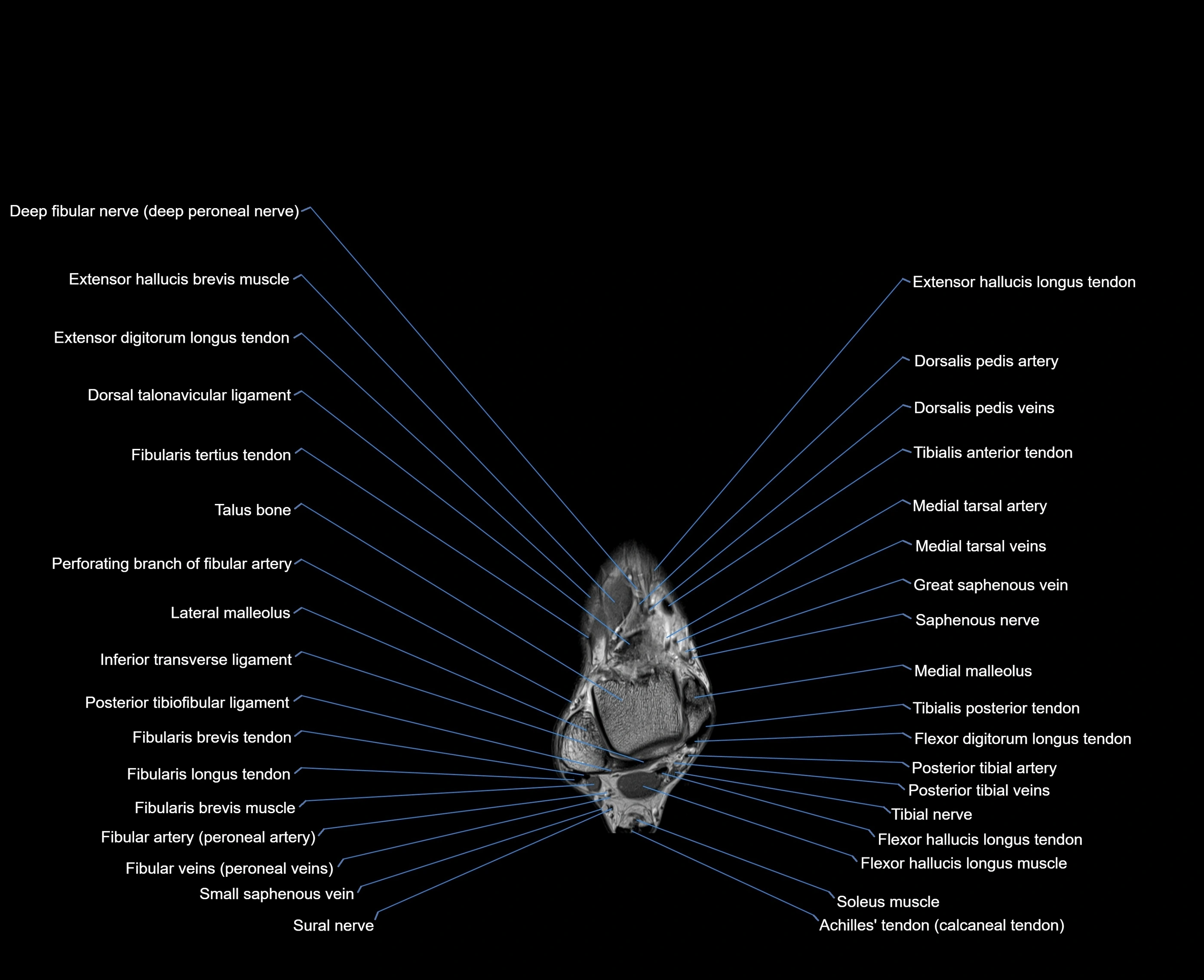
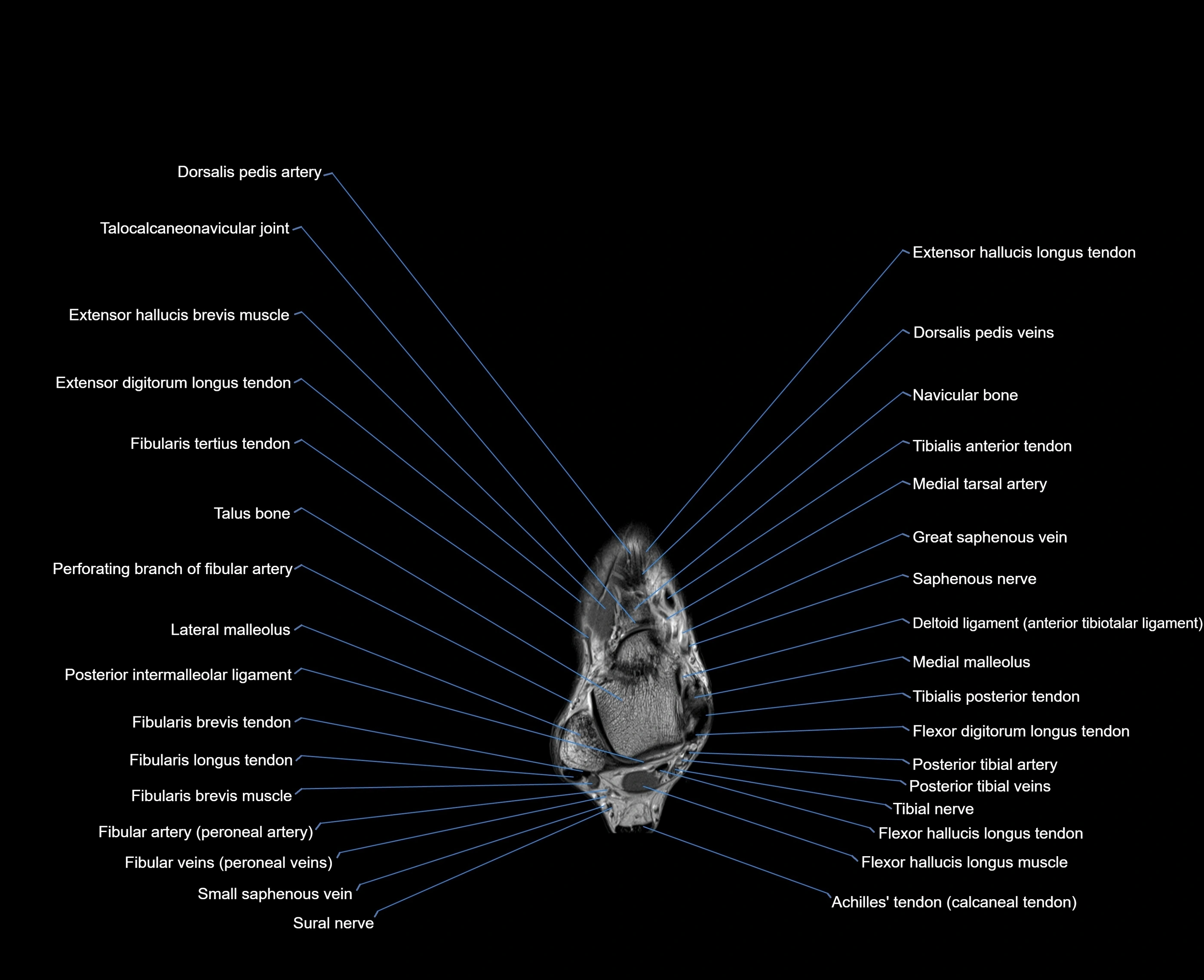
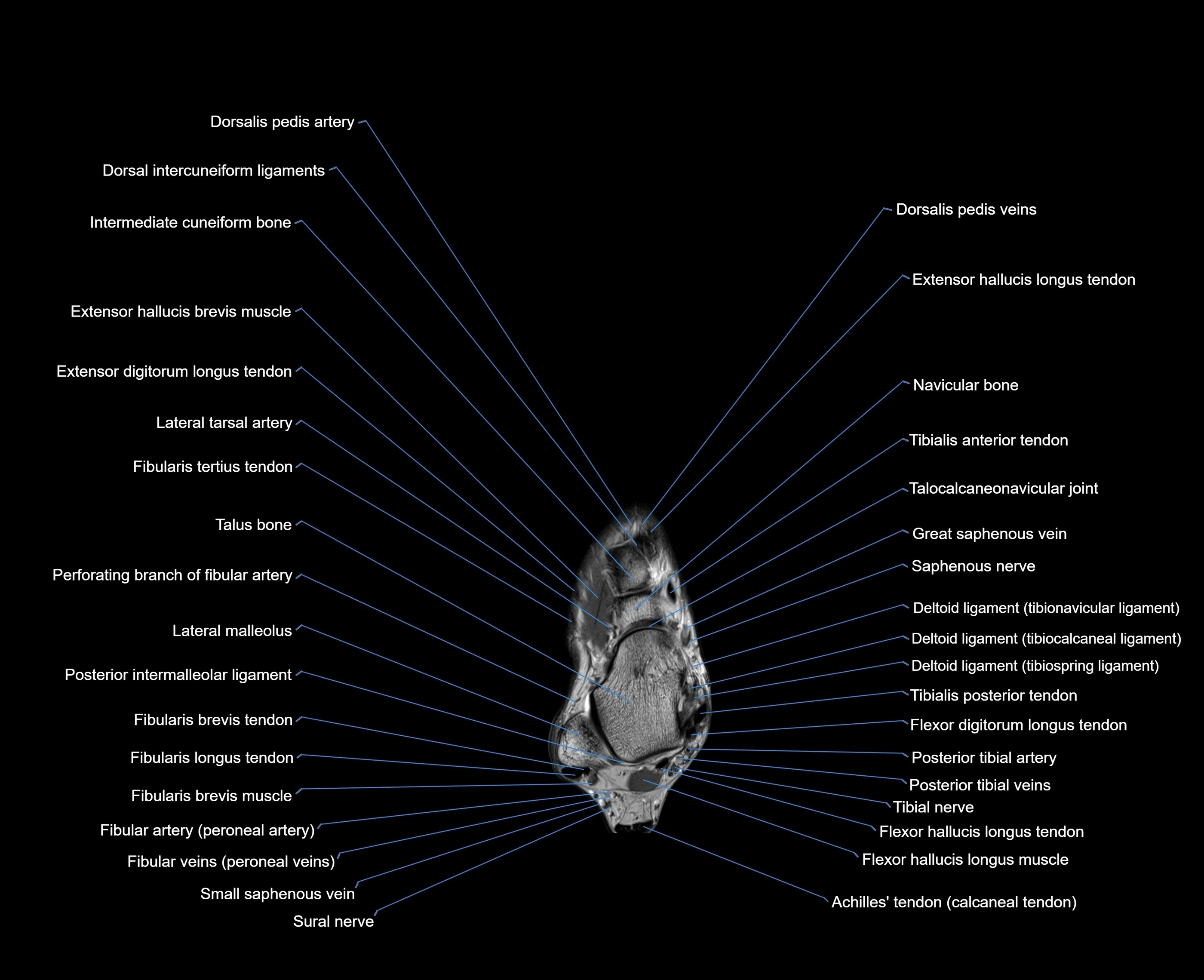
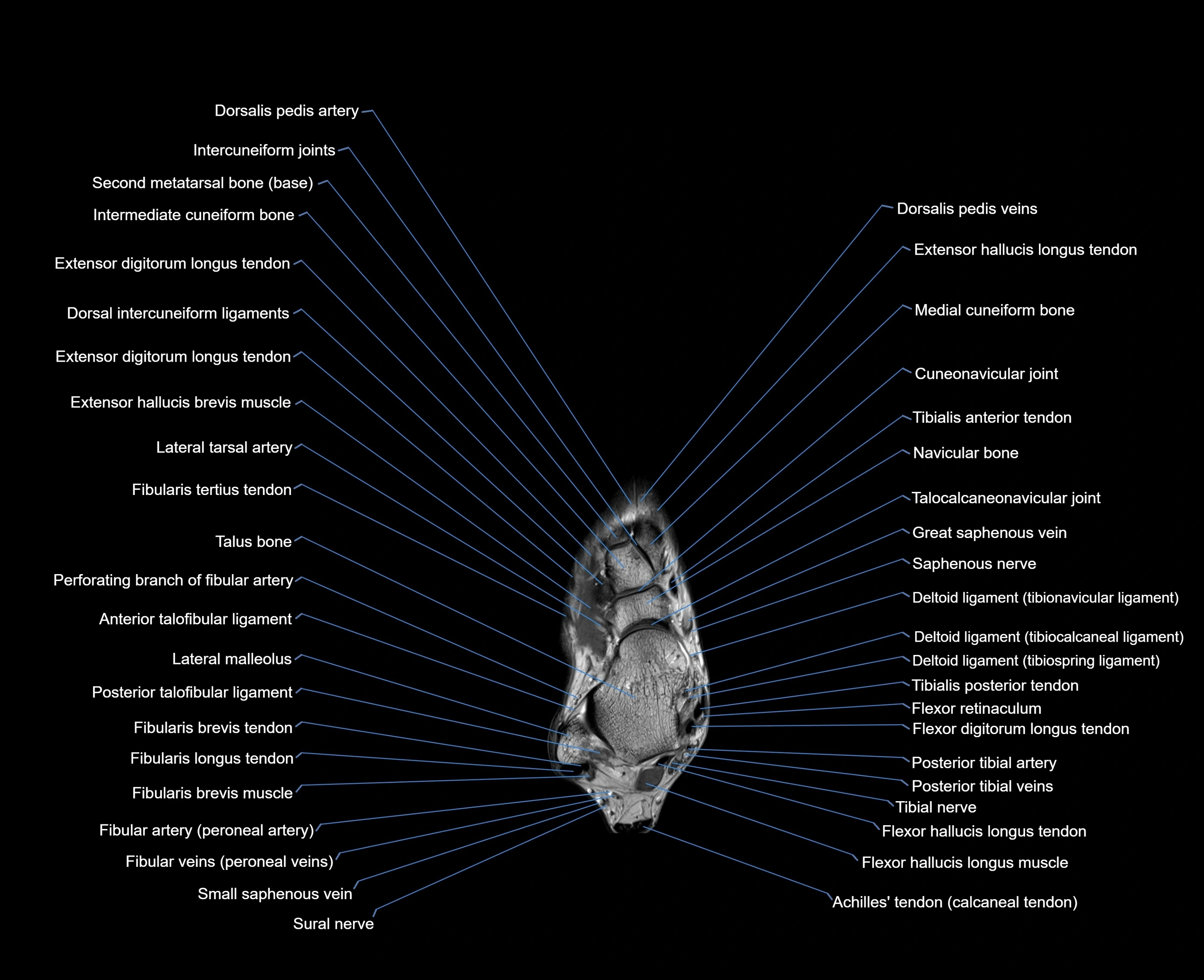
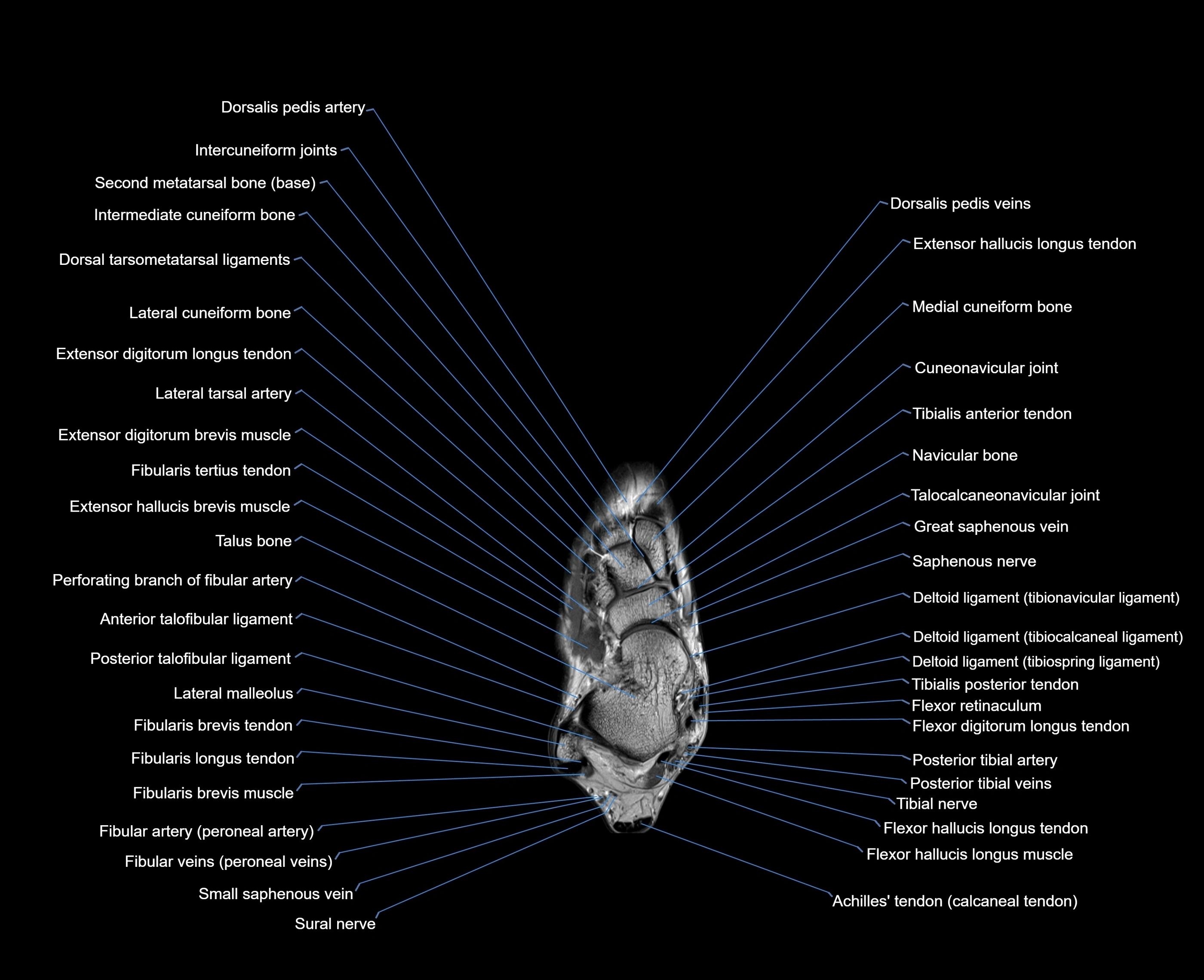
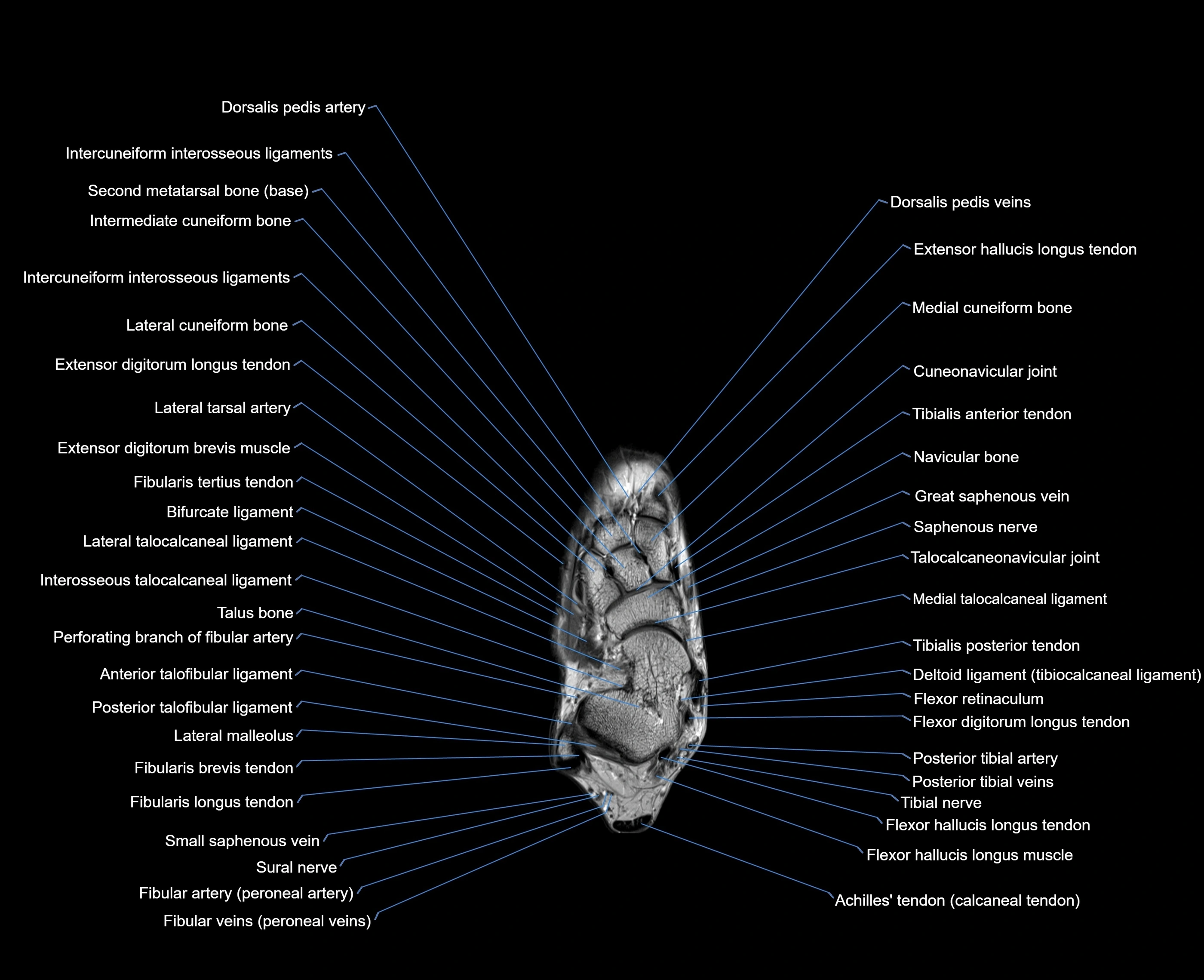
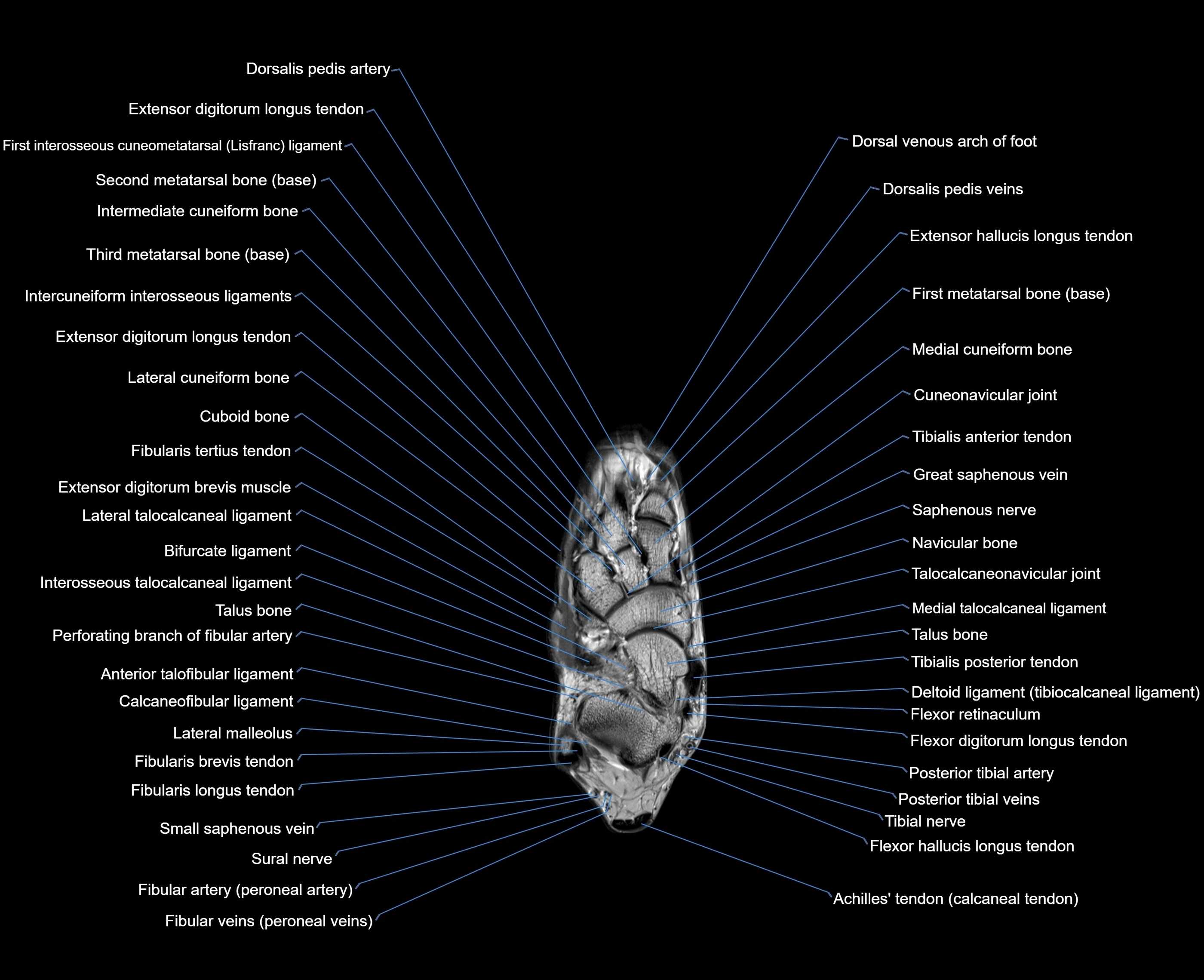
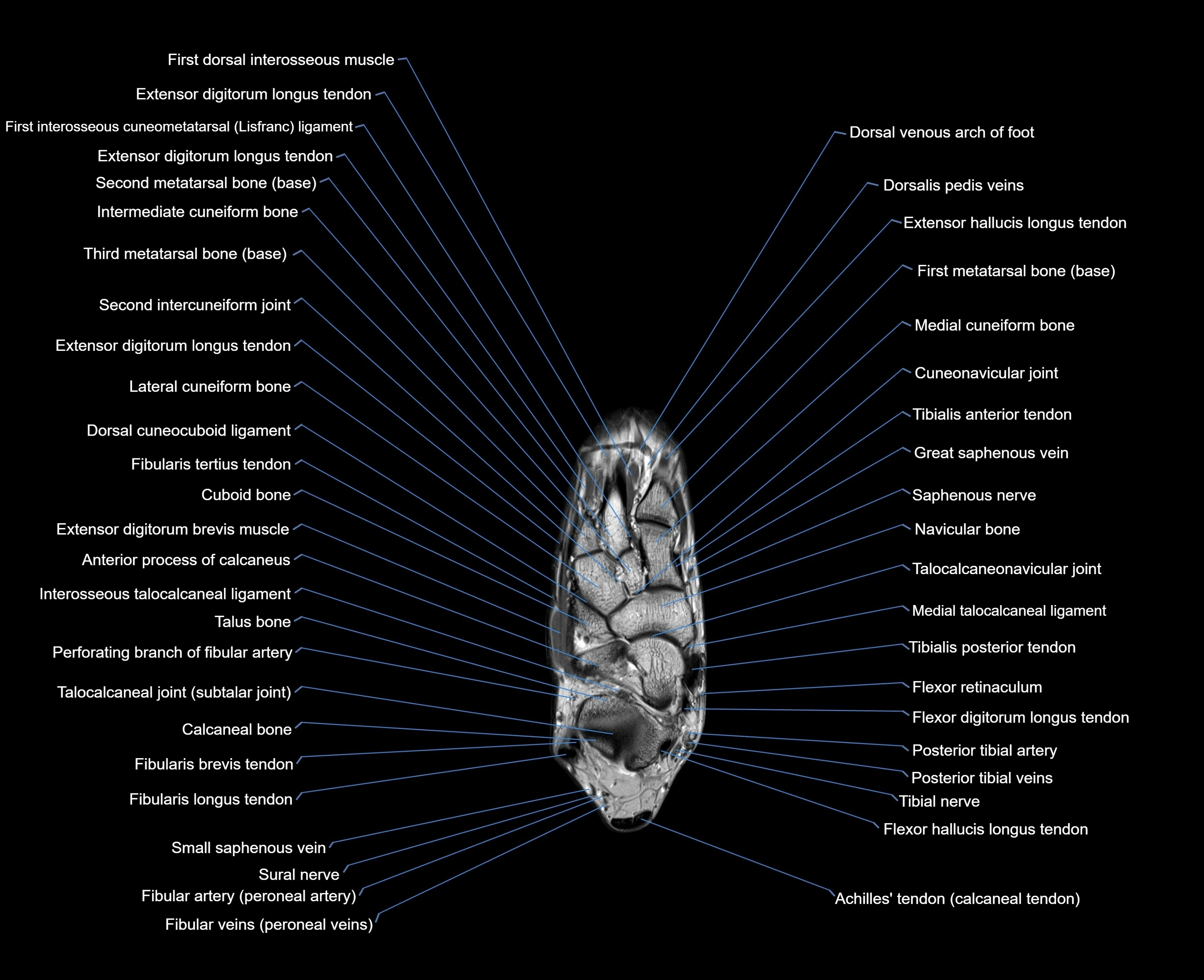
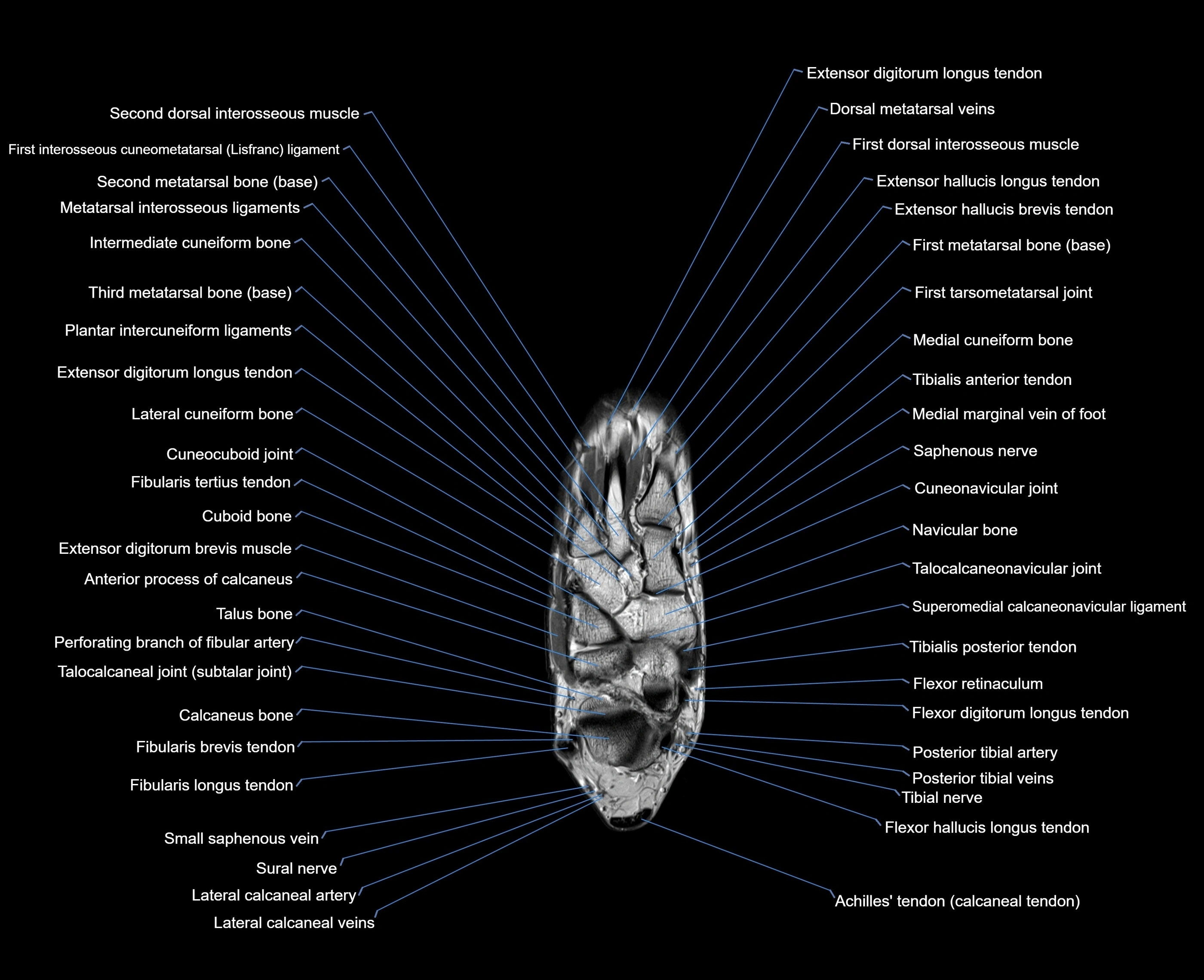
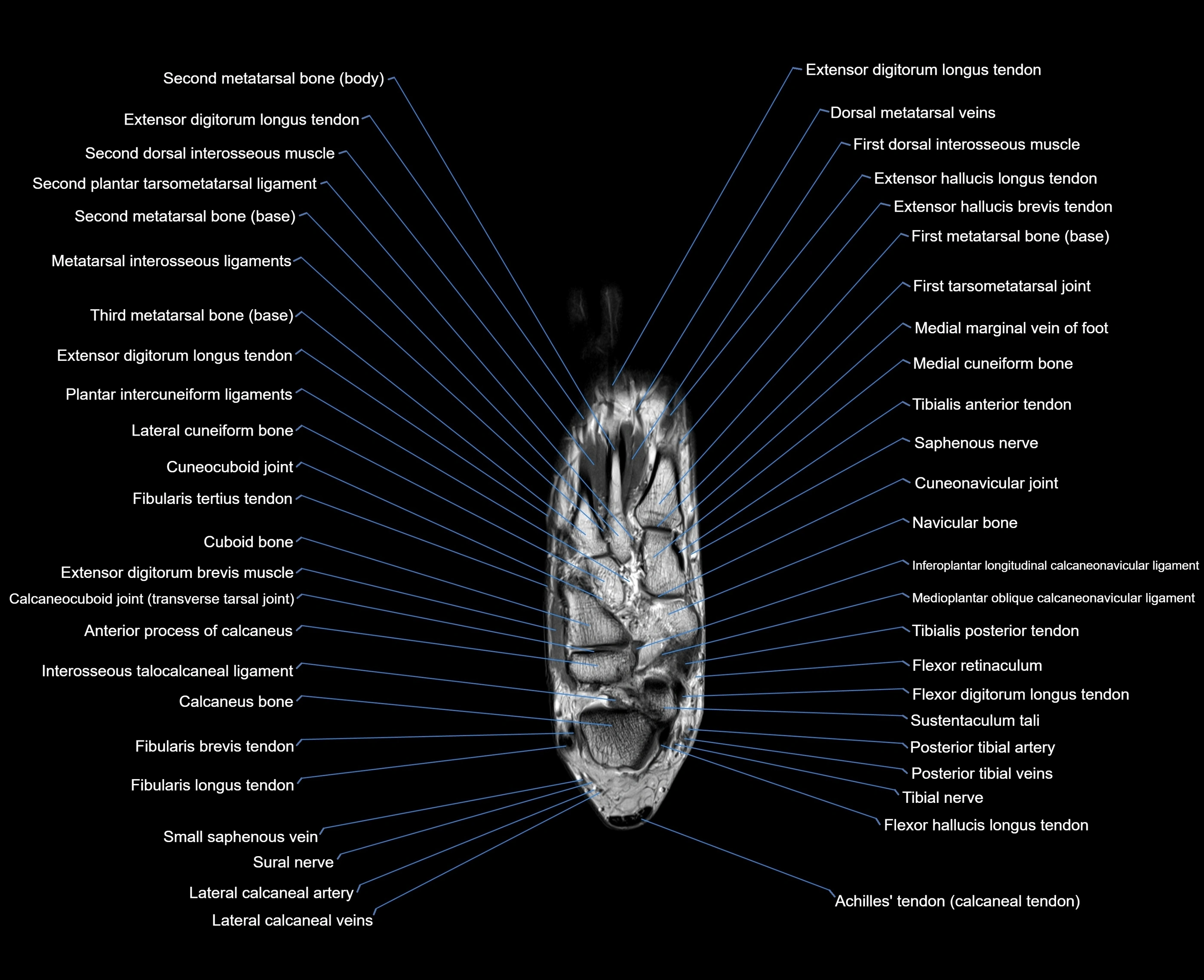
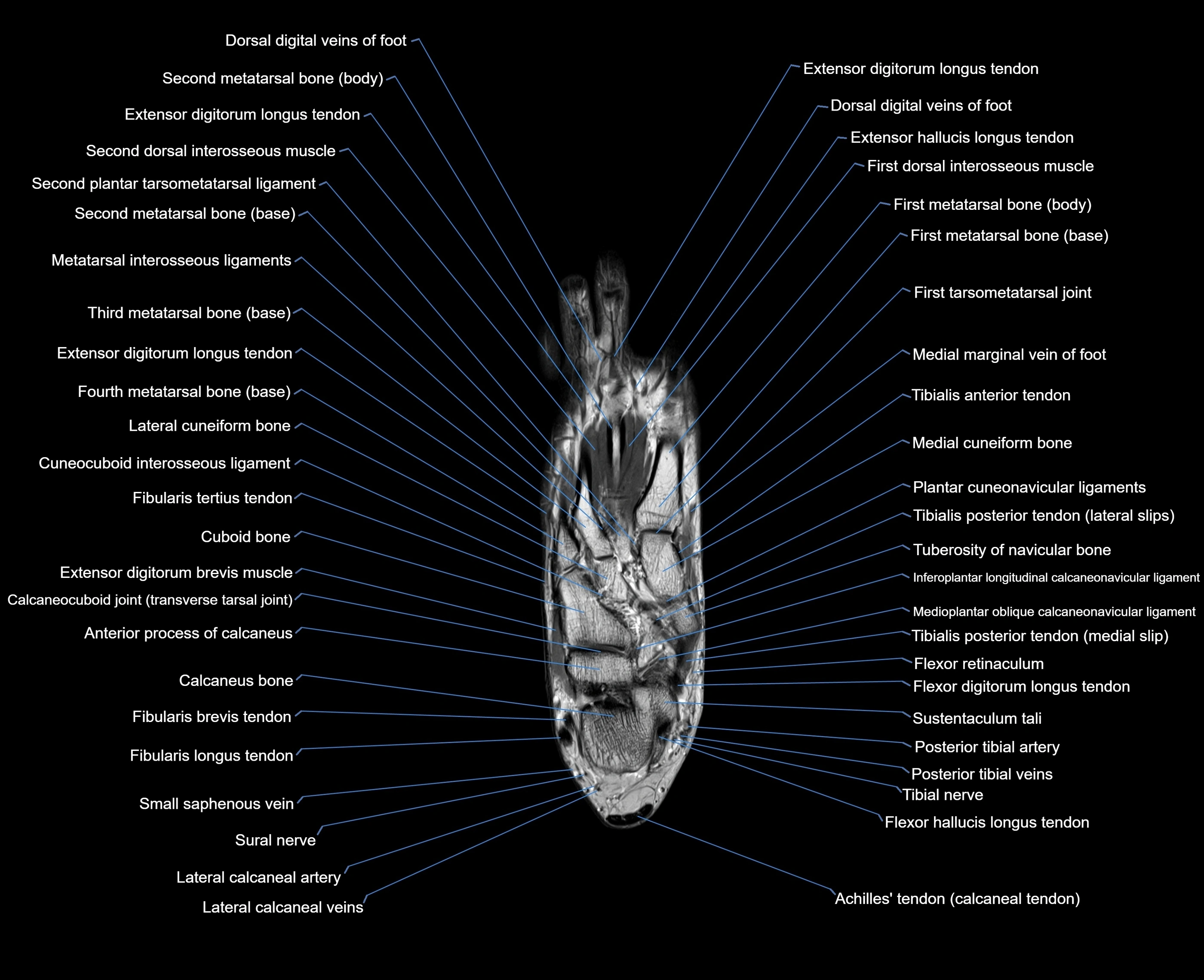
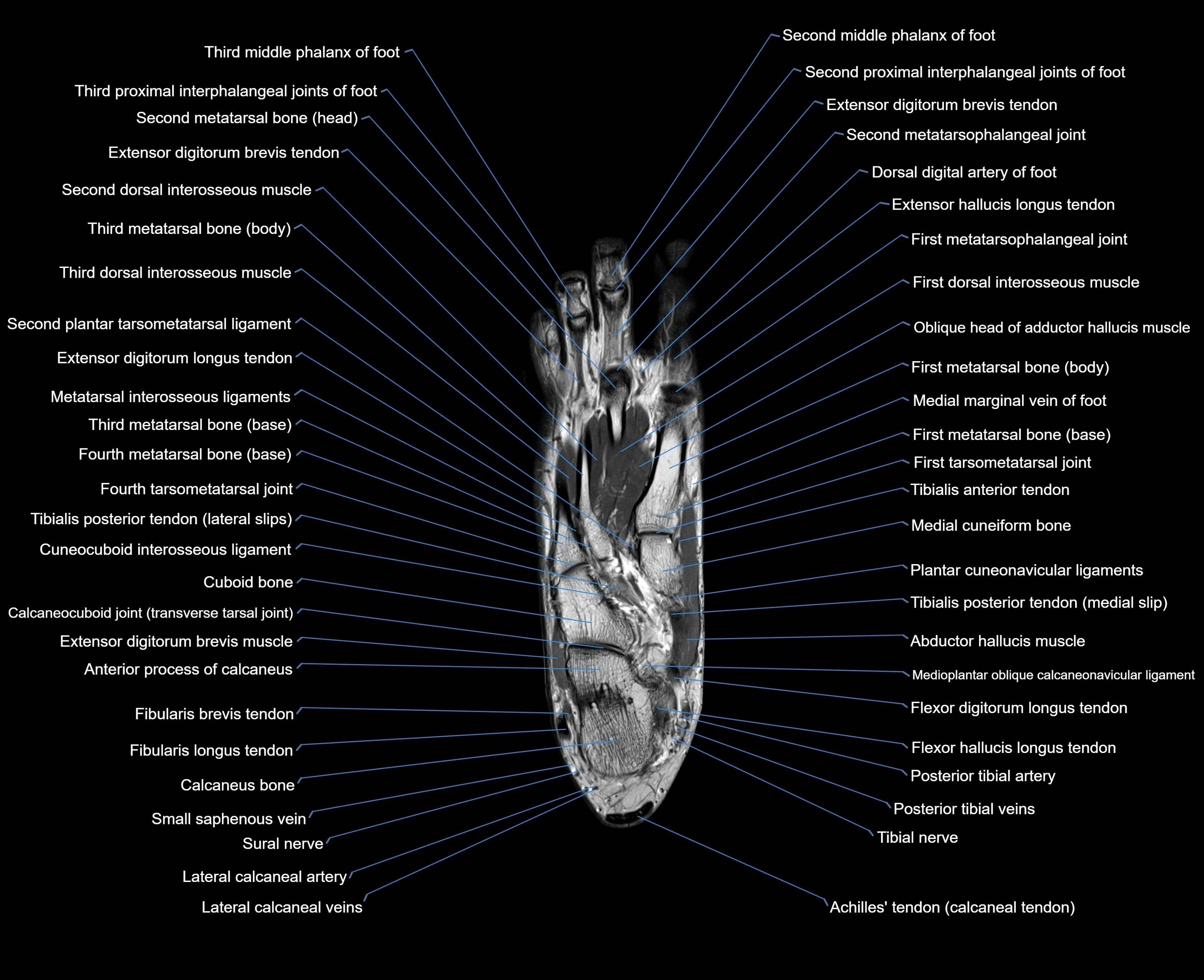
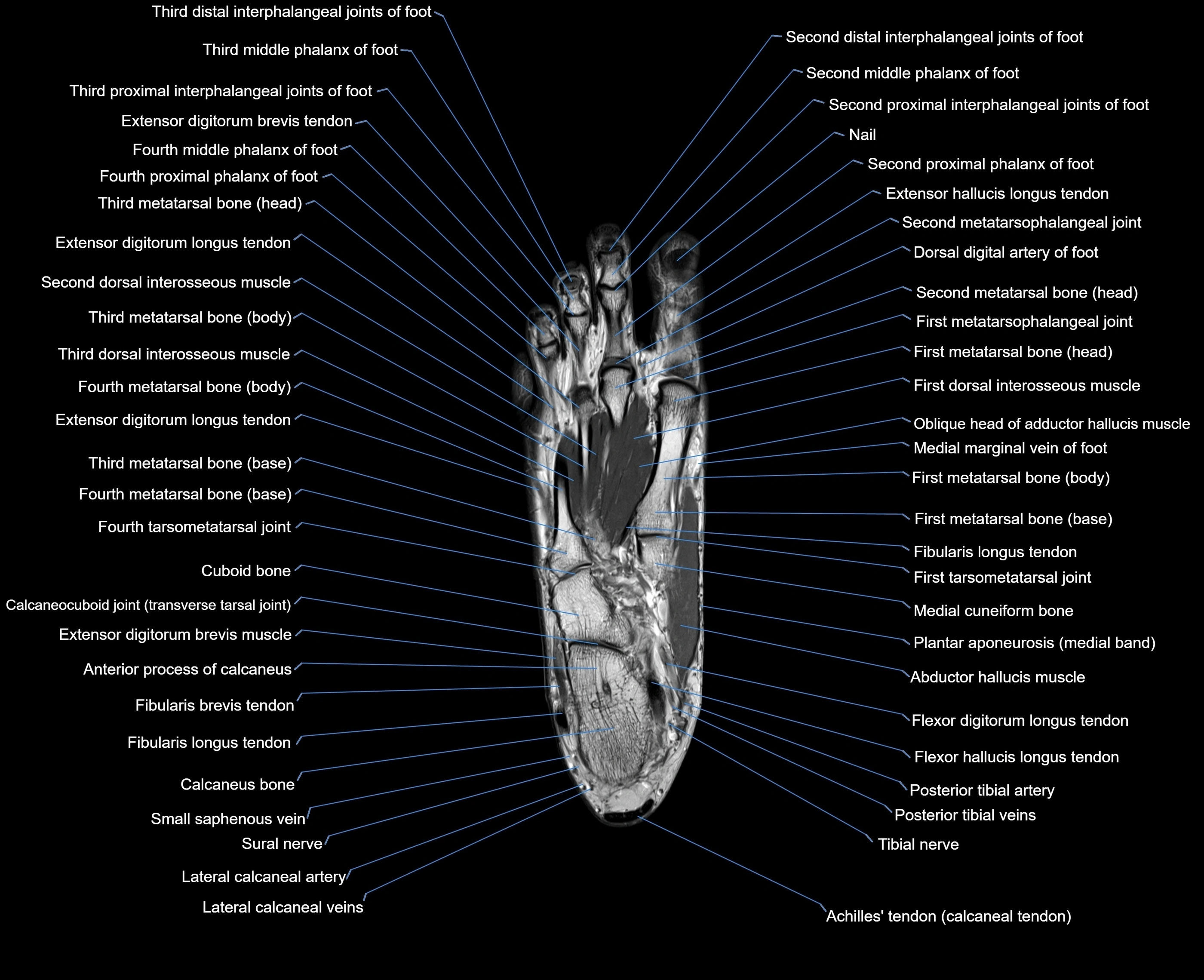
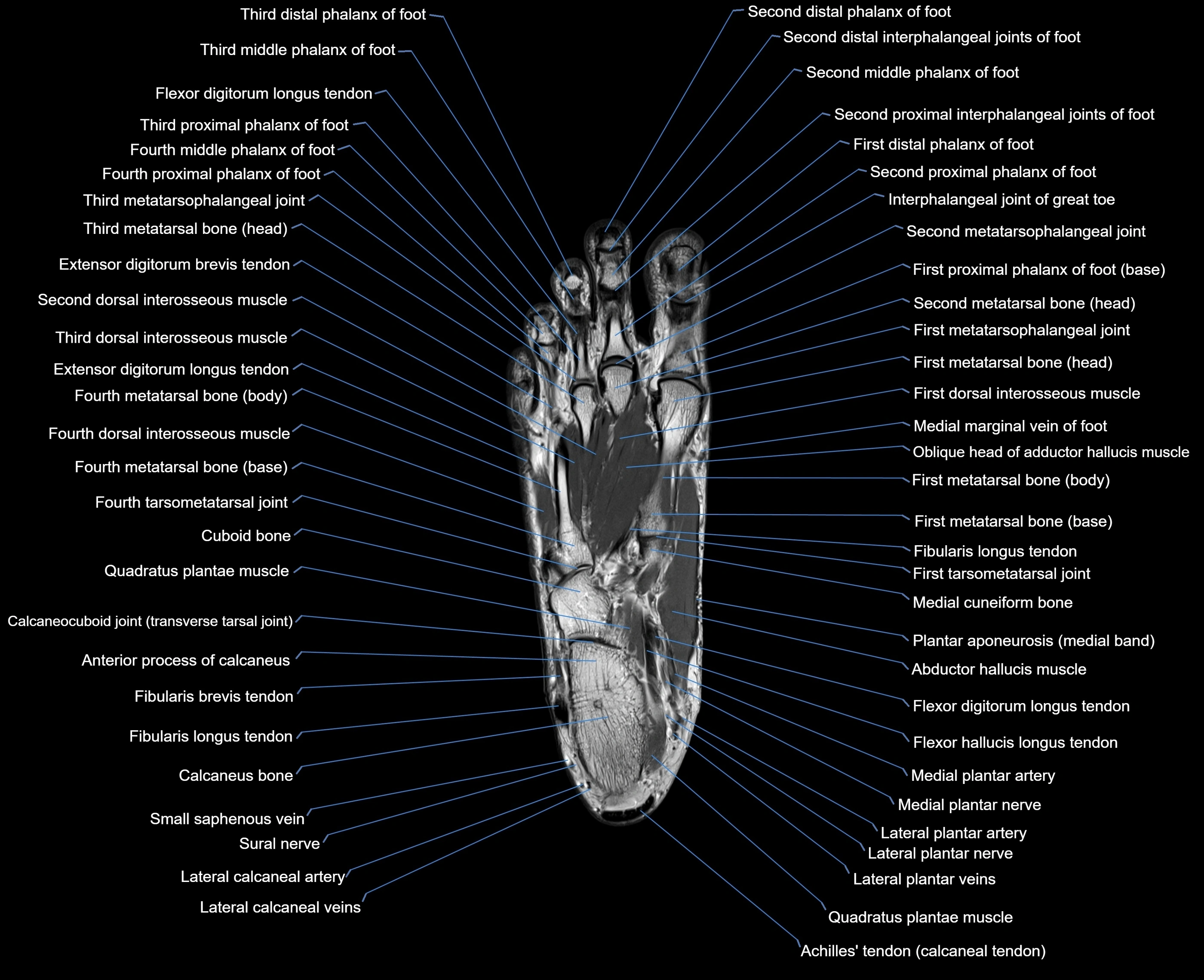
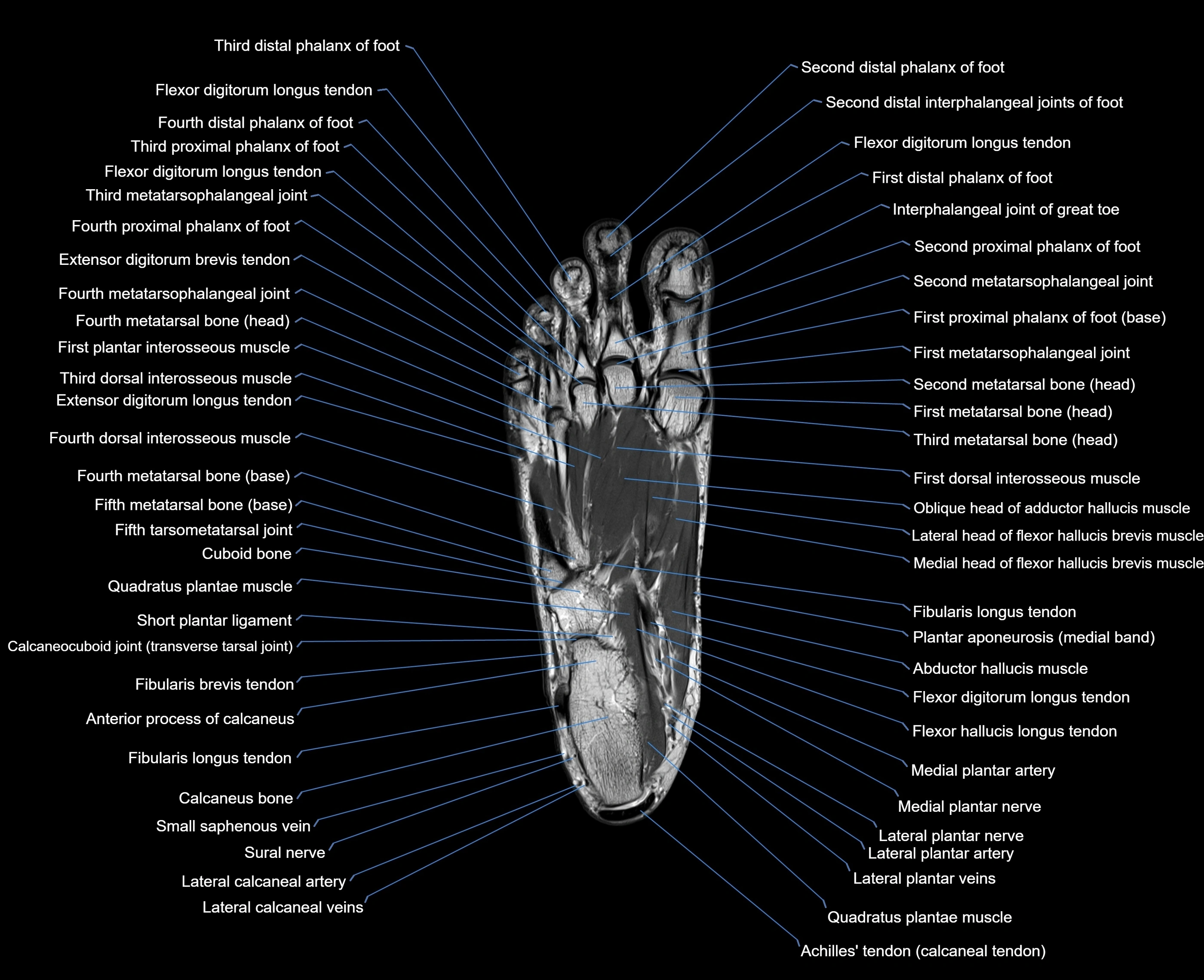
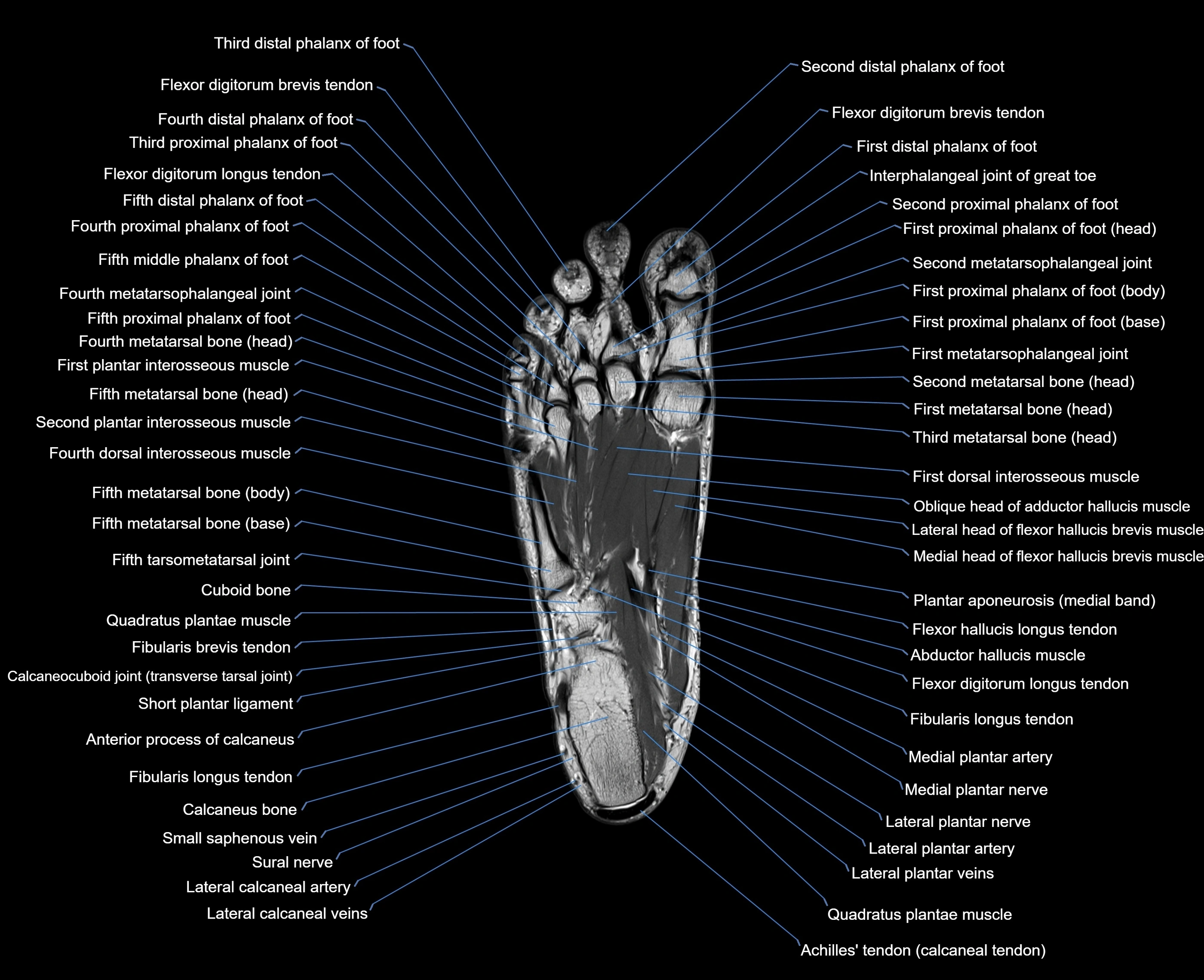
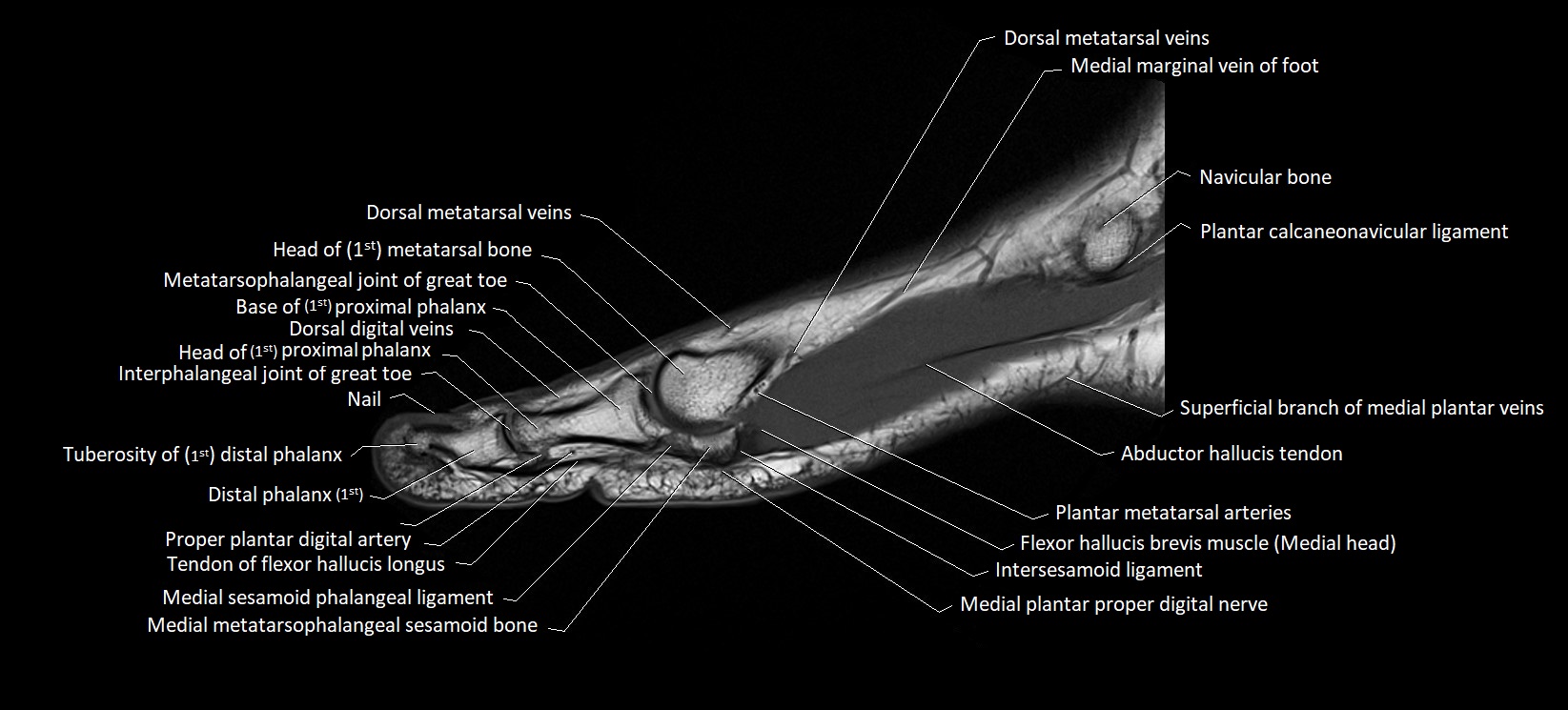
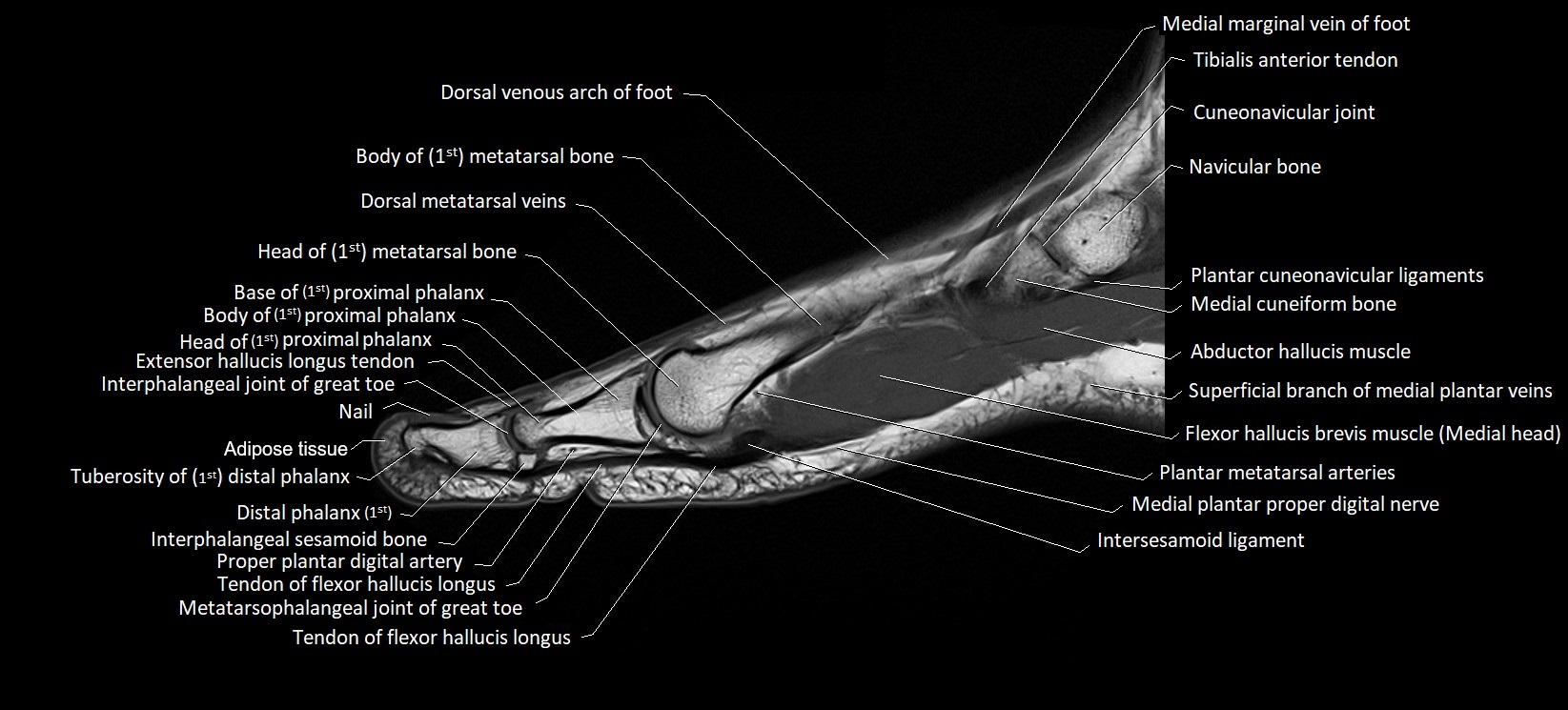
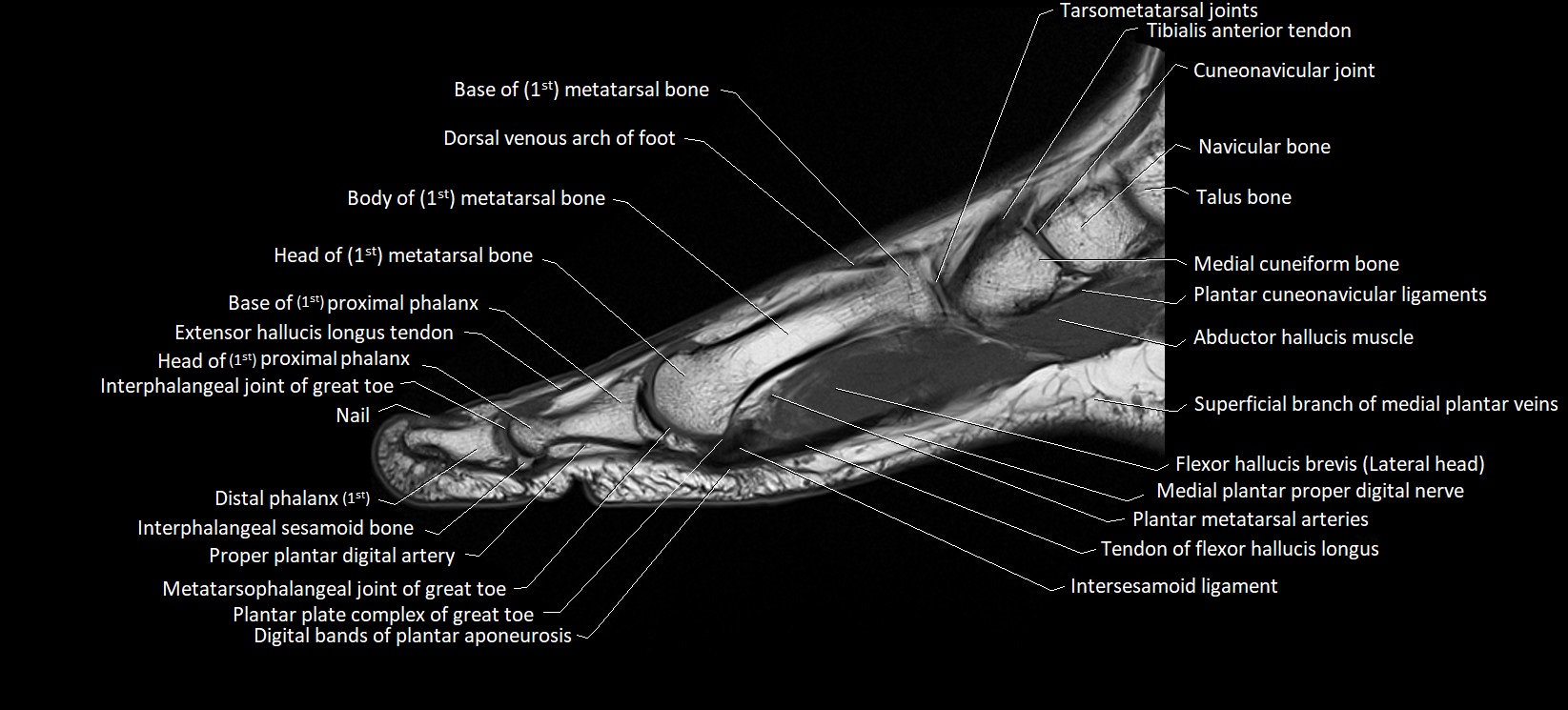
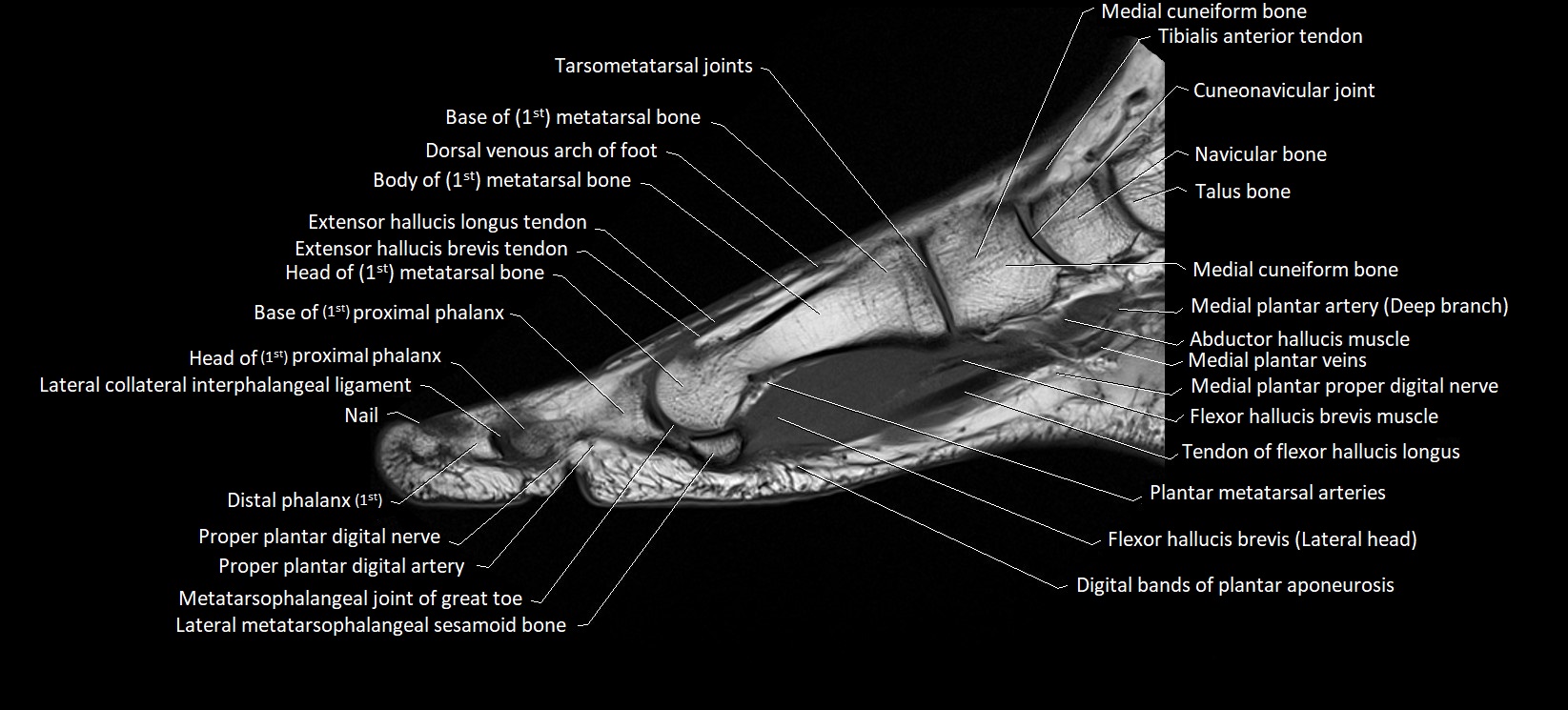
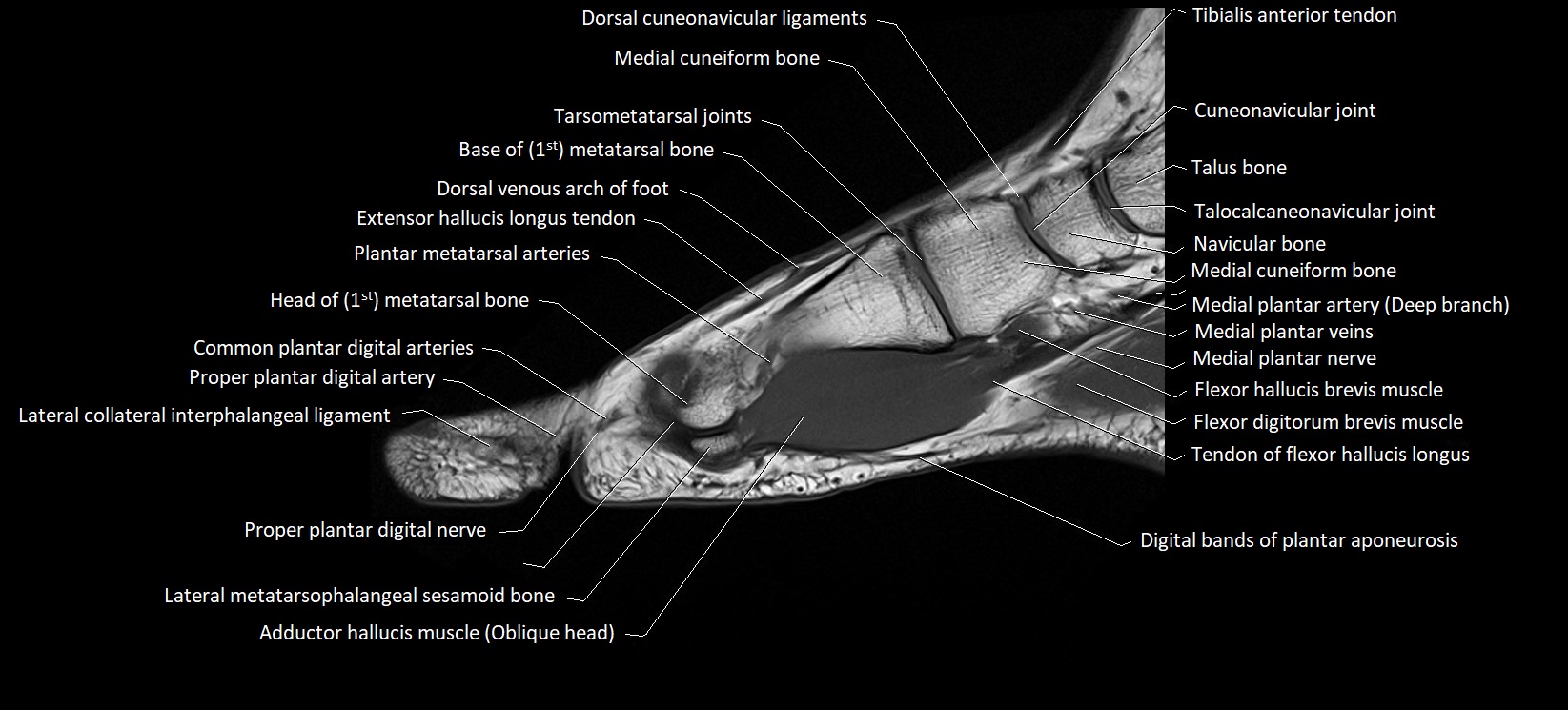
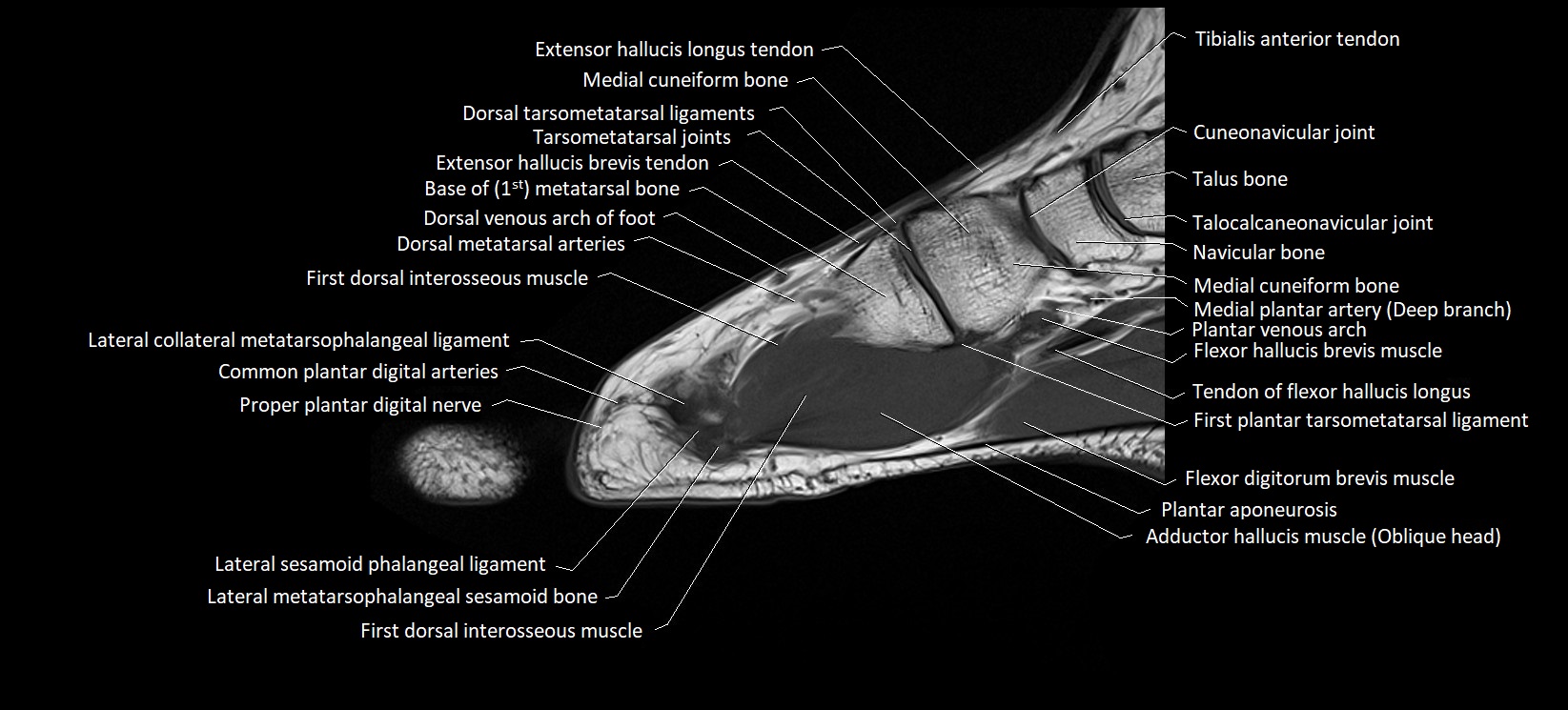
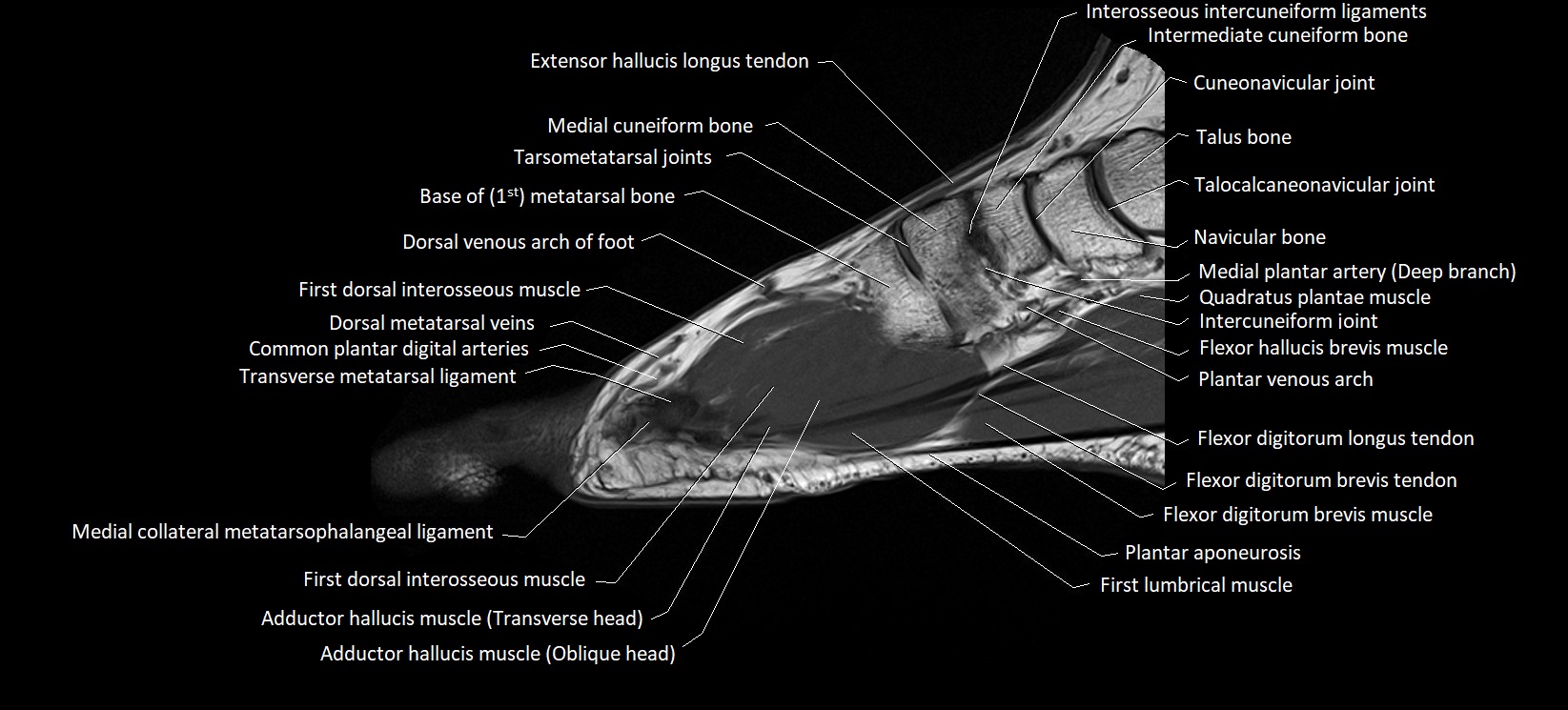
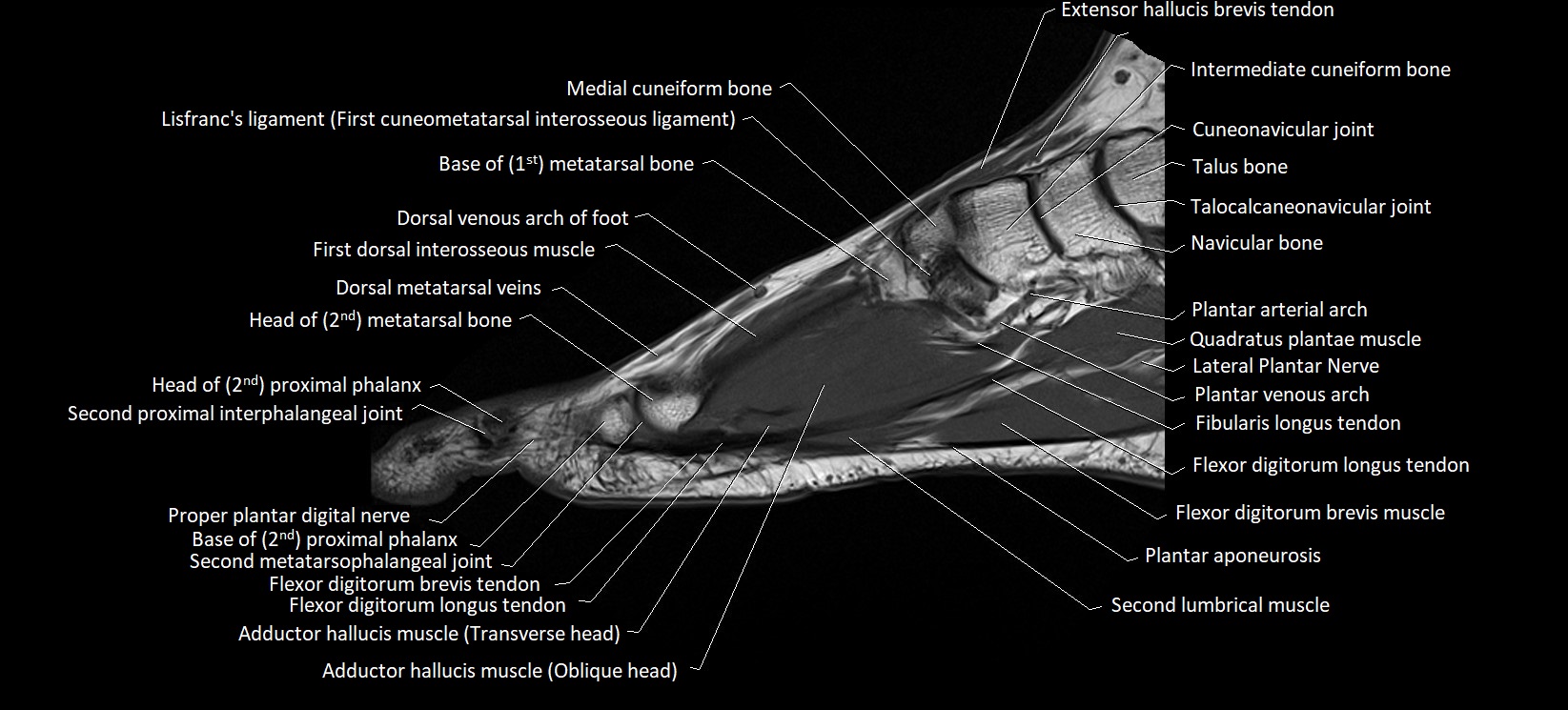
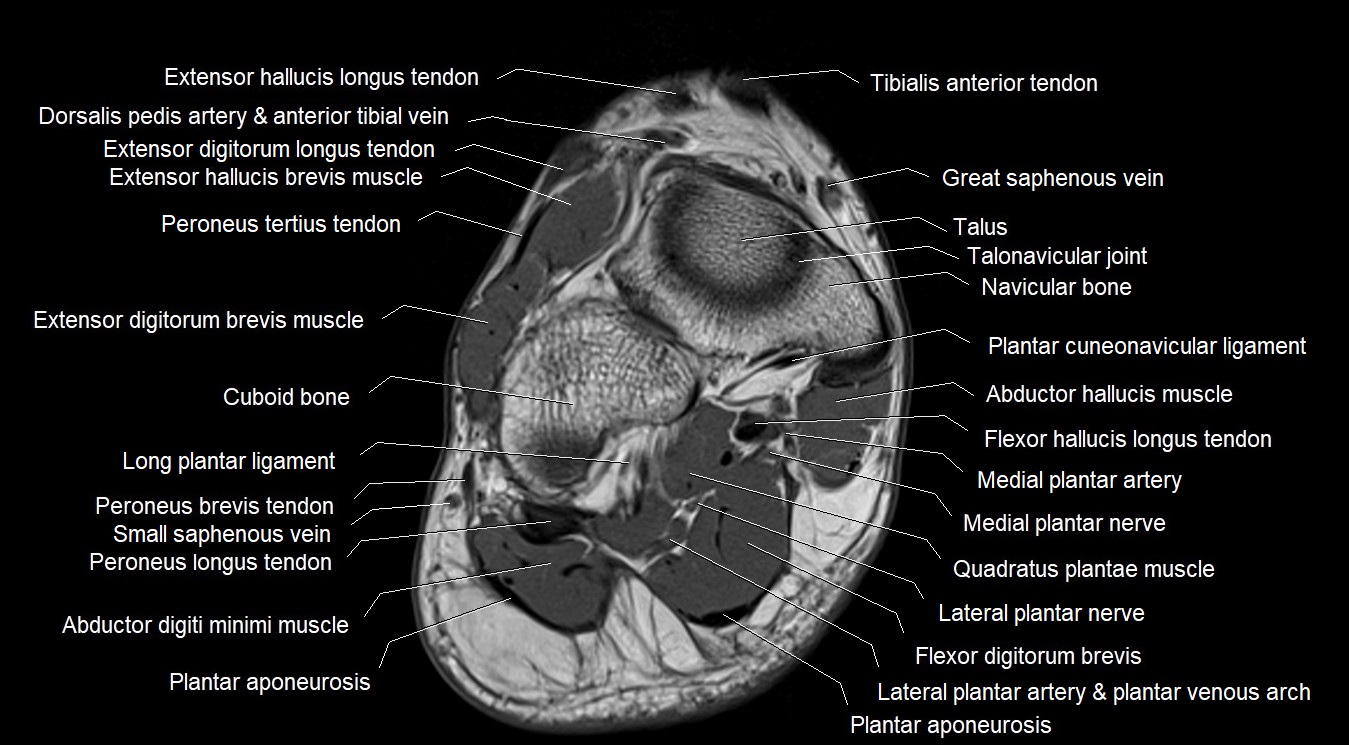
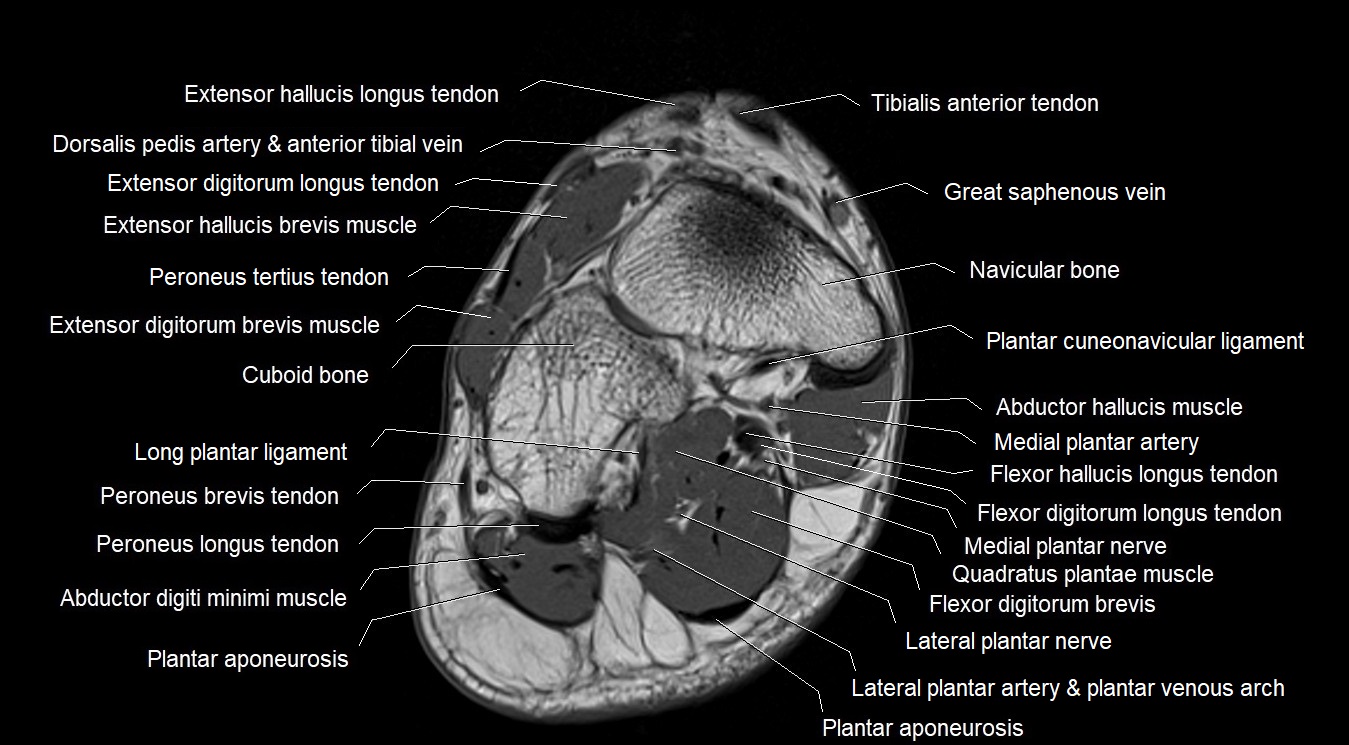
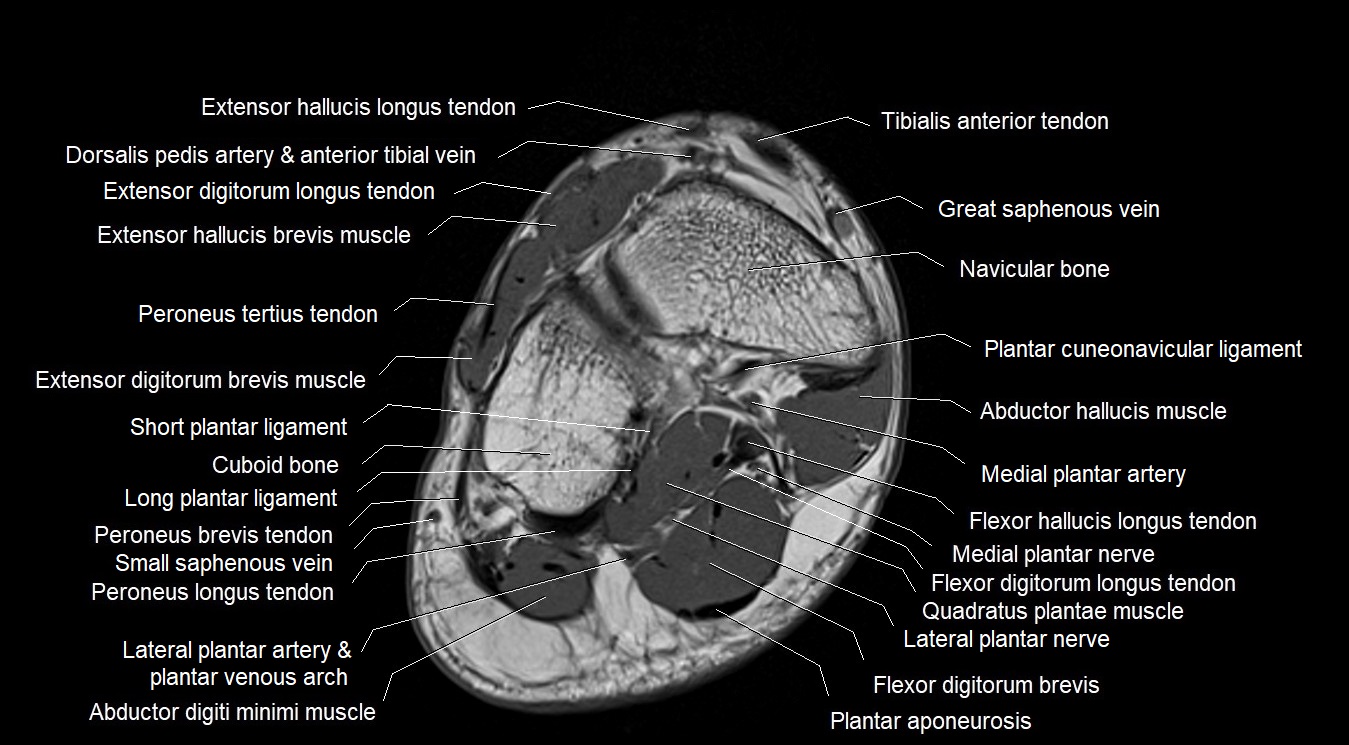
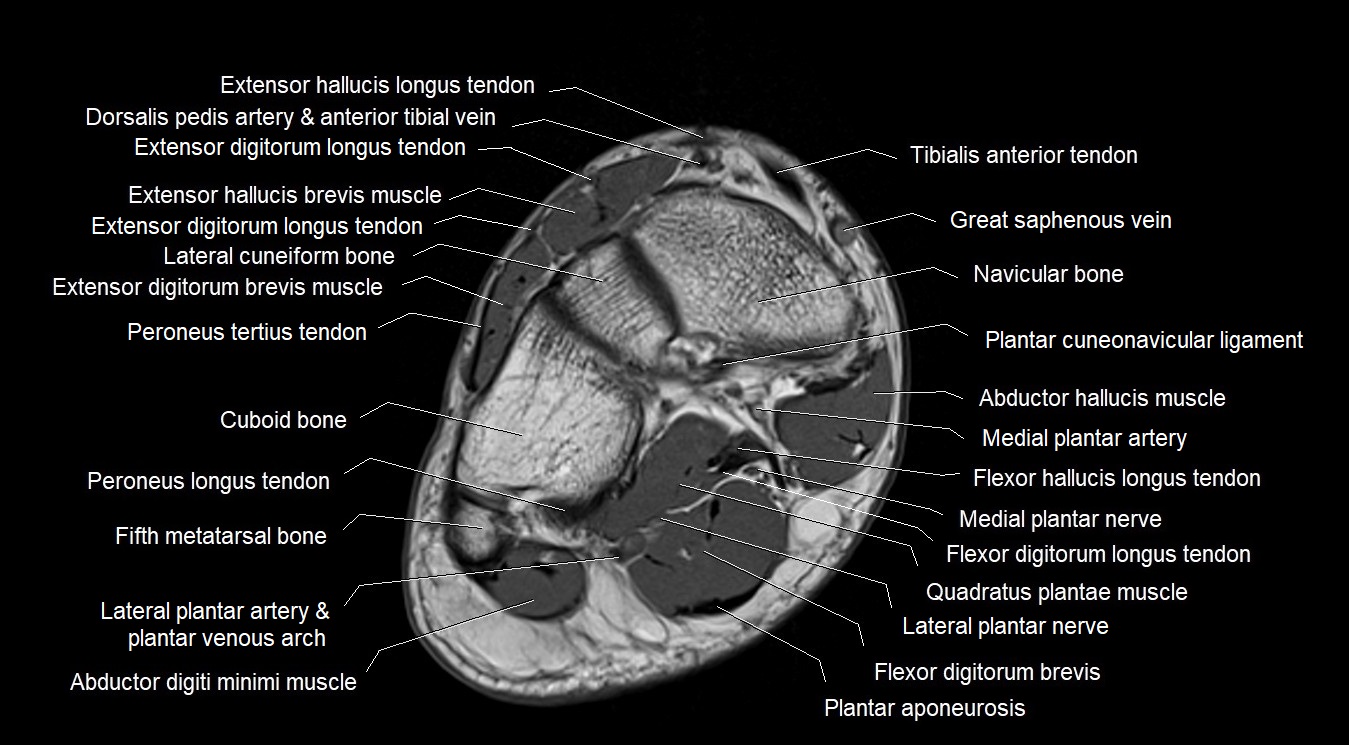
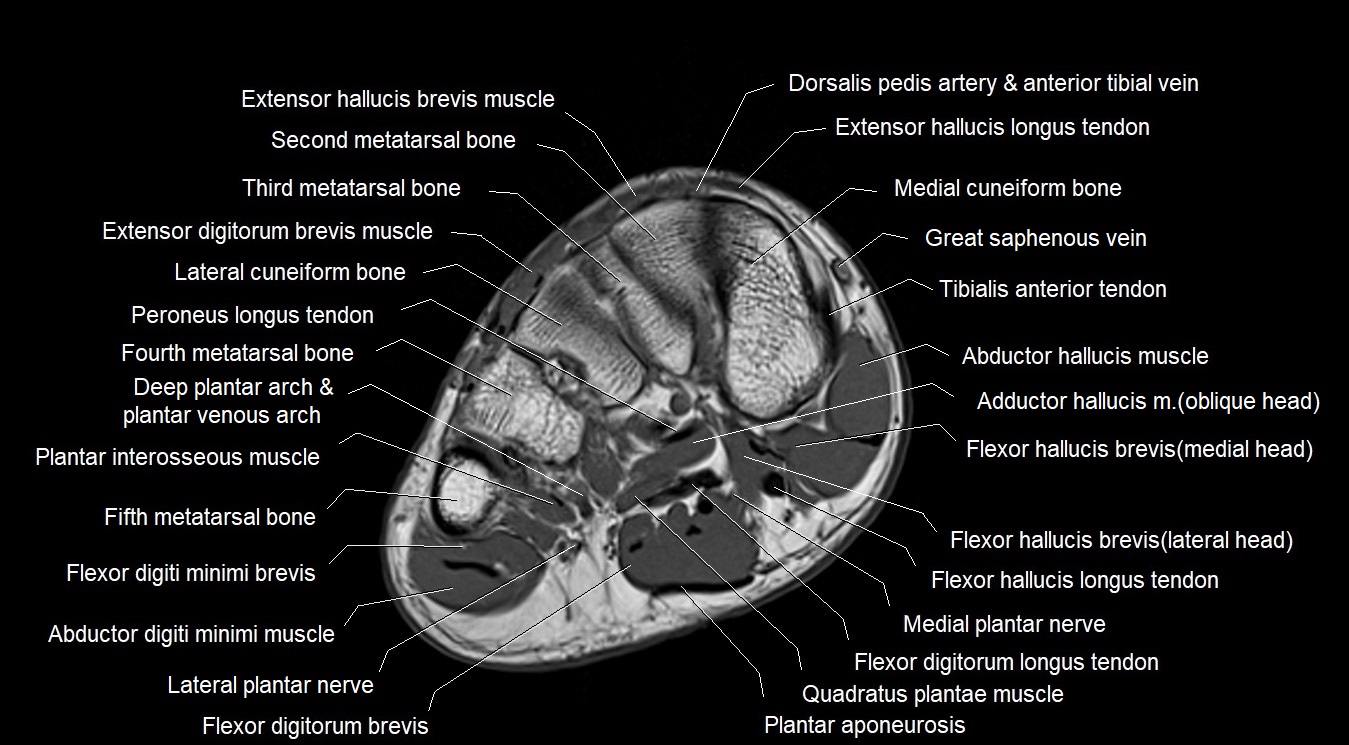
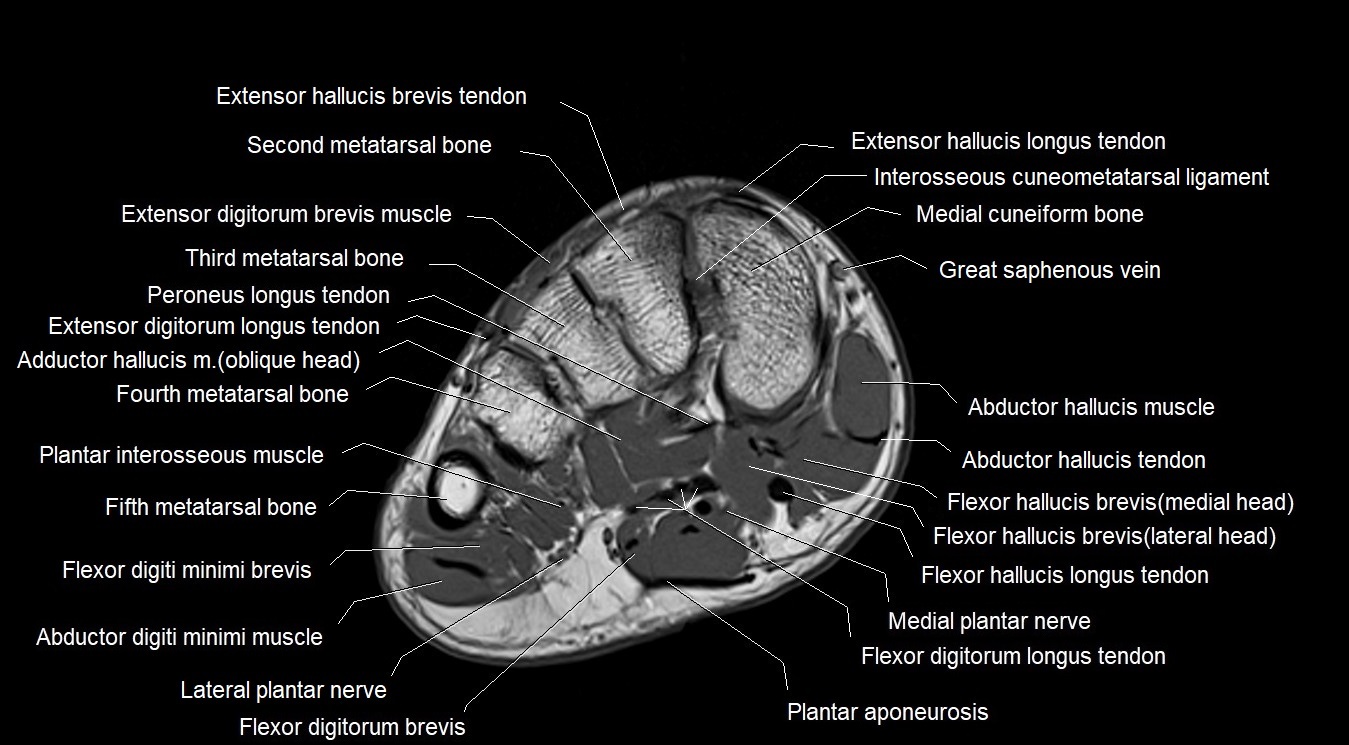
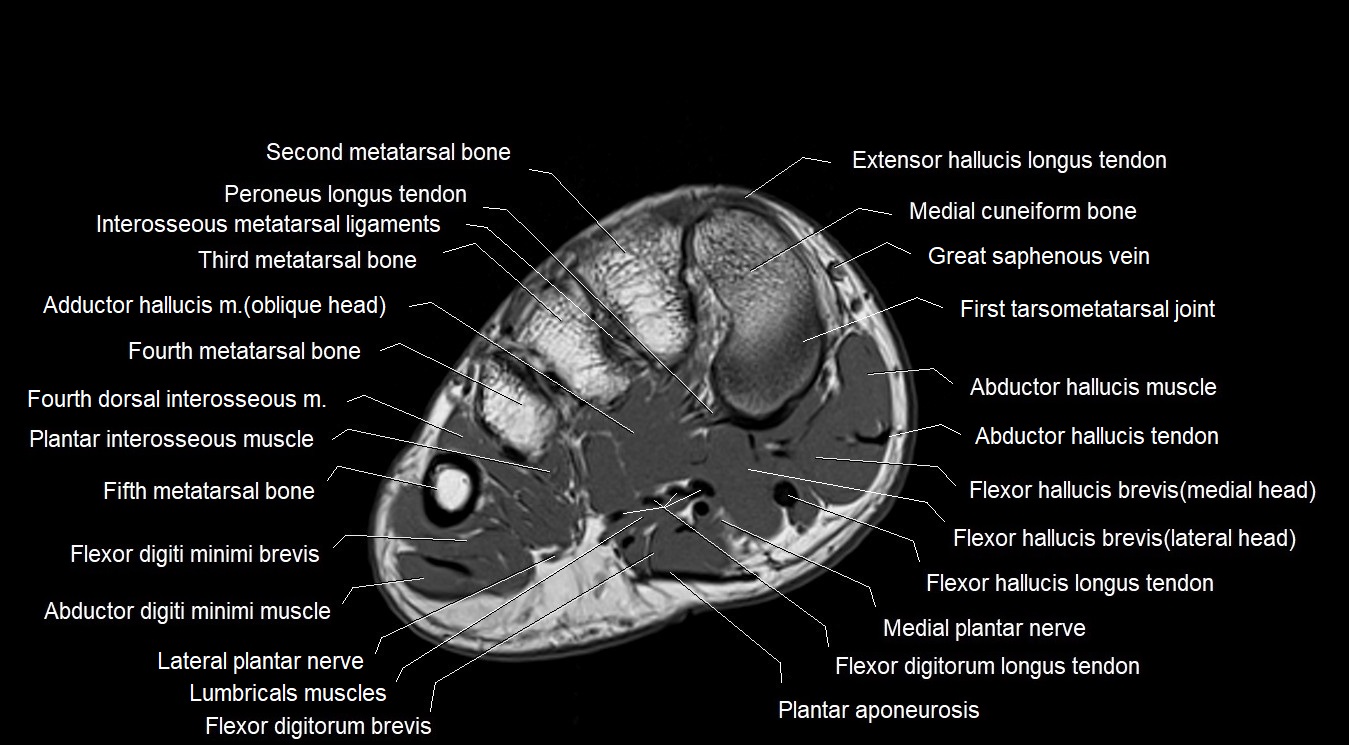
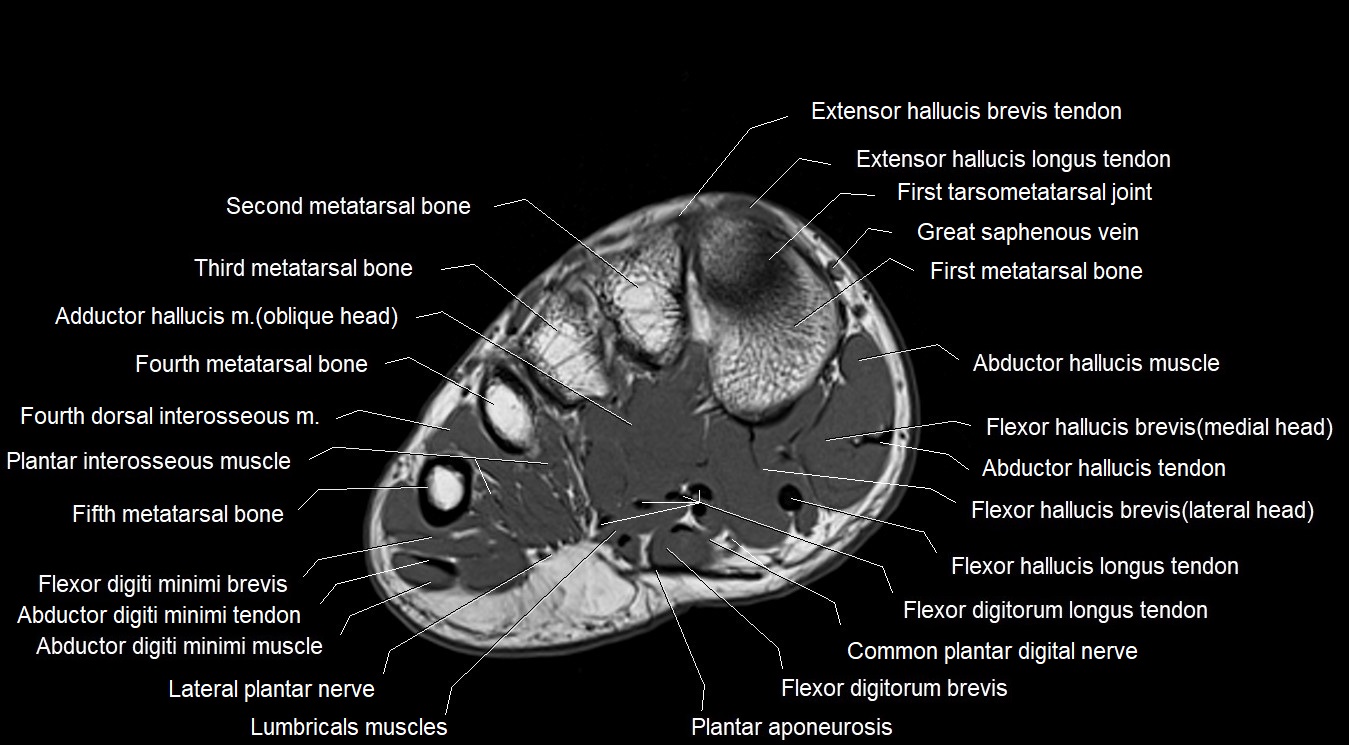
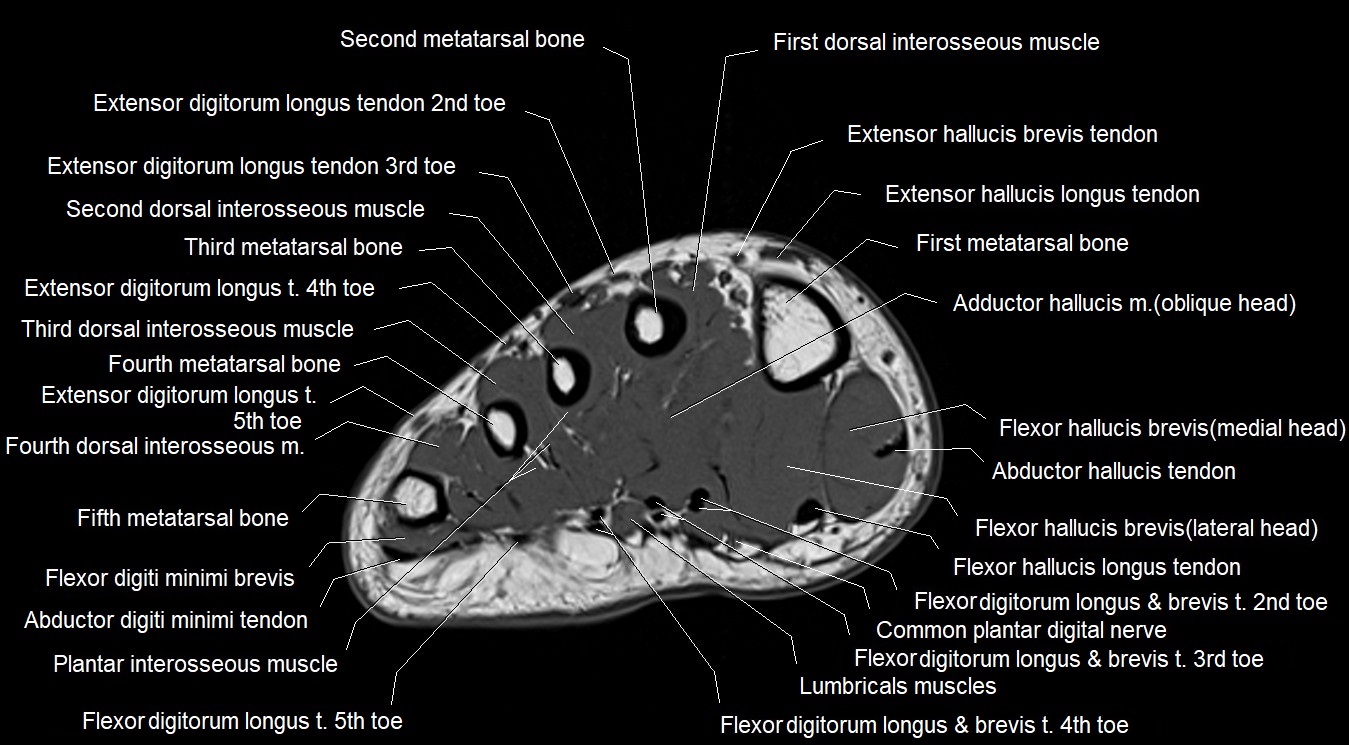
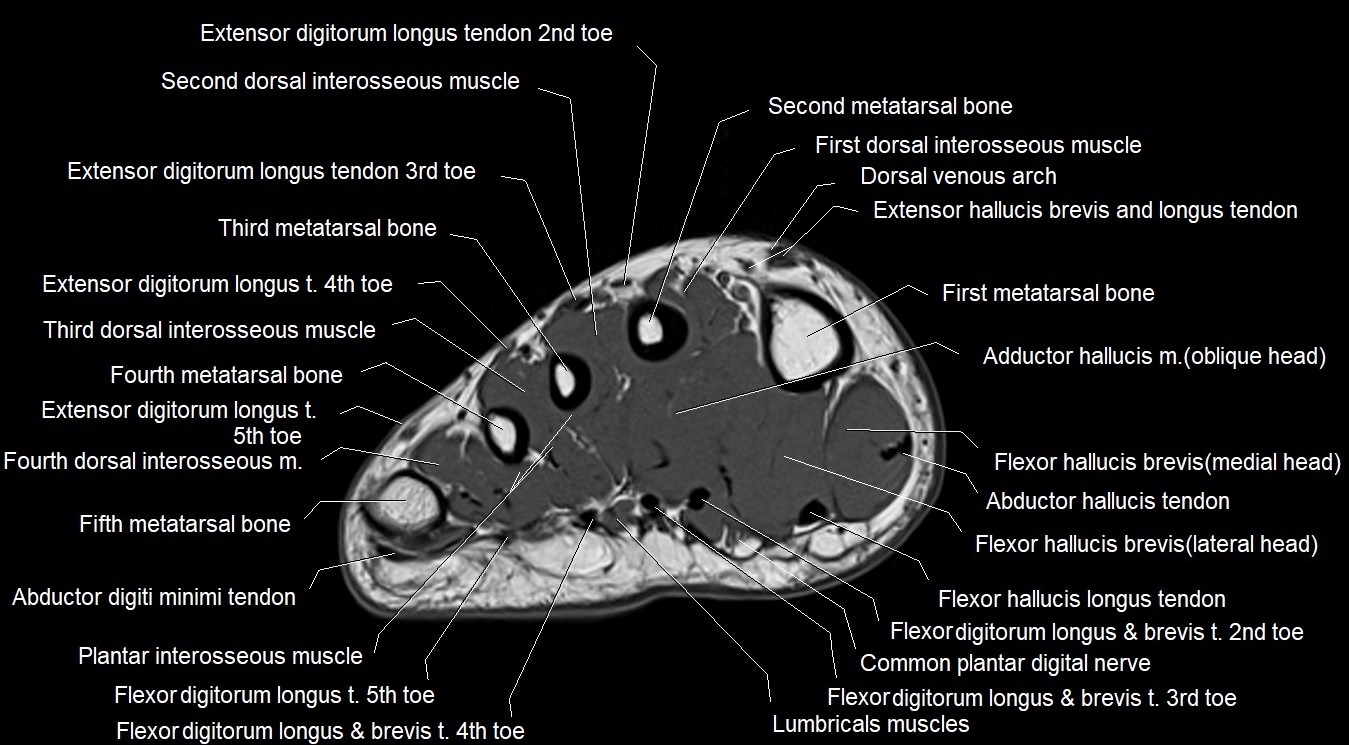
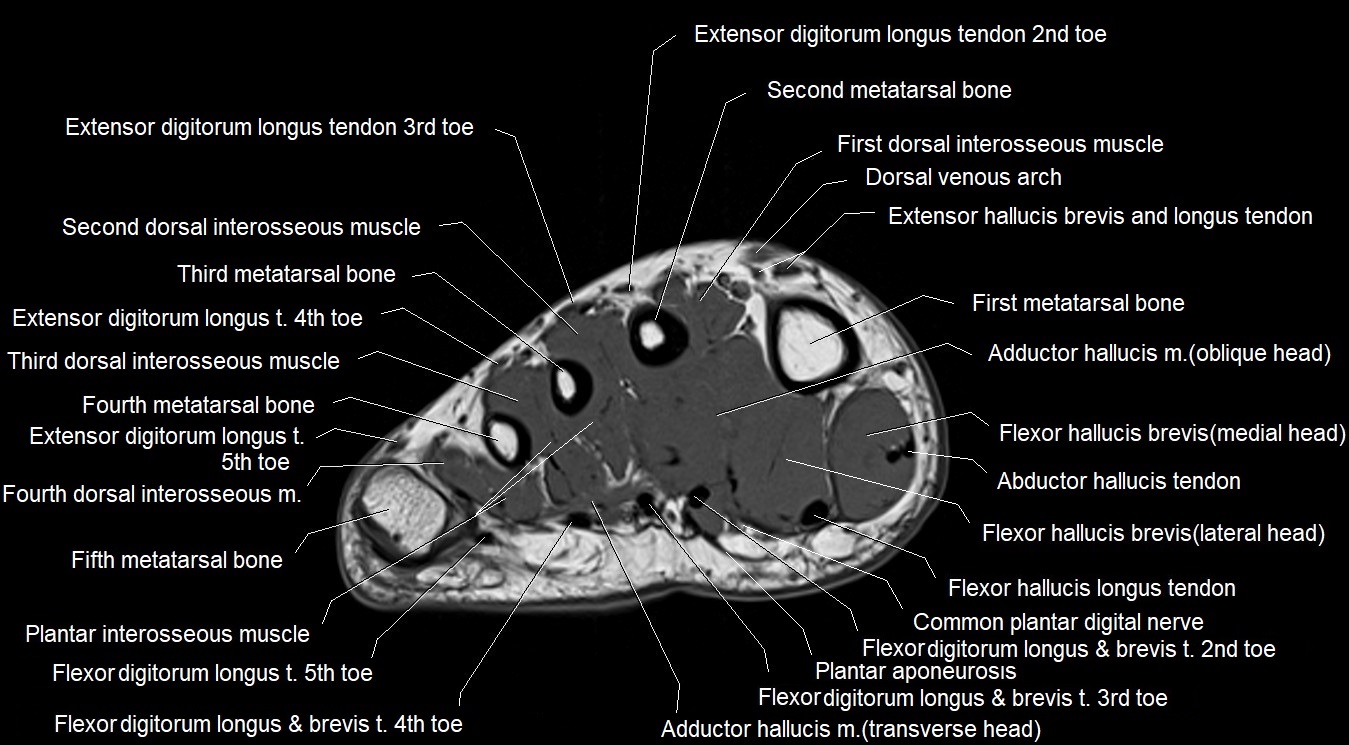
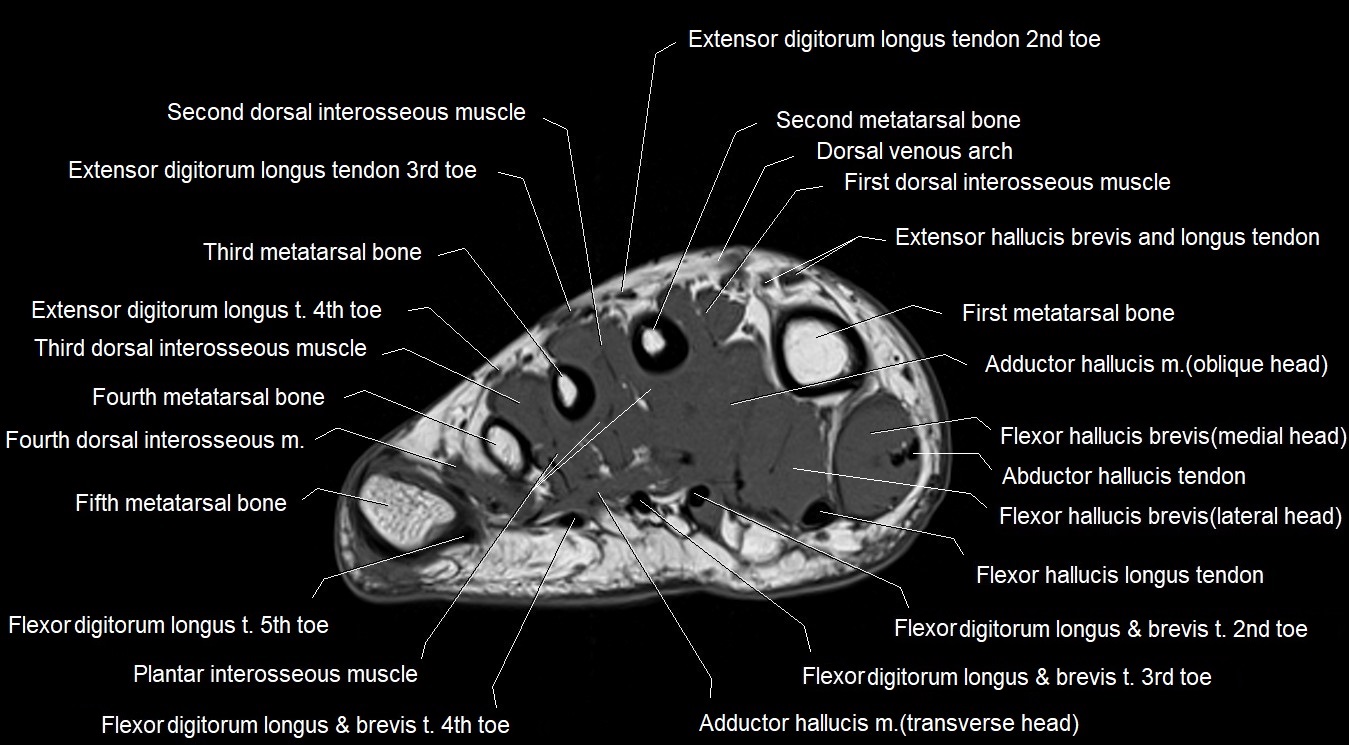
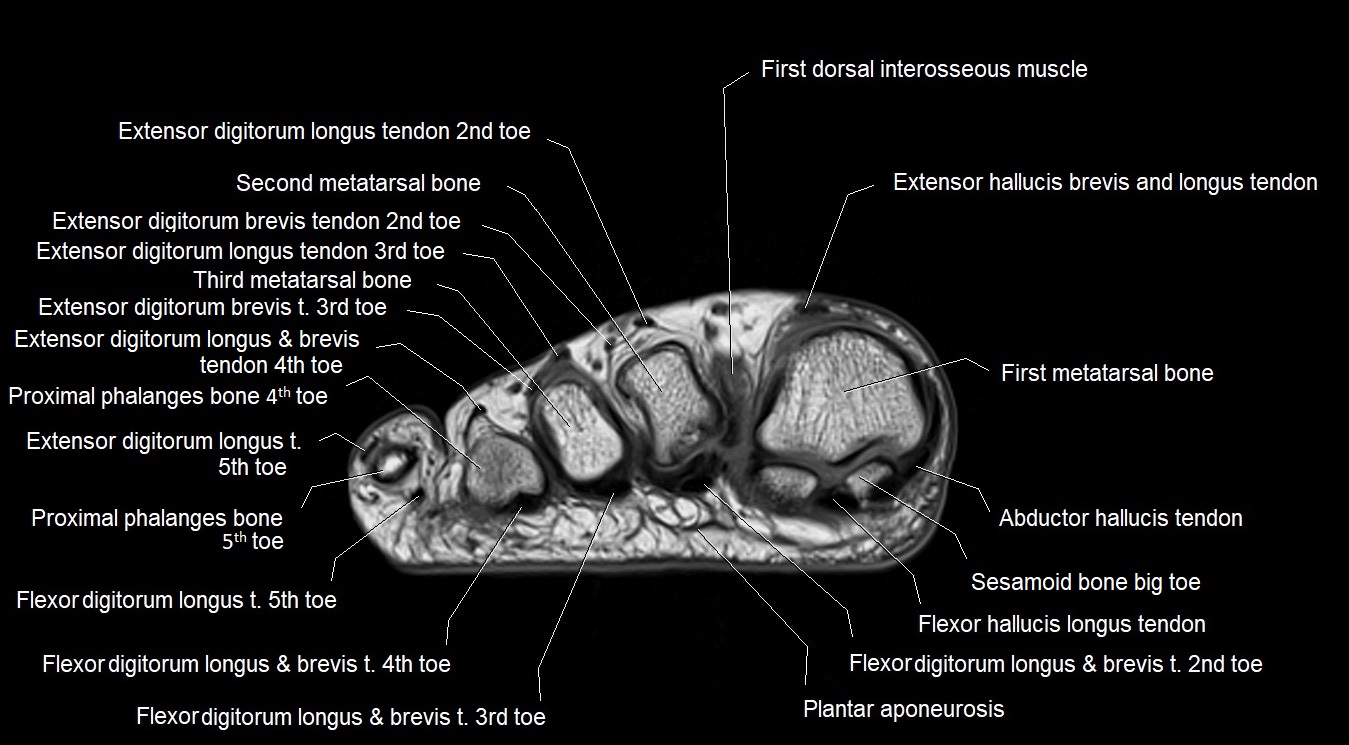
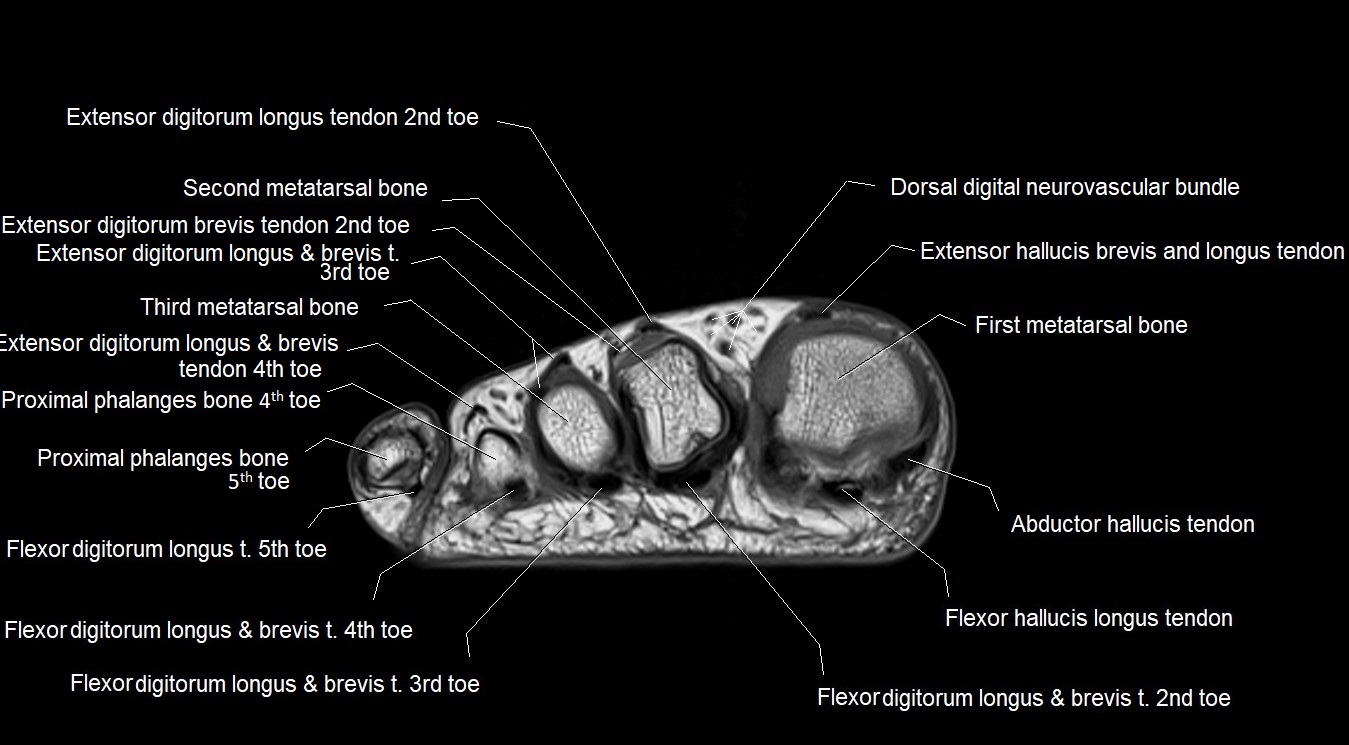
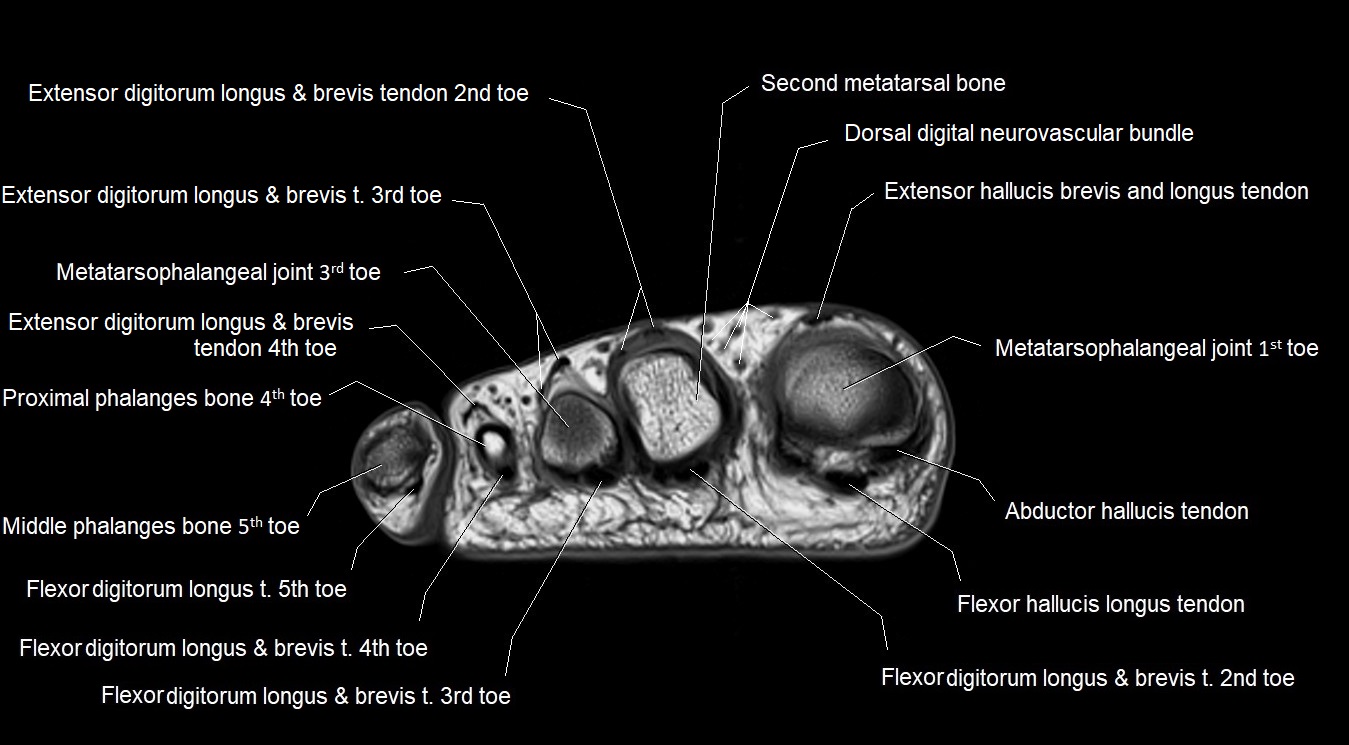
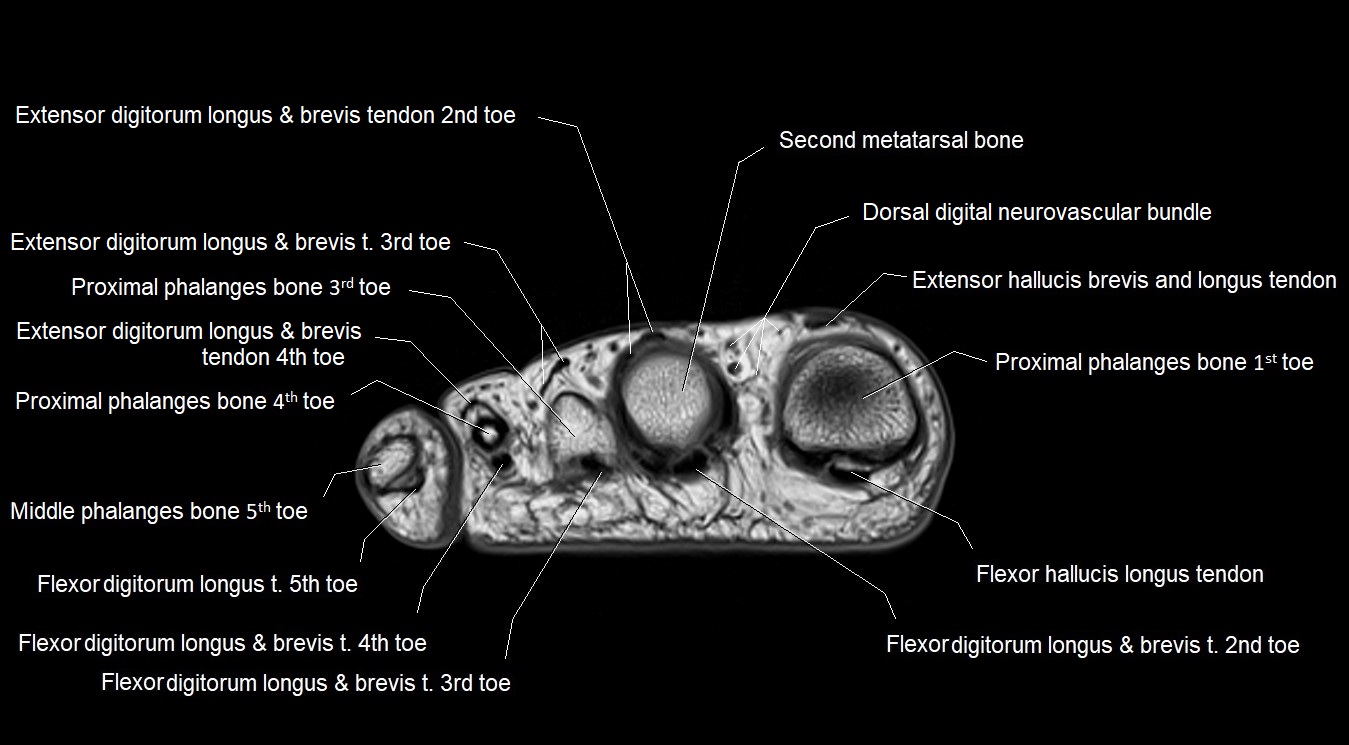
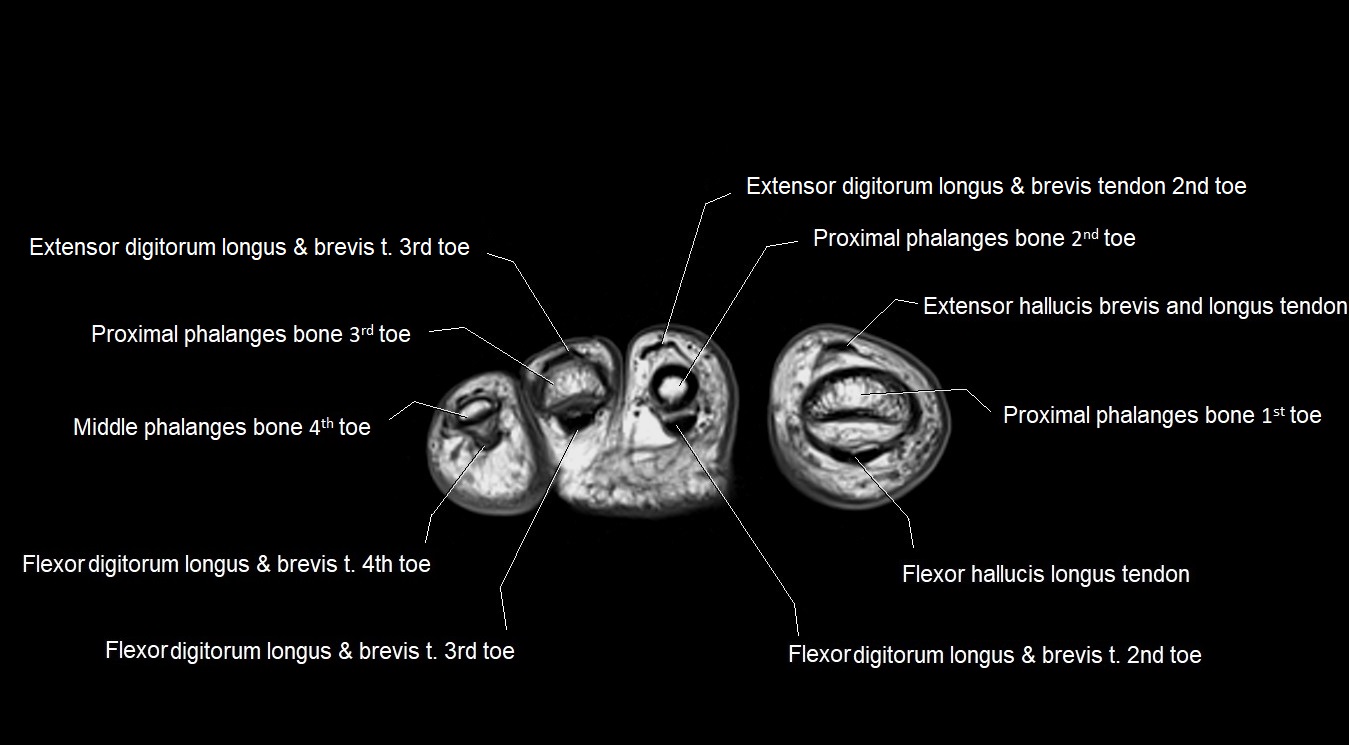
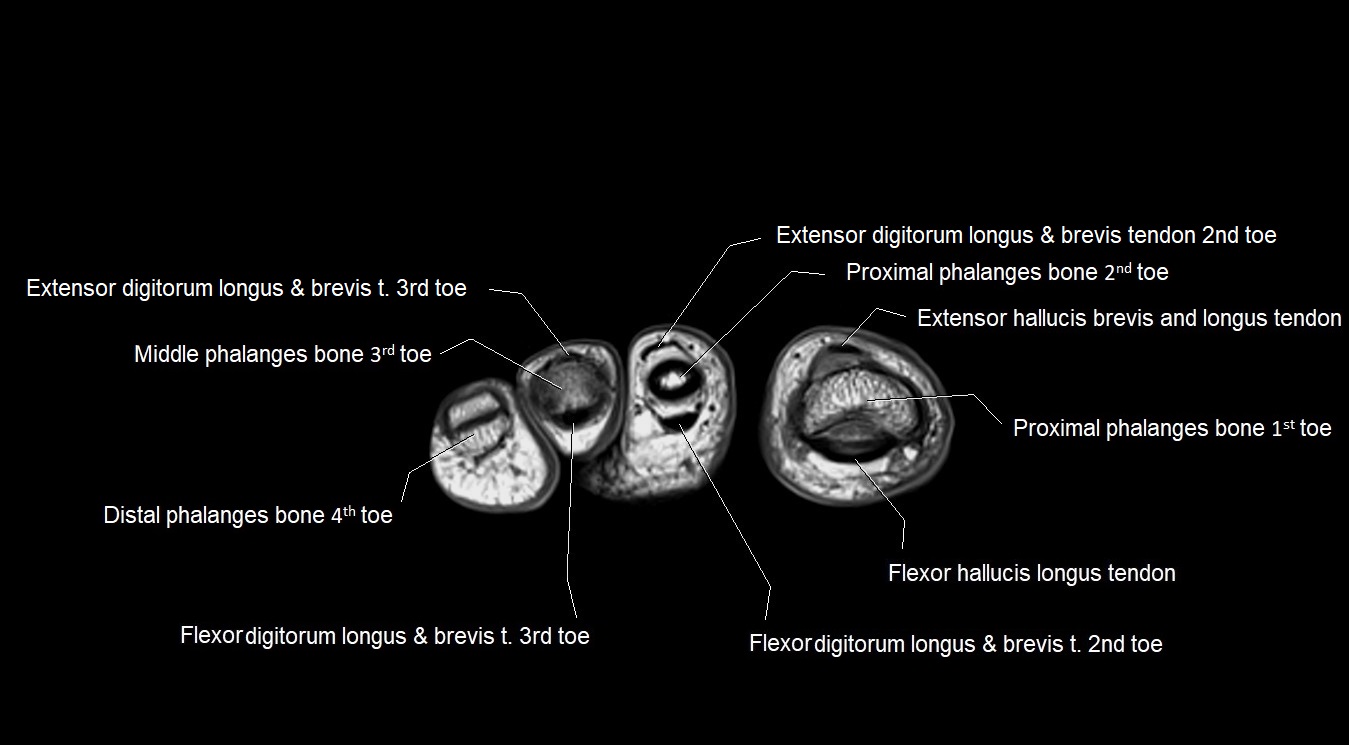
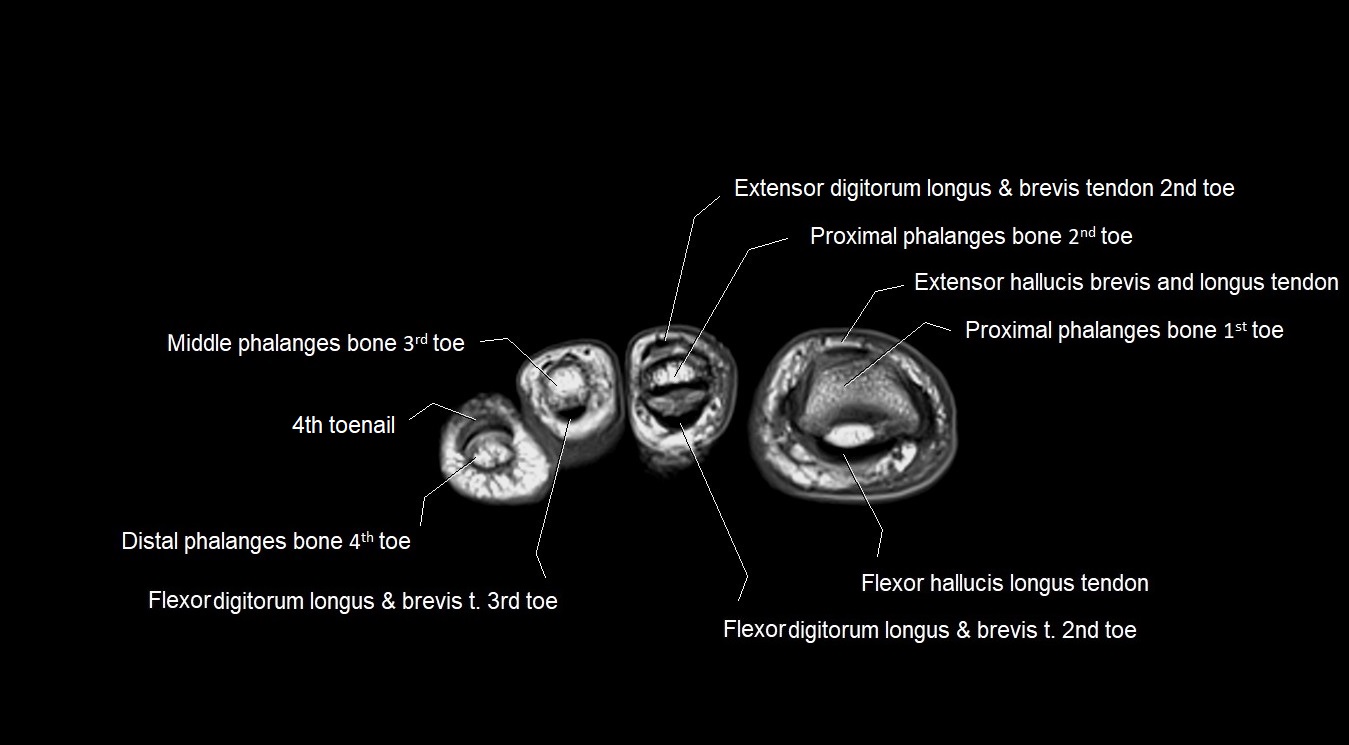
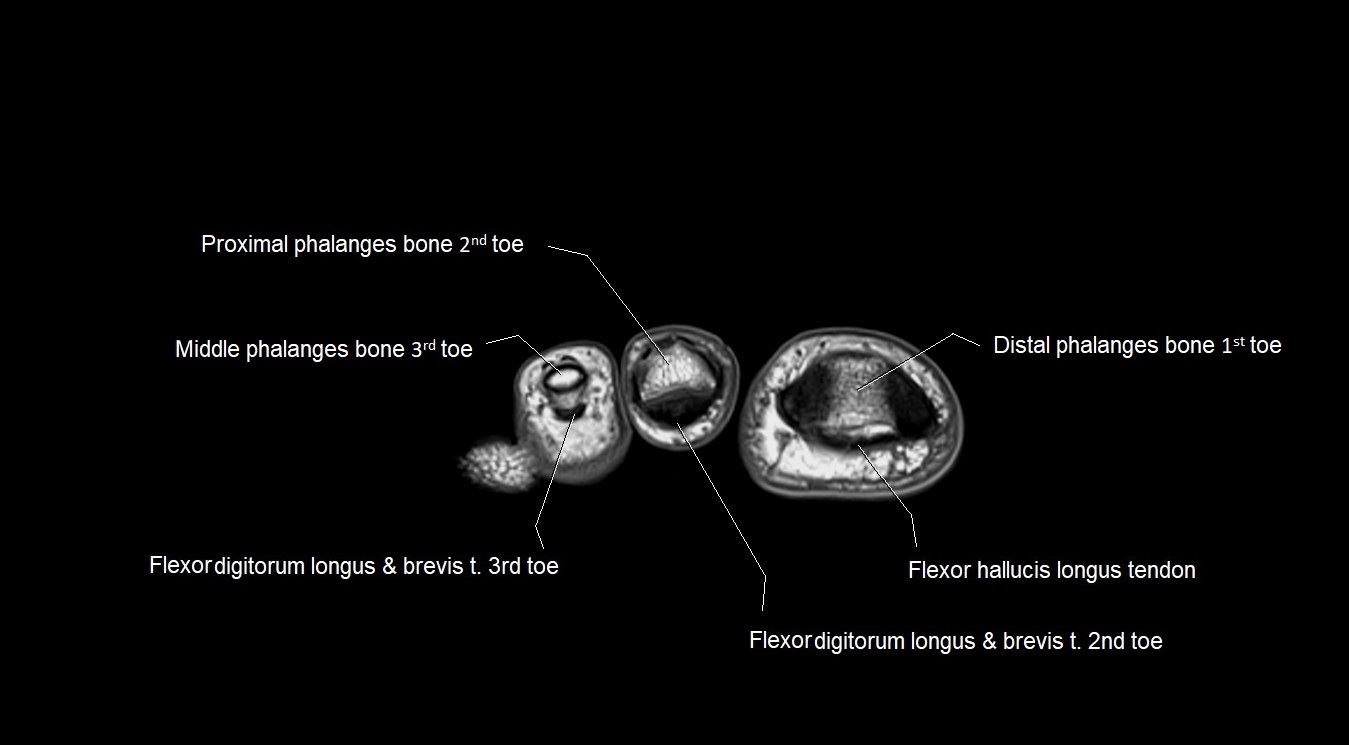
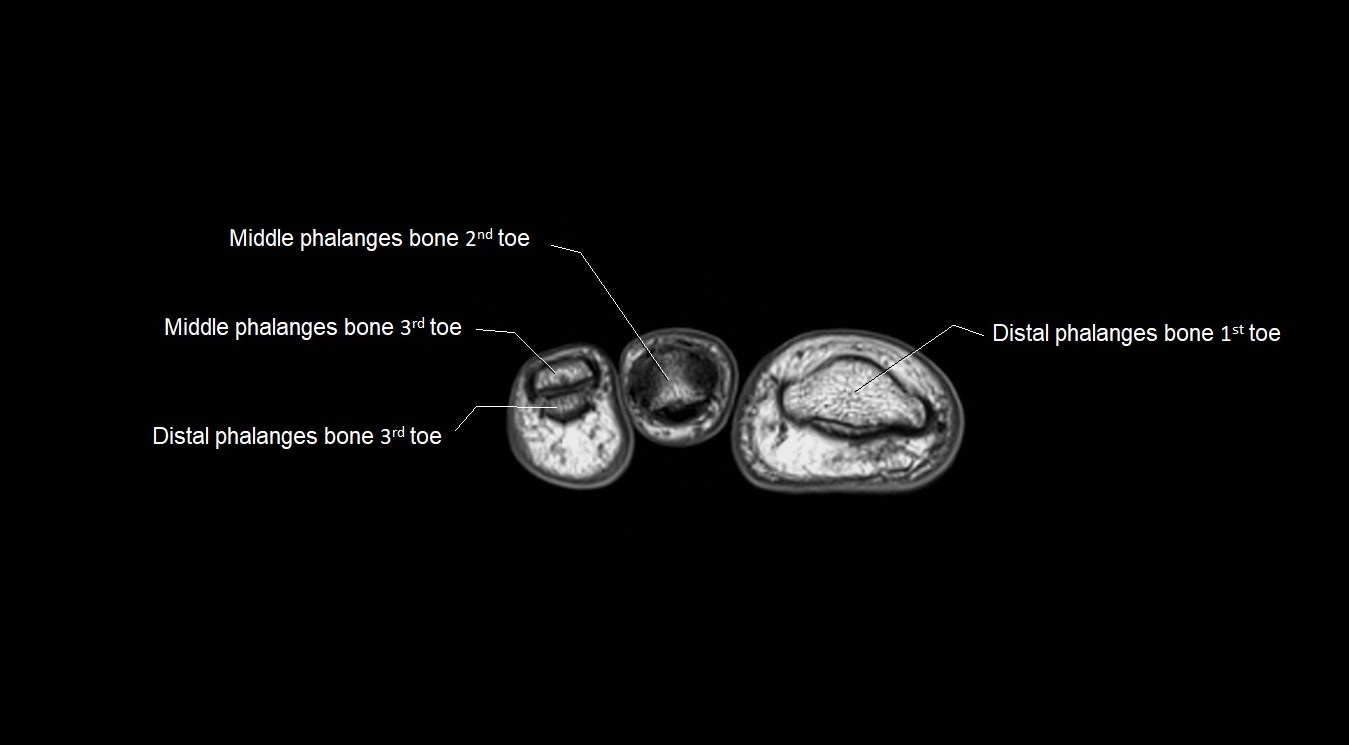
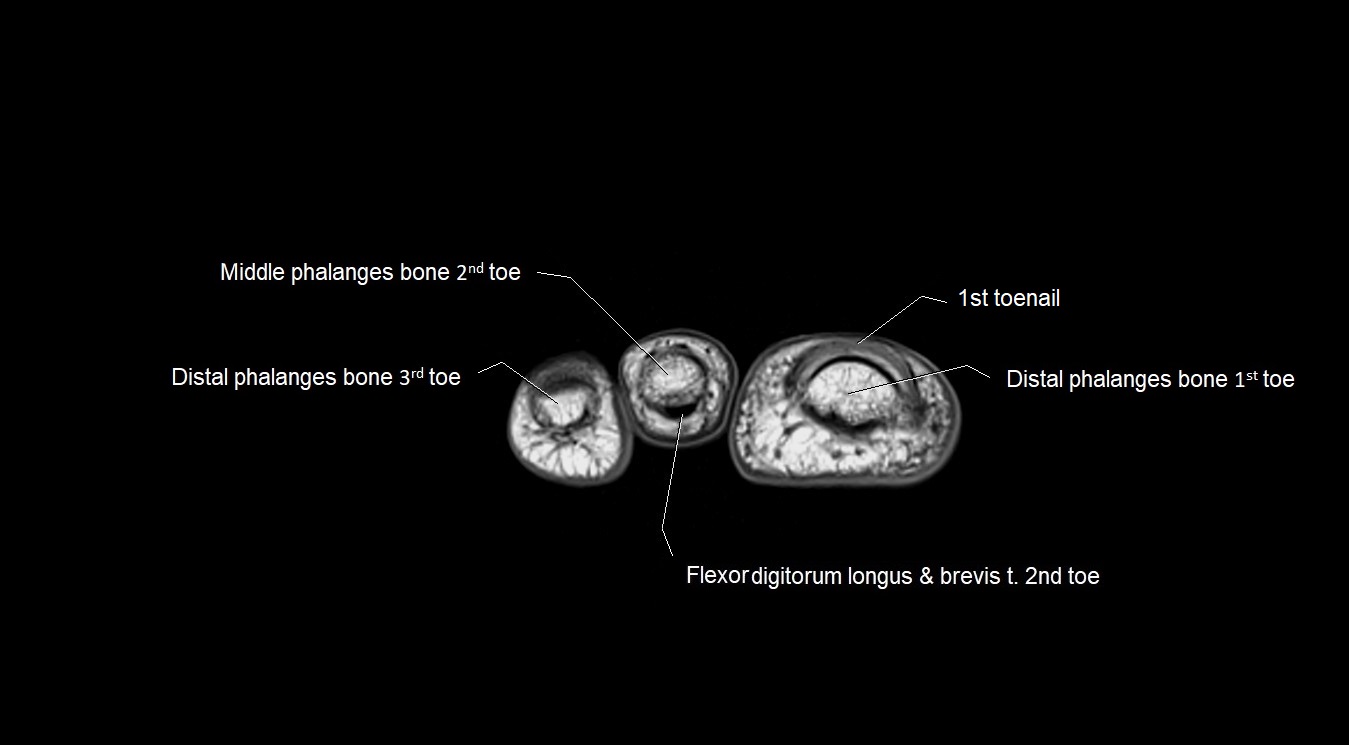
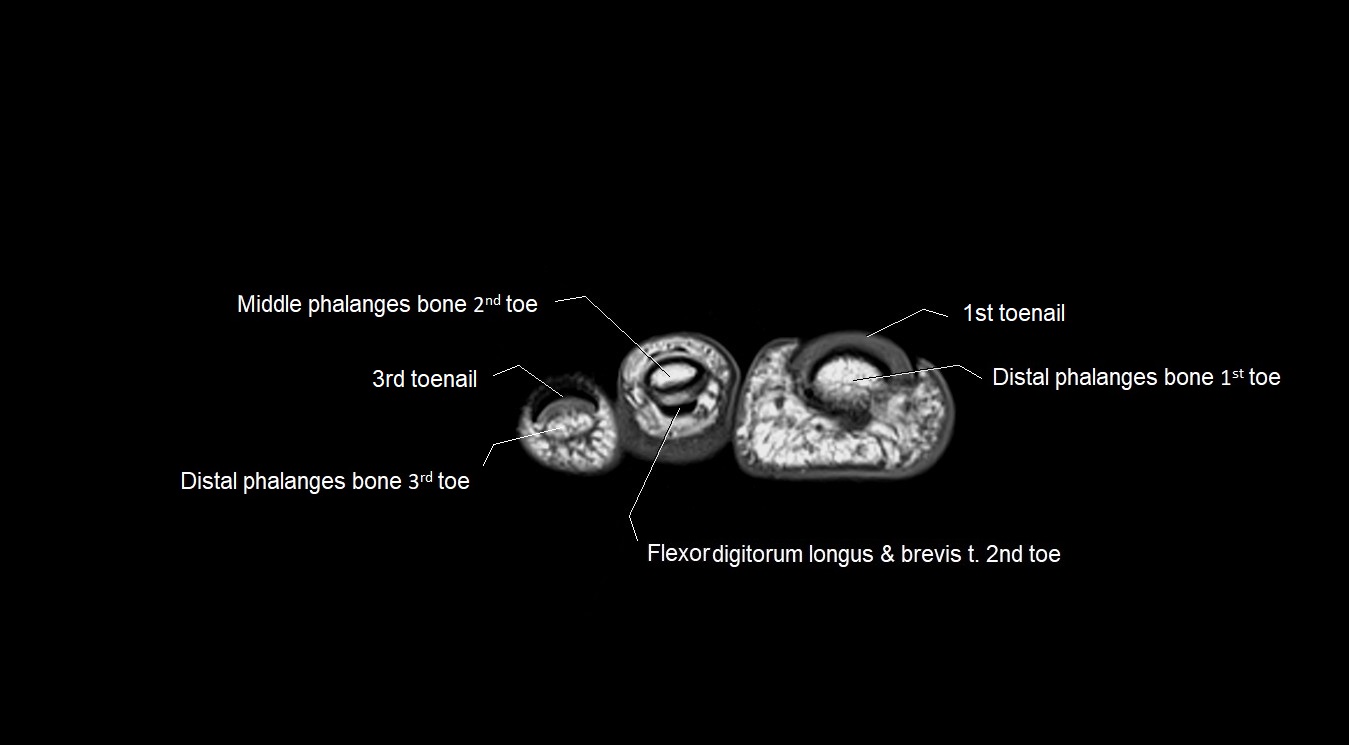
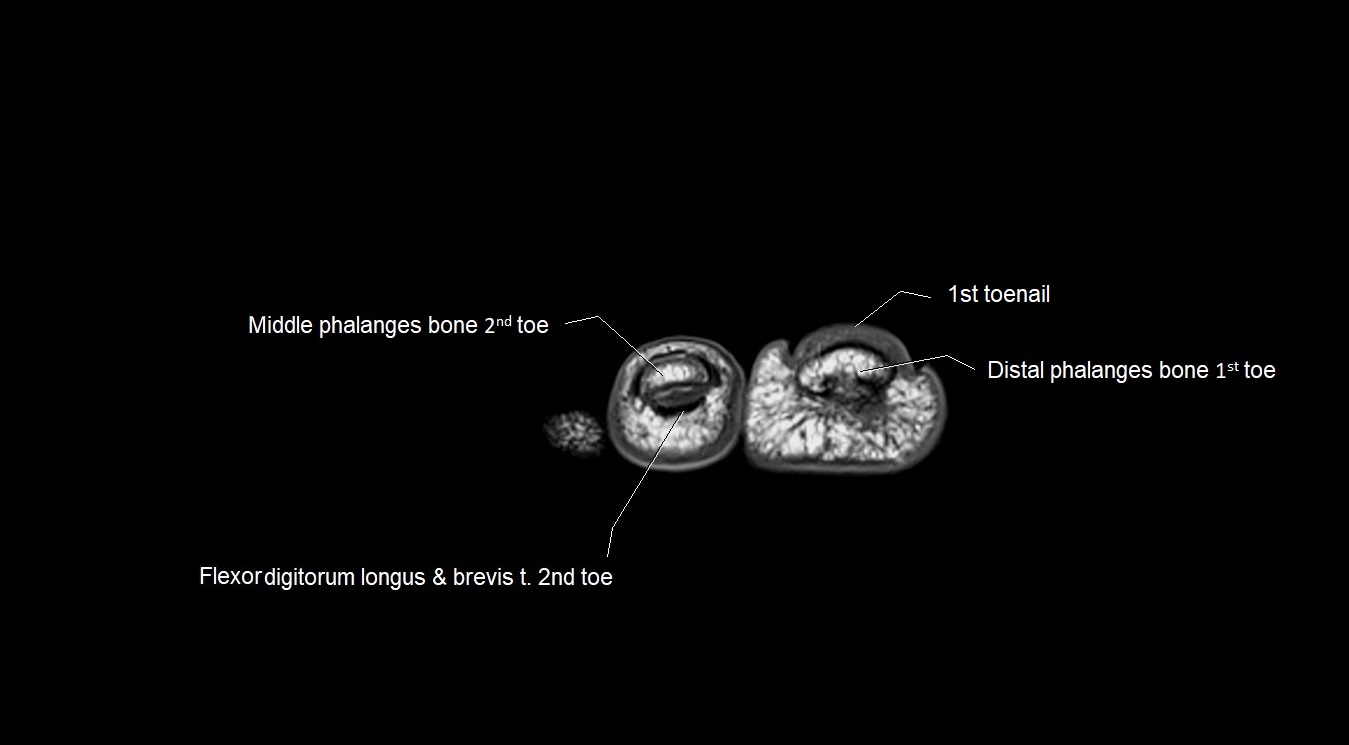
Topic
- Abductor digiti minimi muscle
- Abductor digiti minimi tendon
- Abductor hallucis muscle
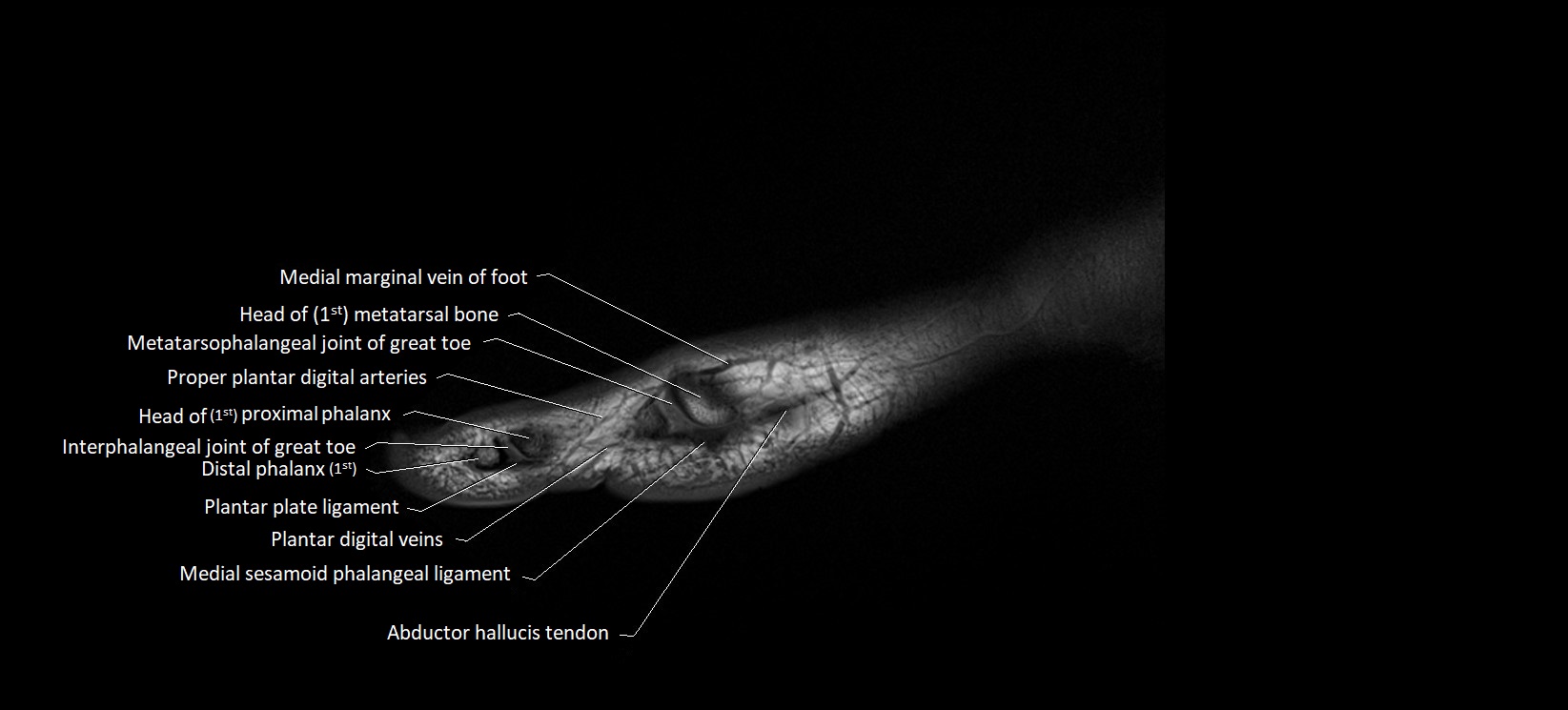
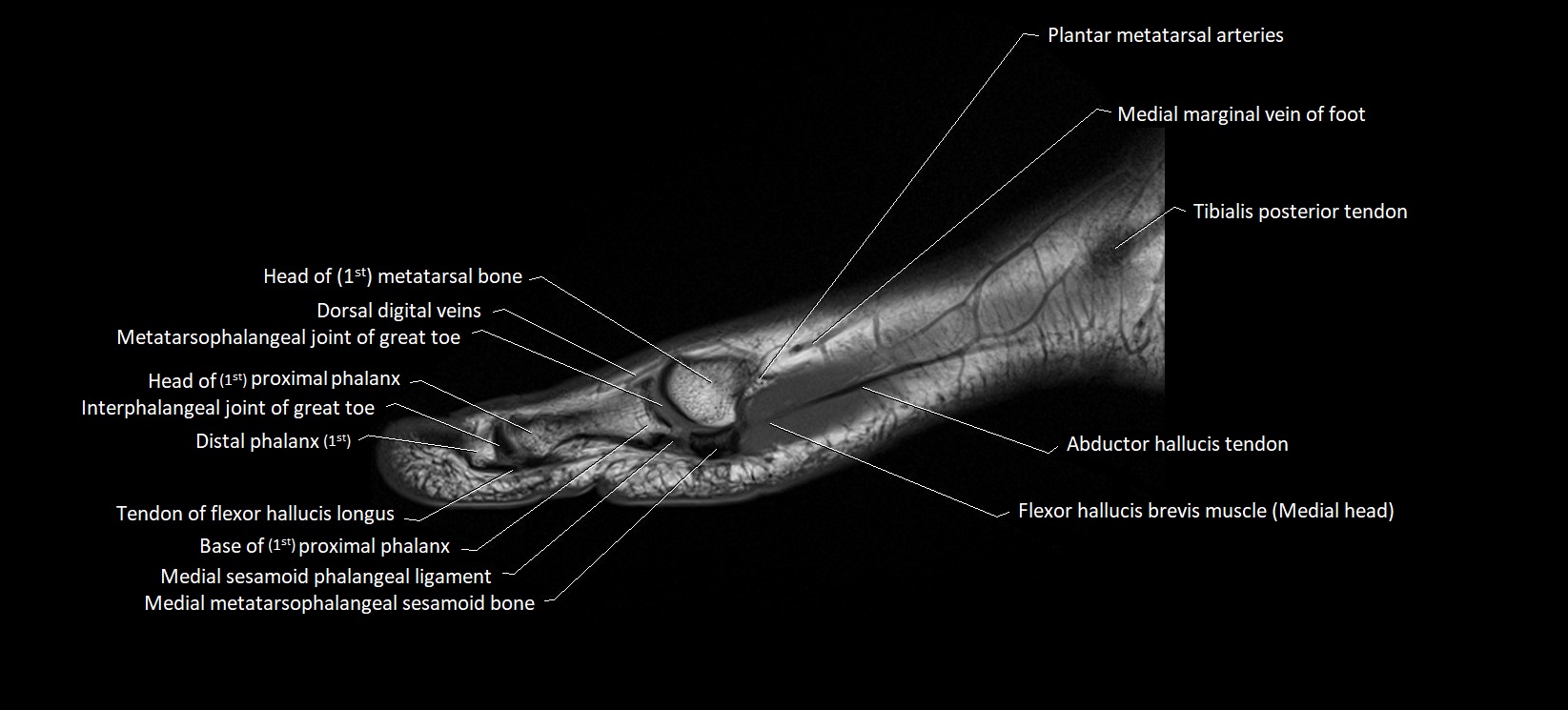
- Abductor hallucis tendon
- Accessory anterior inferior tibiofibular (Bassett’s) ligament
- Achilles tendon
- Adductor hallucis muscle
- Anastomotic branch sural nerve
- Ankle joint
- Anterior colliculus of medial malleolus
- Anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament
- Anterior process of calcaneus
- Anterior talar articular surface
- Anterior talofibular ligament
- Anterior tibial artery
- Anterior tibial veins
- Anterior tibiotalar ligament
- Apex of lateral malleolus
- Apex of medial malleolus
- Articular facet of lateral malleolus
- Articular facet of medial malleolus
- Articular surface for cuboid bone
- Base of distal phalanx of great toe
- Base of first metatarsal bone
- Base of metatarsal bone
- Base of phalanx of foot
- Base of proximal phalanx of great toe
- Bifurcate ligament
- Body of distal phalanx of great toe
- Body of first metatarsal bone
- Body of metatarsal bone
- Body of phalanx of foot
- Body of proximal phalanx of great toe
- Body of talus
- Body of the metatarsal bone
- Calcaneal perforator veins
- Calcaneal process of cuboid bone
- Calcaneal tubercle
- Calcaneal tuberosity
- Calcaneocuboid joint
- Calcaneocuboid ligament (Bifurcate ligament)
- Calcaneofibular ligament
- Calcaneonavicular ligament (Bifurcate ligament)
- Calcaneus
- Cockett’s perforator veins
- Cuboid articular surface
- Cuboid bone
- Cuboideonavicular joint
- Cuneiform perforator veins
- Cuneocuboid Joint
- Cuneocuboid interosseous ligament
- Cuneonavicular joint
- Deep fibular nerve
- Deep plantar arterial arch
- Deep posterior tibiotalar ligament
- Deltoid ligament complex
- Dermis of skin
- Digital slips of plantar aponeurosis
- Distal interphalangeal joint of foot
- Distal phalanx of foot
- Distal phalanx of great toe
- Dorsal calcaneocuboid ligament
- Dorsal cuneocuboid ligament
- Dorsal cuneonavicular ligaments
- Dorsal digital nerve of foot
- Dorsal digital nerves
- Dorsal fascia of foot
- Dorsal intercuneiform ligaments
- Dorsal interossei tendons of foot
- Dorsal interosseous muscles
- Dorsal metatarsal arteries
- Dorsal metatarsal ligaments
- Dorsal metatarsal veins
- Dorsal perforator veins
- Dorsal talonavicular ligament
- Dorsal tarsometatarsal ligaments
- Dorsal venous arch of foot
- Dorsalis pedis artery
- Dorsalis pedis veins
- Epidermis
- Extensor digitorum brevis muscle
- Extensor digitorum brevis tendons
- Extensor digitorum longus tendon
- Extensor digitorum longus tendons
- Extensor hallucis brevis muscle
- Extensor hallucis brevis tendon
- Extensor hallucis longus muscle
- Extensor hallucis longus tendon
- Extensor hood of foot
- Fascia cruris
- Fibula
- Fibula shaft
- Fibular artery
- Fibular notch of tibia
- Fibular trochlea
- Fibular veins
- Fibularis brevis muscle
- Fibularis brevis tendon
- Fibularis longus tendon
- Fibularis tertius muscle
- Fibularis tertius tendon
- Fifth metatarsal bone
- Fifth toe
- First dorsal cuneometatarsal ligament (Dorsal lisfranc ligament)
- First dorsal interosseous muscle of foot
- First intercuneiform joint
- First lumbrical muscle of foot
- First metatarsal bone
- First plantar cuneometatarsal ligament (Plantar lisfranc ligament)
- First plantar interosseous muscle of foot
- First tarsometatarsal joint
- Flexor digiti minimi brevis muscle
- Flexor digitorum brevis muscle
- Flexor digitorum brevis tendons
- Flexor digitorum longus muscle
- Flexor digitorum longus tendon
- Flexor digitorum longus tendons
- Flexor hallucis brevis muscle
- Flexor hallucis brevis tendons
- Flexor hallucis longus muscle
- Flexor hallucis longus tendon
- Flexor retinaculum
- Fourth dorsal interosseous muscle of foot
- Fourth lumbrical muscle of foot
- Fourth metatarsal bone
- Fourth toe
- Great toe (Hallux)
- Head of distal phalanx of great toe
- Head of first metatarsal bone
- Head of metatarsal bone
- Head of phalanx of foot
- Head of proximal phalanx of great toe
- Head of talus
- Hypodermis of skin
- Inferior articular surface of tibia
- Inferior calcaneal nerve (Baxter’s nerve)
- Inferior extensor retinaculum
- Inferior peroneal retinaculum
- Inferior tibiofibular joint
- Inferior transverse ligament
- Inferoplantar longitudinal calcaneonavicular ligament
- Intercuneiform ligaments
- Intermediate cuneiform bone
- Intermediate dorsal cutaneous nerve
- Intermetatarsal joints
- Interosseous cuneometatarsal Ligament (Lisfranc Proper Ligament)
- Interosseous intercuneiform ligaments
- Interosseous membrane (middle tibiofibular ligament)
- Interosseous membrane of leg
- Interphalangeal joint of great toe
- Interphalangeal sesamoid of great toe
- Intersesamoid ligament
- Kager fat pad (pre-Achilles fat pad)
- Kager’s fat pad
- Knot of Henry
- Lateral branch of deep fibular nerve
- Lateral calcaneal artery
- Lateral calcaneal branches of sural nerve
- Lateral calcaneal veins
- Lateral collateral ligament of big toe (lateral metatarsophalangeal collateral ligament)
- Lateral collateral ligament of interphalangeal joint of foot
- Lateral cuneiform bone
- Lateral dorsal cutaneous nerve
- Lateral head of flexor hallucis brevis muscle
- Lateral malleolar facet of talus
- Lateral malleolus
- Lateral marginal vein of foot
- Lateral nail fold (toe)
- Lateral perforator veins of leg
- Lateral plantar artery
- Lateral plantar nerve
- Lateral plantar veins
- Lateral process of calcaneal tuberosity
- Lateral process of talus
- Lateral sesamoid bone
- Lateral sesamoid phalangeal ligament
- Lateral talocalcaneal ligament
- Lateral tarsal artery
- Lateral tarsal veins
- Lateral tubercle of talus
- Lisfranc complex
- Lisfranc ligament
- Long plantar ligament
- Lumbrical muscles
- Malleolar fossa
- Medial branch of deep fibular nerve
- Medial calcaneal nerve
- Medial calcaneal nerve (anterior cutaneous branches)
- Medial calcaneal nerve (posterior cutaneous branches)
- Medial collateral ligament of big toe (medial metatarsophalangeal collateral ligament)
- Medial collateral ligament of interphalangeal joint of foot
- Medial cuneiform bone
- Medial dorsal cutaneous nerve
- Medial head of flexor hallucis brevis muscle
- Medial malleolar facet of talus
- Medial malleolus
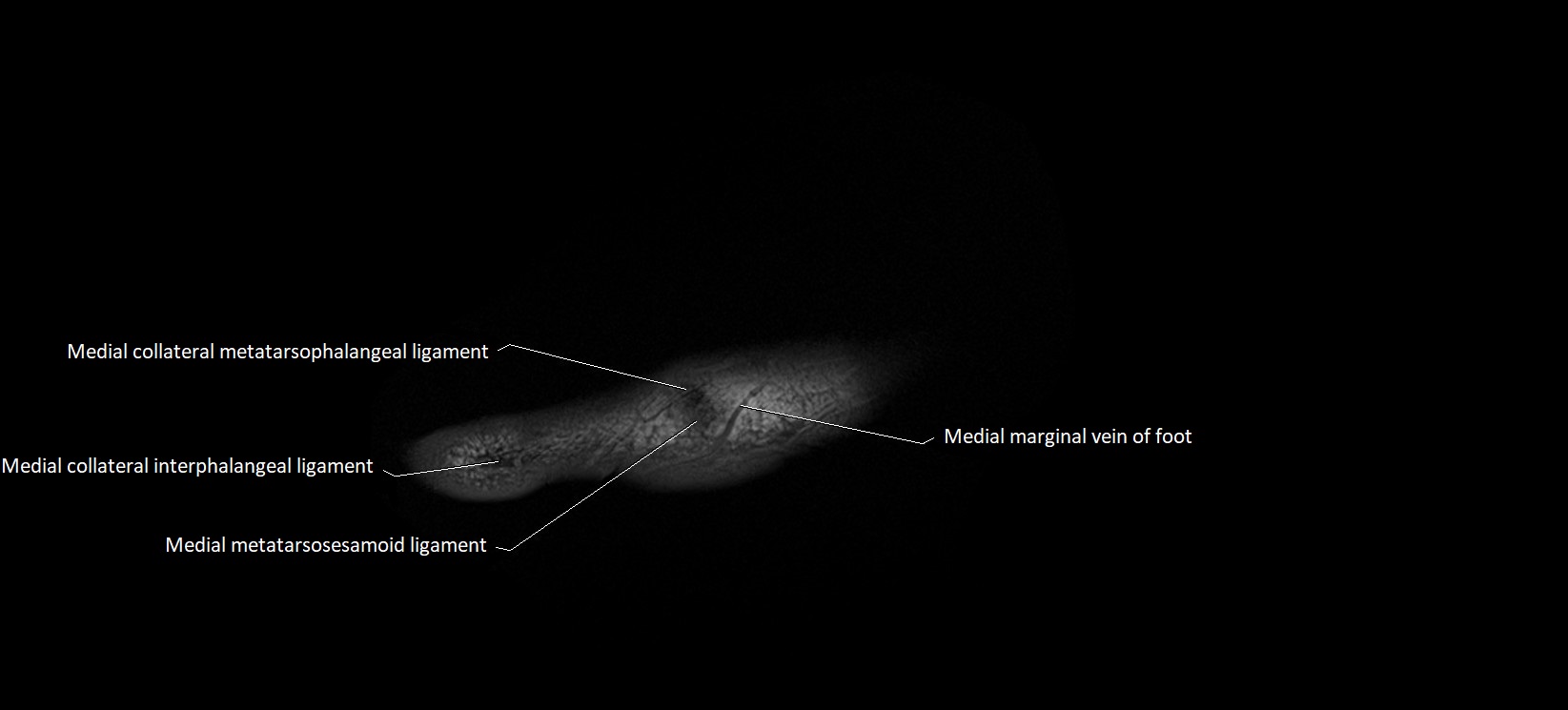
- Medial marginal vein of foot
- Medial perforator veins of leg
- Medial plantar artery
- Medial plantar nerve
- Medial plantar veins
- Medial process of calcaneal tuberosity
- Medial sesamoid bone
- Medial sesamoid phalangeal ligament
- Medial talocalcaneal ligament
- Medial tarsal arteries
- Medial tarsal veins
- Medial tubercle of talus
- Medioplantar oblique calcaneonavicular ligament
- Metatarsal Bones (MT)
- Metatarsal interosseous ligaments
- Metatarsophalangeal joint of great toe
- Metatarsophalangeal joints
- Middle phalanx of foot
- Middle talar articular surface
- Nail (toe)
- Nail bed (toe)
- Nail root (toe)
- Navicular articular surface
- Navicular bone
- Navicular perforator veins
- Neck of talus
- Oblique head of adductor hallucis muscle
- Opponens digiti minimi muscle of foot
- Plantar aponeurosis
- Plantar calcaneocuboid ligament (short plantar ligament)
- Plantar cuboideonavicular ligament
- Plantar cuneocuboid ligament
- Plantar cuneonavicular ligaments
- Plantar intercuneiform ligaments
- Plantar interossei tendons of foot
- Plantar interosseous muscles
- Plantar metatarsal arteries
- Plantar metatarsal ligaments
- Plantar plate ligament
- Plantar tarsometatarsal ligaments
- Plantar venous arch
- Plantaris tendon
- Posterior calcaneal articular facet
- Posterior colliculus of medial malleolus
- Posterior inferior tibiofibular ligament
- Posterior intermalleolar ligament
- Posterior malleolus
- Posterior talar articular surface
- Posterior talofibular ligament
- Posterior tibial artery
- Posterior tibial veins
- Proper plantar digital nerve to great toe
- Proper plantar digital nerves
- Proximal interphalangeal joints of foot
- Proximal nail fold
- Proximal phalanx of foot
- Proximal phalanx of great toe
- Quadratus plantae muscle
- Quadratus plantae tendon
- Saphenous nerve
- Second dorsal interosseous muscle of foot
- Second intercuneiform joint
- Second lumbrical muscle of foot
- Second metatarsal bone
- Second plantar interosseous muscle of foot
- Second tarsometatarsal joint
- Second toe
- Sesamoid bone of great toe
- Small saphenous vein
- Spring ligament complex
- Submalleolar foot perforator veins
- Subtalar joint
- Superficial fibular nerve
- Superficial plantar venous plexus
- Superficial posterior tibiotalar ligament
- Superior extensor retinaculum
- Superior facet of talus
- Superior peroneal retinaculum
- Superomedial calcaneonavicular ligament
- Sural nerve
- Sustentaculum tali
- Synovial fluid
- Talocalcaneal interosseous ligament
- Talocalcaneal joint
- Talocalcaneonavicular joint
- Talonavicular joint
- Talus
- Tarsal sinus
- Tarsometatarsal joints
- Tendon sheath
- Third dorsal interosseous muscle of foot
- Third lumbrical muscle of foot
- Third metatarsal bone
- Third plantar interosseous muscle of foot
- Third toe
- Tibia
- Tibial nerve
- Tibialis anterior tendon
- Tibialis posterior muscle
- Tibialis posterior tendon
- Tibialis posterior tendon (cuneiform insertions)
- Tibialis posterior tendon (lateral slips)
- Tibialis posterior tendon (medial slip)
- Tibialis posterior tendon (metatarsal insertions)
- Tibiocalcaneal ligament
- Tibiofemoral joint space
- Tibionavicular ligament
- Tibiospring Ligament
- Transverse head of adductor hallucis muscle
- Transverse tarsal joint
- Trochlea of phalanx
- Trochlea of phalanx of great toe
- Trochlea of talus
- Tuberosity of cuboid bone
- Tuberosity of distal phalanx of foot
- Tuberosity of distal phalanx of great toe
- Tuberosity of fifth metatarsal bone
- Tuberosity of first metatarsal bone
- Tuberosity of navicular bone
- great saphenous vein
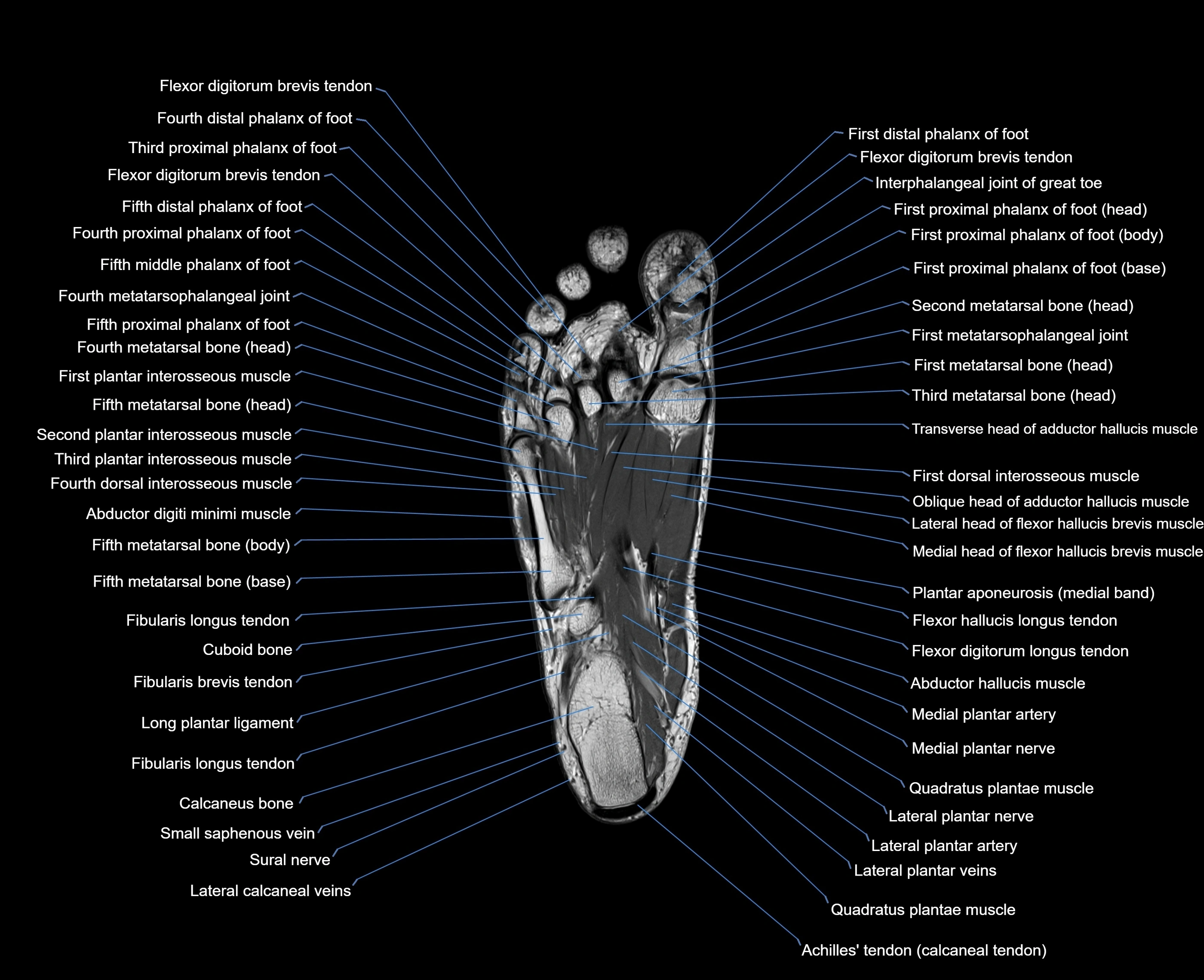
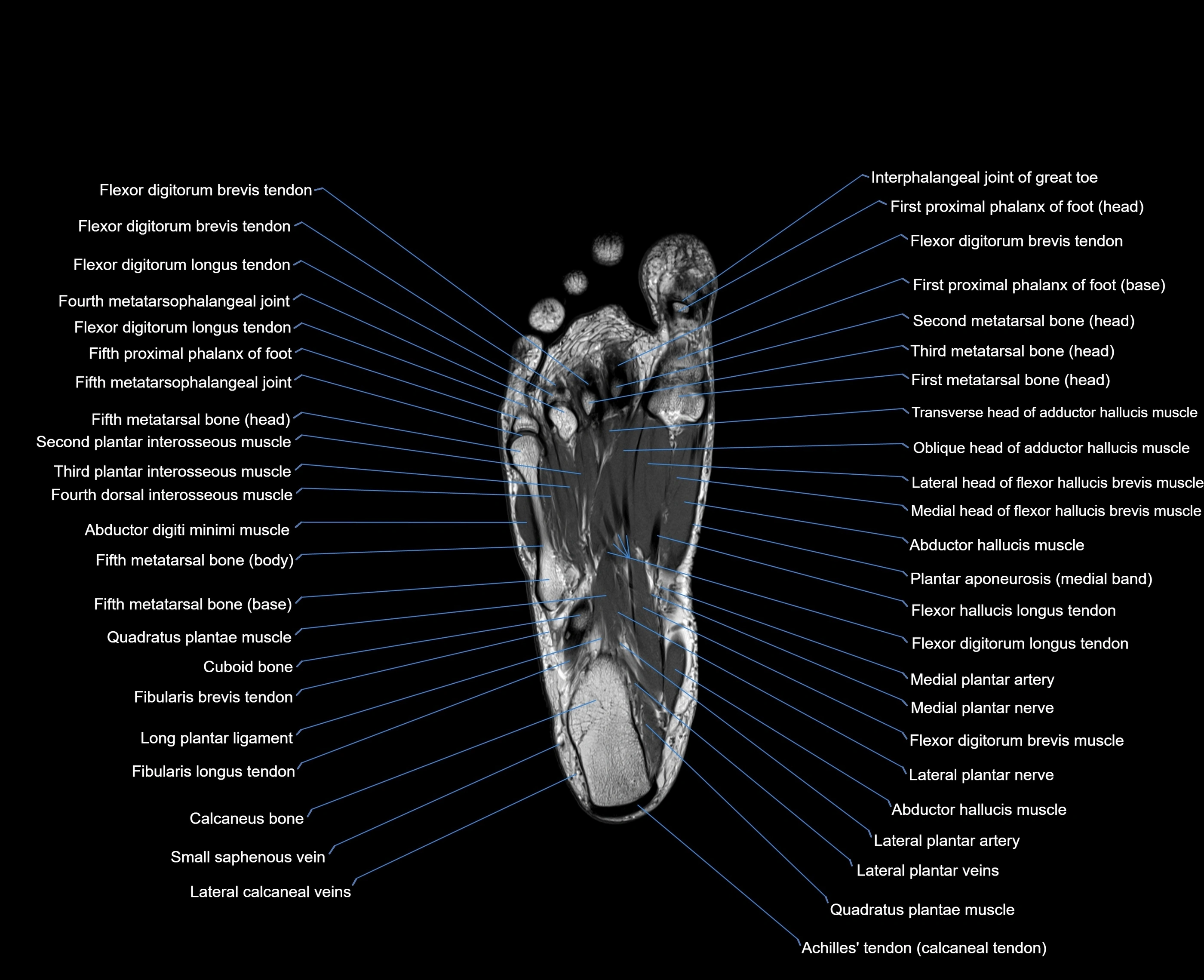
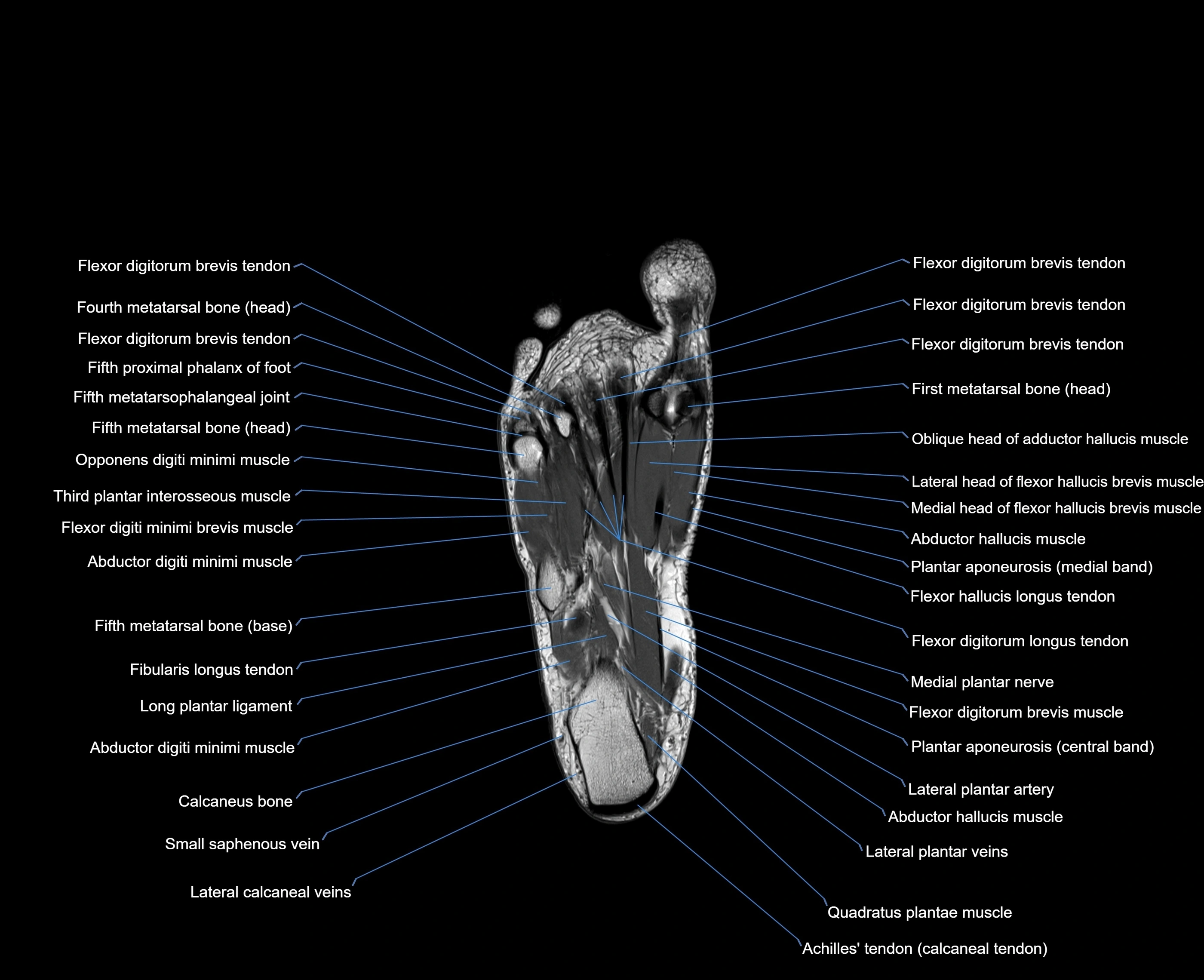
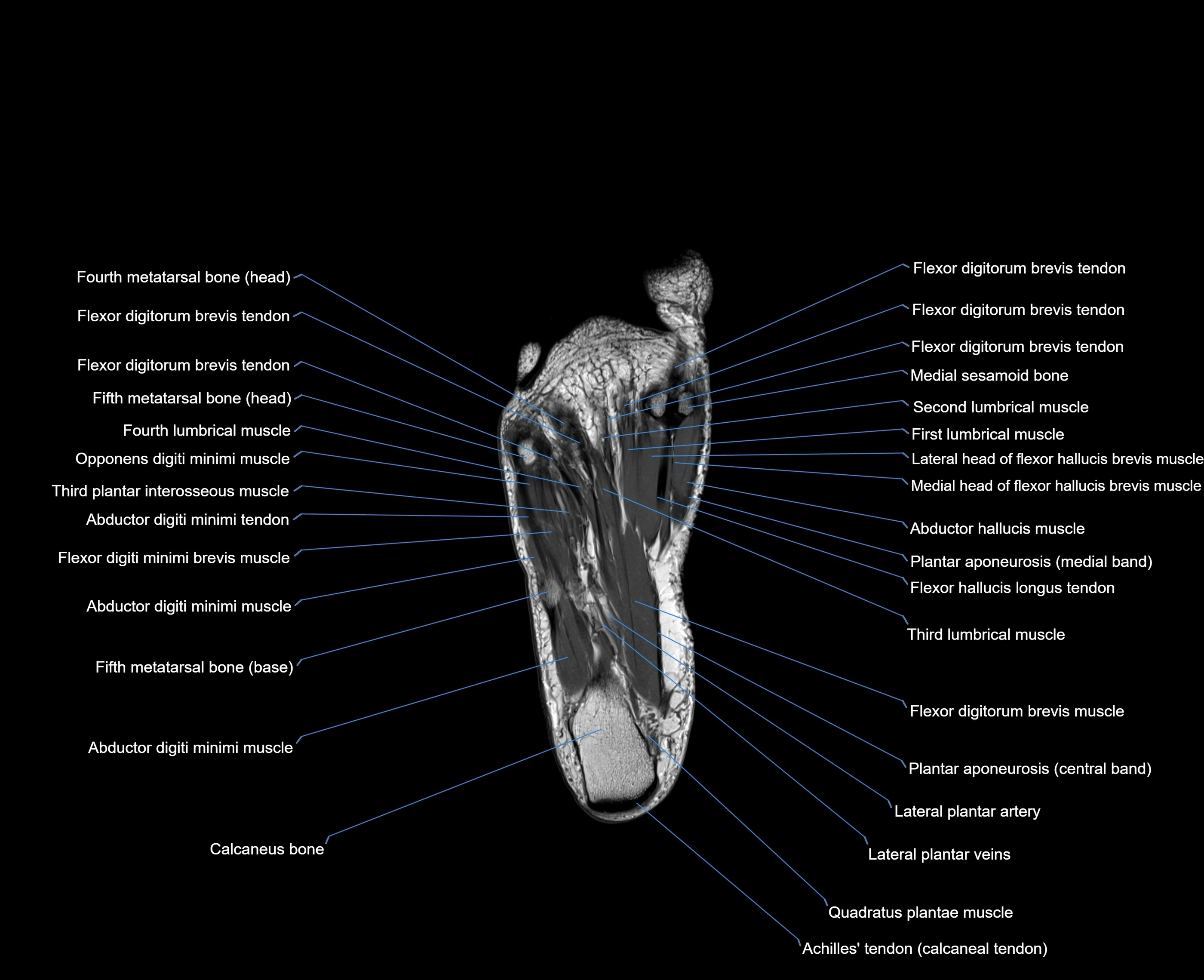
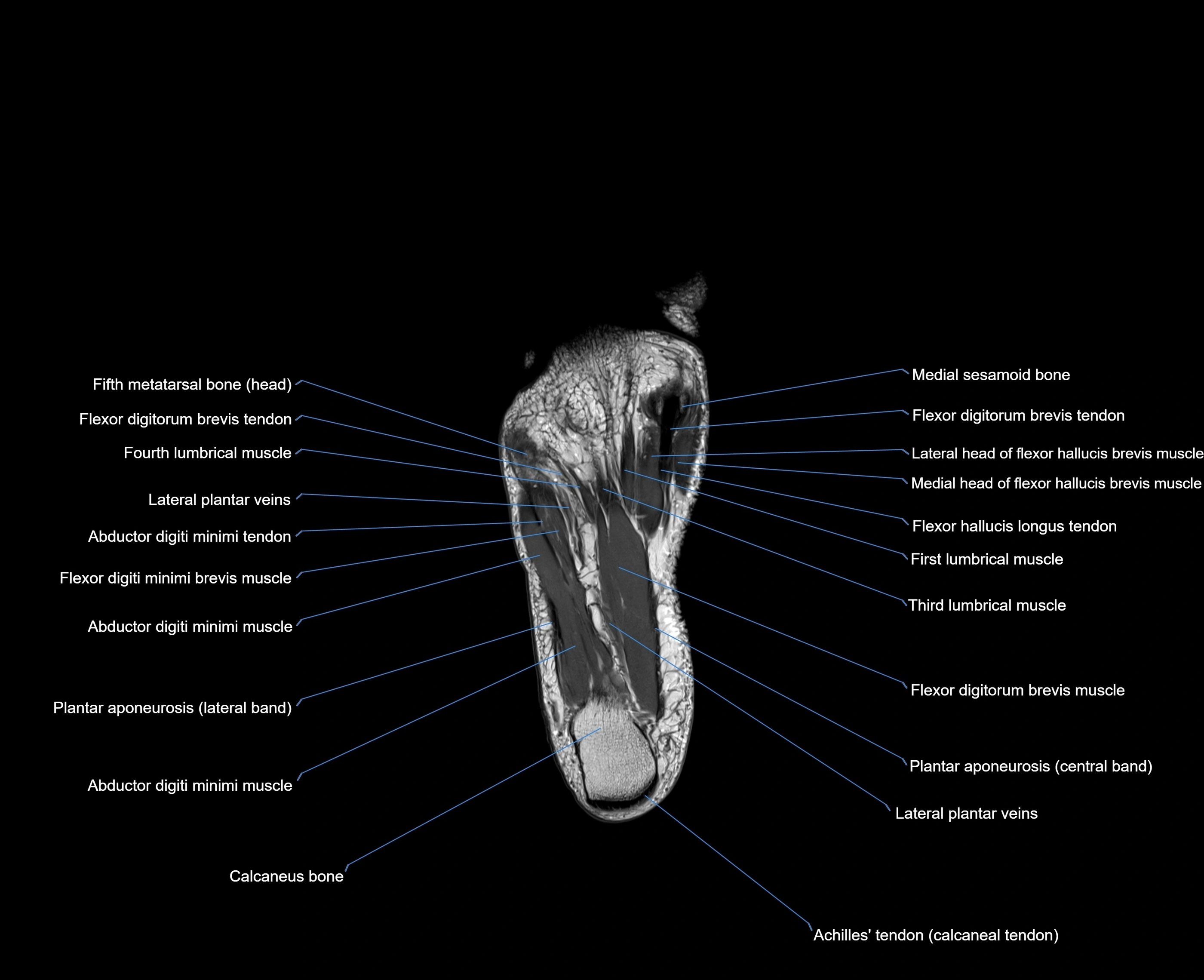
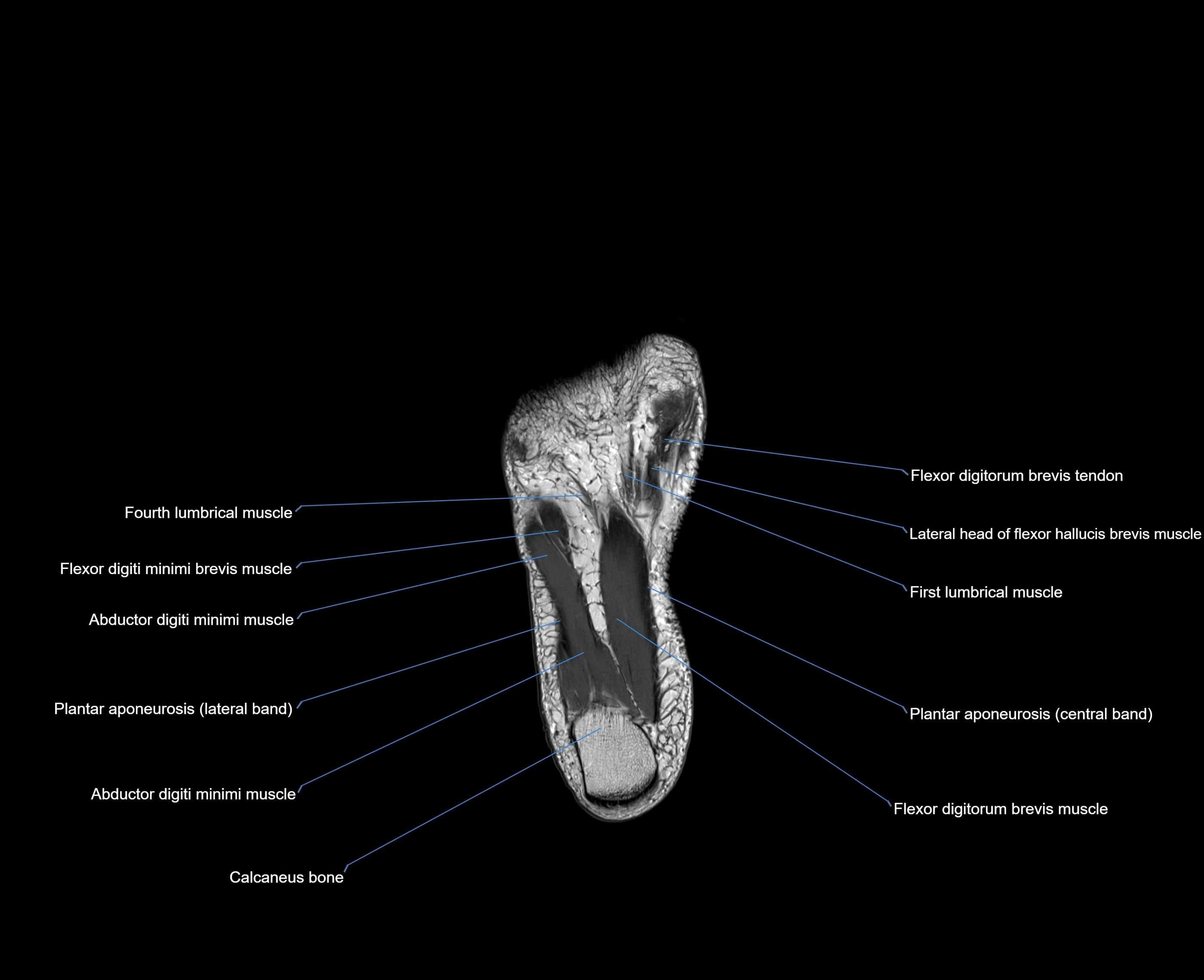
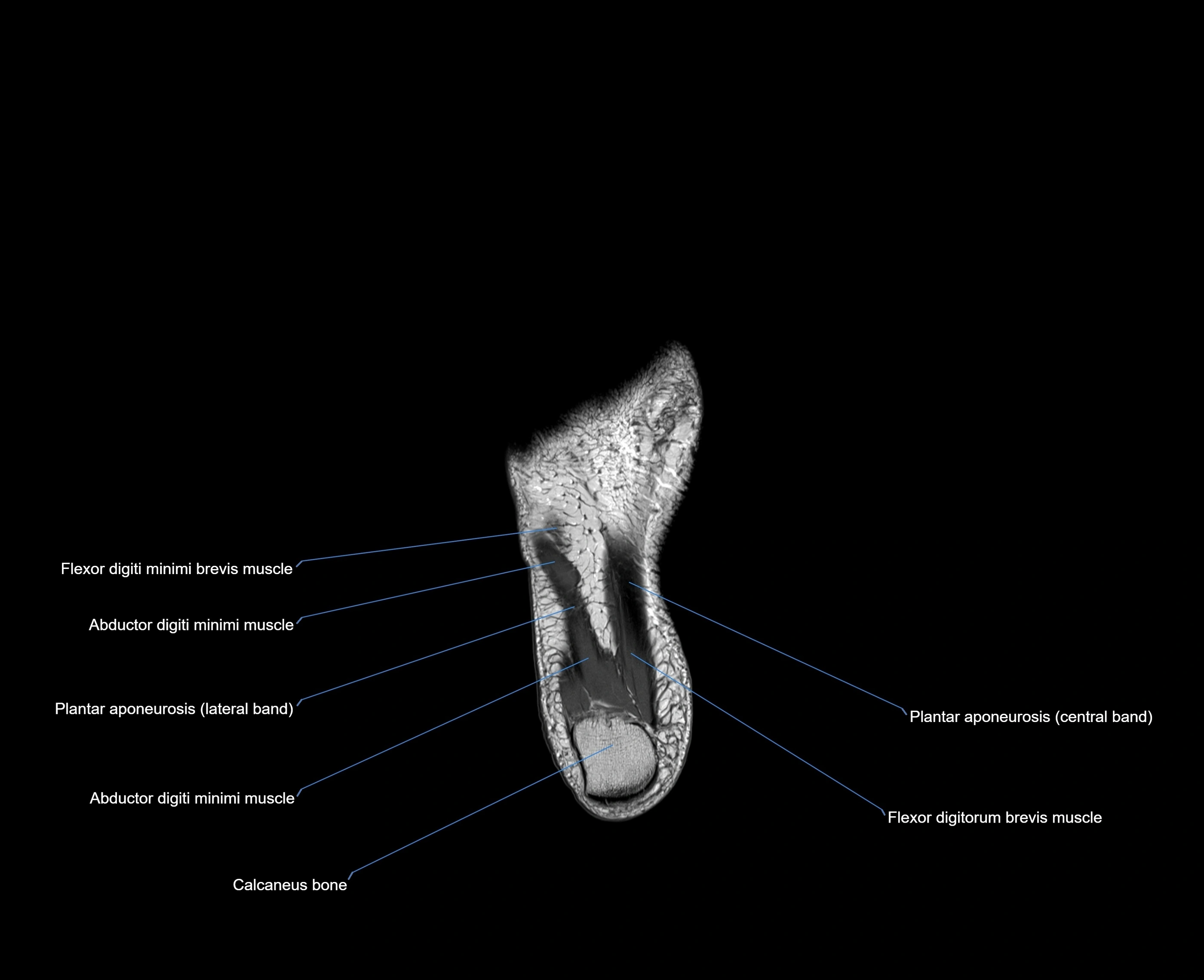
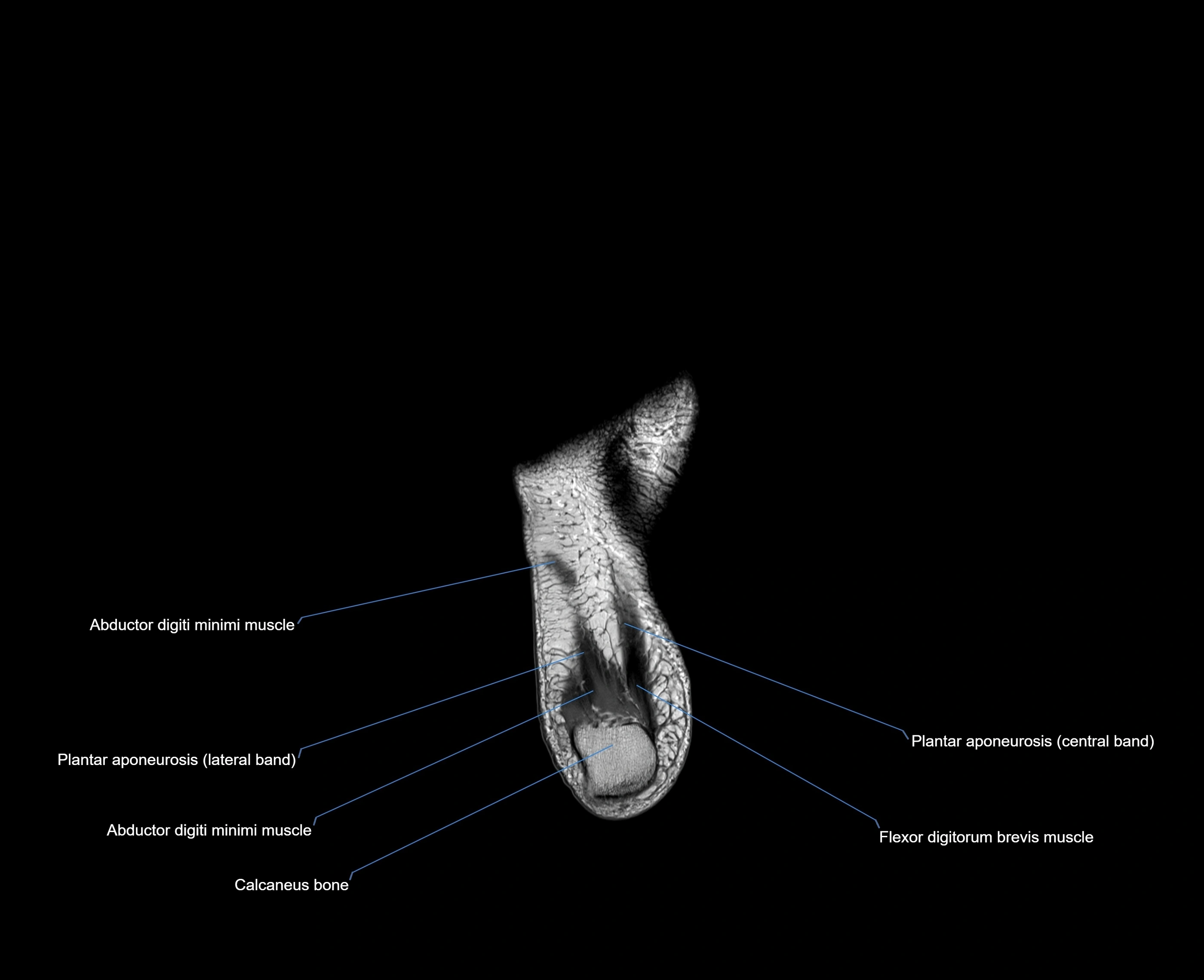
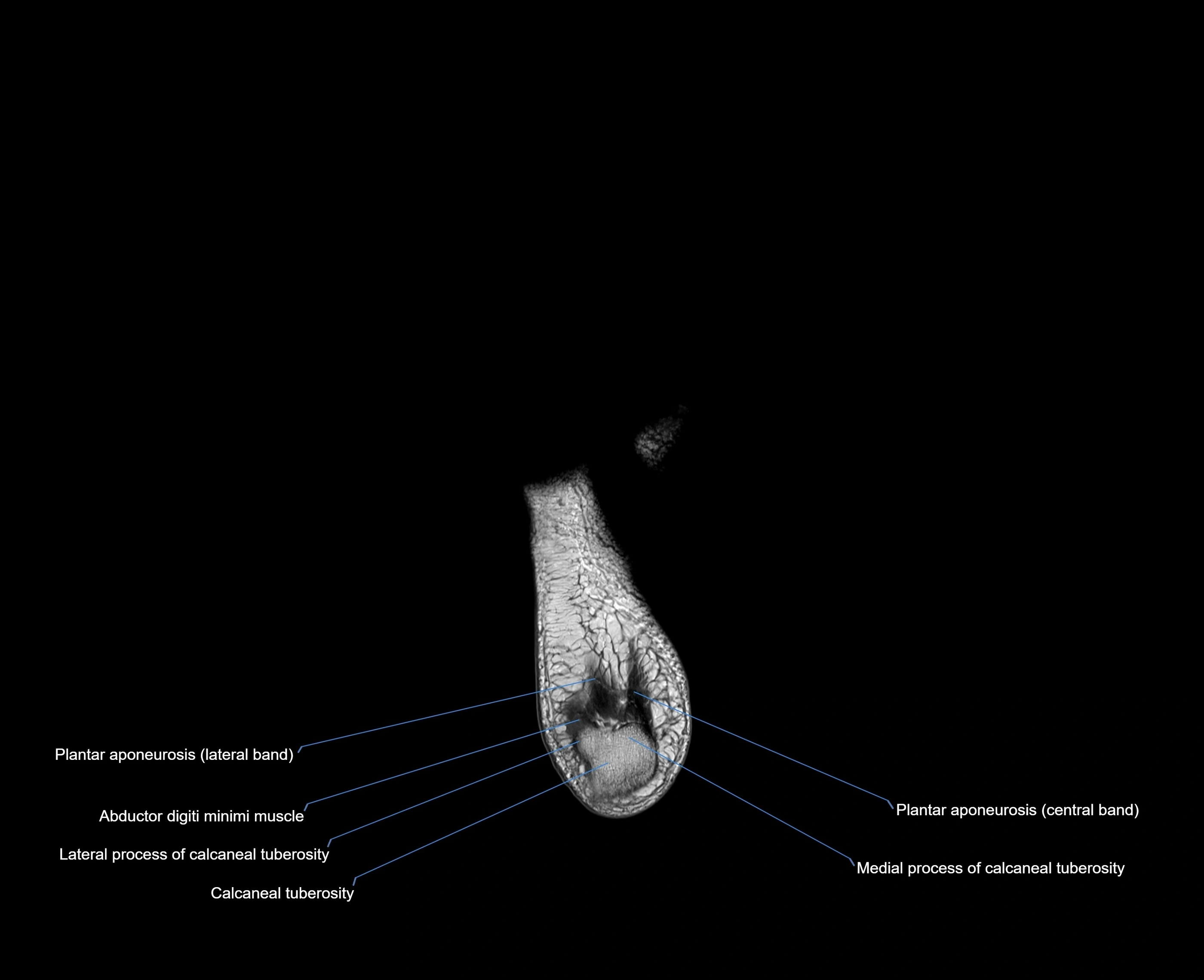
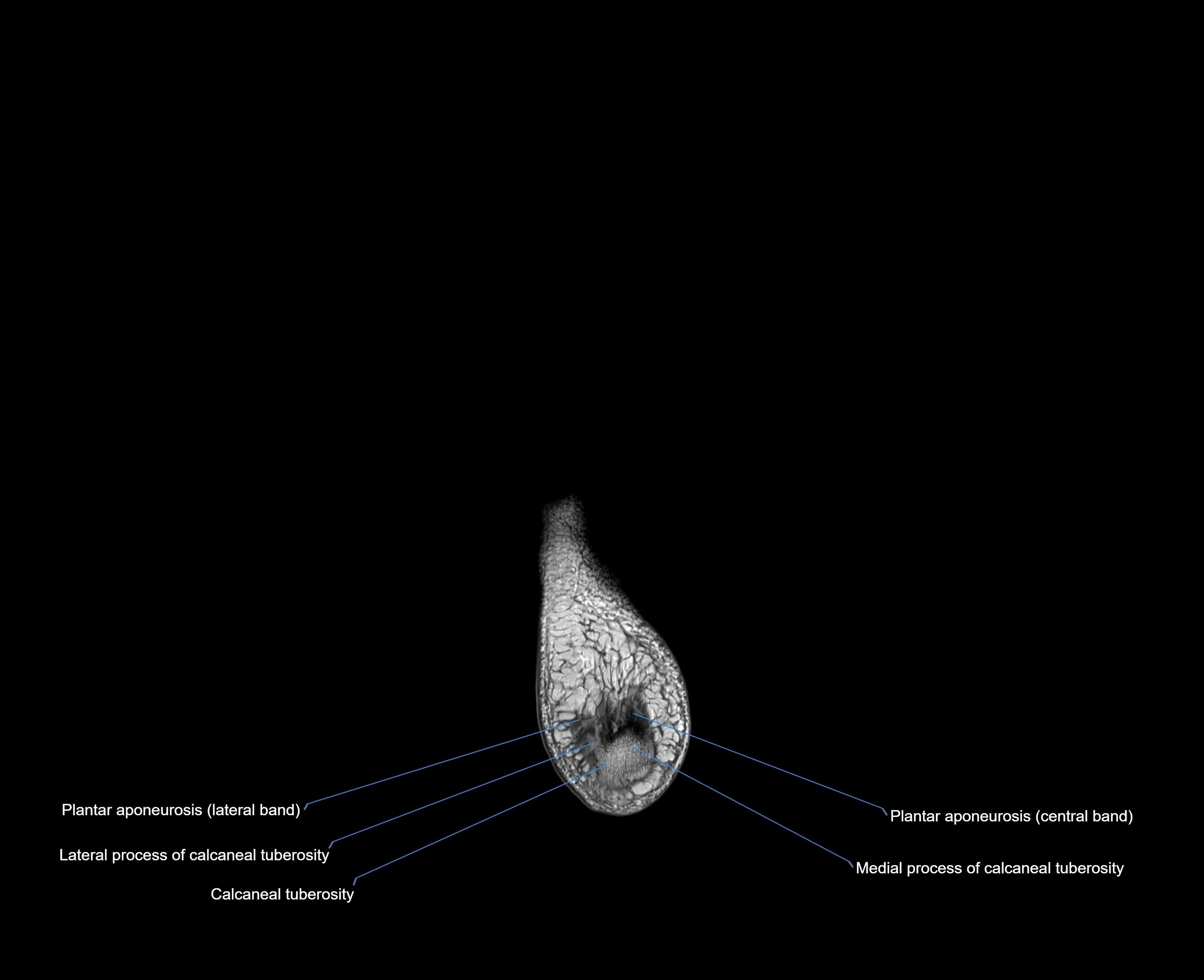
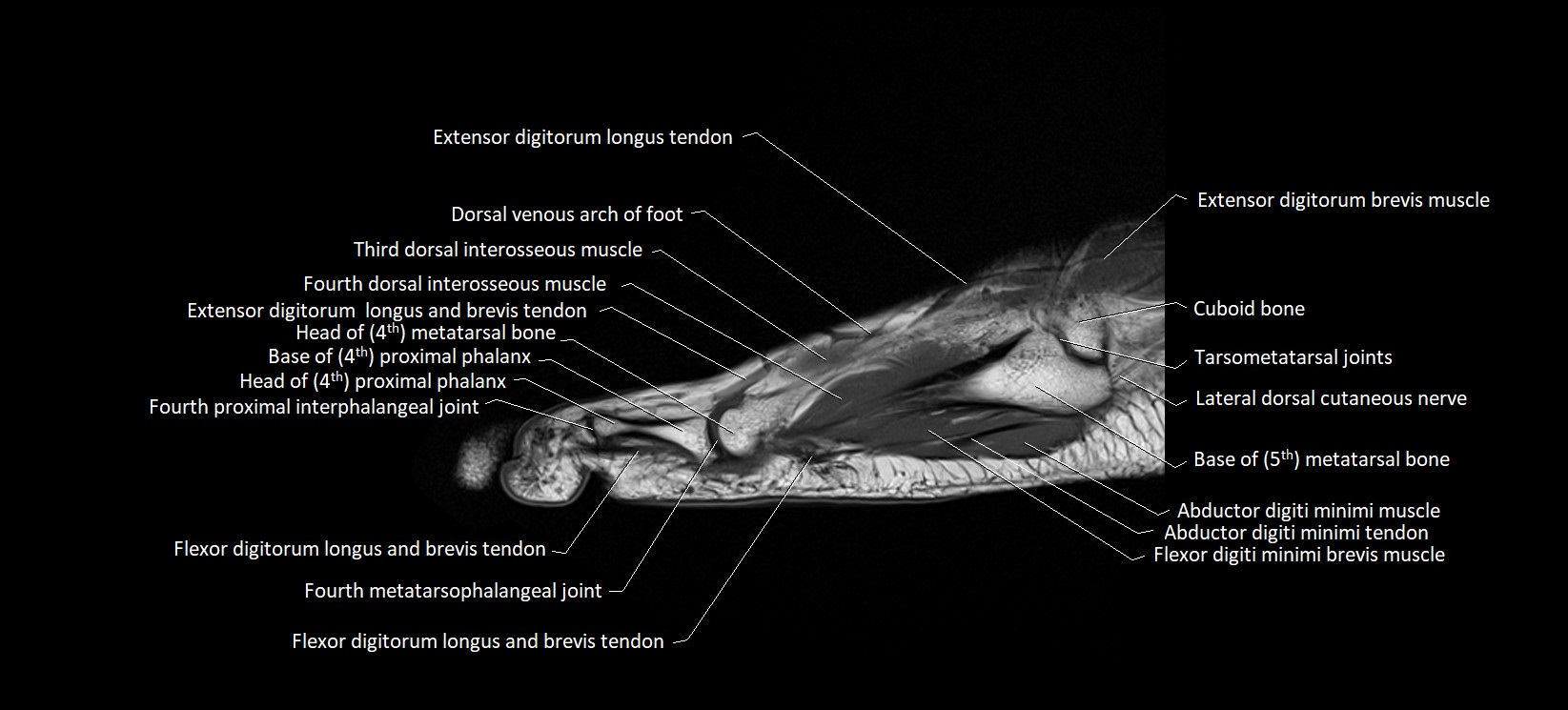
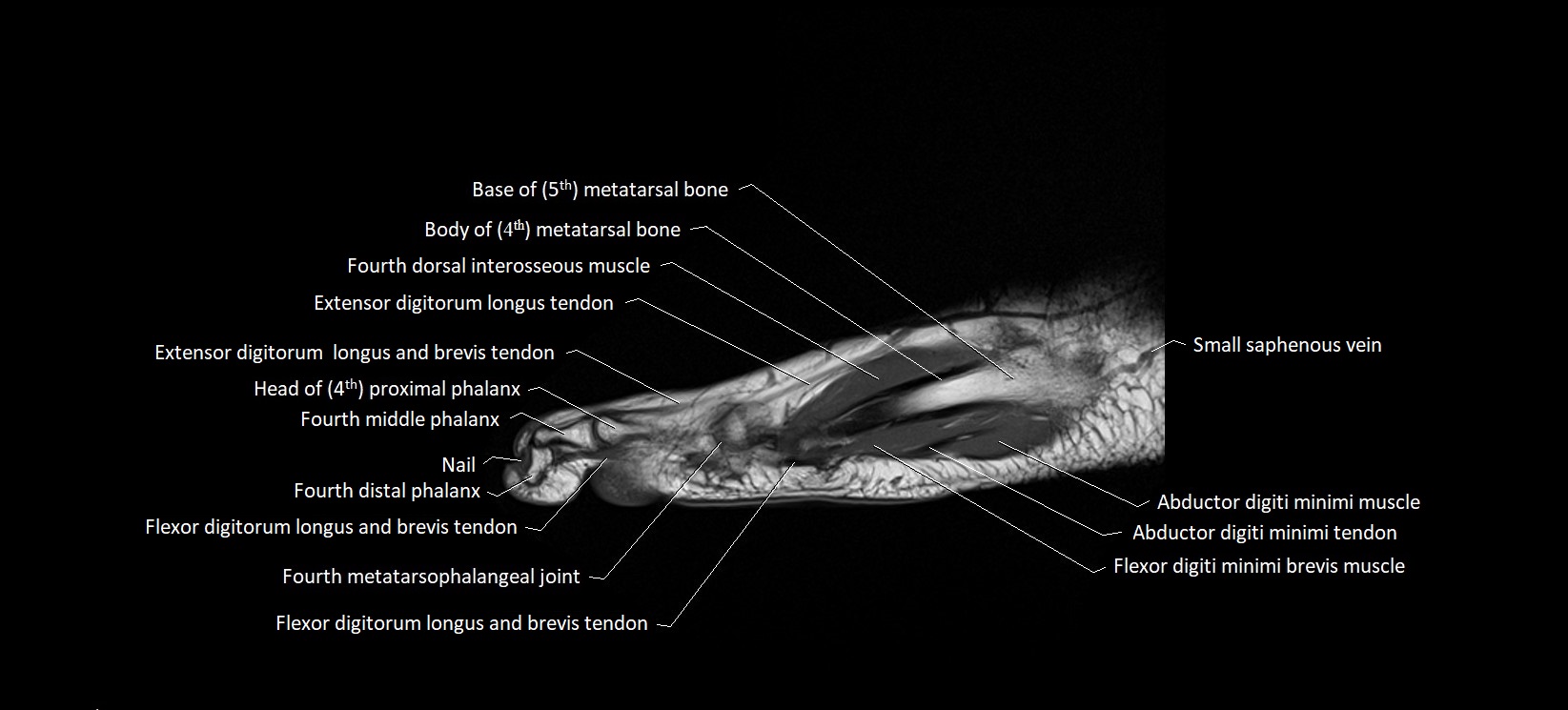
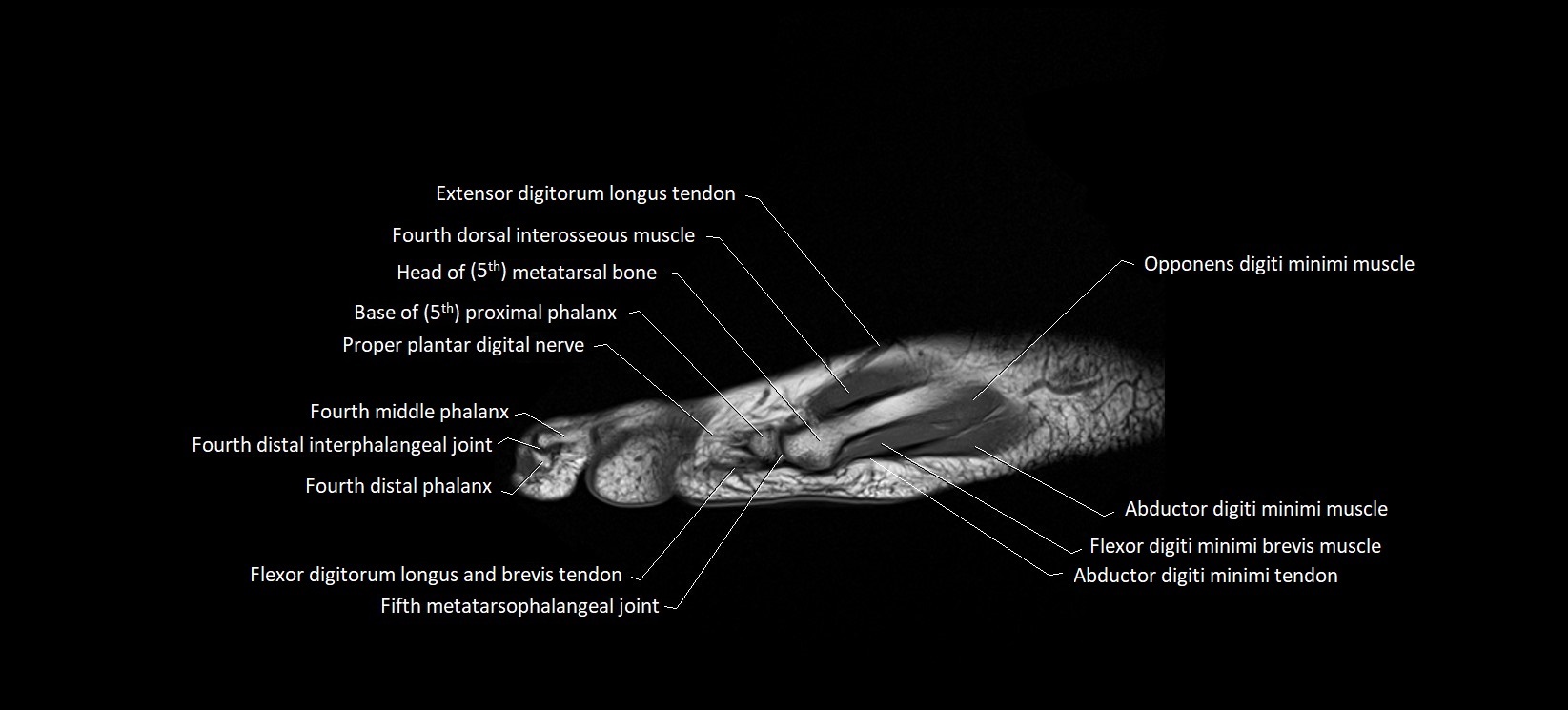
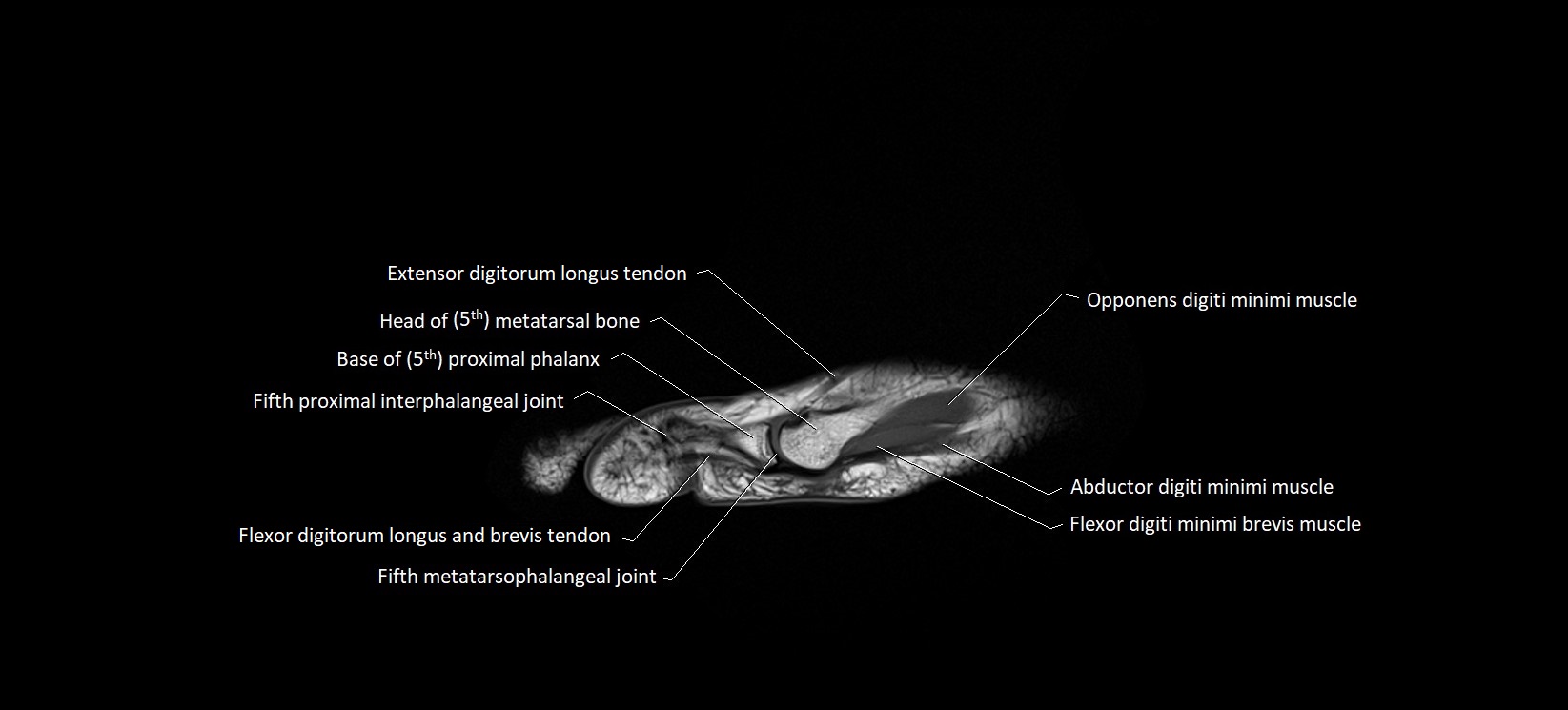
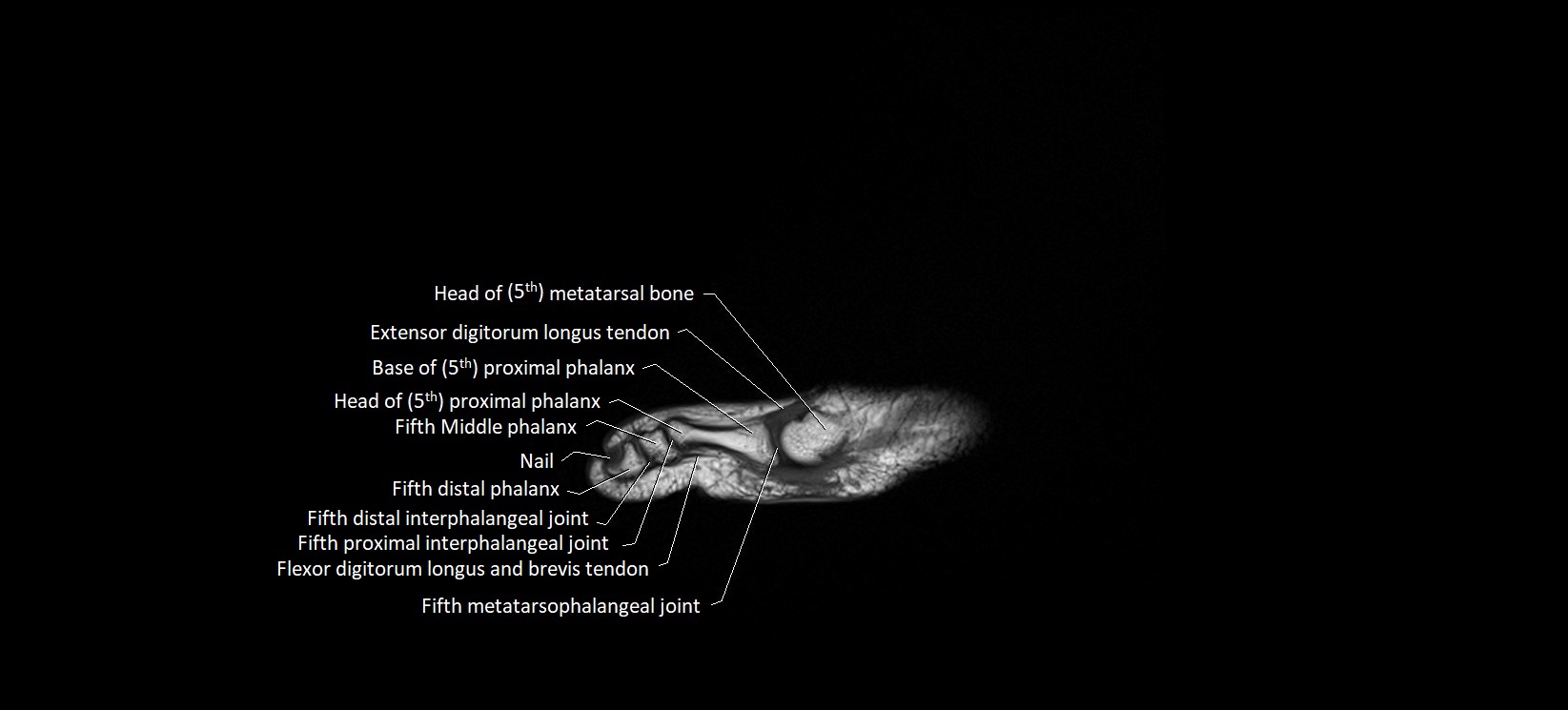
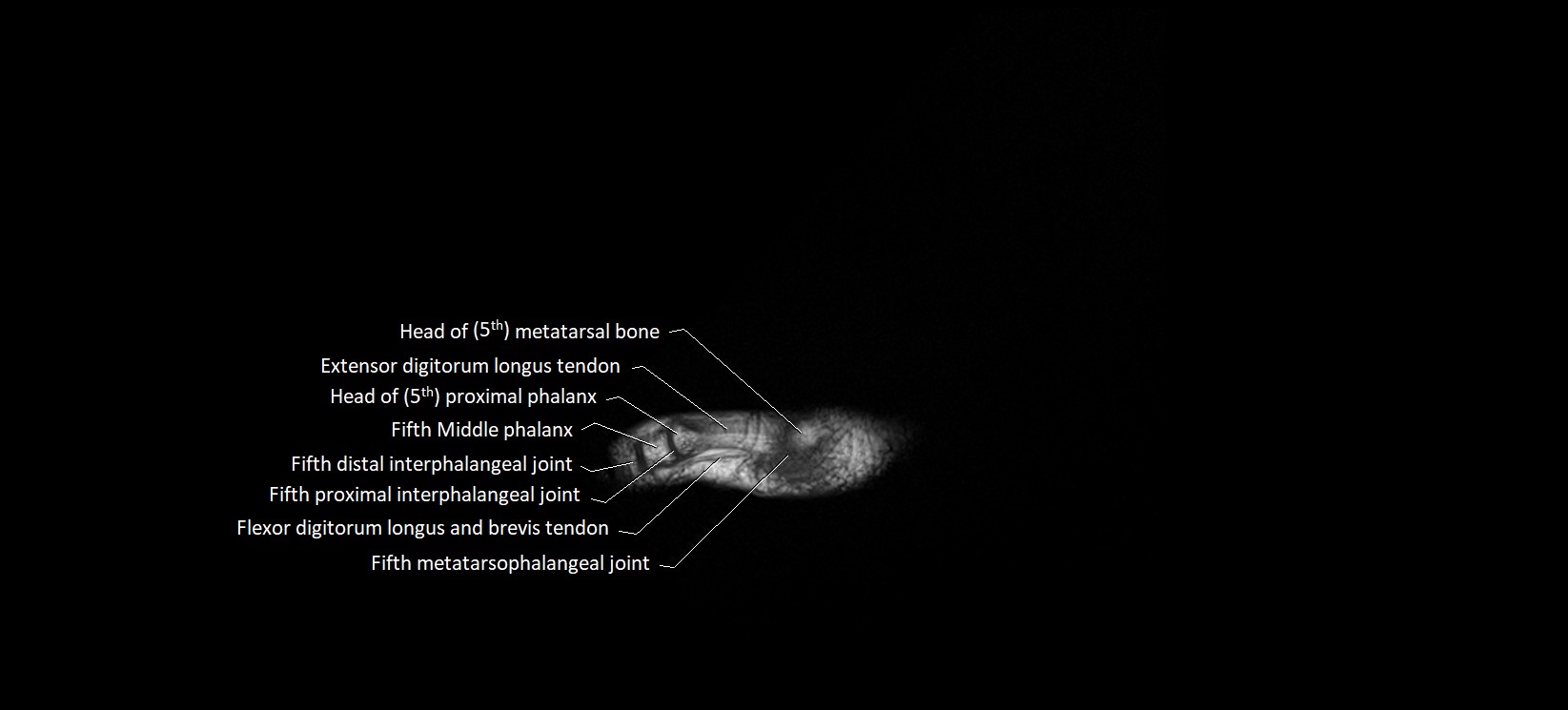
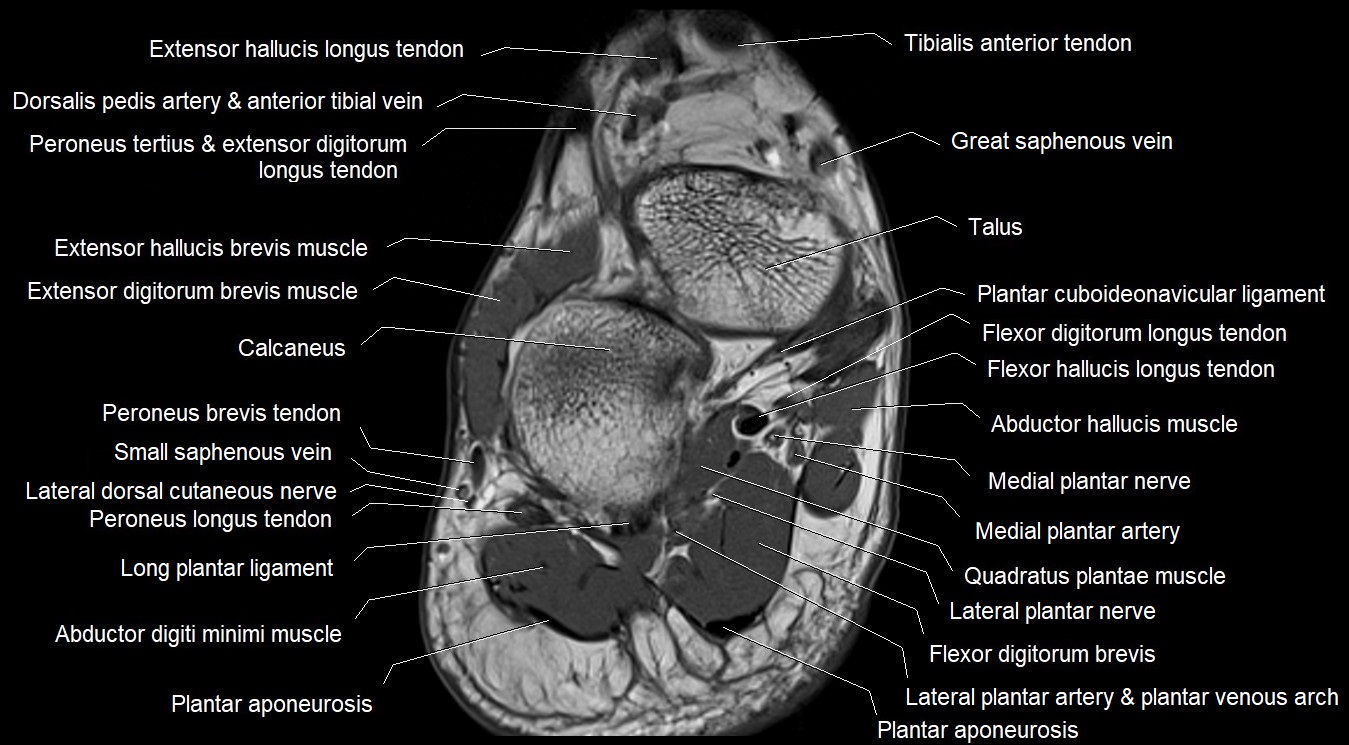
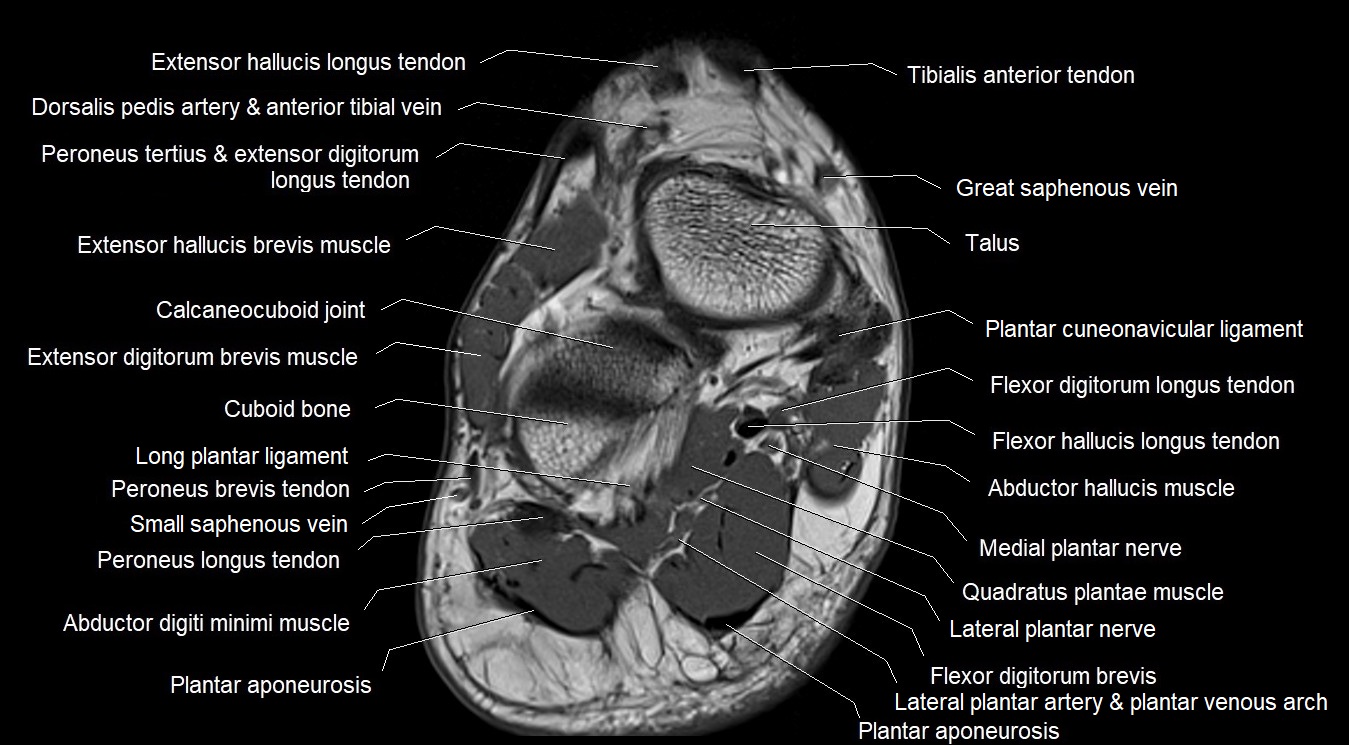
The abductor digiti minimi (ADM) is a superficial intrinsic muscle of the sole of the foot, located along the lateral border. It forms the most medial muscle of the lateral plantar compartment. The ADM abducts and flexes the fifth toe (little toe) at the metatarsophalangeal joint and provides lateral stability to the foot during gait.
It is clinically relevant in plantar fasciitis, heel pain syndromes, and nerve entrapments such as Baxter’s neuropathy, which affects the first branch of the lateral plantar nerve.
Synonyms
-
Abductor of the little toe
-
Abductor of the fifth digit
Origin, Course, and Insertion
-
Origin: Medial and lateral processes of the calcaneal tuberosity, plantar aponeurosis, and intermuscular septum
-
Course: Fibers run forward along the lateral margin of the foot
-
Insertion: Lateral aspect of the base of the proximal phalanx of the 5th toe; sometimes attaches to the tendon of the flexor digiti minimi brevis
Tendon Attachments
-
Attaches distally into the lateral base of the proximal phalanx of the fifth toe
-
Occasionally merges with the tendon of flexor digiti minimi brevis for reinforcement
Relations
-
Superficial: Plantar fascia
-
Deep: Flexor digitorum brevis, quadratus plantae, lateral plantar vessels and nerve
-
Medial: Flexor digitorum brevis
-
Lateral: Lateral margin of foot and skin
Nerve Supply
-
Lateral plantar nerve (first branch), from tibial nerve (S1–S3)
Arterial Supply
-
Lateral plantar artery, branch of posterior tibial artery
Venous Drainage
-
Tributaries of the lateral plantar vein, draining into the posterior tibial vein
Function
-
Abduction of the 5th toe: Moves toe laterally at the metatarsophalangeal joint
-
Flexion: Assists in flexion of the 5th toe at the MTP joint
-
Support: Helps maintain the lateral longitudinal arch of the foot
-
Stabilization: Provides lateral balance during stance and gait
Clinical Significance
-
Baxter’s neuropathy: Entrapment of the inferior calcaneal branch of the lateral plantar nerve may cause selective ADM atrophy, seen on MRI
-
Heel pain syndromes: Often involved in chronic plantar fasciitis
-
Tears or strain: Can occur with trauma or overuse, presenting with lateral plantar foot pain
-
Atrophy: Early marker of peripheral neuropathy and chronic compression
MRI Appearance
-
T1-weighted images:
-
Normal ADM: intermediate signal intensity muscle belly
-
Fat planes and subcutaneous tissue: bright signal
-
Chronic denervation: fatty replacement with bright signal
-
-
T2-weighted images:
-
Normal muscle: intermediate-to-dark signal (darker than on T1)
-
Acute injury or denervation: hyperintense changes in muscle belly
-
Chronic tendinopathy or strain: irregular bright signal at origin or insertion
-
-
STIR (Short Tau Inversion Recovery):
-
Normal muscle: intermediate to dark signal
-
Pathology: bright hyperintensity in edema, tears, or nerve-related denervation
-
-
Proton Density Fat-Saturated (PD FS):
-
Normal: intermediate-to-dark muscle signal
-
Tears or inflammation: bright hyperintense signal within muscle fibers
-
Excellent for detecting subtle denervation or tendon injury
-
-
T1 Fat-Sat Post-Contrast:
-
Normal muscle: minimal enhancement
-
Pathology: focal or diffuse enhancement in myositis, tendon origin inflammation, or post-surgical change
-
CT Appearance
Non-Contrast CT:
-
Muscle appears as a soft tissue density on the lateral sole
-
Calcifications may indicate chronic tendinopathy or trauma
-
Atrophy manifests as reduced bulk compared to contralateral side
Post-Contrast CT:
-
Normal ADM enhances homogeneously
-
Pathology such as inflammation or soft tissue tumor shows focal or diffuse increased enhancement
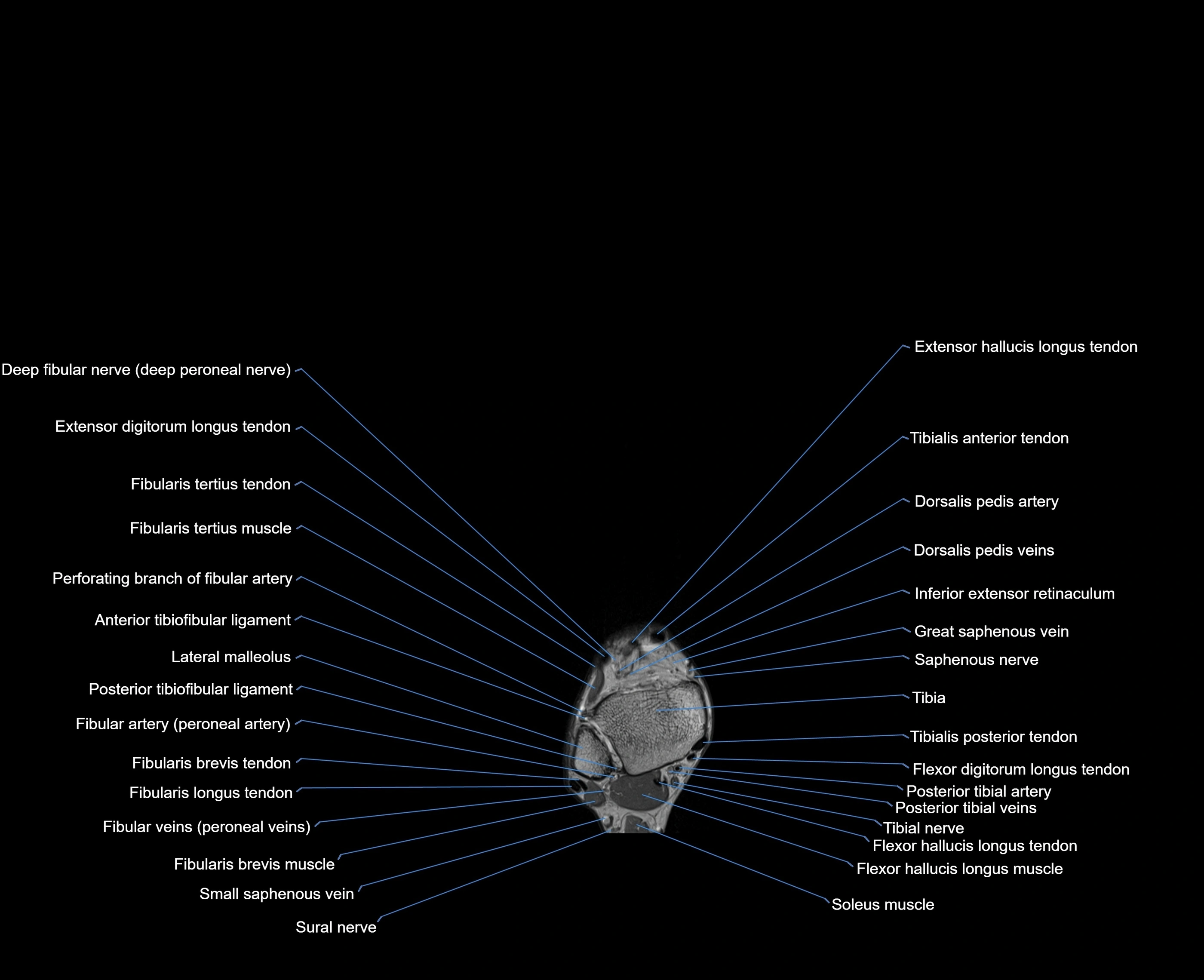
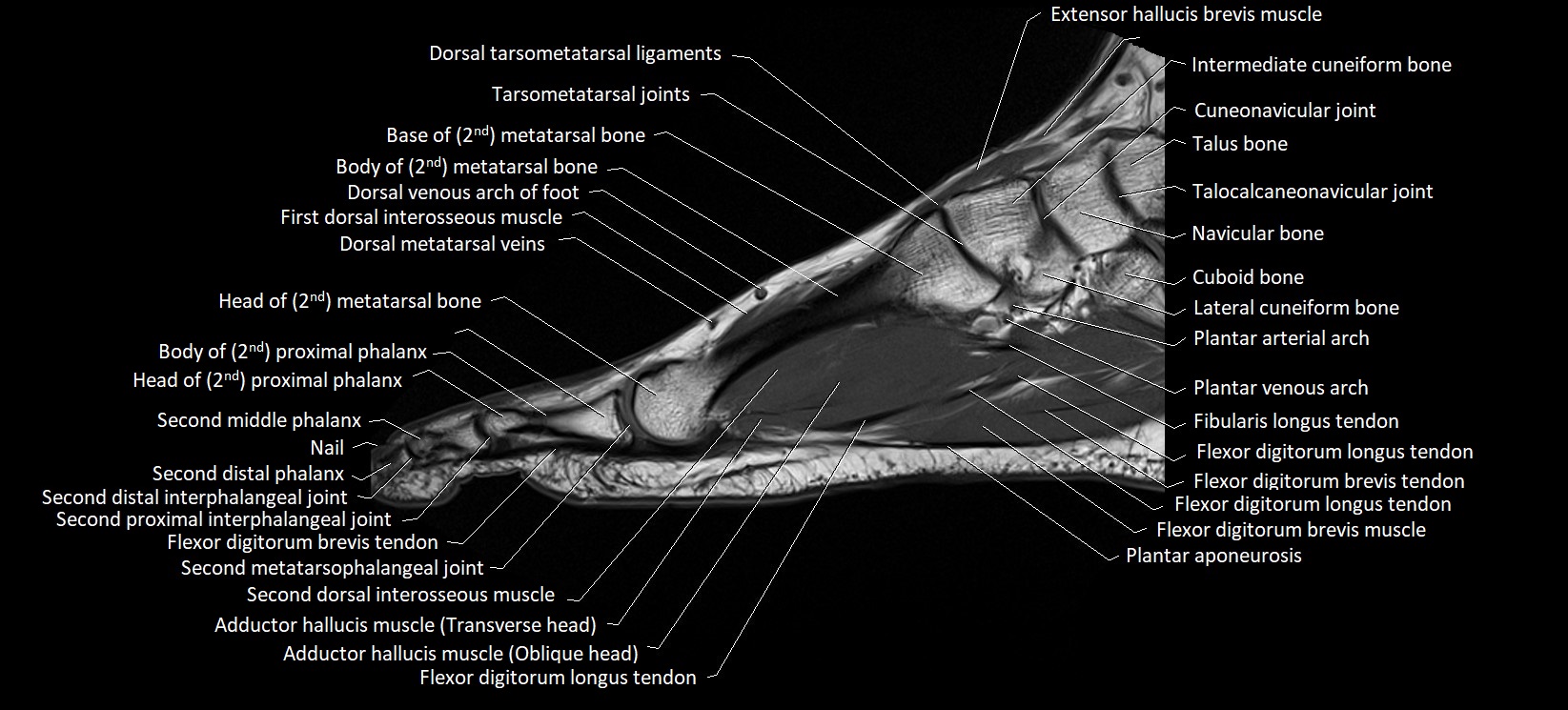
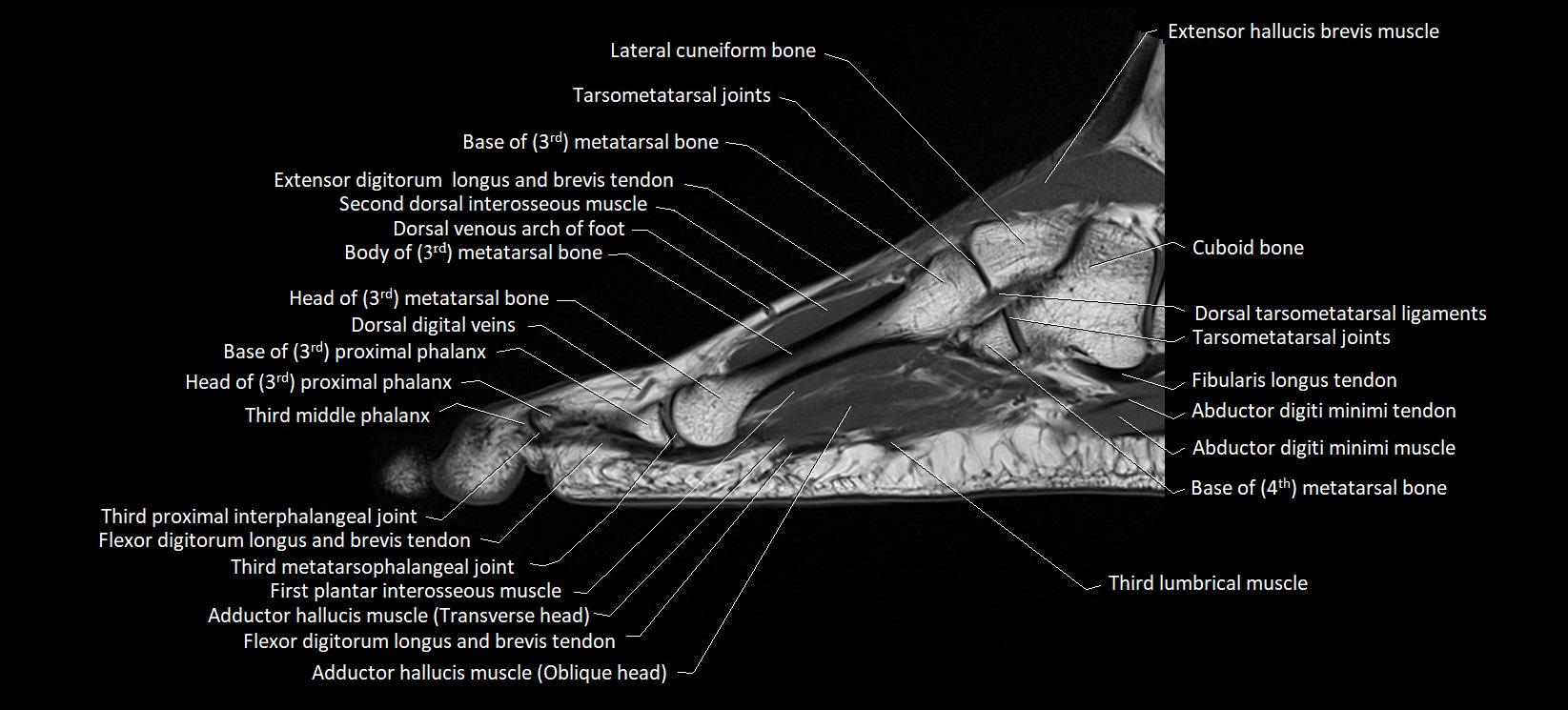
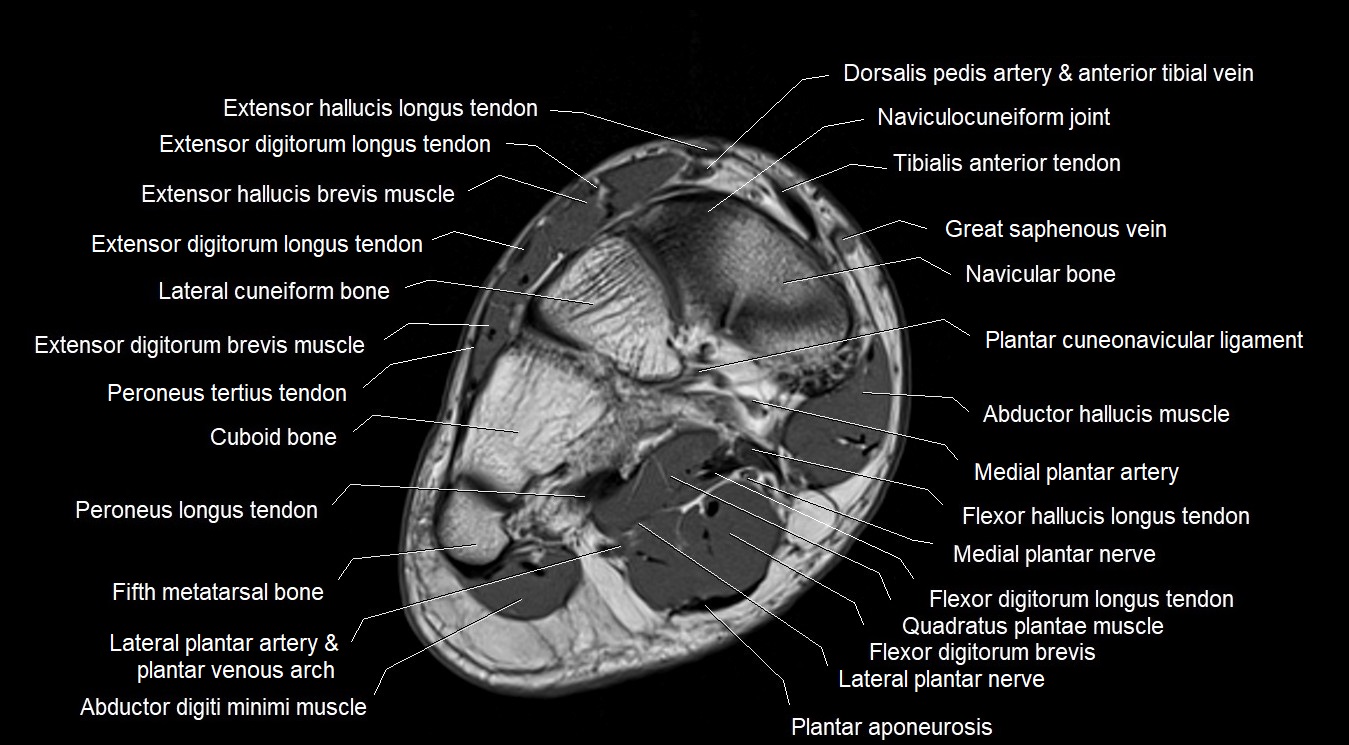
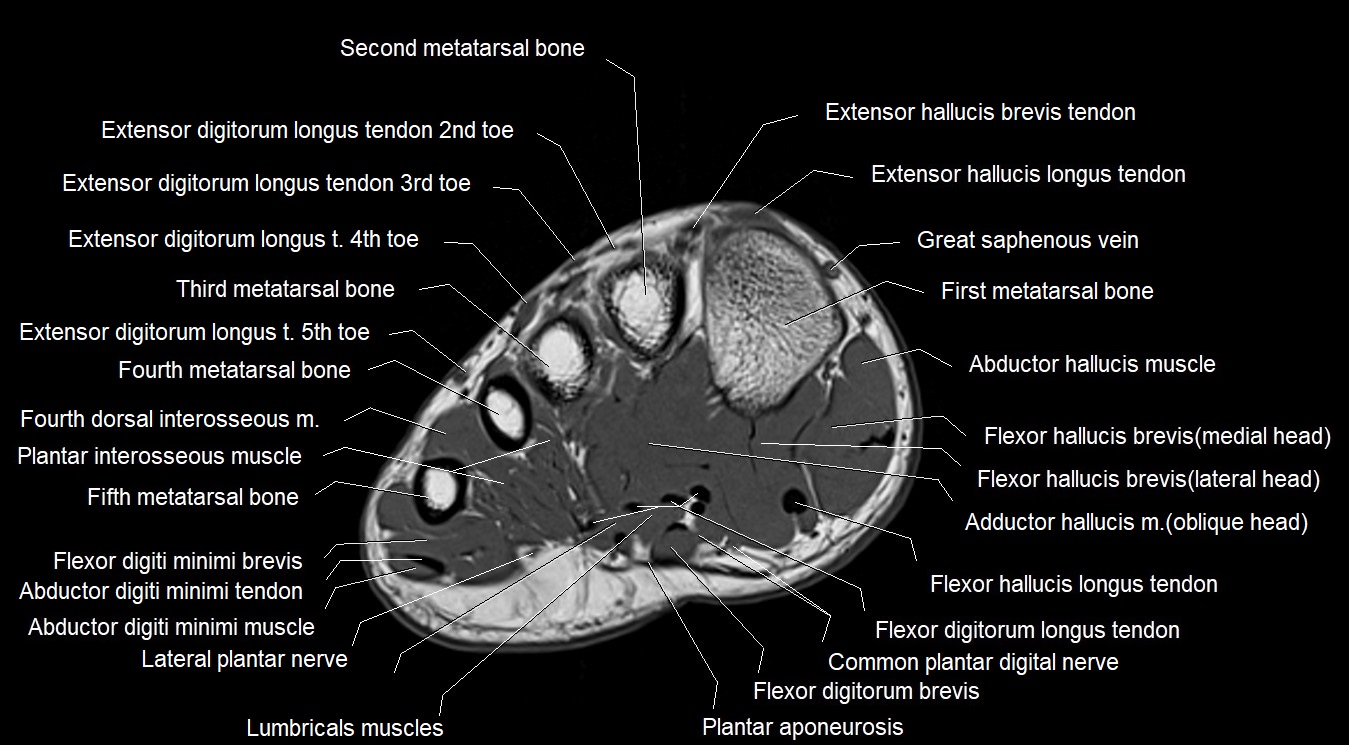
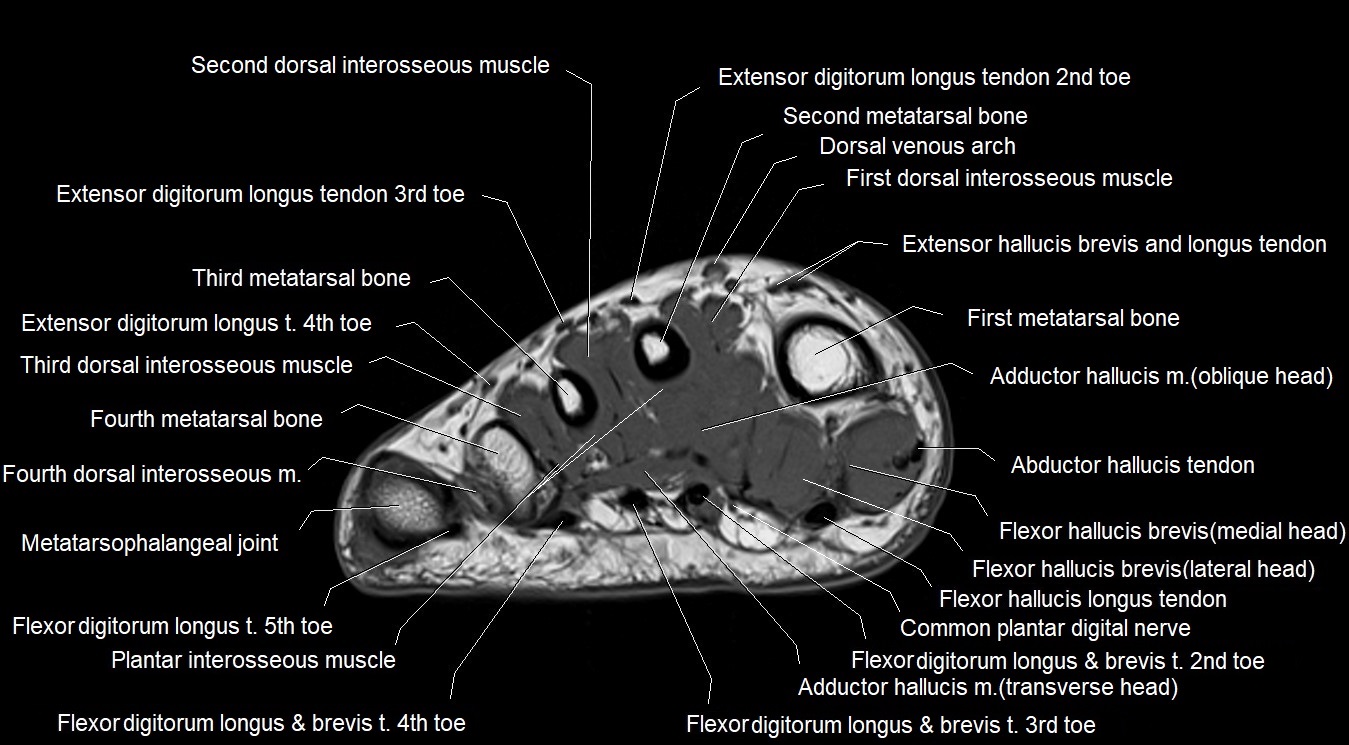
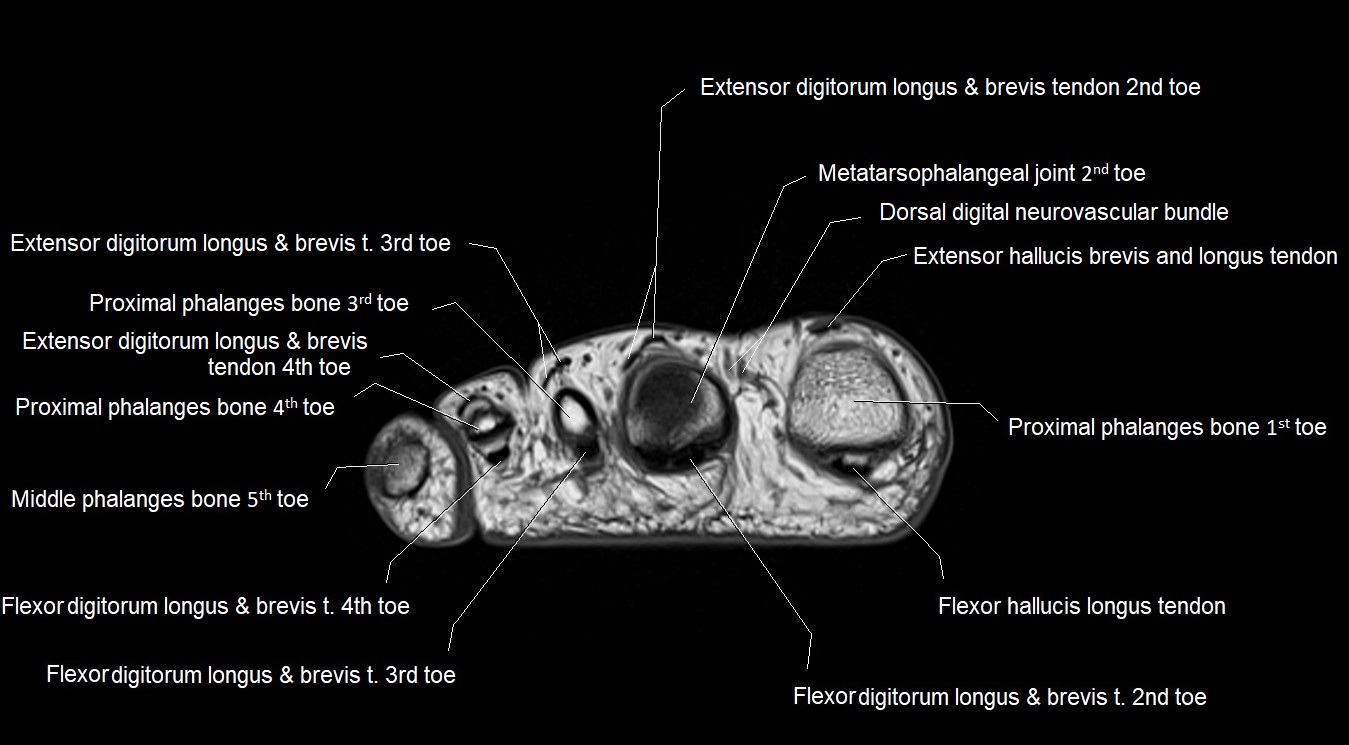
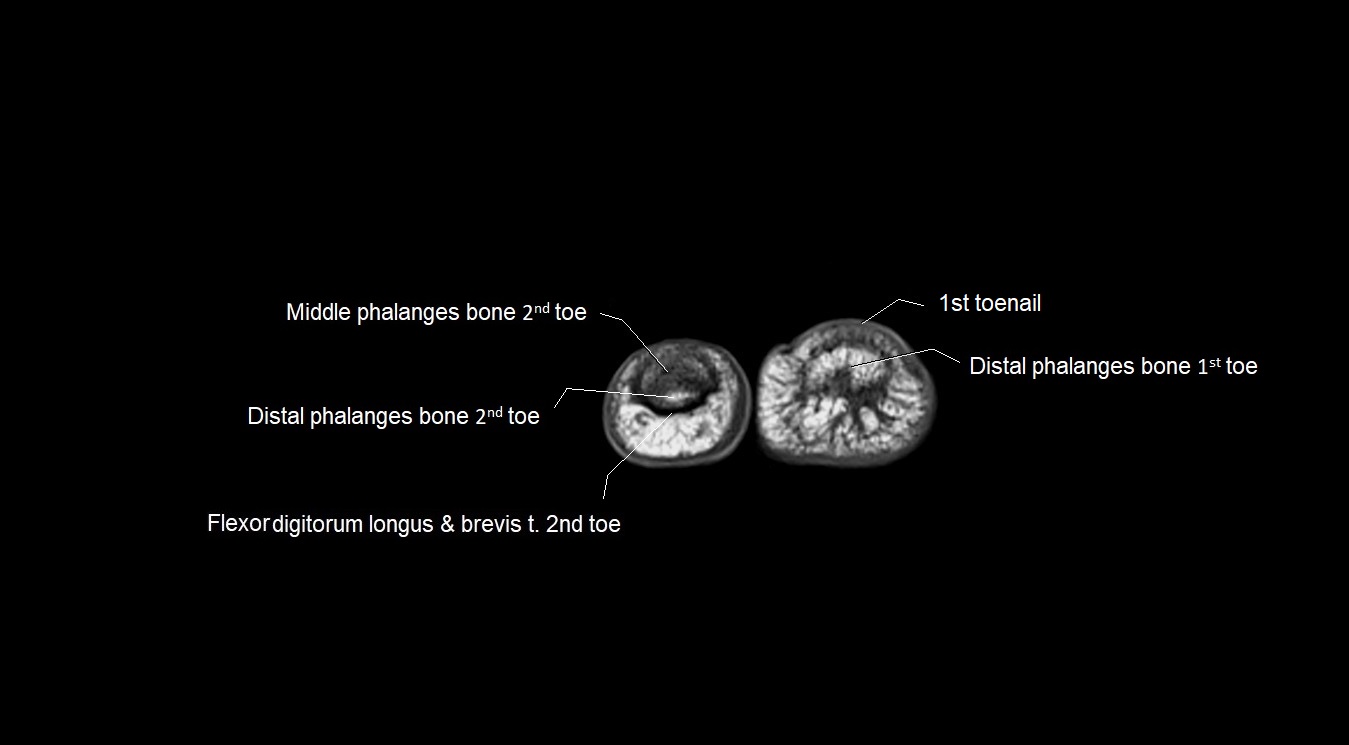
MRI image

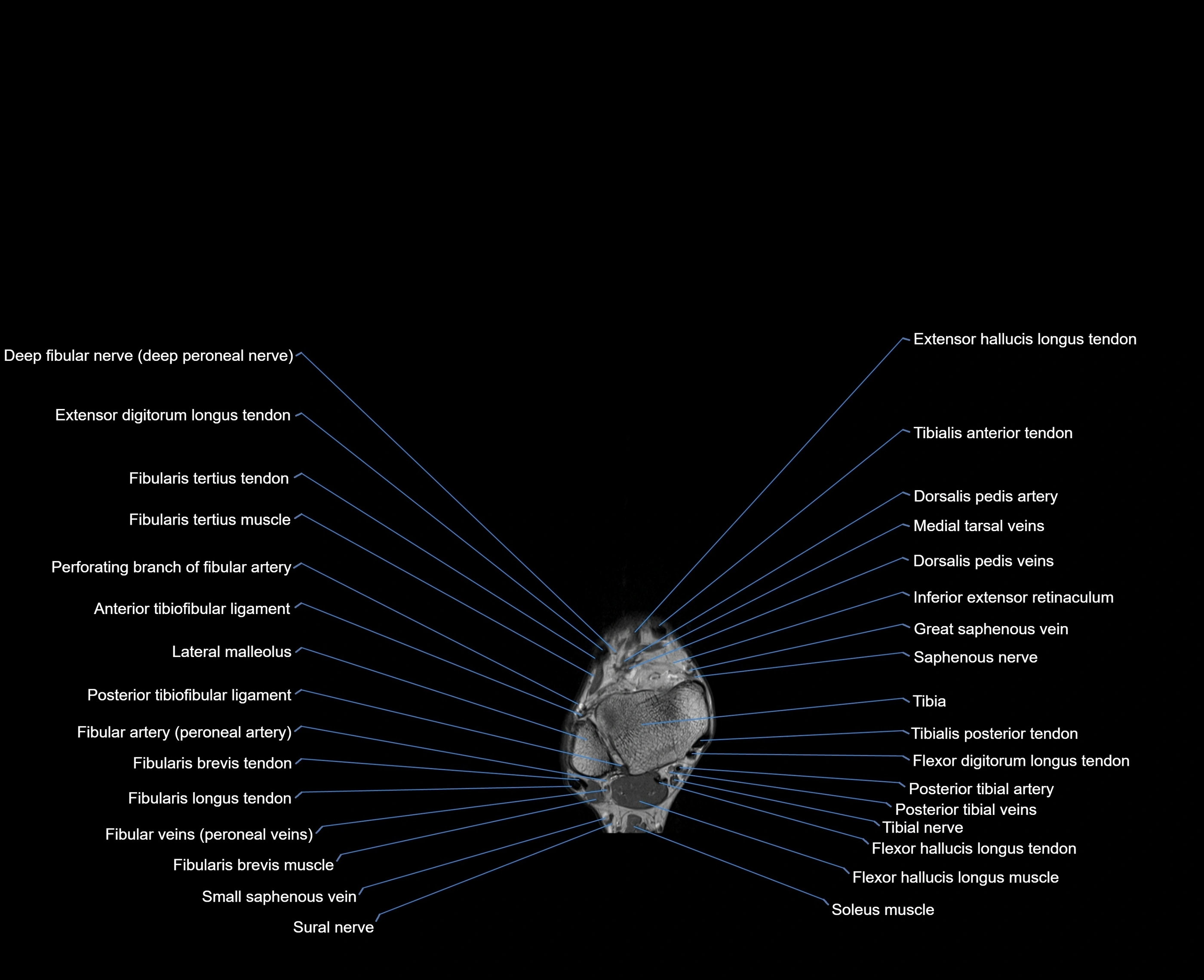
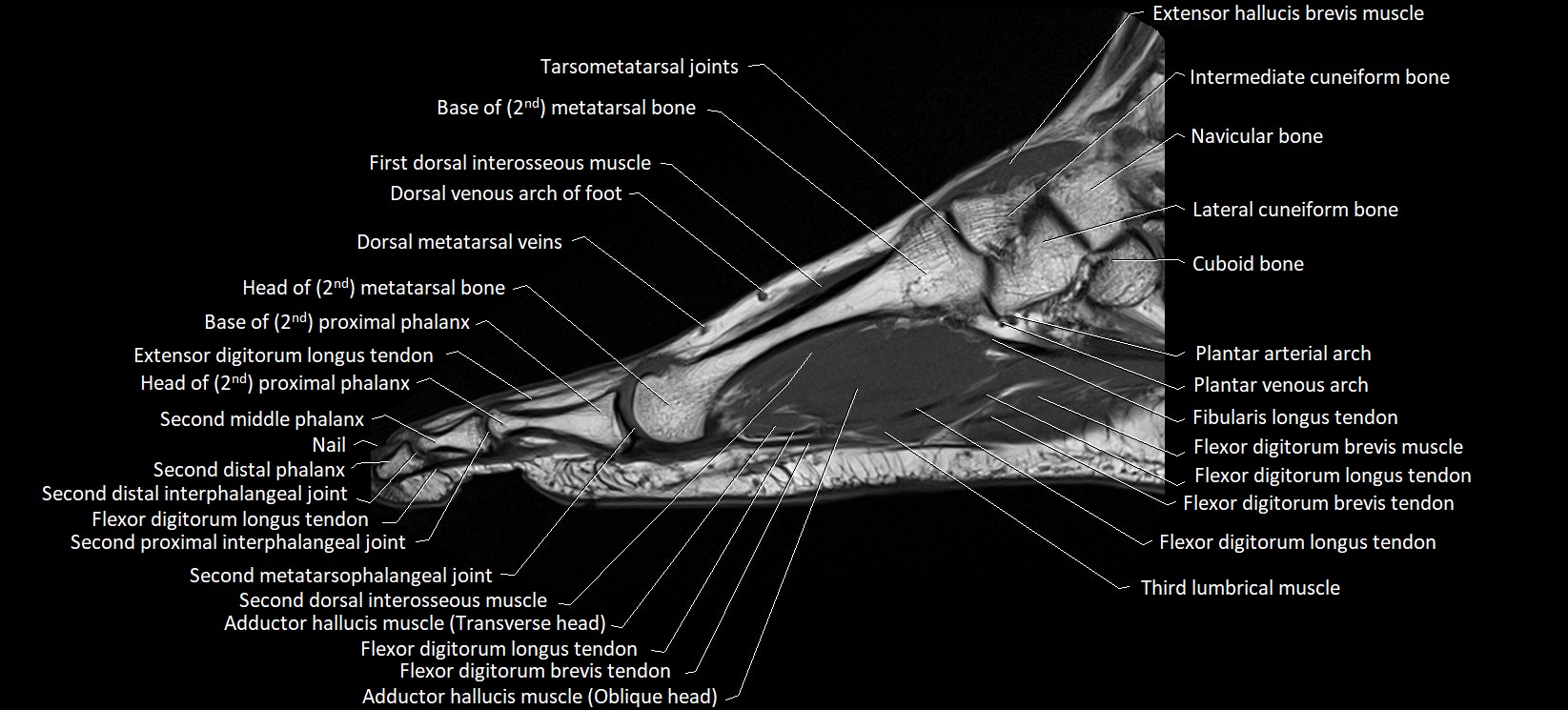
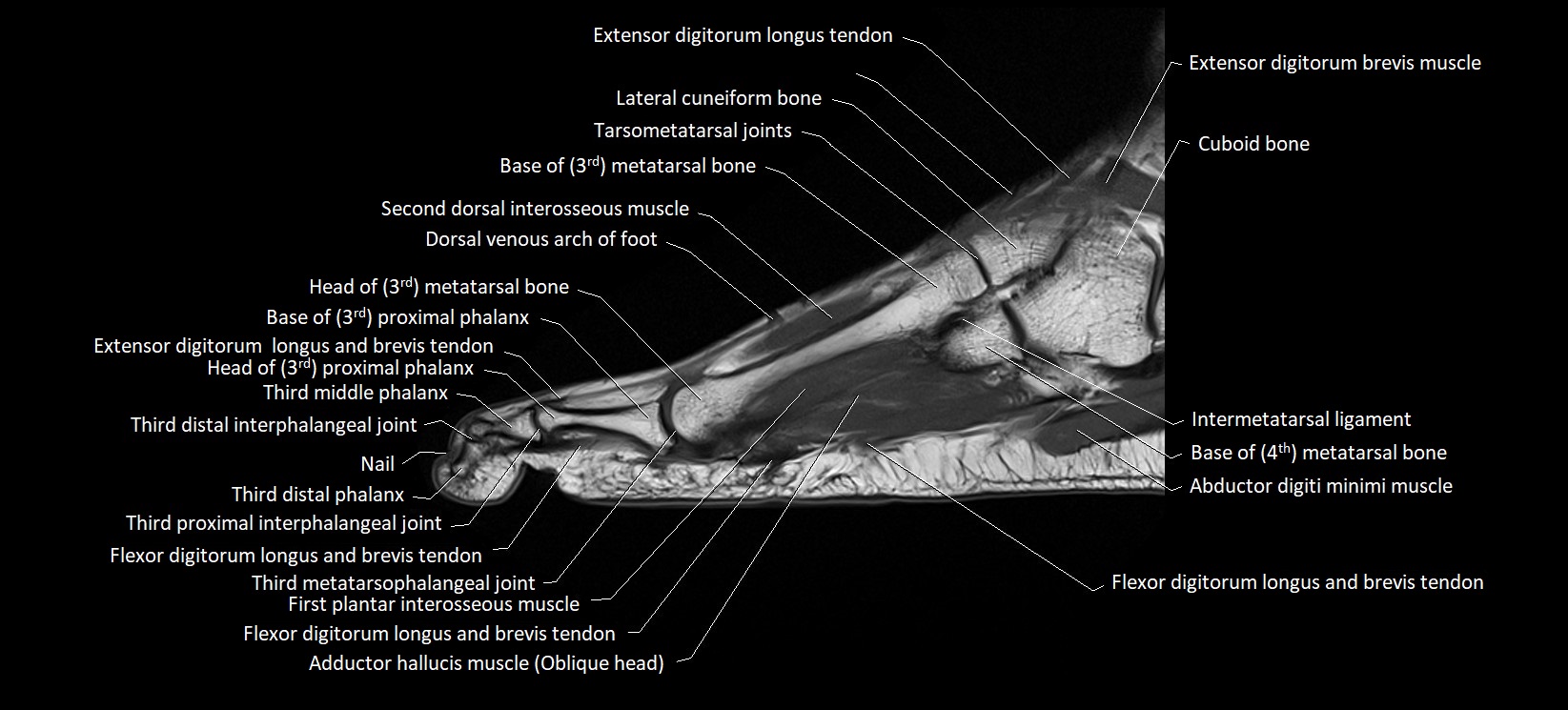
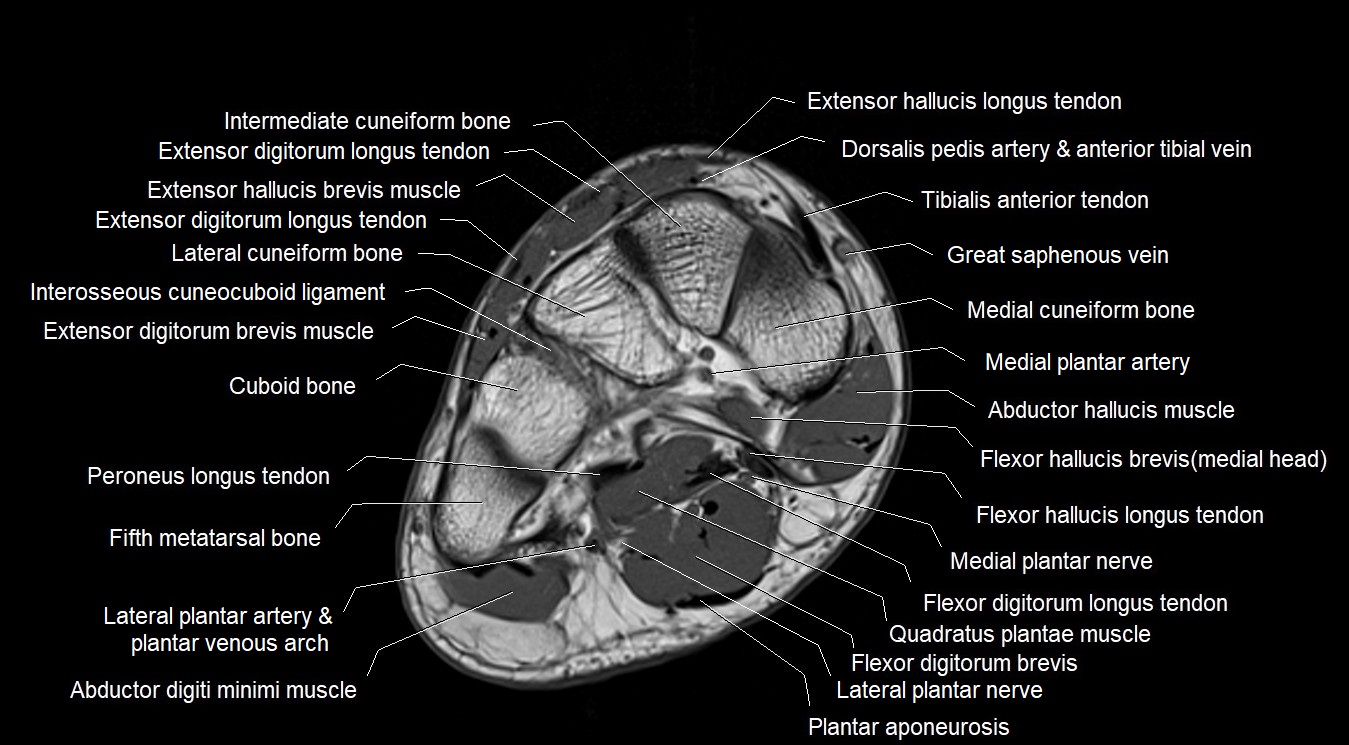
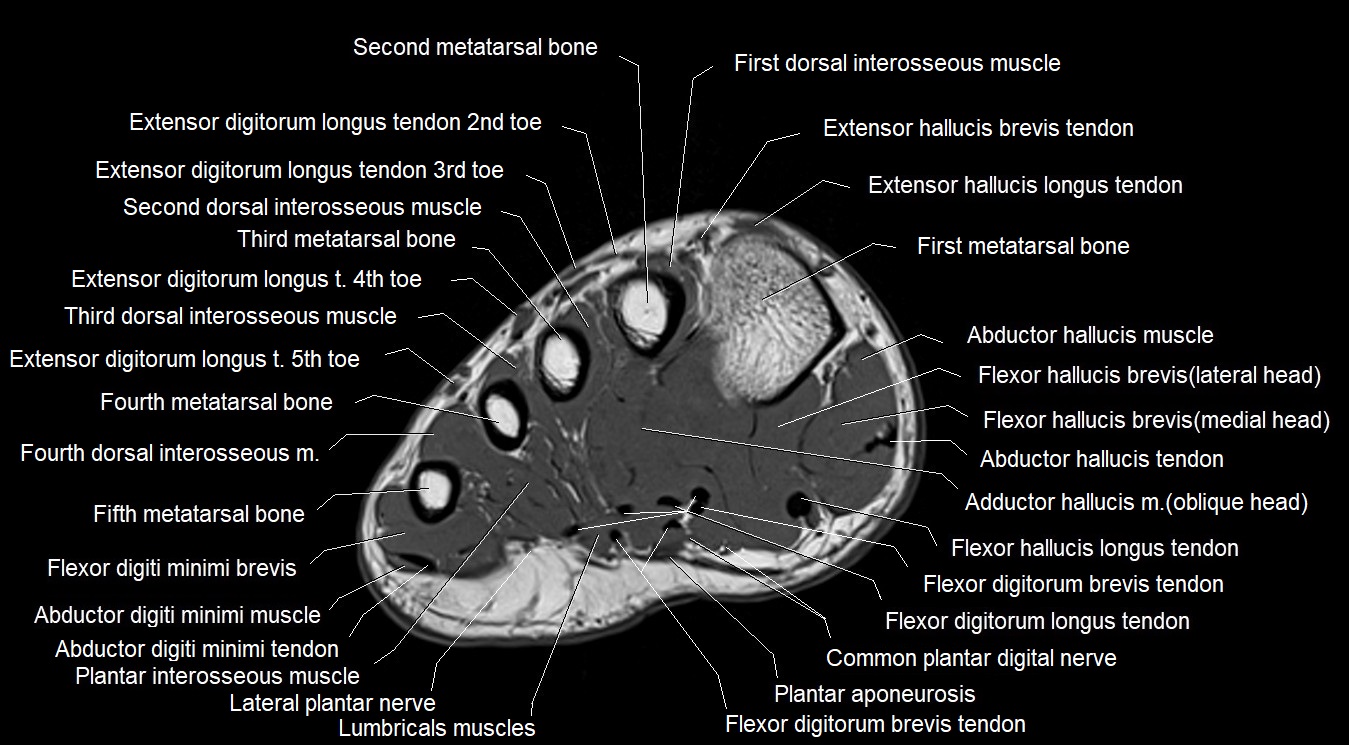
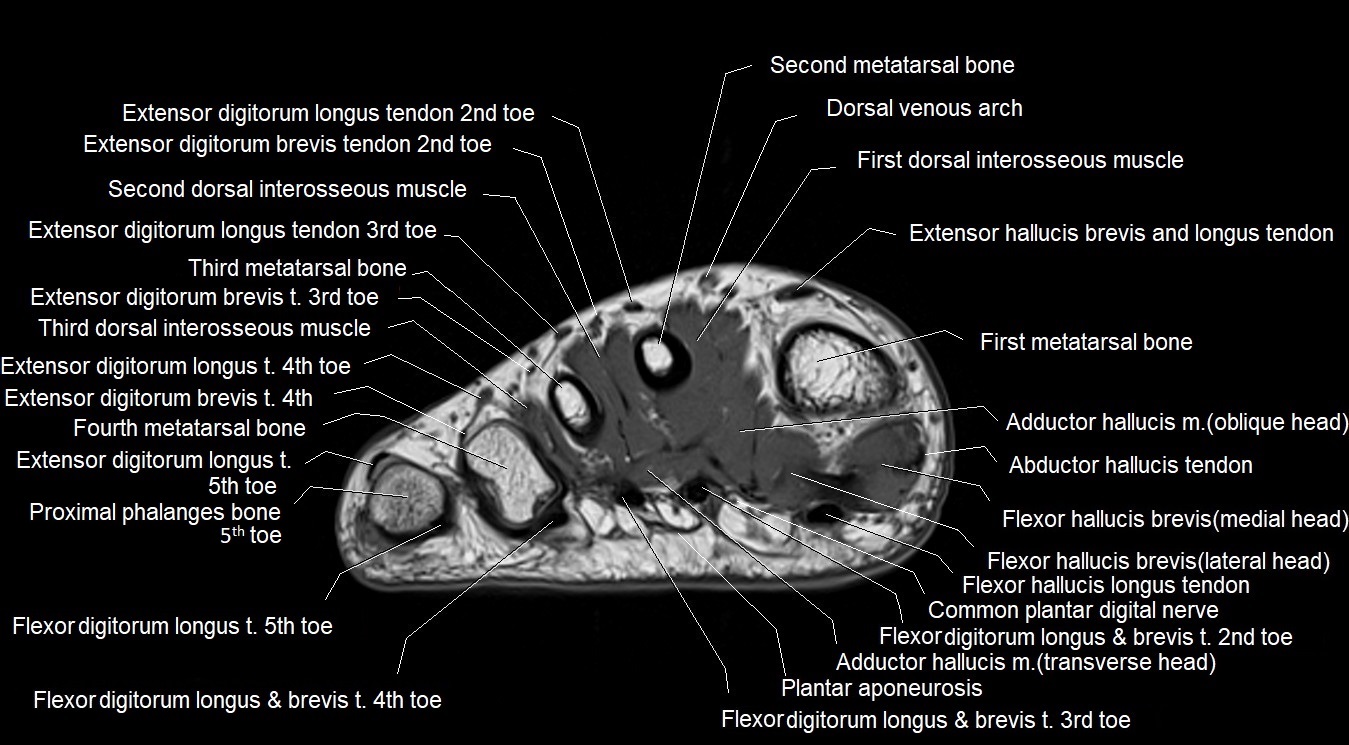
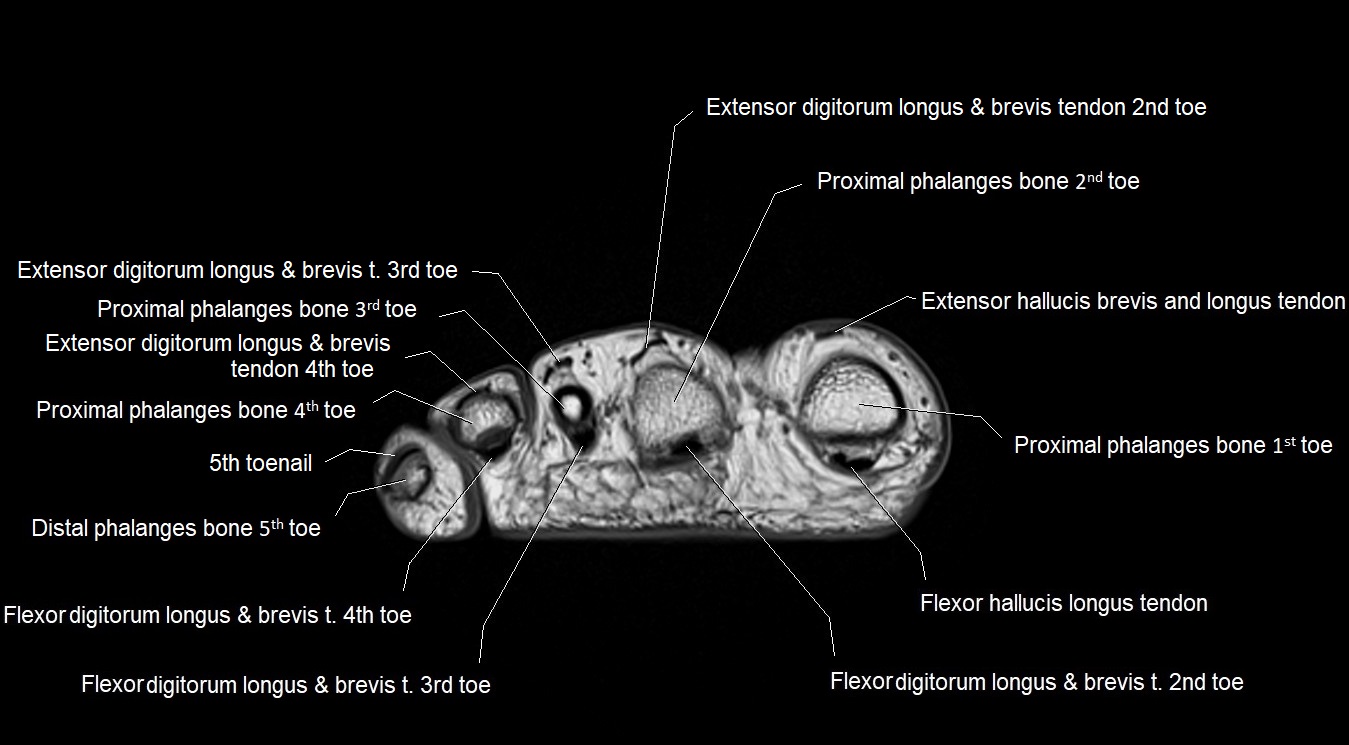
MRI image

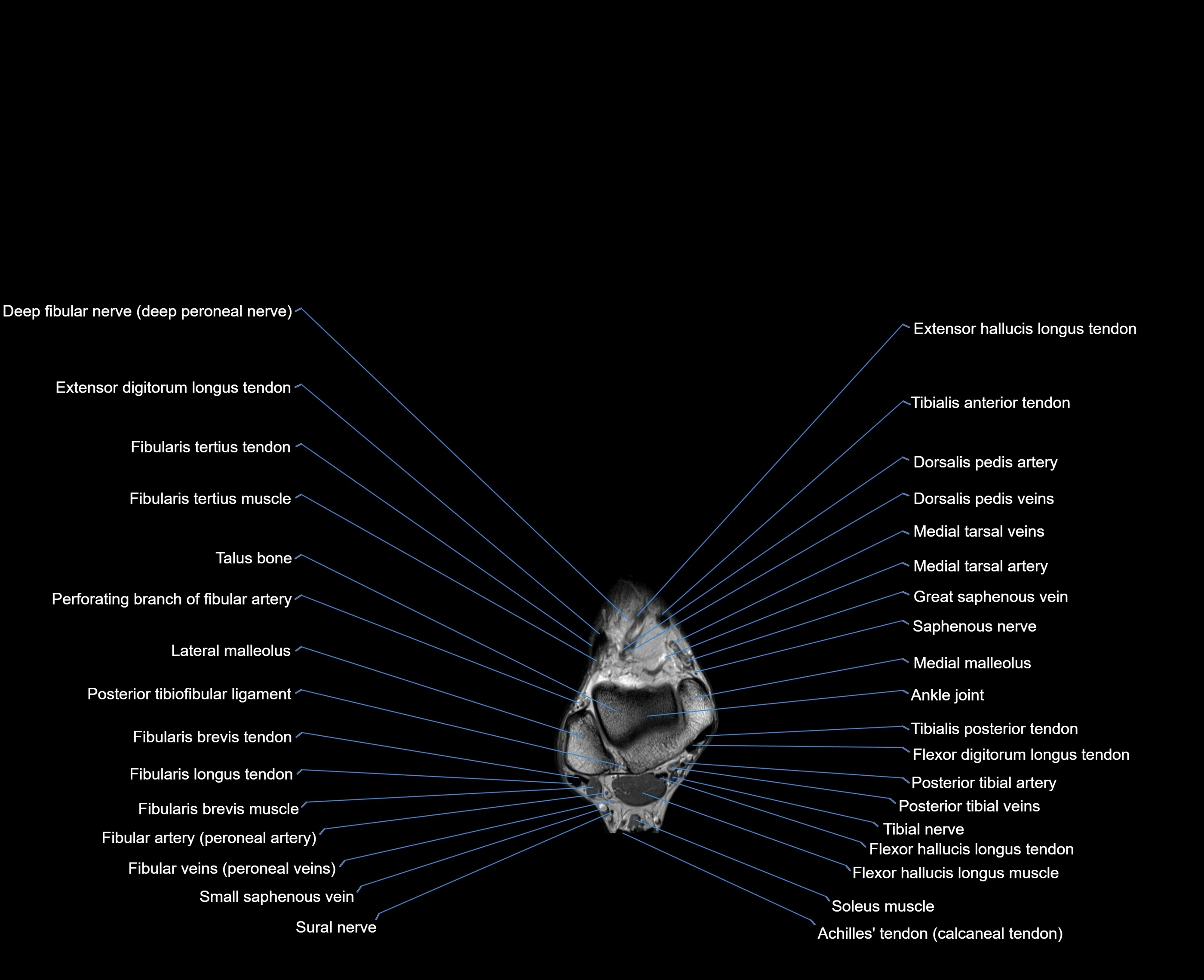
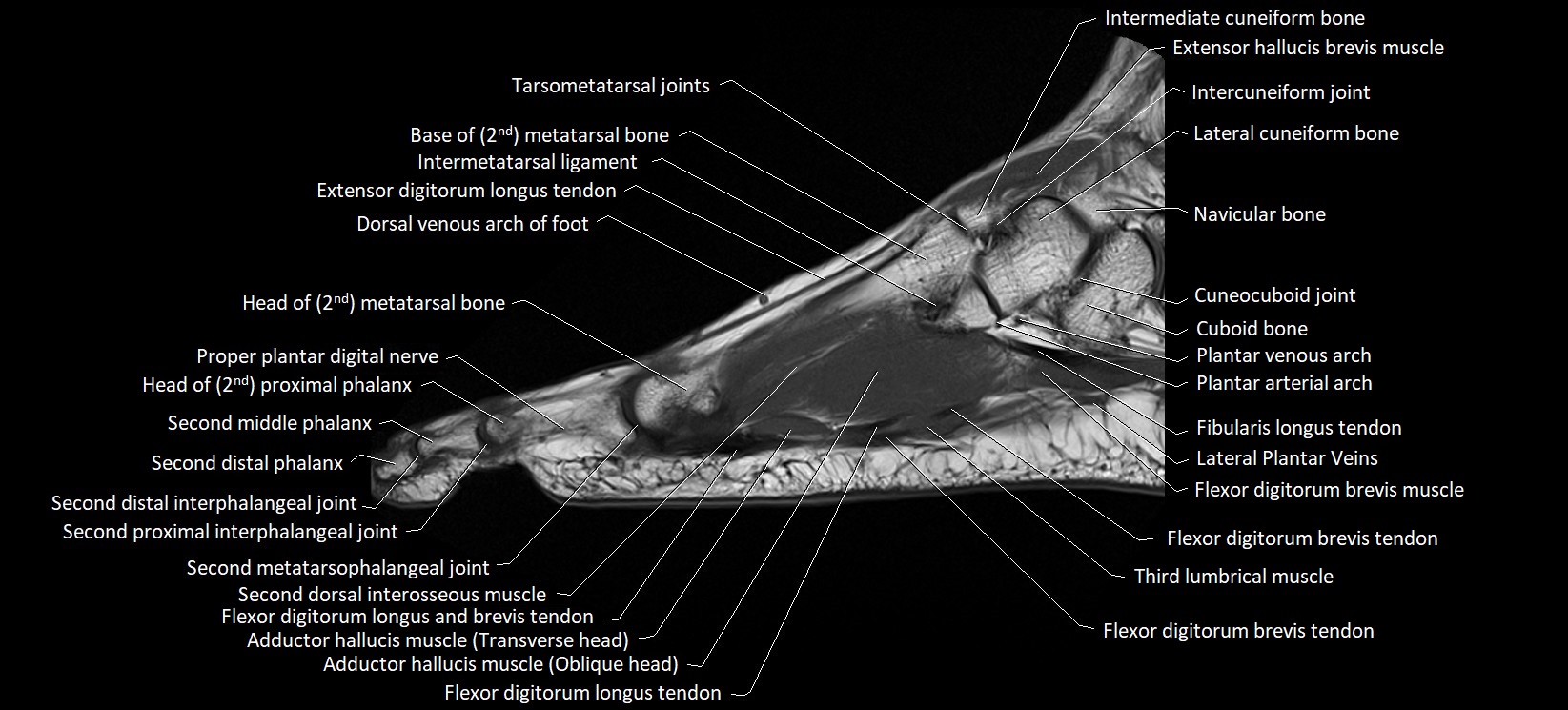
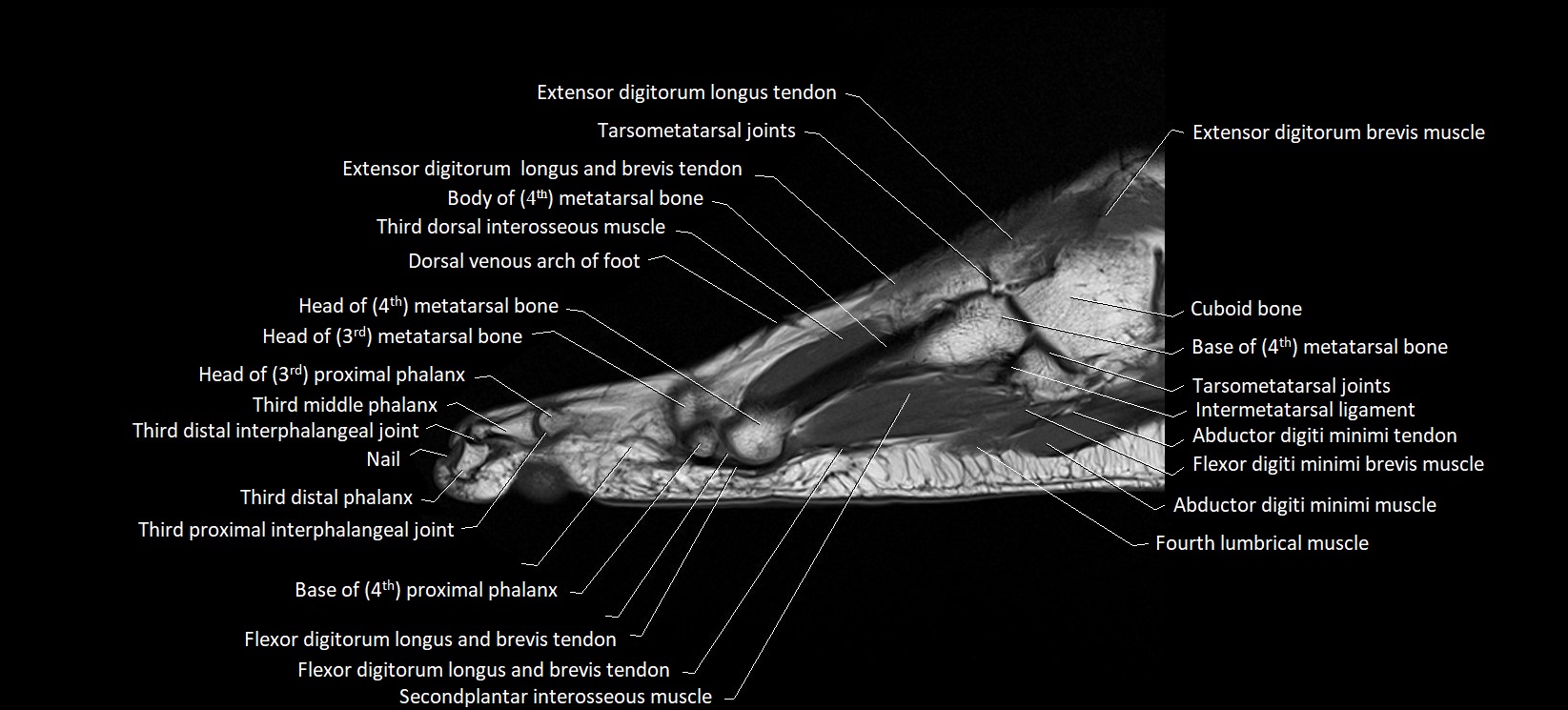
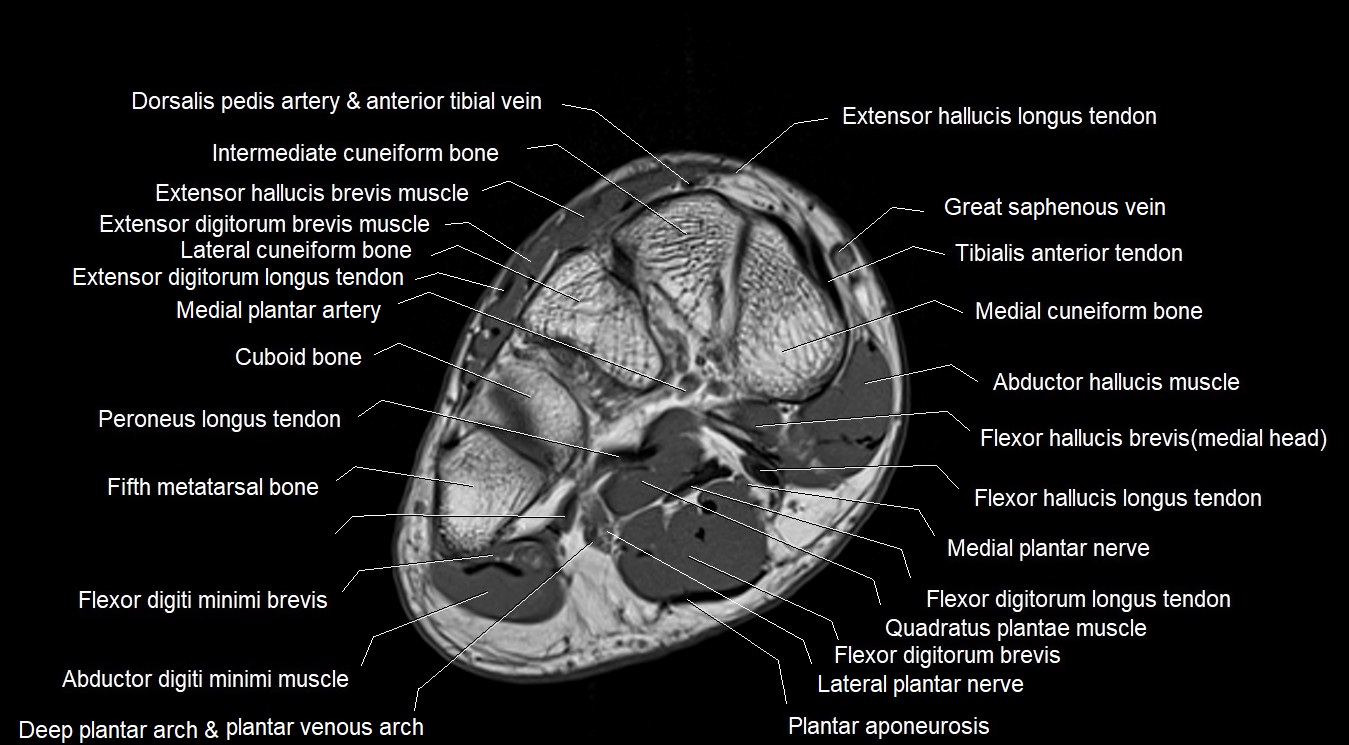
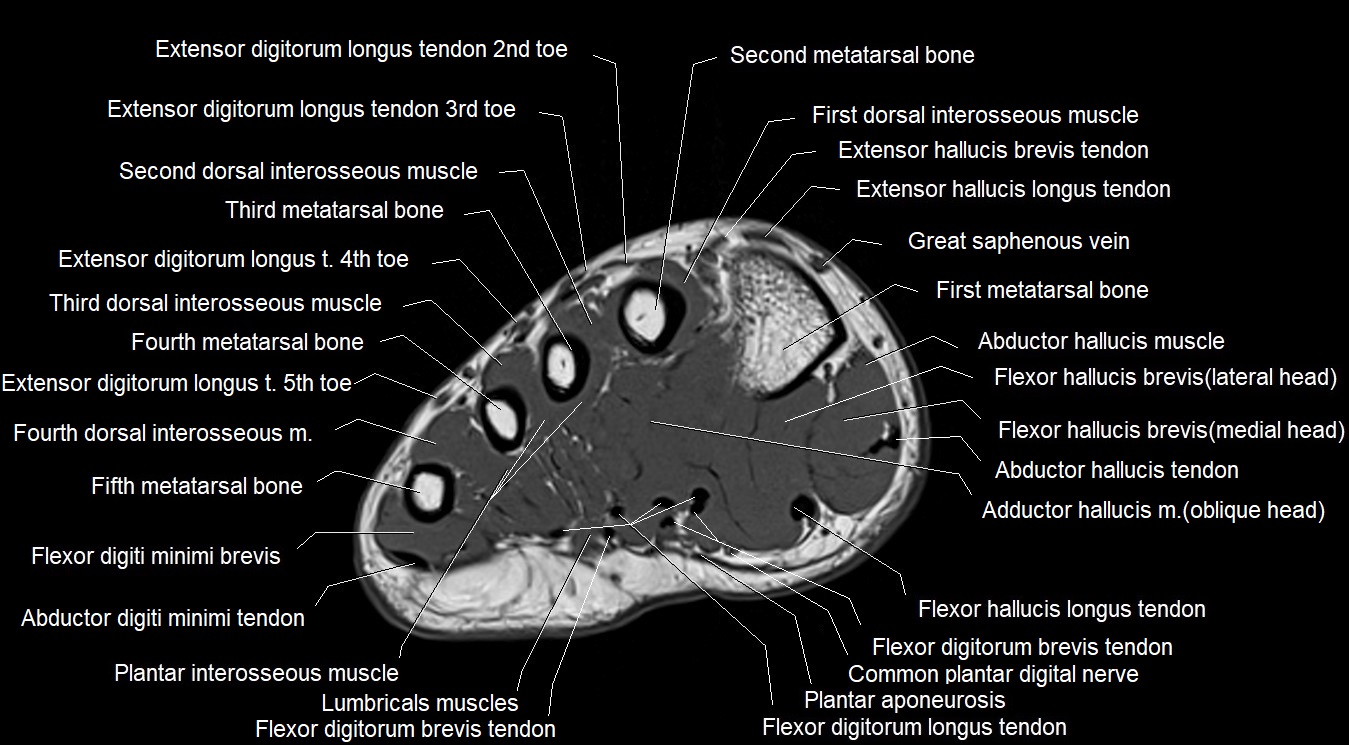
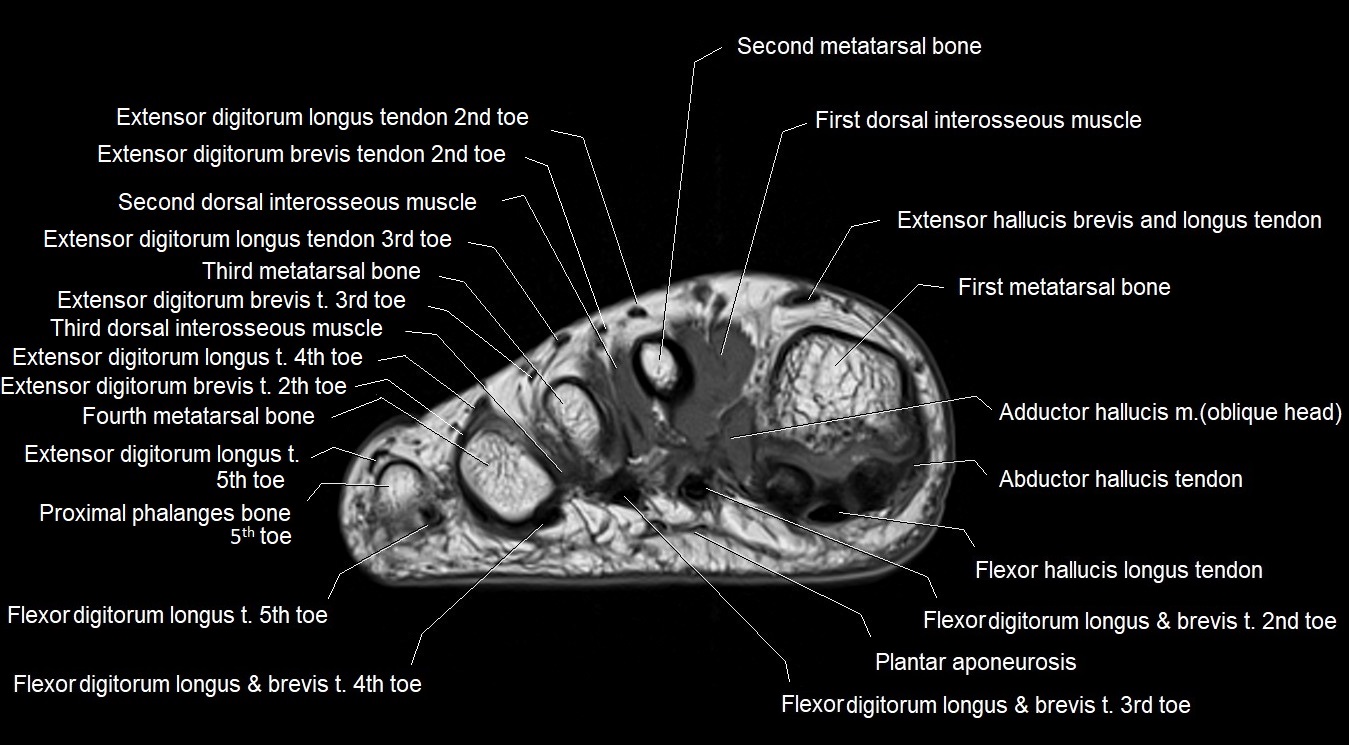
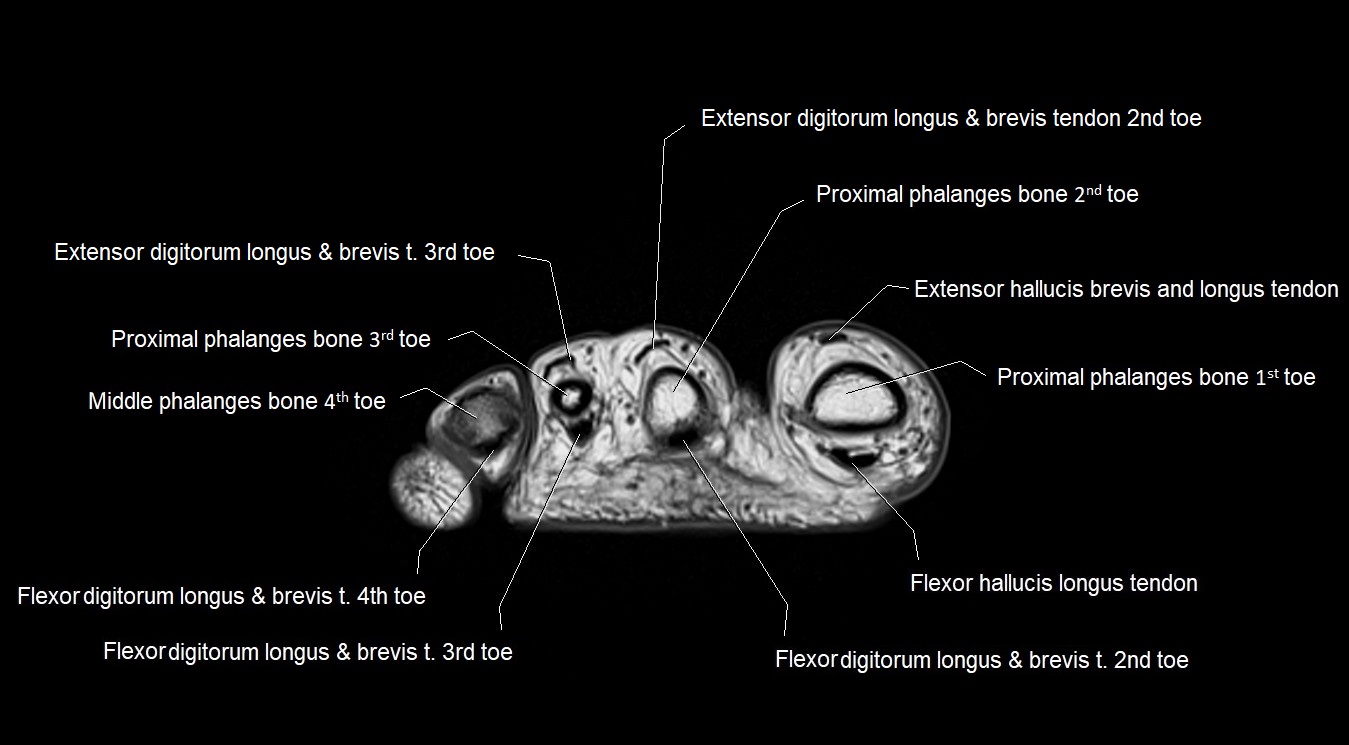
MRI image

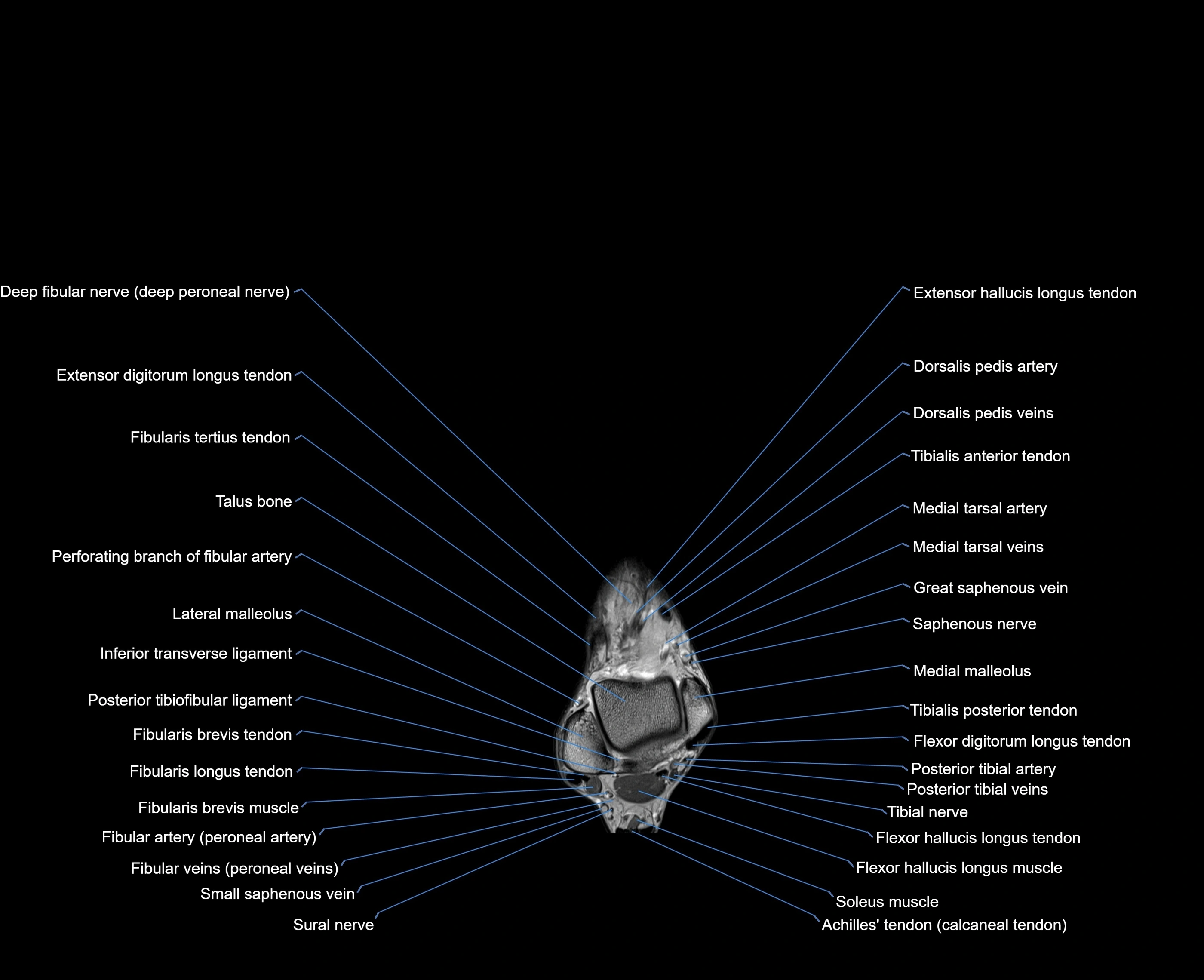
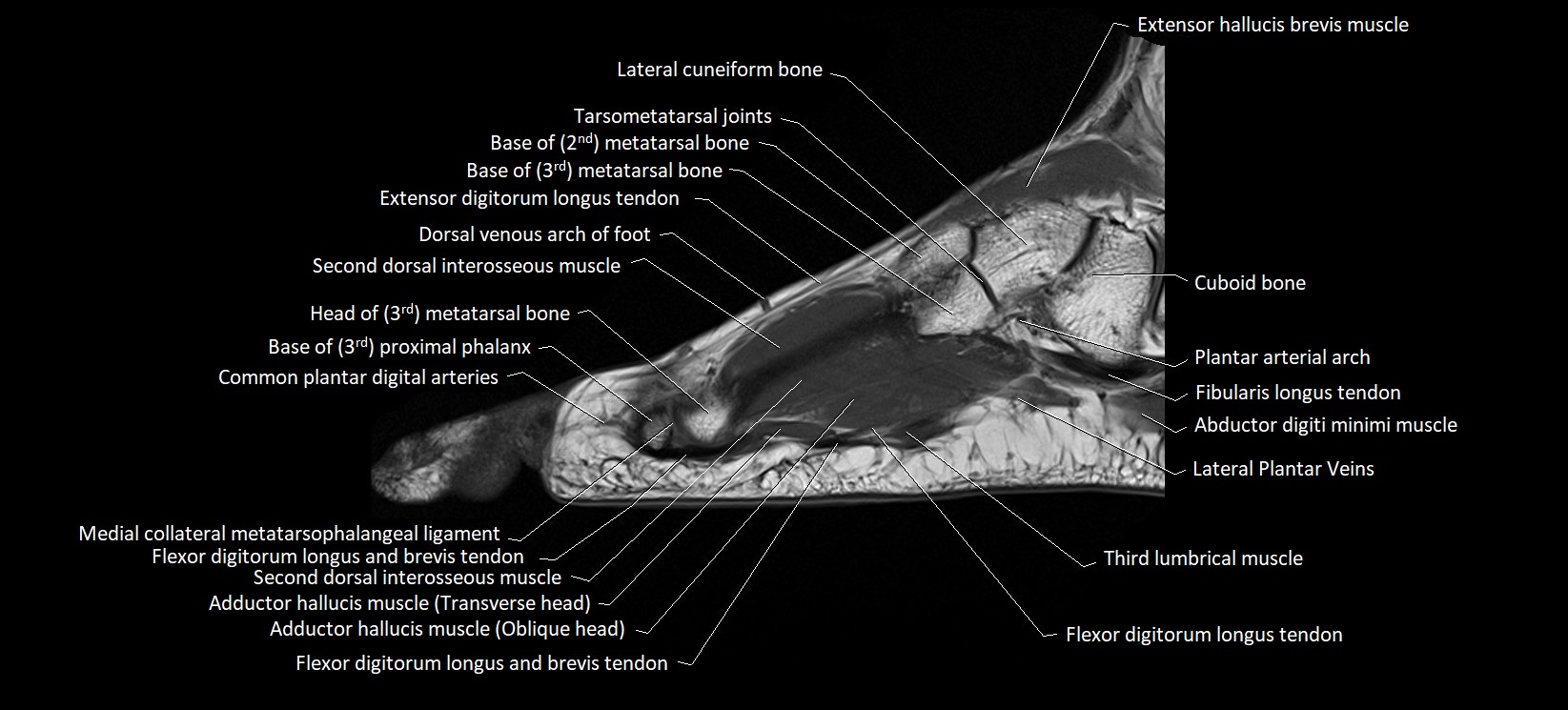
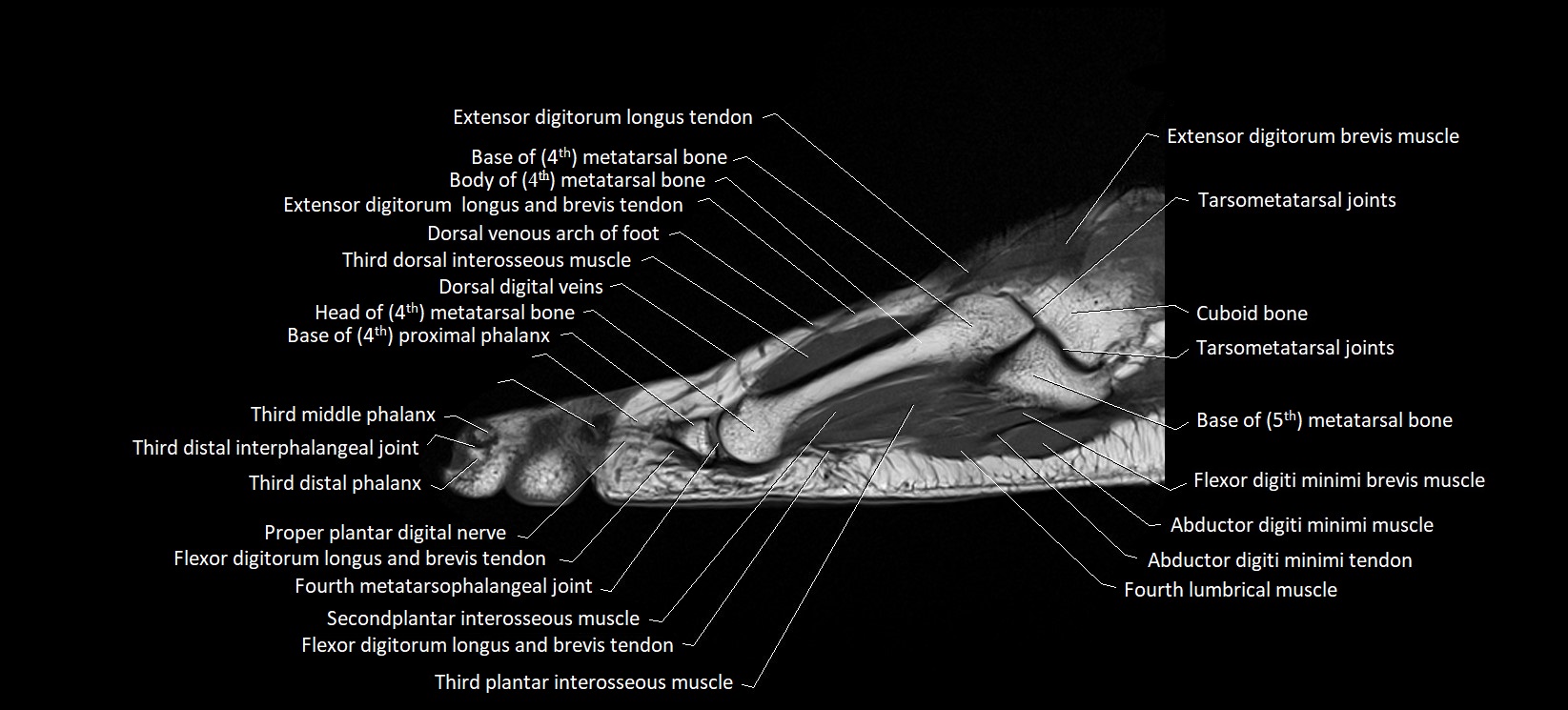
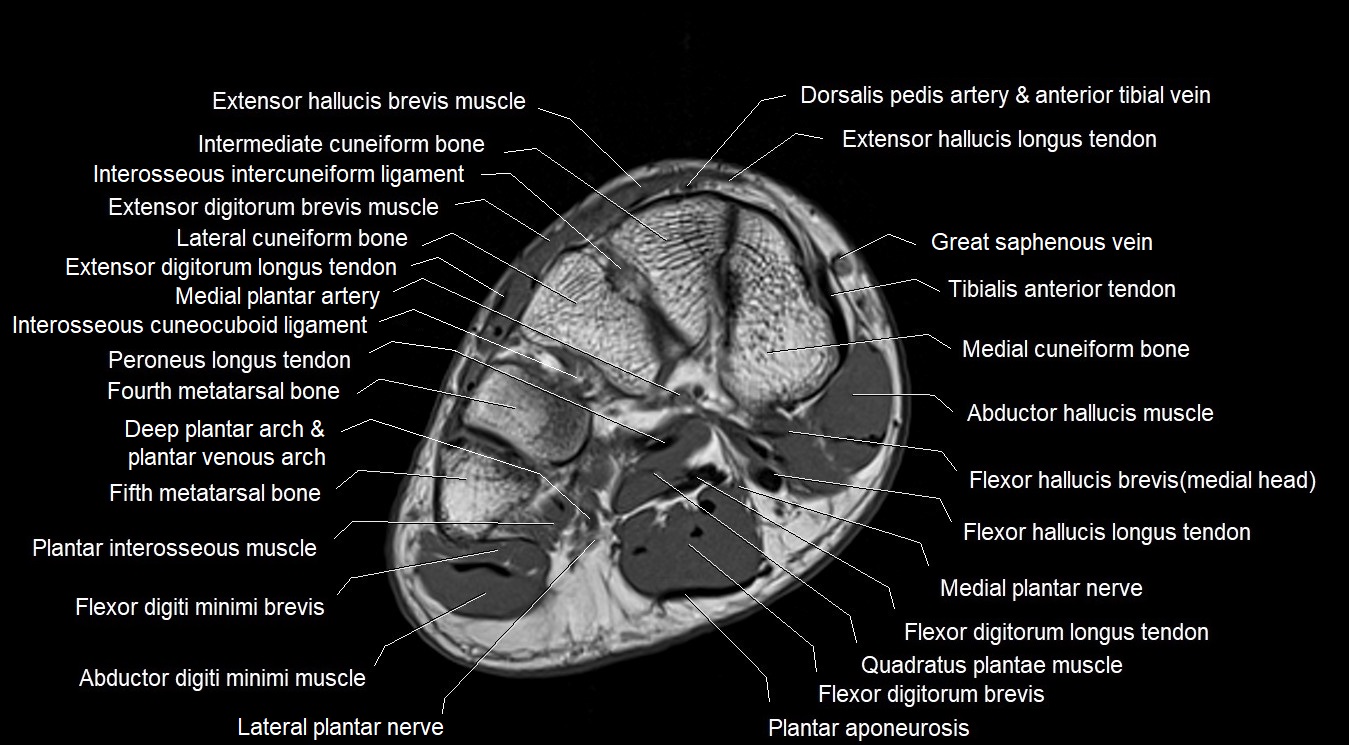
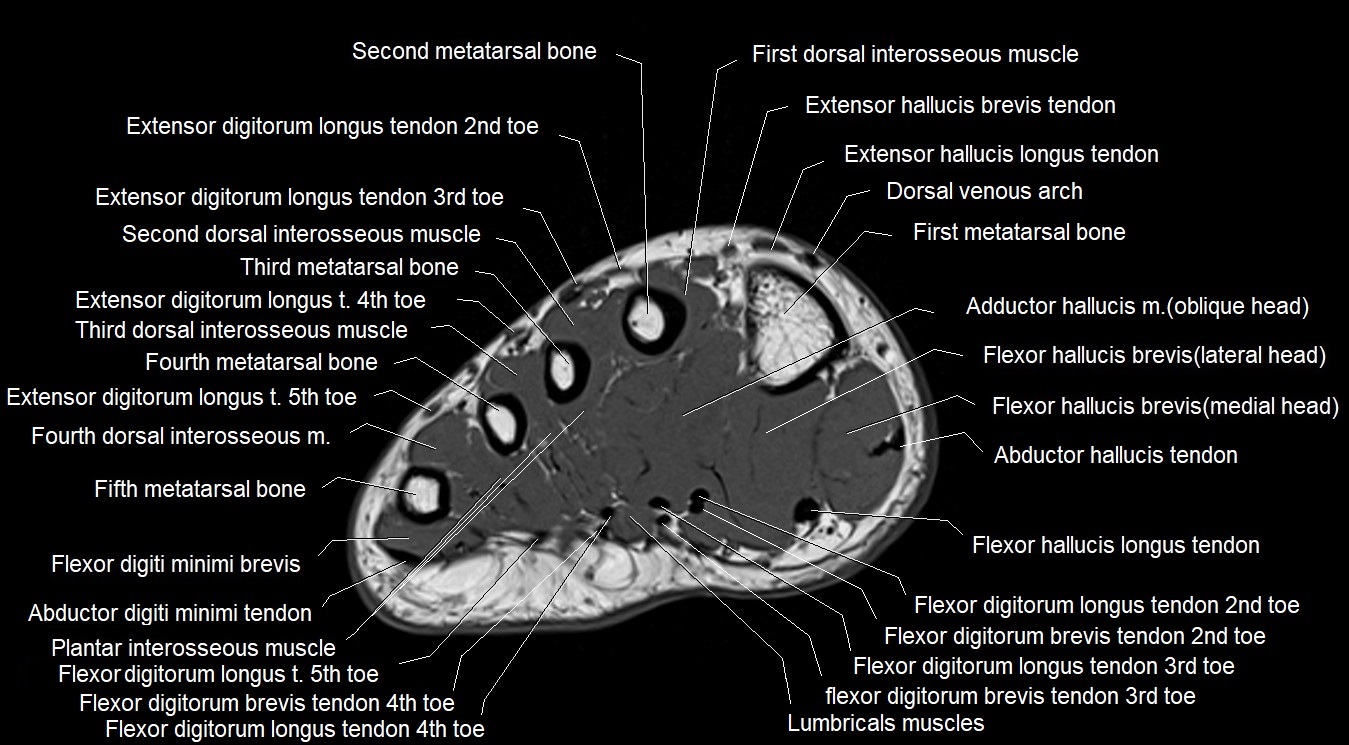
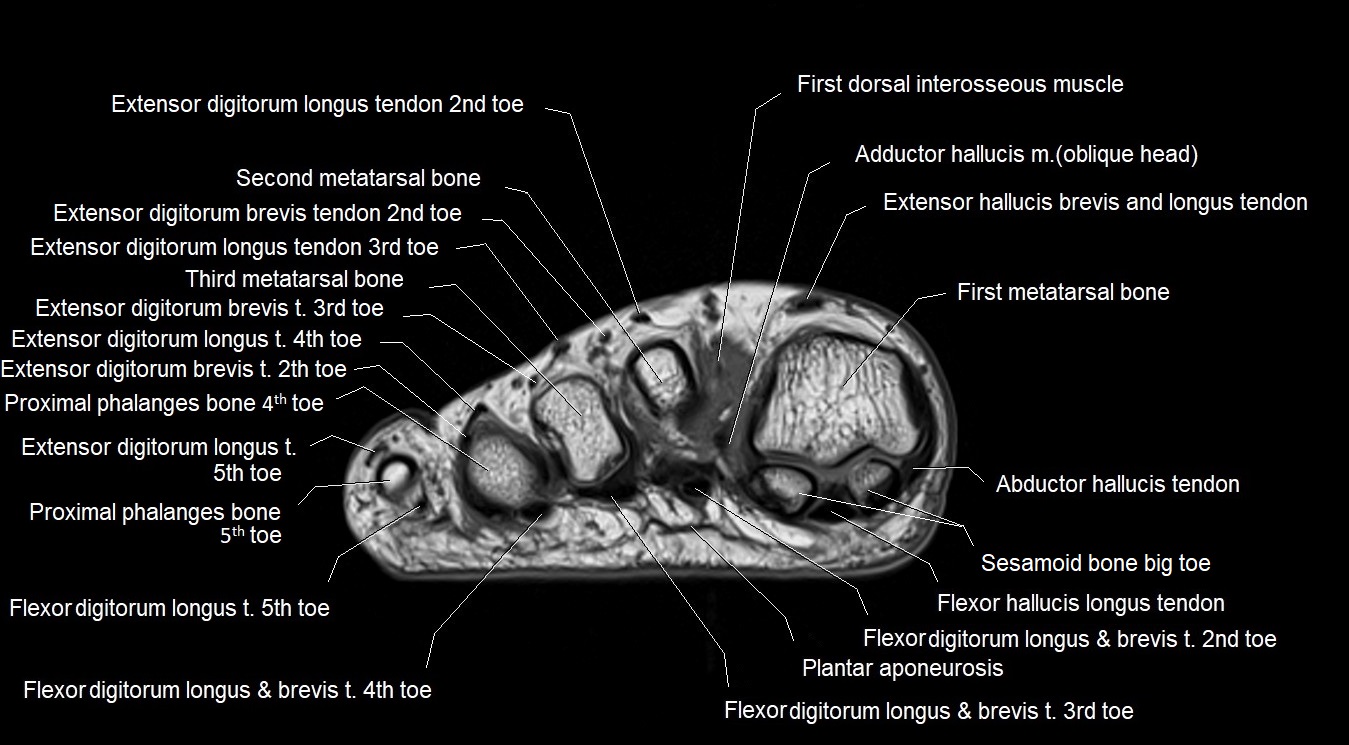
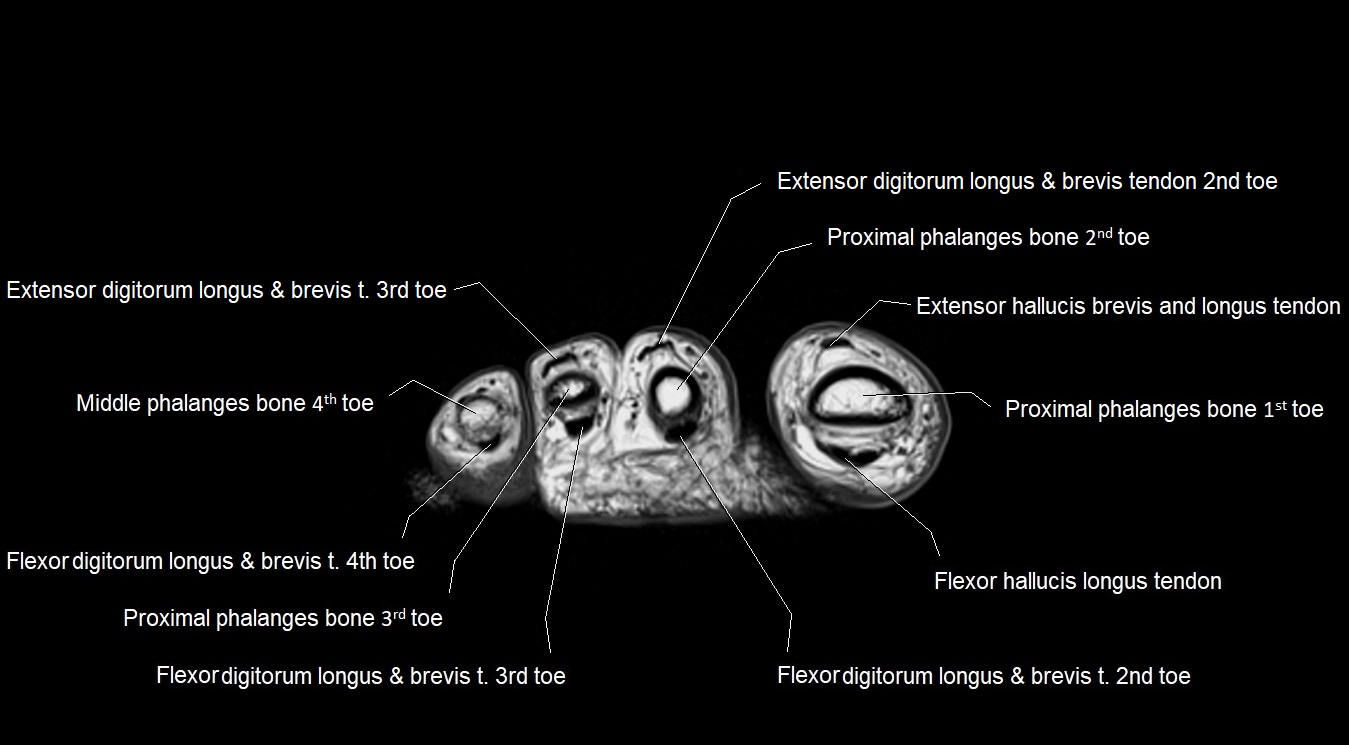
MRI image

CT image