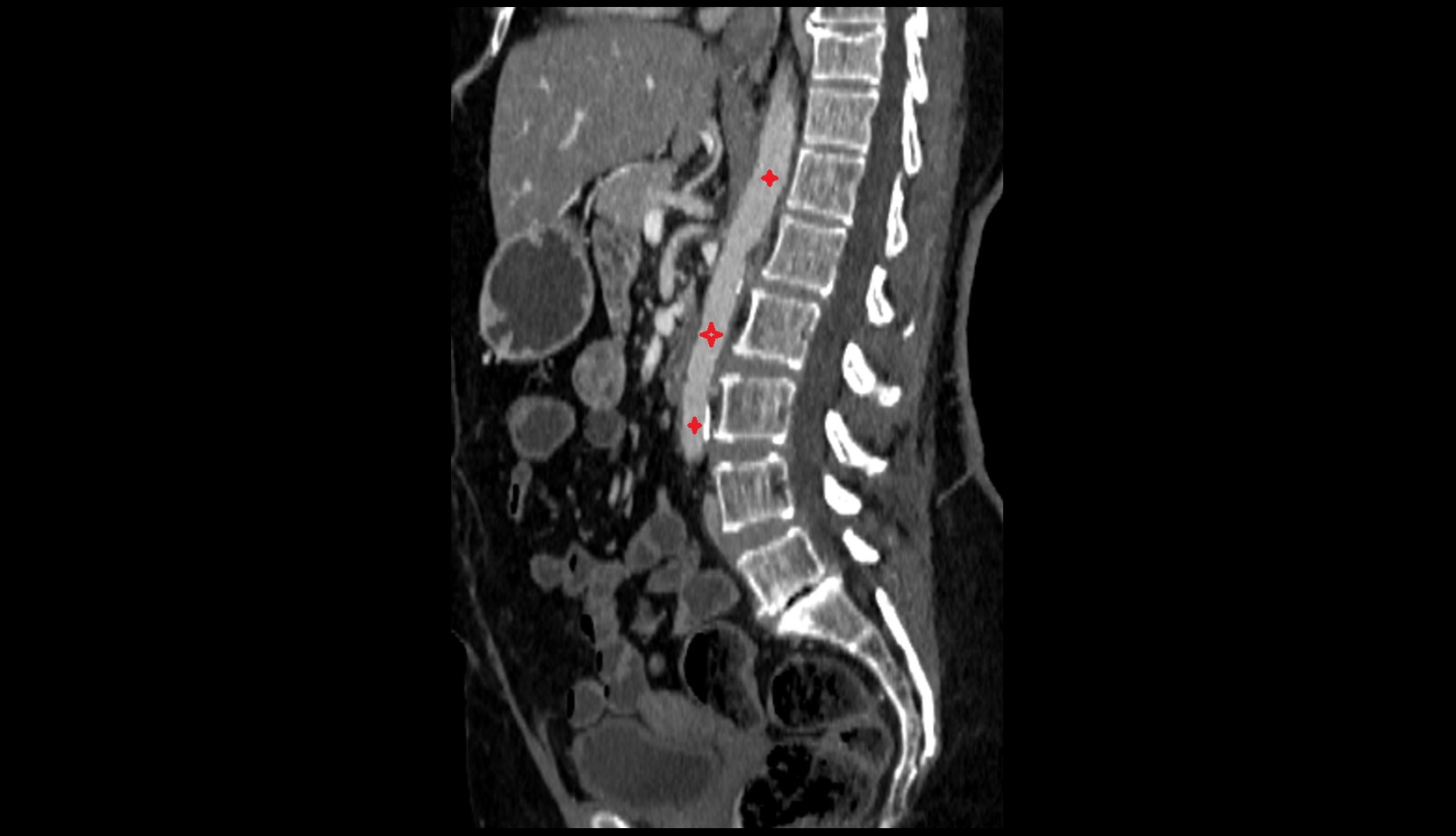
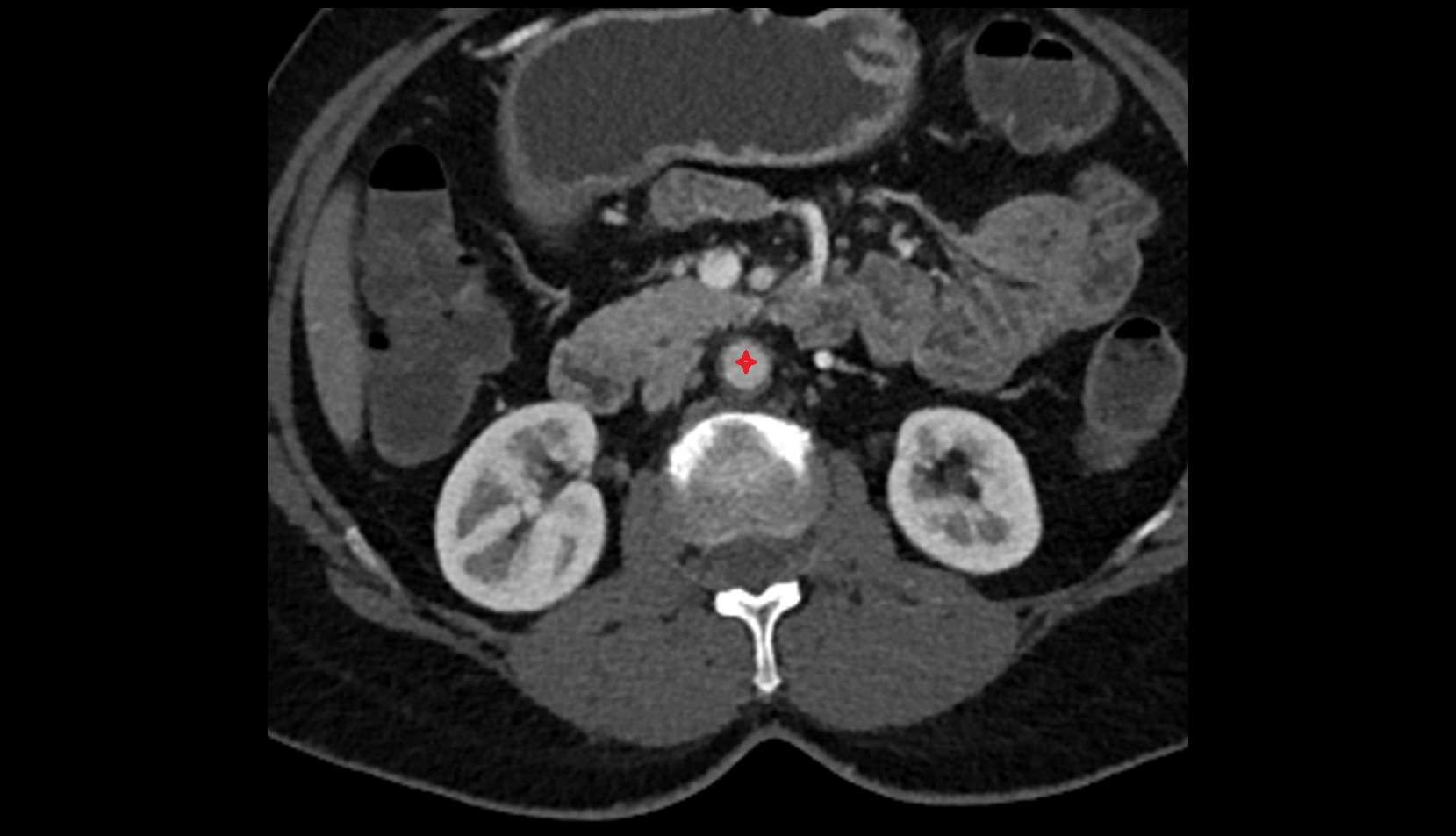
Topic
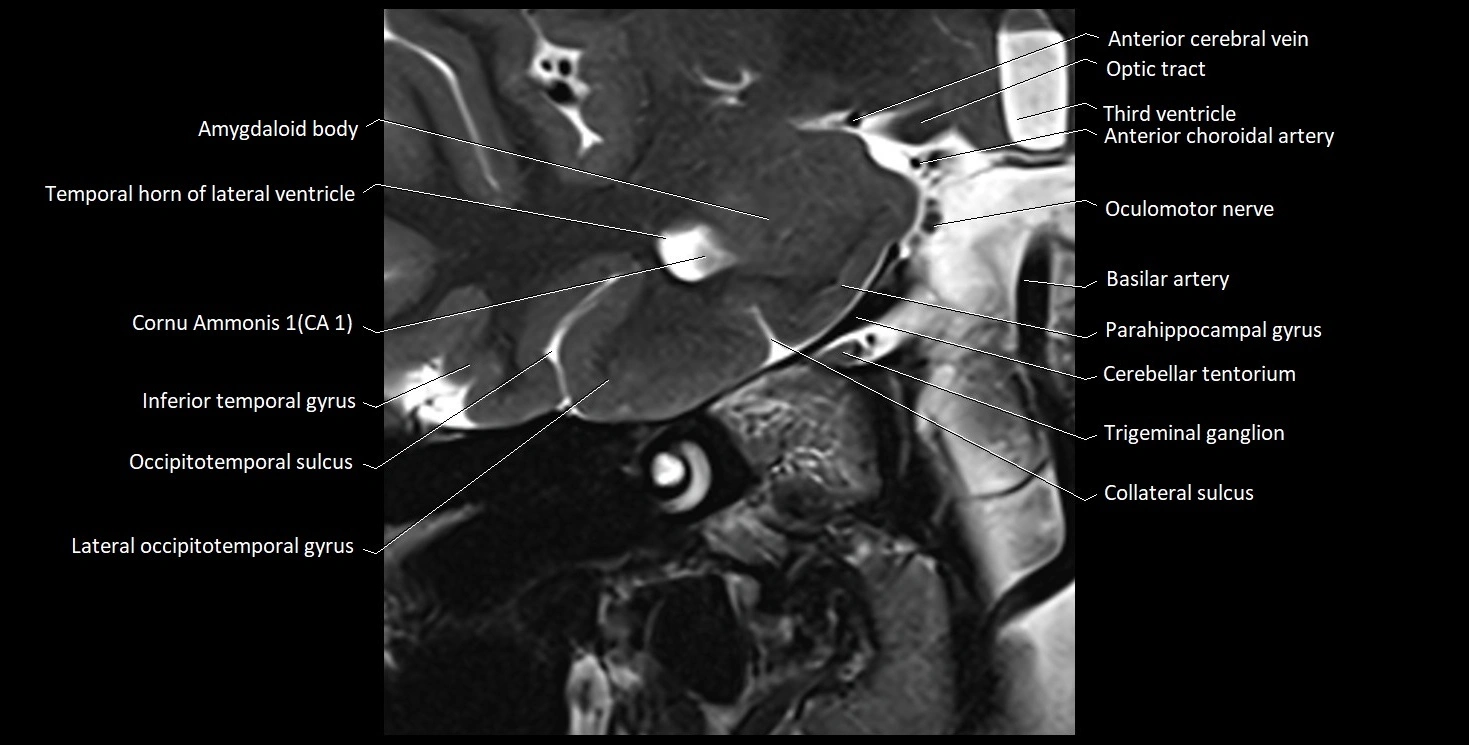
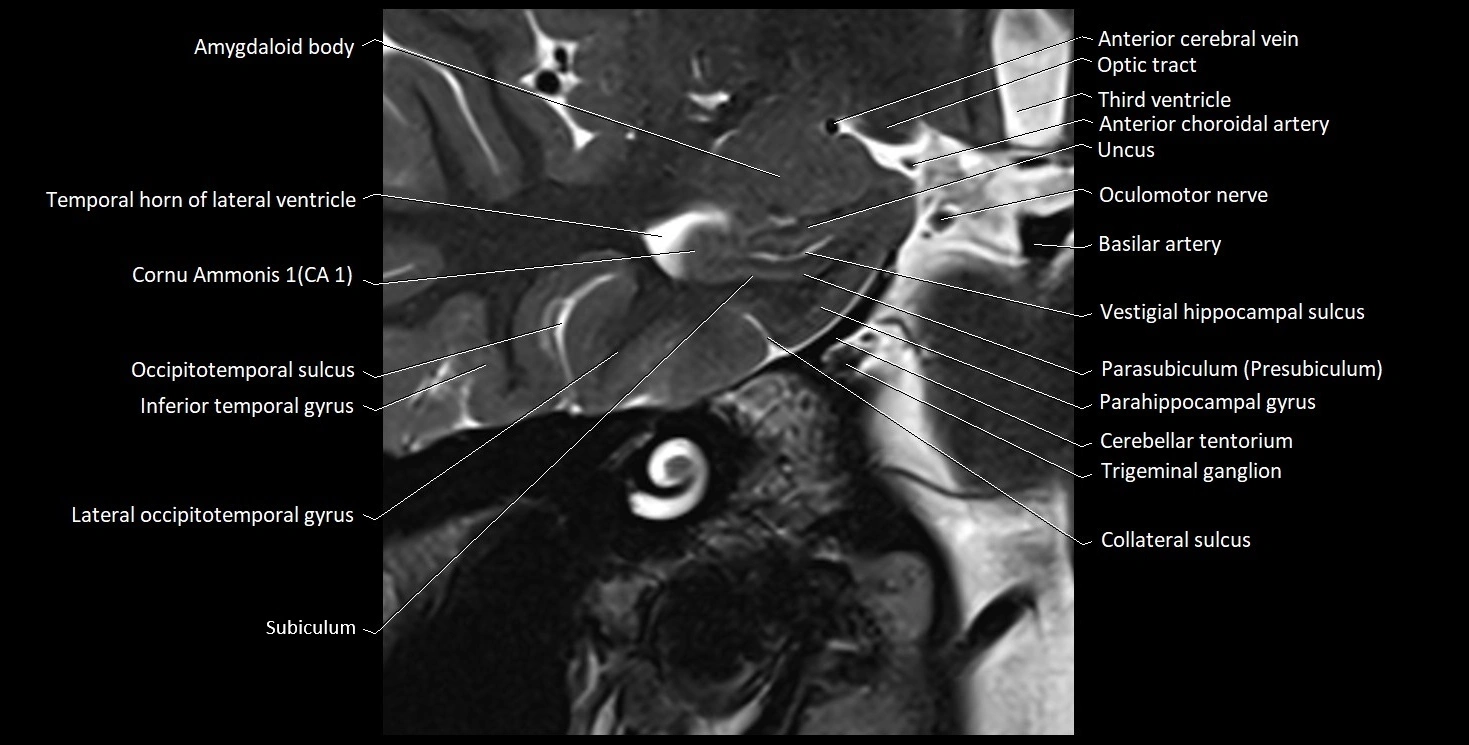
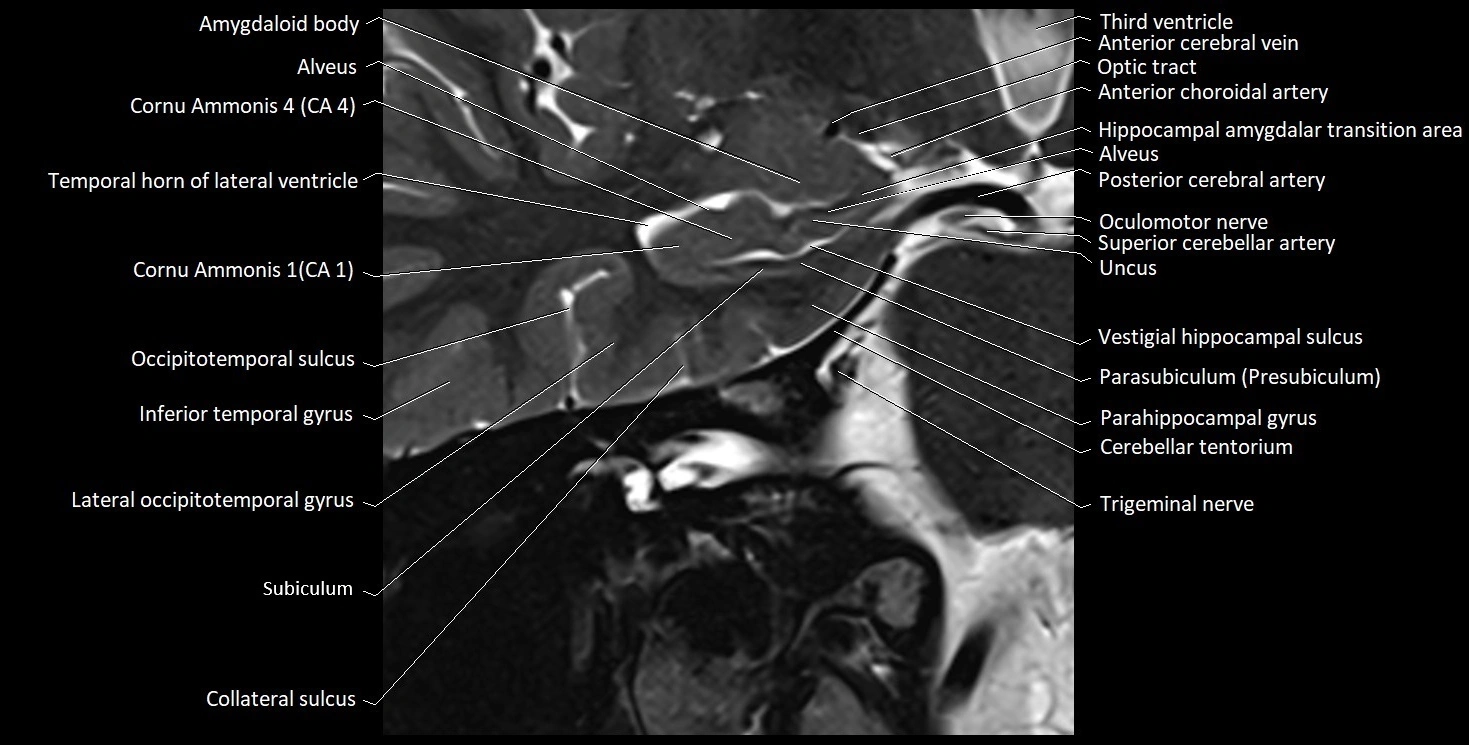
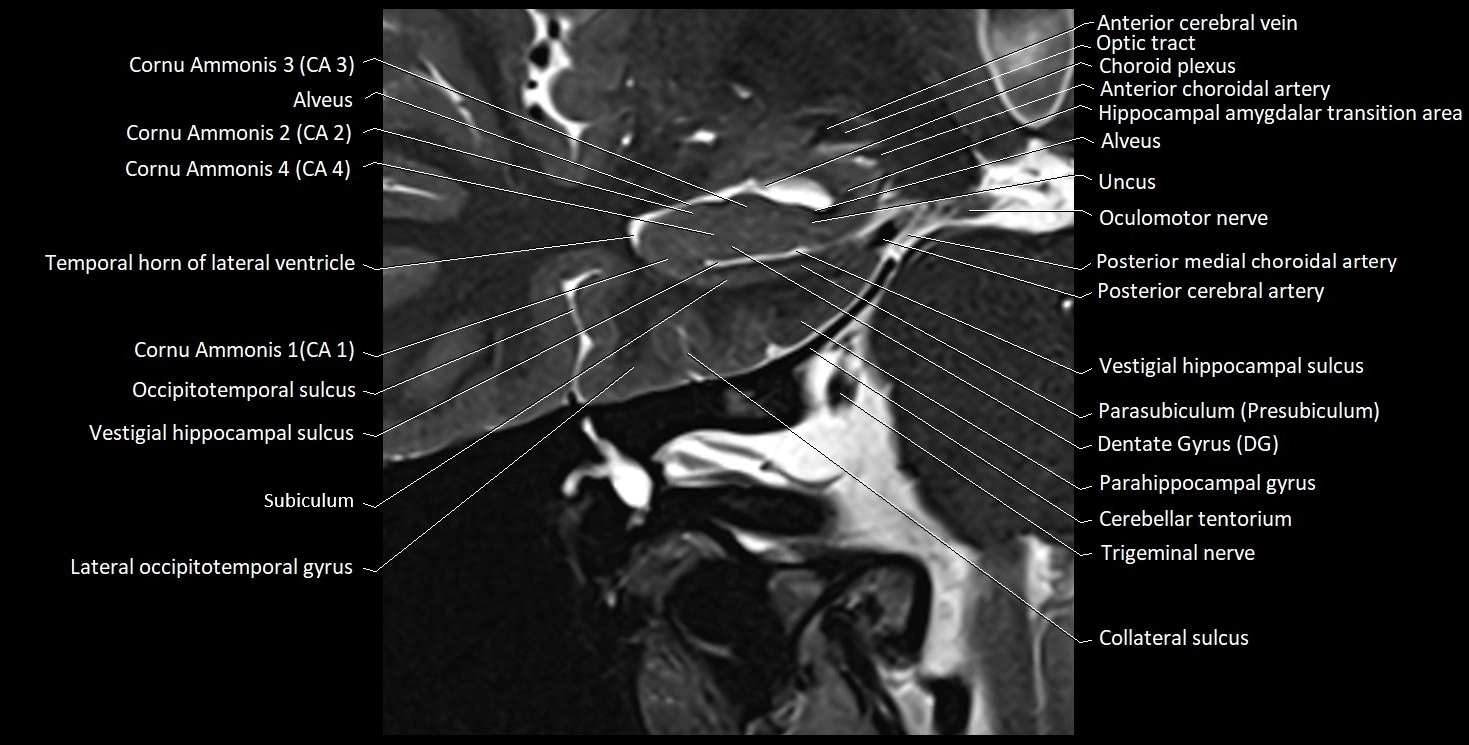
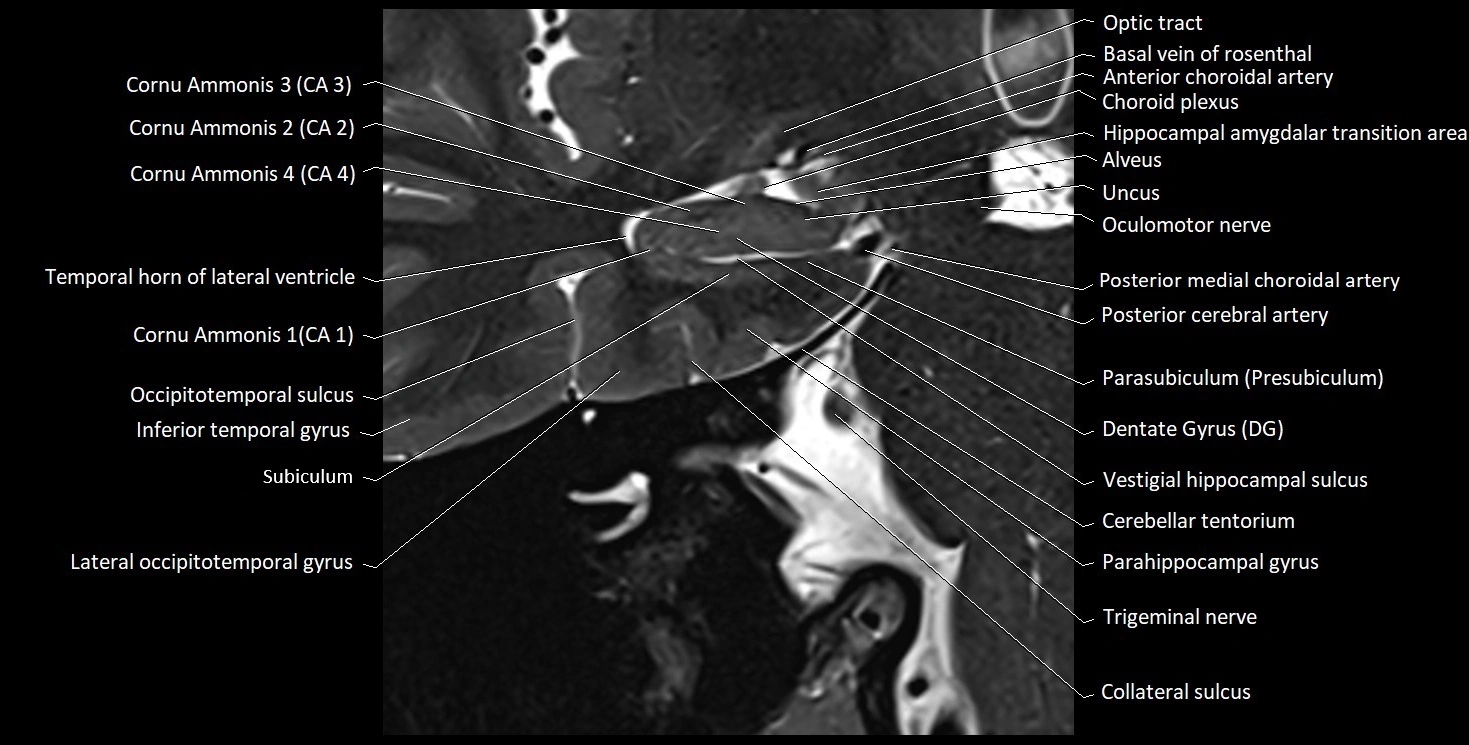
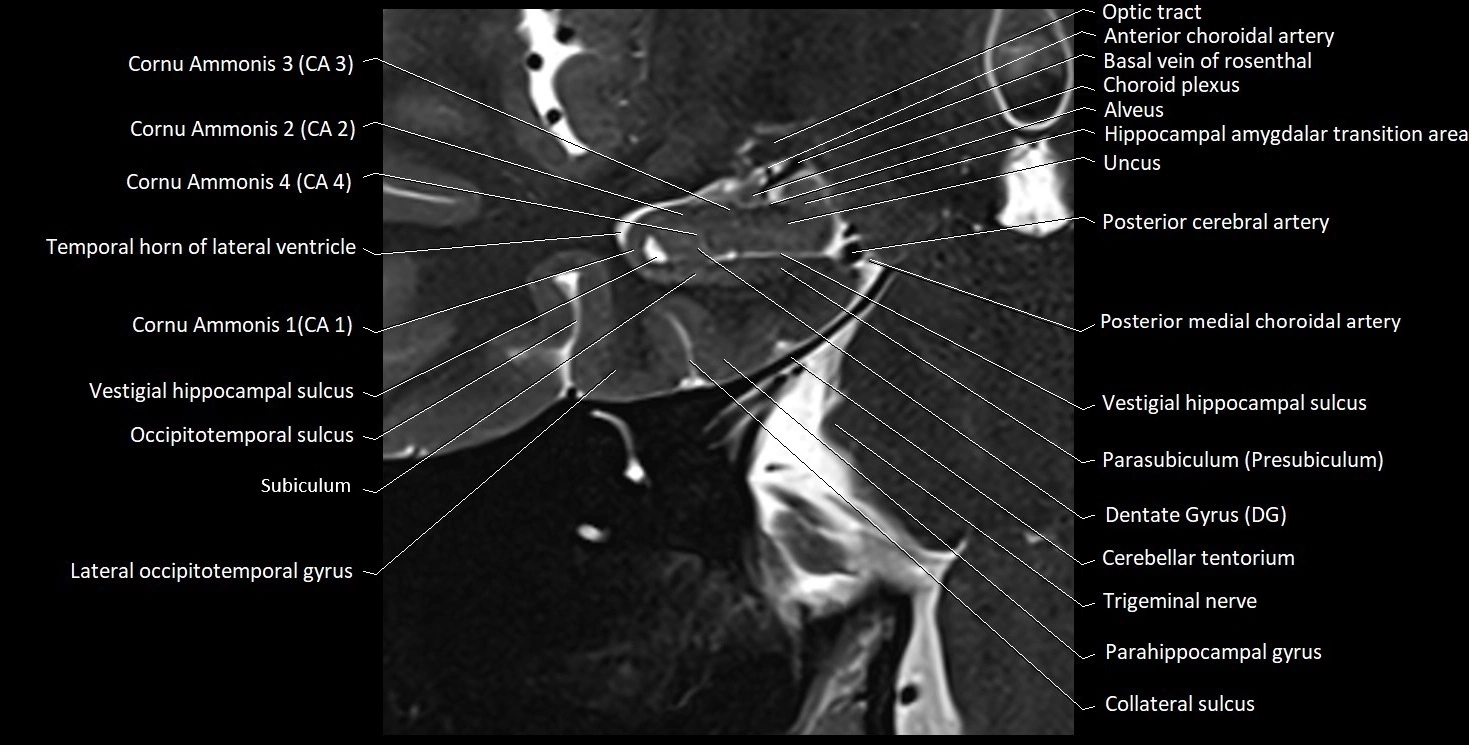
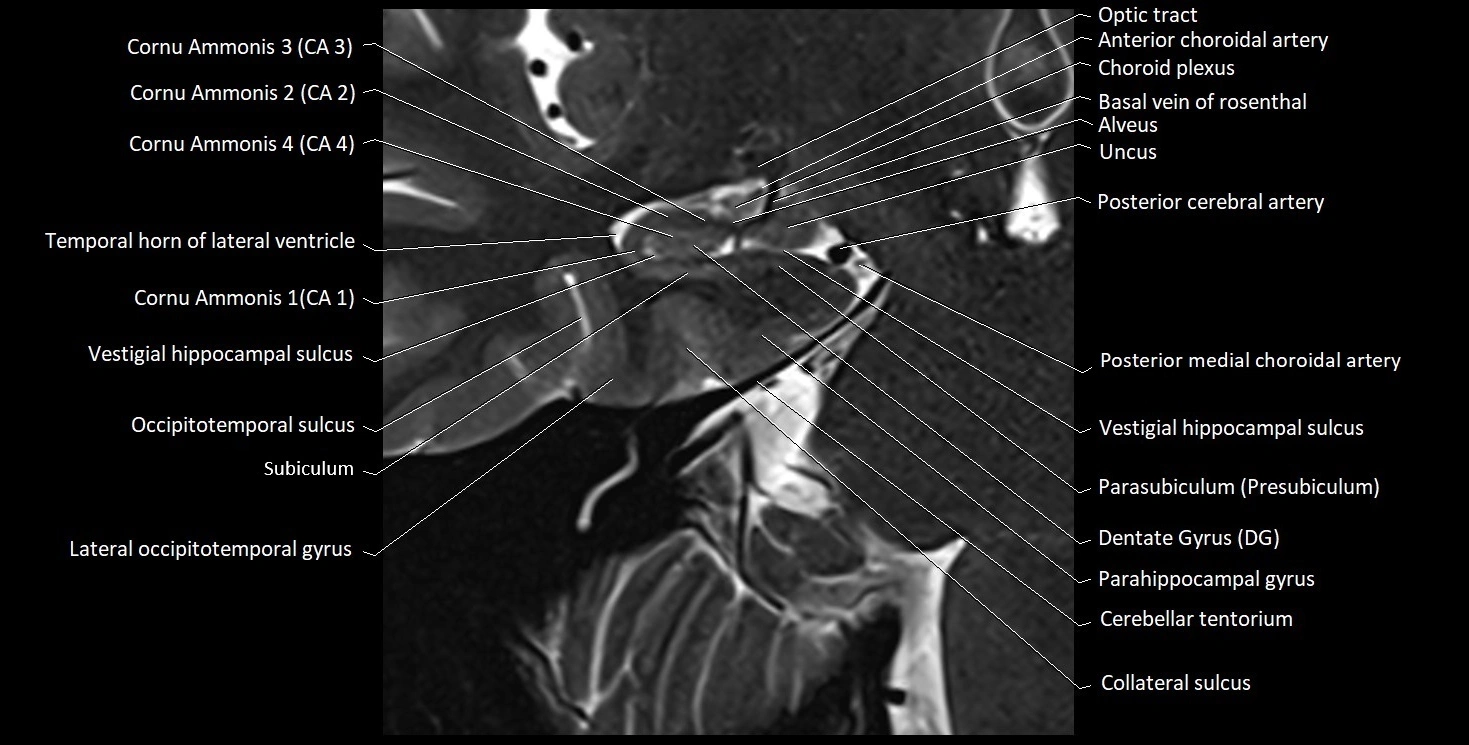
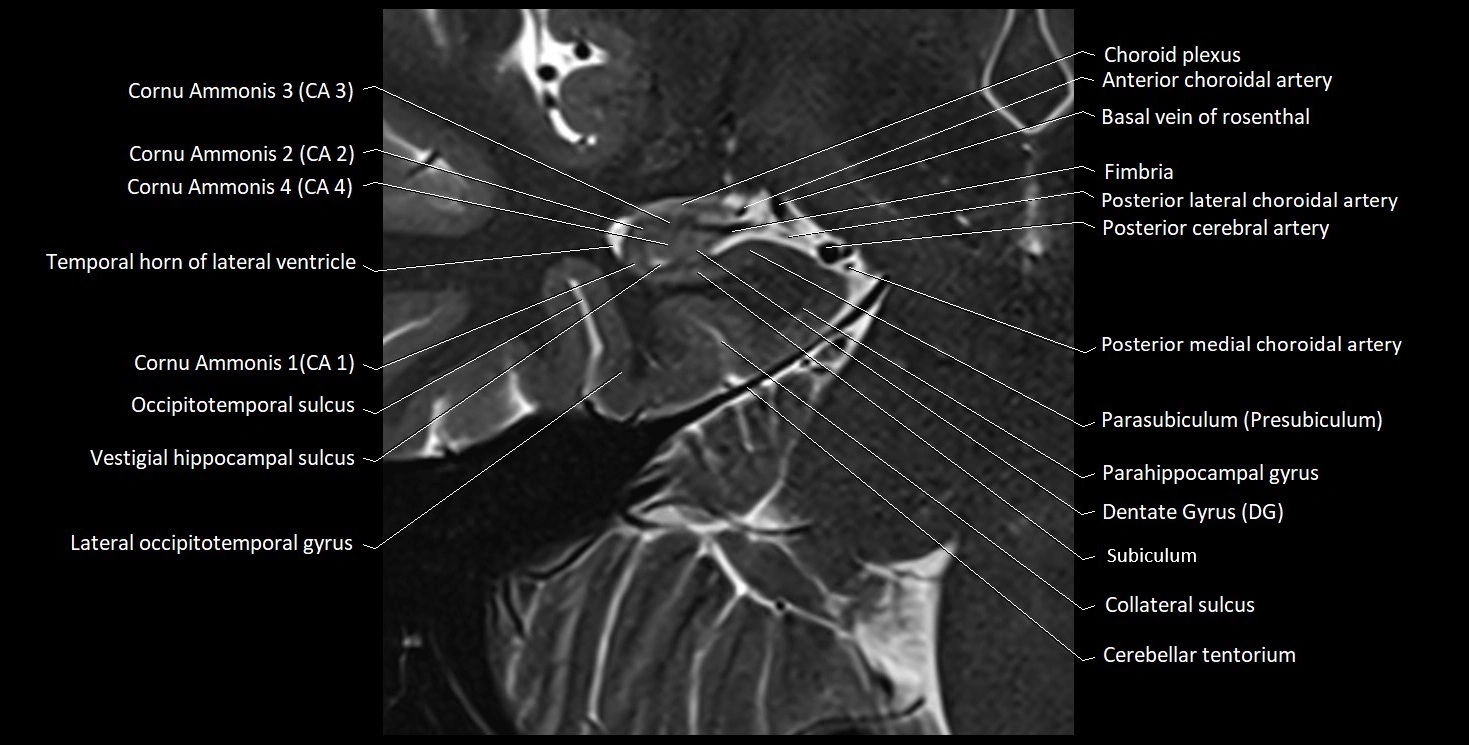
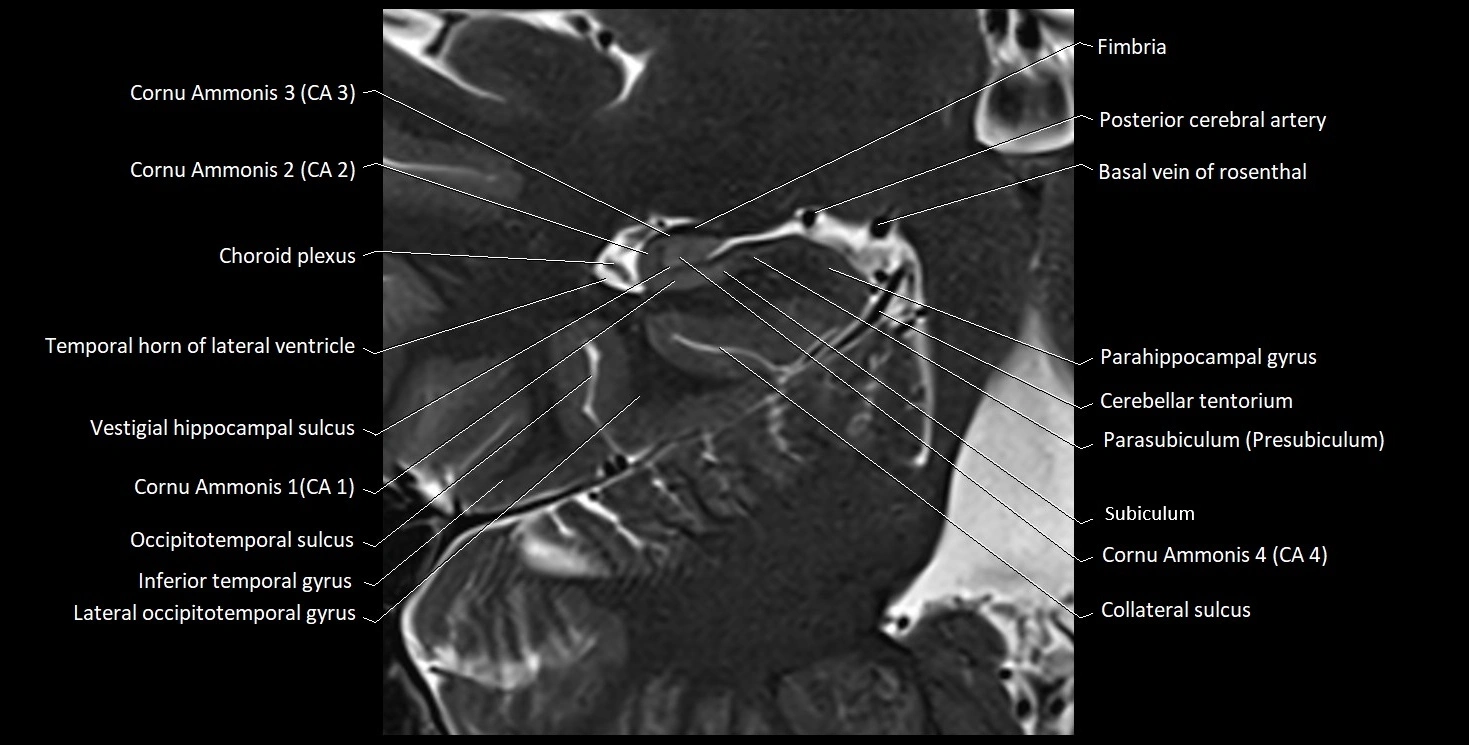
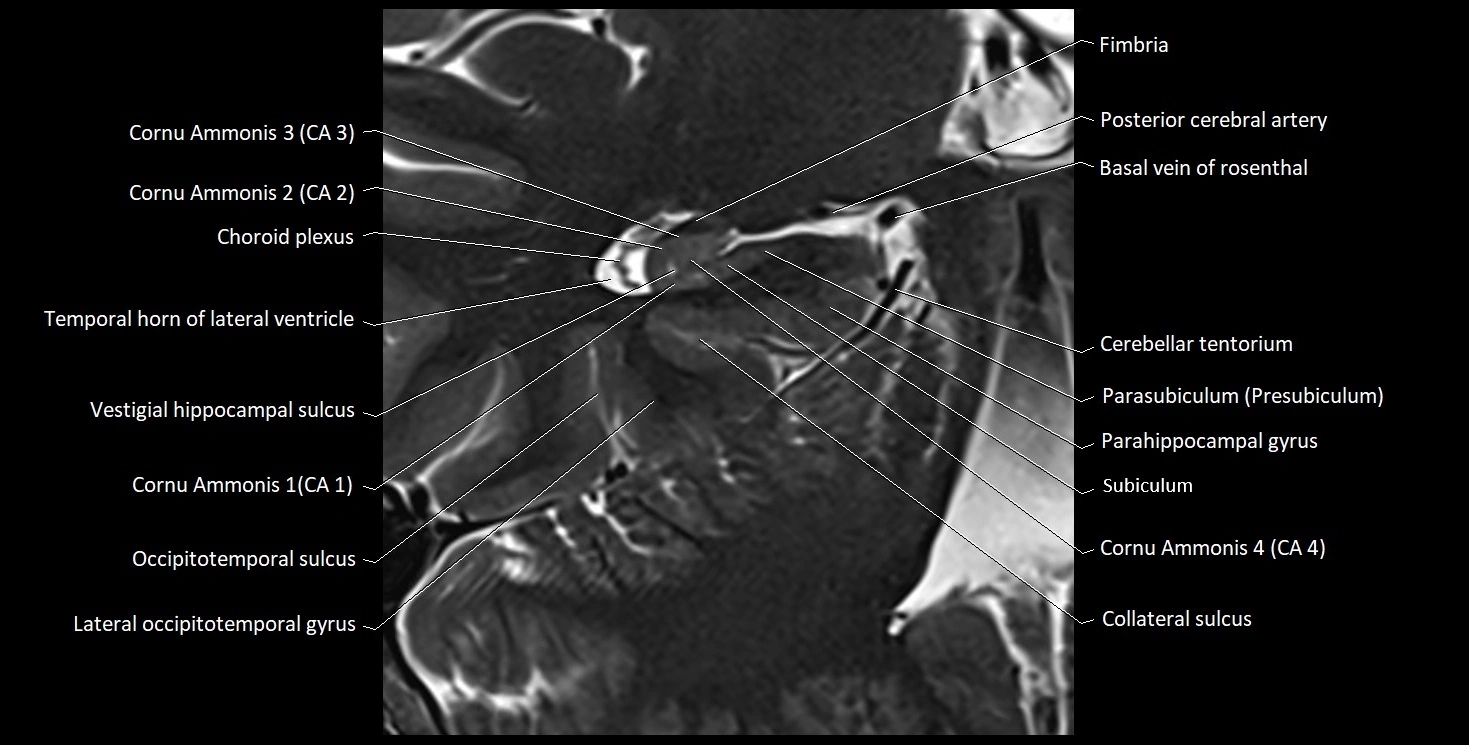
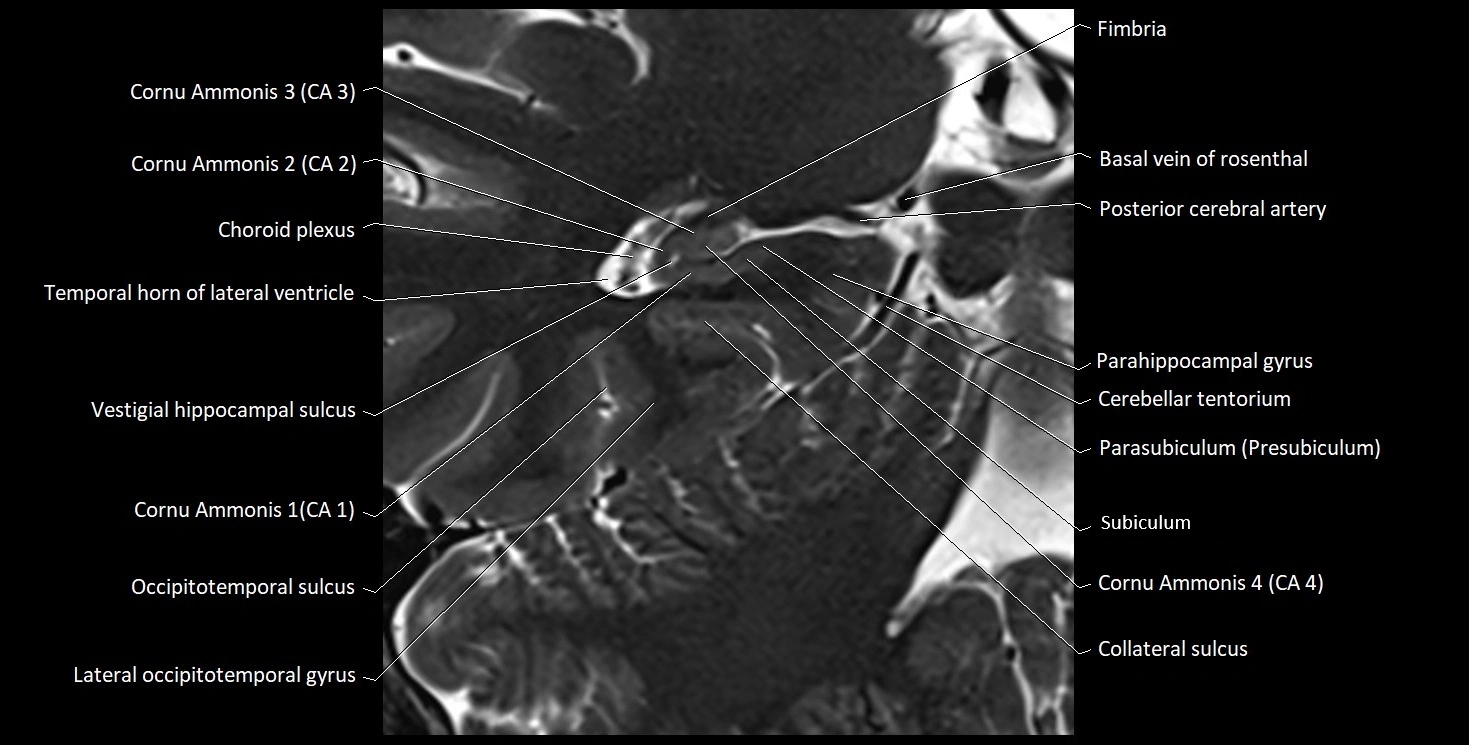
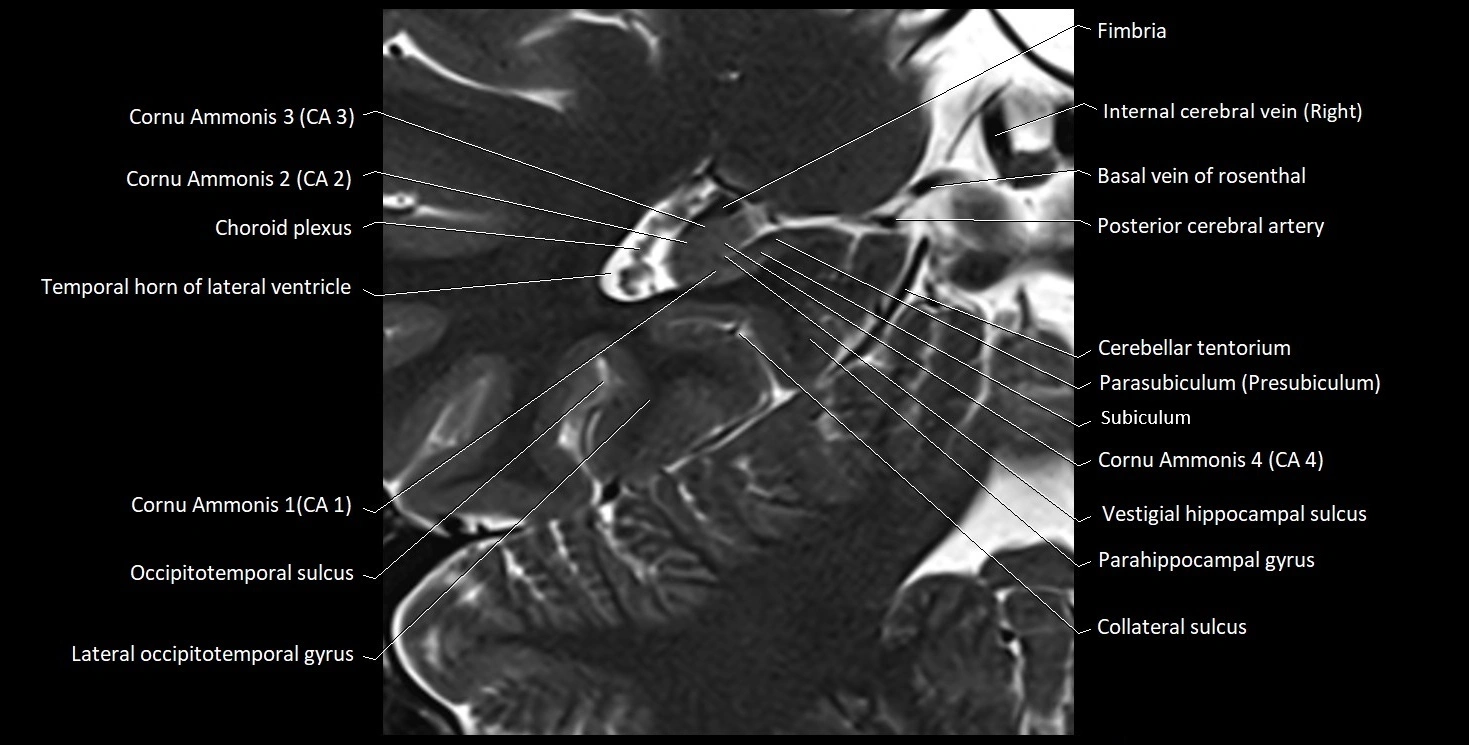
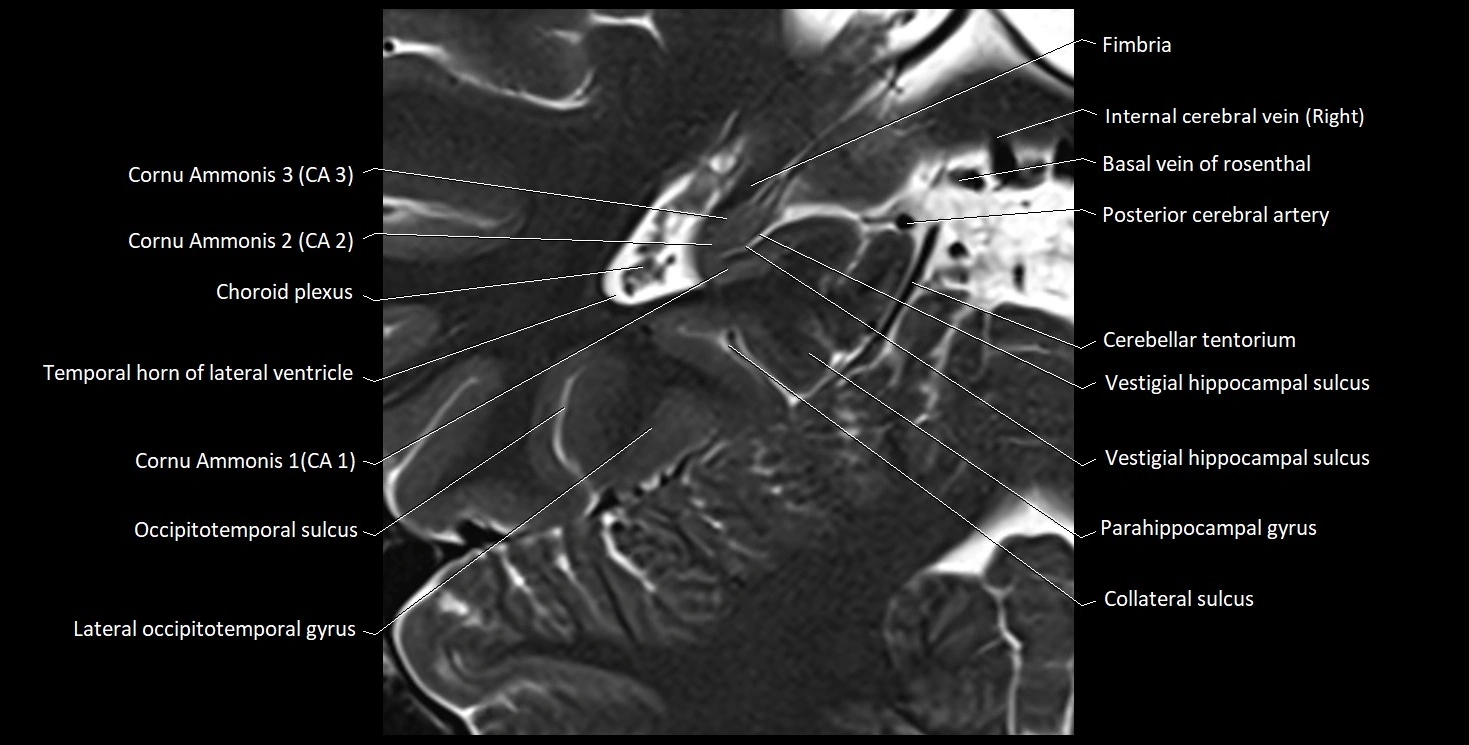
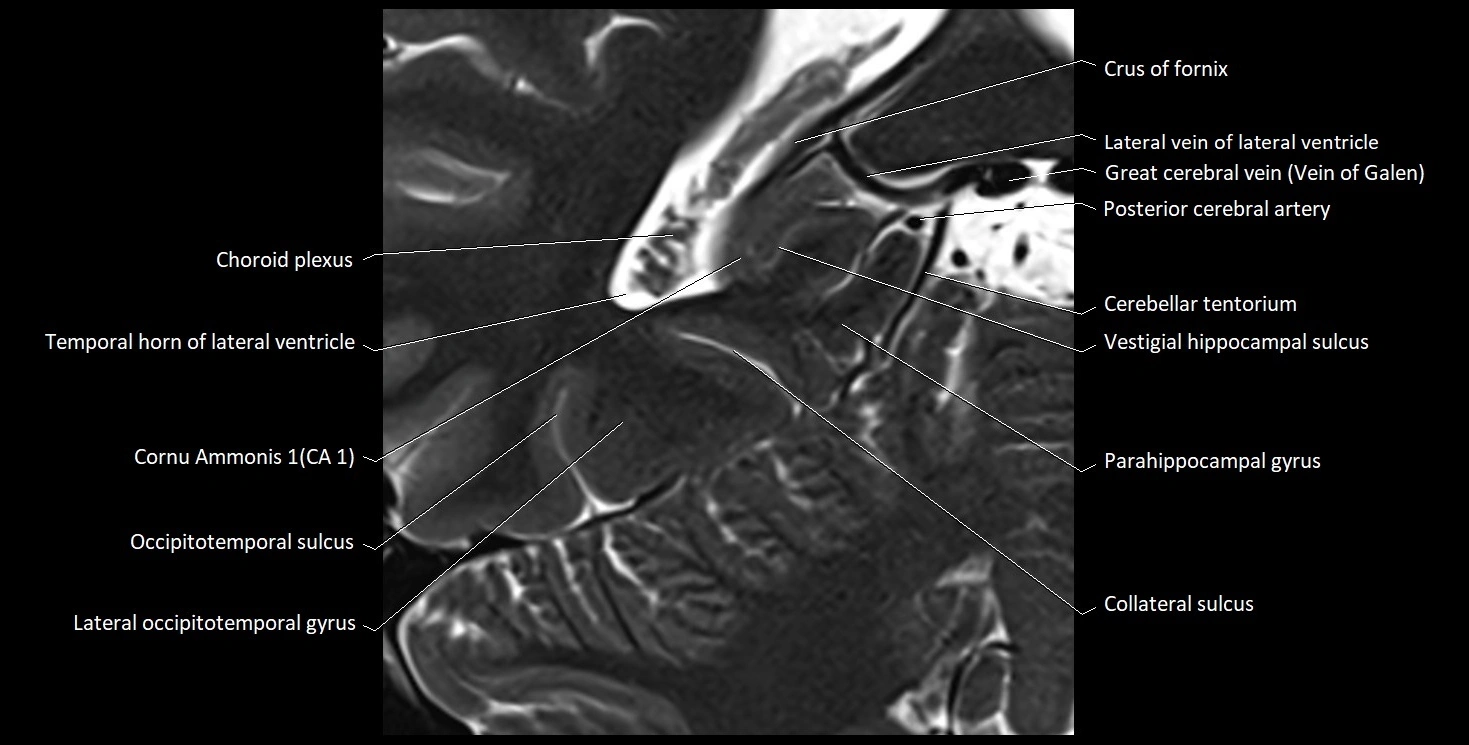
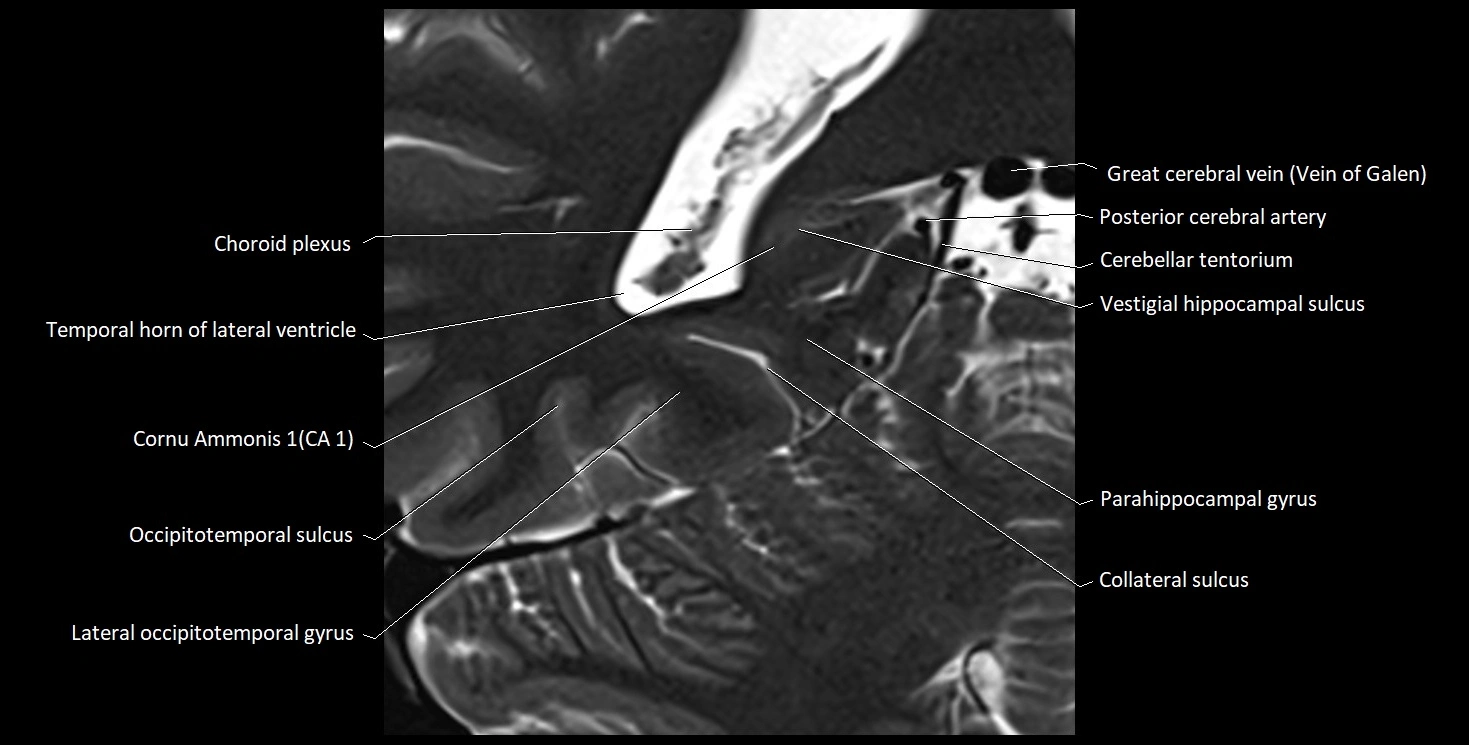
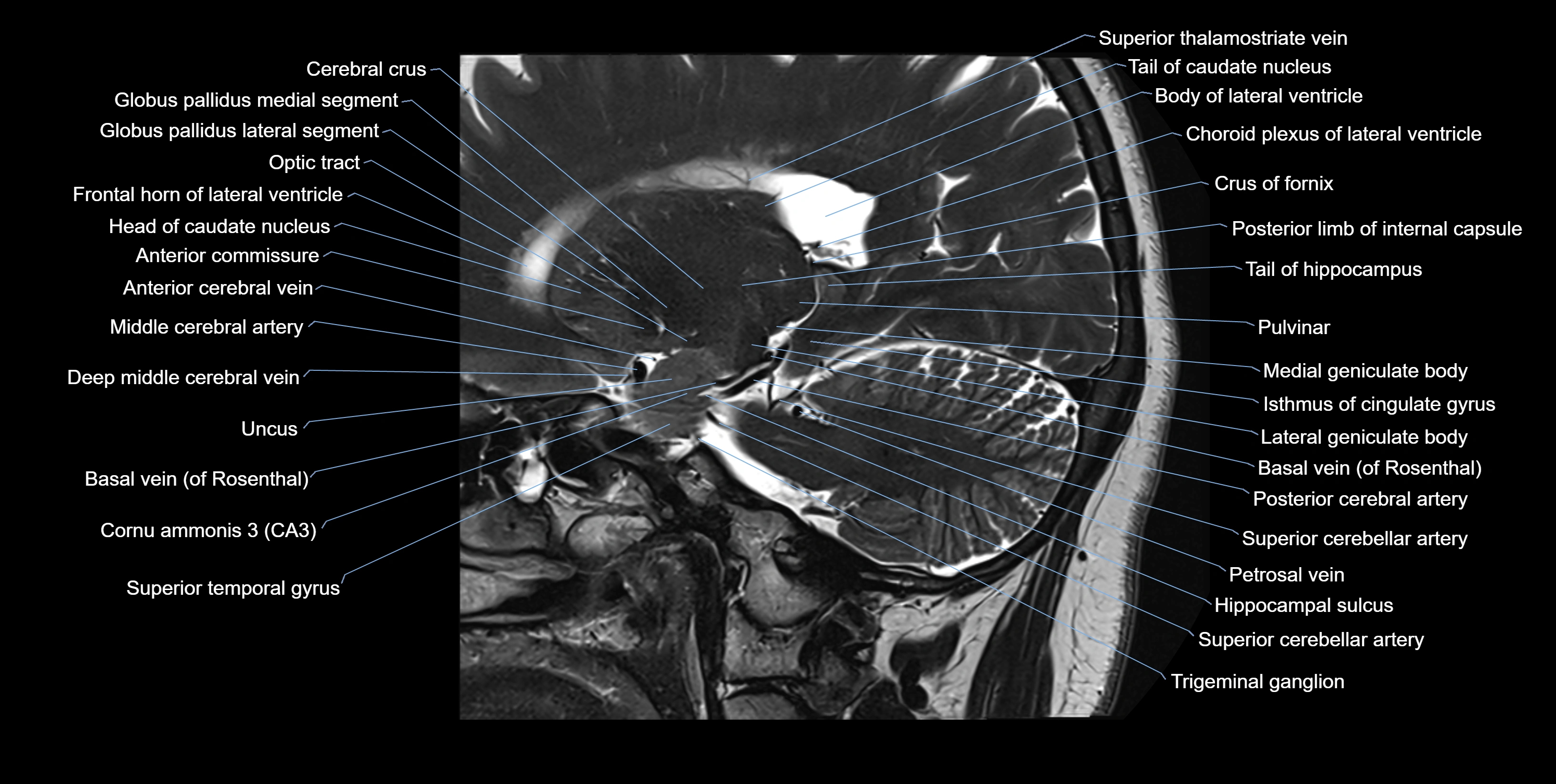
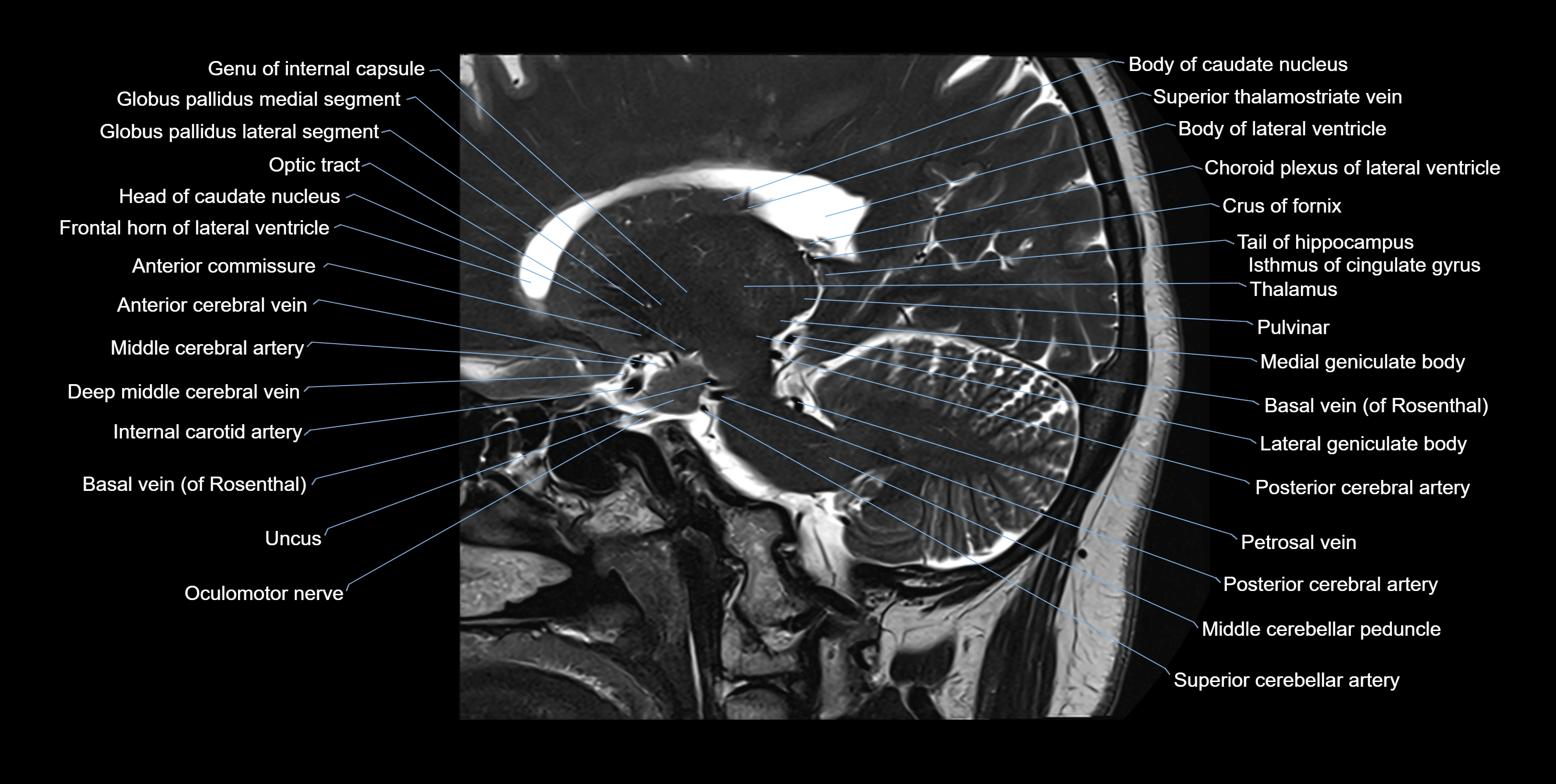
The alveus of the hippocampus is a thin, white matter layer covering the superior (ventricular) surface of the hippocampus within the temporal horn of the lateral ventricle. It consists of myelinated efferent fibers arising primarily from the pyramidal neurons of the hippocampus. These fibers converge medially to form the fimbria of the hippocampus, which continues posteriorly into the fornix, forming a crucial part of the Papez circuit involved in memory consolidation and emotional processing.
The alveus serves as the initial output pathway of the hippocampal formation, linking it to other limbic structures including the hypothalamus, mammillary bodies, and cingulate gyrus. Because of its intimate relationship with the hippocampal head and tail, it is often evaluated in cases of temporal lobe epilepsy, hippocampal sclerosis, and neurodegenerative diseases.
Synonyms
-
Hippocampal alveus
-
White matter layer of hippocampus
-
Subependymal hippocampal fibers
Location and Structure
-
Position: Lies on the ventricular (superior) surface of the hippocampus, beneath the ependyma of the inferior horn of the lateral ventricle.
-
Composition: A thin sheet of myelinated axons derived mainly from hippocampal pyramidal cells.
-
Course: Fibers run medially along the hippocampal surface to form the fimbria of the hippocampus, which curves upward and backward into the fornix.
-
Relations:
-
Superiorly: Ependyma and CSF of the temporal horn of the lateral ventricle
-
Inferiorly: Pyramidal cell layer of the hippocampus (CA1 region)
-
Medially: Fimbria and fornix
-
Laterally: Temporal lobe white matter and parahippocampal gyrus
-
Function
-
Efferent conduction: Acts as the main output pathway from hippocampal pyramidal neurons to the fimbria and fornix.
-
Integration: Connects hippocampus with other limbic system components for memory encoding and retrieval.
-
White matter tract: Ensures transmission of processed signals to hypothalamic and thalamic nuclei within the Papez circuit.
-
Clinical role: Structural and signal abnormalities may indicate hippocampal sclerosis, ischemia, or demyelination.
Clinical Significance
-
Hippocampal sclerosis: Common in temporal lobe epilepsy; the alveus may appear thinned or with altered signal intensity.
-
Atrophy: Seen in Alzheimer’s disease and medial temporal lobe atrophy syndromes.
-
Tumor invasion: Gliomas or metastases may involve the hippocampal alveus region.
-
Surgical relevance: Key landmark in selective amygdalohippocampectomy procedures.
-
Imaging relevance: Evaluated in volumetric hippocampal MRI, epilepsy mapping, and neurodegenerative disease imaging.
MRI Appearance
T1-weighted images:
-
Alveus: Thin linear high signal band (due to myelinated fibers) overlying the hippocampal gray matter.
-
Hippocampal gray matter: Intermediate signal intensity.
-
CSF of lateral ventricle: Dark (low signal).
-
Pathology:
-
Sclerosis: Alveus becomes indistinct, with reduced T1 signal and hippocampal atrophy.
-
Edema or gliosis: Diffuse hypointensity and blurring of alvear margins.
-
T2-weighted images:
-
Alveus: Low signal line overlying brighter hippocampal gray matter.
-
CSF: Bright hyperintense.
-
Pathology:
-
Gliosis or demyelination: Causes increased signal in the alvear region.
-
Hippocampal sclerosis: Gray-white differentiation becomes indistinct.
-
Edema: Hyperintense change surrounding alveus.
-
FLAIR (Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery):
-
Normal alveus: Appears as a thin hypointense line beneath dark ventricular CSF.
-
Hippocampal sclerosis: Shows hyperintense hippocampal parenchyma with loss of alvear definition.
-
Ischemia or inflammation: Hyperintense periventricular signal with cortical thinning.
-
Neoplasm: May appear as focal hyperintensity with mass effect or architectural distortion.
DWI (Diffusion-Weighted Imaging):
-
Normal alveus: Isointense to adjacent white matter with no restricted diffusion.
-
Acute ischemia: Bright restricted diffusion along hippocampal ridge and alvear layer with low ADC.
-
Tumor infiltration: Variable restriction depending on cellular density.
-
Encephalitis: Patchy restricted diffusion within hippocampal head and alveus.
T1 Fat-Sat Post-Contrast:
-
Normal alveus: No enhancement.
-
Enhancing pathology:
-
Tumor invasion or encephalitis: Focal linear or patchy enhancement along alvear region.
-
Post-surgical or inflammatory change: Mild enhancement at margins of hippocampal head.
-
Vascular lesions: May show curvilinear enhancement along hippocampal sulcus.
-
CT Appearance
Non-Contrast CT:
-
Alveus: Not individually visualized; merges with hippocampal gray-white matter.
-
Hippocampus: Homogeneous gray matter density within medial temporal lobe.
-
Pathology:
-
Infarct: Subtle hypodensity or loss of gray-white distinction.
-
Calcification or hemorrhage: Hyperdense foci within hippocampal formation.
-
Atrophy: Temporal horn dilation and volume loss in hippocampal area.
-
Post-Contrast CT:
-
Normal alveus: No visible enhancement.
-
Enhancing lesions:
-
Glioma or metastasis: Focal cortical or subcortical enhancement near medial temporal horn..
-
Vascular malformations: Curvilinear enhancing structures adjacent to alvear surface.
-
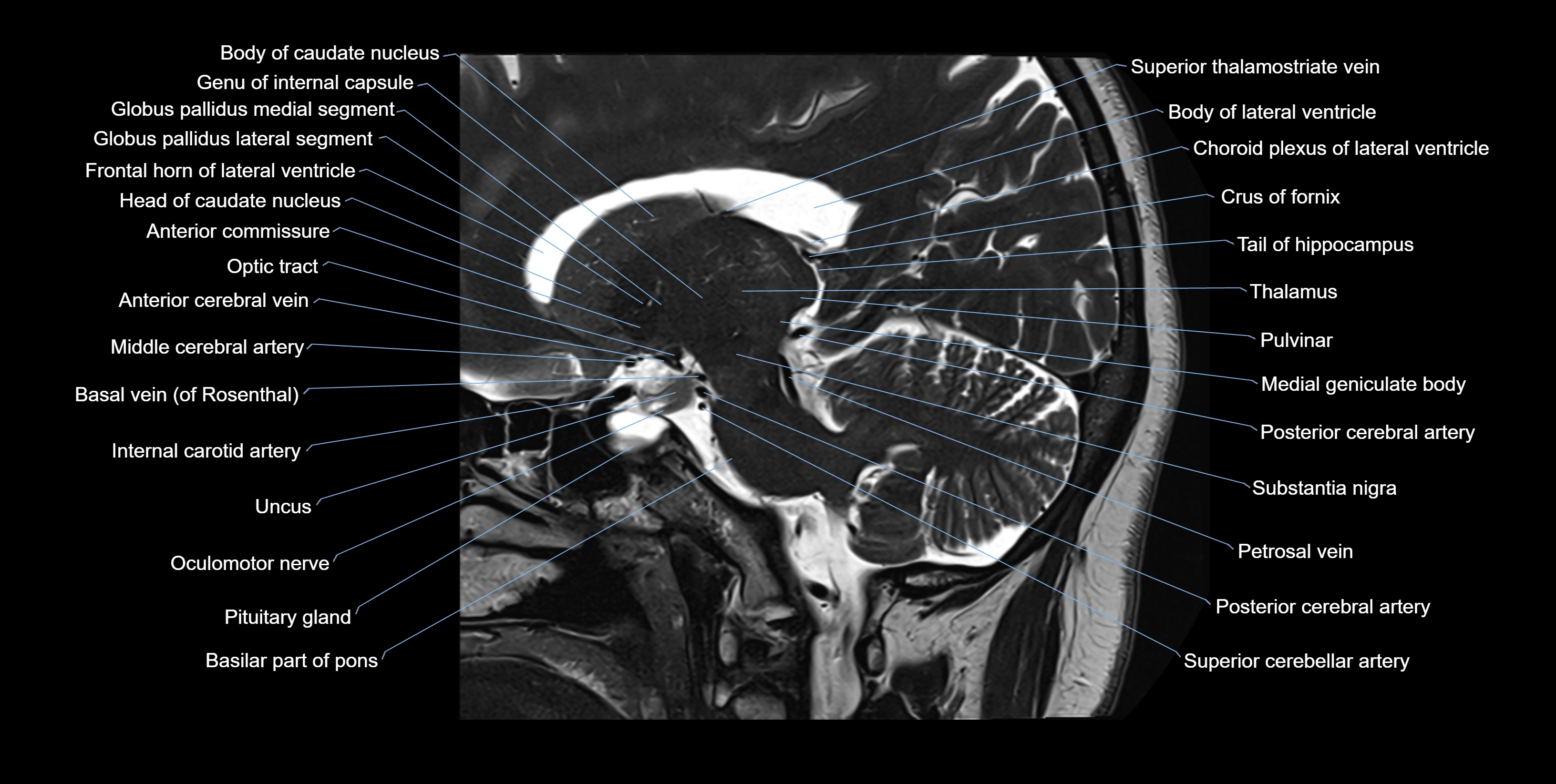
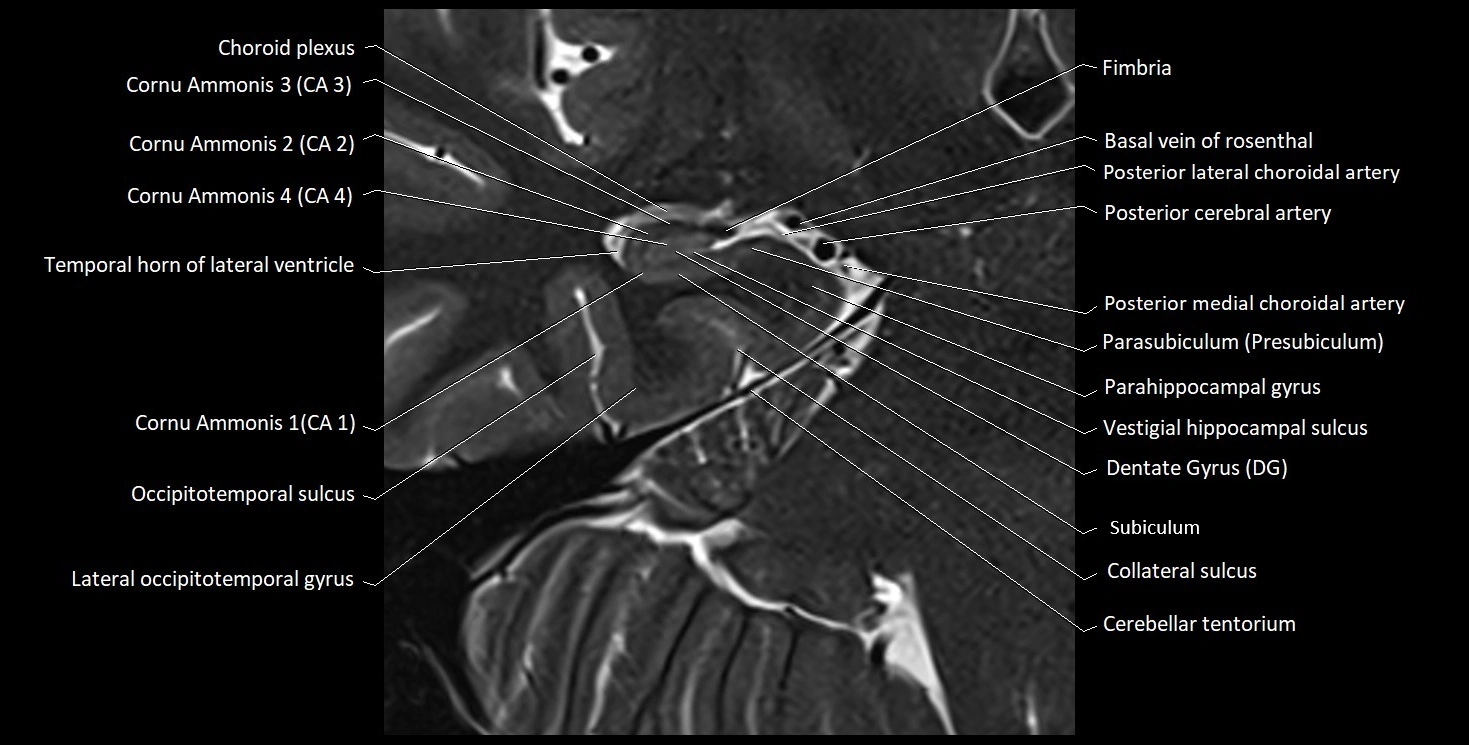
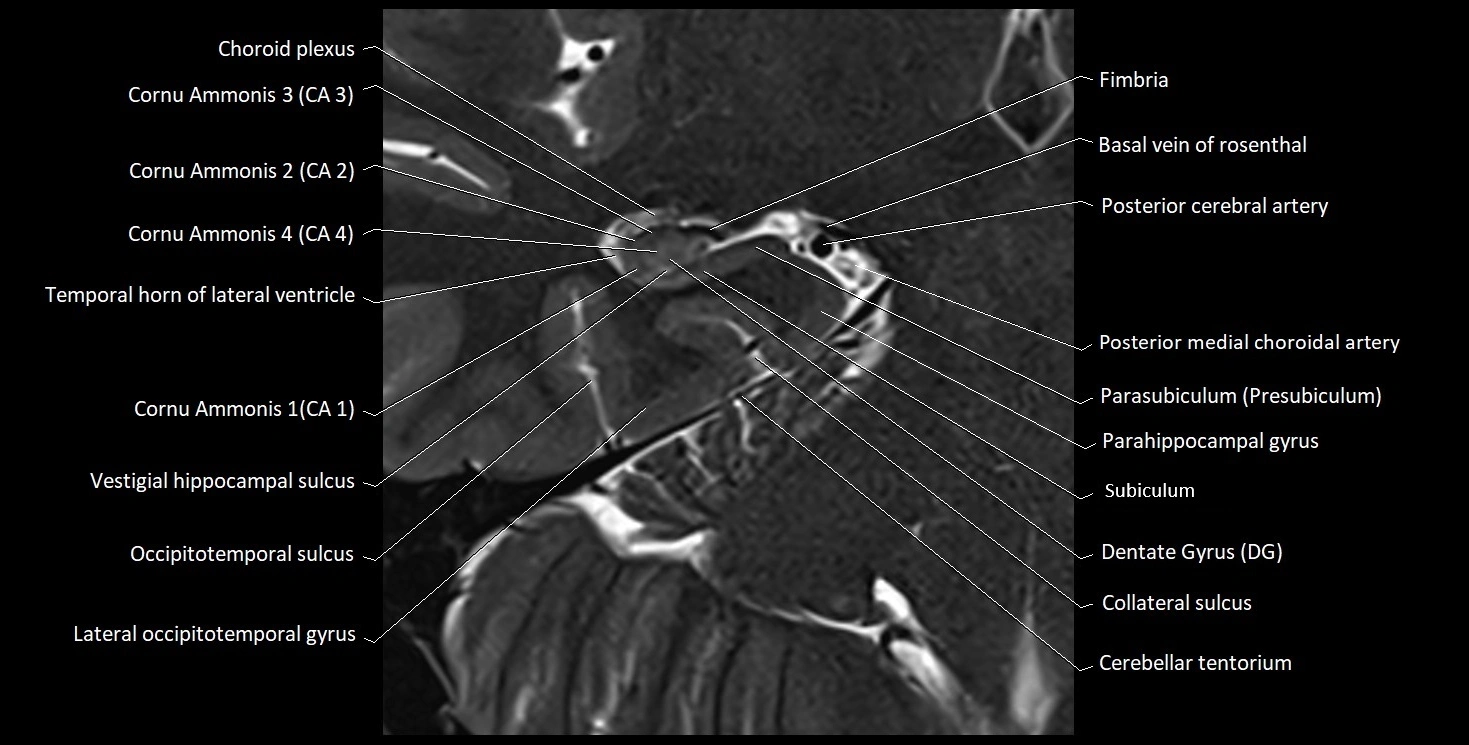
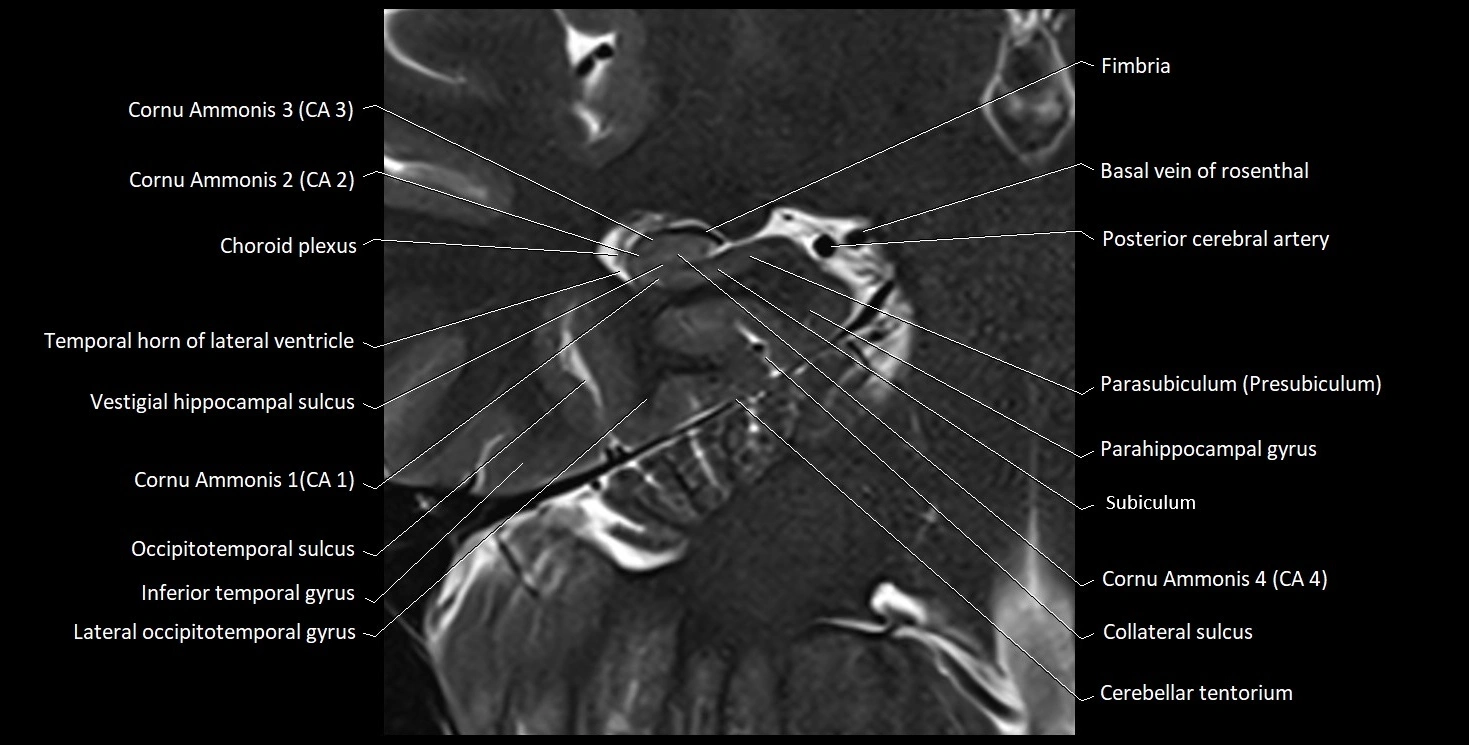
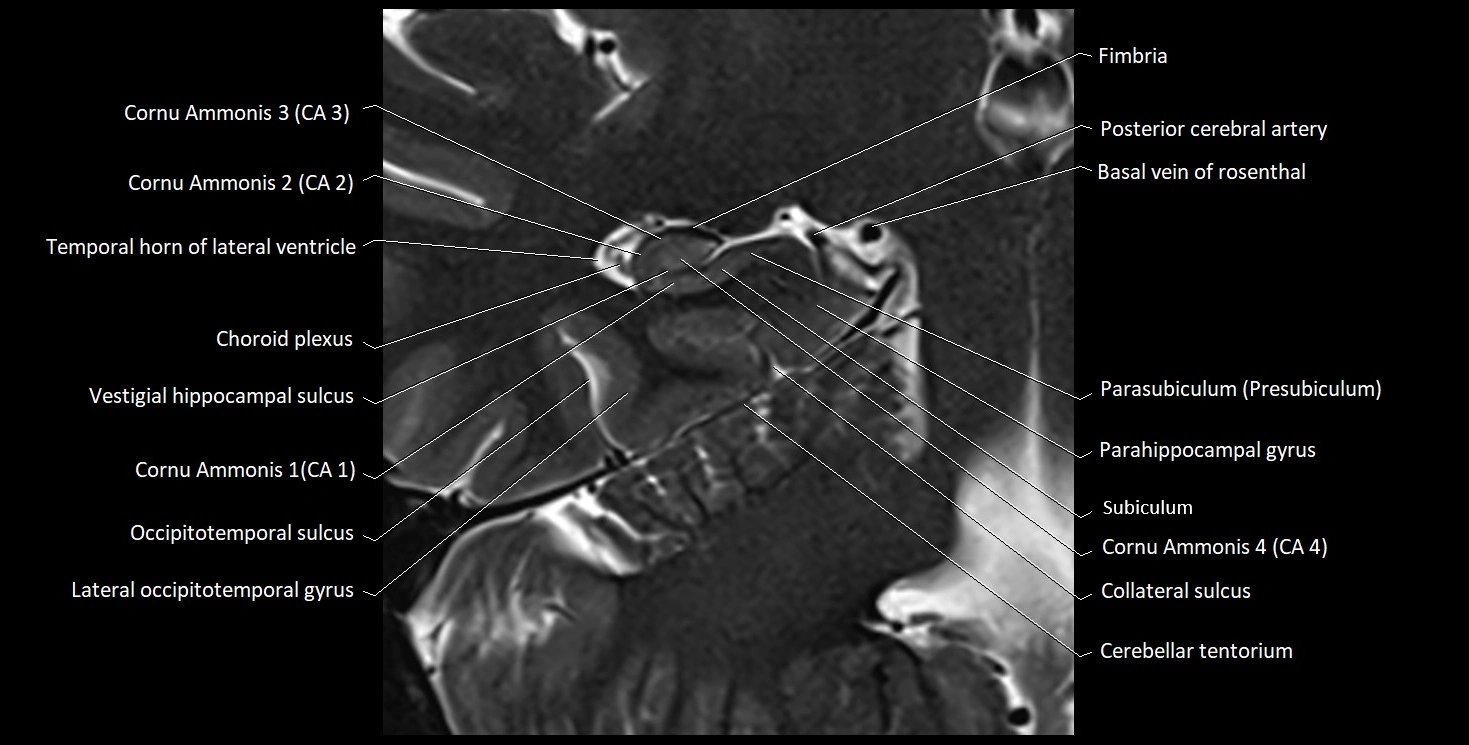
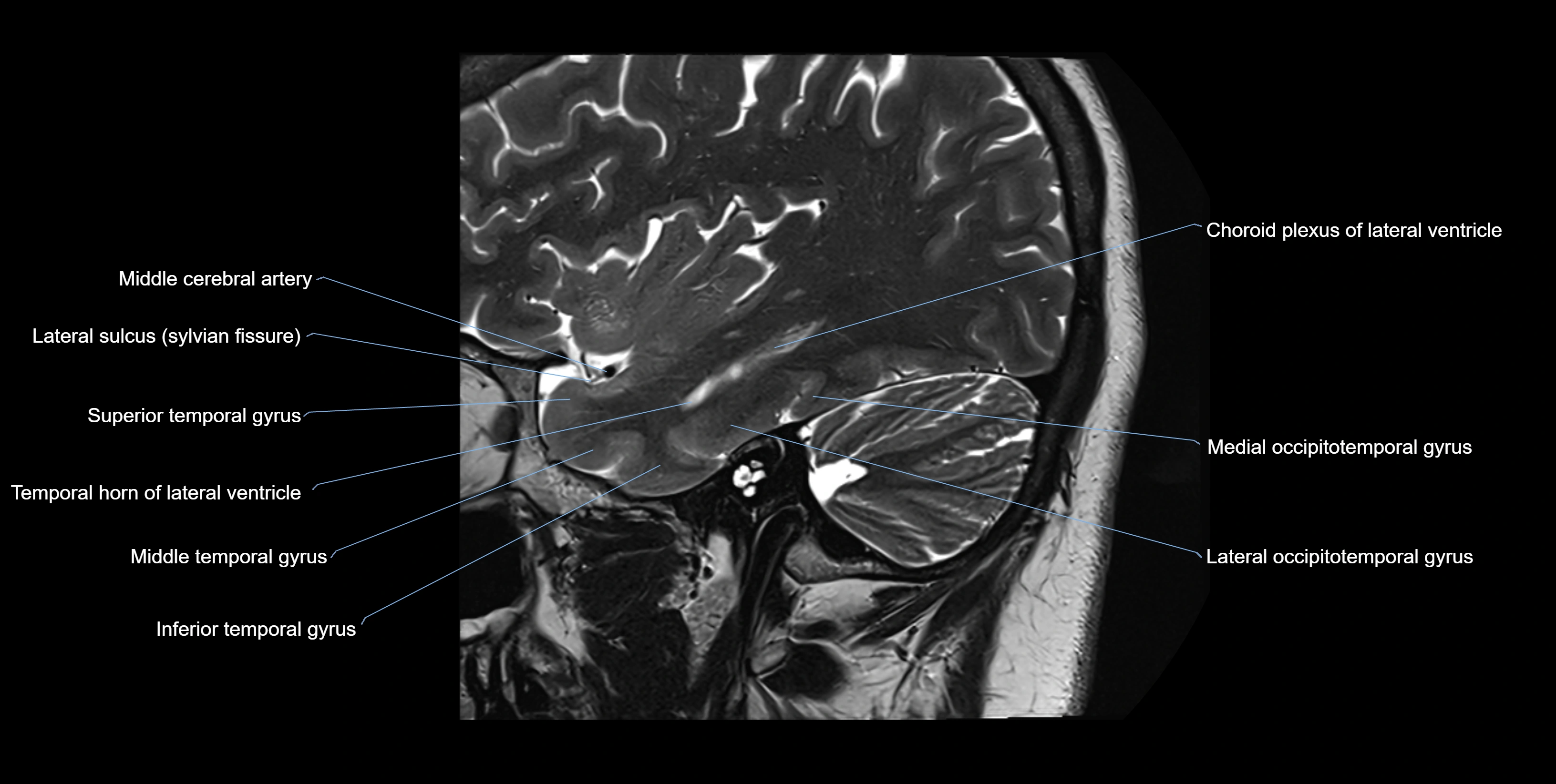
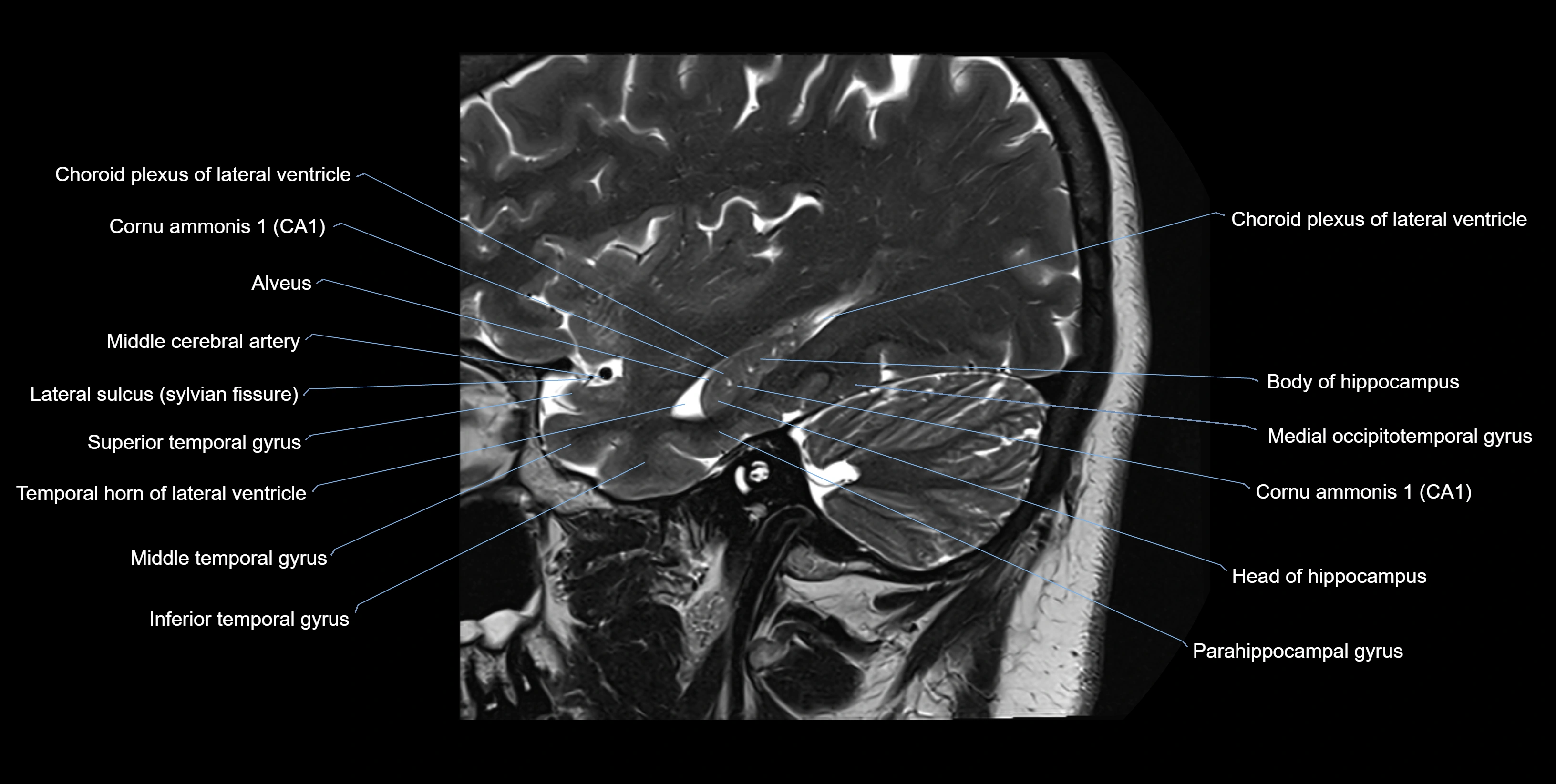
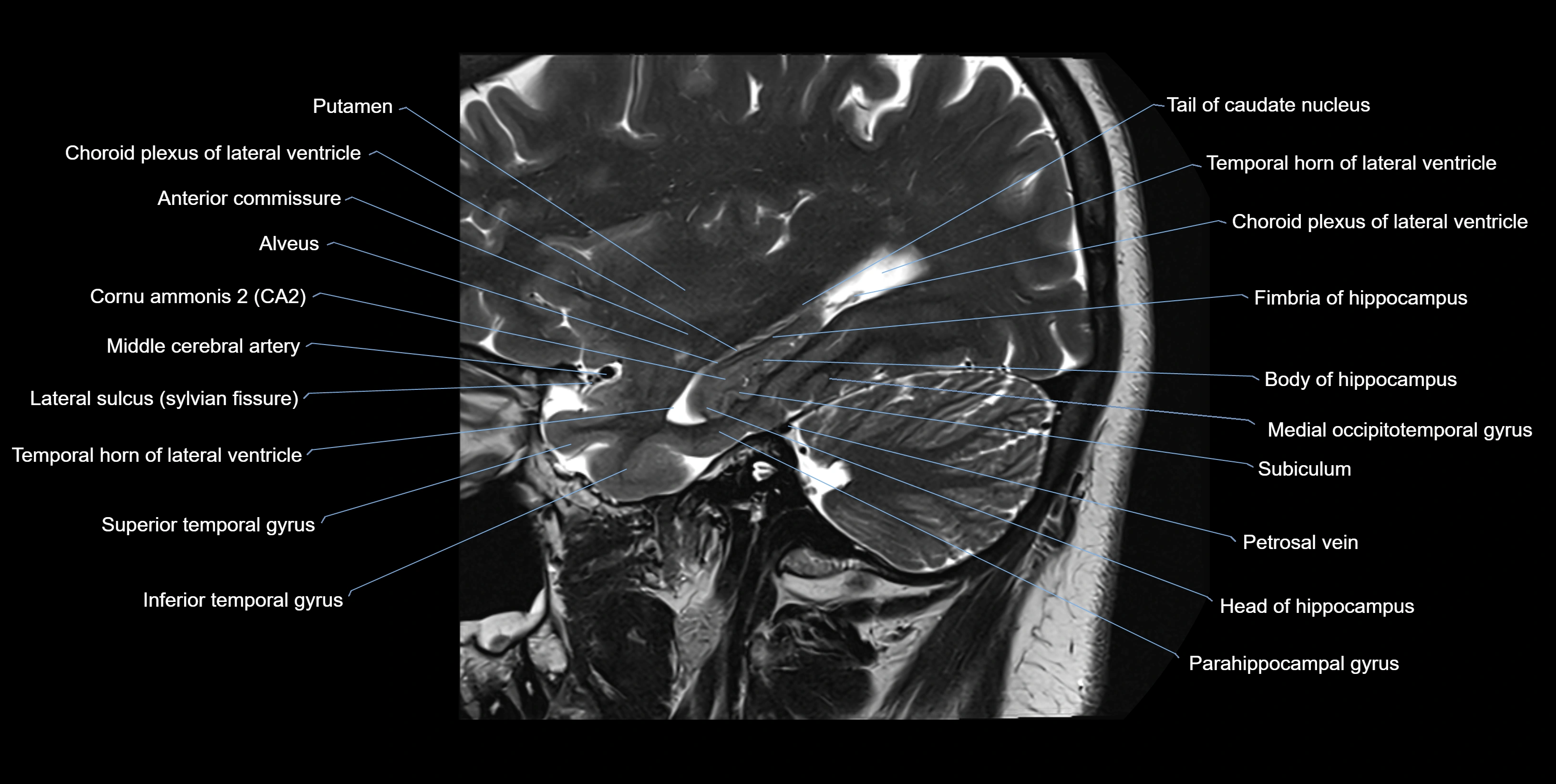
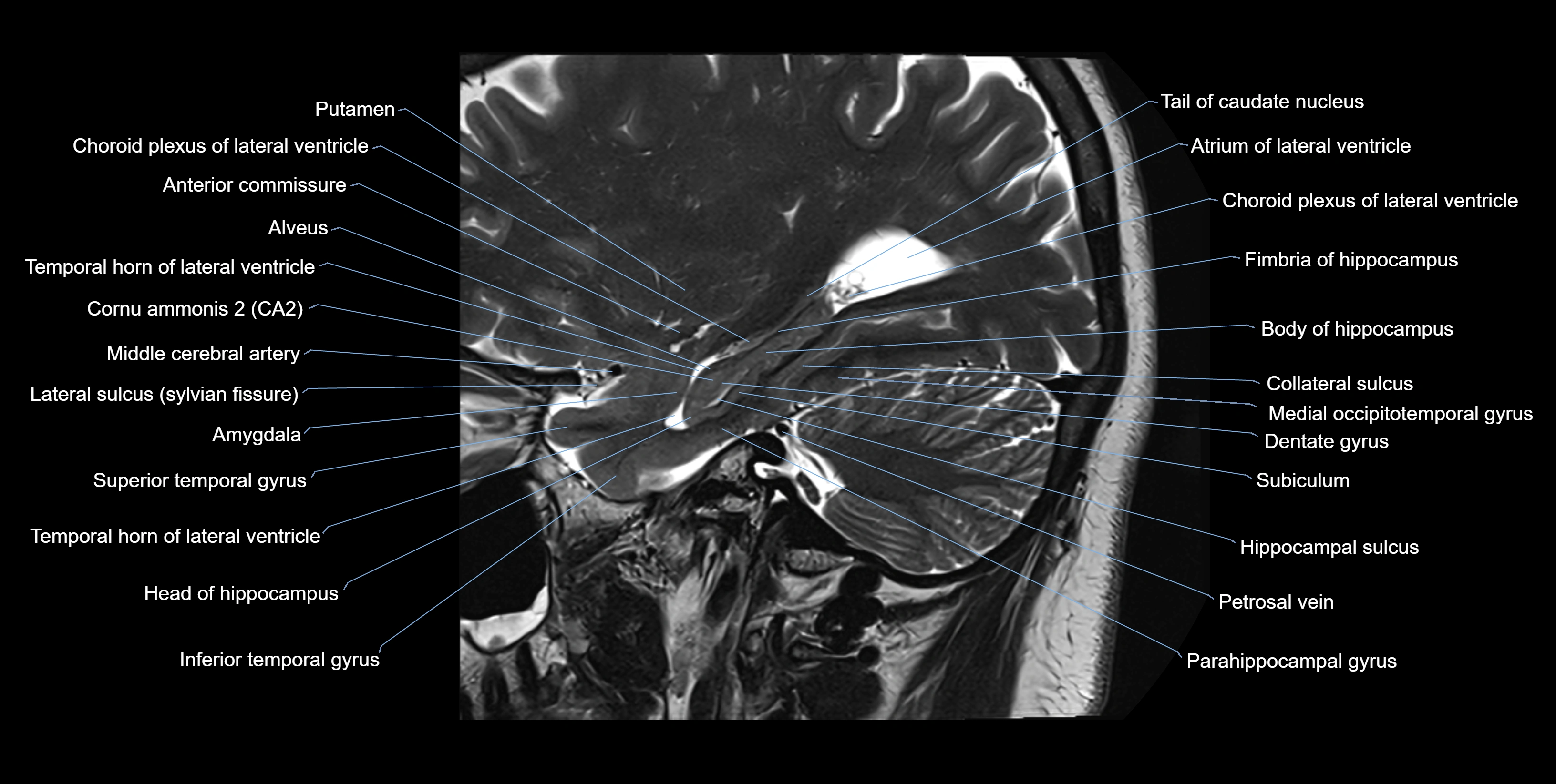
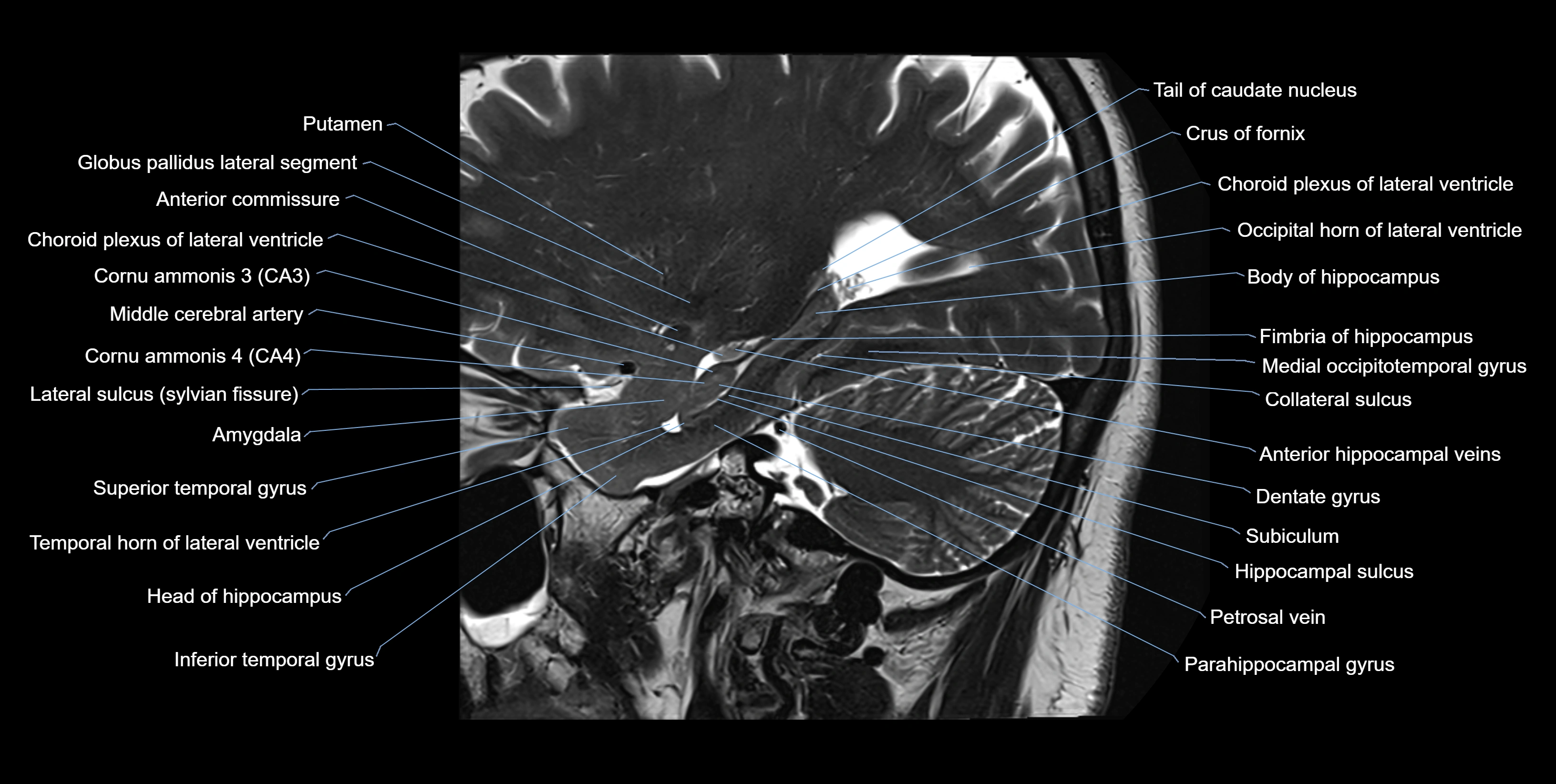
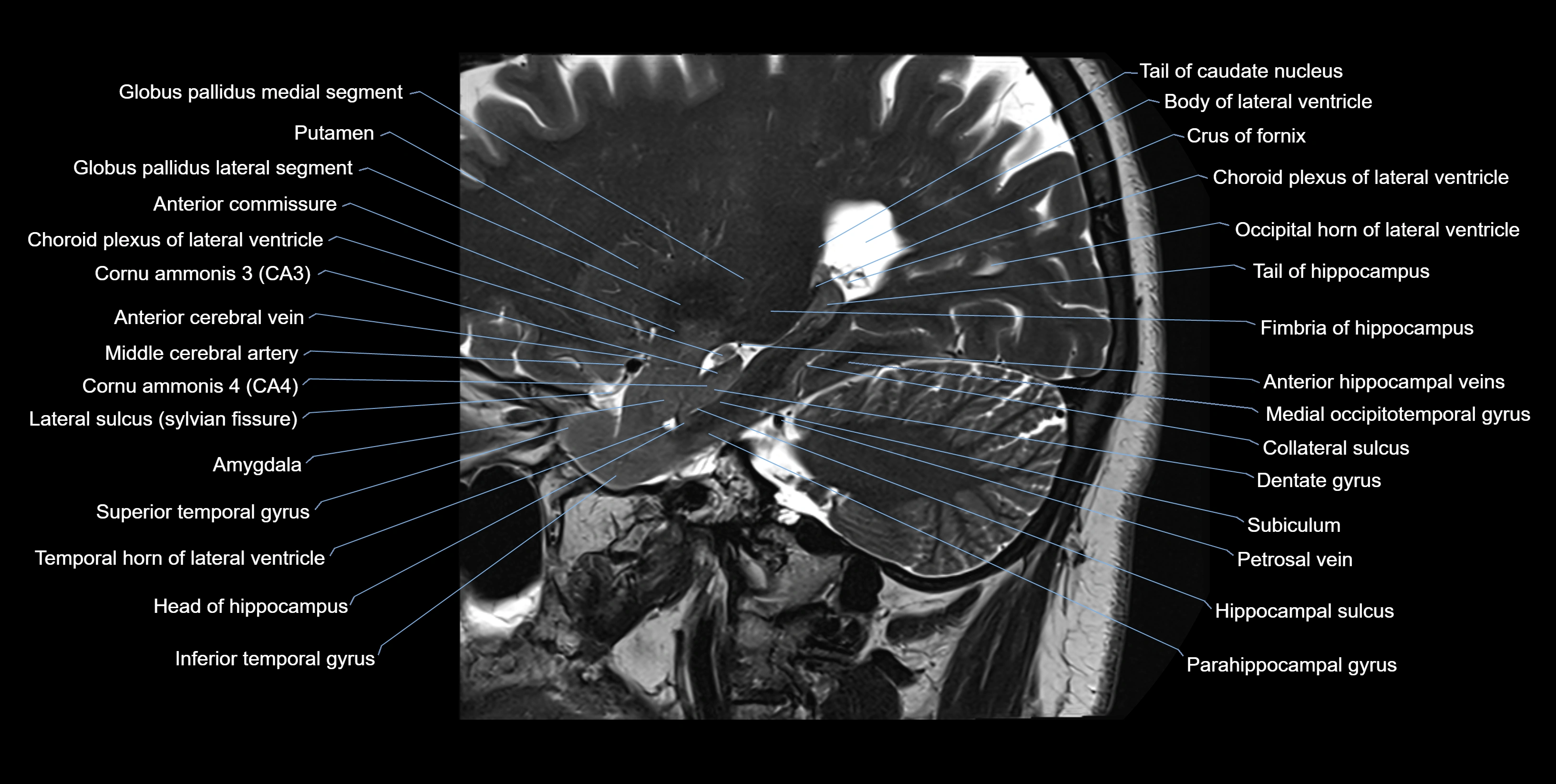
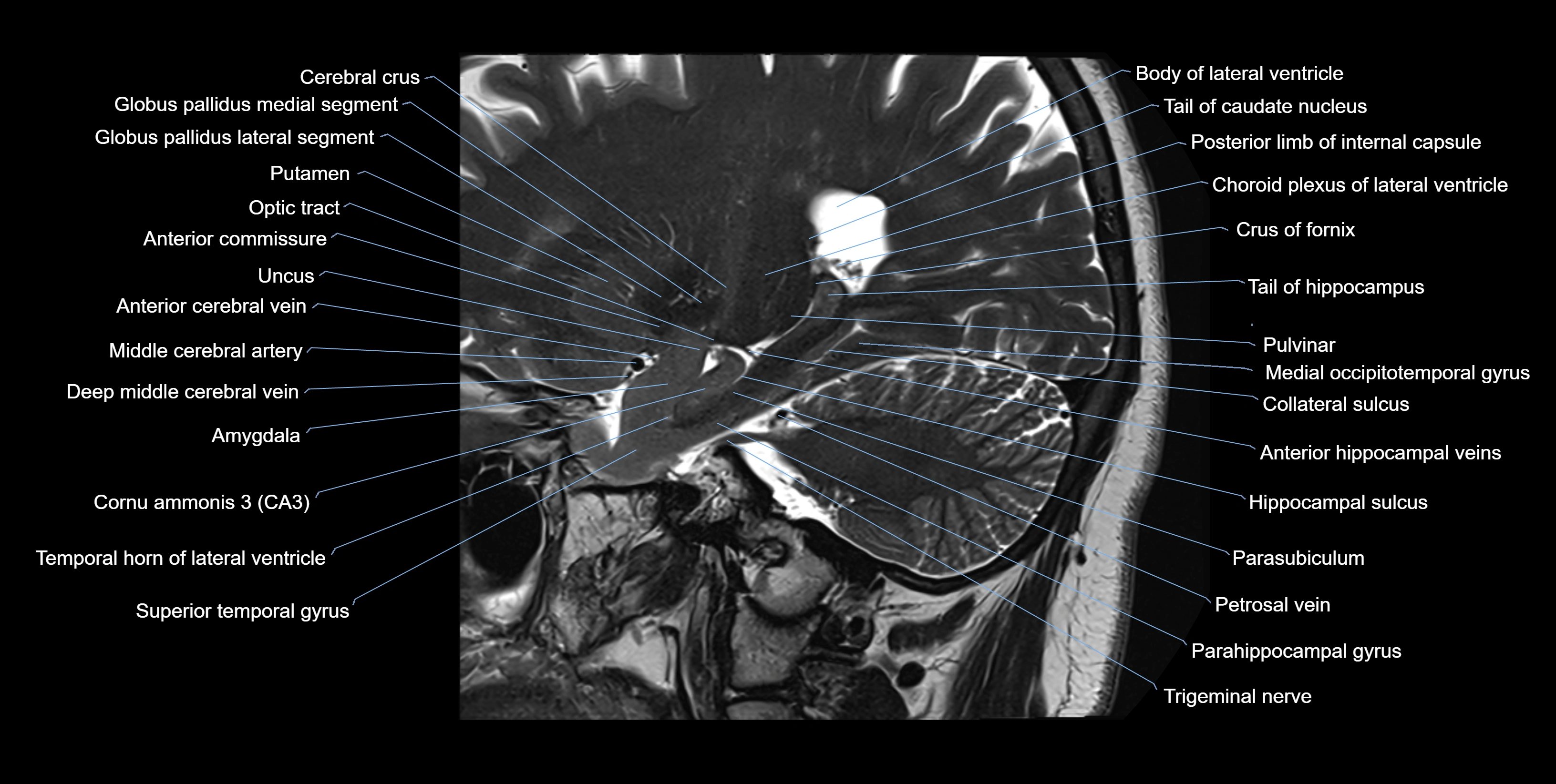
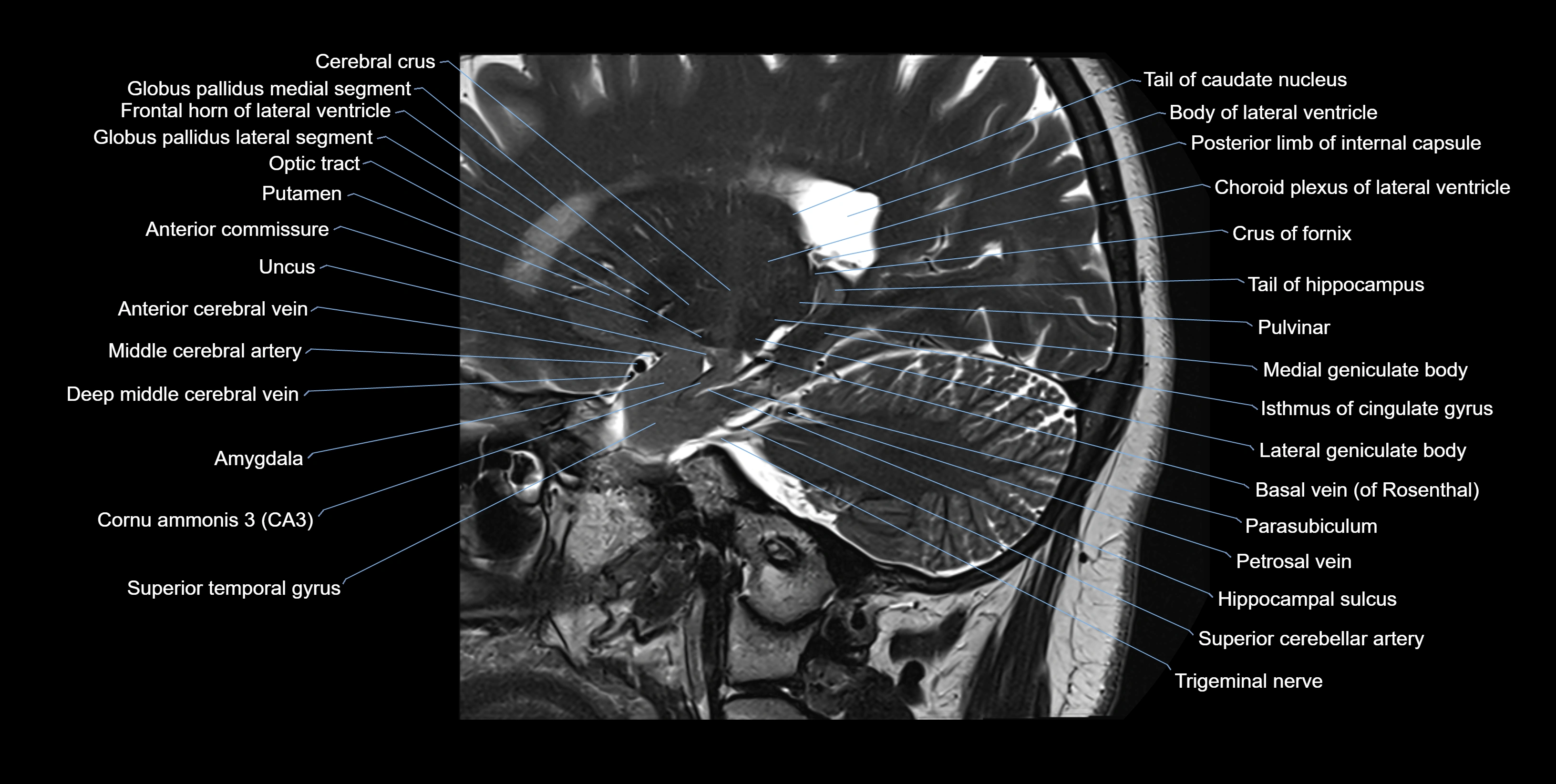
MRI images

MRI images