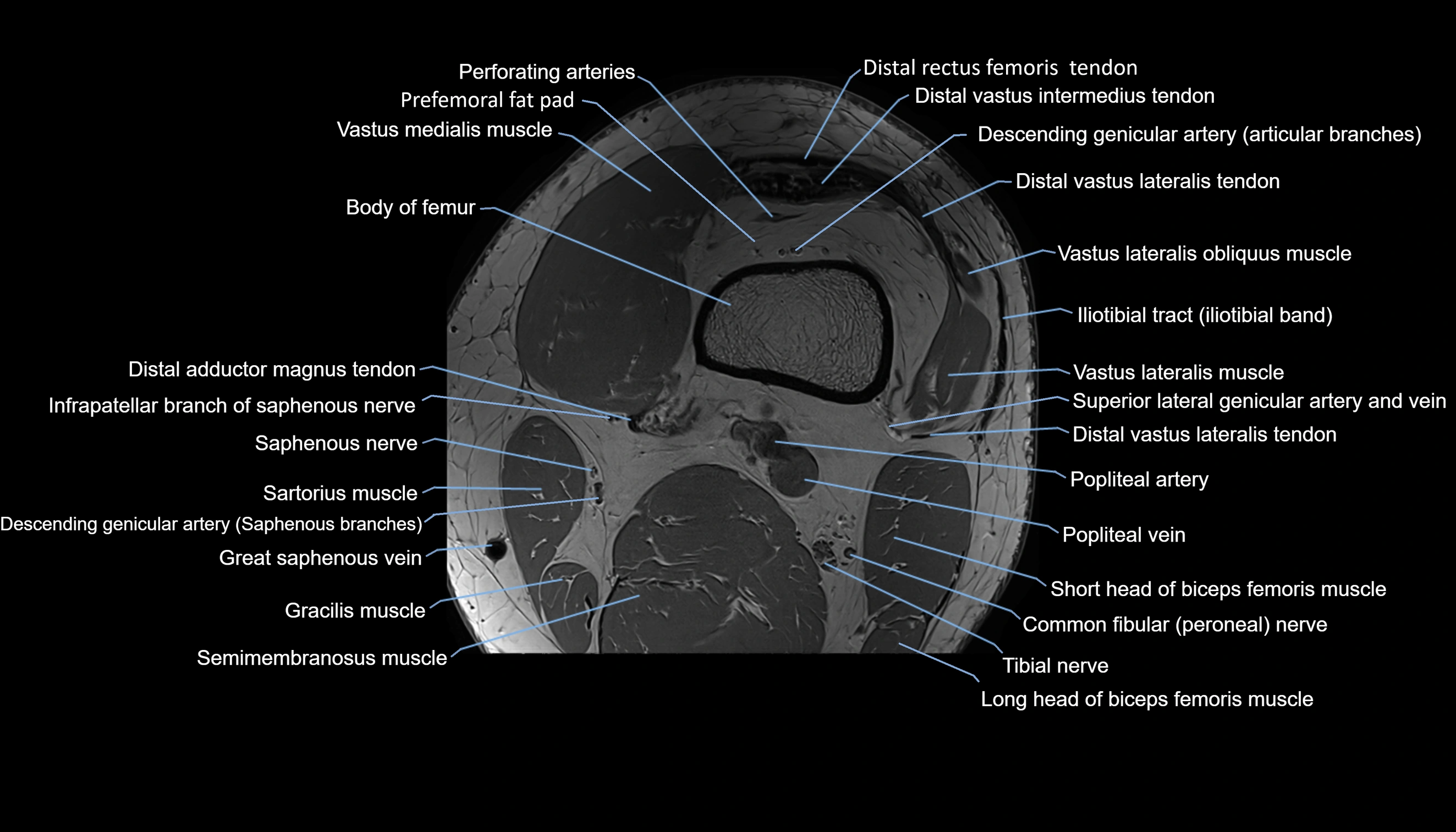
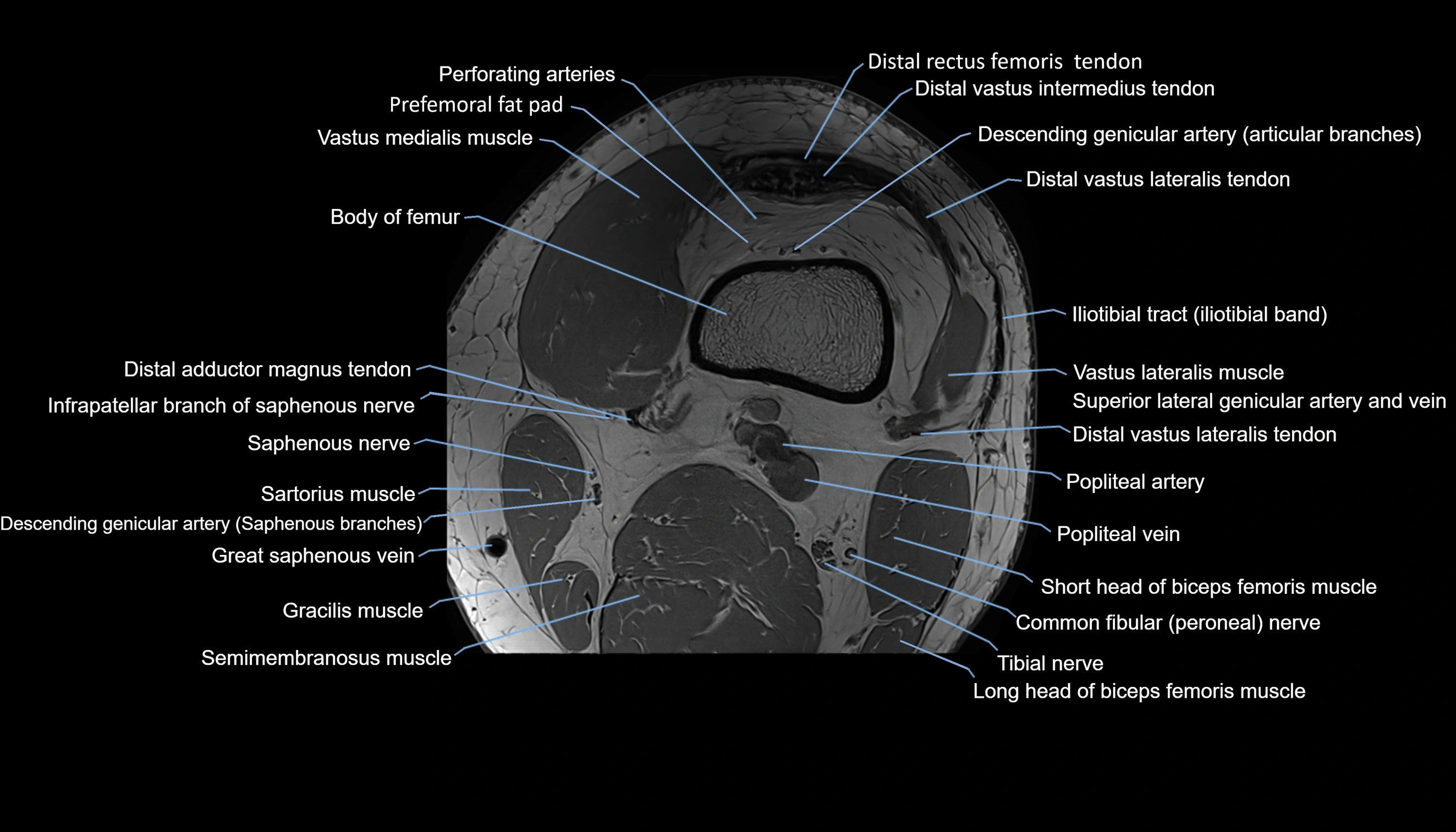
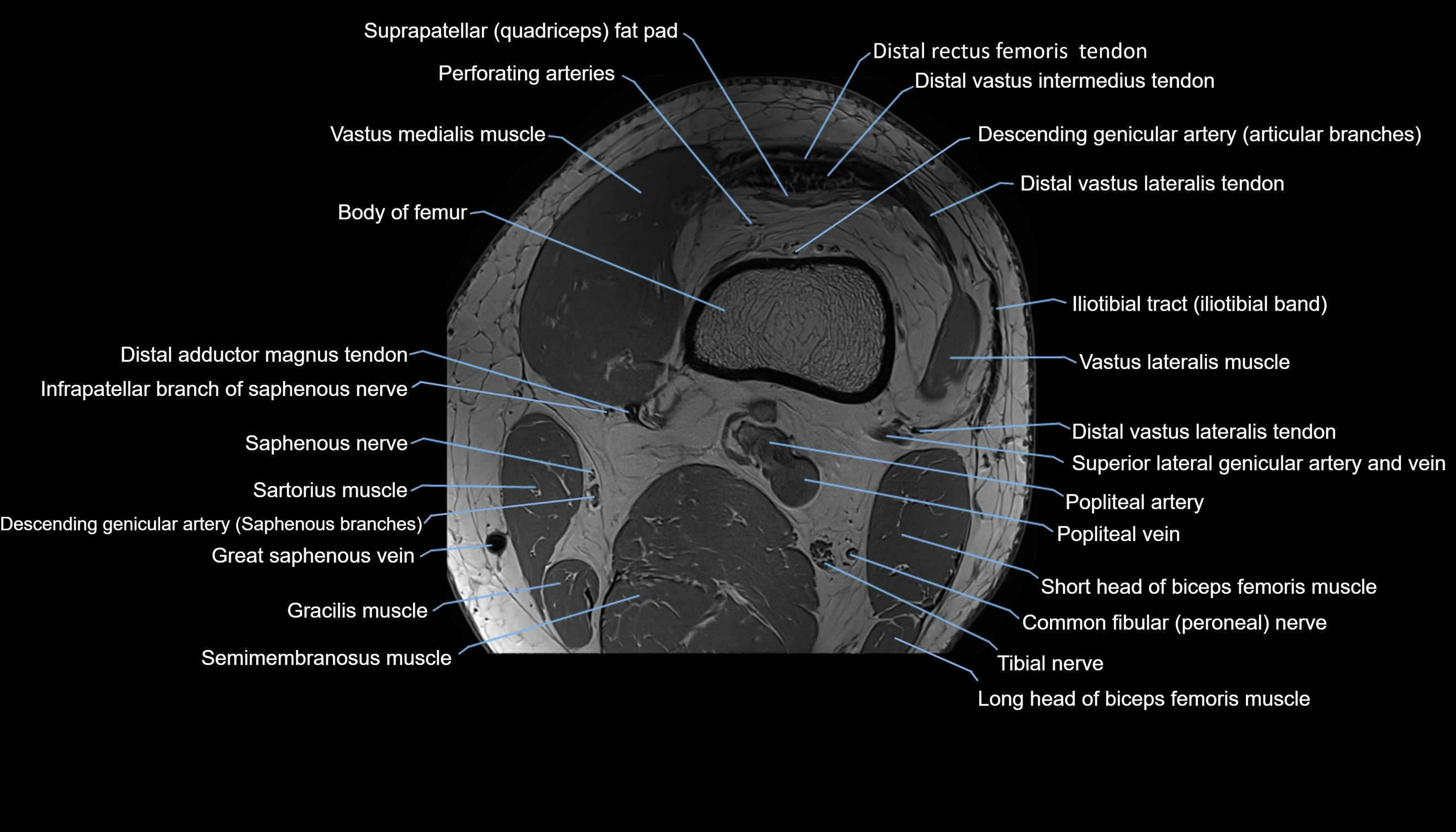
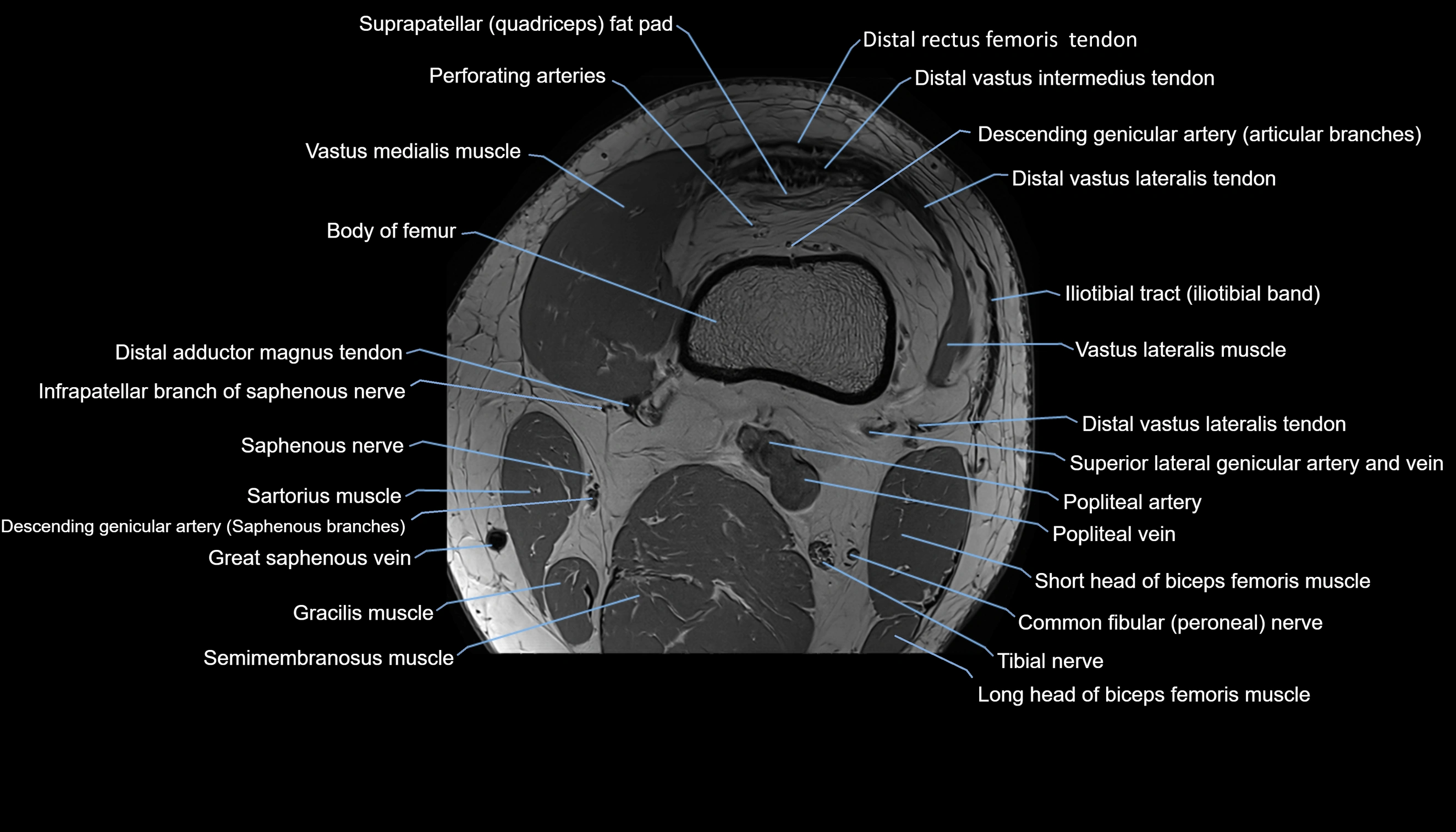
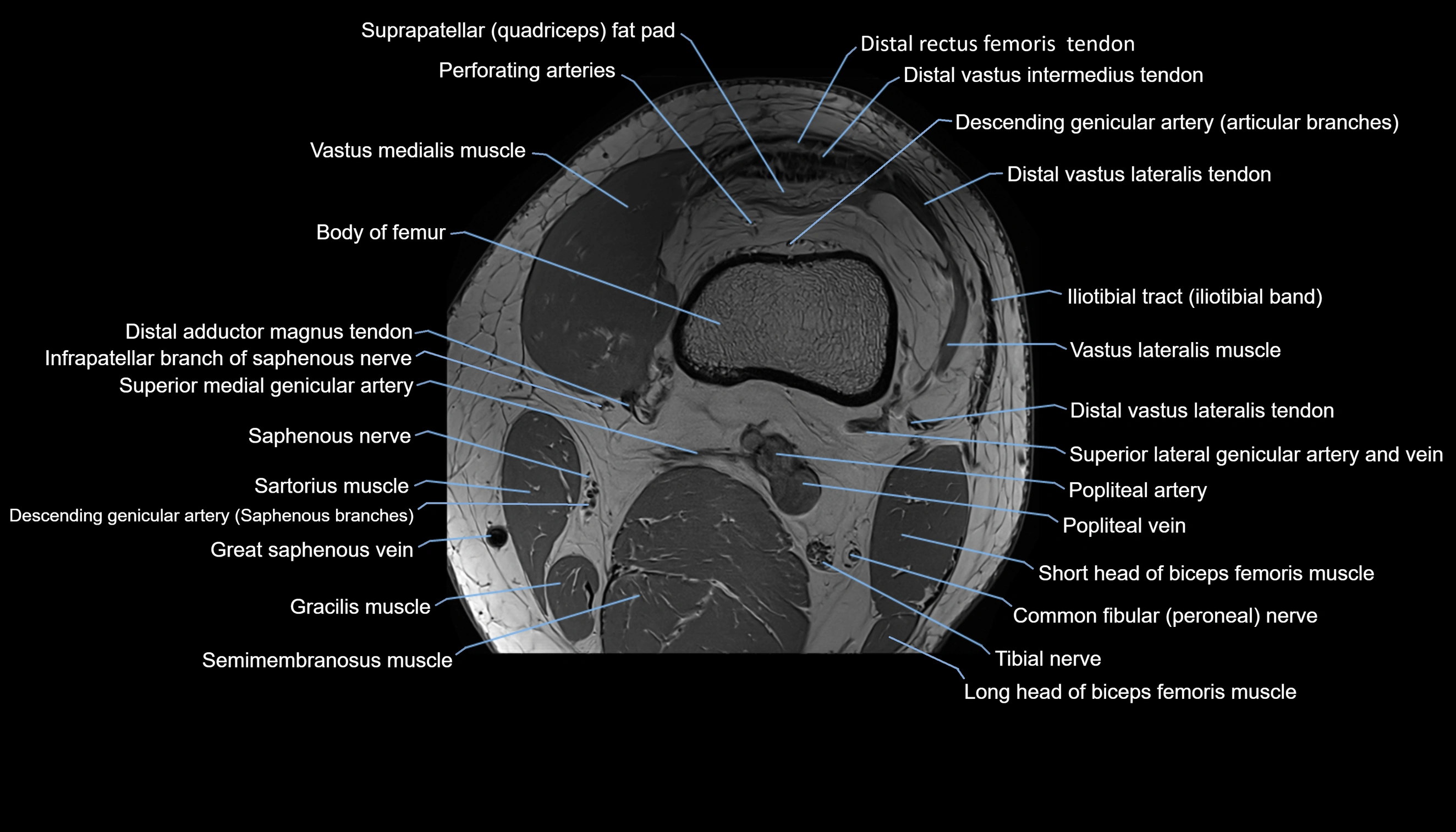
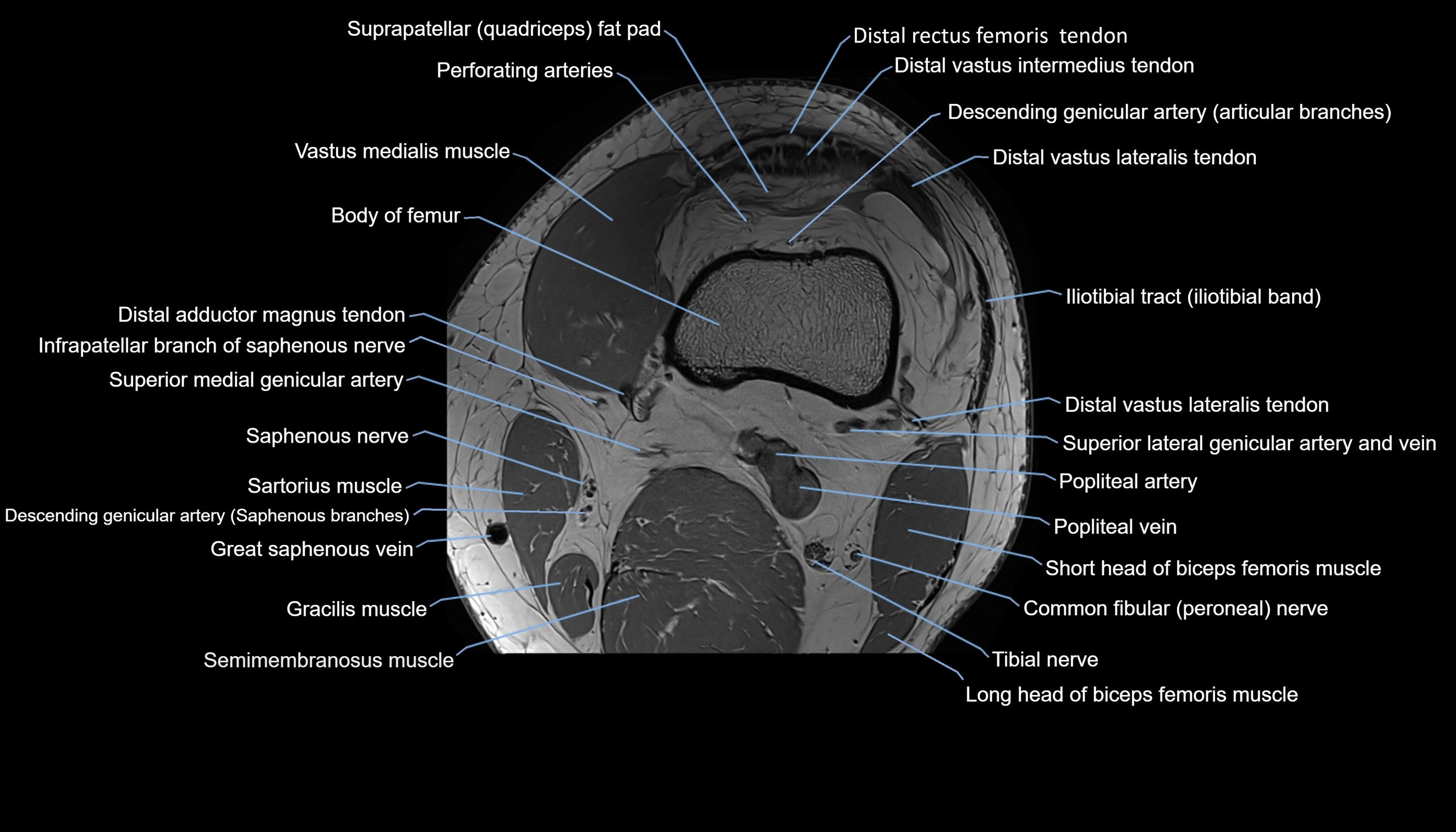
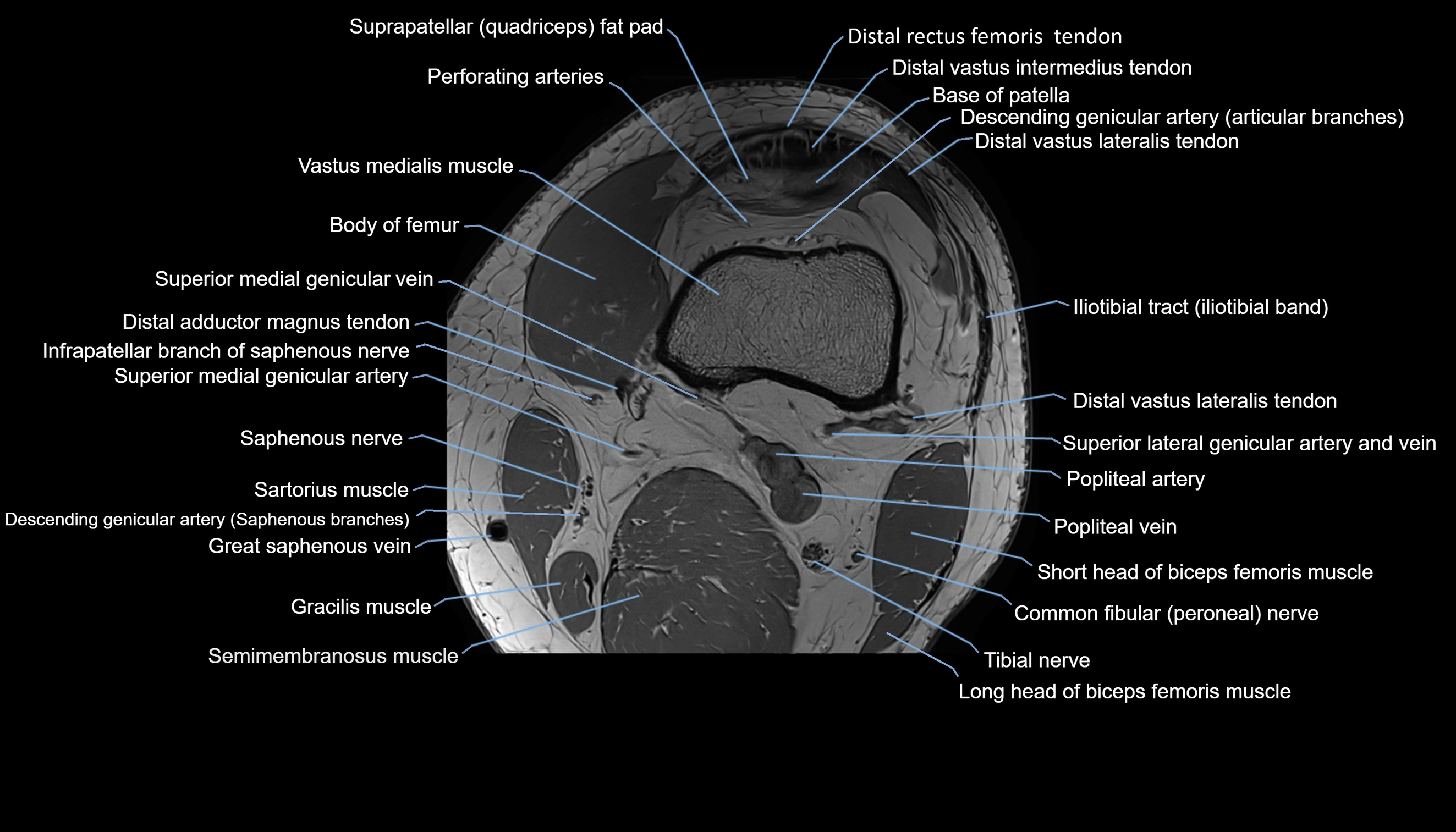
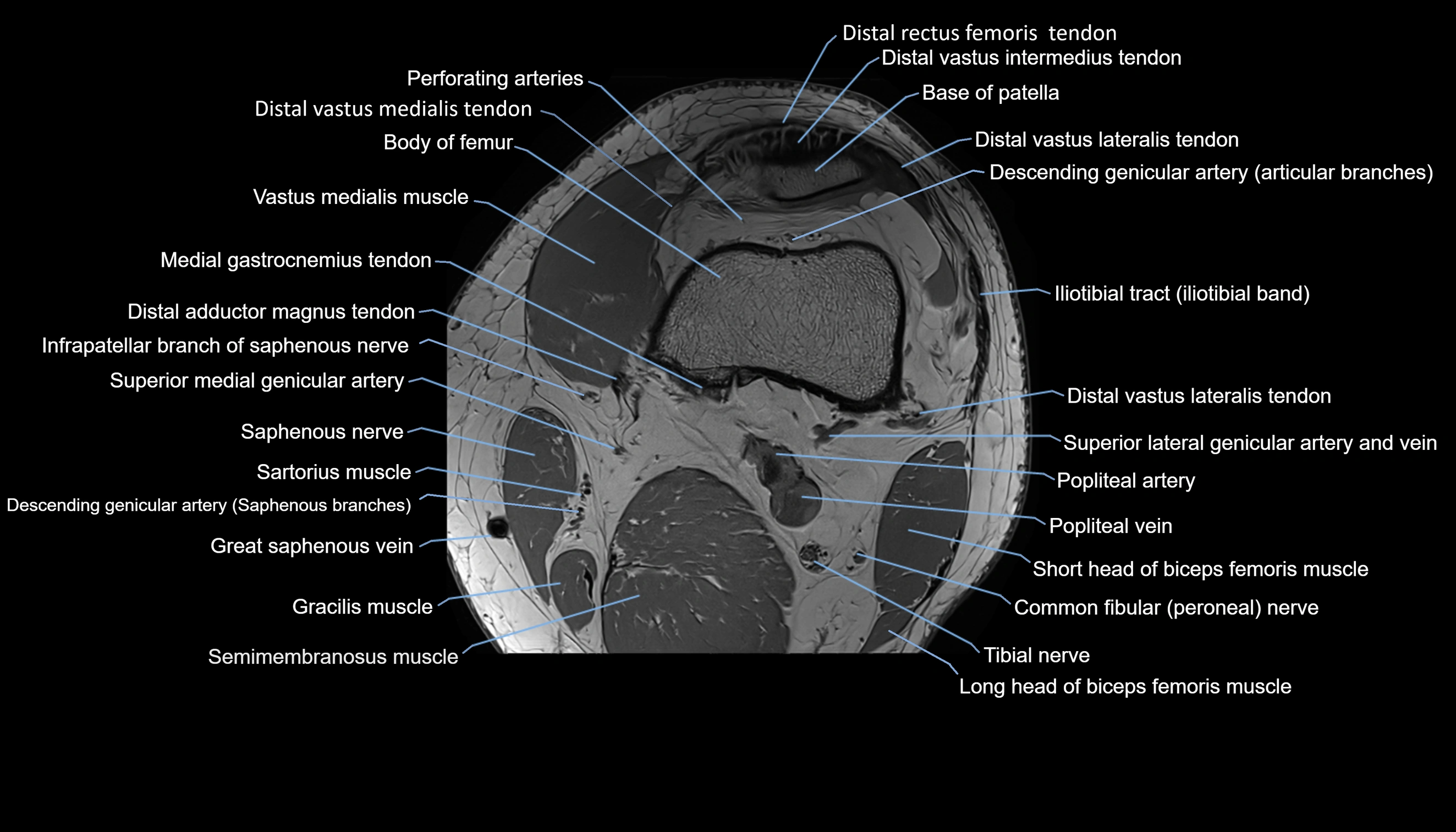
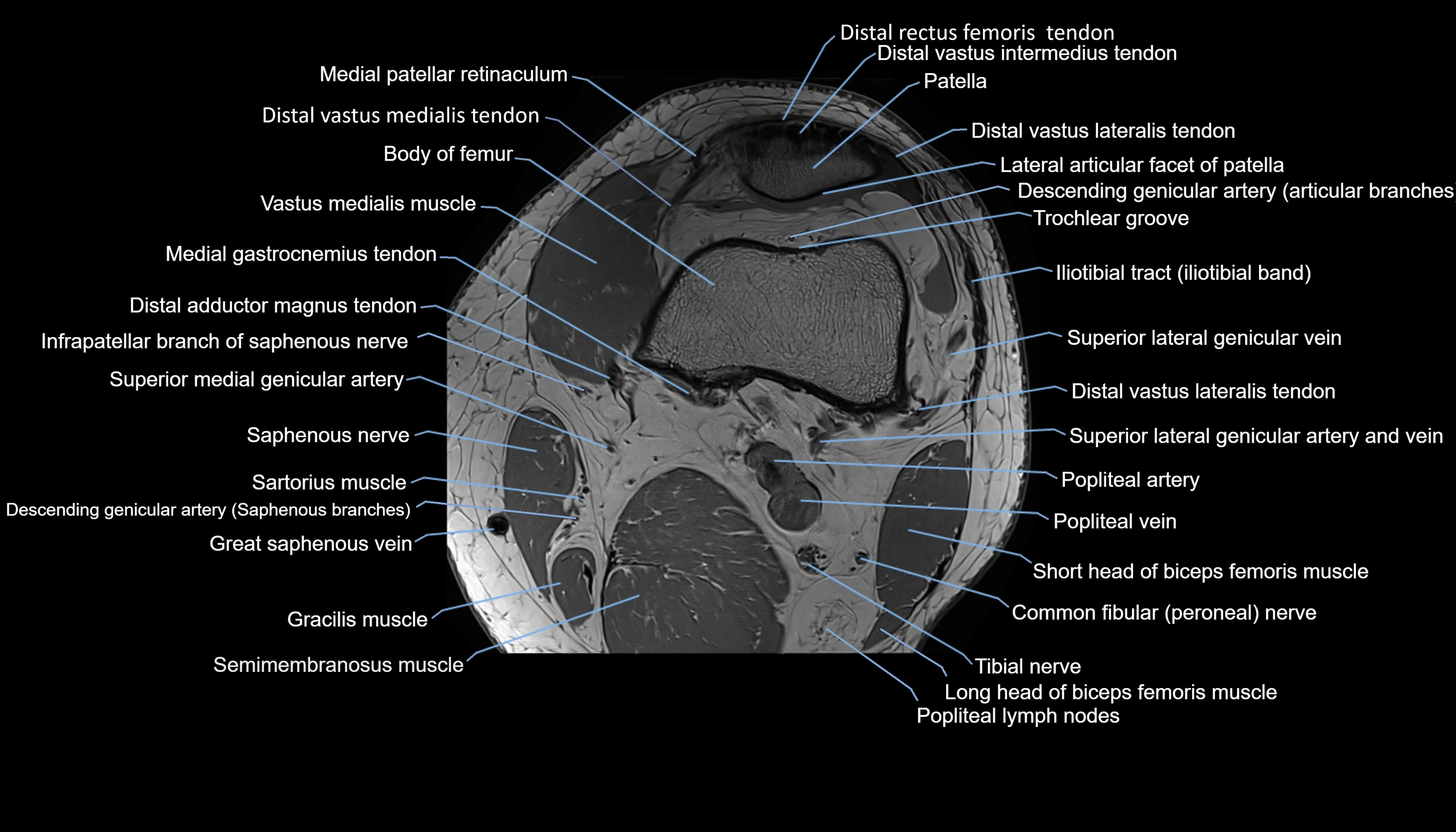
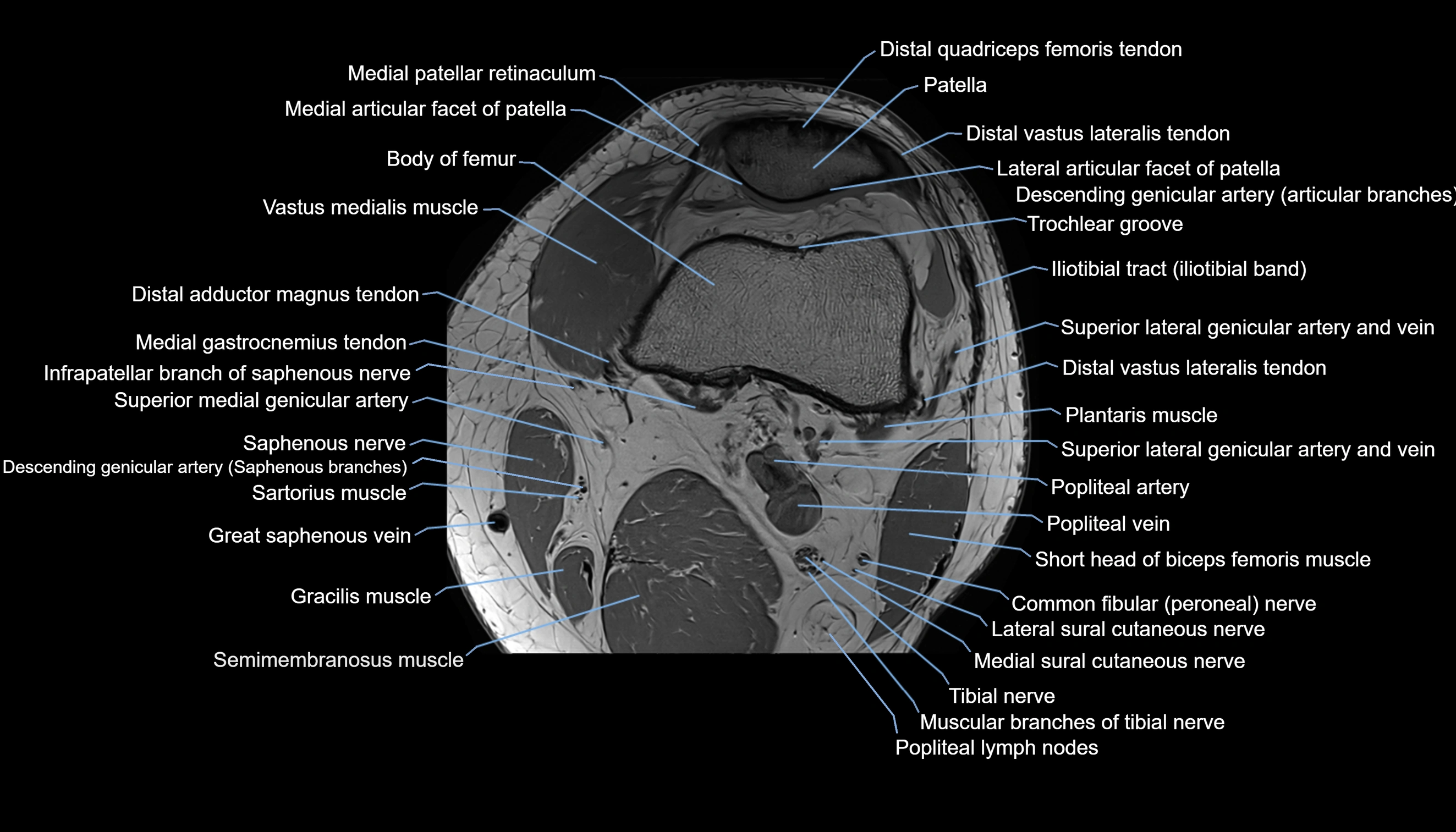
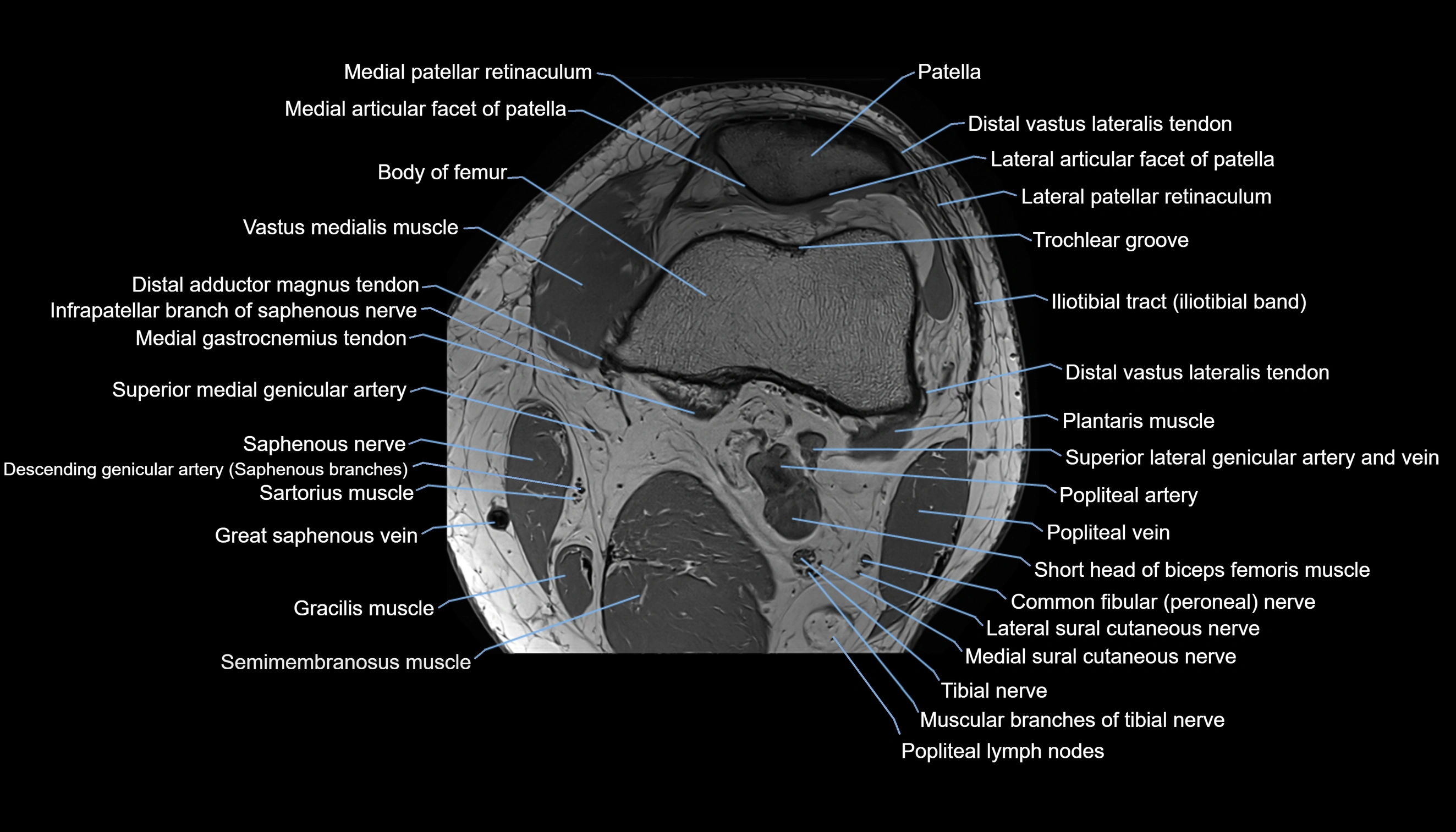
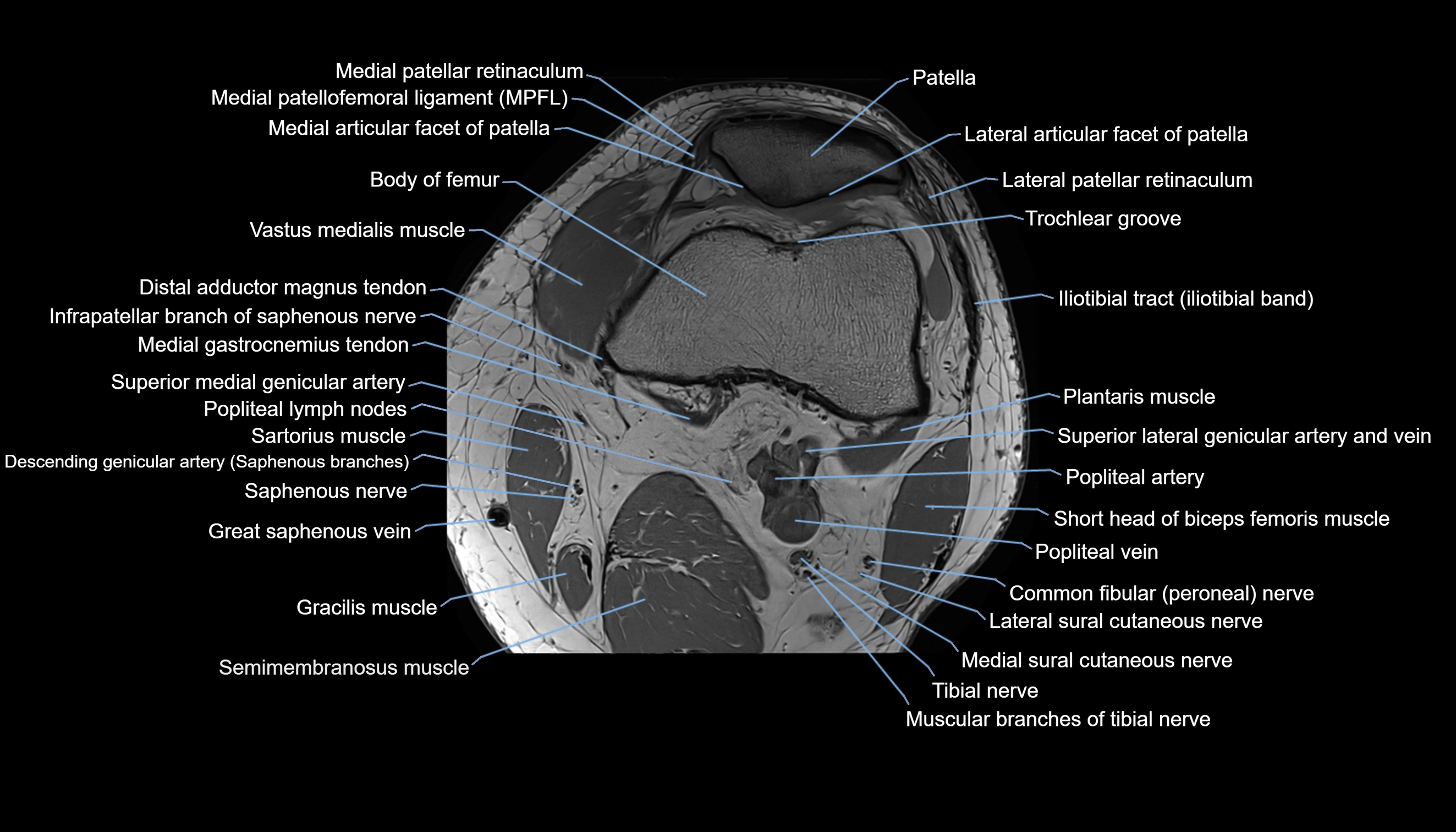
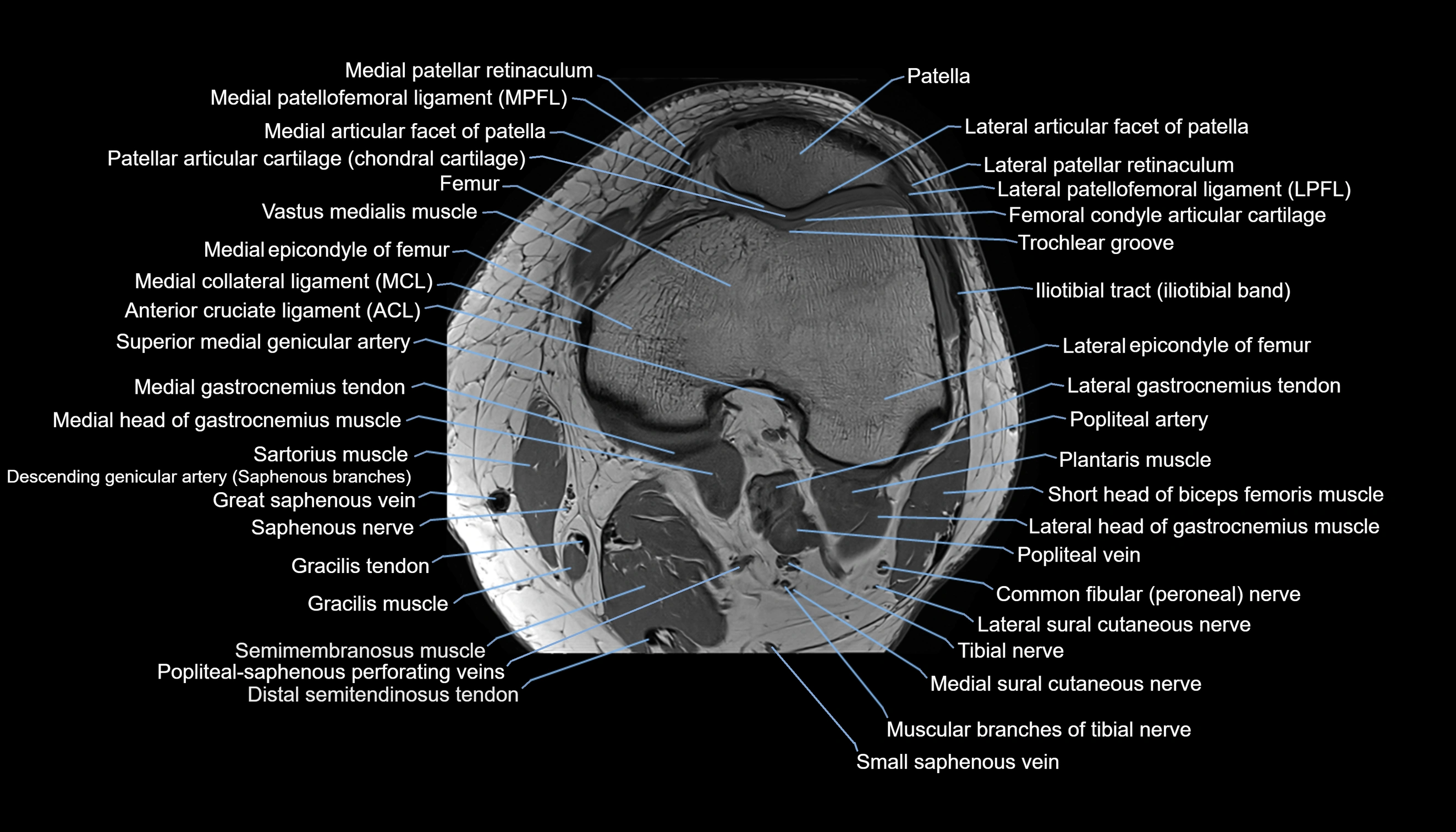
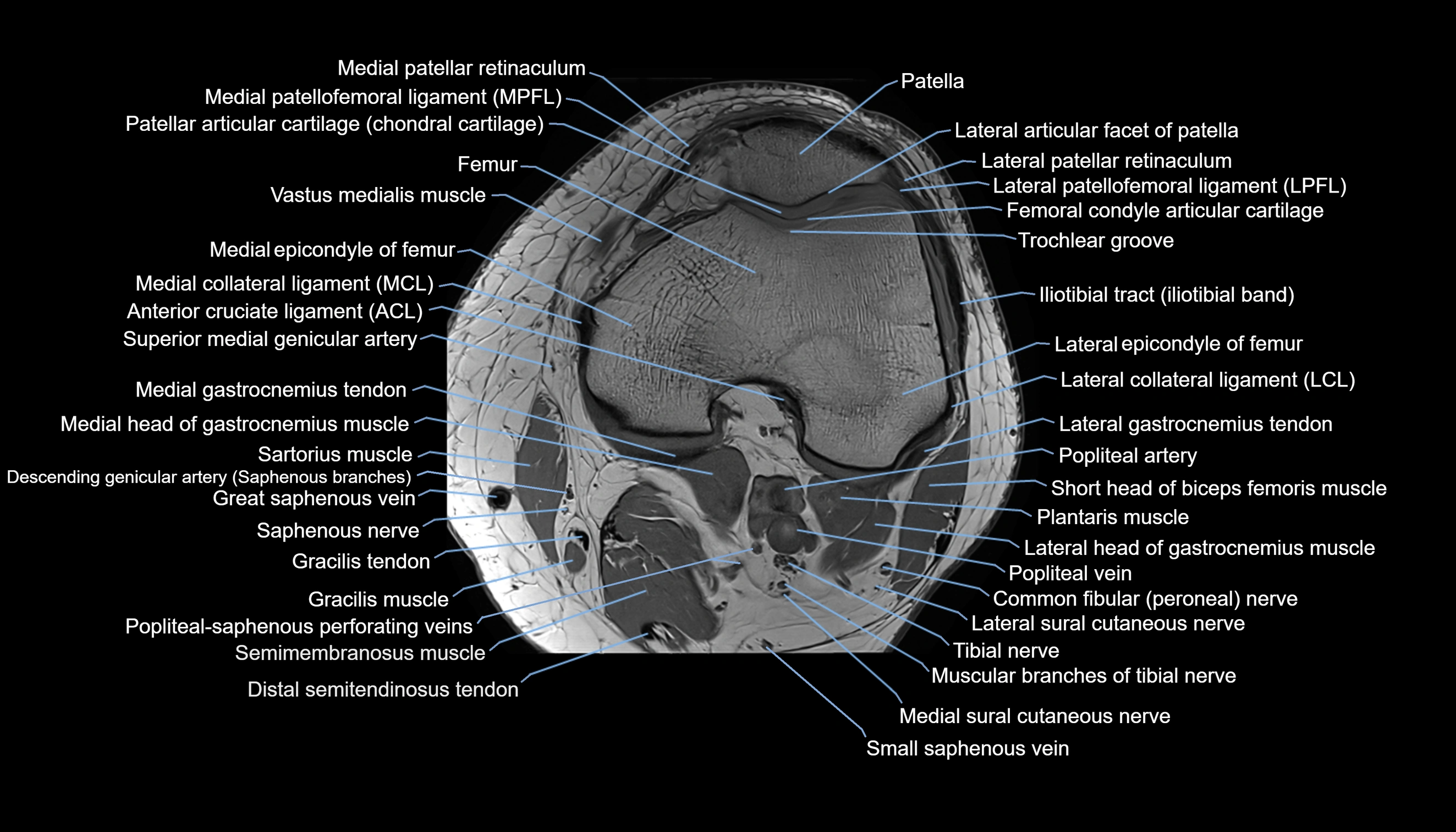
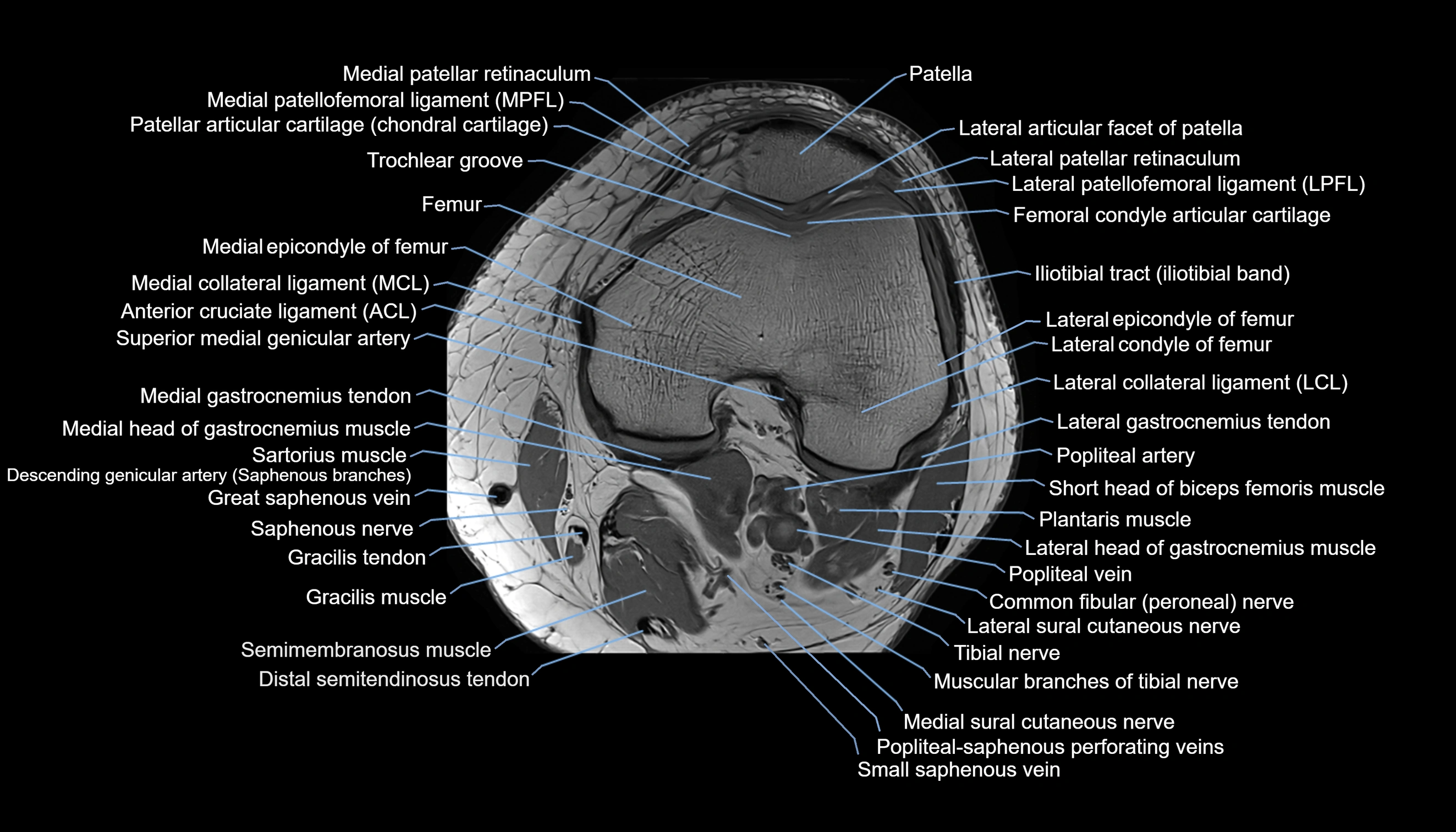
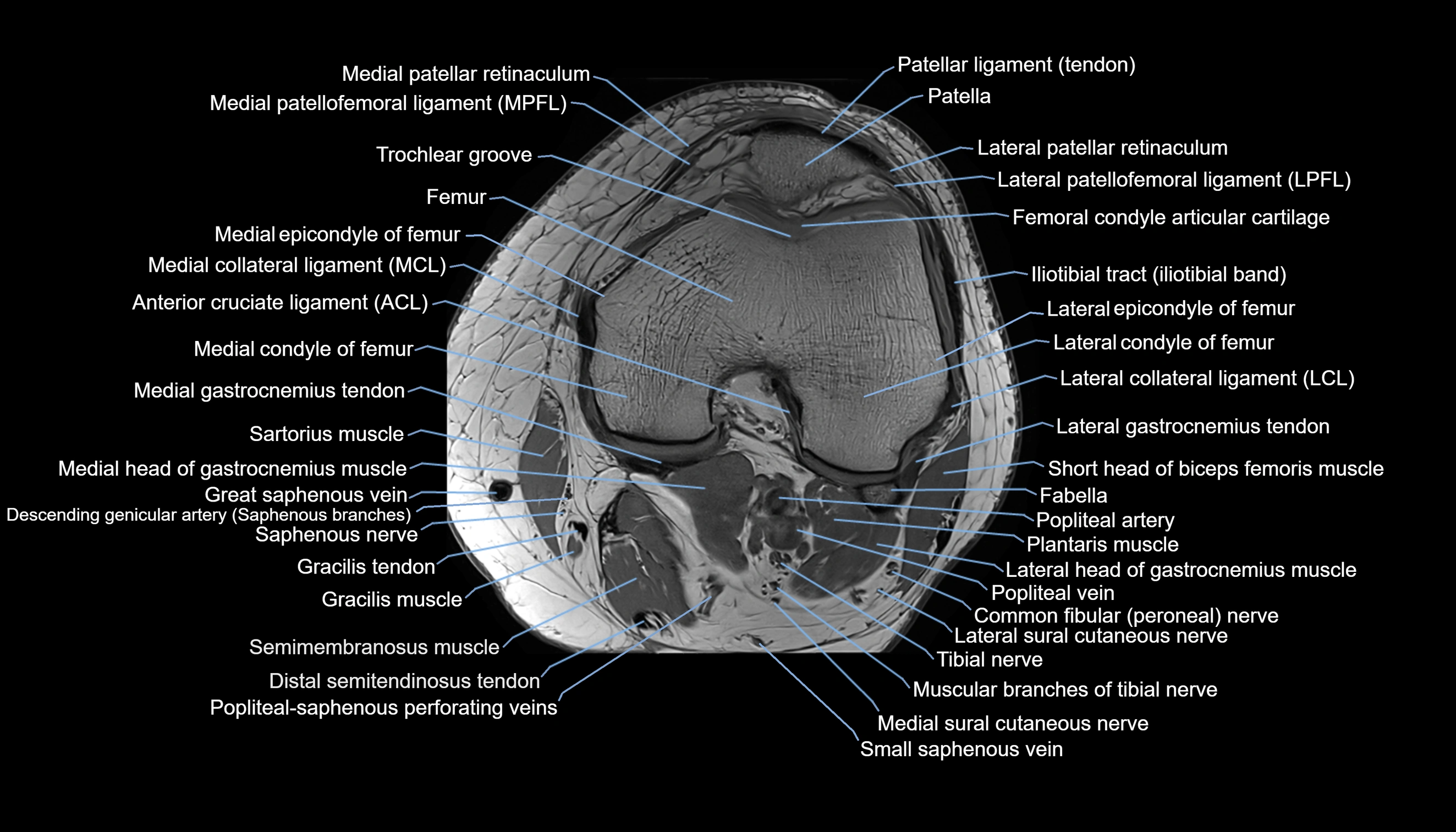
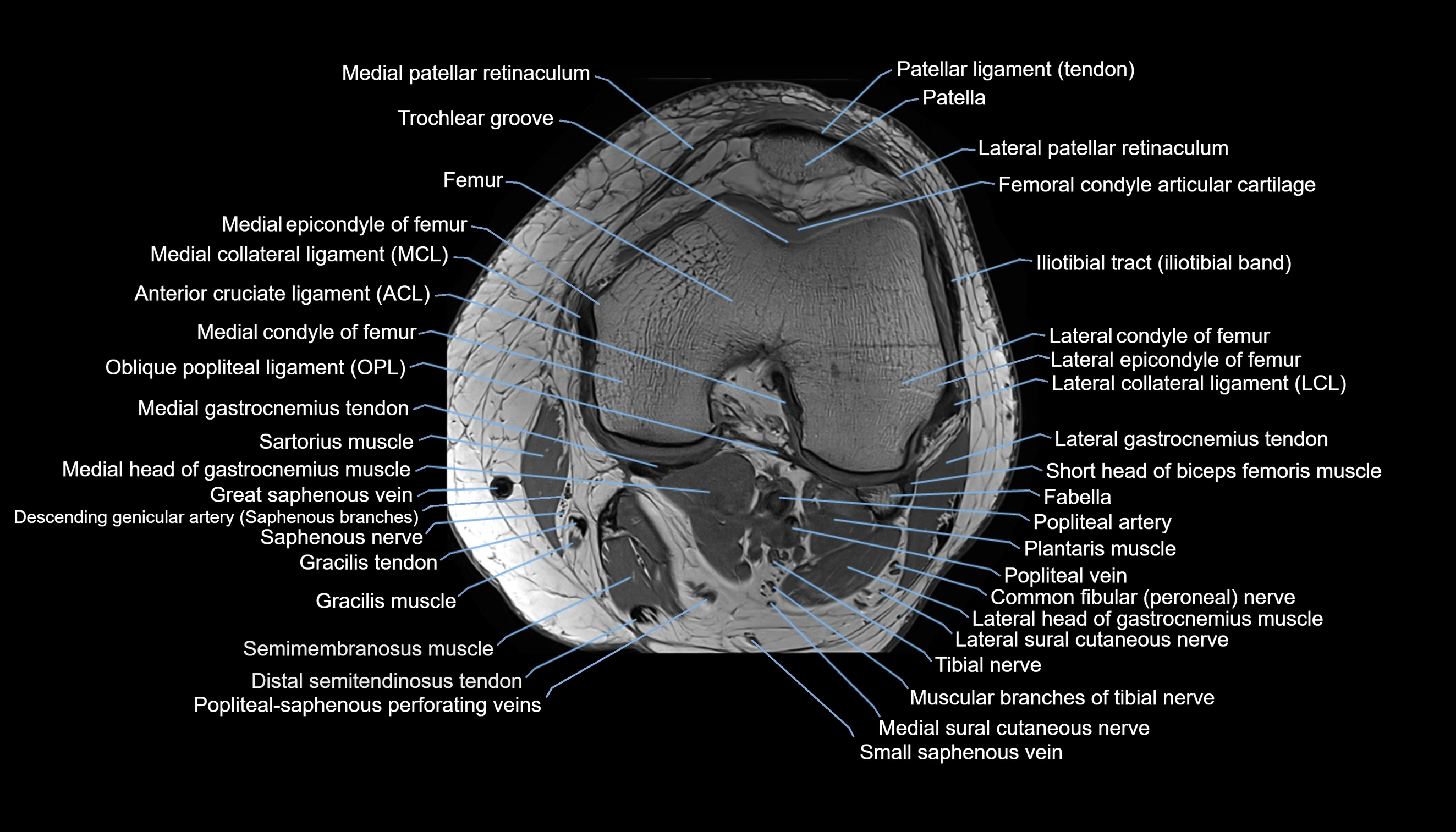
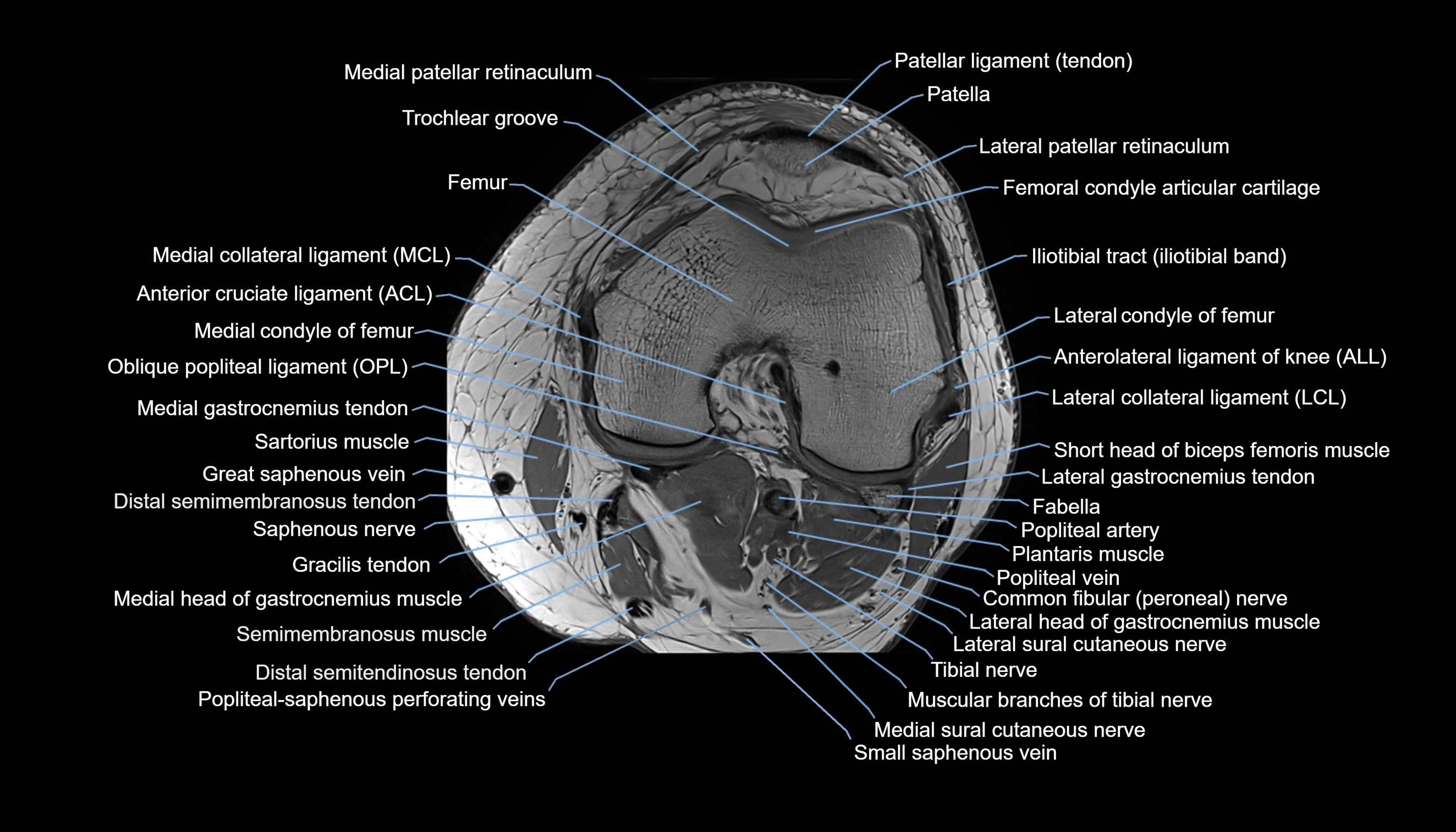
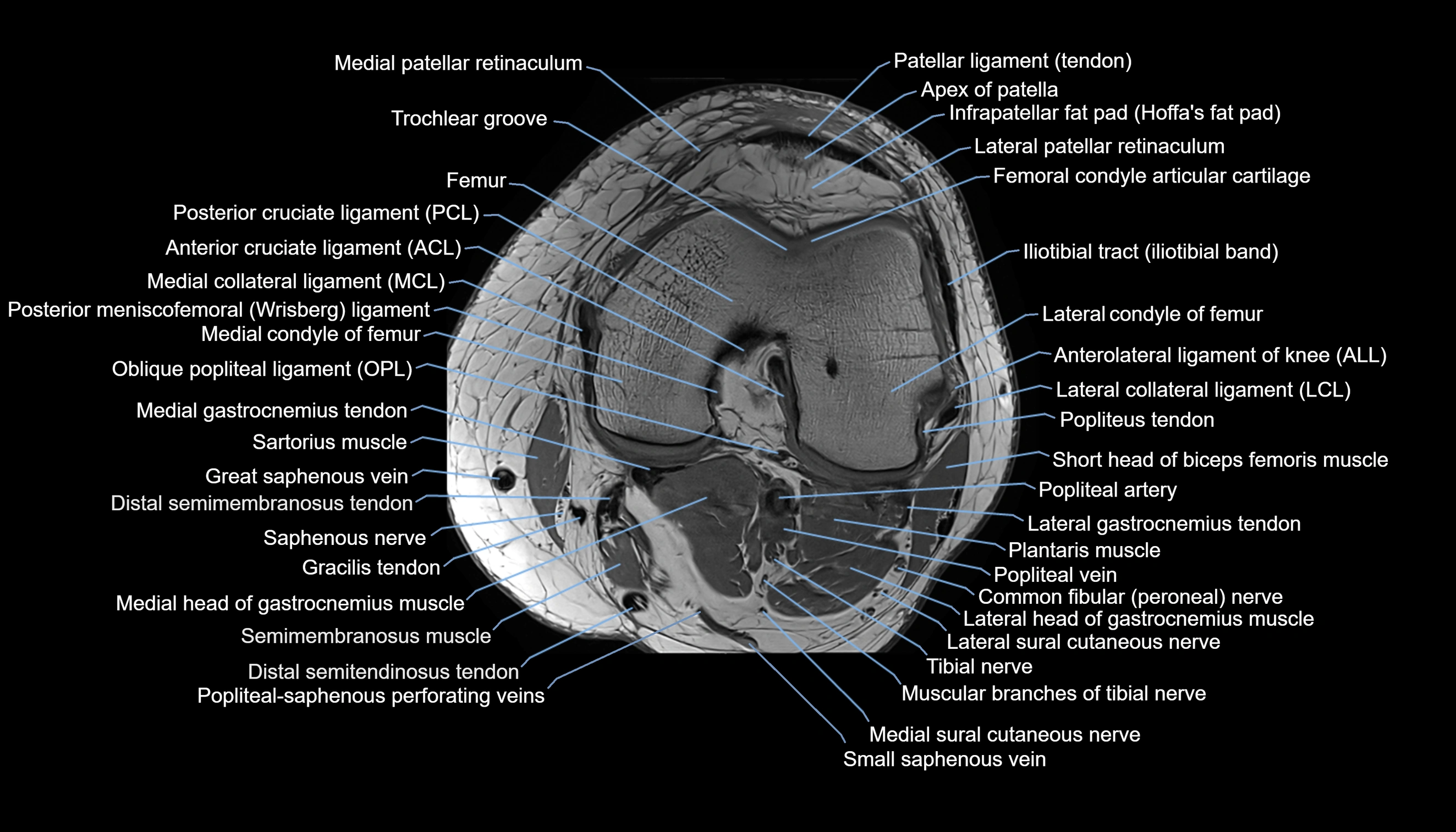
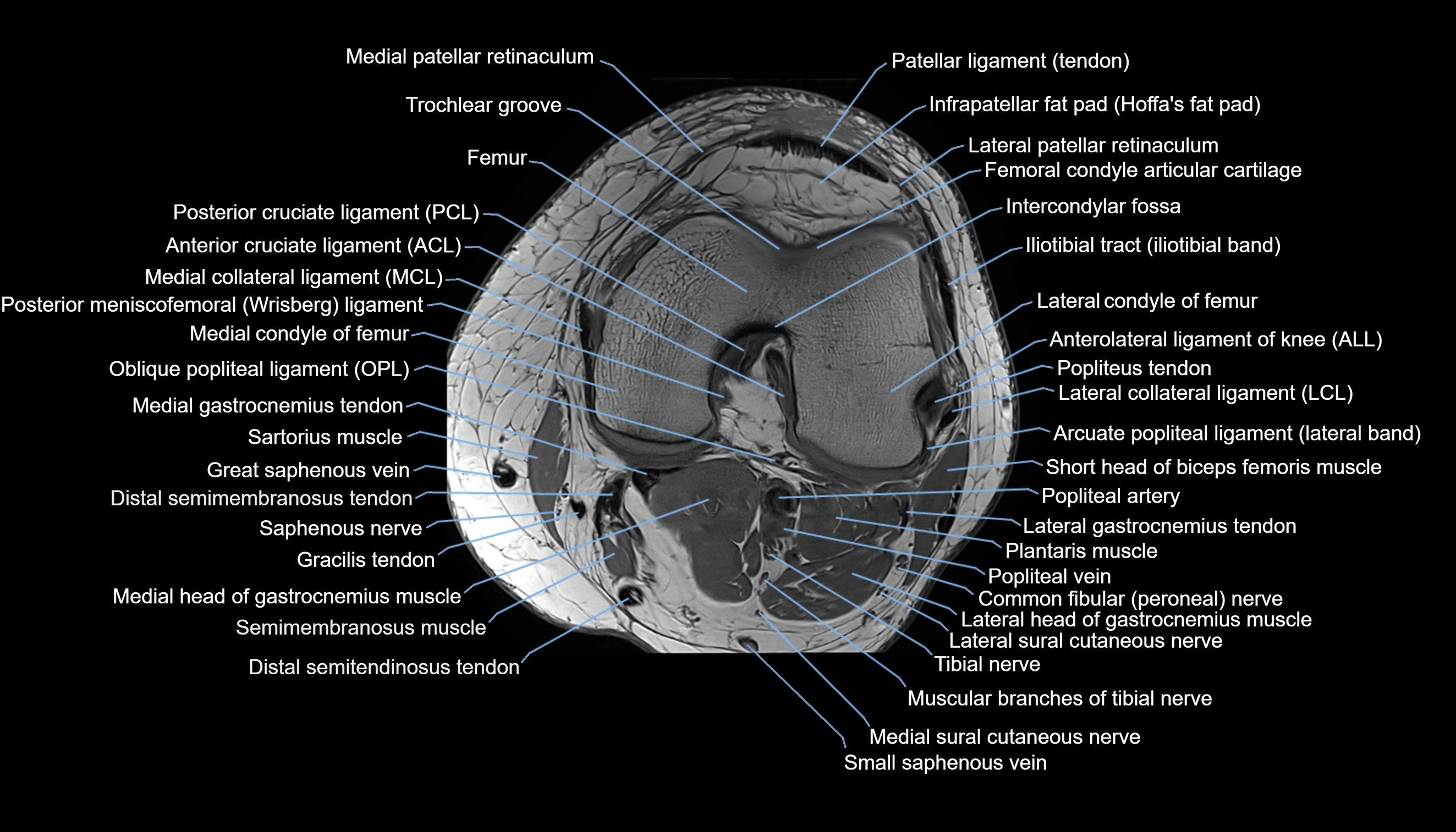
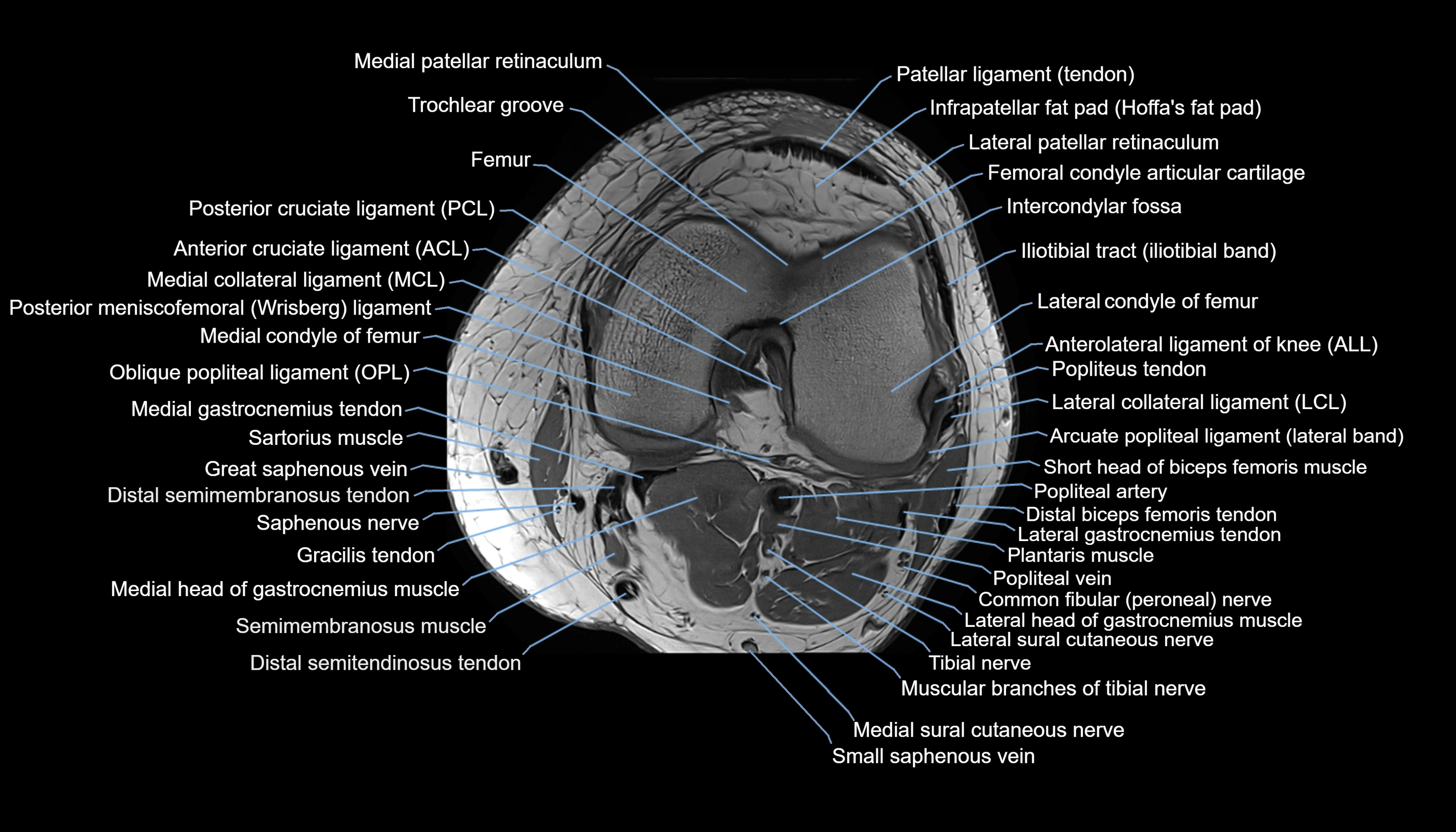
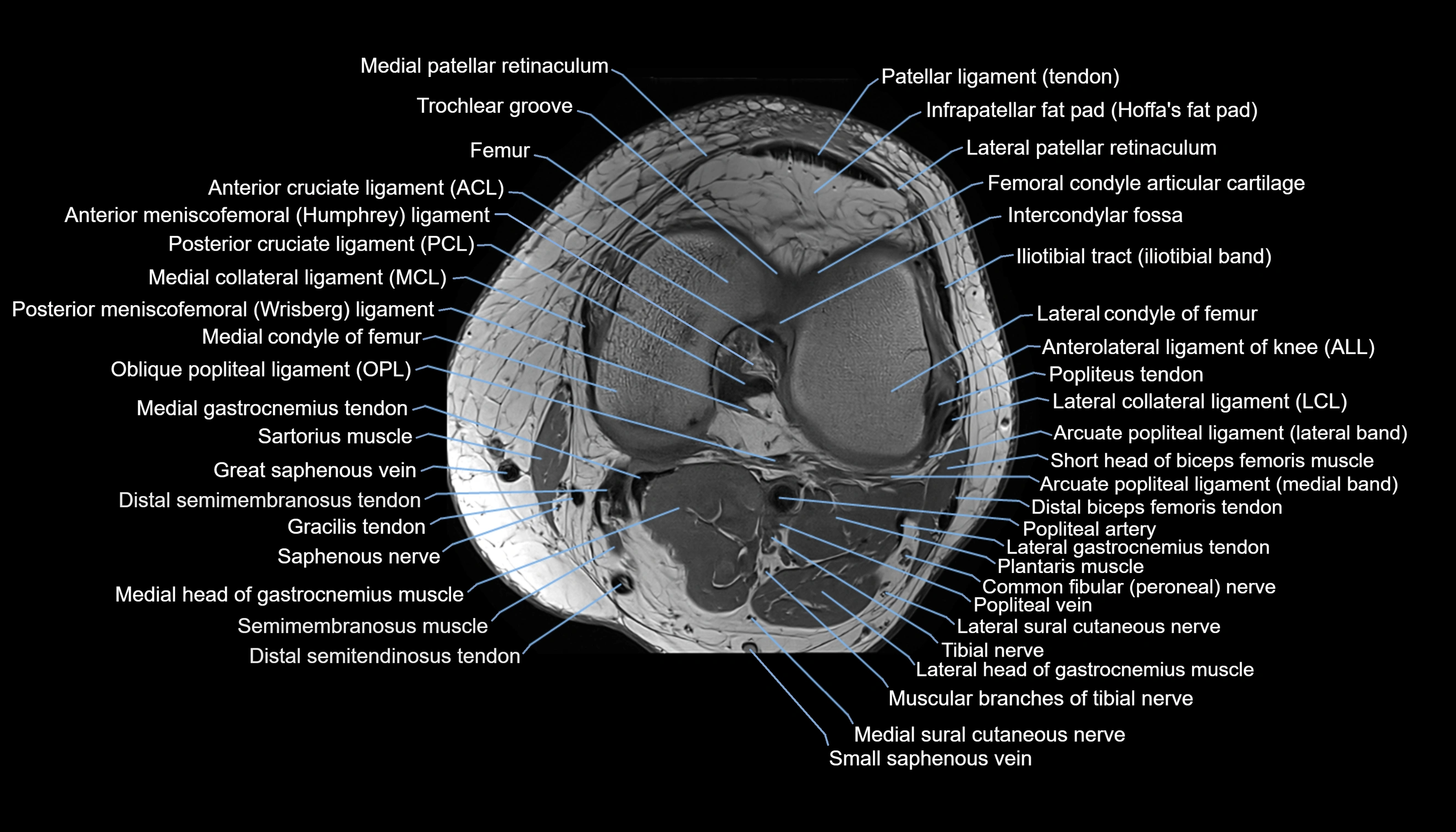
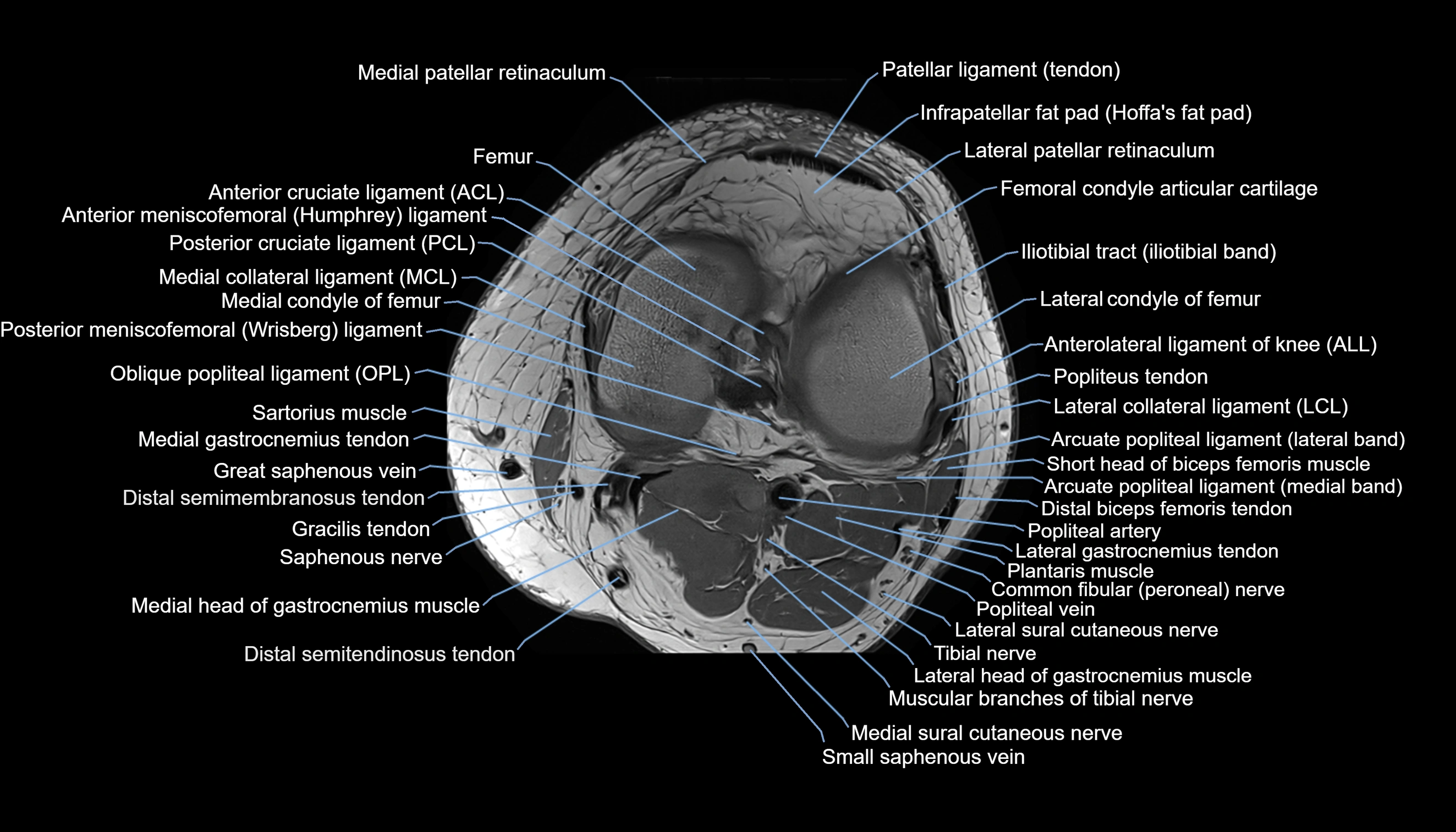
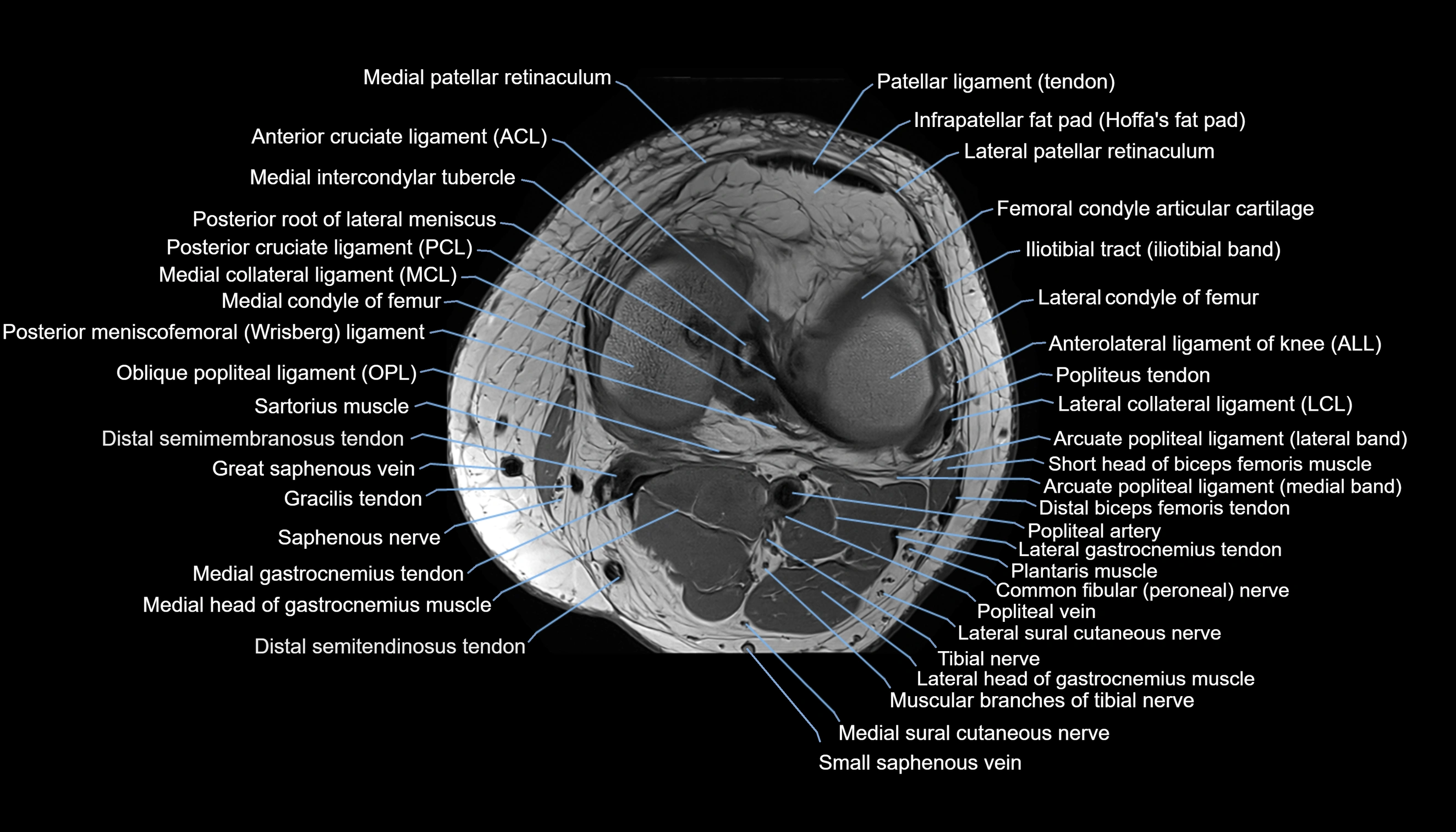
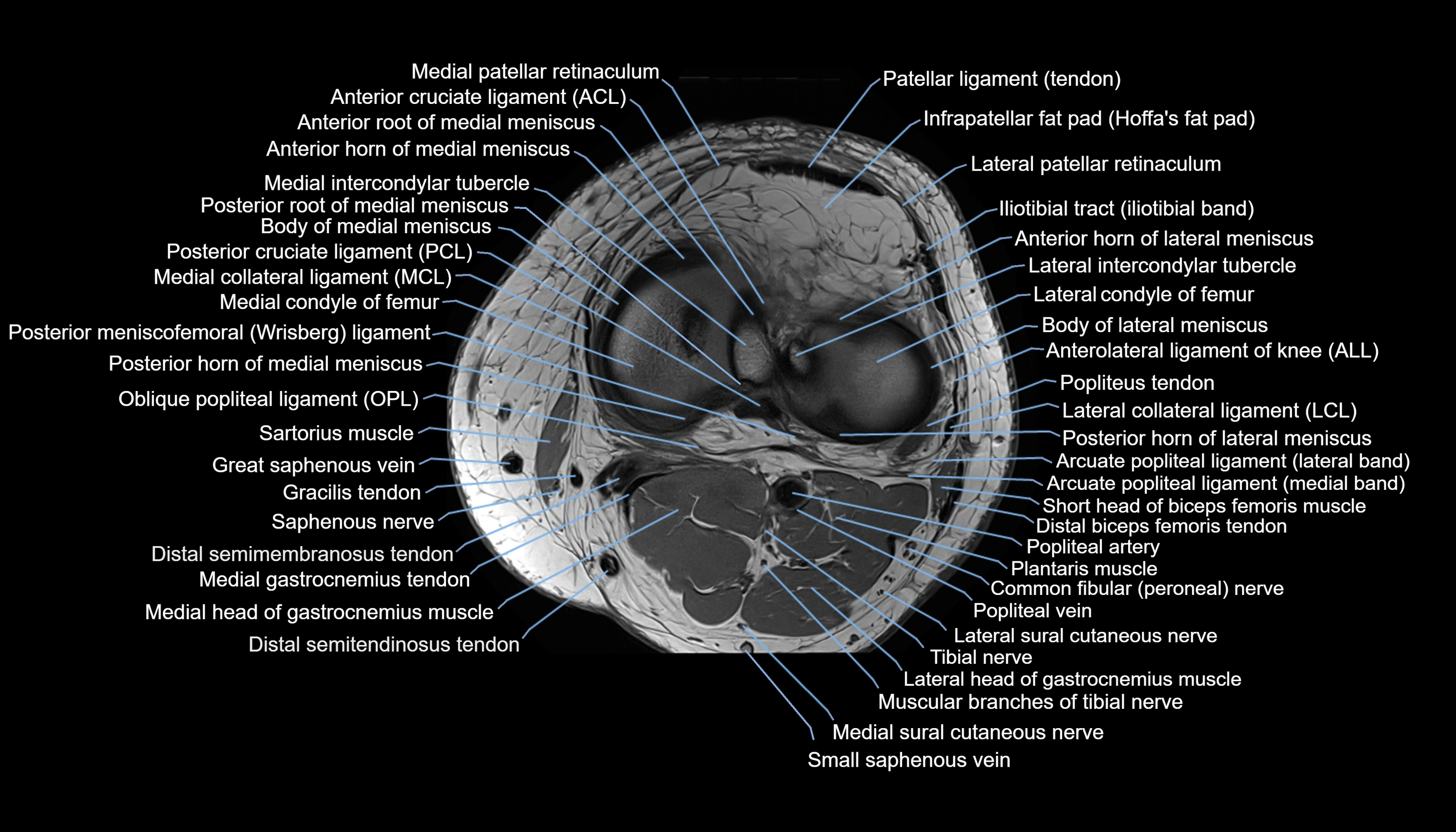
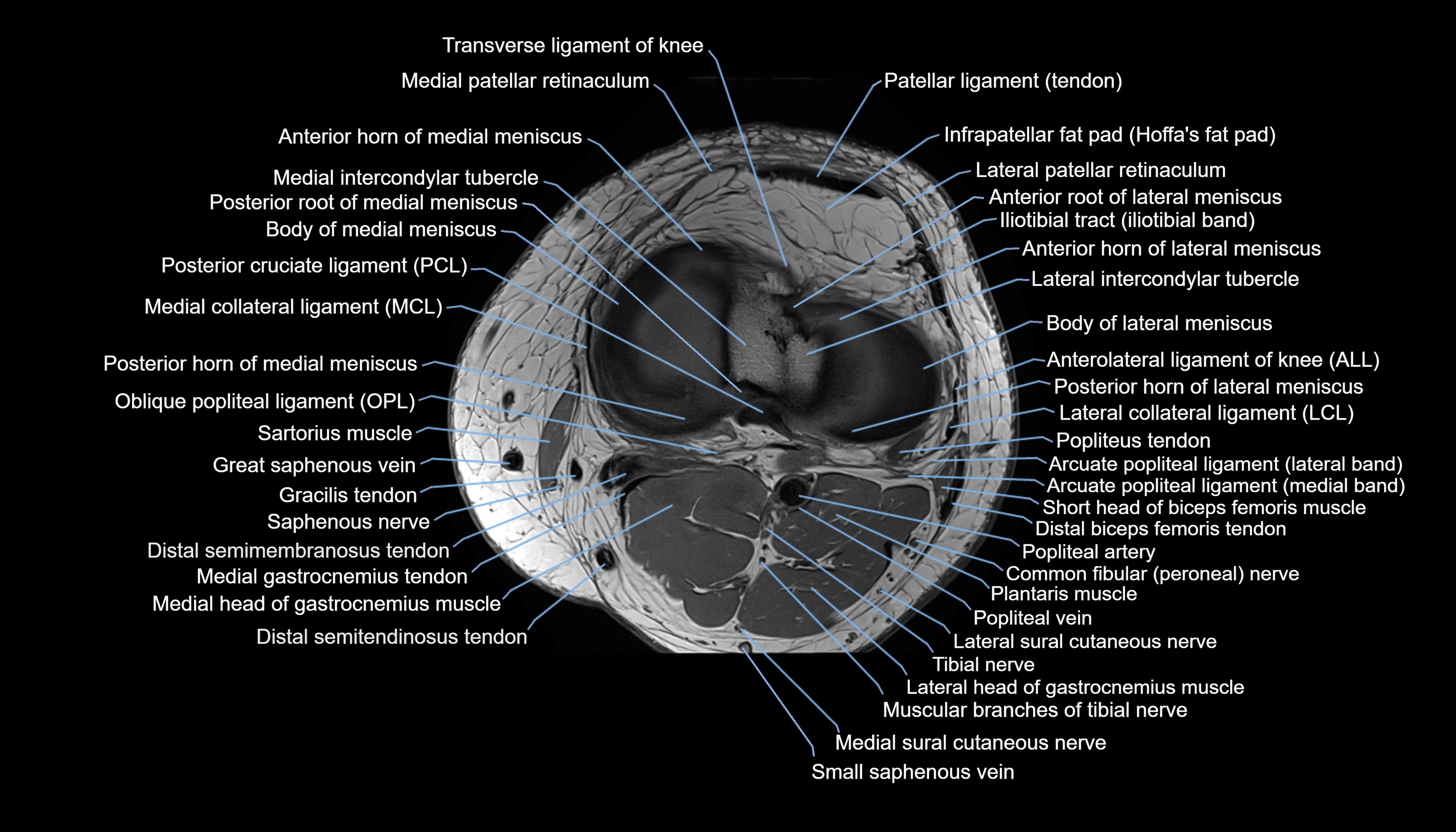
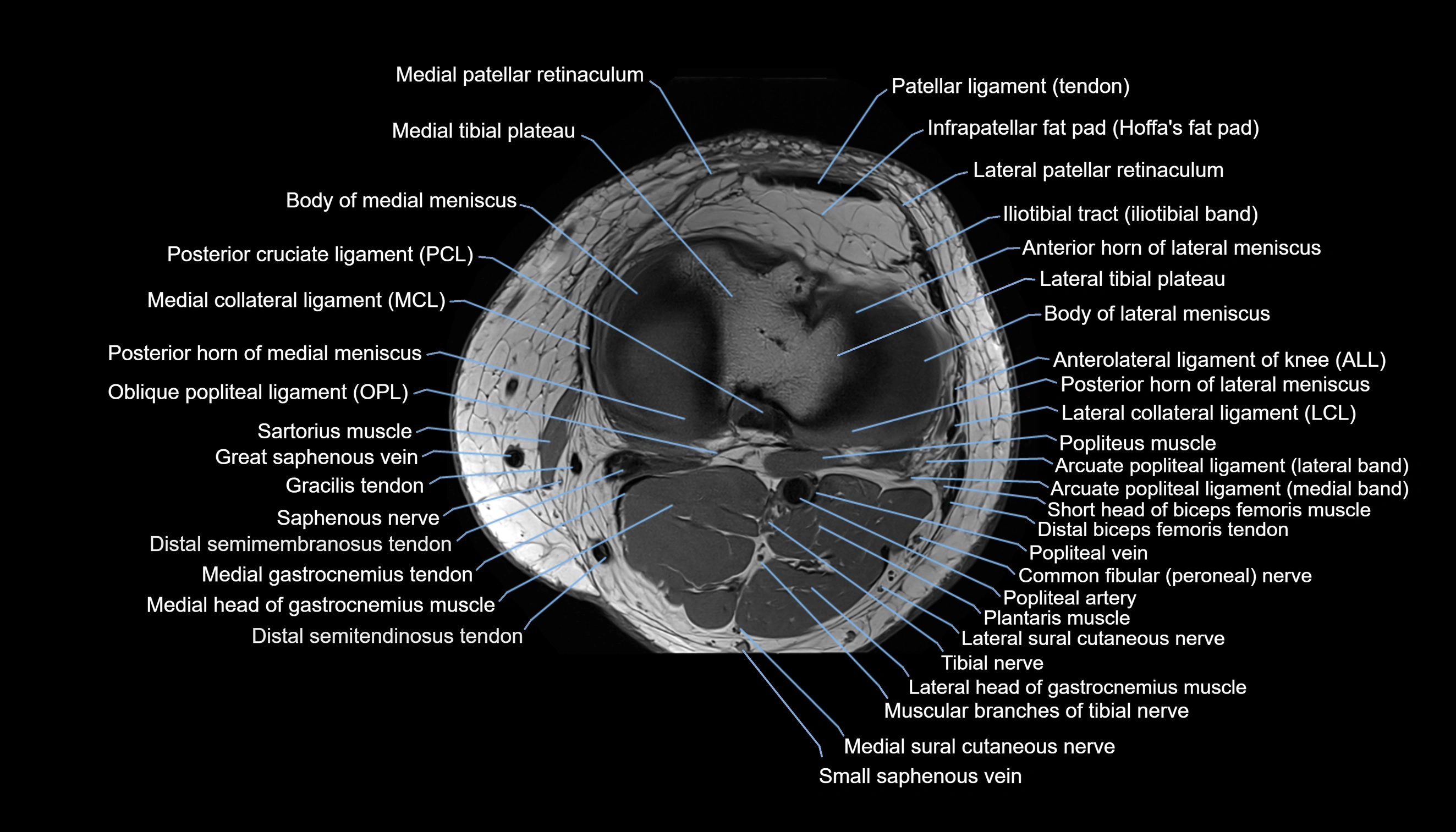
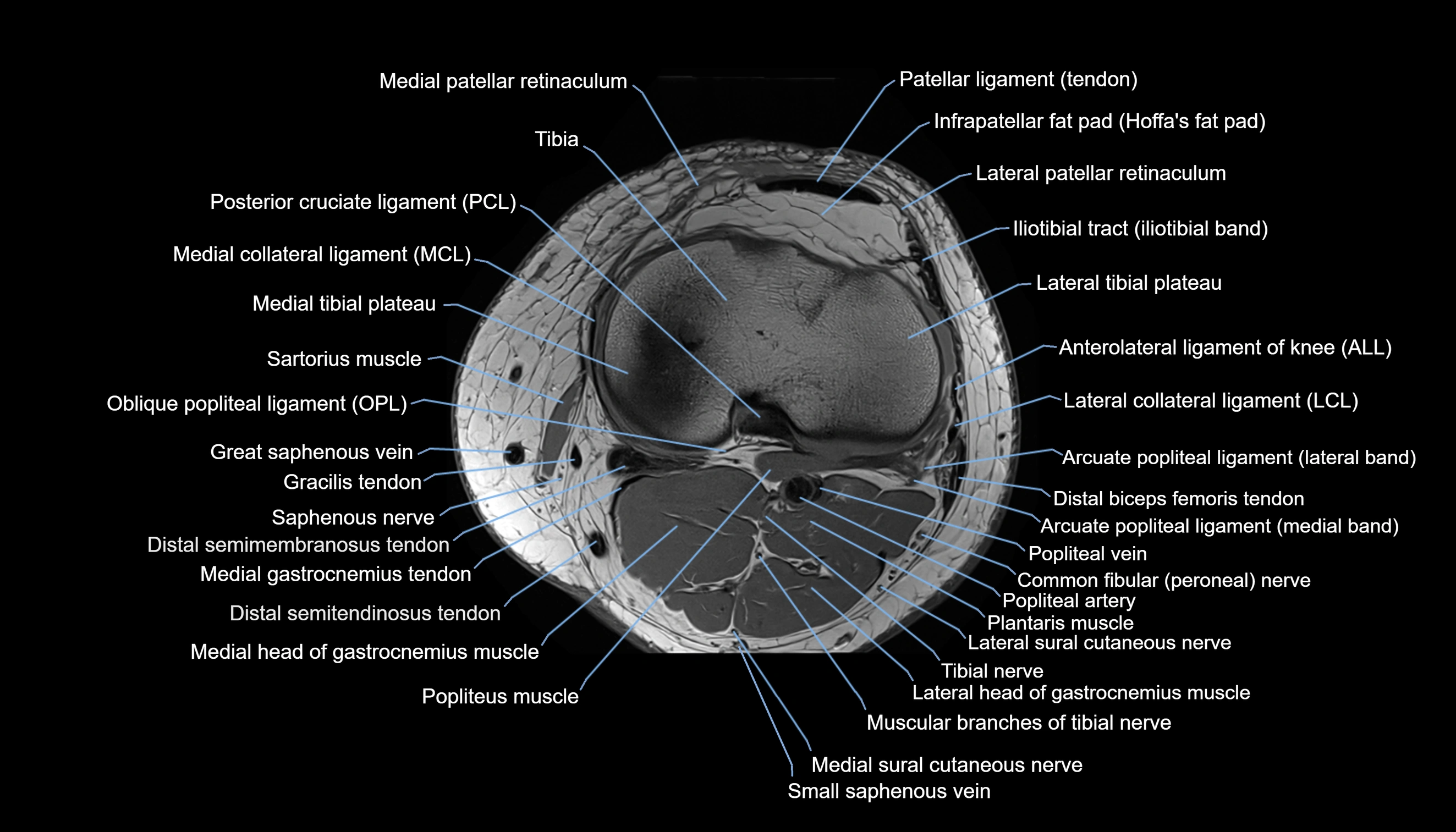
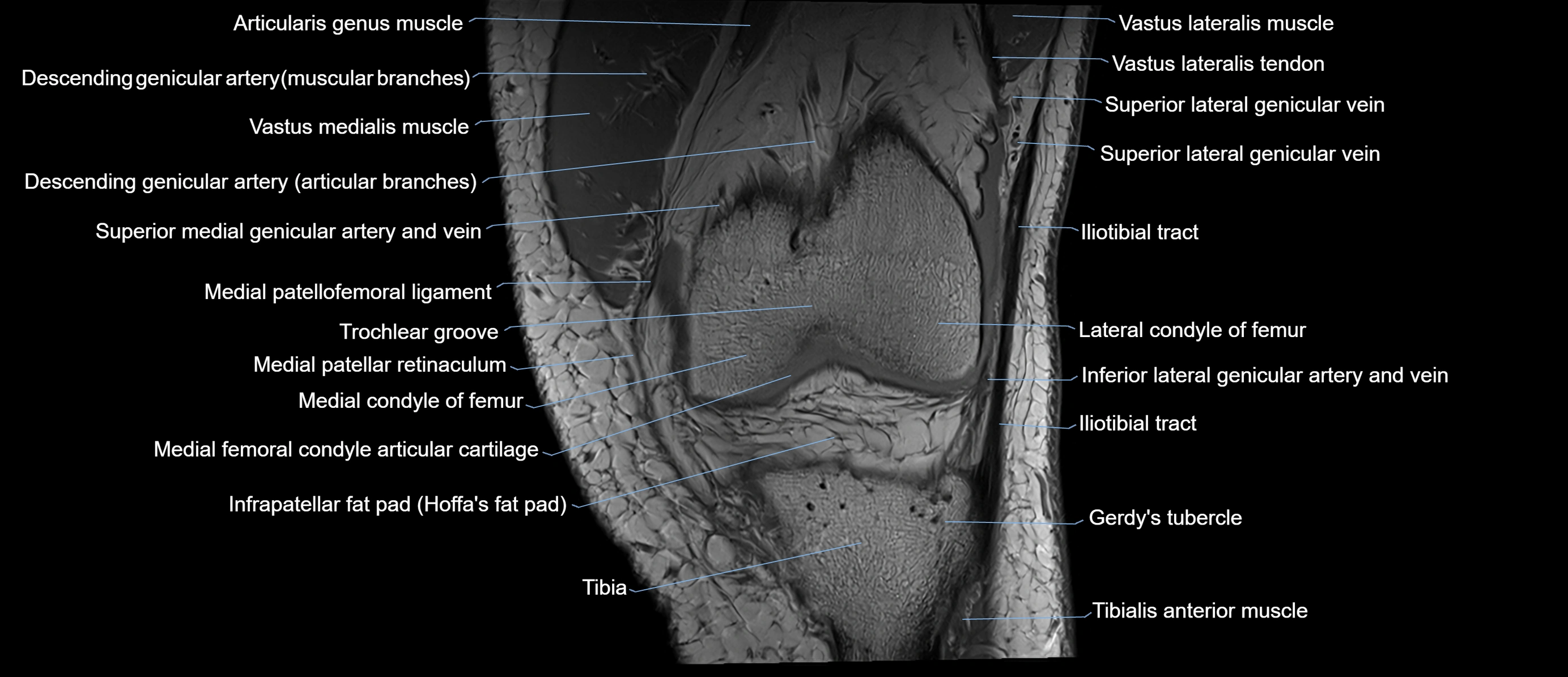
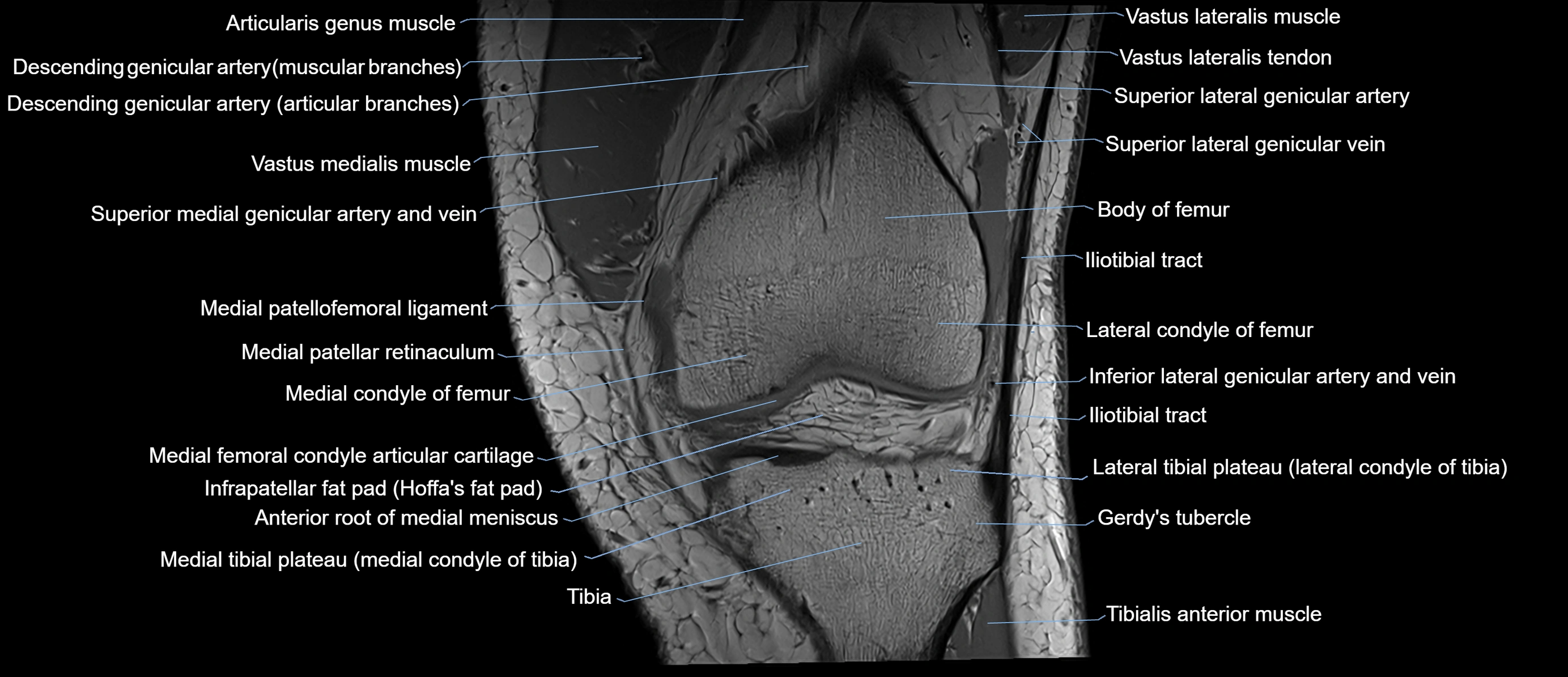
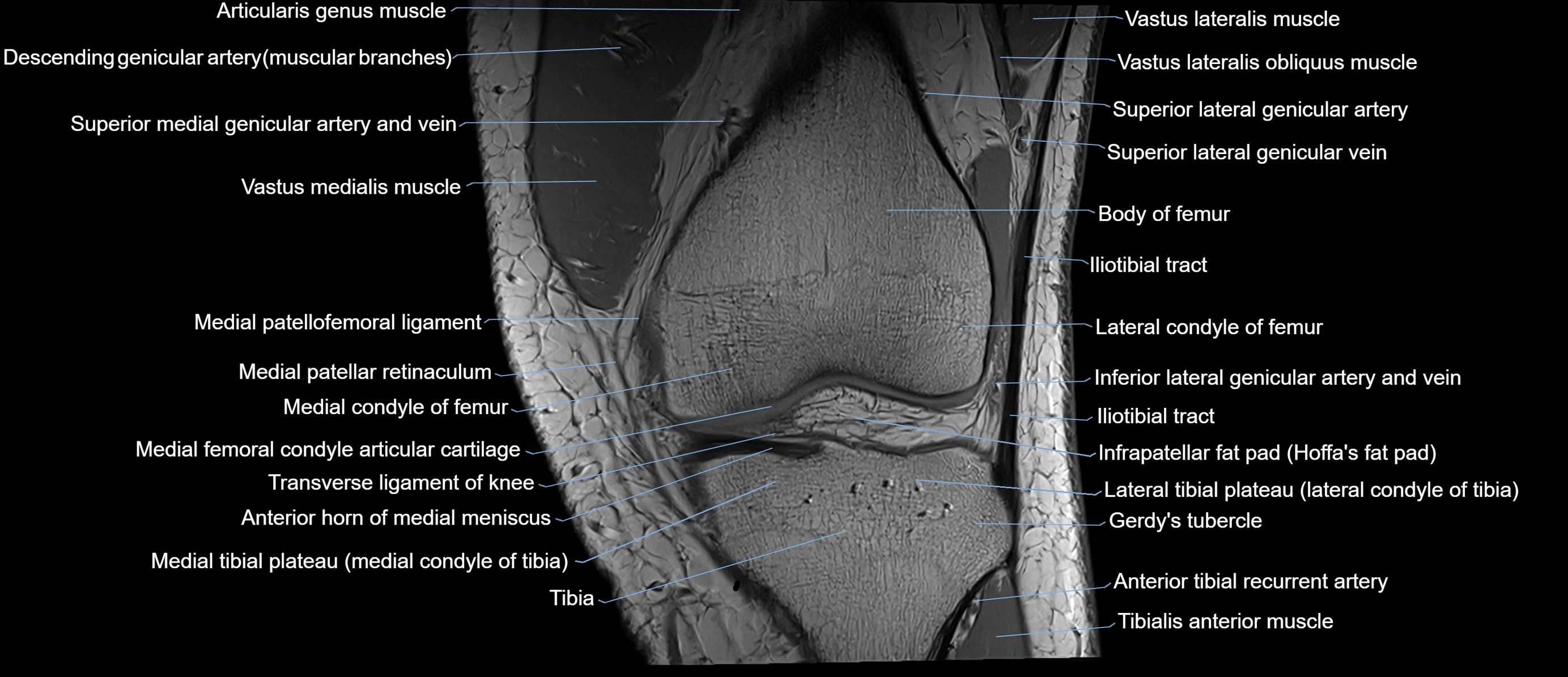
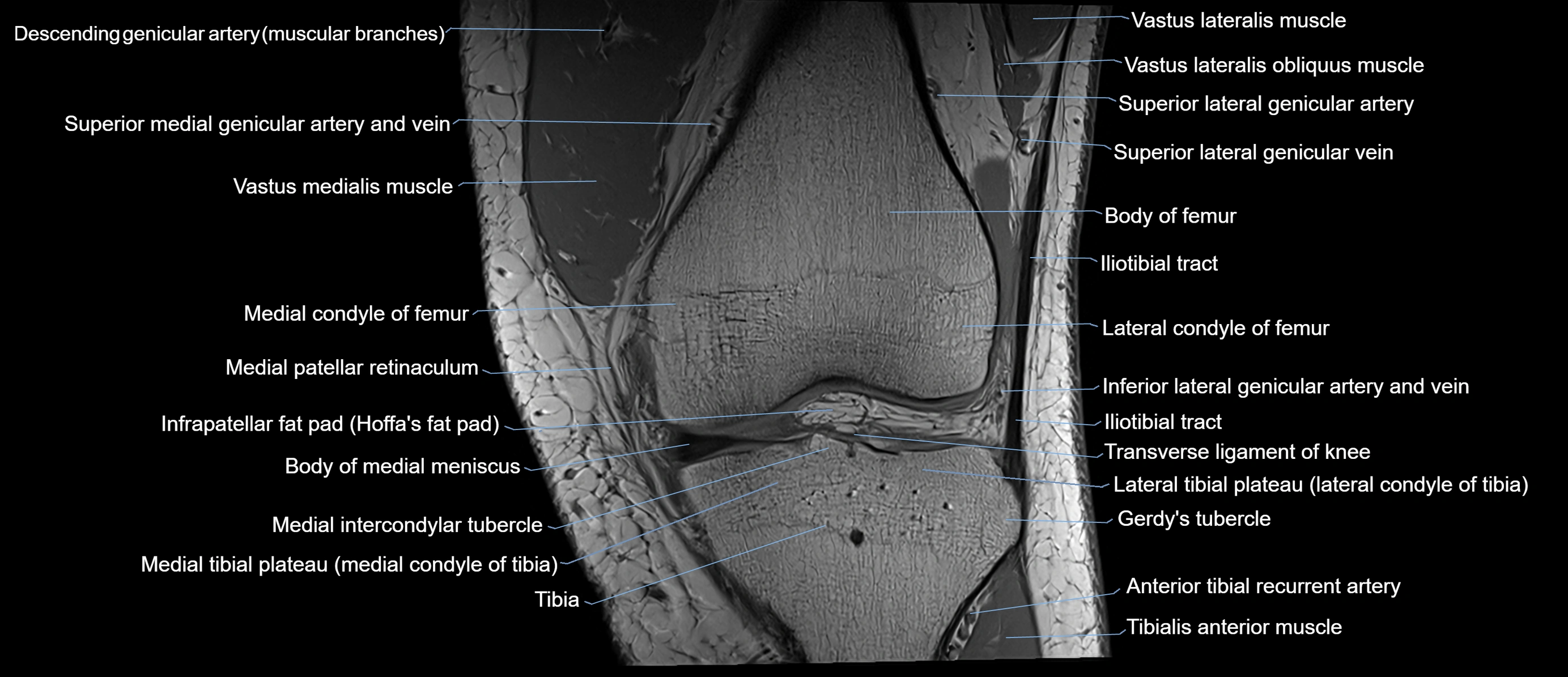
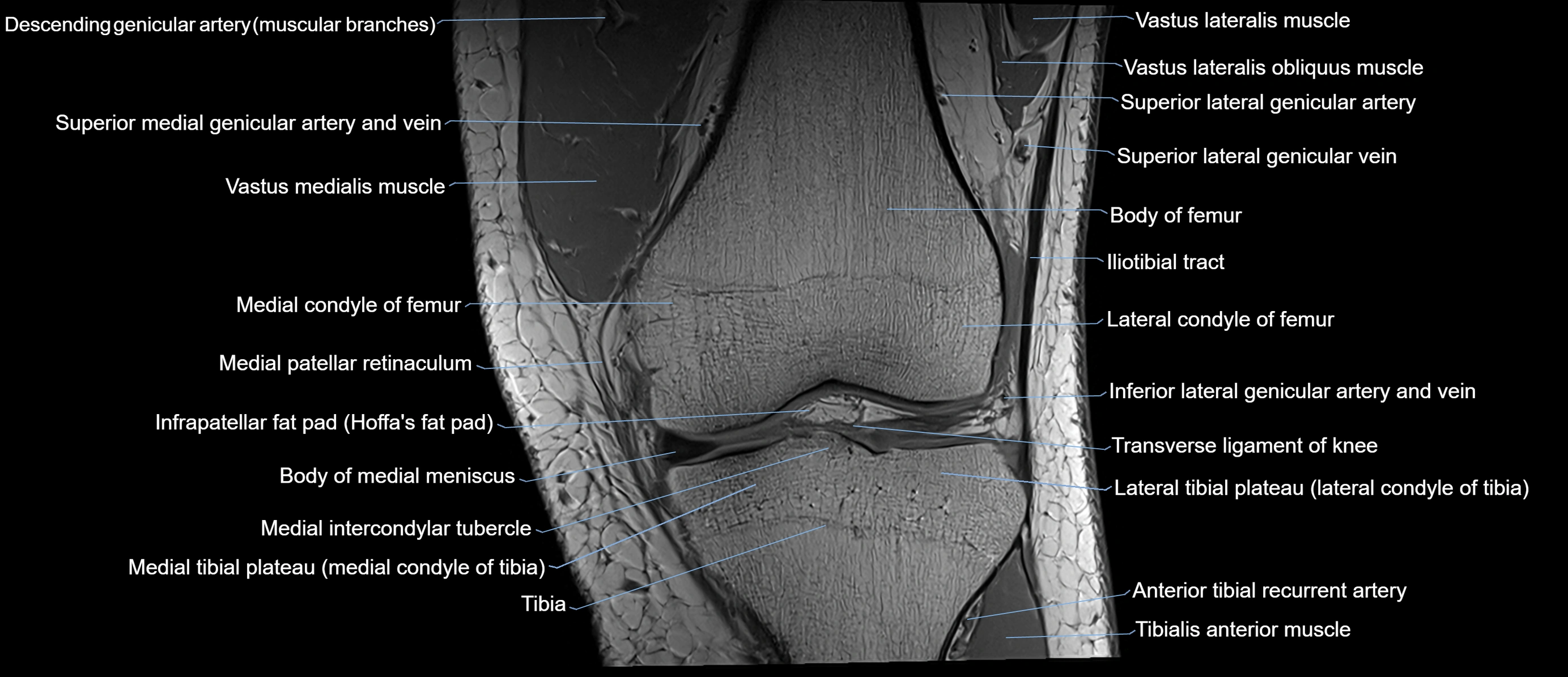
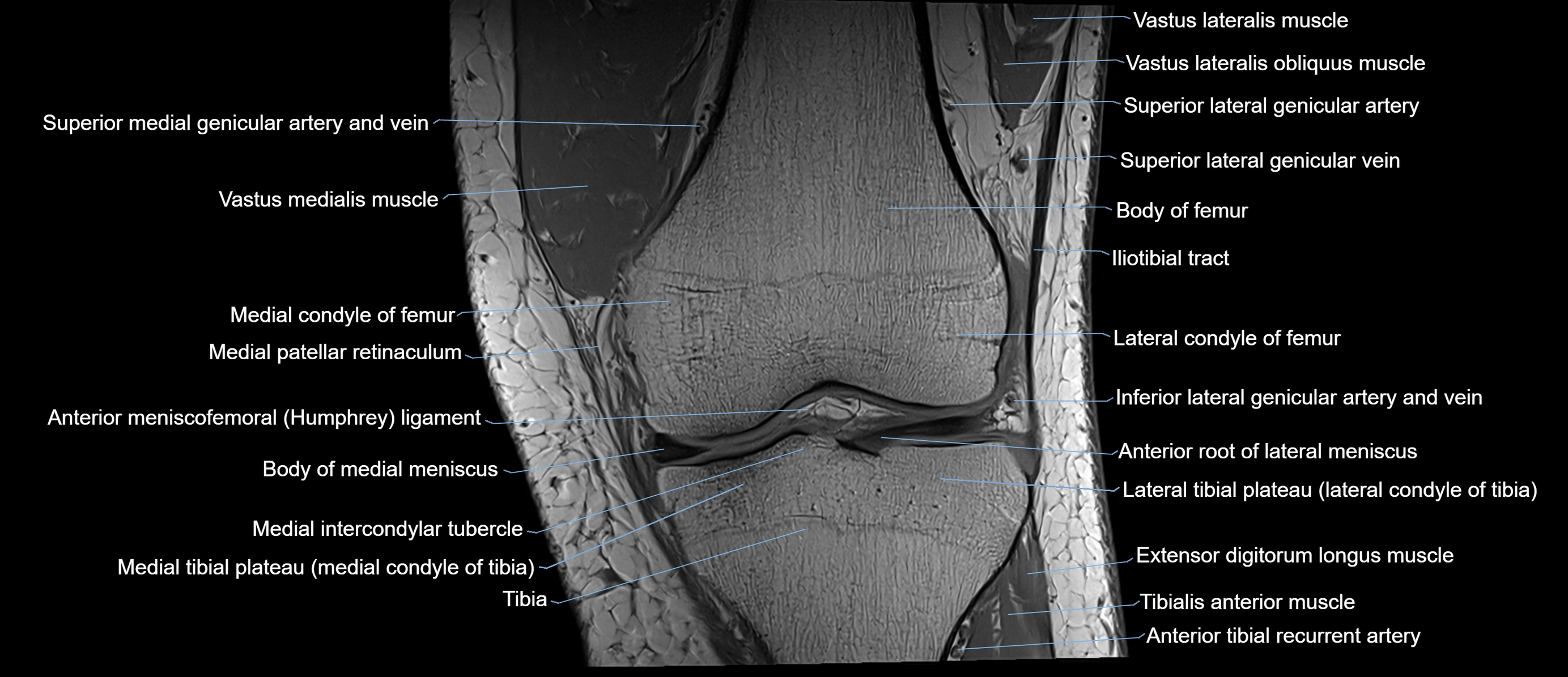
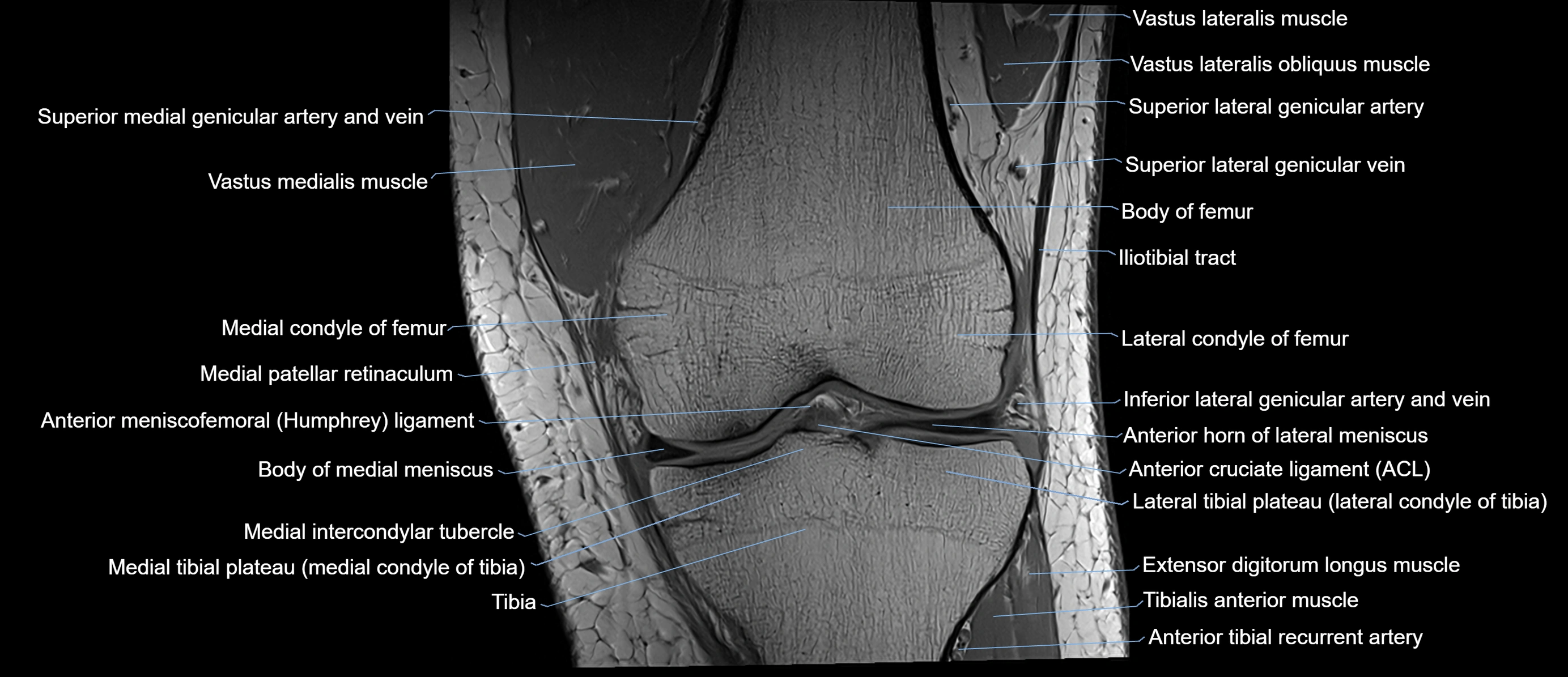
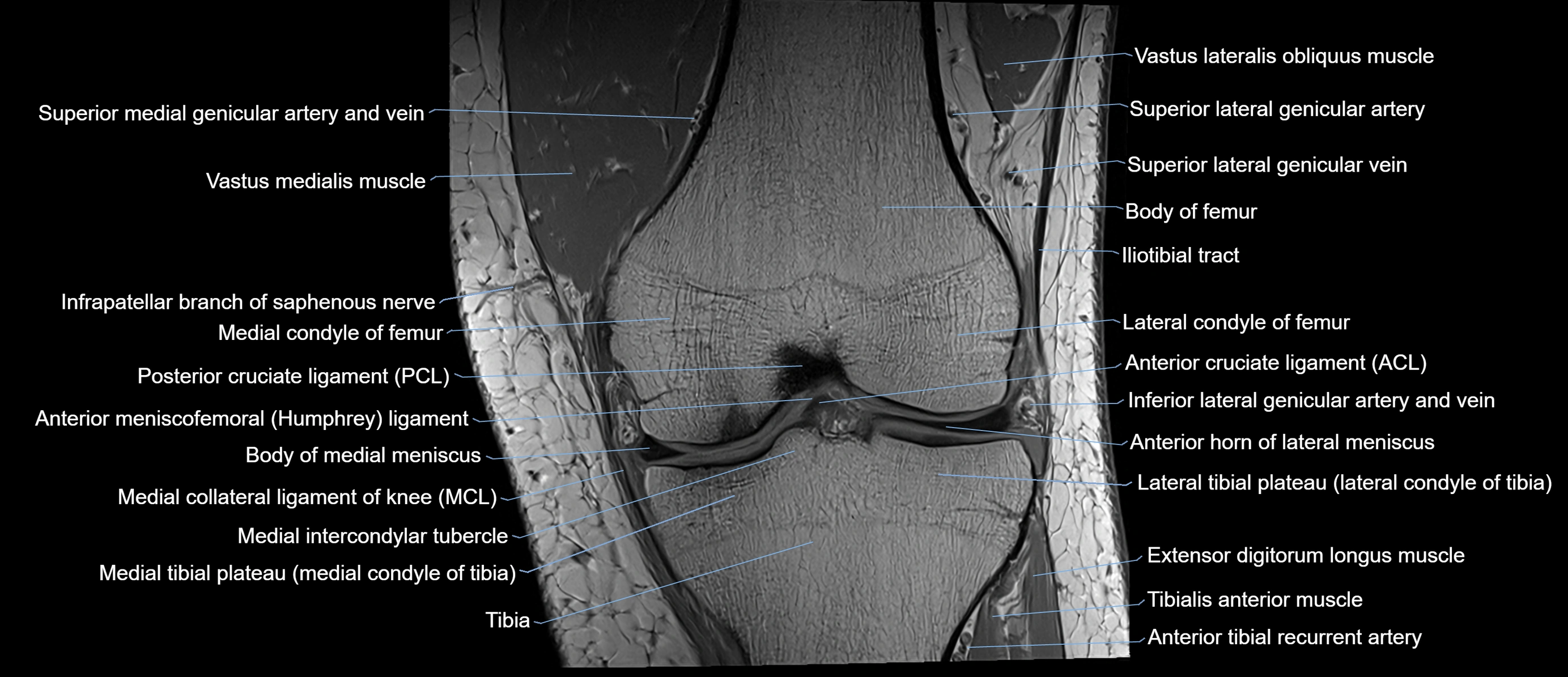
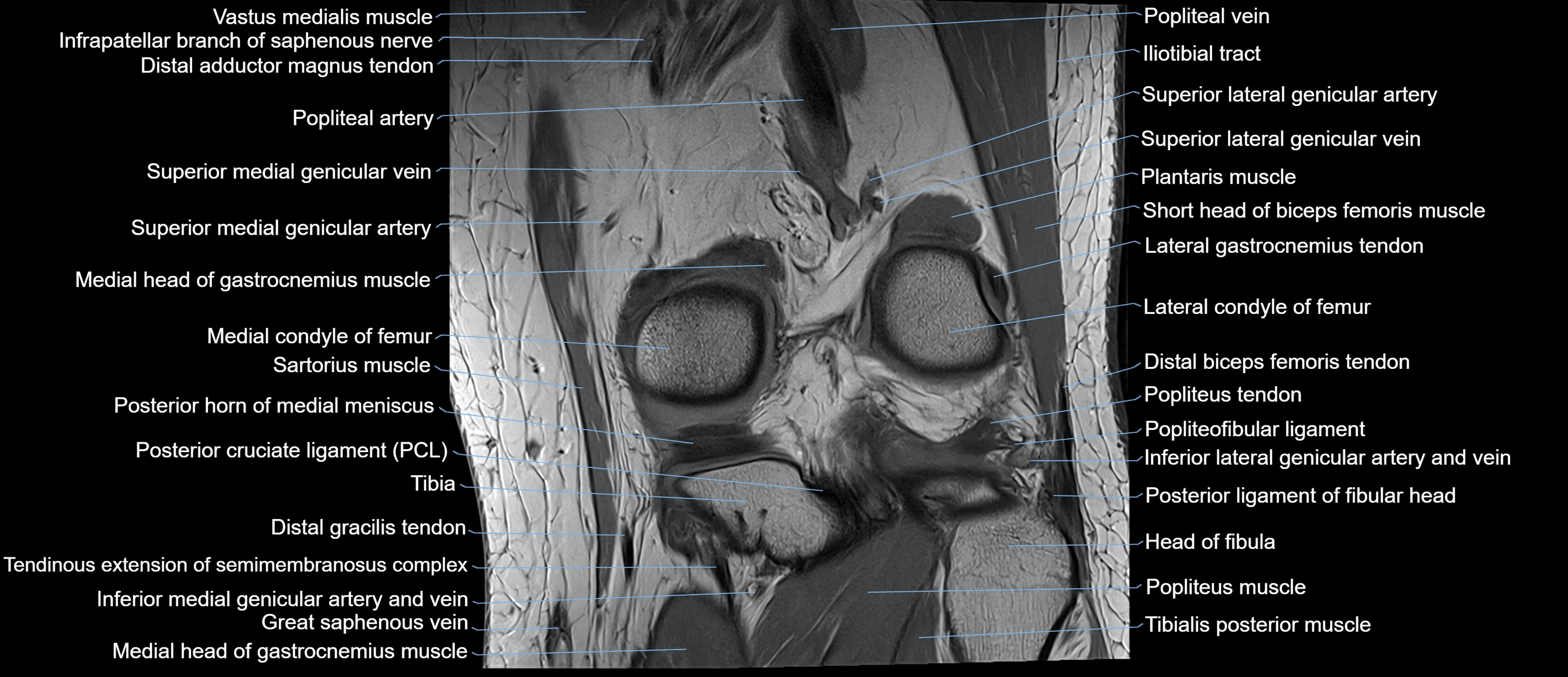
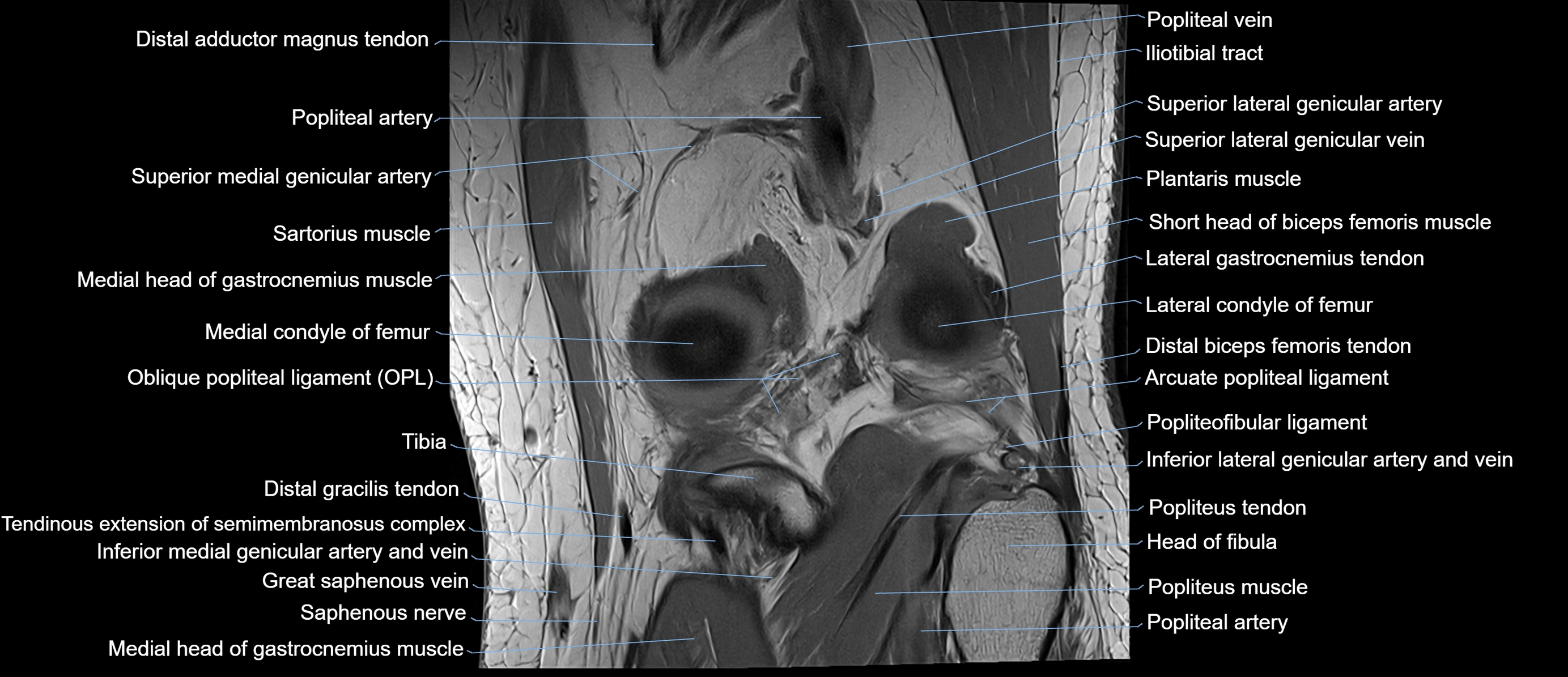
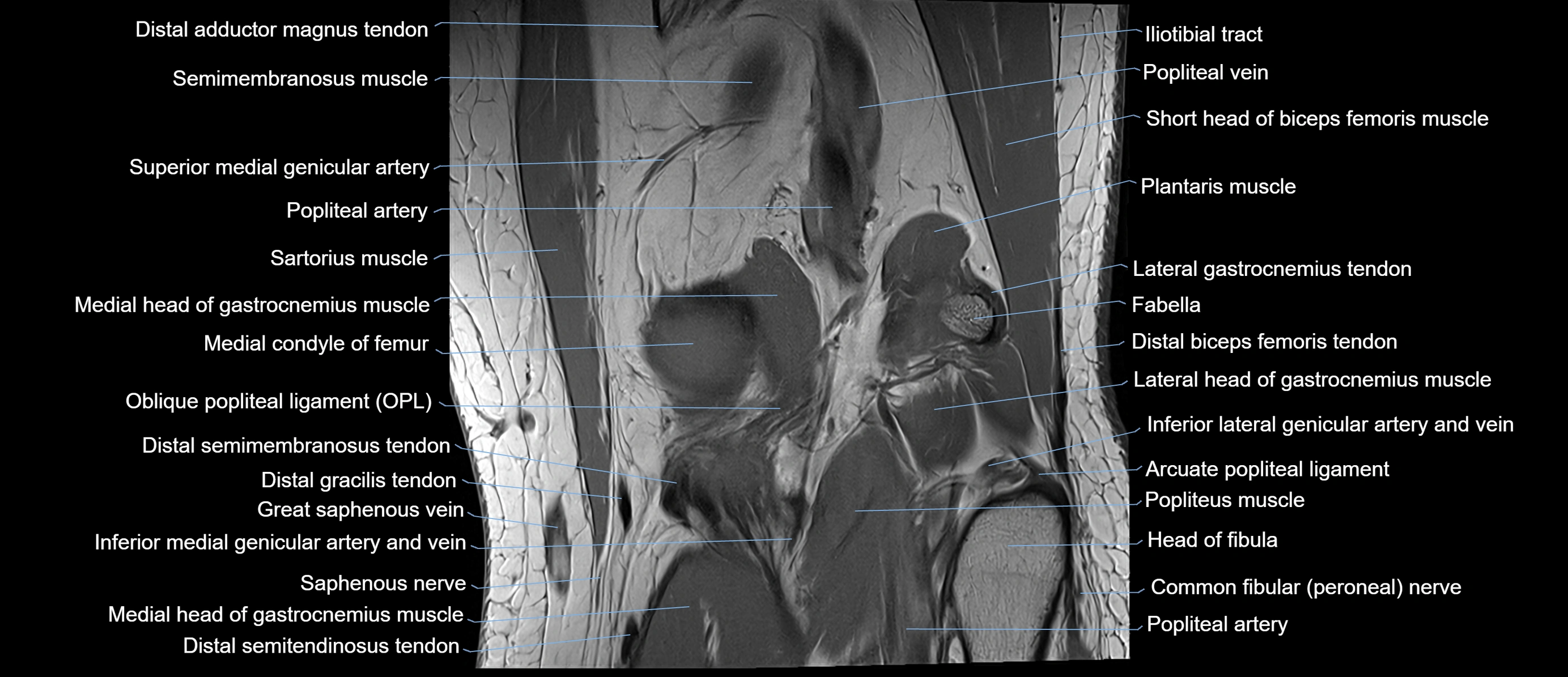
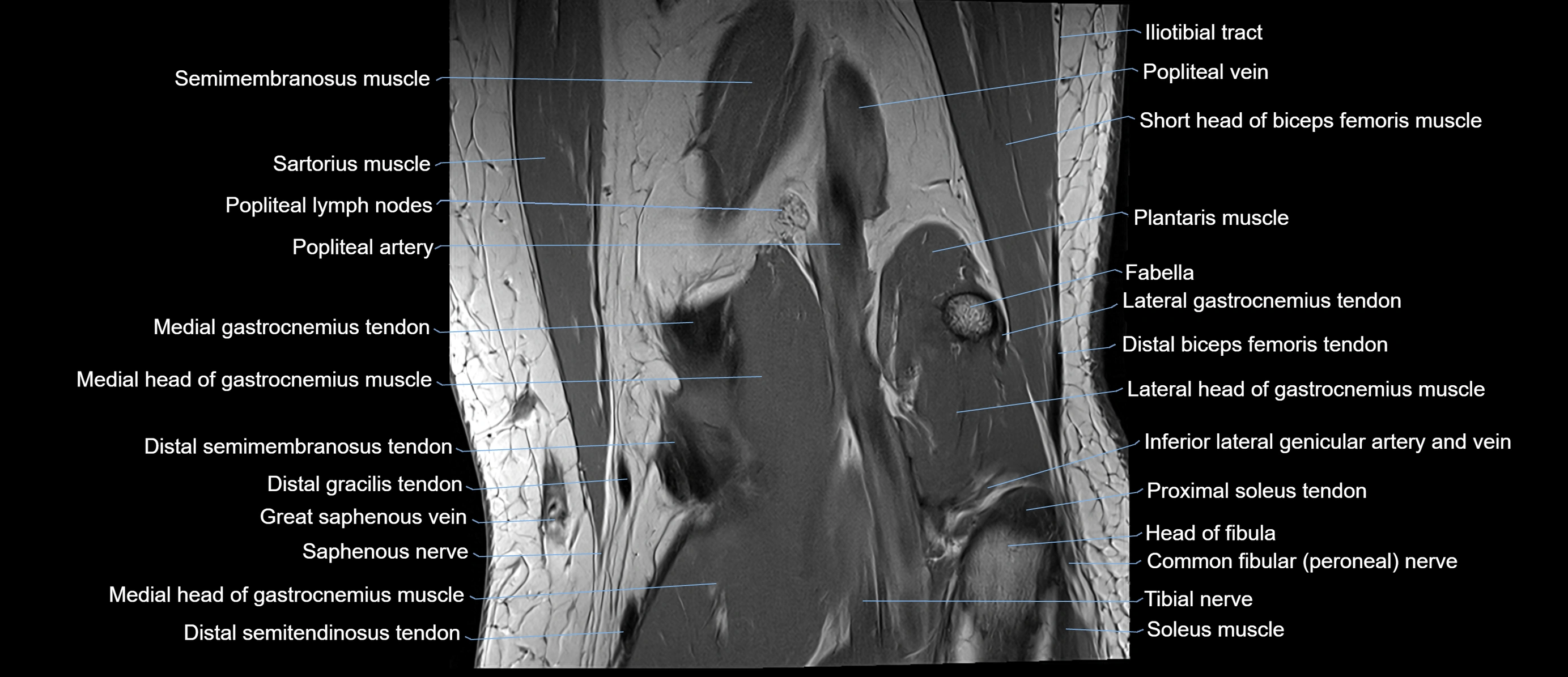
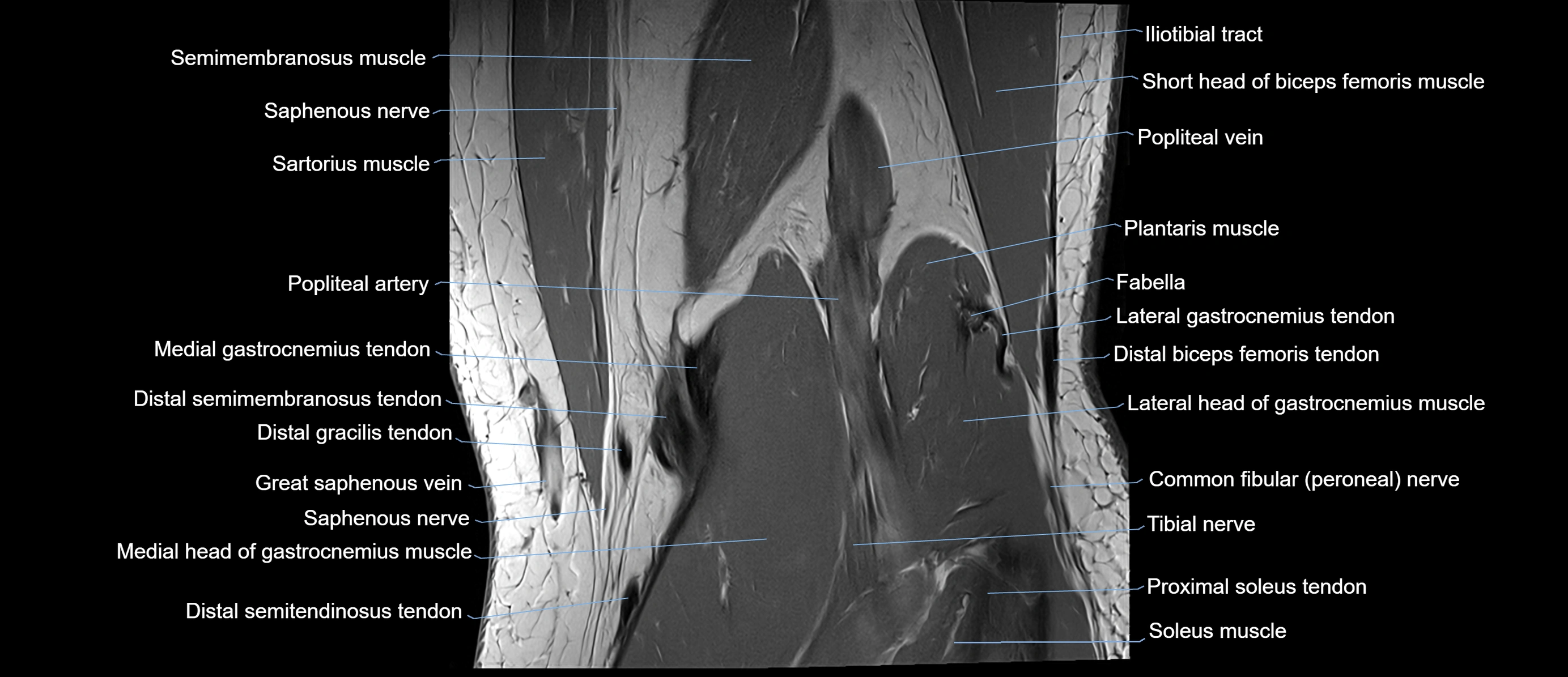
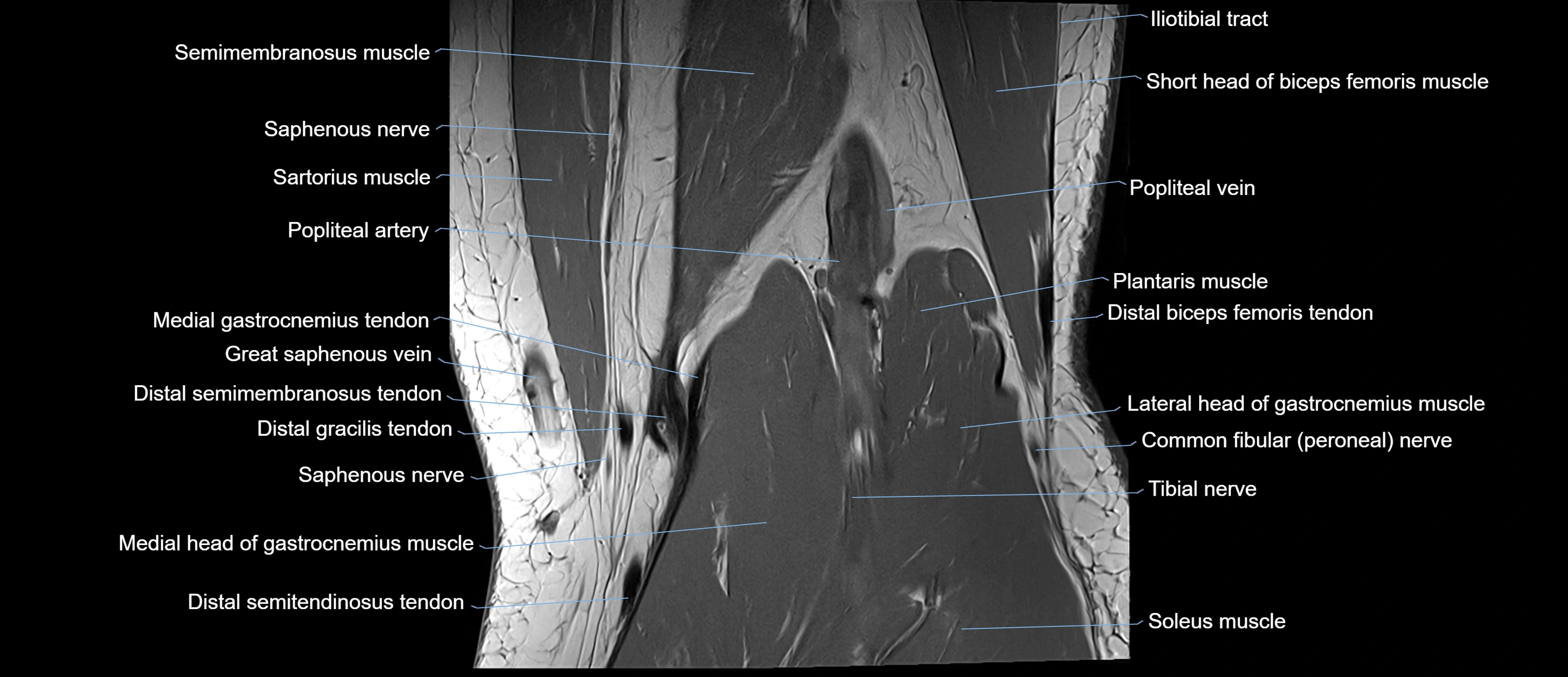
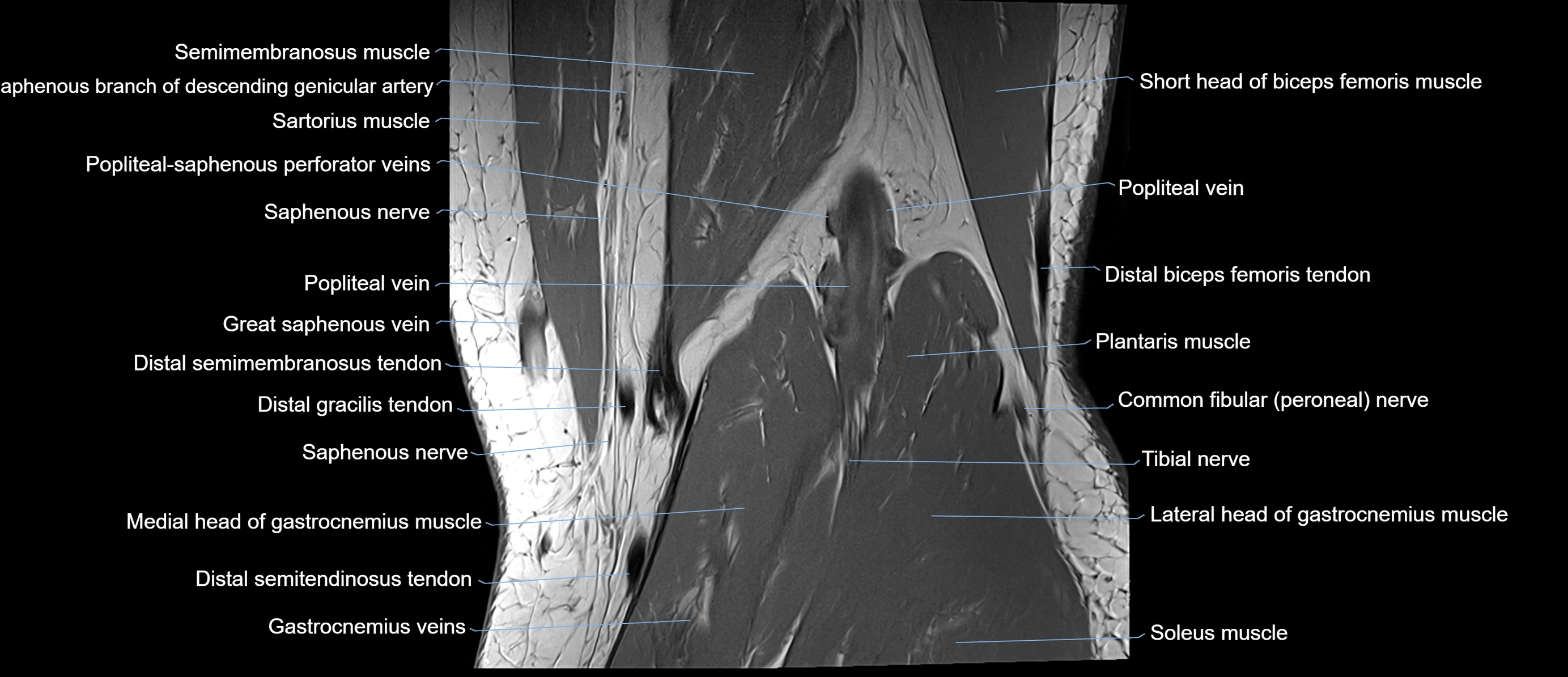
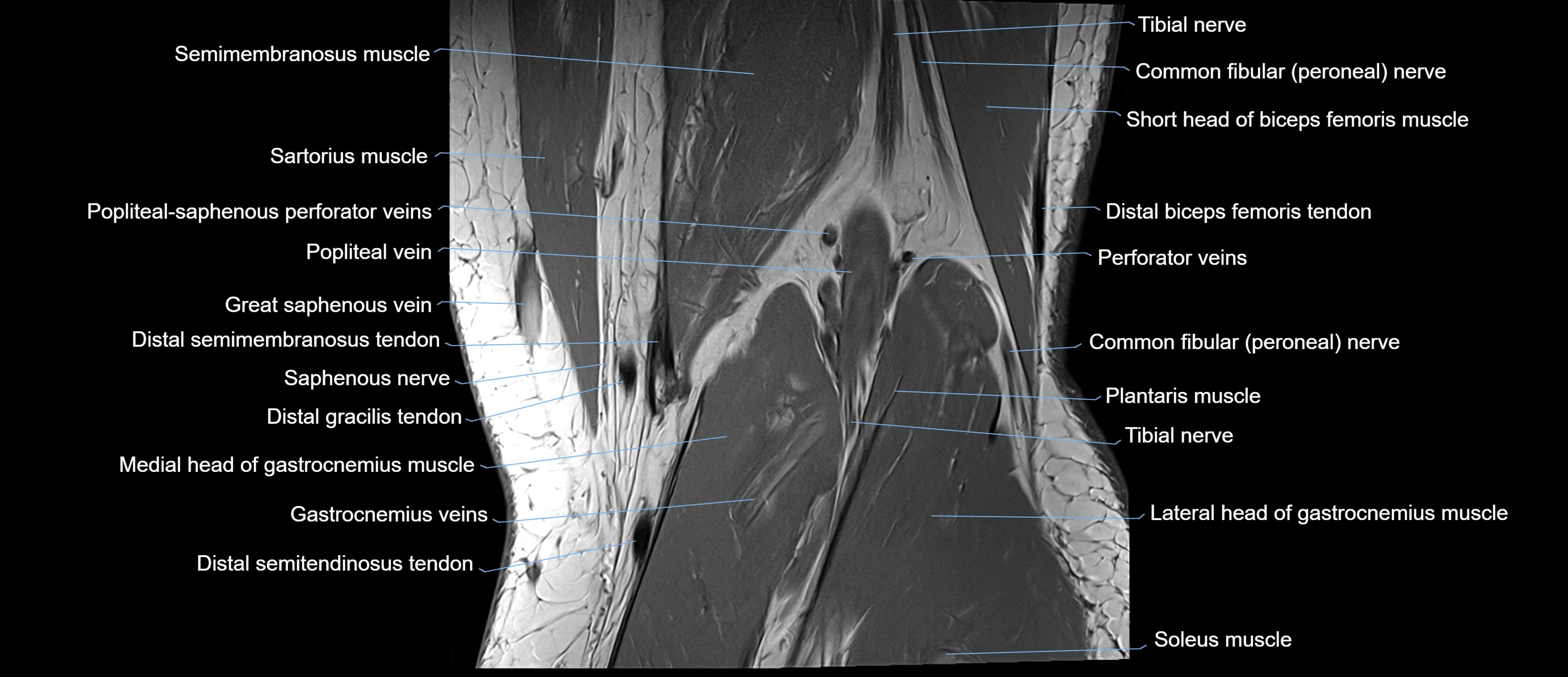
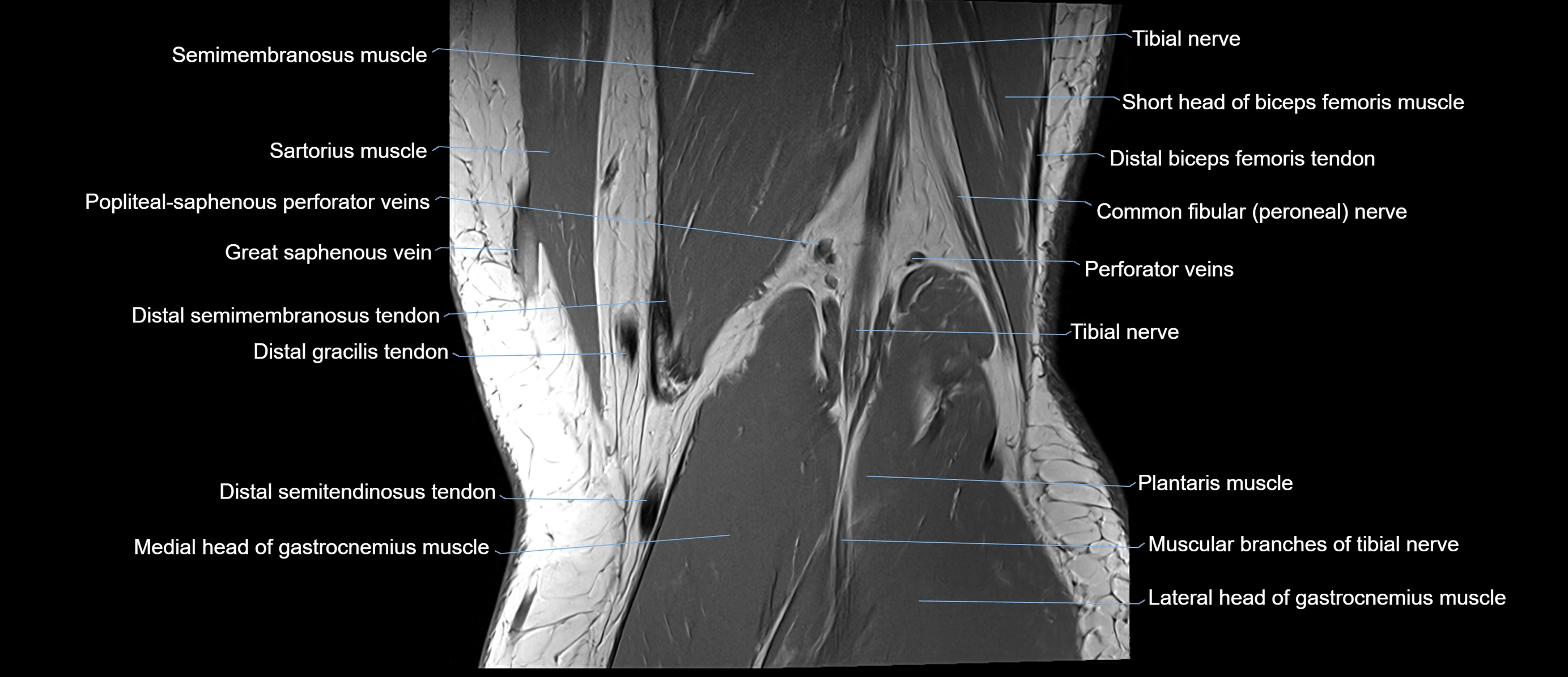
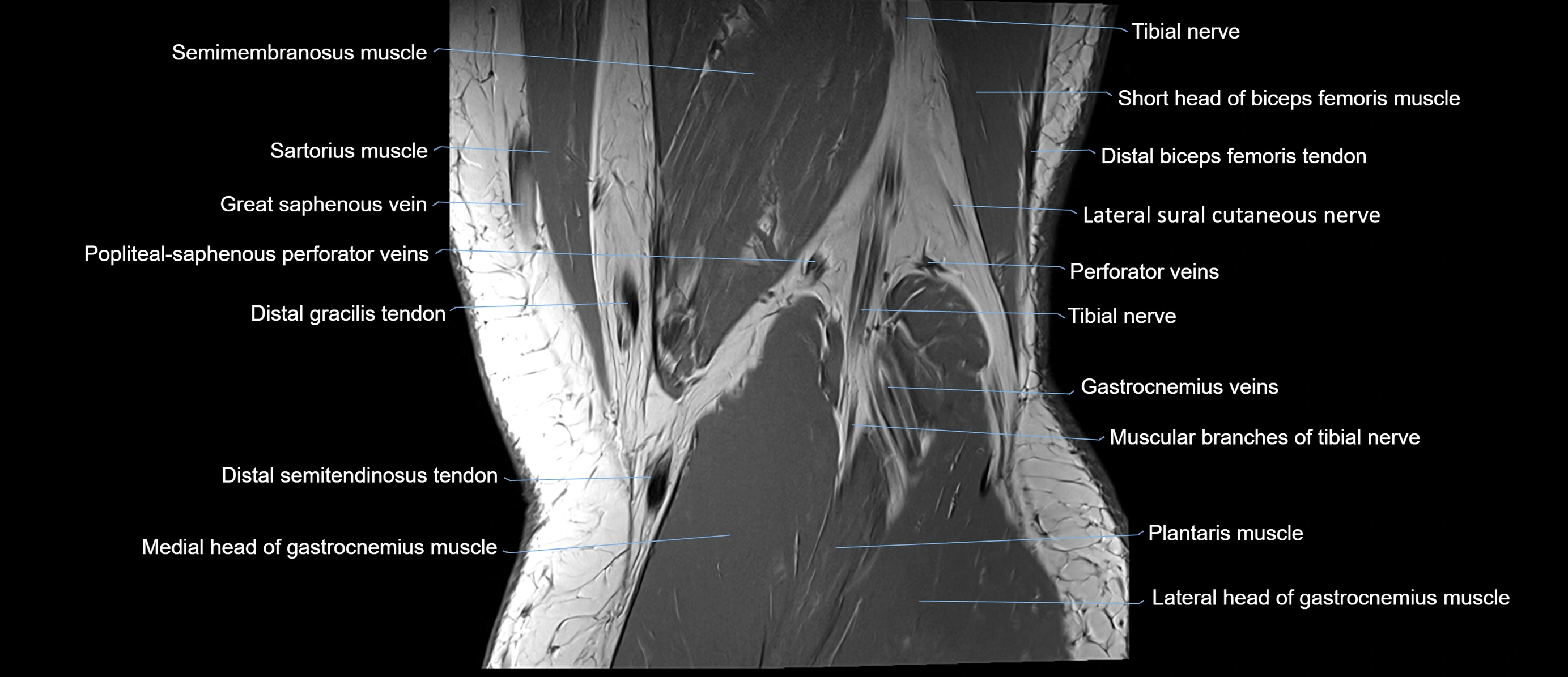
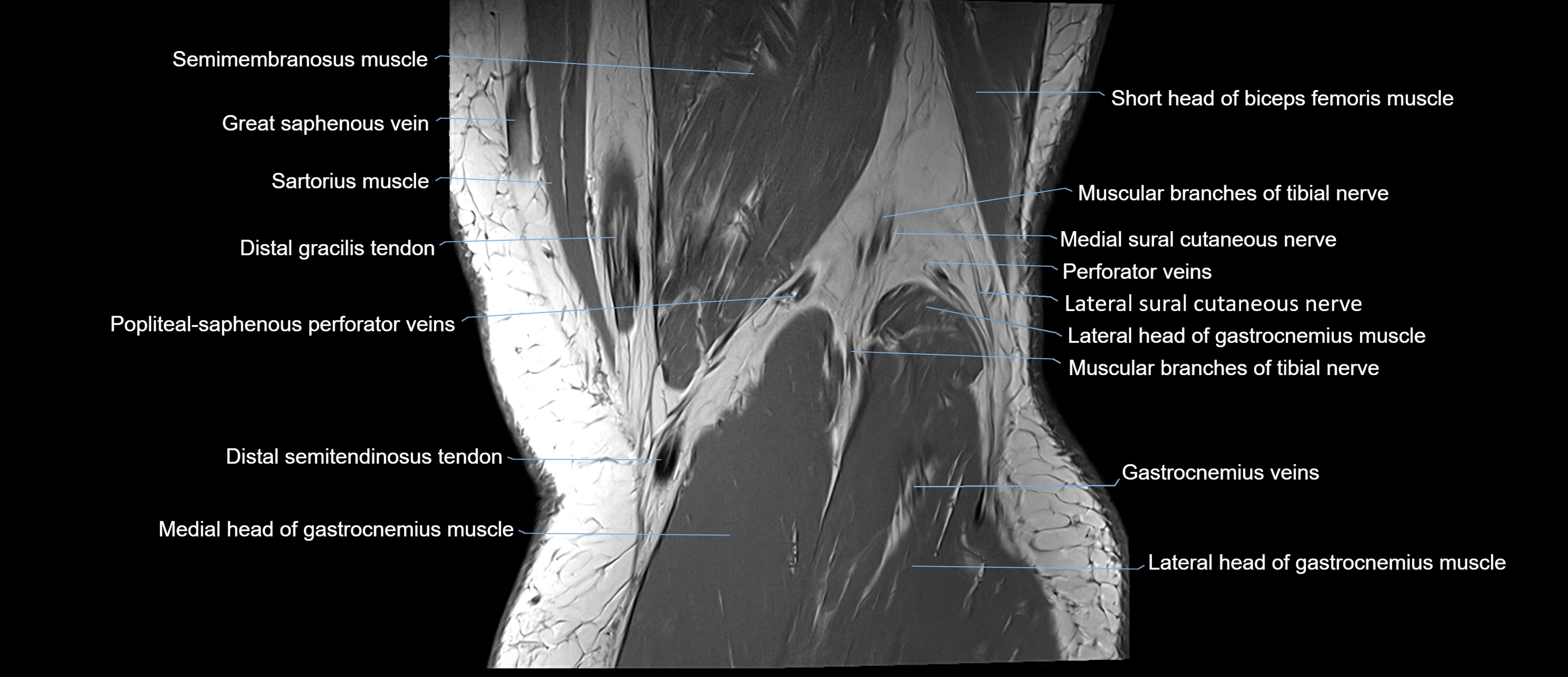
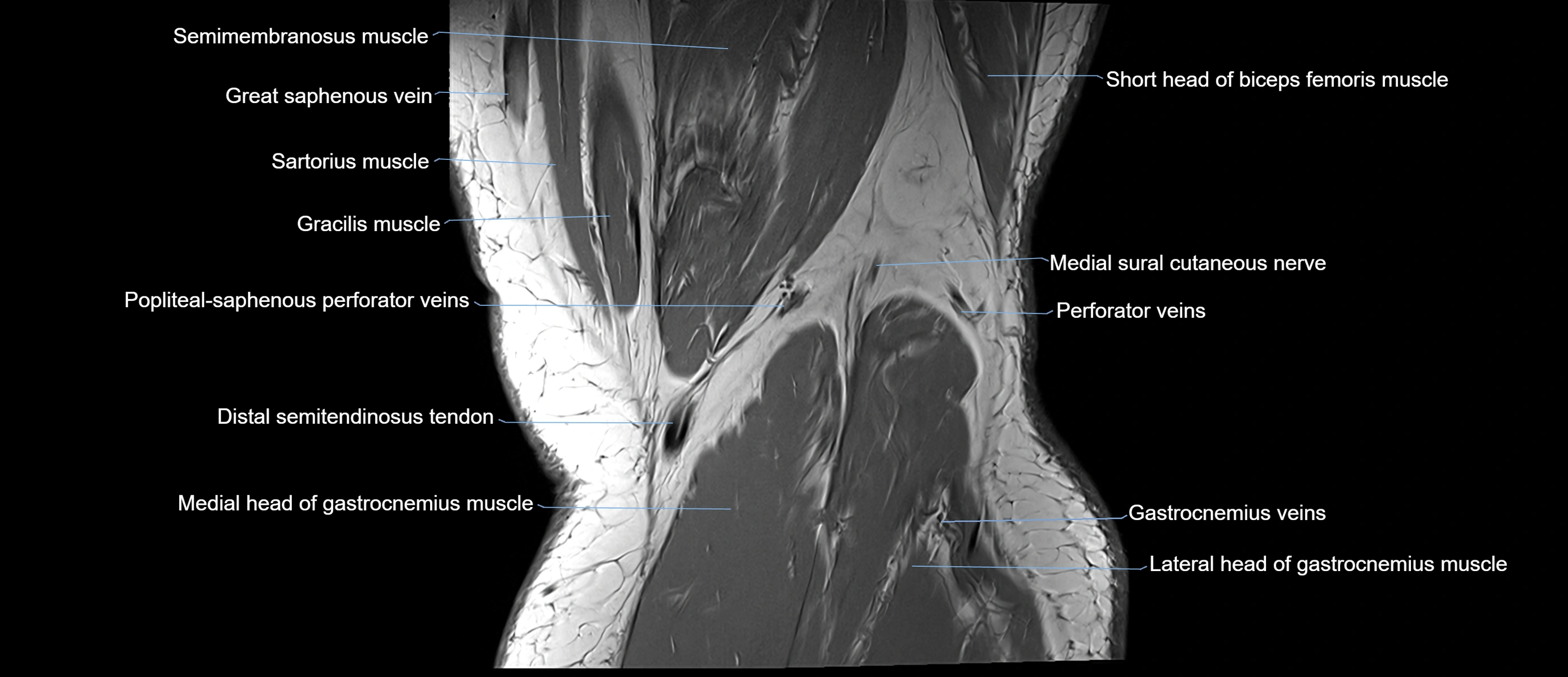
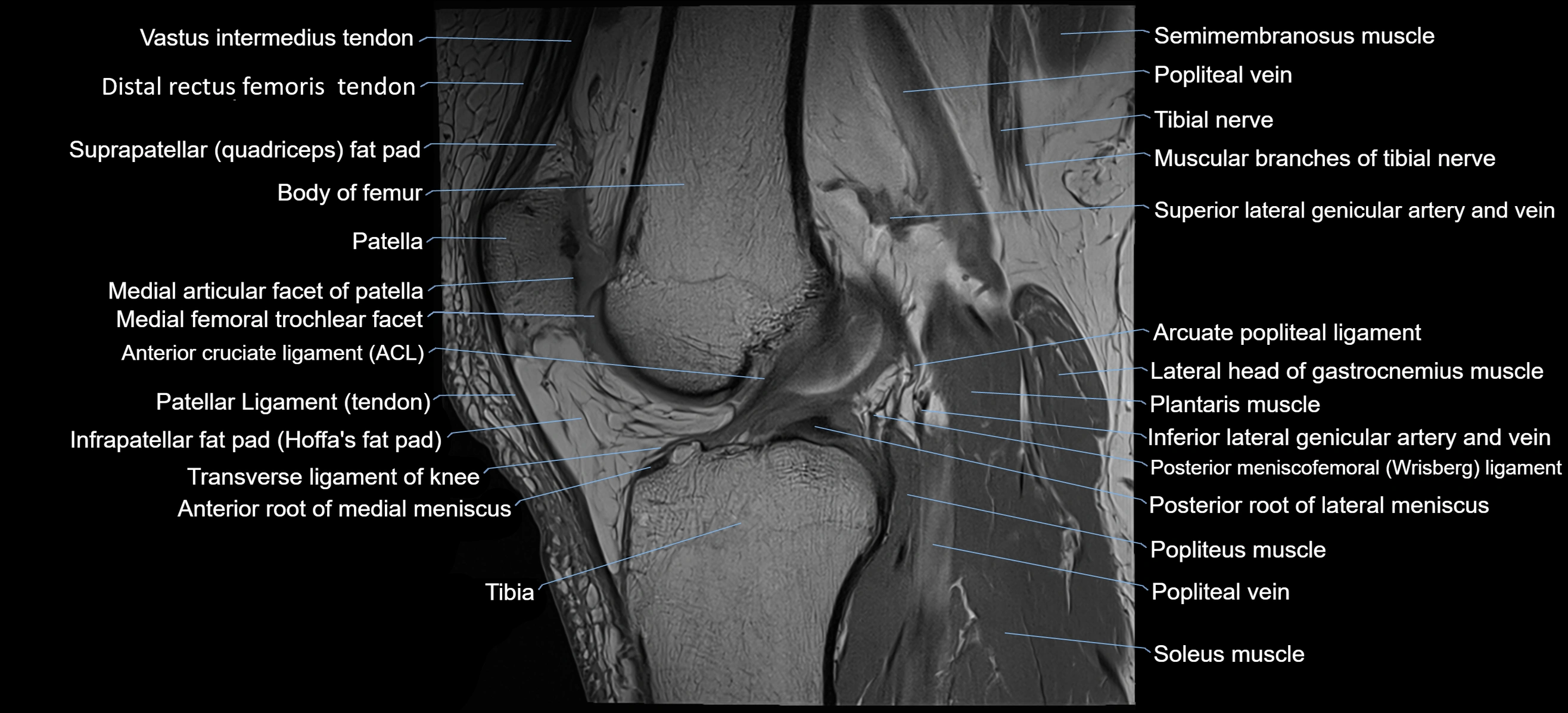
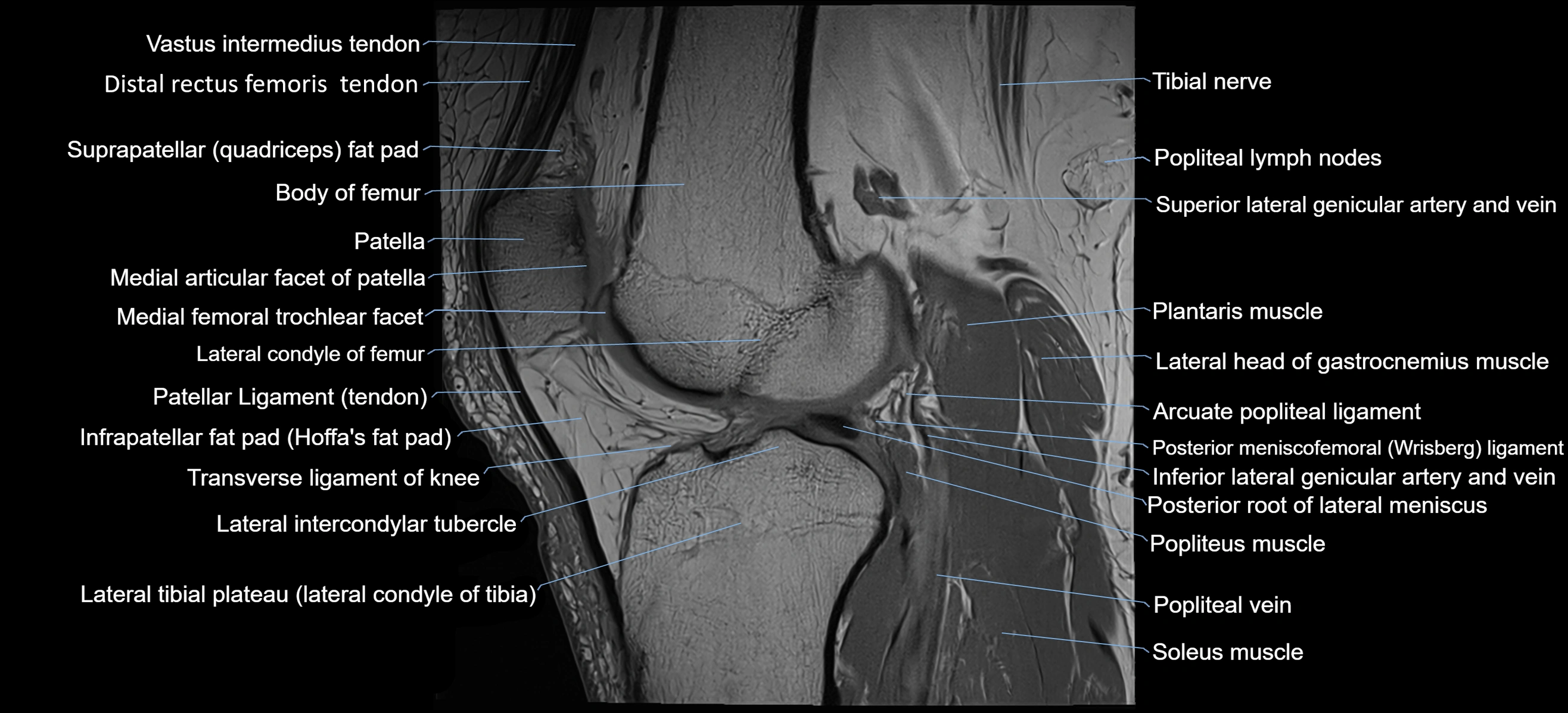
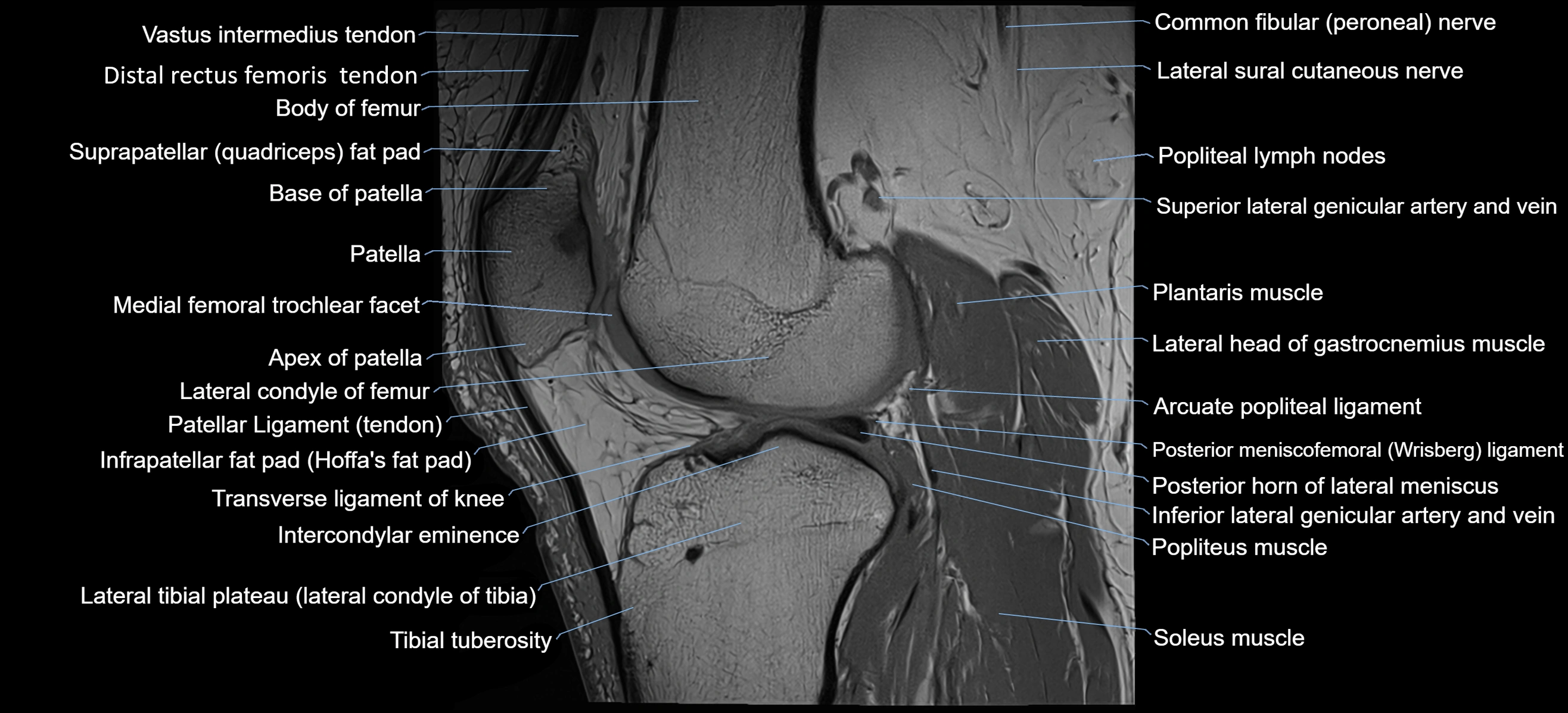
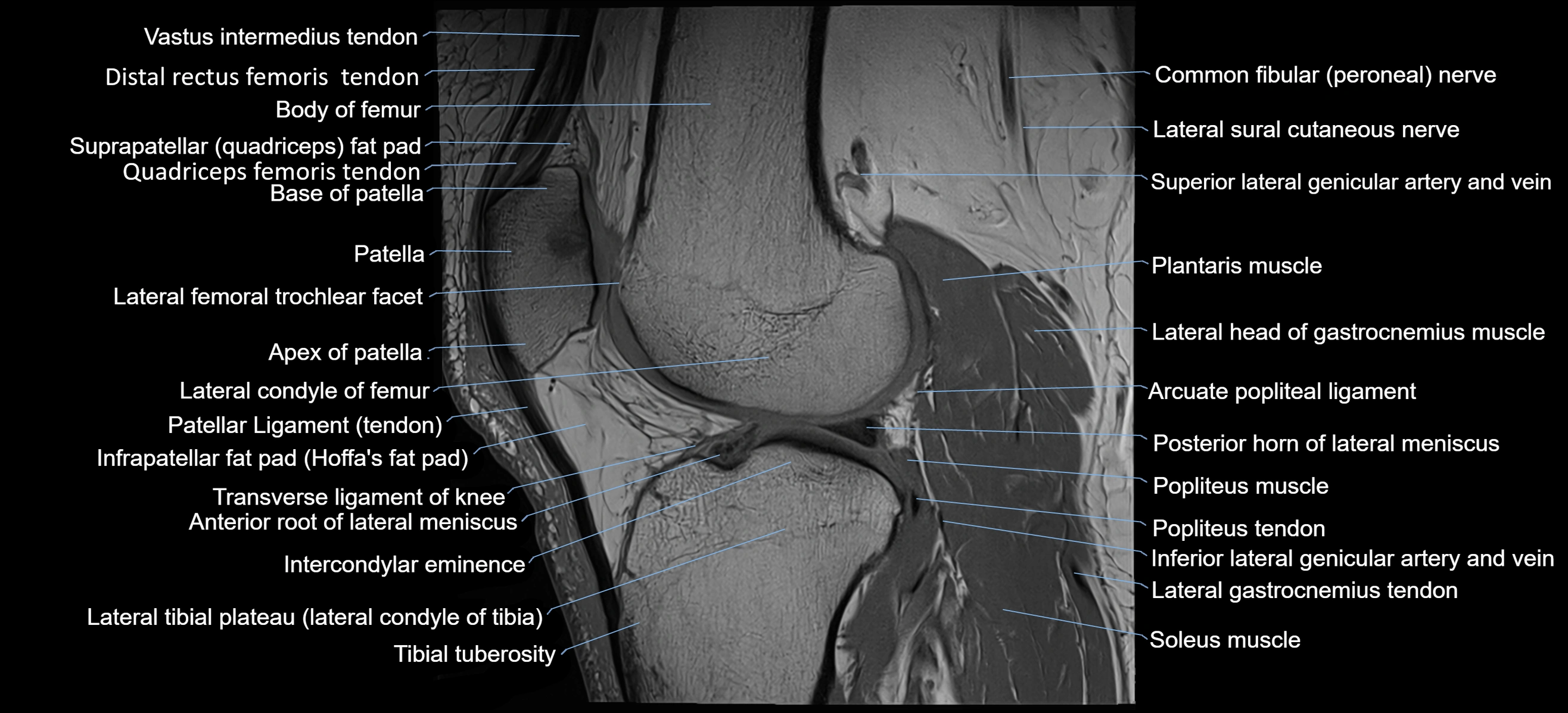
Topic
- Adductor tubercle
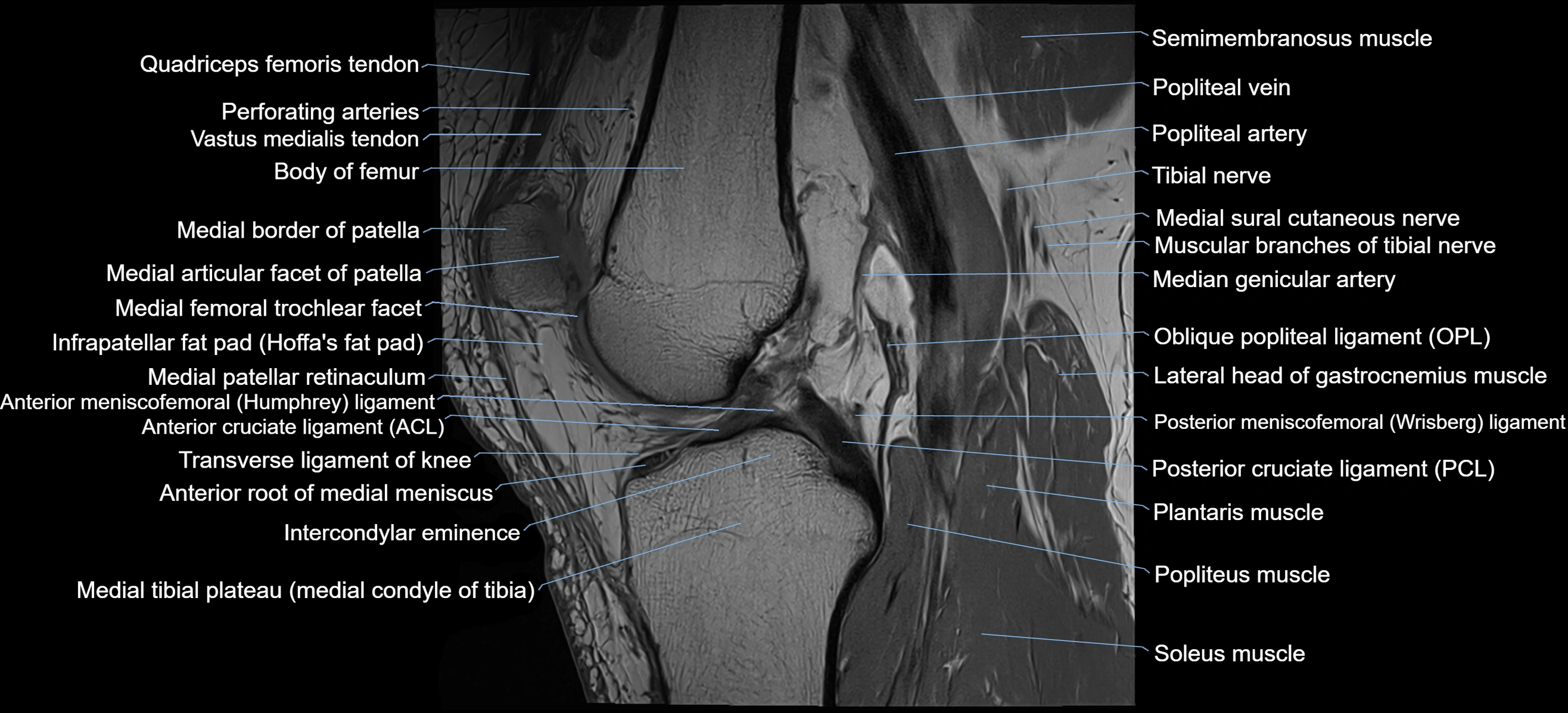
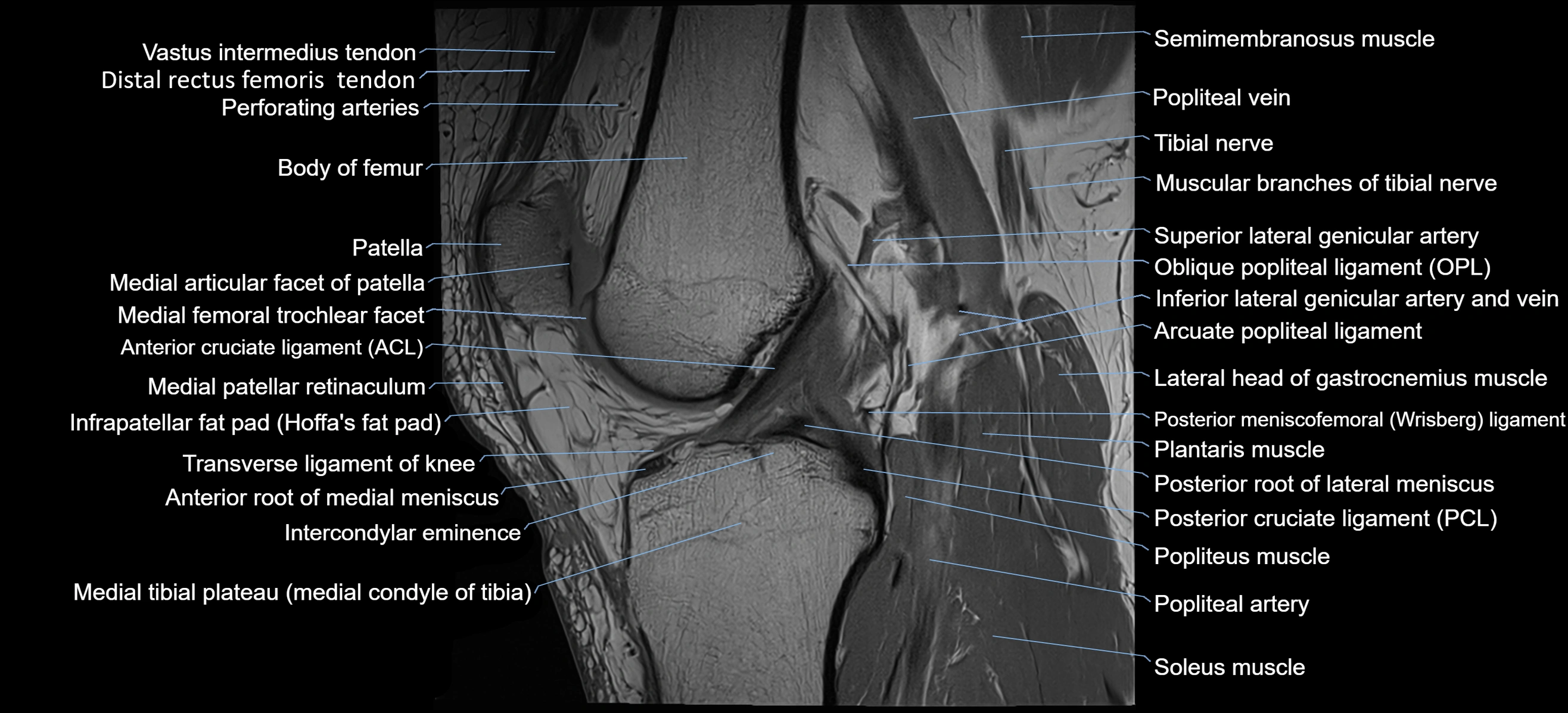
- Anterior cruciate ligament
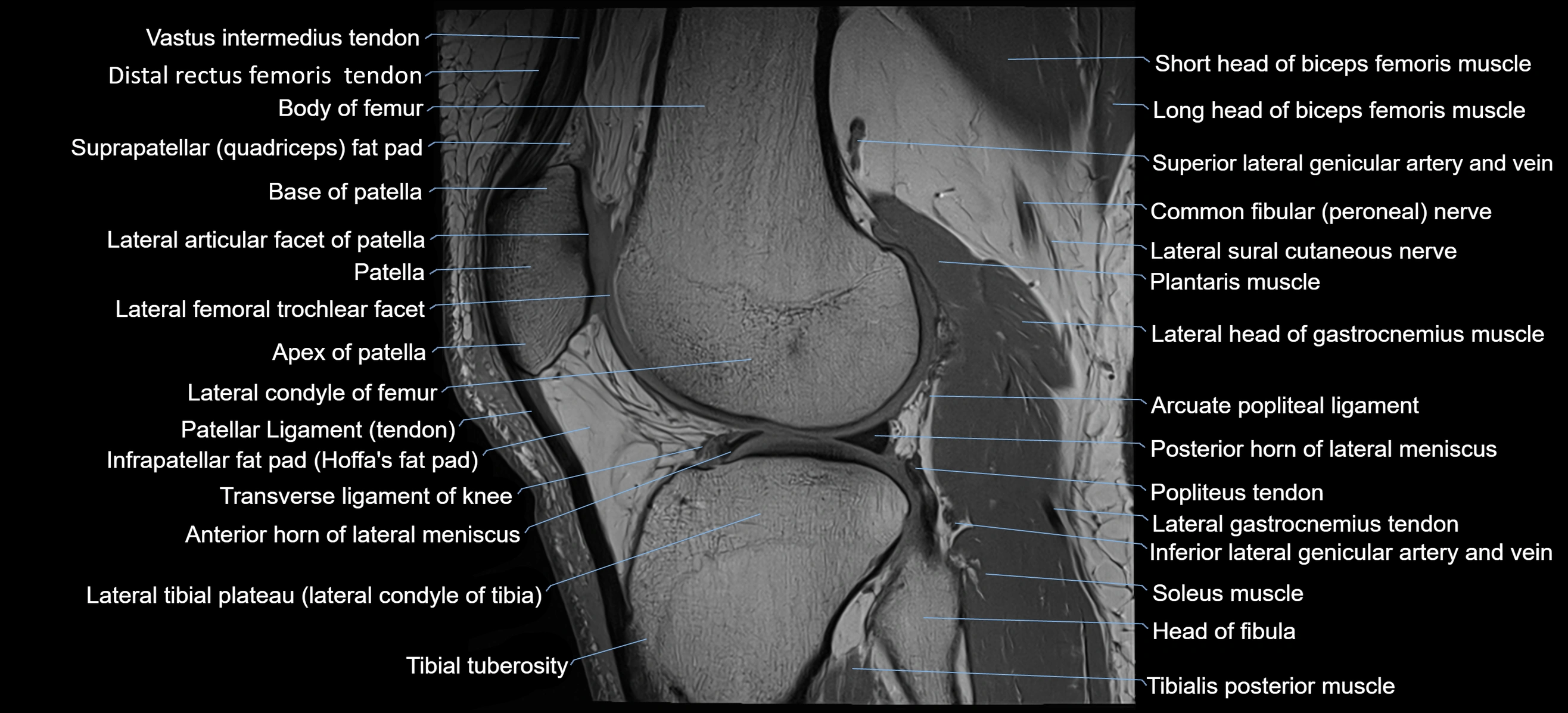
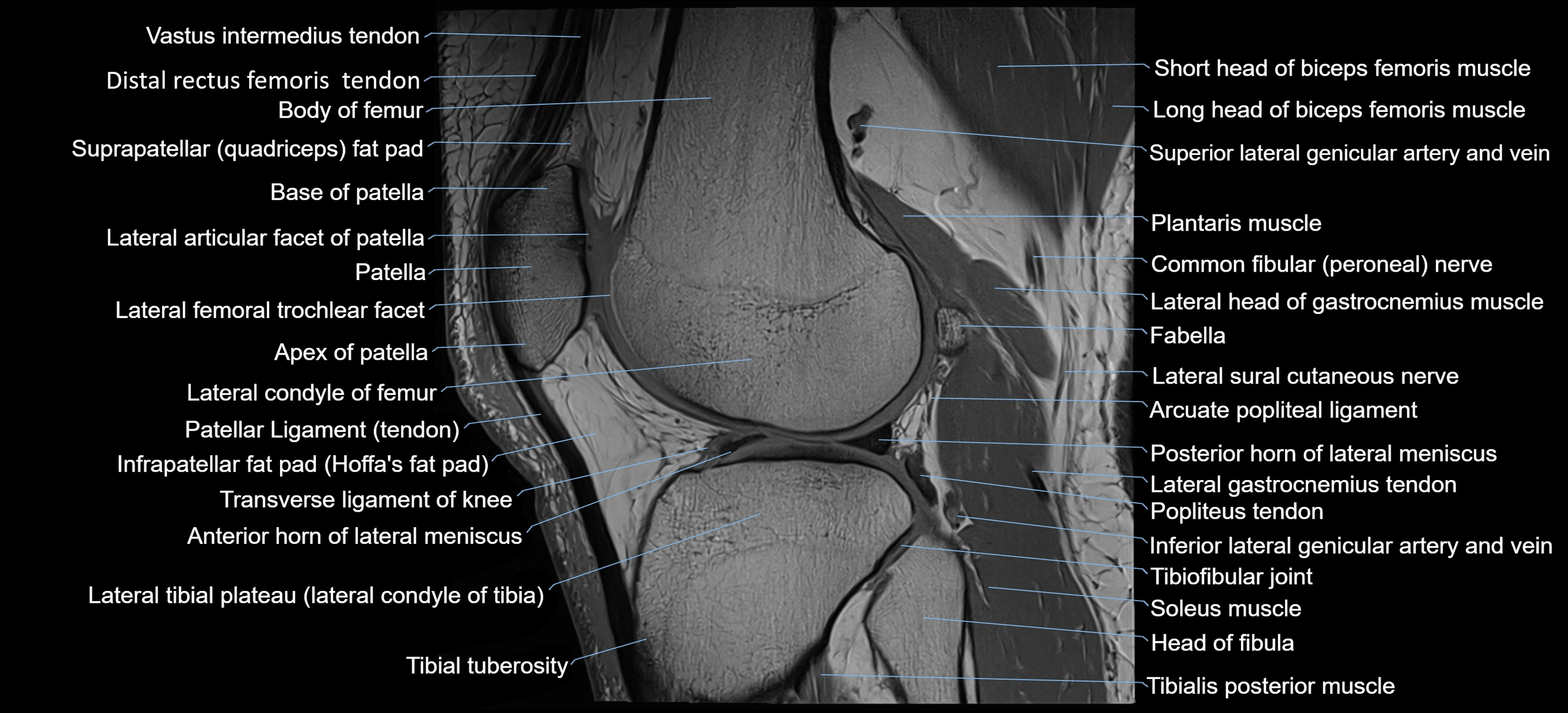
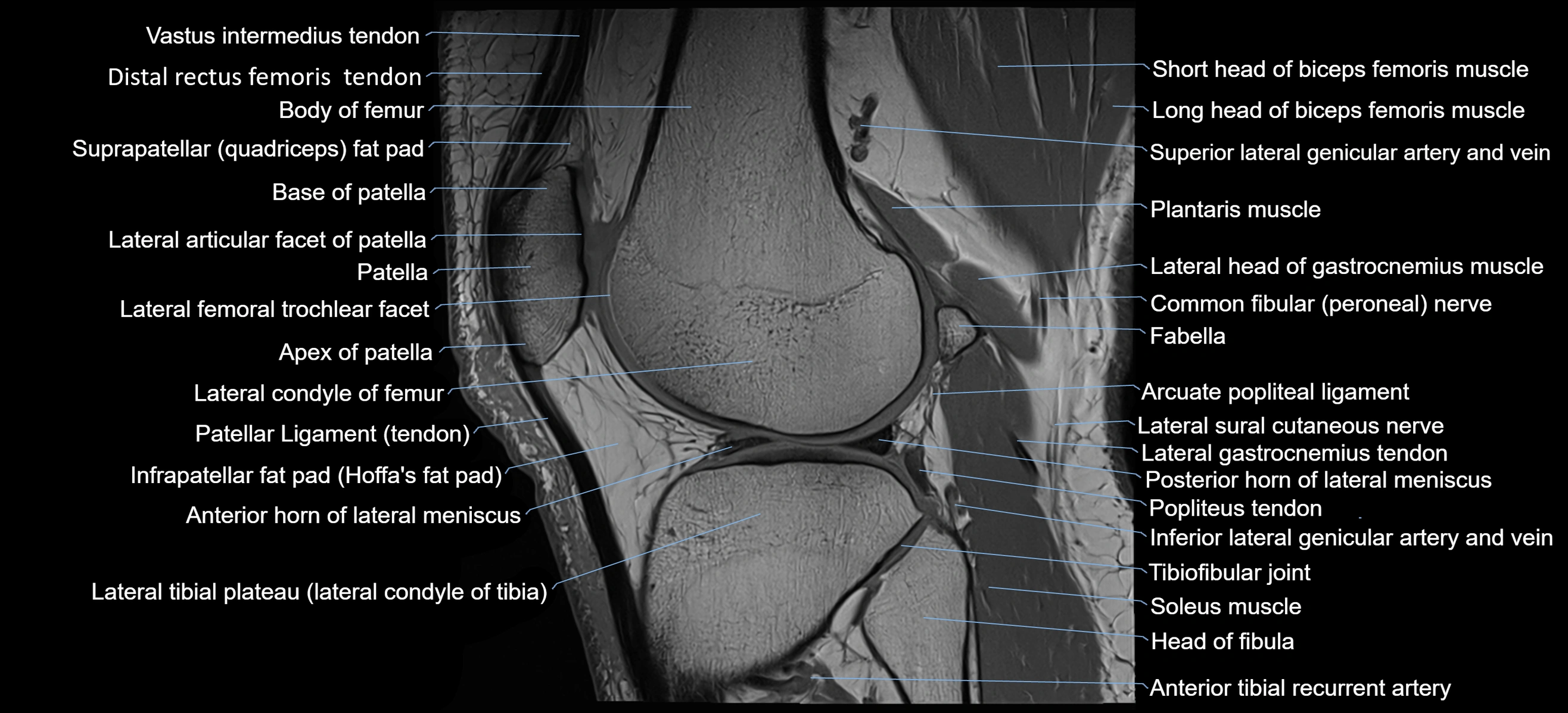
- Anterior horn of lateral meniscus
- Anterior horn of medial meniscus
- Anterior ligament of fibular head
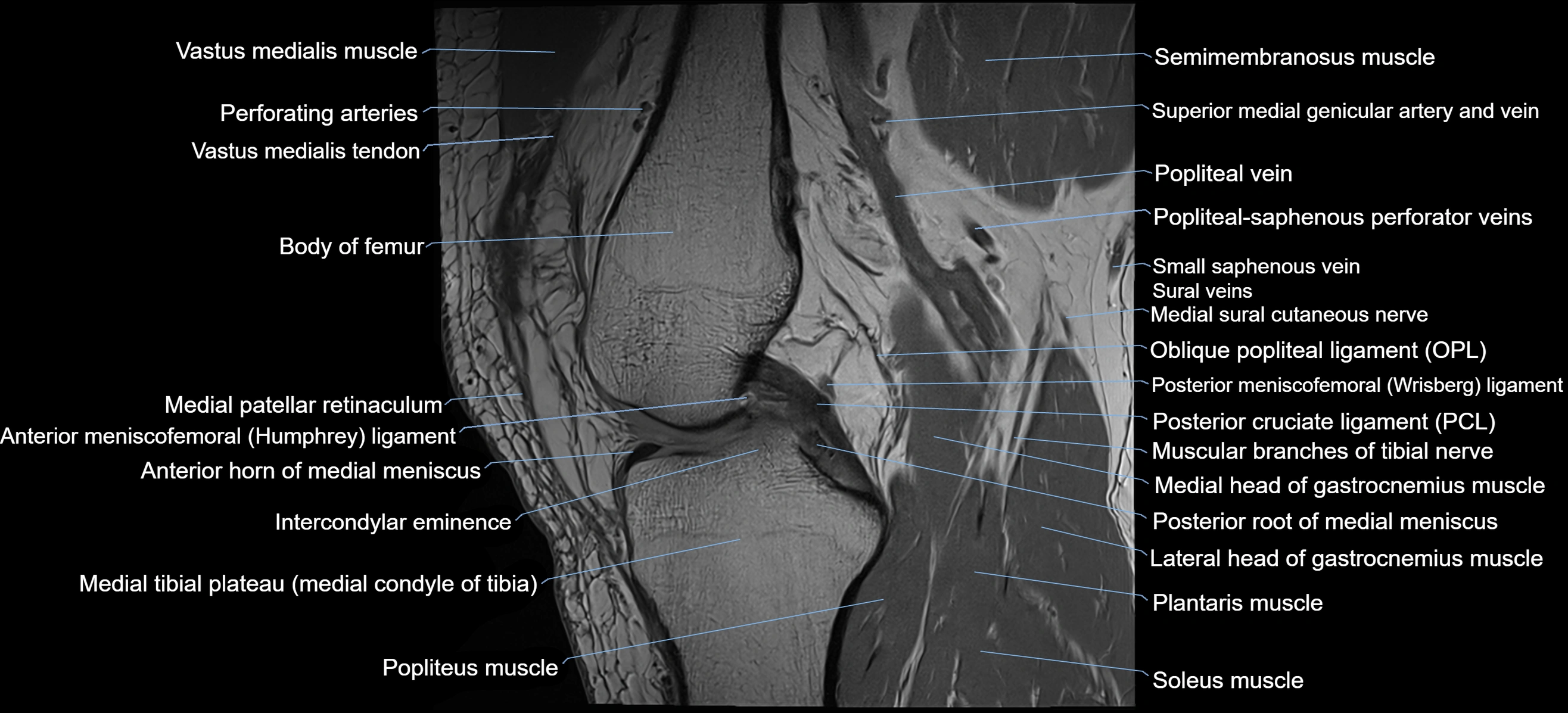
- Anterior meniscofemoral ligament
- Anterior rim of acetabulum
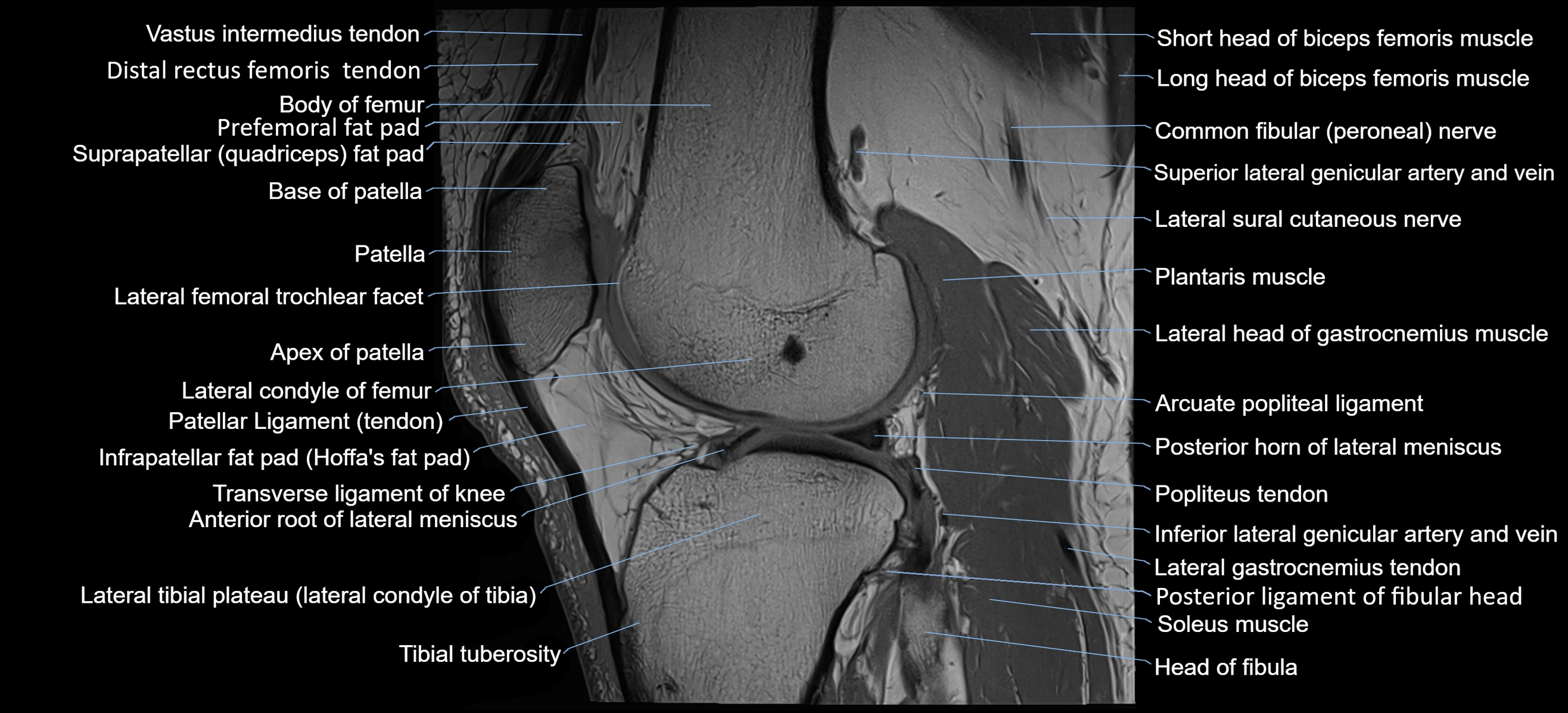
- Anterior root of lateral meniscus
- Anterior root of medial meniscus
- Anterolateral ligament of knee
- Apex of head of fibula
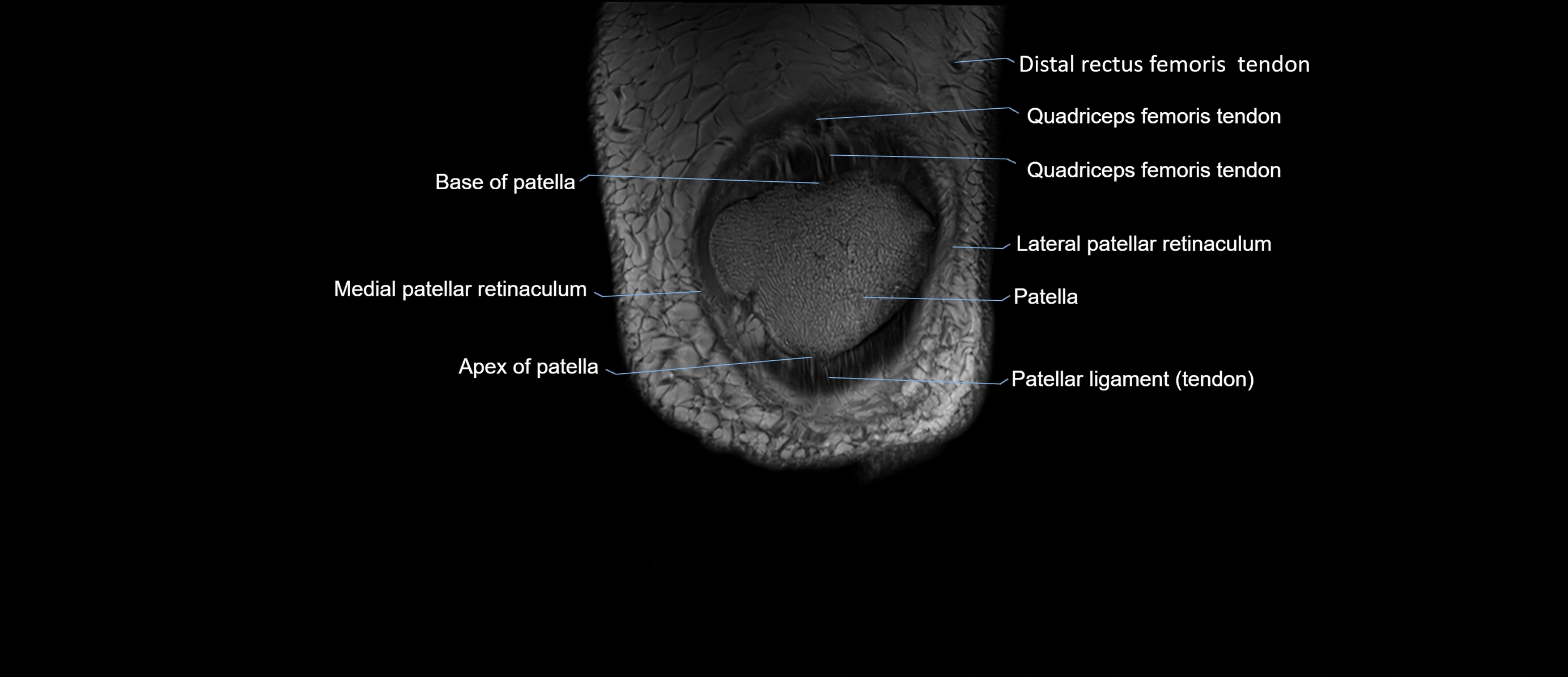
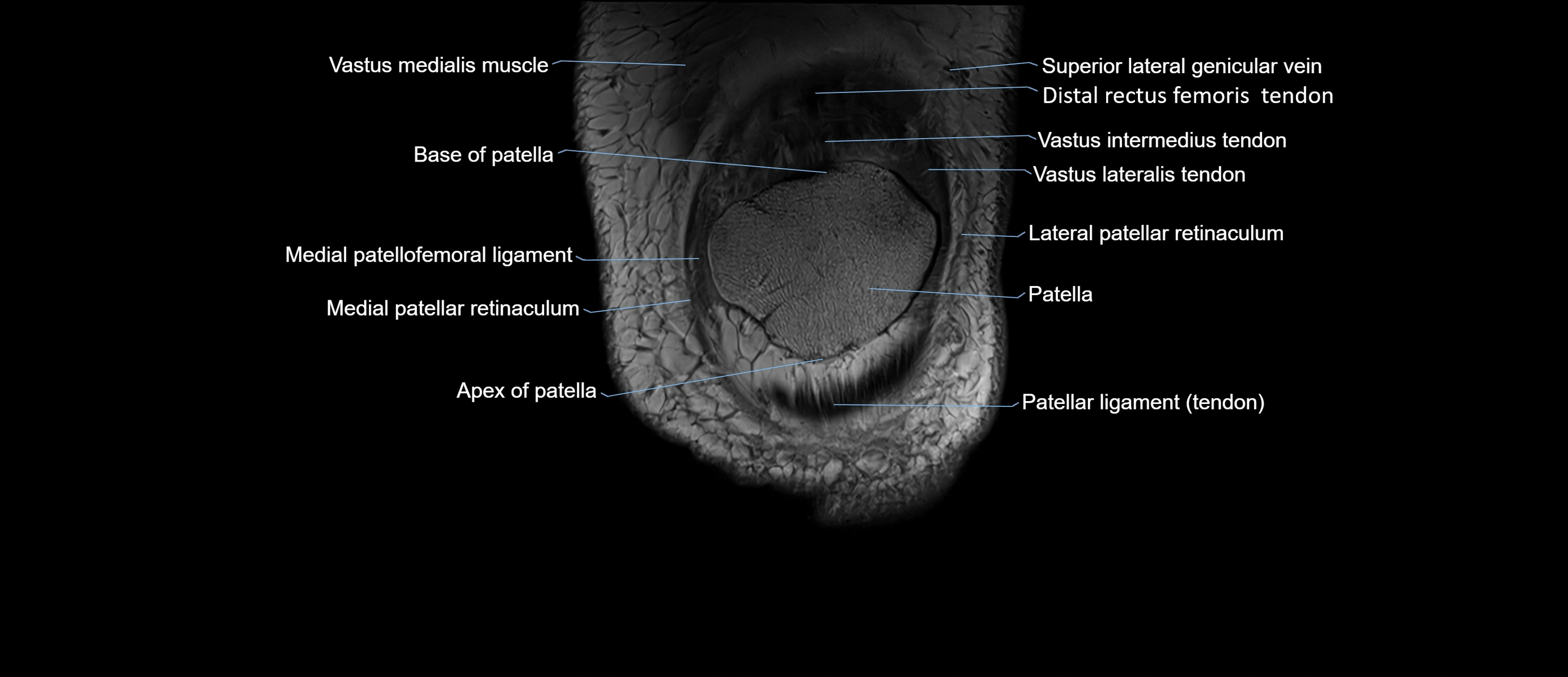
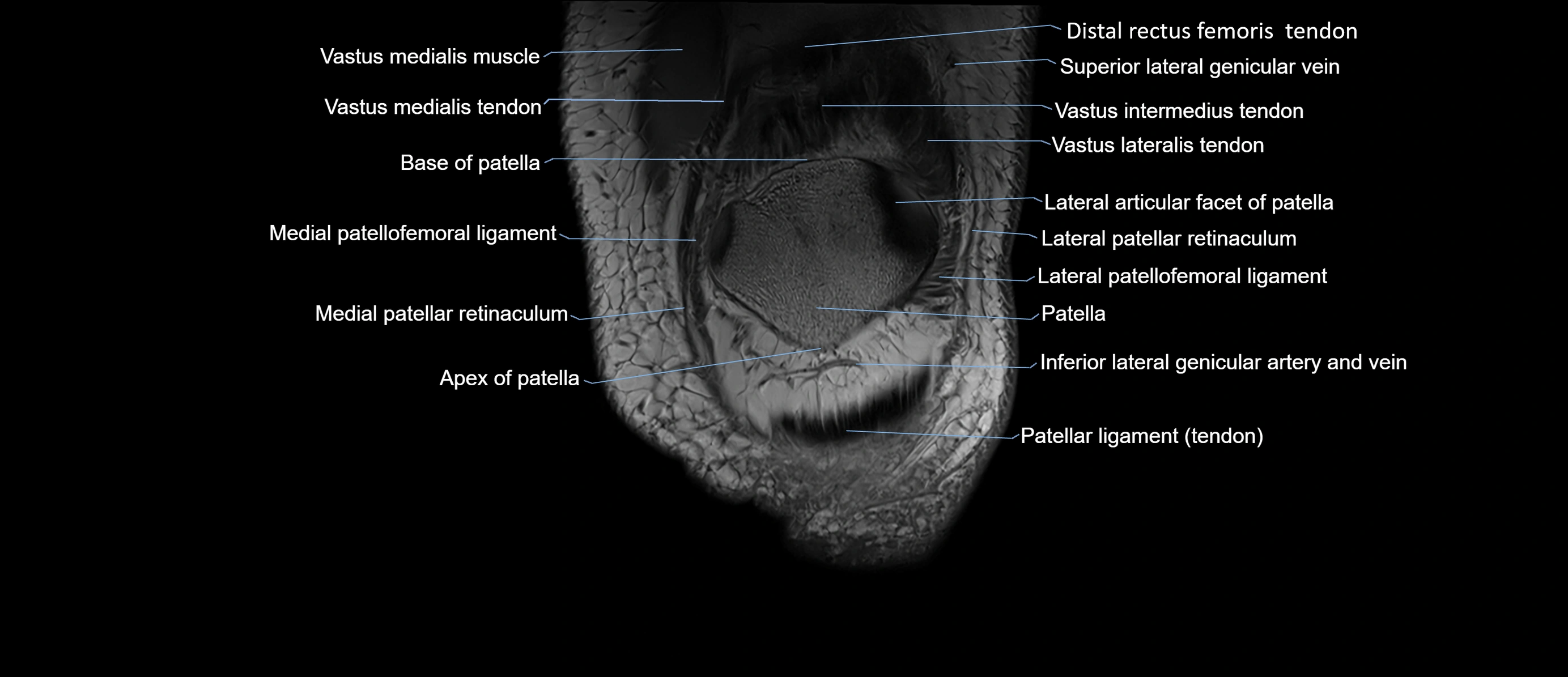
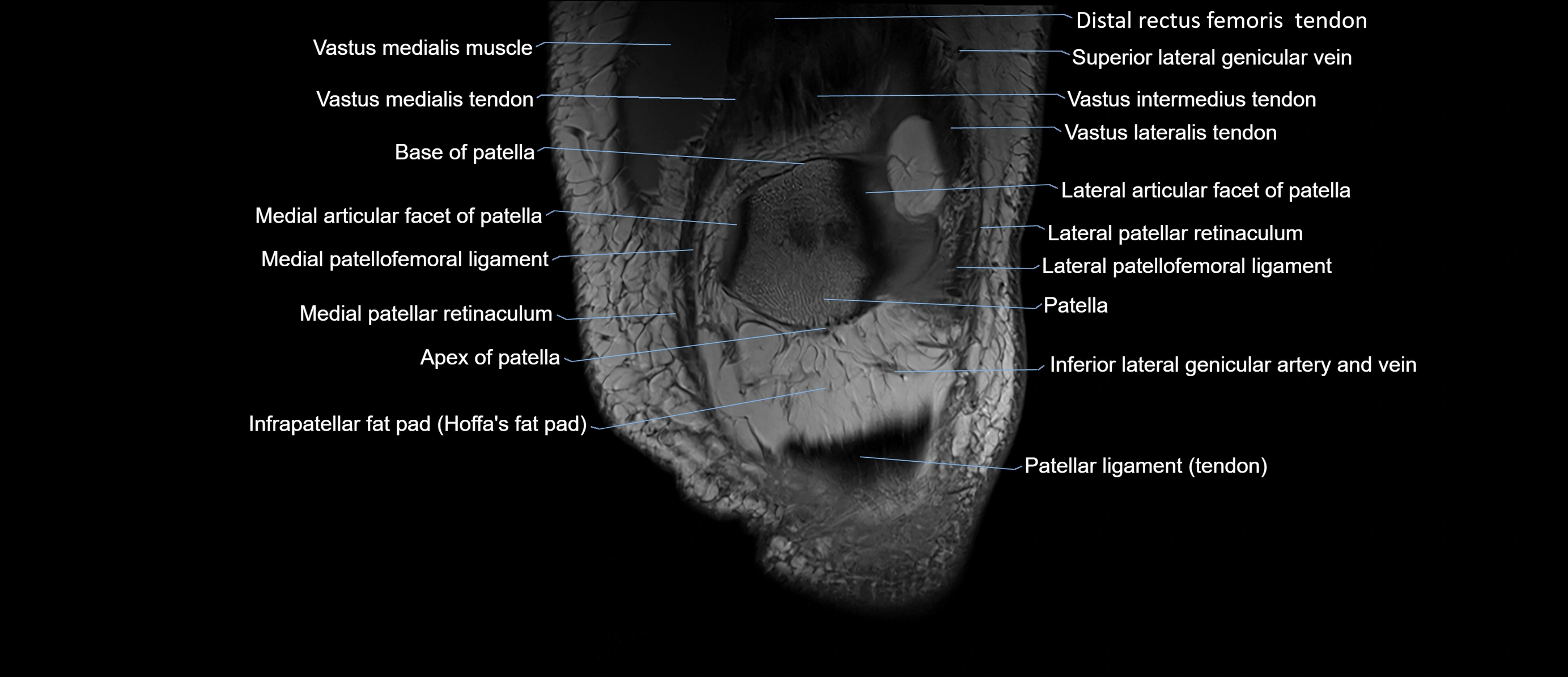
- Apex of patella
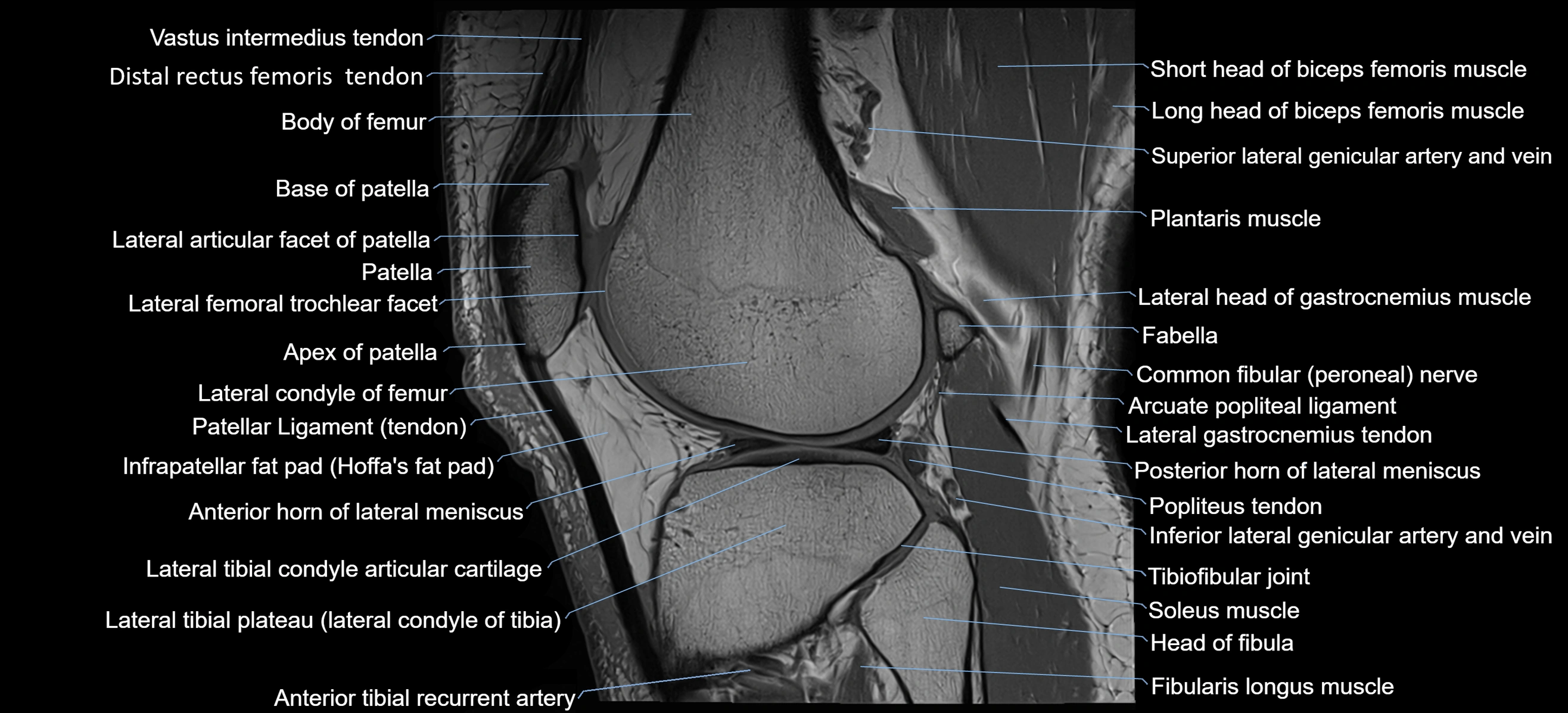
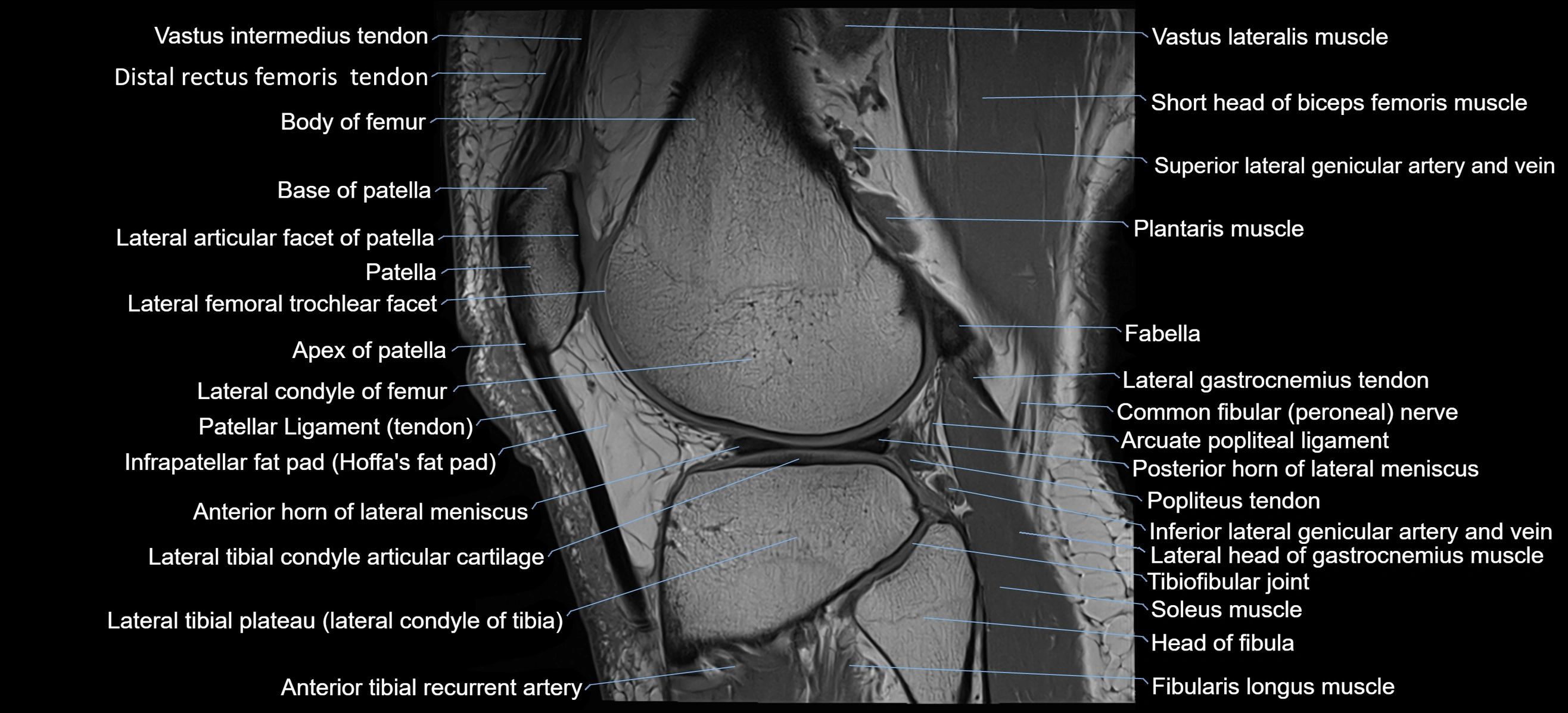
- Arcuate popliteal ligament
- Articular facet of head of fibula
- Articular surface of lateral femoral condyle
- Articular surface of lateral tibial condyle
- Articular surface of medial femoral condyle
- Articular surface of medial tibial condyle
- Base of patella
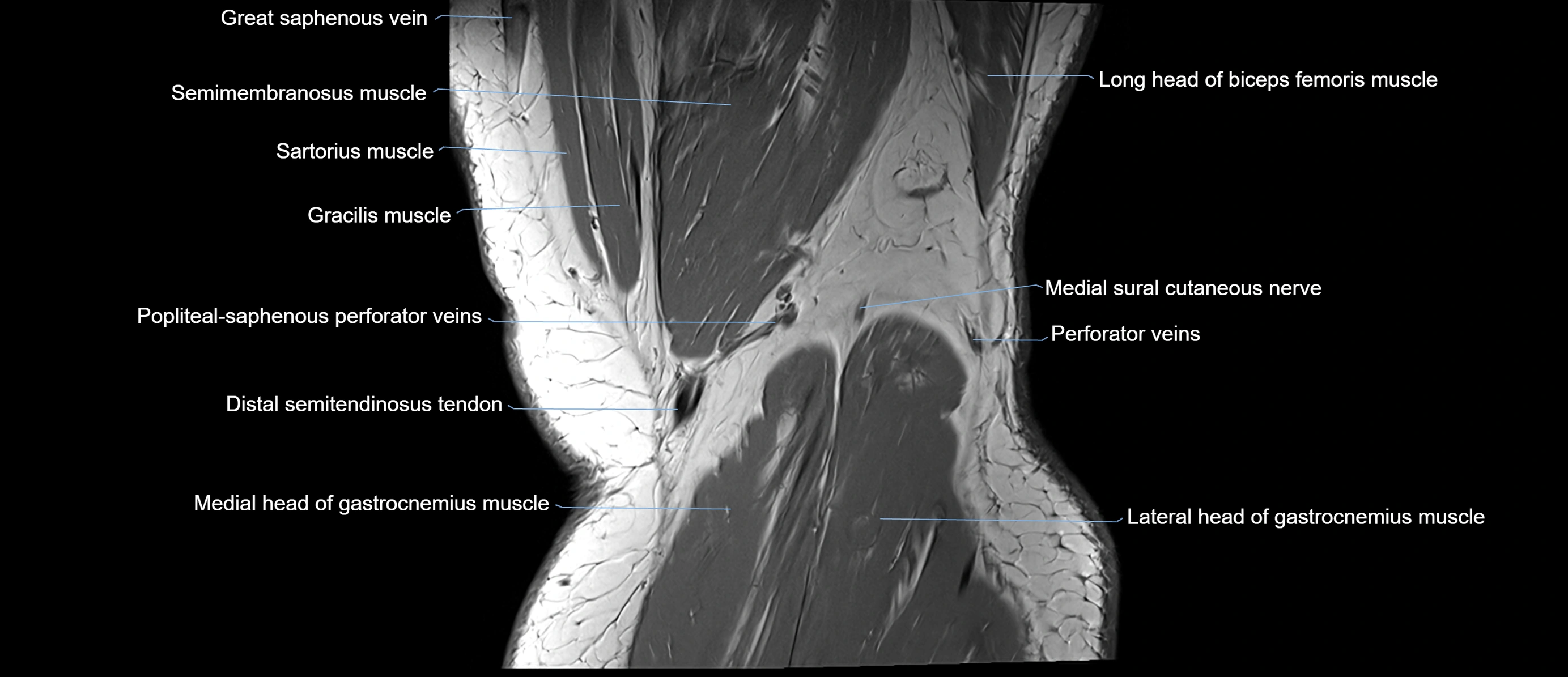
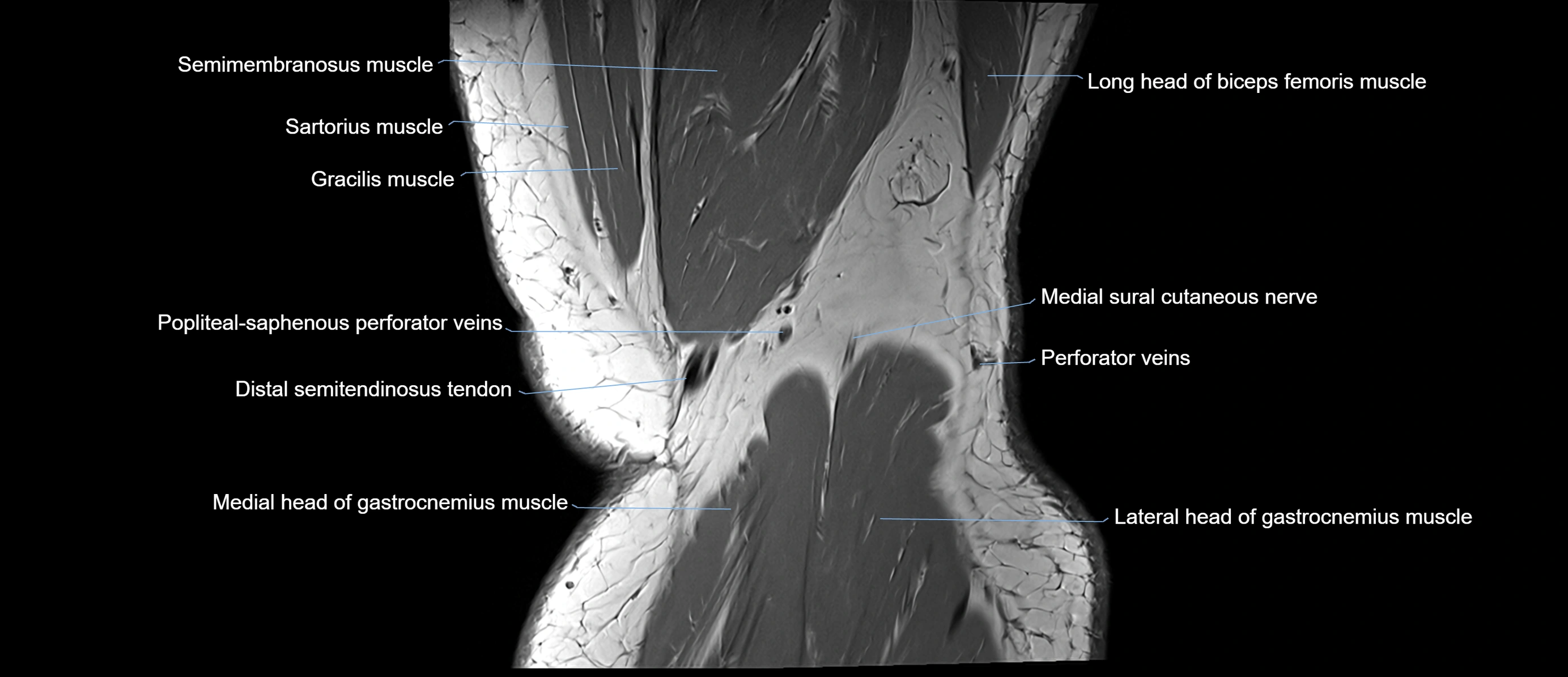
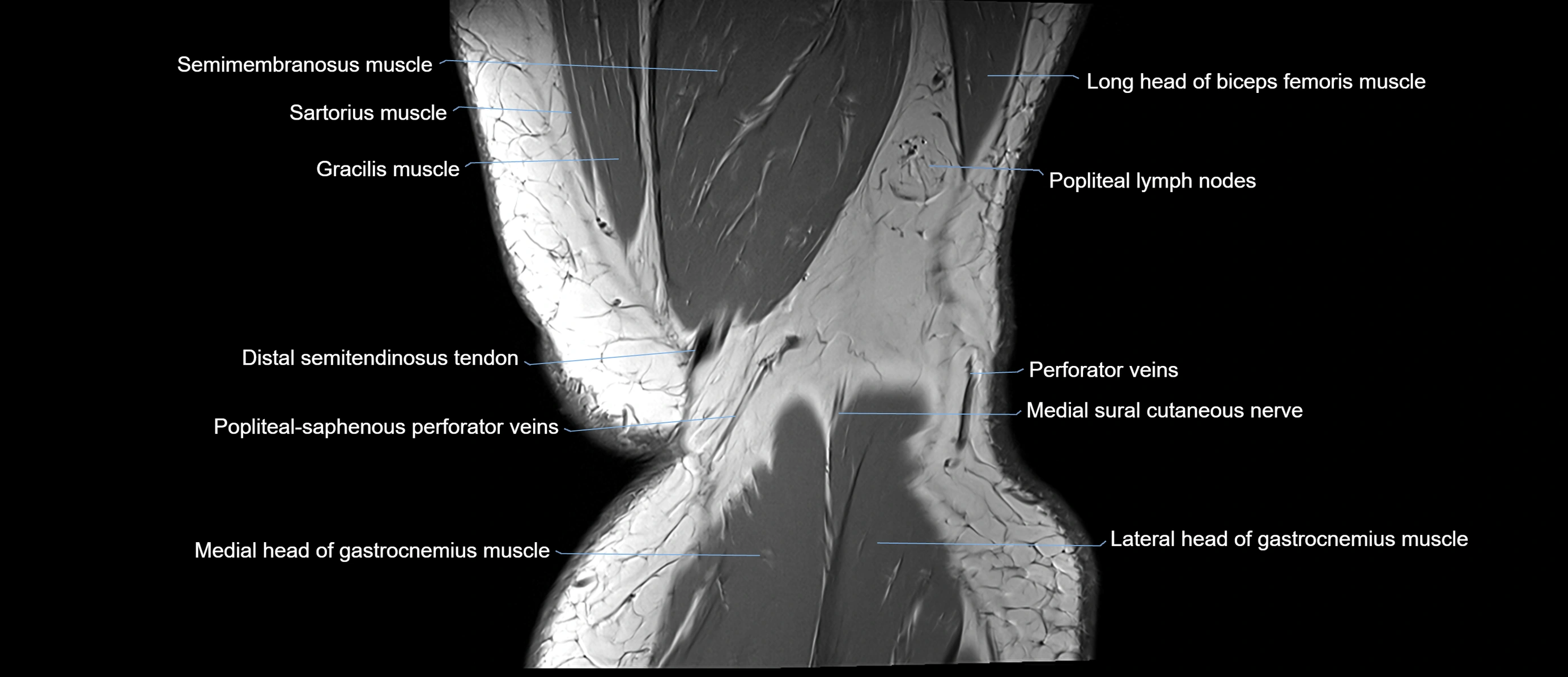
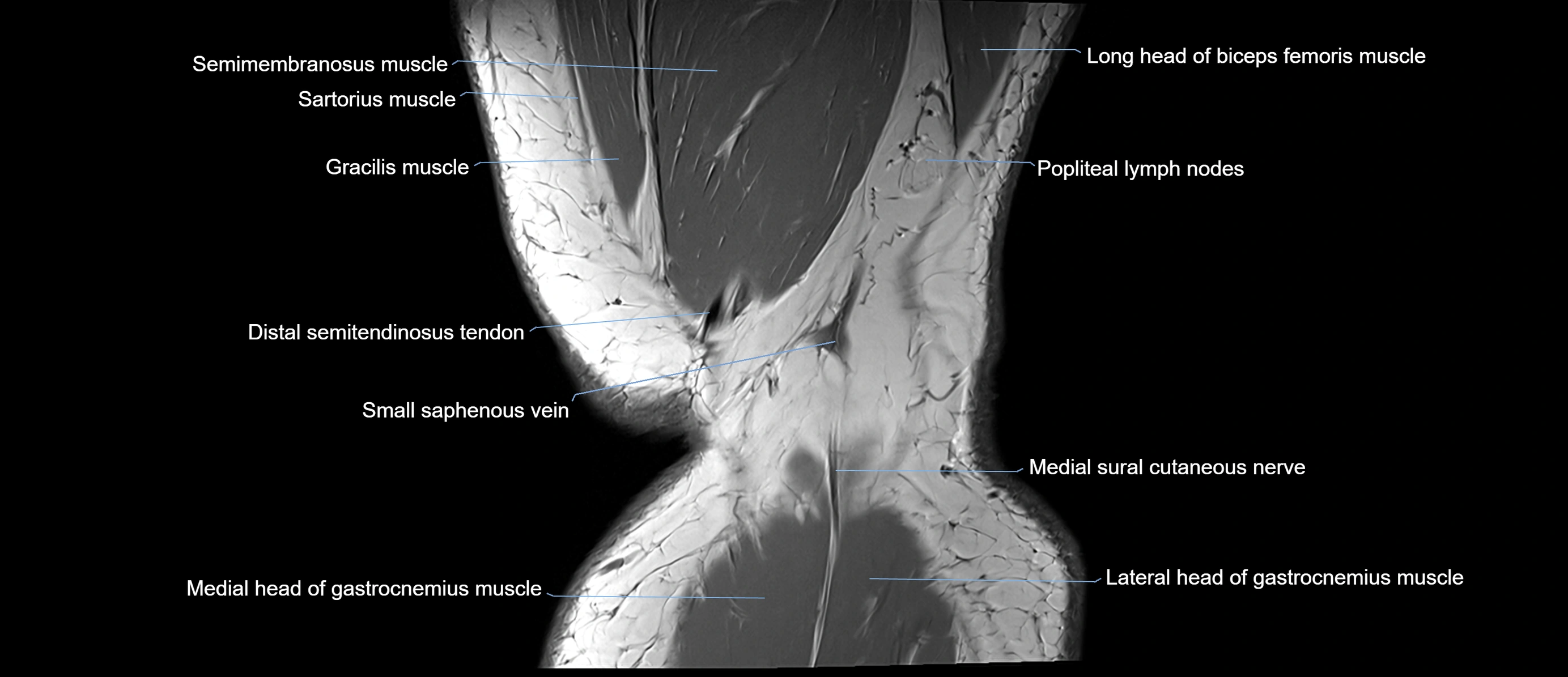
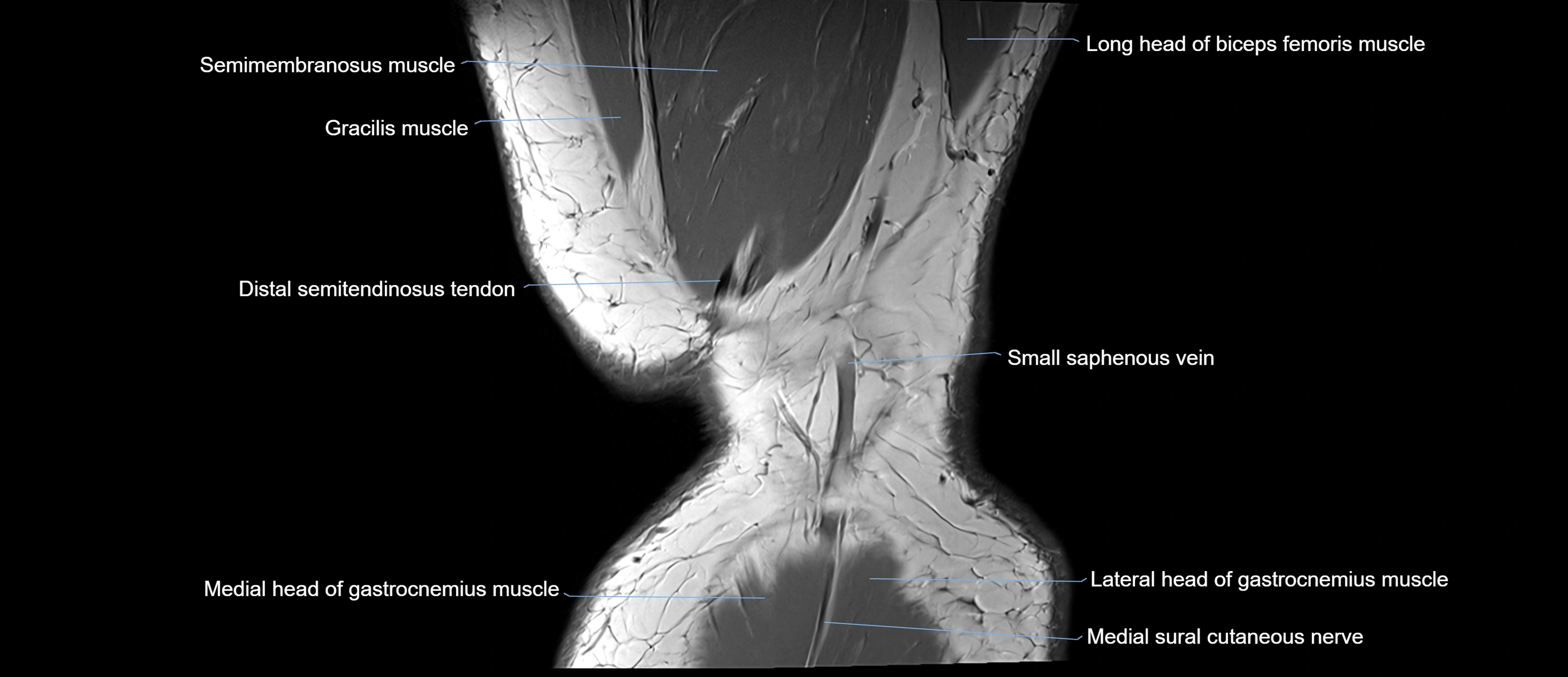
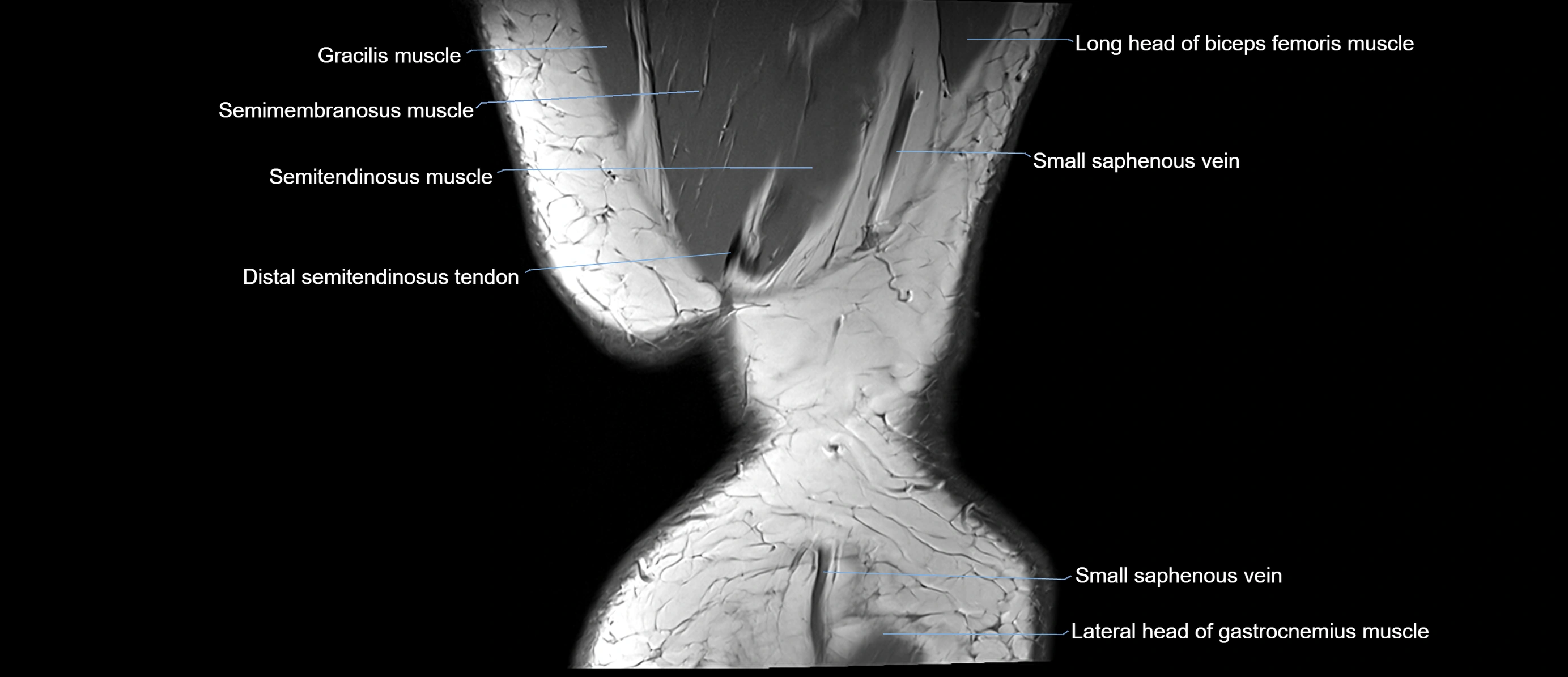
- Biceps femoris muscle (Long head)
- Biceps femoris muscle (Short head)
- Body of femur
- Body of fibula
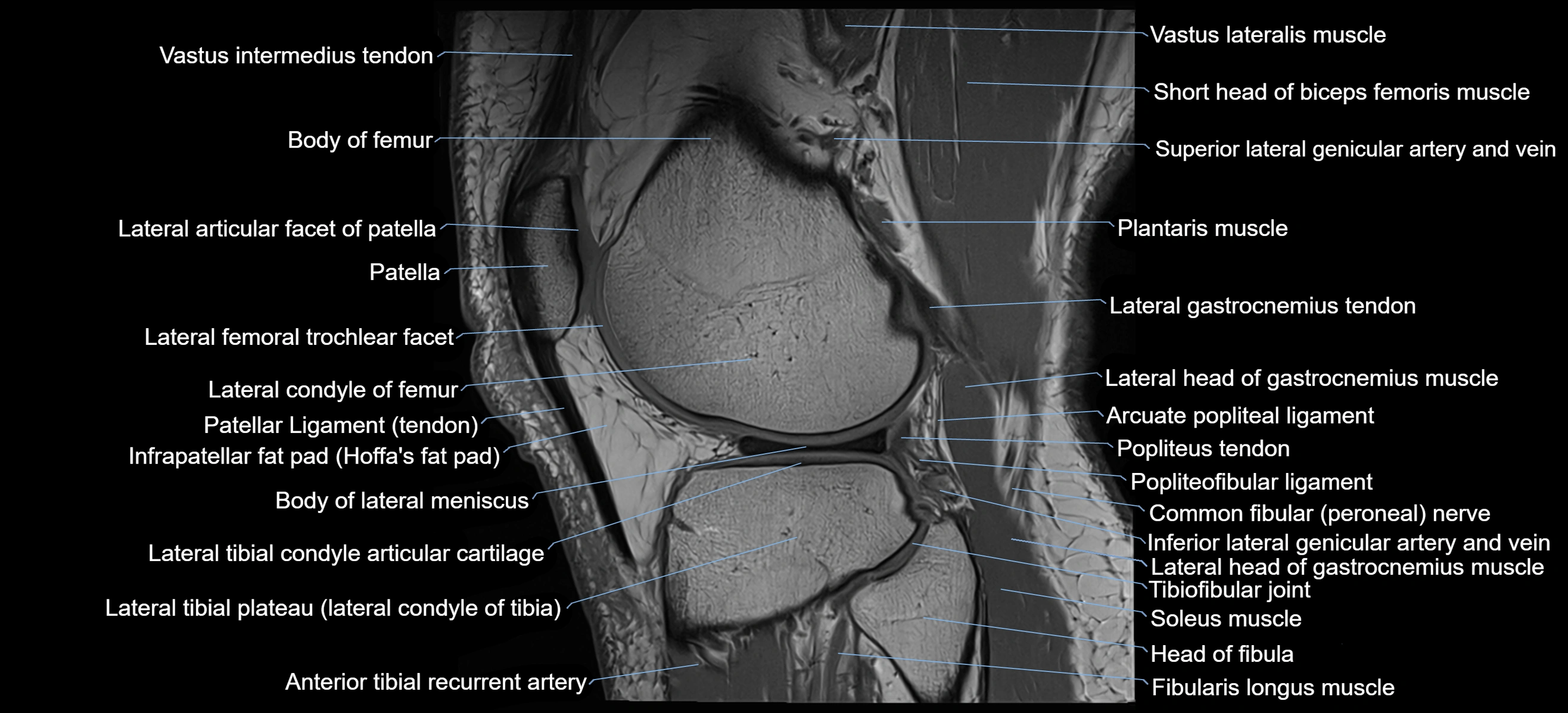
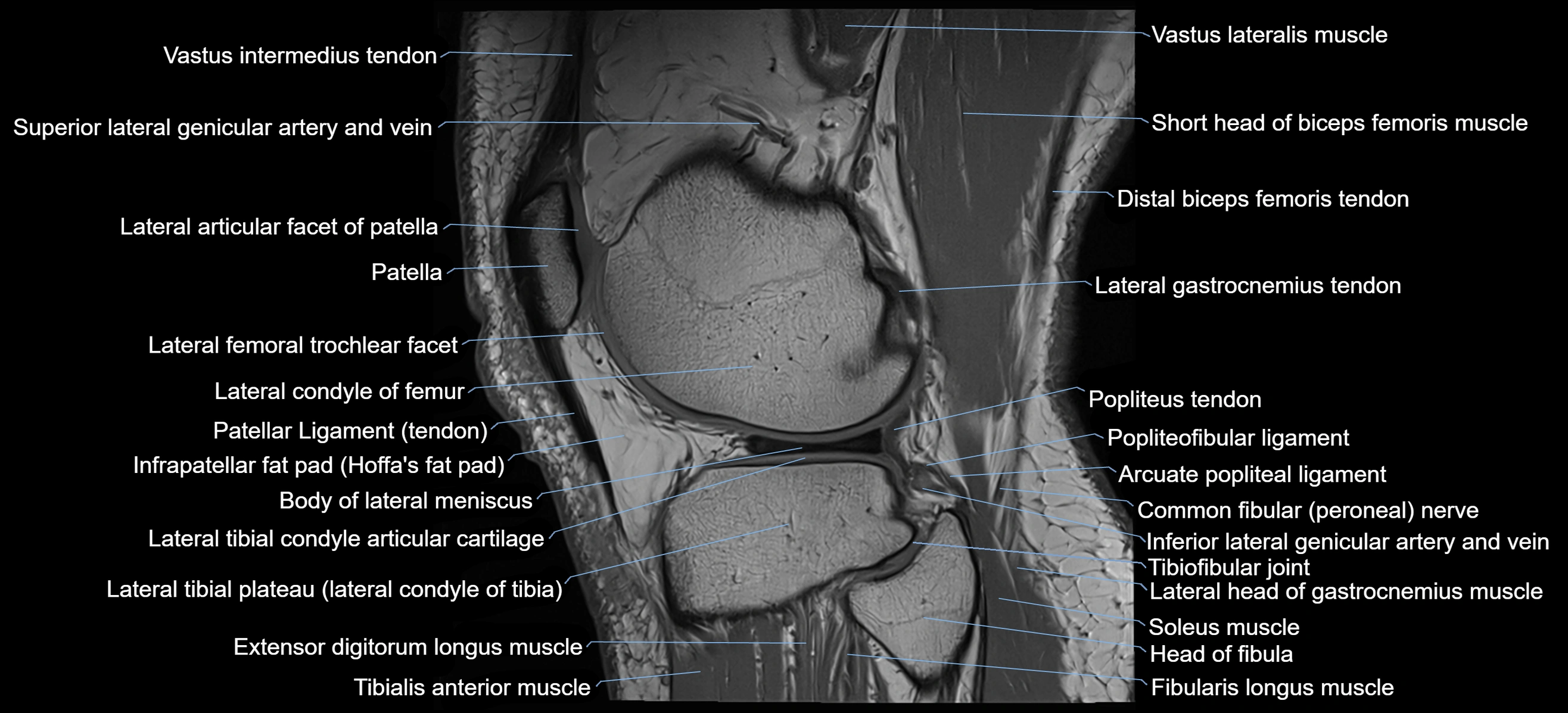
- Body of lateral meniscus
- Body of medial meniscus
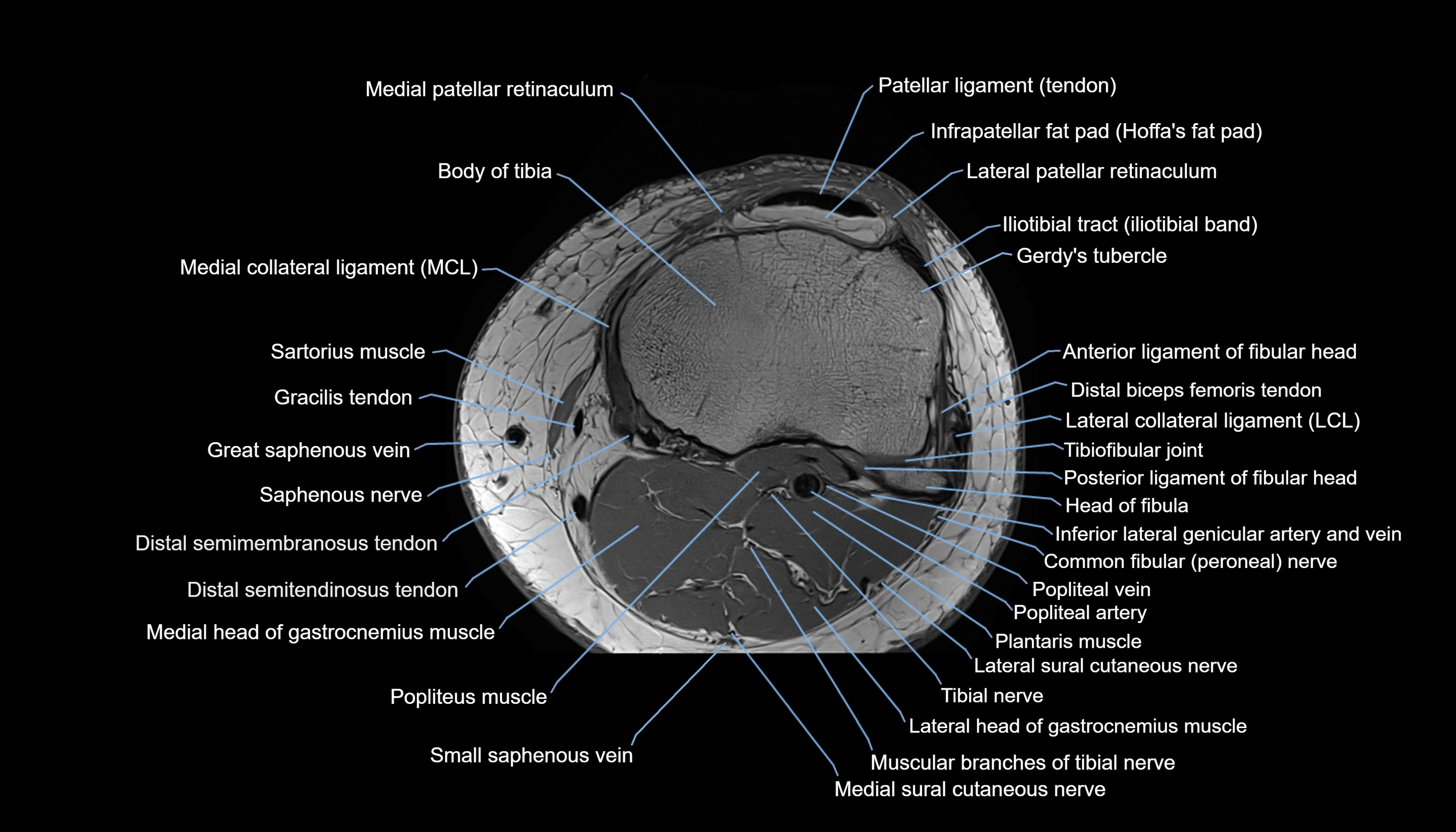
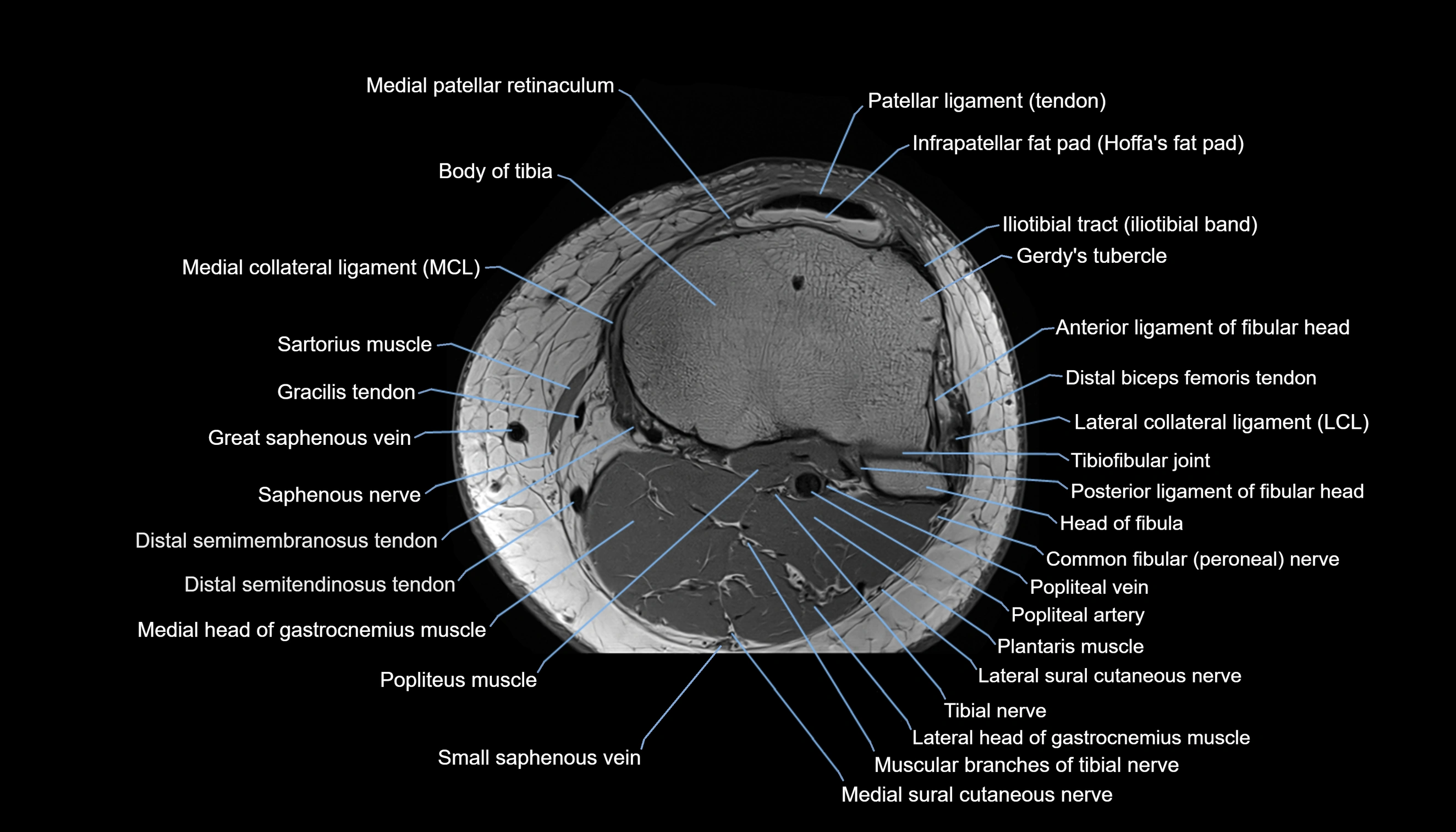
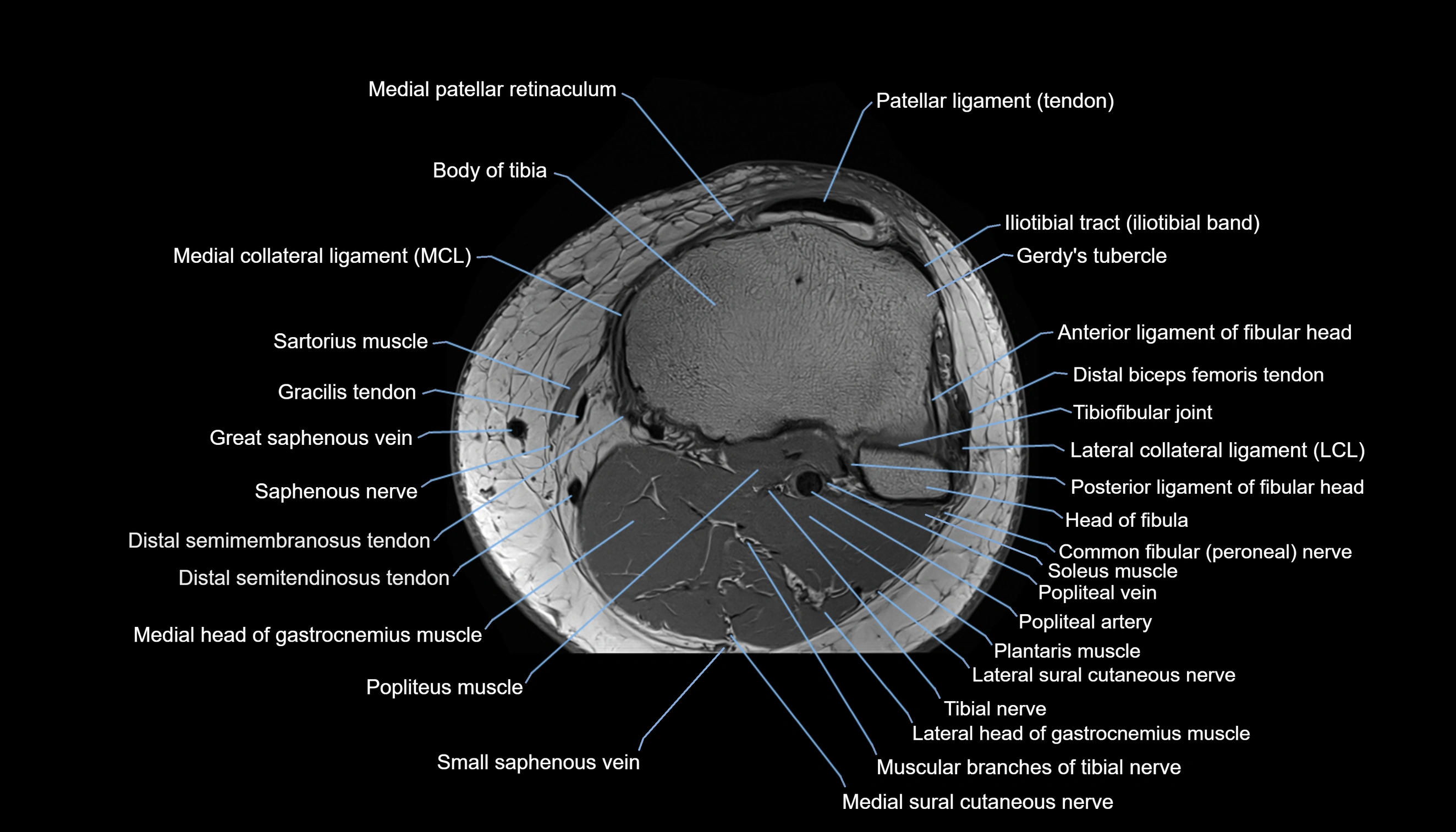
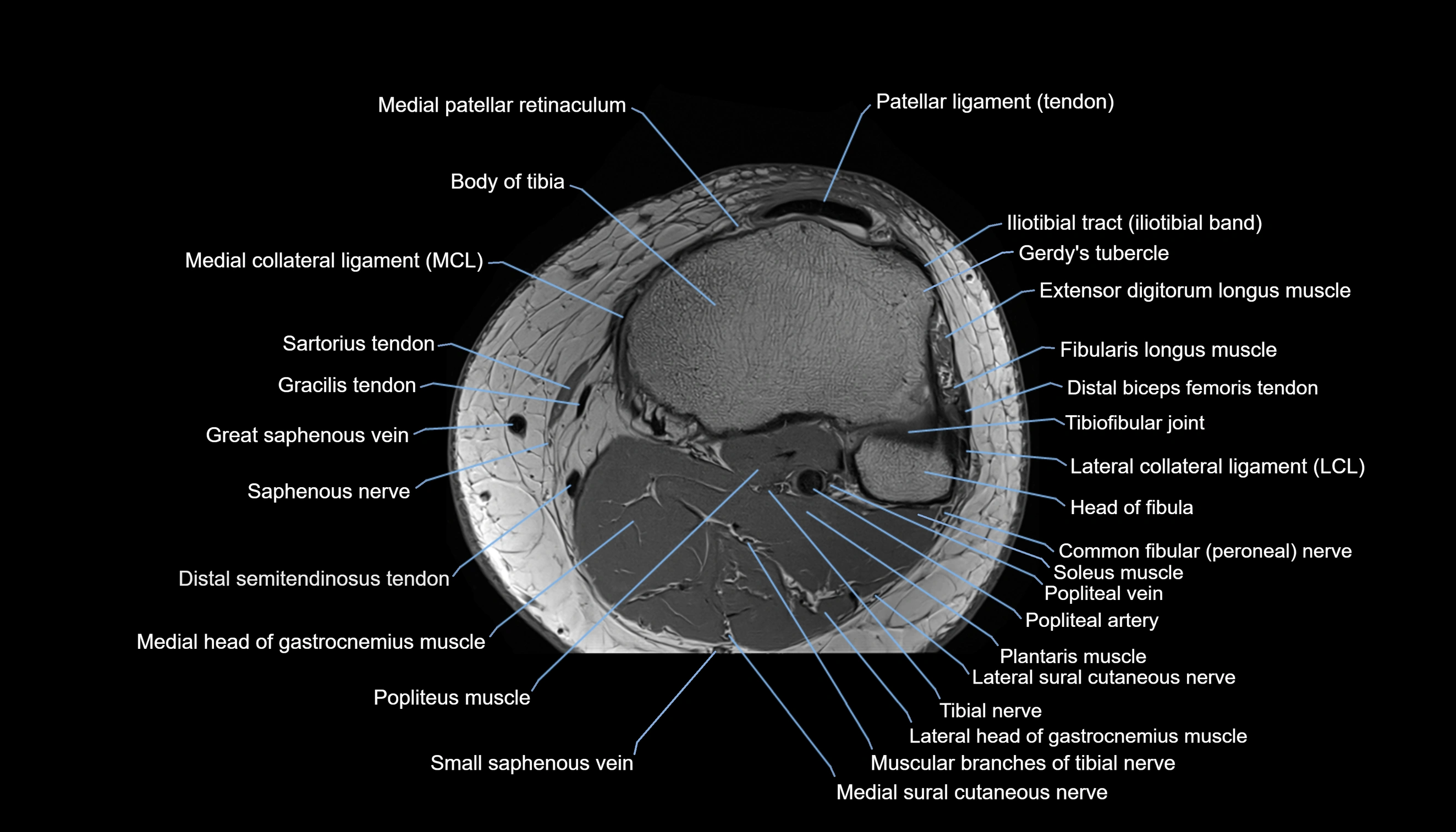
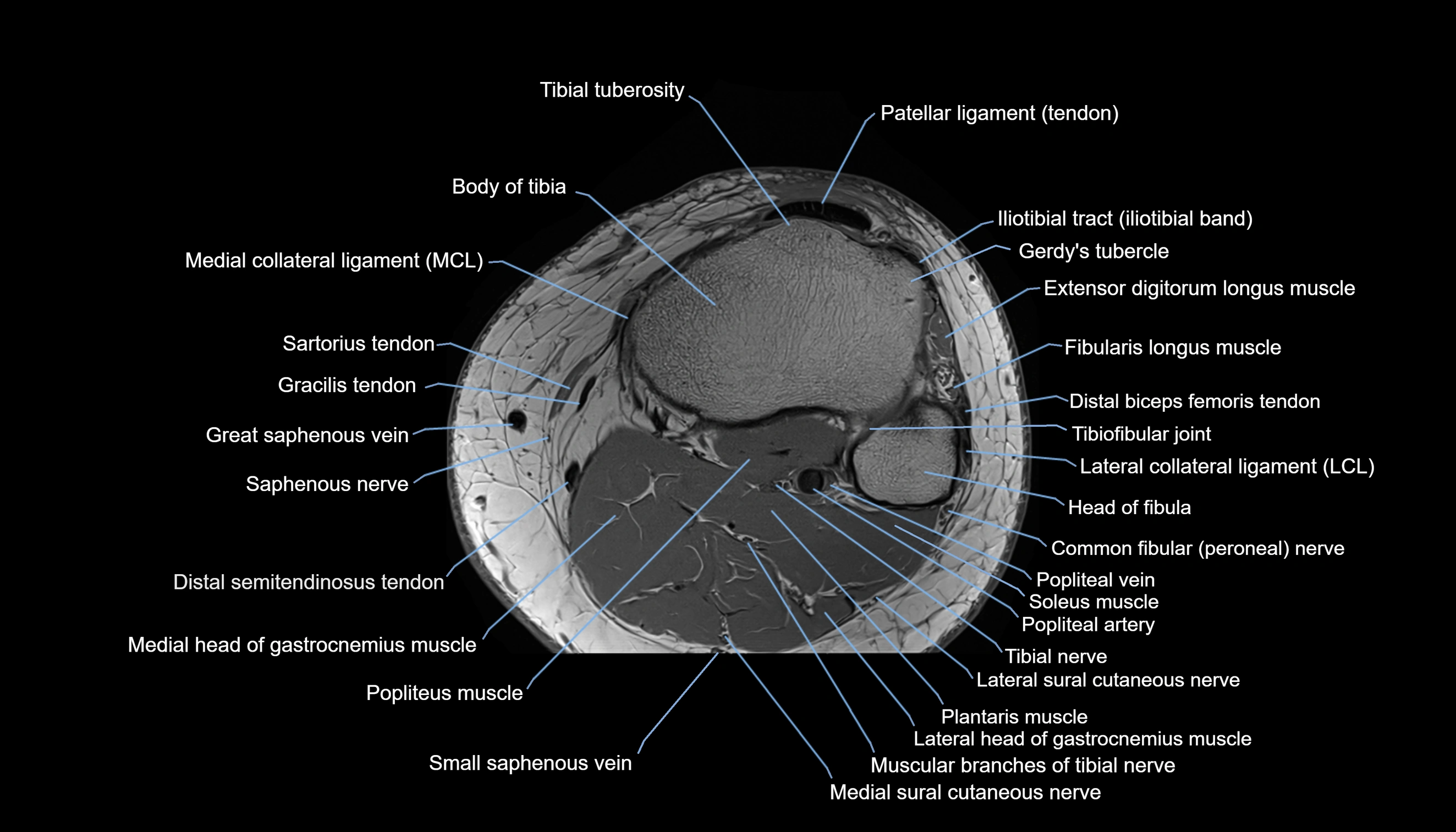
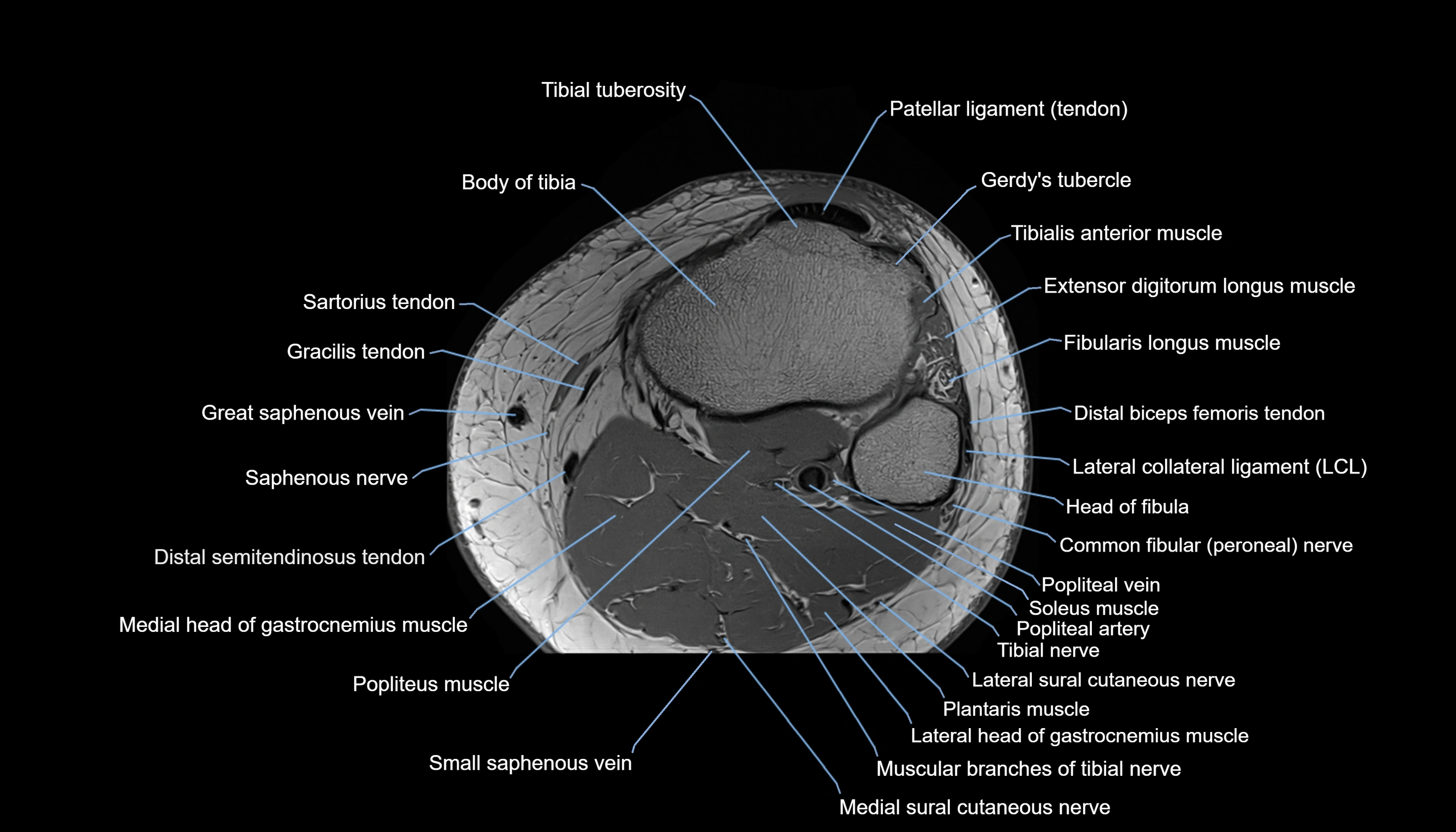
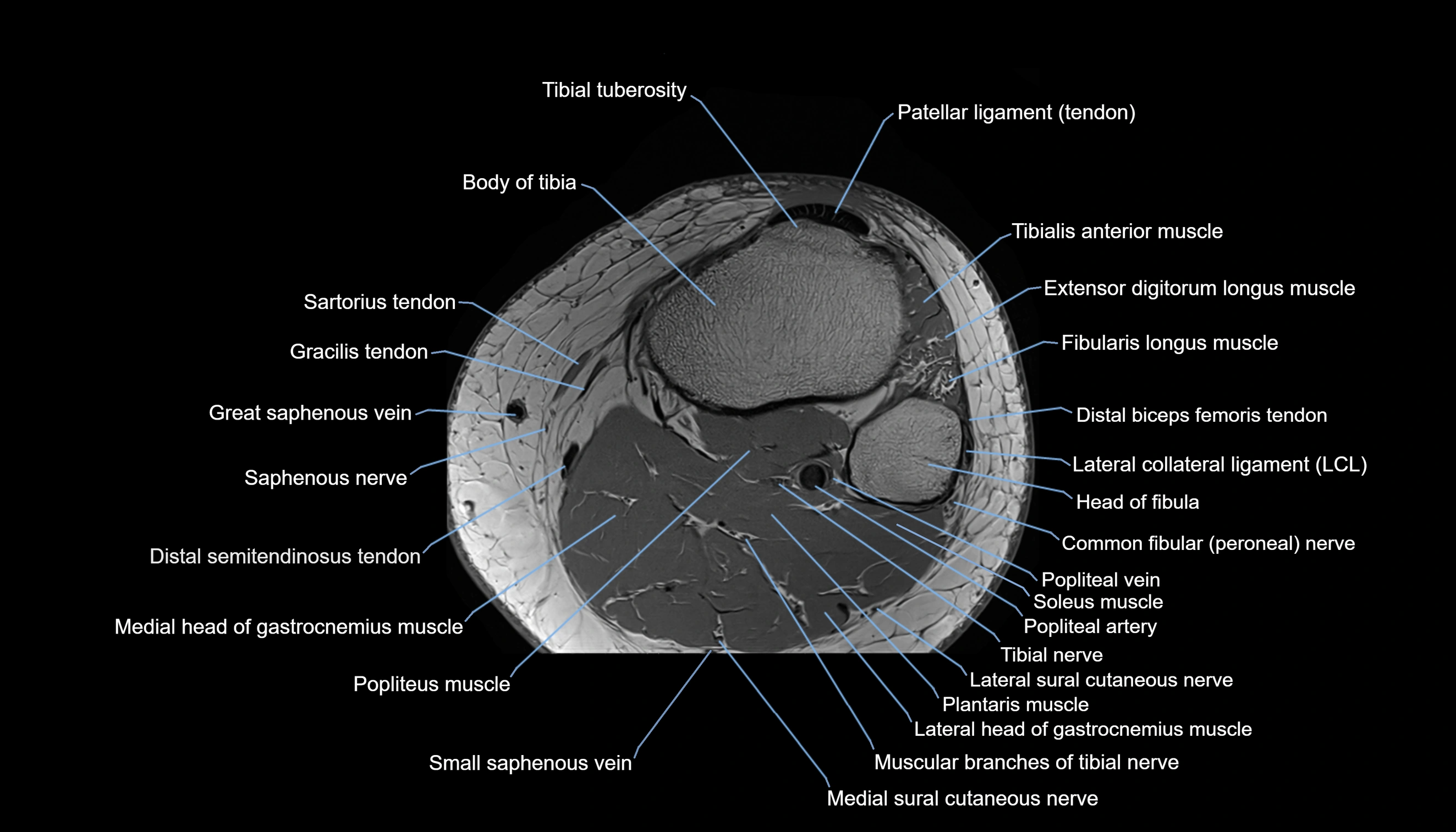
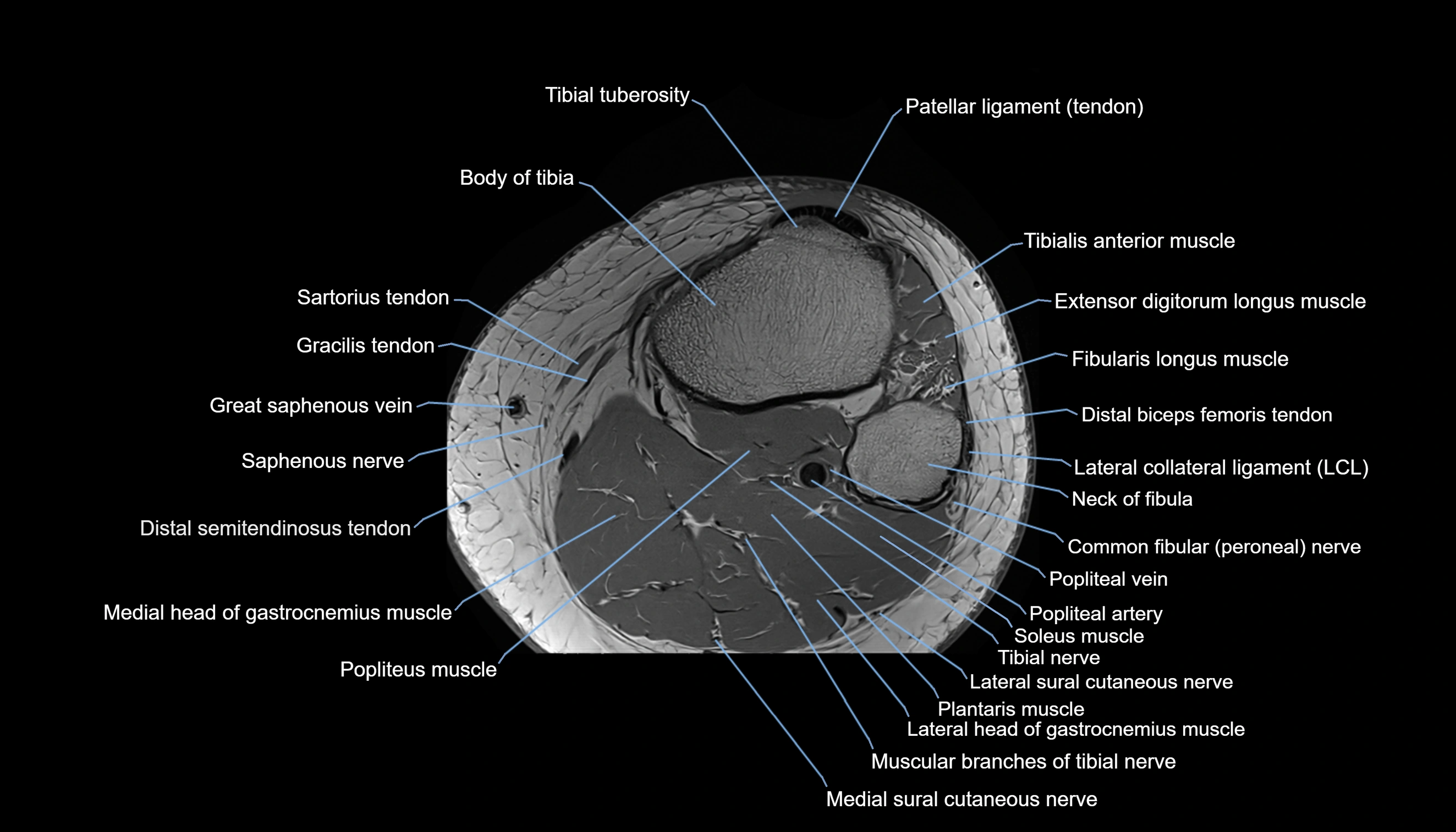
- Body of tibia
- Common fibular nerve
- Dermis of skin
- Descending genicular artery (Articular branches)
- Descending genicular artery (Saphenous branch)
- Distal adductor magnus tendon
- Distal biceps femoris tendon
- Distal quadriceps femoris tendon
- Distal rectus femoris tendon
- Distal semimembranosus tendon
- Distal semitendinosus tendon
- Distal vastus intermedius tendon
- Distal vastus lateralis tendon
- Distal vastus medialis tendon
- Epidermis
- Extensor digitorum longus muscle
- Extensor hood of foot
- Femoral condyle articular cartilage
- Fibula
- Fibular articular facet of tibia
- Fibularis longus muscle (peroneus longus muscle)
- Gastrocnemius muscle
- Gerdy’s tubercle
- Gracilis Tendon (Proximal)
- Gracilis tendon (Distal)
- Groove for popliteus muscle
- Head of fibula
- Hypodermis of skin
- Inferior lateral genicular artery
- Inferior lateral genicular vein
- Inferior rim of acetabulum
- Infrapatellar branch of saphenous nerve
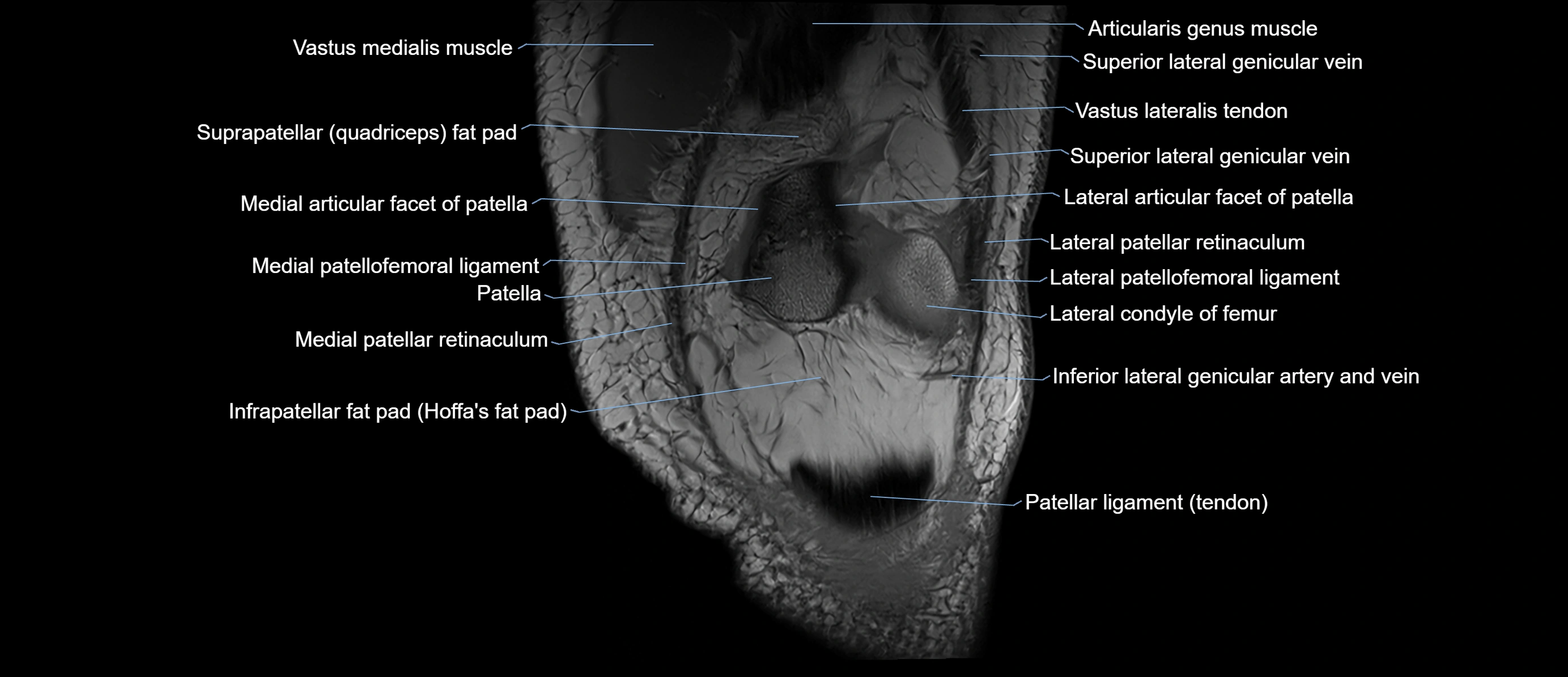
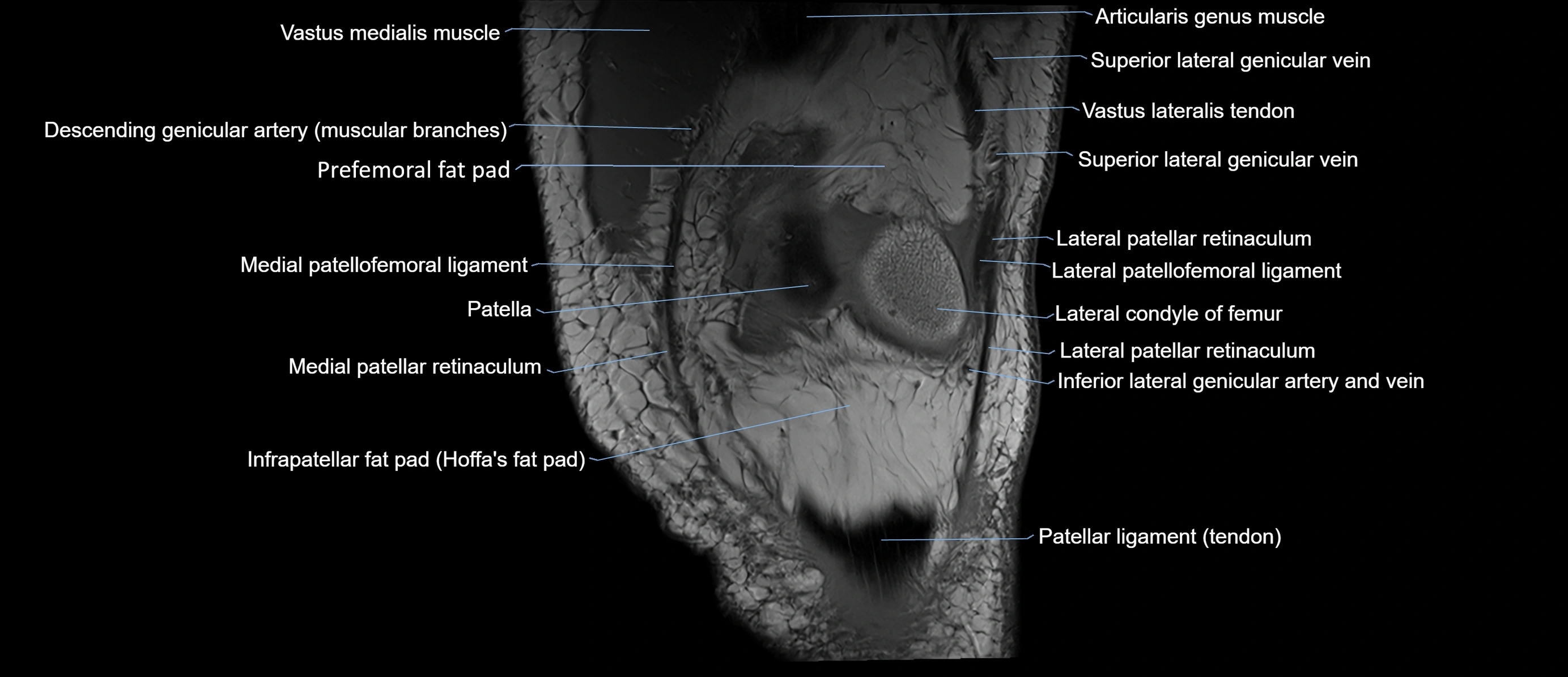
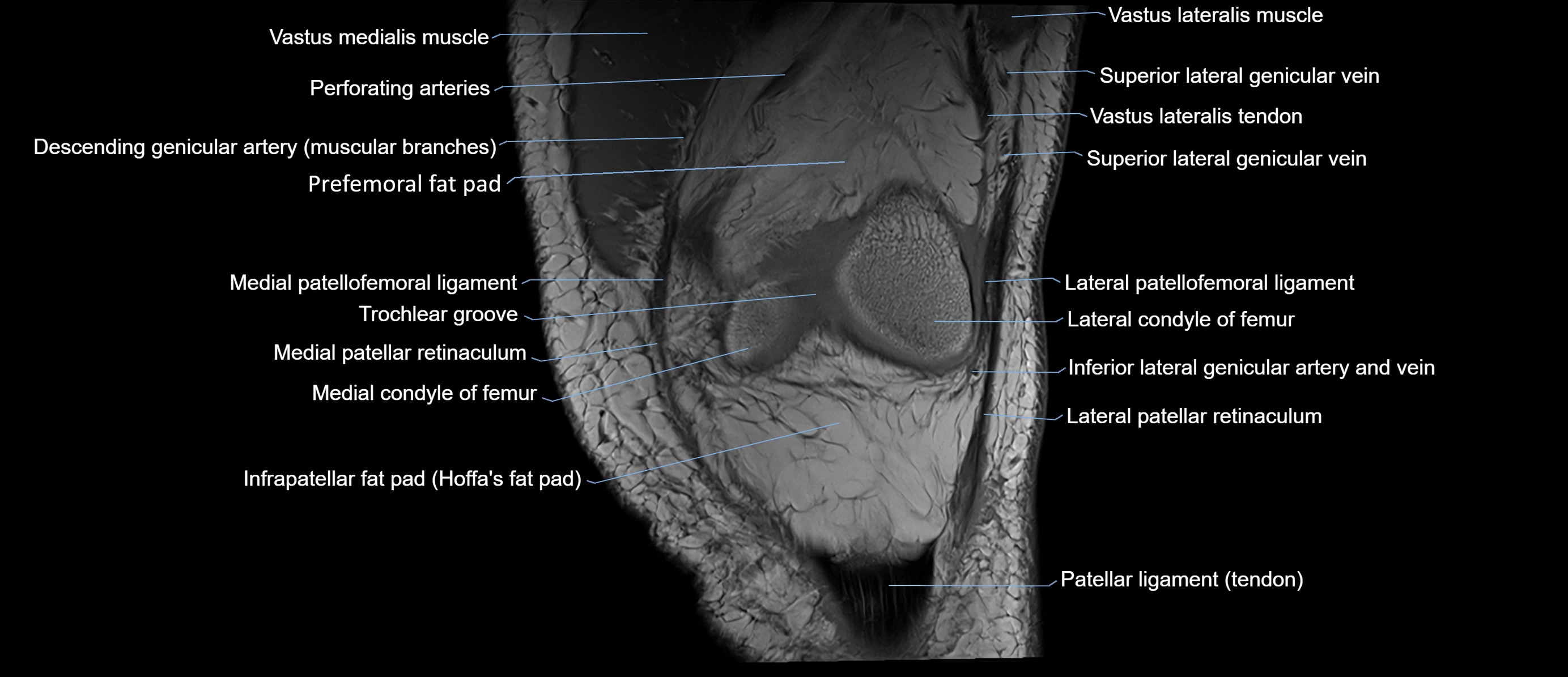
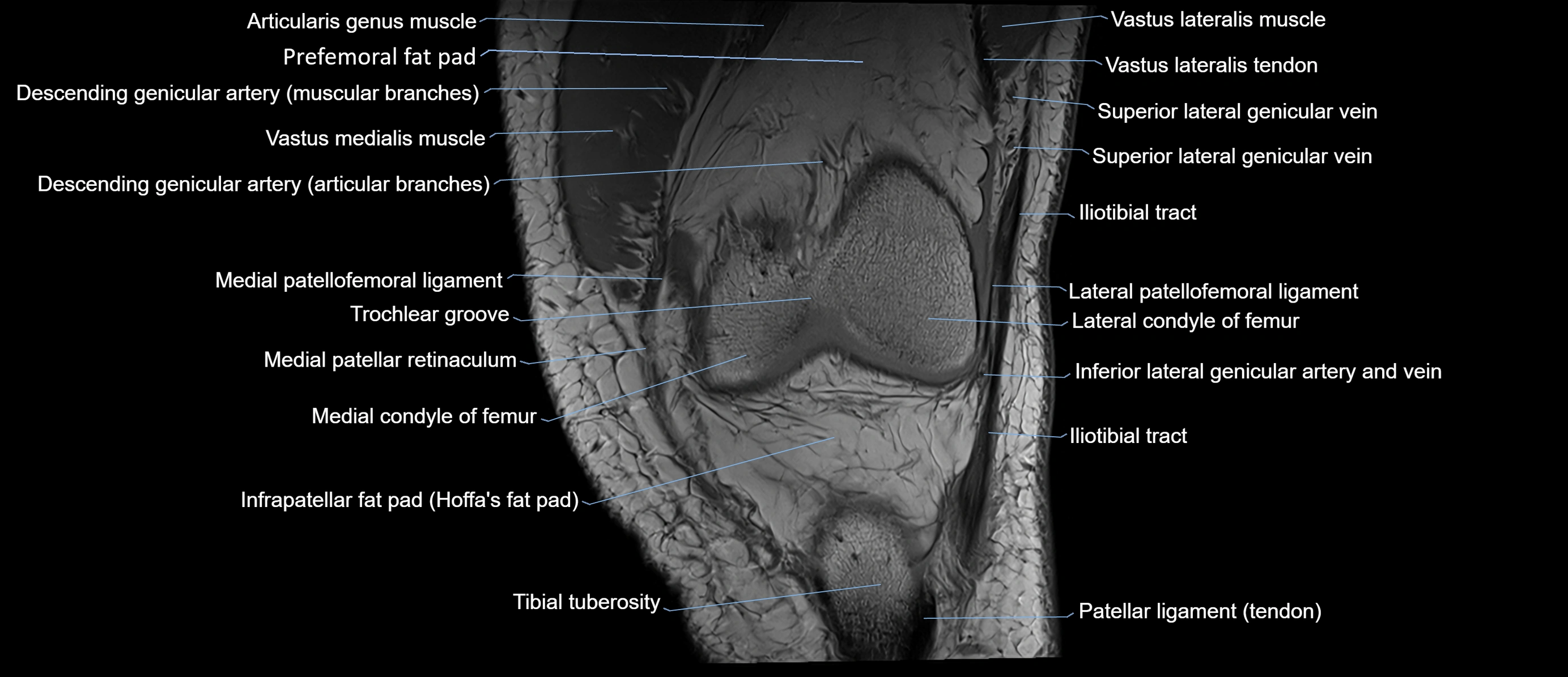
- Infrapatellar fat pad
- Intercondylar eminence
- Intercondylar fossa
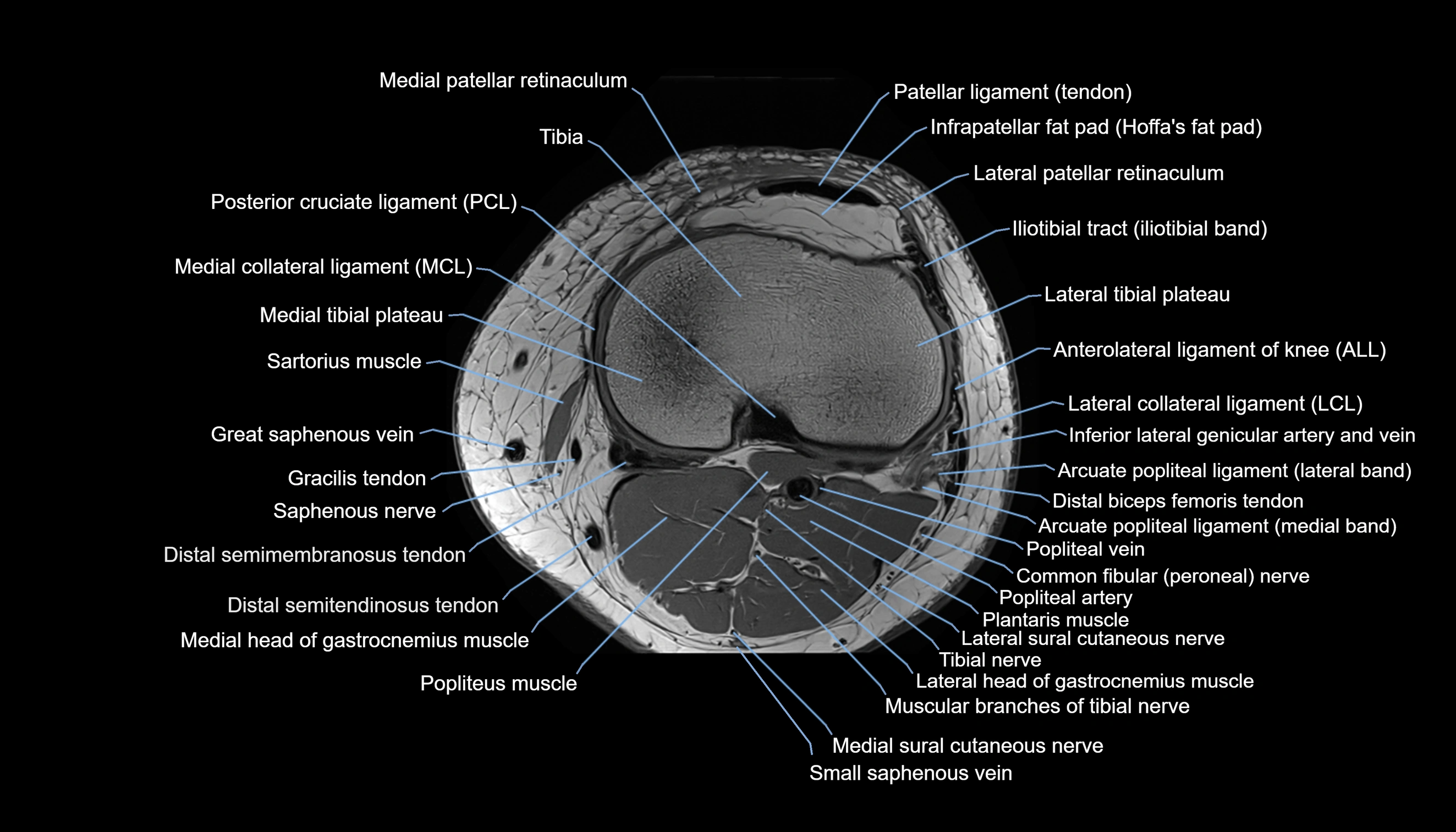
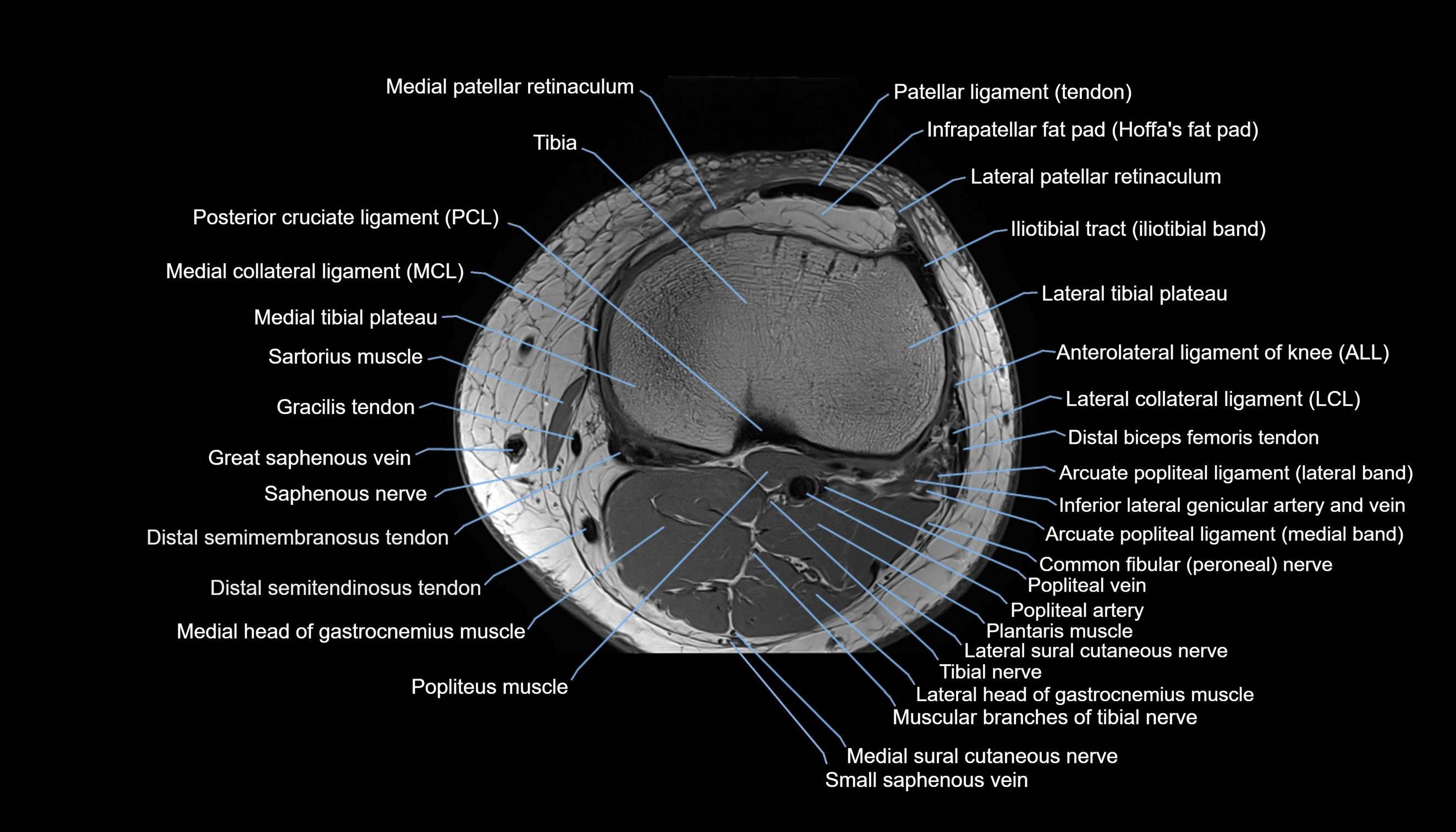
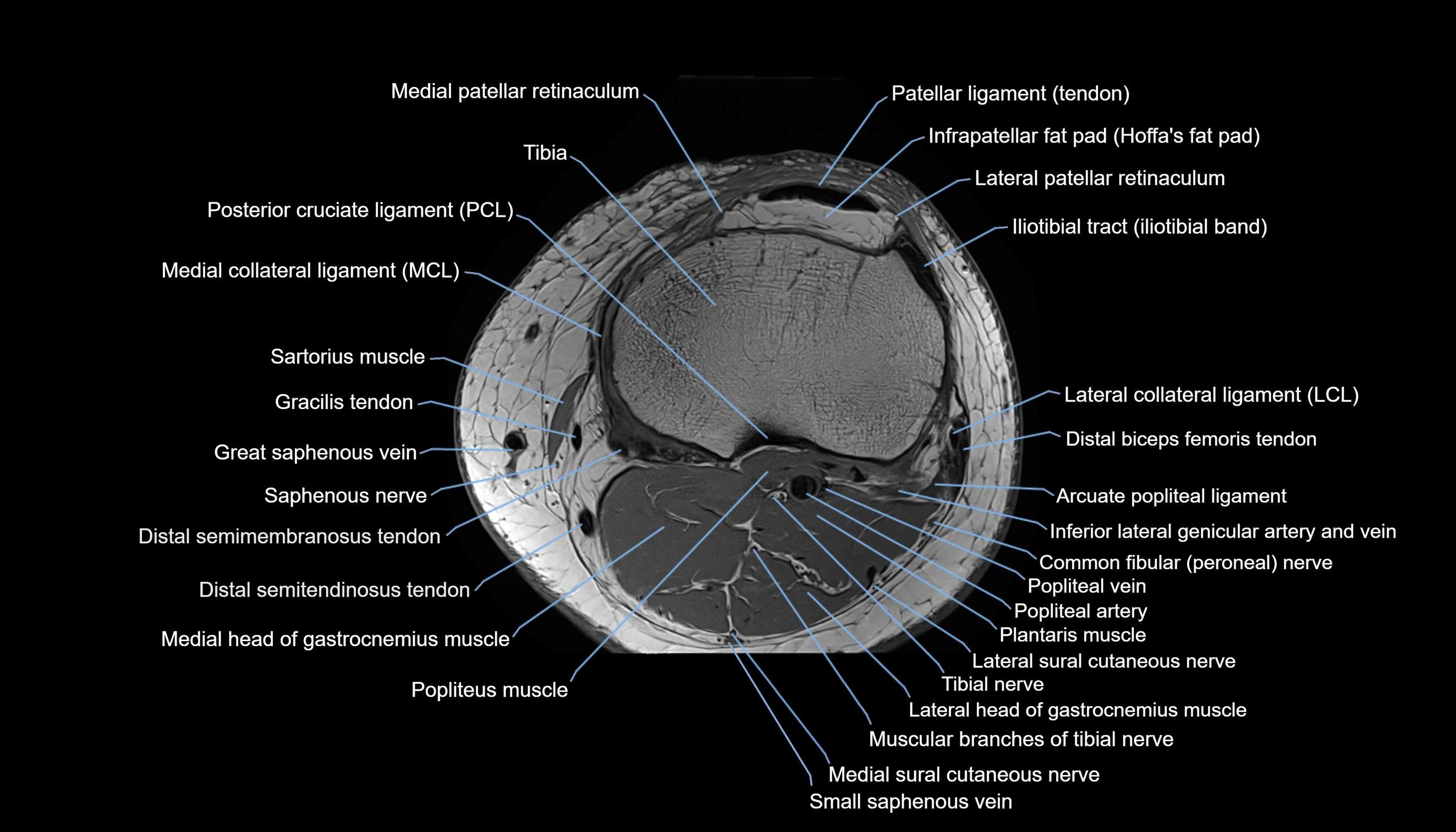
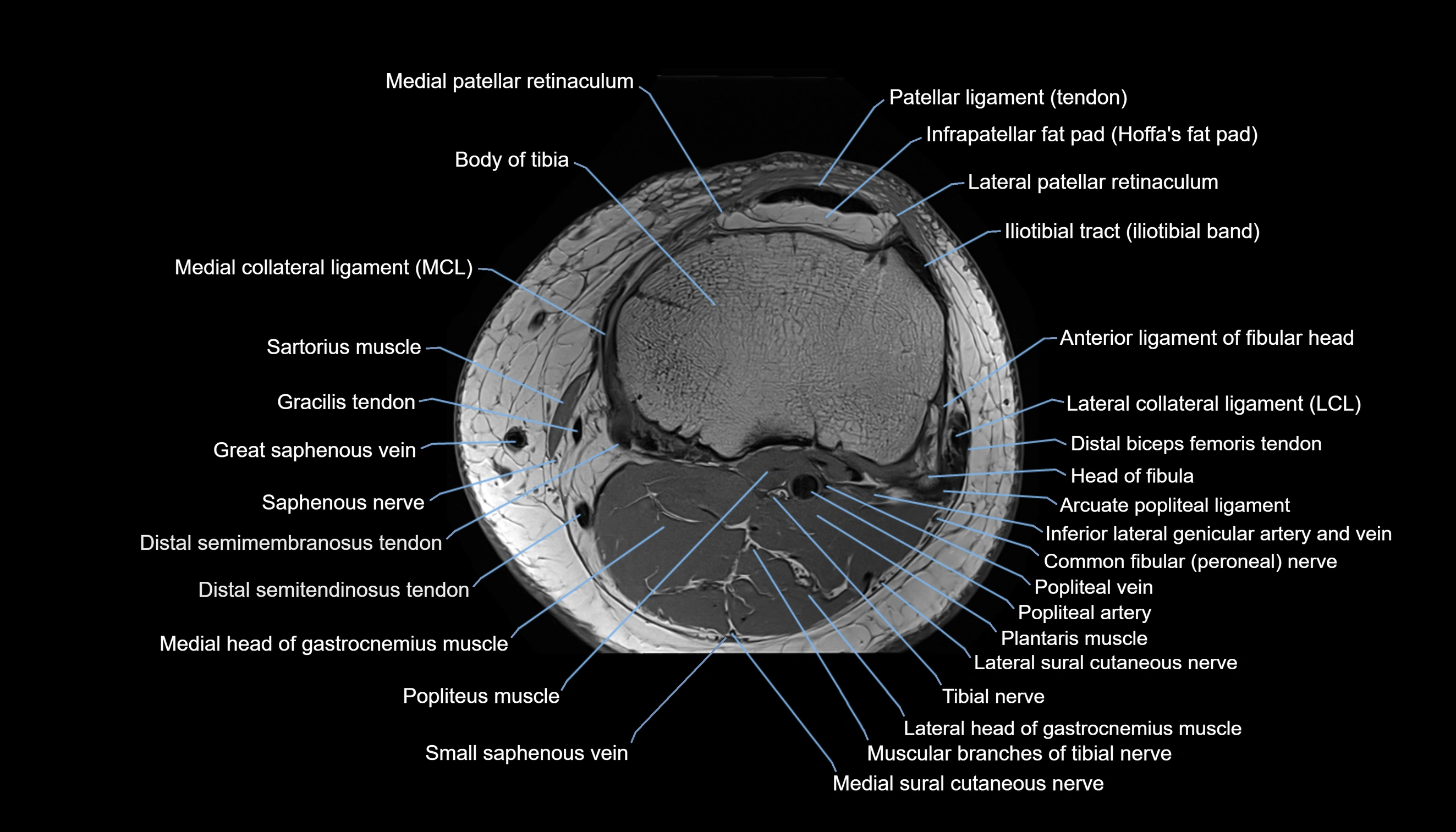
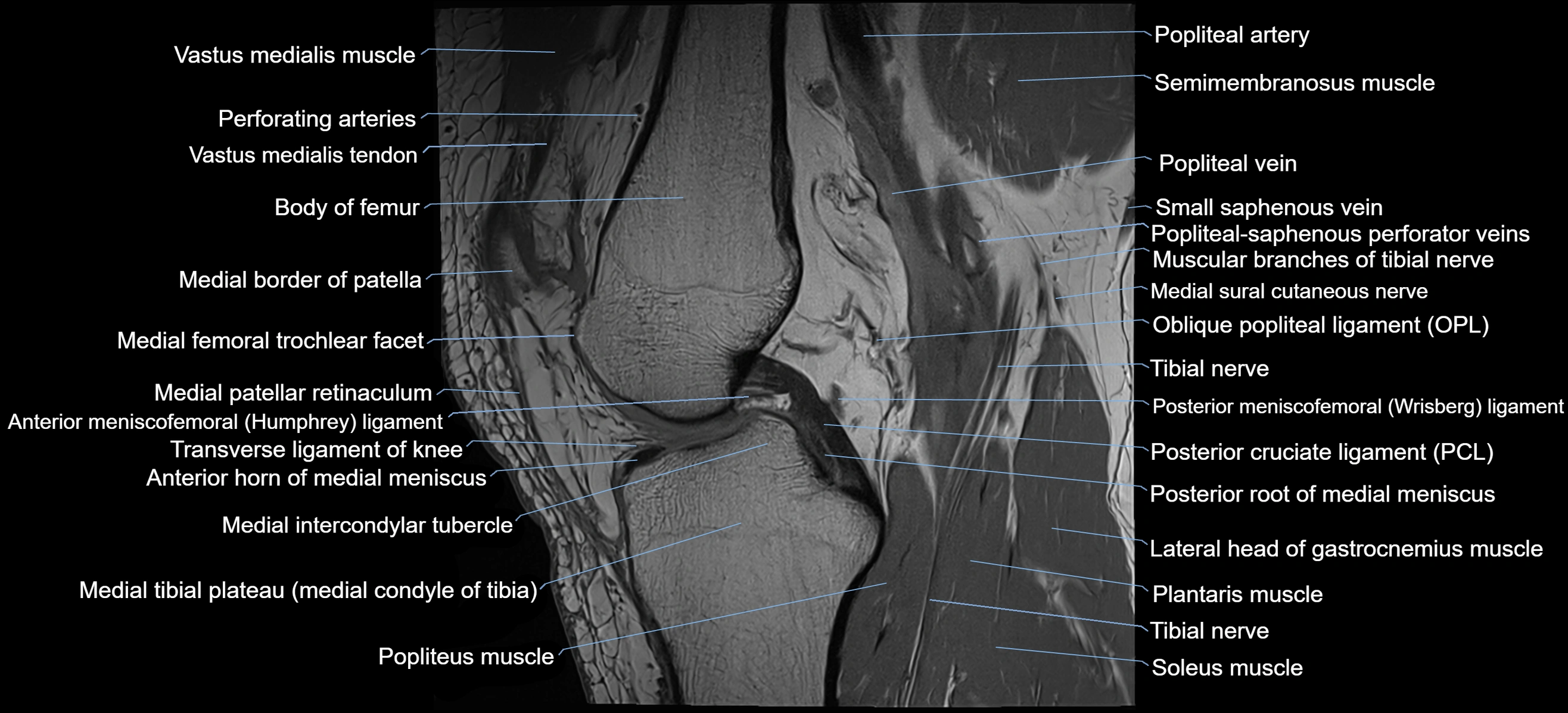
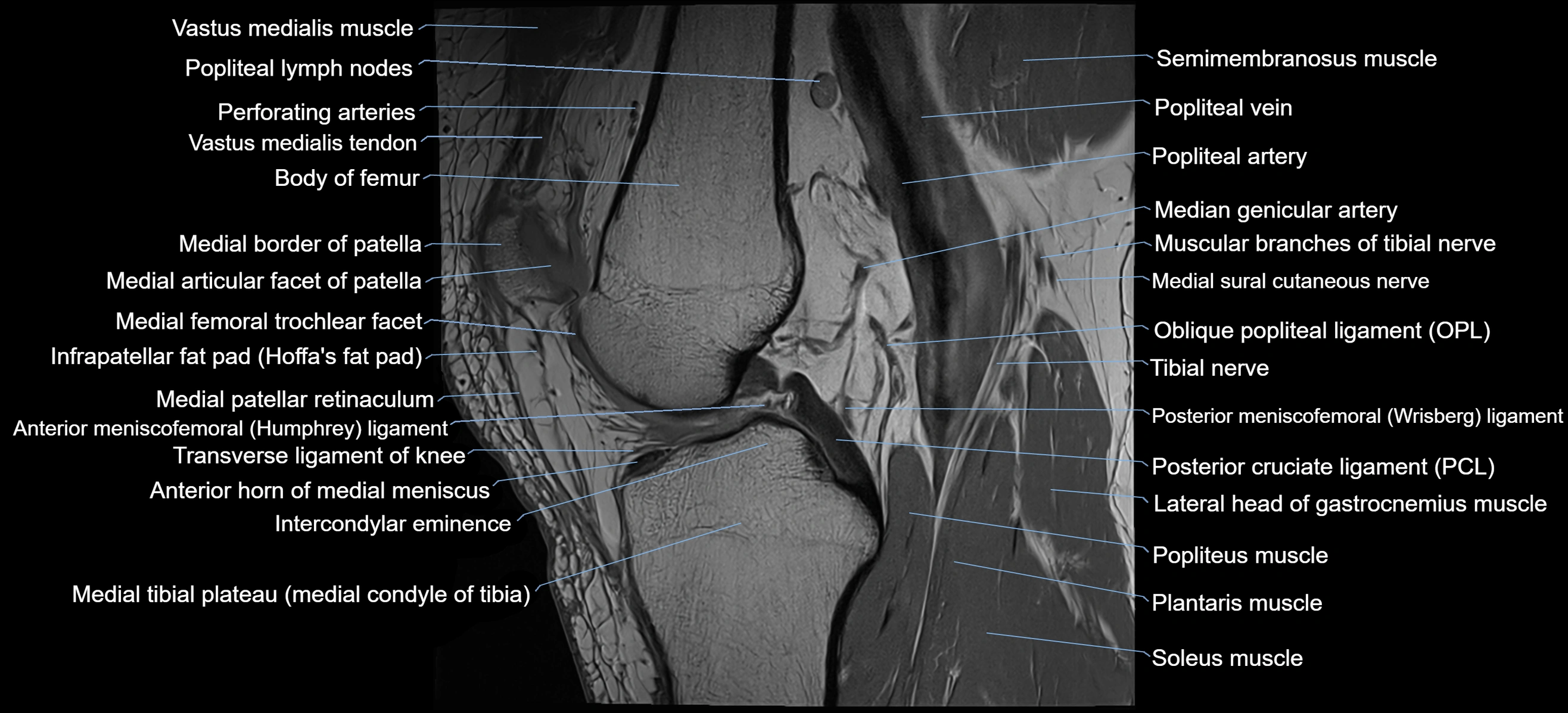
- Knee Joint
- Lateral articular facet of patella
- Lateral border of patella
- Lateral collateral ligament
- Lateral condyle of femur
- Lateral condyle of tibia
- Lateral epicondyle of femur
- Lateral gastrocnemius tendon
- Lateral head of gastrocnemius muscle
- Lateral intercondylar tubercle
- Lateral meniscus
- Lateral nail fold (toe)
- Lateral patellar retinaculum
- Lateral patellofemoral ligament
- Lateral supracondylar line
- Lateral sural cutaneous nerve
- Lateral tibial plateau
- Lateral tibiofemoral joint space
- Medial articular facet of patella
- Medial border of patella
- Medial collateral ligament
- Medial condyle of femur
- Medial condyle of tibia
- Medial epicondyle of femur
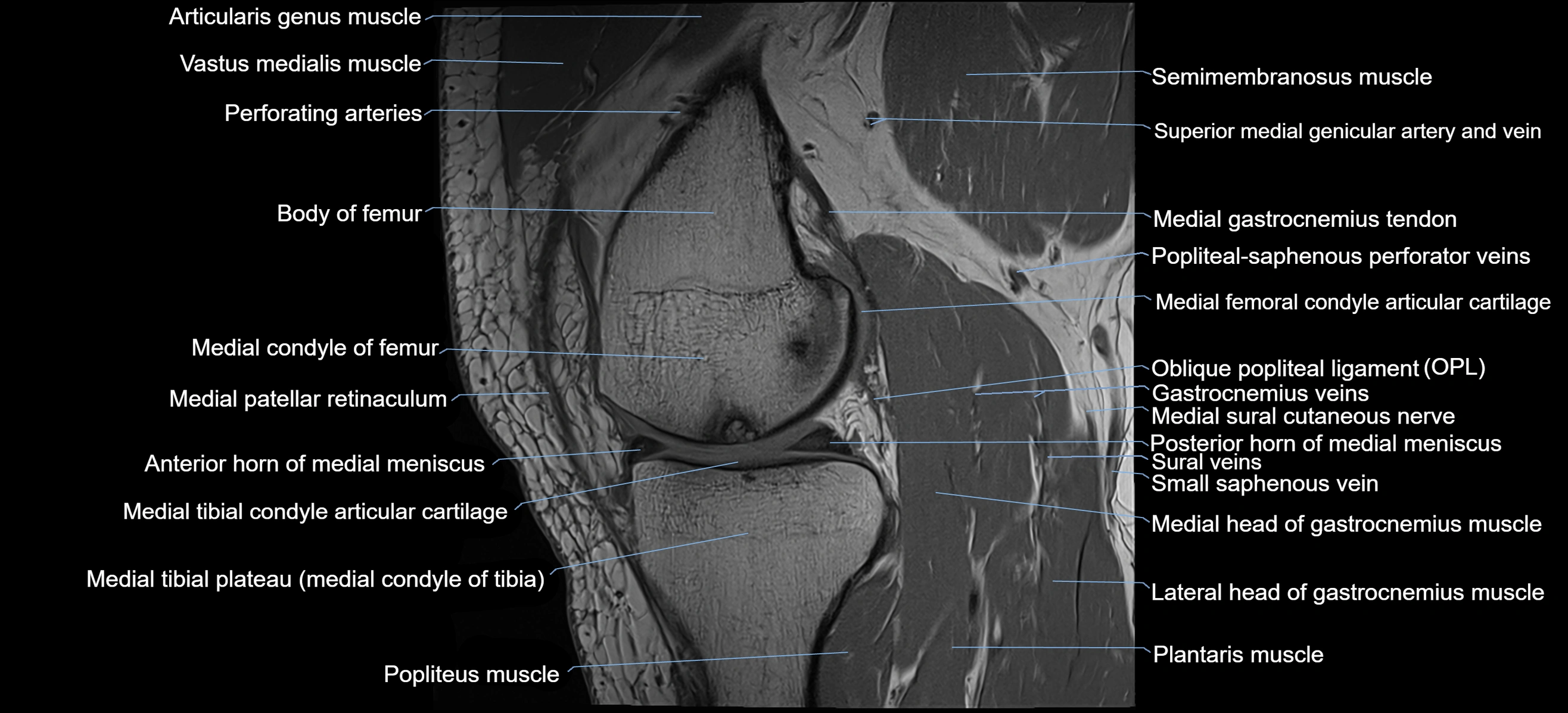
- Medial gastrocnemius tendon
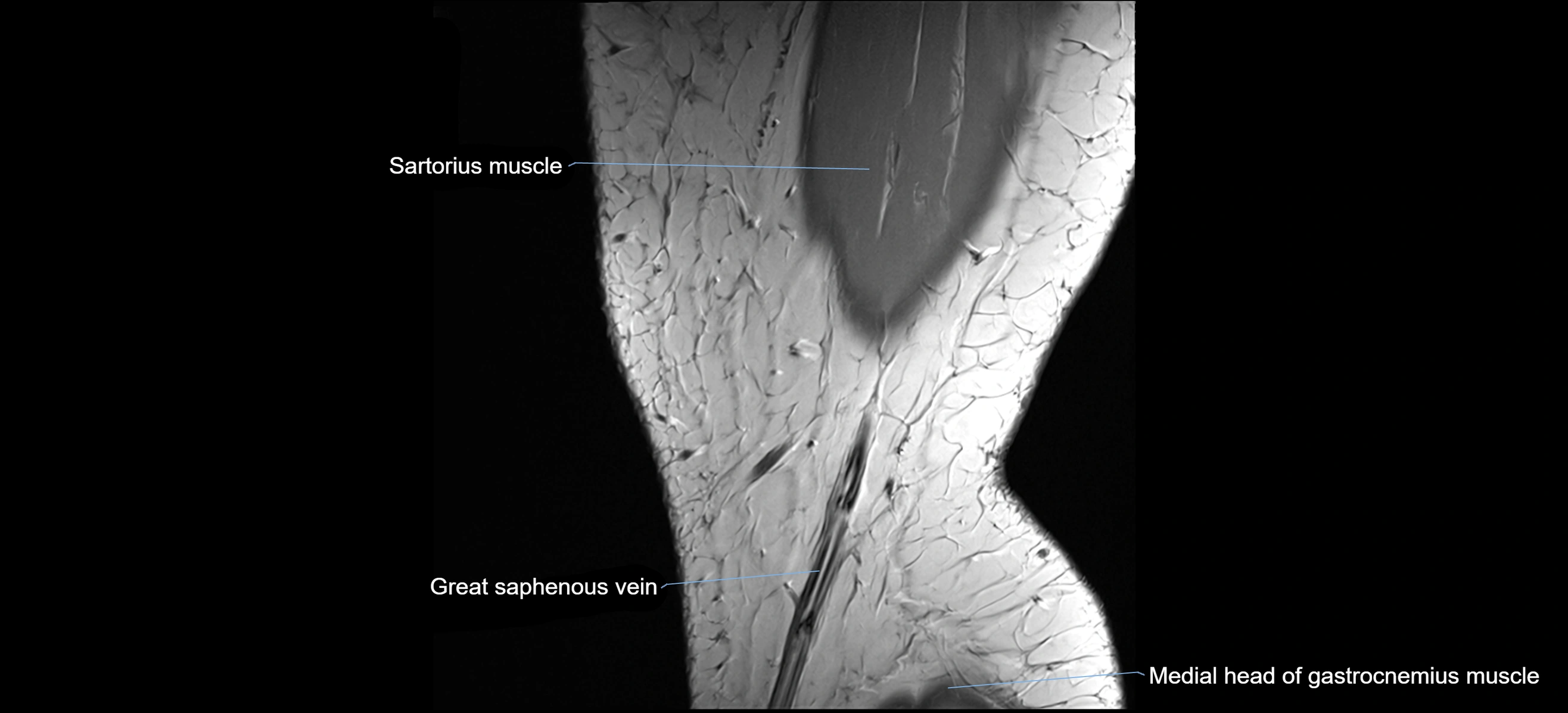
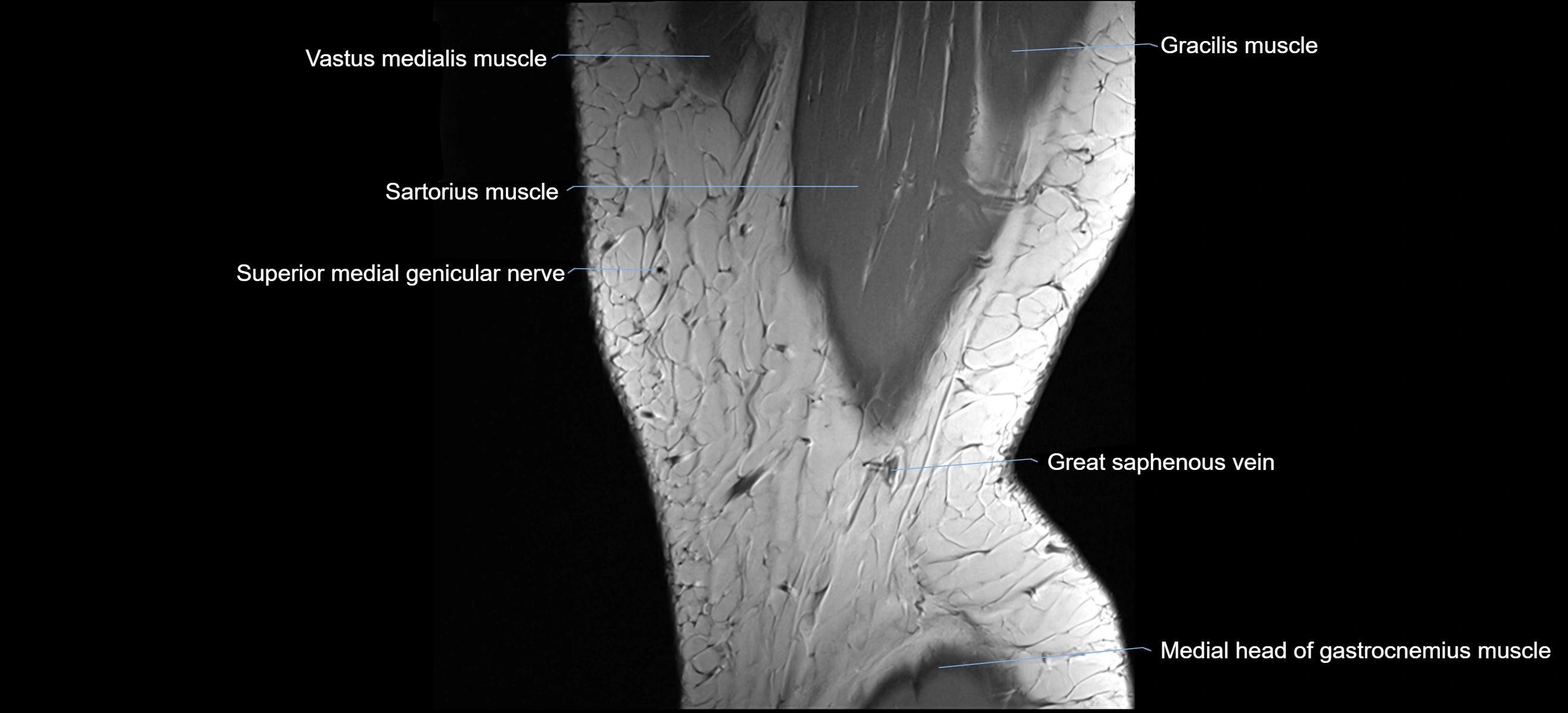
- Medial head of gastrocnemius muscle
- Medial intercondylar tubercle
- Medial meniscus
- Medial patellar retinaculum
- Medial patellofemoral ligament
- Medial supracondylar line
- Medial sural cutaneous nerve
- Medial tibial plateau
- Medial tibiofemoral joint space
- Meniscus cartilage
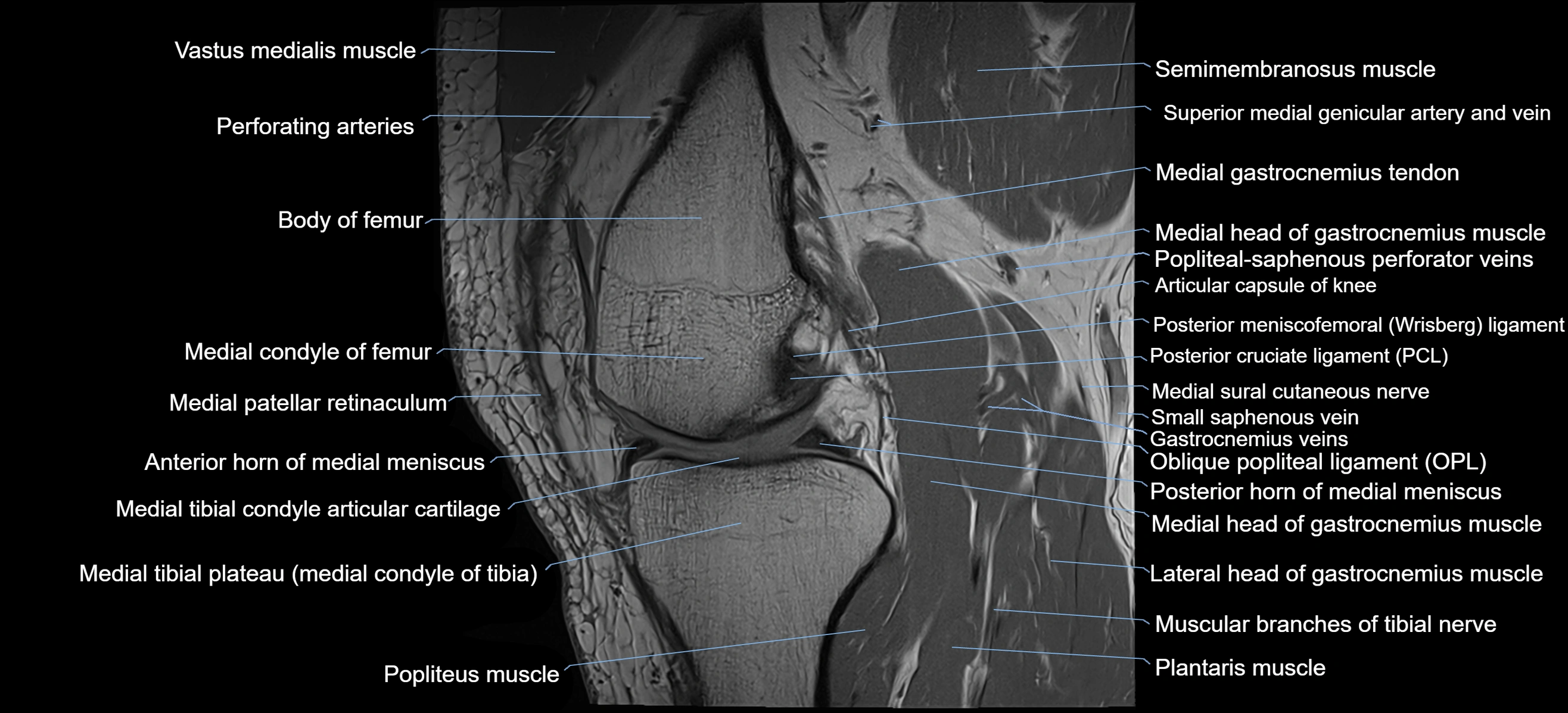
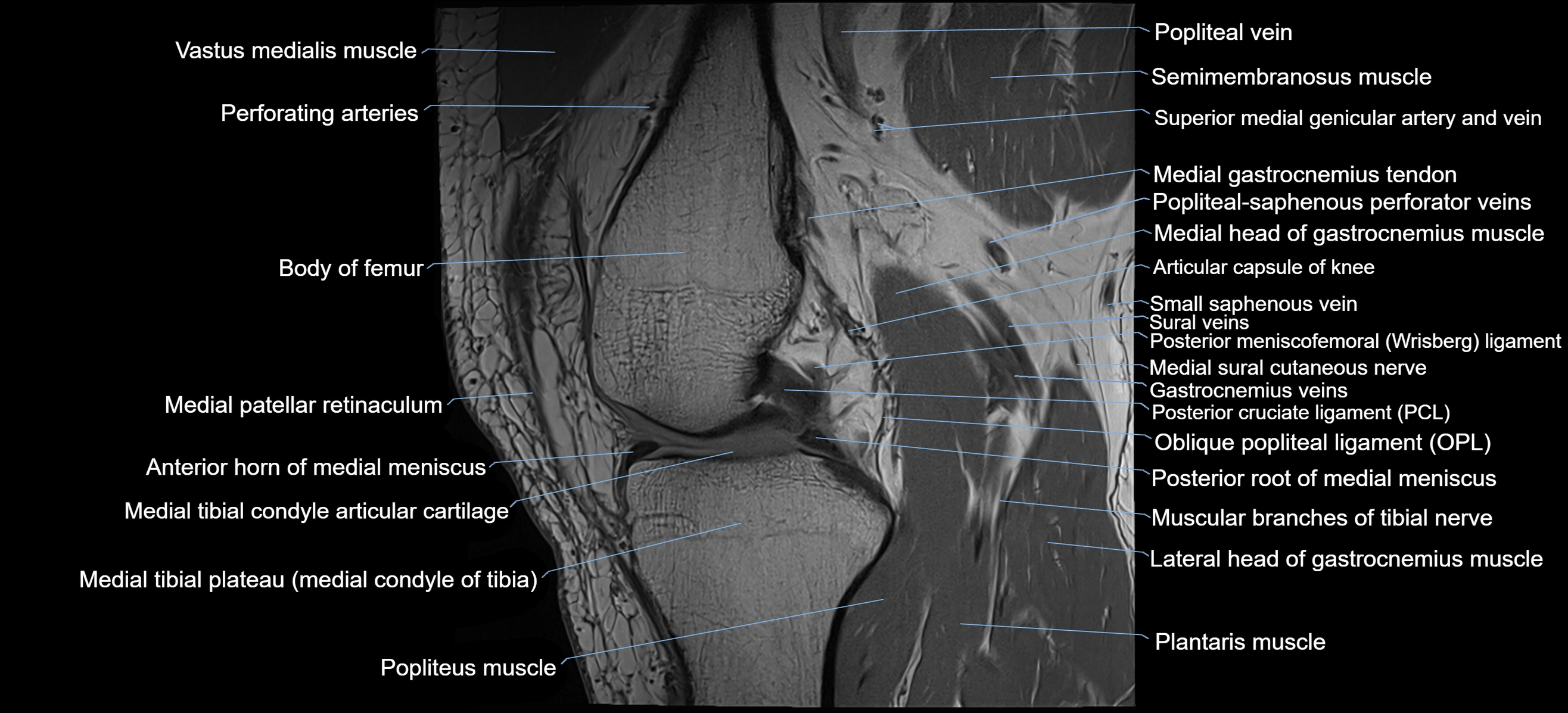
- Muscular branches of tibial nerve
- Nail (toe)
- Nail bed (toe)
- Nail root (toe)
- Neck of fibula
- Oblique popliteal ligament
- Patella
- Patellar articular cartilage
- Patellar tendon (patellar ligament)
- Perforating Arteries (Knee joint)
- Plantaris muscle
- Popliteal artery
- Popliteal lymph nodes
- Popliteal vein
- Popliteal–Saphenous perforating veins
- Popliteus muscle
- Popliteus tendon
- Posterior cruciate ligament
- Posterior horn of lateral meniscus
- Posterior horn of medial meniscus
- Posterior ligament of fibular head
- Posterior meniscofemoral ligament
- Posterior rim of acetabulum
- Posterior root of lateral meniscus
- Posterior root of medial meniscus
- Prefemoral fat pad
- Proximal nail fold
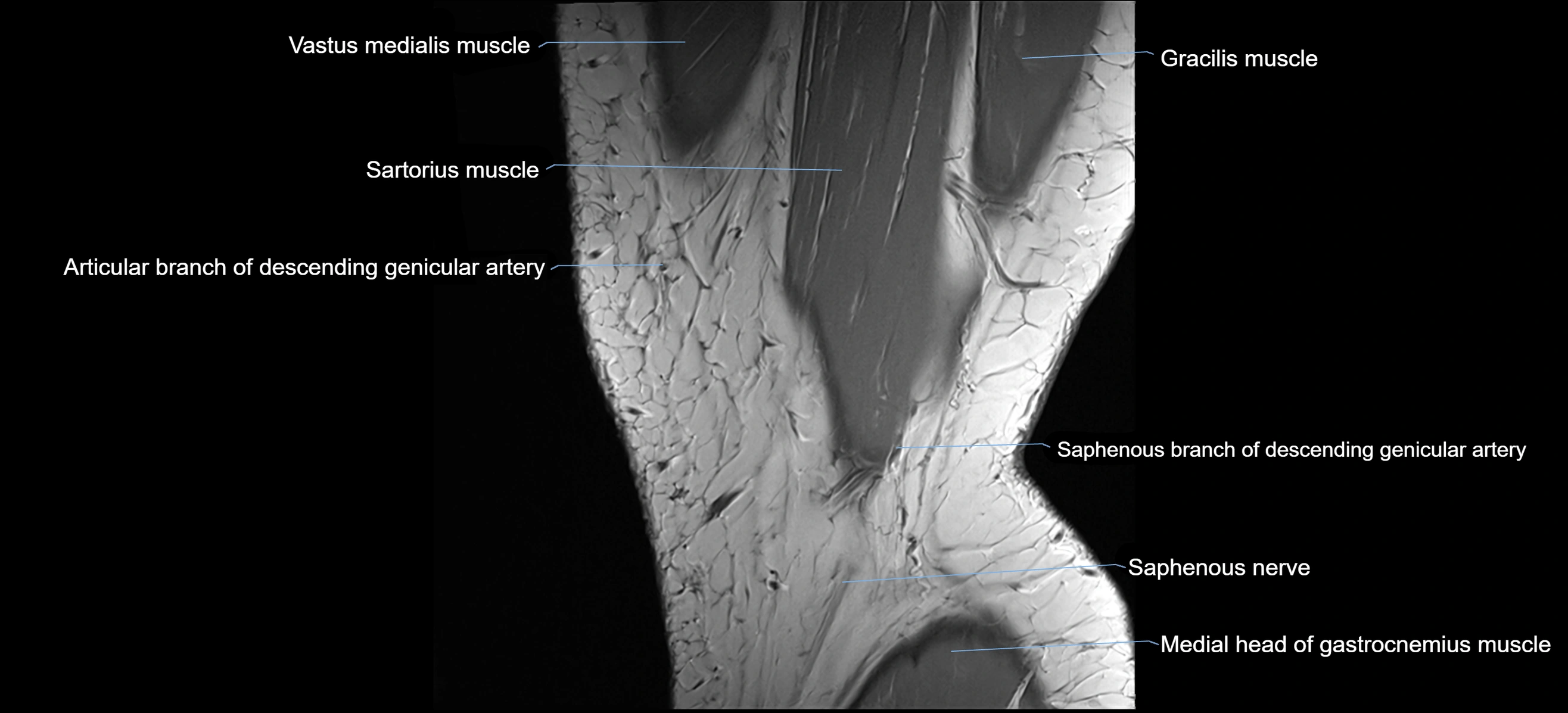
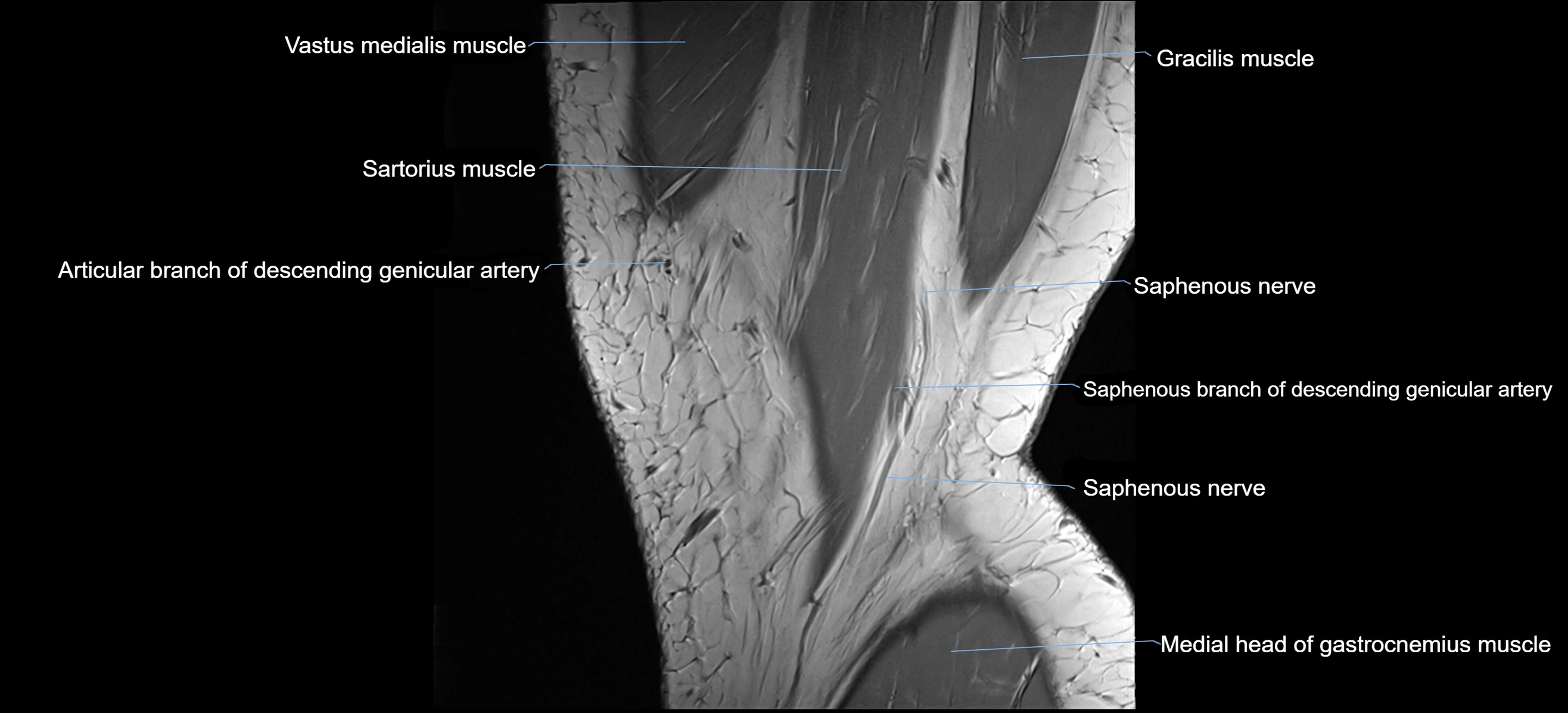
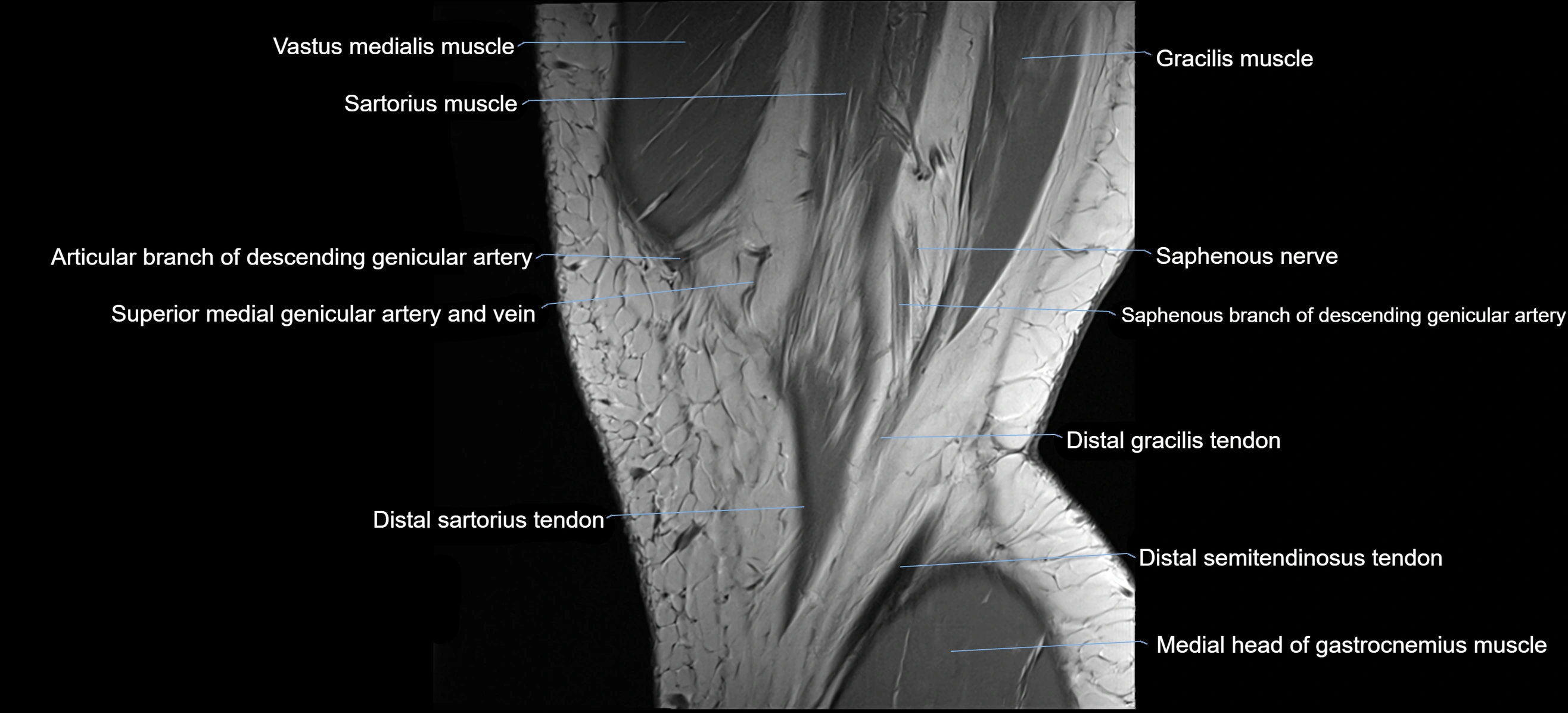
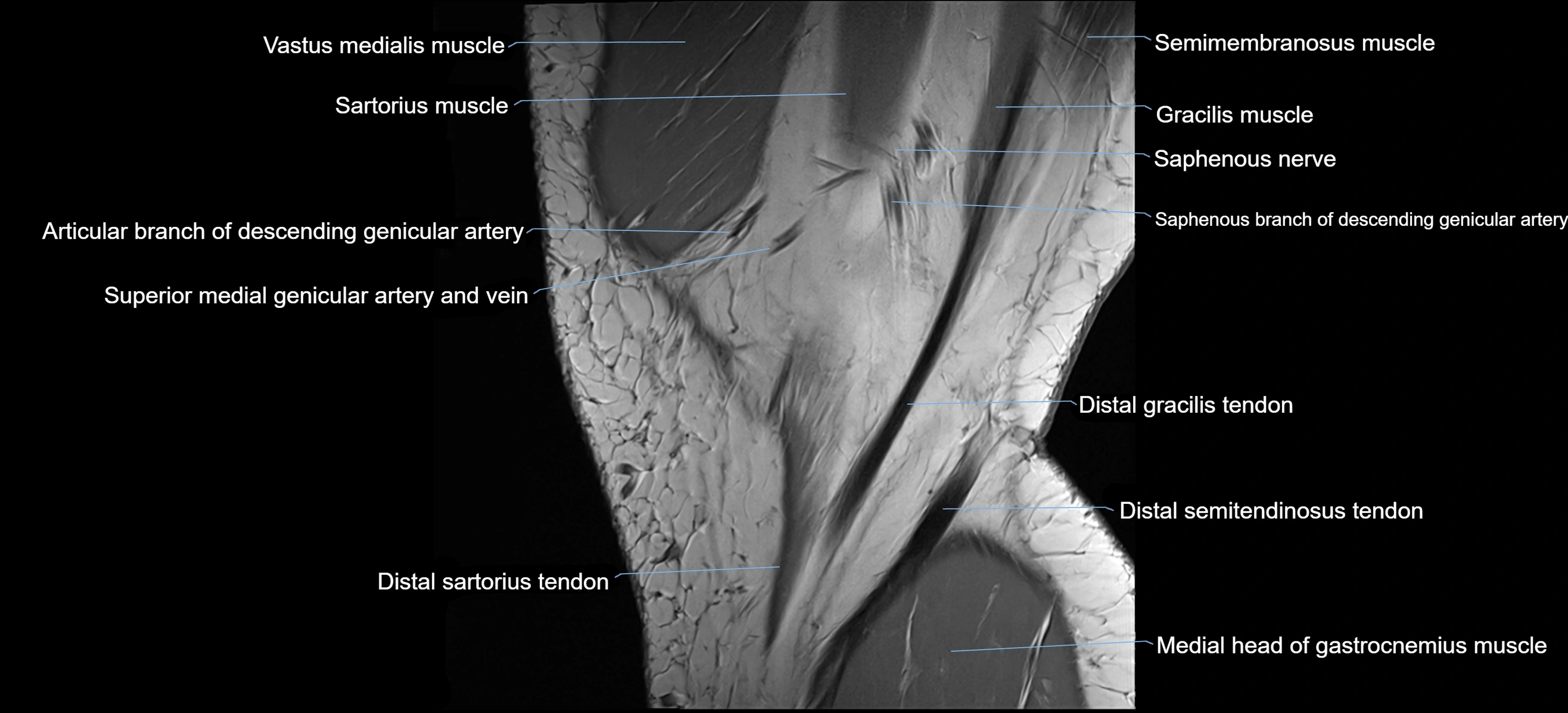
- Saphenous nerve
- Sartorius muscle
- Sartorius tendon (Distal)
- Semimembranosus muscle
- Semitendinosus muscle
- Small saphenous vein
- Soleus muscle
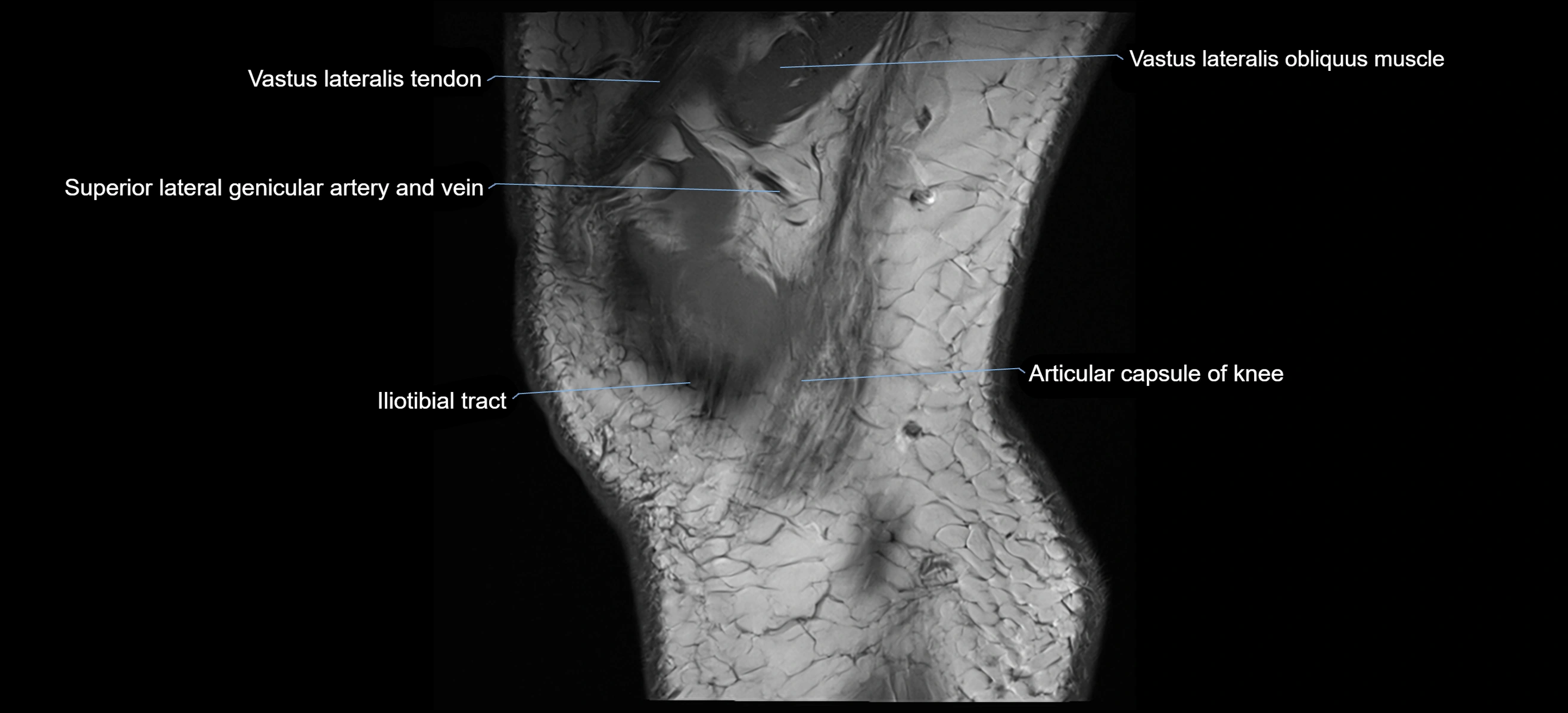
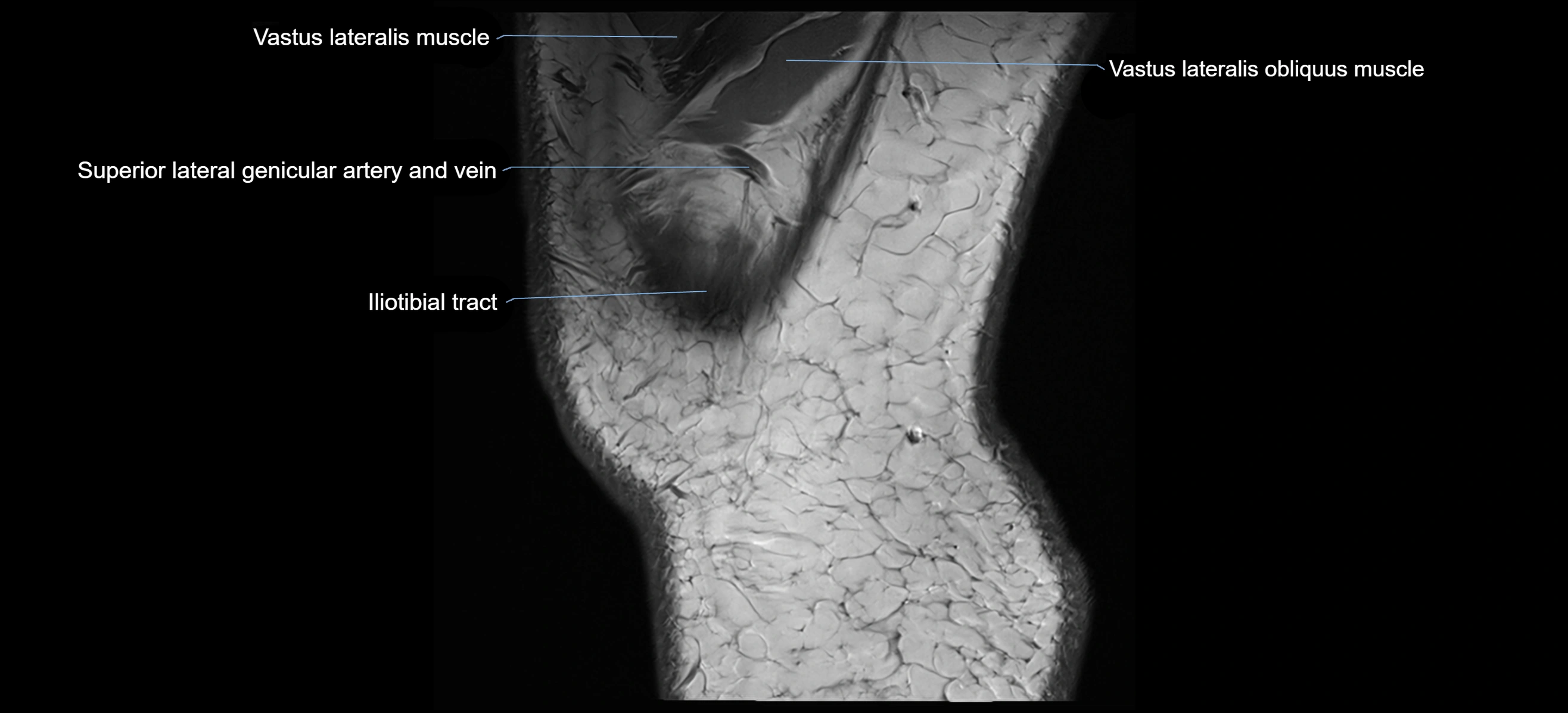
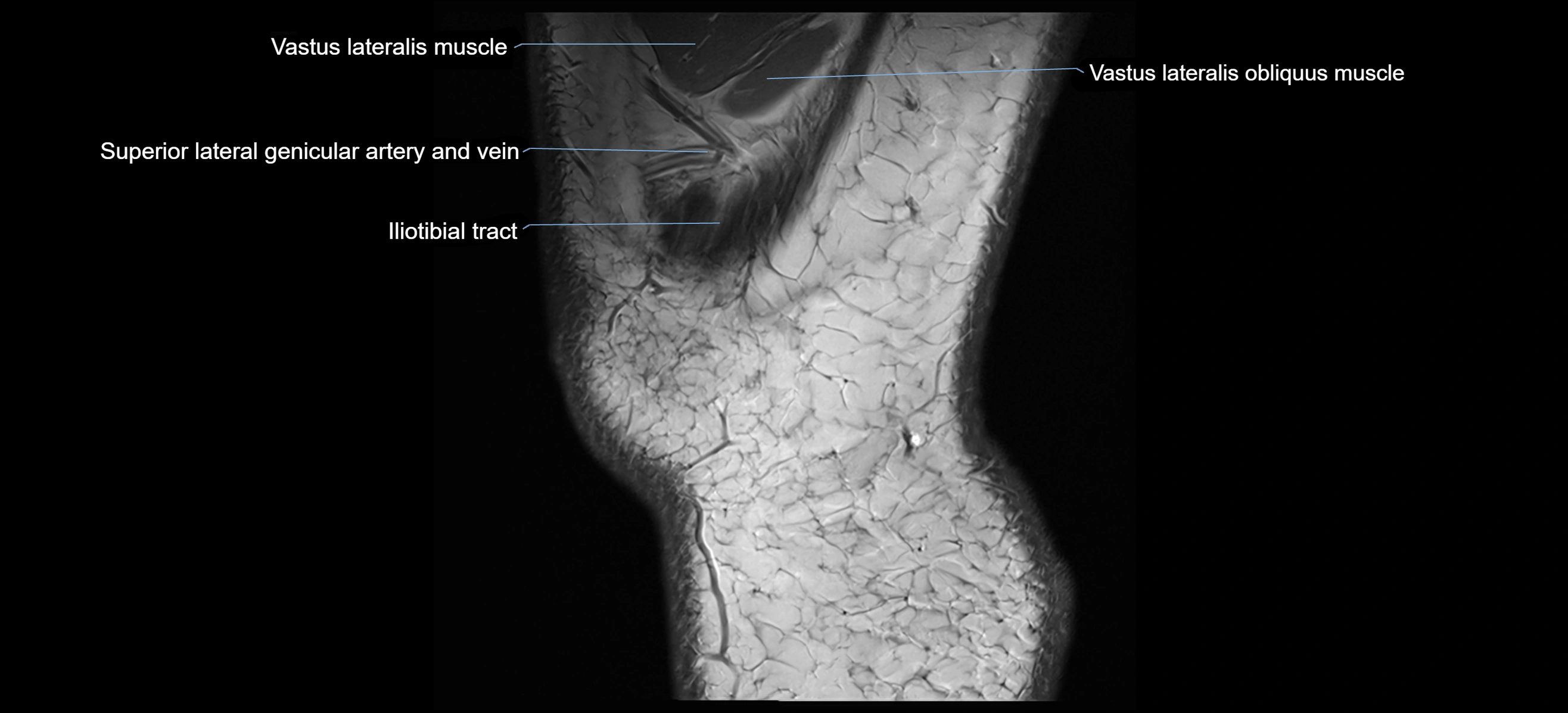
- Superior lateral genicular artery
- Superior lateral genicular vein
- Superior medial genicular artery
- Superior medial genicular vein
- Superior rim of acetabulum
- Superior tibiofibular joint
- Suprapatellar fat pad
- Synovial fluid
- Tendon sheath
- Tensor fasciae latae muscle
- Tibia
- Tibial condyle articular cartilage
- Tibial nerve
- Tibial tuberosity
- Tibialis anterior muscle
- Tibiofibular joint (proximal)
- Transverse ligament of knee
- Trochlear groove
- Tubercle of iliotibial tract
- Vastus Lateralis Obliquus Muscle
- Vastus lateralis muscle
- Vastus medialis muscle
- great saphenous vein
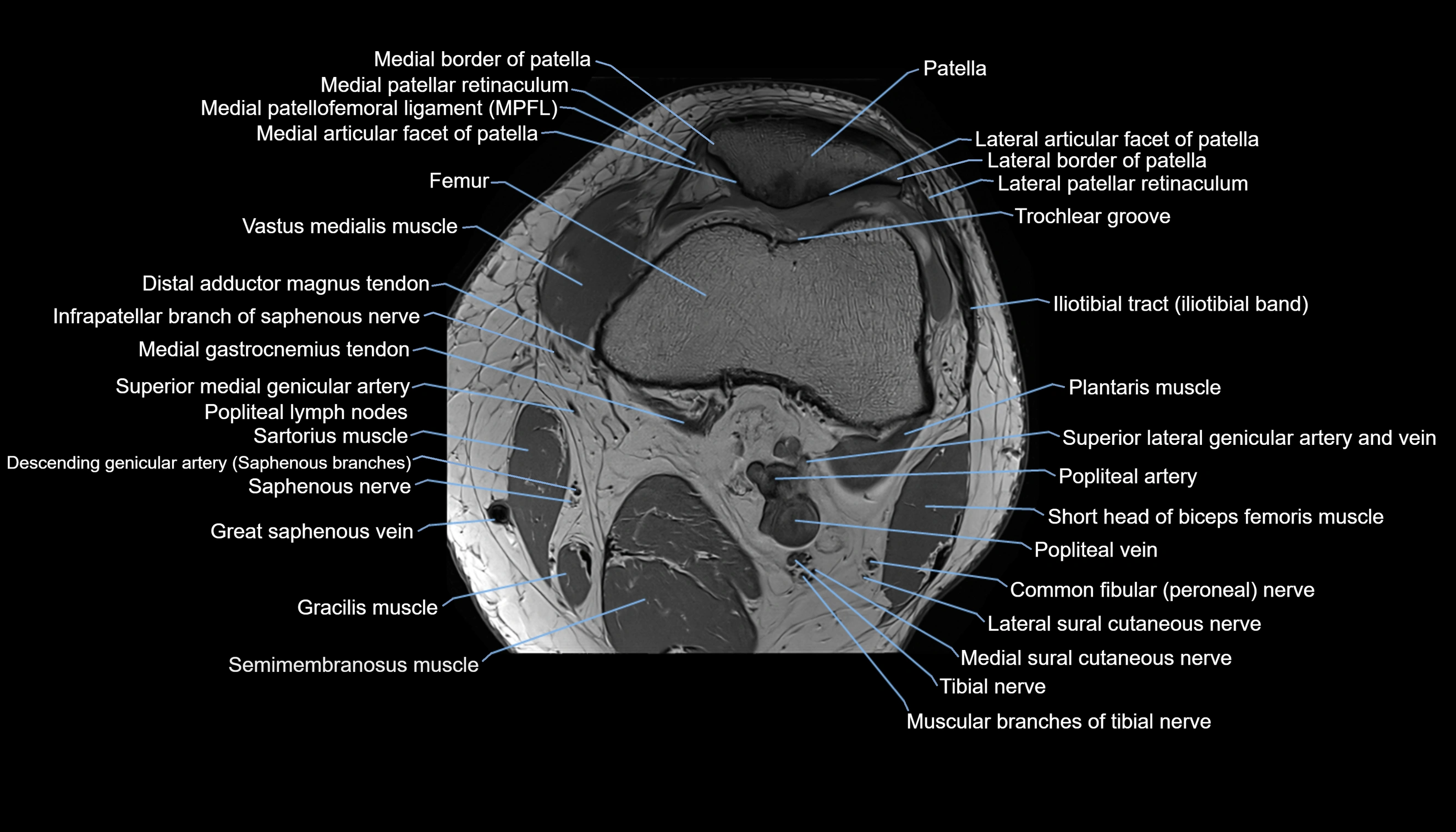
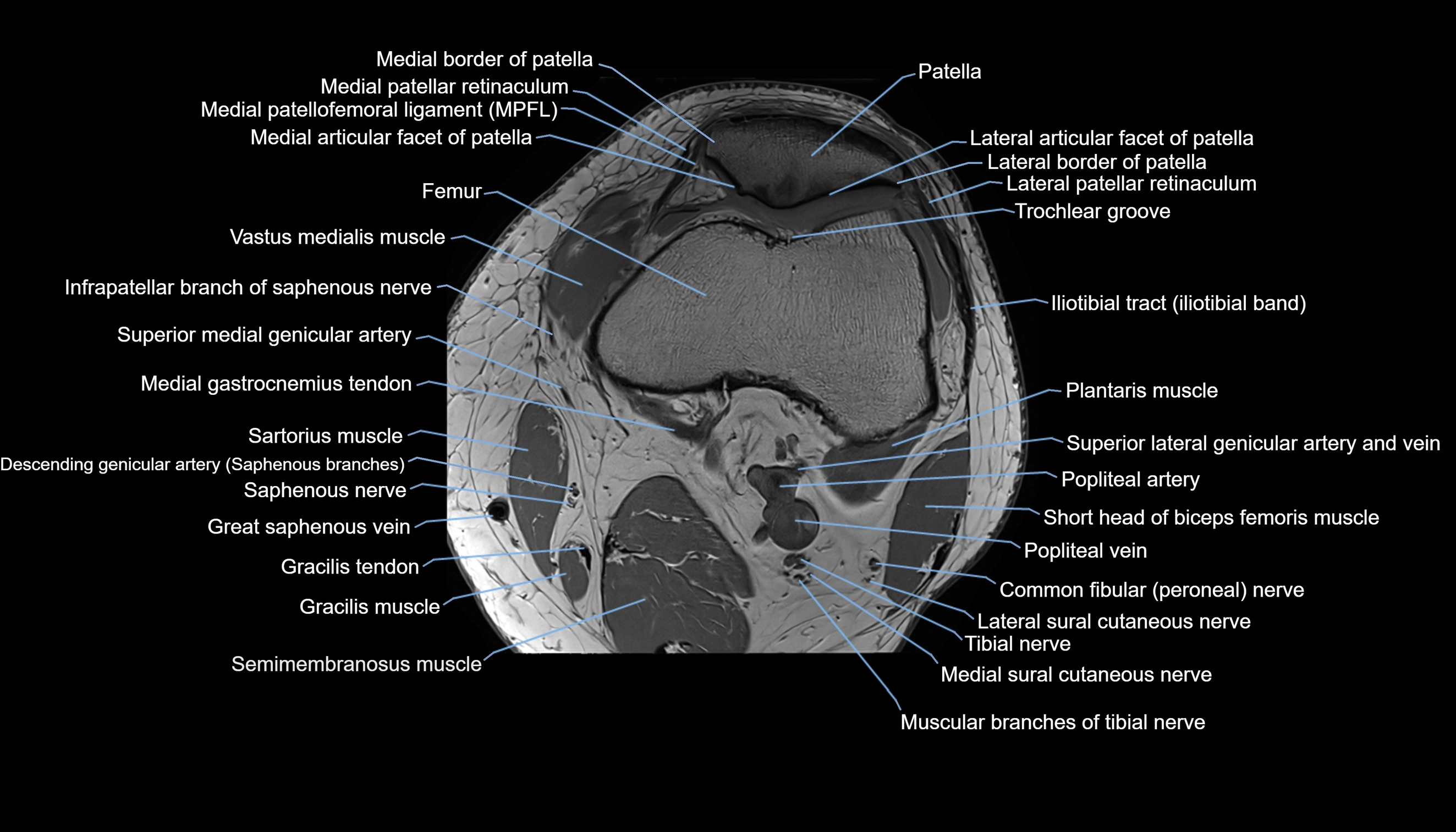
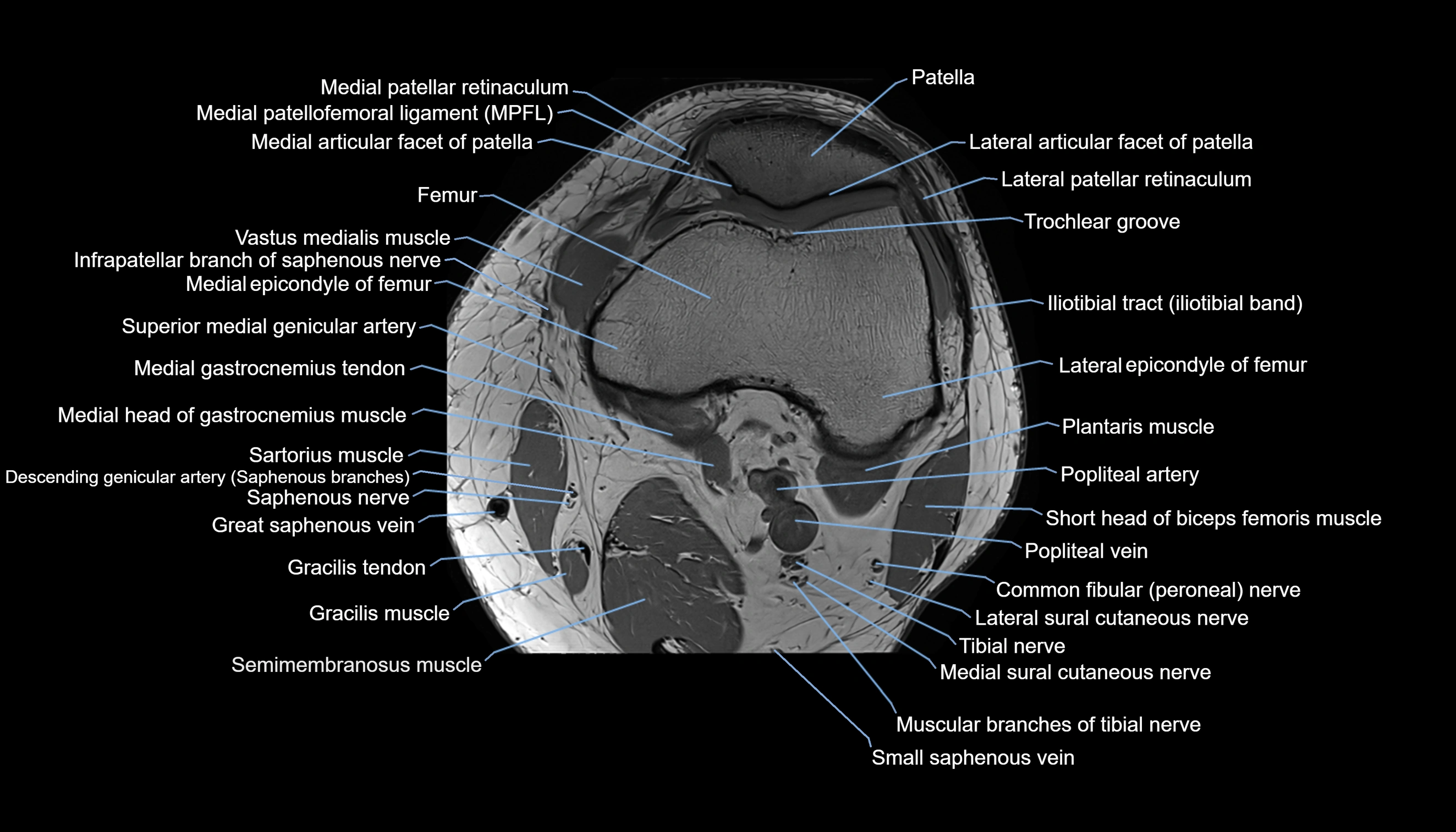
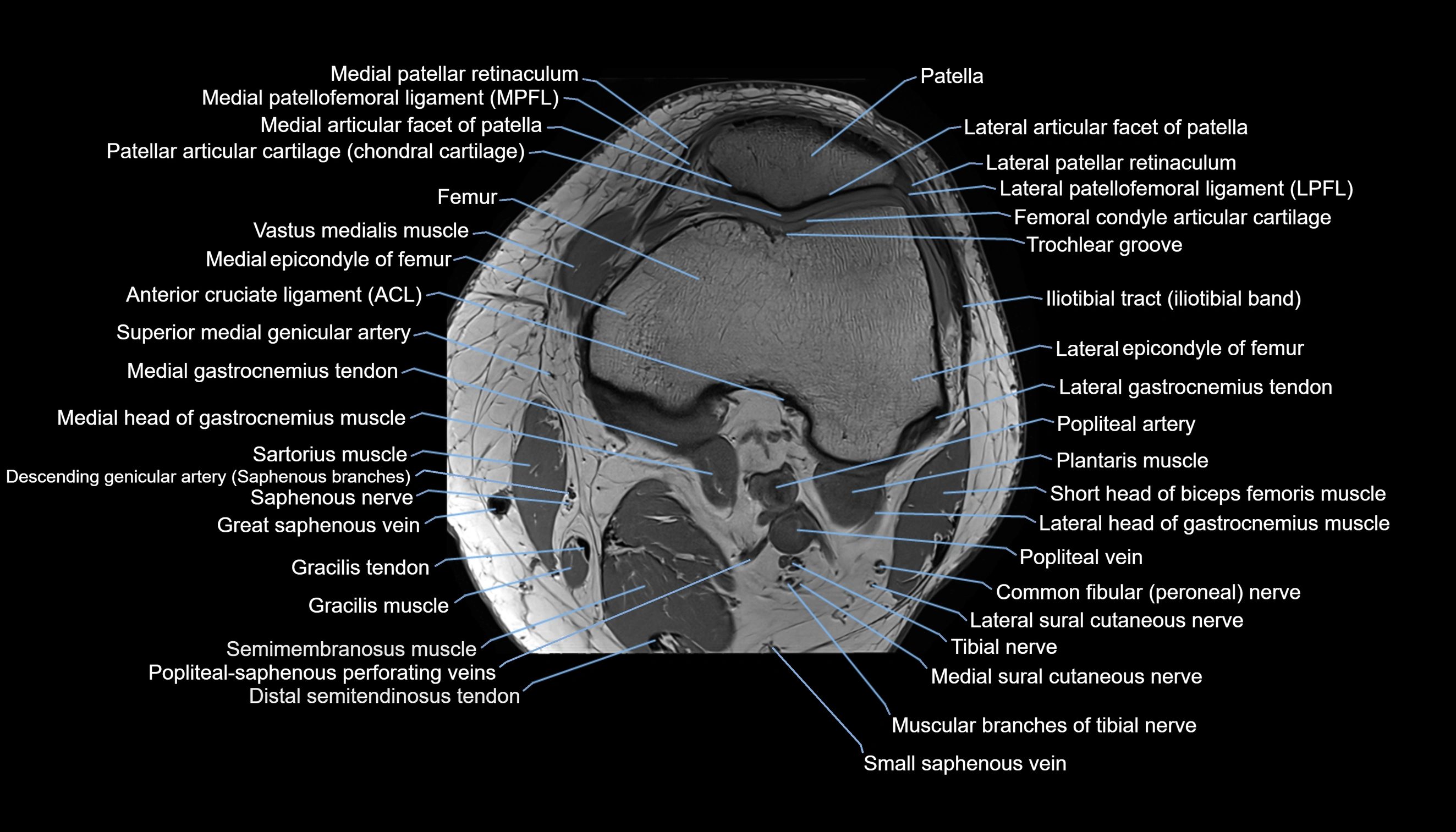
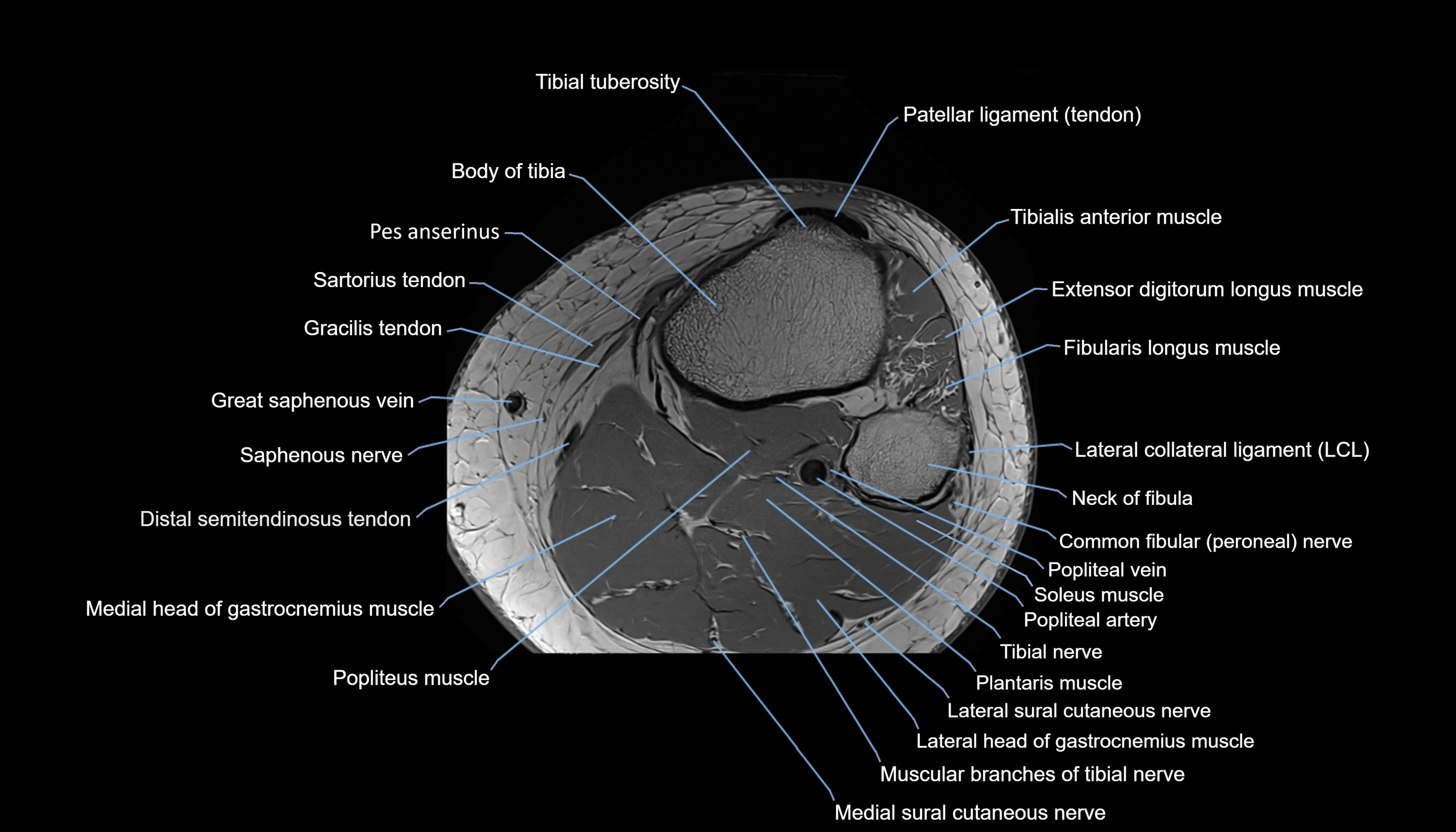
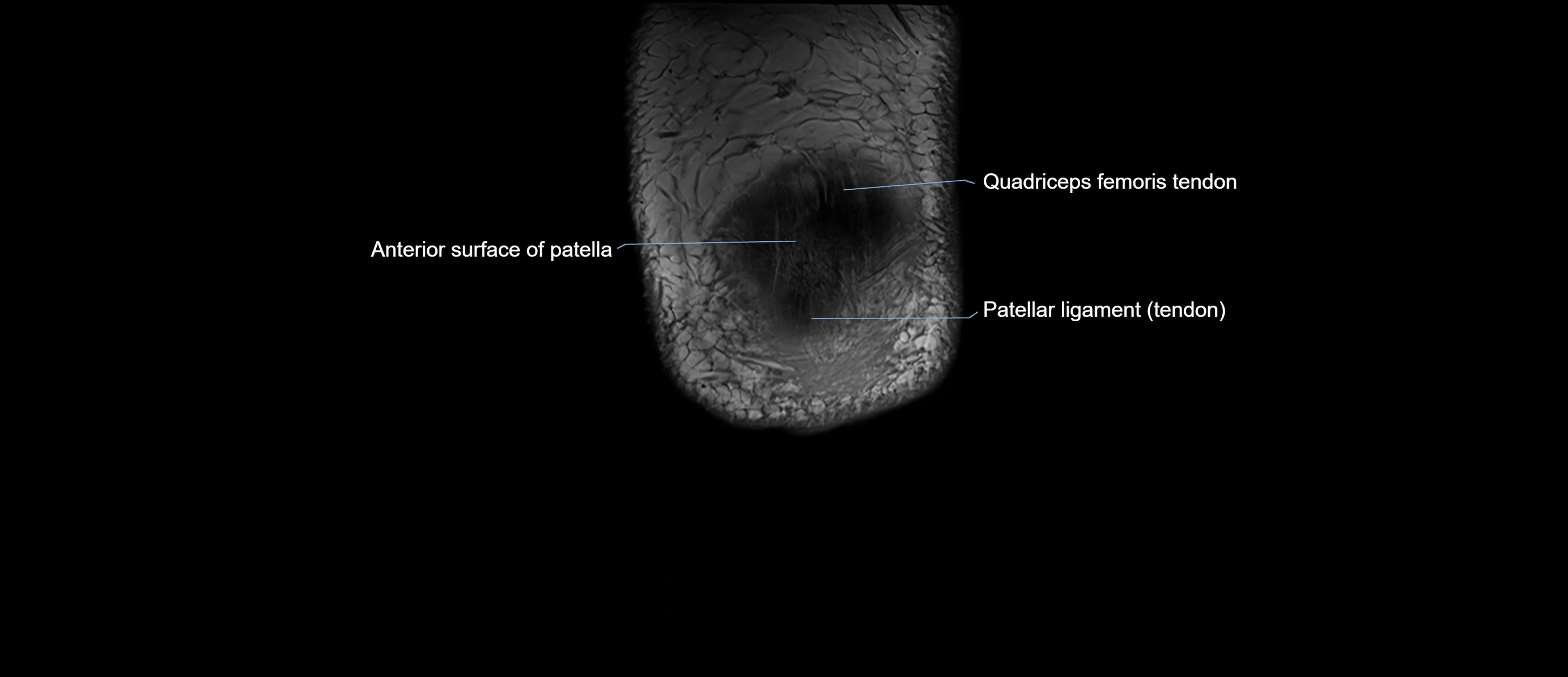
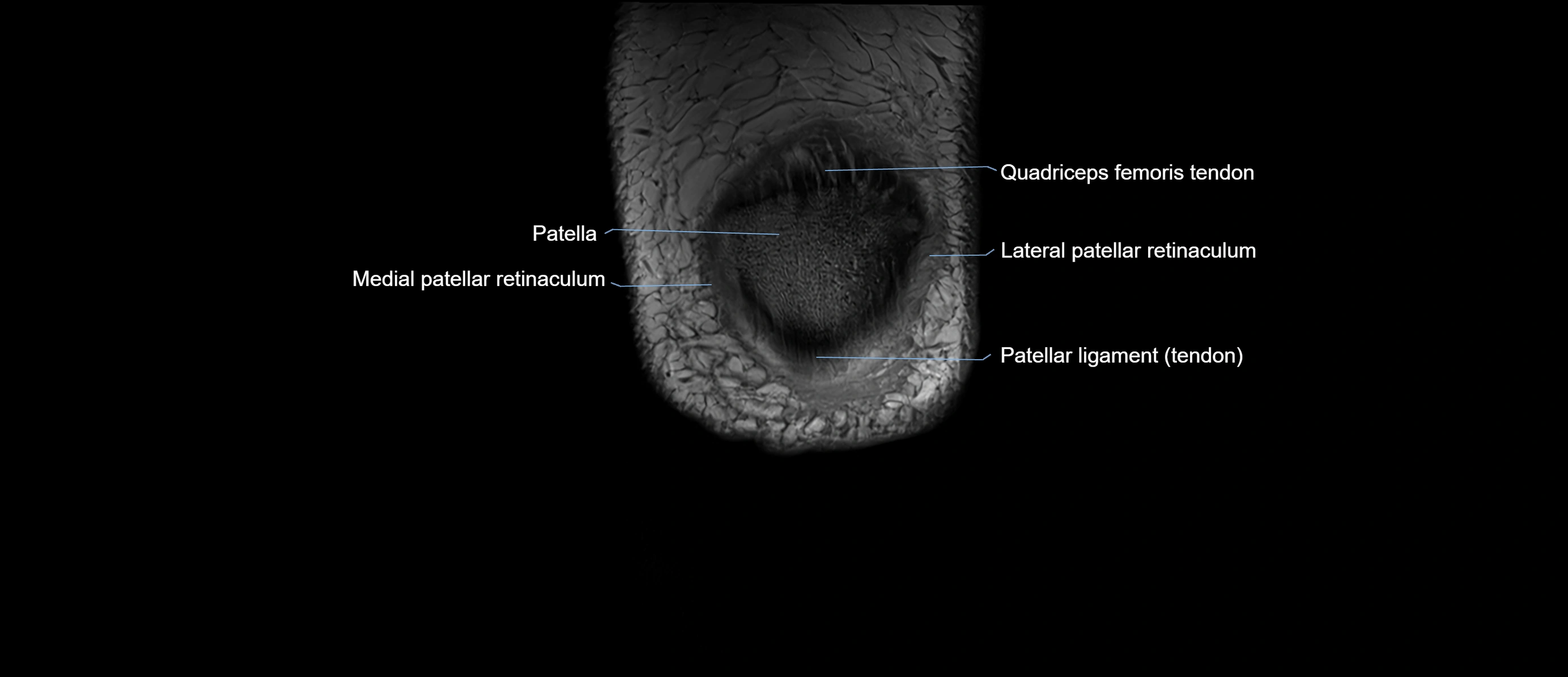
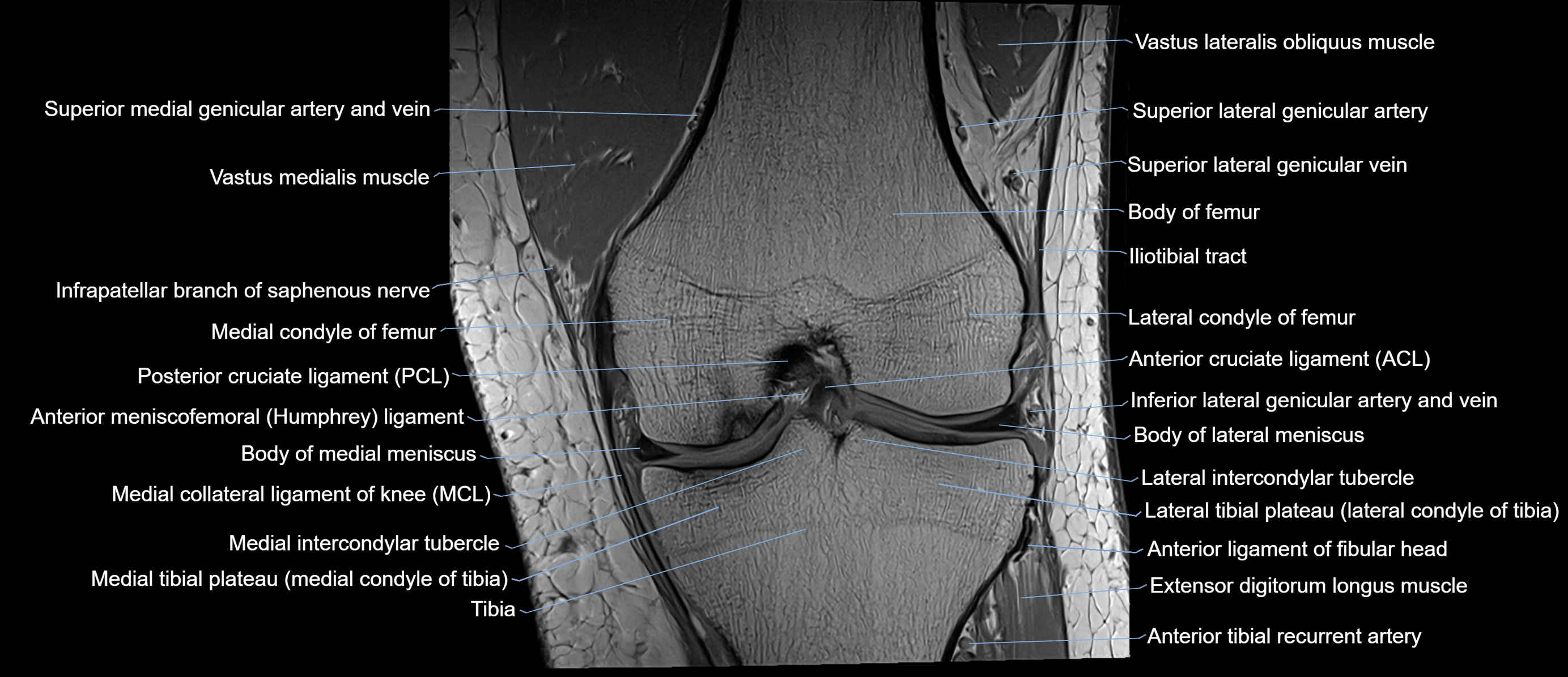
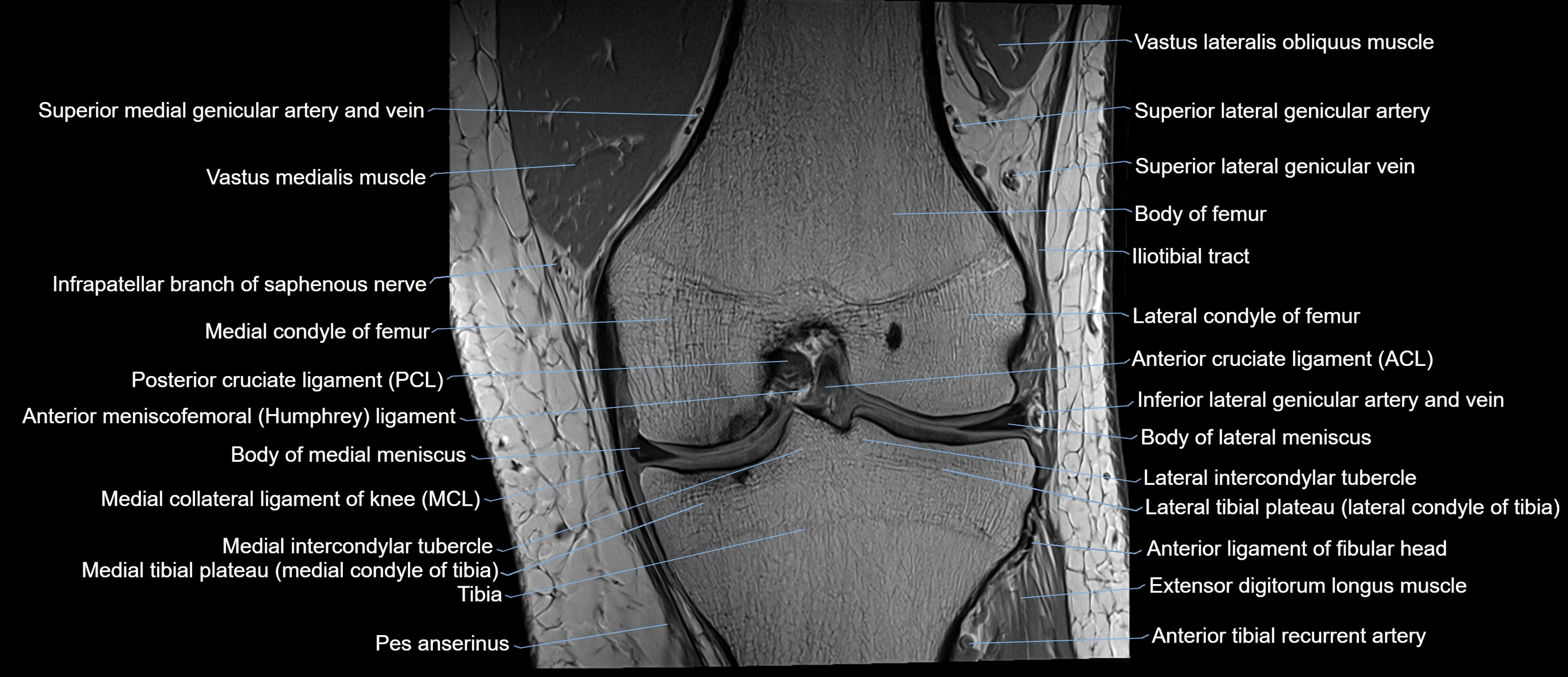
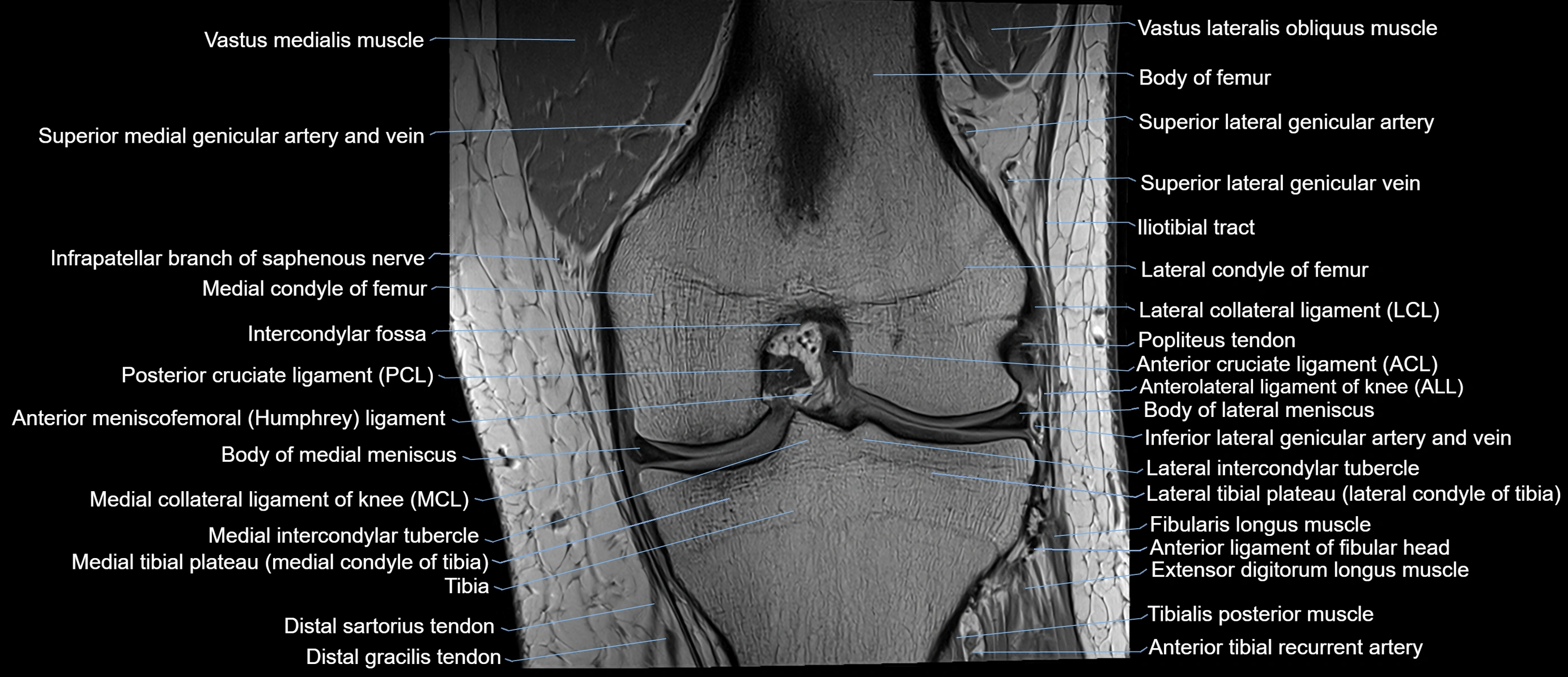
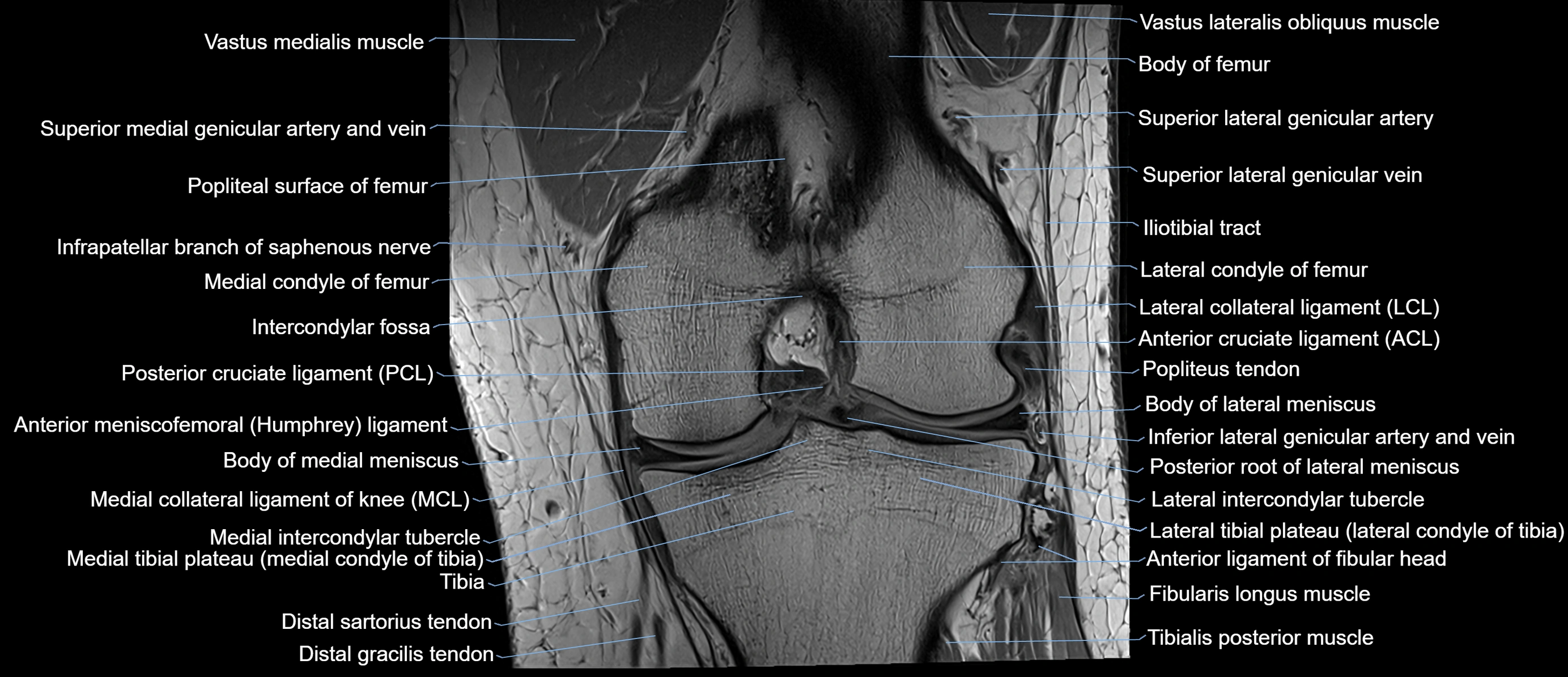
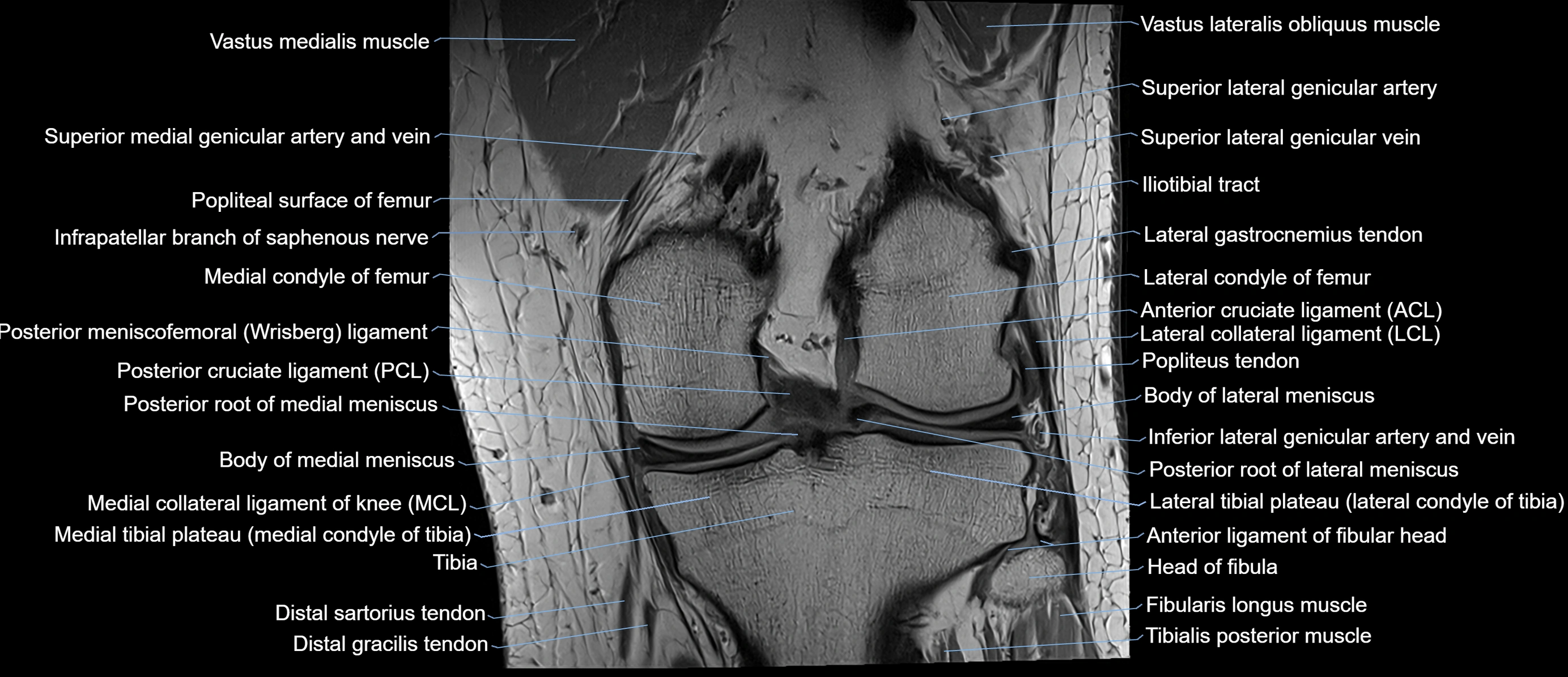
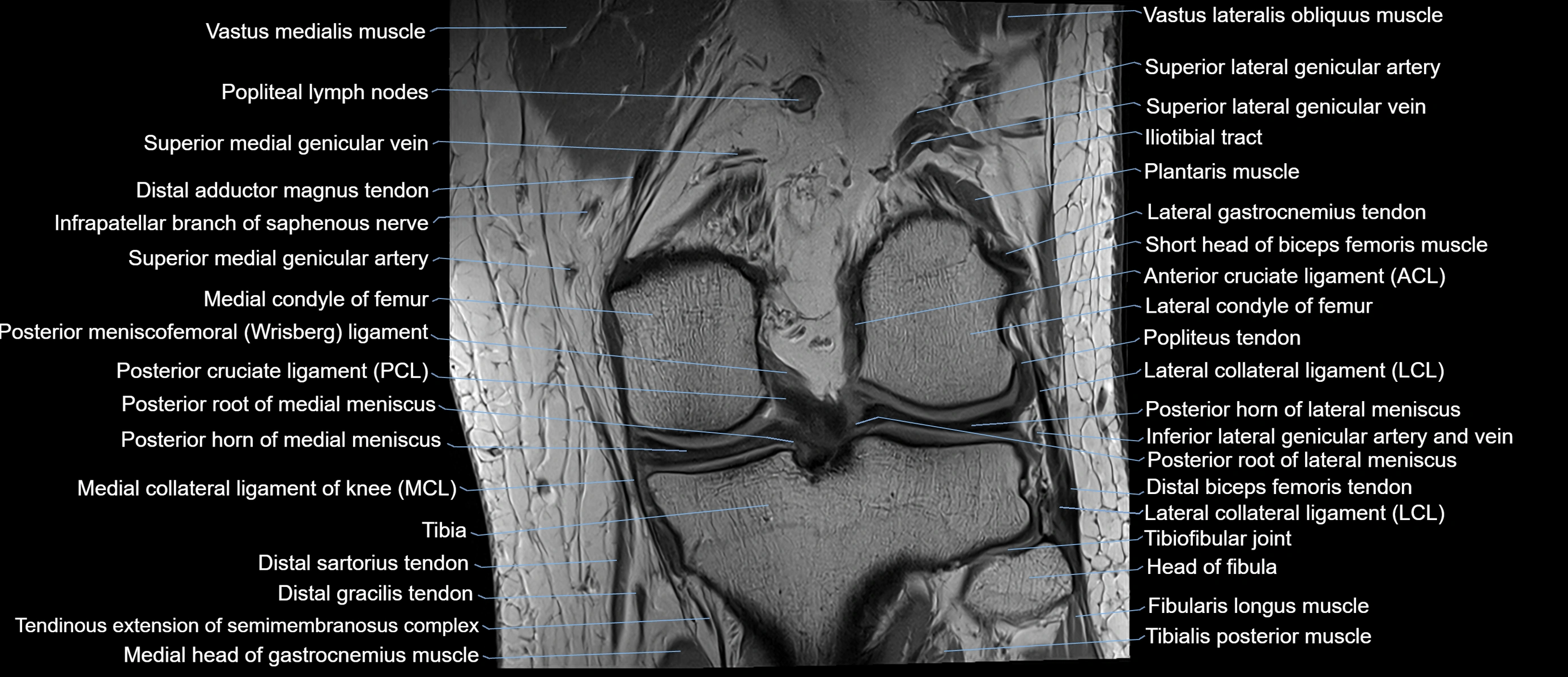
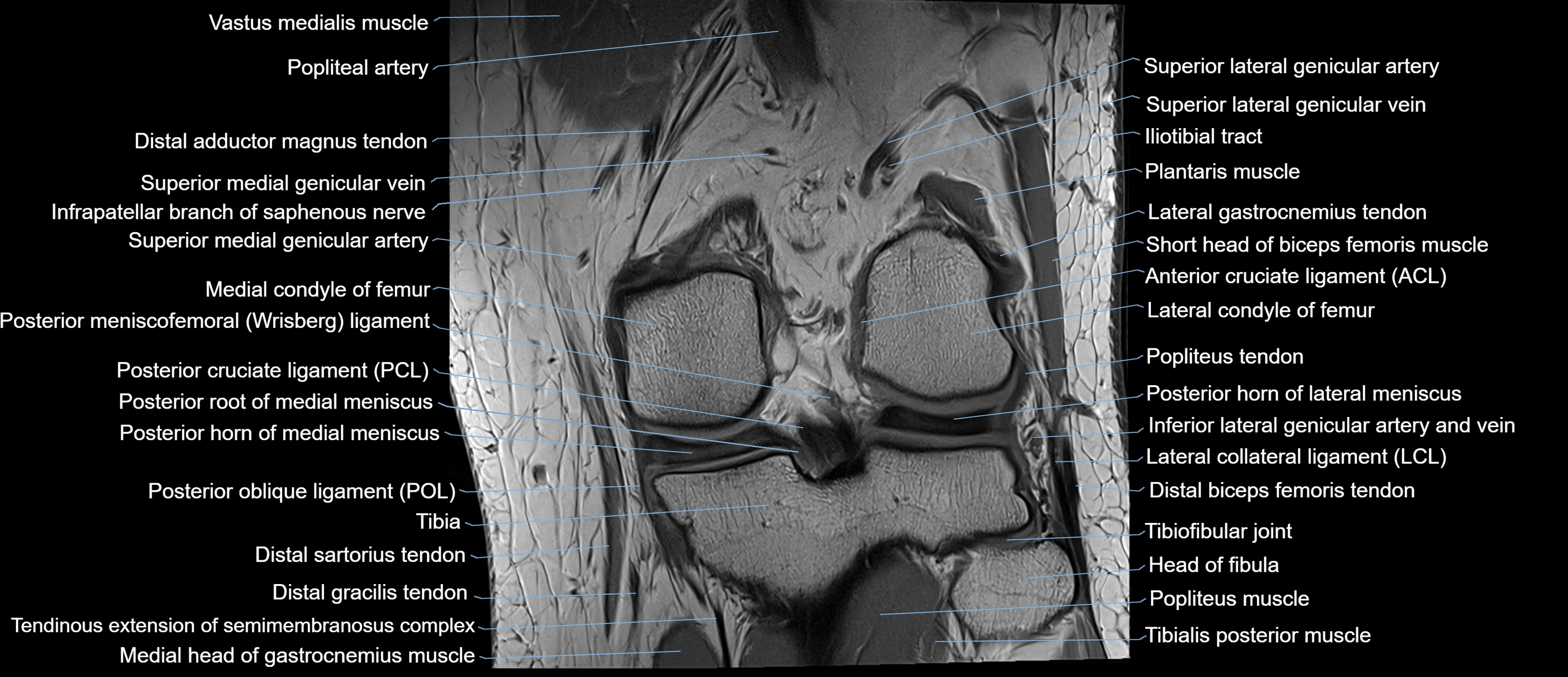
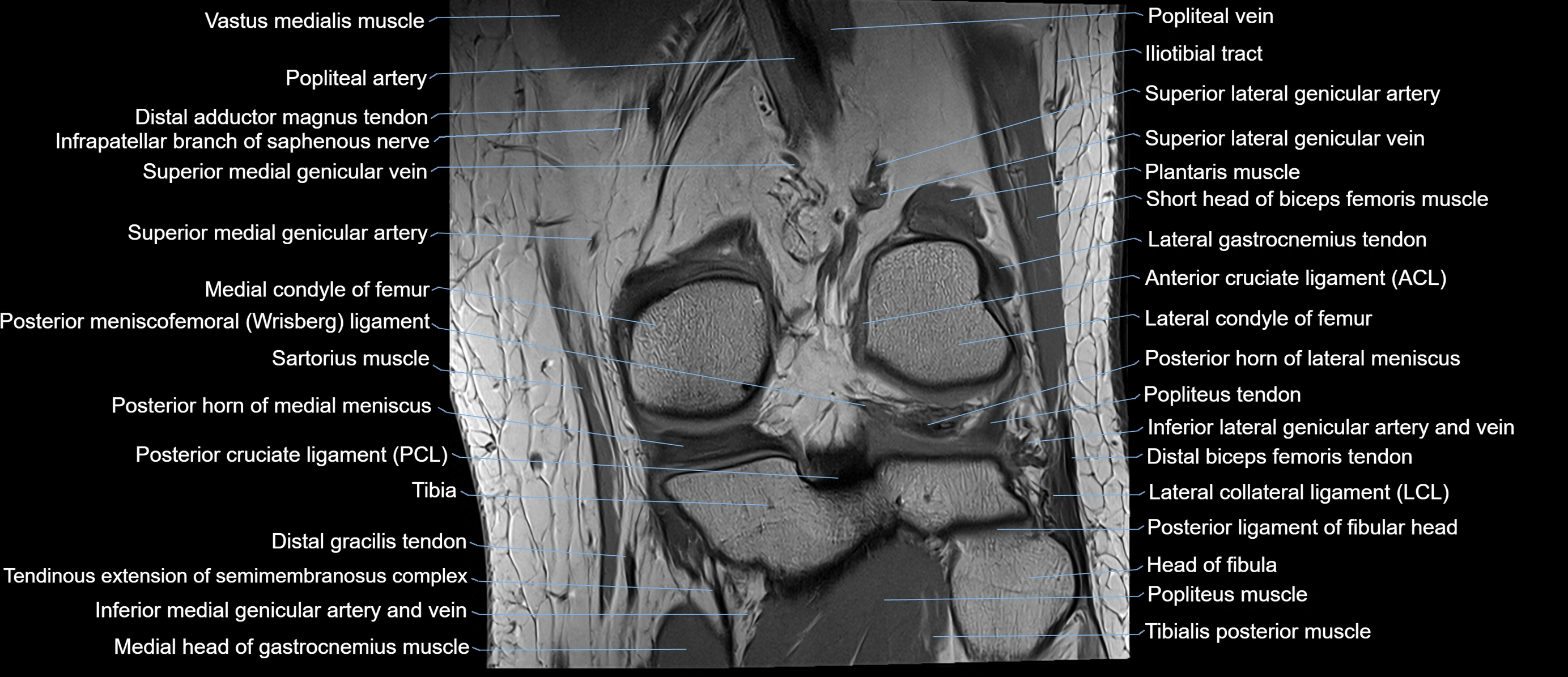
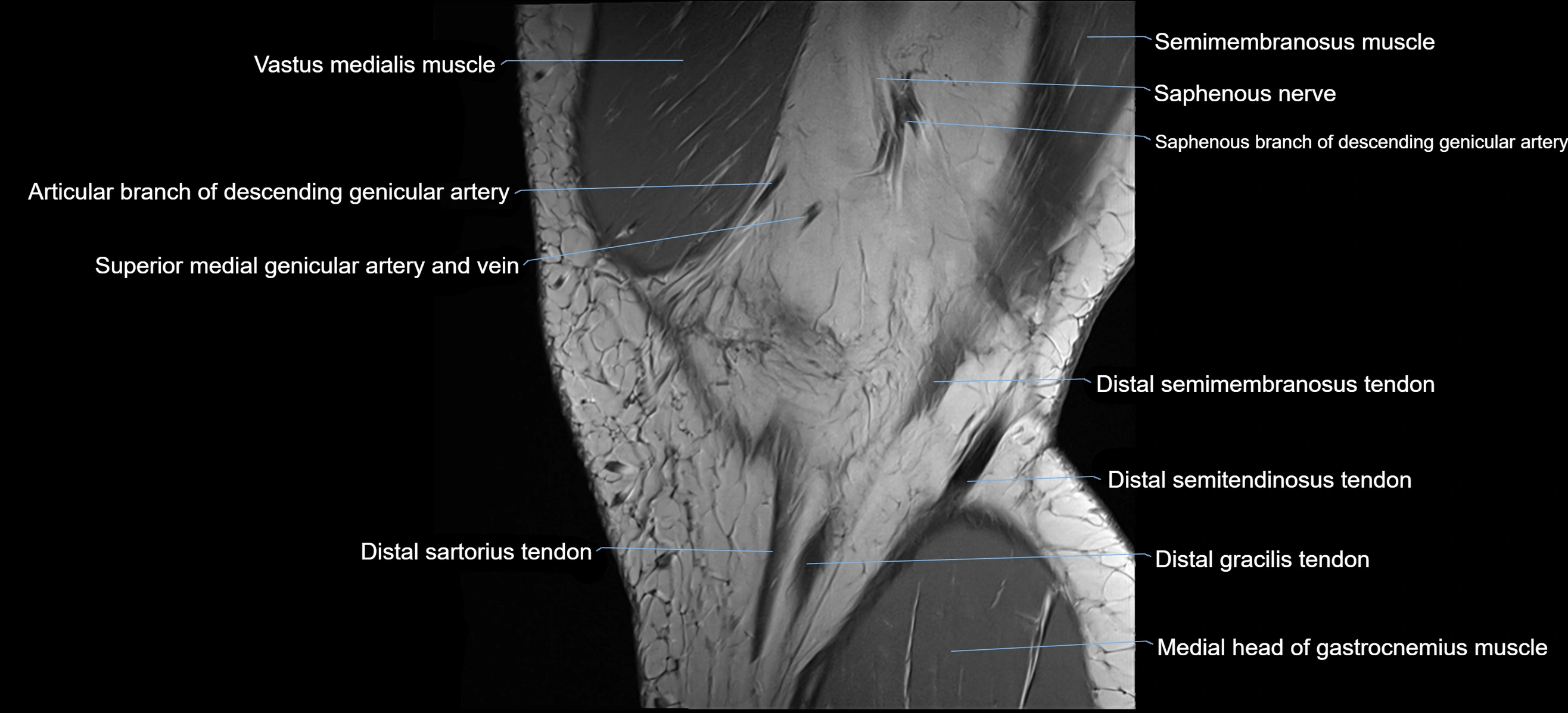
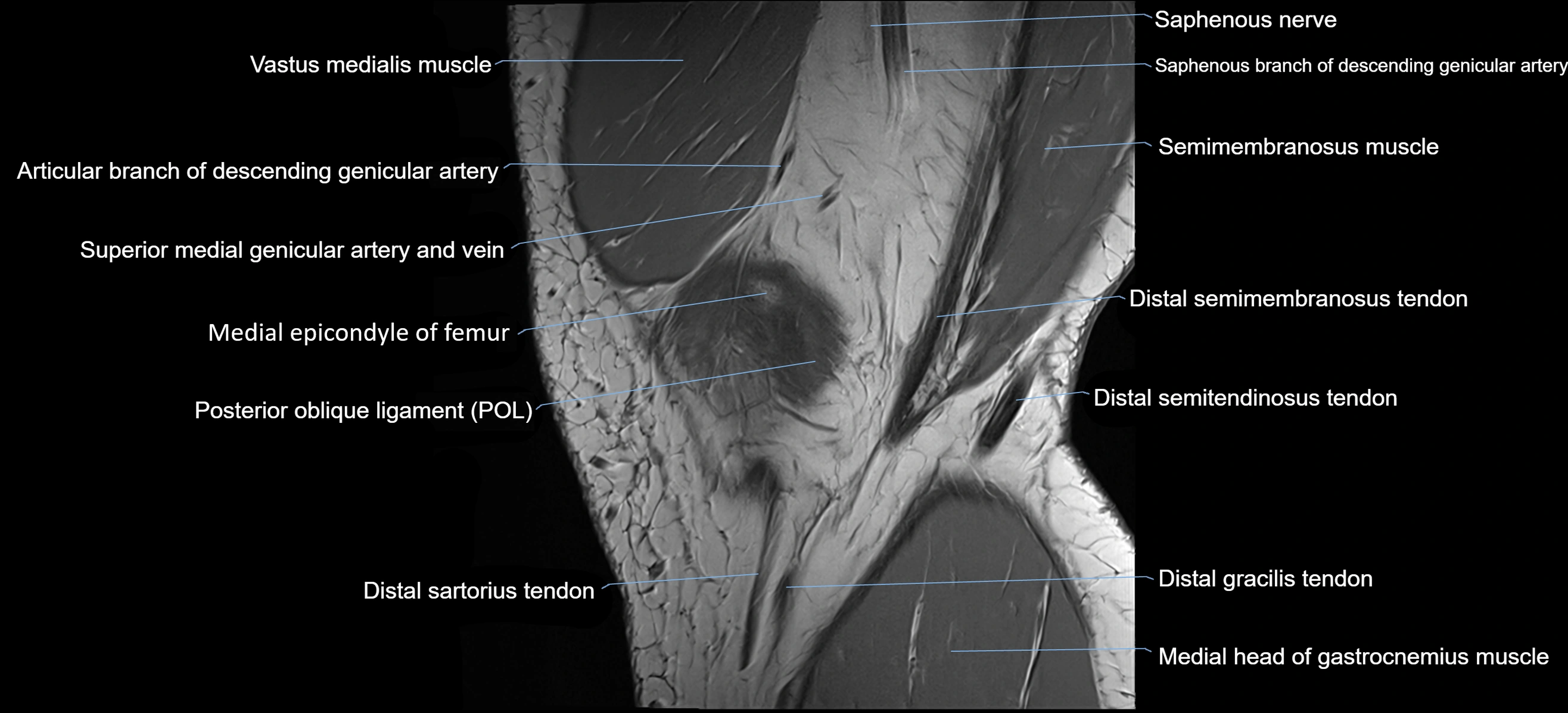
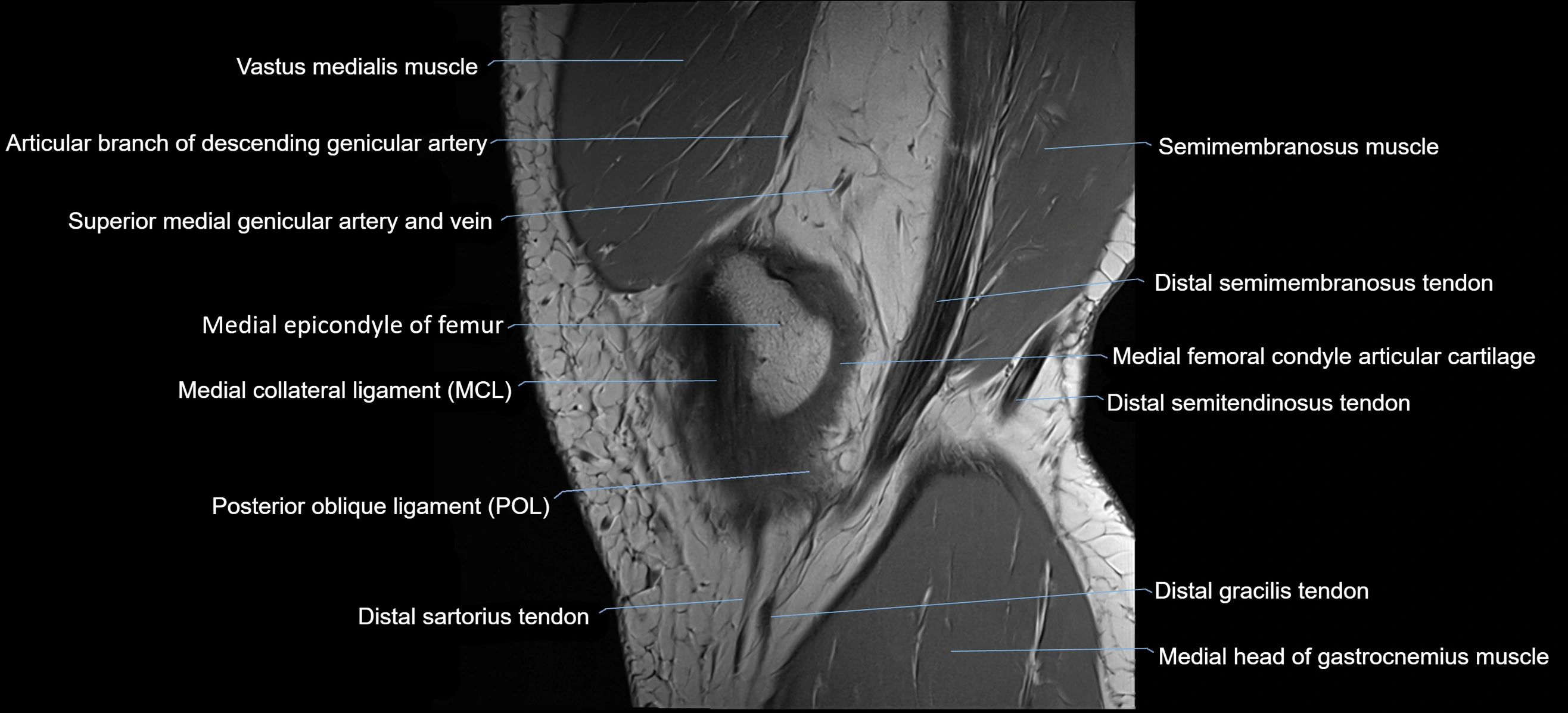
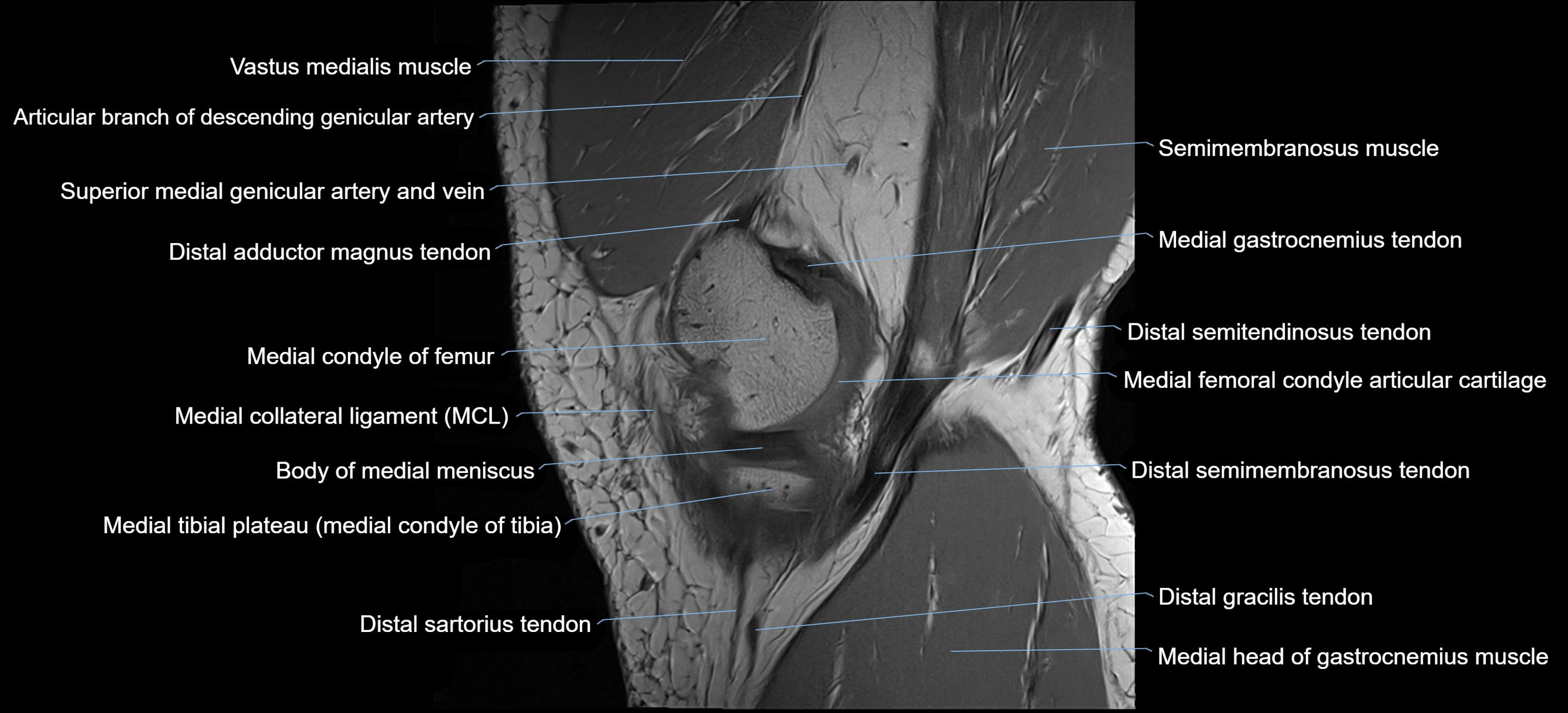
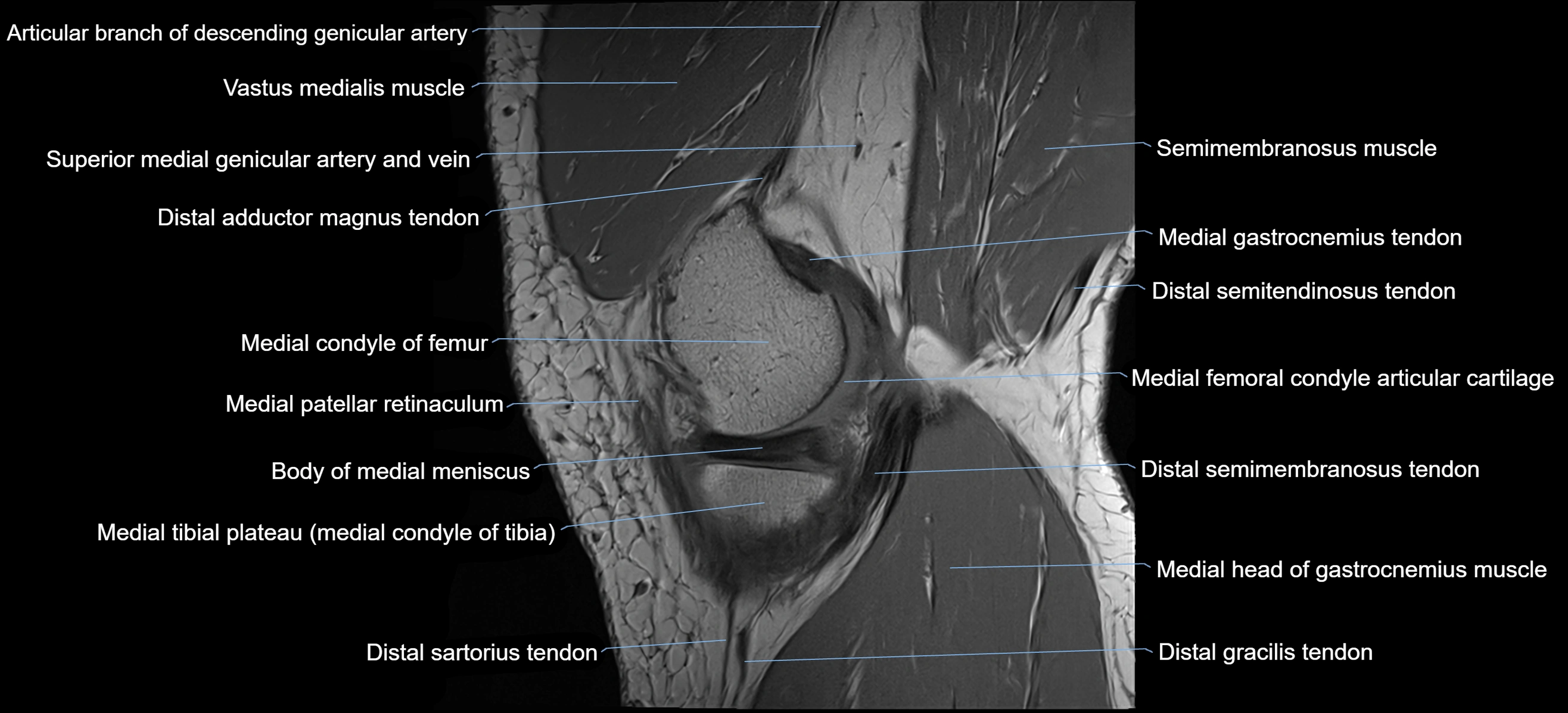
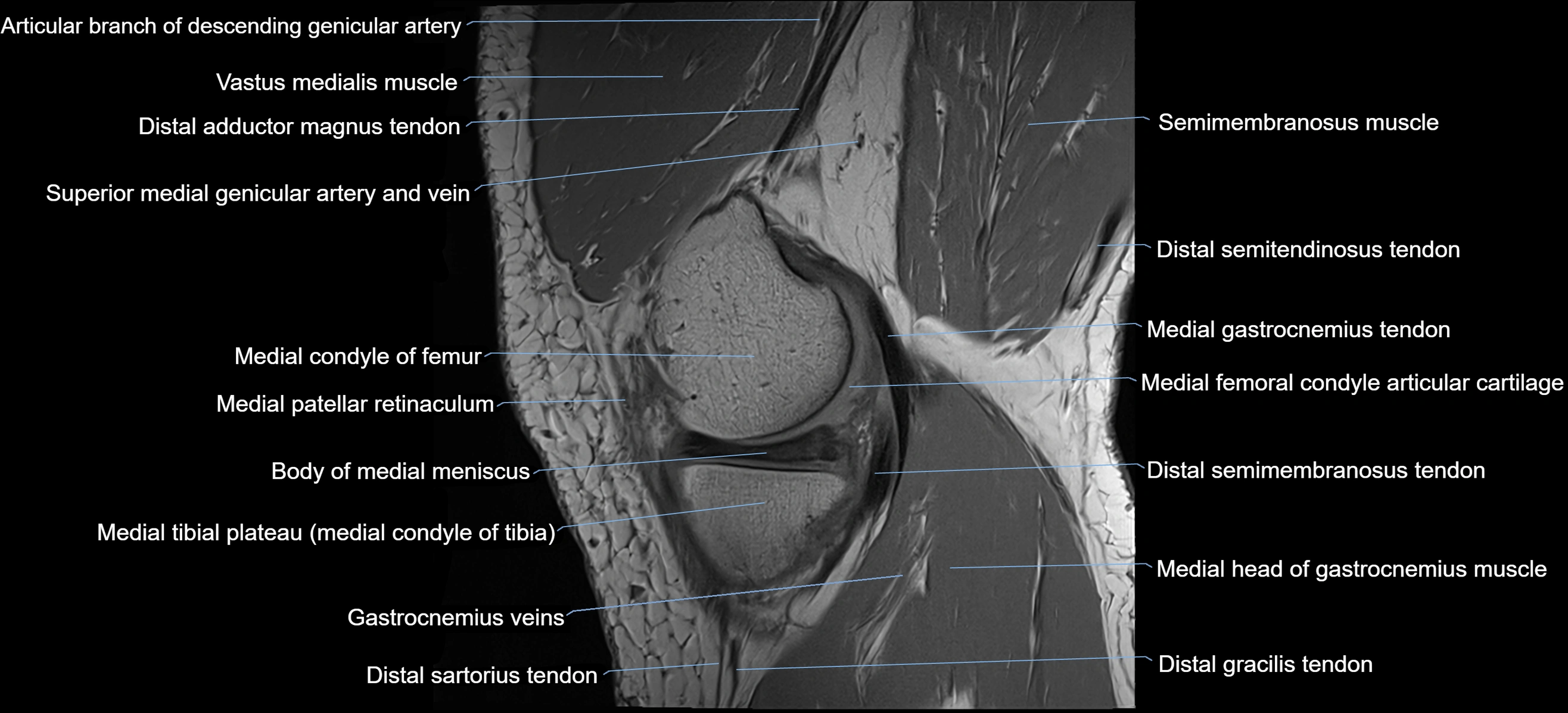
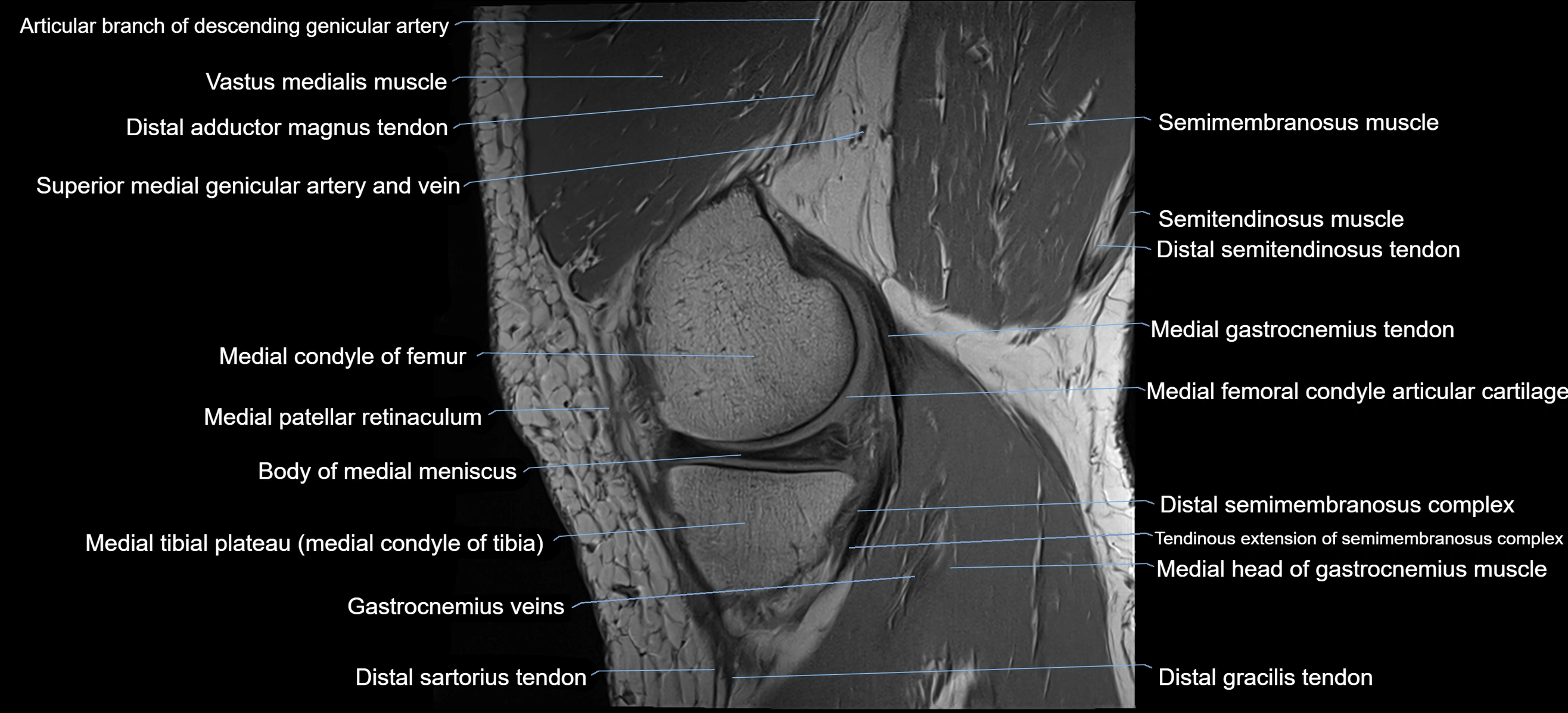
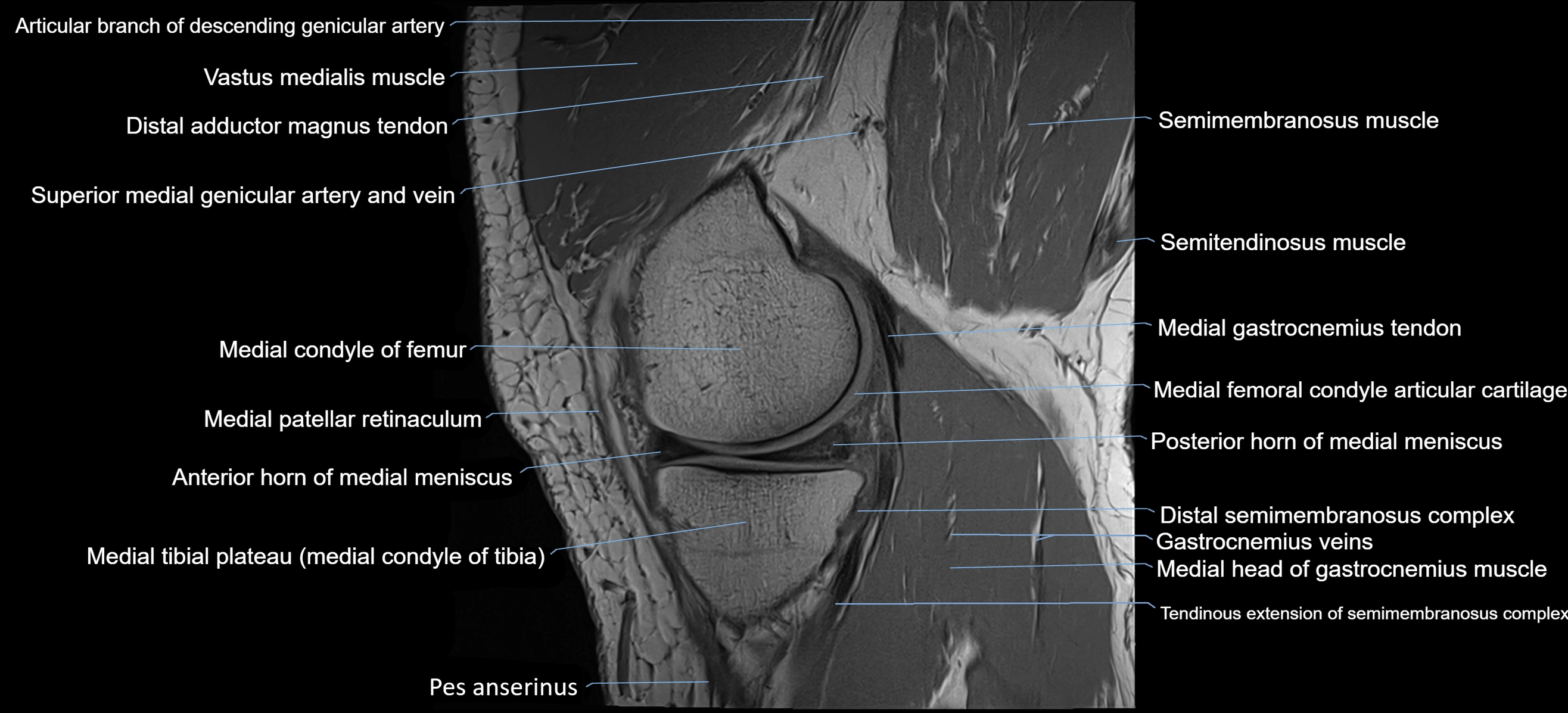
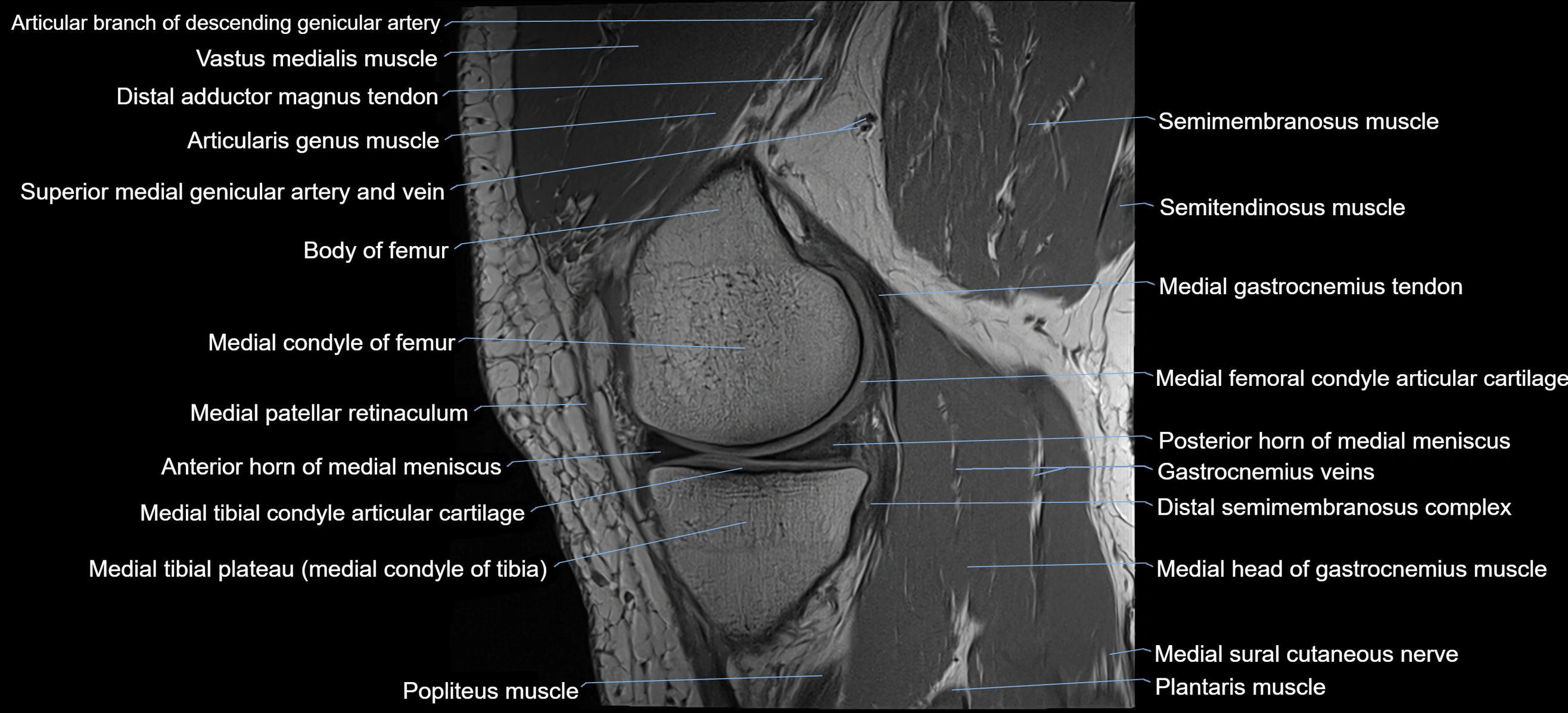
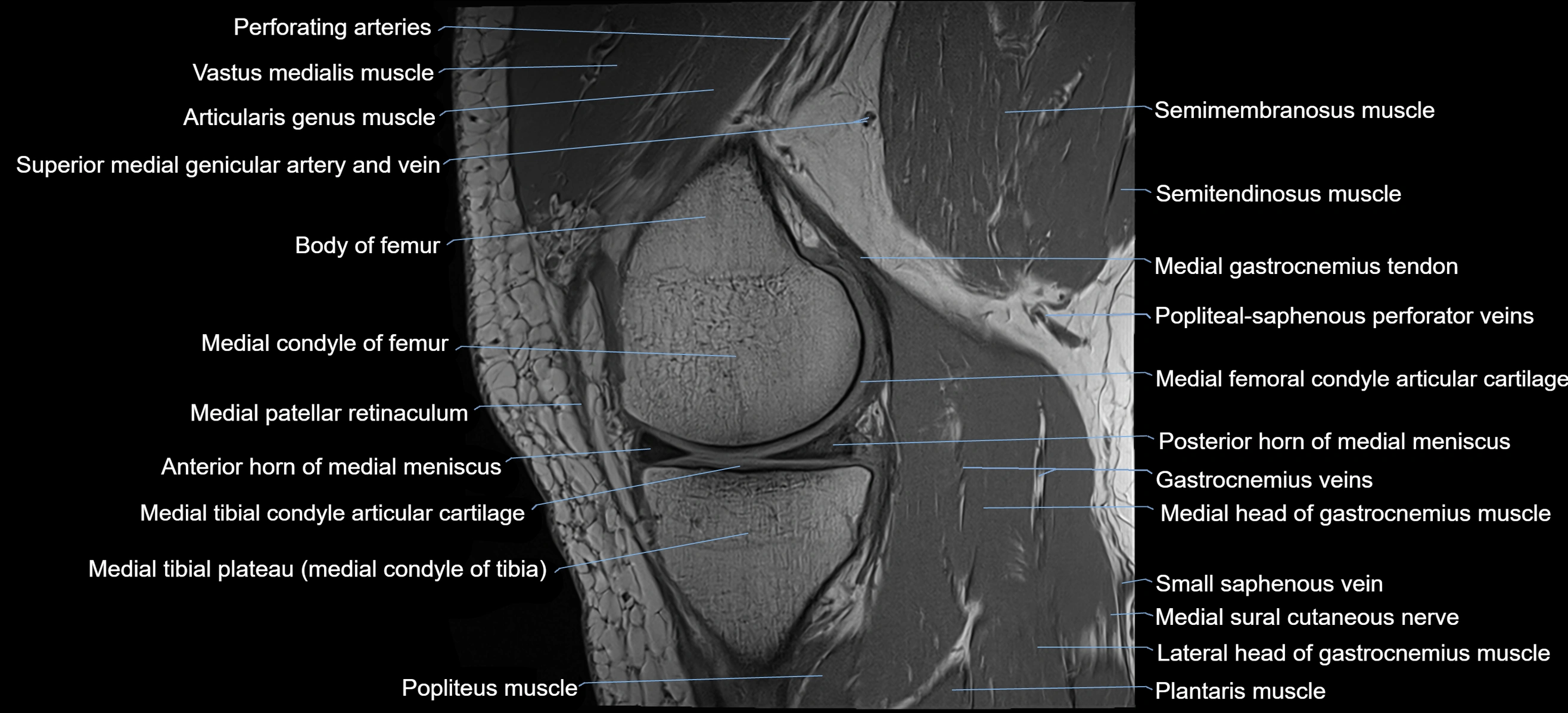
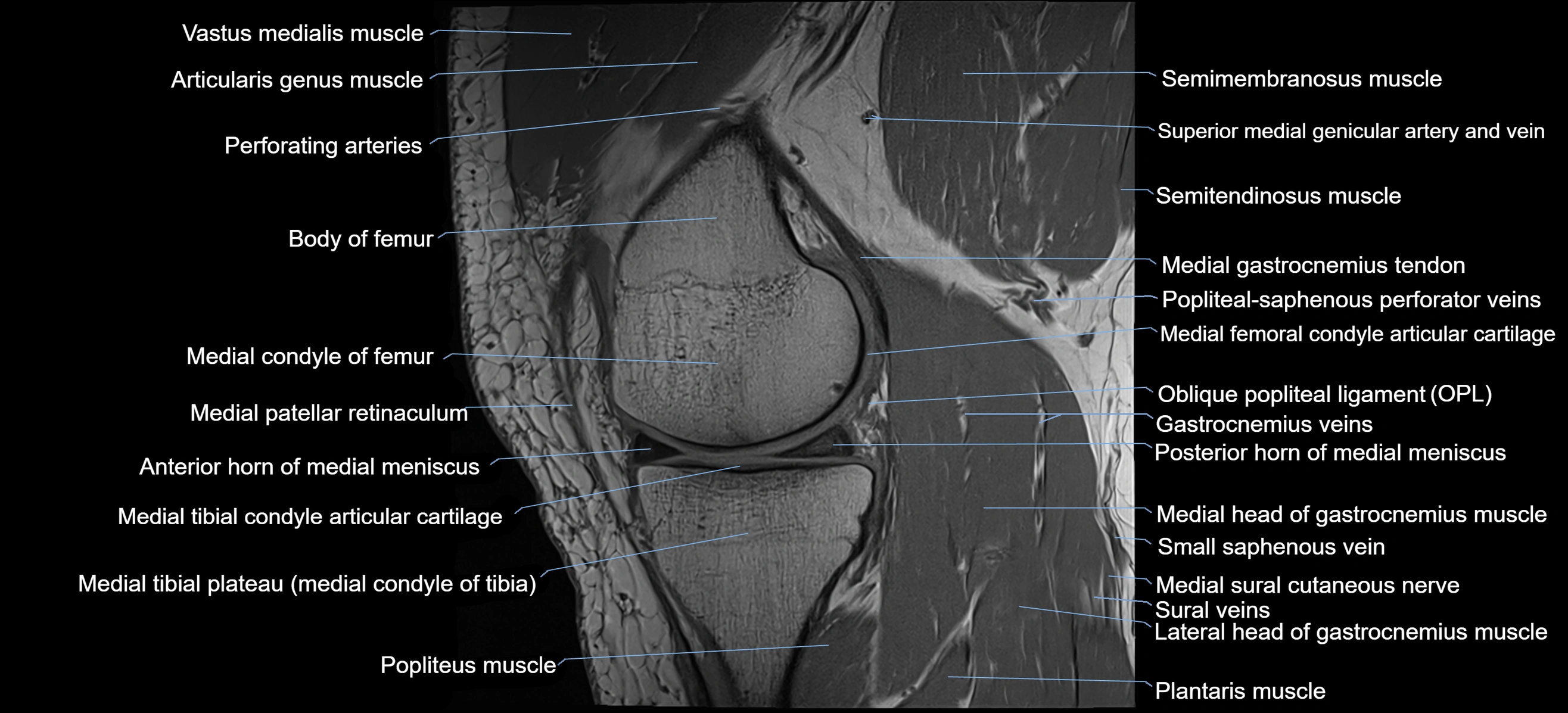
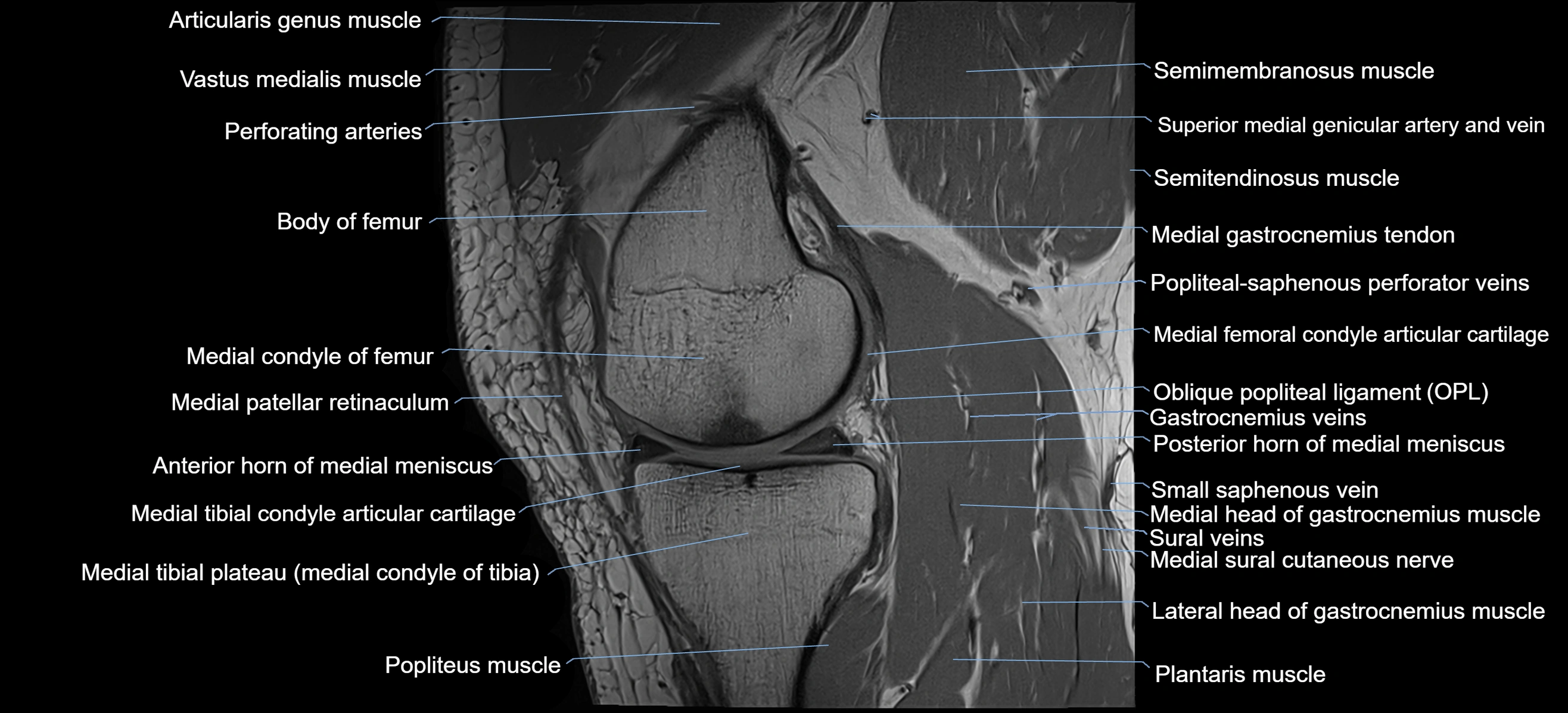
The adductor tubercle is a small but prominent bony projection located on the superior aspect of the medial femoral condyle. It serves as an important anatomical landmark in the distal femur and marks the insertion of the adductor magnus muscle (hamstring part). The adductor tubercle is clinically significant in orthopedic surgery, knee imaging, and anatomical localization around the medial distal femur.
It is particularly useful for identifying the level of the knee joint line and distinguishing between the medial epicondyle and condylar regions.
Synonyms
-
Tuberculum adductorium
-
Adductor tuberosity (less commonly used)
Location
-
Situated on the superior aspect of the medial femoral condyle
-
Just proximal to the medial epicondyle
-
Posterior to the medial supracondylar line
-
At the transition between the shaft and distal femur
-
On the medial side of the distal femur
Anatomical components
-
Osseous prominence of the distal femur
-
Attachment site of the hamstring (ischiocondylar) part of adductor magnus
-
Separates the medial epicondyle (ligamentous attachment) from the condylar articular region
Relations
Anteriorly:
-
Medial supracondylar ridge
-
Vastus medialis muscle
Posteriorly:
-
Popliteal surface of femur
-
Adductor hiatus (just superior and posterior)
Inferiorly:
-
Medial epicondyle of femur
-
Medial collateral ligament attachment nearby
Superiorly:
-
Femoral shaft (distal metaphysis)
Medially:
-
Adductor magnus tendon insertion
Laterally:
-
Medial femoral condyle articular surface
Function
-
Muscle attachment landmark: Serves as the insertion site for the adductor magnus (hamstring portion)
-
Surgical reference point: Used to identify knee joint line and medial distal femoral anatomy
-
Biomechanical role: Contributes to medial stabilization forces transmitted through adductor magnus
X-ray appearance
Plain radiographs (AP and lateral knee views):
-
Adductor tubercle: Small bony prominence on the superior-medial aspect of the distal femur
-
Cortical outline: Well-defined and continuous with femoral cortex
-
Best visualized: On oblique or lateral projections
CT appearance (pre-contrast)
Non-contrast CT:
-
Tubercle: Cortical bony protuberance arising from the medial femoral condyle
-
Margins: Smooth and sharply defined
-
Trabecular continuity: Continuous with medullary cavity
-
Useful for: Precise delineation of bony anatomy and preoperative planning
MRI appearance
T1-weighted images:
-
Tubercle: Low signal cortical bone with intermediate marrow signal centrally
-
Adductor magnus insertion: Seen as low-signal tendon attaching to the tubercle
-
Adjacent marrow: Normal fatty signal
T2-weighted images:
-
Cortical bone: Low signal
-
Surrounding soft tissues: Intermediate signal
-
Tendon insertion: Low-signal linear structure
STIR:
-
Bone cortex: Low signal
-
Bone marrow: Normally suppressed signal
CT VRT 3D image

CT image