Topic
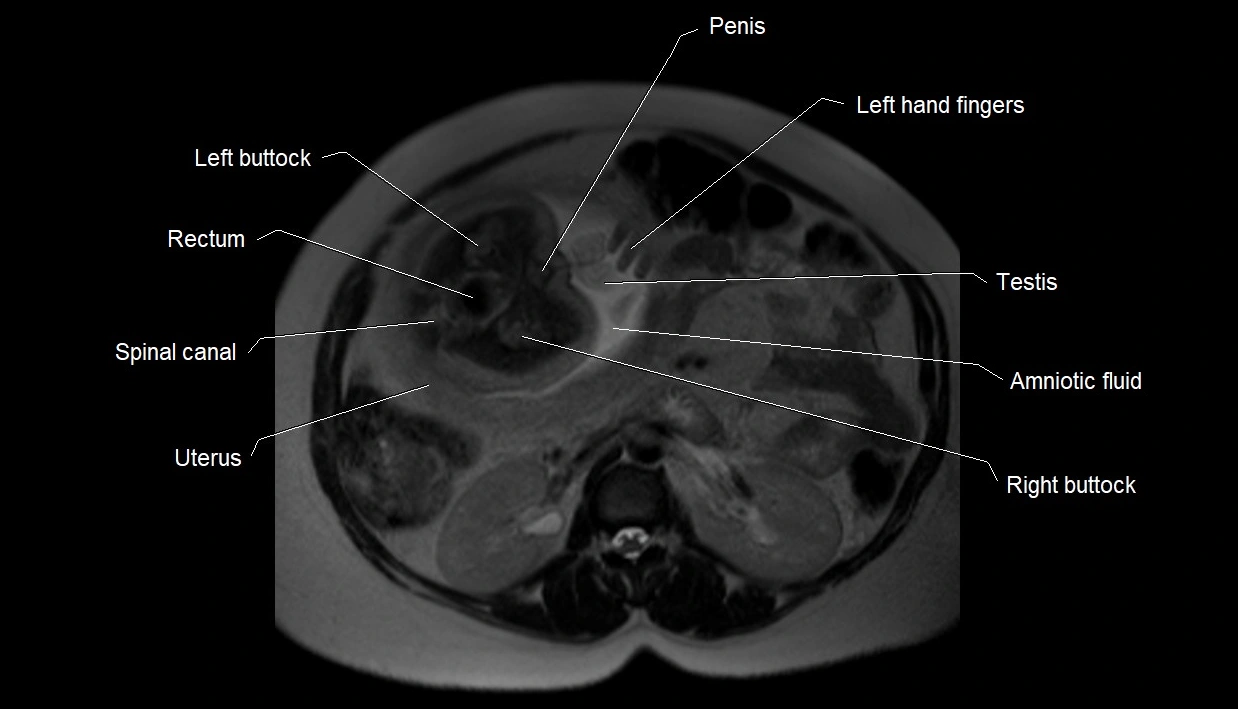
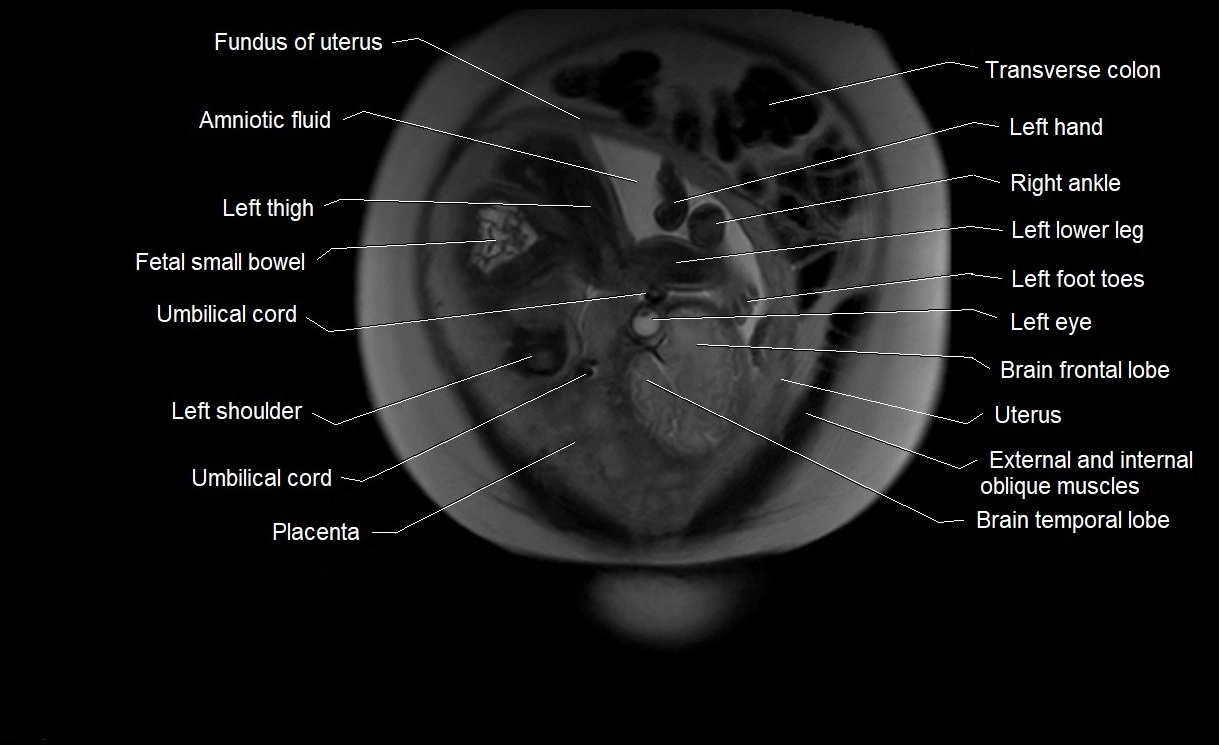
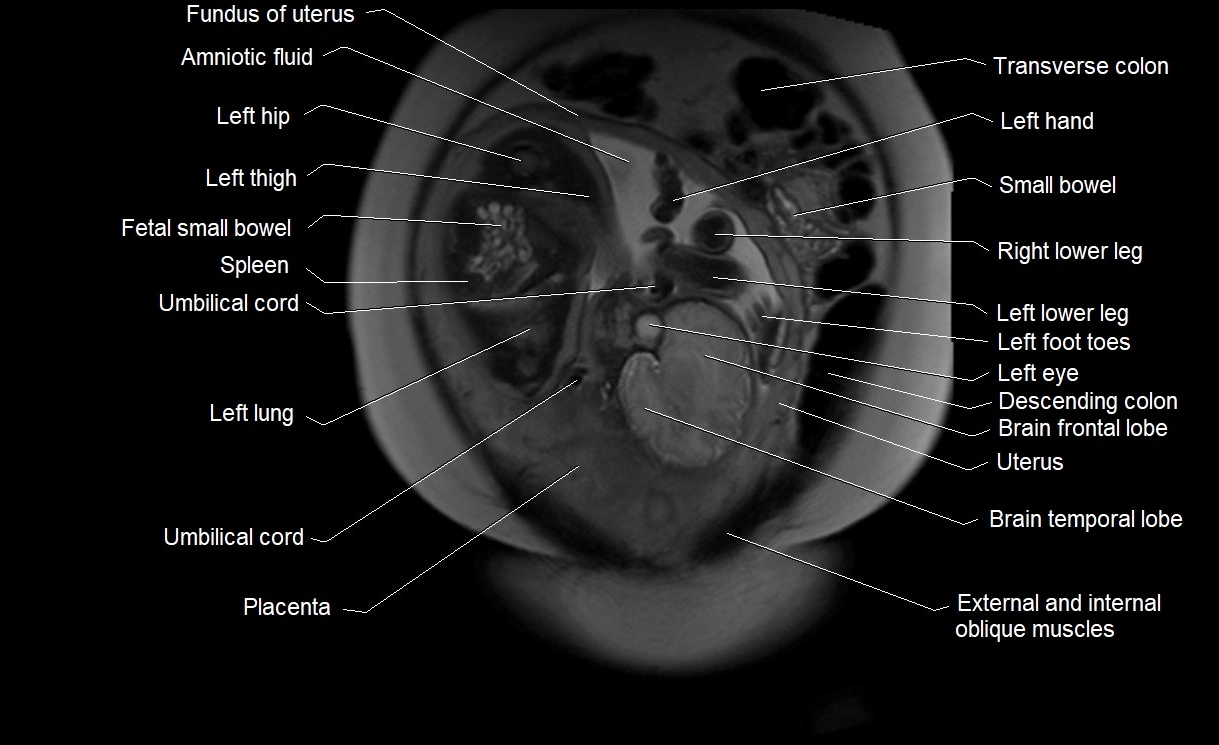
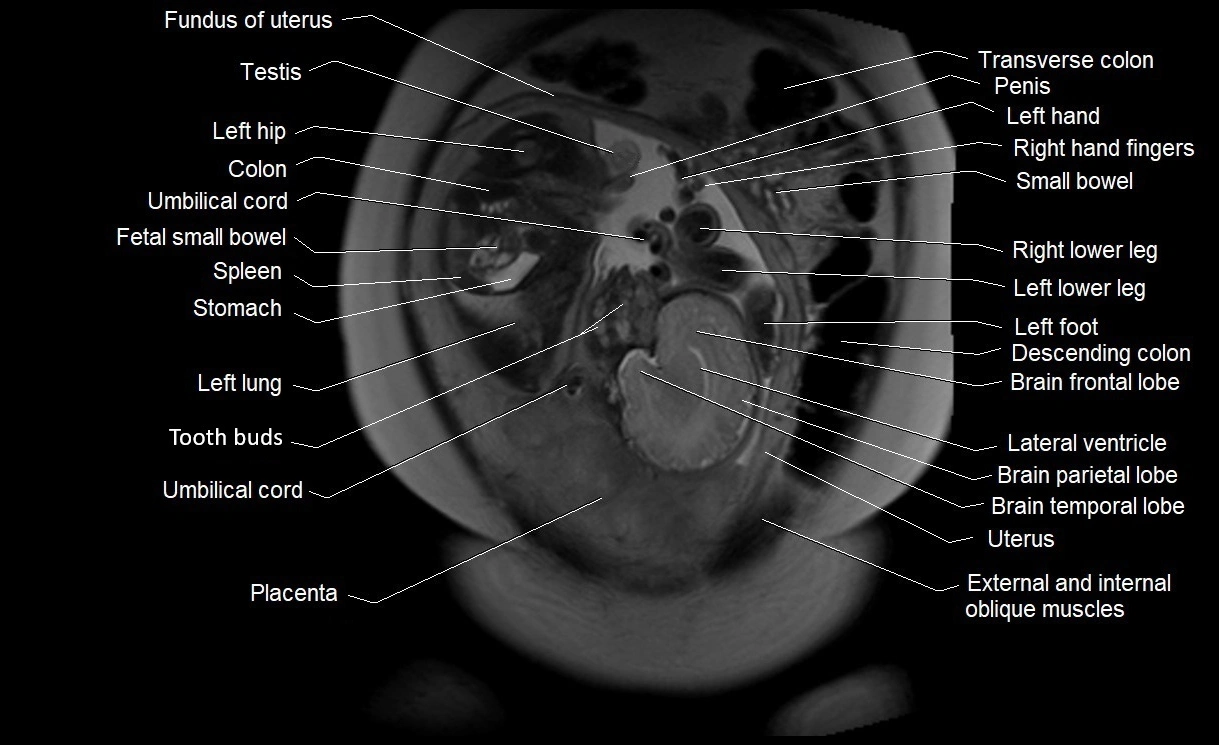
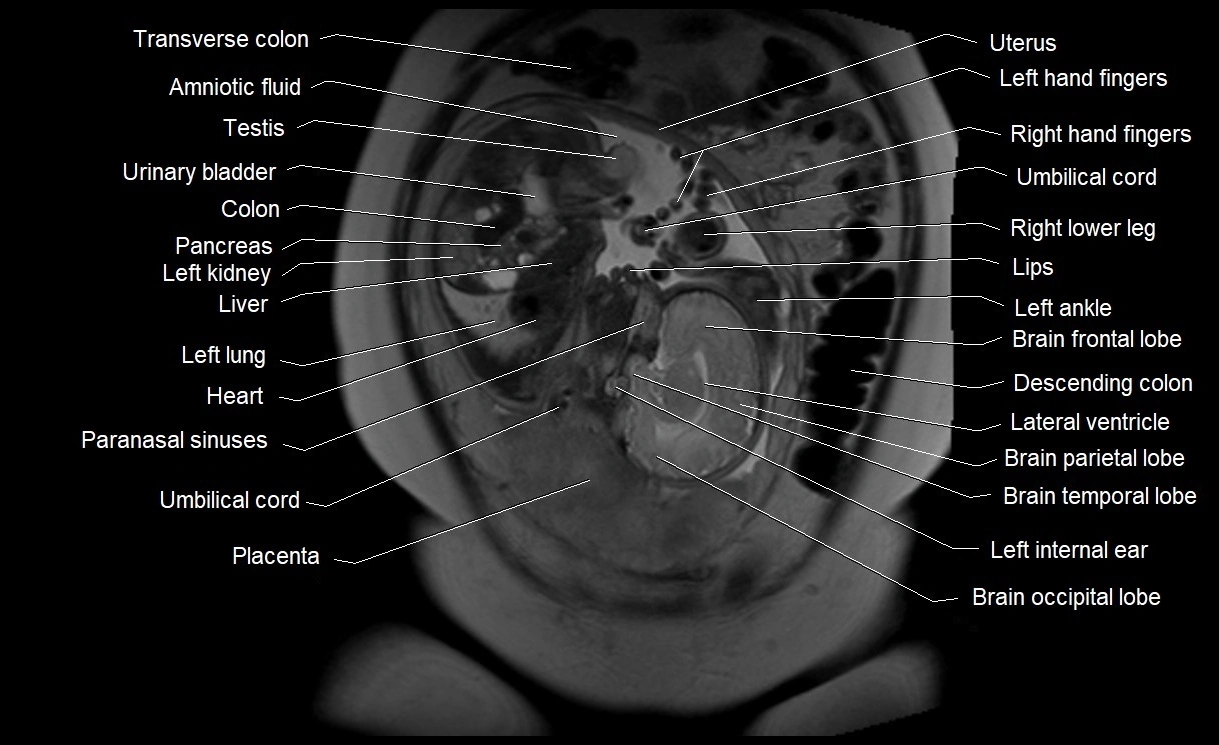
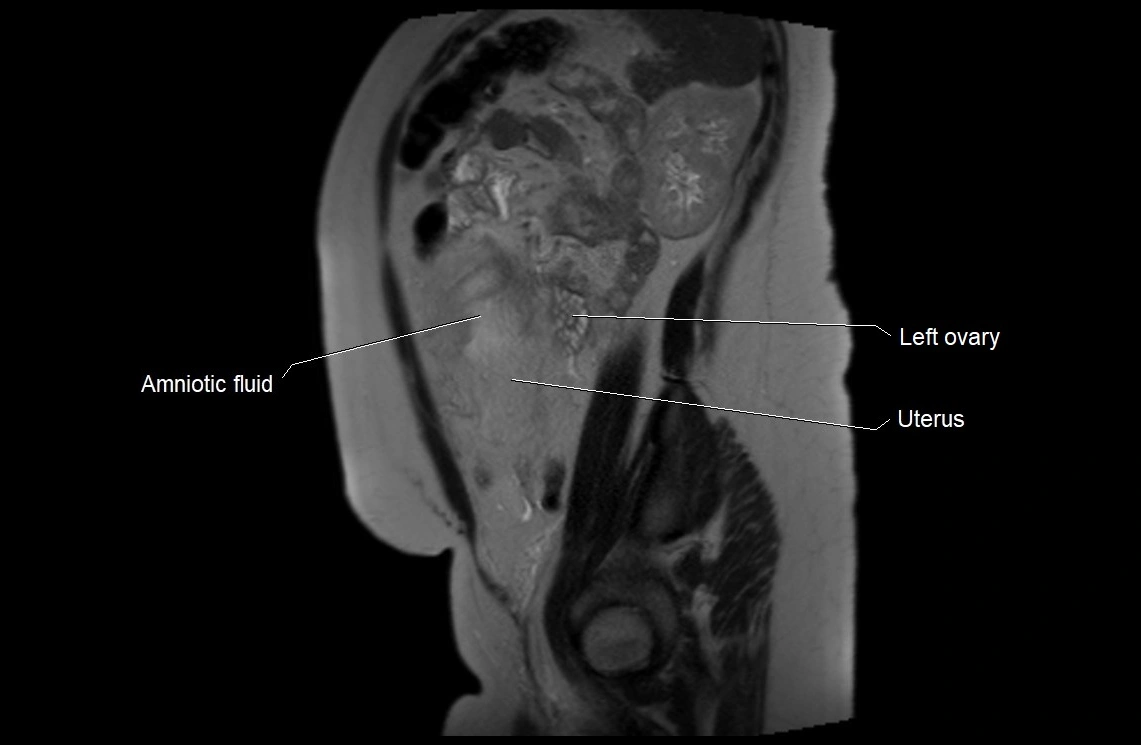
Amniotic fluid is the protective liquid surrounding the fetus within the amniotic sac. It plays an essential role in cushioning the fetus, enabling fetal movement, maintaining temperature stability, and allowing for normal lung and musculoskeletal development.
The volume and composition of amniotic fluid change throughout pregnancy. It is mainly derived from maternal plasma in early pregnancy, while in later stages, it consists largely of fetal urine, lung secretions, and transmembrane exchanges.
Synonyms
-
Liquor amnii
-
Amniotic liquor
-
Fetal water
Structure and Composition
-
Water: ~98% of amniotic fluid
-
Electrolytes: Sodium, potassium, chloride, calcium
-
Proteins, carbohydrates, lipids
-
Hormones and enzymes
-
Fetal cells and vernix caseosa (shed epithelial cells, lanugo, sebaceous material)
Relations
-
Enclosed within the amniotic sac, bounded by the amnion and chorion
-
Surrounds and cushions the developing fetus
-
In continuity with maternal circulation through placental and transmembrane exchanges
Function
-
Protects fetus from trauma by cushioning external shocks
-
Prevents adherence of amniotic membranes to fetus
-
Permits fetal movement and musculoskeletal development
-
Maintains stable intrauterine temperature
-
Essential for normal lung development via fetal breathing movements
-
Provides a medium for biochemical assessment of fetal well-being
Clinical Significance
-
Oligohydramnios: Abnormally low fluid → associated with renal agenesis, placental insufficiency, premature rupture of membranes
-
Polyhydramnios: Excess fluid → associated with maternal diabetes, fetal swallowing disorders, GI obstruction
-
Amniotic fluid embolism: Rare but life-threatening maternal complication
-
Infections: Chorioamnionitis may affect amniotic fluid composition
-
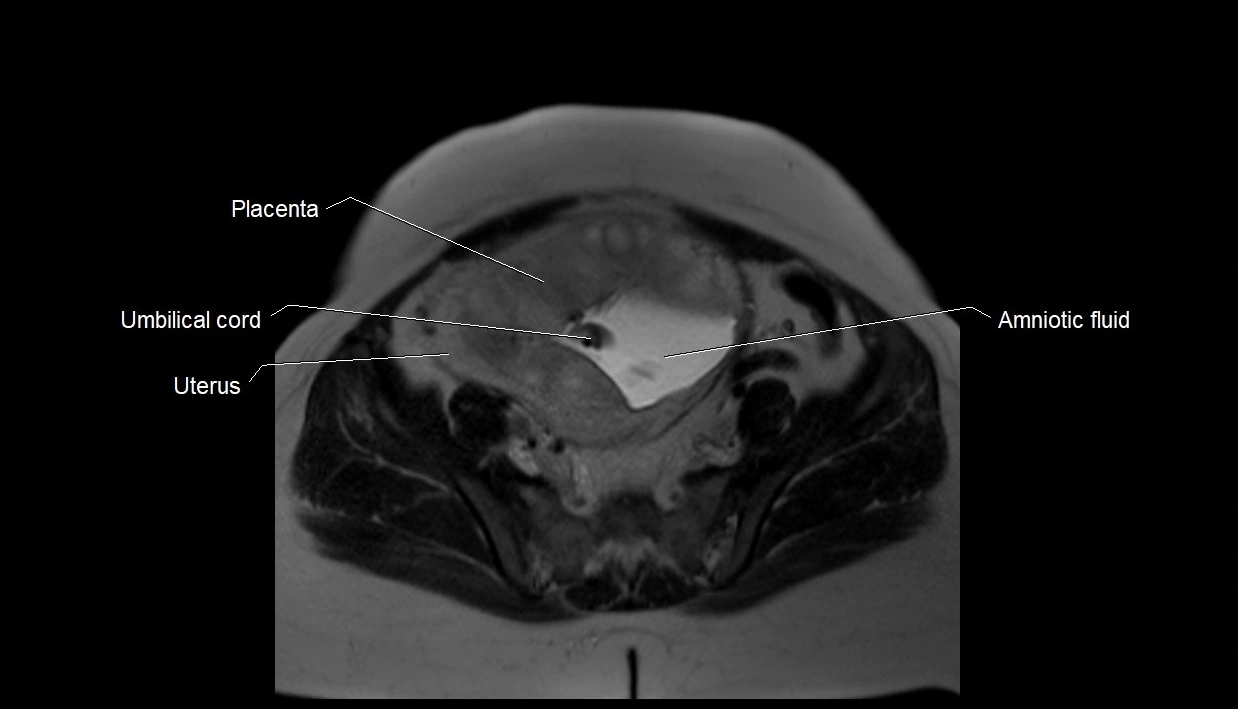
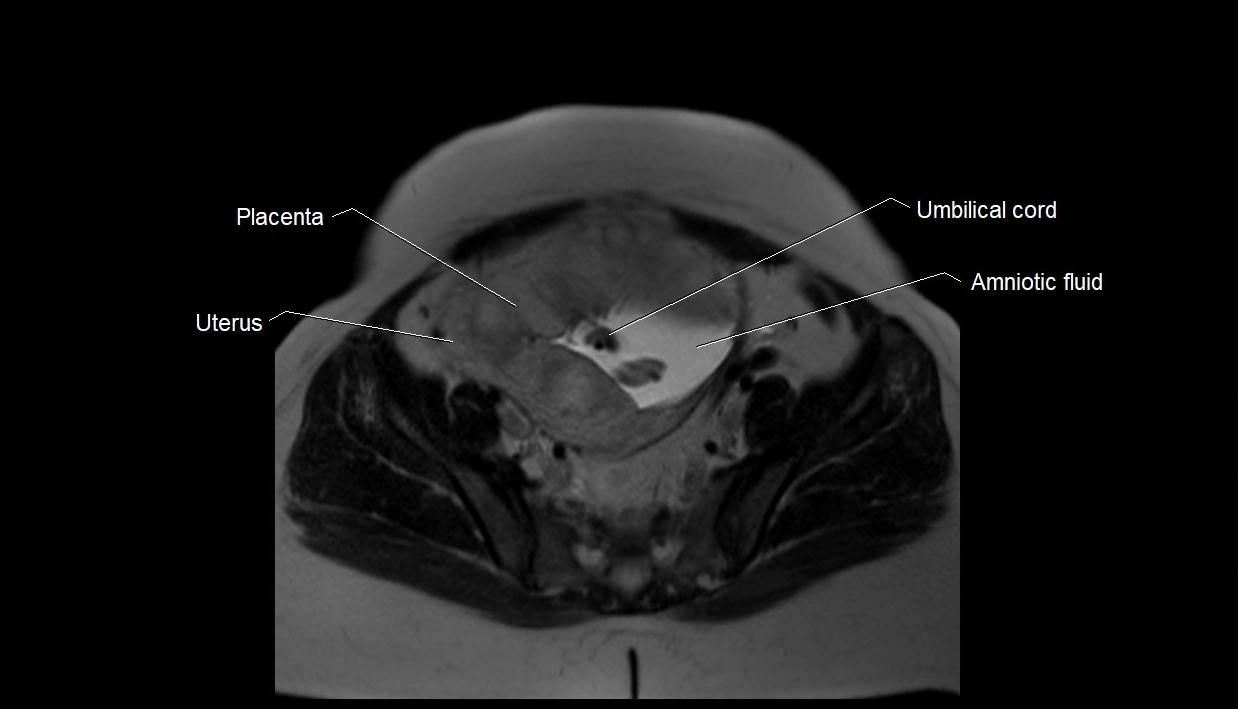
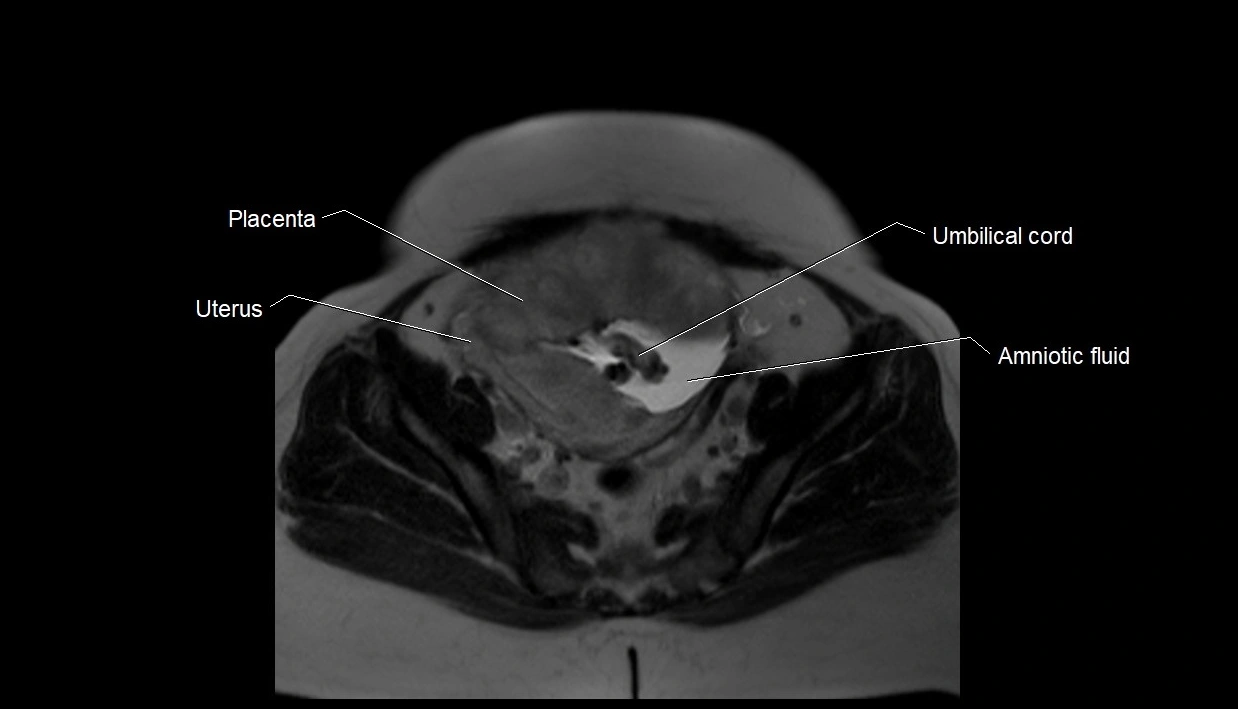
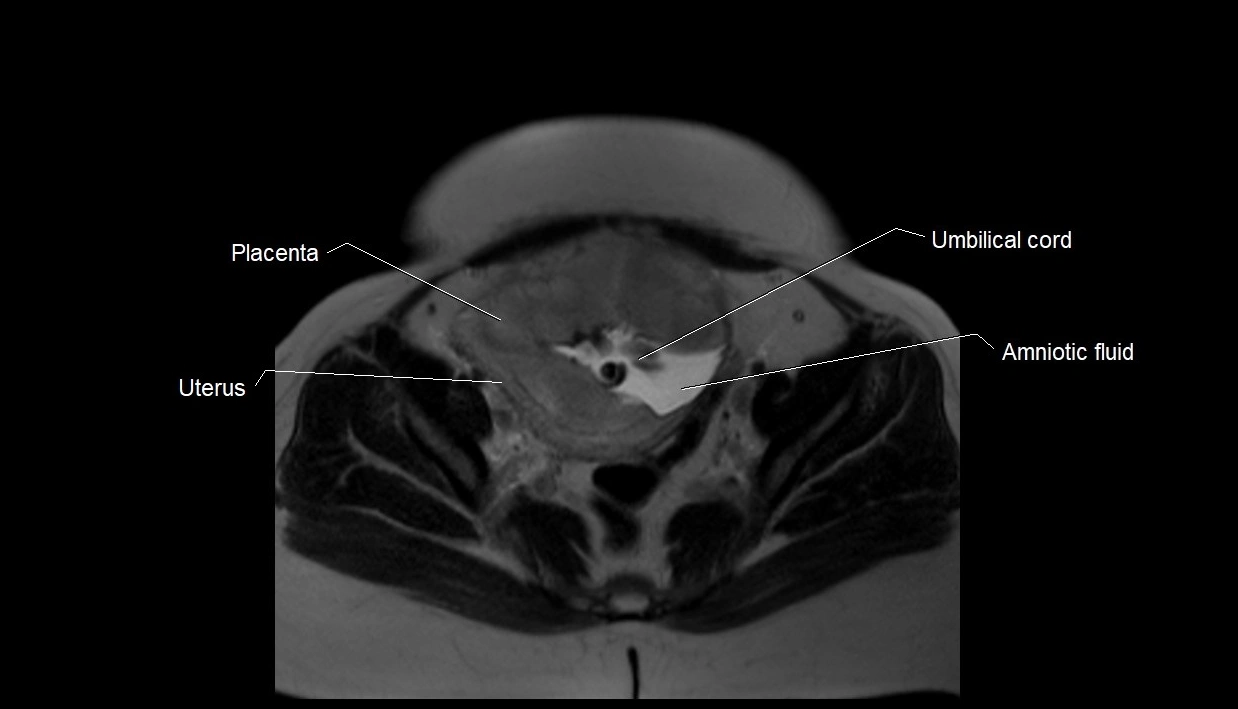
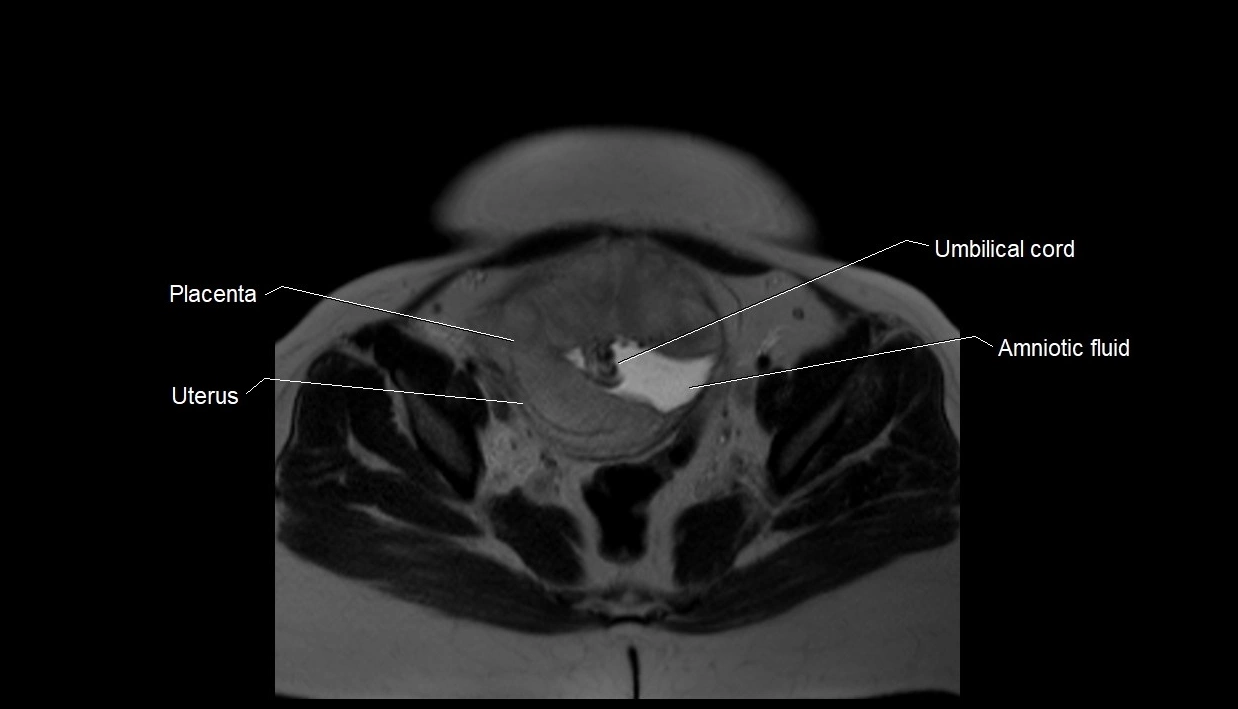
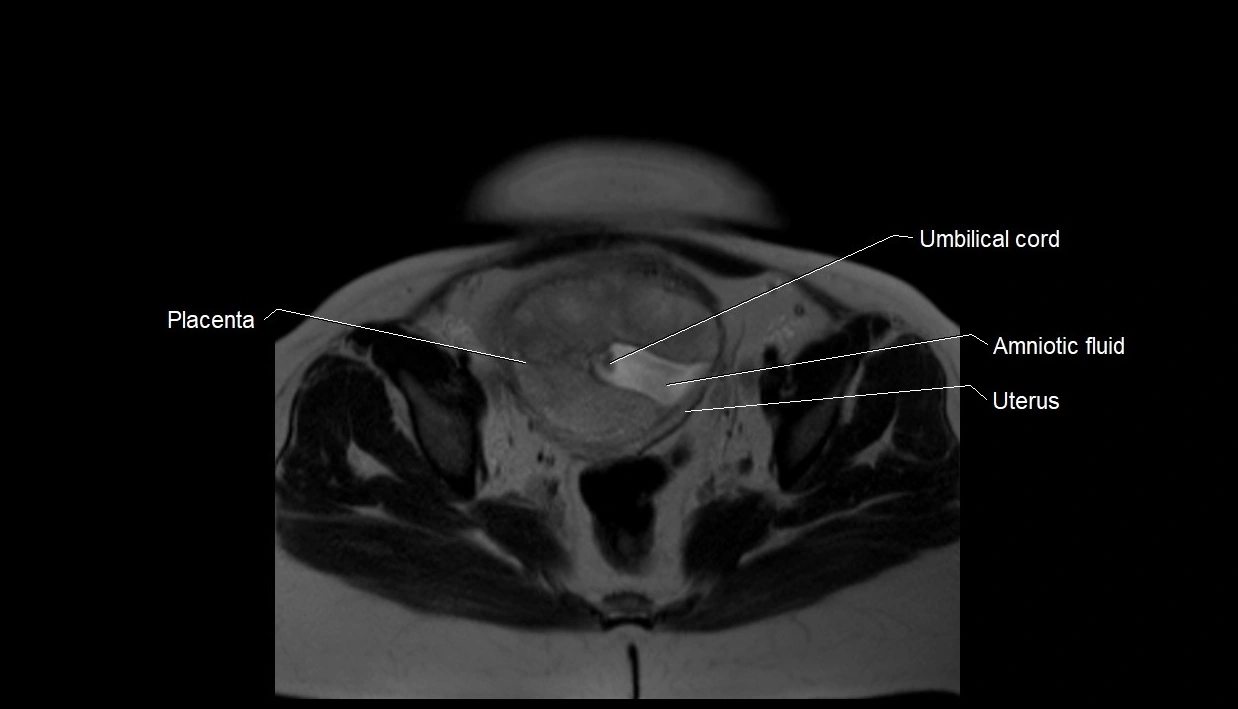
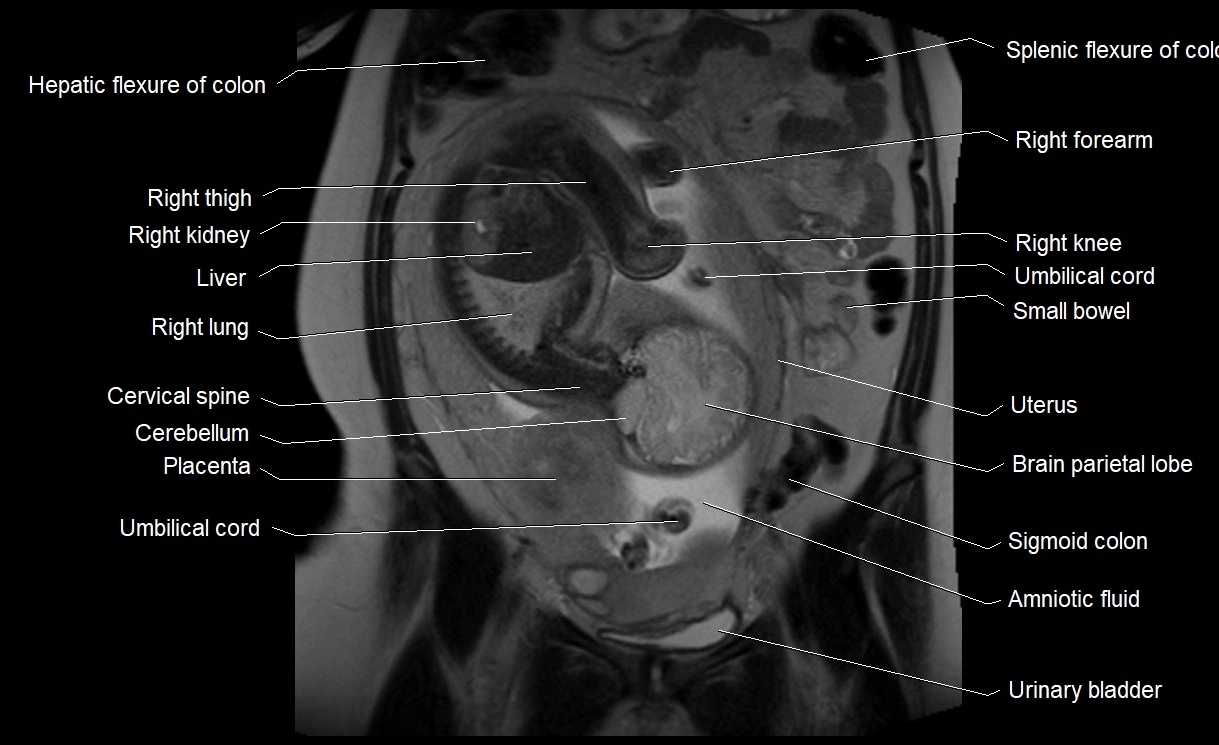
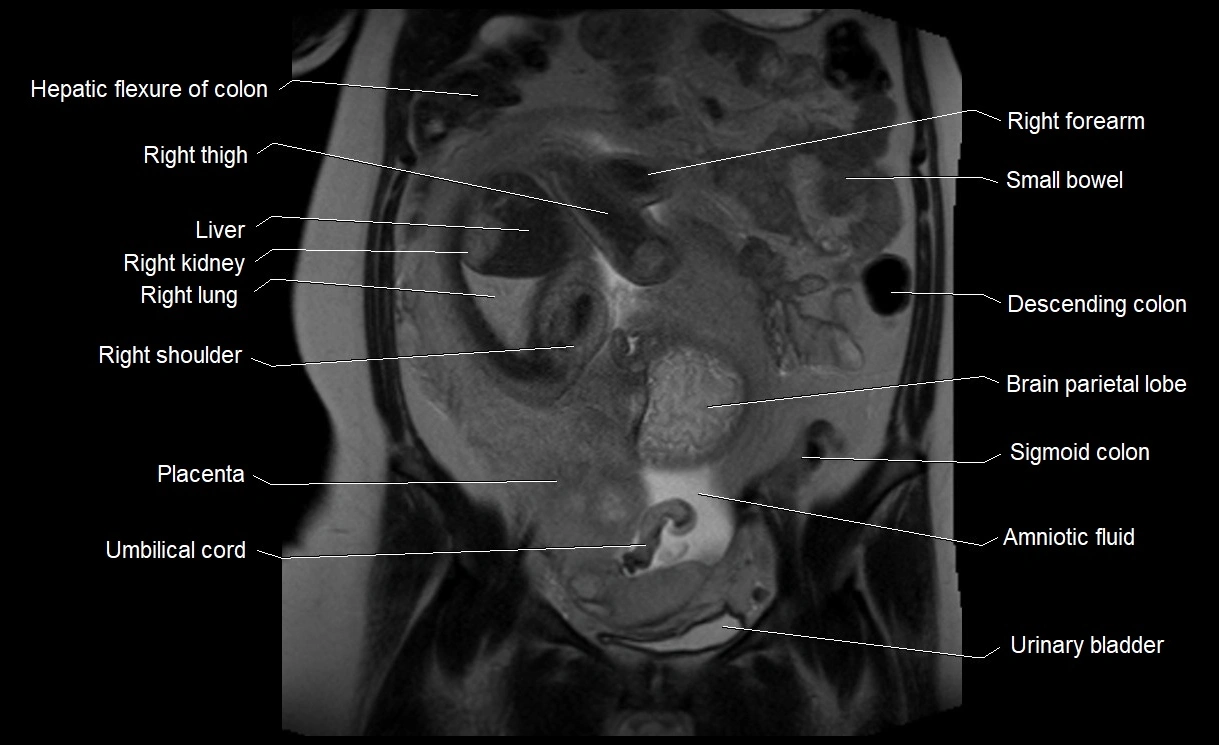
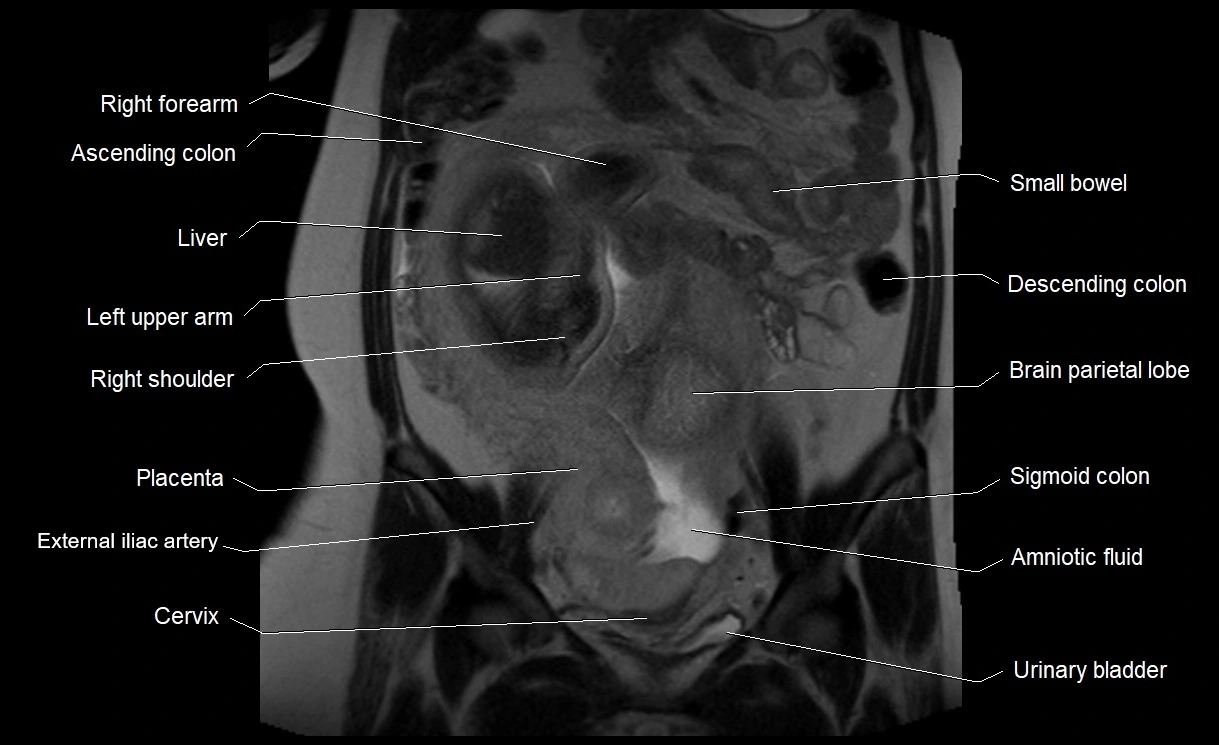
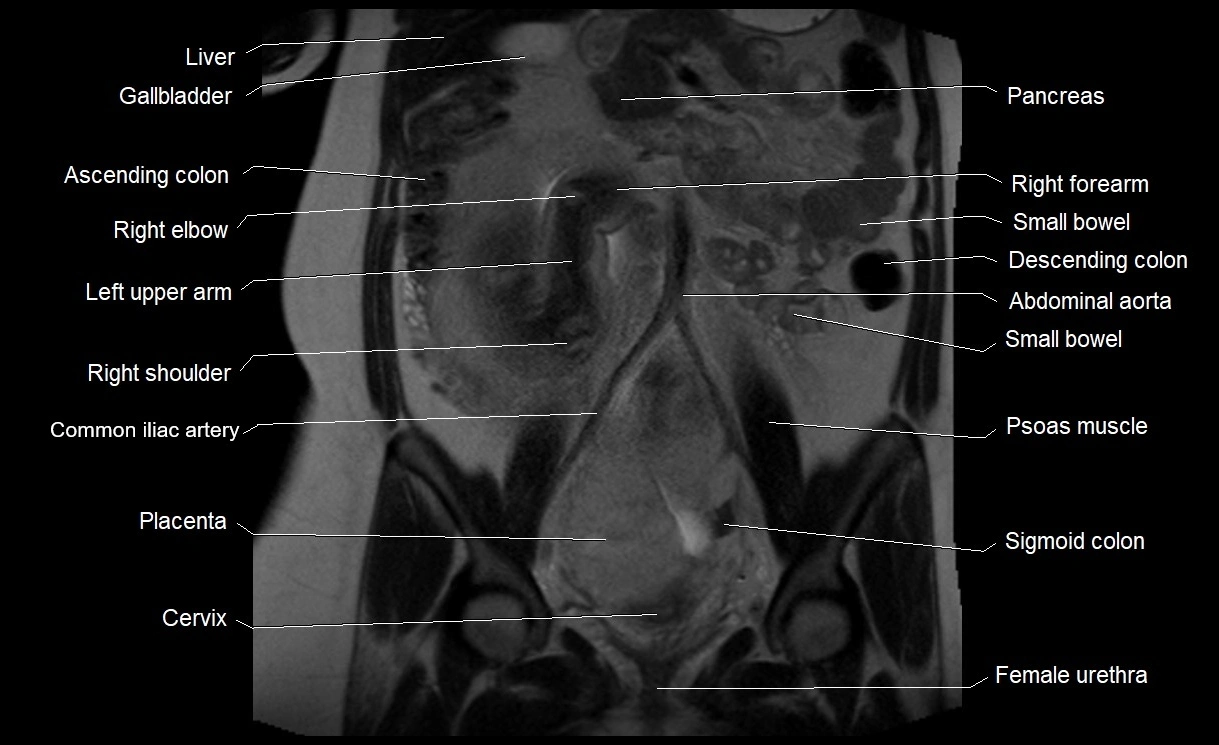
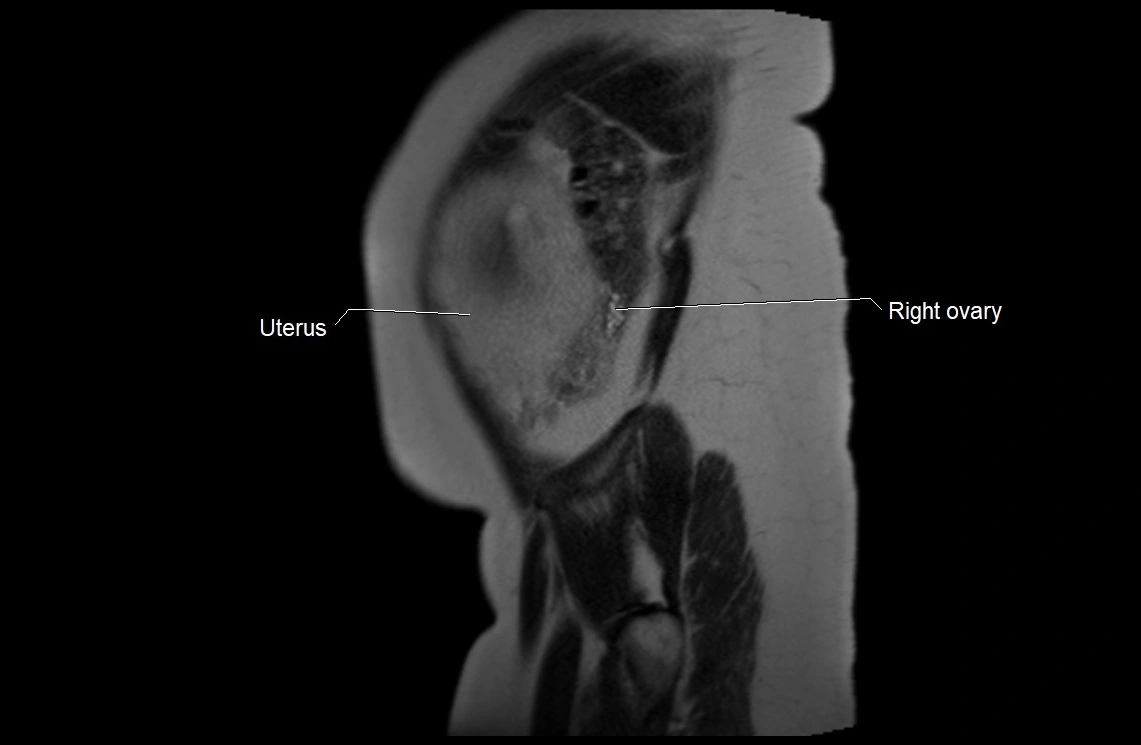
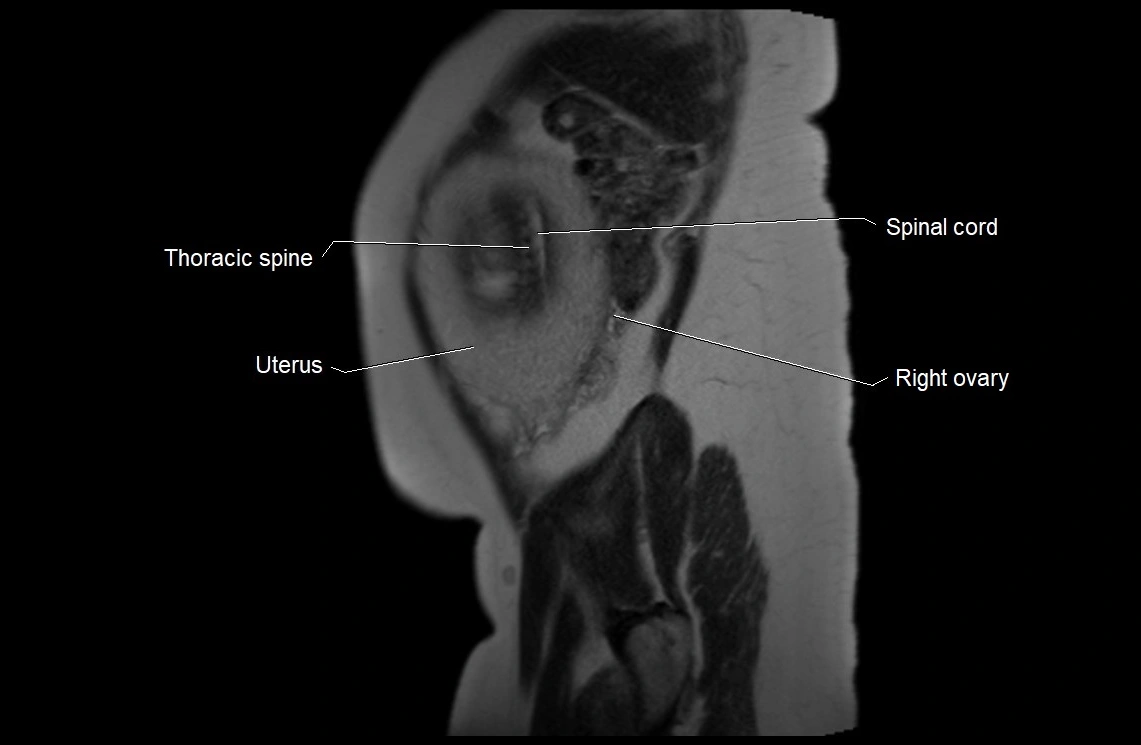
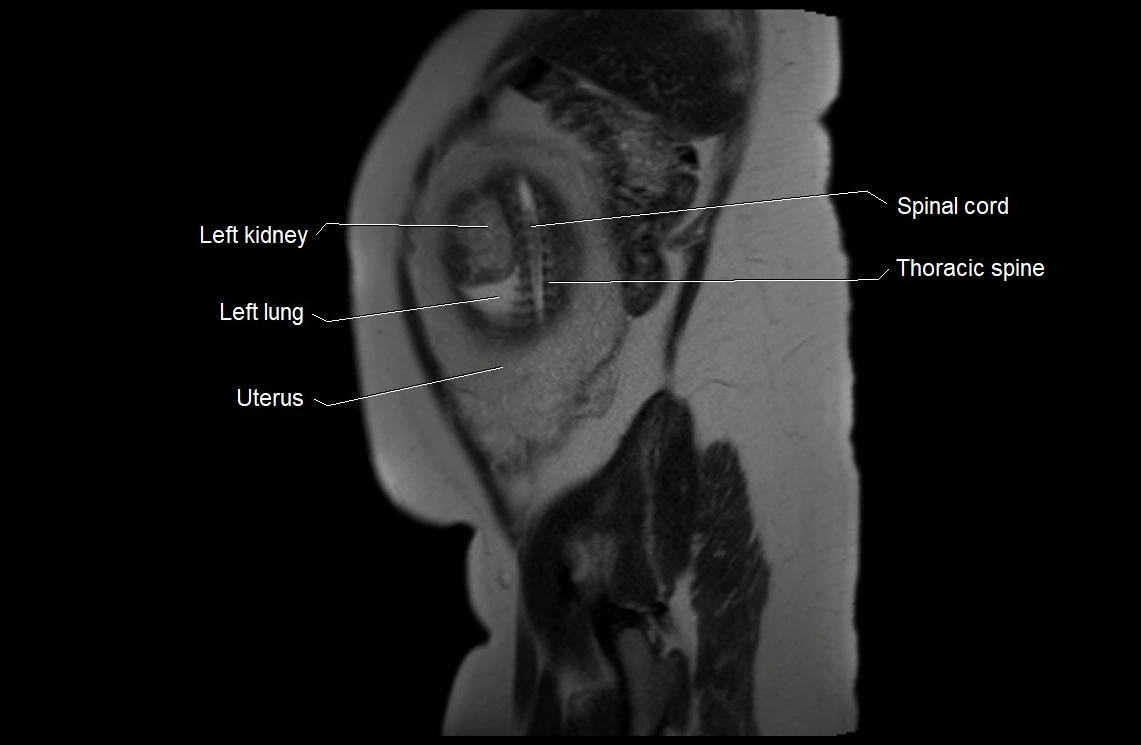
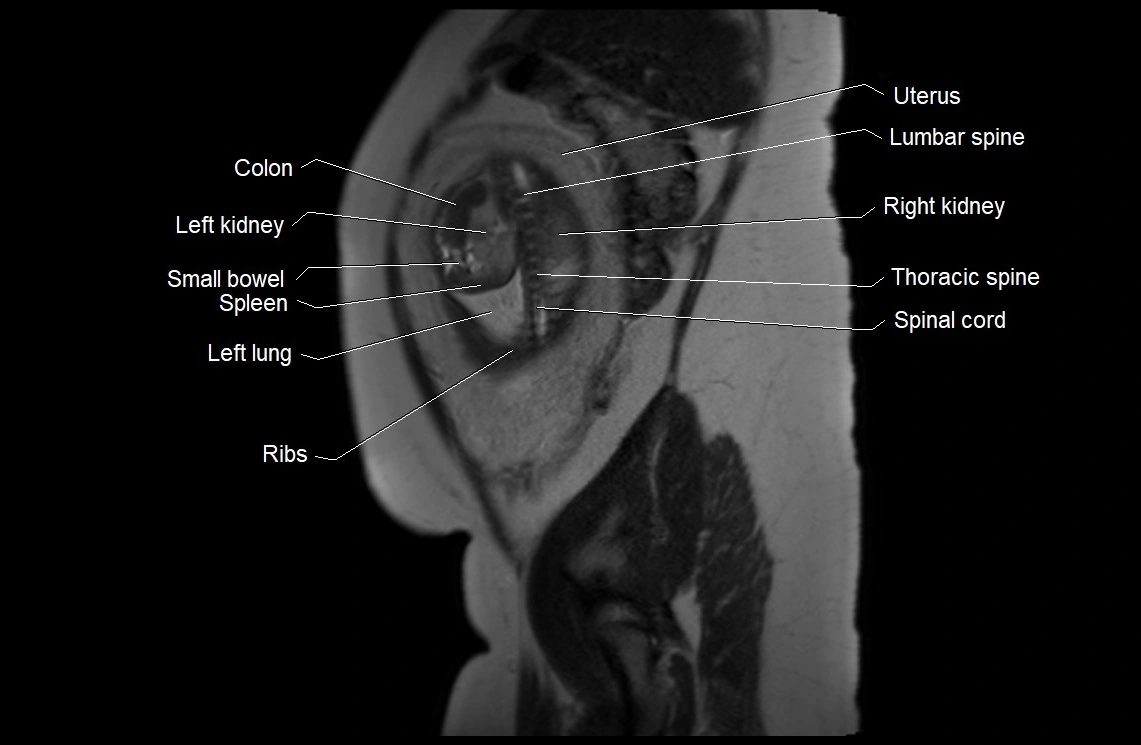
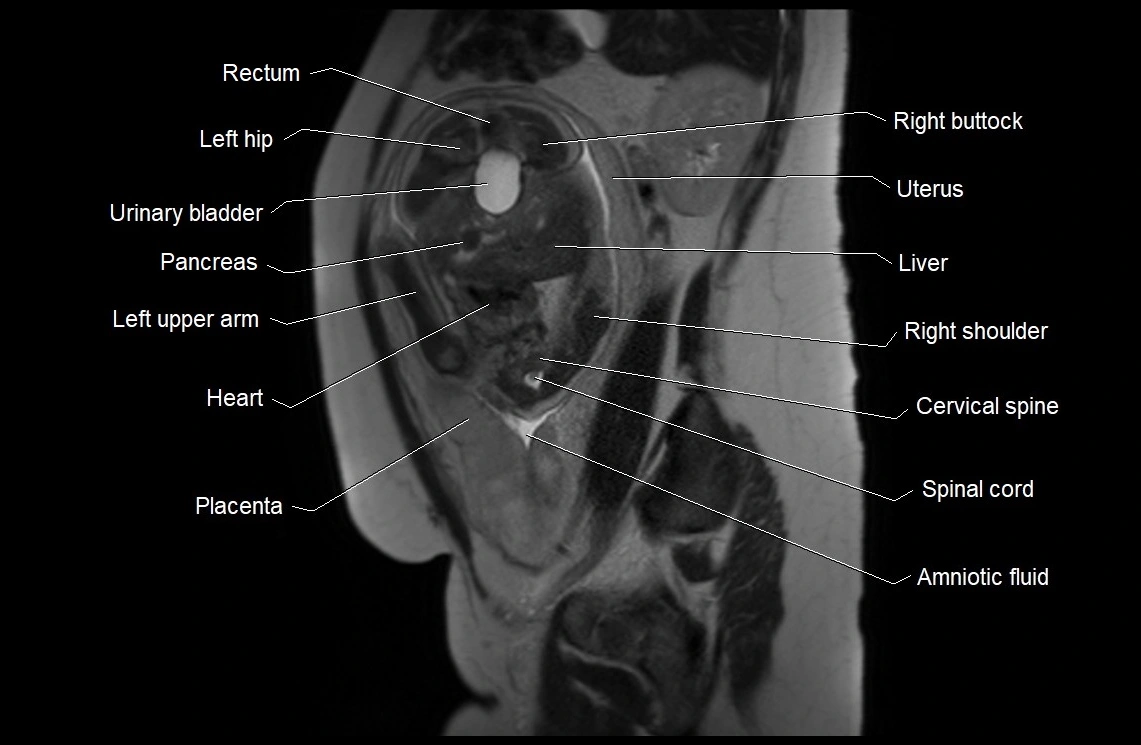
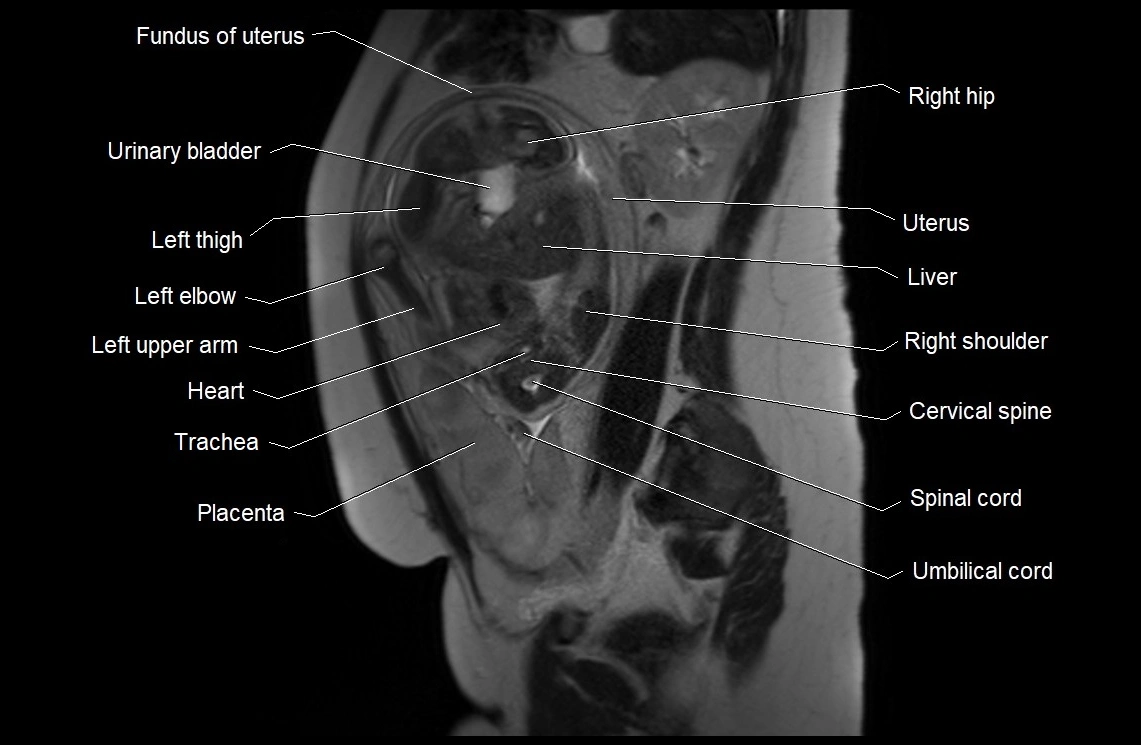
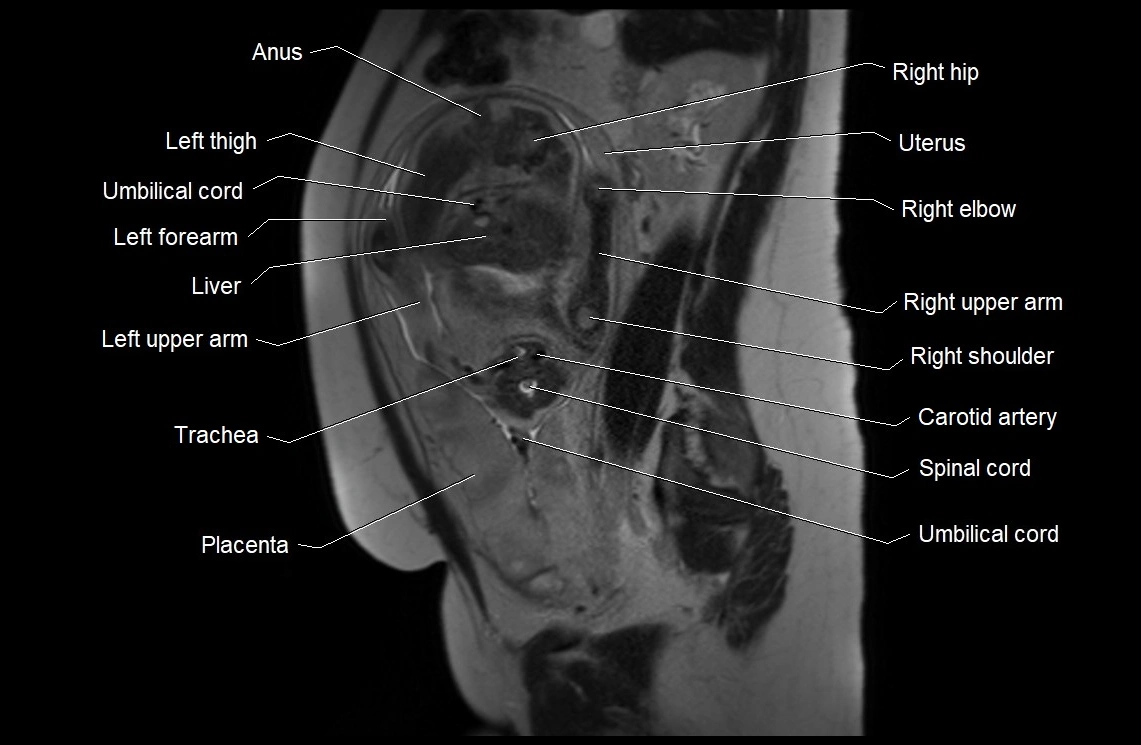
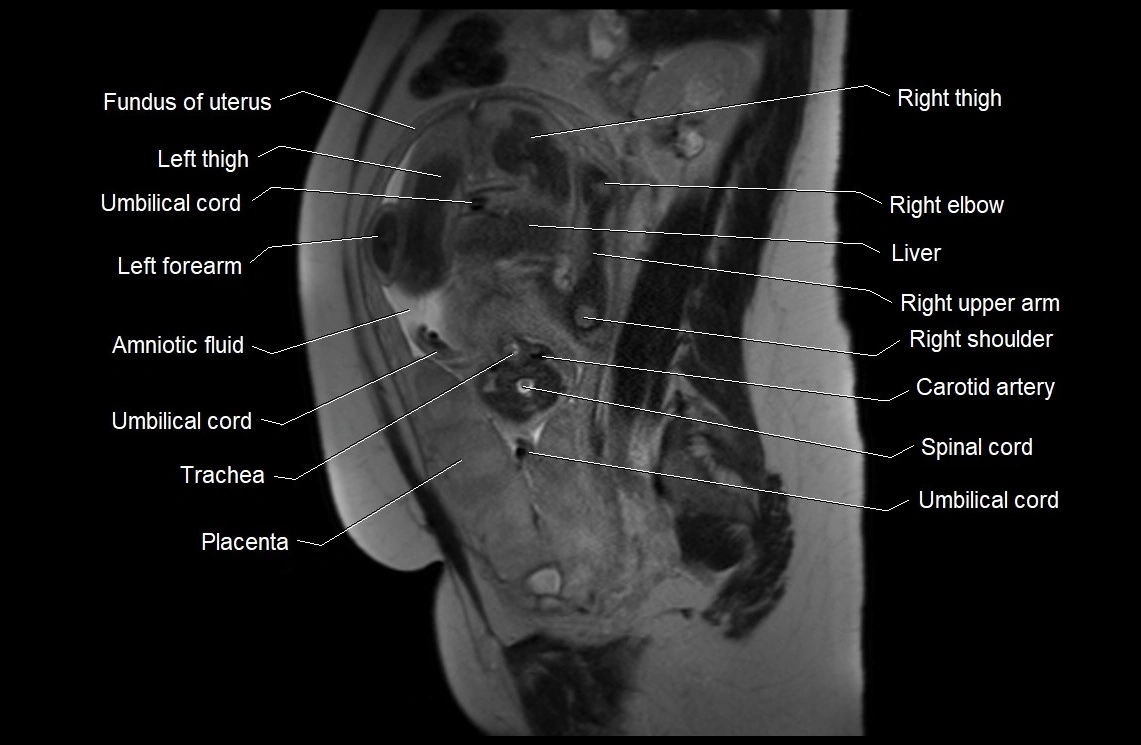
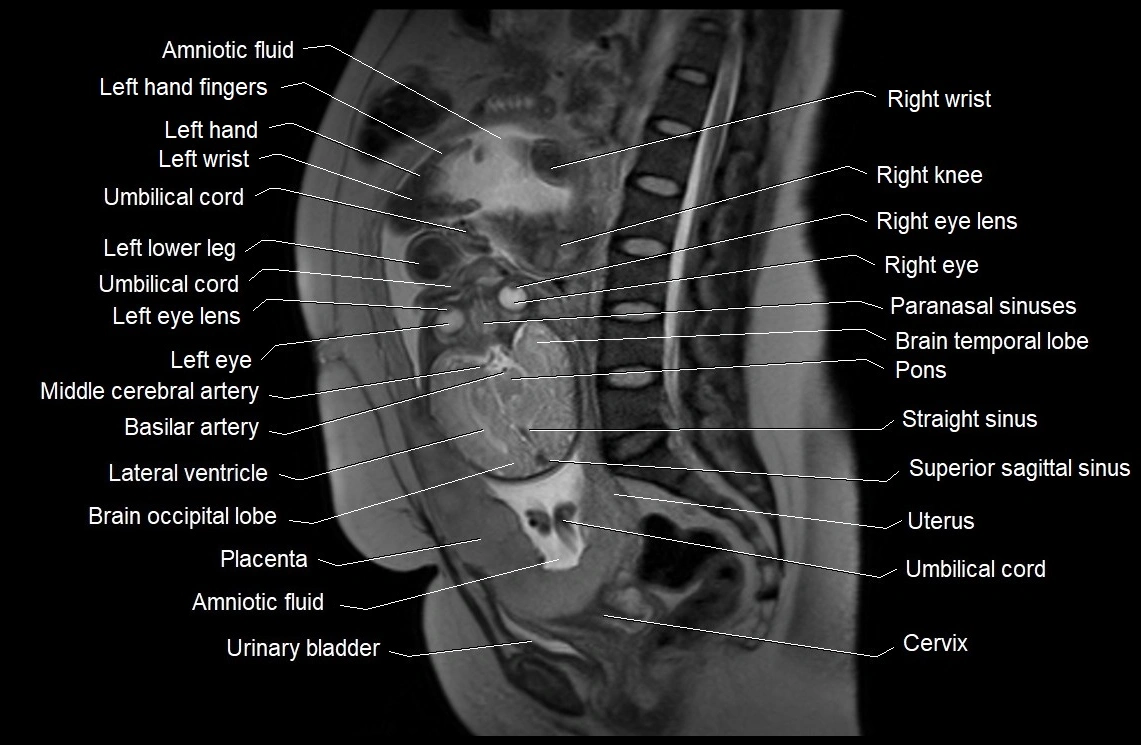
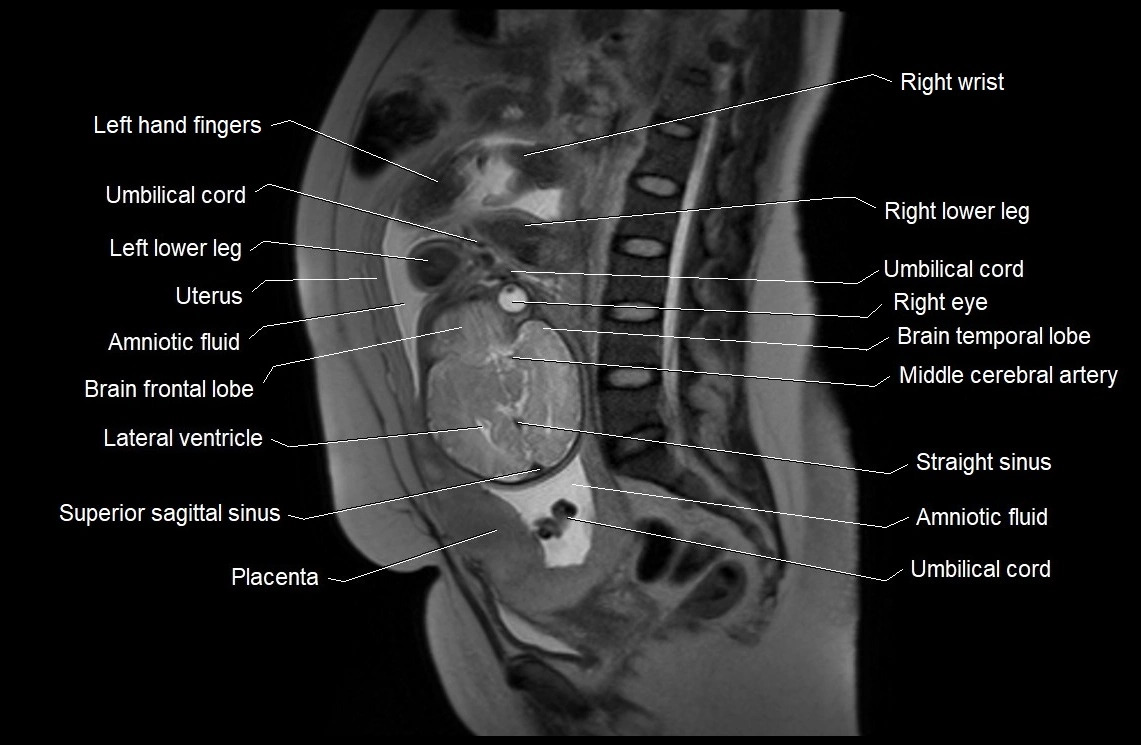
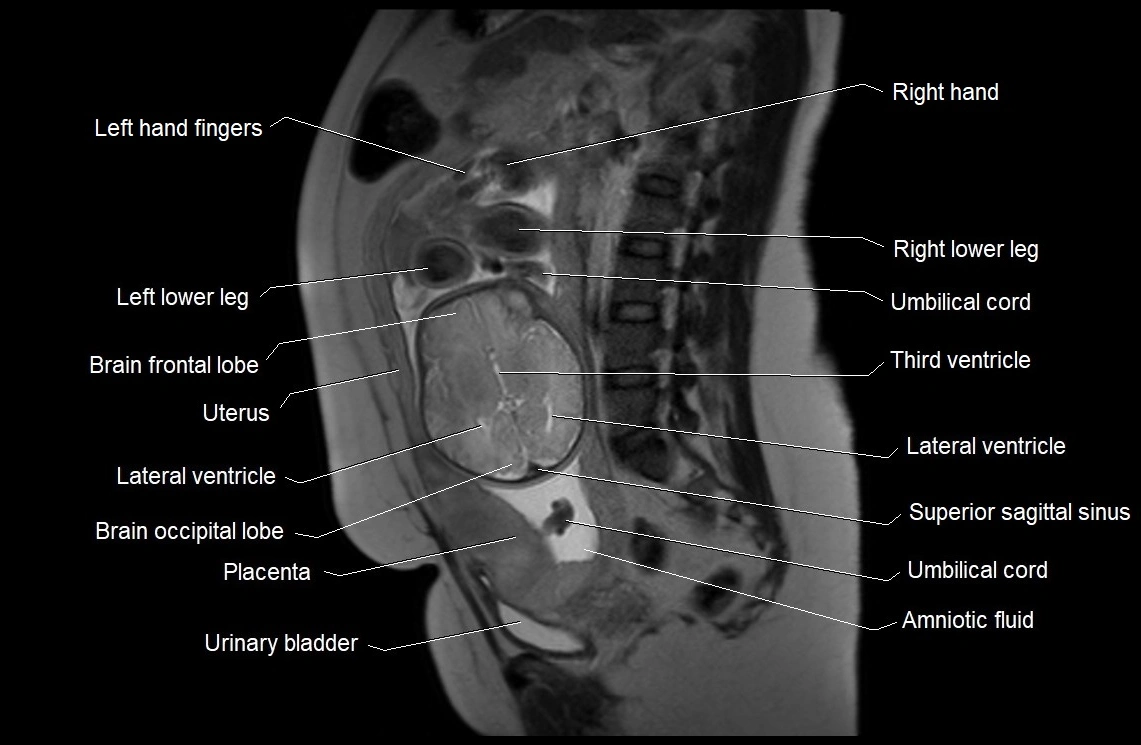
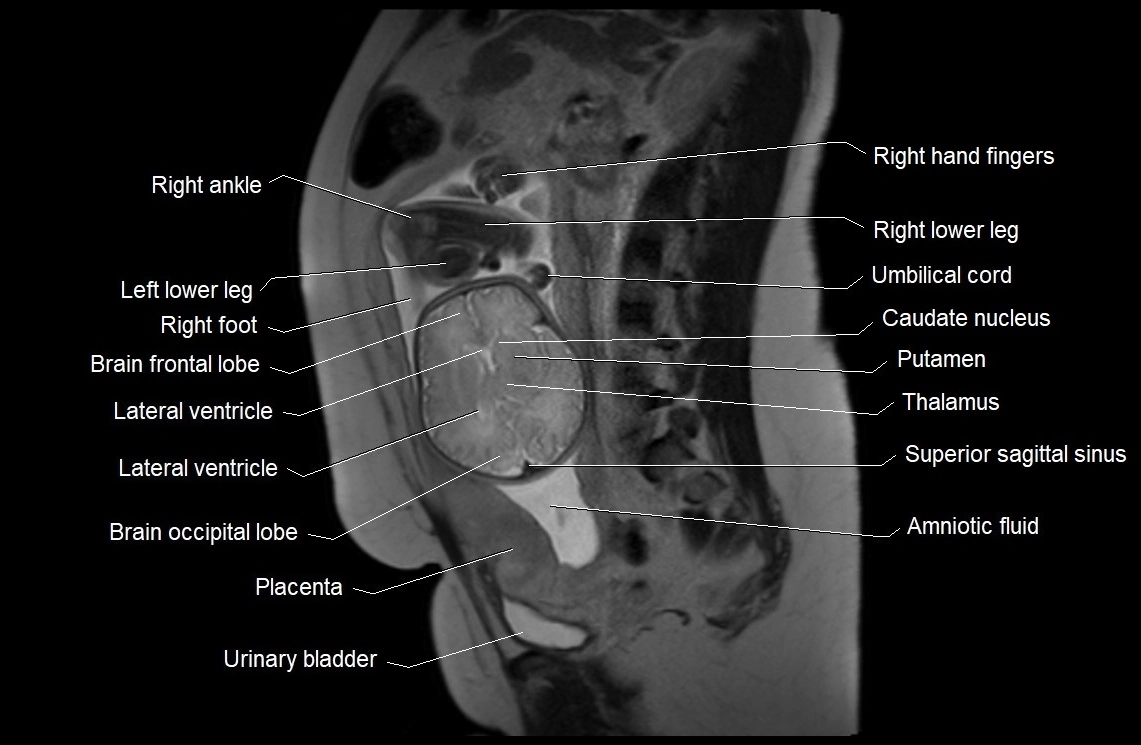
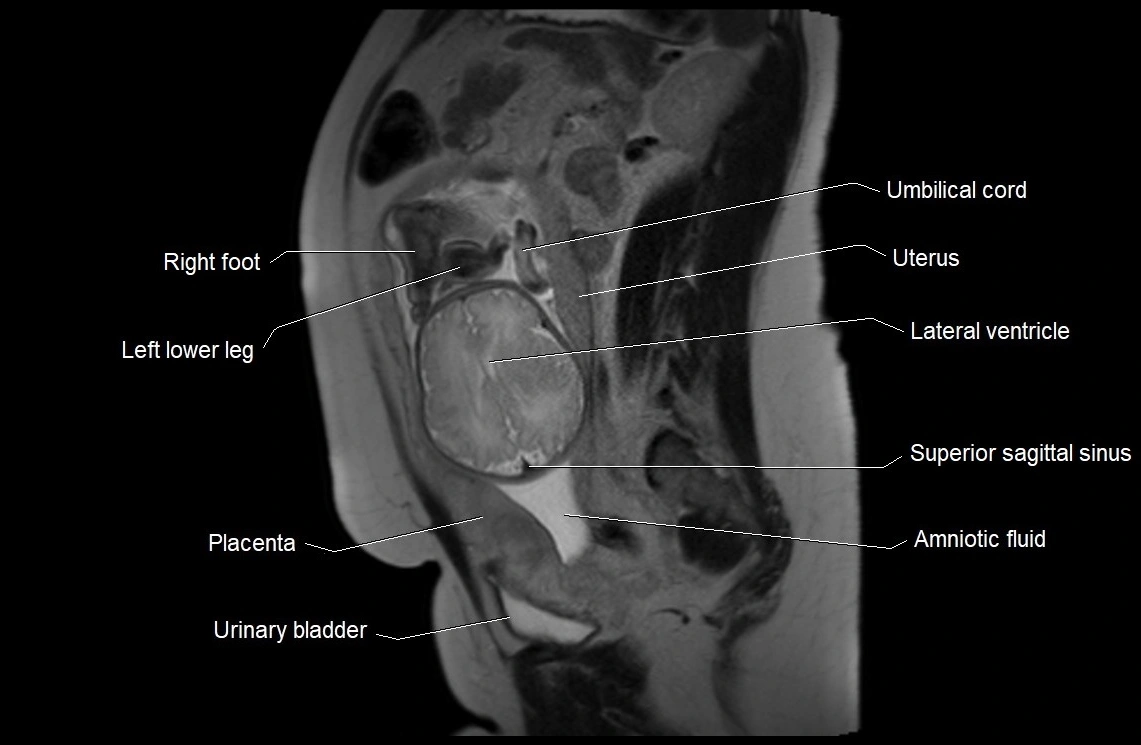
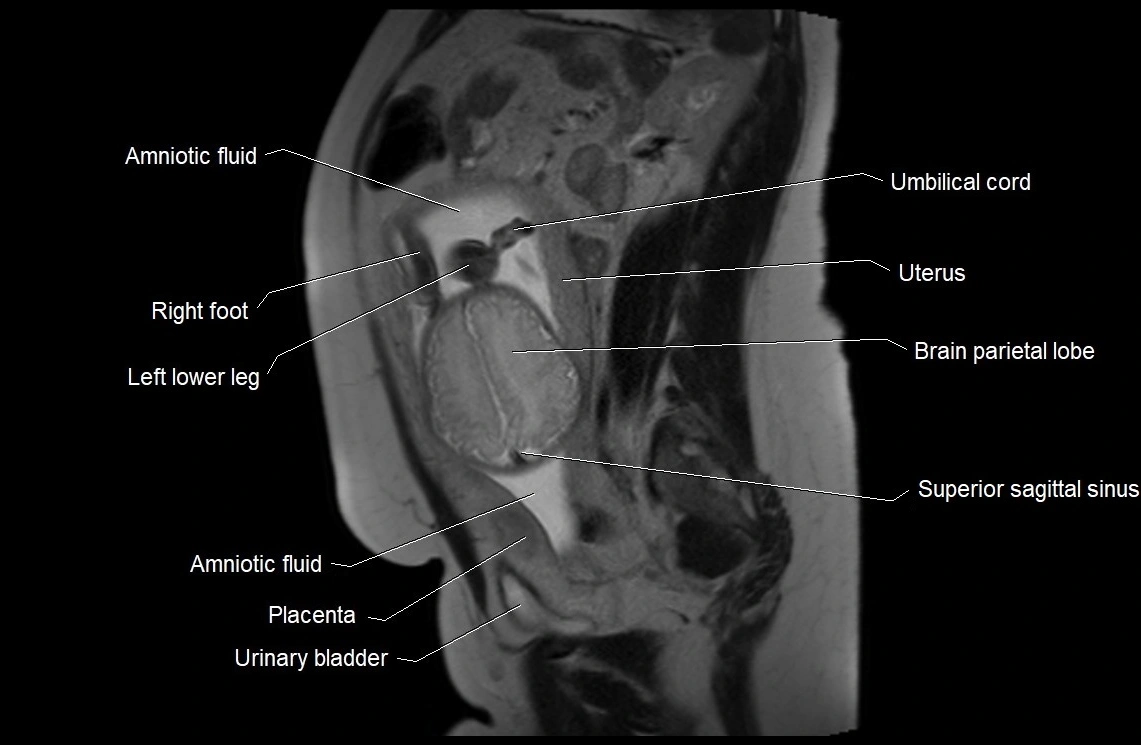
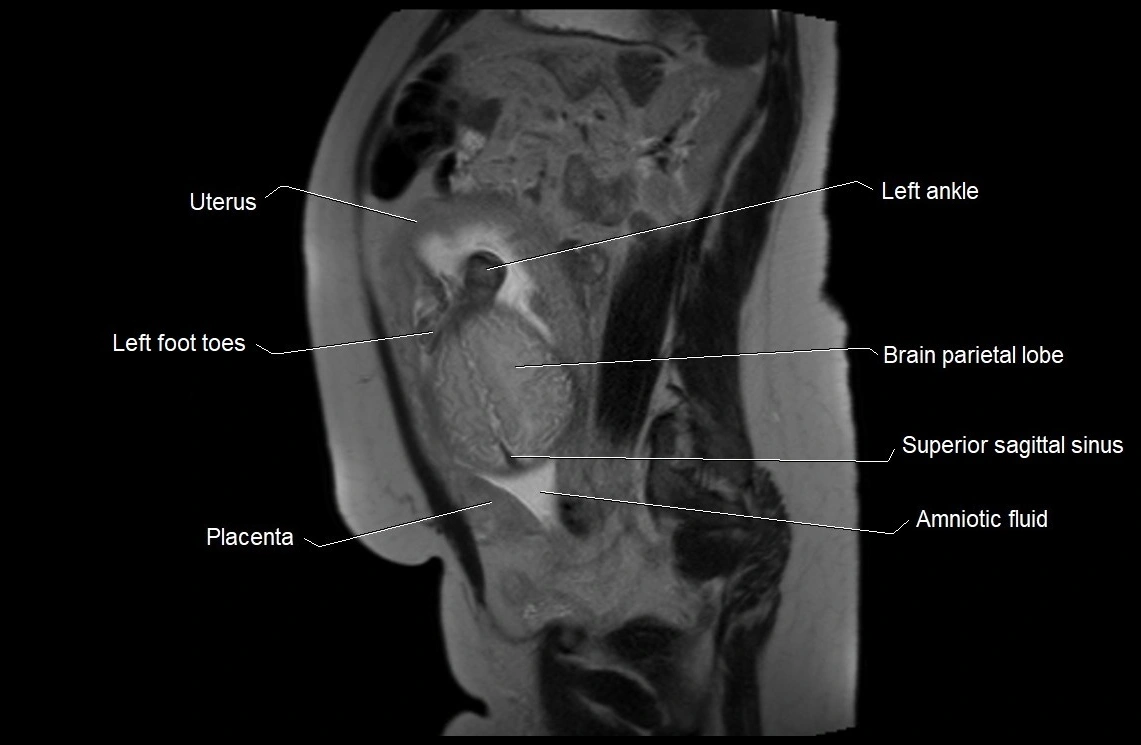
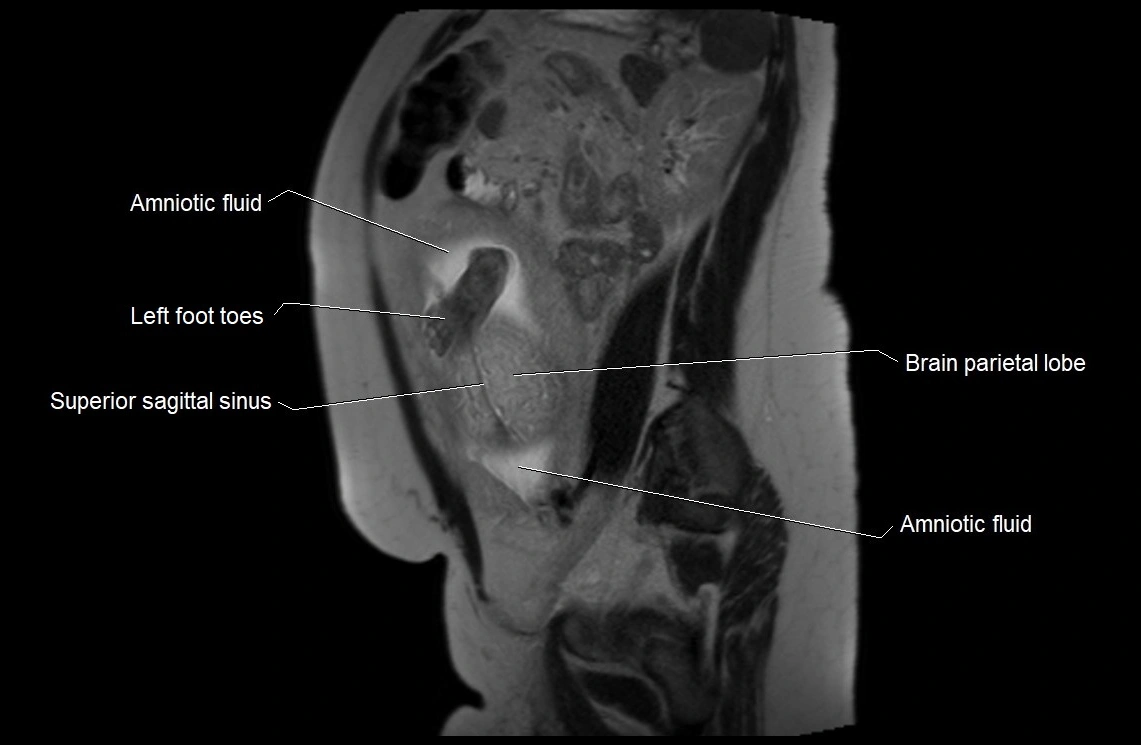
Imaging relevance: MRI used for fetal visualization and assessing oligohydramnios/polyhydramnios when ultrasound is inconclusive
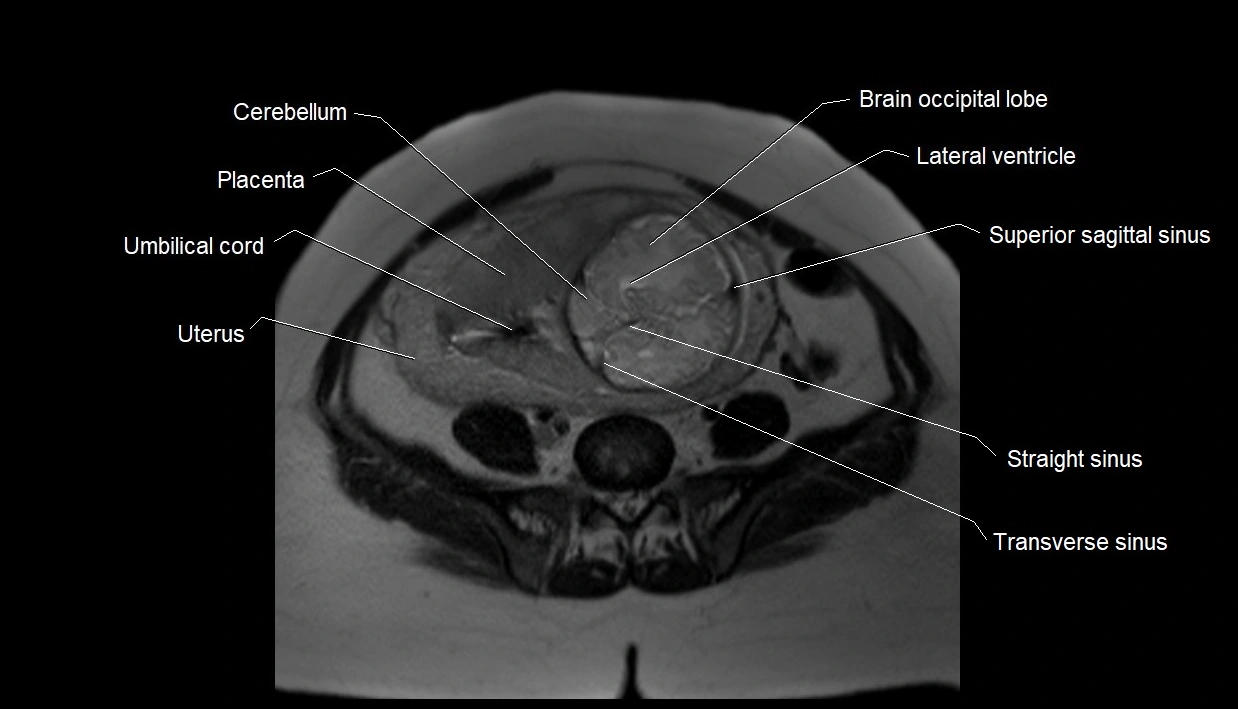
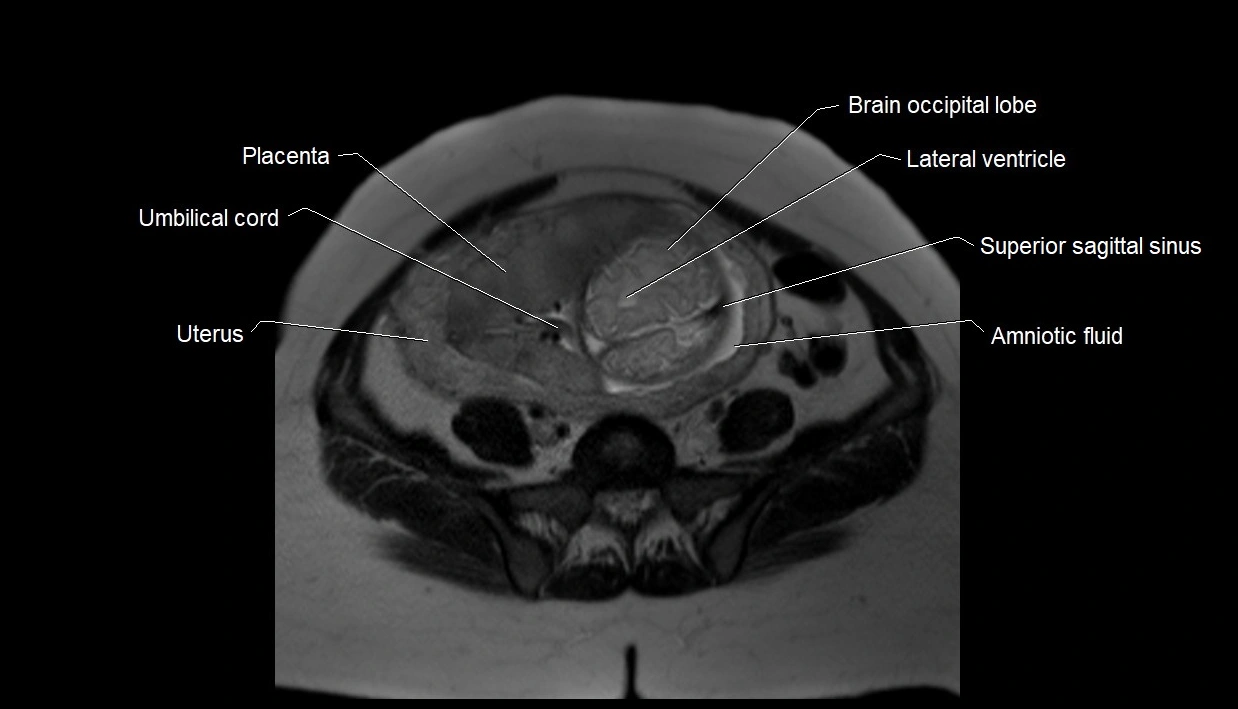
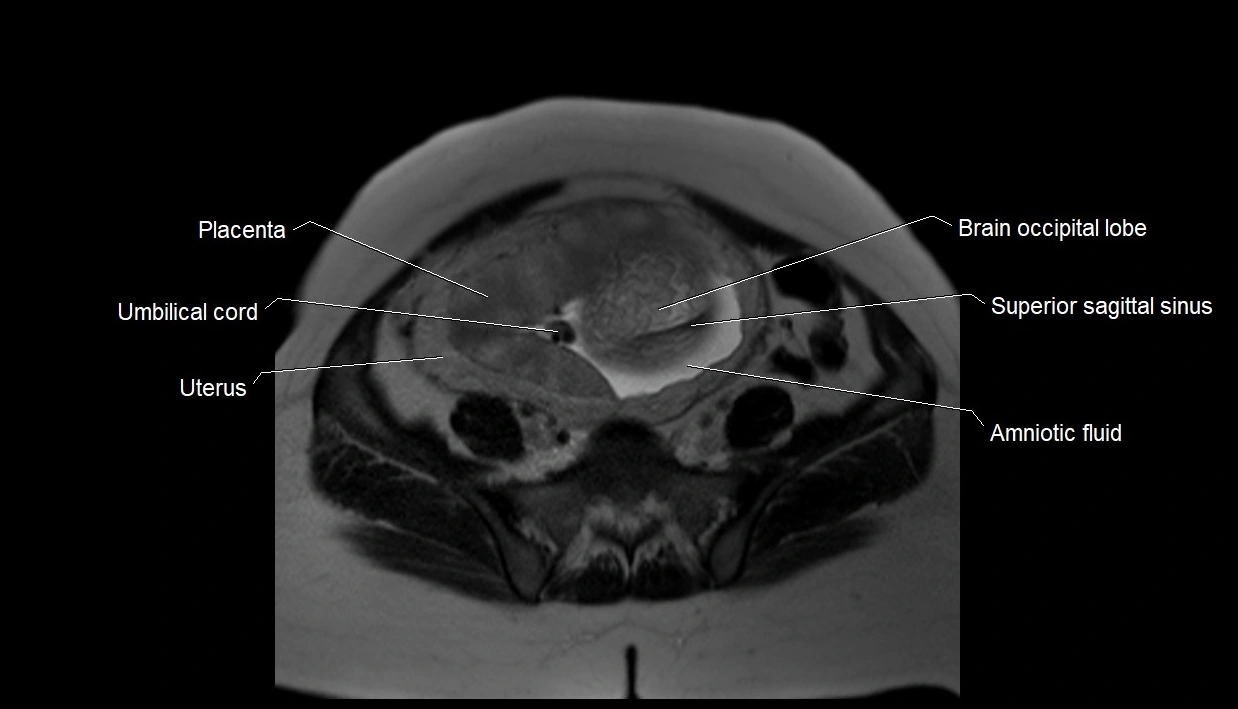
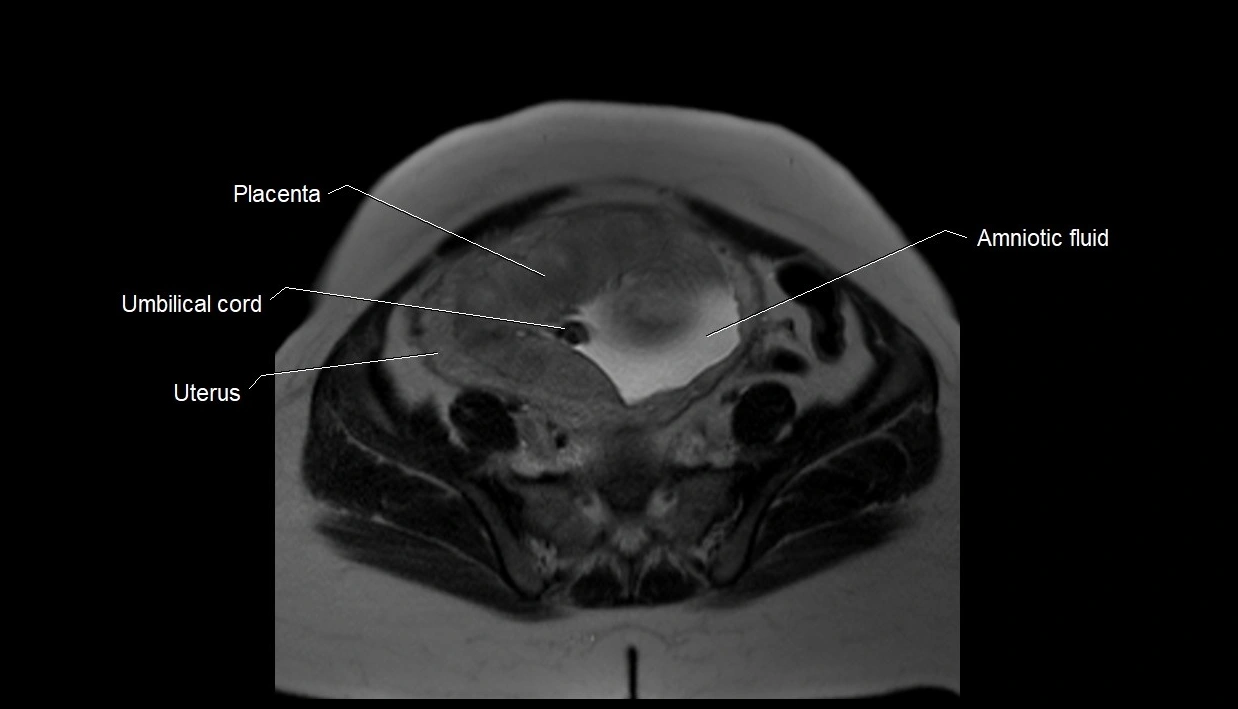
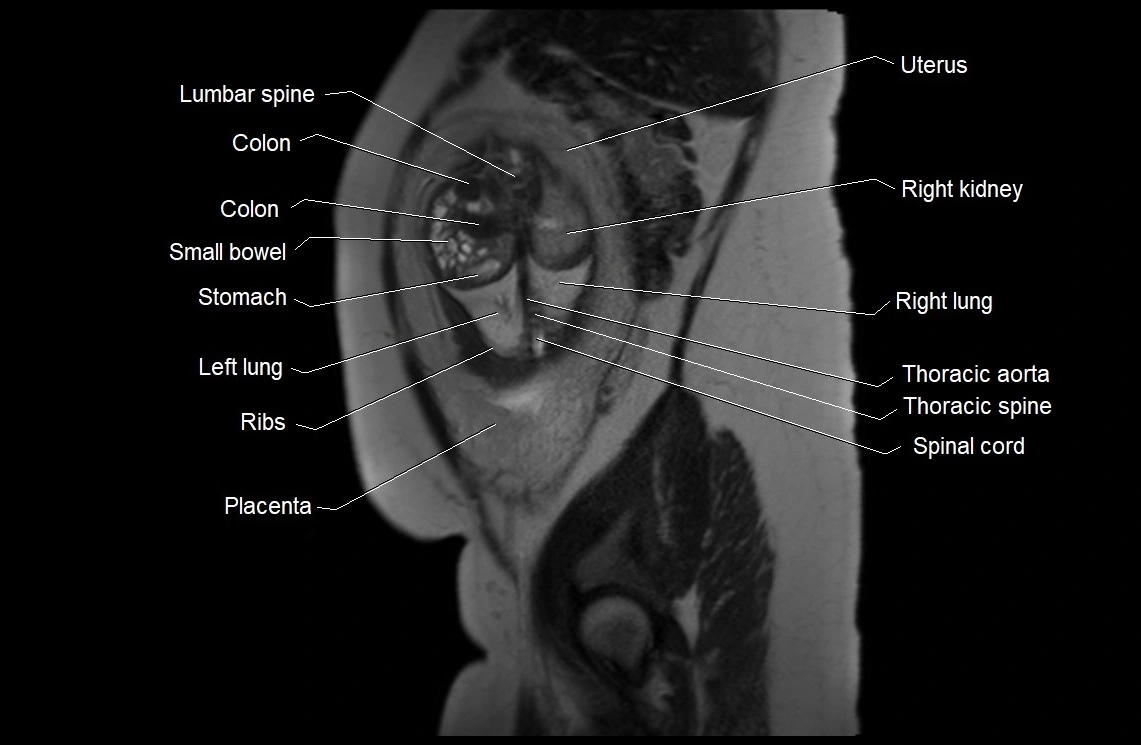
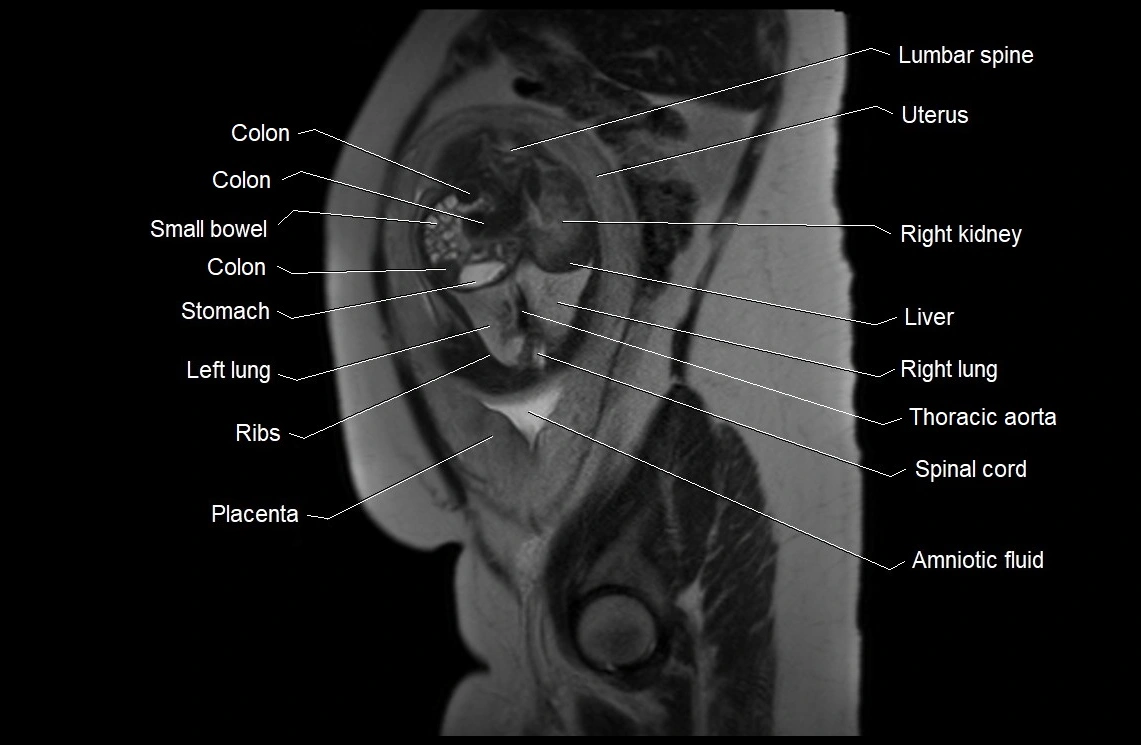
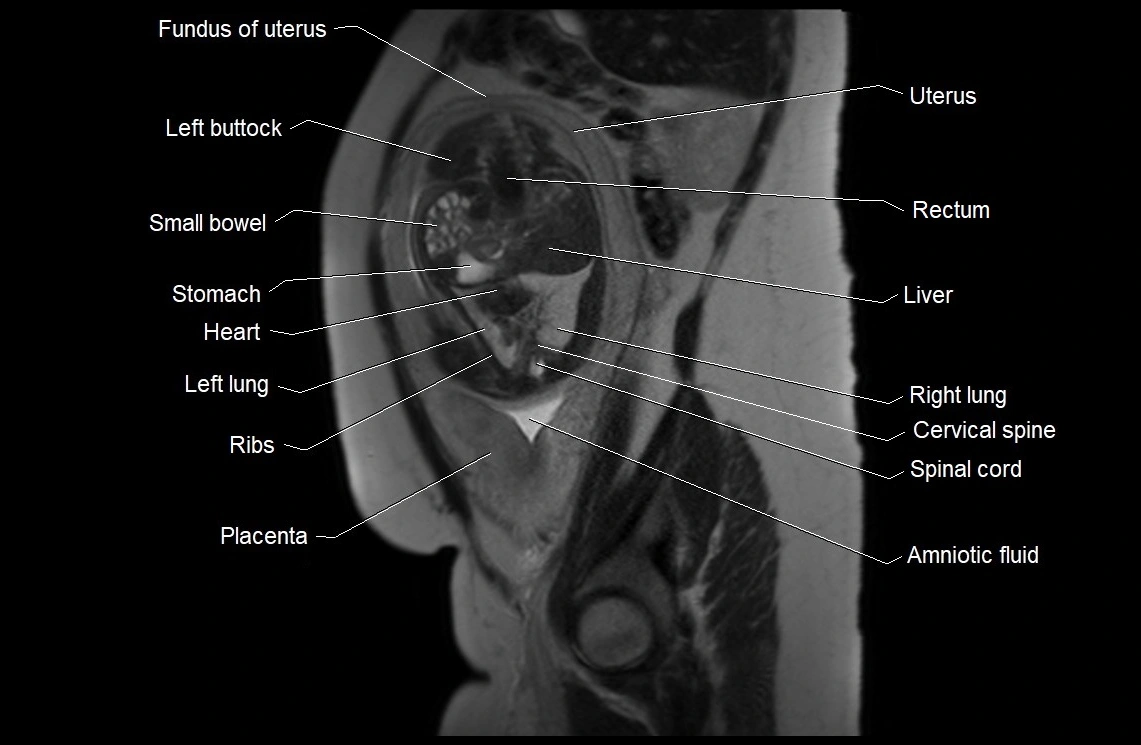
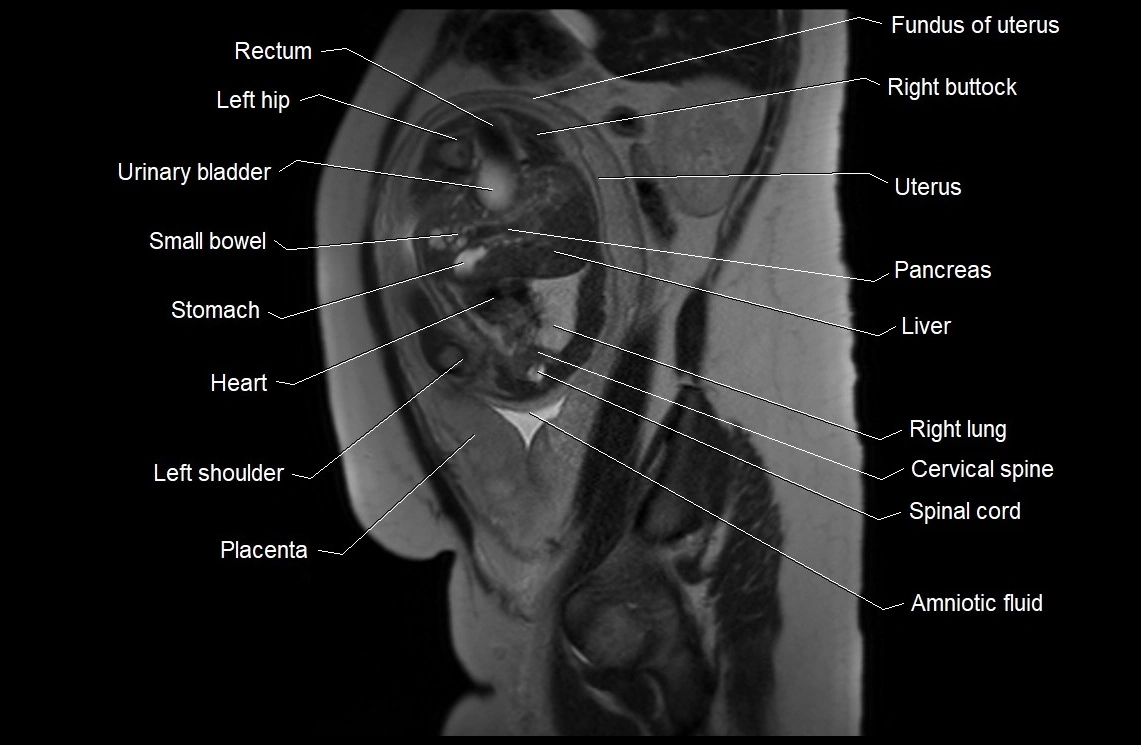
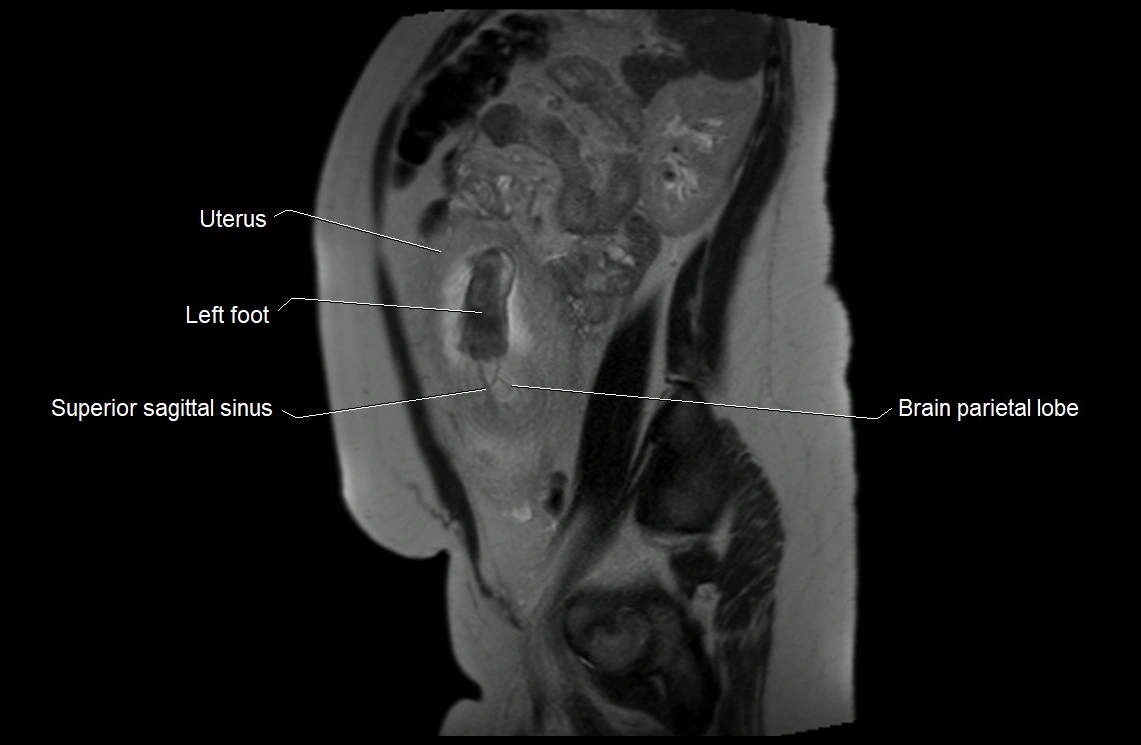
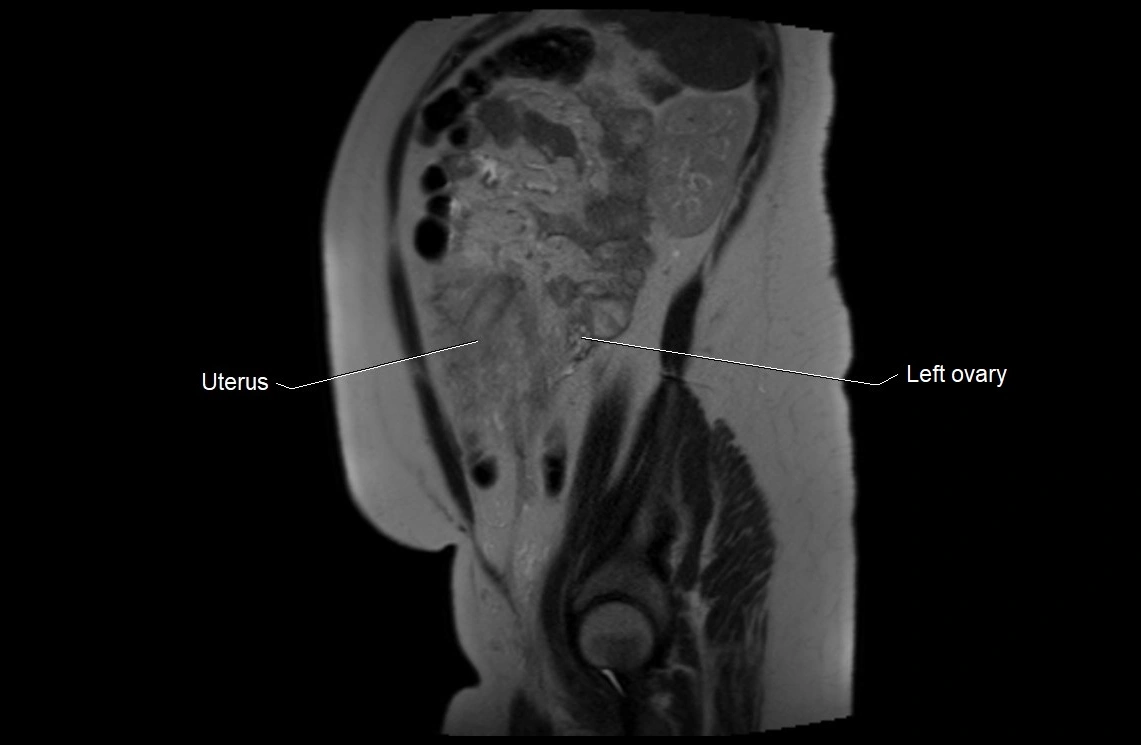
MRI Appearance
T2 HASTE (T2 GRE):
-
Amniotic fluid shows very bright hyperintense signal
-
Provides natural contrast against fetus and placenta
-
Small particles (vernix) may appear as scattered hypointense foci within bright fluid
T1 GRE:
-
Amniotic fluid shows low signal intensity (dark)
-
Hemorrhage, infection, or proteinaceous content may cause focal or diffuse high signal intensity
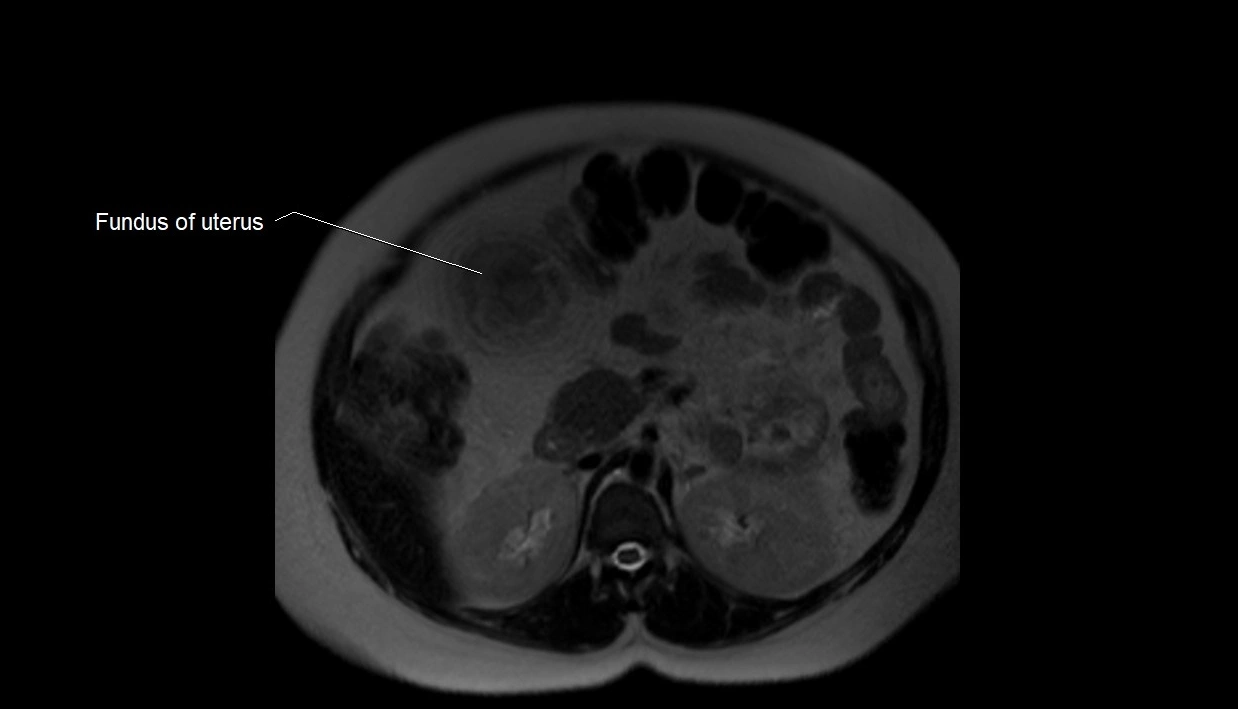
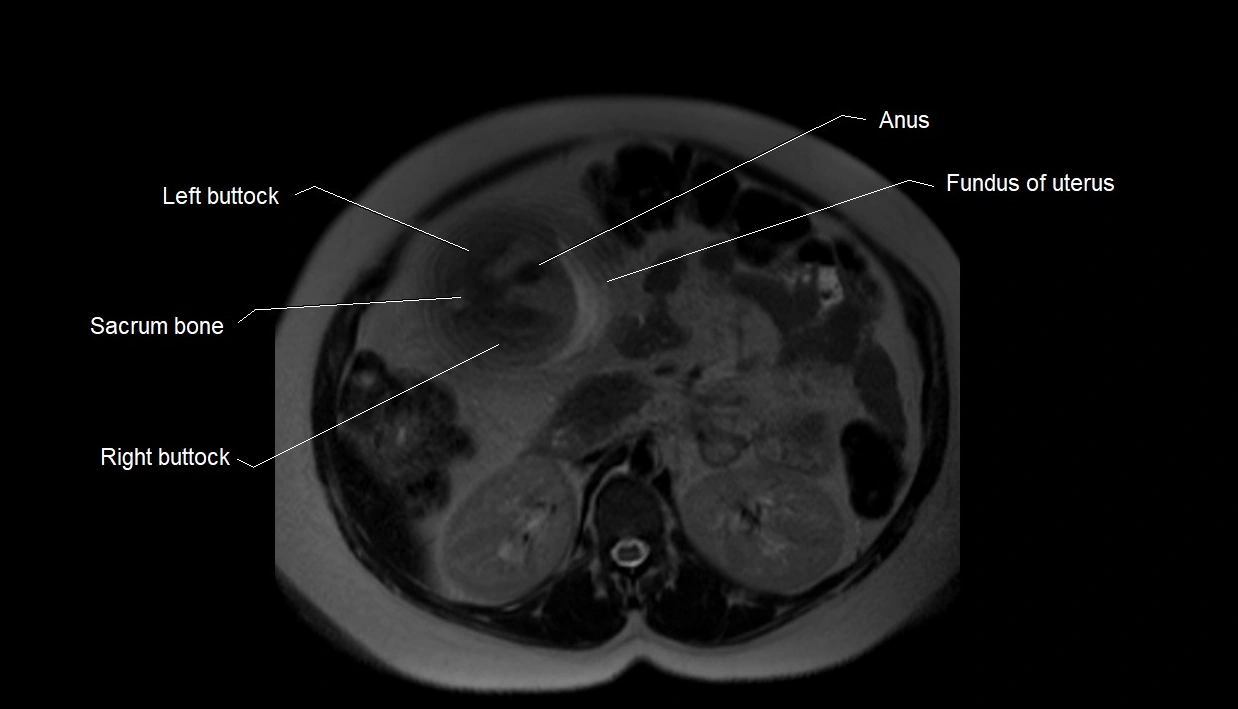
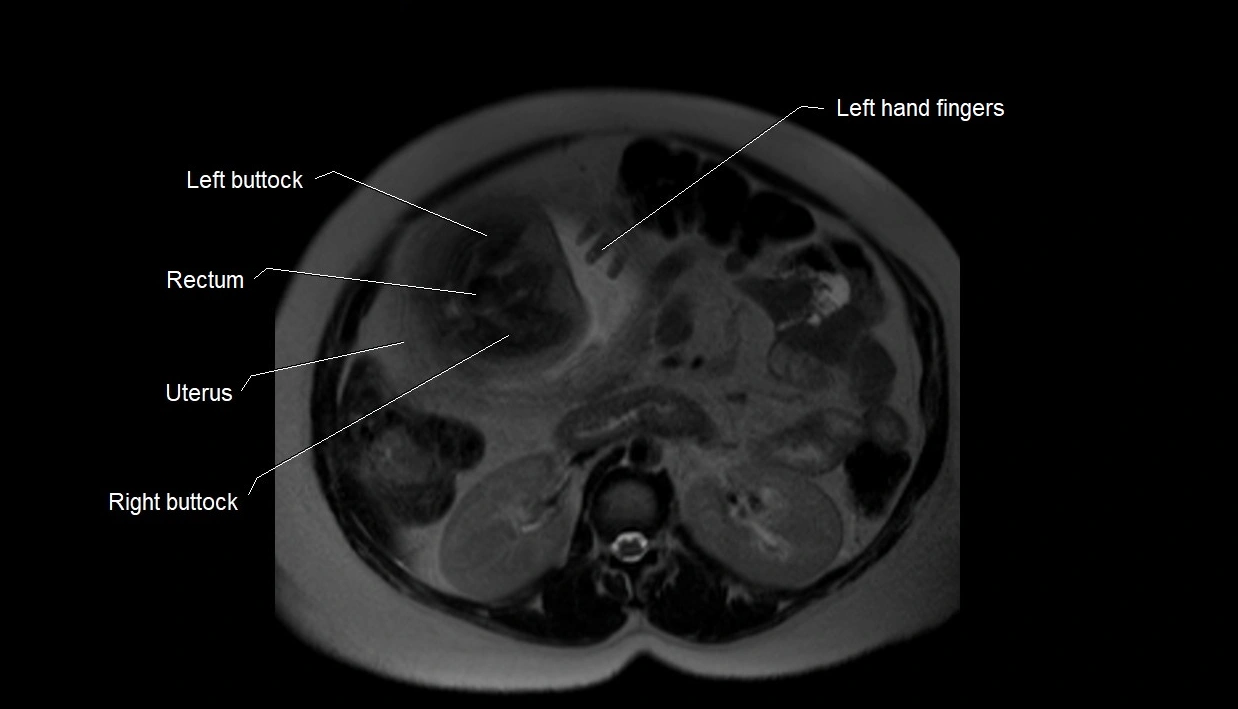
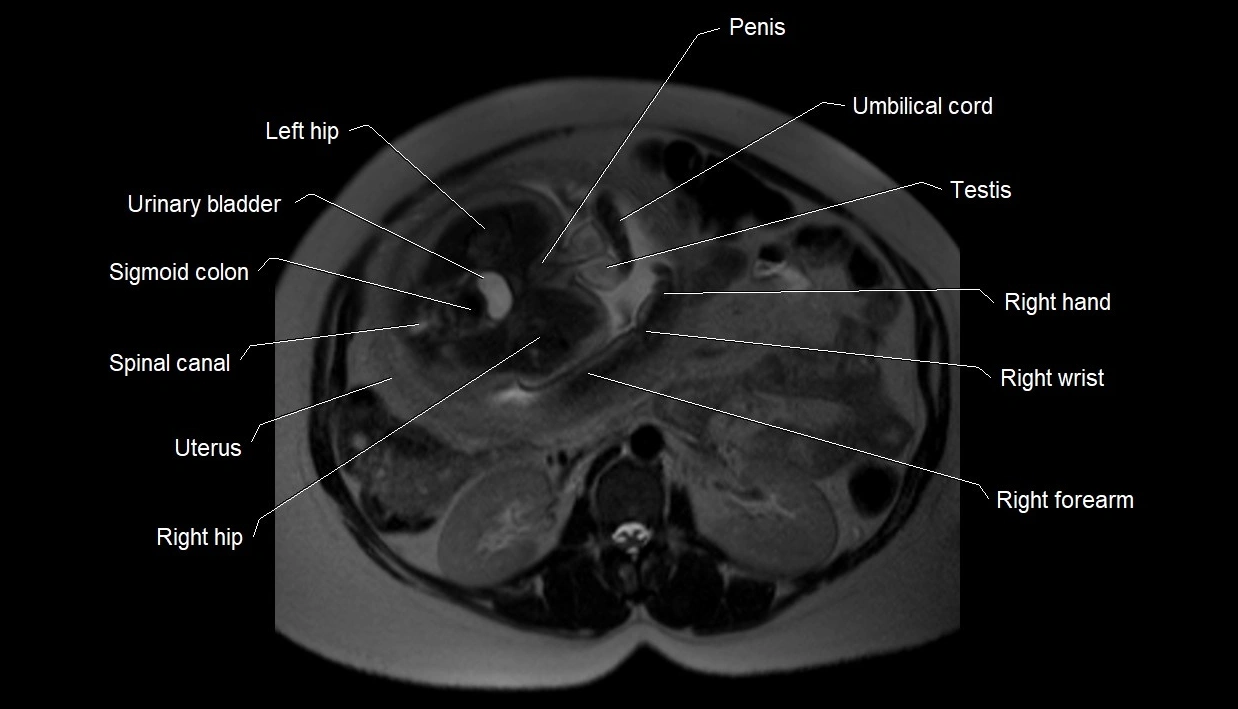
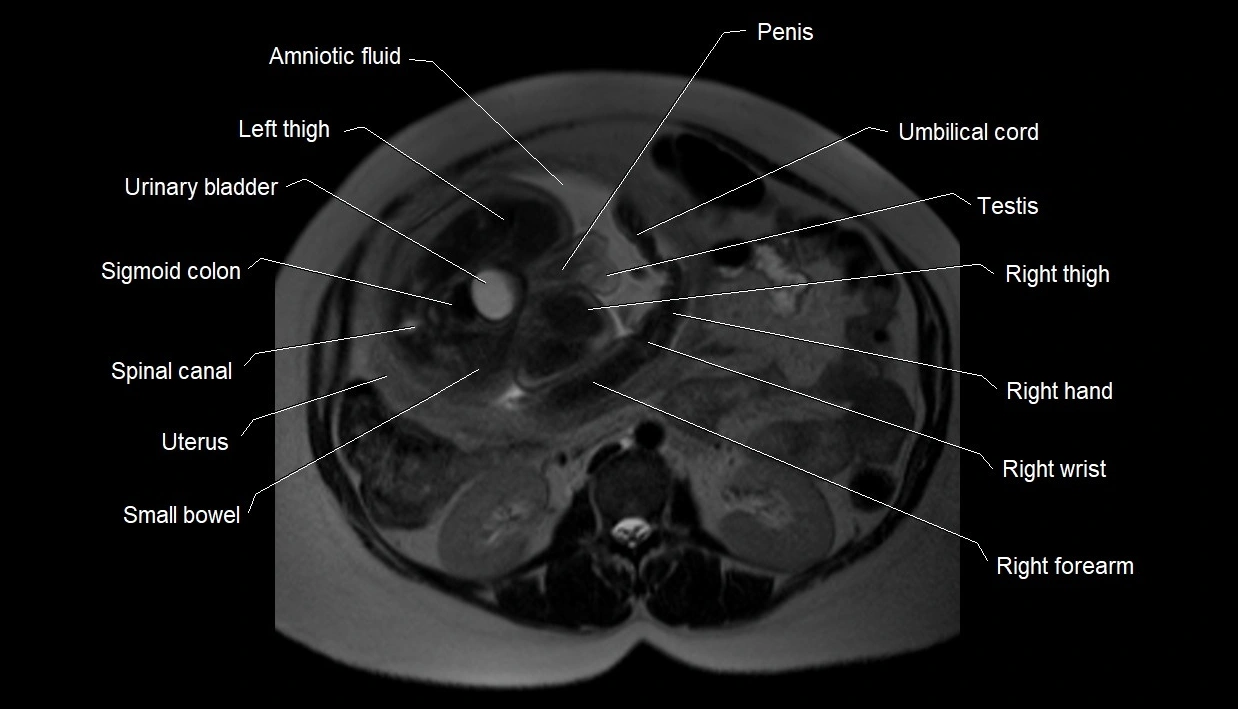
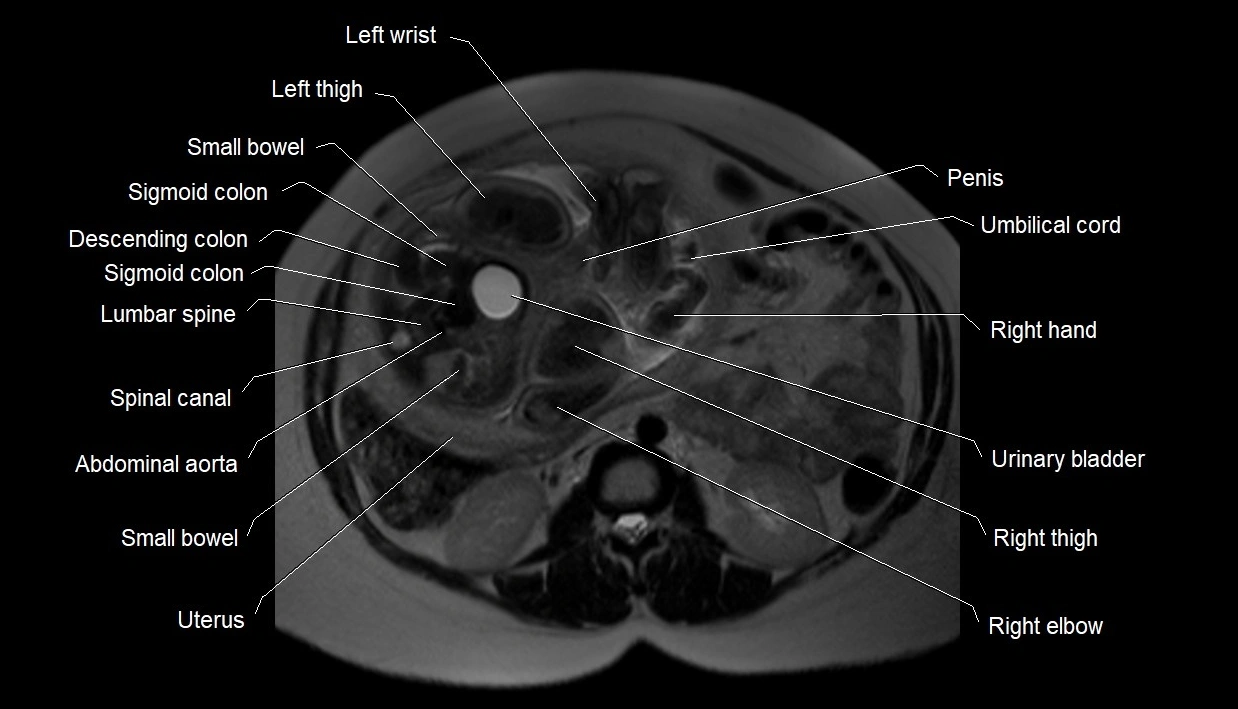
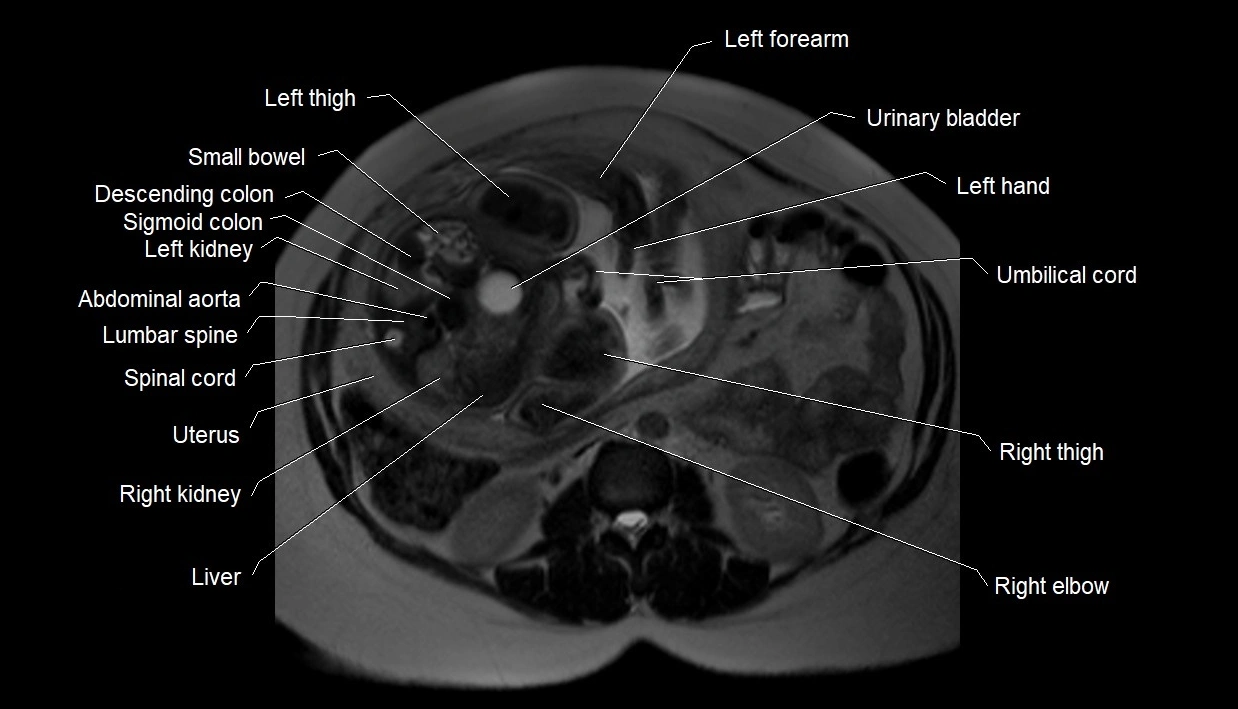
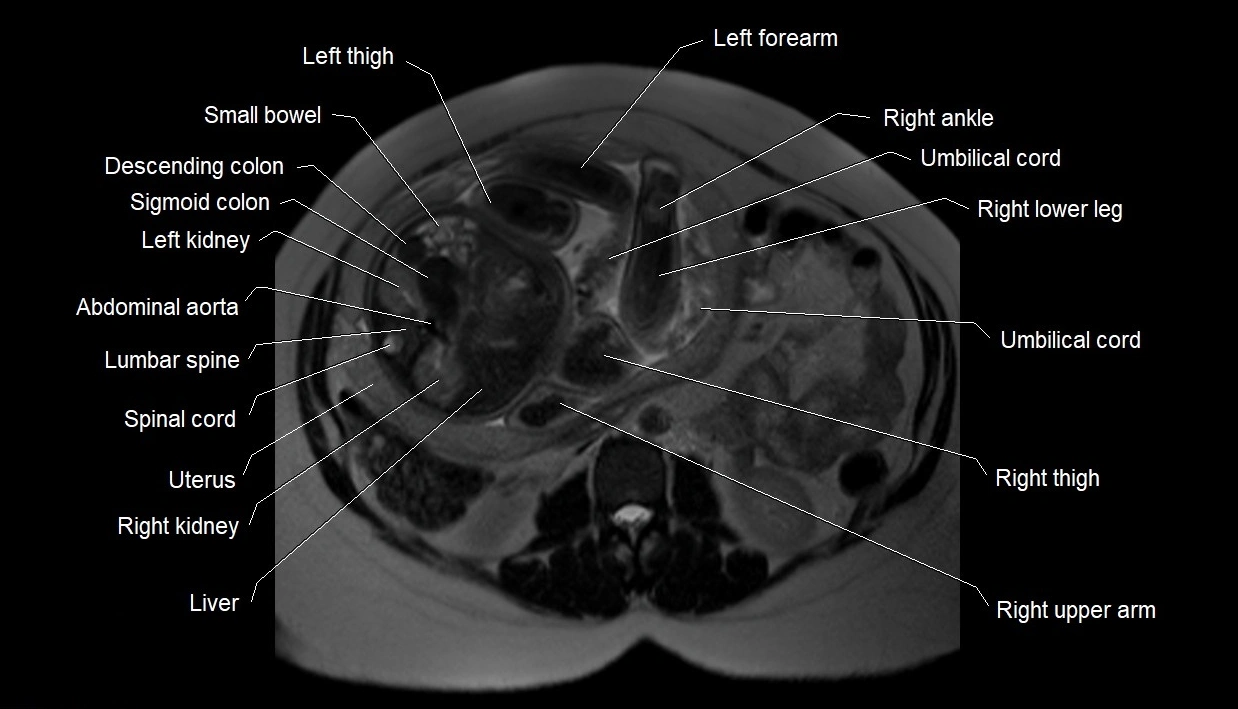
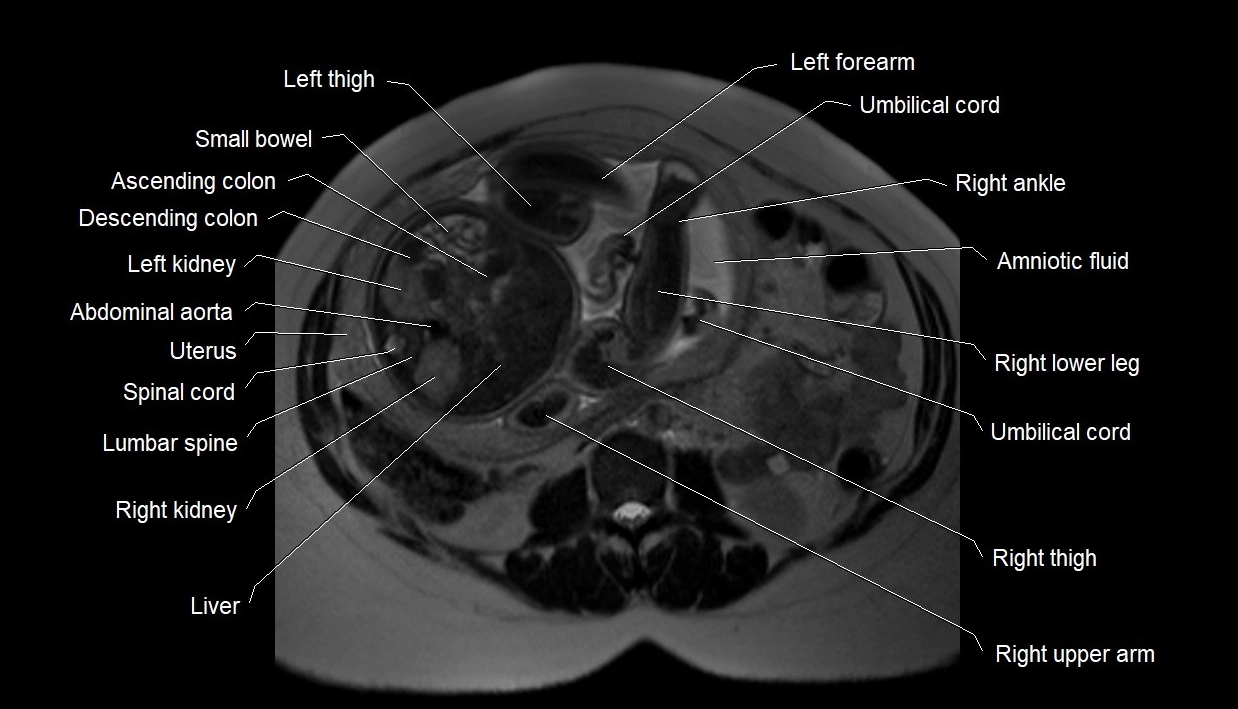
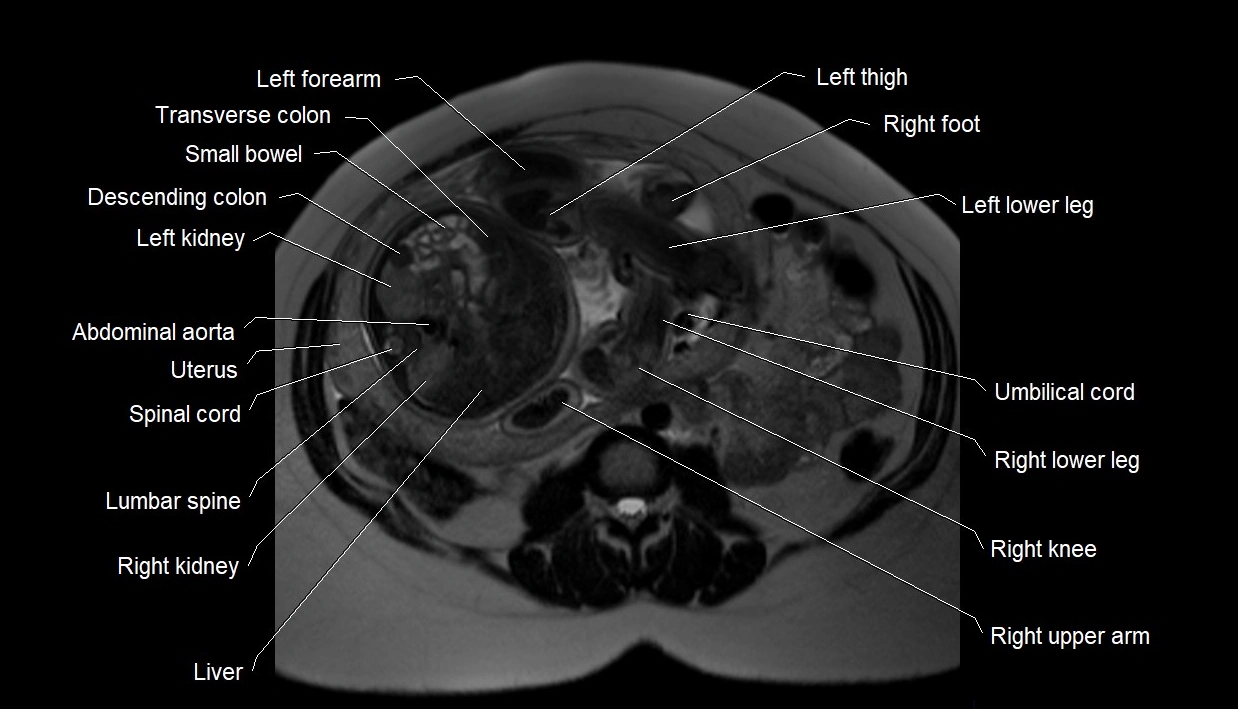
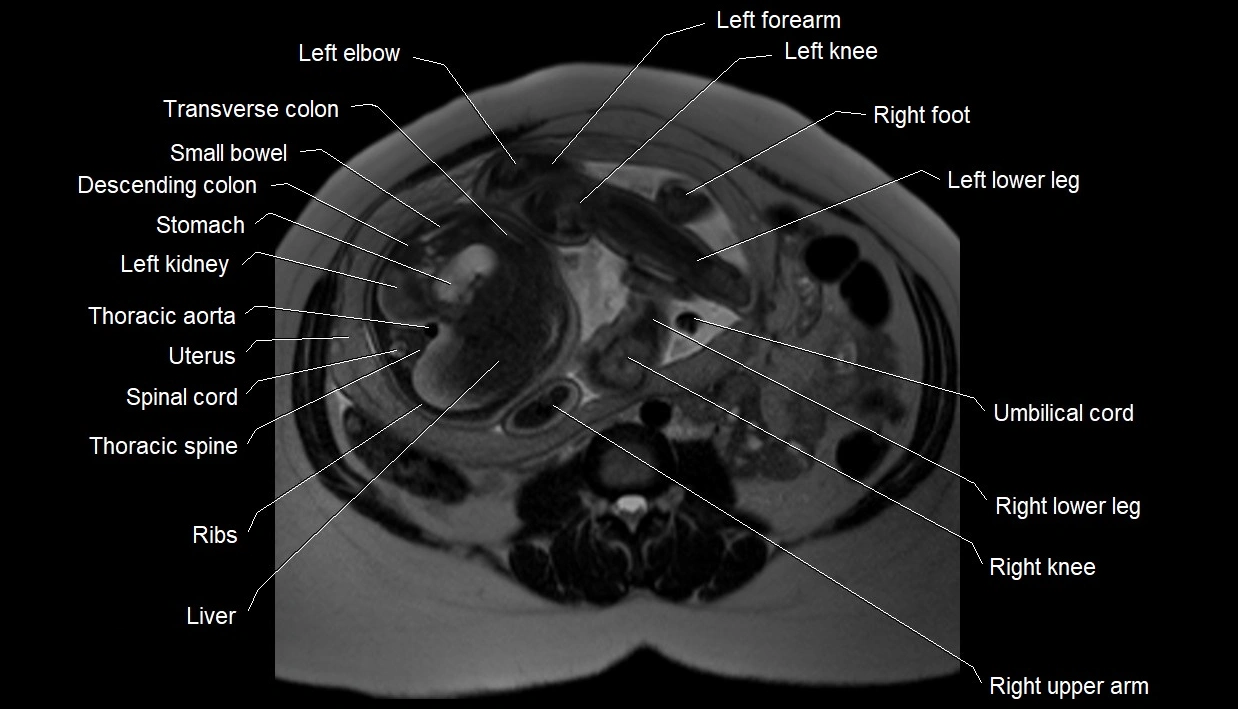
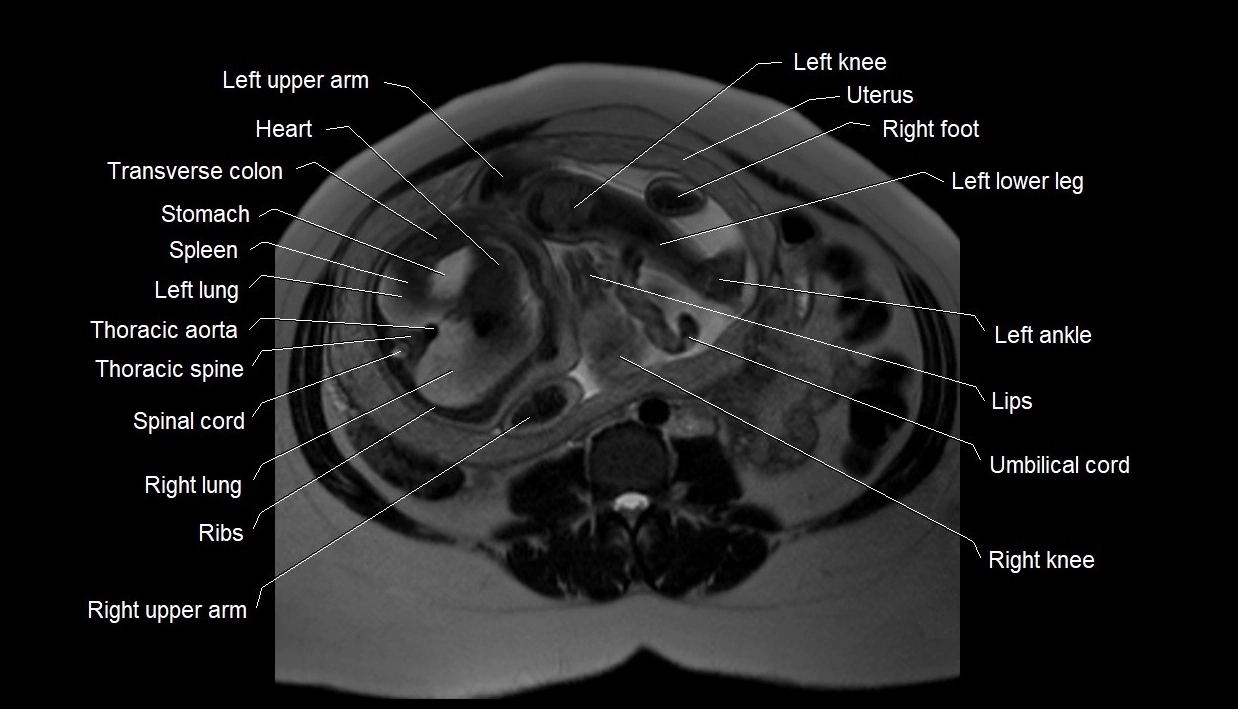
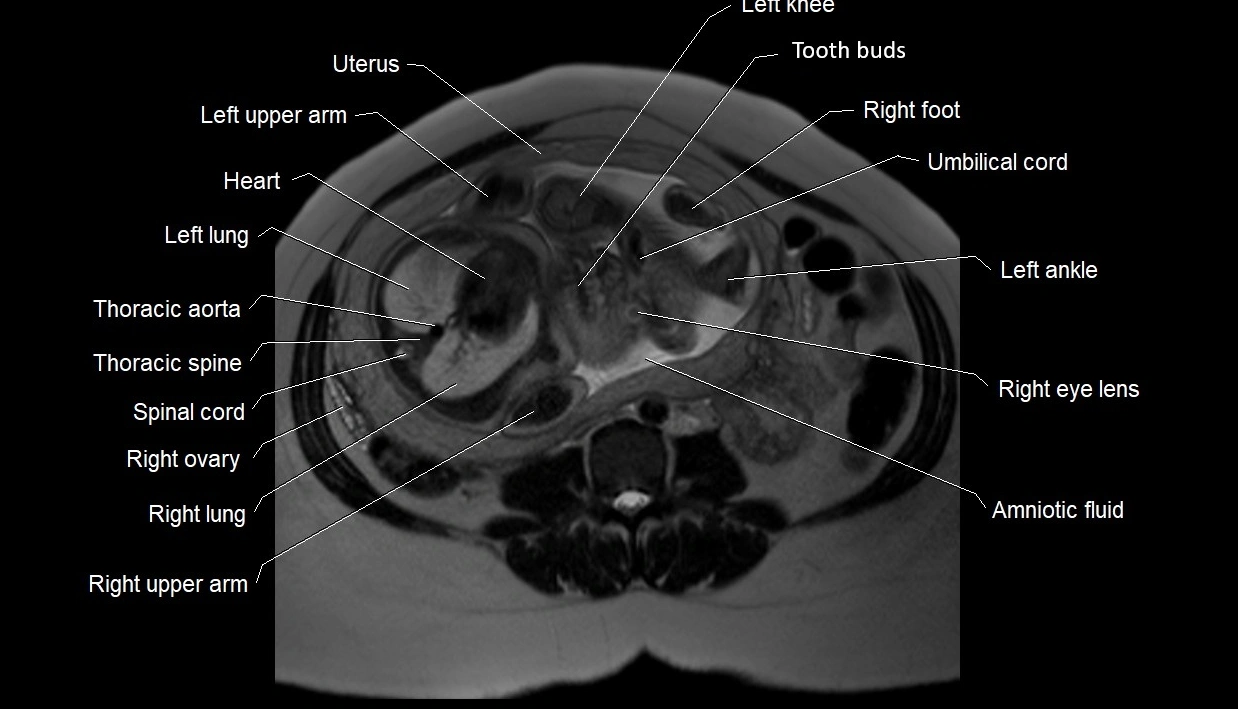
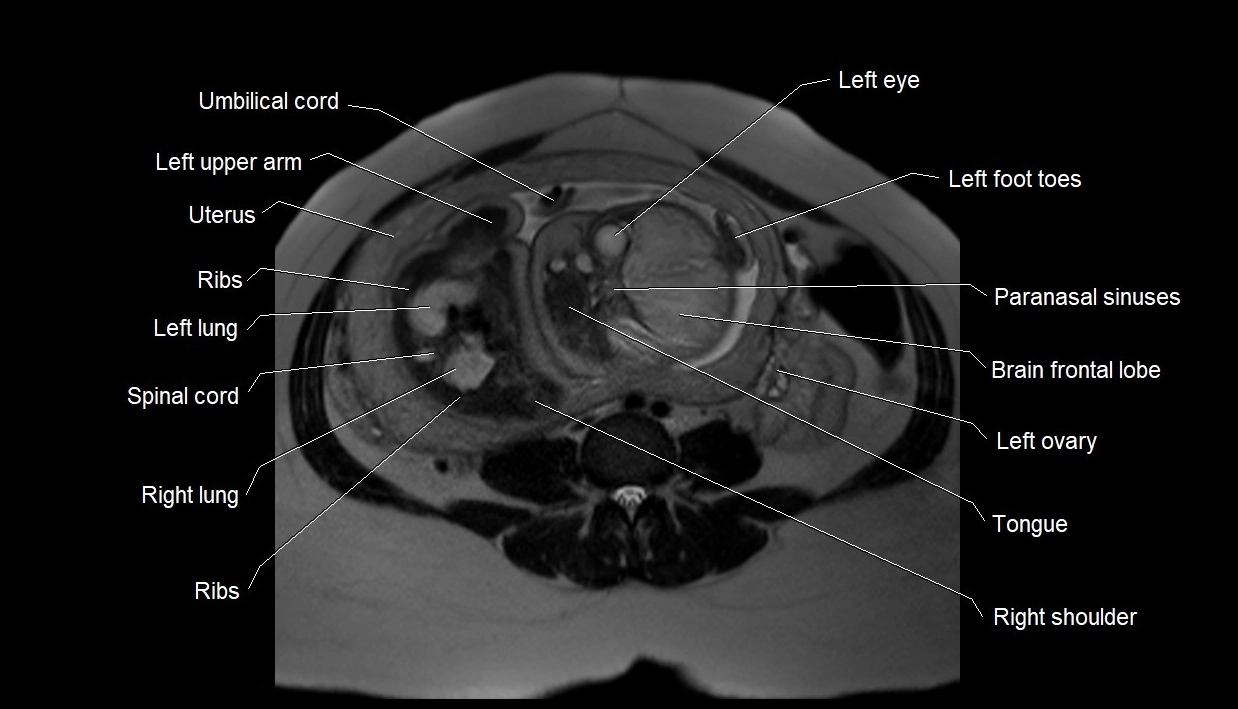
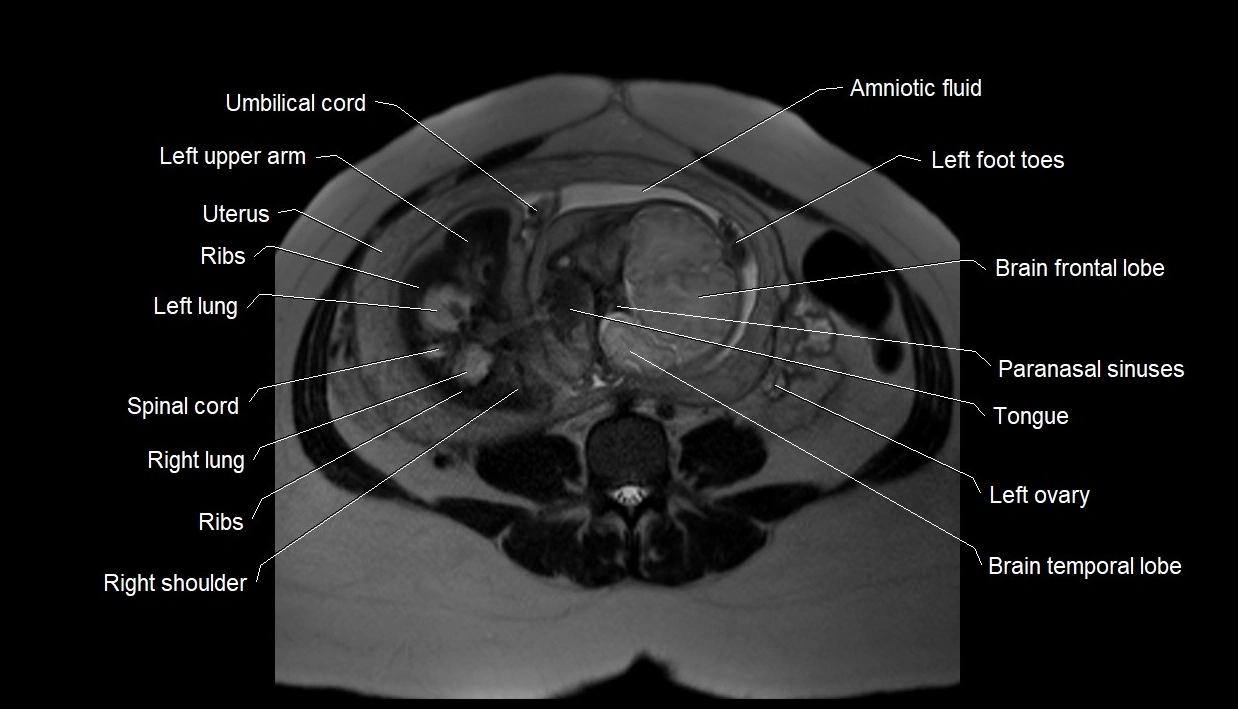
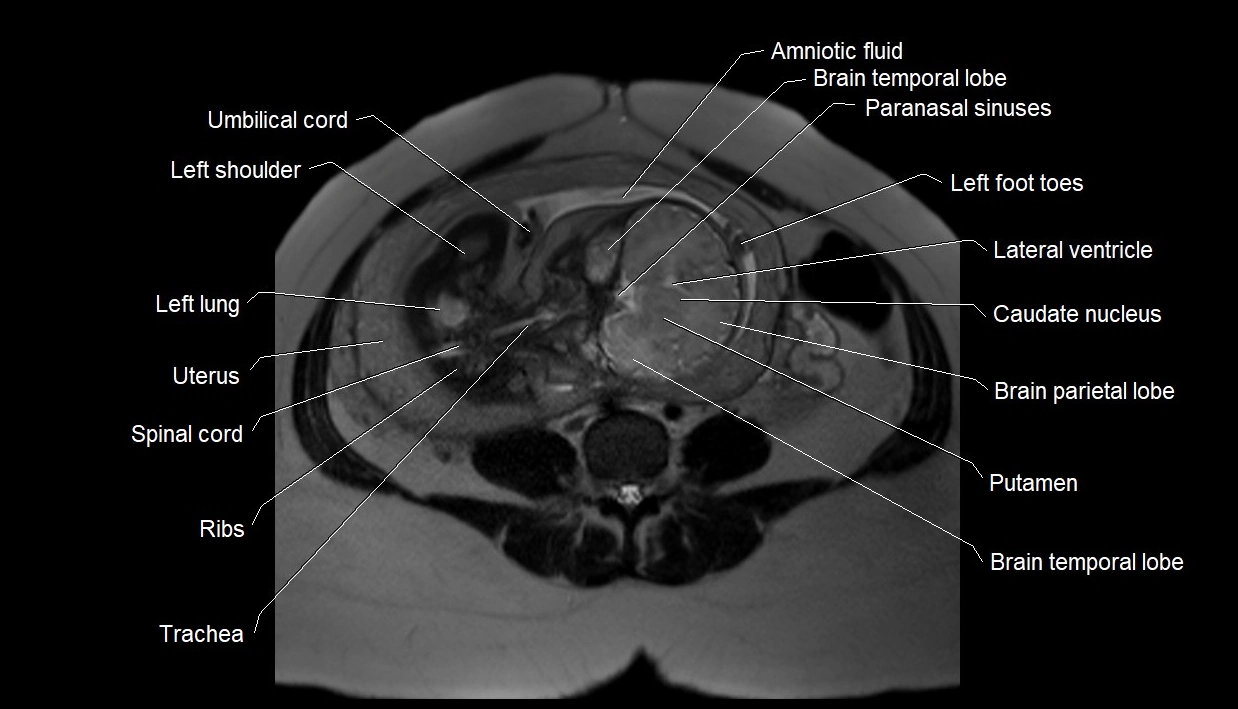
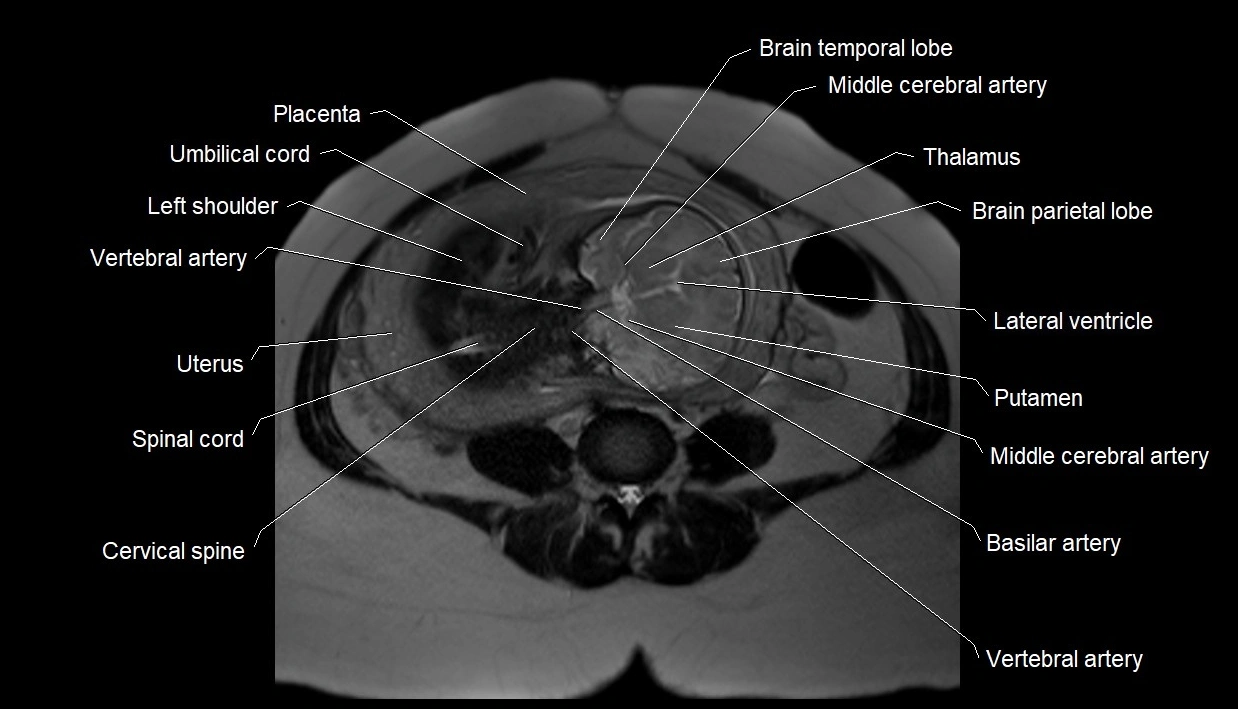
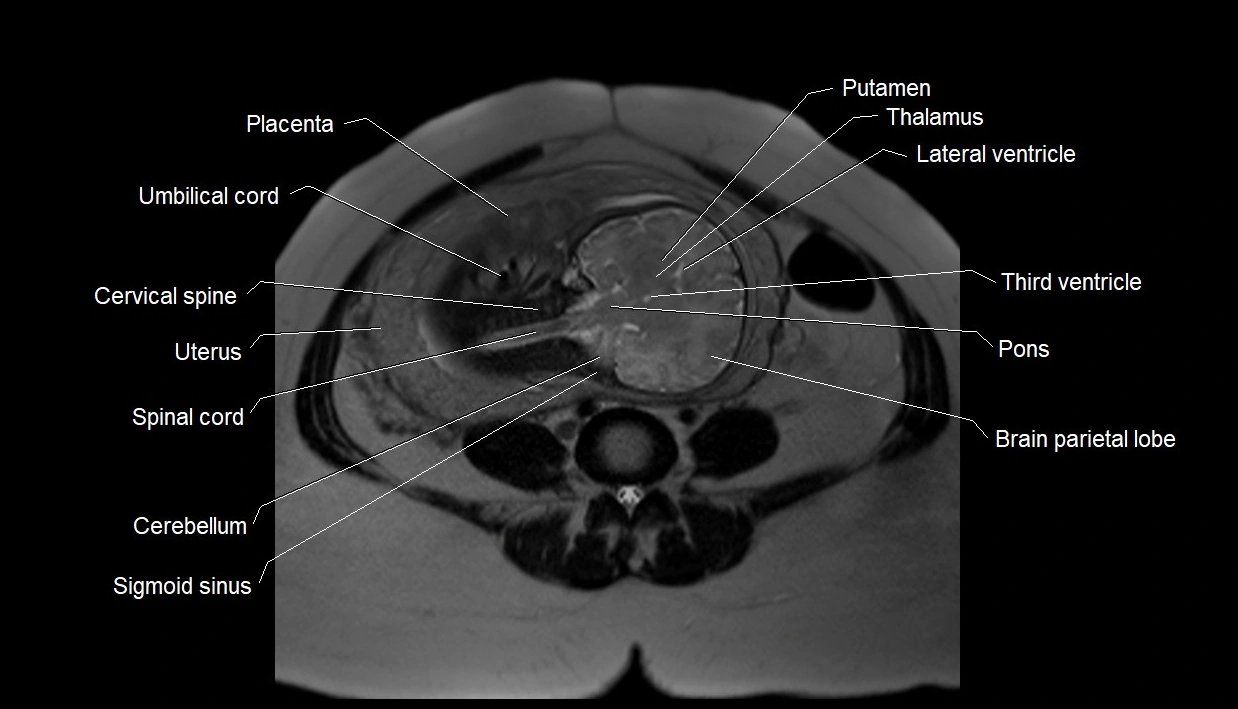
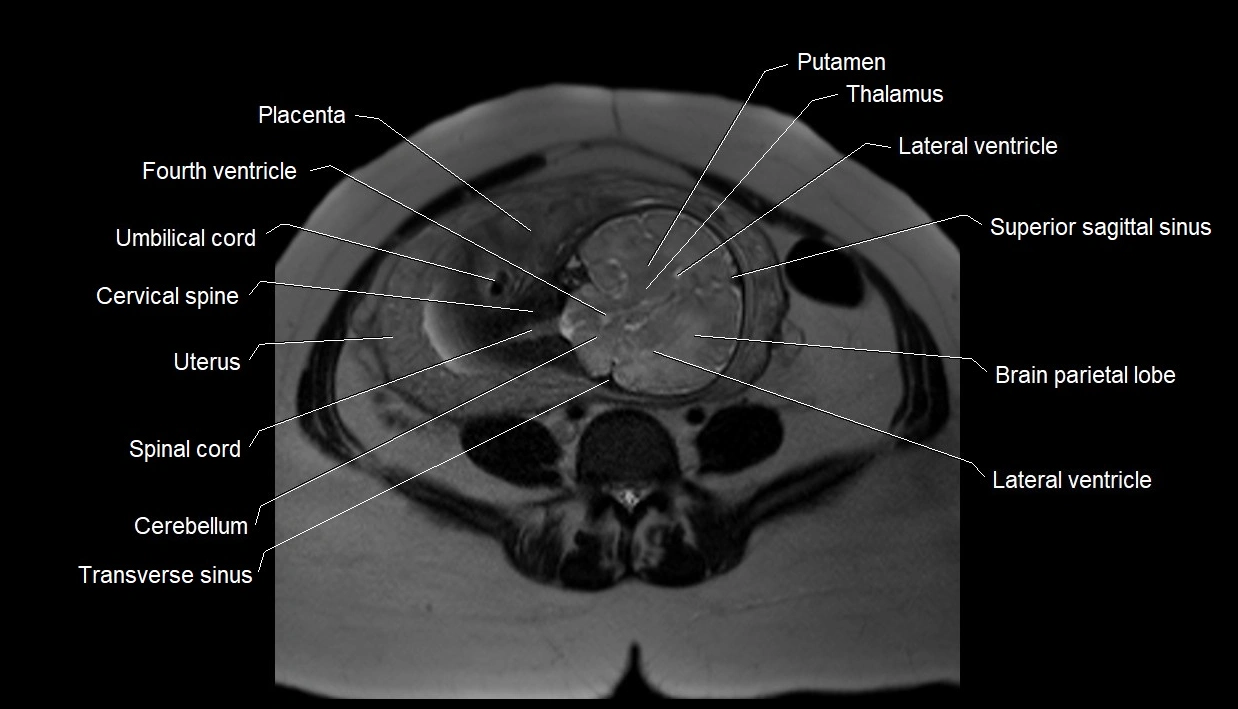
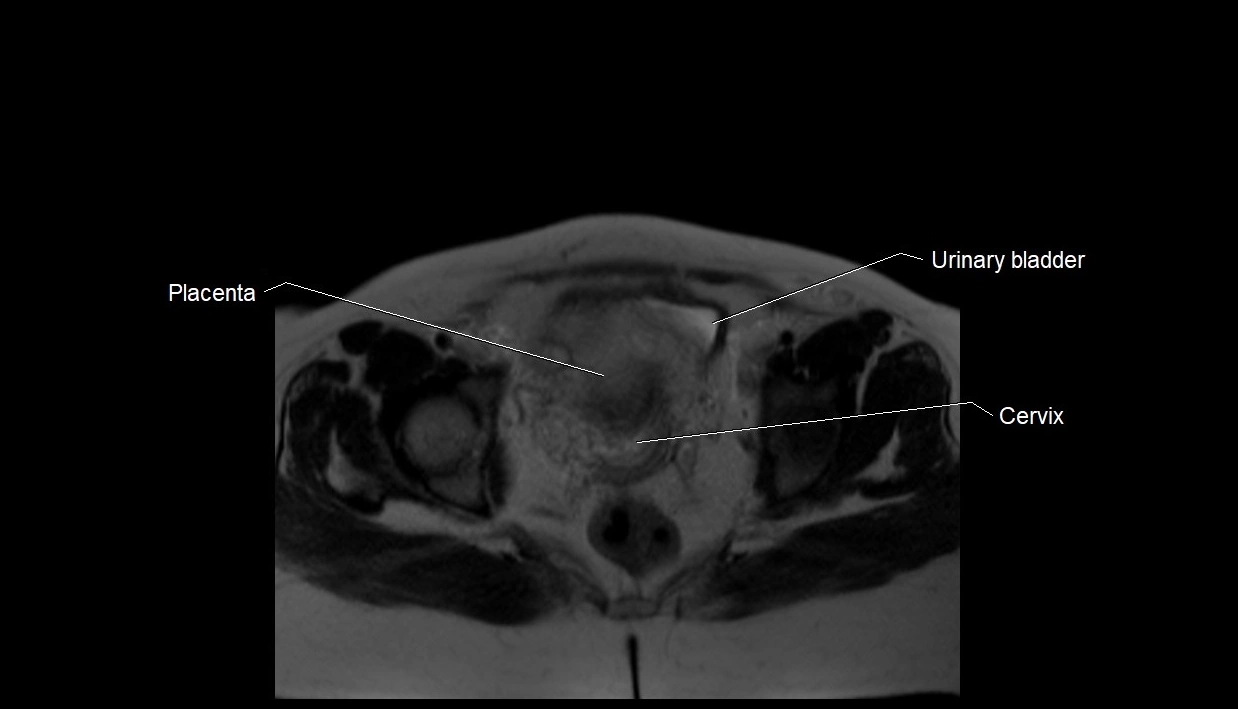
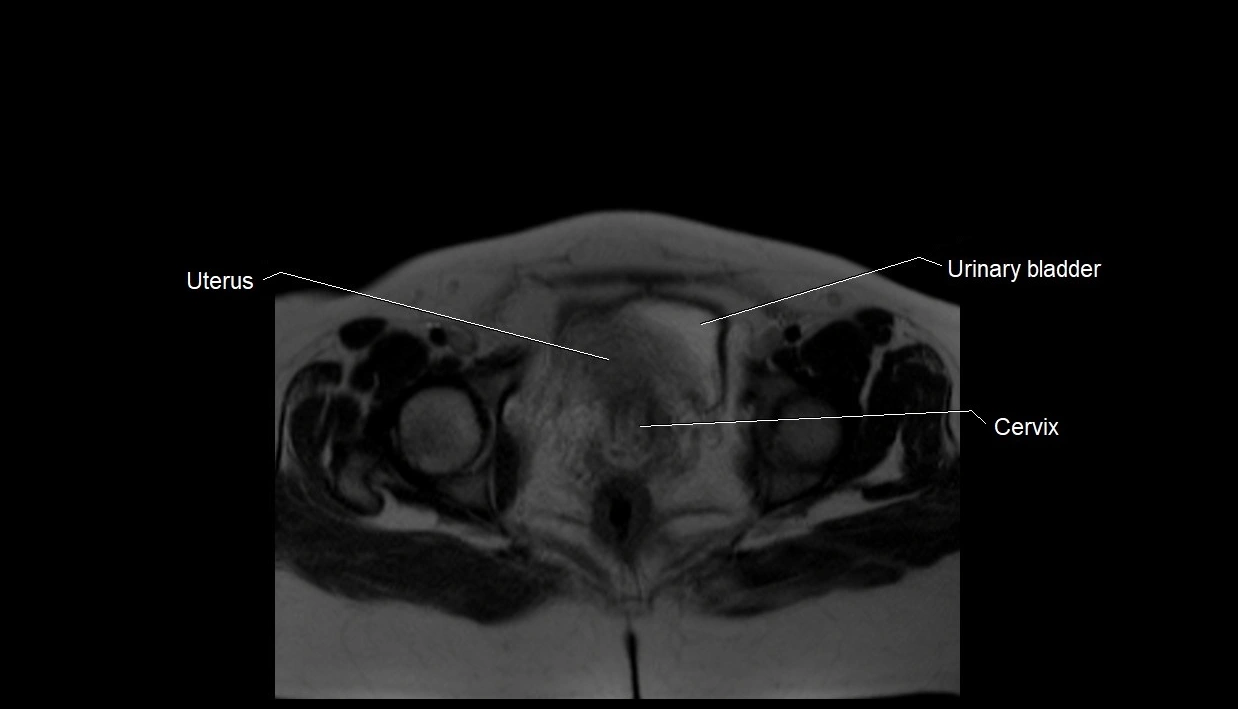
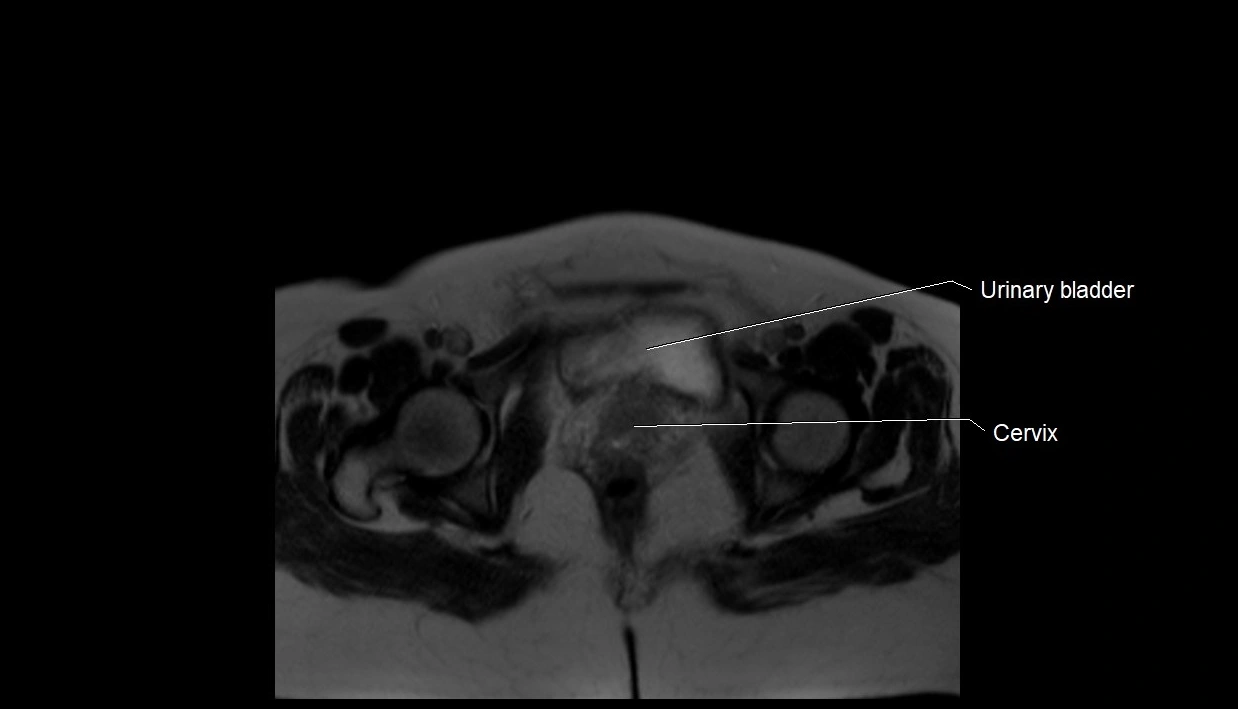
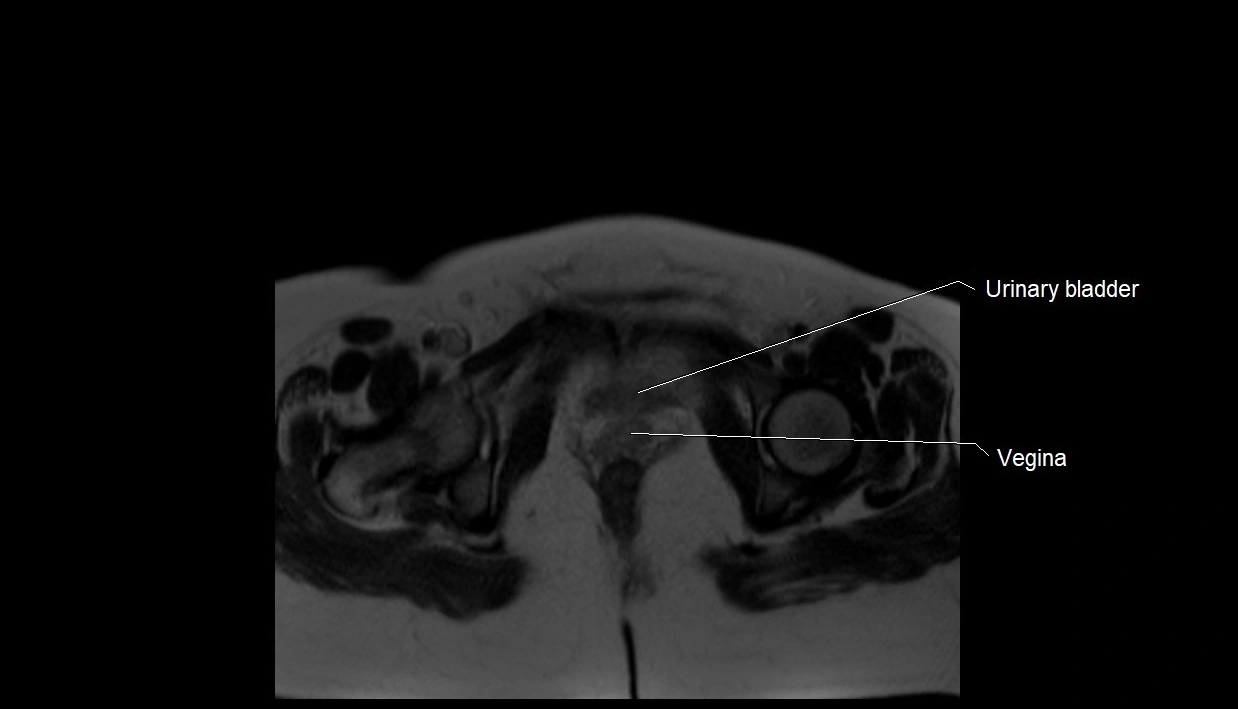
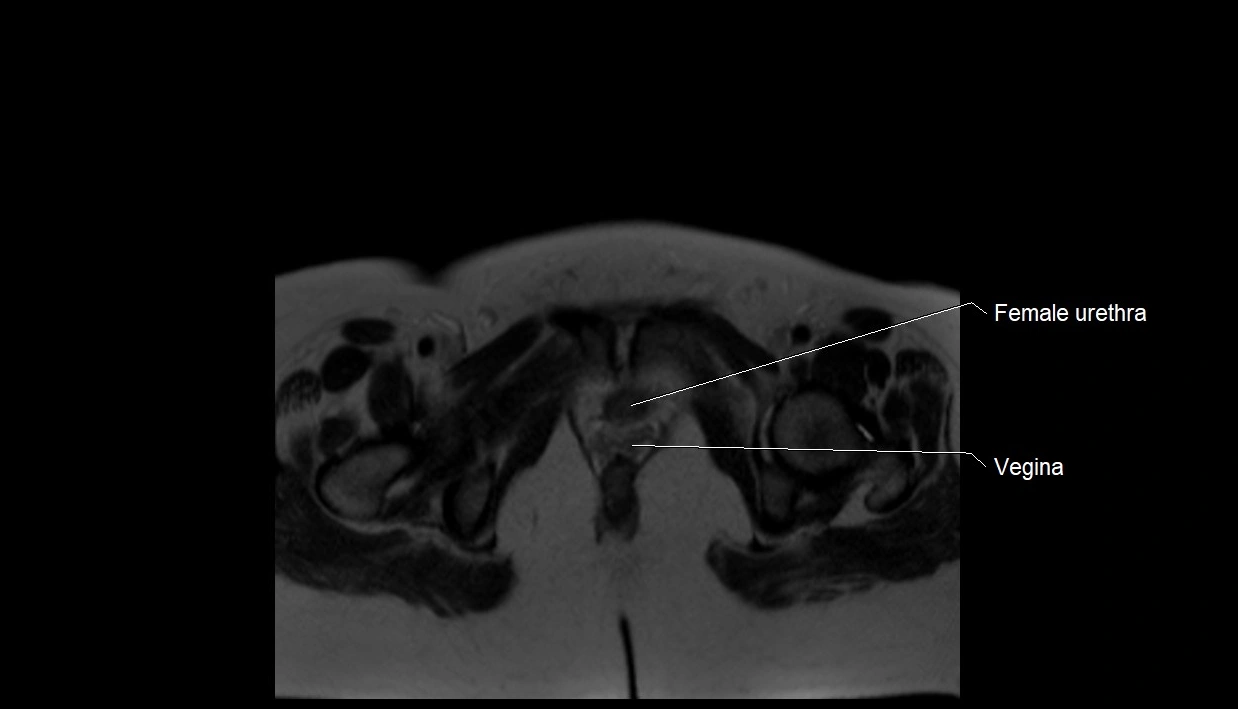
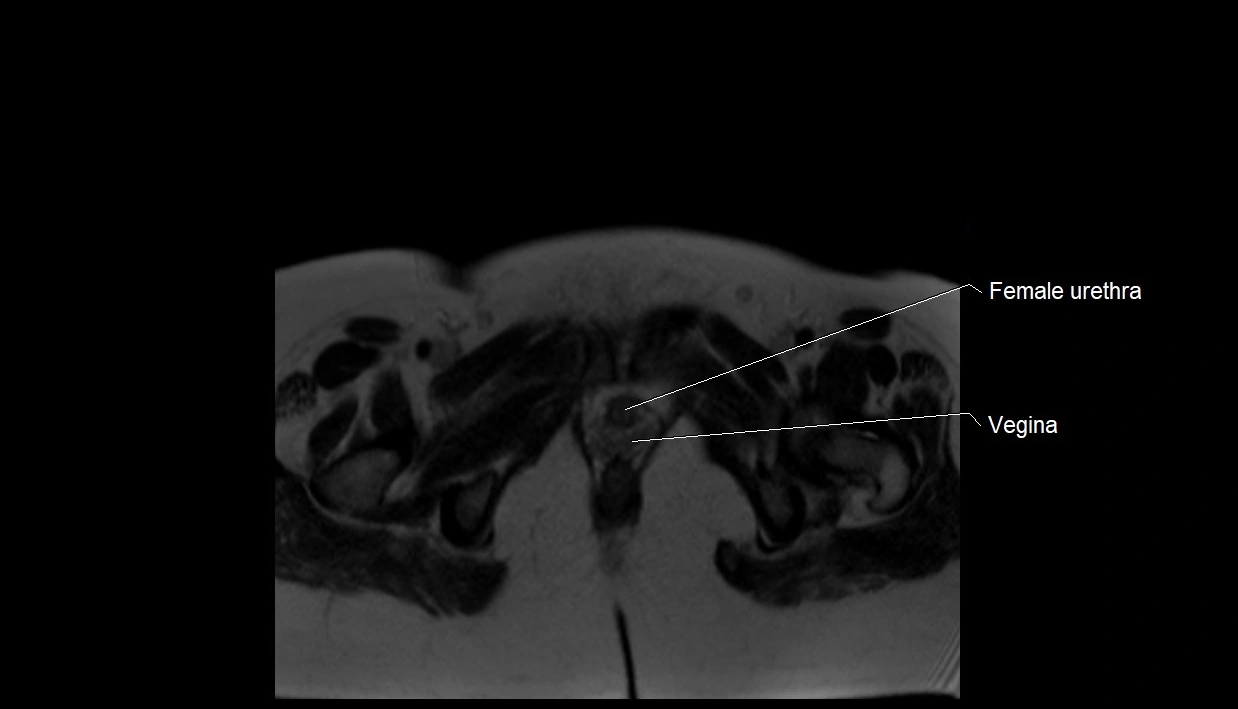
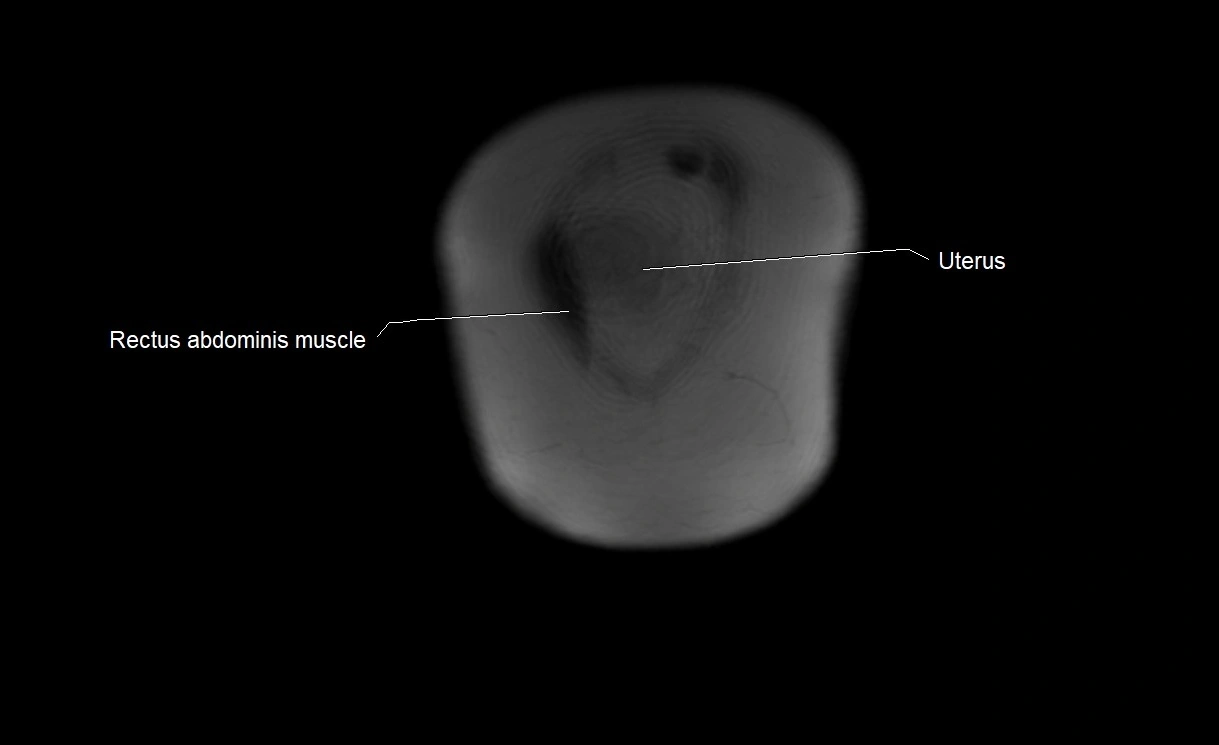
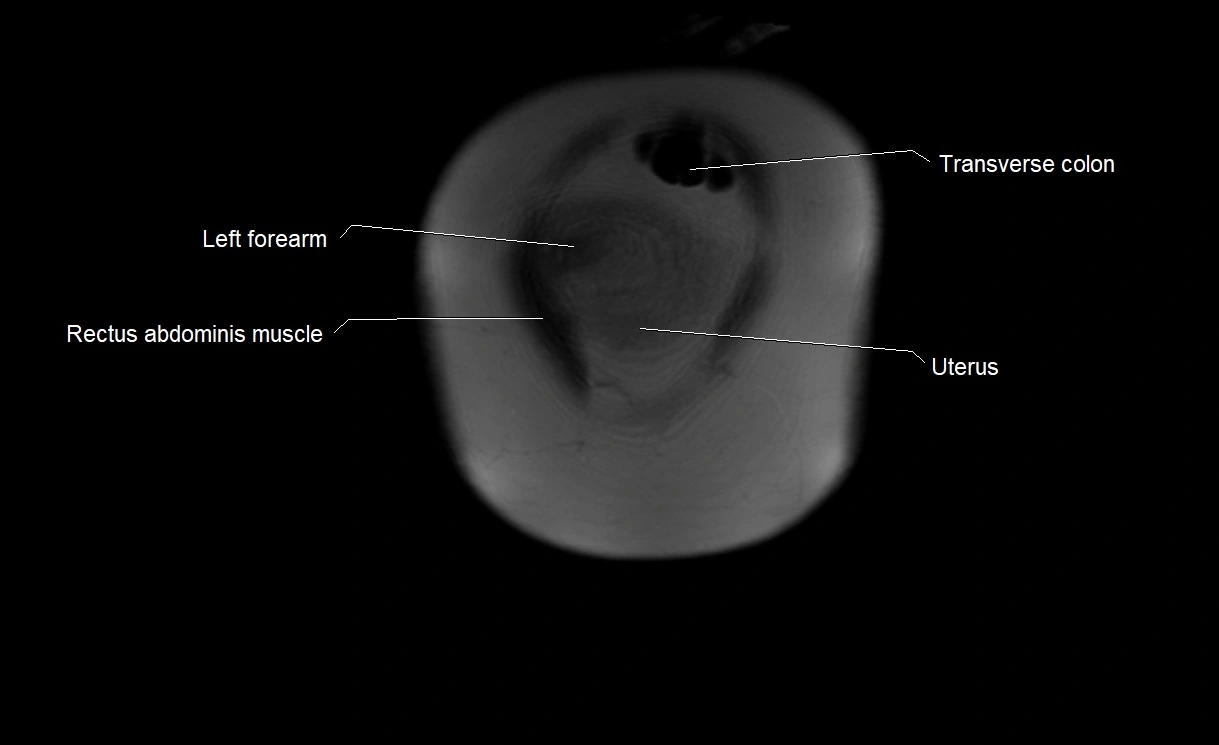
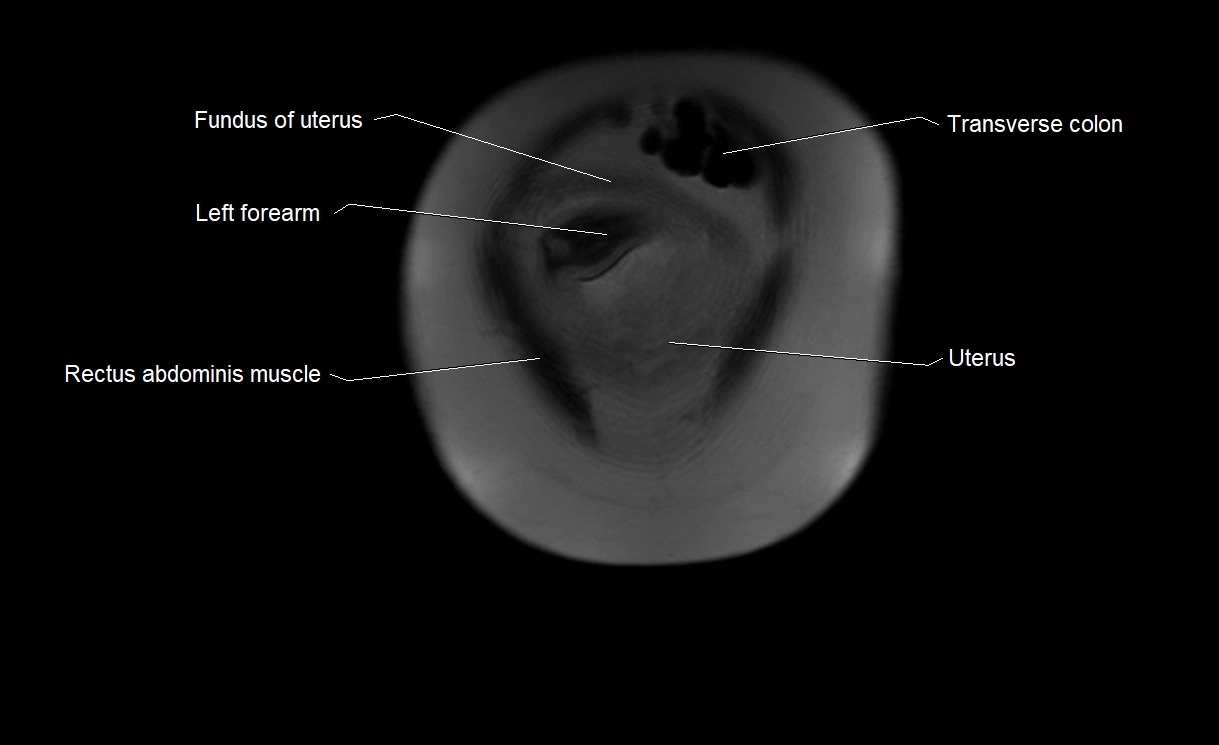
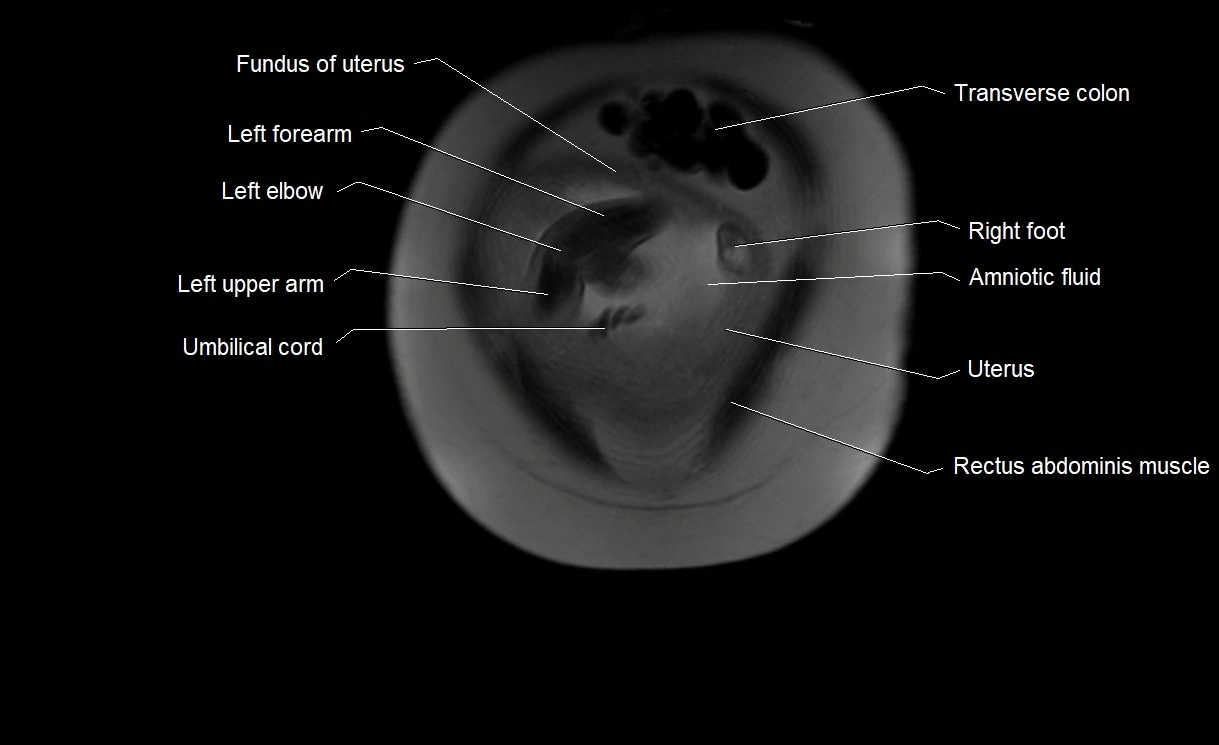
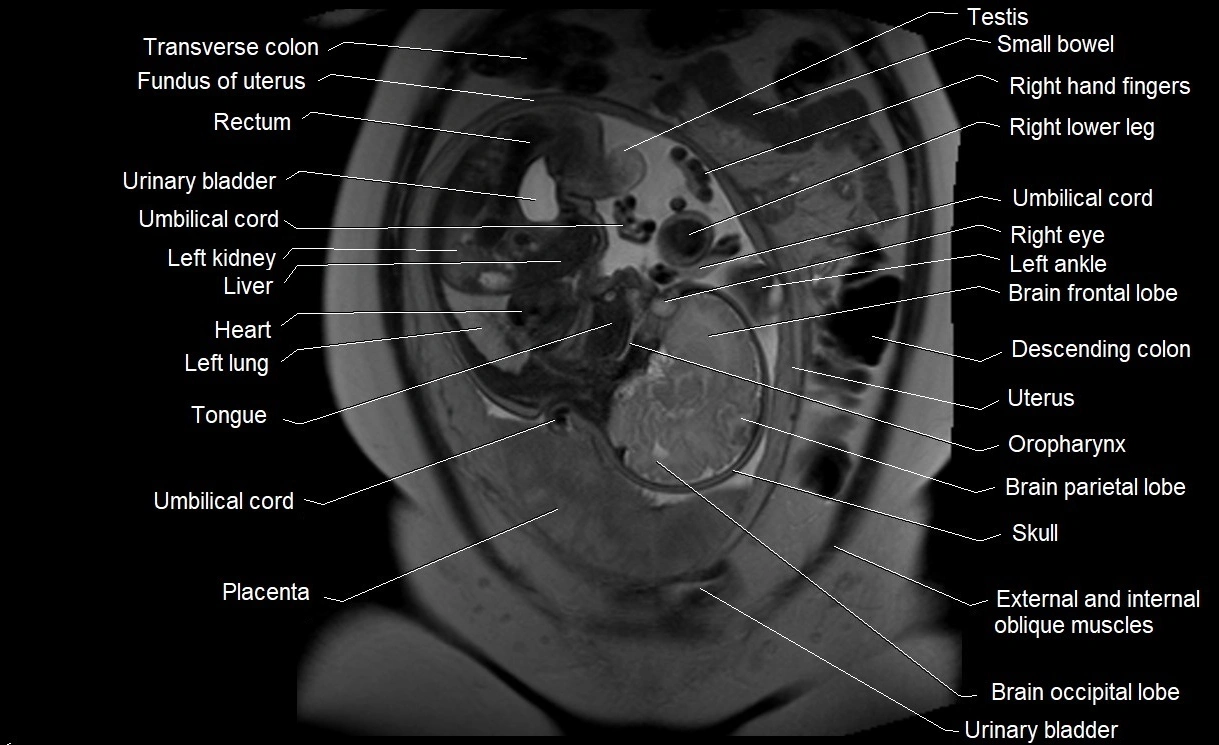
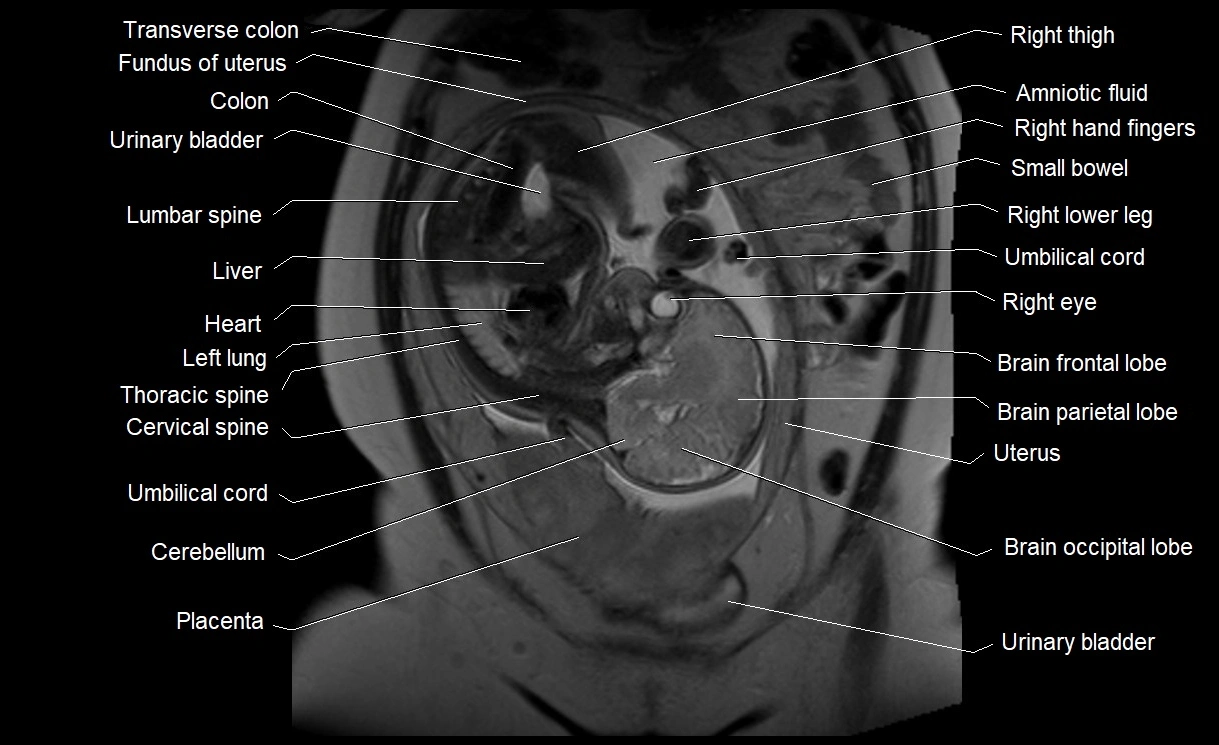
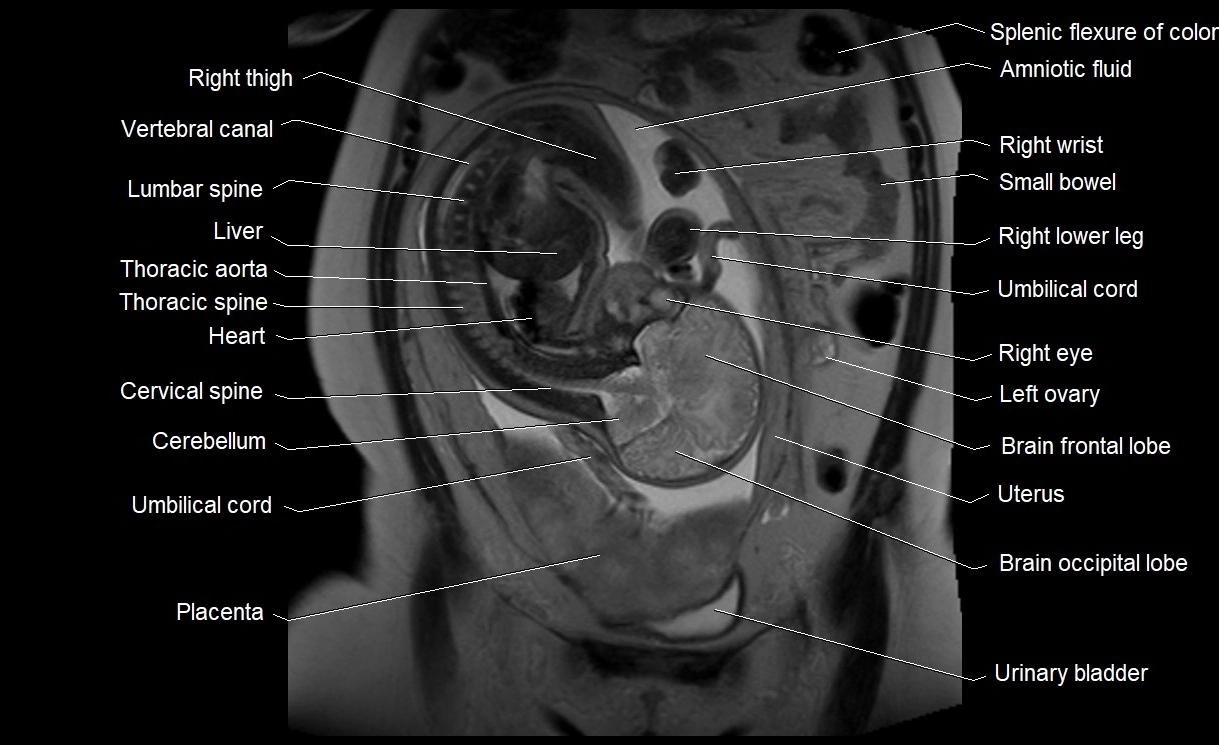
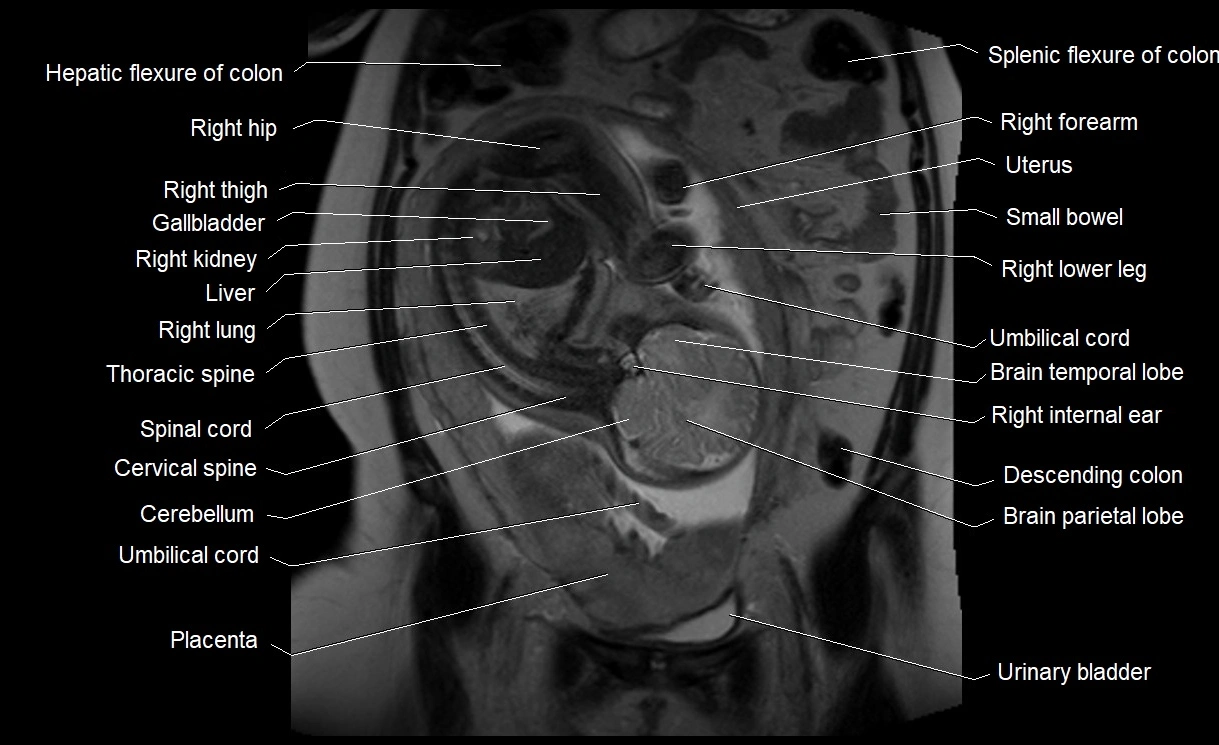
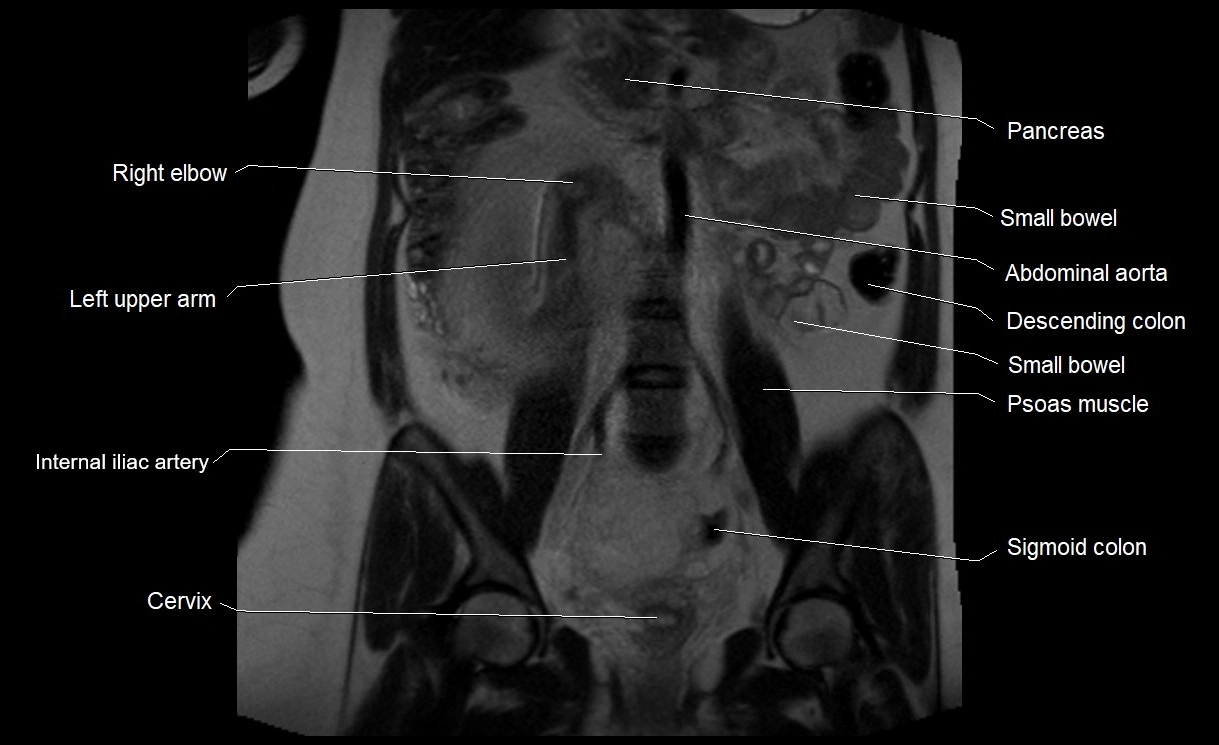
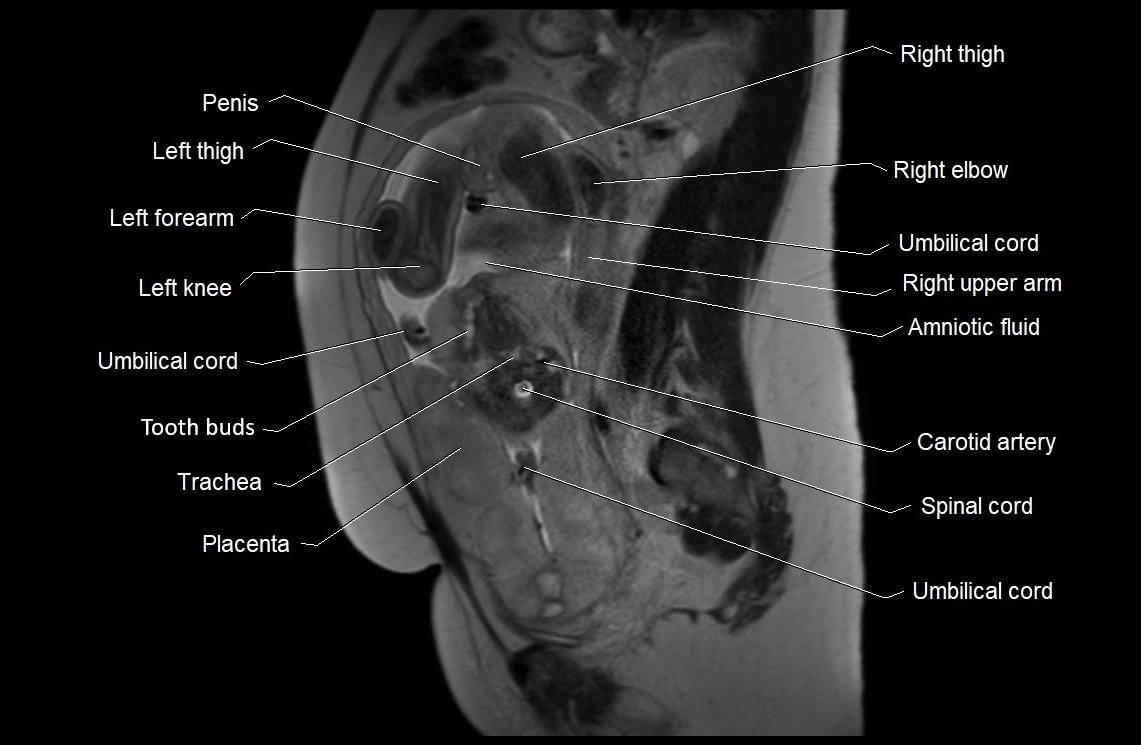
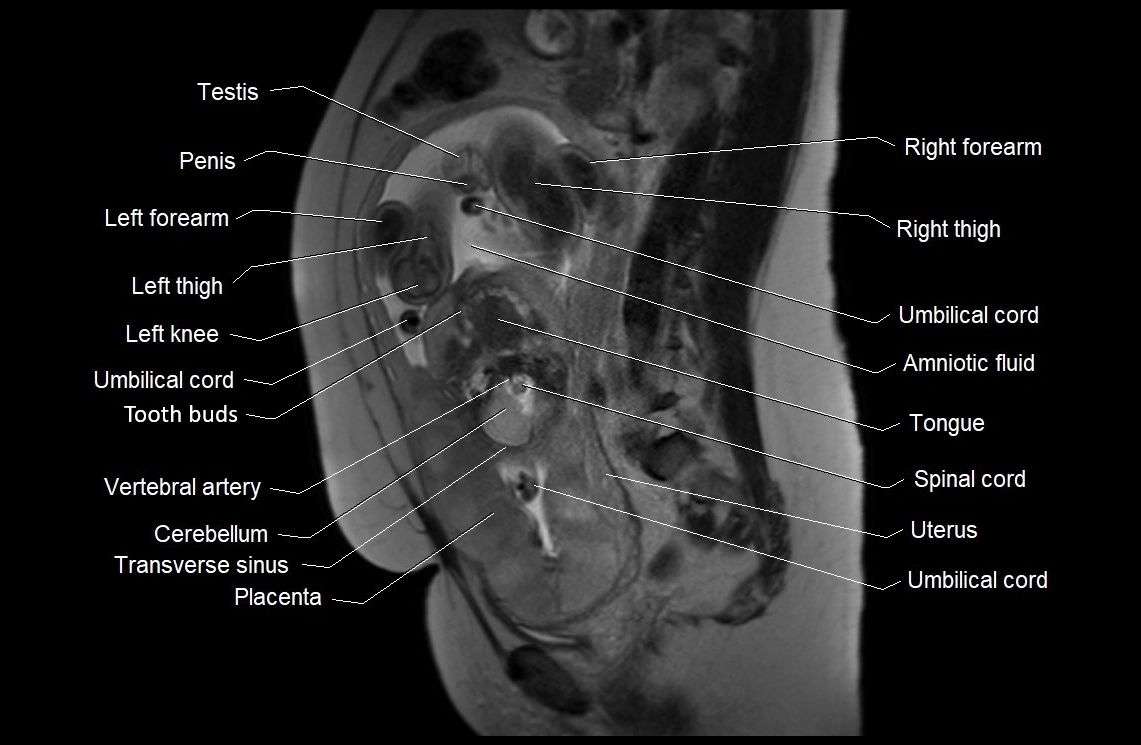
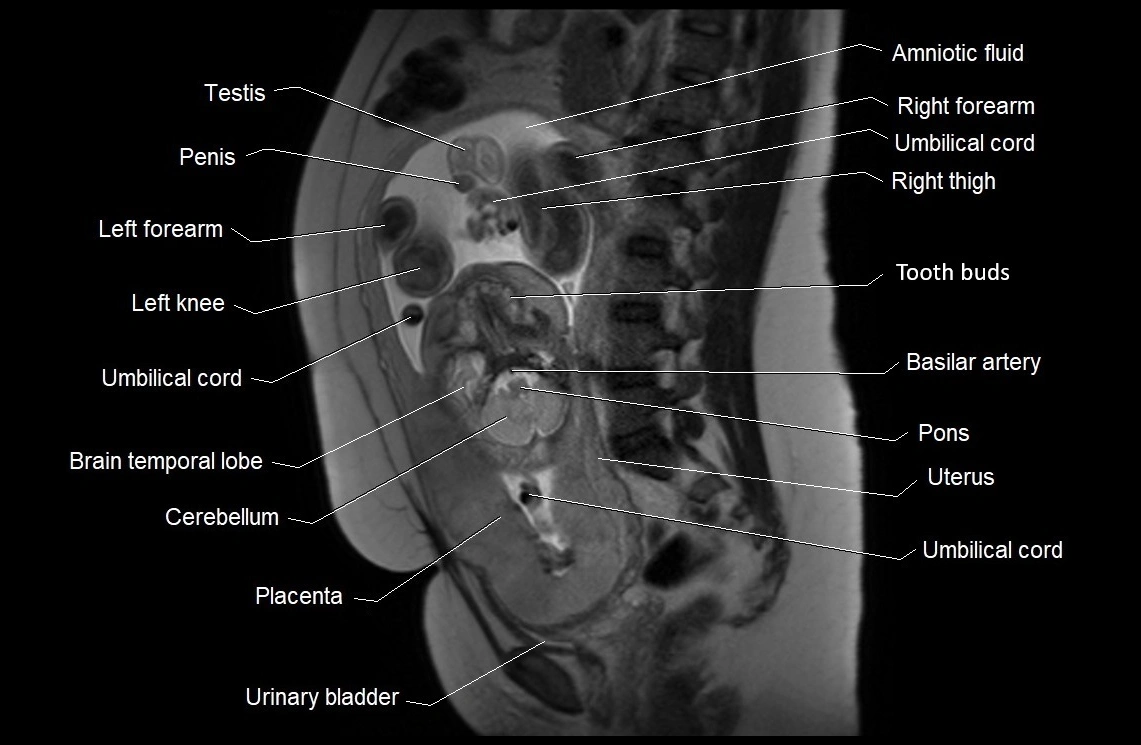
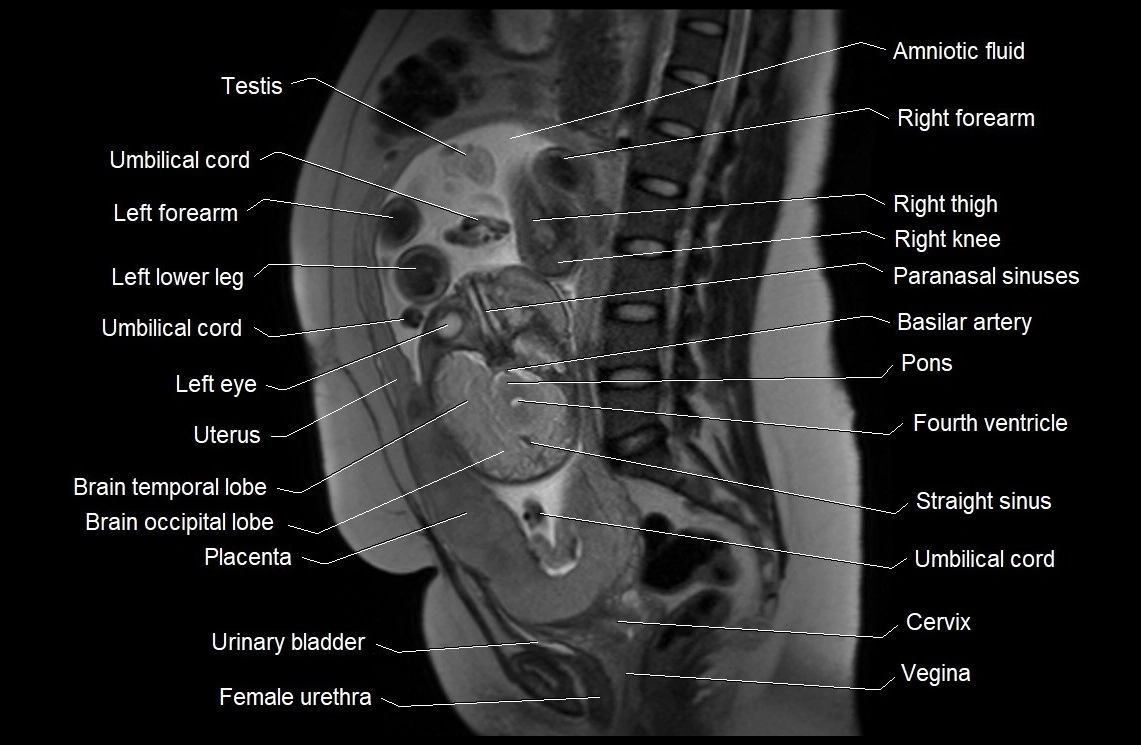
MRI image

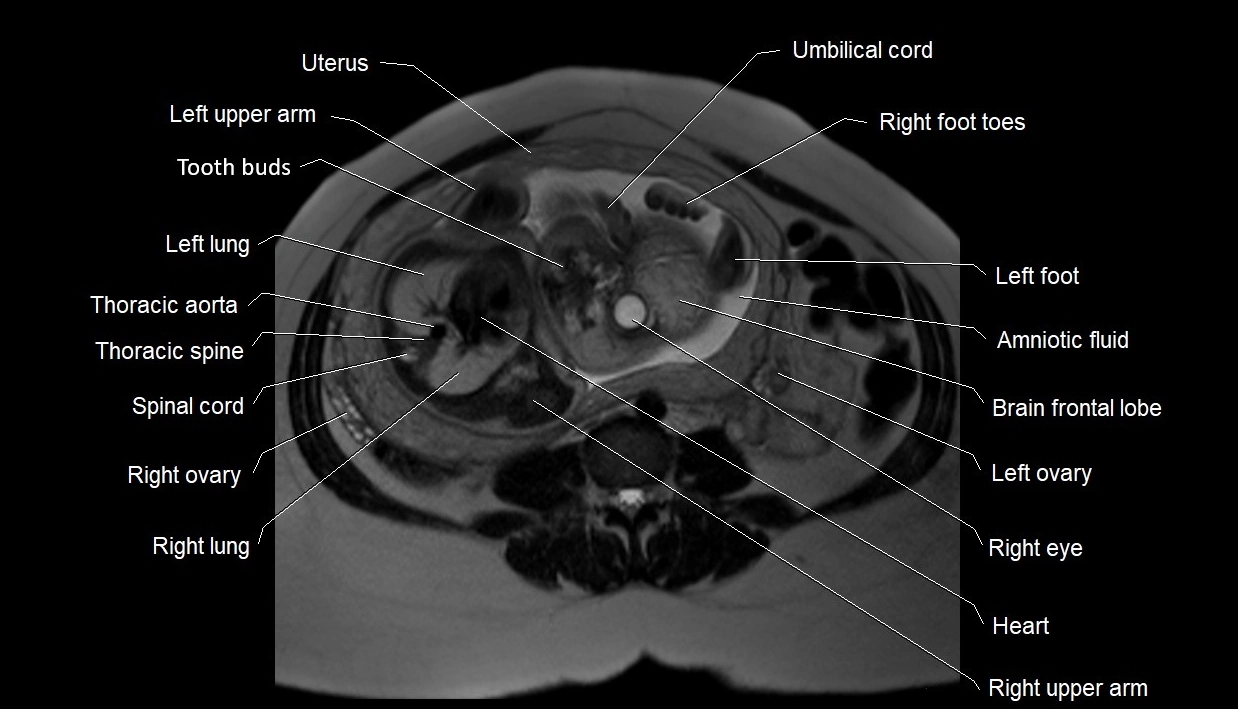
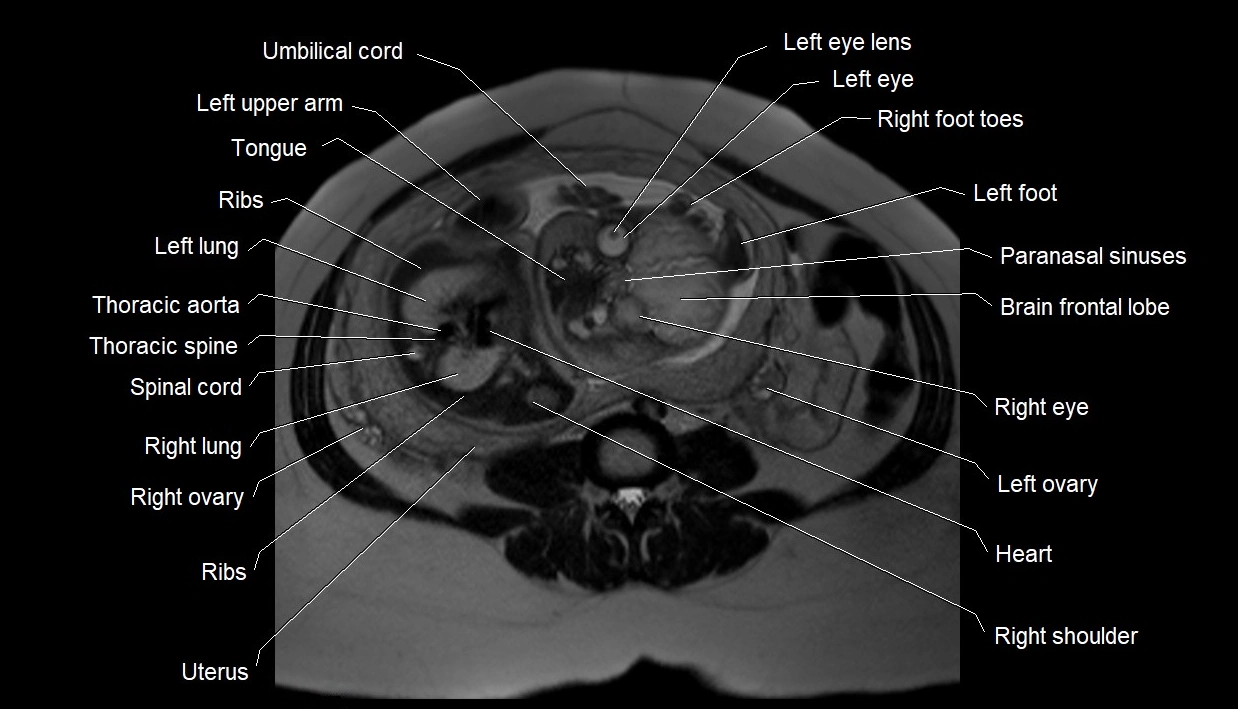
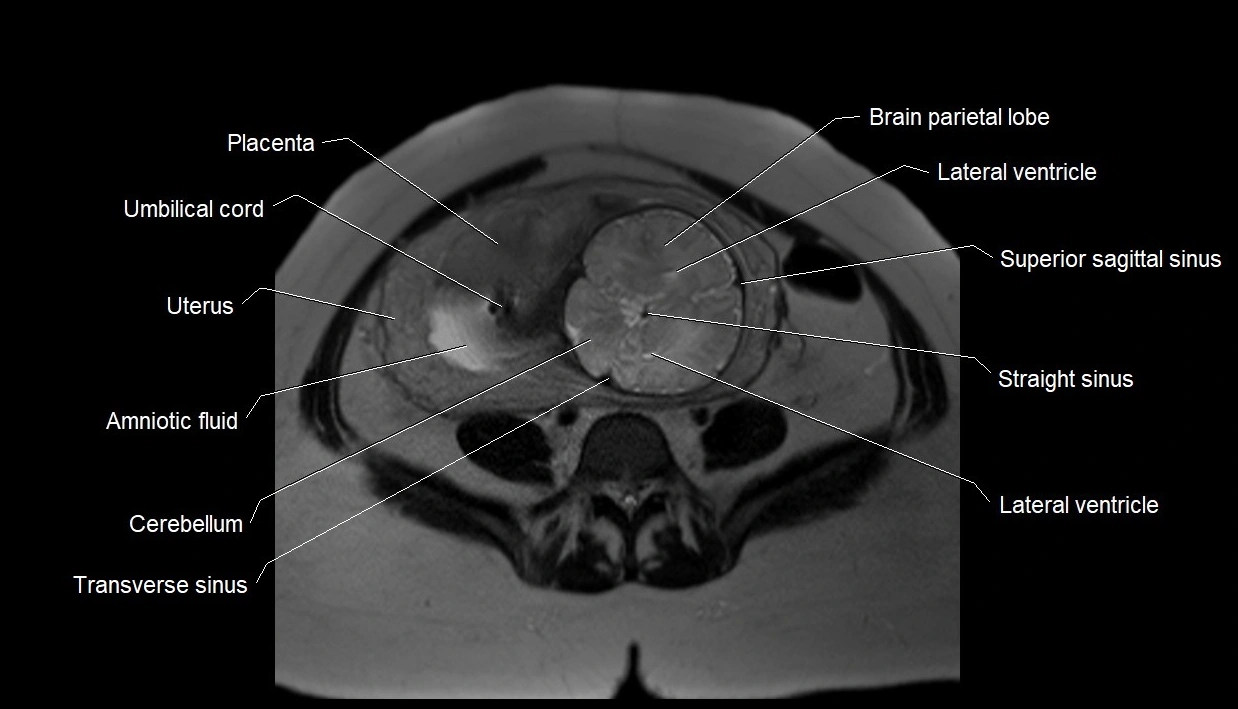
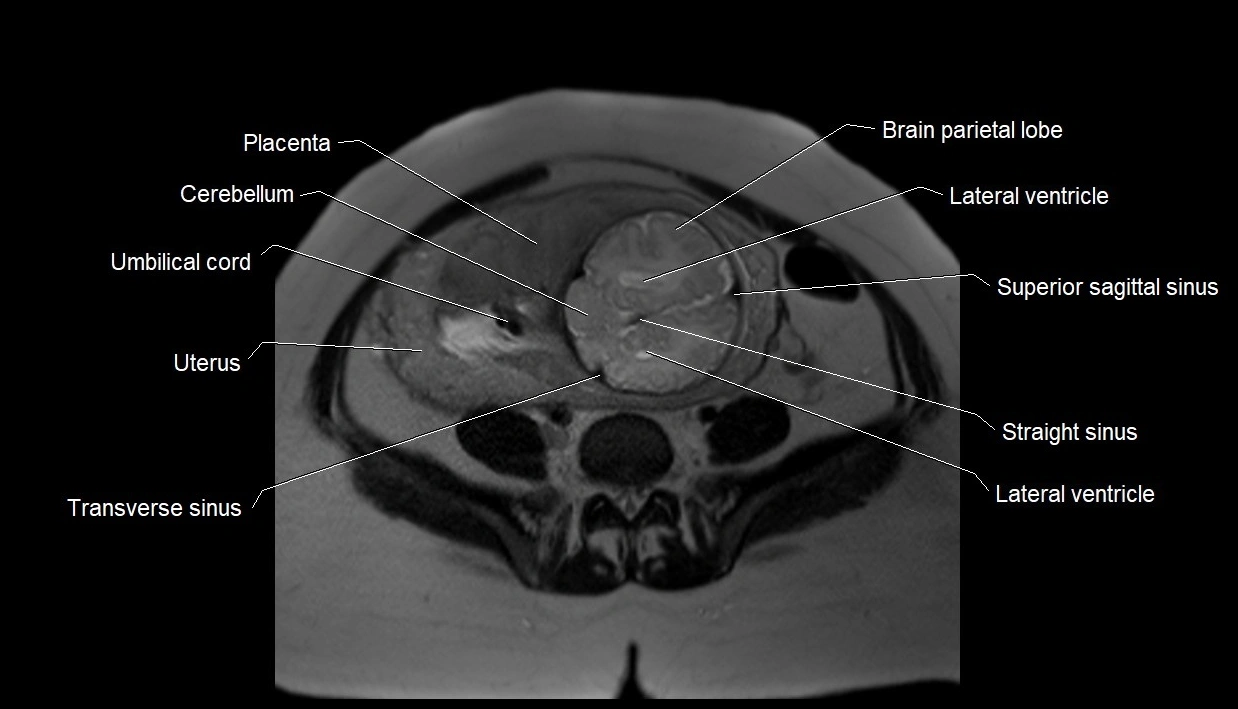
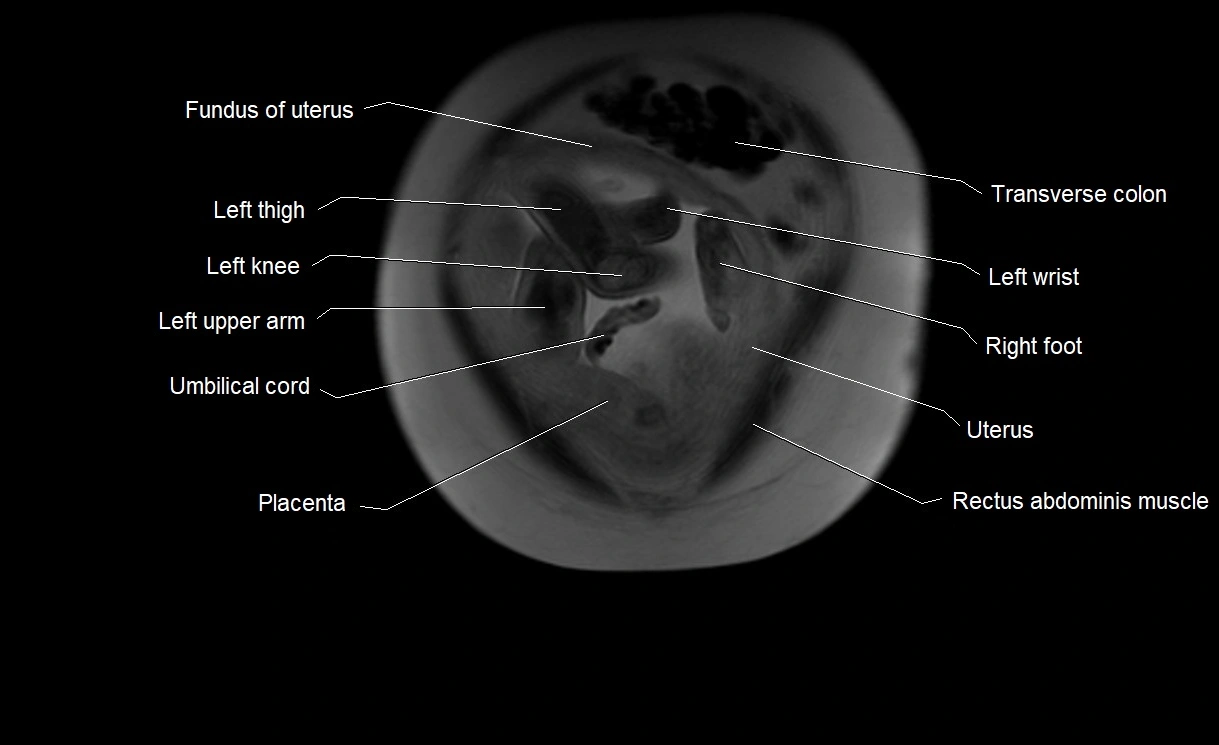
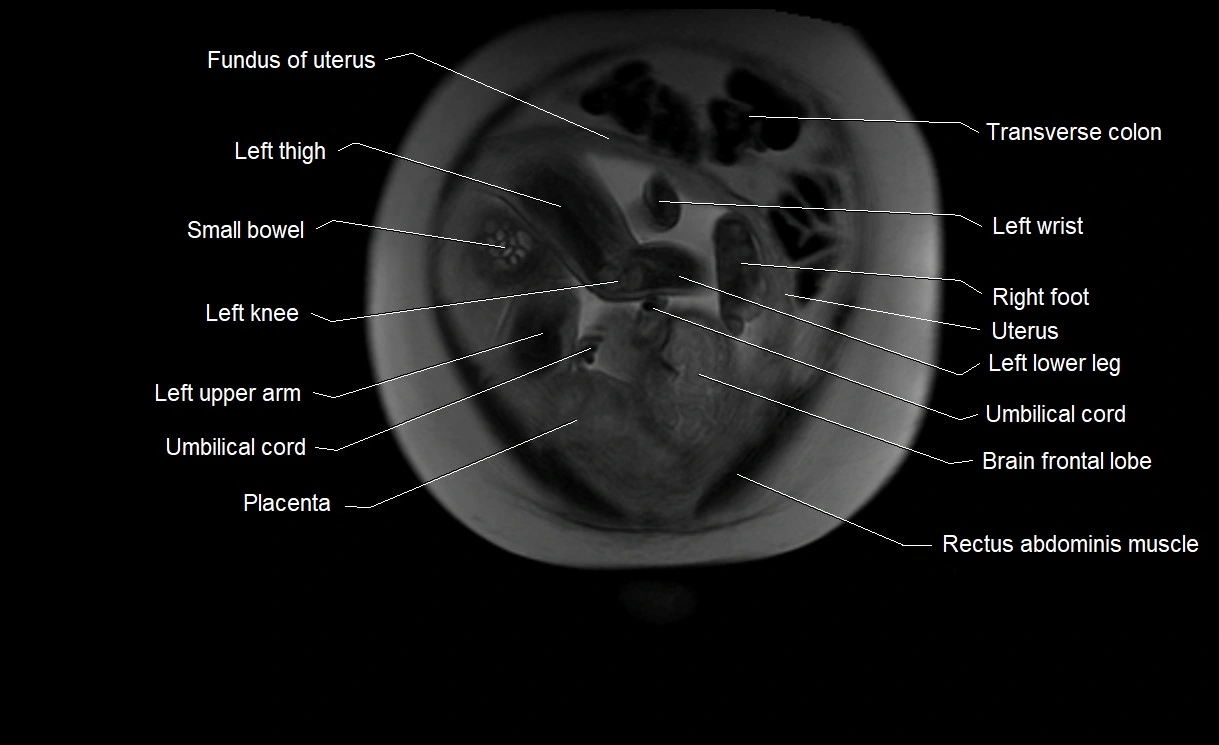
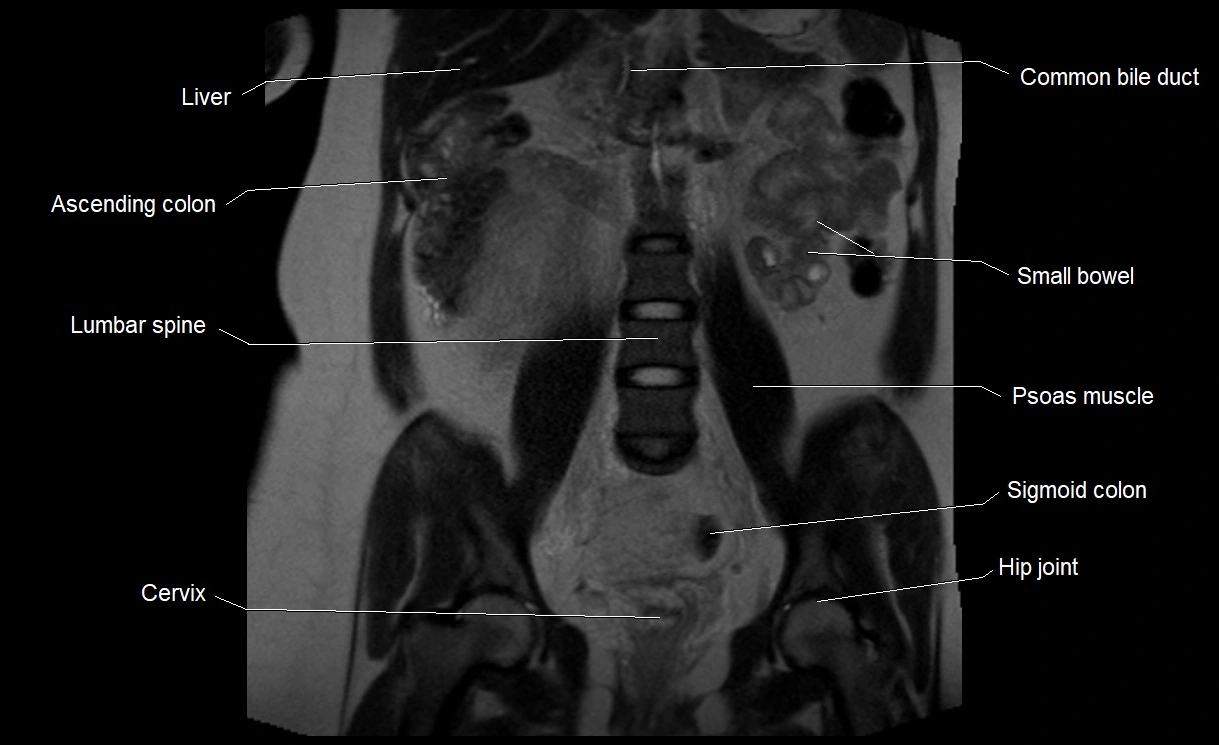
MRI image