Topic
- Accessory obturator artery
- Accessory obturator vein
- Accessory saphenous vein
- Acetabular labrum
- Acetabular margin (Acetabular rim)
- Acetabular notch
- Acetabulum
- Adductor brevis muscle
- Adductor longus muscle
- Adductor magnus muscle
- Adductor minimus muscle
- Ala of ilium (wing of ilium)
- Ala of sacrum
- Anal canal
- Anococcygeal body (anococcygeal ligament)
- Anococcygeal nerve
- Anterior acetabular wall
- Anterior cecal artery
- Anterior division of obturator nerve (Anterior branch of obturator nerve)
- Anterior fornix of cervix
- Anterior inferior iliac spine
- Anterior longitudinal ligament
- Anterior rim of acetabulum
- Anterior sacral foramina
- Anterior sacroiliac ligament
- Anterior superior iliac spine
- Aortic bifurcation
- Apex of urinary bladder
- Appendicular artery
- Articular capsule of hip joint
- Ascending colon
- Ascending mesocolon
- Body of femur
- Body of ilium
- Body of ischium
- Body of pubis
- Body of urinary bladder
- Body of uterus
- Body of vertebra
- Broad ligament of uterus
- Bulbospongiosus muscle (Female)
- Caudate lobe of liver
- Cecum
- Cervix of uterus
- Clitoris
- Co (Coccyx)
- Coccygeal nerve
- Coccygeal plexus
- Coccygeus muscle
- Coccyx
- Common iliac lymph nodes
- Common iliac vein
- Conjoint tendon of biceps femoris & semitendinosus
- Cystic artery
- Deep circumflex iliac artery
- Deep femoral artery (profunda femoris)
- Deep femoral vein (profunda femoris vein)
- Deep transverse perineal muscle
- Descending mesocolon
- Dorsal ramus of spinal nerve
- Endocervical canal
- Endometrium of uterus
- Erector spinae muscles
- Exiting nerve root of spinal nerve S1
- Exiting nerve root of spinal nerve S2
- Exiting nerve root of spinal nerve S3
- Exiting nerve root of spinal nerve S4
- Exiting nerve root of spinal nerve S5
- External anal sphincter
- External iliac artery
- External iliac lymph nodes
- External iliac vein
- External os of the cervix
- External urethral orifice
- External urethral sphincter (female)
- Fallopian tube
- Female urethra
- Femoral artery
- Femoral nerve
- Femoral shaft
- Femoral vein
- Femur
- Filum terminale internum
- Fornix of the vagina
- Fovea for ligament of head of femur
- Fundus of urinary bladder
- Fundus of uterus
- Genitofemoral nerve
- Gluteus maximus muscle
- Gluteus medius muscle
- Gluteus medius tendon
- Gluteus minimus muscle
- Gluteus minimus tendon
- Gracilis muscle
- Greater sciatic notch
- Greater trochanter
- Head of femur
- Hip joint
- Ileal arteries
- Ileocolic artery
- Ileocolic artery colic branches
- Ileocolic artery ileal branches
- Ileum
- Iliac bone
- Iliac crest
- Iliac fossa
- Iliac tubercle
- Iliac tuberosity
- Iliococcygeus muscle
- Iliocostalis lumborum muscle
- Iliofemoral Ligament inferior band (vertical band, medial band)
- Iliofemoral Ligament superior band (transverse band, lateral band)
- Iliofemoral ligament
- Iliohypogastric nerve
- Ilioinguinal nerve
- Iliolumbar ligament
- Iliopsoas muscle
- Iliopsoas tendon
- Iliopubic eminence
- Iliotibial tract
- Ilium bone
- Inferior articular process of L5 vertebra
- Inferior epigastric artery
- Inferior epigastric veins
- Inferior gemellus muscle
- Inferior gluteal artery
- Inferior gluteal nerve
- Inferior gluteal vein
- Inferior mesenteric artery (IMA)
- Inferior mesenteric vein
- Inferior pubic ligament
- Inferior pubic ramus
- Inferior rectal nerve
- Inferior rim of acetabulum
- Inferior vesical artery
- Inguinal ligament
- Inguinal lymph nodes
- Intercommunicating branches of L3–L4 nerves
- Intermediate lacunar external iliac lymph nodes
- Intermediate sacral crest
- Internal anal sphincter
- Internal iliac artery
- Internal iliac lymph nodes
- Internal iliac vein
- Internal oblique muscle
- Internal os of the cervix
- Internal pudendal artery
- Internal pudendal vein
- Internal urethral orifice
- Internal urethral sphincter (female)
- Interosseous sacroiliac ligament
- Interspinales lumborum muscle
- Intertrochanteric line
- Ischial spine
- Ischial tuberosity
- Ischioanal fossa
- Ischiocavernosus muscle (Female)
- Ischiococcygeus muscle
- Ischiofemoral ligament
- Ischiopubic ramus
- Ischium bone
- Isthmus of uterus
- Jejunal arteries
- Junctional zone of uterus
- L (Lumbar spine)
- L1–L2 Intervertebral Disc
- L2–L3 Intervertebral Disc
- L3–L4 Intervertebral Disc
- L4–L5 Intervertebral Disc
- L5–S1 Intervertebral disc
- Labia majora
- Labia minora
- Lateral circumflex femoral artery
- Lateral circumflex femoral veins
- Lateral femoral cutaneous nerve
- Lateral fornix of cervix
- Lateral part of sacrum
- Lateral sacral artery
- Lateral sacral crest
- Lateral sacral vein
- Left colic artery
- Left ovarian vein
- Left ovary
- Left paracolic gutter
- Left ureter
- Lesser trochanter
- Levator ani muscle
- Ligamentum teres (ligament of the head of femur)
- Linea alba
- Liver Segment I – Caudate lobe
- Liver Segment II – Left lateral superior segment
- Liver Segment III – Left lateral inferior segment
- Liver Segment IVa – Left medial superior segment
- Liver Segment IVb – Left medial inferior segment
- Liver Segment V – Right anteroinferior segment
- Liver Segment VI – Right posteroinferior segment
- Liver Segment VII – Right posterosuperior segment
- Liver Segment VIII – Right anterosuperior segment
- Longissimus thoracis muscle
- Lumbar triangle
- Lumbosacral joint
- Lumbosacral trunk
- Marginal artery of Drummond
- Medial circumflex femoral artery
- Medial circumflex femoral vein
- Medial cluneal nerves
- Median sacral crest
- Median sacral vein
- Median umbilical ligament
- Mesorectal fascia
- Mesorectal free fluid
- Mesorectum
- Mons pubis
- Muscular branches of femoral nerve
- Myometrium of uterus
- Neck of femur
- Neck of urinary bladder
- Obturator artery
- Obturator externus muscle
- Obturator foramen
- Obturator internus muscle
- Obturator lymph nodes
- Obturator nerve
- Obturator vein
- Obturator veins
- Ovaries
- Parietal peritoneum
- Pectineus muscle
- Pedicle of vertebra
- Perimetrium of uterus
- Perineal nerves
- Piriformis muscle
- Posterior acetabular wall
- Posterior division of obturator nerve (Posterior branch of obturator nerve)
- Posterior fornix of cervix
- Posterior inferior iliac spine
- Posterior longitudinal ligament
- Posterior rim of acetabulum
- Posterior sacral foramina
- Posterior sacroiliac ligament
- Posterior superior iliac spine
- Preperitoneal space
- Psoas major muscle
- Pubic bone
- Pubic symphysis
- Pubic tubercle
- Puboanalis muscle
- Pubococcygeus muscle
- Pubofemoral ligament
- Puborectalis muscle
- Pudendal artery
- Pudendal nerve
- Pudendal vein
- Pyramidal muscle (pyramidalis muscle)
- Quadrate lobe of liver
- Quadratus femoris muscle
- Quadratus lumborum muscle
- Ramus of ischium
- Rectococcygeal muscle
- Rectouterine pouch (pouch of Douglas)
- Rectovaginal septum (rectovaginal fascia)
- Rectum
- Rectus femoris muscle
- Rectus femoris tendon (Proximal tendon of rectus femoris)
- Retropubic space
- Right ovary
- Right paracolic gutter
- Rotatores lumborum muscles
- Rotatores thoracis muscles
- Round ligament of uterus
- S (Sacral spine)
- Sacral canal
- Sacral cornu (sacral horn)
- Sacral hiatus
- Sacral plexus
- Sacral splanchnic nerves
- Sacroiliac joint
- Sacrospinous ligament
- Sacrotuberous ligament
- Sacrum
- Saphenous nerve
- Sartorius Tendon (Proximal)
- Sartorius muscle
- Sciatic nerve
- Semimembranosus tendon (proximal)
- Sigmoid colon
- Skene’s gland (paraurethral glands)
- Small intestine
- Spinal nerve Co1
- Spinal nerve L2
- Spinal nerve L3
- Spinal nerve L4
- Spinal nerve L5
- Spinal nerve S1
- Spinal nerve S2
- Spinal nerve S3
- Spinal nerve S4
- Spinal nerve S5
- Spinalis thoracis muscle
- Stomach
- Stroma of the cervix
- Superficial circumflex iliac artery
- Superficial circumflex iliac vein
- Superficial femoral artery
- Superficial inguinal lymph nodes
- Superficial transverse perineal muscle
- Superior articular process of S1 vertebra
- Superior articular process of sacrum
- Superior articular process of vertebra
- Superior cluneal nerves
- Superior gemellus muscle
- Superior gluteal artery
- Superior gluteal nerve
- Superior gluteal veins
- Superior pubic ligament
- Superior pubic ramus
- Superior rectal artery
- Superior rectal vein
- Superior rim of acetabulum
- Superior vesical artery
- Suspensory ligament of ovary
- T (Thoracic spine)
- T12–L1 Intervertebral Disc
- Tensor fasciae latae muscle
- Tensor fasciae latae tendon
- Terminal ileum
- Thoracic aorta
- Transverse abdominal muscle
- Transverse acetabular ligament
- Transverse mesocolon
- Transverse process of vertebra
- Transverse processes
- Transverse ridges
- Transversus abdominis muscle
- Traversing nerve root of spinal nerve
- Traversing nerve root of spinal nerve S1
- Traversing nerve root of spinal nerve S2
- Traversing nerve root of spinal nerve S3
- Traversing nerve root of spinal nerve S4
- Trigone of urinary bladder
- Umbilical artery
- Union of common iliac veins
- Ureteric Orifice
- Ureters
- Urethrovaginal space
- Urinary bladder
- Uterine artery
- Uterine horn
- Uterine veins
- Uterine venous plexus
- Uterosacral ligament
- Uterus
- Vagina
- Vaginal venous plexus
- Vastus intermedius muscle
- Vastus lateralis muscle
- Vastus medialis muscle
- Vertebrae
- Vesicouterine pouch
- Vesicovaginal space
- Vestibular fossa
- Zona orbicularis ligament
- Zygapophyseal joint
- common iliac artery
- great saphenous vein
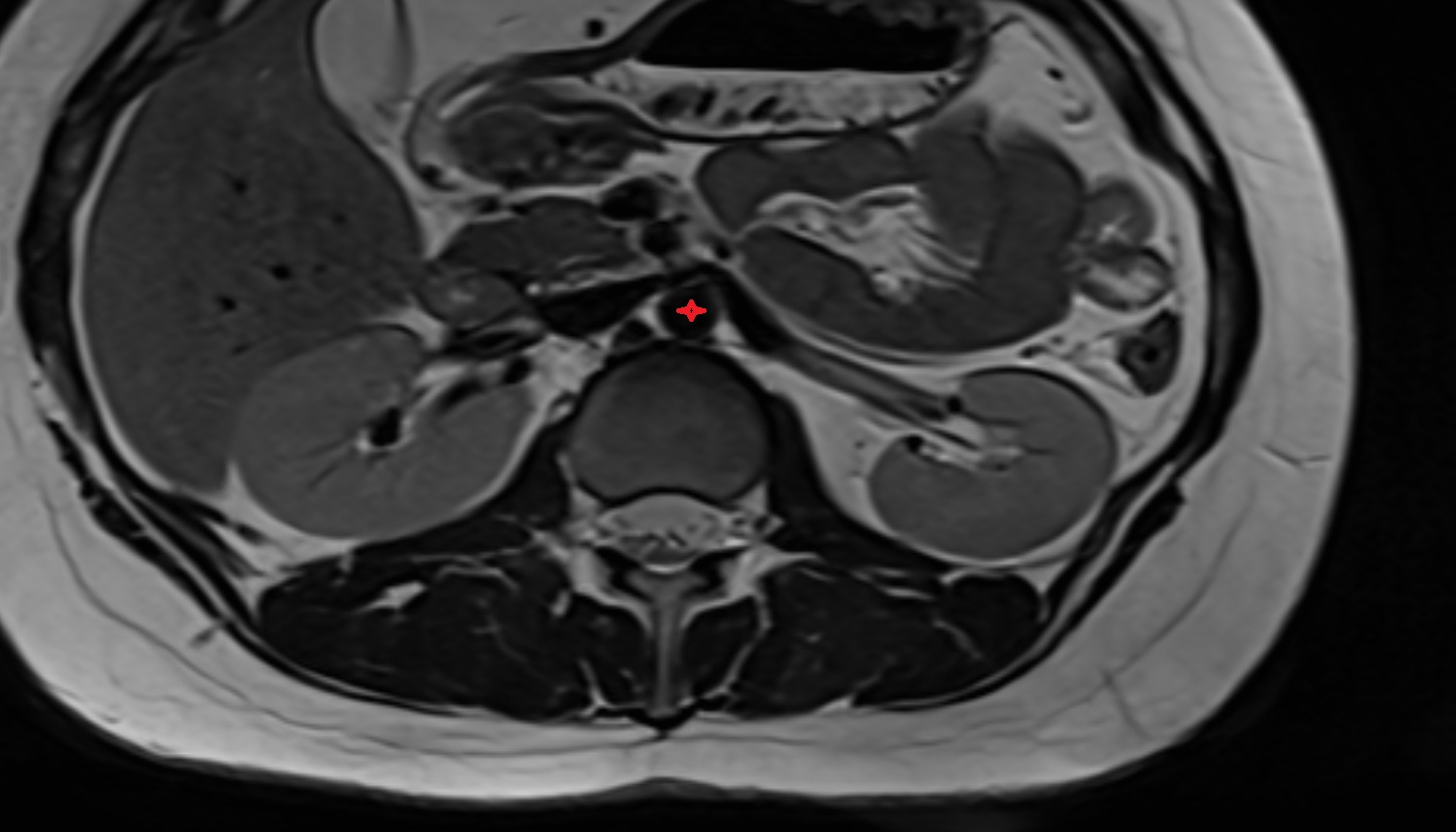
The accessory obturator artery (AOA) is an anatomical variant present in approximately 10–30% of individuals. It typically arises from the external iliac artery or inferior epigastric artery, rather than the internal iliac system. When present, it runs along the superior pubic ramus toward the obturator canal, often forming an anastomosis with the obturator artery.
This artery is clinically significant because it may contribute to the vascularization of the obturator region, pubic bone, and medial thigh, and can create a corona mortis (Latin for "crown of death") when it forms a large pubic anastomosis between the external and internal iliac systems. Injury to this artery during pelvic or hernia surgery can result in life-threatening hemorrhage.
Function
-
Provides collateral circulation to the obturator territory when the main obturator artery is absent, small, or compromised
-
Supplies branches to the pubic bone, hip joint capsule, and adductor muscles
-
Clinically important in pelvic trauma, hernia repairs, orthopedic and gynecological surgery
MRI Appearance
T1-weighted images:
-
Artery appears as a small linear hypointense flow void coursing over the superior pubic ramus
-
Seen within bright perivascular fat of pelvis
T2-weighted images:
-
Artery lumen is a signal void
-
In thrombosed or diseased variants, lumen may appear hyperintense relative to surrounding fat
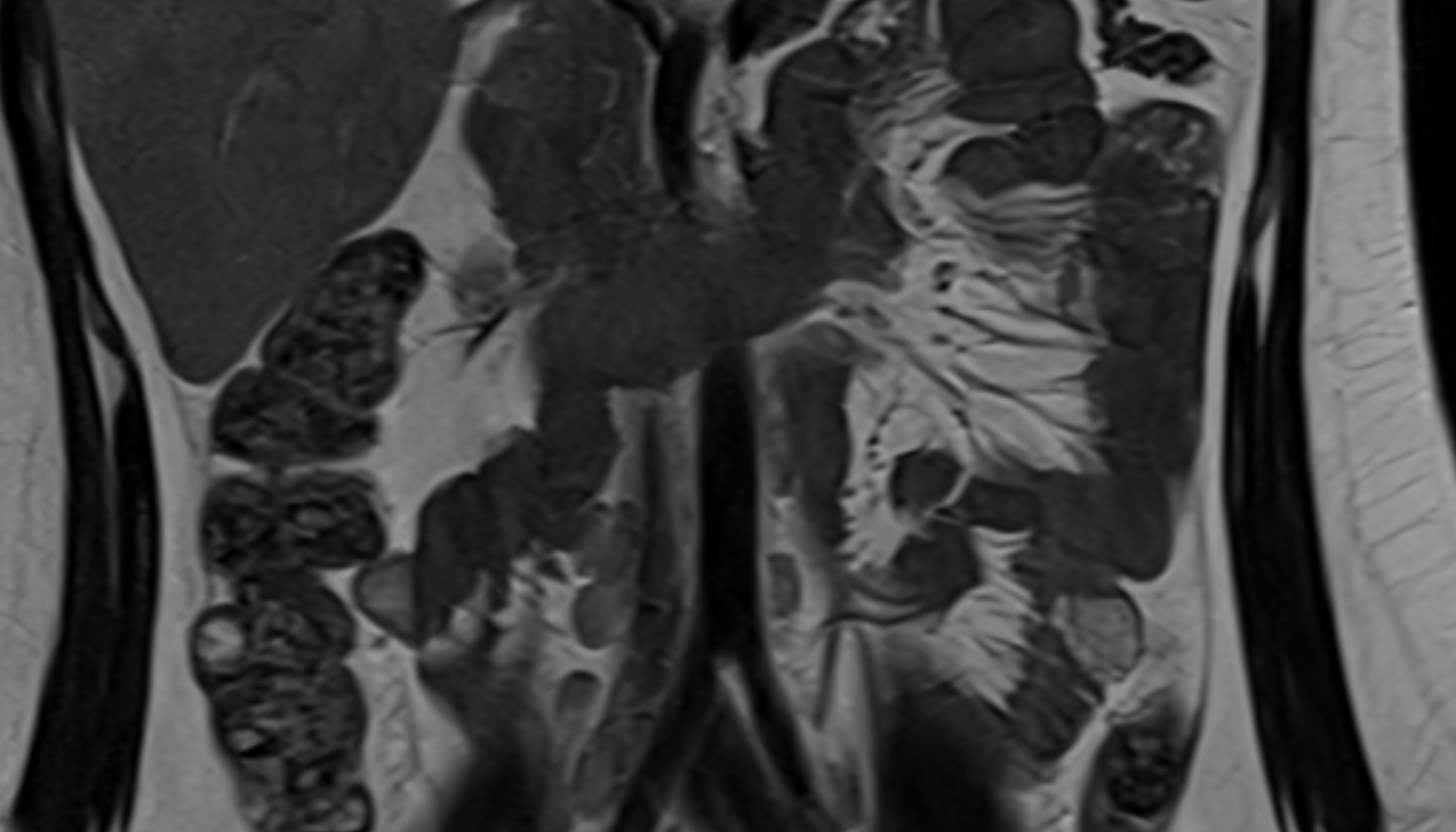
STIR:
-
Fat suppression makes the artery more visible within pelvic fat
-
Helps identify perivascular edema, hematoma, or inflammatory changes
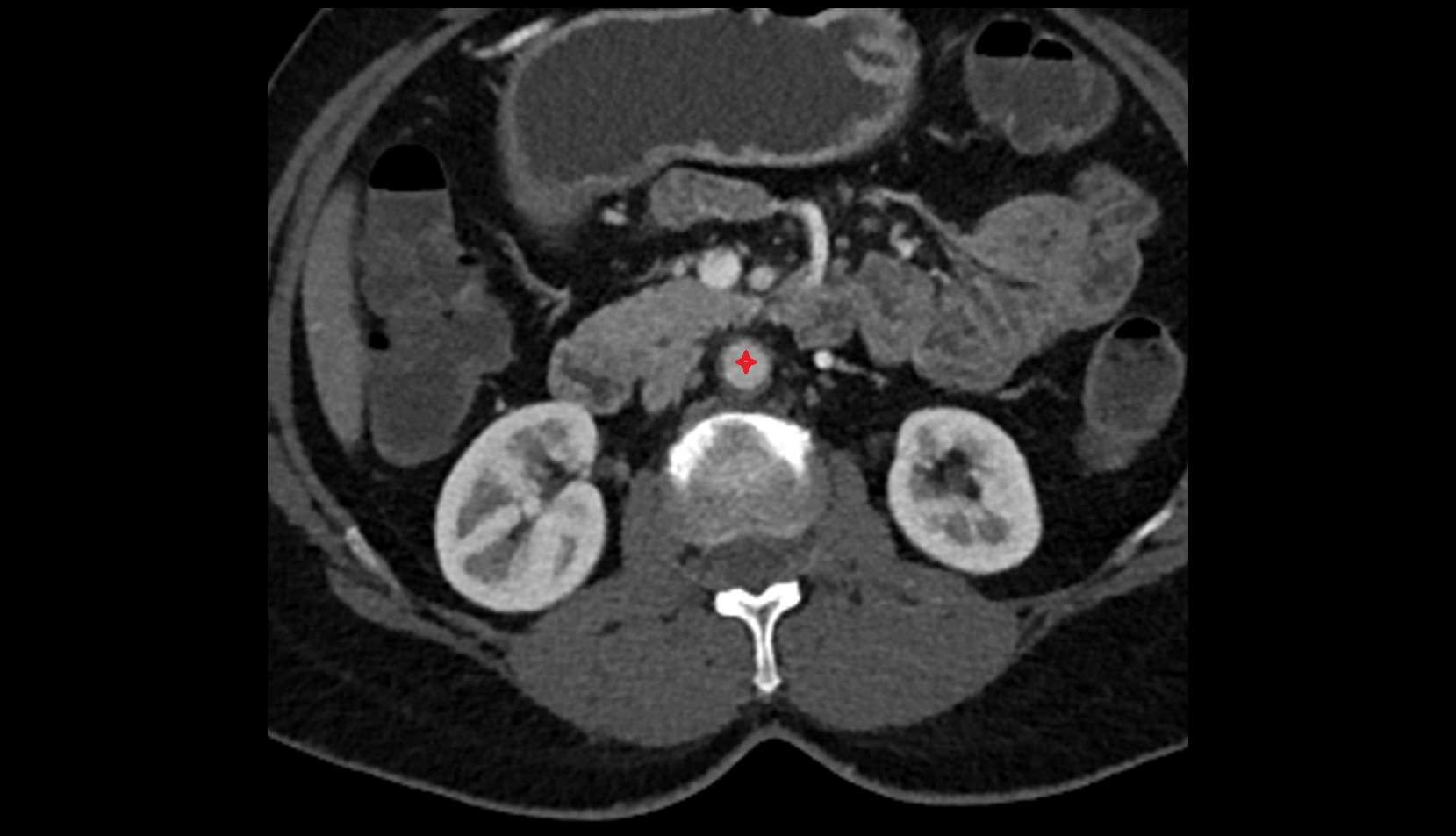
T1 Post-Gadolinium (with fat suppression):
-
Artery enhances brightly and homogeneously
-
Useful for tracing the course, anastomoses, and presence of corona mortis
-
Highlights arterial wall thickening or tumor encasement if present
MRA Pelvis with Gadolinium:
-
Clearly delineates the origin, course, and anastomoses of the accessory obturator artery
-
Identifies connection with inferior epigastric artery, external iliac artery, or obturator artery
-
Excellent for detecting vascular variants prior to surgery
-
Useful in mapping pelvic vasculature in trauma, tumor embolization, or preoperative planning
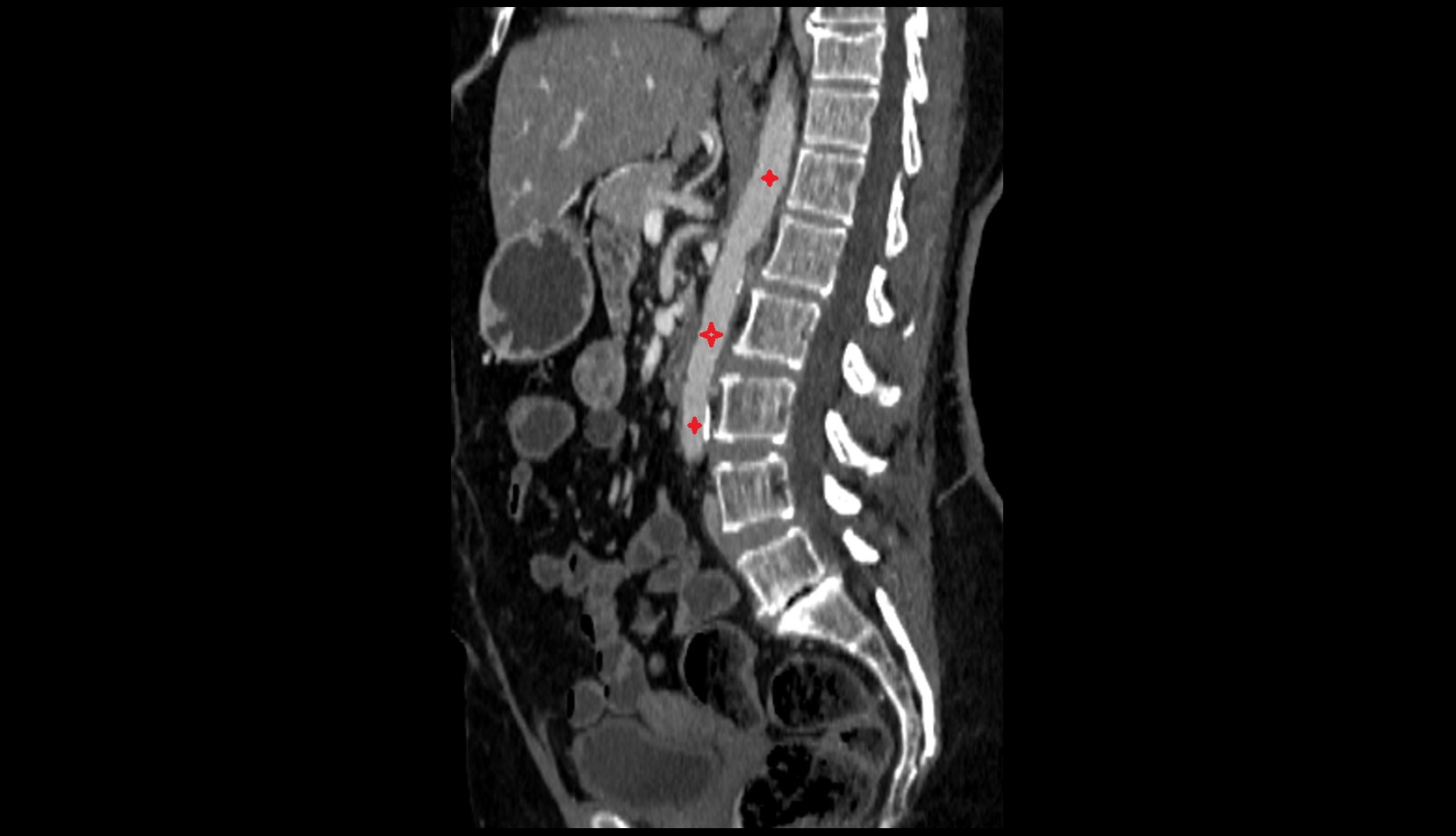
CT Appearance
Non-contrast CT:
-
Artery not well seen without contrast
-
Can suggest its location along the superior pubic ramus by small vessel density
CT Post-Contrast:
-
Vessel opacifies clearly along superior pubic ramus
-
Detects vascular variants, aneurysms, or active bleeding
-
Important in trauma imaging when pelvic fractures are associated with hemorrhage