular joint
- Articular disc of temporomandibular joint
- Articular eminence
- Articular surface of mandibular fossa
- Articular tubercle
- Aryepiglottic fold
- Arytenoid cartilage
- Ascending pharyngeal artery
- Atlantooccipital joint
- Attachment of inferior head of lateral pterygoid muscle
- Attachment of superior head of lateral pterygoid muscle
- Auditory tube
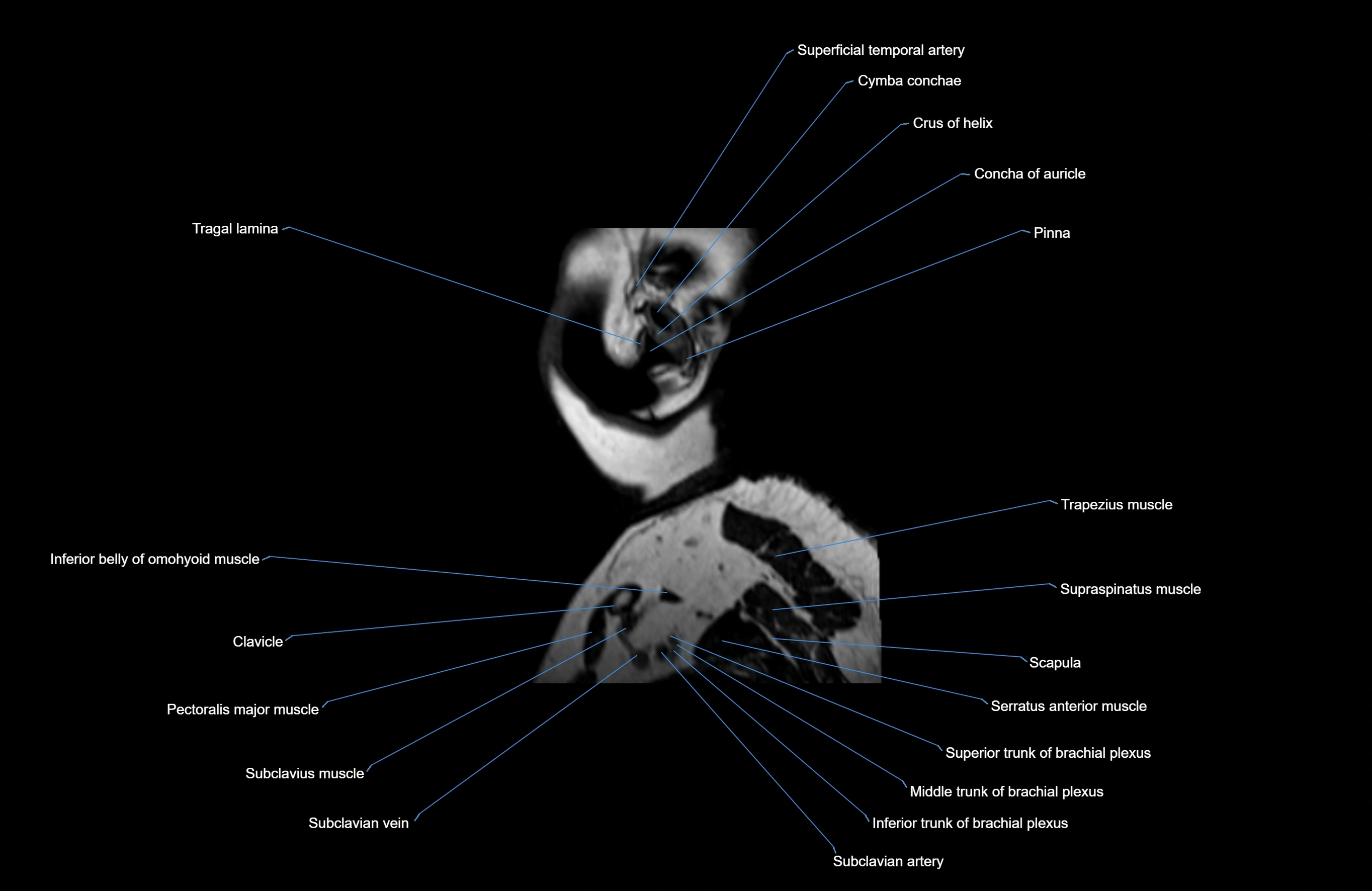
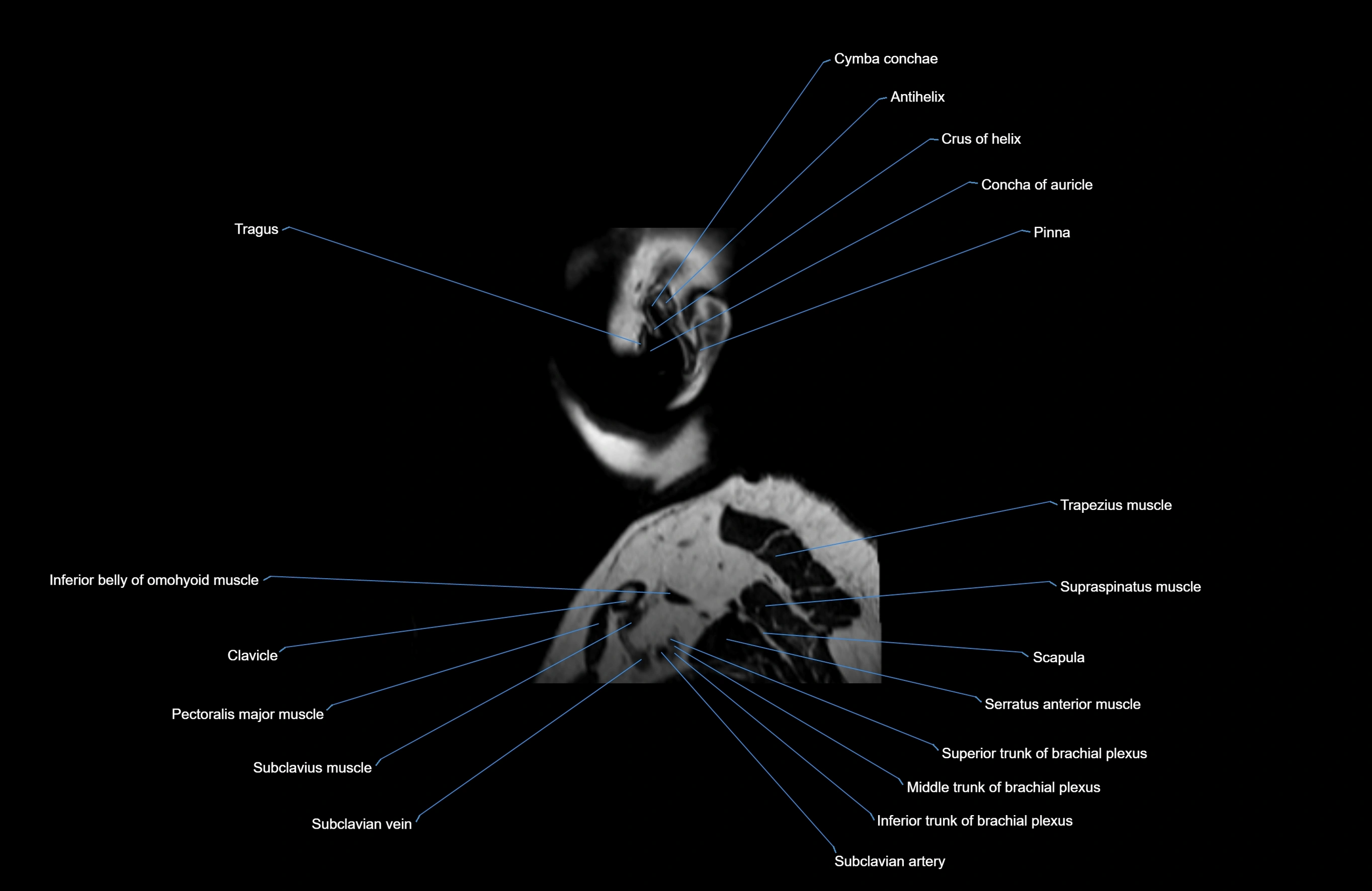
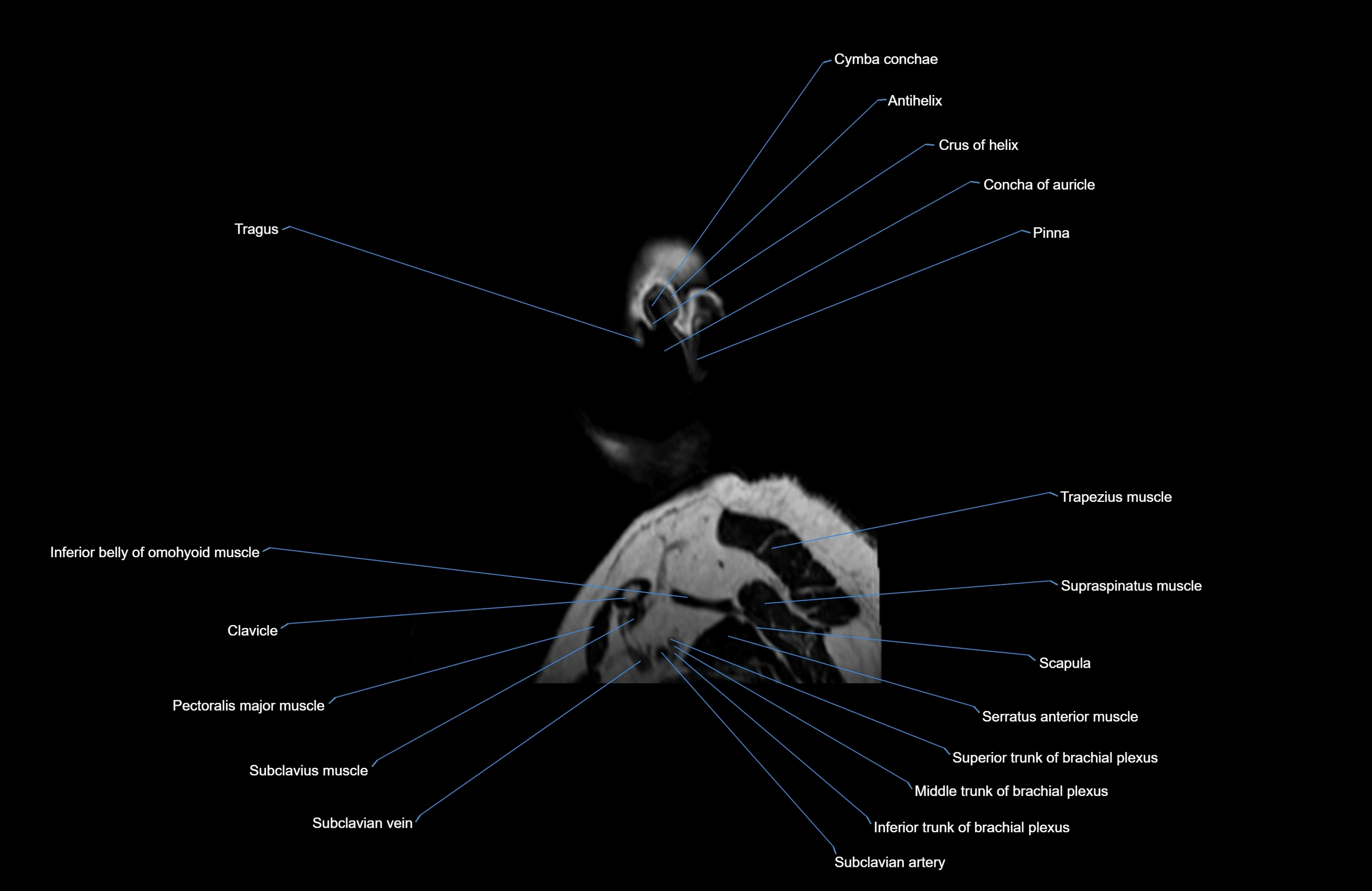
- Auricle (Pinna)
- Auricularis anterior muscle
- Auricularis posterior muscle
- Auriculotemporal nerve
- Axillary artery
- Axillary lymph nodes
- Axillary veins
- Axis (C2 vertebra)
- Basivertebral veins
- Body of hyoid bone
- Body of mandible
- Body of rib
- Body of sternum
- Body of tongue
- Body of vertebra
- Bony nasal septum
- Brachial plexus
- Brachial veins
- Brachiocephalic trunk
- Buccinator lymph nodes
- Buccinator muscle
- Buccopharyngeal fascia
- C3–C4 intervertebral disc
- Carotid bifurcation
- Carotid canal
- Cartilaginous part of nasal septum
- Central inferior incisor tooth
- Central lobule
- Central superior incisor tooth
- Cerebellar commissure
- Cerebellar tentorium
- Cerebellopontine angle
- Cerebellopontine cistern
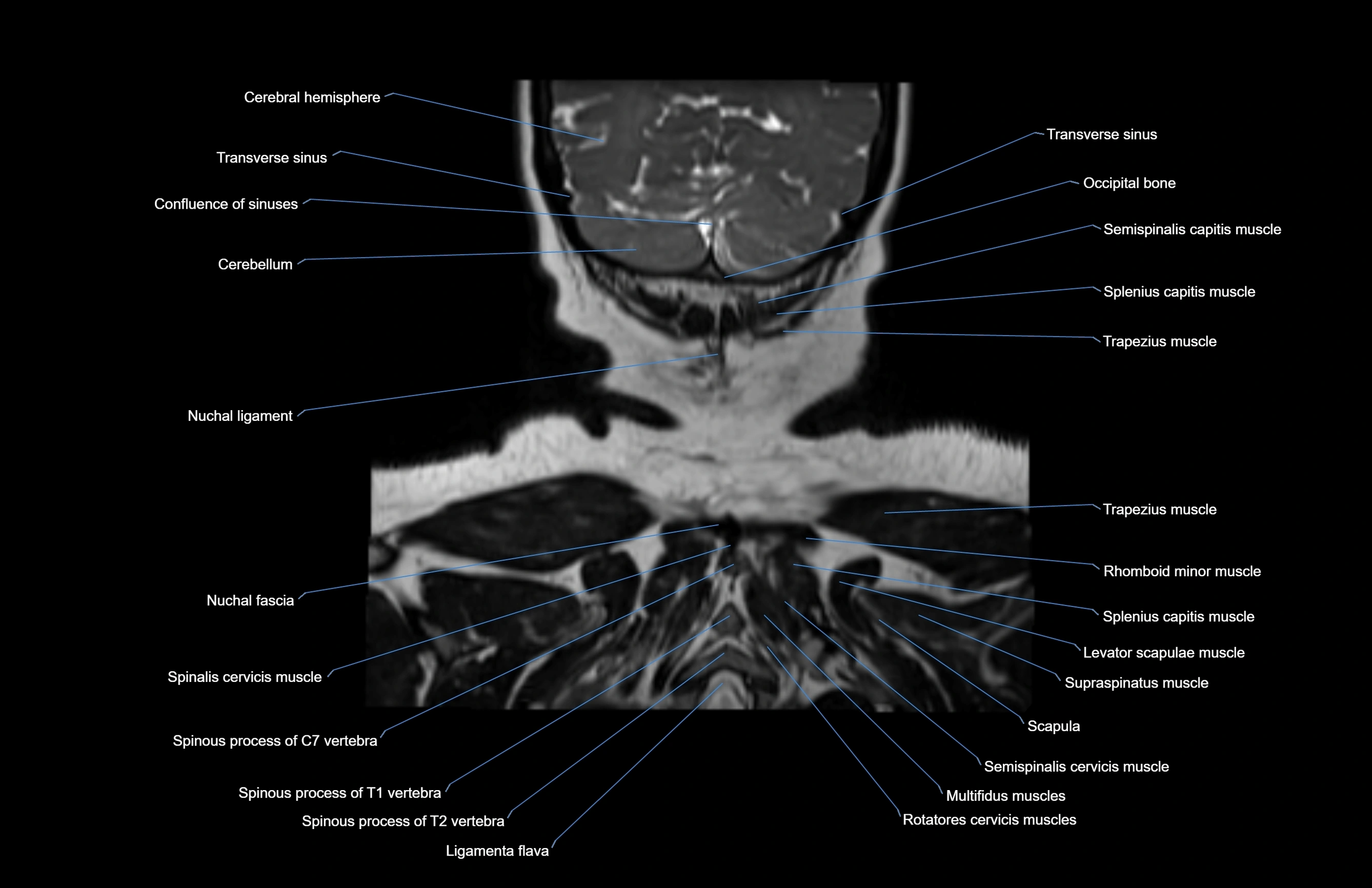
- Cerebellum
- Cerebral aqueduct
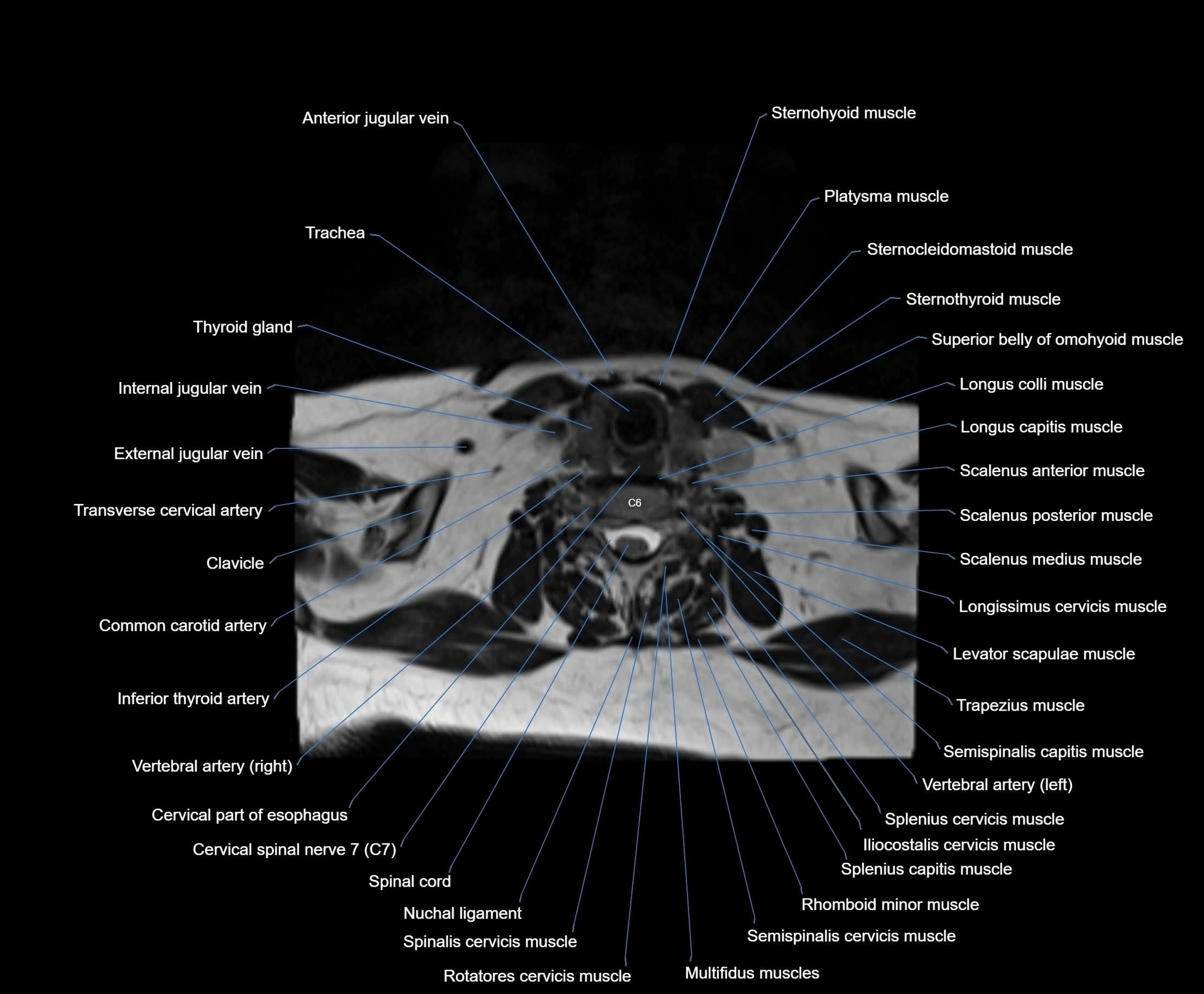
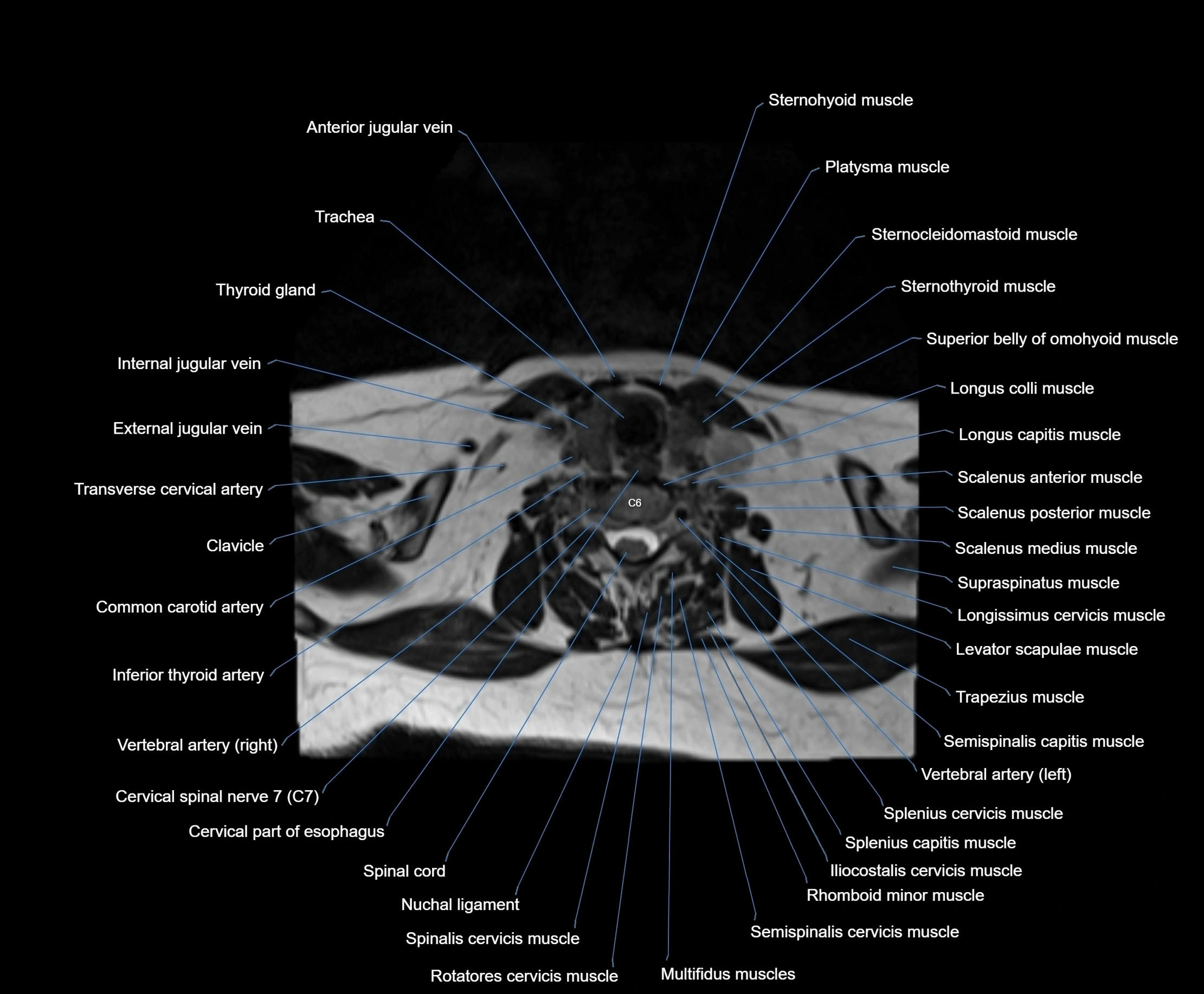
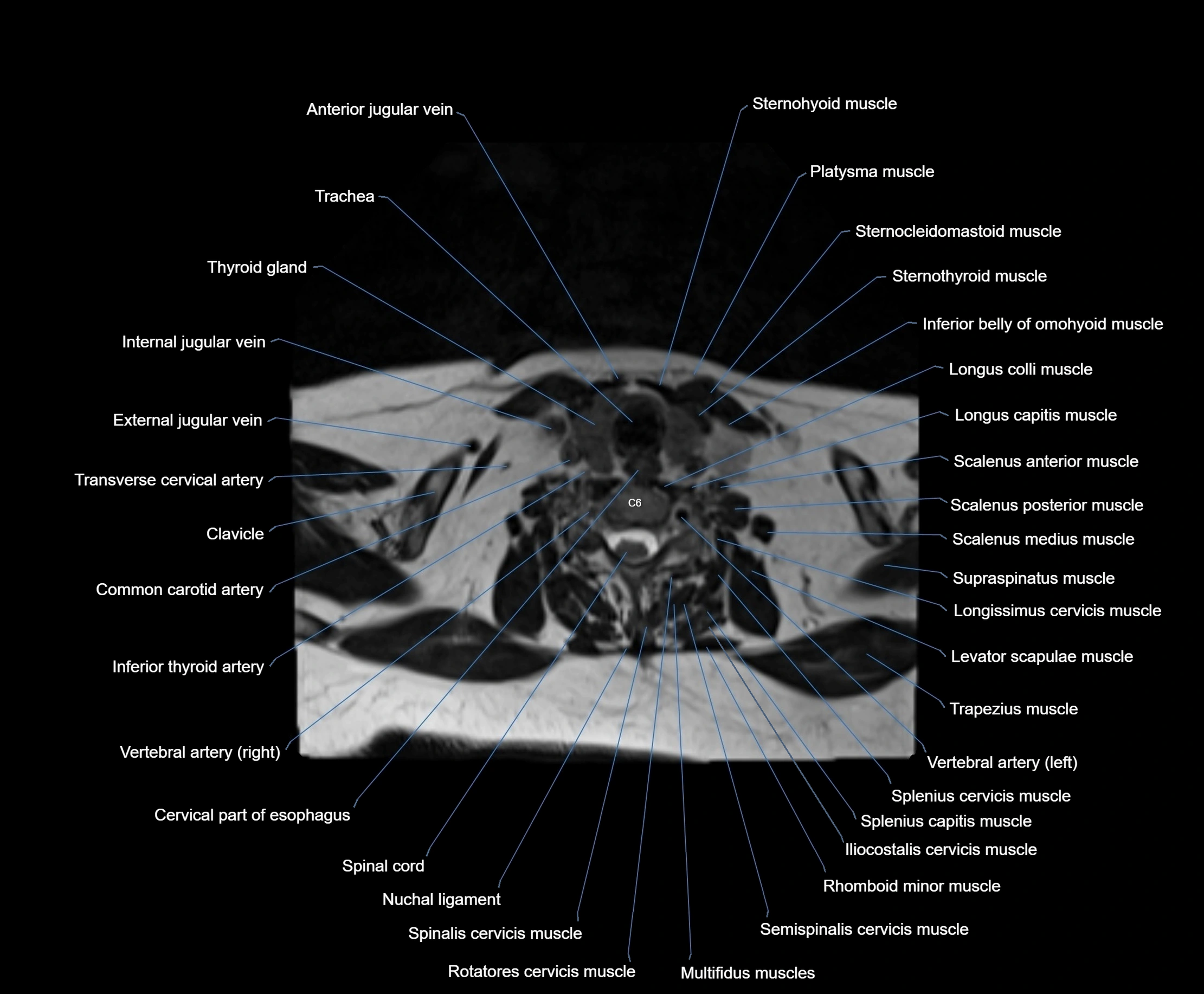
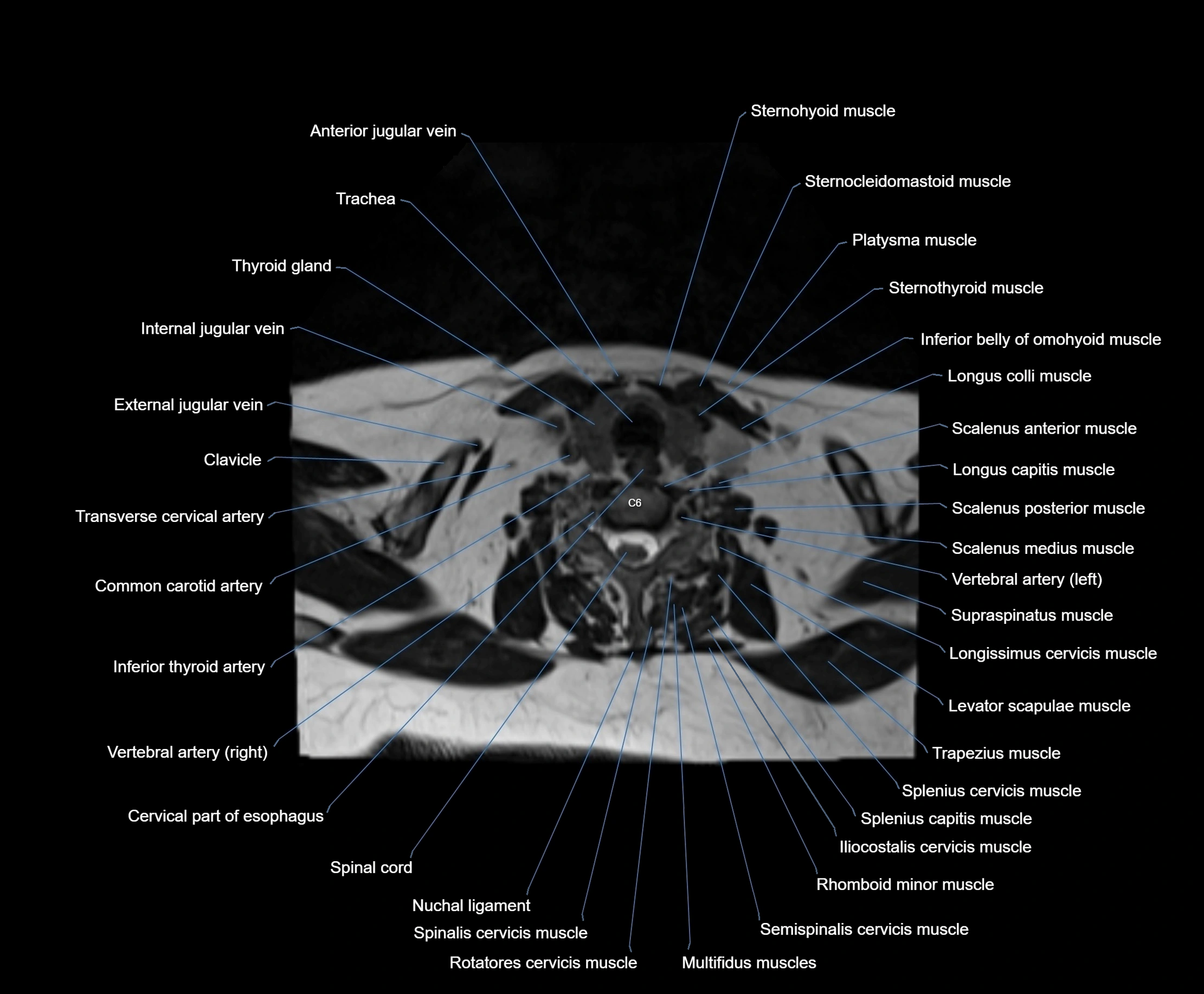
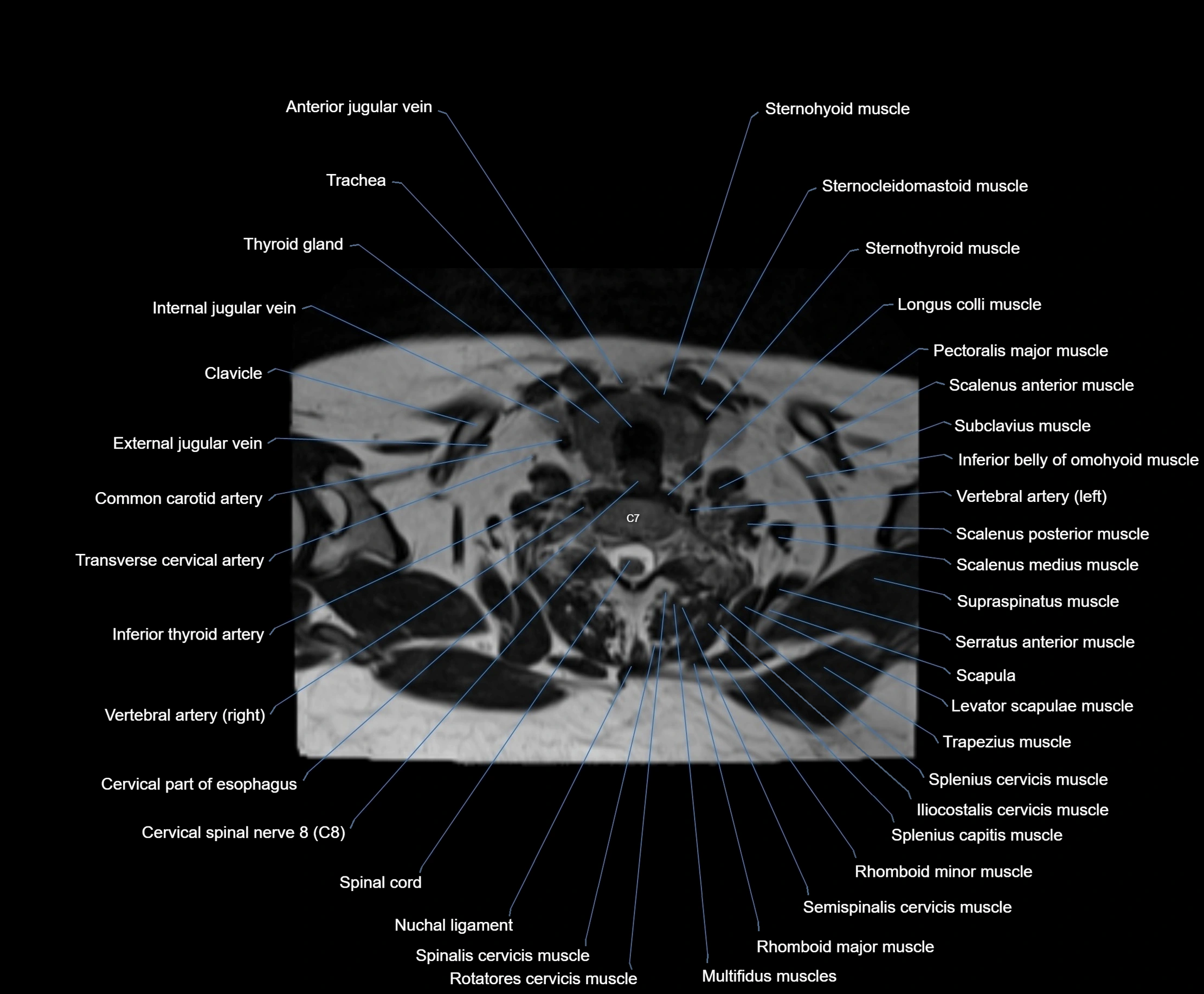
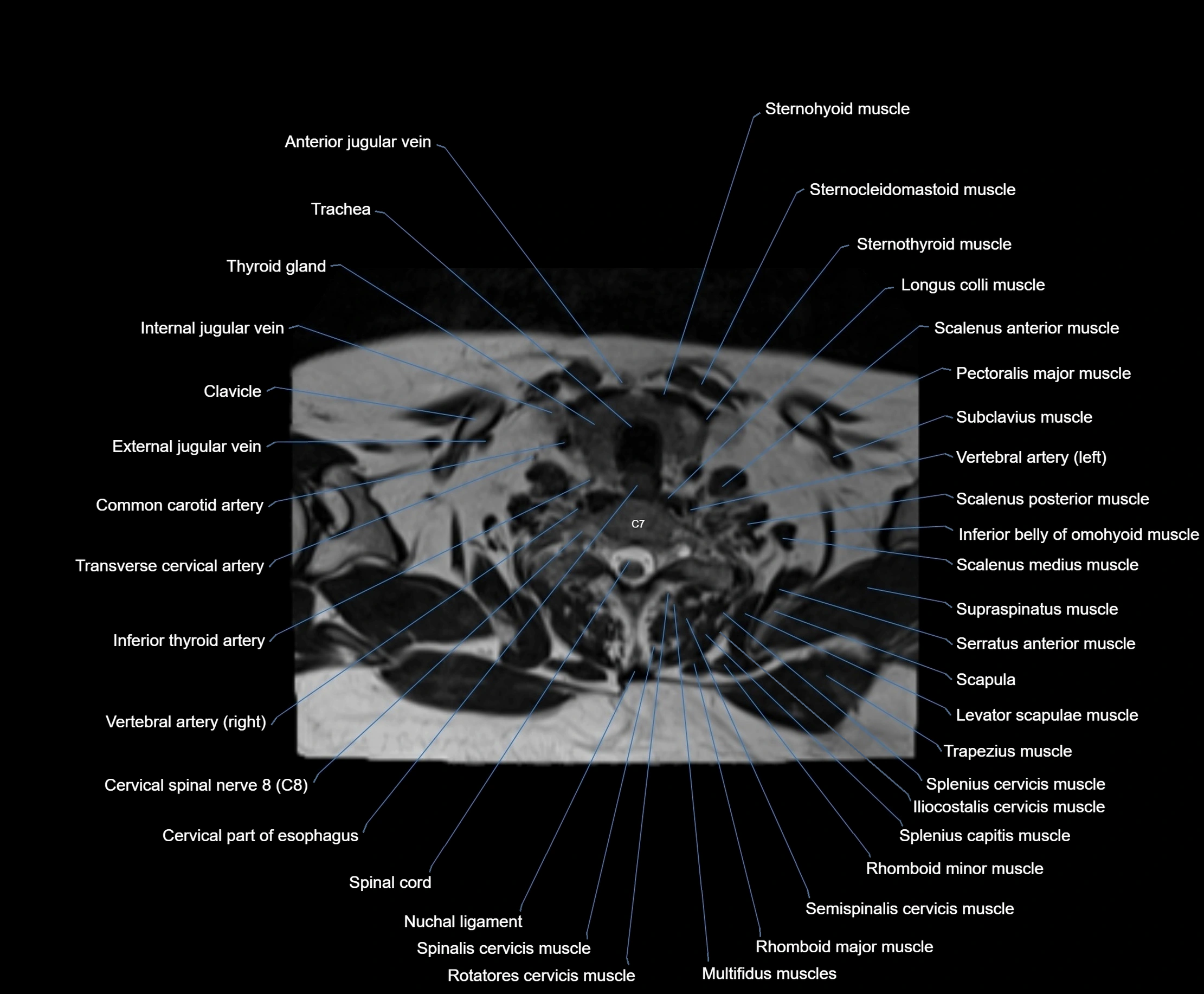
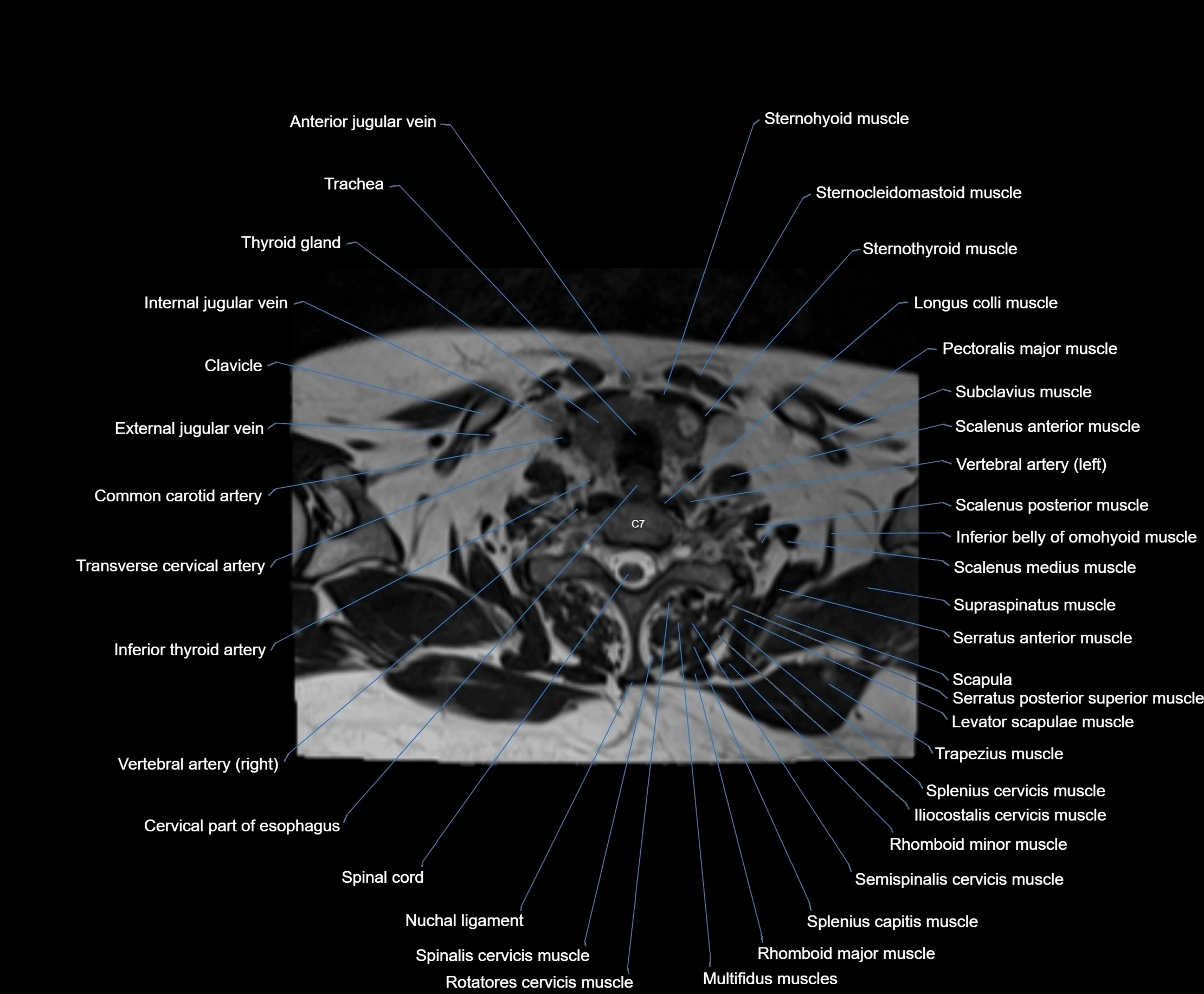
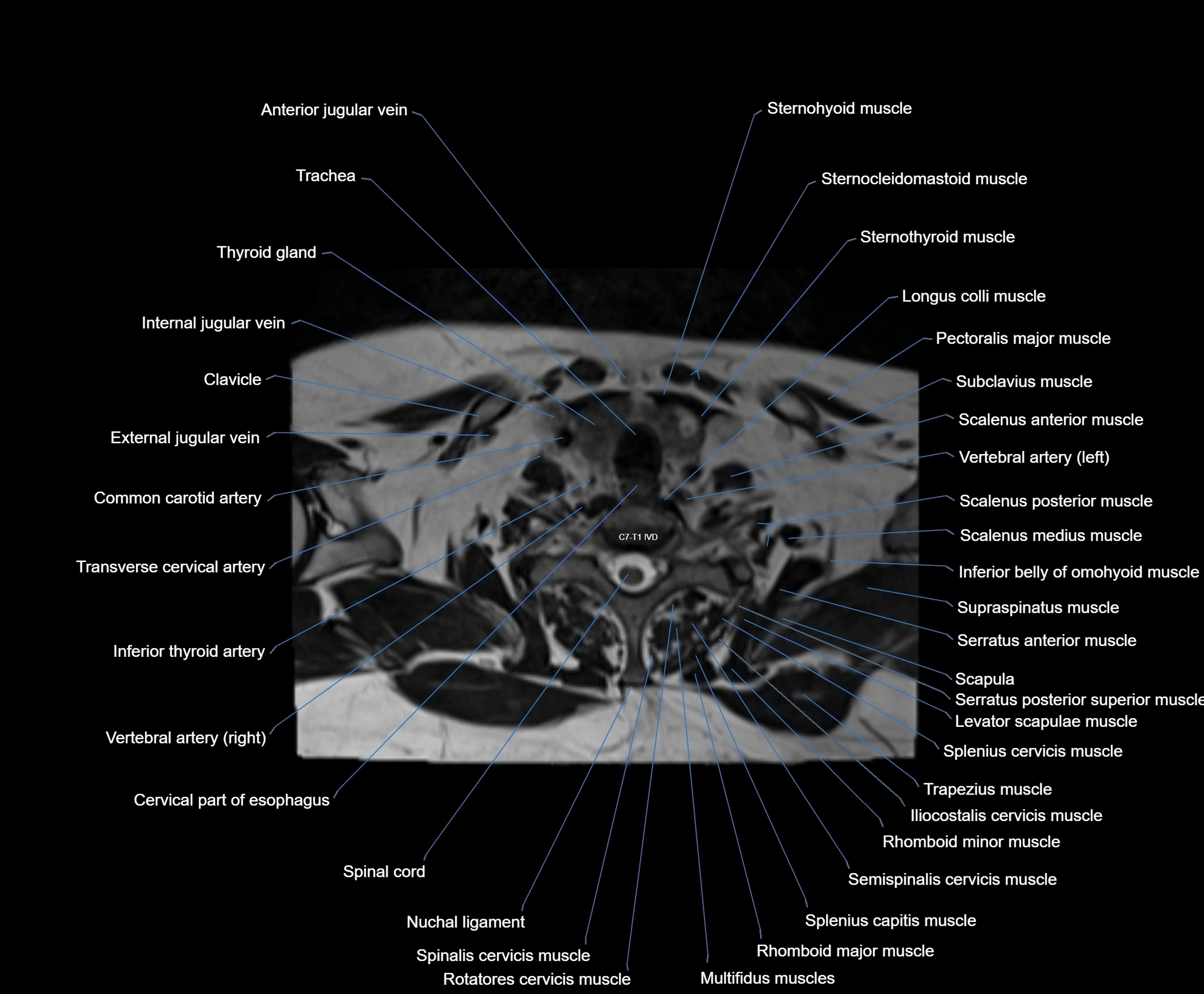
- Cervical part of esophagus
- Cervical spinal nerve 1 (C1)
- Cervical spinal nerve 2 (C2)
- Cervical spinal nerve 3 (C3)
- Cervical spinal nerve 4 (C4)
- Cervical spinal nerve 5 (C5)
- Cervical spinal nerve 6 (C6)
- Cervical spinal nerve 7 (C7)
- Cervical spinal nerve 8 (C8)
- Choana
- Choroid
- Choroid fissure
- Circumflex scapular artery
- Cisterna magna
- Clavicle
- Clavicular notch
- Clivus
- Cochlea
- Cochlear nerve (Cranial nerve VIII)
- Collateral trigone
- Common carotid artery
- Common nasal meatus
- Common tendinous ring (Annulus of zinn)
- Condylar canal
- Conus elasticus
- Cornea
- Coronoid process of mandible
- Costal notches
- Costochondral joints
- Costotransverse joint
- Costotransverse ligament
- Costovertebral joint
- Cribriform plate
- Cricoid cartilage
- Cricothyroid muscle
- Crista galli
- Cruciate ligament of the atlas
- Crus helix of ear
- Culmen
- Declive
- Deep parotid lymph nodes
- Deep part of masseter muscle
- Dens of axis
- Dental branches of inferior alveolar artery, vein, & nerve
- Dental pulp of upper molar tooth
- Dental pulp of upper premolar tooth
- Dental pulp of lower molar tooth
- Dentate nucleus
- Depressor anguli oris muscle
- Depressor labii inferioris muscle
- Depressor septi nasi muscle
- Dorsal root of spinal nerve
- Dorsal scapular artery
- Dorsal scapular vein
- Dorsum of nose
- Dorsum of tongue
- Enamel of lower molar tooth
- Enamel of upper molar tooth
- Enamel of canines tooth
- Enamel of lower incisor tooth
- Enamel of lower canines tooth
- Enamel of lower premolar tooth
- Enamel of upper incisor tooth
- Epiglottic vallecula
- Epiglottis
- Ethmoid sinus
- Ethmoidal air cells
- Exit foramina
- External acoustic meatus
- External carotid artery
- External jugular vein
- External occipital protuberance
- Eyeball
- Facet joint of vertebra (Zygapophyseal joints)
- Facial Nerve (Cranial nerve VII)
- Facial artery
- Facial vein
- First rib
- Flocculonodular lobe
- Folium of Vermis
- Foramen cecum of tongue
- Foramen ovale
- Foramen spinosum
- Frontal bone
- Frontal nerve
- Frontal process (zygomatic bone)
- Frontal process of zygomatic bone
- Frontal sinus
- Frontonasal suture
- Genioglossus muscle
- Glenoid process of parotid gland
- Glossopharyngeal nerve (Cranial nerve IX)
- Glottis
- Greater alar cartilage
- Greater horn of hyoid bone
- Greater wing of sphenoid bone
- Gum (gingiva)
- Hard palate
- Head of rib
- Horizontal fissure (cerebellum)
- Hyoepiglottic ligament
- Hyoglossus
- Hyoglossus muscle
- Hyoid bone
- Hypoglossal Nerve (Cranial nerve XII)
- Iliocostalis cervicis muscle
- Incisive duct
- Inferior alveolar foramen (mandibular foramen)
- Inferior alveolar nerve
- Inferior articular process of vertebra
- Inferior belly of omohyoid muscle
- Inferior branch vestibular nerve
- Inferior canine tooth
- Inferior cerebellar peduncle
- Inferior cerebellar veins
- Inferior constrictor muscle of pharynx
- Inferior cornu of thyroid cartilage
- Inferior deep cervical lymph nodes
- Inferior eyelid
- Inferior first premolar tooth
- Inferior head of lateral pterygoid muscle
- Inferior longitudinal lingual muscle
- Inferior longitudinal muscle of tongue
- Inferior nasal concha
- Inferior nasal meatus
- Inferior oblique muscle
- Inferior ophthalmic vein
- Inferior orbital fissure
- Inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscle
- Inferior rectus muscle
- Inferior salivatory nucleus
- Inferior second molar tooth
- Inferior second premolar tooth
- Inferior semilunar lobule
- Inferior tarsus
- Inferior third molar tooth
- Inferior thyroid artery
- Inferior thyroid vein
- Inferior vestibular nucleus
- Infraclavicular lymph nodes
- Infraglottic cavity
- Infraorbital nerve
- Intercostal muscles
- Intercostal space
- Intermediate zone of articular disc
- Internal carotid artery
- Internal carotid artery (cavernous part)
- Internal carotid artery (cervical part)
- Internal carotid artery (petrous part)
- Internal occipital crest
- Internal thoracic artery
- Interspinales muscles
- Interspinous ligament
- Intervertebral Disc
- Intervertebral foramen
- Intervertebral foramina
- Intracanalicular part of optic nerve
- Intracranial part of optic nerve
- Intraculminate fissure
- Iris
- Jugular foramen
- Jugular foramen pars vascularis
- Jugular venous arch
- Jugulodigastric lymph nodes
- Lacrimal artery
- Lacrimal bone
- Lacrimal canaliculi
- Lacrimal gland
- Lacrimal nerve
- Lacrimal nucleus
- Lacrimal vein
- Lamina of cricoid cartilage
- Lamina of thyroid cartilage
- Lamina of vertebra
- Laryngeal inlet
- Laryngeal ventricle
- Laryngeal vestibule
- Laryngopharynx
- Lateral aperture of fourth ventricle (foramen of Luschka)
- Lateral atlantoaxial joint
- Lateral canthal ligament
- Lateral cricoarytenoid muscle
- Lateral glossoepiglottic fold
- Lateral inferior incisor tooth
- Lateral mass of atlas
- Lateral nasal cartilage
- Lateral pterygoid muscle
- Lateral rectus muscle
- Lateral superior incisor tooth
- Lateral temporomandibular ligament
- Lateral thoracic artery
- Lateral vestibular nucleus
- Lateral wall of maxillary sinus
- Left Vertebral Artery (Intracranial Part)
- Left brachiocephalic vein
- Left common carotid artery
- Left lobe of liver
- Left lobe of thyroid gland
- Left recurrent laryngeal nerve
- Left subclavian artery
- Left subclavian vein
- Left vertebral artery
- Left vertebral artery (atlantic part)
- Left vertebral artery (cervical part)
- Lesser wing of sphenoid
- Levator anguli oris muscle
- Levator labii superioris alaeque nasi muscle
- Levator labii superioris muscle
- Levator palpebrae superioris muscle
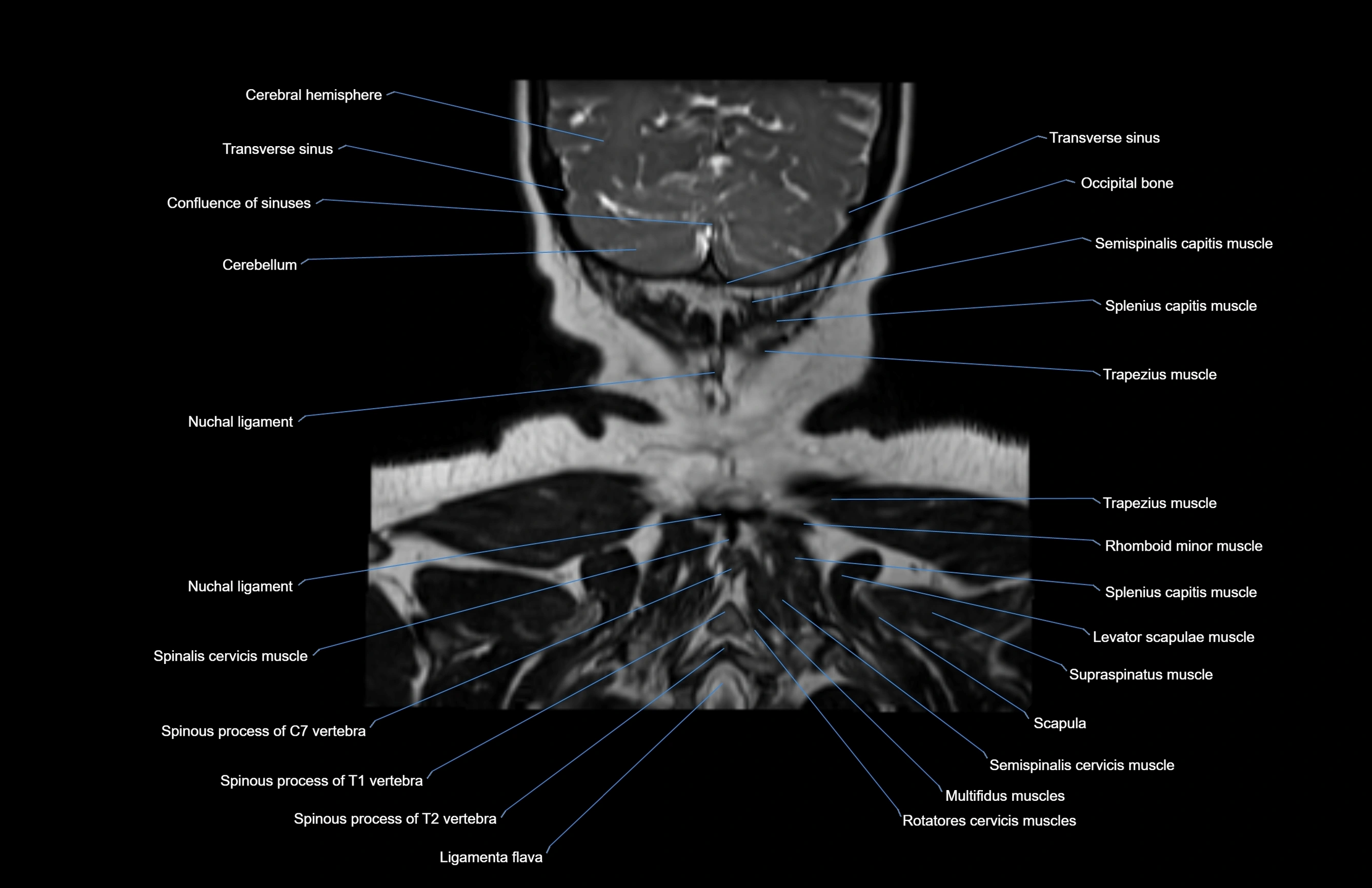
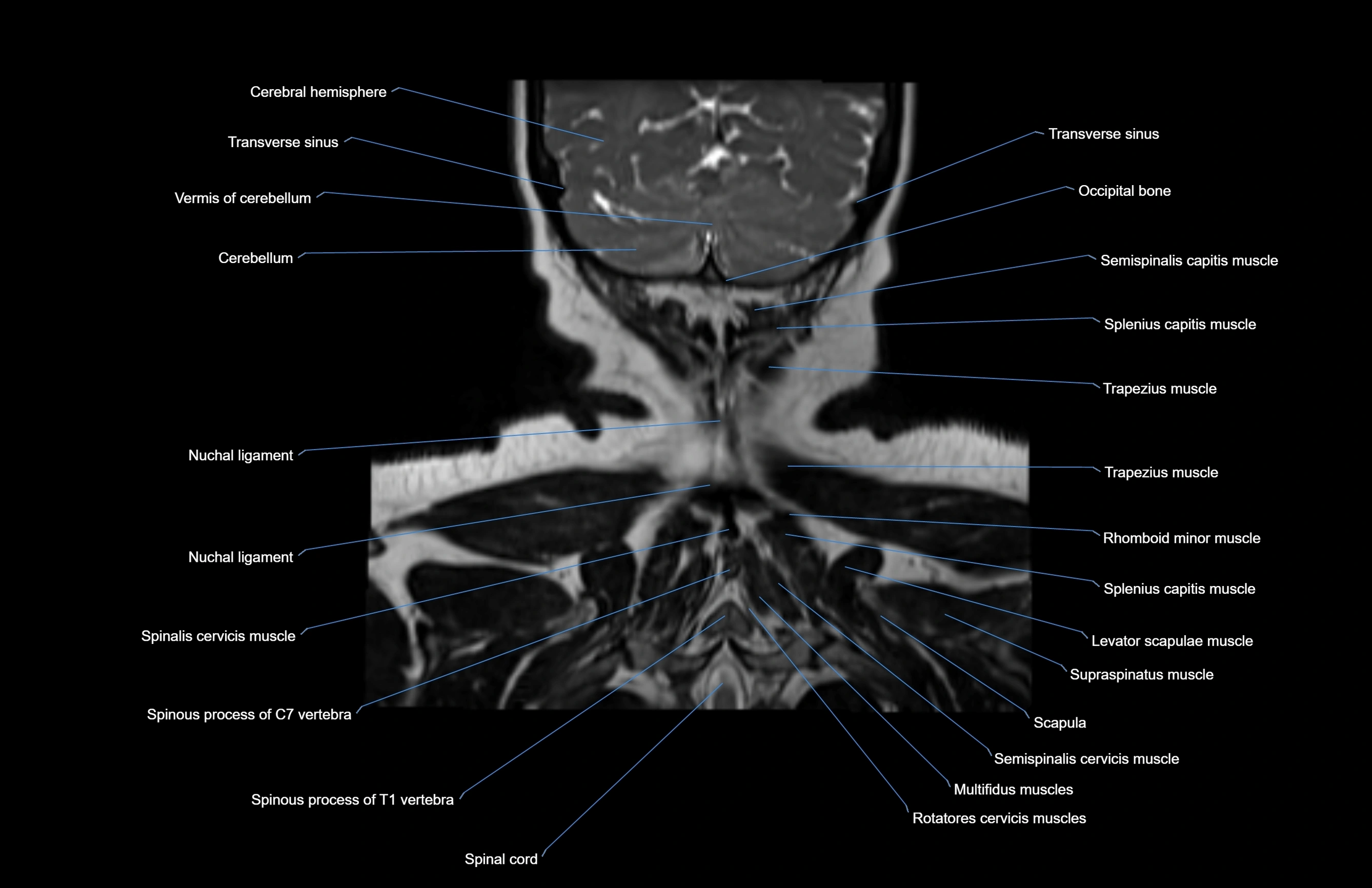
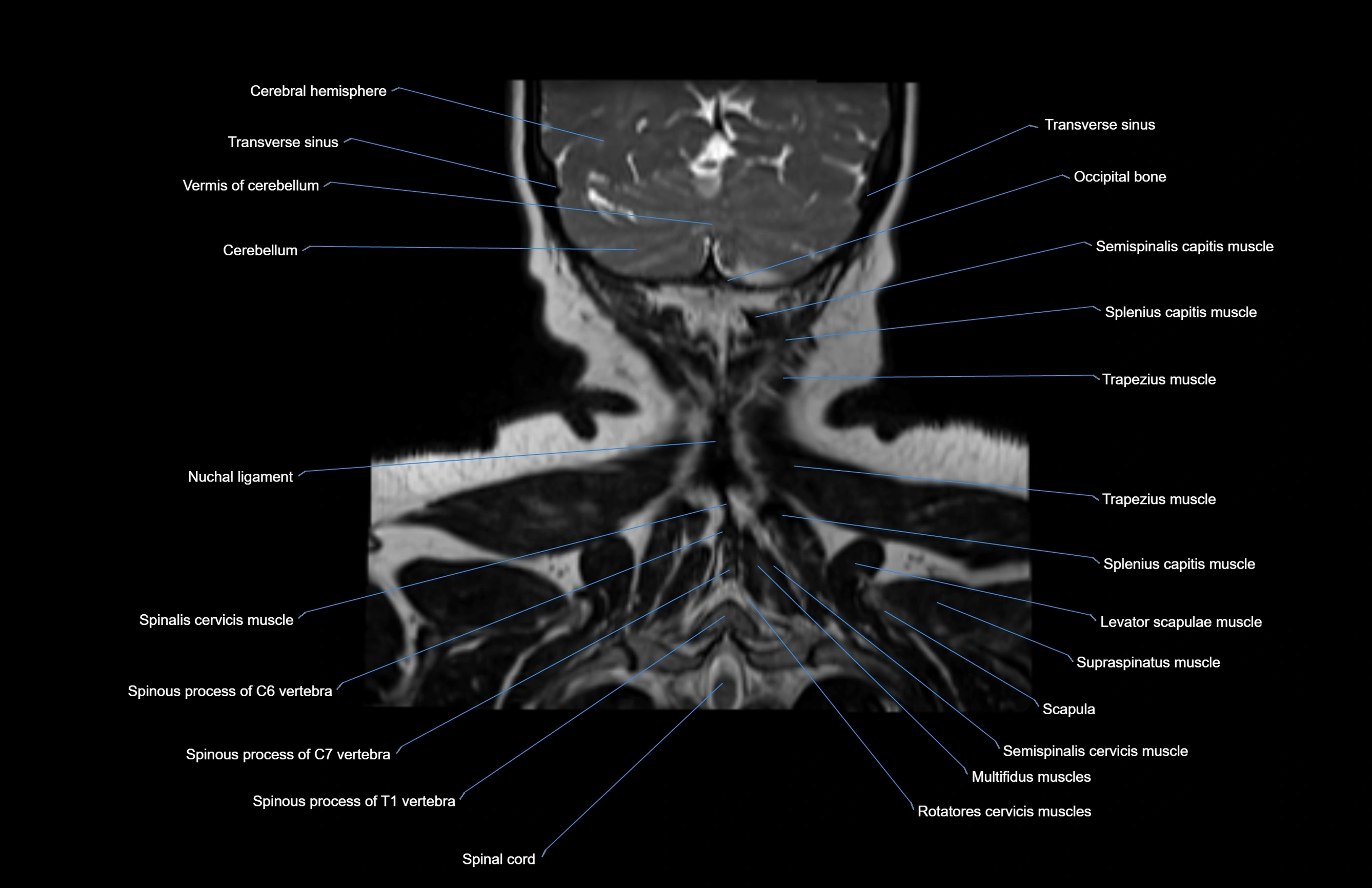
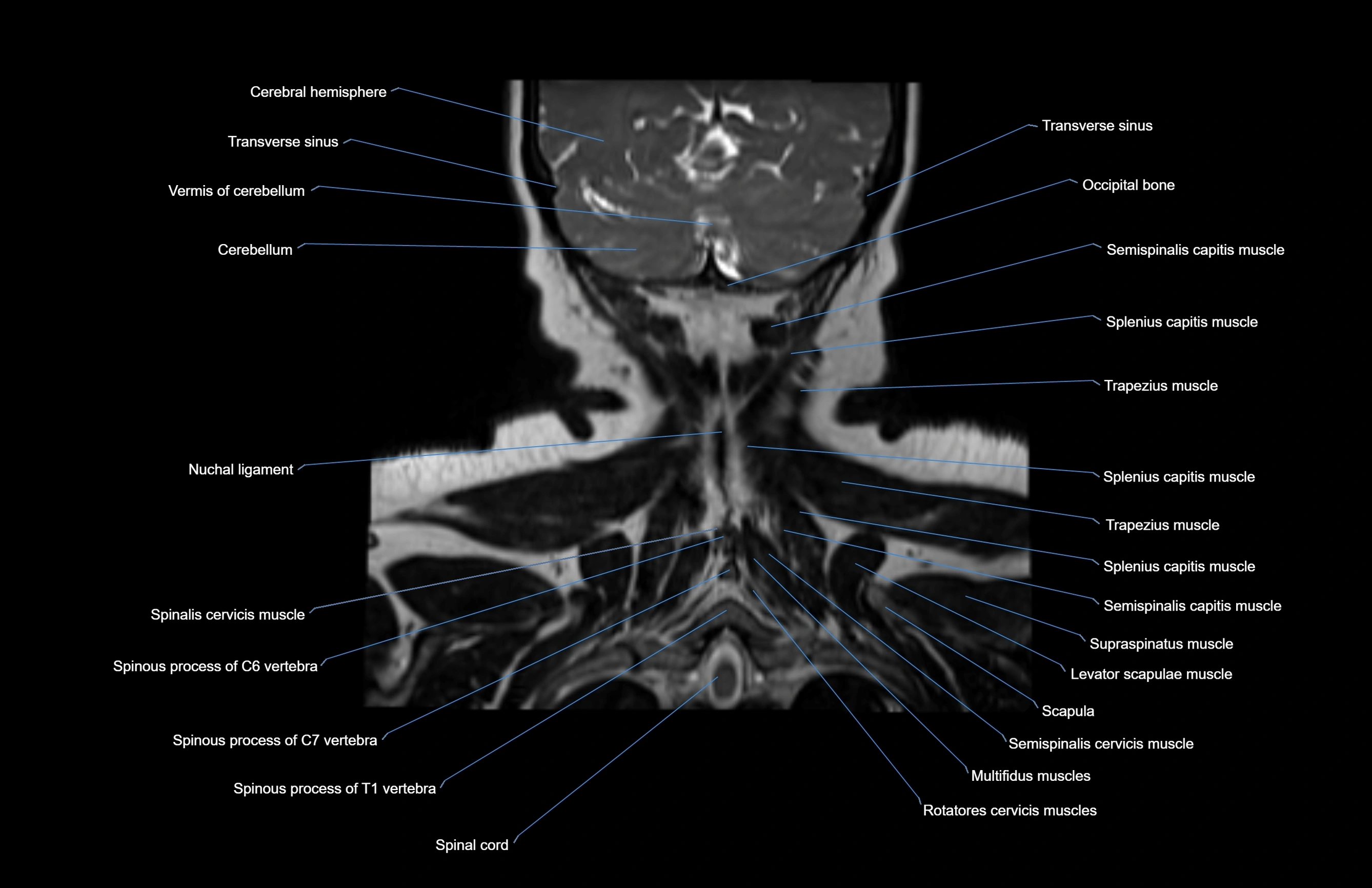
- Levator scapulae muscle
- Levator veli palatini muscle
- Ligamenta flava (Ligamentum flavum)
- Lingual Septum
- Lingual artery
- Lingual lymph nodes
- Lingual tonsil
- Lingula of cerebellum
- Lockwood’s ligament
- Longissimus capitis muscle
- Longissimus cervicis muscle
- Longus capitis muscle
- Longus colli muscle
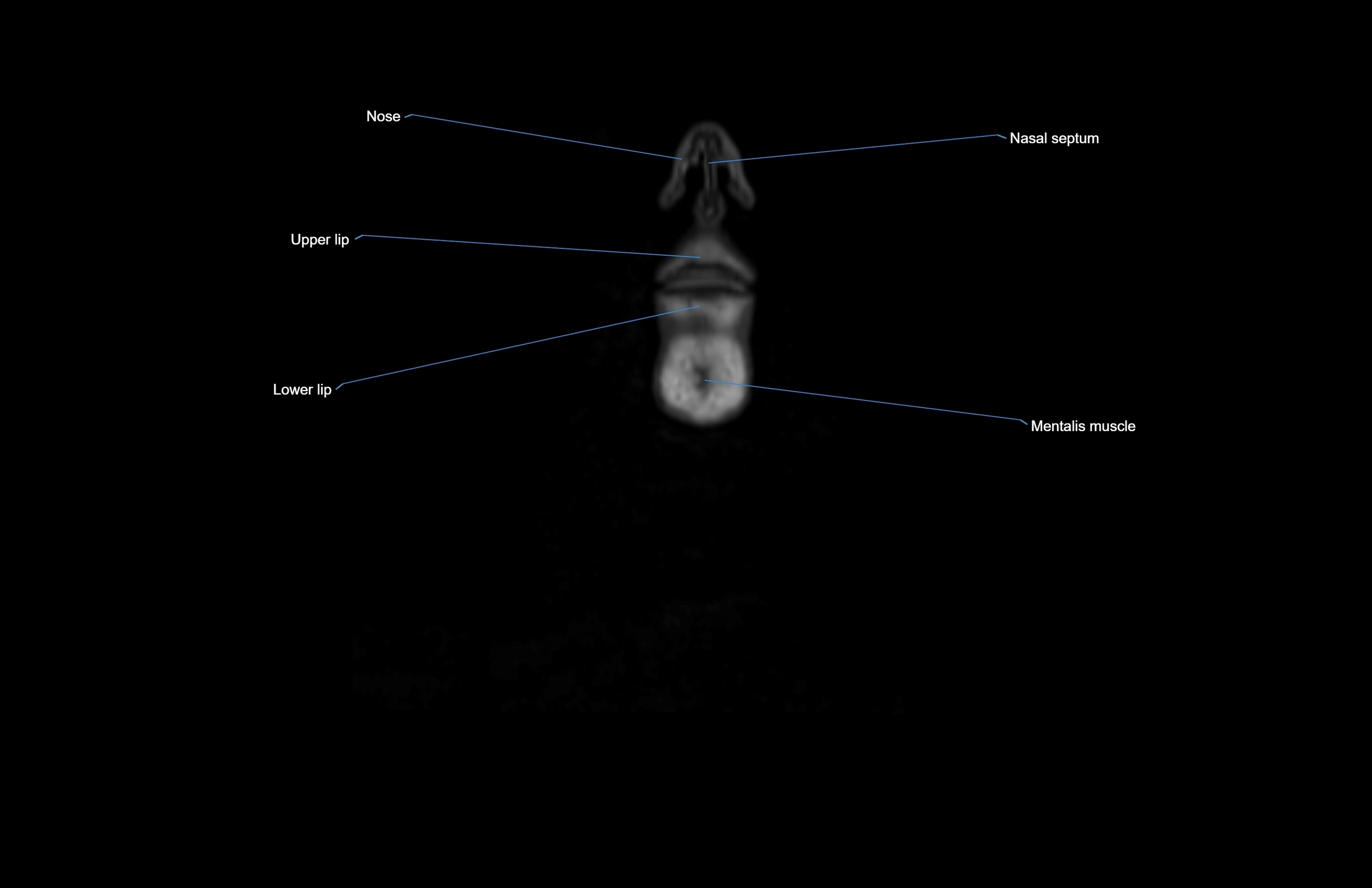
- Lower lip
- Lower molar apical foramen
- Lower premolar apical foramen
- Lunogracle fissure
- Major alar cartilage
- Malar (zygomatic) lymph nodes
- Mandible
- Mandibular canal
- Mandibular condyle
- Mandibular foramen
- Mandibular fossa
- Mandibular lymph nodes
- Mandibular nerve
- Margin of tongue
- Masseter muscle
- Masseter muscle (Deep part)
- Masseter muscle (Superficial part)
- Mastoid air cells
- Mastoid lymph nodes
- Mastoid process
- Maxilla
- Maxillary artery
- Maxillary bone
- Maxillary nerve
- Maxillary sinus
- Maxillary veins
- Meckel’s cave (Trigeminal cave)
- Medial atlantoaxial joint
- Medial canthal ligament
- Medial pterygoid muscle
- Medial rectus muscle
- Medial vestibular nucleus
- Median aperture of fourth ventricle (foramen of Magendie)
- Median atlantoaxial joint
- Median glossoepiglottic fold
- Median sulcus of rhomboid fossa
- Mental foramen
- Mental nerve
- Mentalis muscle
- Mesencephalic nucleus of trigeminal nerve
- Middle Nasal Meatus
- Middle cerebellar peduncle
- Middle constrictor muscle of pharynx
- Middle deep cervical lymph nodes
- Middle nasal concha
- Middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle
- Middle superior alveolar nerve
- Minor alar cartilage
- Motor nucleus of facial nerve
- Motor nucleus of trigeminal nerve
- Multifidus muscles
- Mylohyoid muscle
- Nasal bones
- Nasal crest of maxilla
- Nasal part of frontal bone
- Nasal septum
- Nasal spine of frontal bone
- Nasal vestibule
- Nasalis muscle
- Nasofrontal vein
- Nasolabial lymph nodes
- Nasolacrimal duct (Tear duct)
- Nasopharynx
- Neck of mandible
- Neck of rib
- Nodule of vermis
- Nuchal ligament
- Nucleus of abducens nerve
- Nucleus of hypoglossal nerve
- Nucleus of oculomotor nerve
- Nucleus of solitary tract
- Nucleus of trochlear nerve
- Nucleus pulposus of intervertebral disc
- Oblique and transverse arytenoid muscles
- Oblique arytenoid muscle
- Obliquus inferior capitis muscle
- Obliquus superior capitis muscle
- Occipital bone
- Occipital condyle
- Occipital lymph nodes
- Oculomotor Nerve (Cranial Nerve III)
- Oculomotor nerve (Superior branch)
- Oculomotor nerve (inferior branch)
- Odontoid process
- Olfactory Nerve (Cranial Nerve I)
- Olfactory bulb
- Olfactory tract
- Opening of nasolacrimal duct
- Optic Nerve (Cranial Nerve II)
- Optic canal
- Optic chiasm
- Optic disc
- Optic nerve sheath
- Orbicularis oculi muscle
- Orbicularis oculi muscle (Orbital part)
- Orbicularis oculi muscle (Preseptal part)
- Orbicularis oris muscle
- Orbital part of optic nerve
- Orbital part of orbicularis oculi muscle
- Orbital plate
- Orbital surface of maxilla
- Oropharynx
- Palatine glands
- Palatine process of maxilla
- Palatine tonsil
- Palatoglossus muscle
- Palatopharyngeus muscle
- Paramedian lobule
- Paratracheal lymph nodes
- Parotid duct
- Parotid gland
- Pectoralis major muscle
- Pedicle of vertebra
- Perpendicular plate
- Petrous part of temporal bone
- Pharyngeal raphe
- Pharyngeal tonsil
- Platysma muscle
- Pleura
- Posterior arch of atlas
- Posterior atlanto-occipital ligament
- Posterior atlantooccipital membrane
- Posterior auricular artery
- Posterior auricular vein
- Posterior band of articular disc, TMJ
- Posterior belly of digastric muscle
- Posterior chamber of eyeball
- Posterior cochlear nucleus
- Posterior cricoarytenoid muscle
- Posterior lobe of cerebellum
- Posterior longitudinal ligament
- Posterior sternoclavicular ligament
- Posterior superior alveolar nerve
- Posterior superior fissure
- Posterolateral fissure
- Preauricular lymph nodes
- Prebiventral fissure
- Precentral fissure
- Preculminate fissure
- Premedullary cistern
- Preseptal part of orbicularis oculi muscle
- Primary fissure
- Principal sensory nucleus of the trigeminal nerve
- Pterygoid venous plexus
- Pterygomandibular raphe
- Pupil
- Pyramis of vermis
- Ramus of mandible
- Rectus capitis anterior muscle
- Rectus capitis lateralis muscle
- Rectus capitis posterior major muscle
- Rectus capitis posterior minor muscle
- Retina
- Retrobulbar fat
- Retromandibular vein
- Retropharyngeal lymph nodes
- Rhomboid major muscle
- Rhomboid minor muscle
- Right Vertebral Artery (Intracranial Part)
- Right brachiocephalic vein
- Right lobe of liver
- Right lobe of thyroid gland
- Right subclavian artery
- Right subclavian vein
- Right vertebral artery
- Right vertebral artery (atlantic part)
- Right vertebral artery (cervical part)
- Risorius muscle
- Root canal of lower canines tooth
- Root canal of lower premolar tooth
- Root canal of upper canines tooth
- Root canal of upper molar tooth
- Root canal of upper premolar tooth
- Root of lower canines tooth
- Root of lower molar tooth
- Root of tongue
- Root of upper molar tooth
- Rotatores cervicis muscle
- Rotatores cervicis muscles
- Salpingopalatine fold
- Salpingopharyngeal fold
- Scalenus anterior muscle (Anterior scalene muscle)
- Scalenus medius muscle (middle scalene muscle)
- Scalenus posterior muscle (Posterior scalene muscle)
- Scapula
- Sclera
- Secondary fissure
- Sella turcica
- Semicircular Canals
- Semispinalis capitis muscle
- Semispinalis cervicis muscle
- Septum of sphenoid sinus
- Serratus anterior muscle
- Serratus posterior superior muscle
- Sheath of styloid process
- Simple lobule
- Sphenoid sinus
- Spinal cord
- Spinal nerves
- Spinal nucleus of trigeminal nerve
- Spinalis cervicis muscle
- Spinous process of vertebra
- Splenius capitis muscle
- Splenius cervicis muscle
- Squamous part of temporal bone
- Sternal end of the clavicle
- Sternocleidomastoid muscle
- Sternocostal synchondrosis of first rib
- Sternohyoid muscle
- Sternothyroid muscle
- Styloglossus muscle
- Stylohyoid muscle
- Styloid process
- Stylopharyngeus muscle
- Subarachnoid space of optic nerve
- Subclavian artery
- Subclavius muscle
- Sublingual gland
- Submandibular duct
- Submandibular gland
- Submandibular lymph nodes
- Submental lymph nodes
- Submental vein
- Subscapular artery
- Superciliary arch
- Superficial anterior cervical lymph nodes
- Superficial head of medial pterygoid muscle
- Superficial lateral cervical lymph nodes
- Superficial parotid lymph nodes
- Superficial part of masseter
- Superficial temporal artery
- Superficial temporal vein
- Superior articular process of vertebra
- Superior belly of omohyoid muscle
- Superior branch of vestibular nerve
- Superior bulb of internal jugular vein
- Superior constrictor muscle of pharynx
- Superior cornu of thyroid cartilage
- Superior deep cervical lymph nodes
- Superior dental plexus
- Superior eyelid
- Superior first molar tooth
- Superior first premolar tooth
- Superior head of lateral pterygoid muscle
- Superior intercostal artery
- Superior longitudinal lingual muscle
- Superior longitudinal muscle of tongue
- Superior medullary velum
- Superior nasal concha
- Superior nasal meatus
- Superior oblique muscle
- Superior opening of cerebral aqueduct
- Superior ophthalmic vein
- Superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle
- Superior rectus muscle
- Superior retrodiscal layer
- Superior salivatory nucleus
- Superior second molar tooth
- Superior second premolar tooth
- Superior semilunar lobule of cerebellum
- Superior synovial membrane of temporomandibular joint
- Superior tarsus
- Superior third molar tooth
- Superior vestibular nucleus
- Superior wall of the maxillary sinus
- Supraclavicular lymph nodes
- Supraorbital artery
- Supraorbital nerve
- Supraorbital vein
- Suprascapular artery
- Suprascapular vein
- Supraspinatus muscle
- Supraspinous ligament
- Supratrochlear artery
- Supratrochlear nerve
- Supratrochlear vein
- Sylvian cistern
- Tectorial Membrane
- Teeth
- Temporalis muscle
- Temporalis muscle (face)
- Temporomandibular joint
- Tensor veli palatini muscle
- Thoracic part of esophagus
- Thoracoacromial artery
- Thoracodorsal artery
- Thoracodorsal vein
- Thyroarytenoid muscle
- Thyrocervical trunk
- Thyroepiglottic ligament
- Thyrohyoid membrane
- Thyrohyoid muscle
- Thyroid cartilage
- Thyroid gland
- Thyroid lymph nodes
- Tonsil of cerebellum
- Tonsillar fossa
- Trachea
- Tragus of ear
- Transverse arytenoid muscle
- Transverse cervical artery
- Transverse facial artery
- Transverse facial vein
- Transverse foramen
- Transverse muscle of the tongue
- Transverse muscle of tongue
- Transverse pontine vein
- Transverse process of atlas
- Transverse process of vertebra
- Trapezius muscle
- Trigeminal ganglion
- Trigeminal nerve (Cranial nerve V)
- Trochlear nerve (Cranial nerve IV)
- Tuber of vermis
- Tympanic part of temporal bone
- Upper premolar apical foramen
- Uvula of palate
- Uvula of vermis
- Vagus nerve (Cranial nerve X)
- Ventral root of spinal nerve
- Vertebral artery
- Vertebral vein
- Vestibular fold & vestibular ligament
- Vestibular ganglion
- Vestibule
- Vestibulocochlear nerve (Cranial nerve VIII)
- Vitreous chamber of eyeball
- Vocalis muscle
- Vomer
- Whitnall's ligament
- Wing of central lobule
- Zygomatic arch
- Zygomatic bone
- Zygomatic nerve
- Zygomatic process of frontal bone
- Zygomatic process of temporal bone
- Zygomaticus major muscle
- Zygomaticus minor muscle
- inferior alveolar artery
- jugular foramen pars nervosa
- lens of the eye
- subarachnoid space of spinal cord
- superior canine tooth
The Abducens nerve (Cranial nerve VI) is a purely motor cranial nerve responsible for innervating the lateral rectus muscle of the eye, which is crucial for lateral movement (abduction) of the eyeball. It arises from the abducens nucleus in the dorsal pons, emerges at the pontomedullary junction, and travels a long intracranial course before entering the orbit via the superior orbital fissure. Because of its long path and proximity to the clivus, it is particularly susceptible to injury from increased intracranial pressure or trauma.
Synonyms
-
Sixth cranial nerve
-
CN VI
-
N. abducens (Latin)
-
Nervus abducens
Function
-
Innervates the lateral rectus muscle of the eye
-
Responsible for abduction of the eyeball (moving the eye outward, away from the midline)
-
Is a purely motor nerve (no sensory or autonomic fibers)
-
Lesion results in inability to abduct the affected eye, leading to horizontal diplopia (double vision)
MRI Appearance
-
The abducens nerve is a small, thin, linear structure
-
Best visualized on high-resolution T2-weighted 3D MRI sequences (e.g., FIESTA or CISS)
-
Seen as a hypointense (dark) line running from the brainstem at the pontomedullary junction, traversing the prepontine cistern, and entering Dorello’s canal under the petrosphenoidal ligament, then into the cavernous sinus, and finally the orbit
-
May be challenging to visualize in standard MRI due to its small size
-
Pathology may be inferred by absence, displacement, or enhancement of the nerve
CT Appearance
-
The nerve itself is not directly visualized on conventional CT due to its small size and soft tissue density
-
Indirect signs: assessment of the bony course, such as the Dorello’s canal, superior orbital fissure, or adjacent pathologies (fractures, masses, or inflammation) that could impinge the nerve
-
CT is mainly used to exclude structural lesions or fractures that might affect the course of CN VI
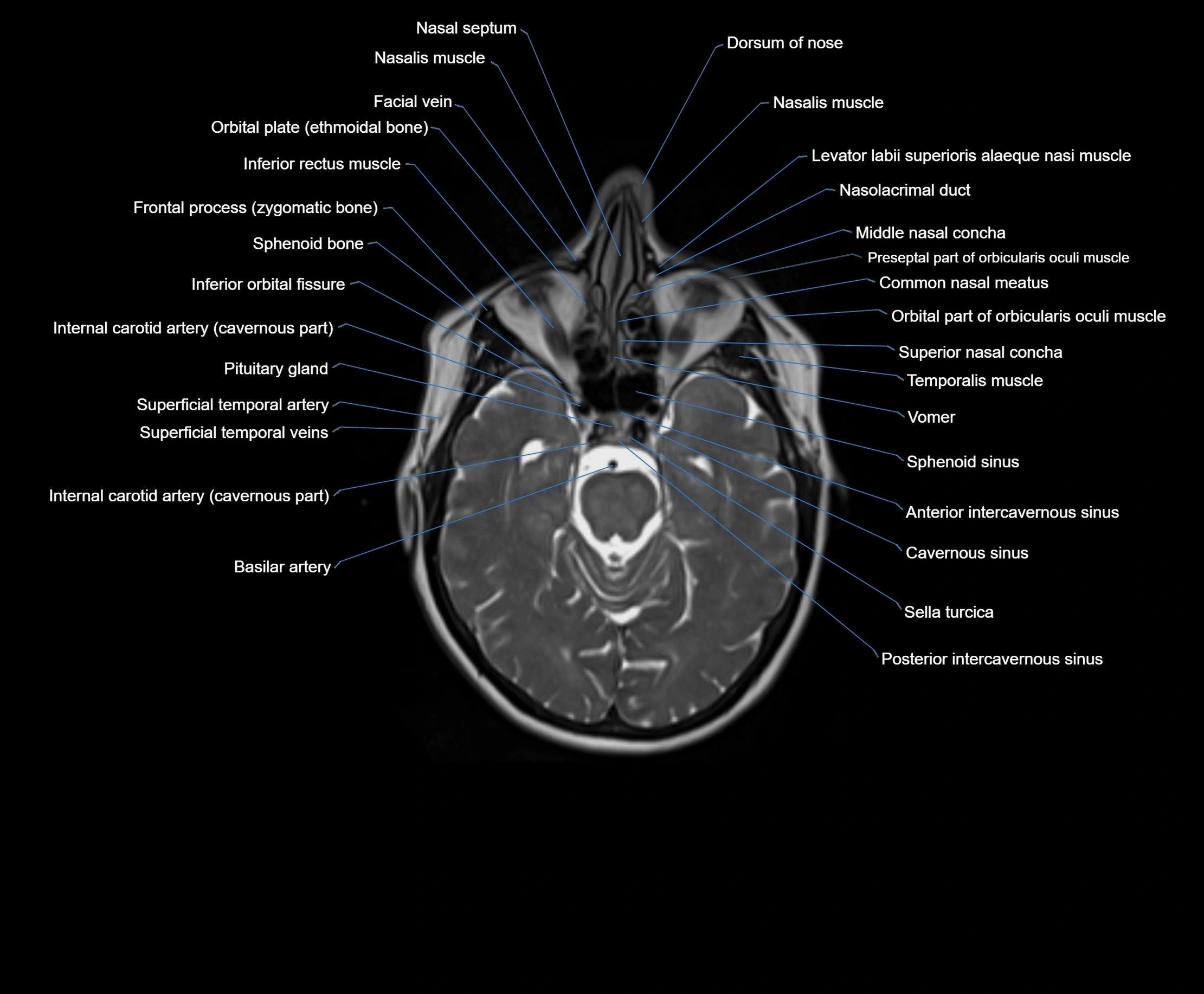
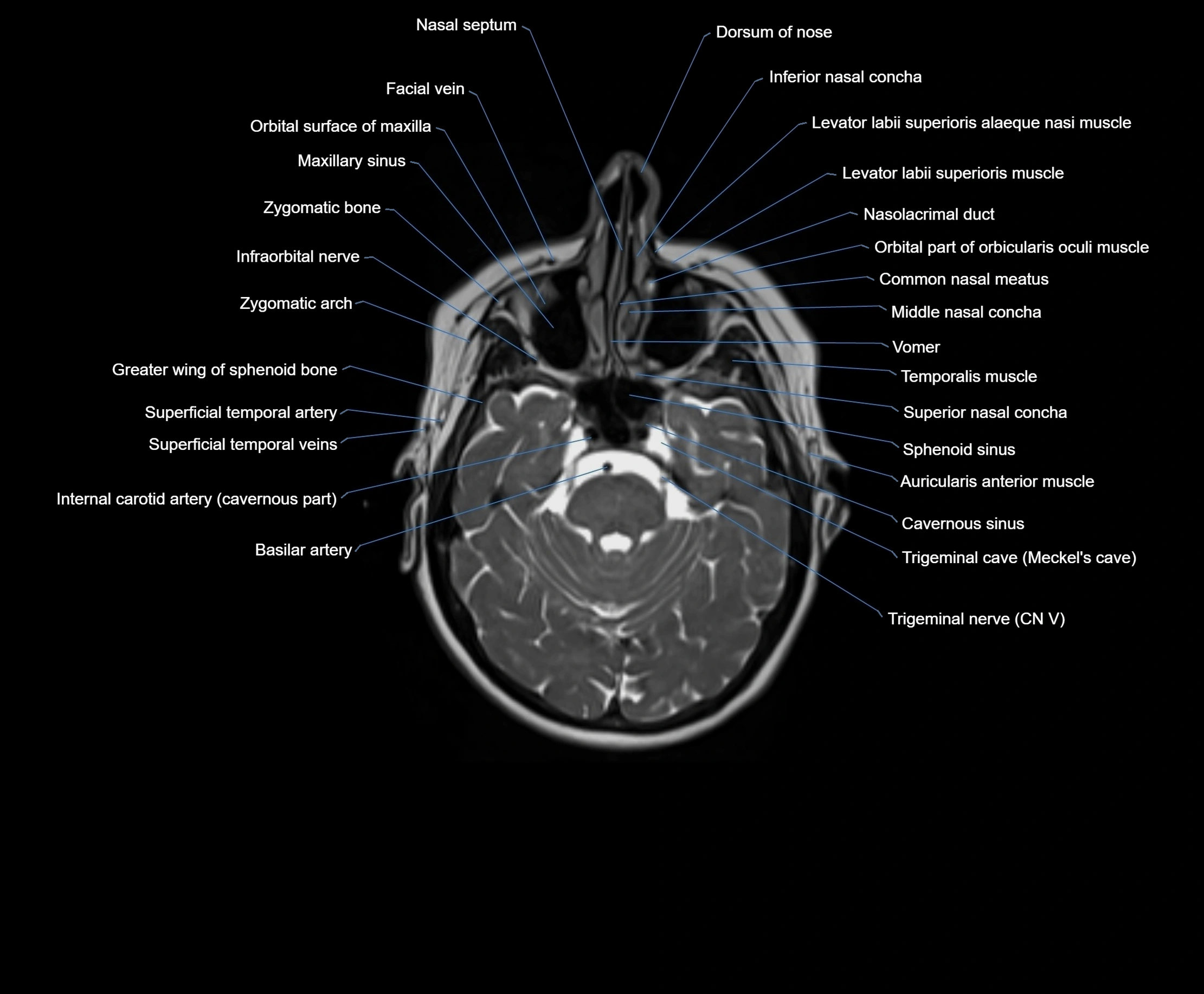
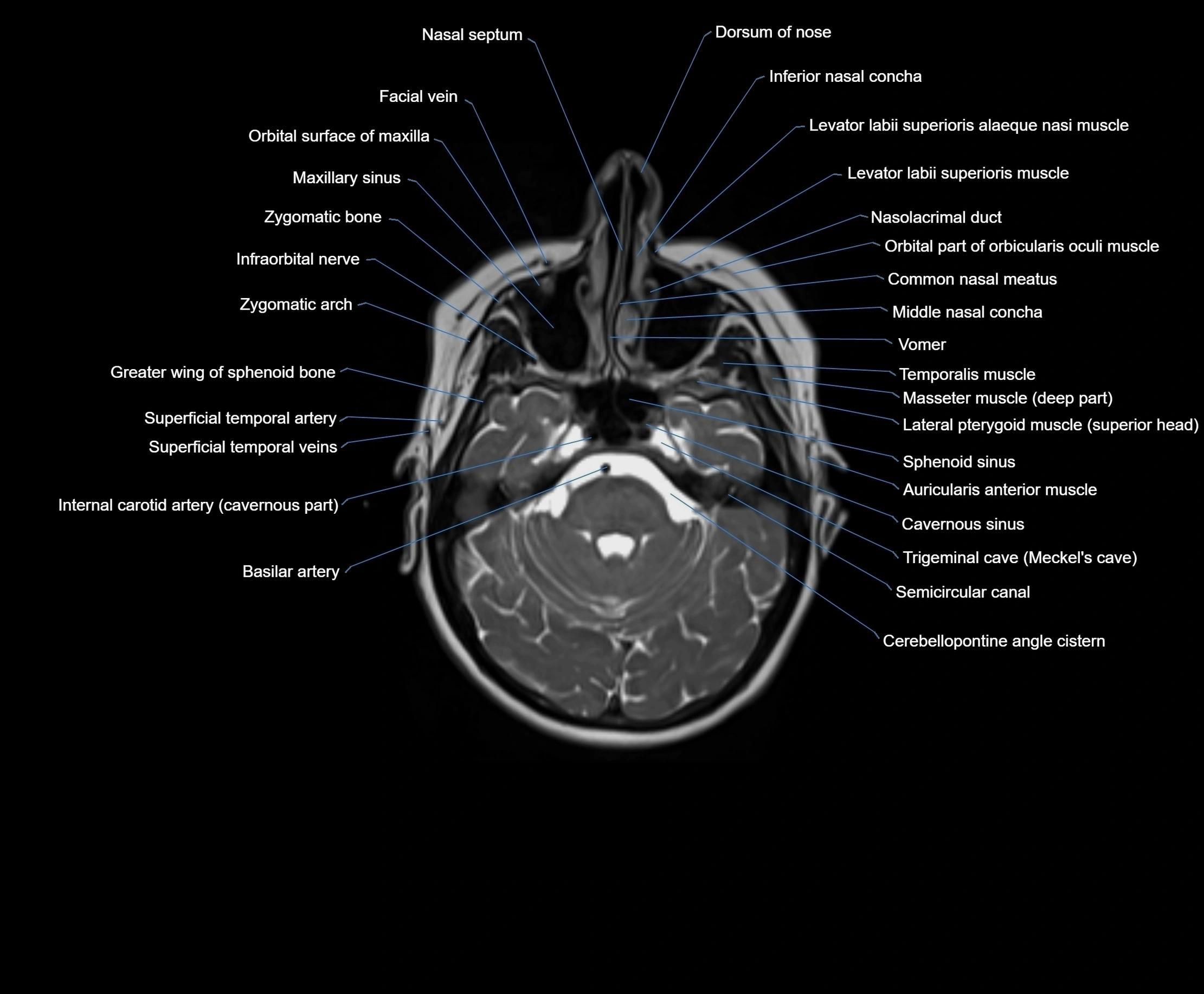
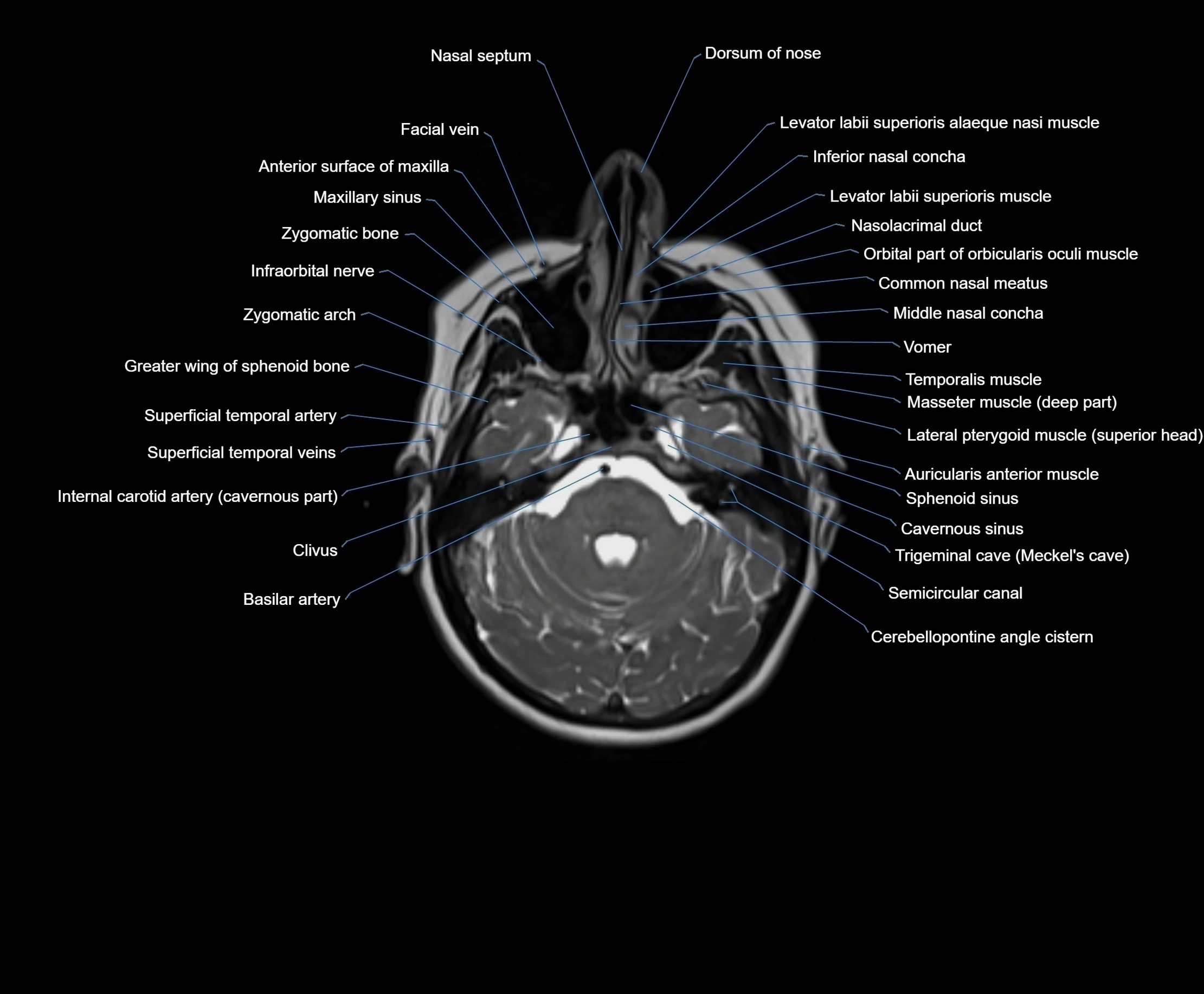
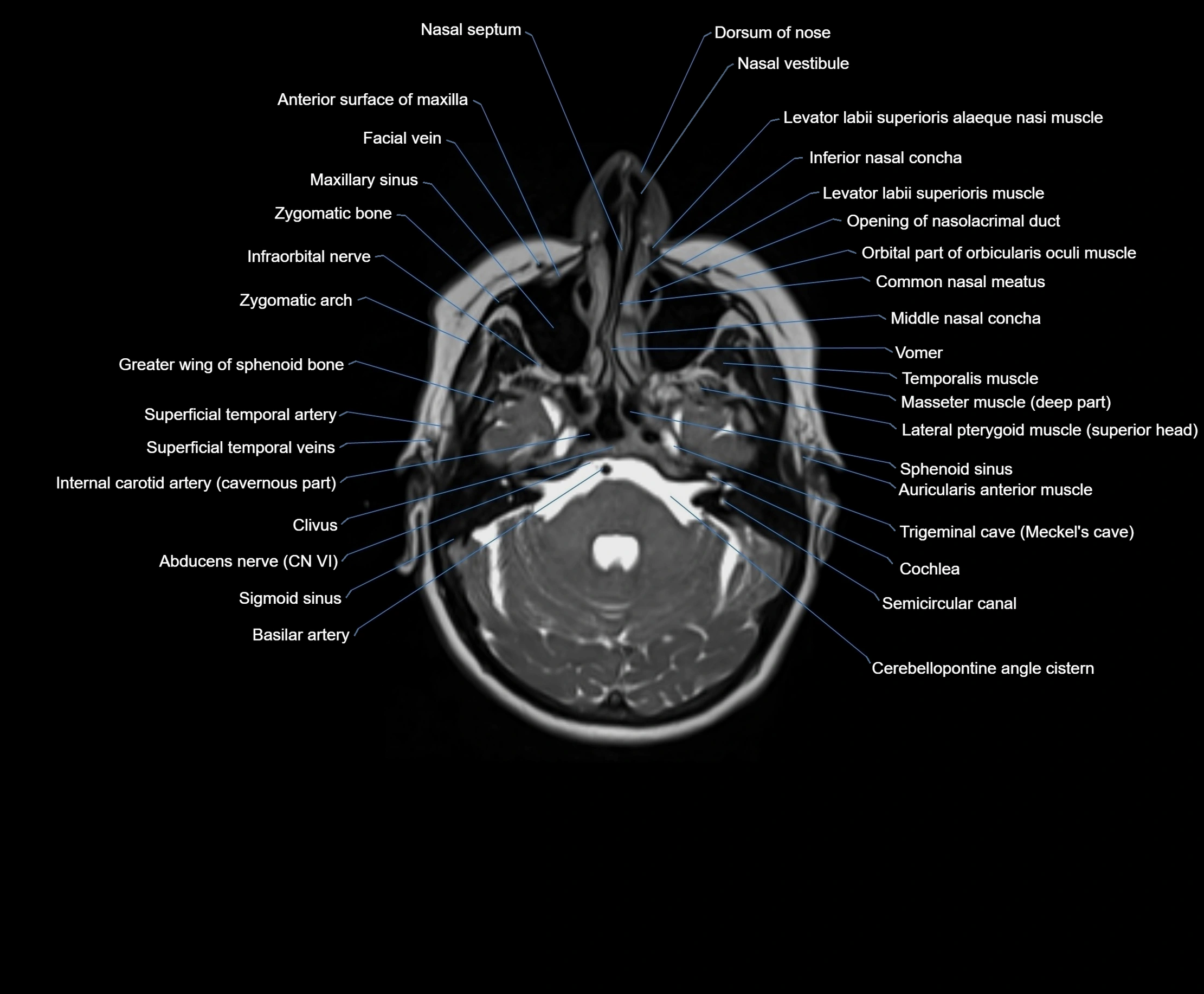
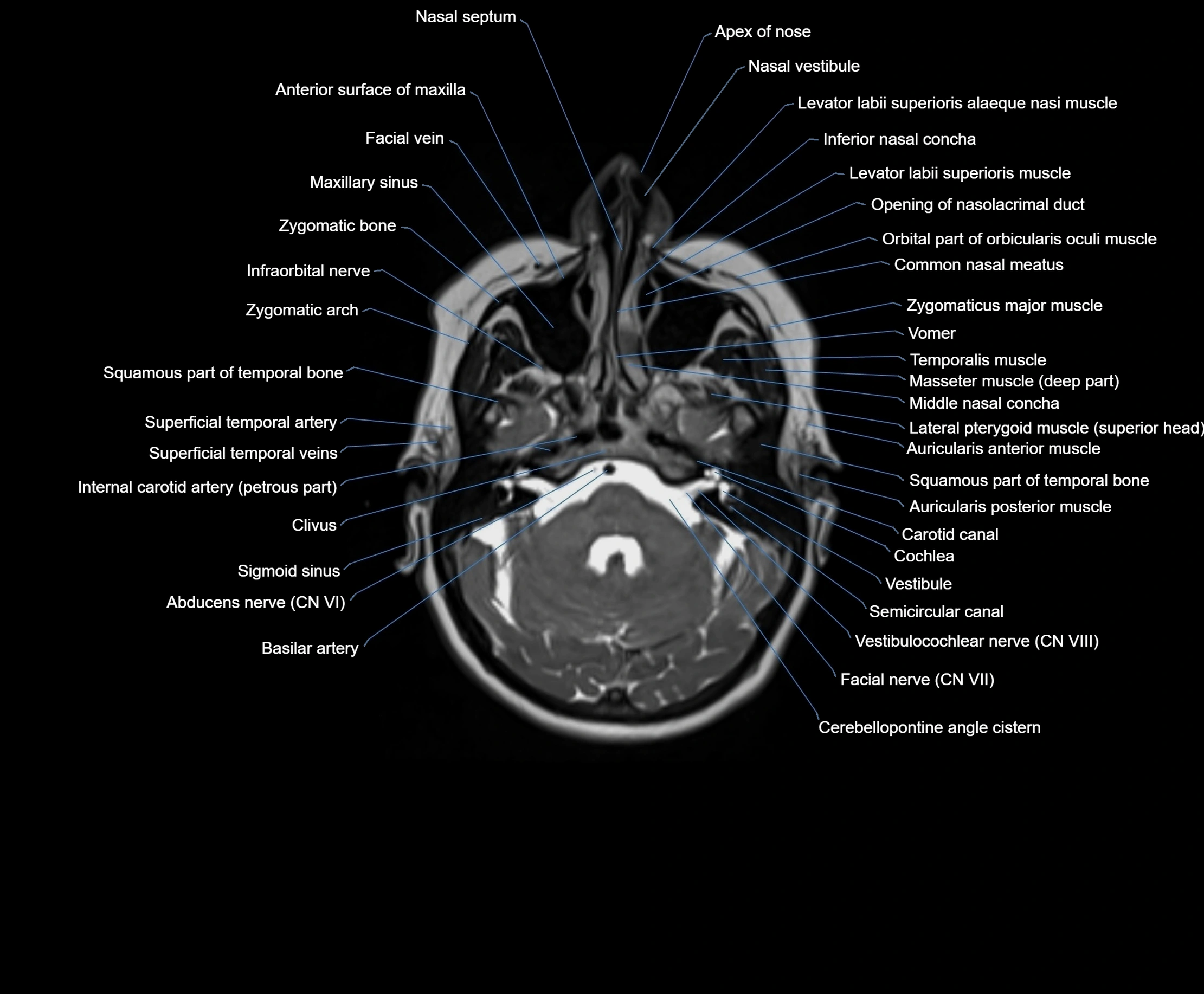
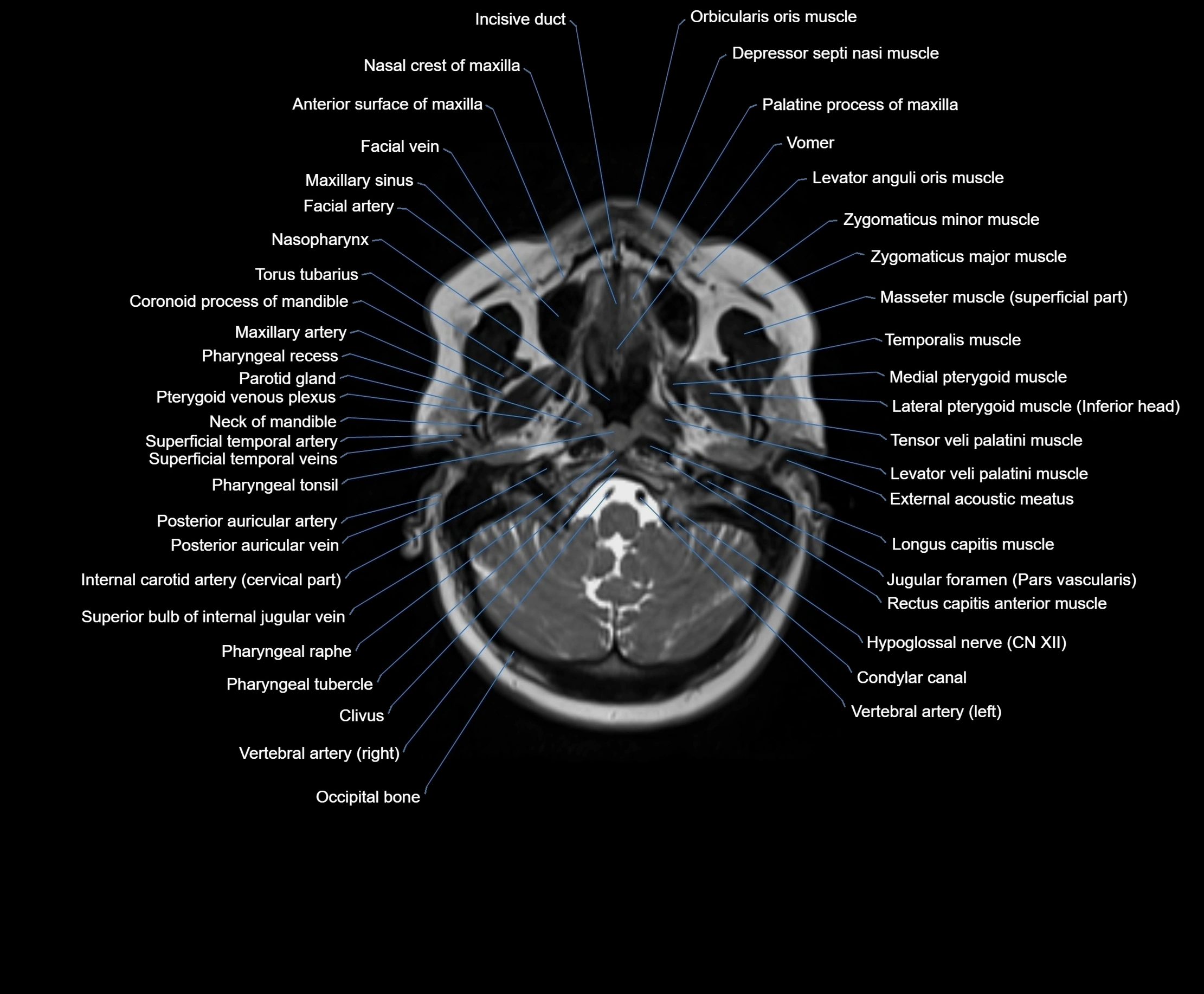
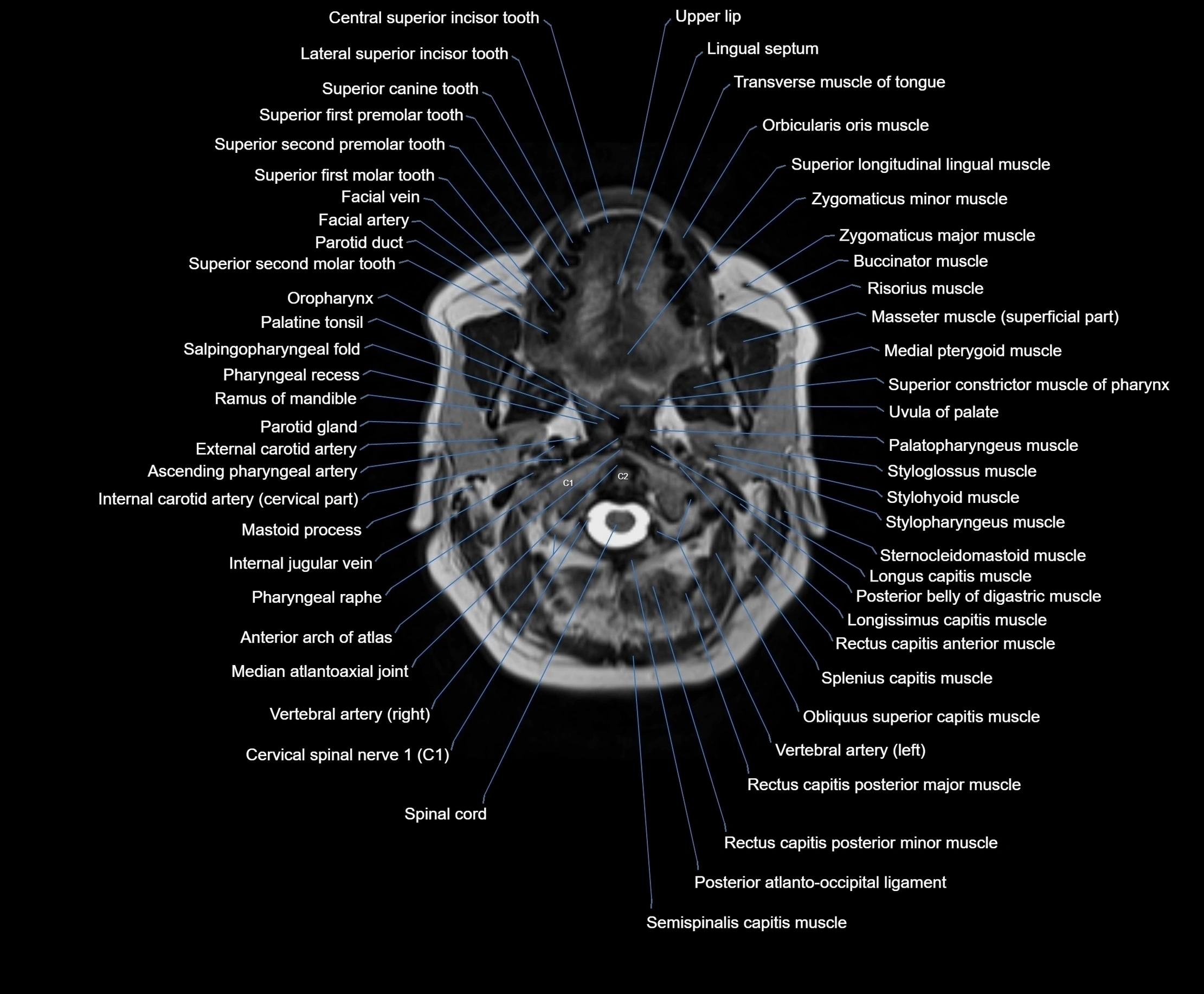
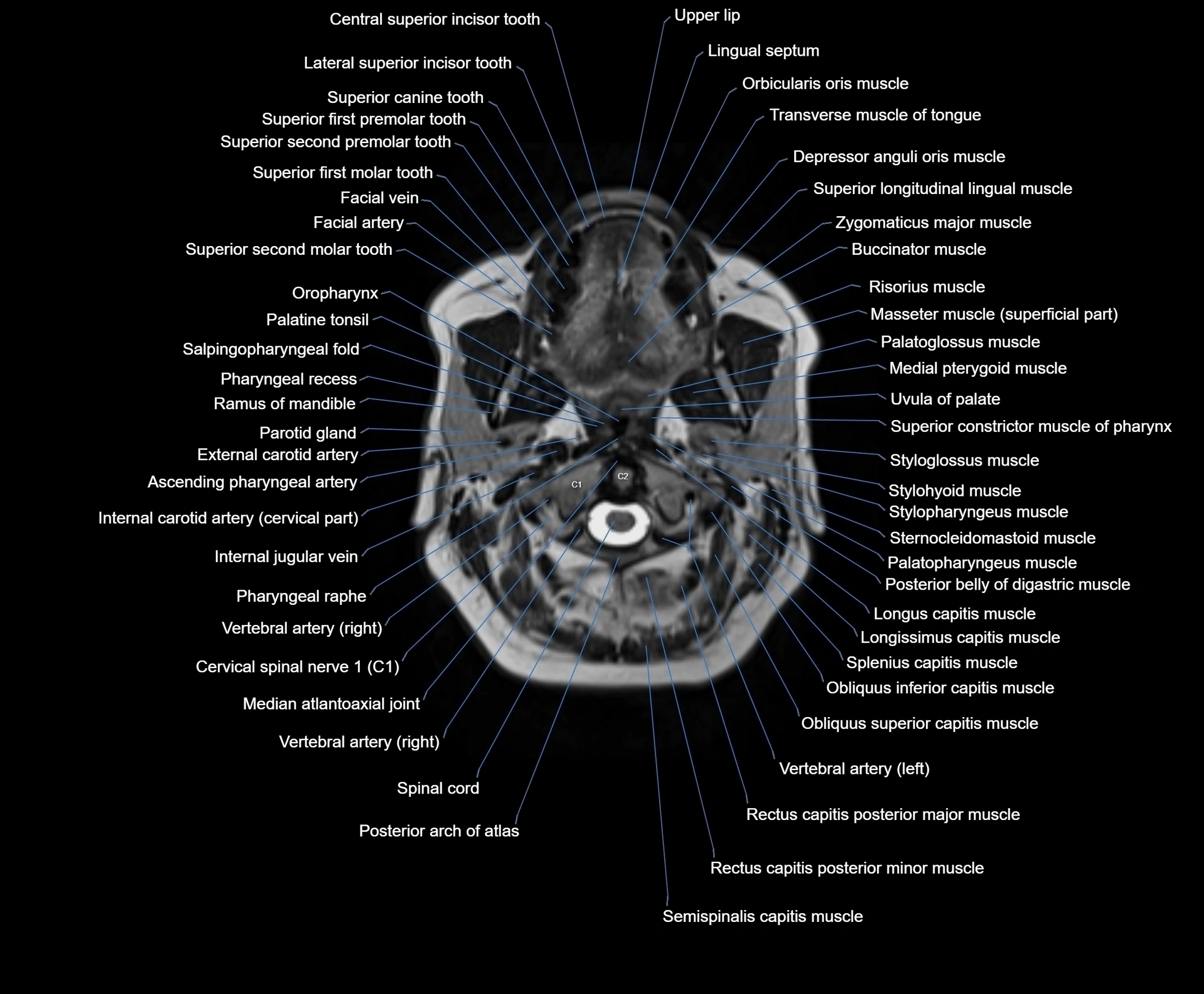
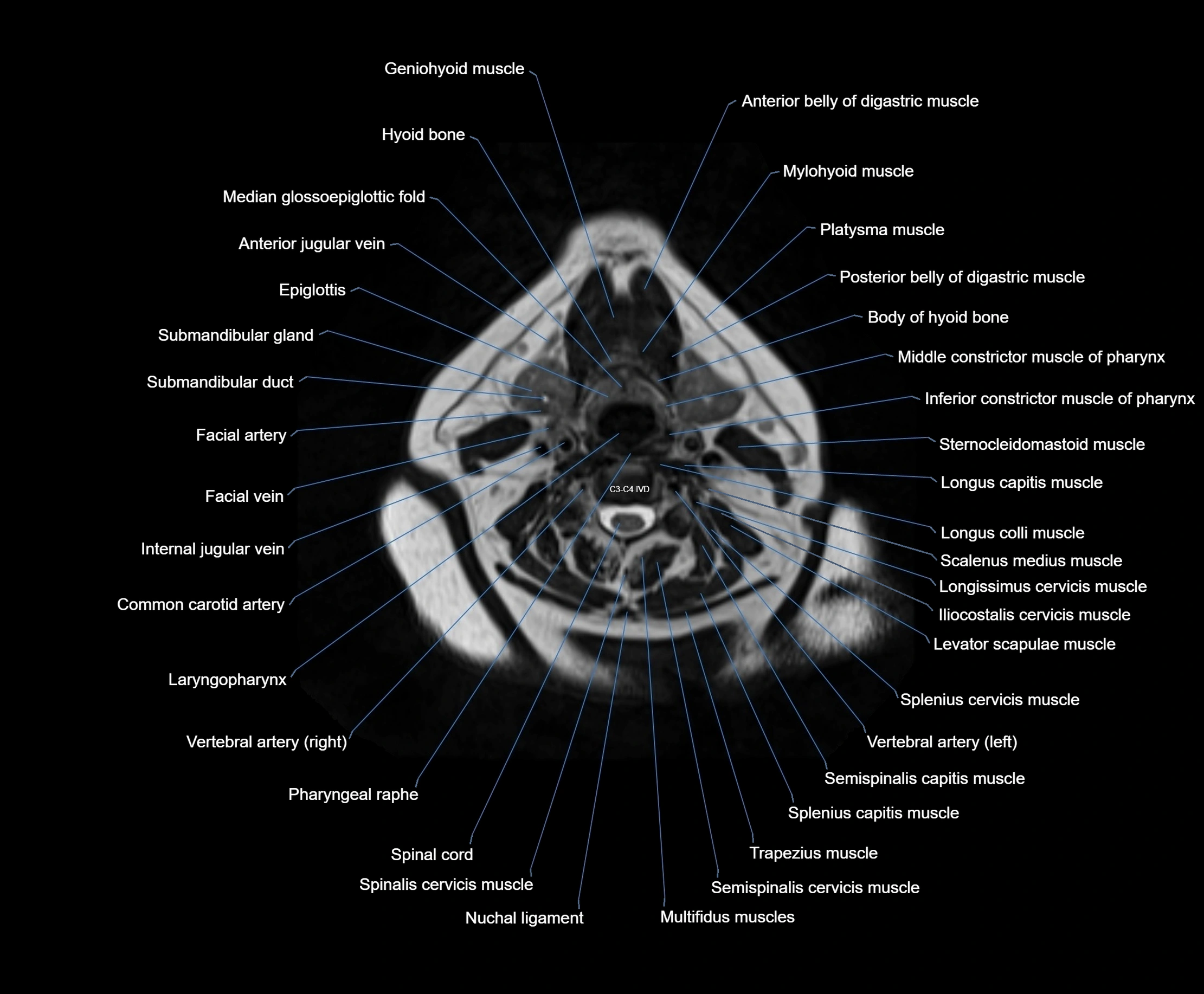
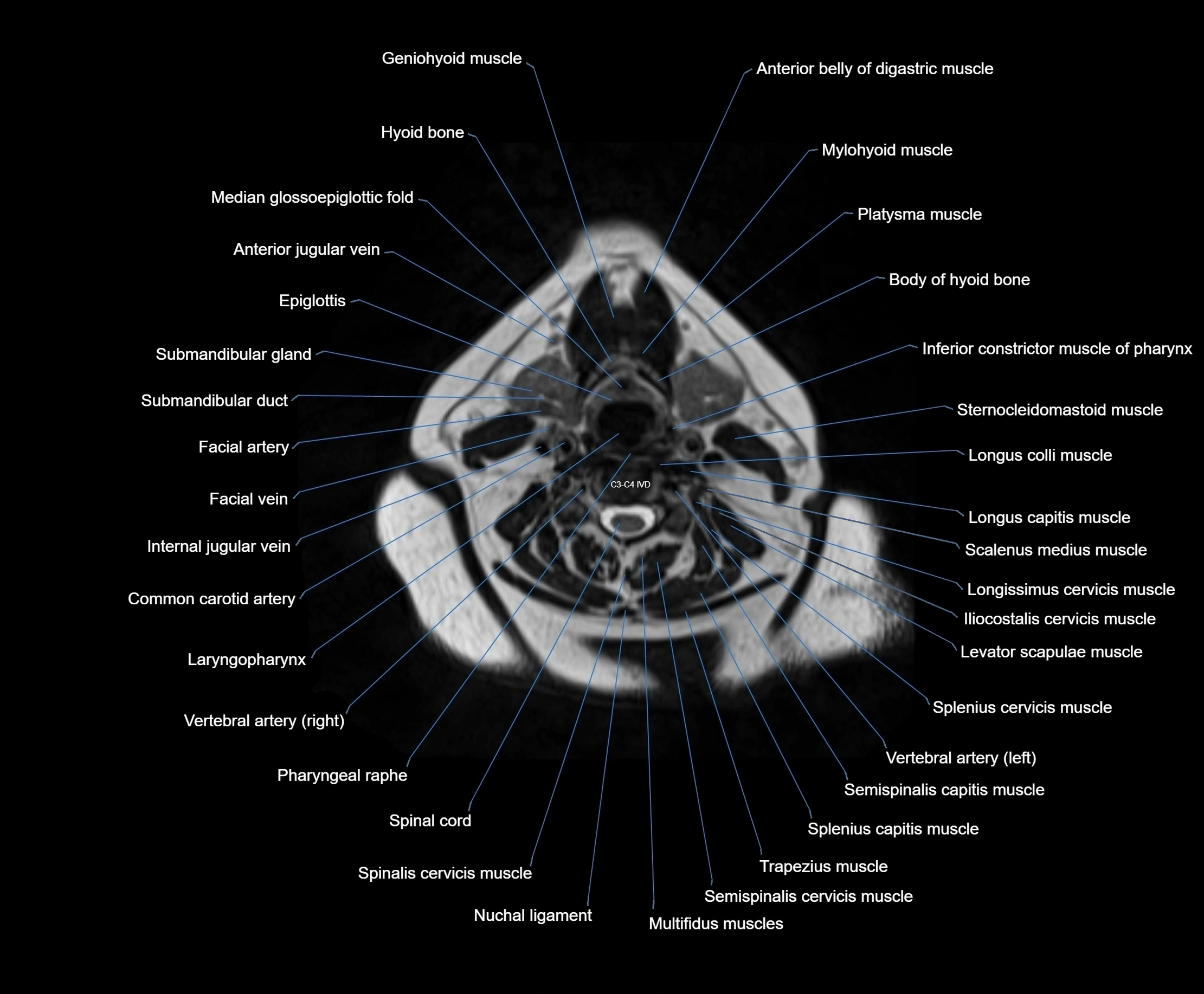
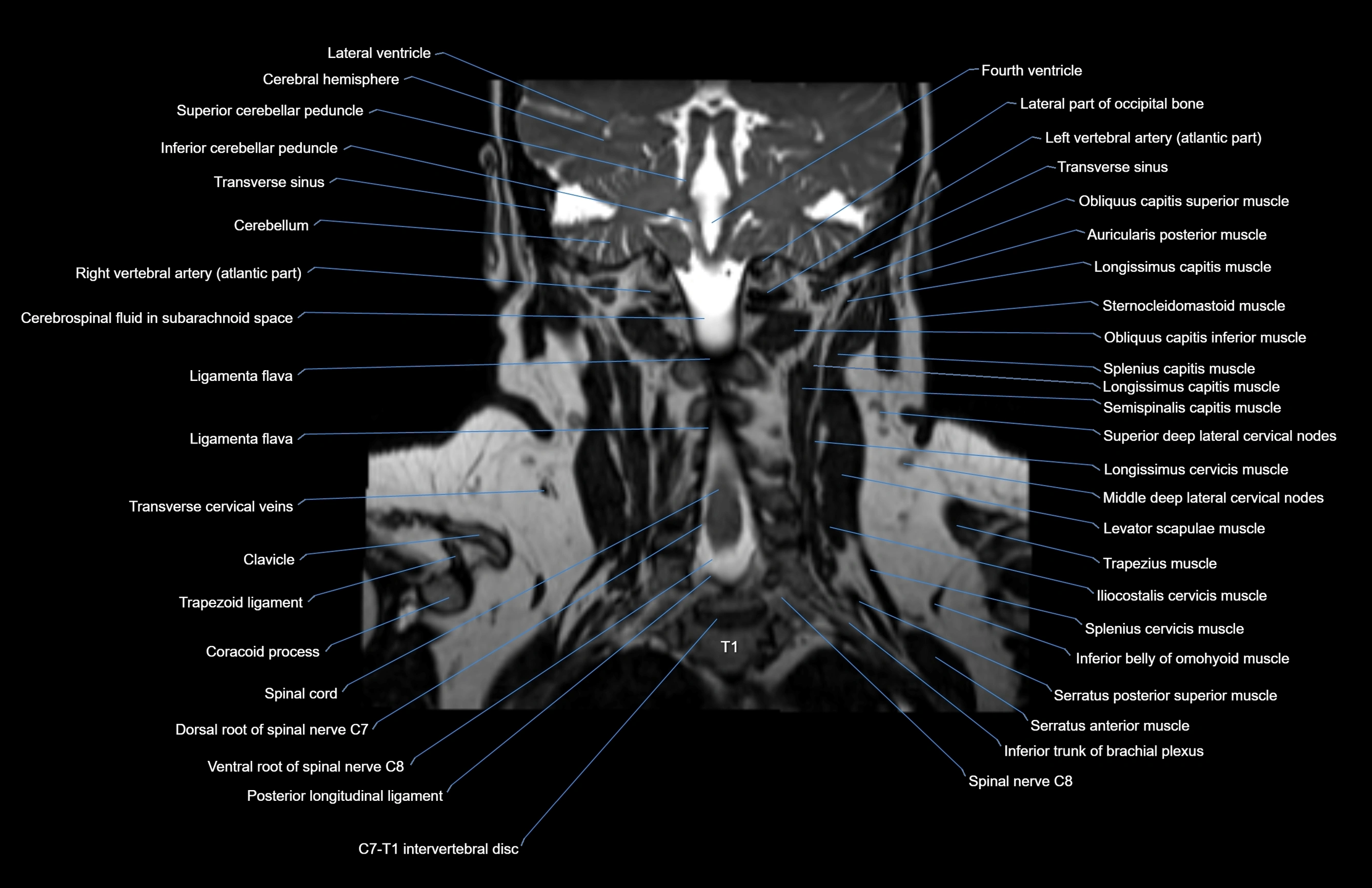
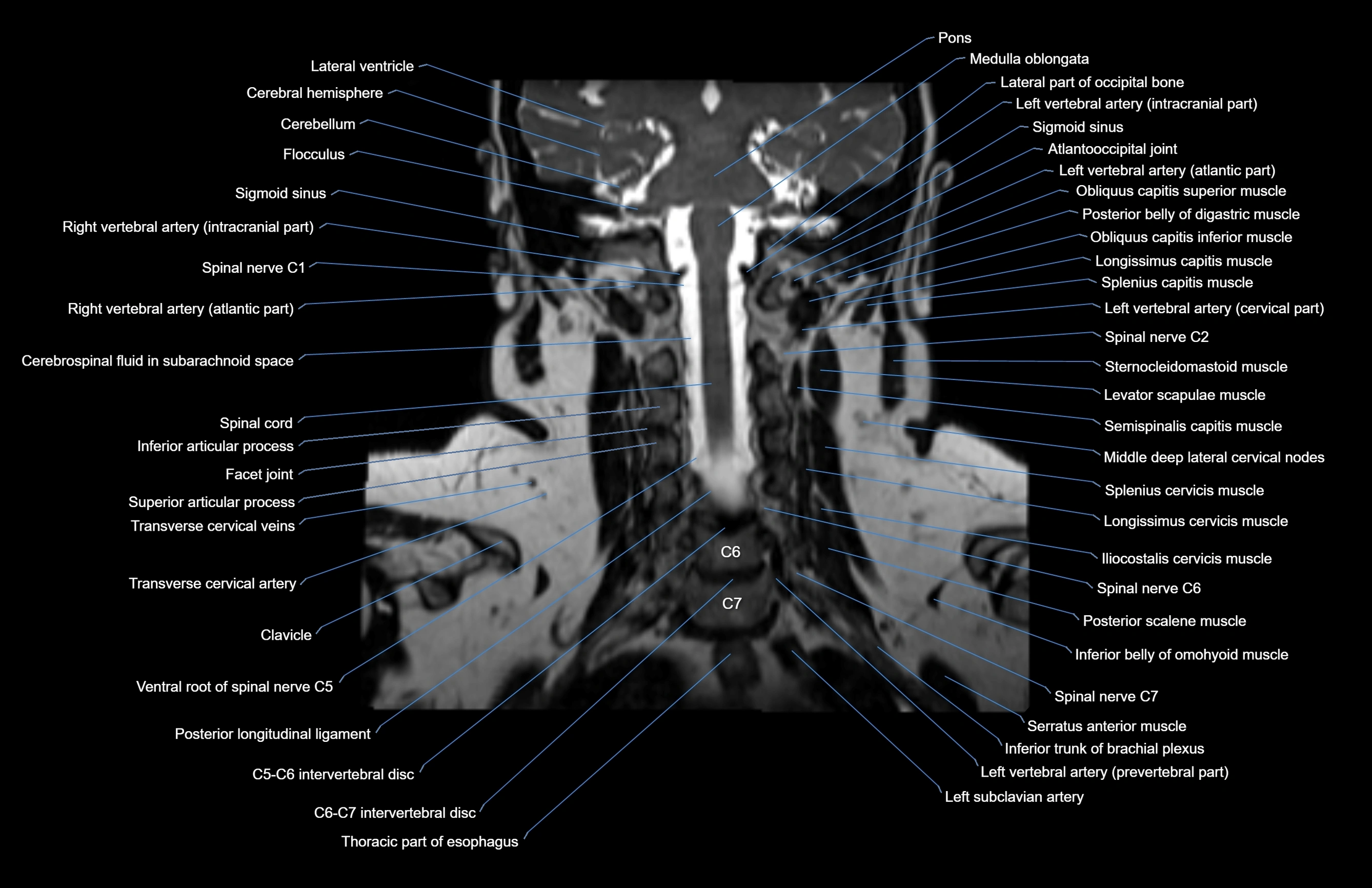
MRI images

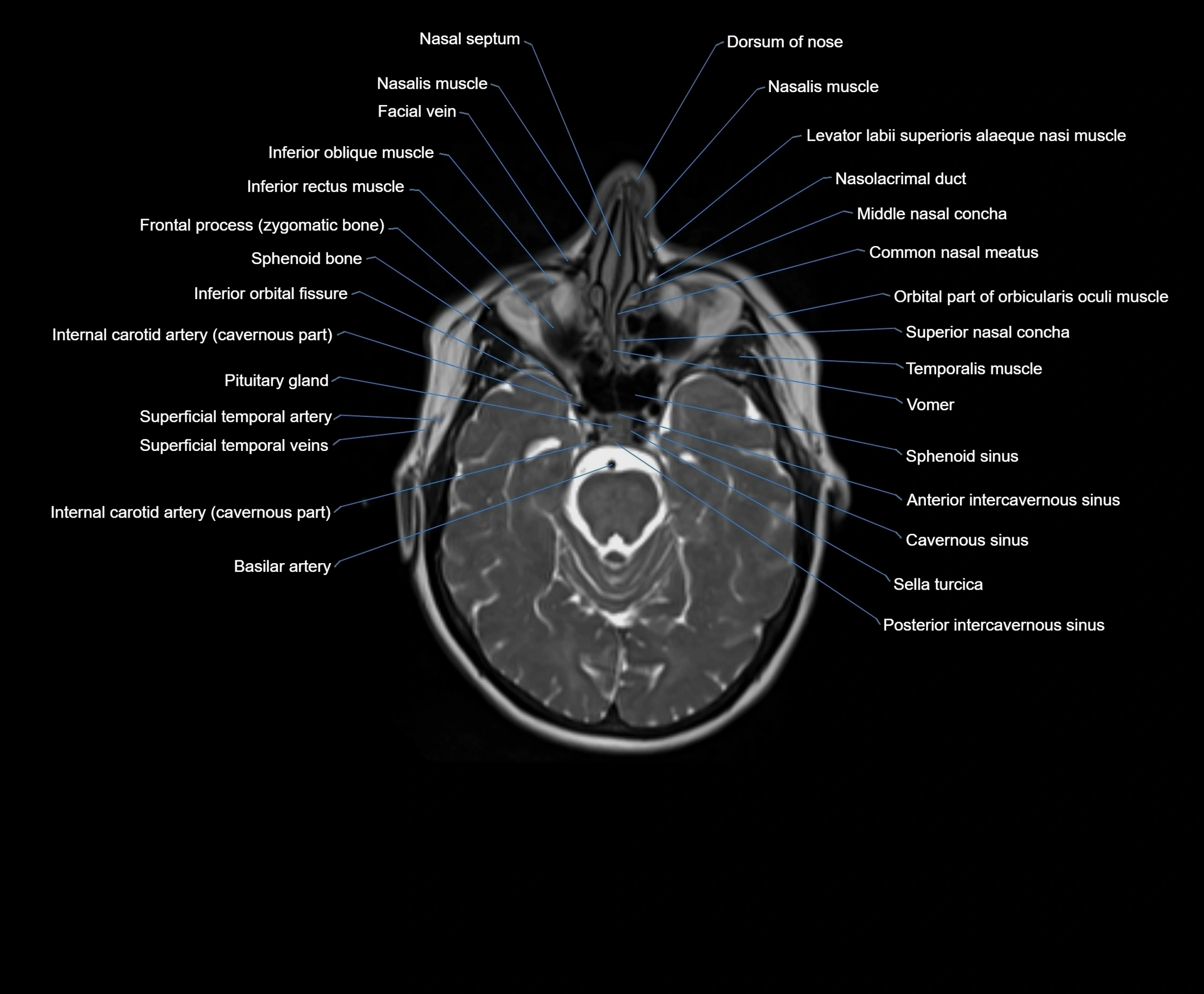
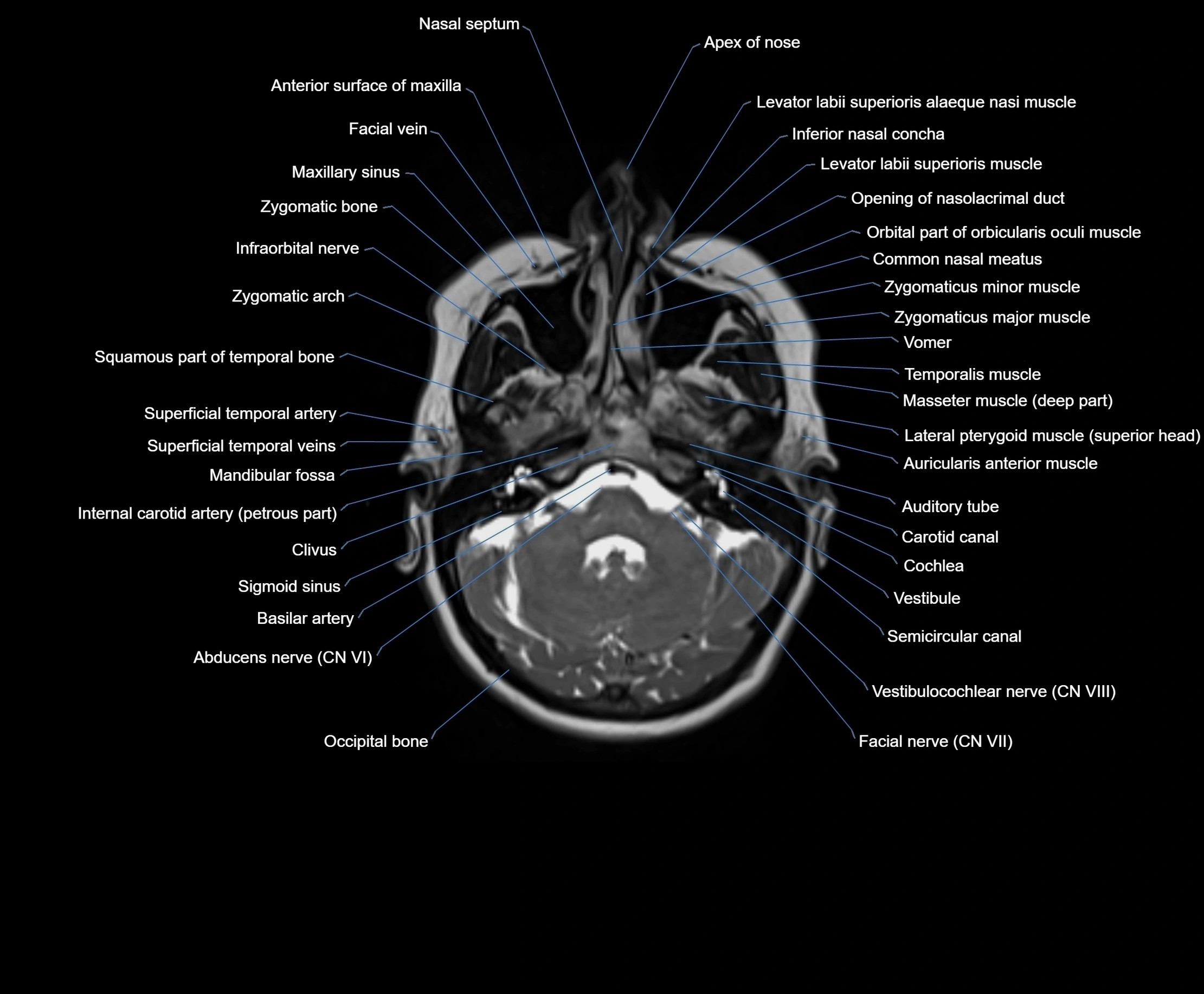
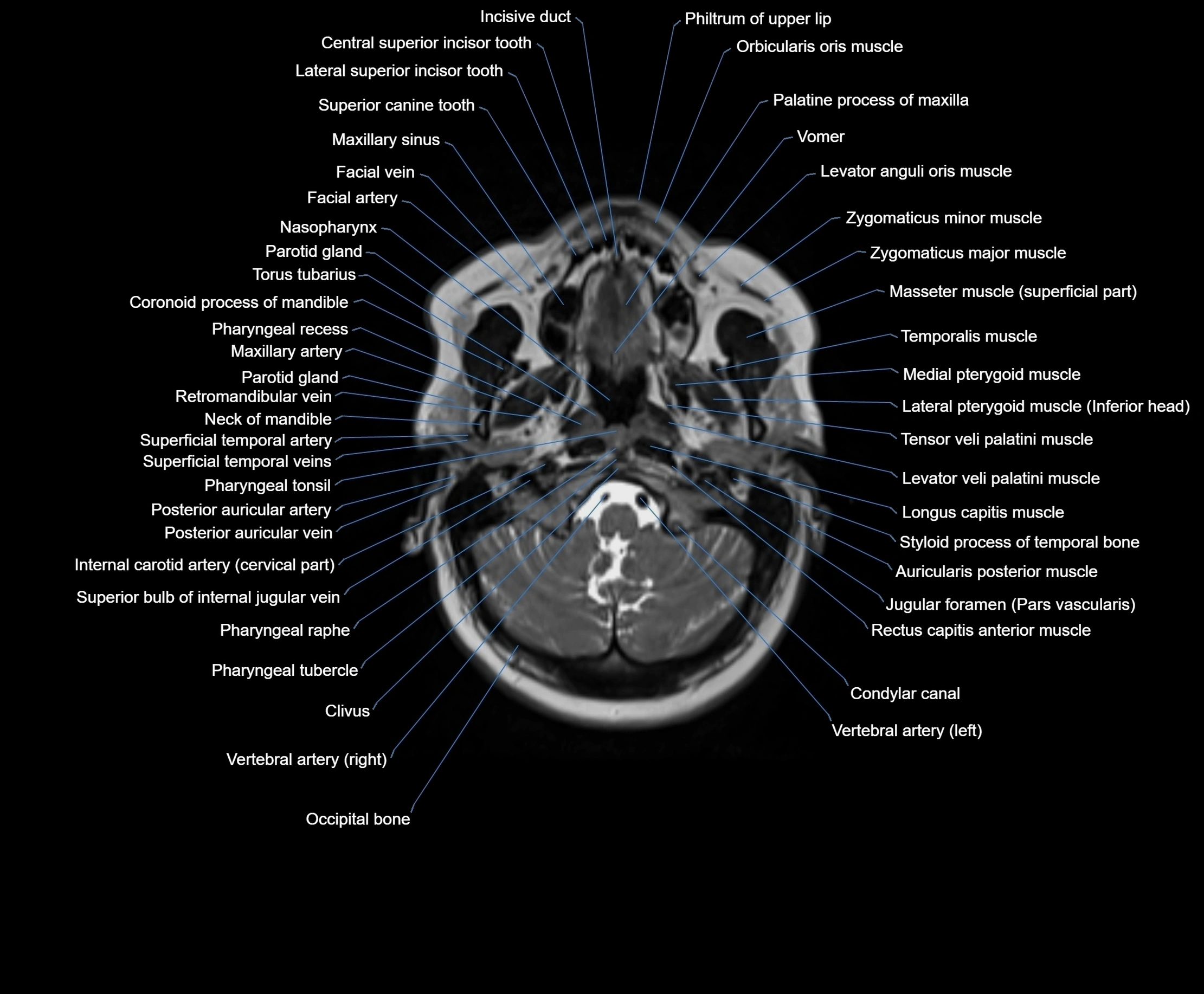
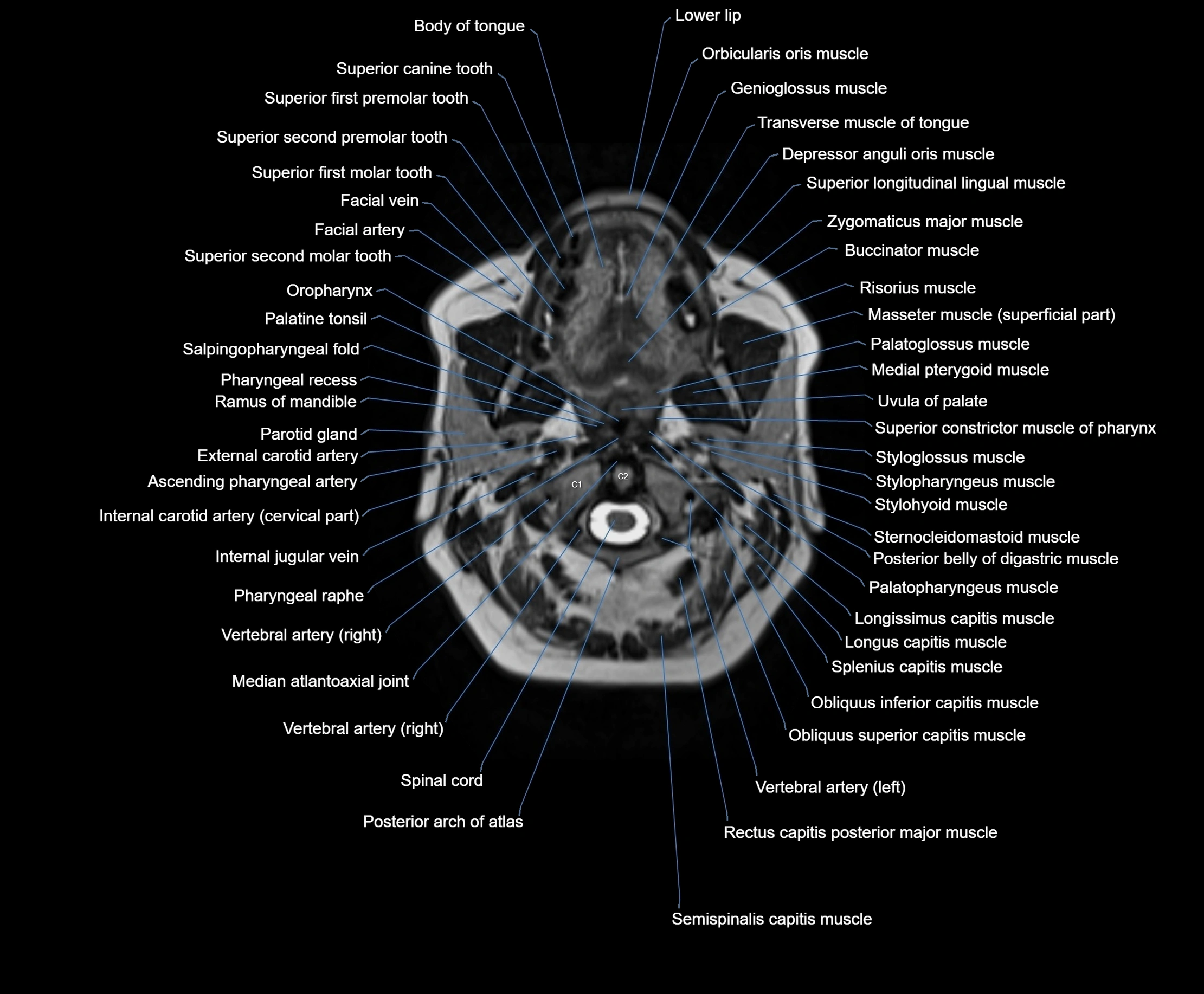
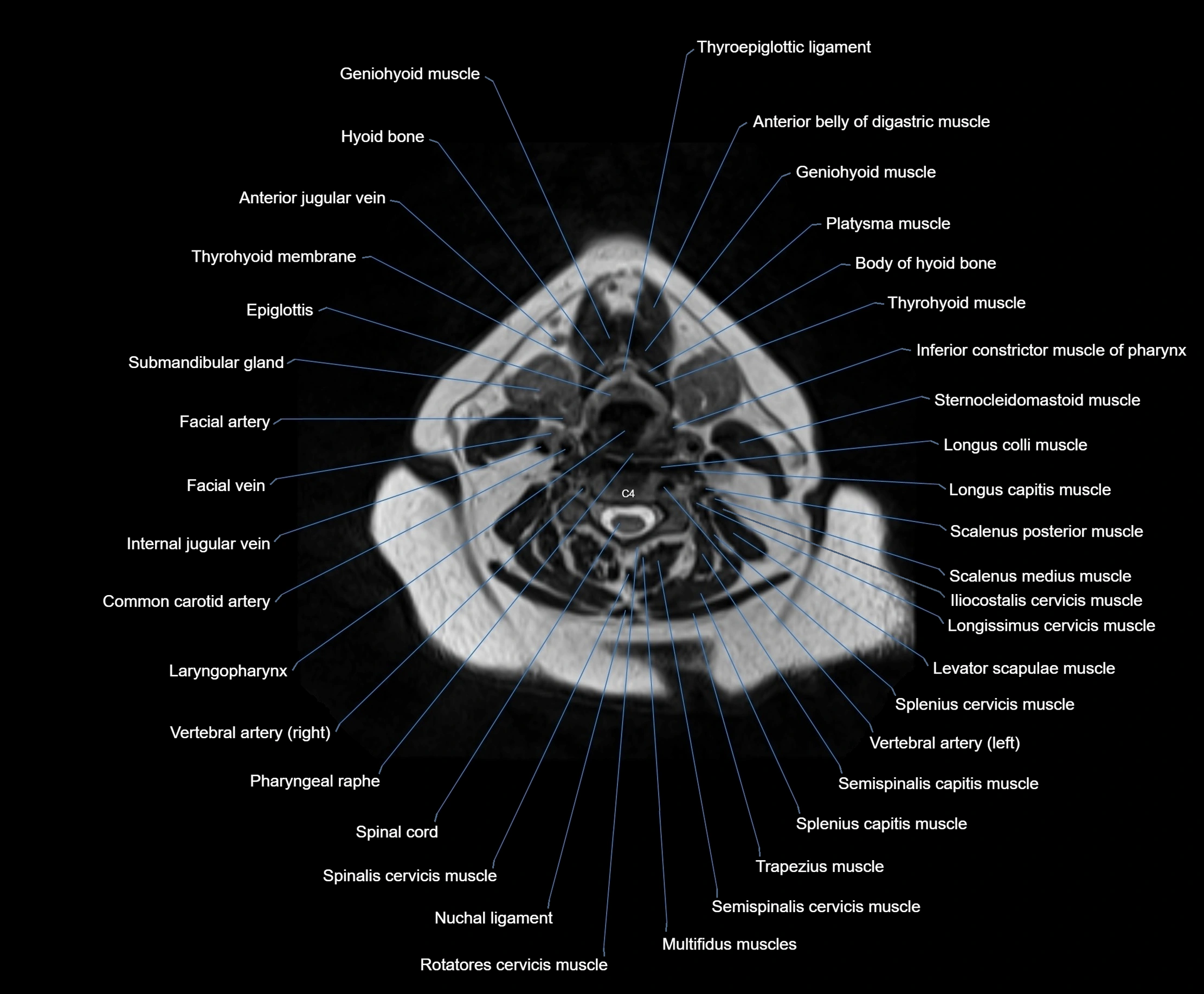
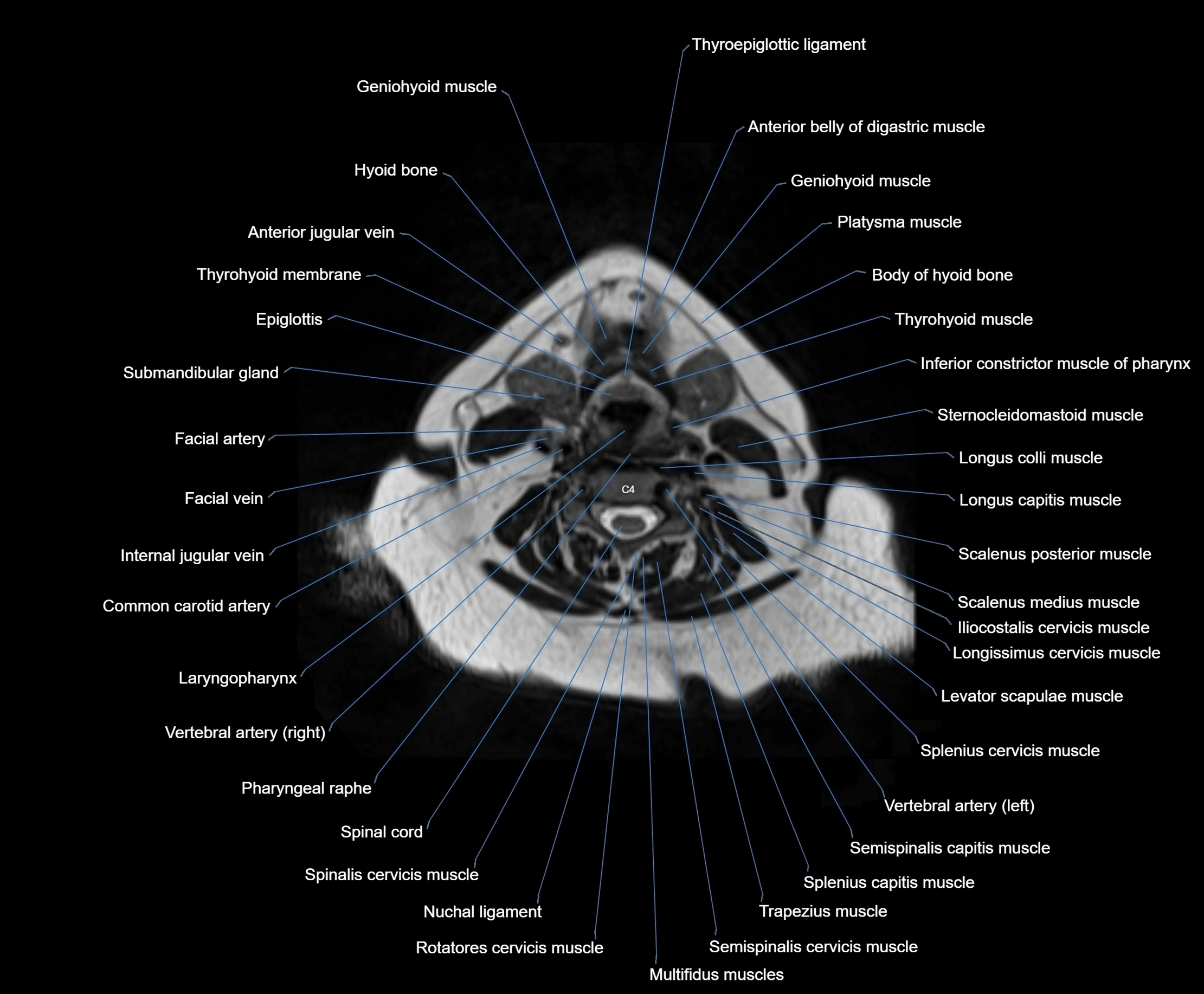
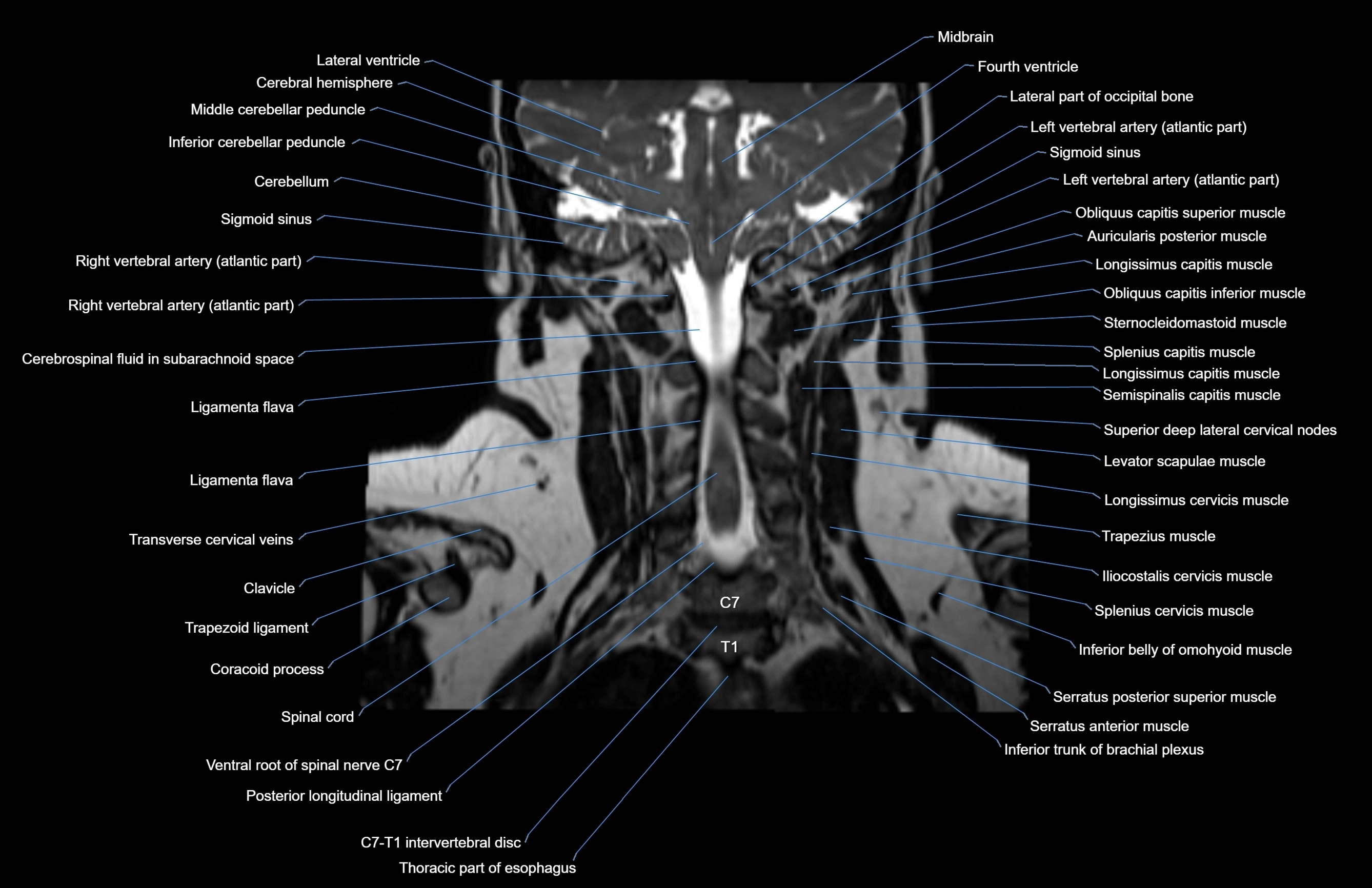
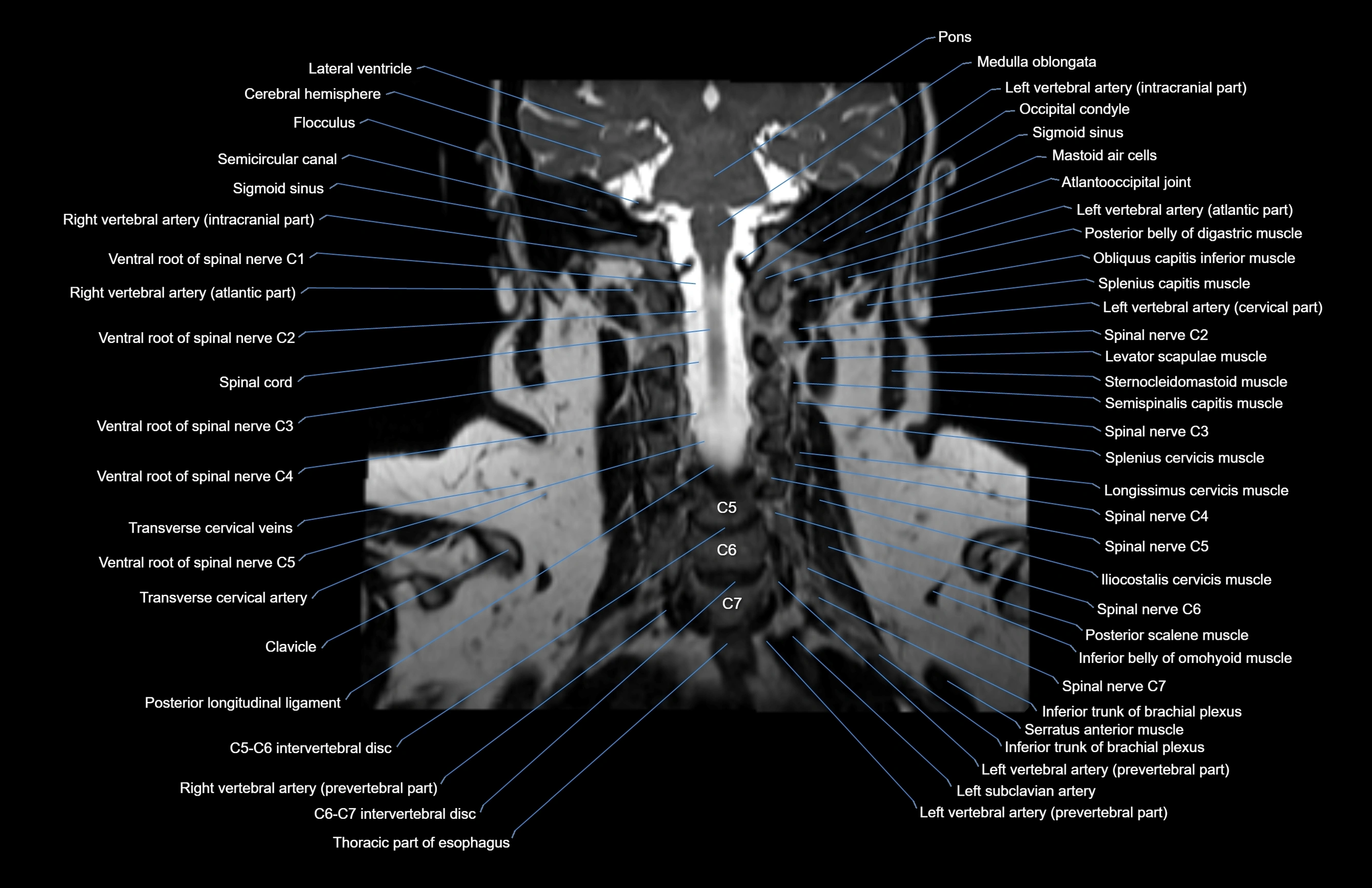
MRI images

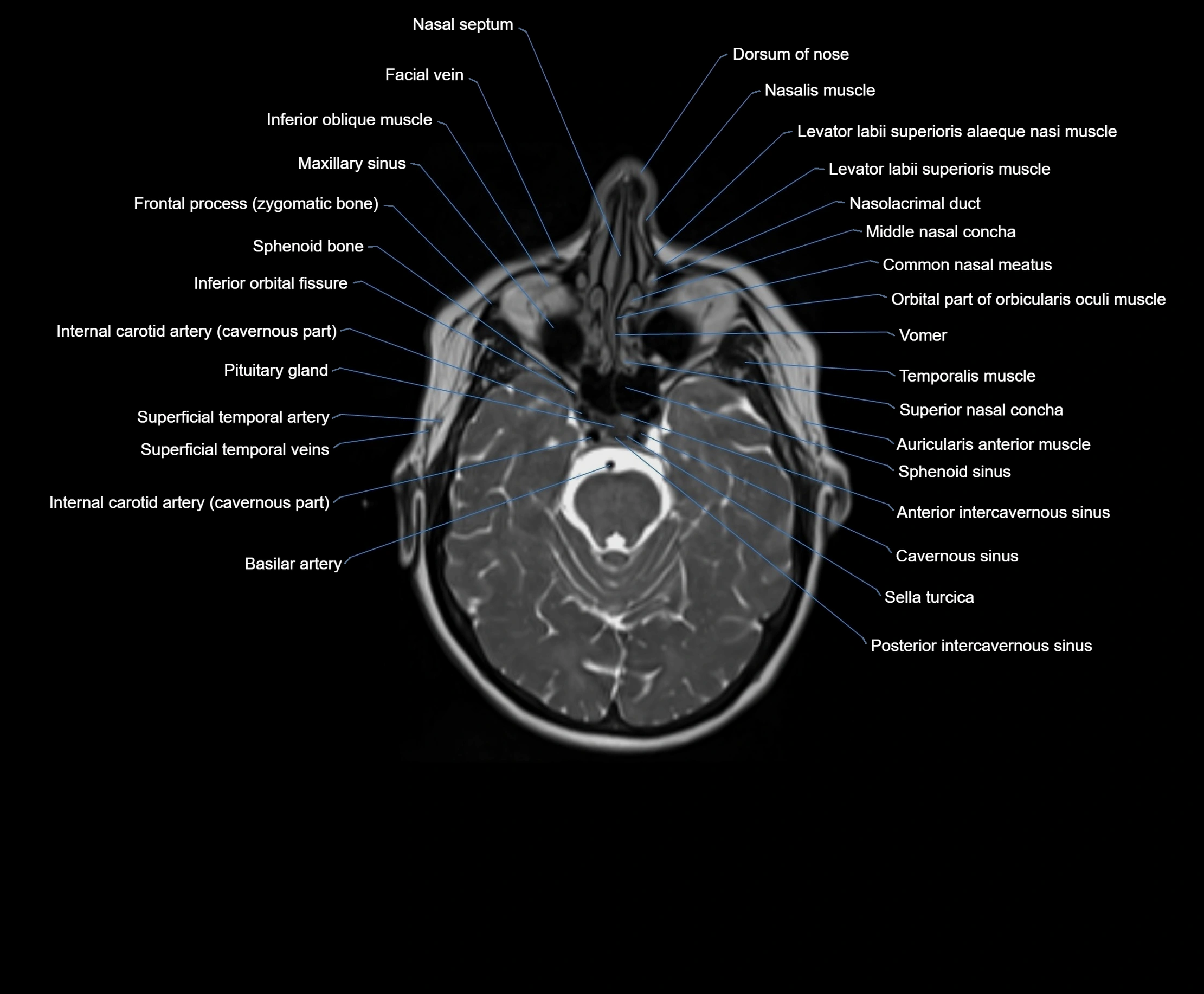
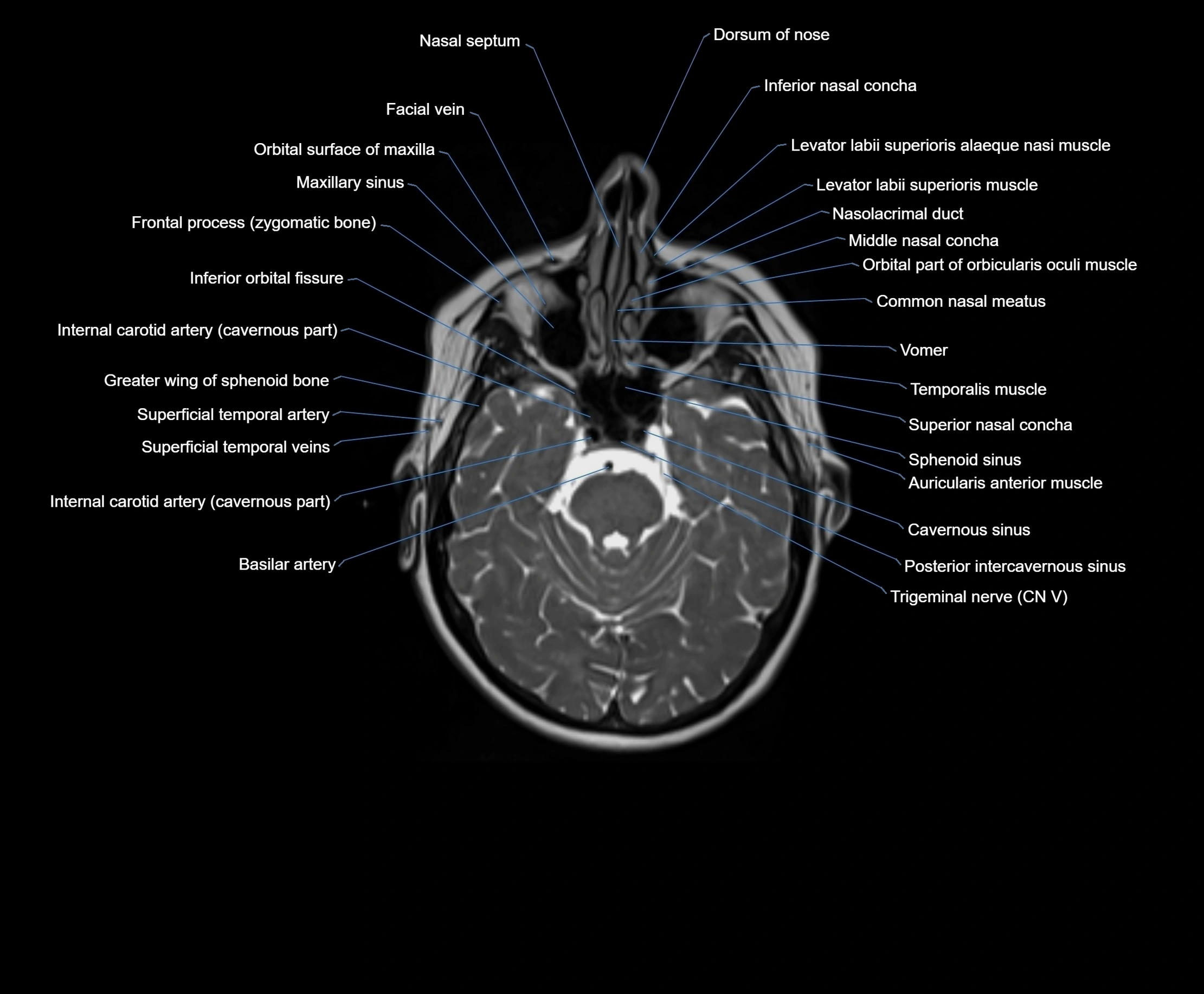
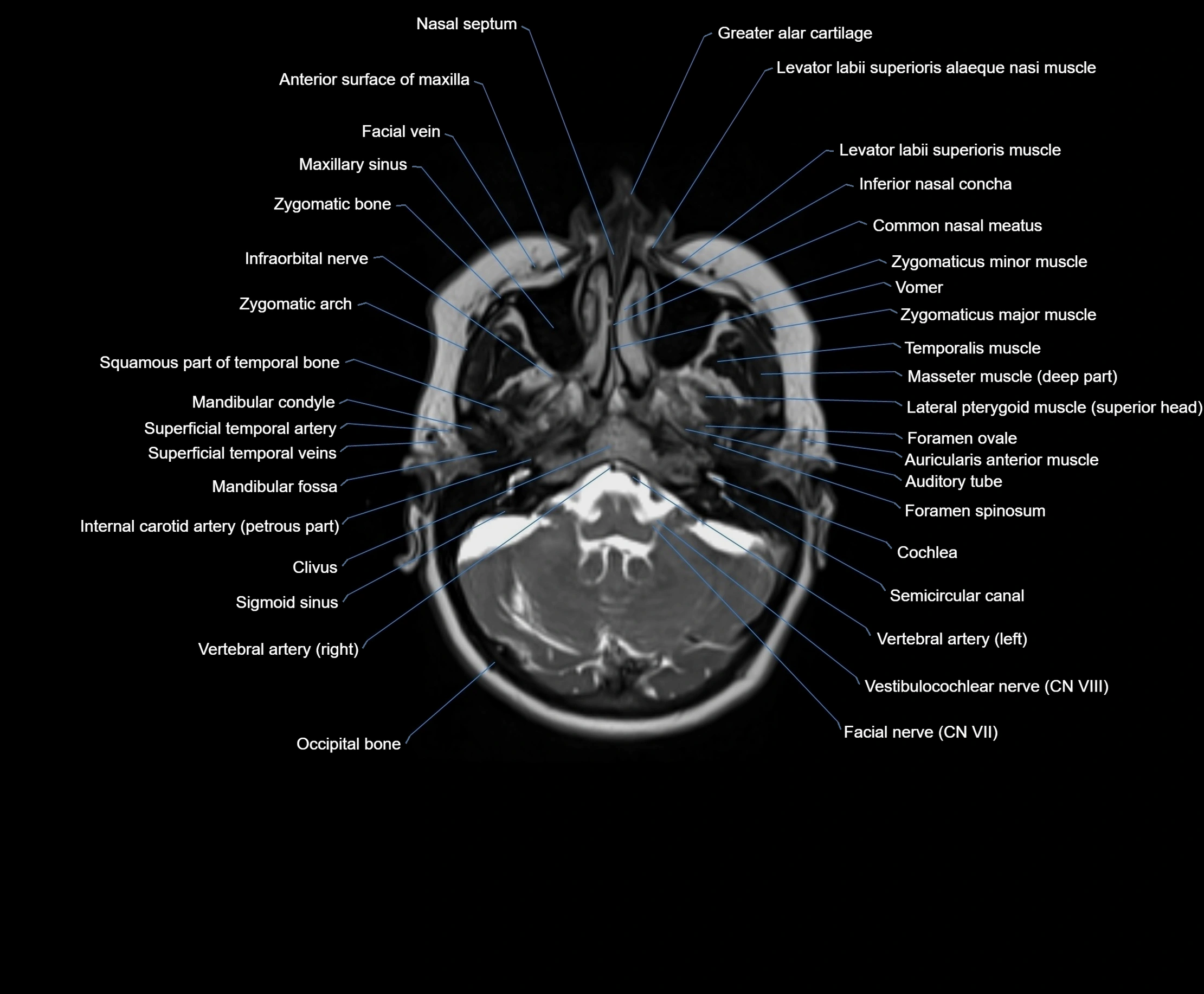
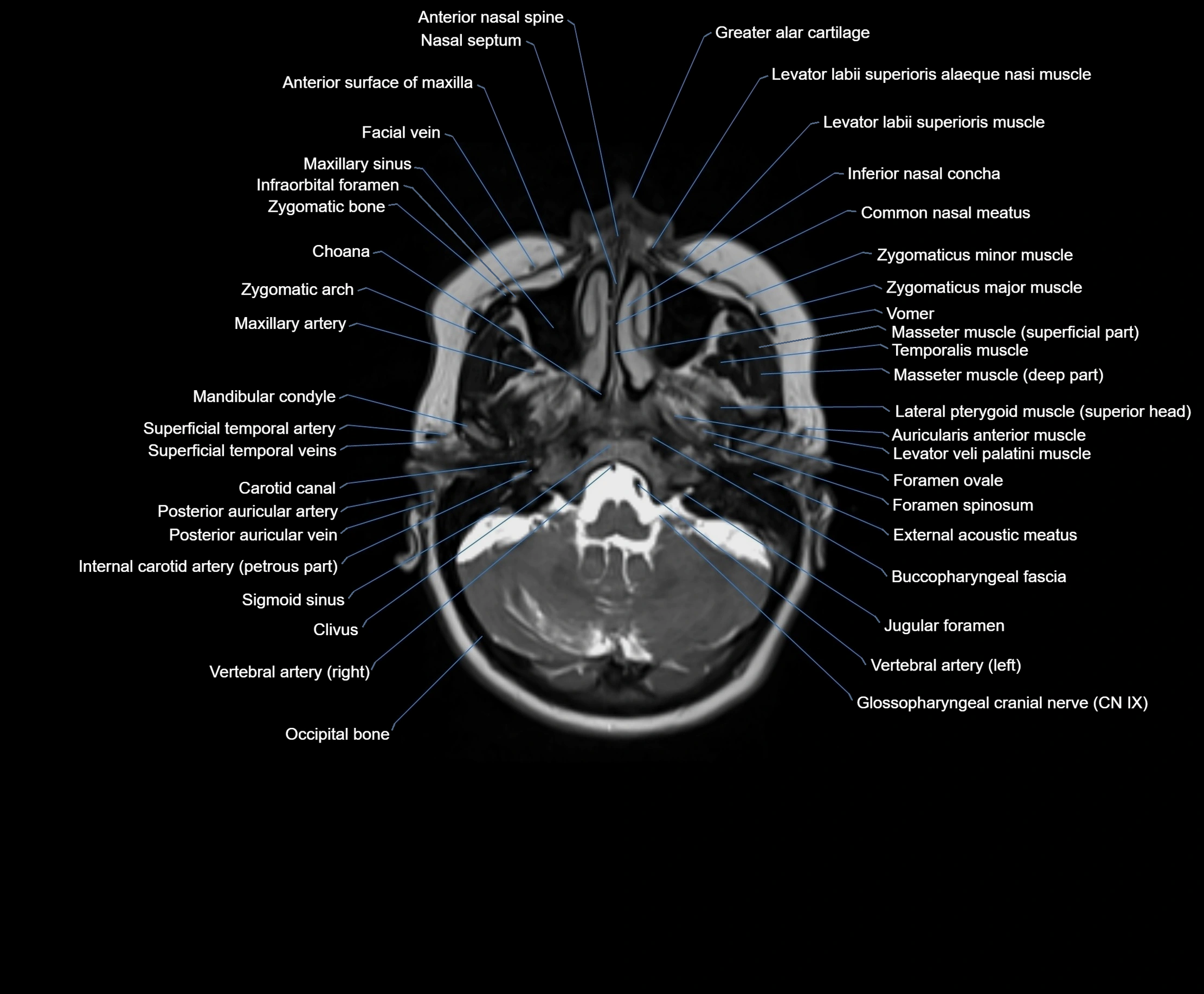
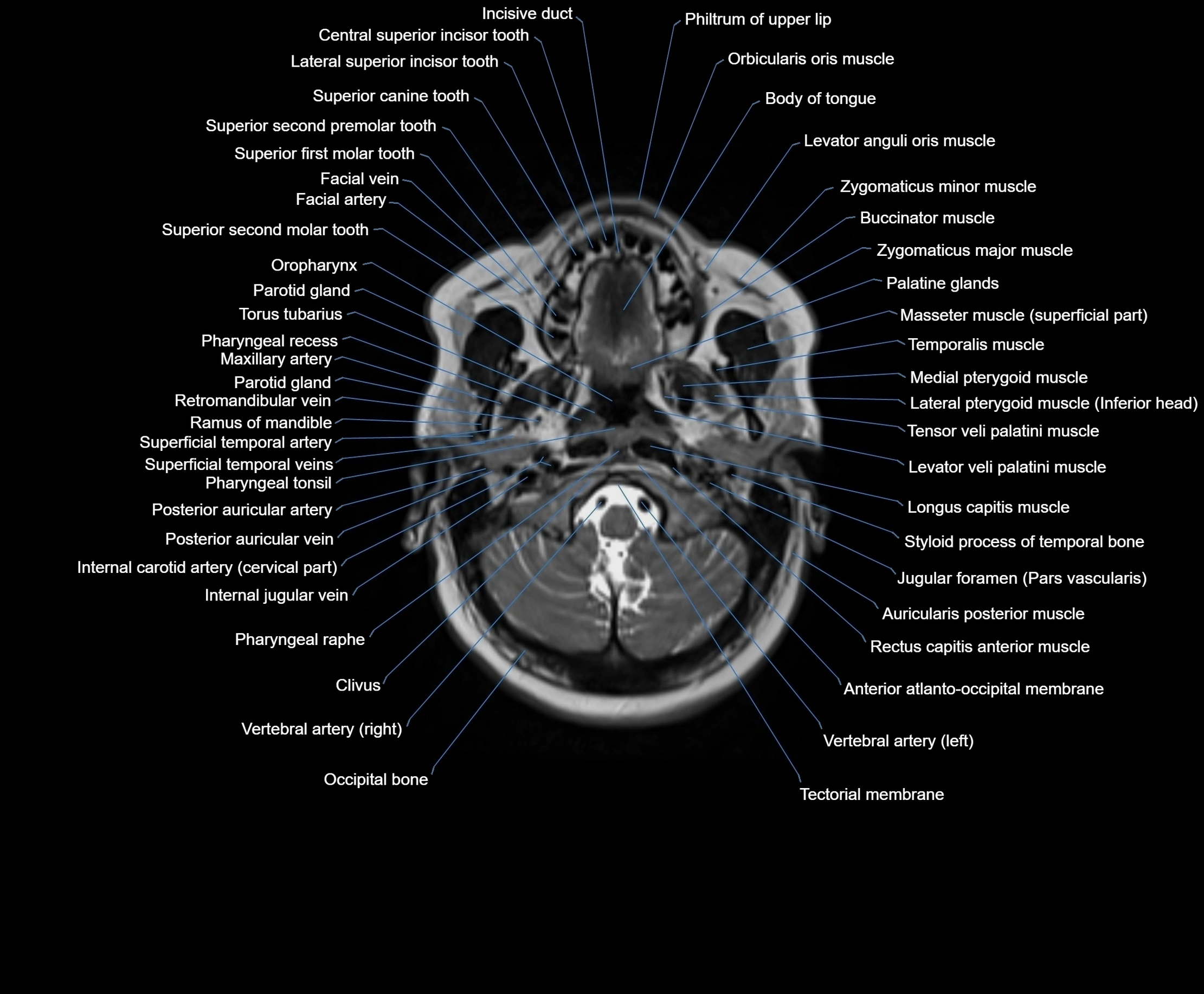
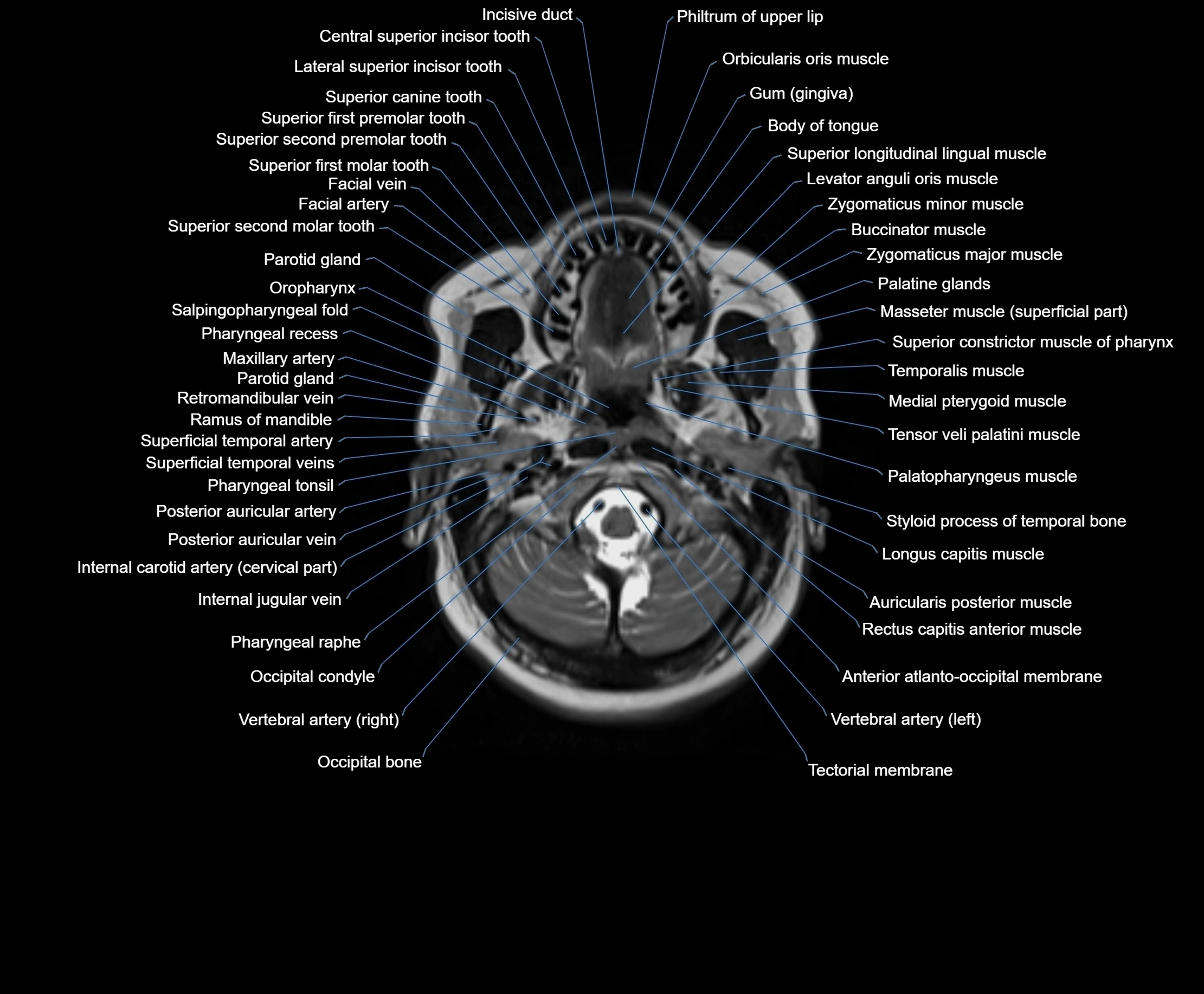
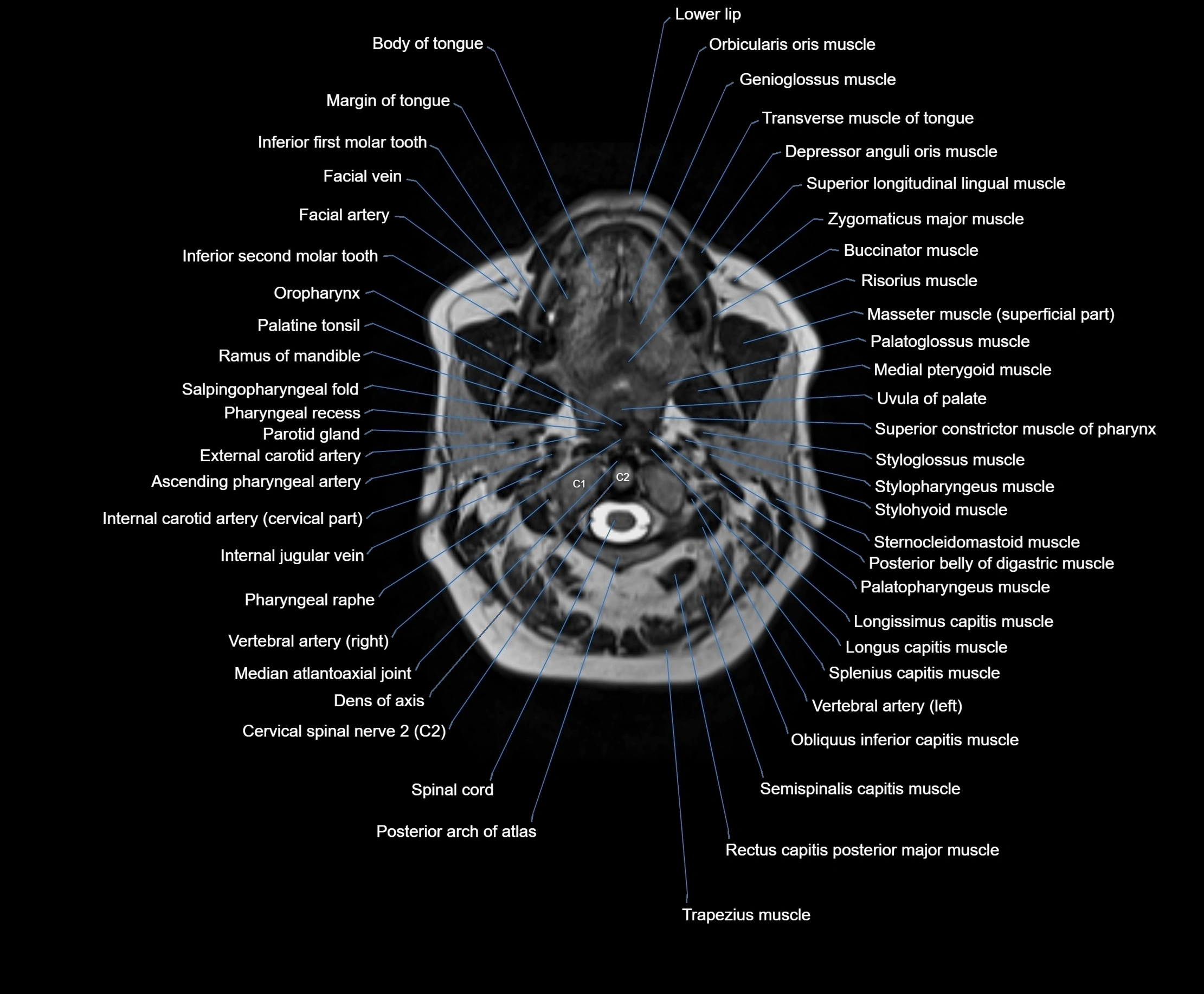
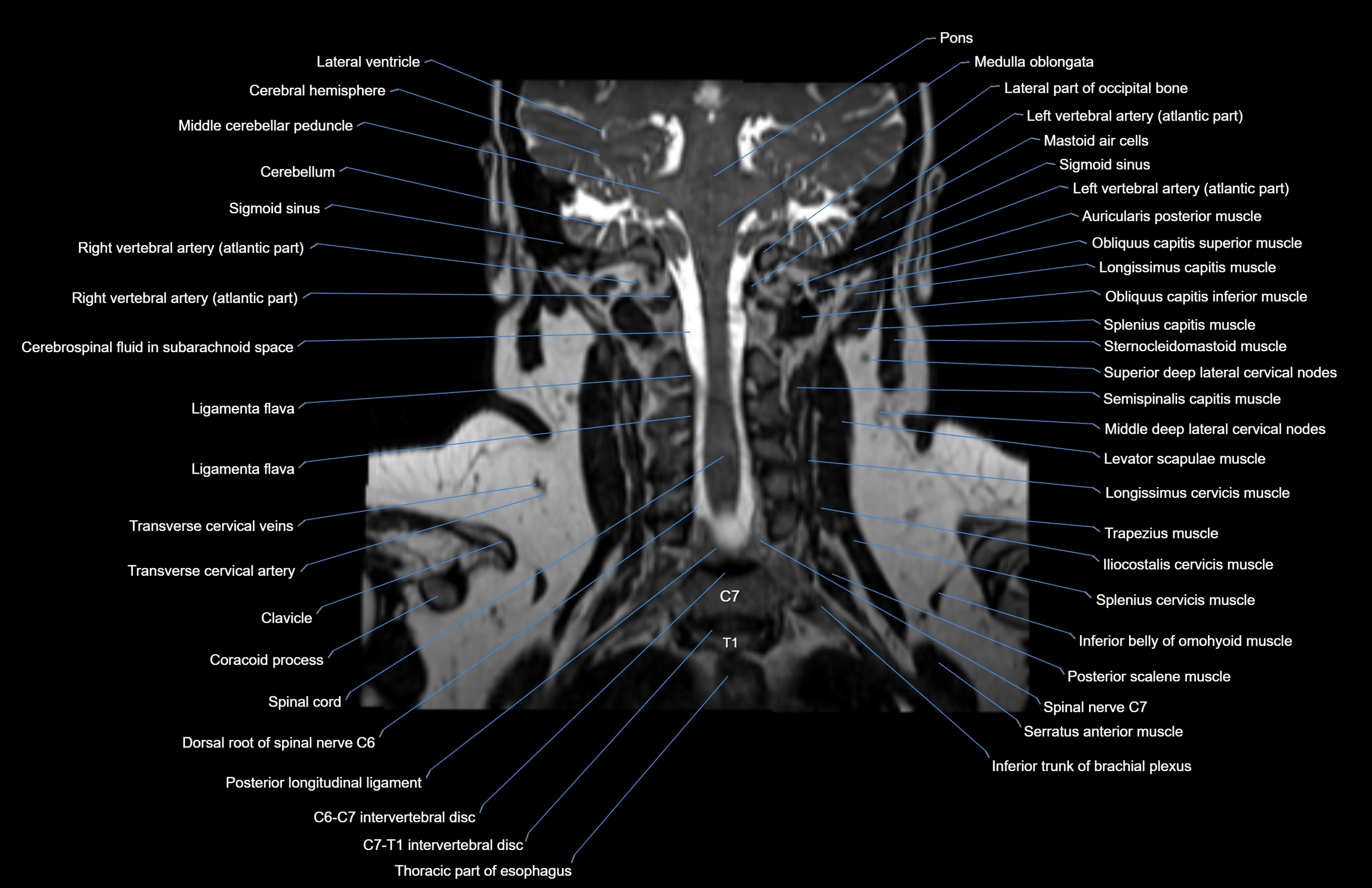
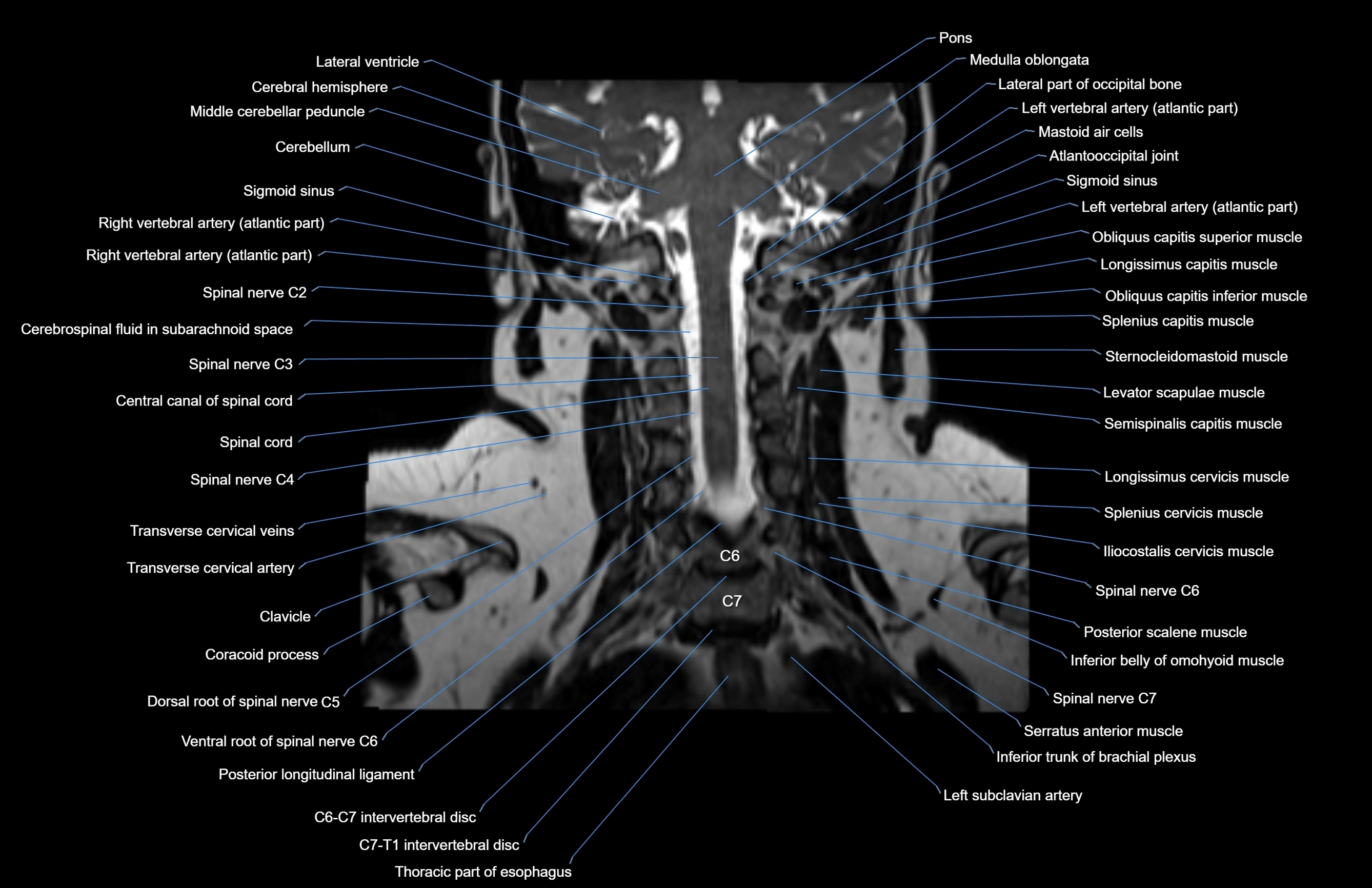
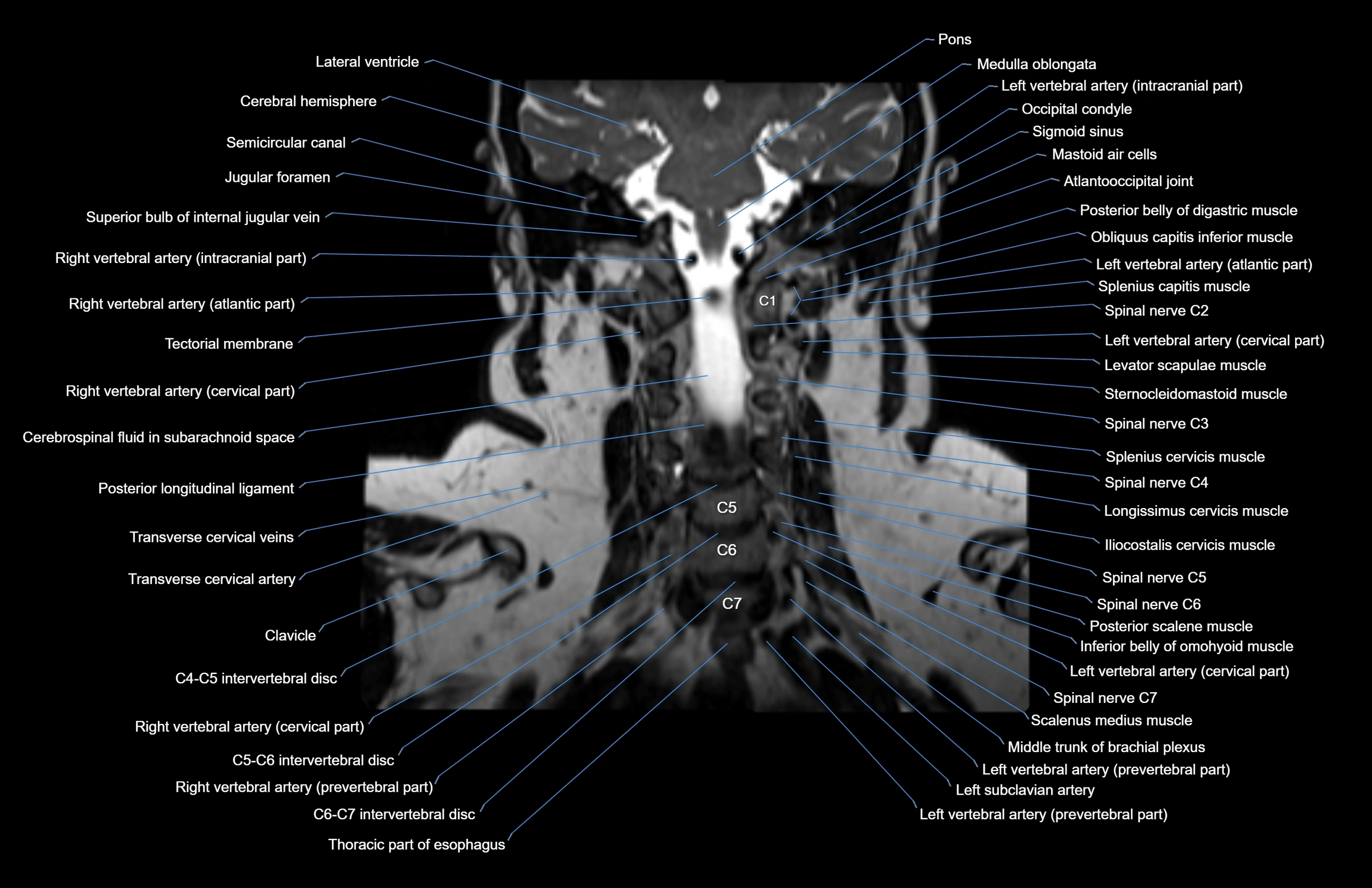
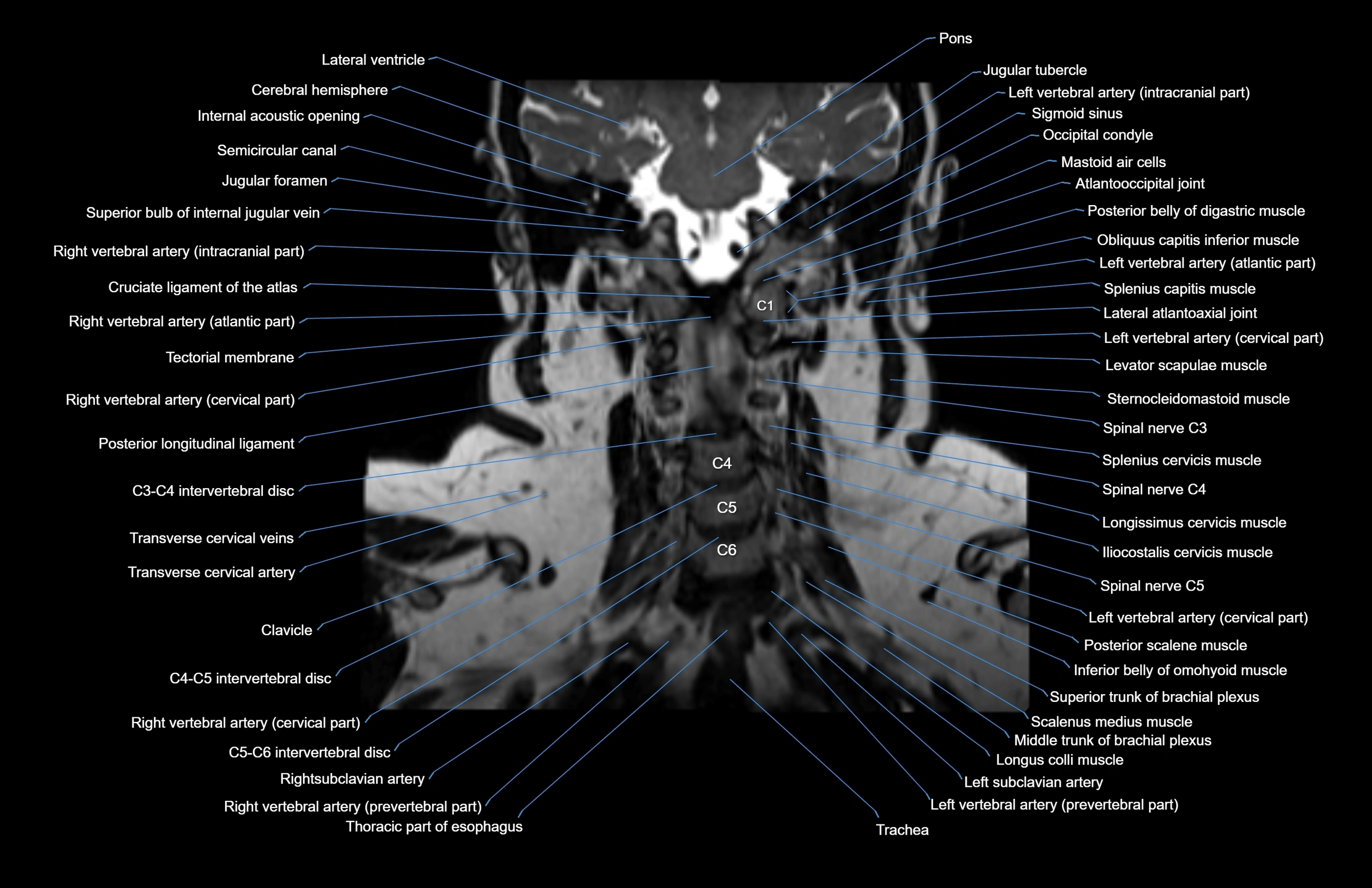
MRI images