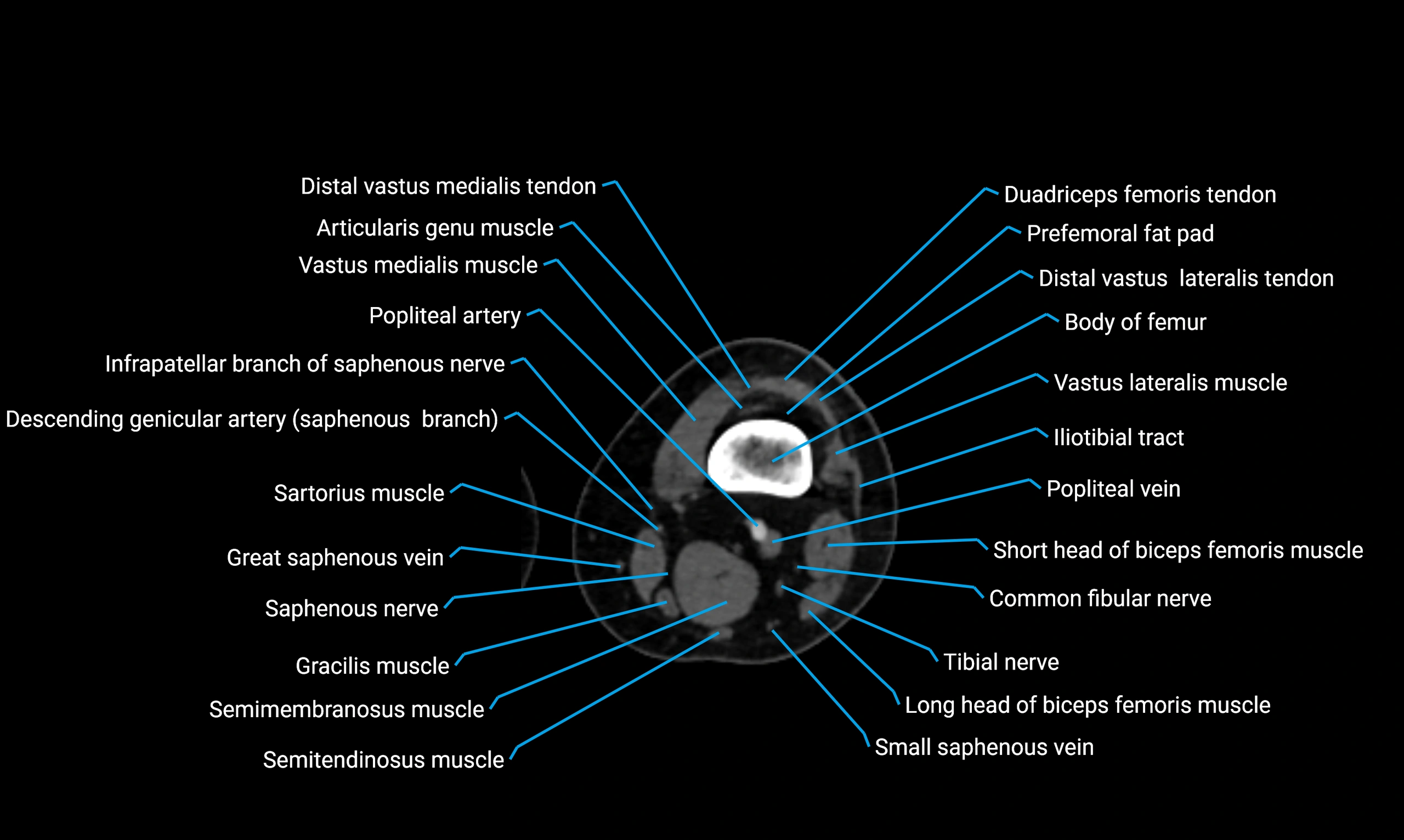
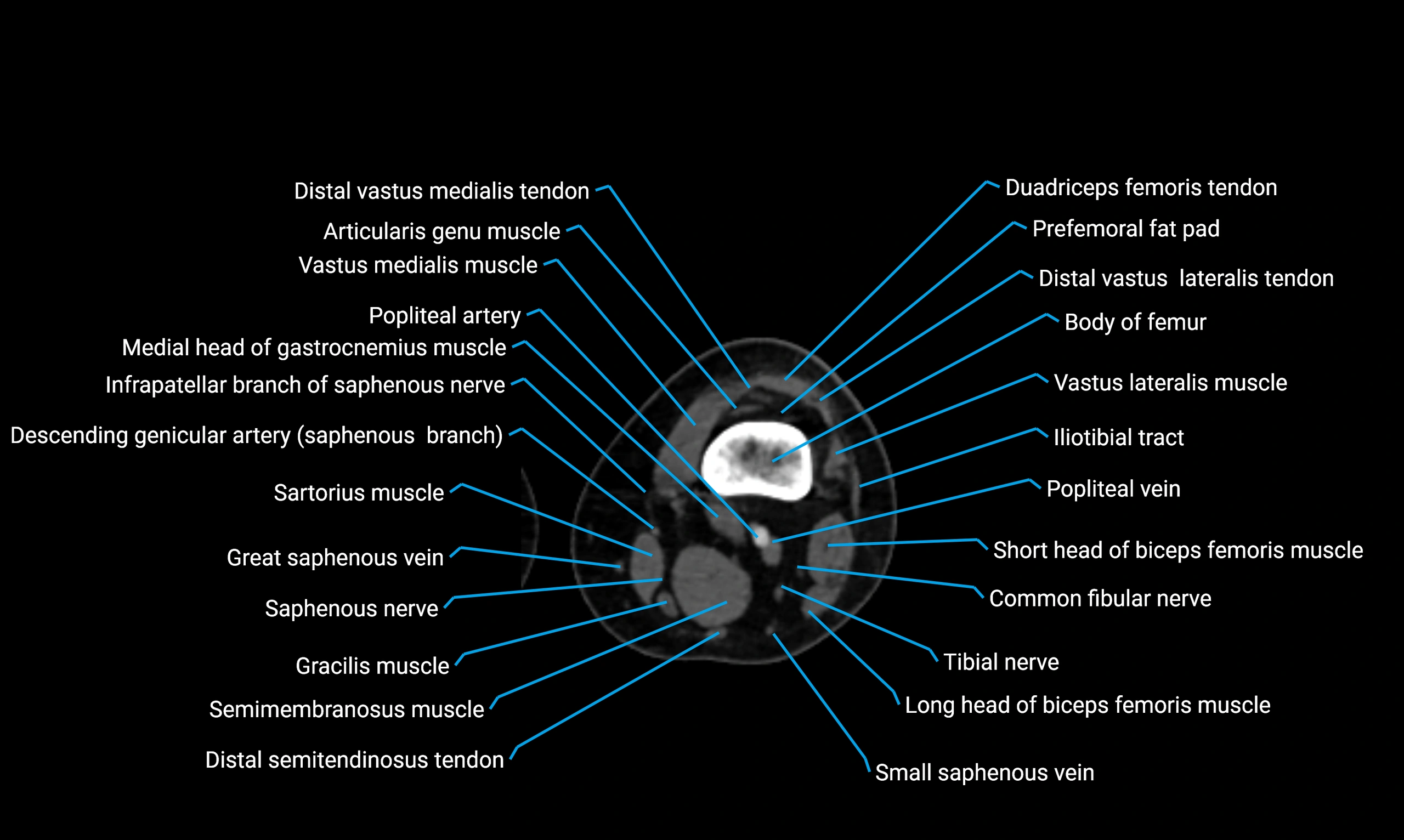
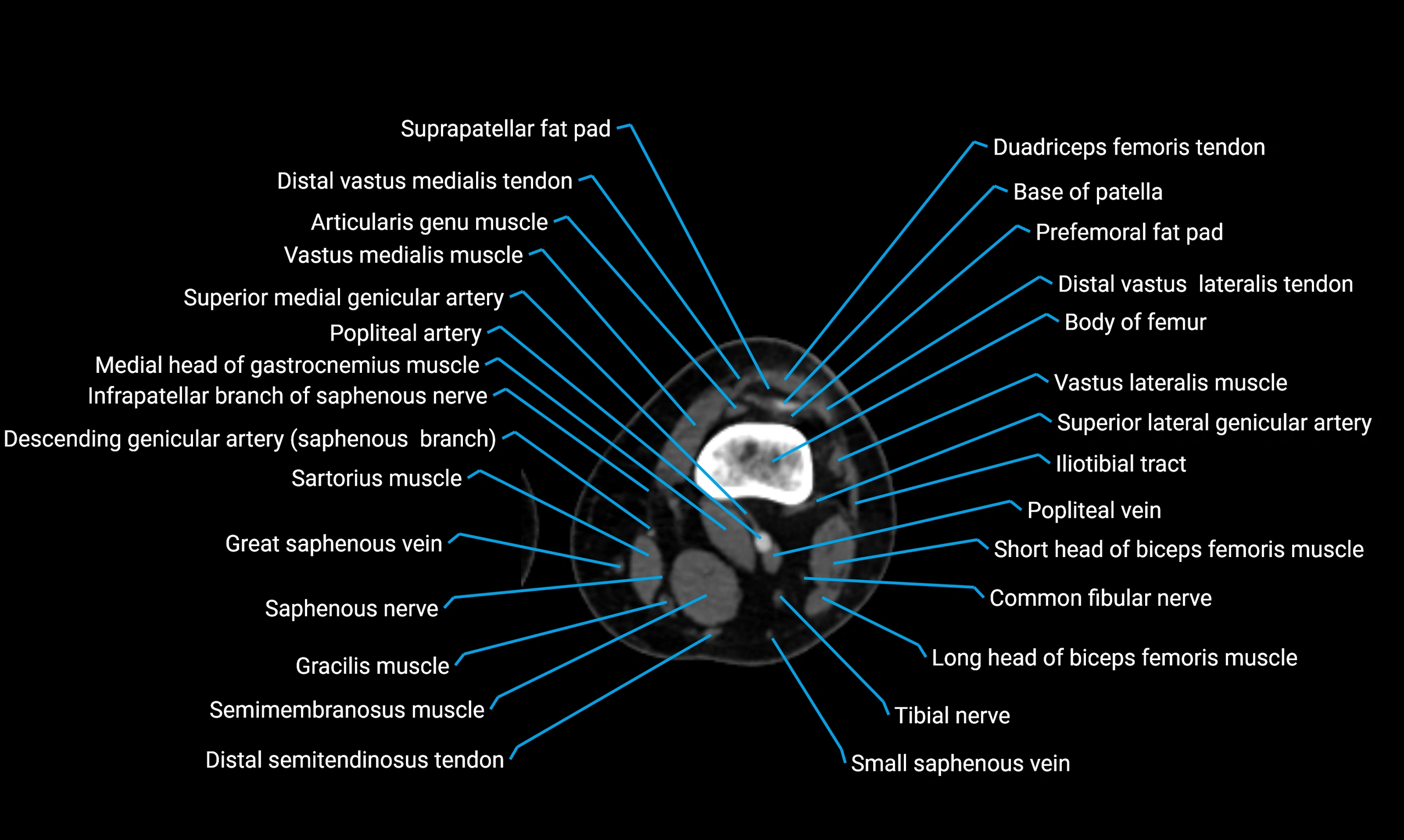
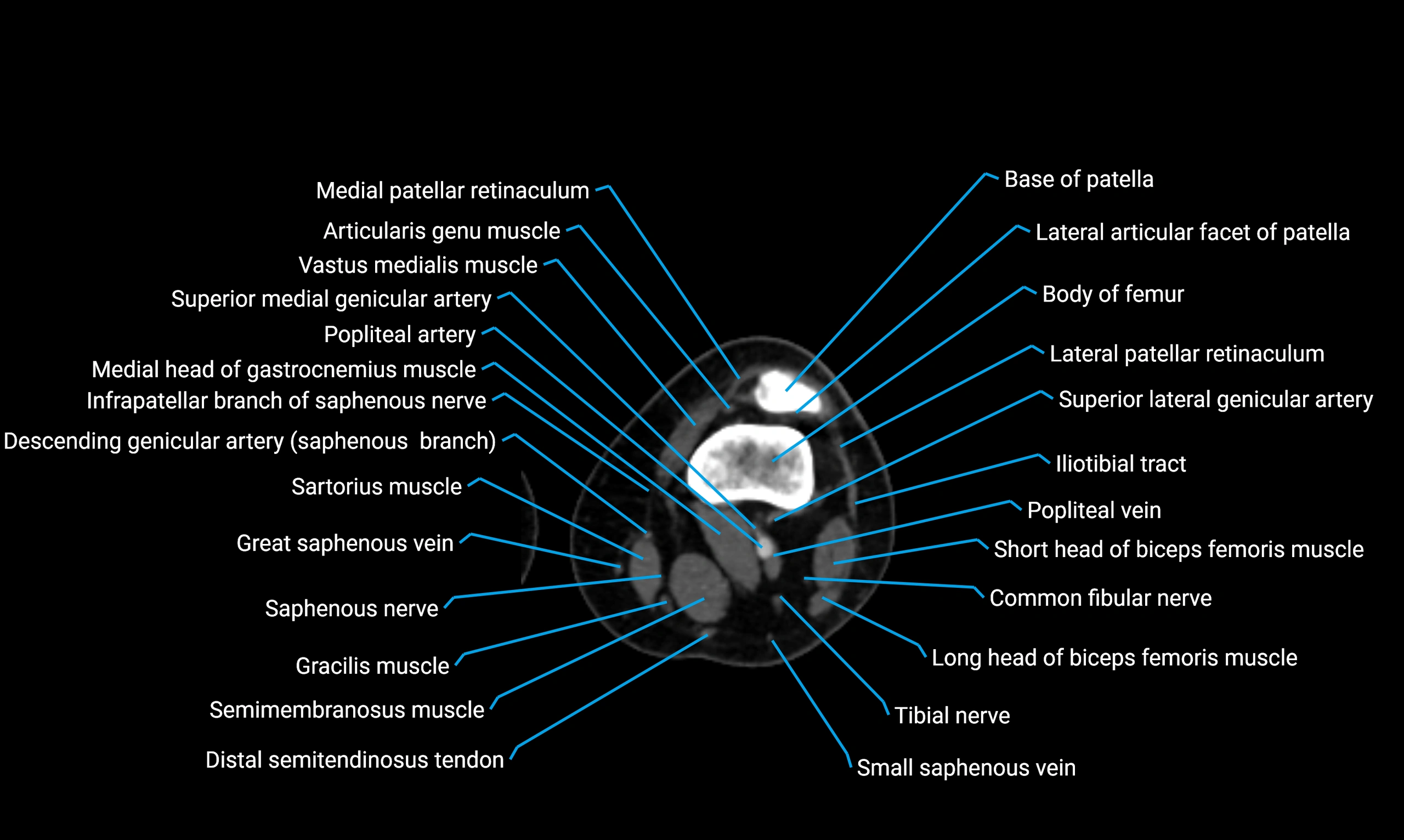
Topic
- Acetabular margin (Acetabular rim)
- Acetabular notch
- Acetabulum
- Adductor brevis muscle
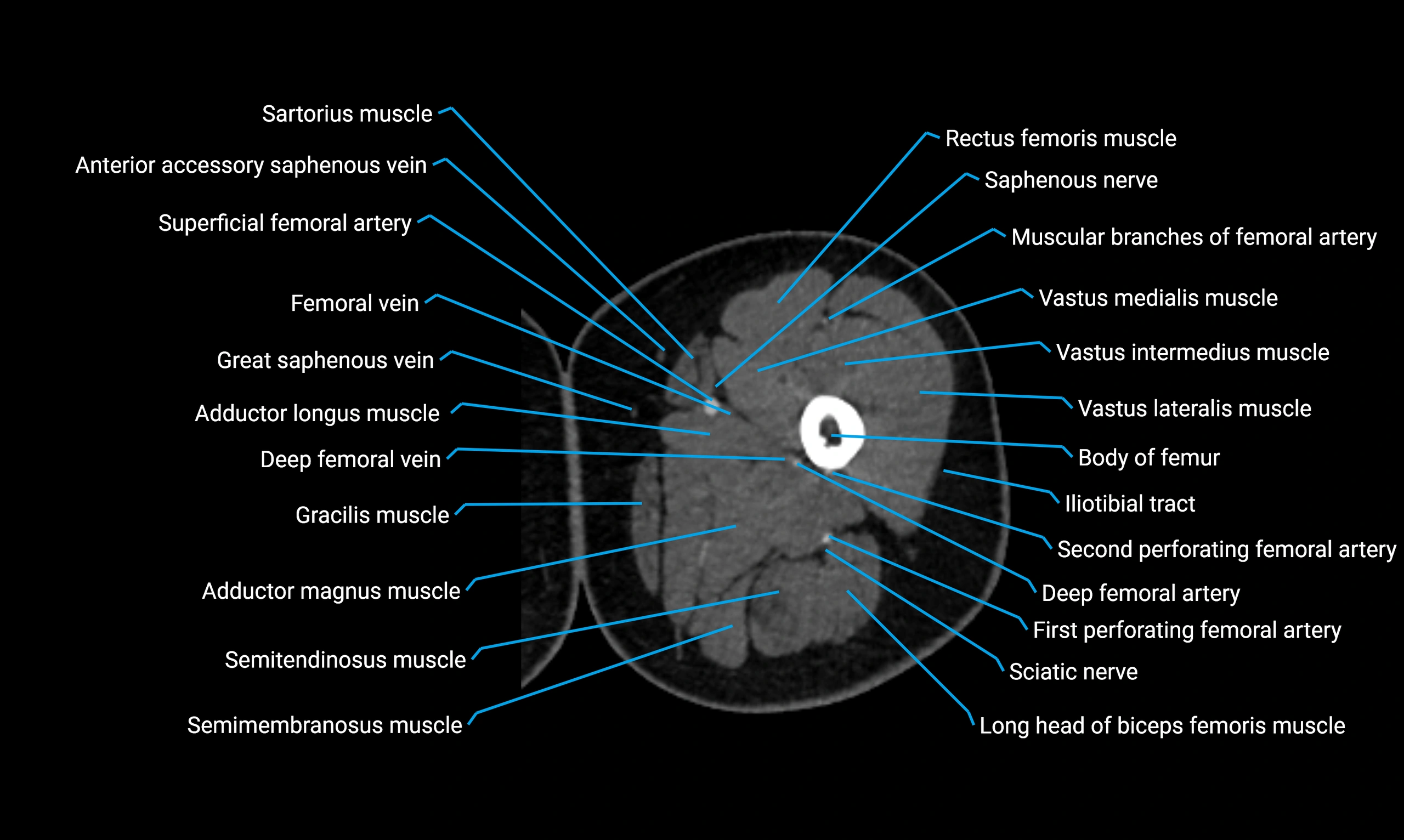
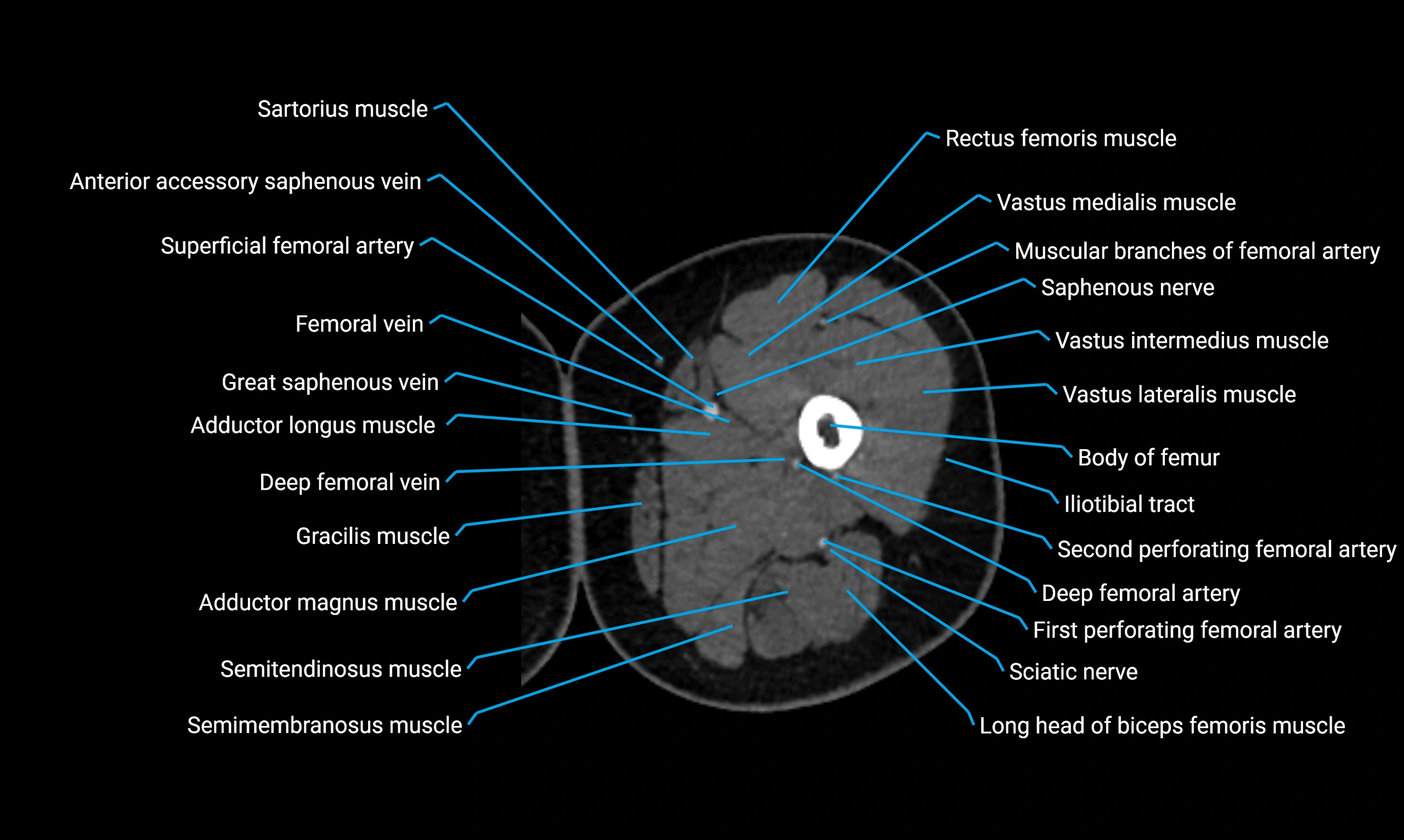
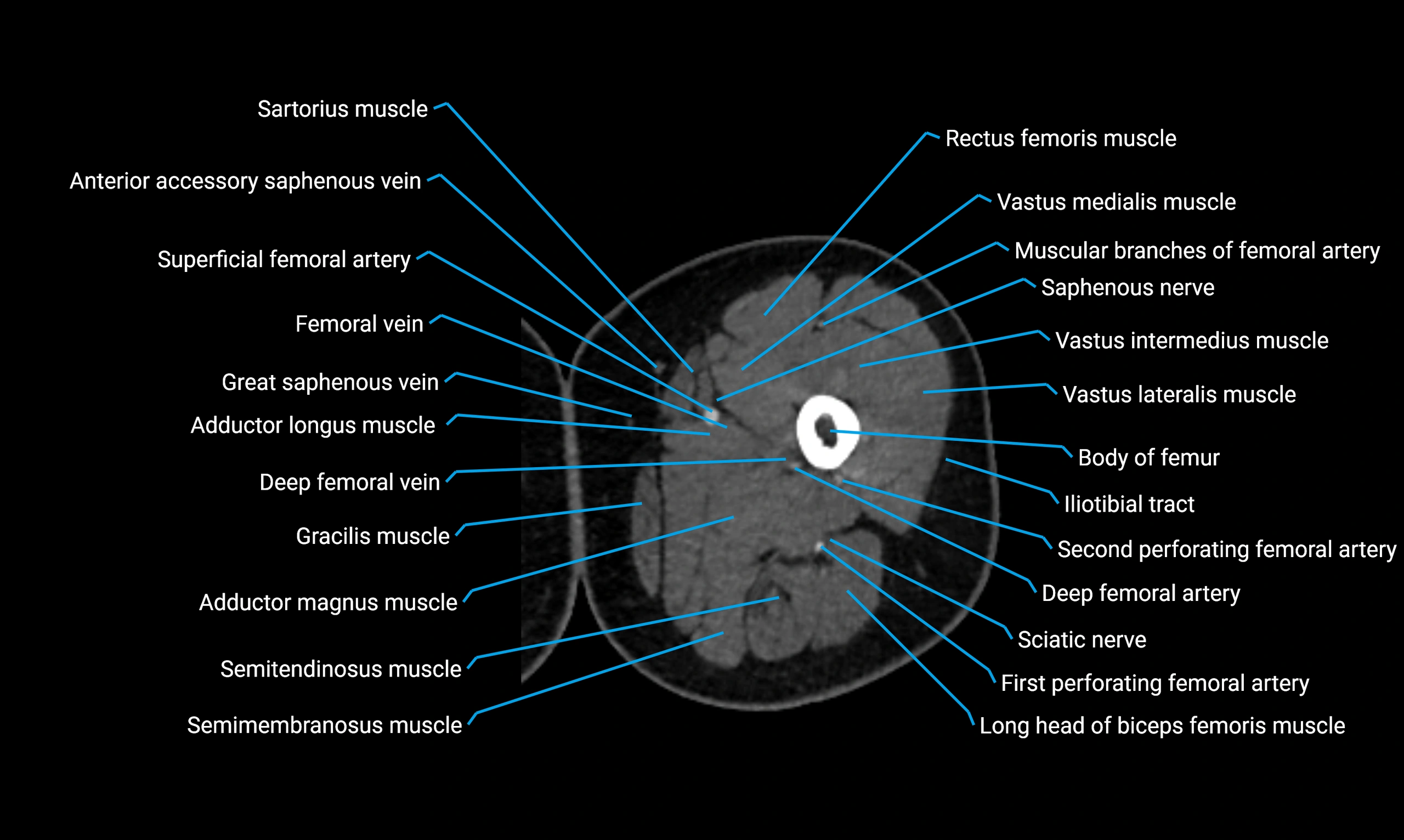
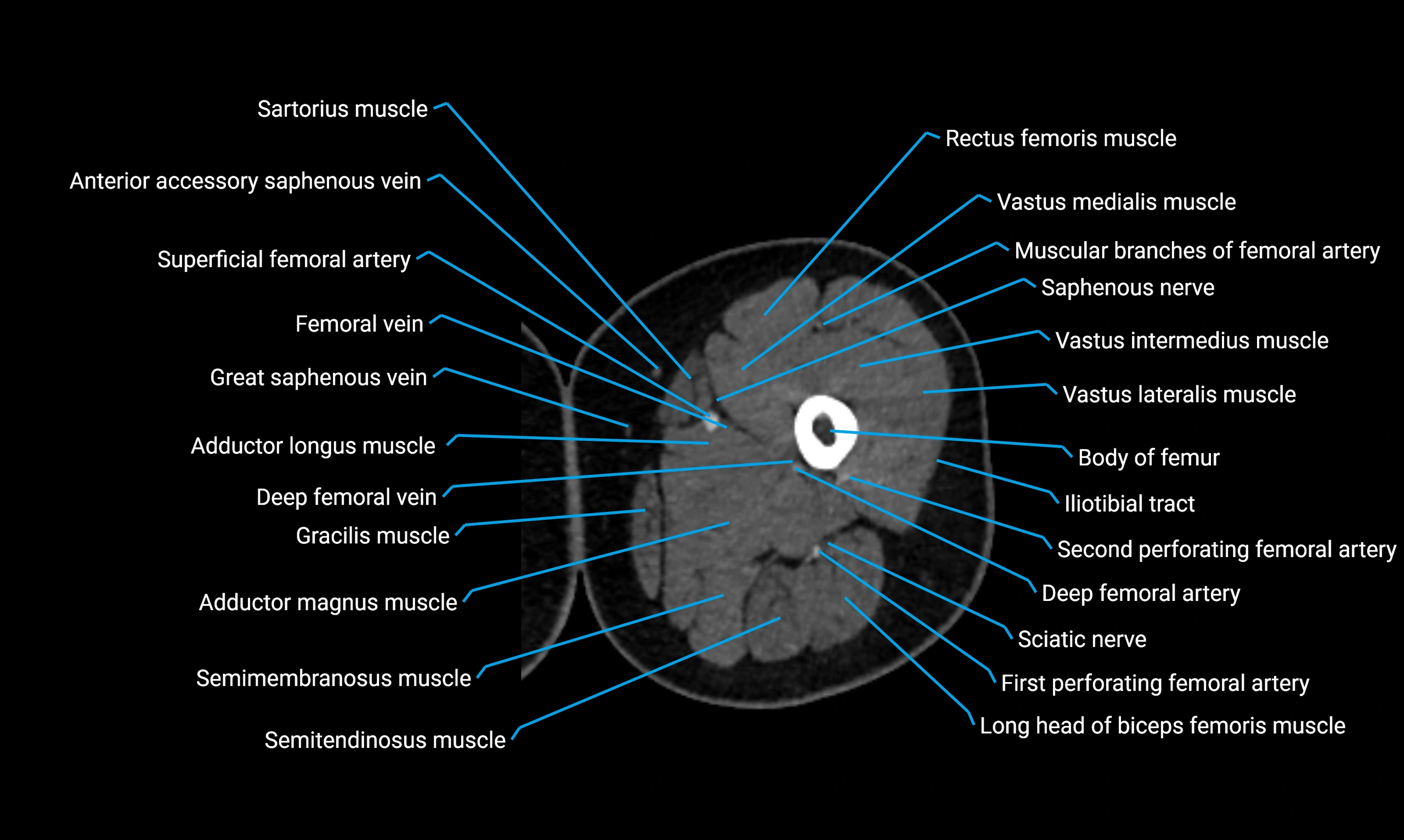
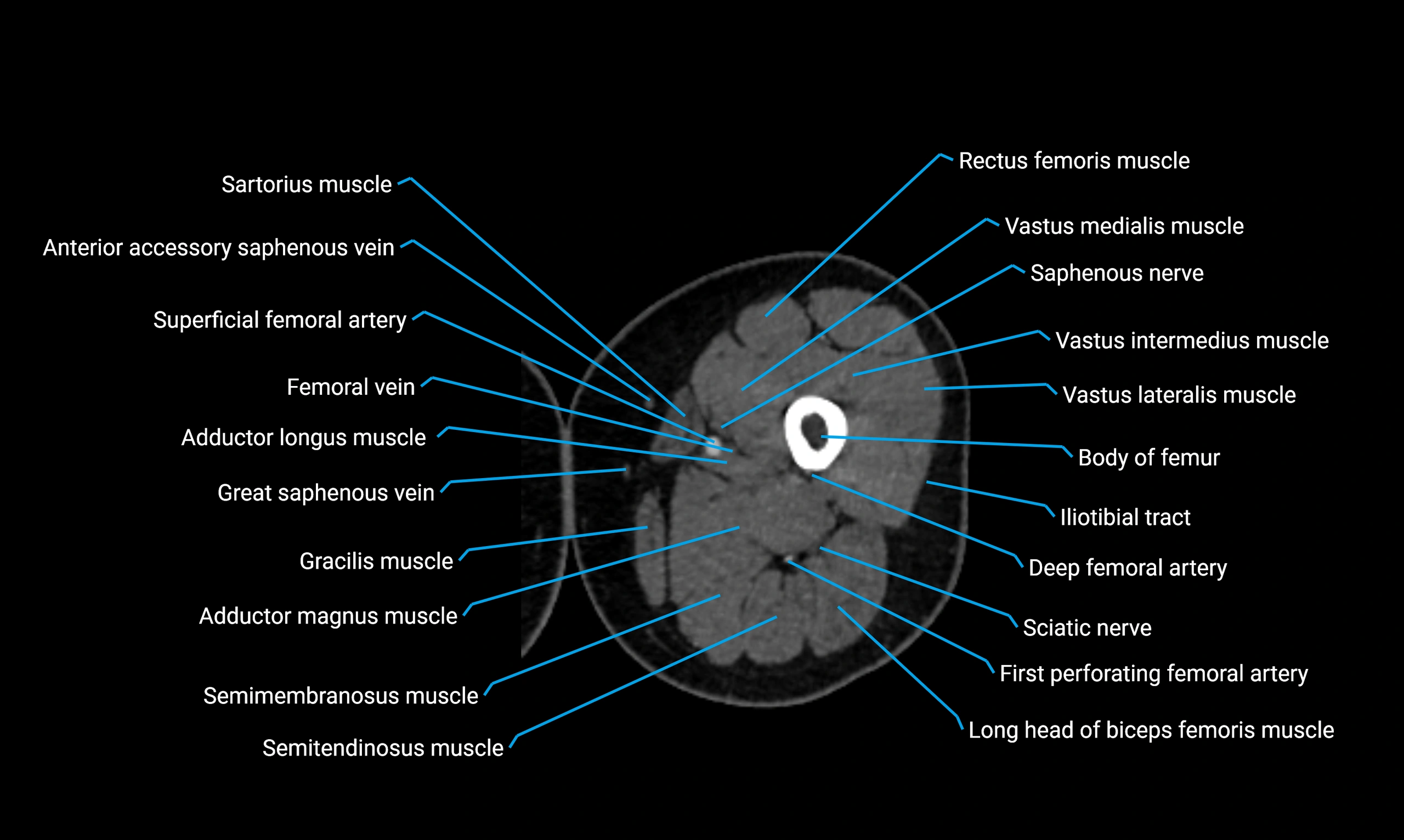
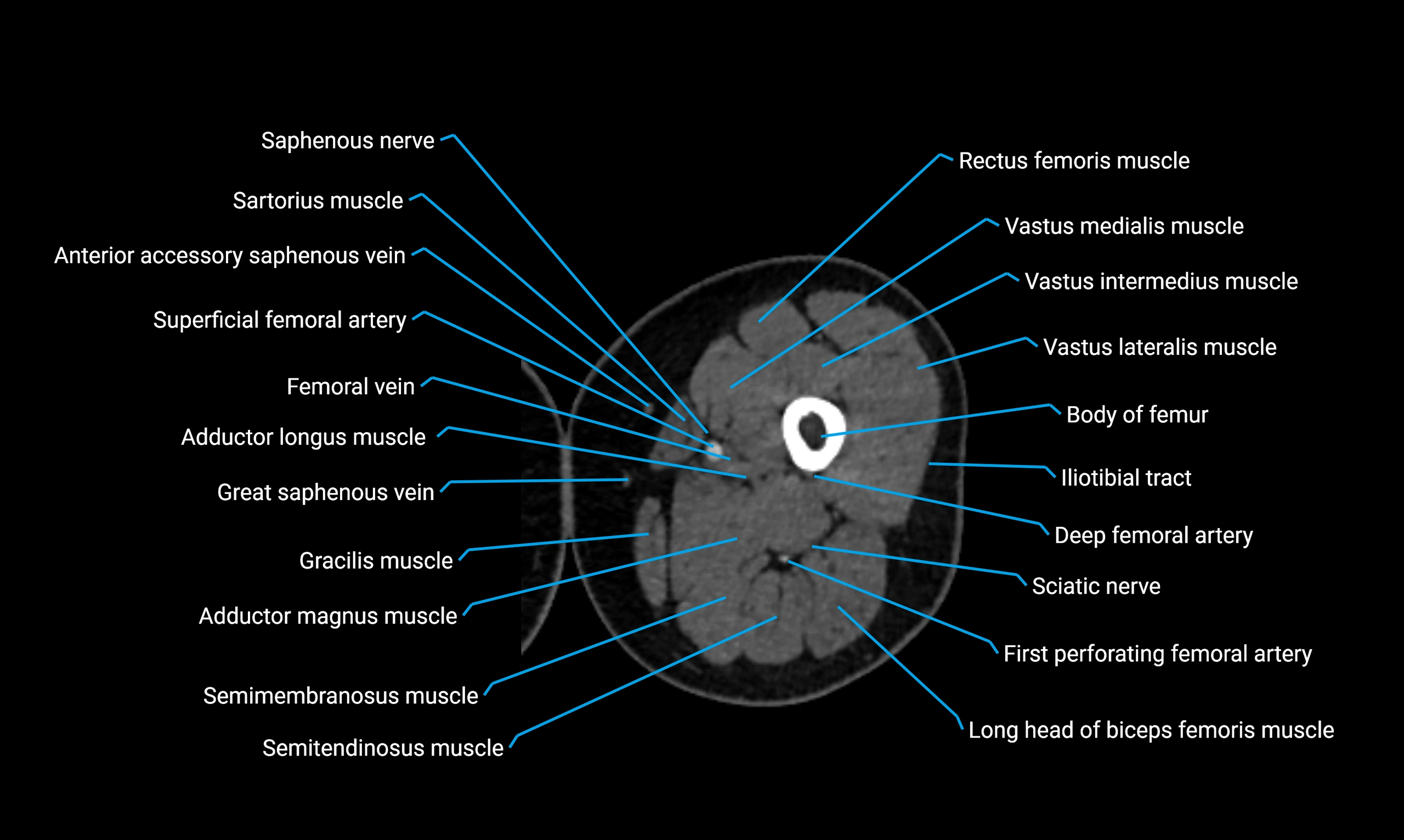
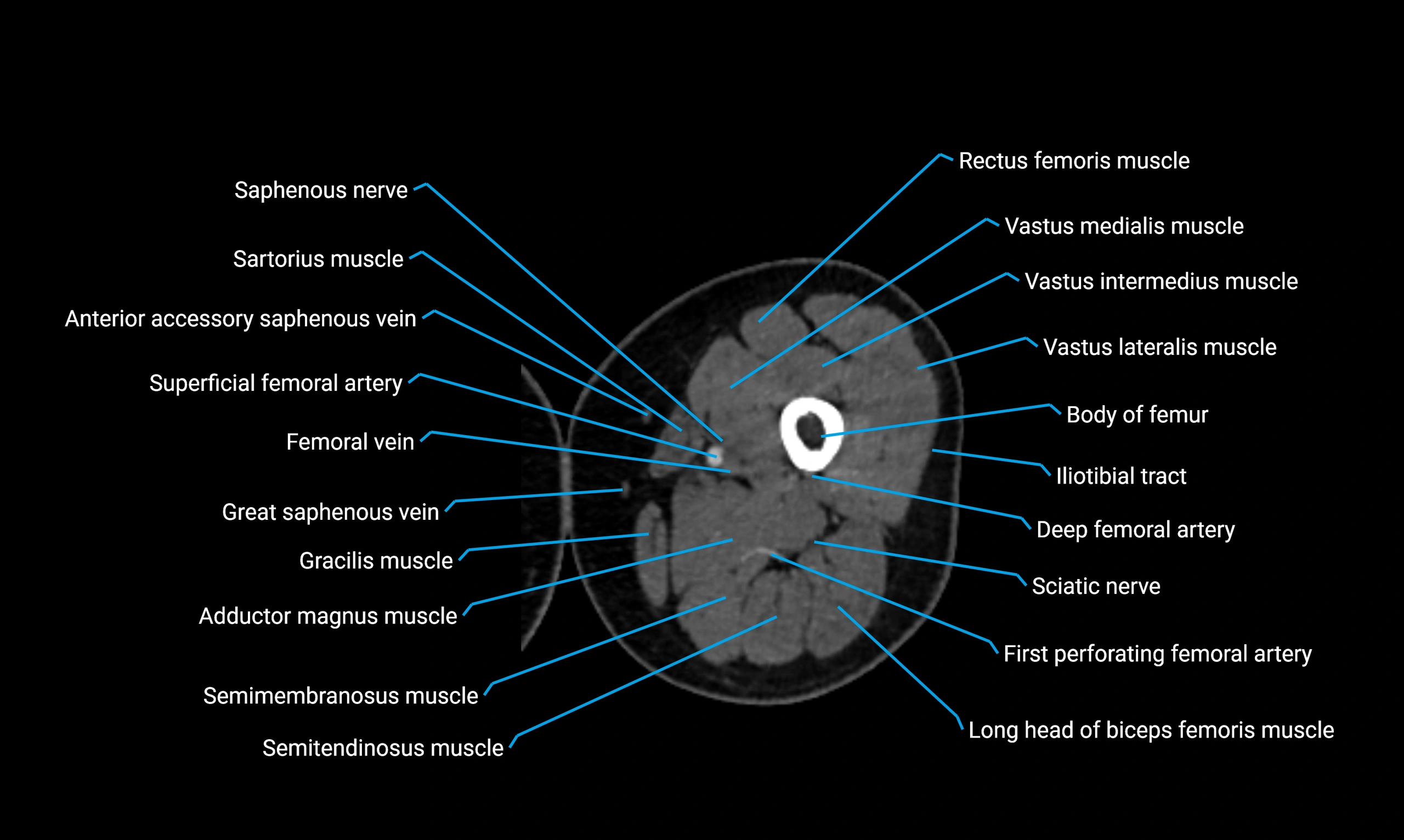
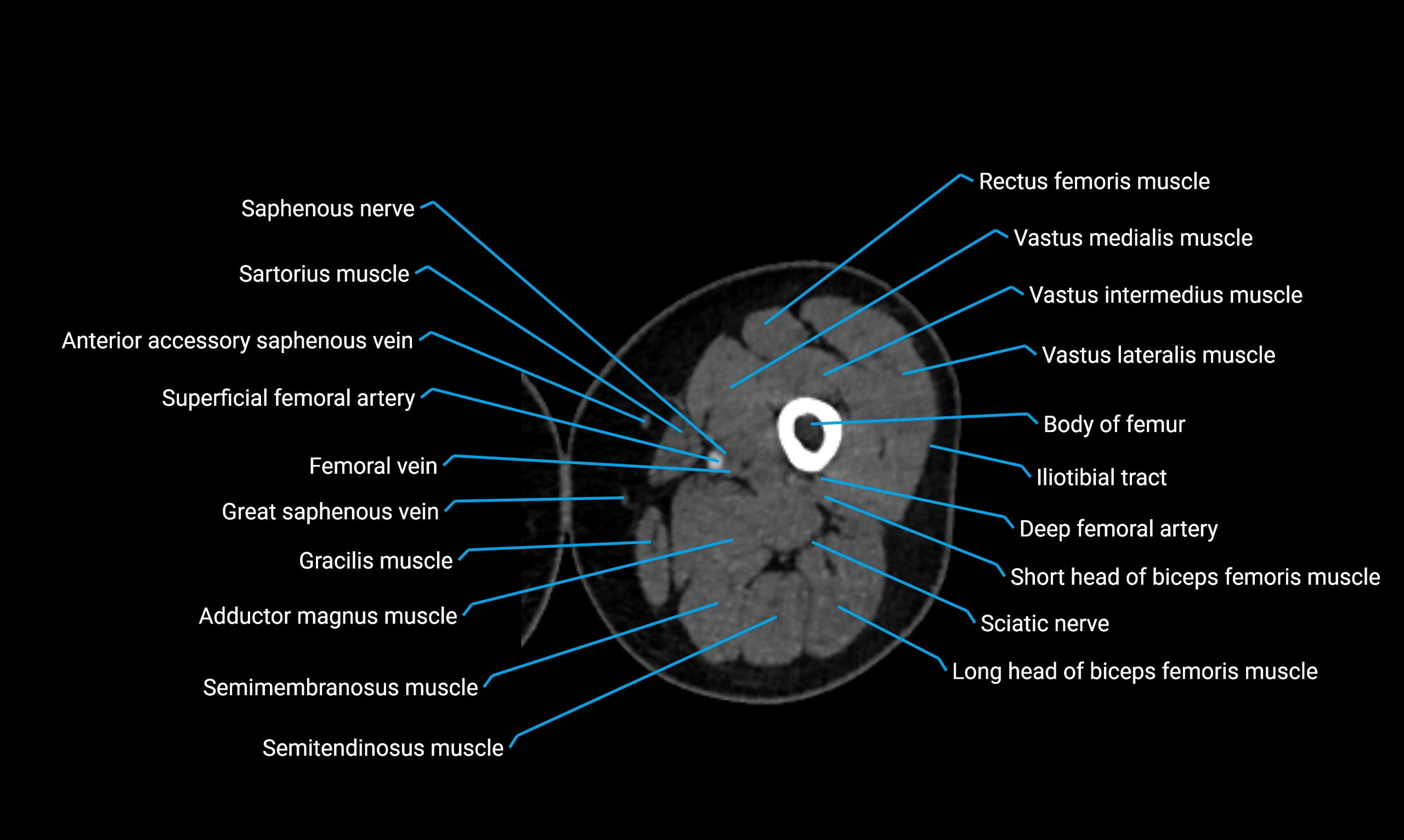
- Adductor longus muscle
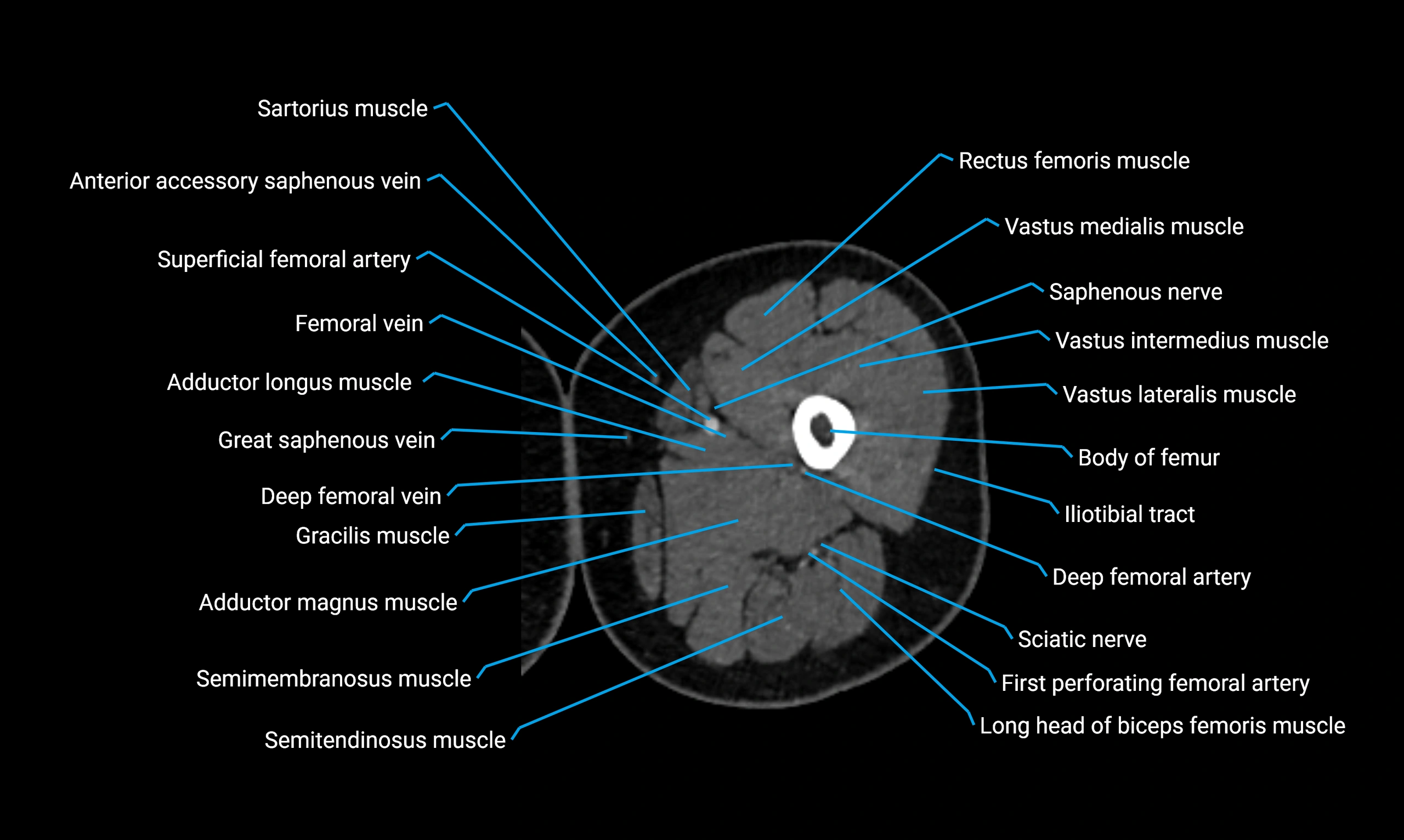
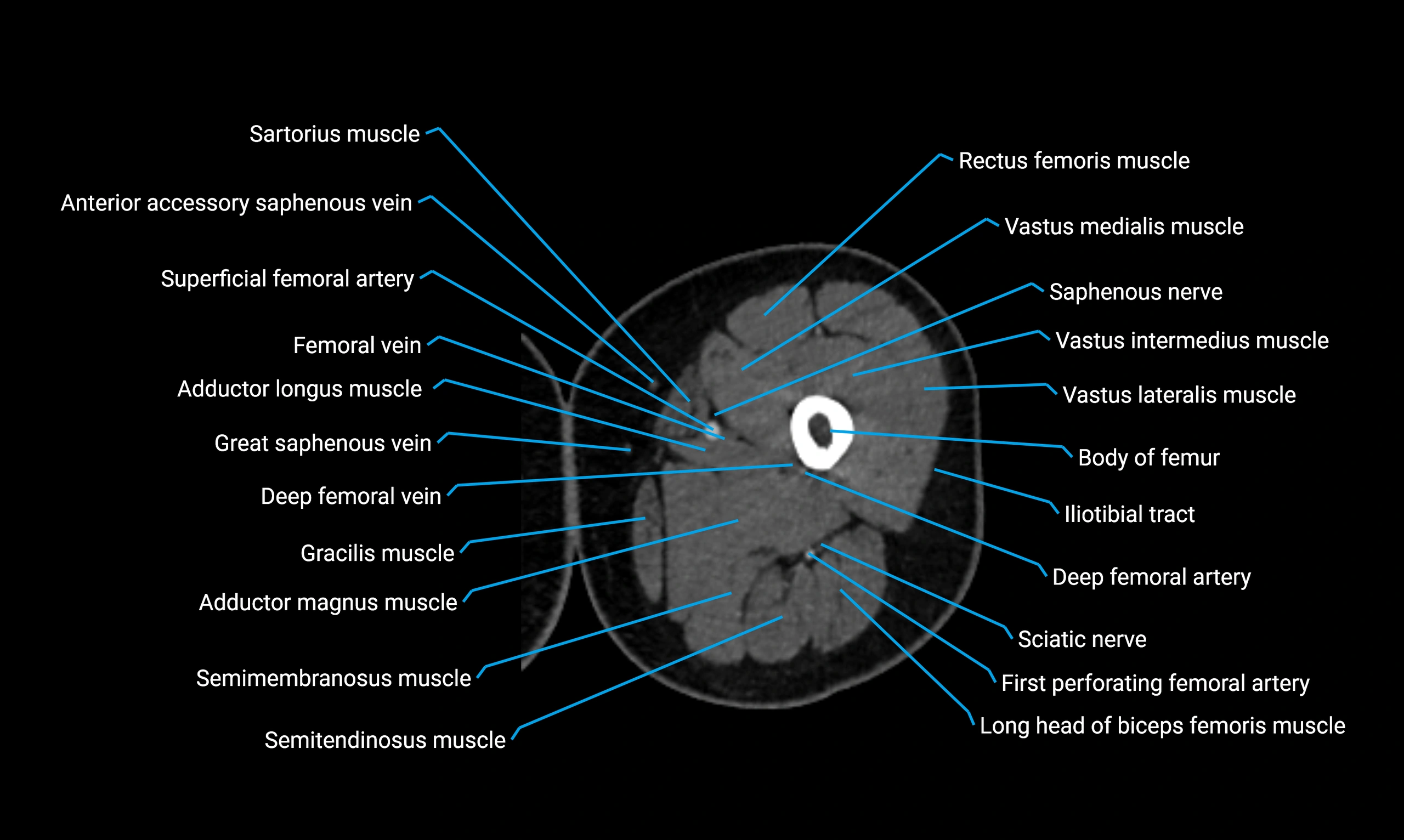
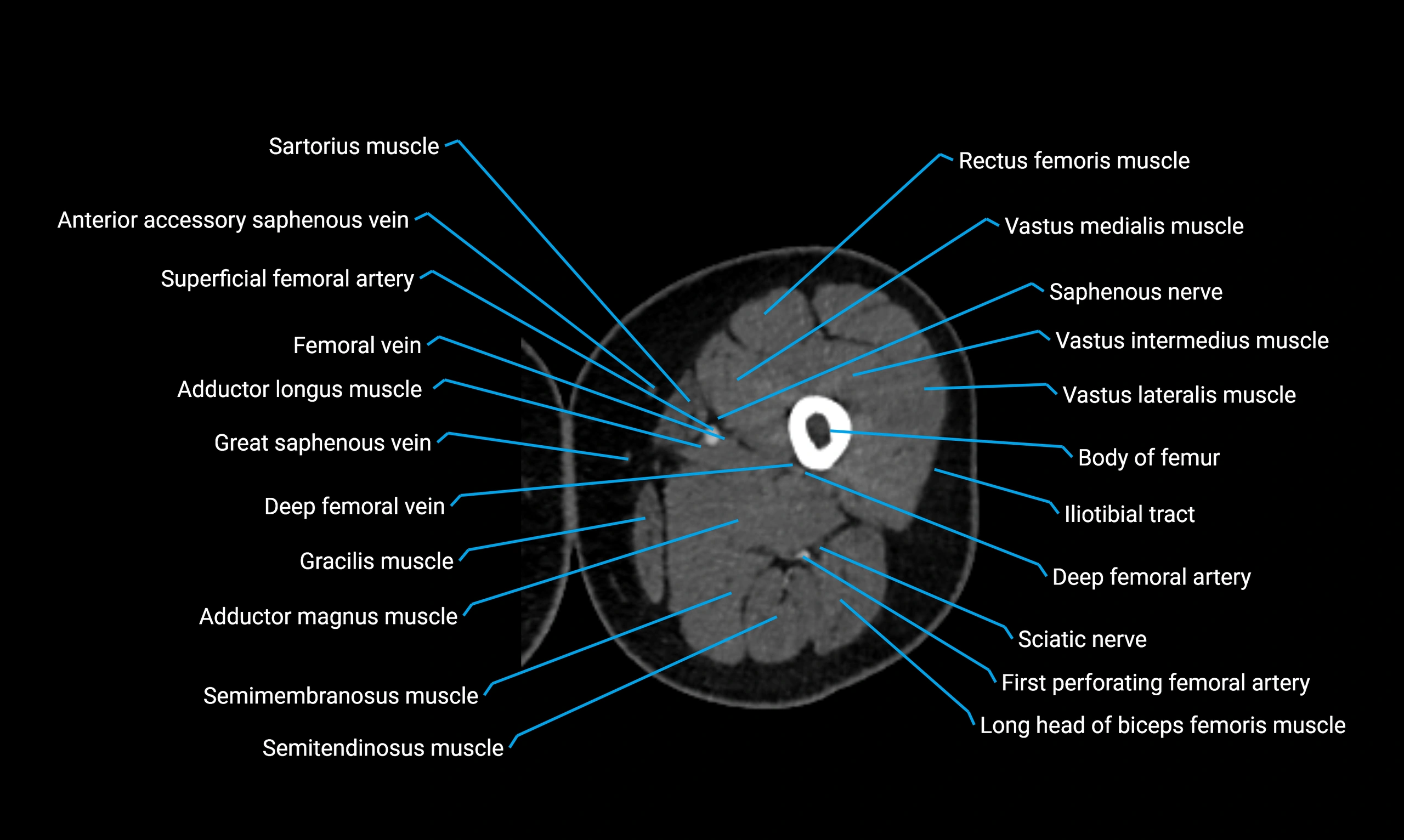
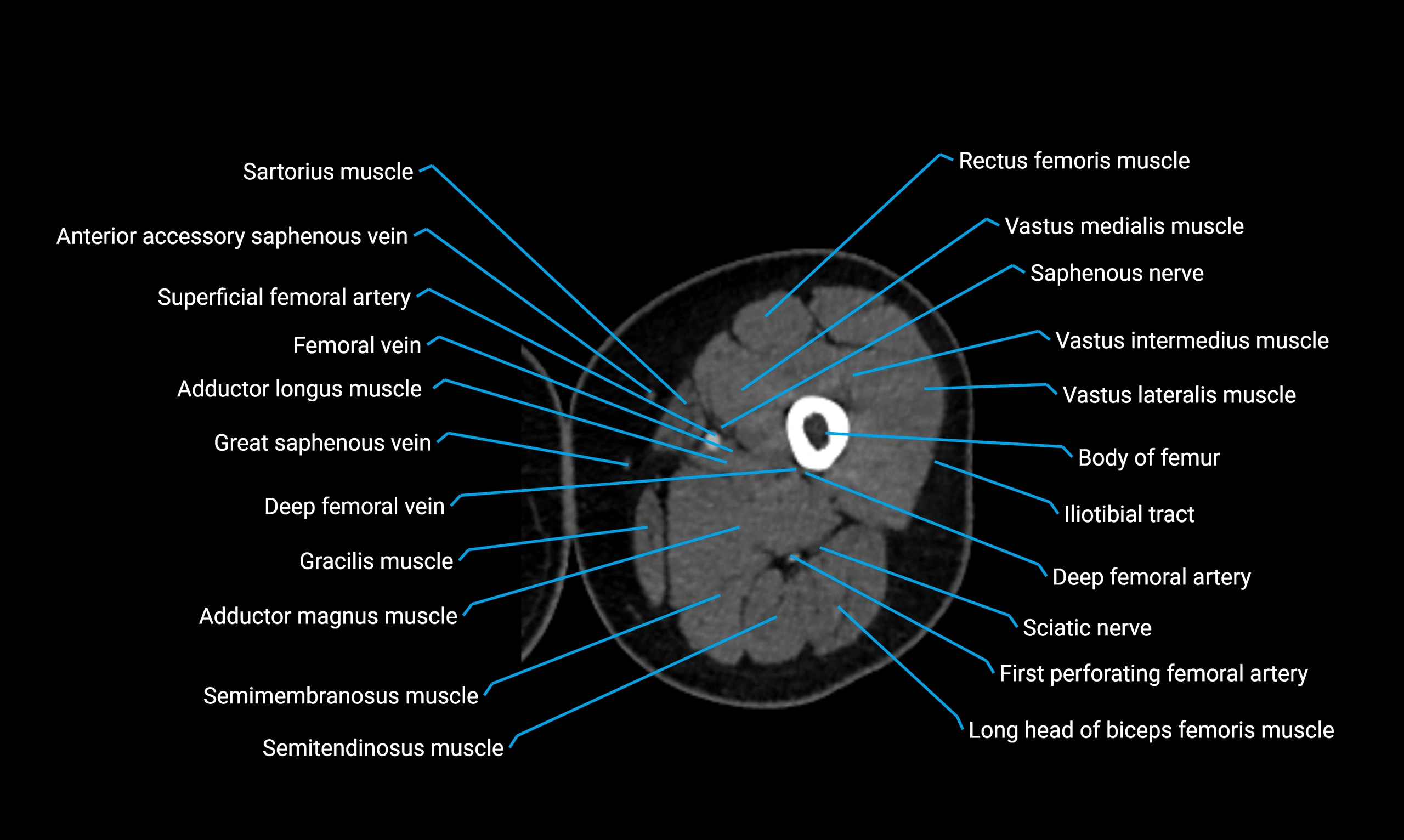
- Adductor magnus muscle
- Adductor minimus muscle
- Adductor tubercle
- Ala of ilium (wing of ilium)
- Anal canal
- Anococcygeal body (anococcygeal ligament)
- Anterior acetabular wall
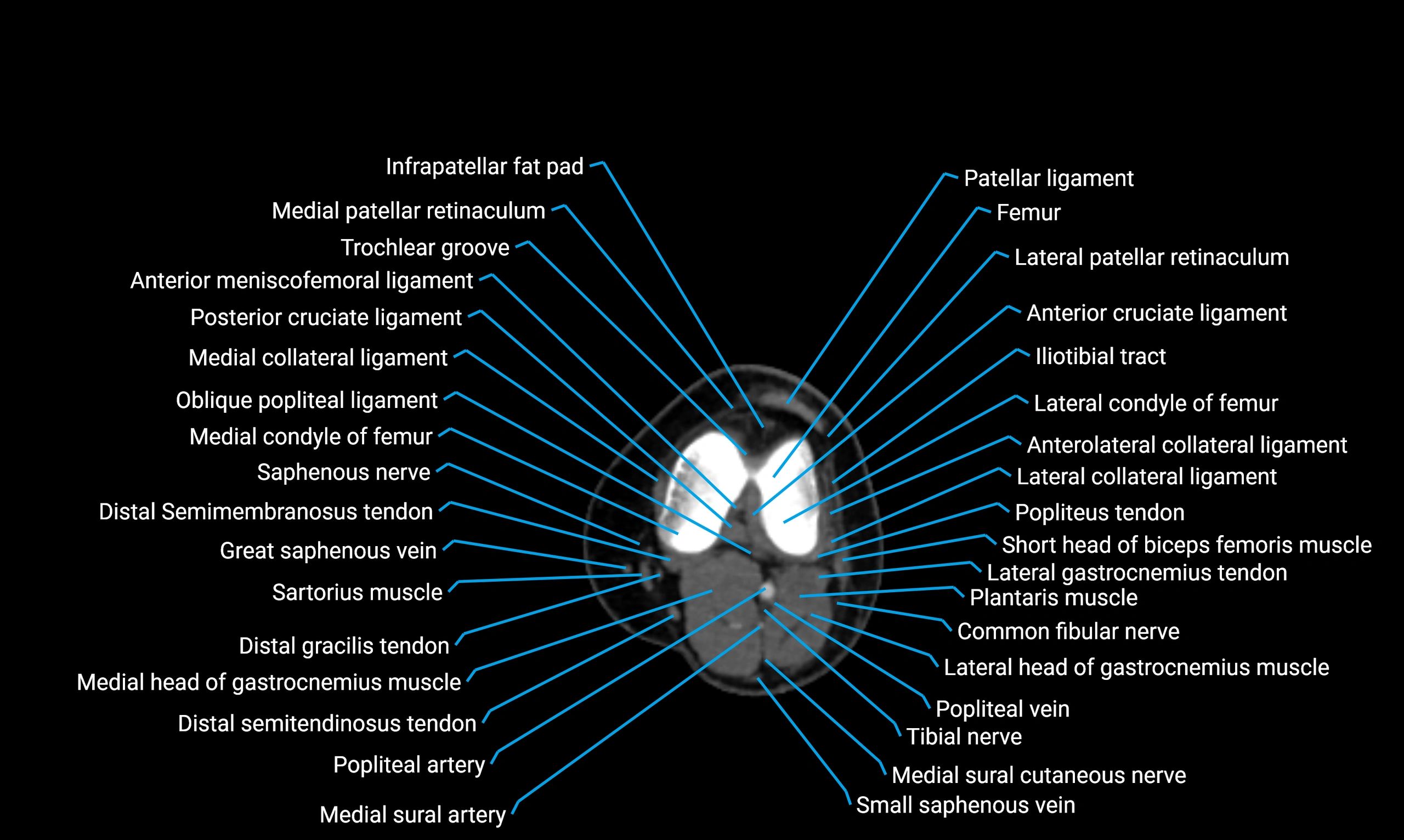
- Anterior cruciate ligament
- Anterior division of obturator nerve (Anterior branch of obturator nerve)
- Anterior horn of lateral meniscus
- Anterior horn of medial meniscus
- Anterior inferior iliac spine
- Anterior lateral femoral cutaneous nerve
- Anterior ligament of fibular head
- Anterior meniscofemoral ligament
- Anterior rim of acetabulum
- Anterior root of lateral meniscus
- Anterior root of medial meniscus
- Anterior sacral foramina
- Anterior superior iliac spine
- Anterior wall of acetabulum
- Anterolateral ligament of knee
- Apex of head of fibula
- Apex of patella
- Arcuate popliteal ligament
- Articular facet of head of fibula
- Articular surface of lateral femoral condyle
- Articular surface of lateral tibial condyle
- Articular surface of medial femoral condyle
- Articular surface of medial tibial condyle
- Base of patella
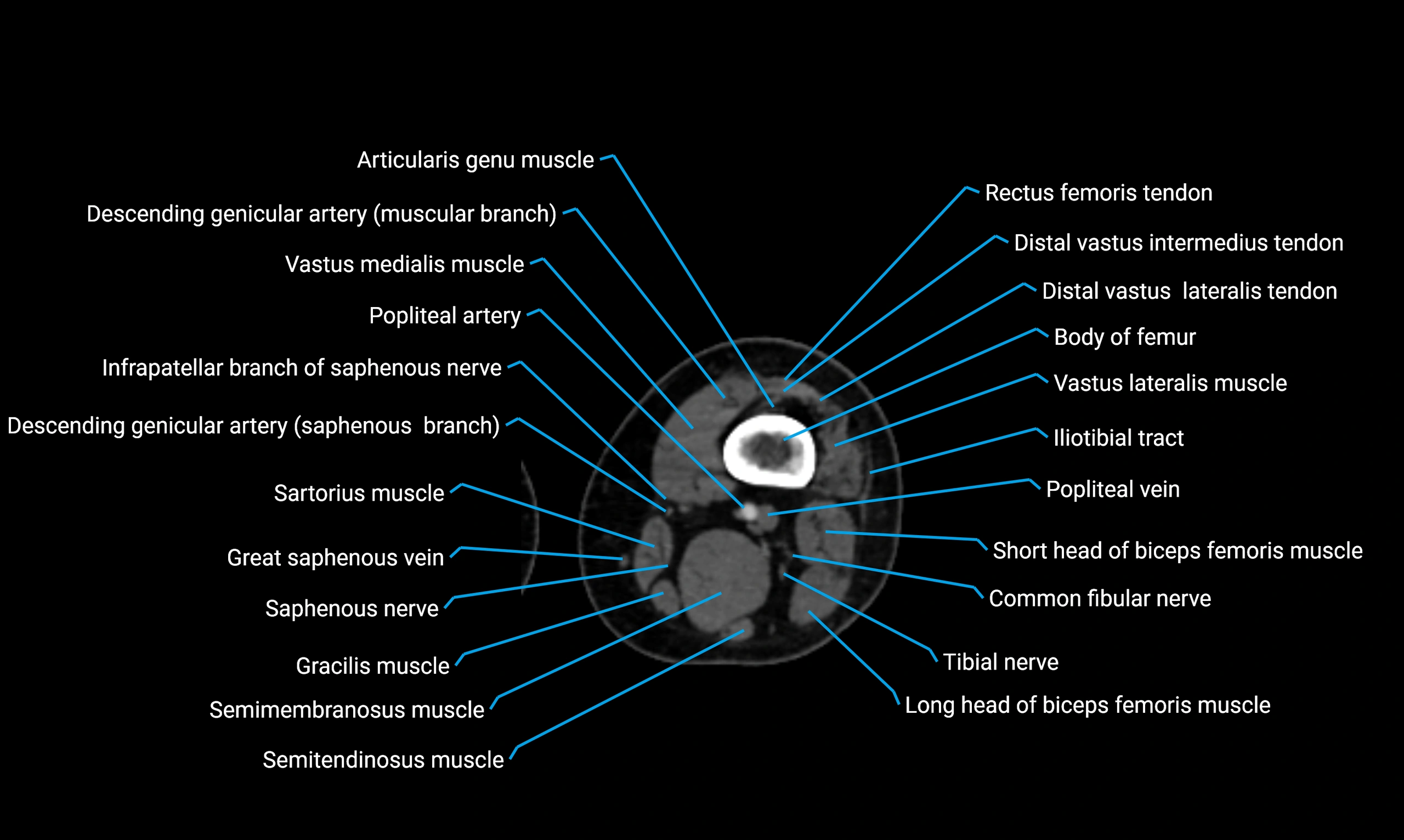
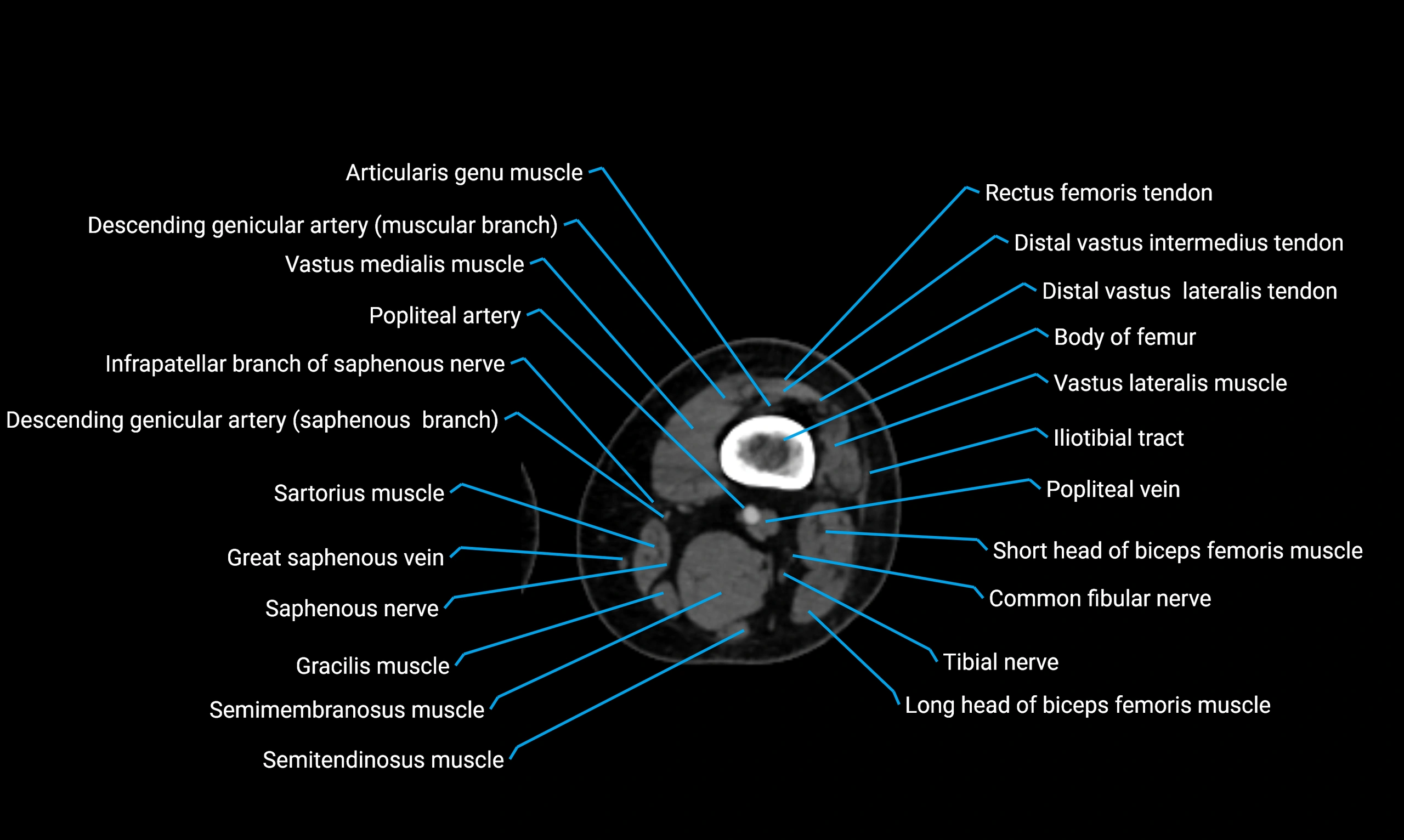
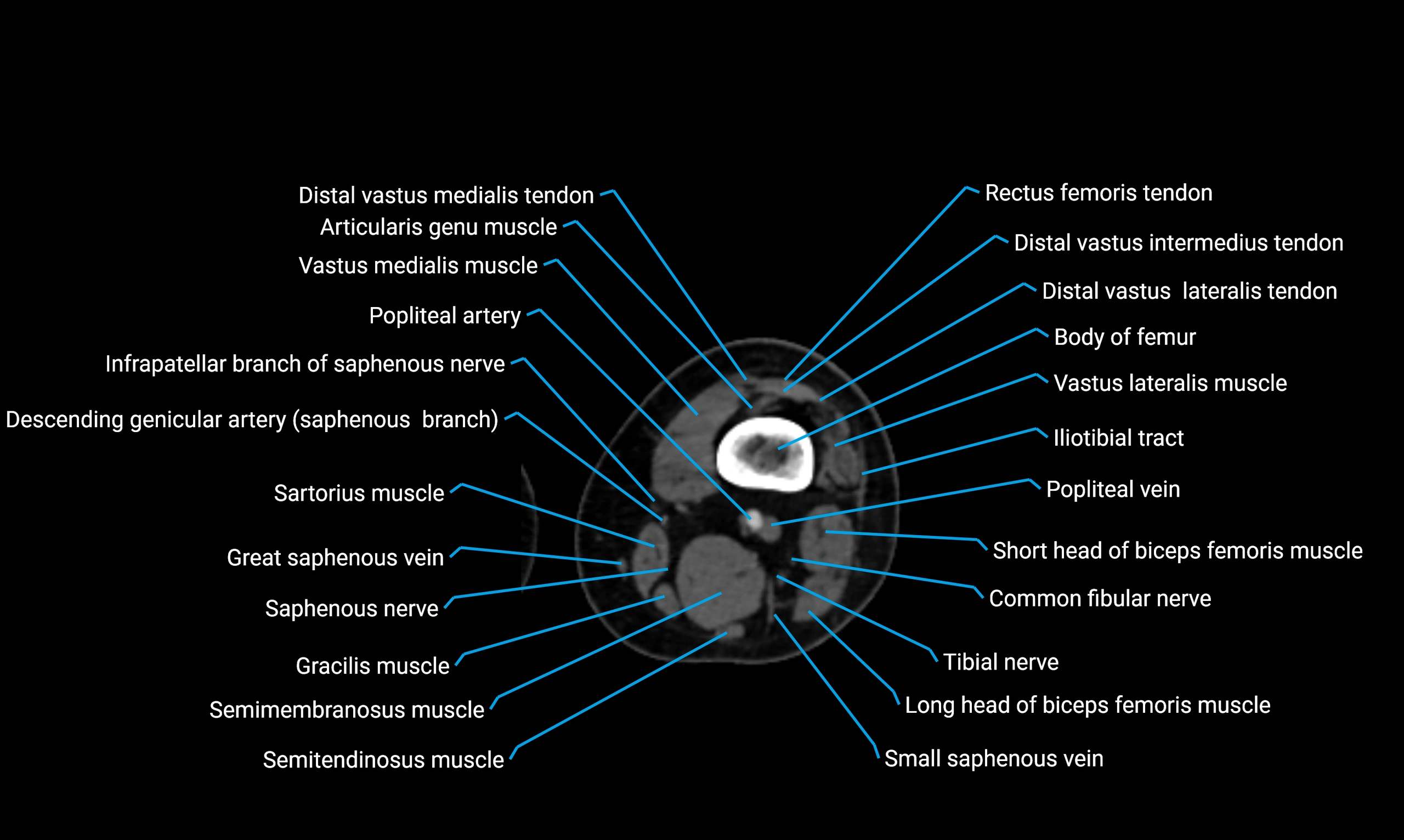
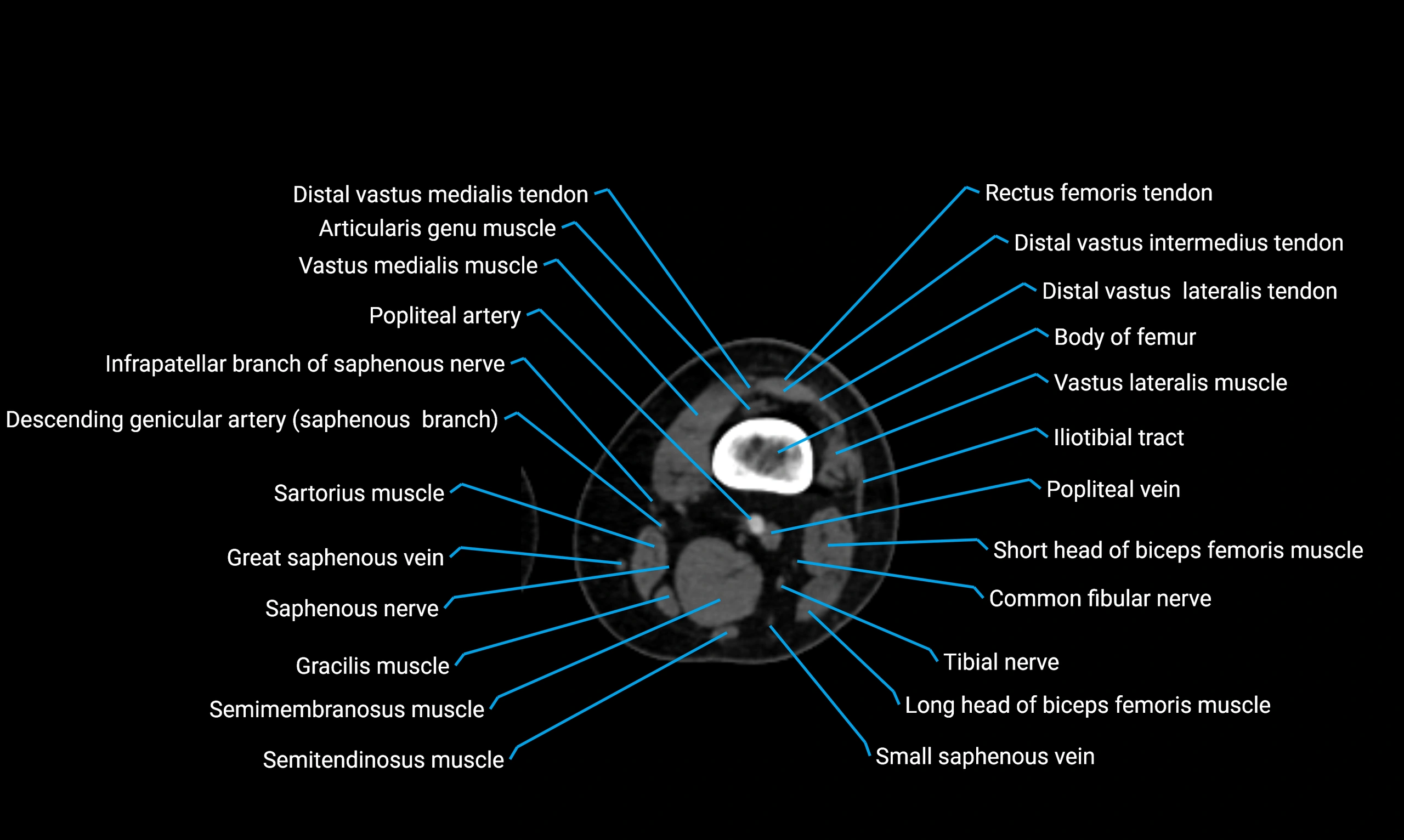
- Biceps femoris muscle (Long head)
- Biceps femoris muscle (Short head)
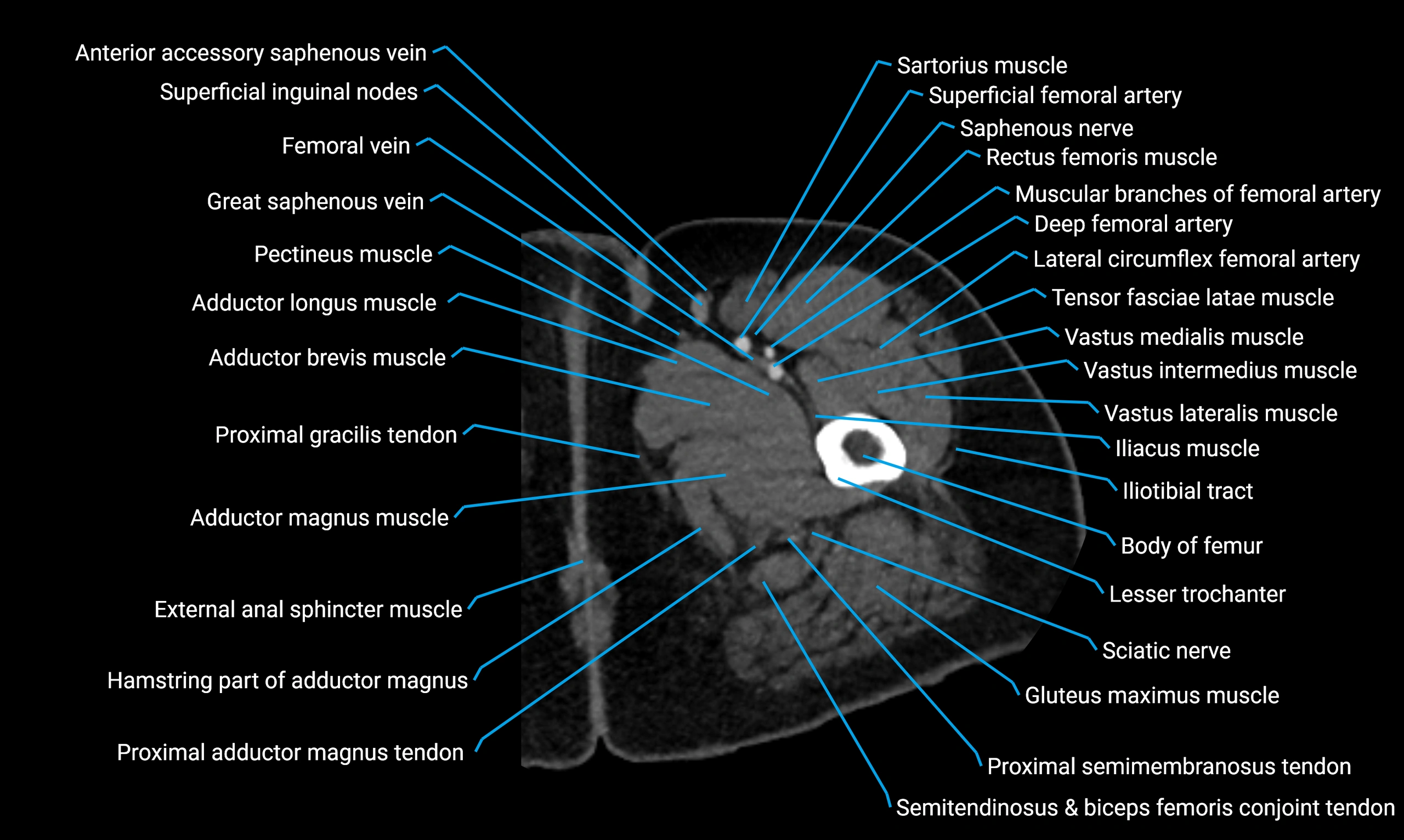
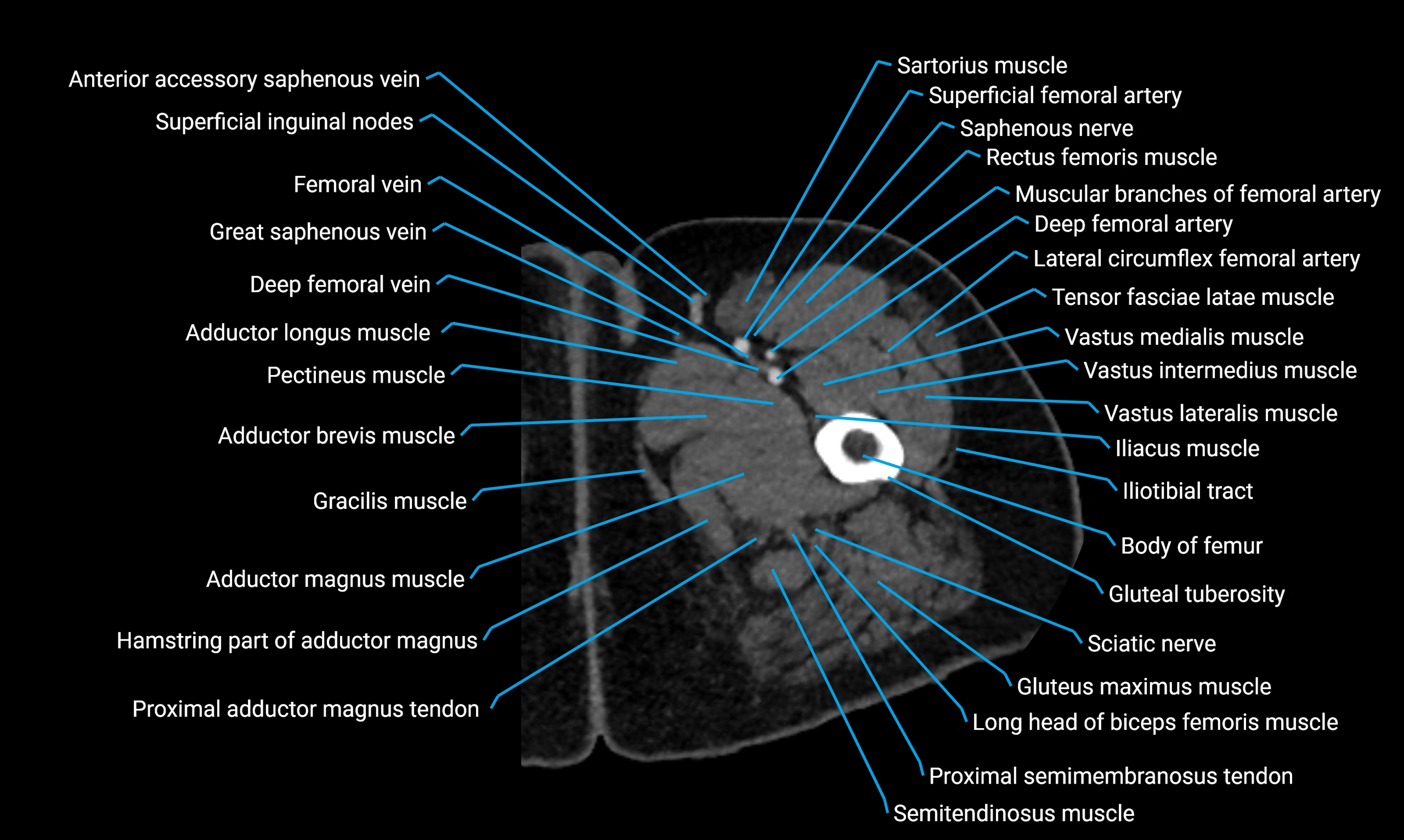
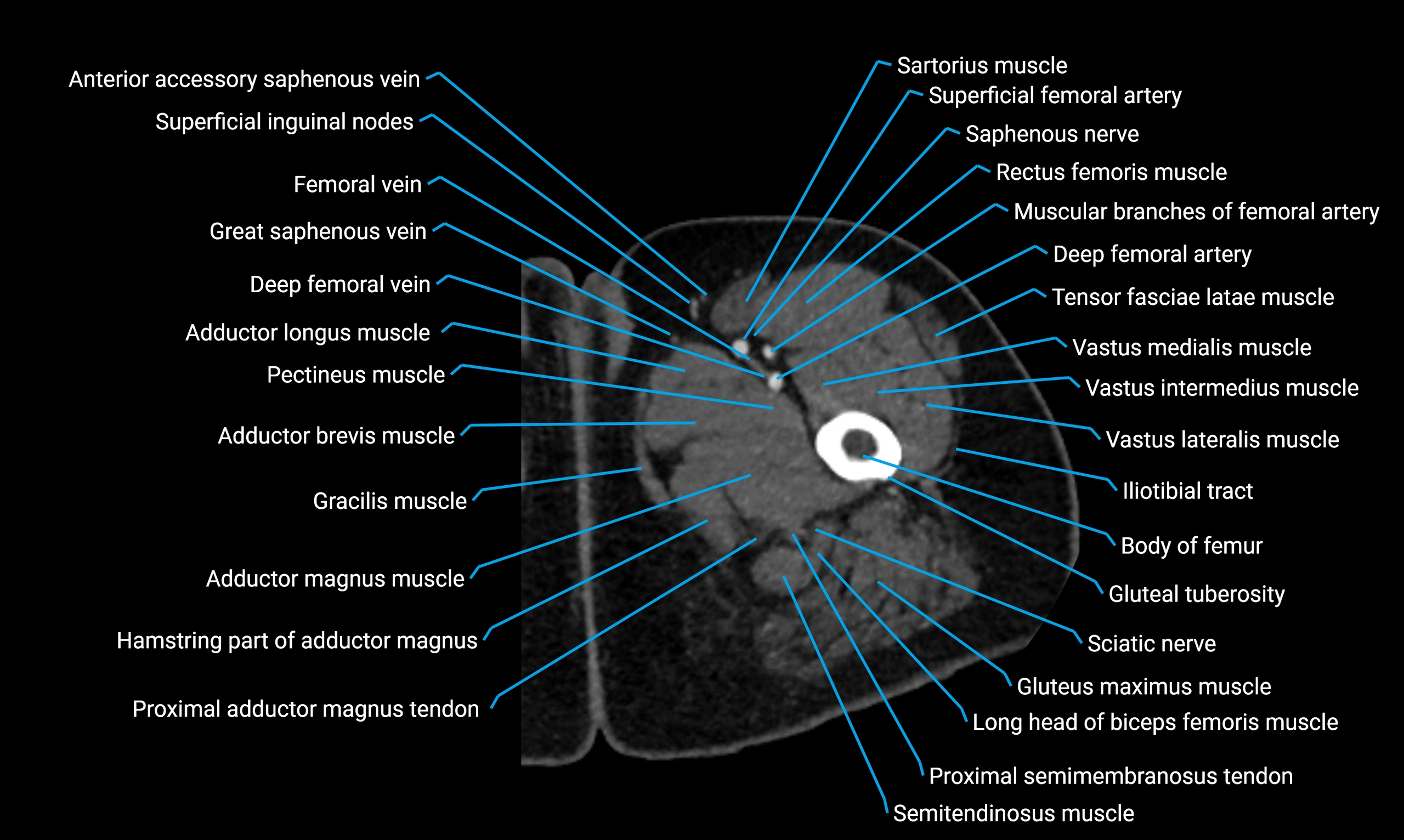
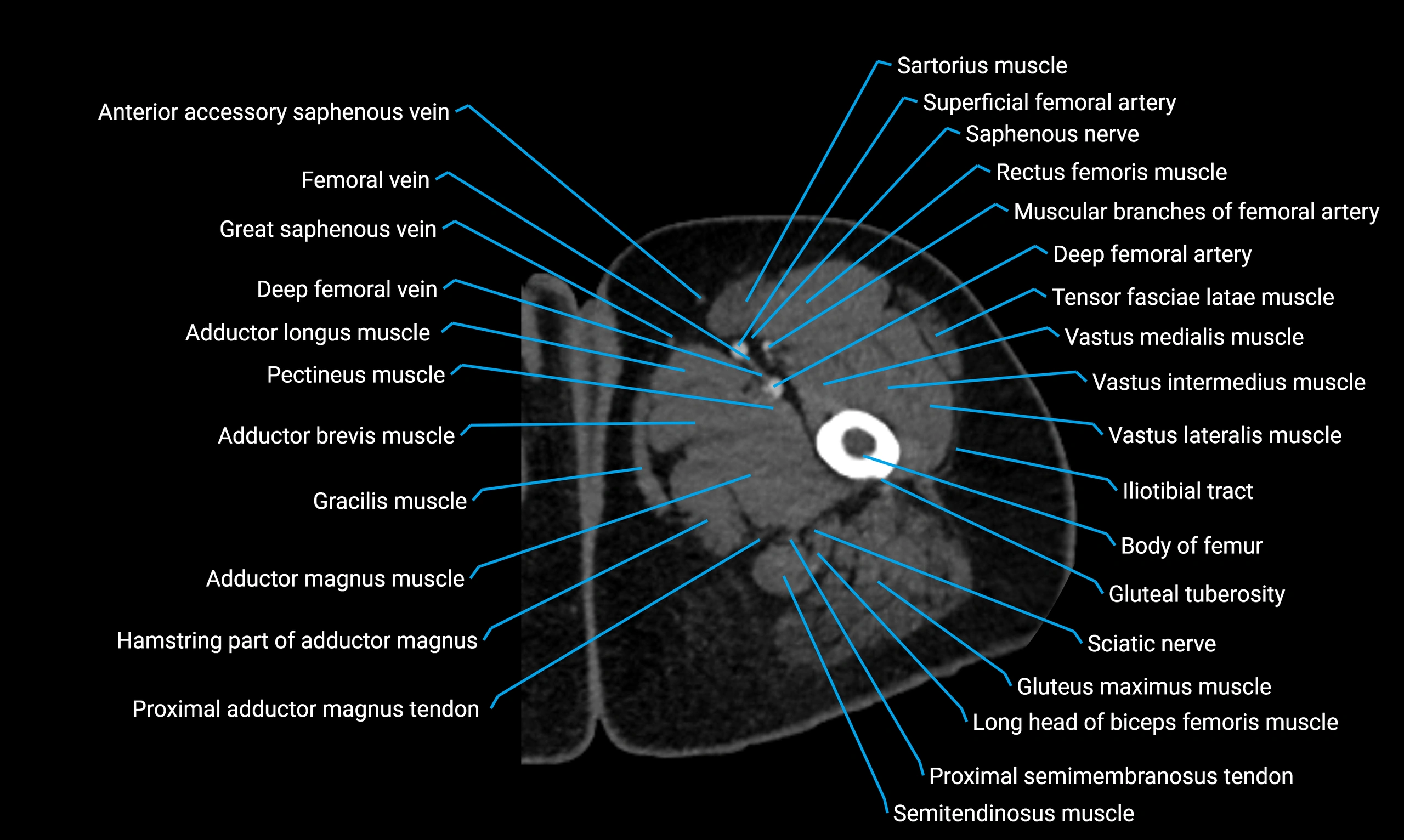
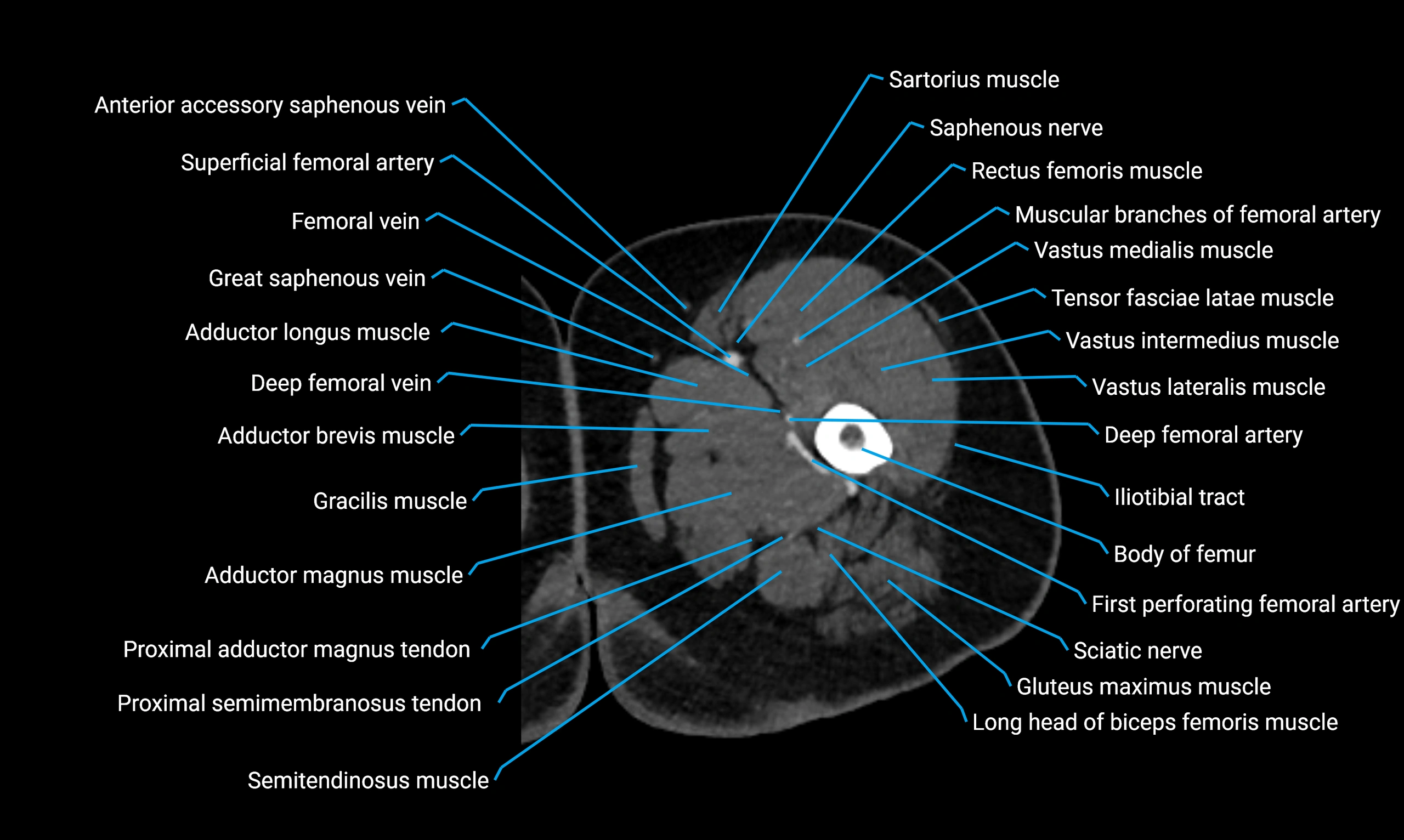
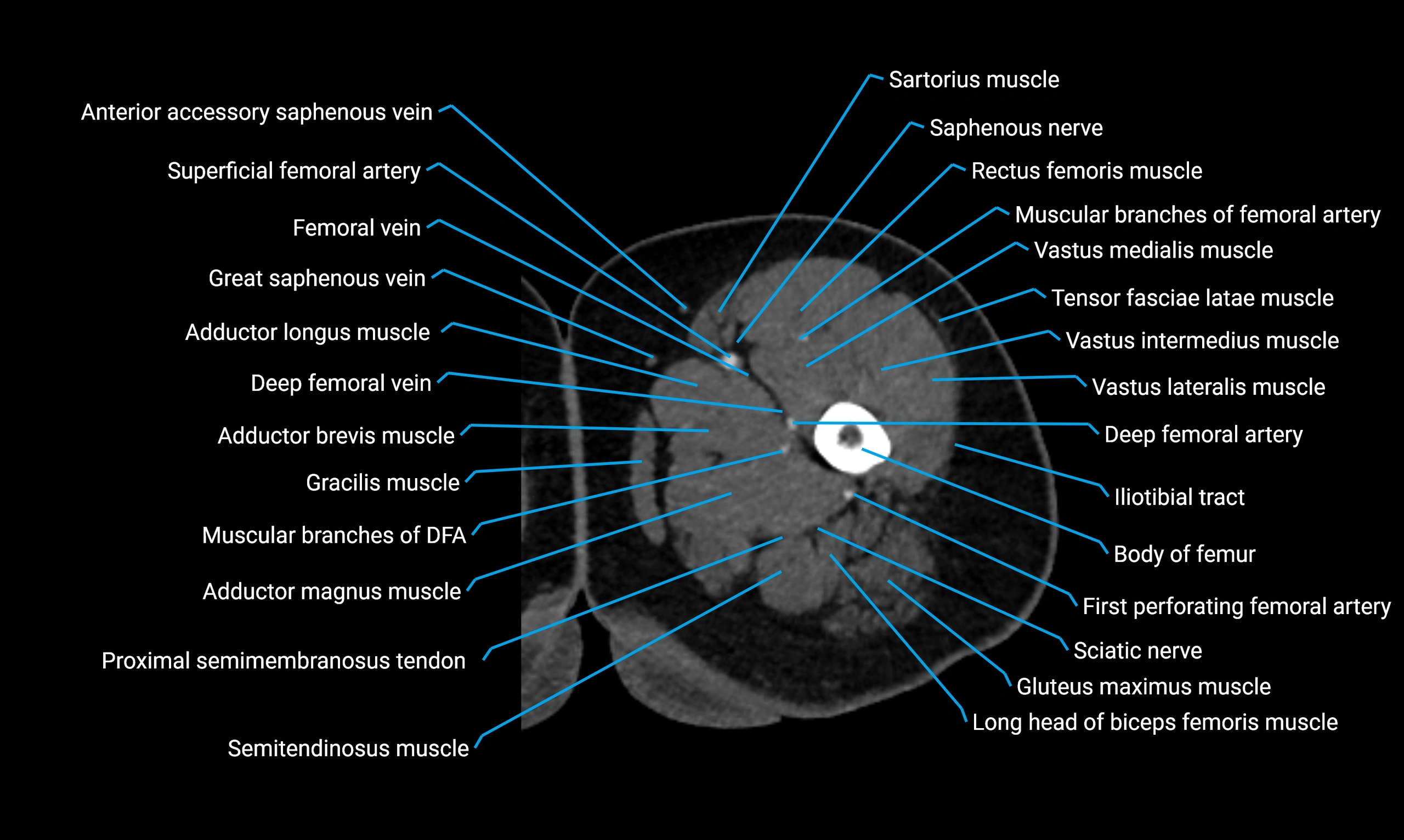
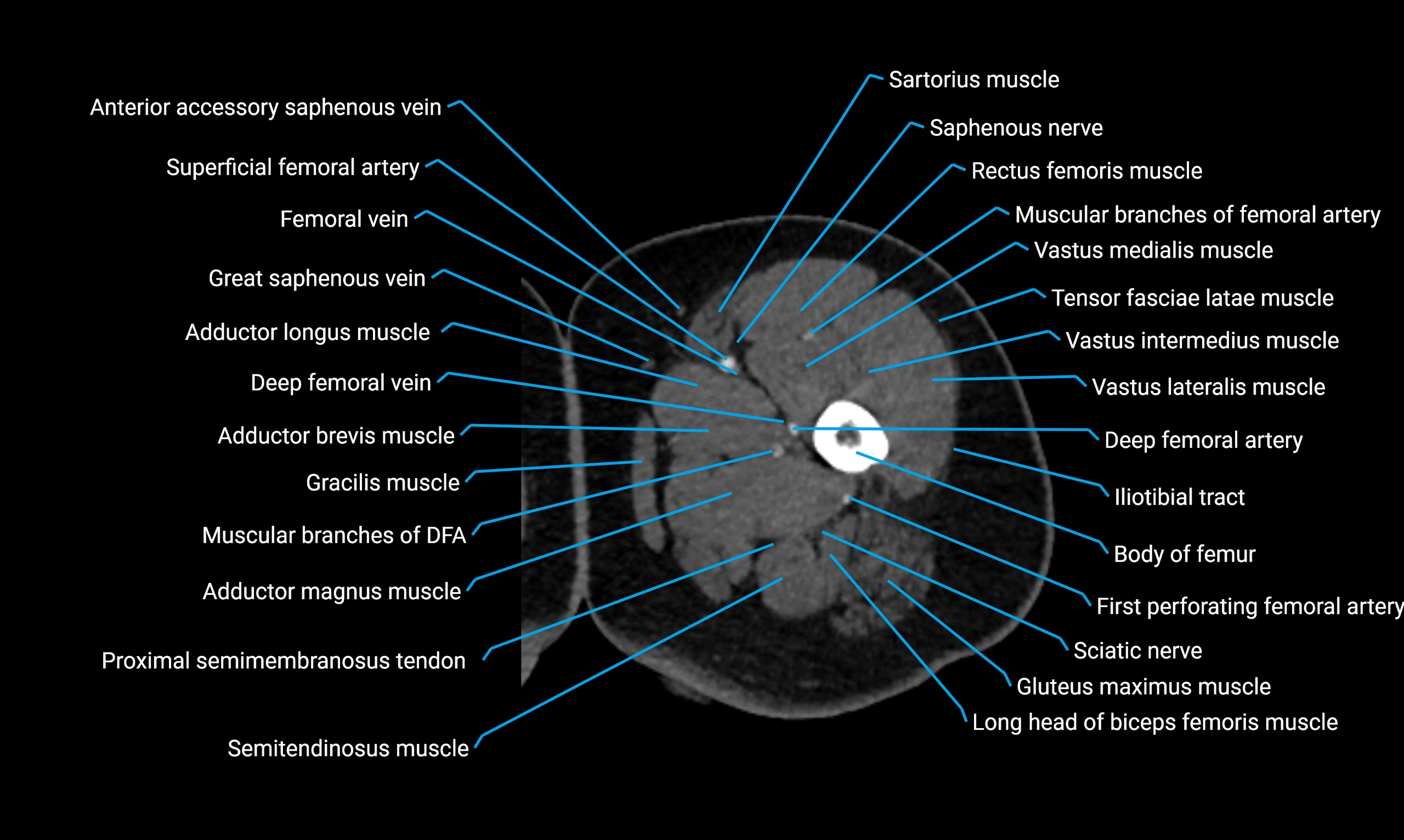
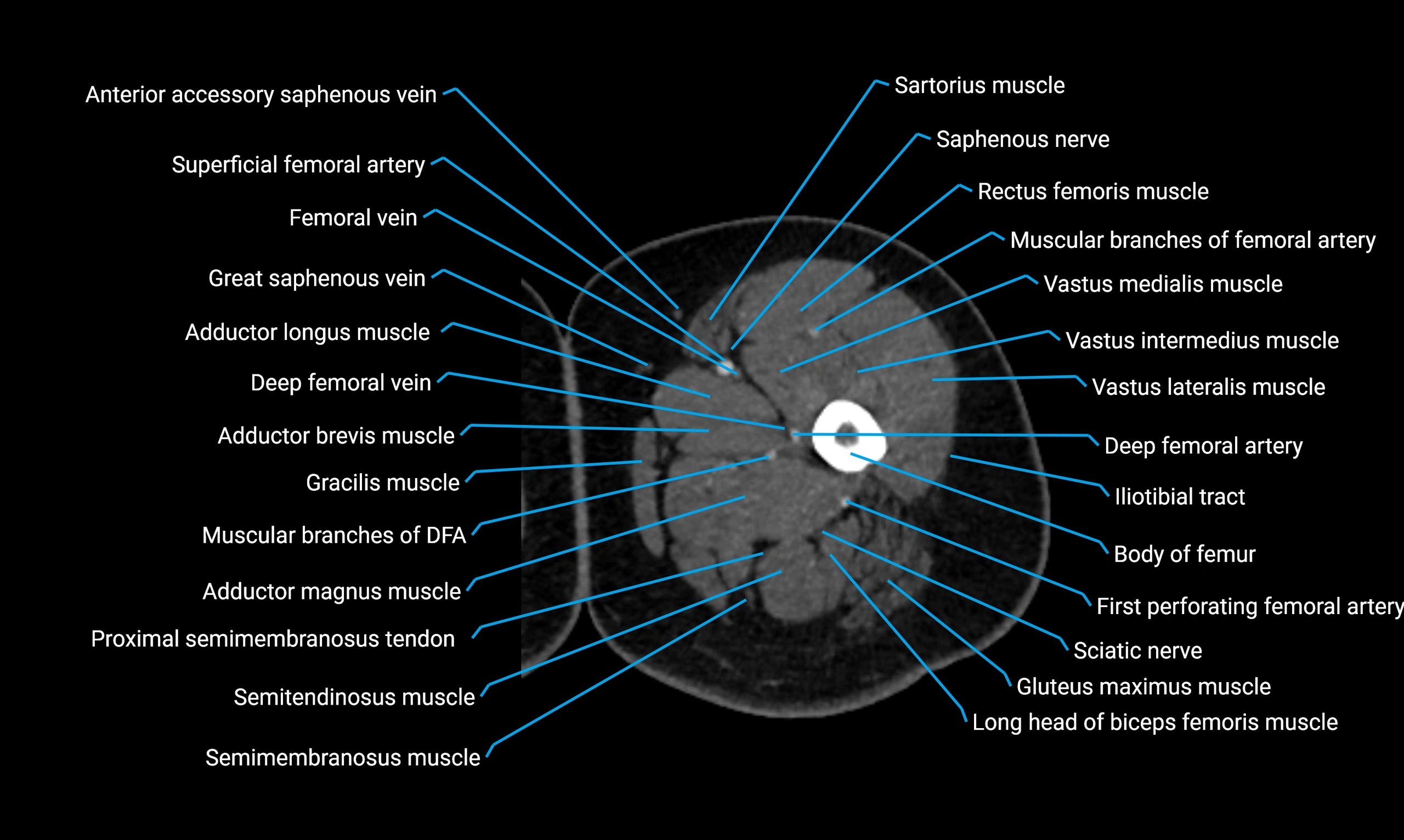
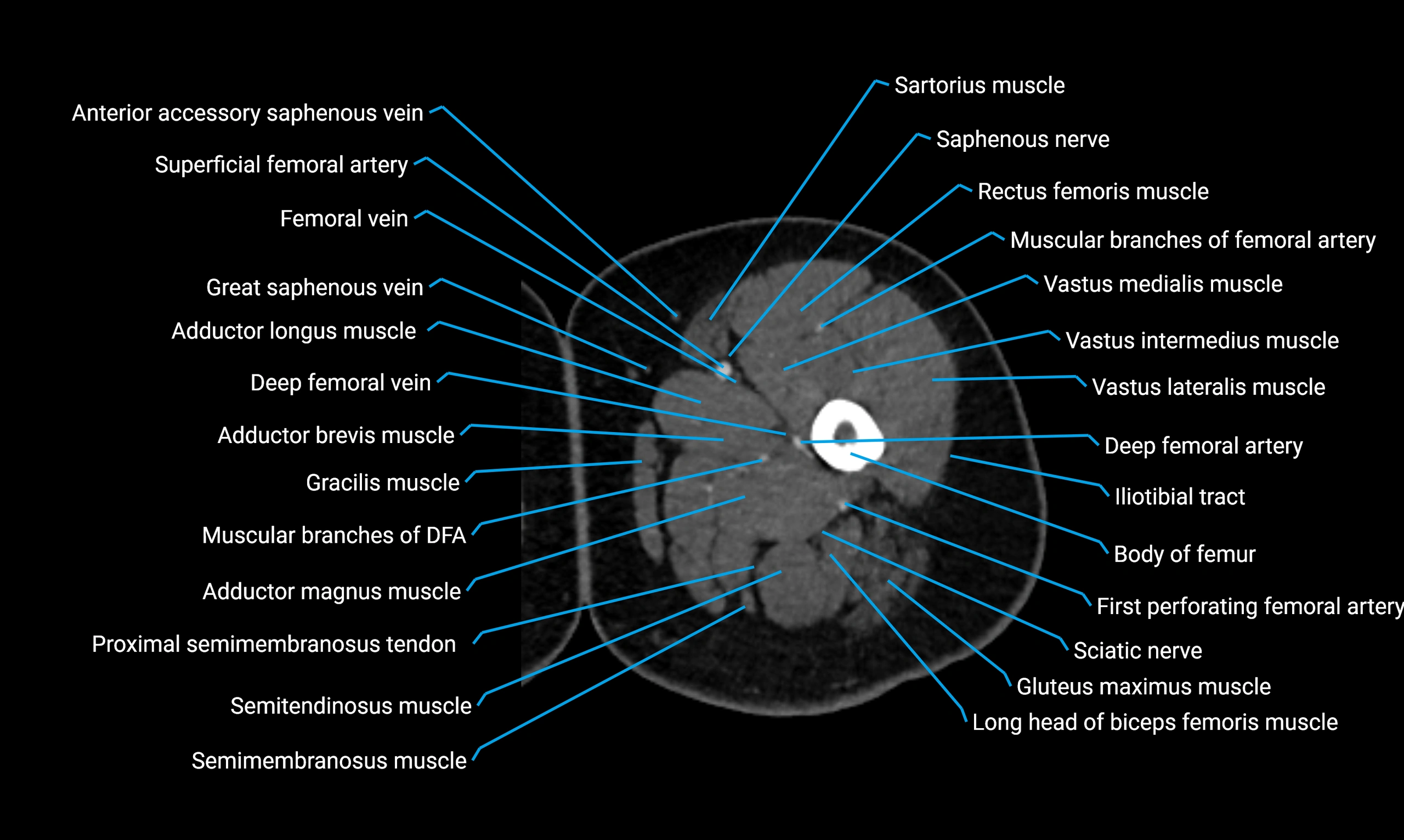
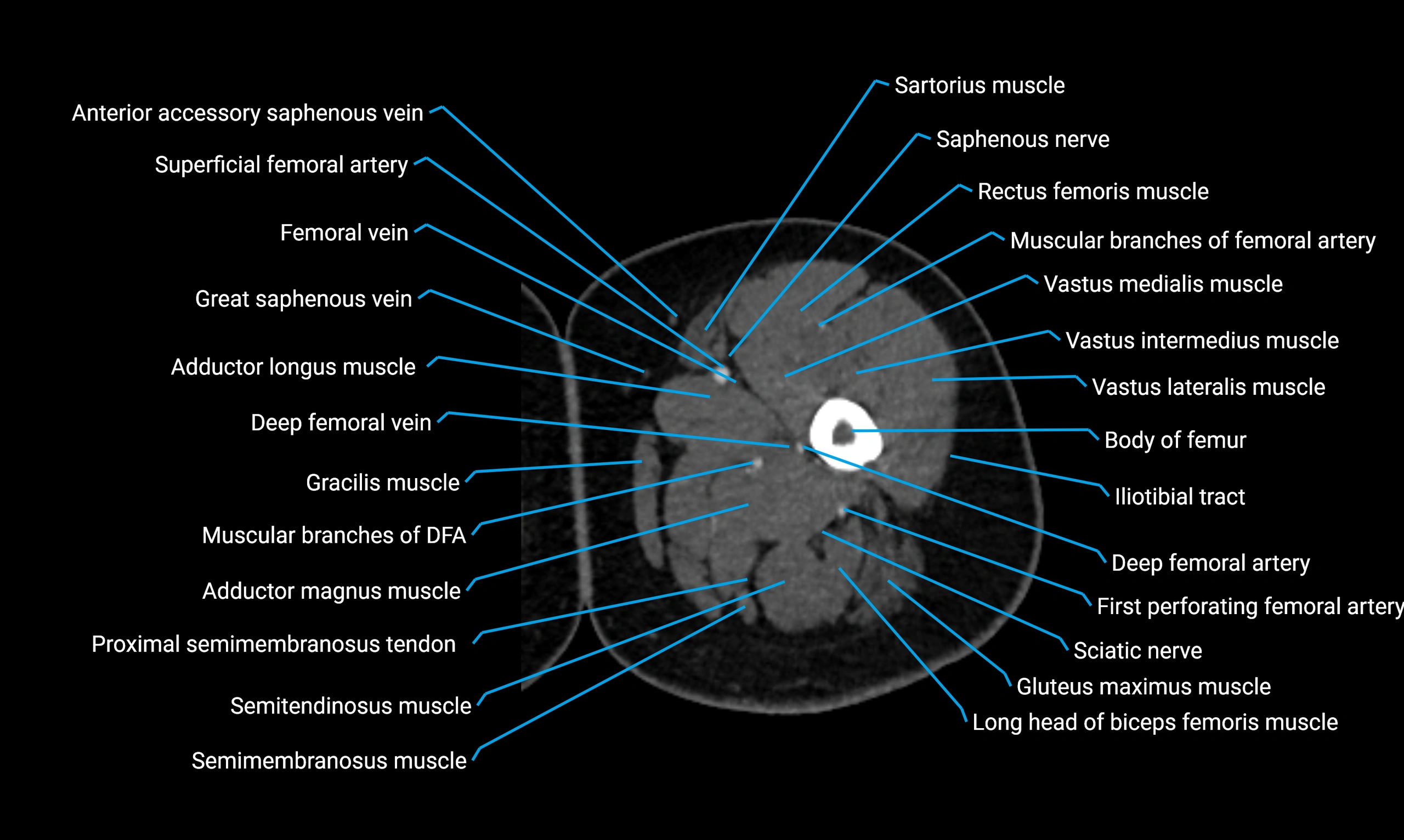
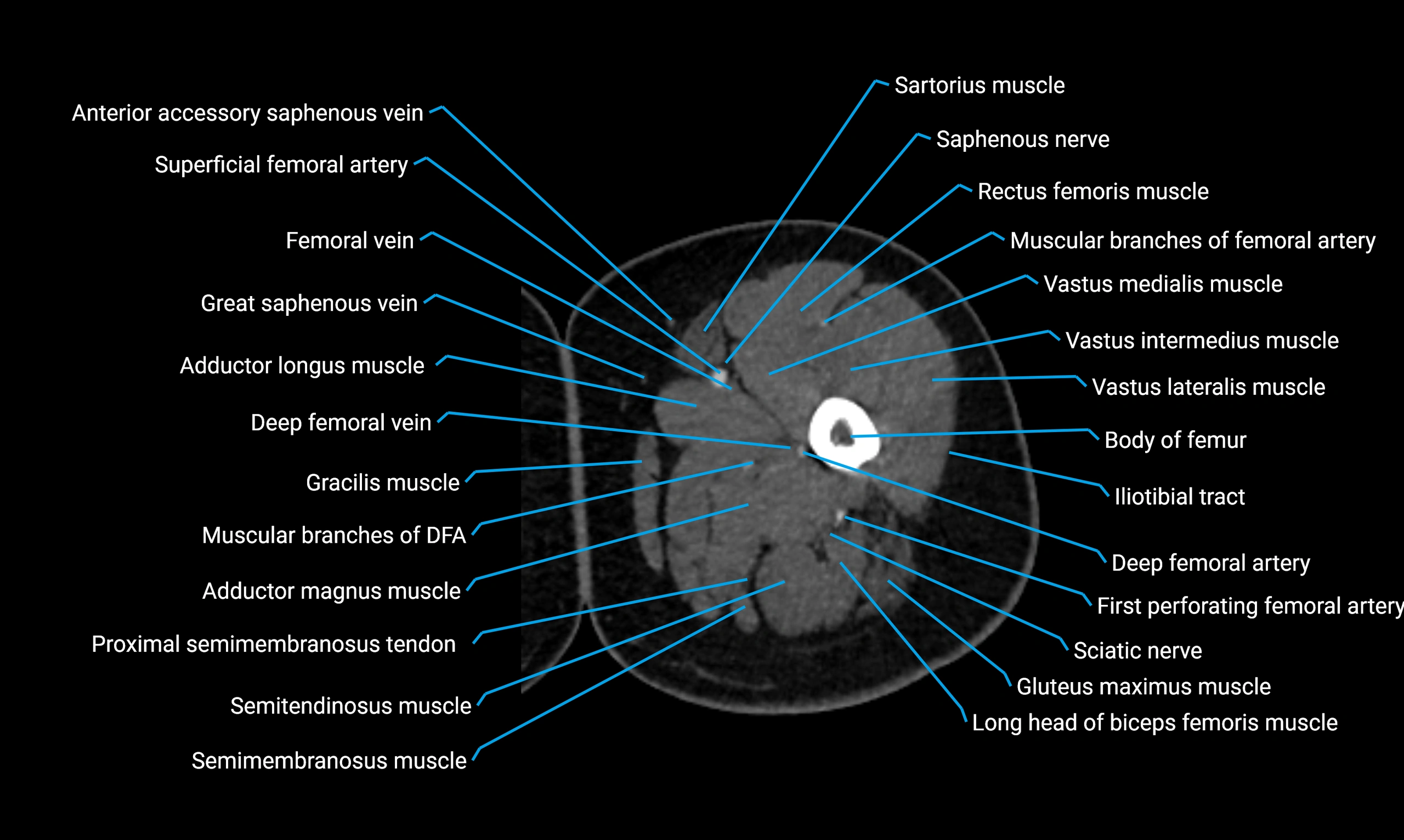
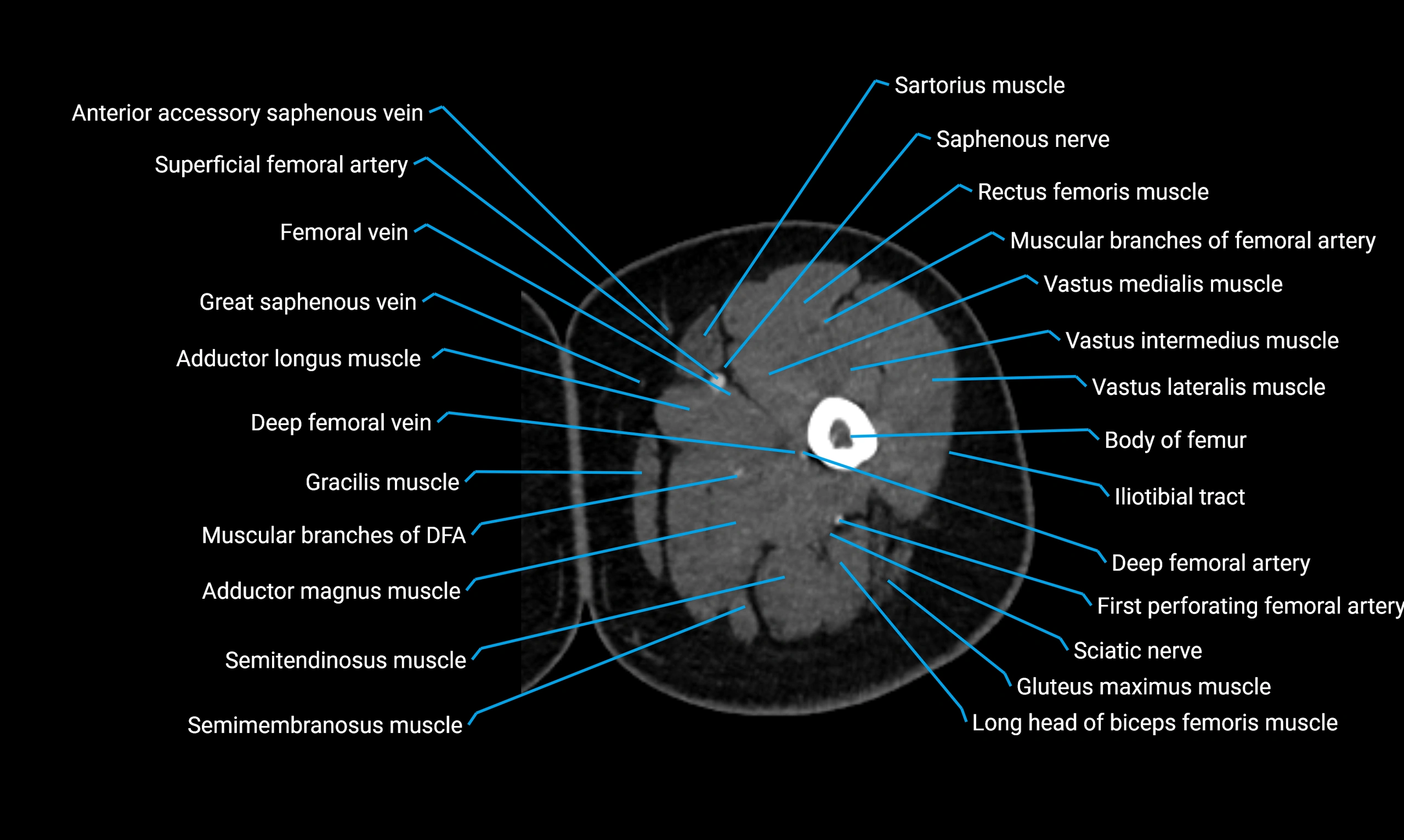
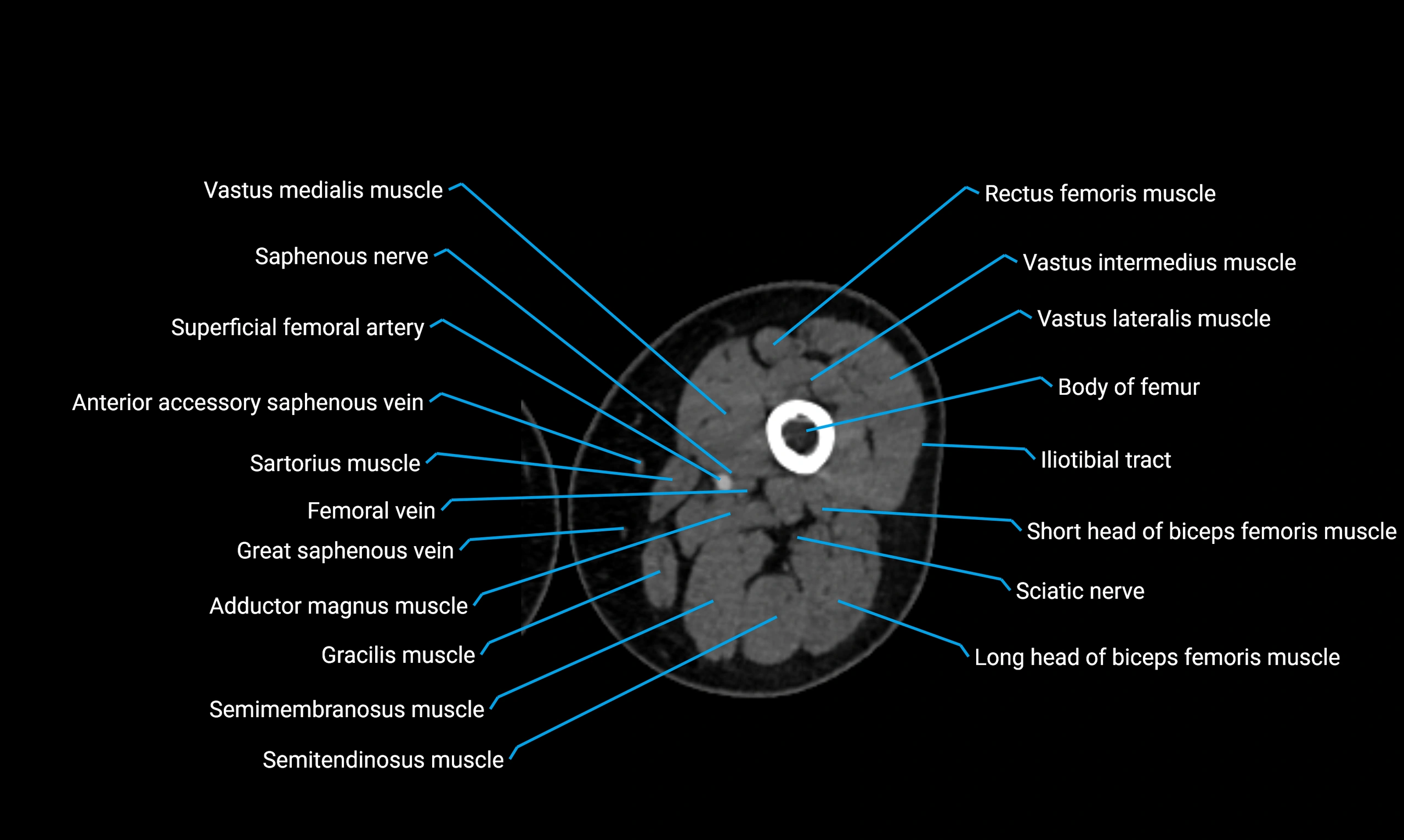
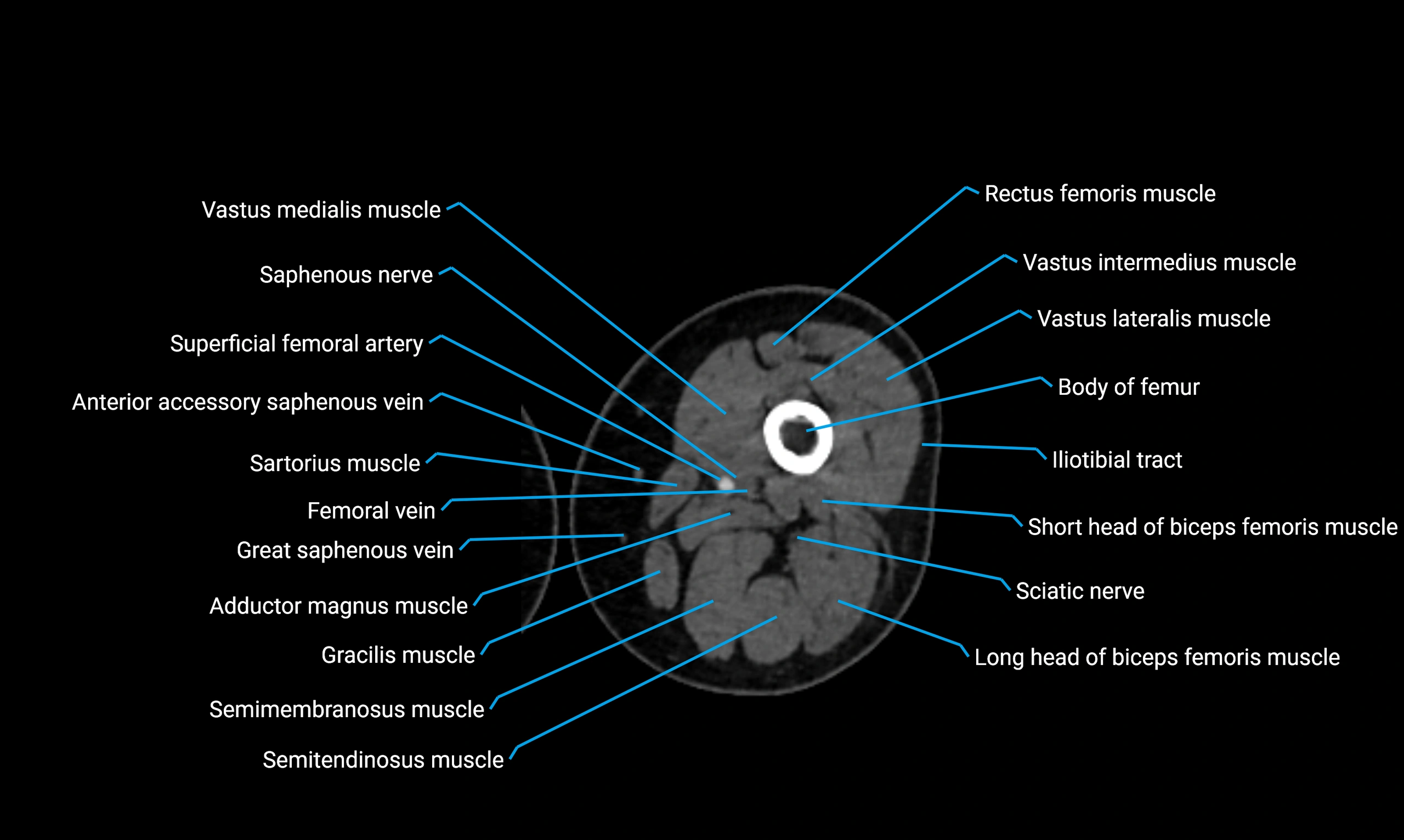
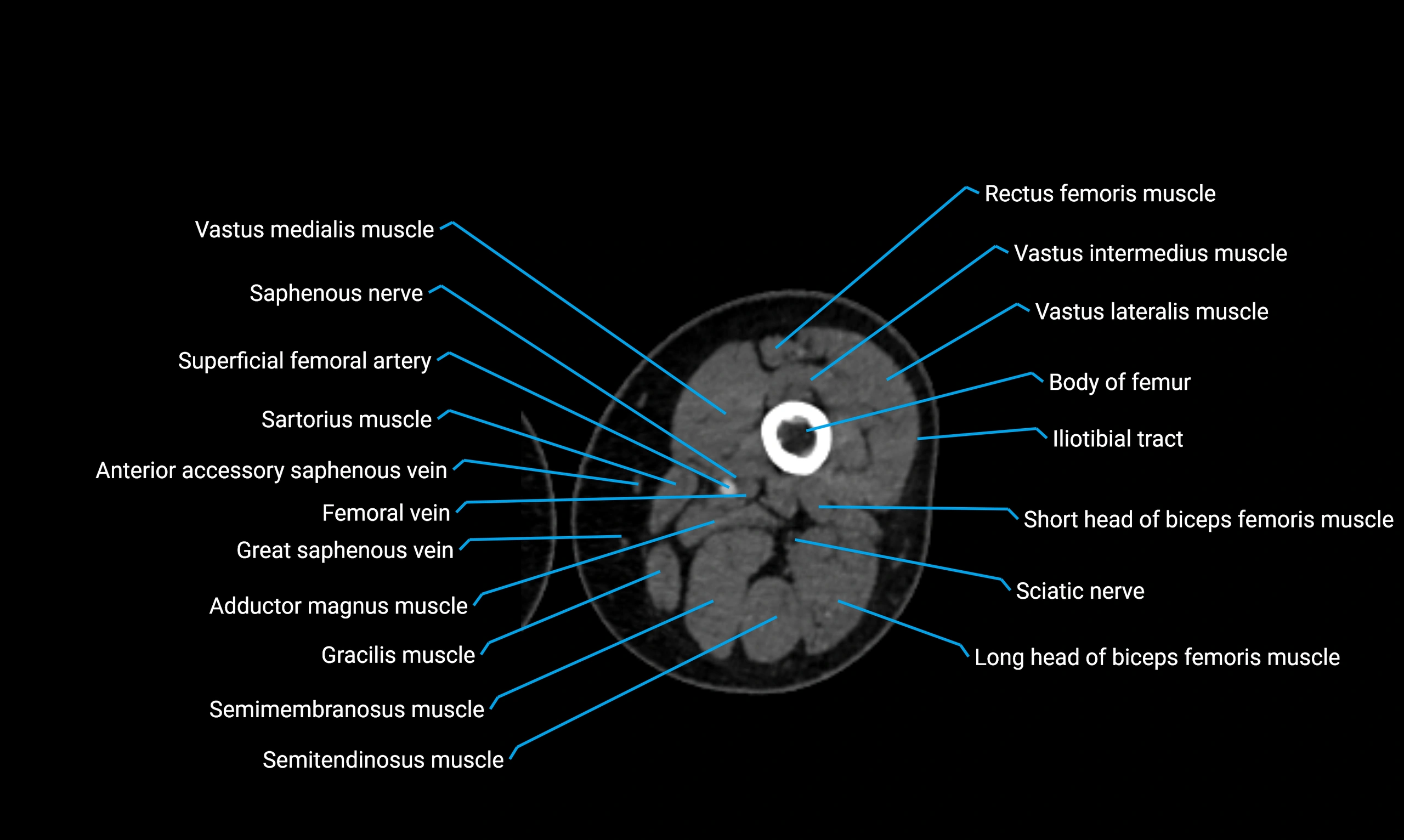
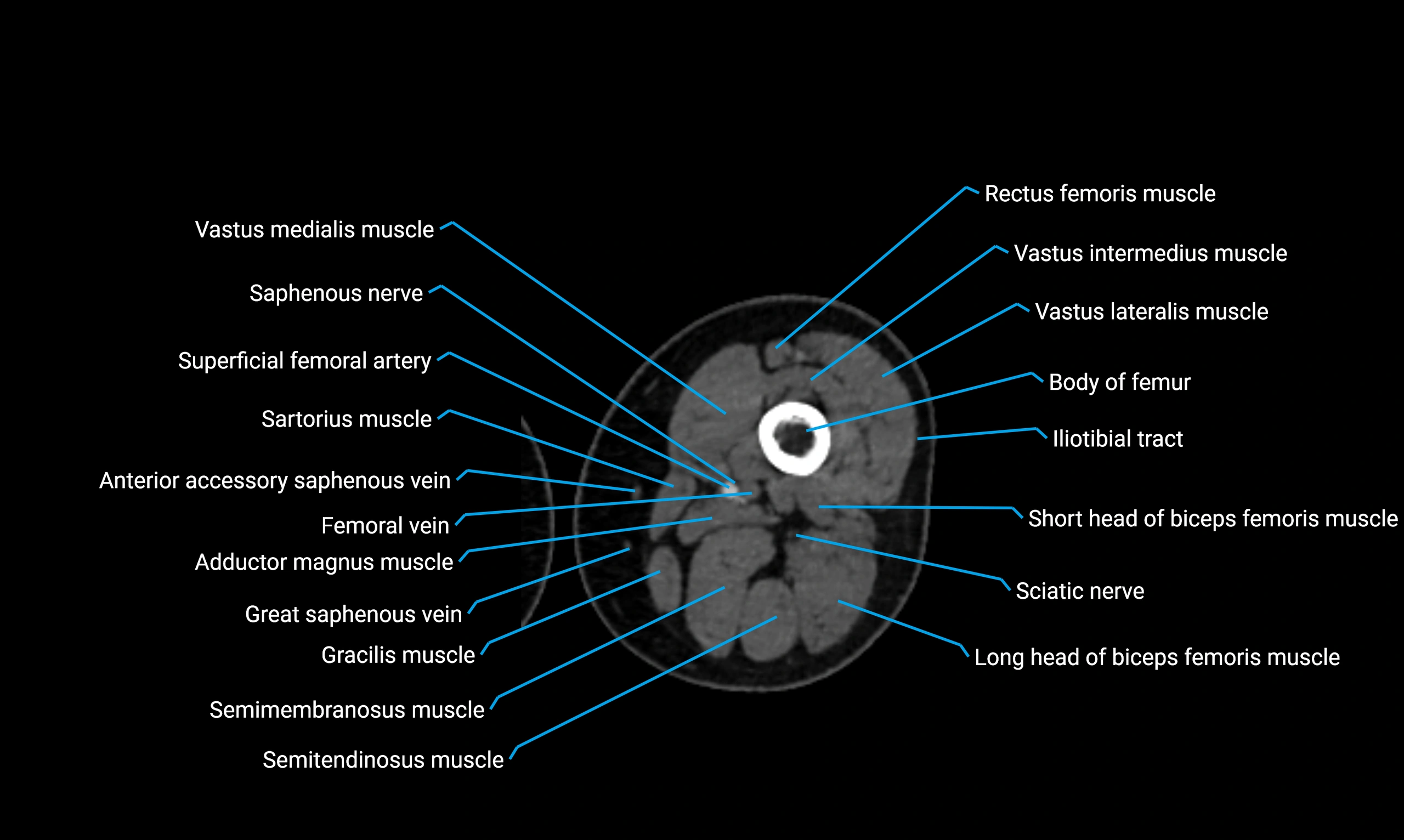
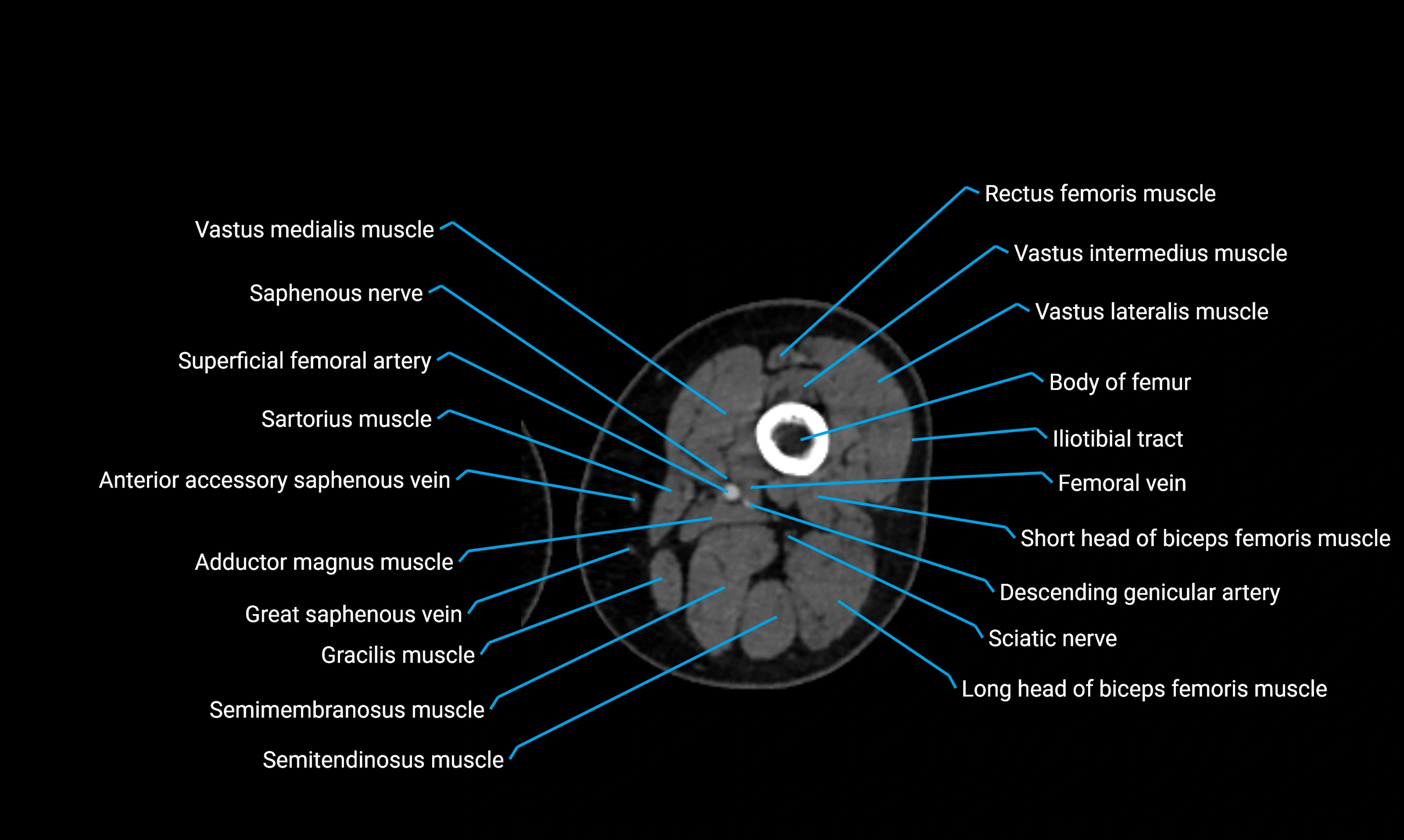
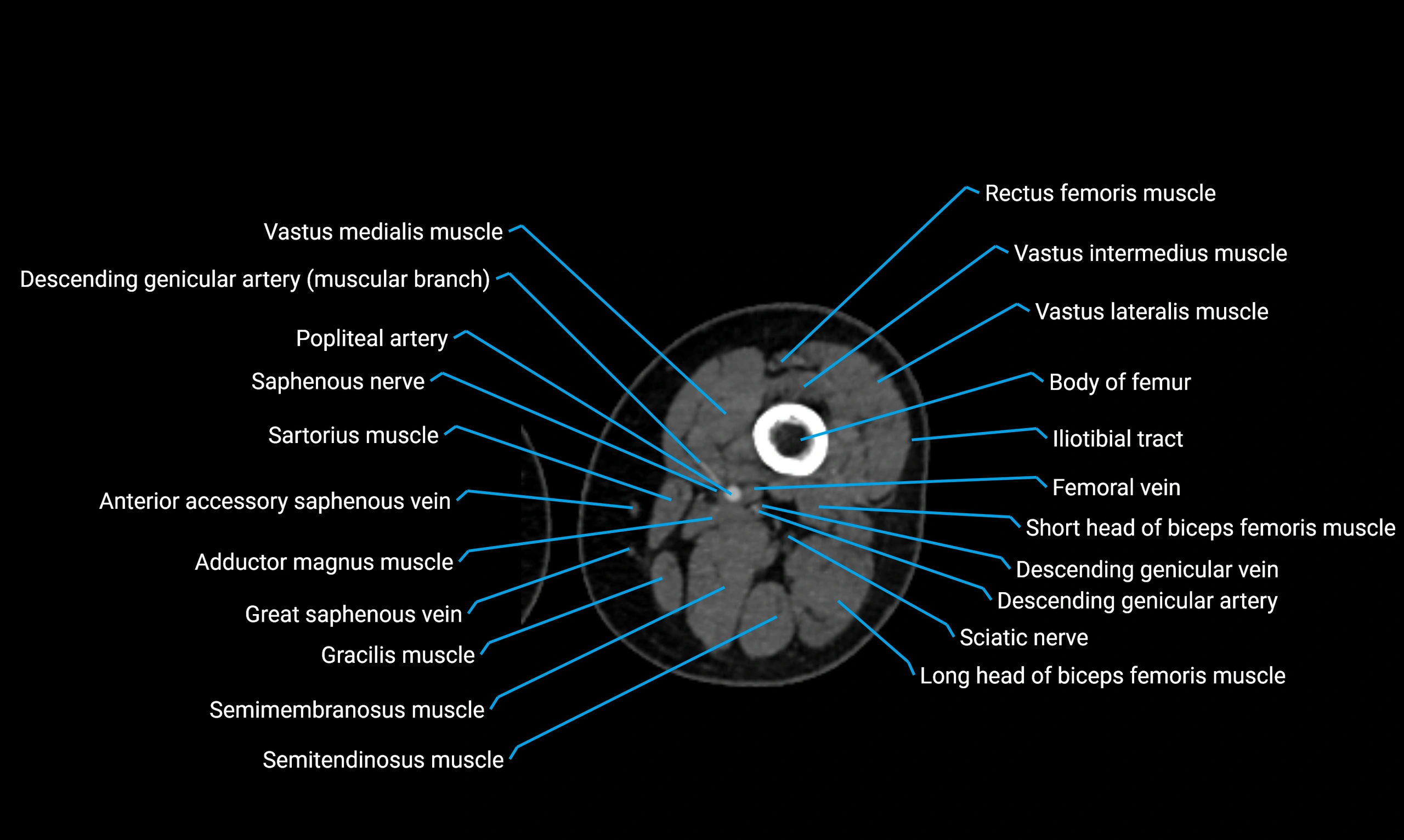
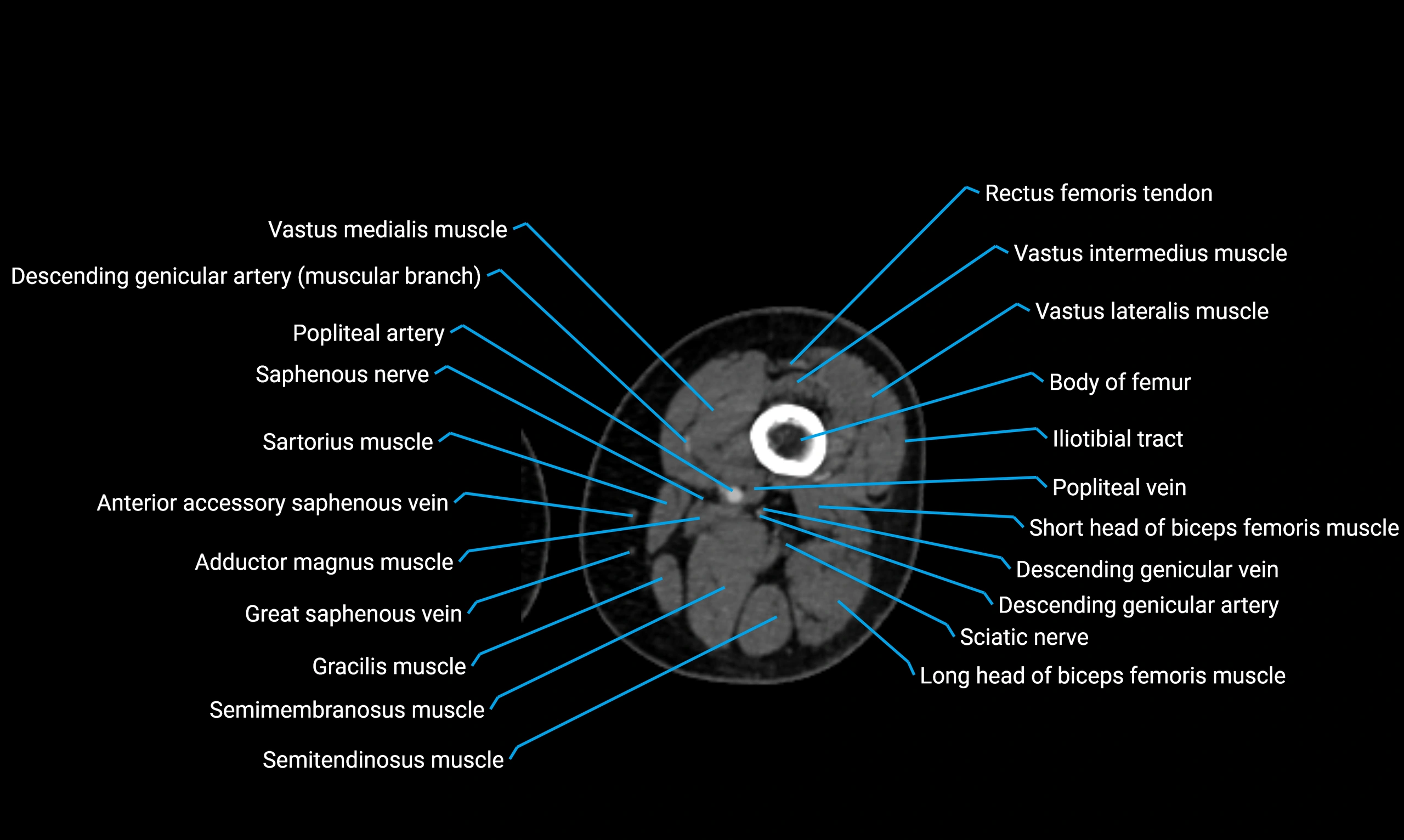
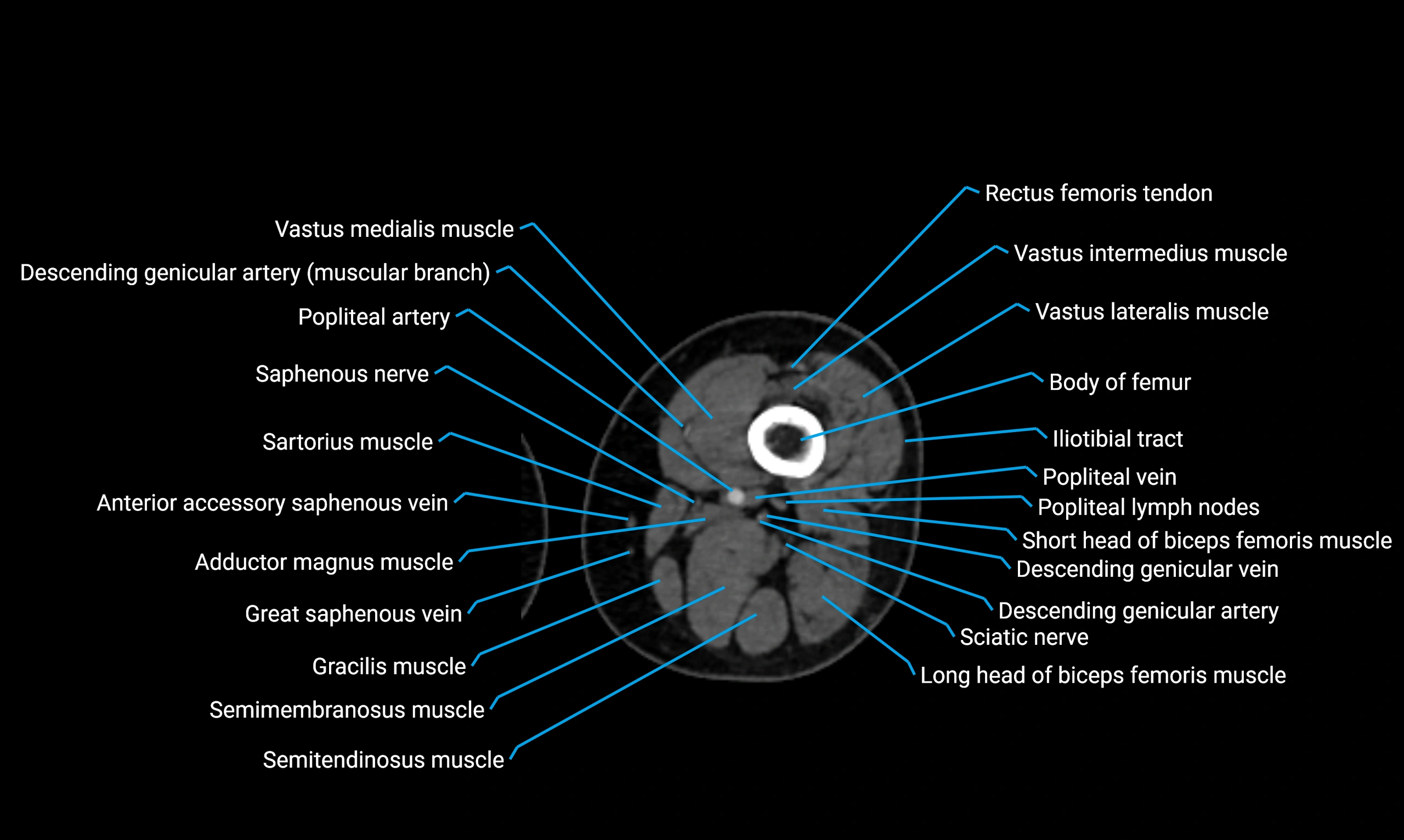
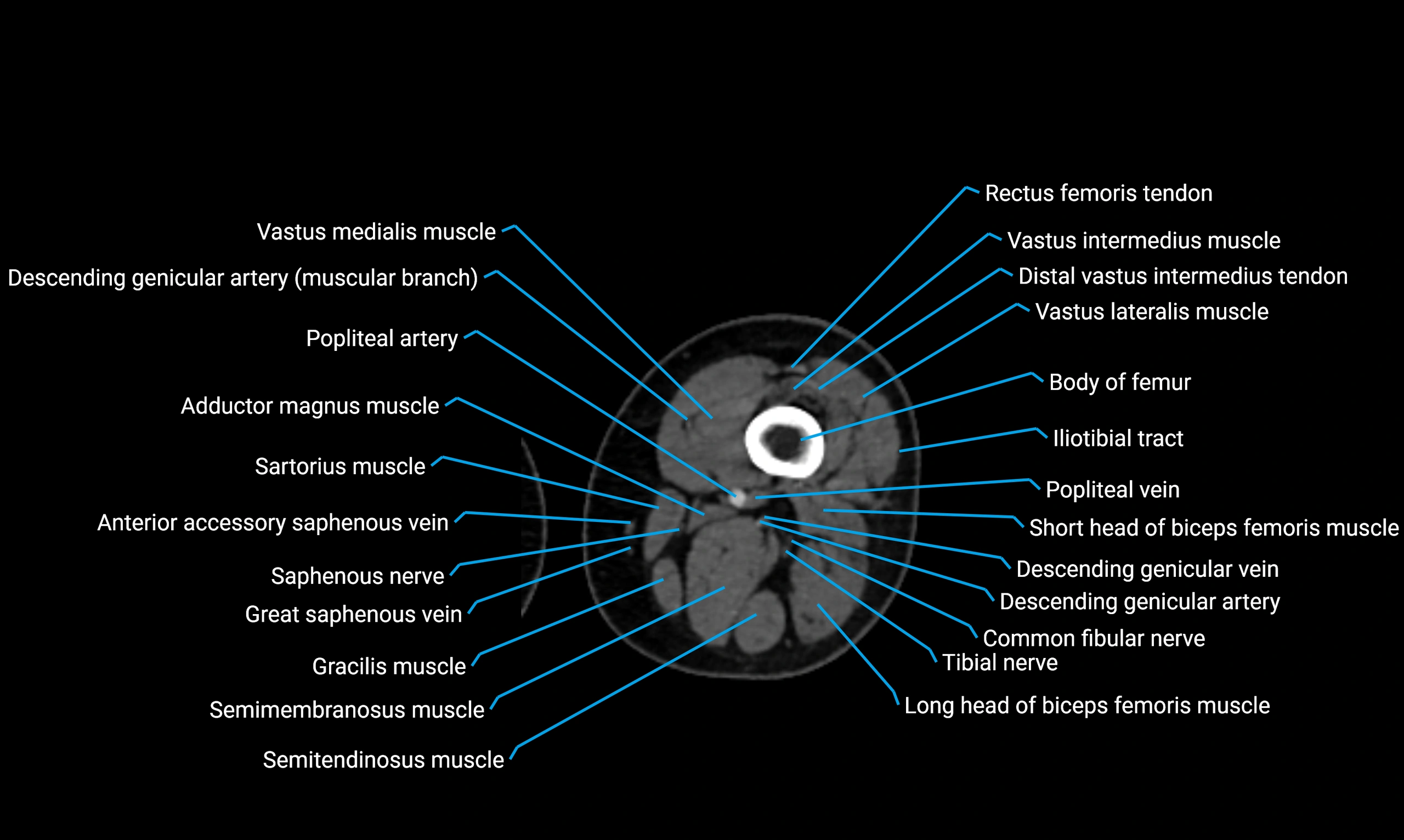
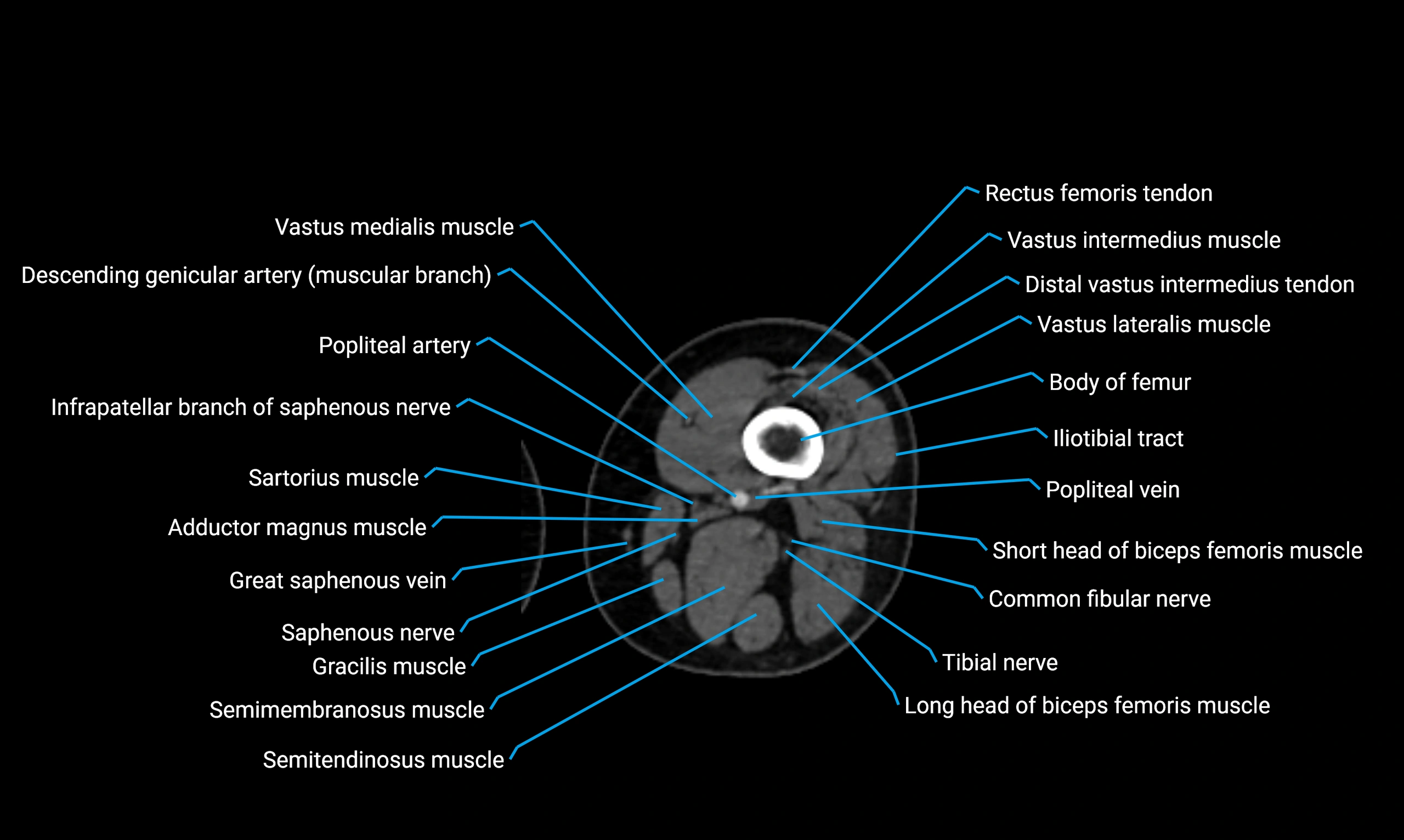
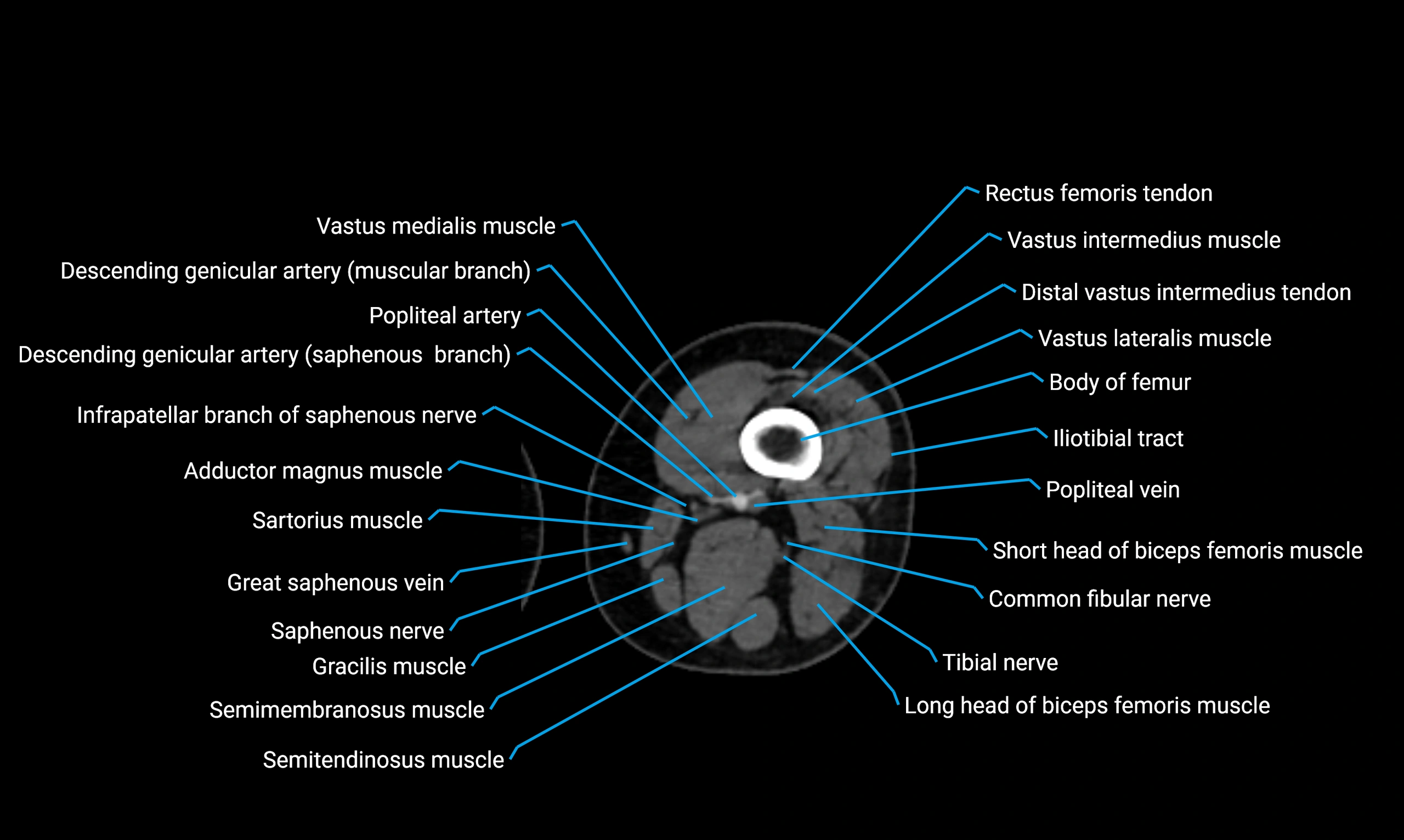
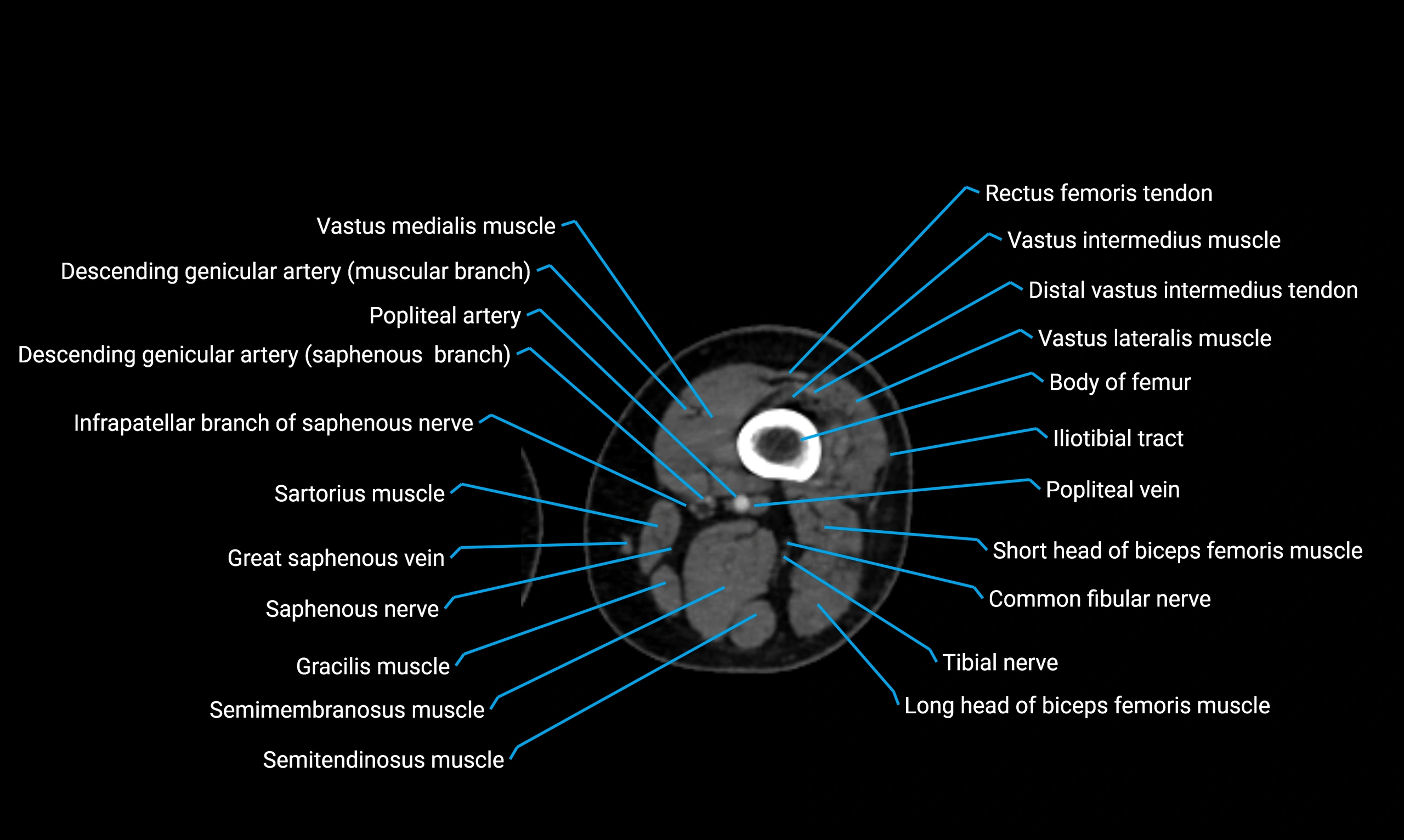
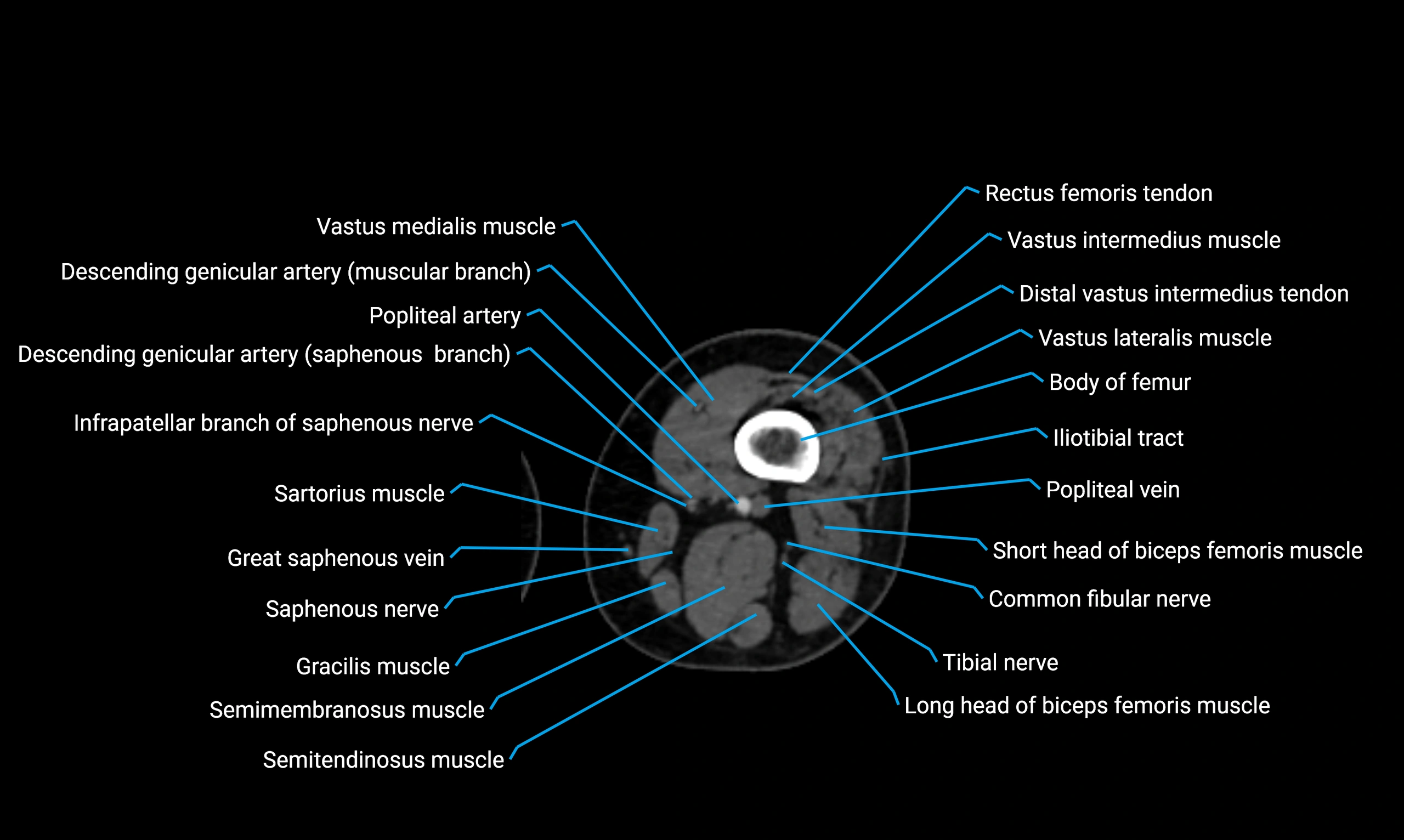
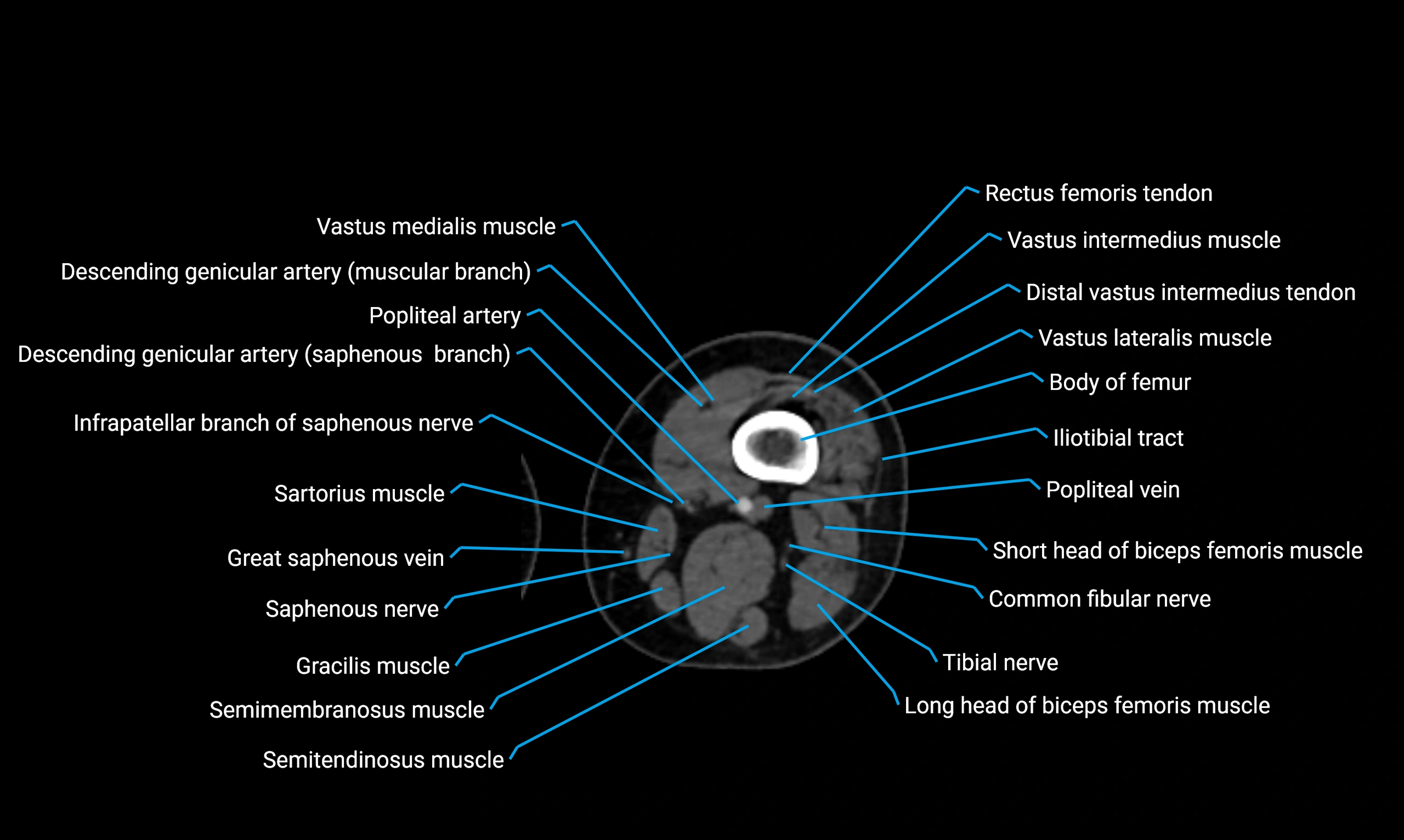
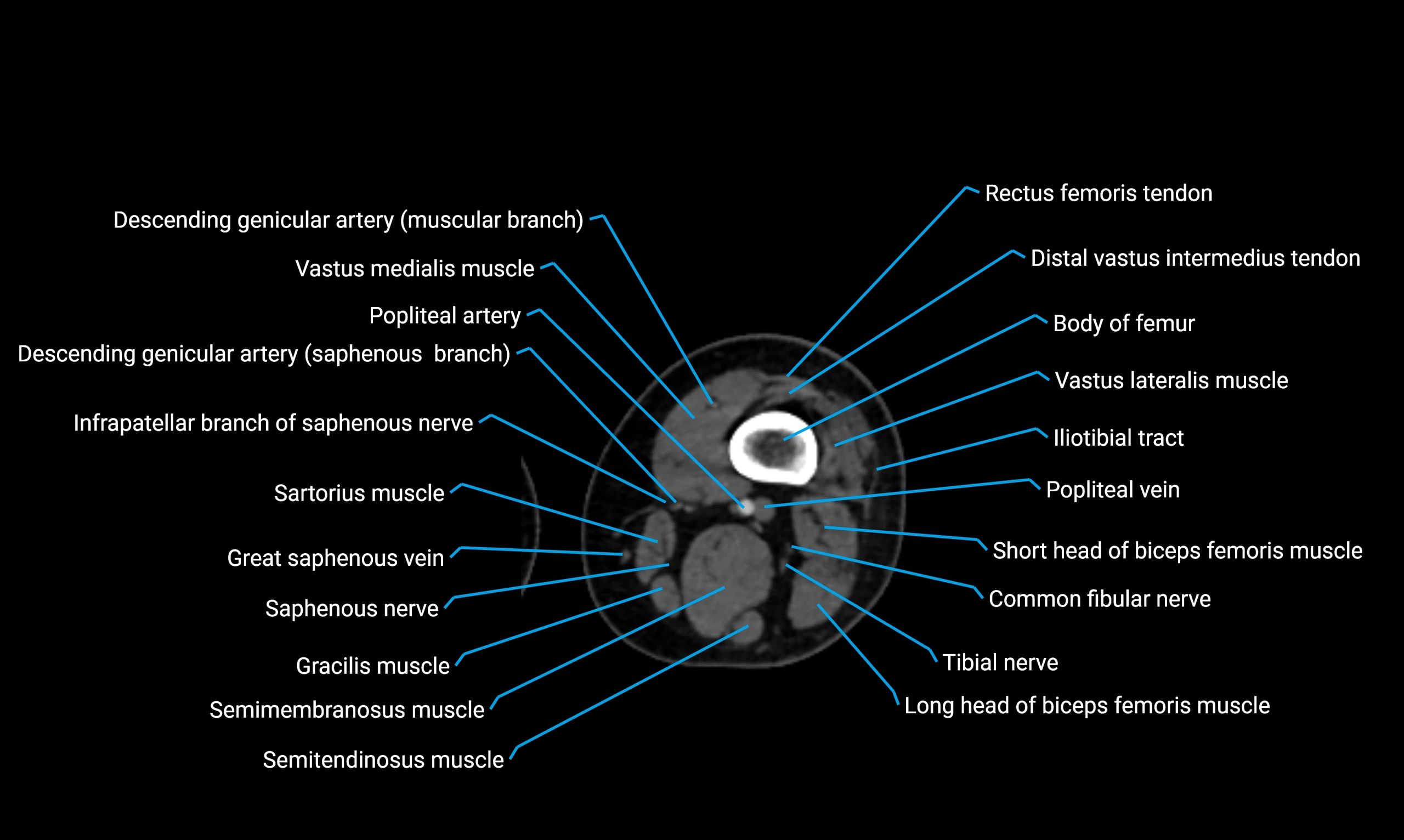
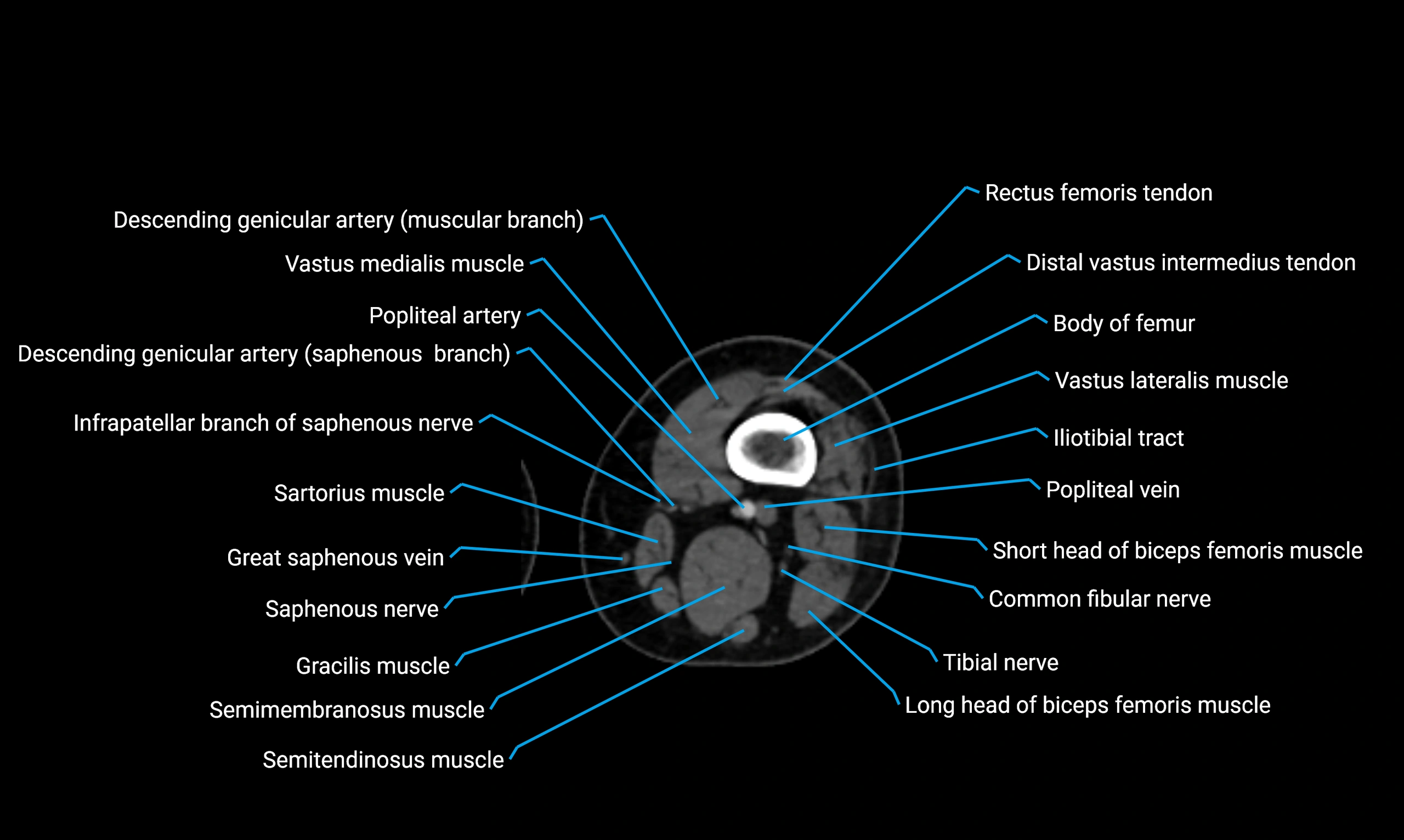
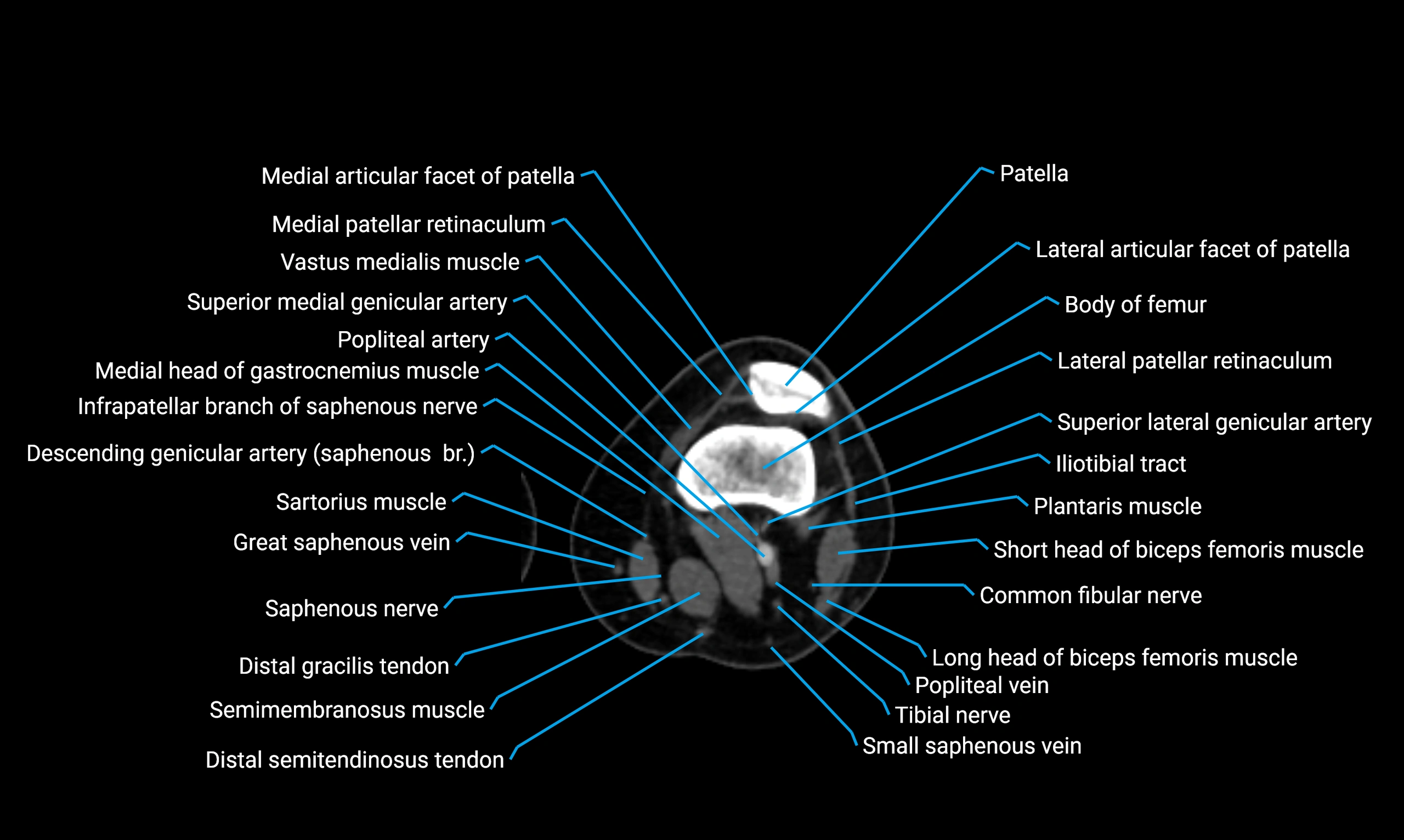
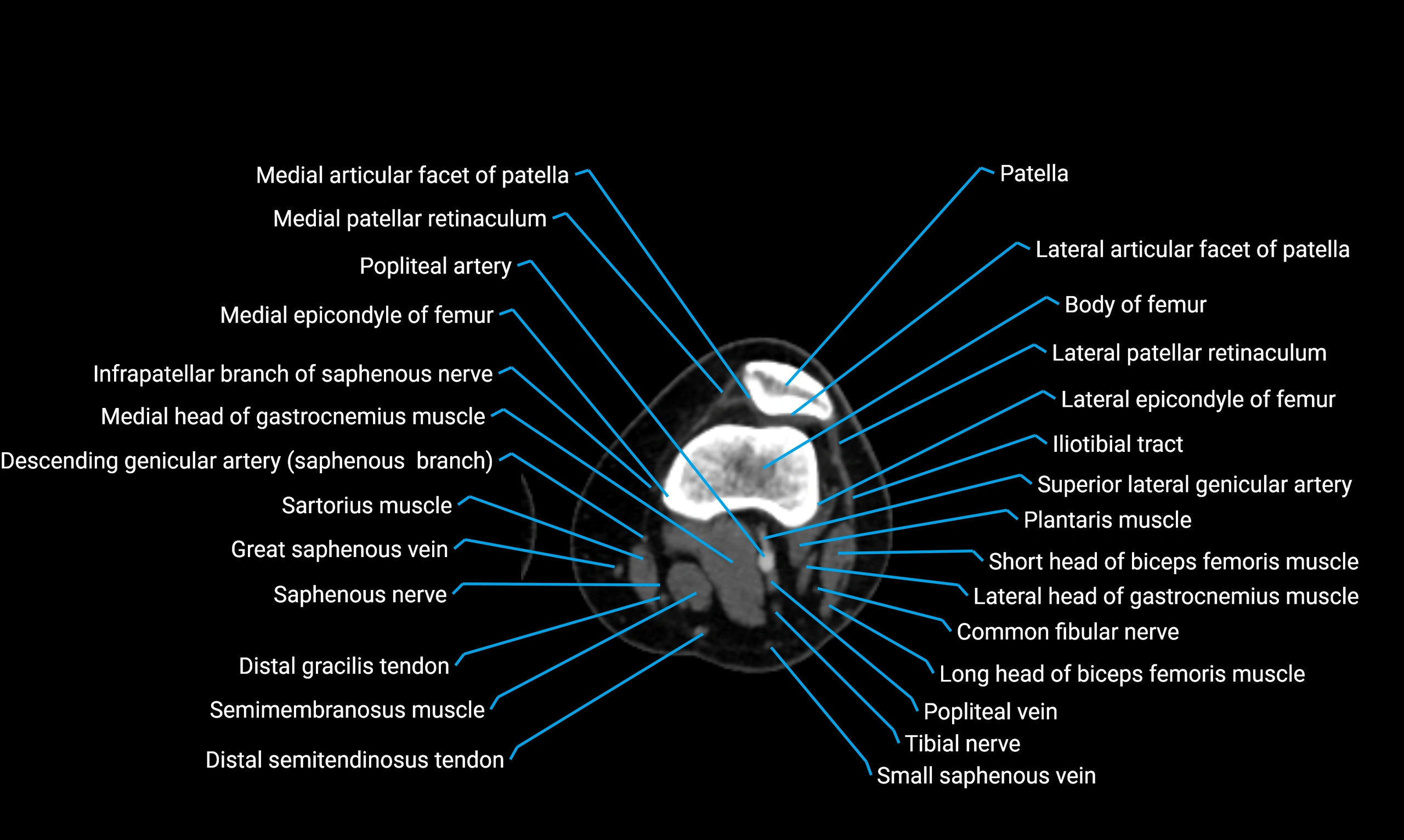
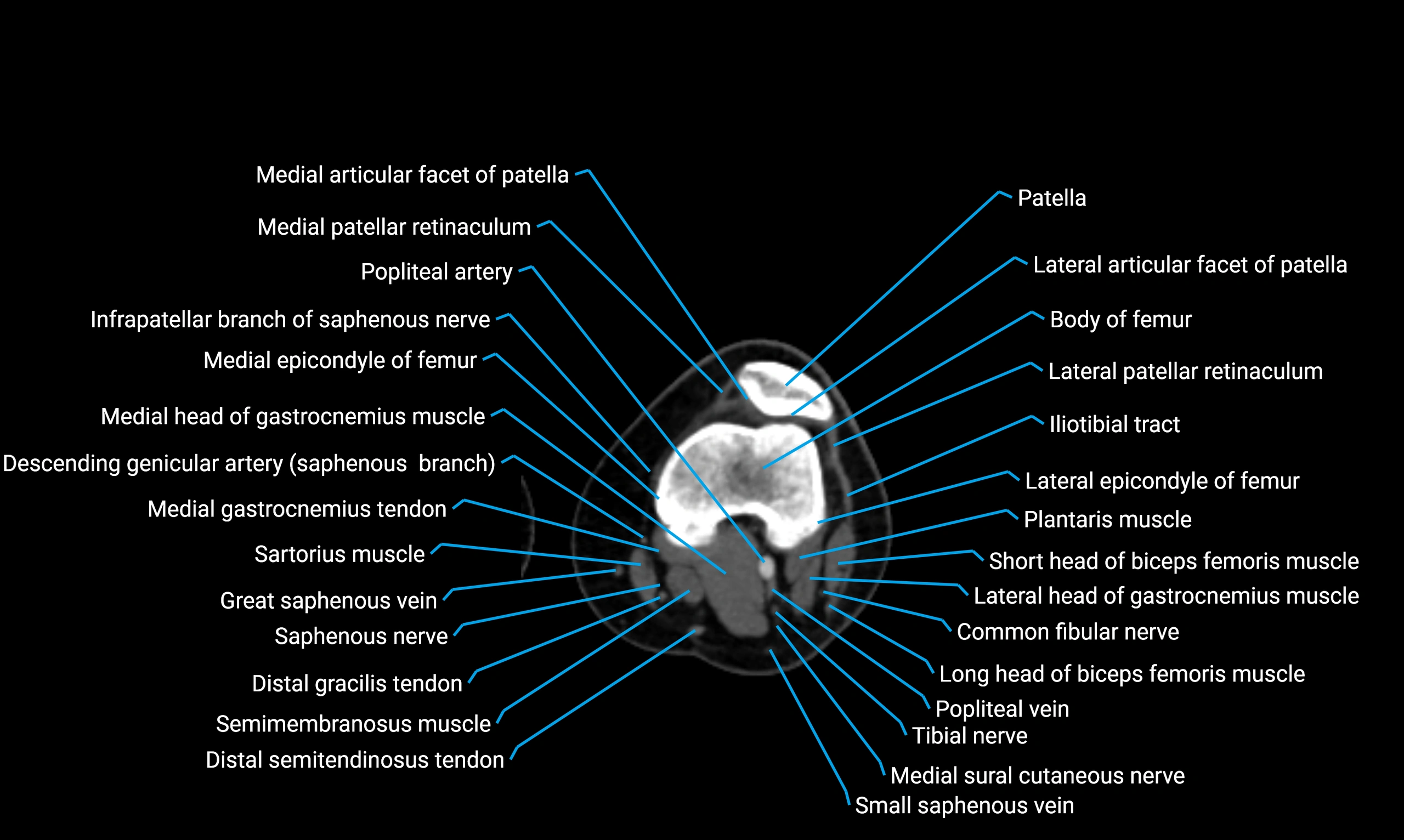
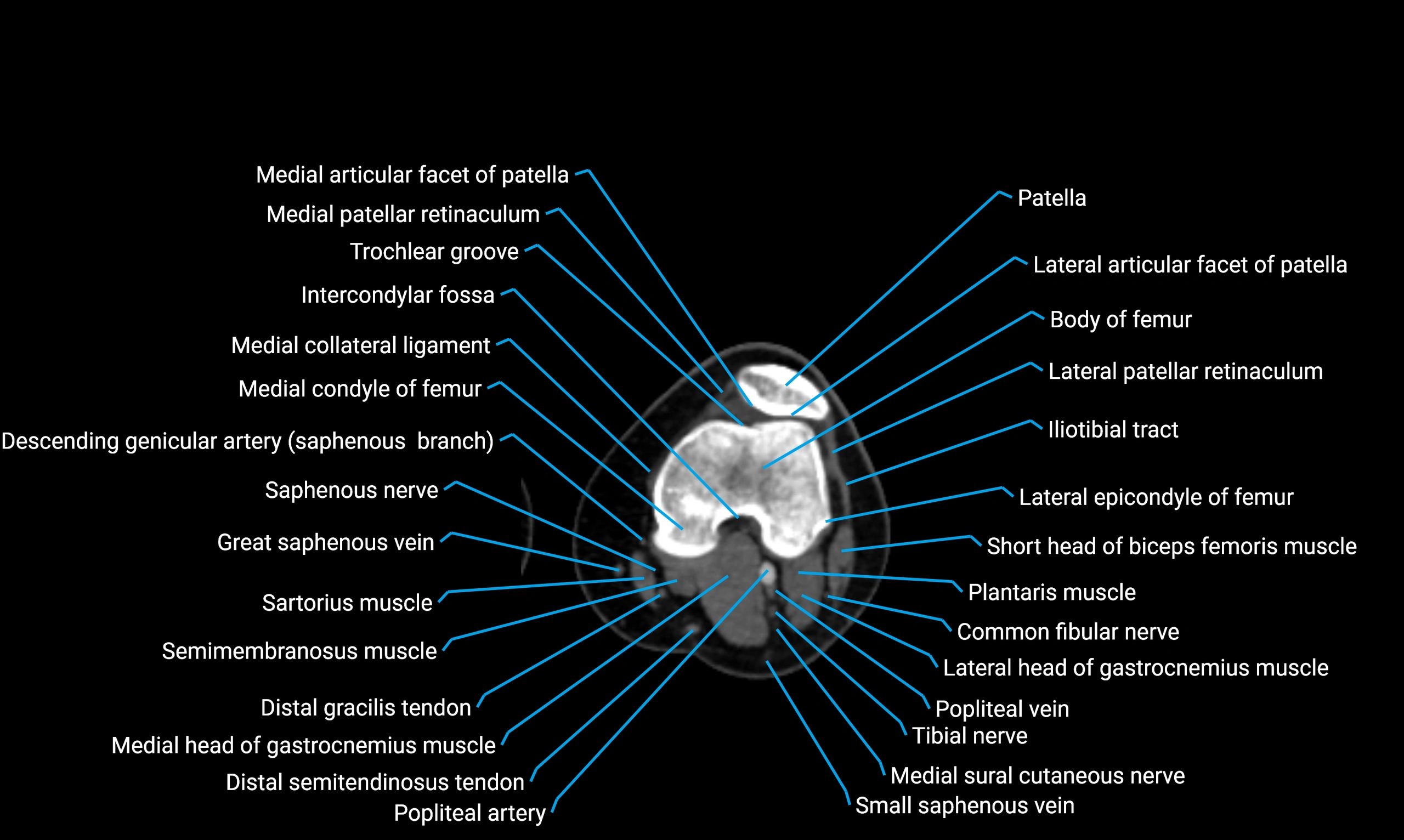
- Body of femur
- Body of fibula
- Body of ilium
- Body of ischium
- Body of lateral meniscus
- Body of medial meniscus
- Body of pubis
- Body of tibia
- Coccygeal nerve
- Coccygeal plexus
- Coccygeus muscle
- Coccyx
- Common fibular nerve
- Common iliac vein
- Conjoint tendon of biceps femoris & semitendinosus
- Deep femoral vein (profunda femoris vein)
- Descending genicular artery (Articular branches)
- Descending genicular artery (Saphenous branch)
- Distal adductor magnus tendon
- Distal biceps femoris tendon
- Distal quadriceps femoris tendon
- Distal rectus femoris tendon
- Distal semimembranosus tendon
- Distal semitendinosus tendon
- Distal vastus intermedius tendon
- Distal vastus lateralis tendon
- Distal vastus medialis tendon
- Erector spinae muscles
- Extensor digitorum longus muscle
- External anal sphincter
- External iliac lymph nodes
- External iliac vein
- Female urethra
- Femoral condyle articular cartilage
- Femoral nerve
- Femoral shaft
- Femur
- Fibula
- Fibular articular facet of tibia
- Fibularis longus muscle (peroneus longus muscle)
- Fovea for ligament of head of femur
- Gastrocnemius muscle
- Gerdy’s tubercle
- Gluteal tuberosity
- Gluteus medius muscle
- Gluteus medius tendon
- Gluteus minimus muscle
- Gluteus minimus tendon
- Gracilis Tendon (Proximal)
- Gracilis muscle
- Gracilis tendon (Distal)
- Greater sciatic notch
- Greater trochanter
- Groove for popliteus muscle
- Hamstring muscles
- Head of femur
- Head of fibula
- Hip joint
- Iliac bone
- Iliopsoas muscle
- Iliopsoas tendon
- Iliopubic eminence
- Ilium bone
- Inferior gemellus muscle
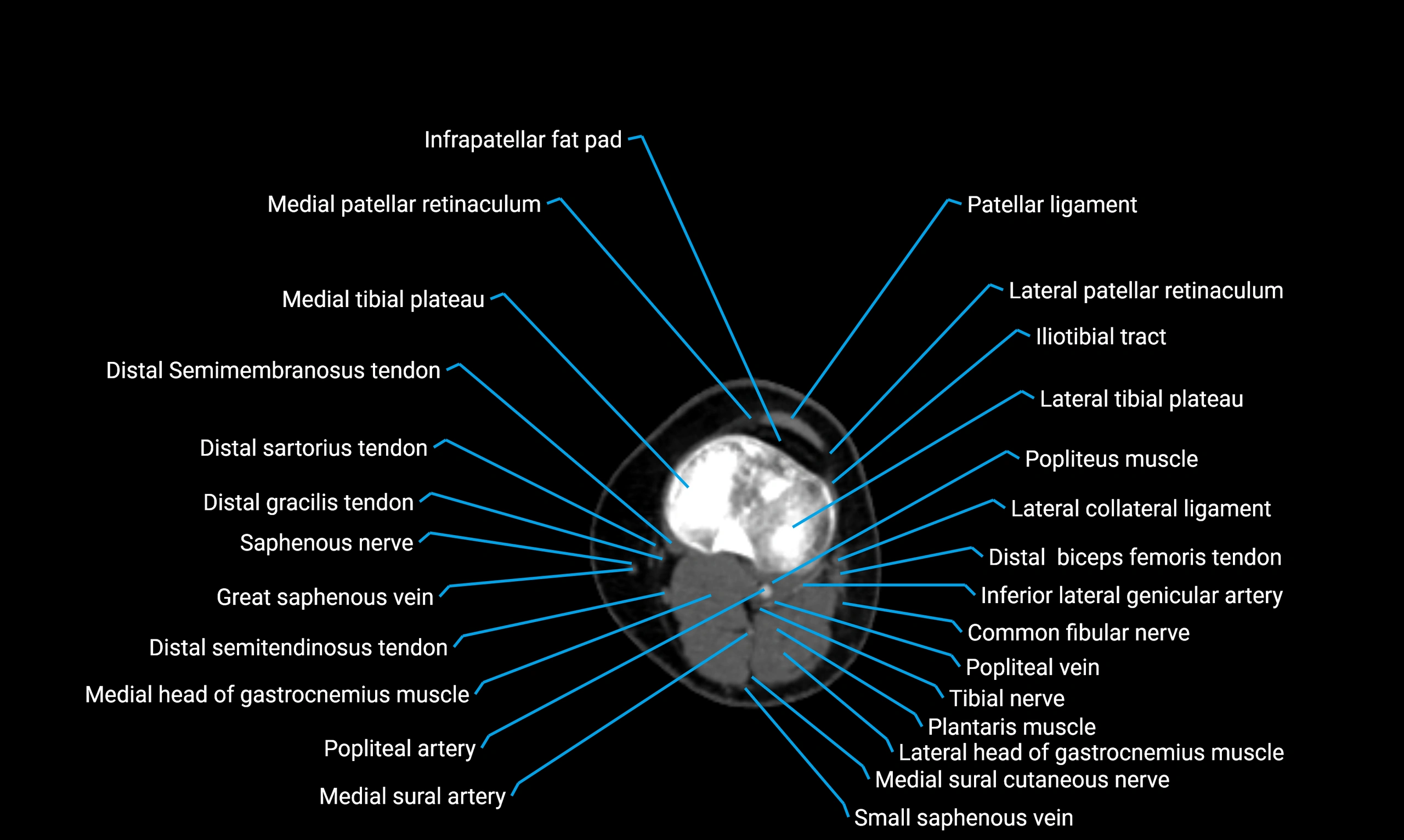
- Inferior lateral genicular artery
- Inferior lateral genicular vein
- Inferior pubic ligament
- Inferior pubic ramus
- Inferior rim of acetabulum
- Infrapatellar branch of saphenous nerve
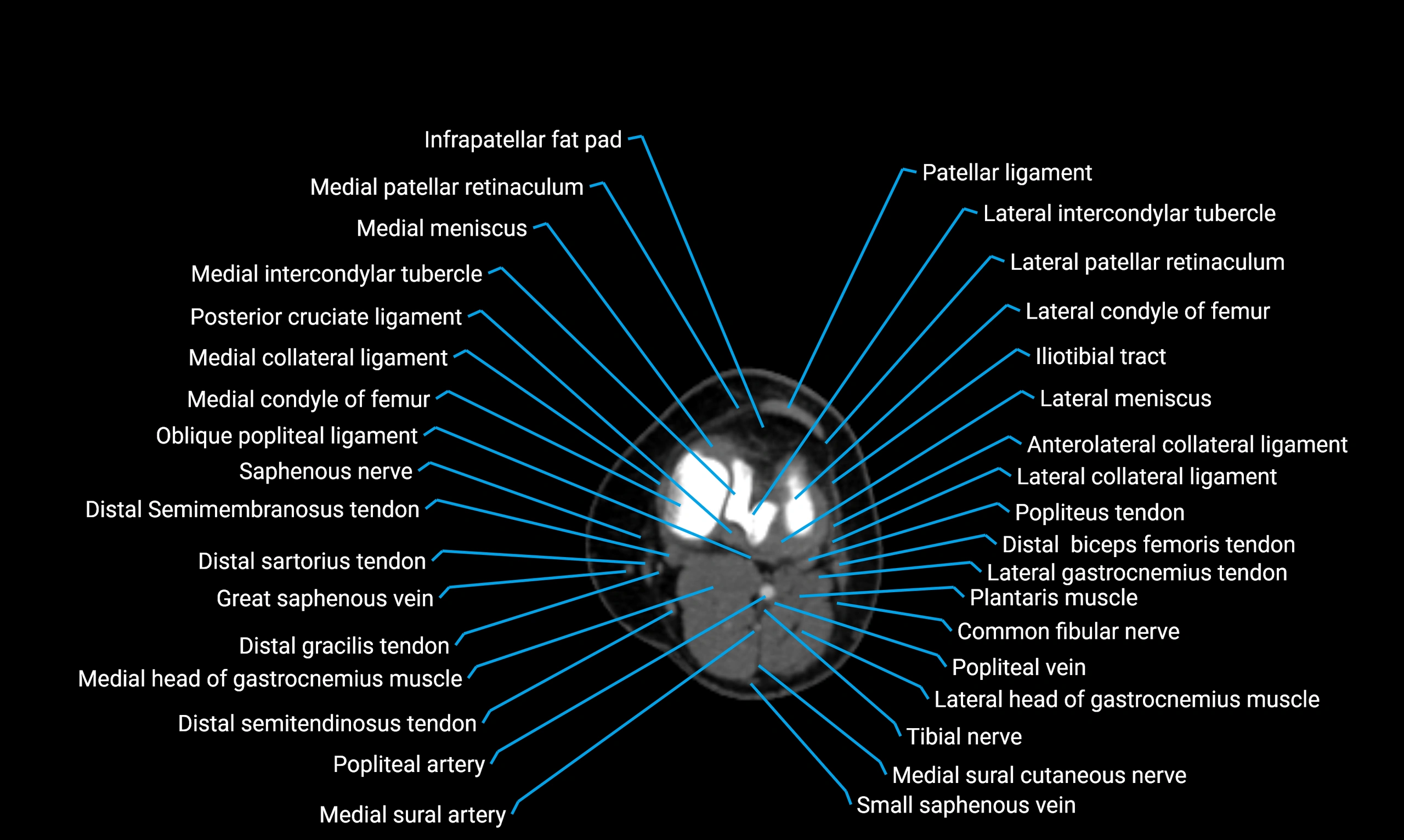
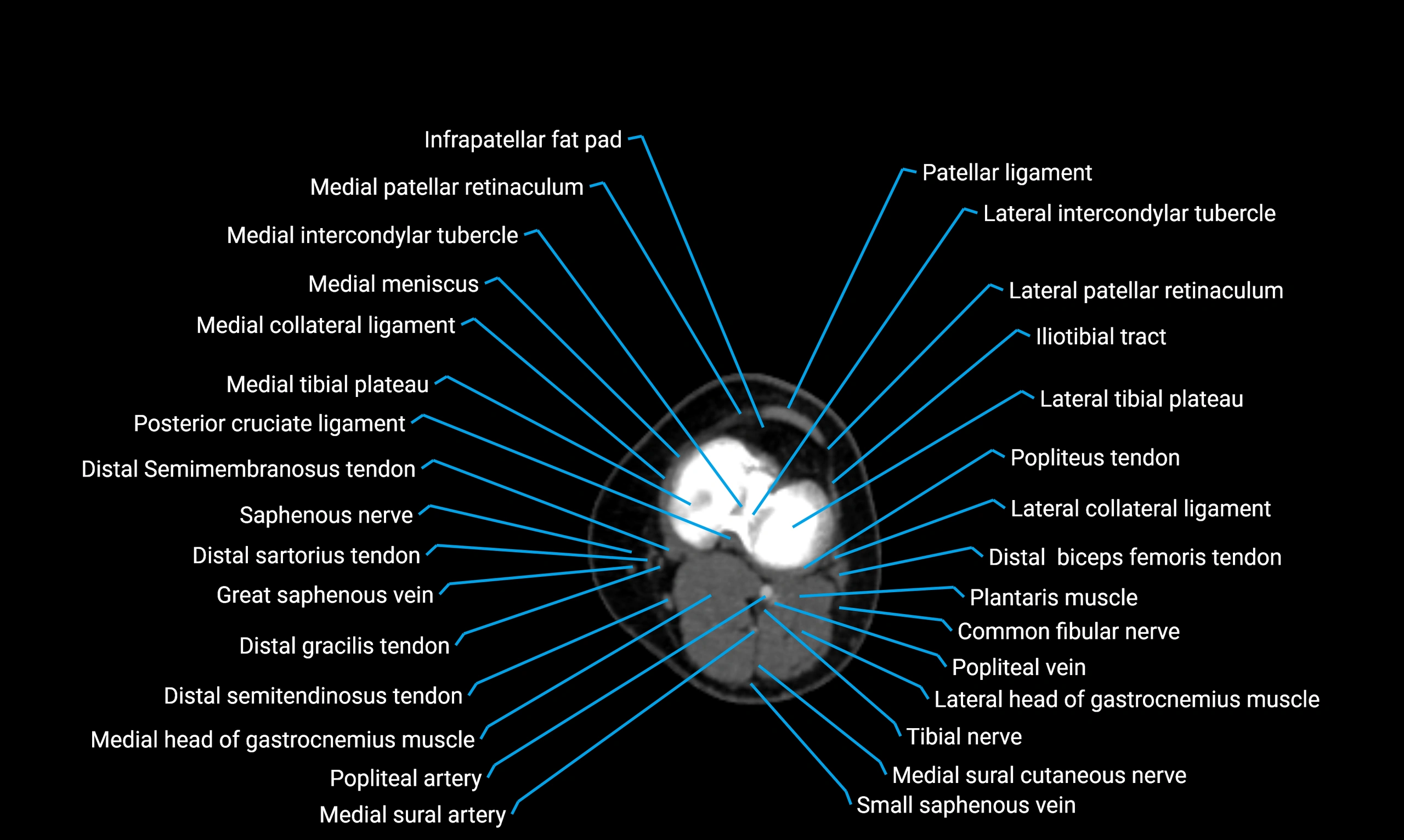
- Infrapatellar fat pad
- Inguinal ligament
- Inguinal lymph nodes
- Intercondylar eminence
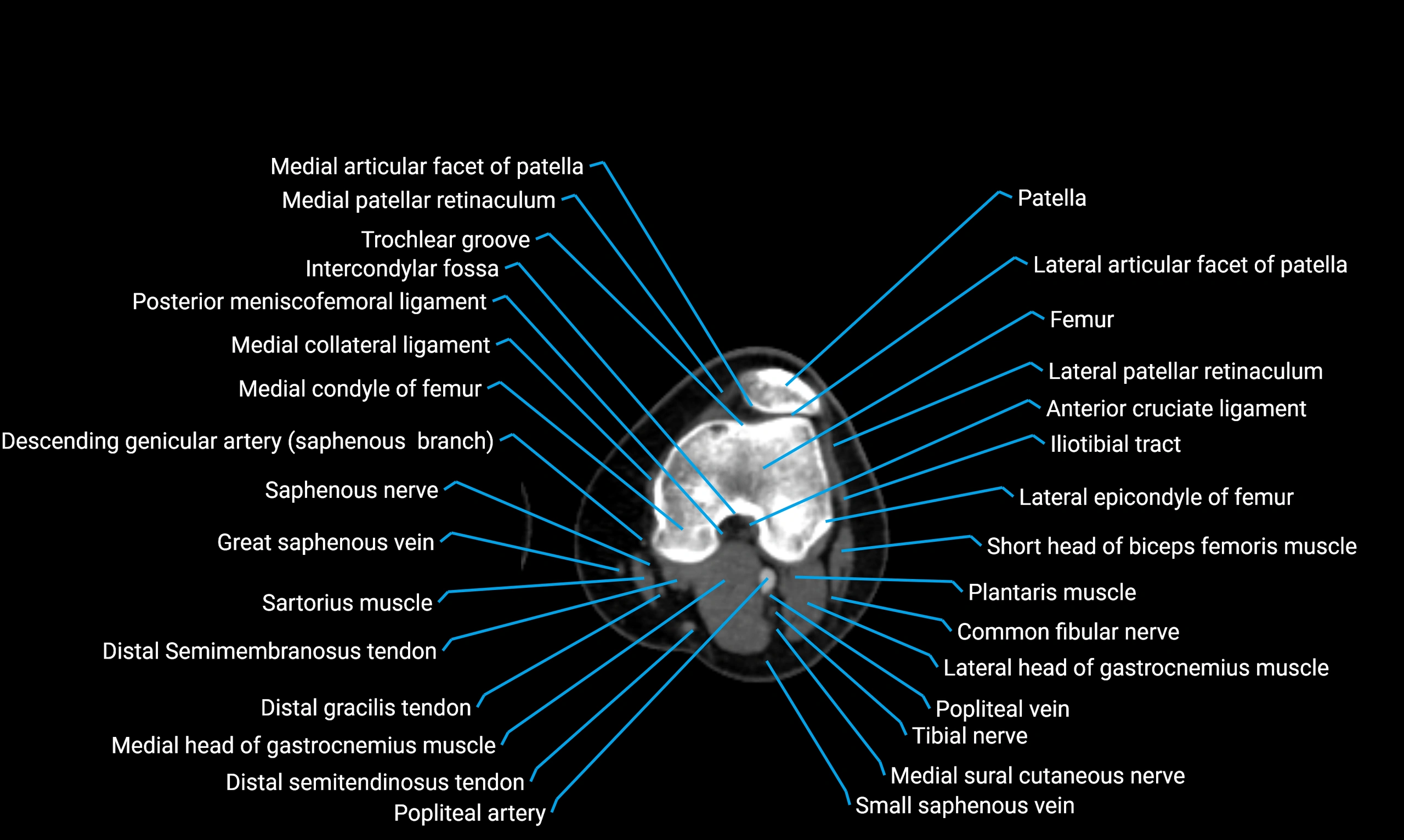
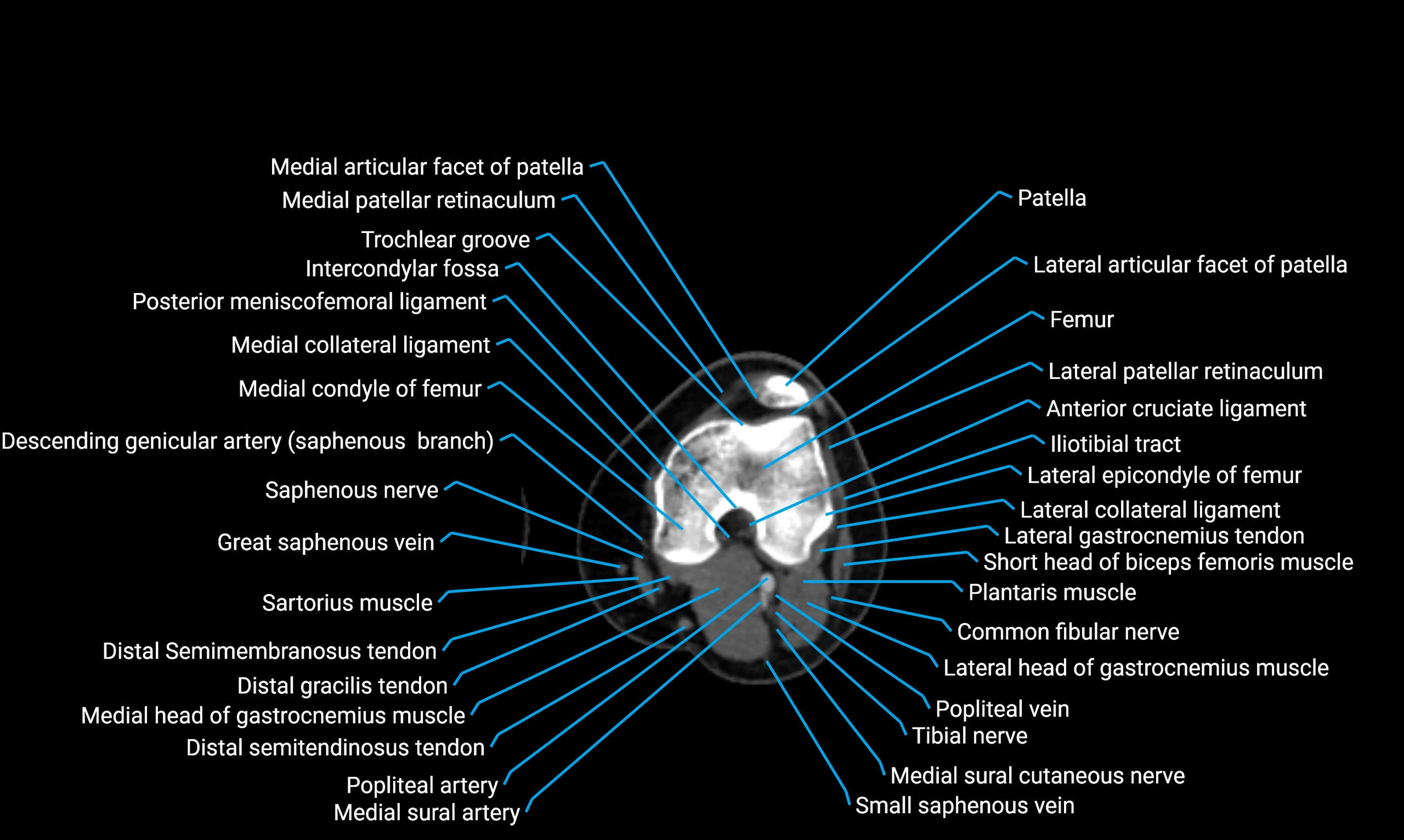
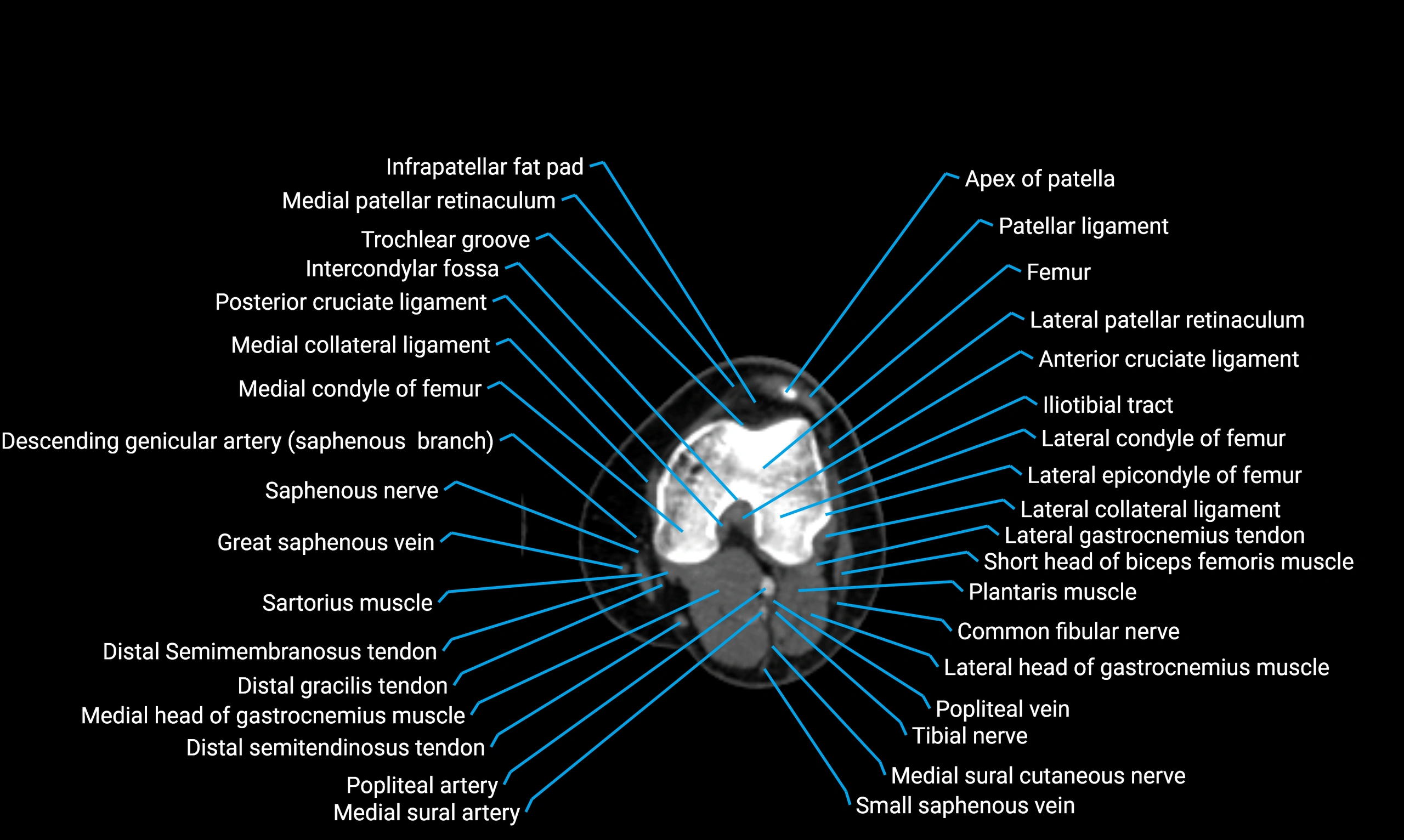
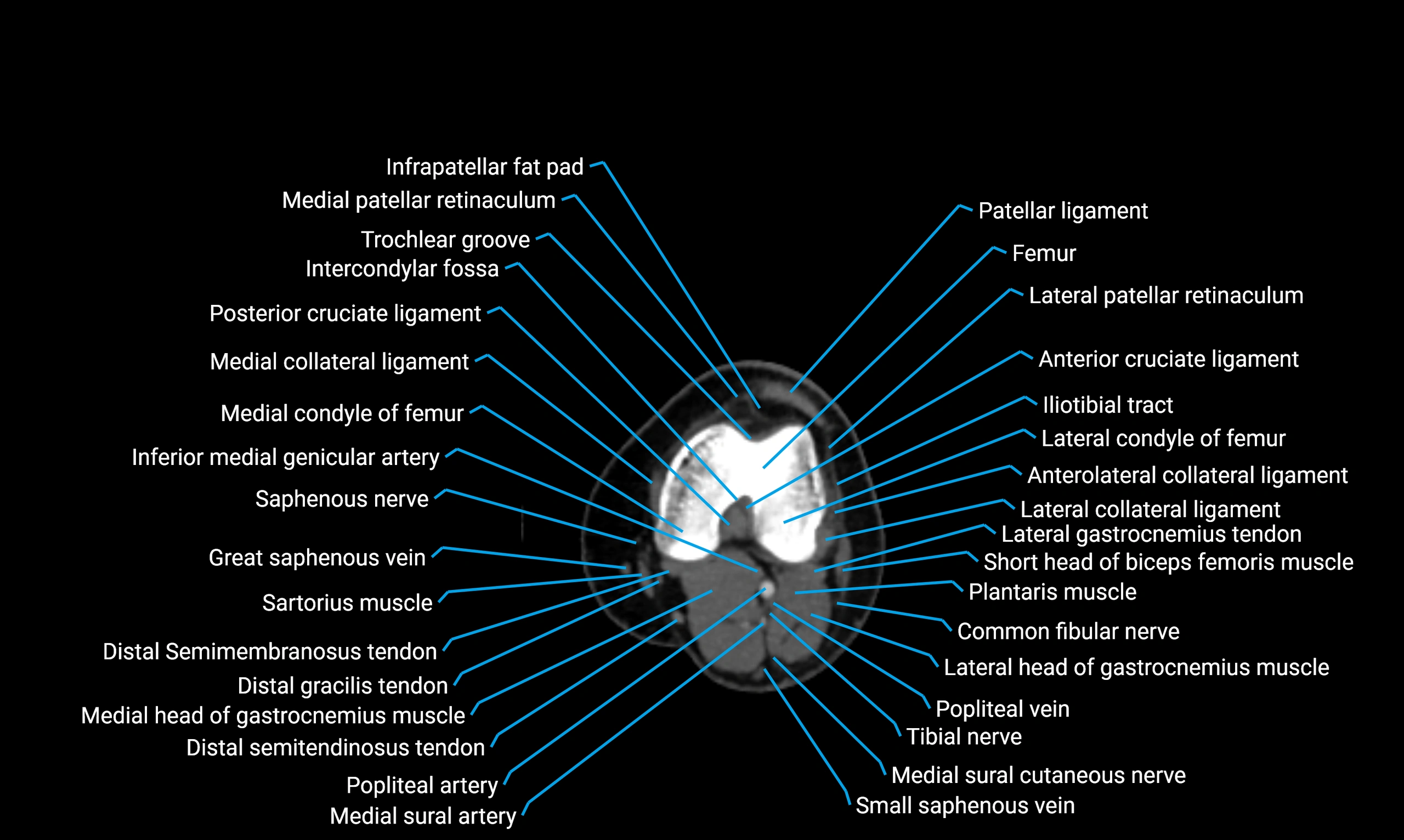
- Intercondylar fossa
- Intermediate lacunar external iliac lymph nodes
- Intermediate sacral crest
- Internal anal sphincter
- Internal iliac lymph nodes
- Internal urethral orifice
- Intertrochanteric crest
- Ischial spine
- Ischial tuberosity
- Ischioanal fossa
- Ischiopubic ramus
- Ischium bone
- Knee Joint
- Lateral articular facet of patella
- Lateral border of patella
- Lateral collateral ligament
- Lateral condyle of femur
- Lateral condyle of tibia
- Lateral epicondyle of femur
- Lateral femoral cutaneous nerve
- Lateral gastrocnemius tendon
- Lateral head of gastrocnemius muscle
- Lateral intercondylar tubercle
- Lateral meniscus
- Lateral part of sacrum
- Lateral patellar retinaculum
- Lateral patellofemoral ligament
- Lateral sacral crest
- Lateral supracondylar line
- Lateral sural cutaneous nerve
- Lateral tibial plateau
- Lateral tibiofemoral joint space
- Levator ani muscle
- Lumbosacral trunk
- Medial articular facet of patella
- Medial border of patella
- Medial collateral ligament
- Medial condyle of femur
- Medial condyle of tibia
- Medial epicondyle of femur
- Medial gastrocnemius tendon
- Medial head of gastrocnemius muscle
- Medial intercondylar tubercle
- Medial meniscus
- Medial patellar retinaculum
- Medial patellofemoral ligament
- Medial supracondylar line
- Medial sural cutaneous nerve
- Medial tibial plateau
- Medial tibiofemoral joint space
- Median sacral crest
- Median umbilical ligament
- Meniscus cartilage
- Mesorectum
- Muscular branches of femoral nerve
- Muscular branches of tibial nerve
- Neck of femur
- Neck of fibula
- Oblique popliteal ligament
- Obturator externus muscle
- Obturator foramen
- Obturator internus muscle
- Obturator lymph nodes
- Obturator nerve
- Obturator veins
- Patella
- Patellar articular cartilage
- Patellar tendon (patellar ligament)
- Pectineus muscle
- Perforating Arteries (Knee joint)
- Perineal nerves
- Plantaris muscle
- Popliteal artery
- Popliteal lymph nodes
- Popliteal vein
- Popliteal–Saphenous perforating veins
- Popliteus muscle
- Popliteus tendon
- Posterior acetabular wall
- Posterior cruciate ligament
- Posterior division of obturator nerve (Posterior branch of obturator nerve)
- Posterior horn of lateral meniscus
- Posterior horn of medial meniscus
- Posterior inferior iliac spine
- Posterior lateral femoral cutaneous nerve
- Posterior ligament of fibular head
- Posterior meniscofemoral ligament
- Posterior rim of acetabulum
- Posterior root of lateral meniscus
- Posterior root of medial meniscus
- Posterior sacral foramina
- Posterior wall of acetabulum
- Prefemoral fat pad
- Pubic symphysis
- Puborectalis muscle
- Pyramidal muscle (pyramidalis muscle)
- Quadratus femoris muscle
- Ramus of ischium
- Rectovaginal septum (rectovaginal fascia)
- Rectus femoris muscle
- Rectus femoris tendon (Proximal tendon of rectus femoris)
- Sacral hiatus
- Sacral plexus
- Sacrotuberous ligament
- Sacrum
- Saphenous nerve
- Sartorius Tendon (Proximal)
- Sartorius muscle
- Sartorius tendon (Distal)
- Semimembranosus muscle
- Semimembranosus tendon (proximal)
- Semitendinosus muscle
- Small saphenous vein
- Soleus muscle
- Spinal nerve L5
- Spinal nerve S1
- Superior gemellus muscle
- Superior lateral genicular artery
- Superior lateral genicular vein
- Superior medial genicular artery
- Superior medial genicular vein
- Superior pubic ligament
- Superior pubic ramus
- Superior rectal artery
- Superior rim of acetabulum
- Suprapatellar fat pad
- Tensor fasciae latae muscle
- Tensor fasciae latae tendon
- Third trochanter
- Tibia
- Tibial condyle articular cartilage
- Tibial nerve
- Tibial tuberosity
- Tibialis anterior muscle
- Tibiofibular joint (proximal)
- Transverse ligament of knee
- Trochanteric fossa
- Trochlear groove
- Tubercle of iliotibial tract
- Urinary bladder
- Uterosacral ligament
- Uterus
- Vastus Lateralis Obliquus Muscle
- Vastus intermedius muscle
- Vastus lateralis muscle
- Vastus medialis muscle
- Vesicovaginal space
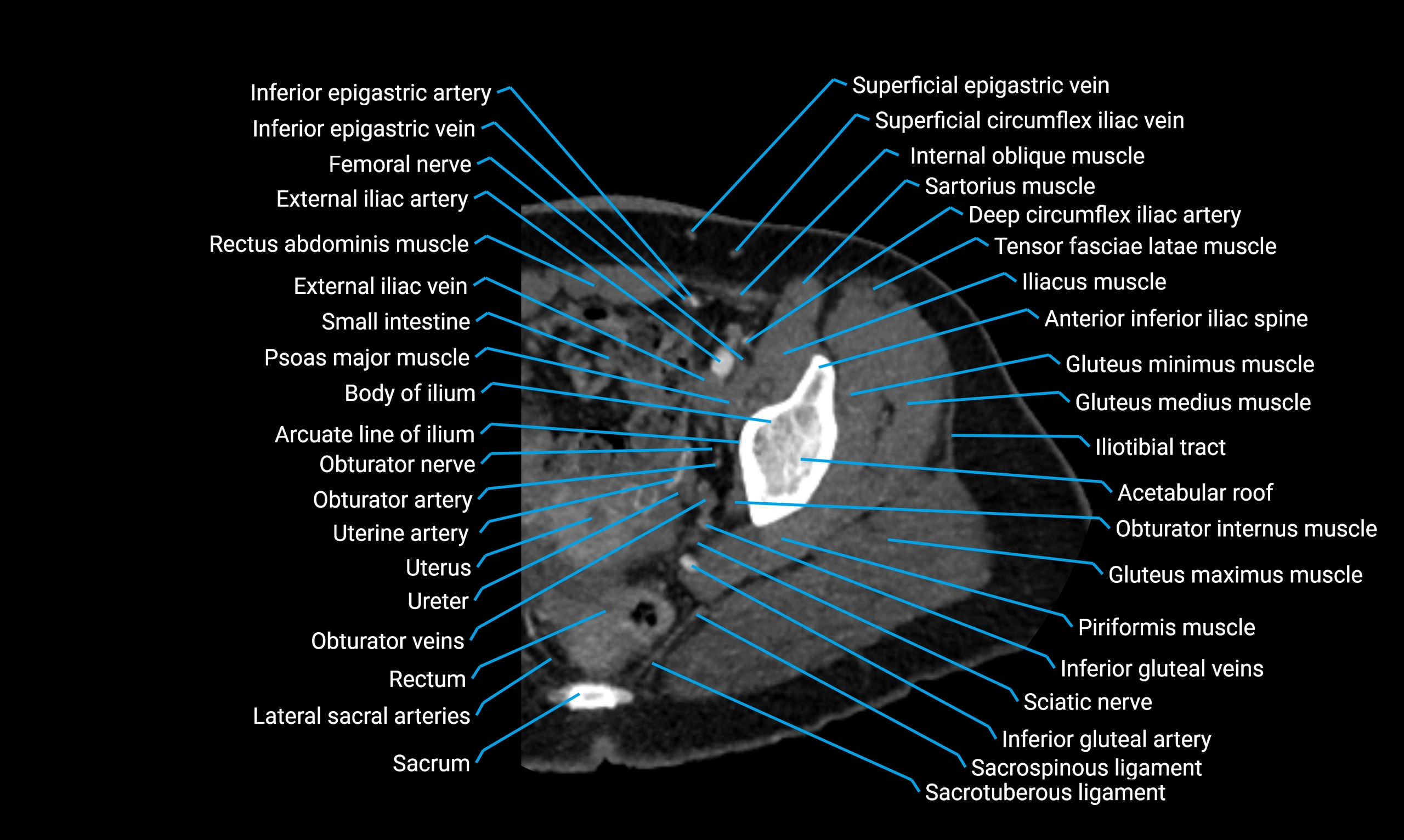
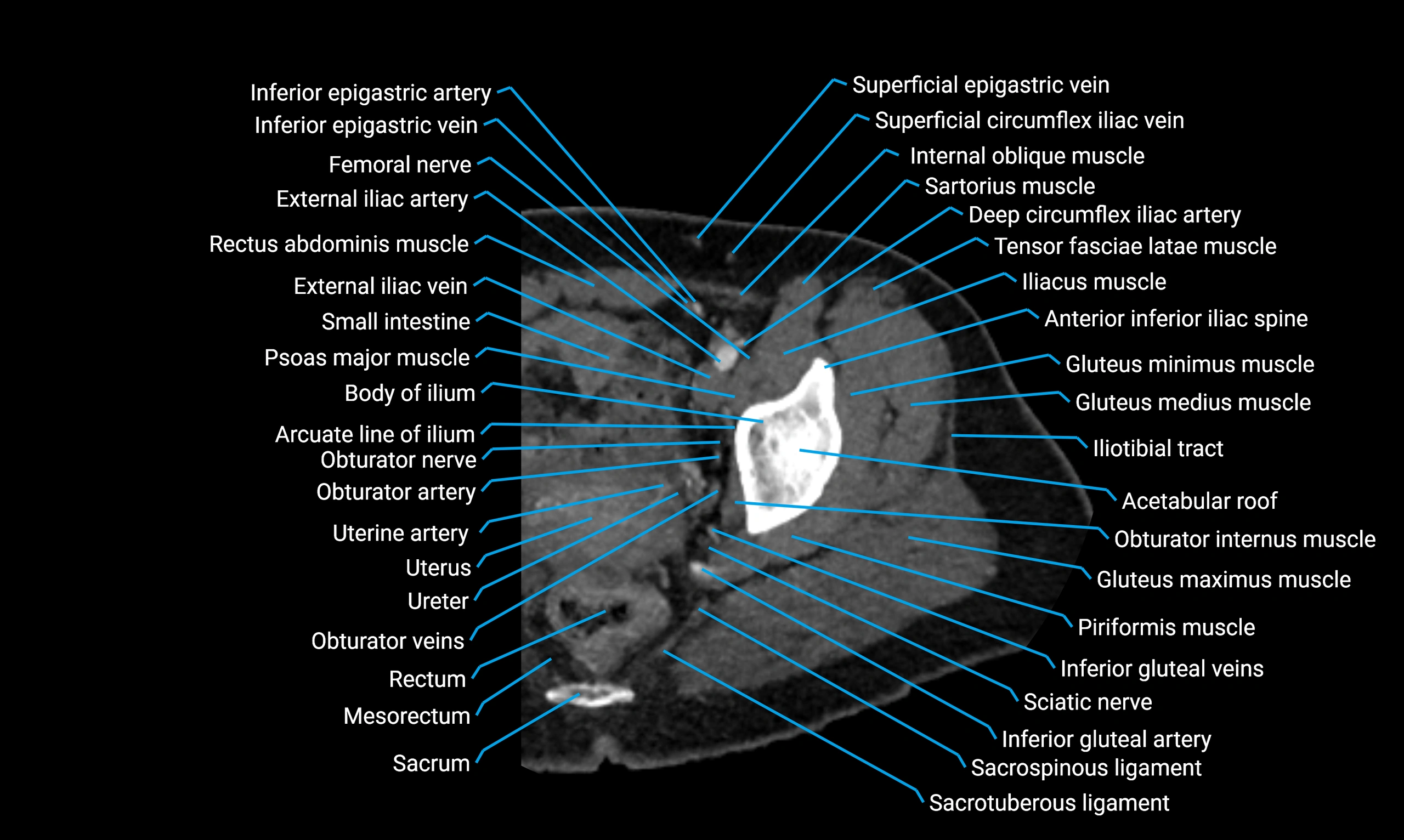
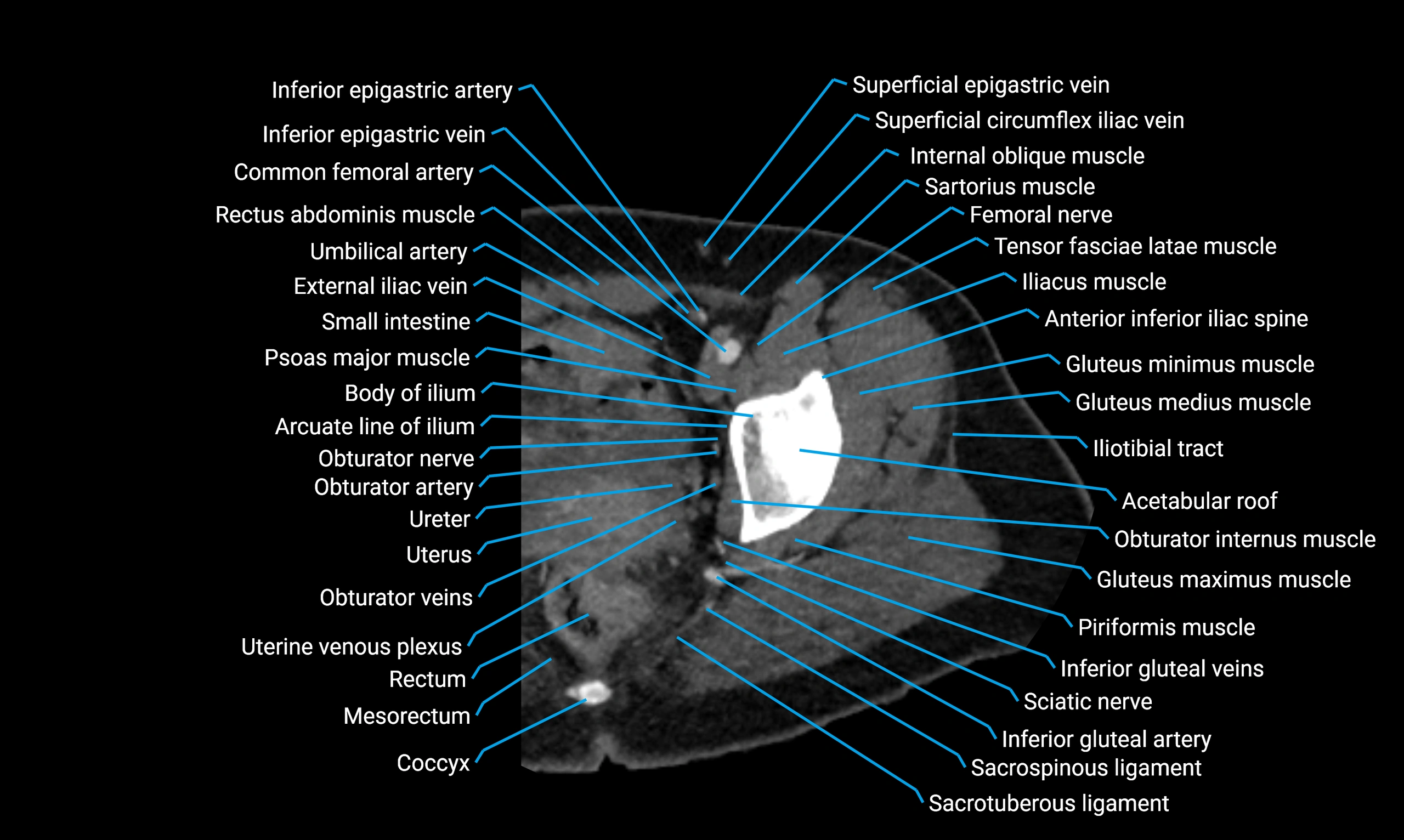
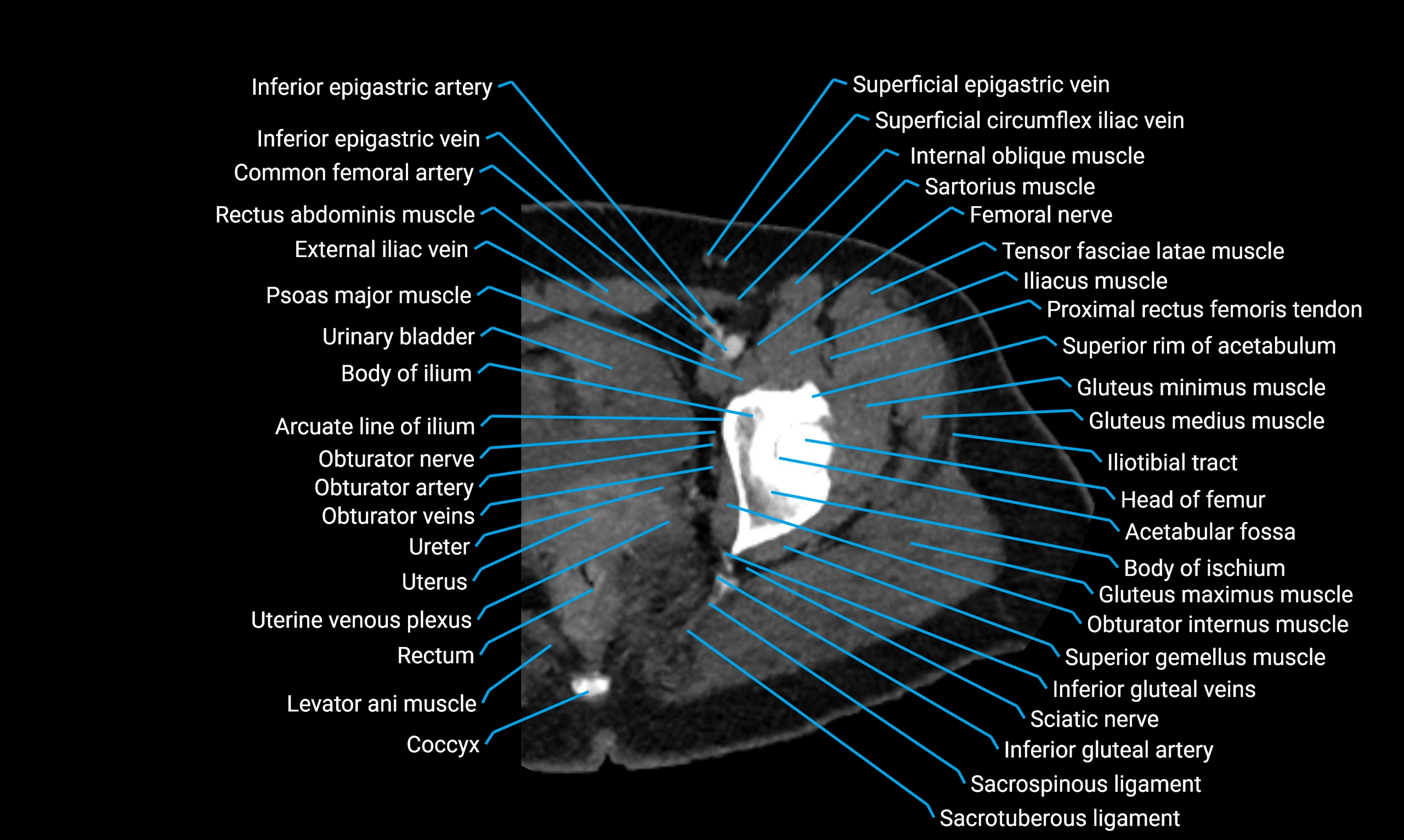
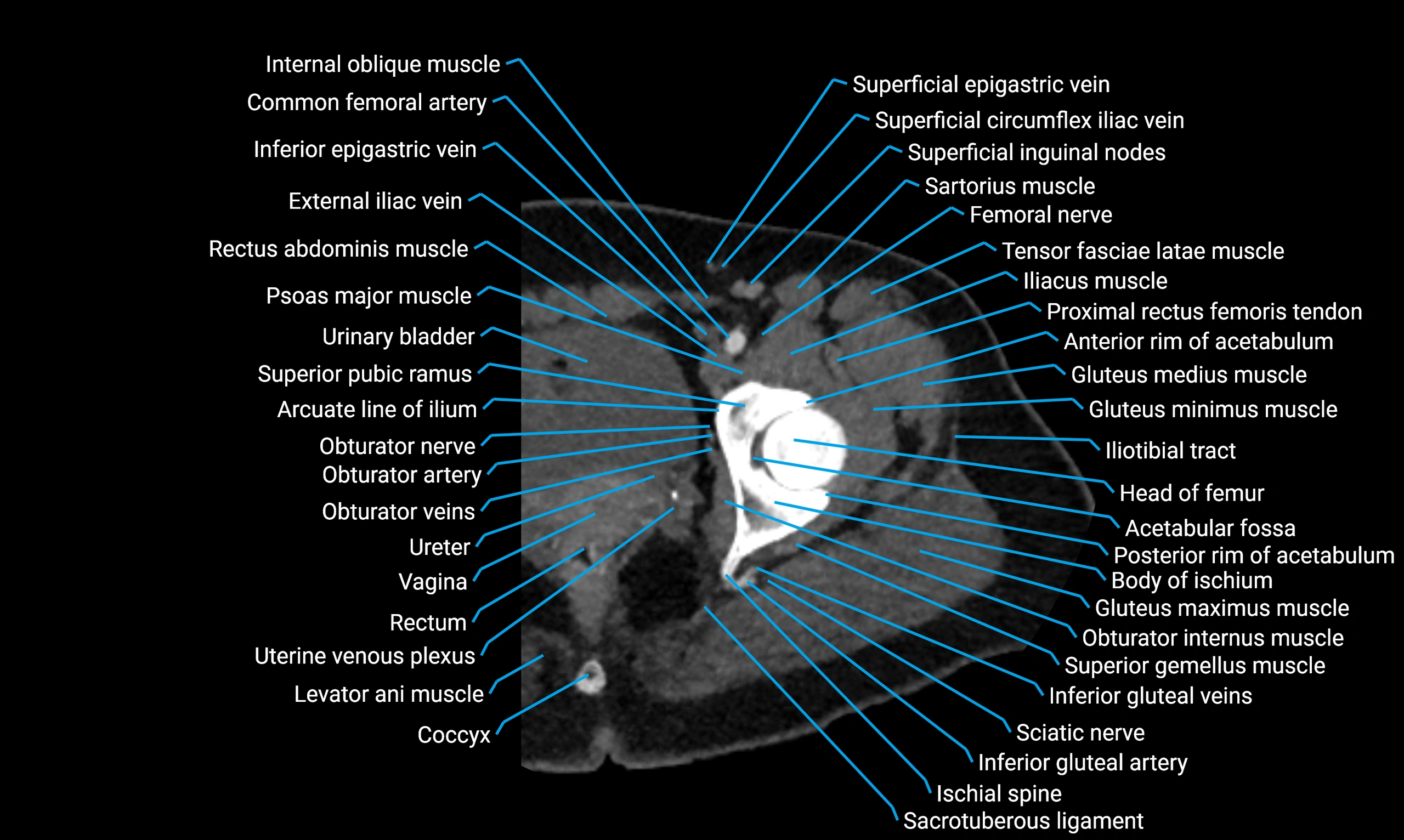
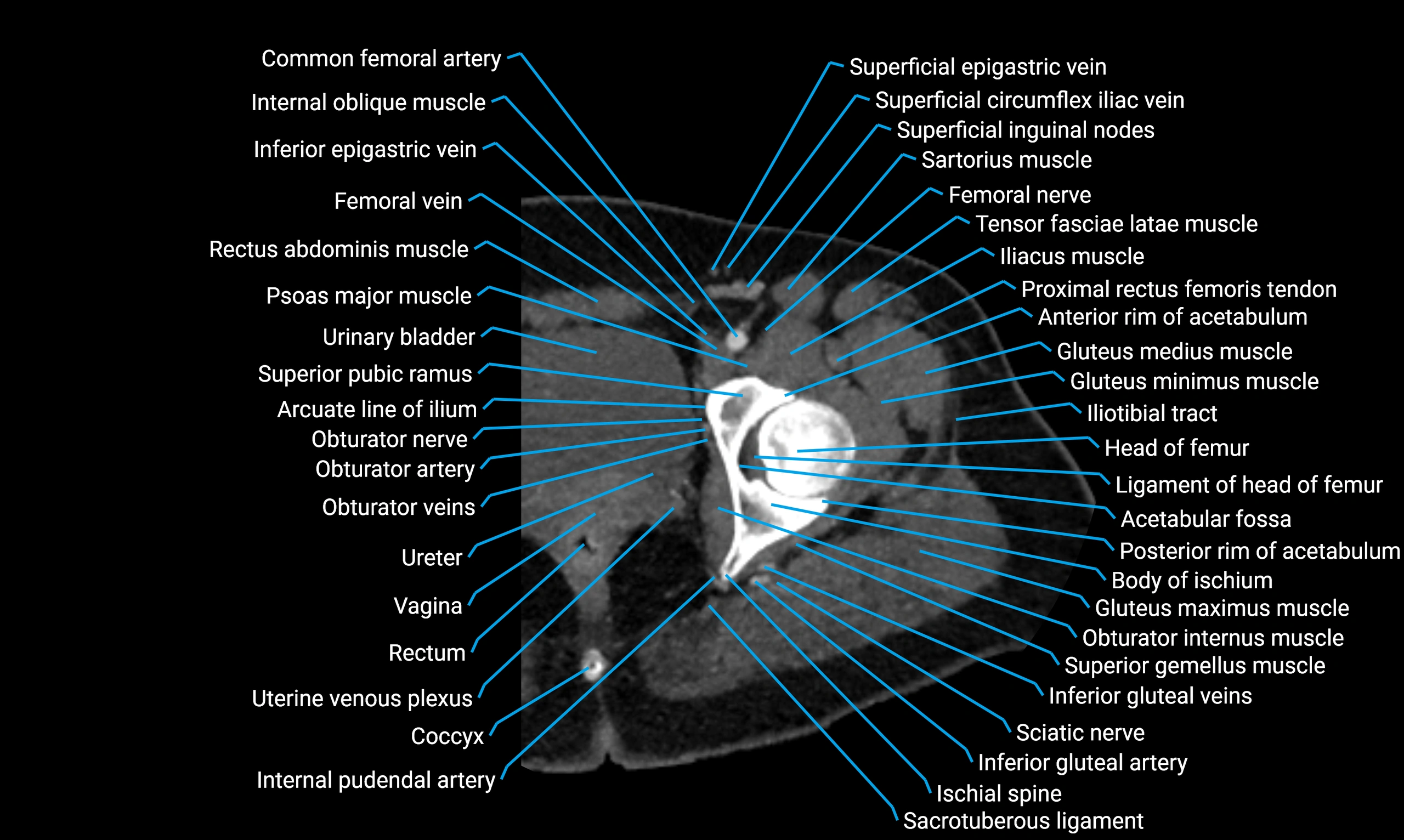
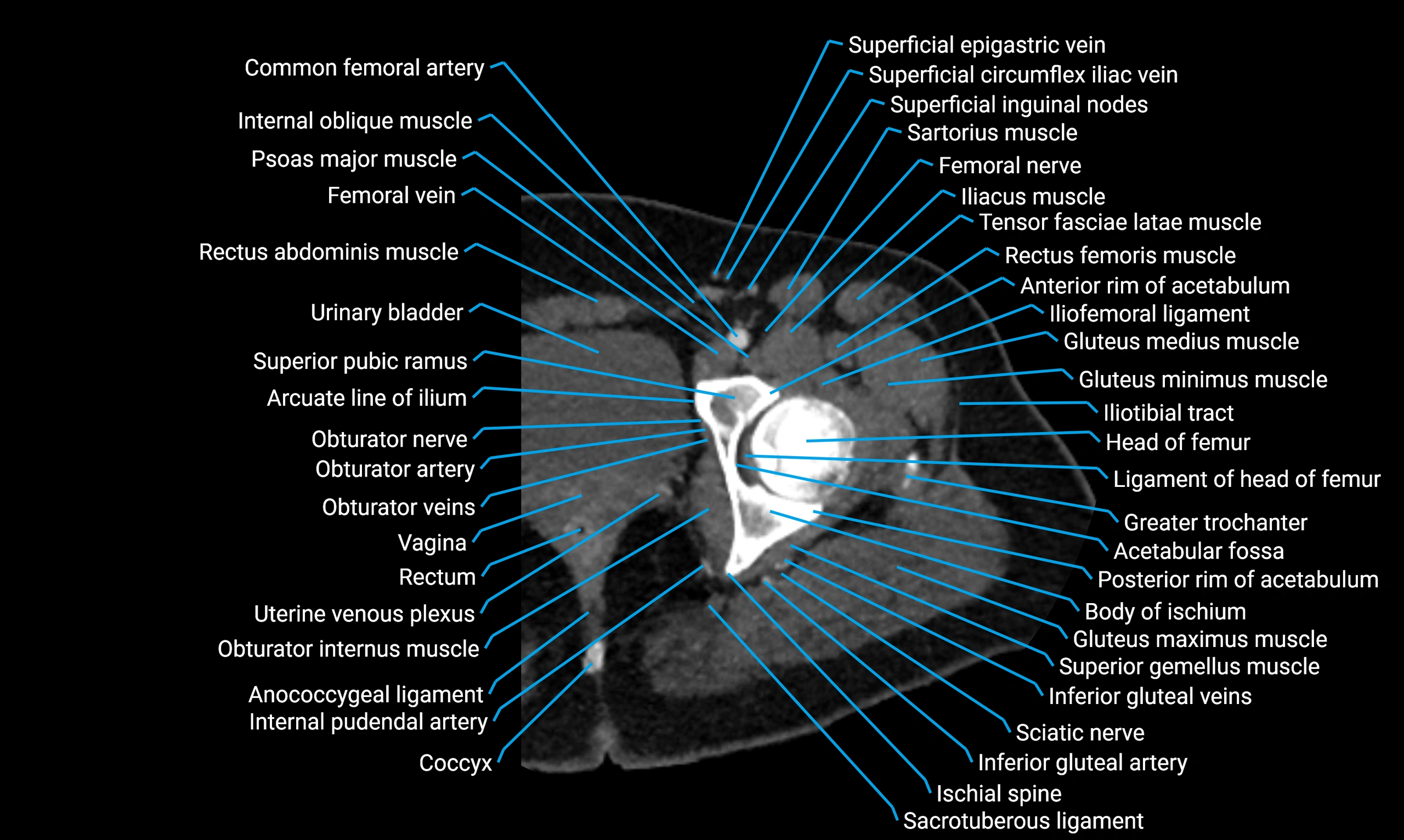
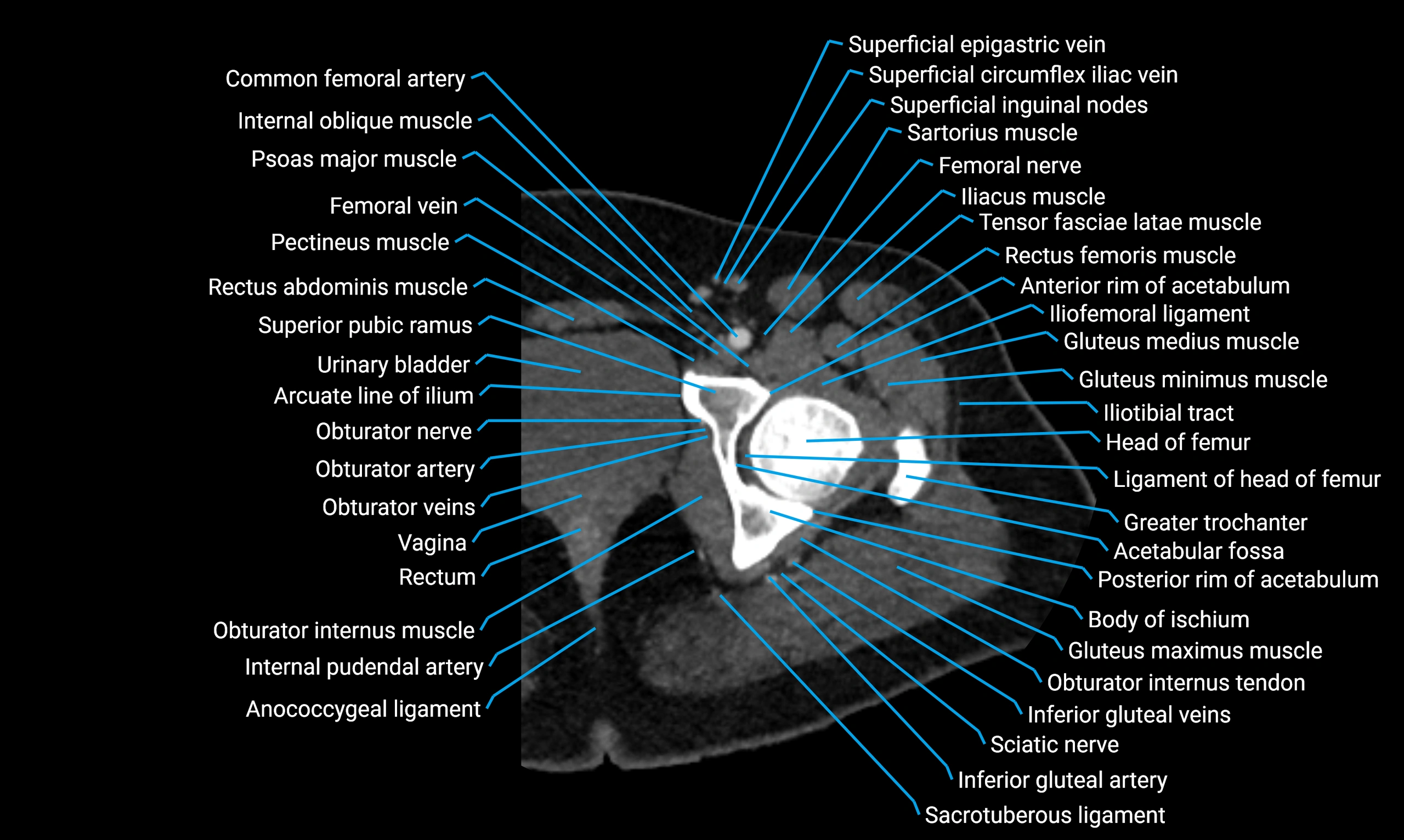
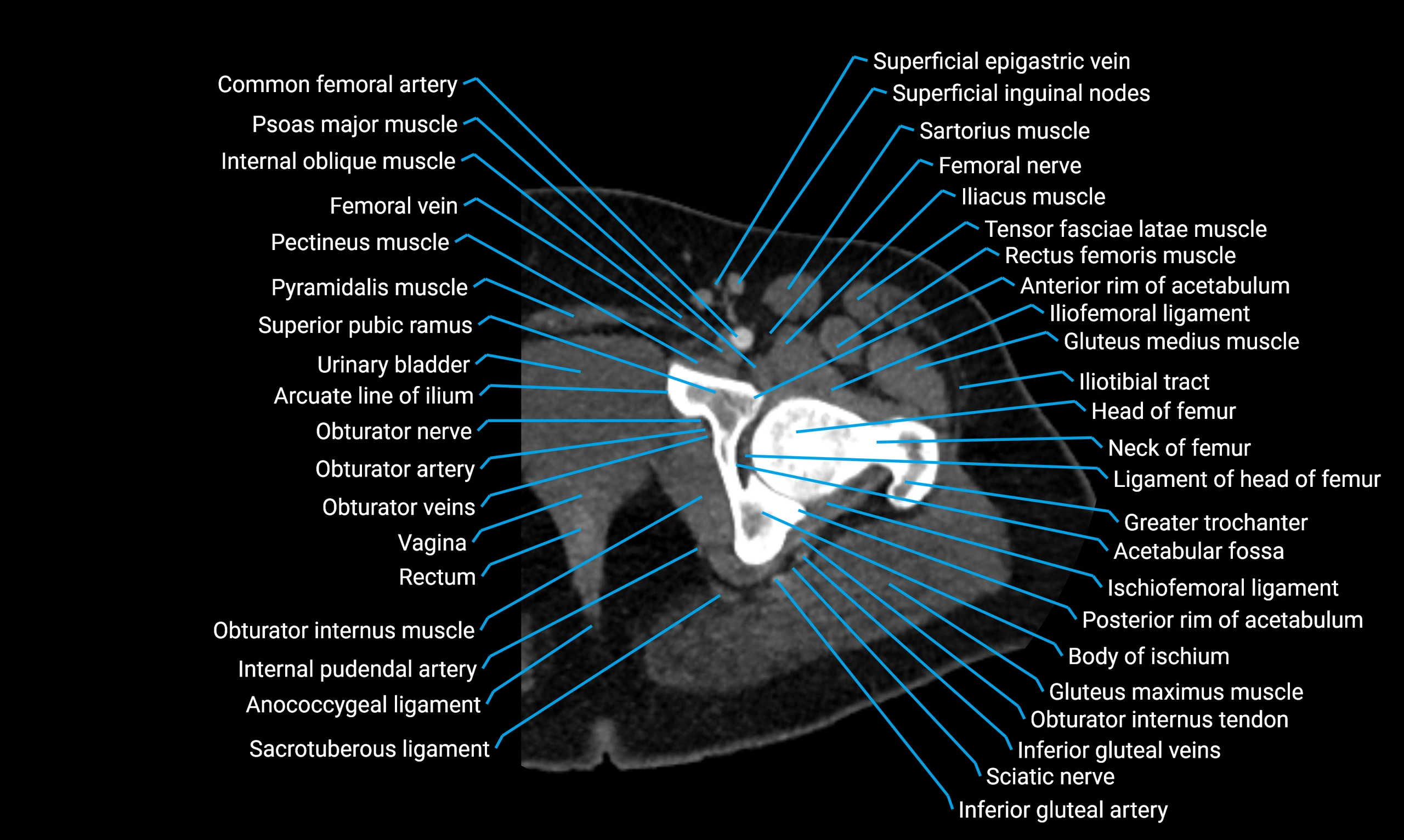
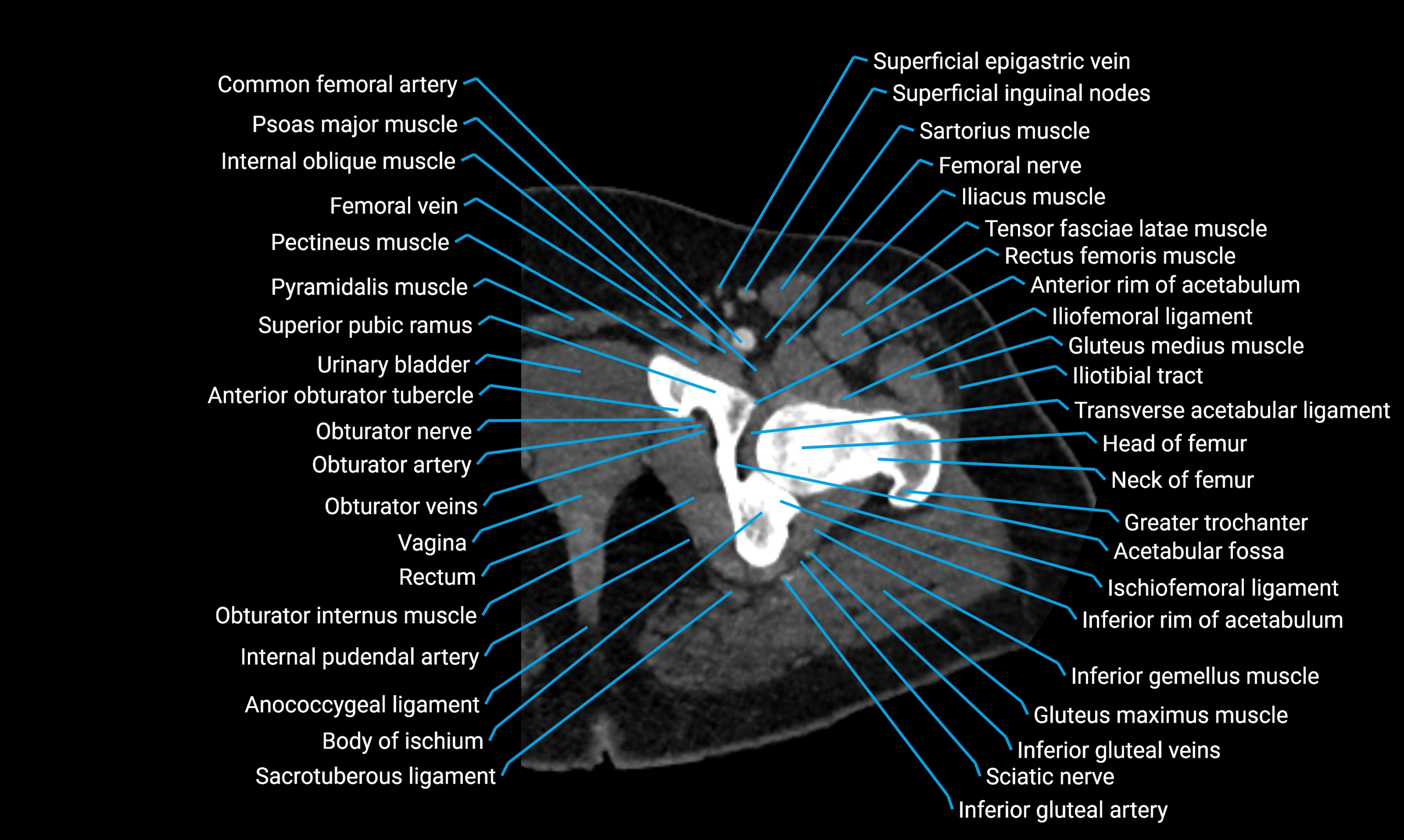
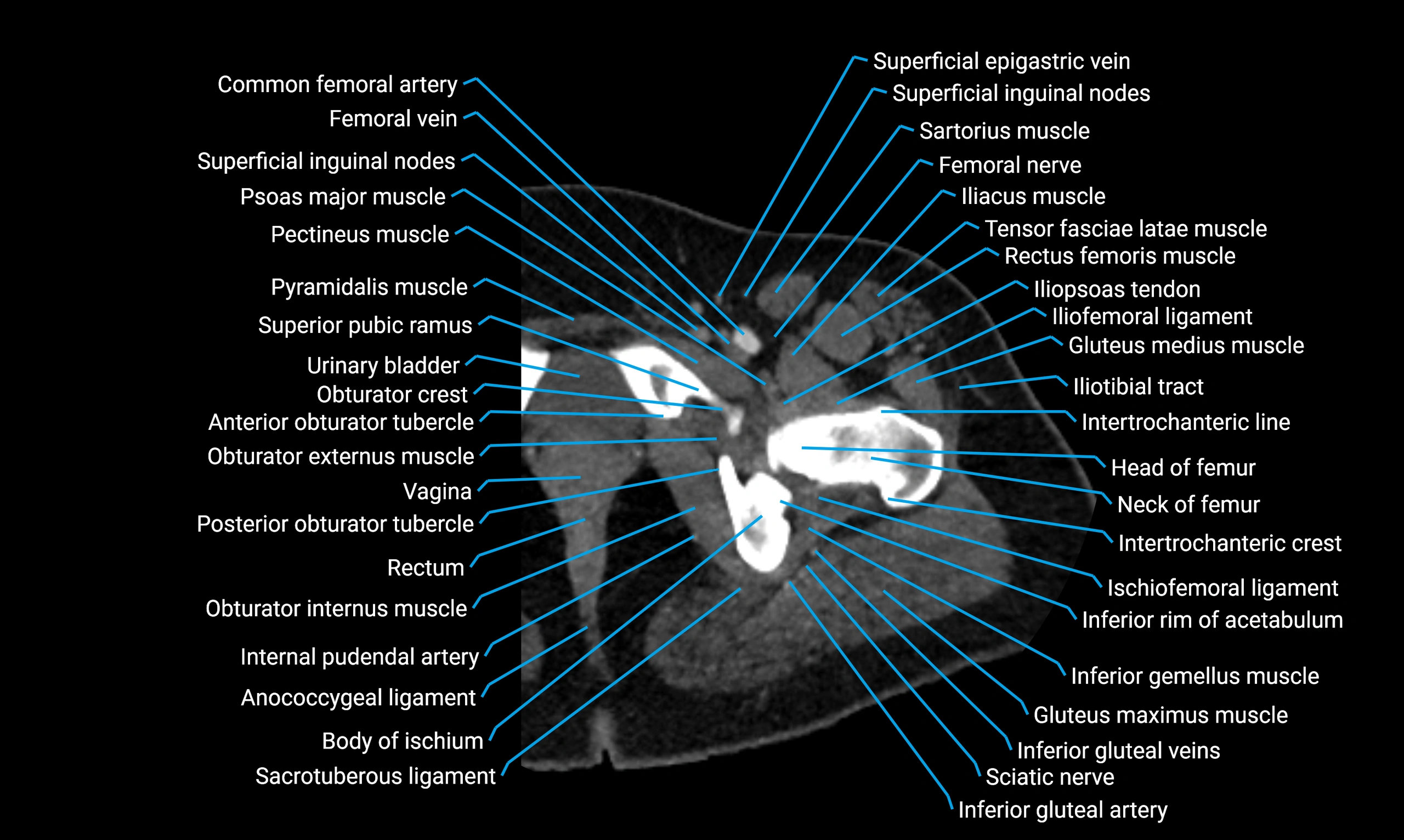
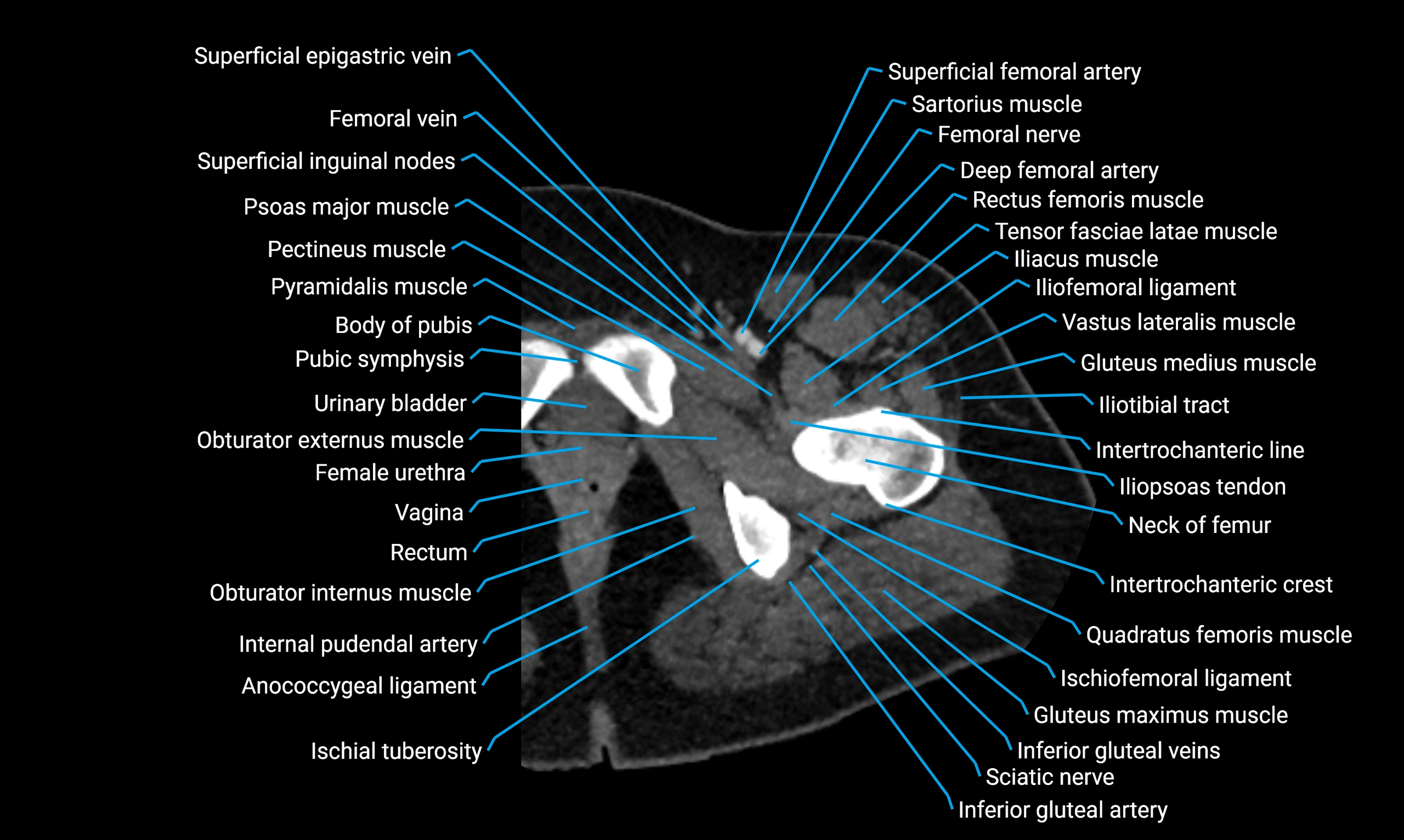
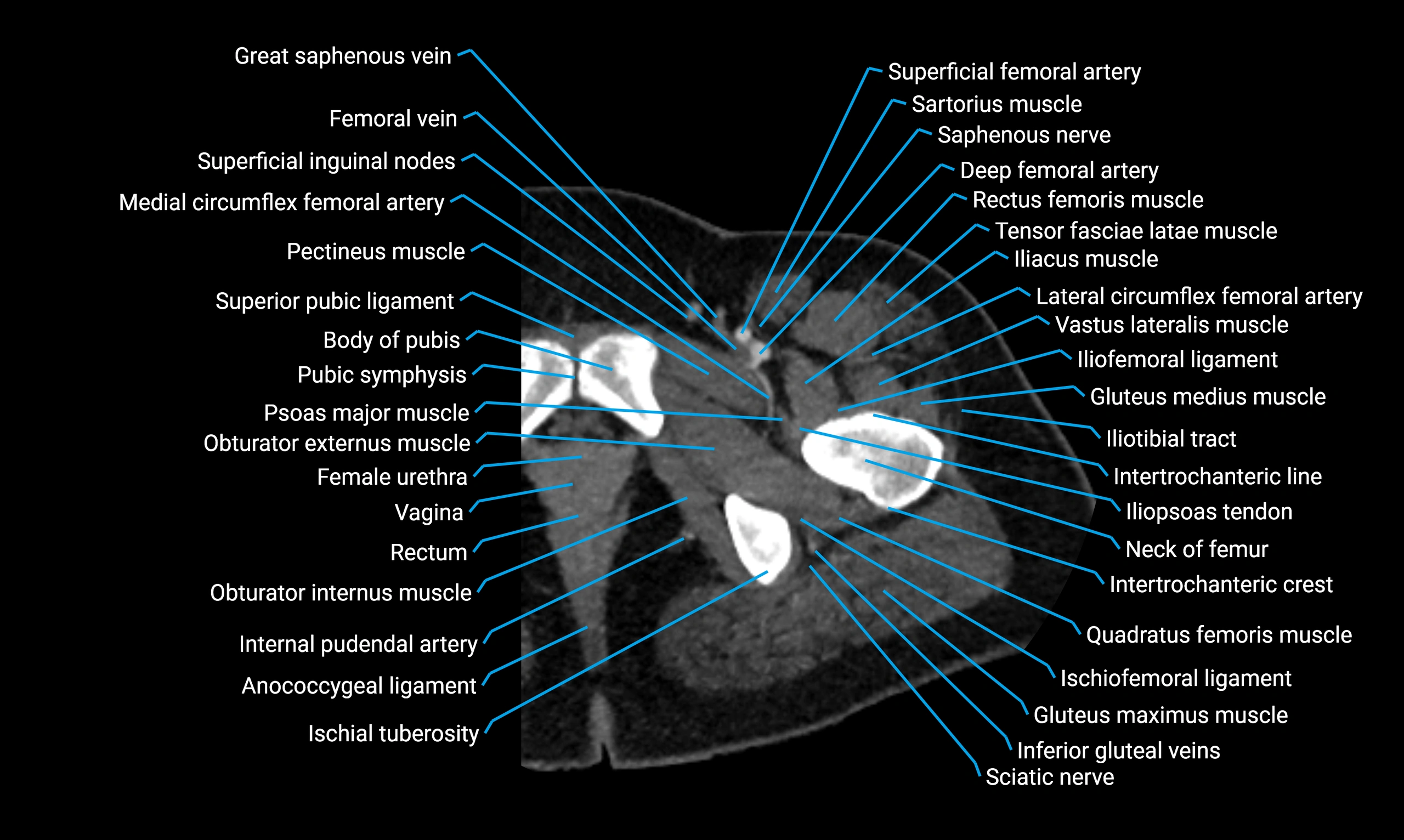
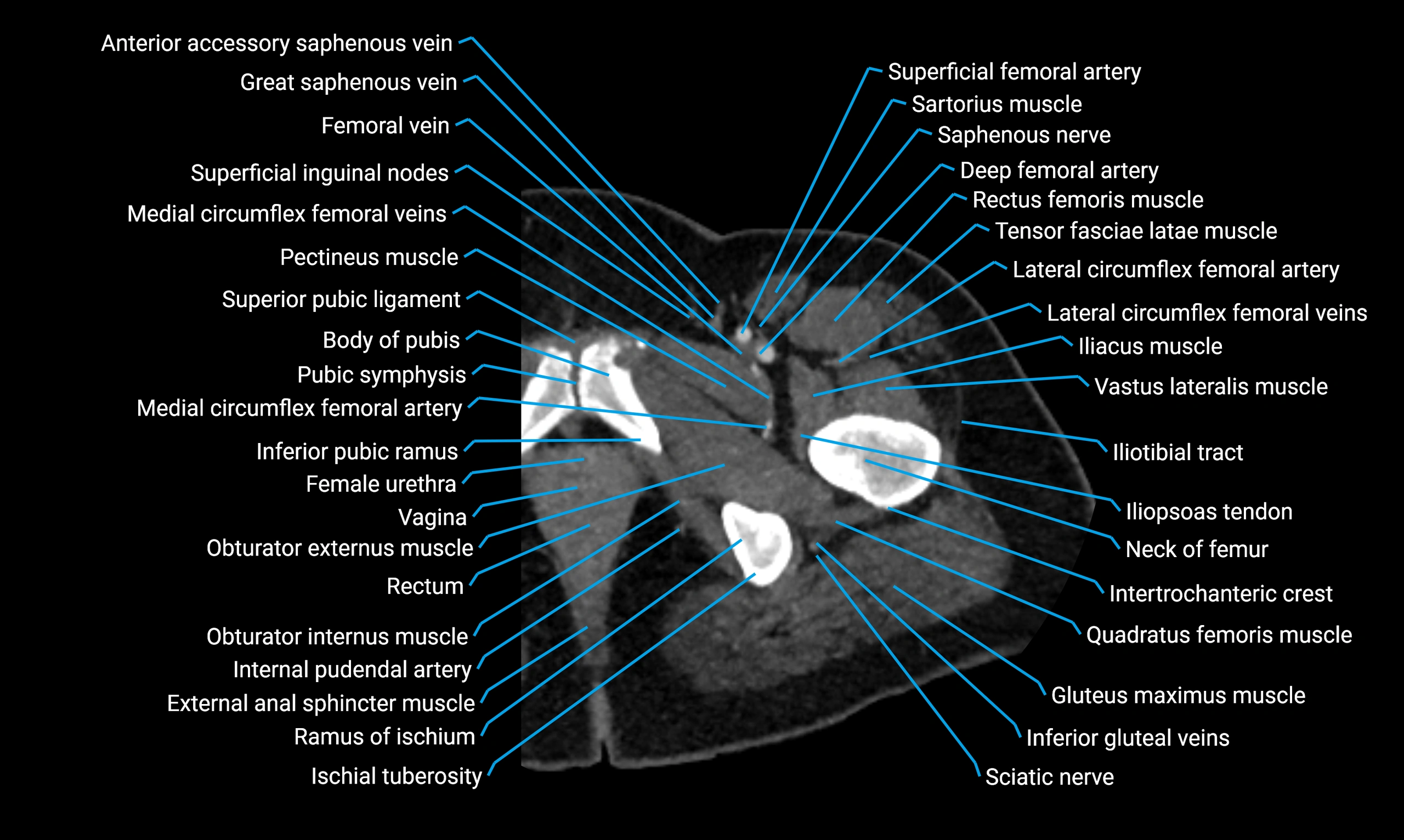
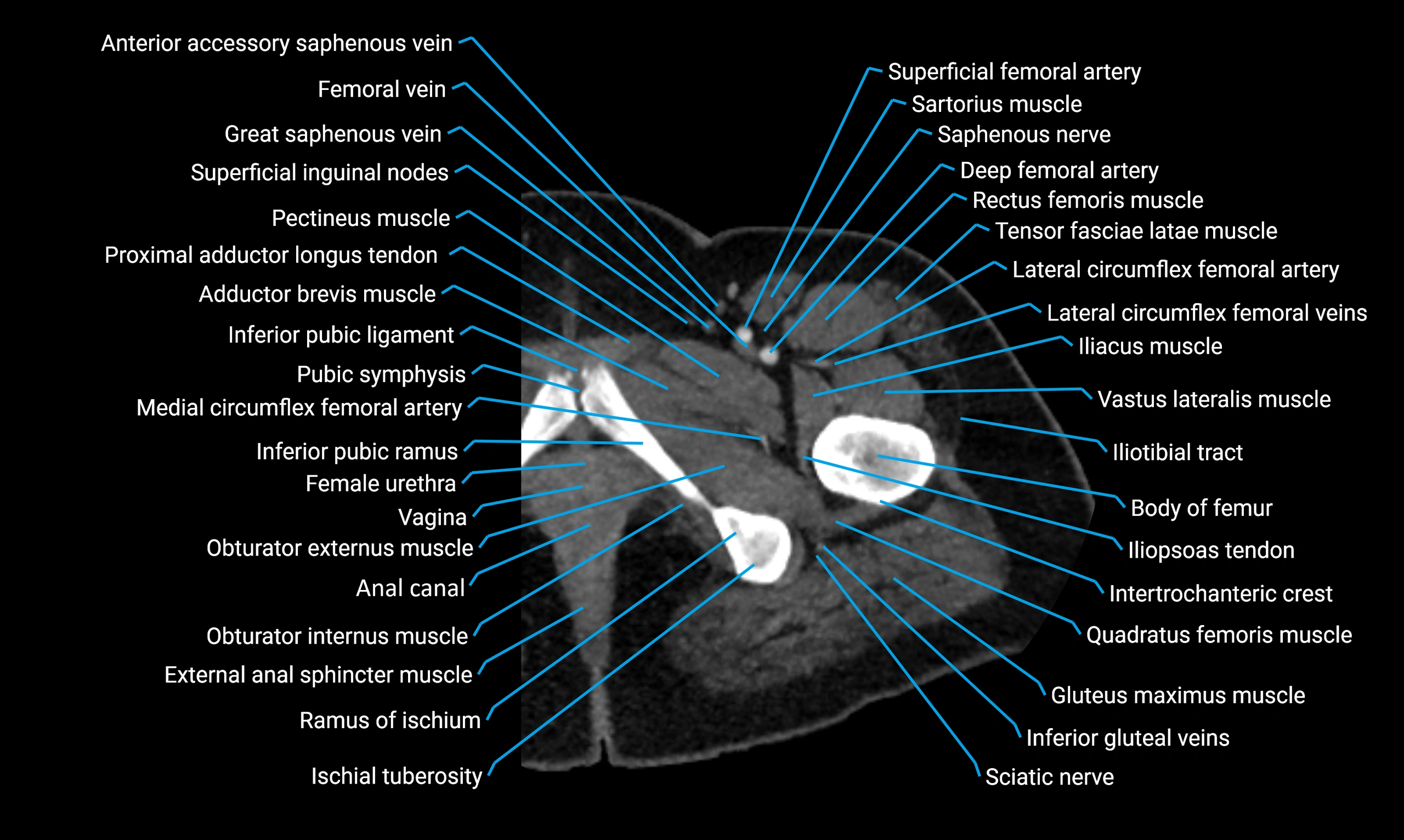
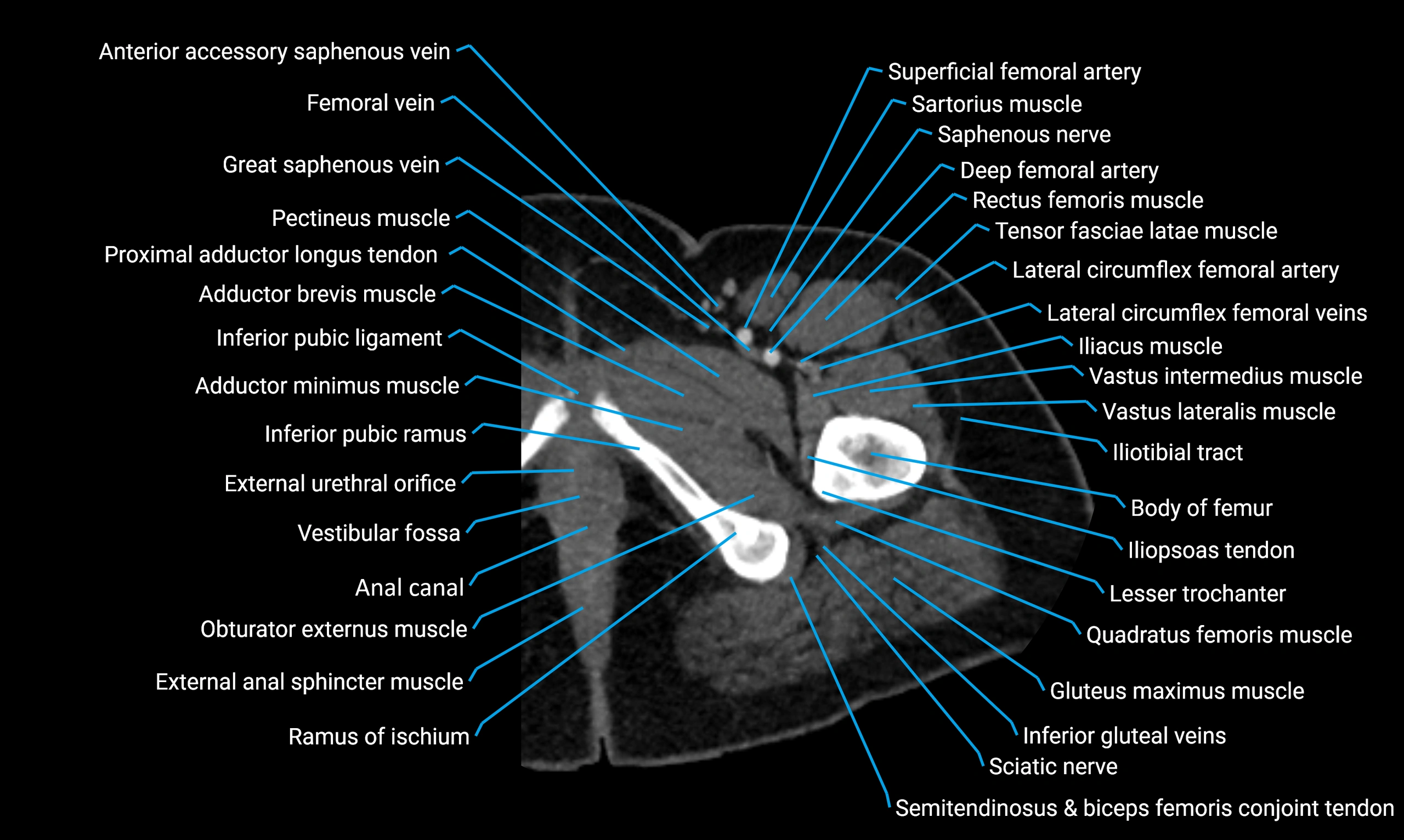
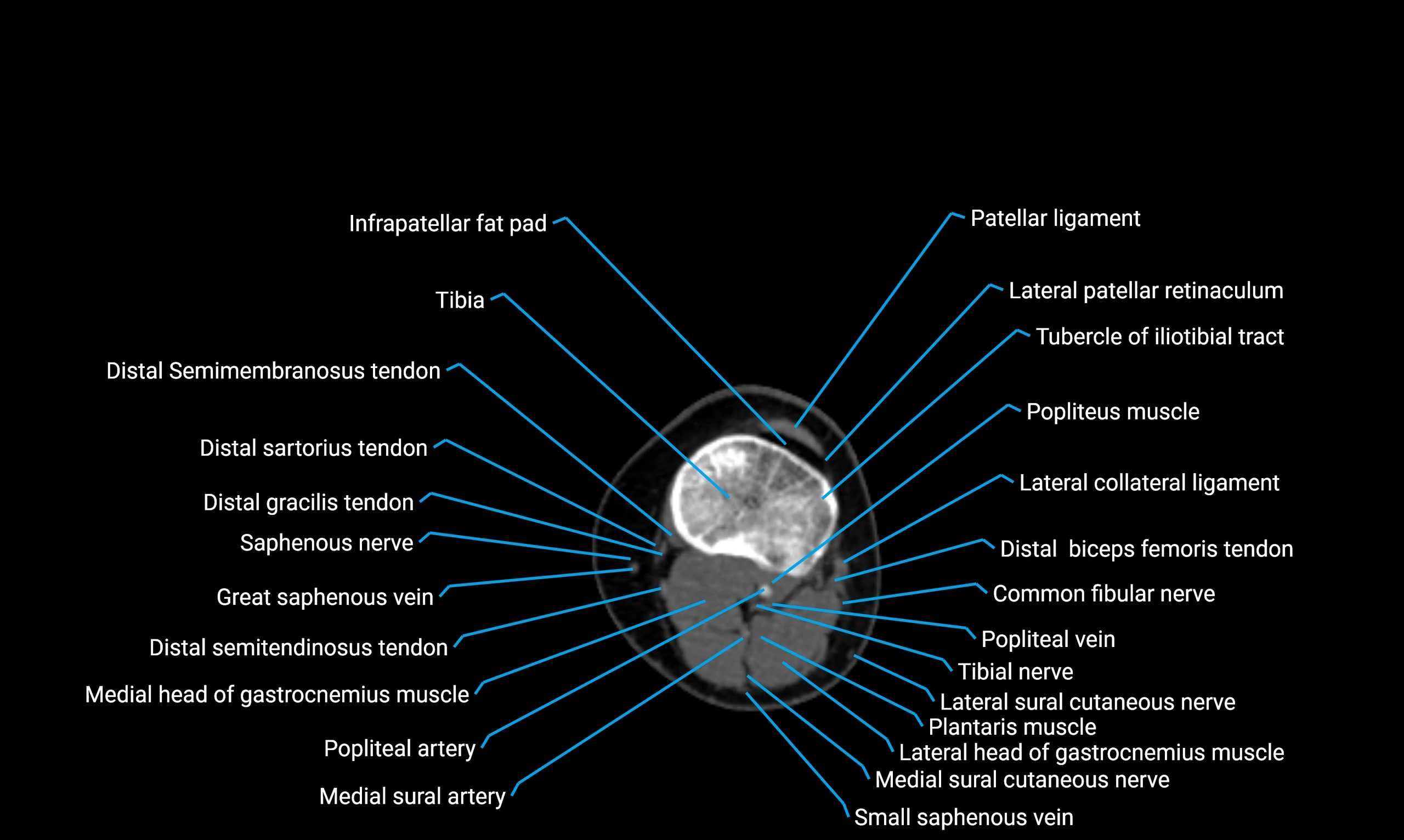
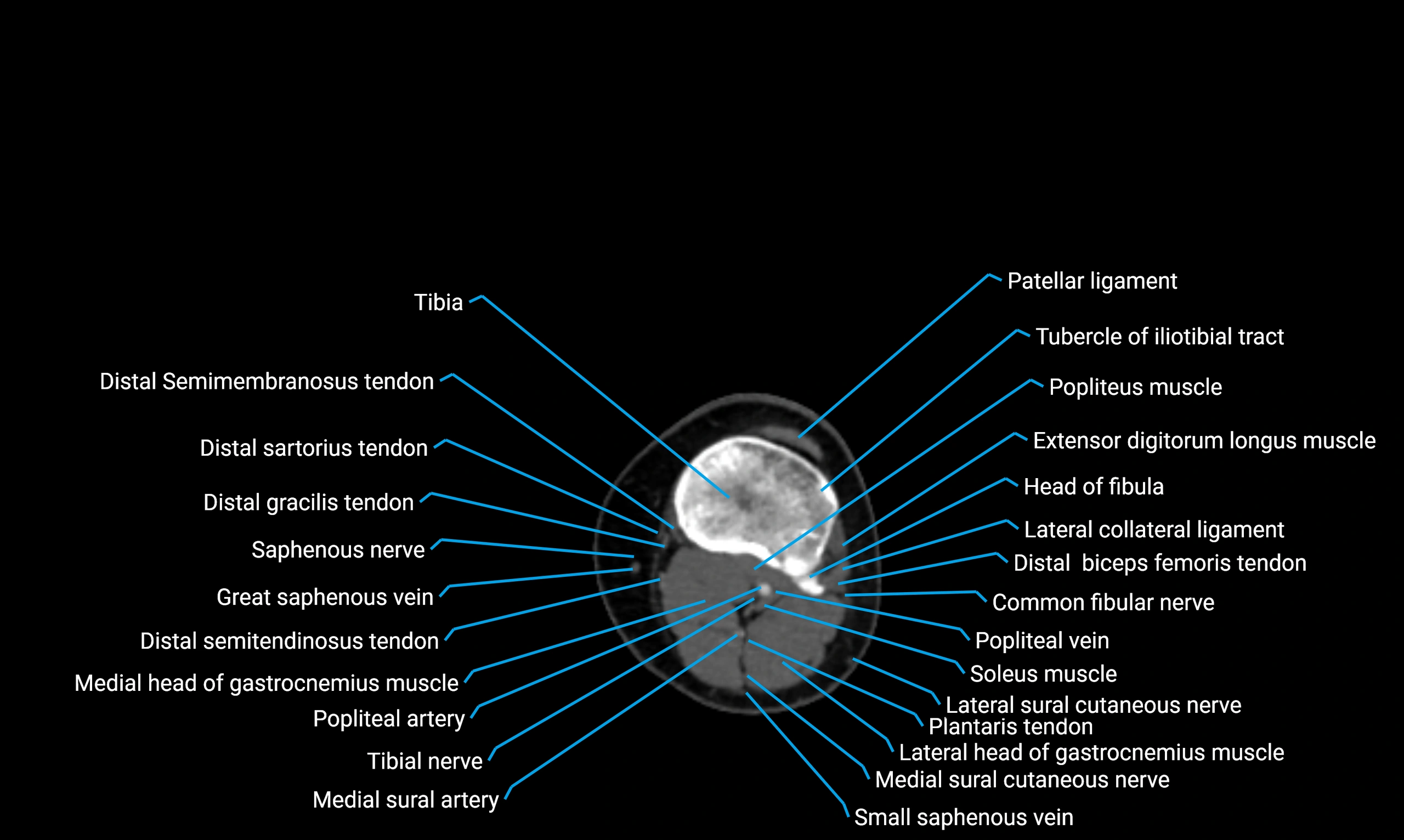
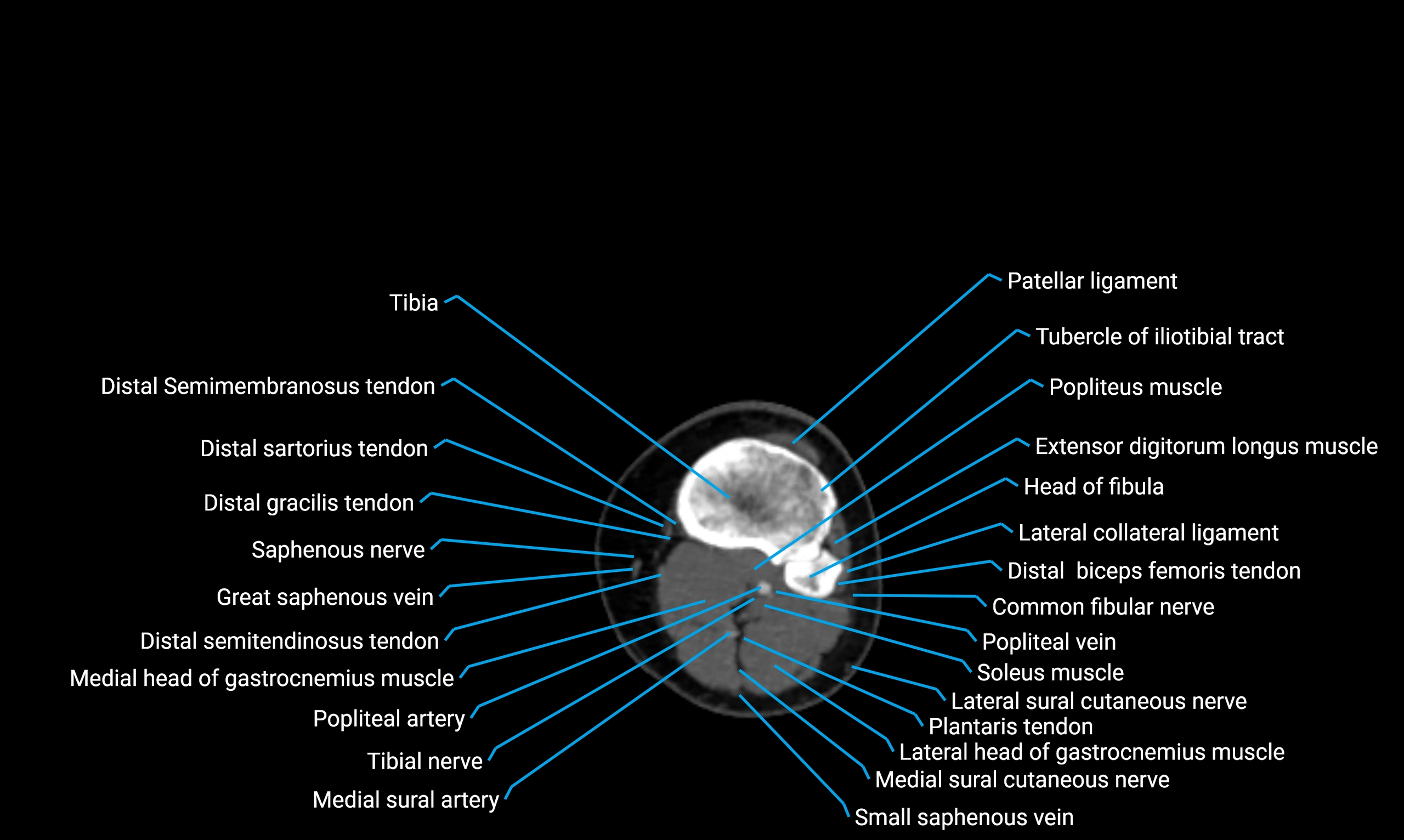
The acetabular margin, also called the acetabular rim, is the bony edge of the acetabulum, the cup-shaped cavity on the lateral aspect of the pelvis that articulates with the head of the femur to form the hip joint. The acetabular margin consists of the superior, anterior, and posterior borders of the acetabulum and is interrupted inferiorly by the acetabular notch.
The rim provides attachment for the acetabular labrum, a fibrocartilaginous structure that deepens the acetabulum, increasing hip joint stability. The transverse acetabular ligament bridges the acetabular notch, completing the bony ring. Superiorly, the margin bears the greatest load during standing and gait, making it the most common site of degenerative changes.
The acetabular margin is clinically significant in femoroacetabular impingement (FAI), acetabular fractures, hip dysplasia, and osteoarthritis. Its morphology (depth, coverage, and orientation) is a key factor in hip biomechanics and surgical planning, especially in arthroscopy and hip preservation surgery.
Synonyms
-
Acetabular rim
-
Acetabular border
-
Margin of acetabulum
Function
-
Forms the boundary of the acetabulum, contributing to the hip joint socket
-
Provides attachment for the acetabular labrum
-
Serves as a load-bearing structure during locomotion
-
Landmark for orthopedic surgery, hip arthroscopy, and imaging evaluation
MRI Appearance
T1-weighted images:
-
Acetabular bone cortex: low signal intensity
-
Marrow within acetabular margin: intermediate signal
-
Labrum appears hypointense, cartilage intermediate
T2-weighted images:
-
Subchondral bone: hypointense
-
Articular cartilage: bright hyperintense
-
Acetabular labrum: dark hypointense triangle at margin
-
Labral tears appear as hyperintense fluid clefts
PD Fat-Saturated (Proton Density with Fat Suppression):
-
Suppresses marrow fat, highlighting cartilage, labrum, and soft tissue pathology
-
Labral tears, cartilage defects, and periacetabular edema appear bright hyperintense
-
Highly sensitive for subtle labral pathology and chondral damage
STIR:
-
Fat suppression highlights bone marrow edema, fractures, or periacetabular inflammation
-
Useful in trauma and early arthritis detection
T1 Post-Gadolinium (MR Arthrography):
-
Contrast fills joint space and extends into labral or chondral tears
-
Enhances delineation of acetabular margin–labrum interface
-
Detects subtle labral detachments and capsular pathology
3D T2-weighted Imaging:
-
Provides isotropic voxels for multiplanar reconstructions of the acetabulum
-
Excellent for visualizing labrum, cartilage surface, and acetabular morphology
-
Essential for arthroscopic planning and evaluation of femoroacetabular impingement
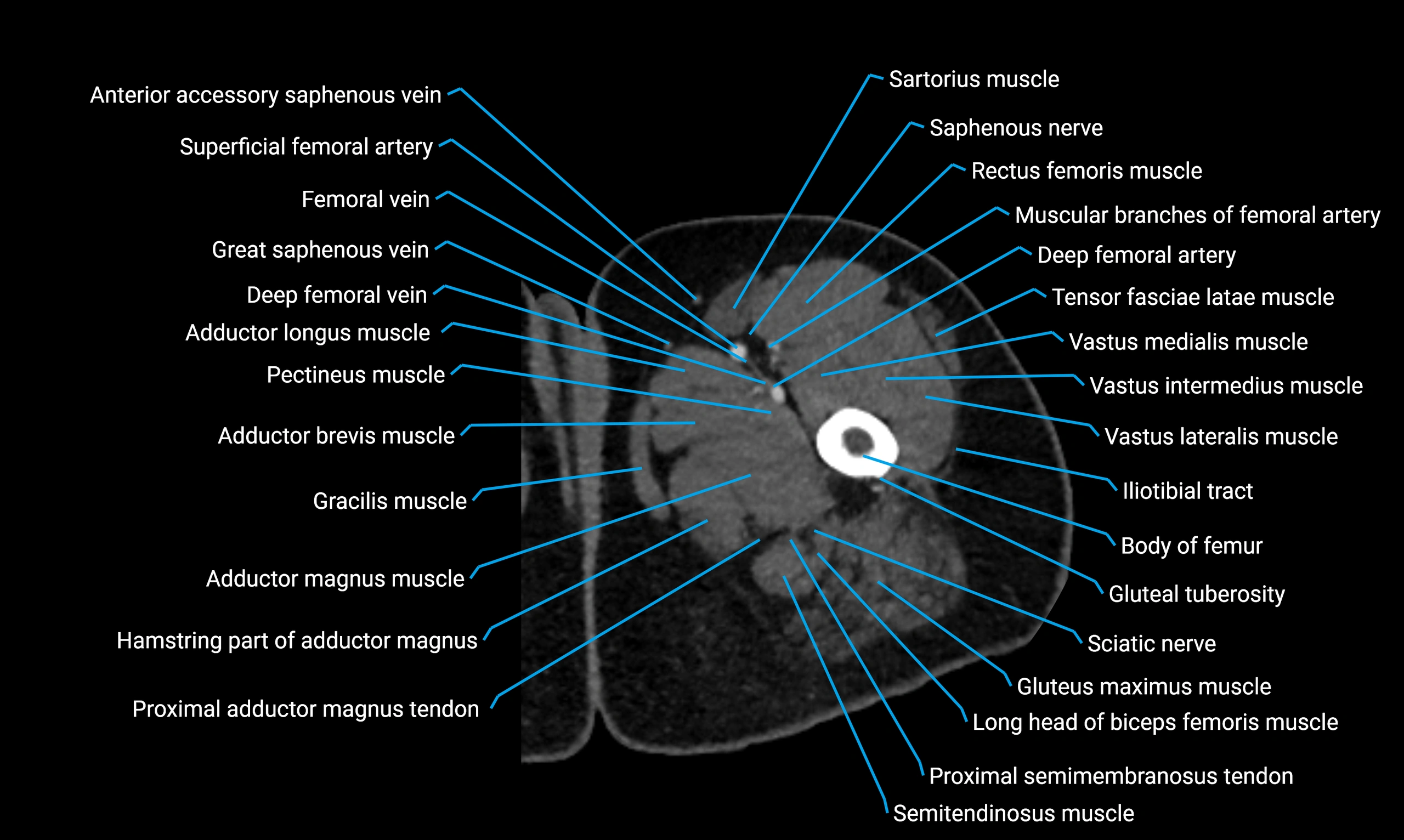
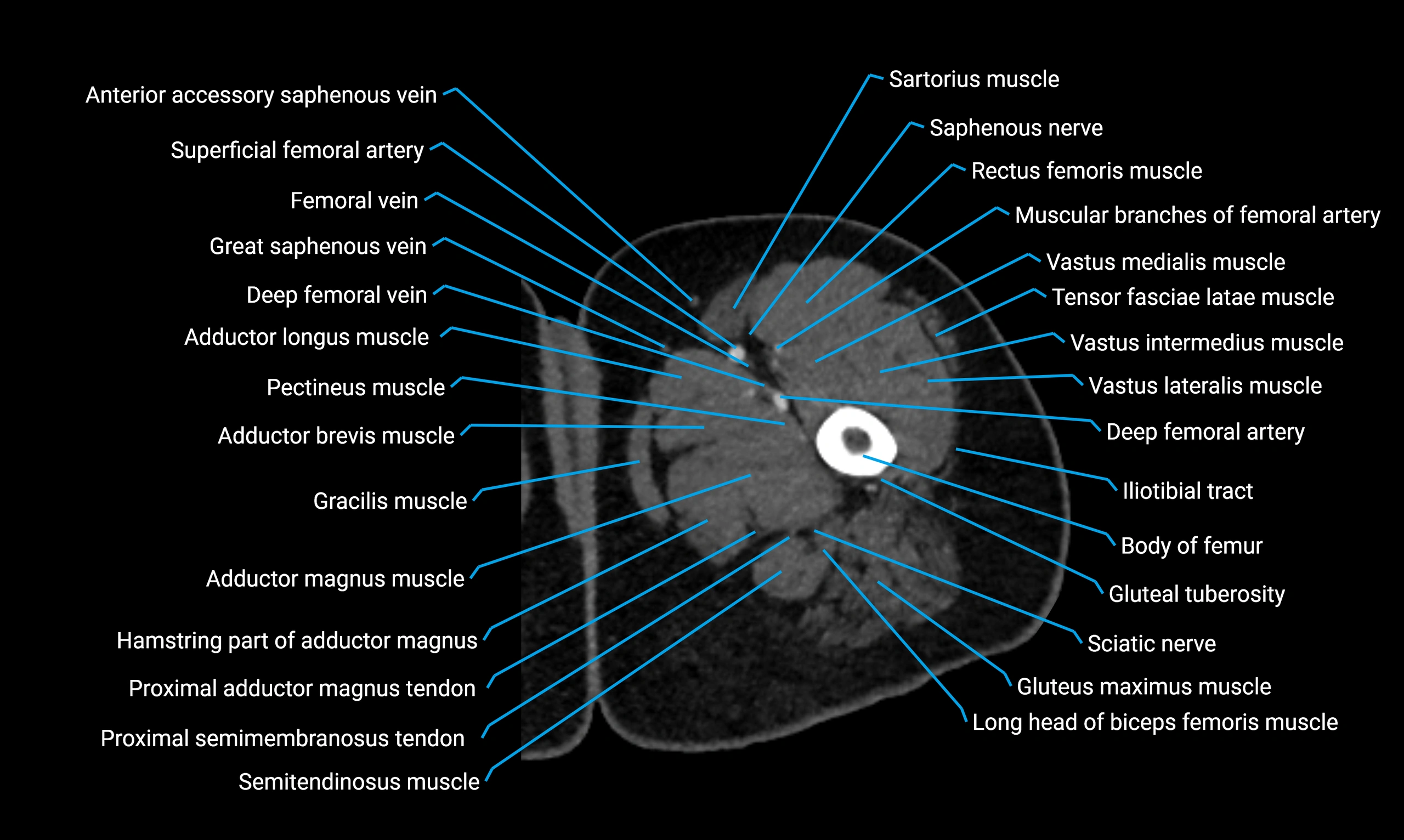
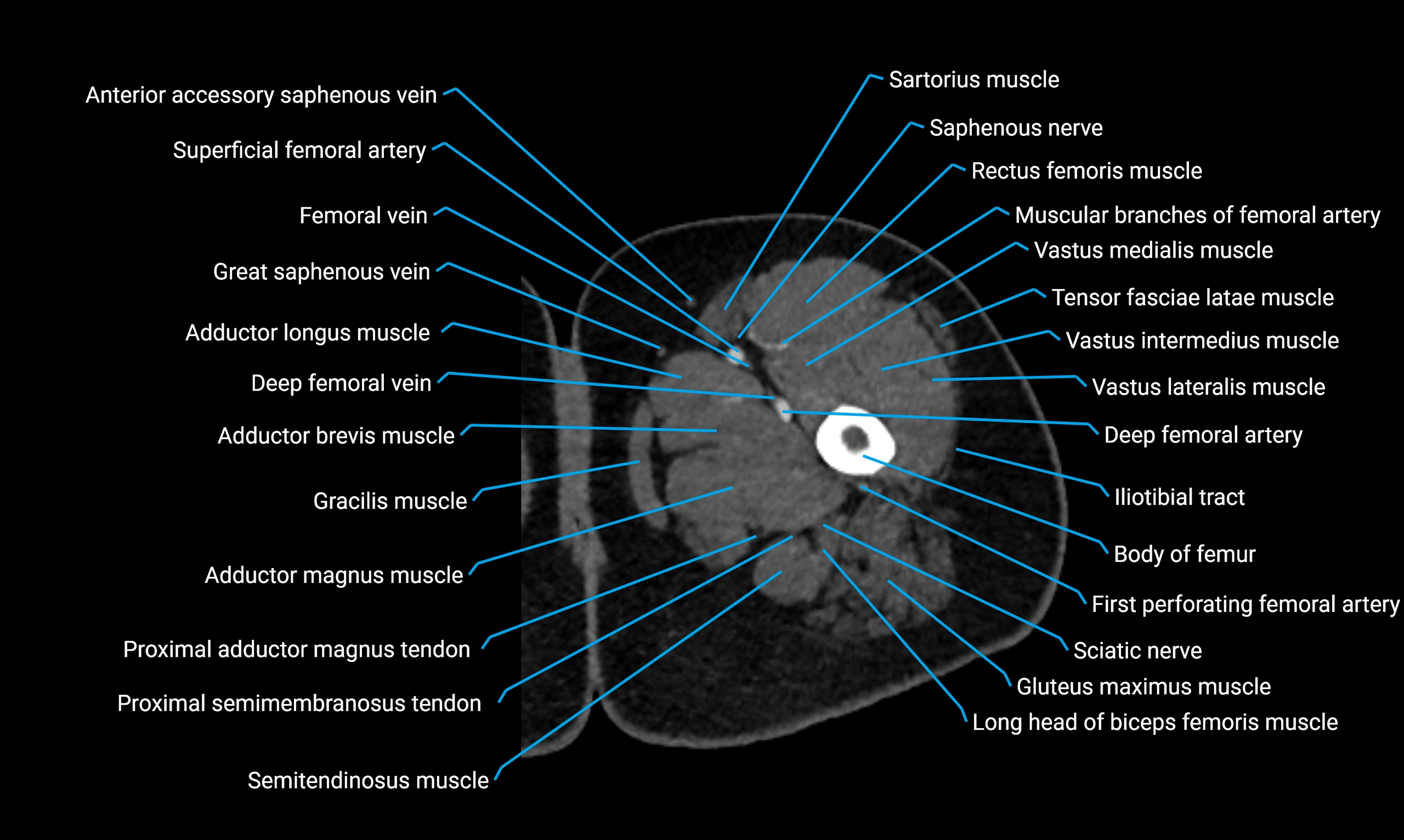
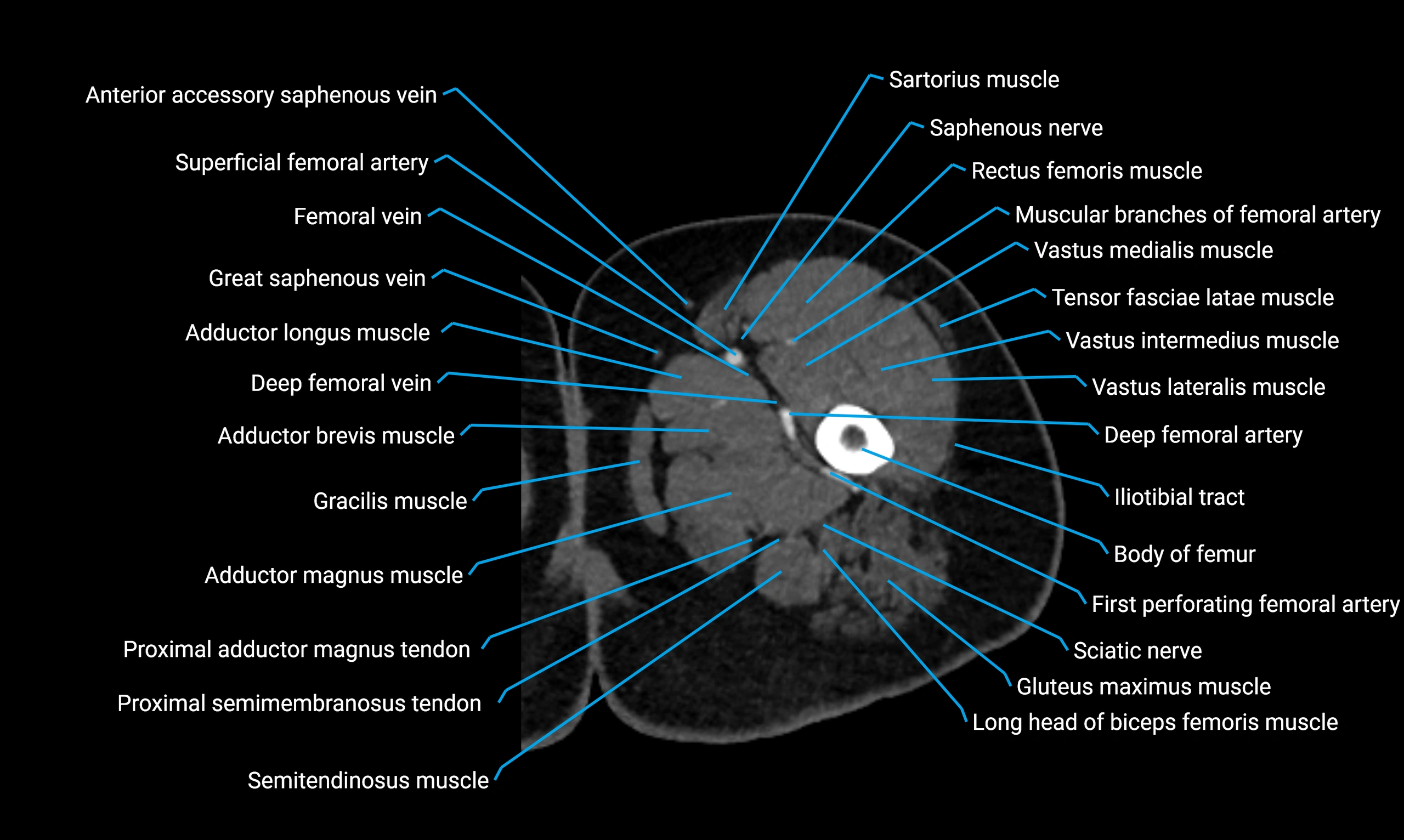
CT Appearance
Non-contrast CT:
-
Demonstrates cortical bone of acetabular rim in excellent detail
-
Detects fractures, dysplasia, retroversion, or bony overcoverage (pincer impingement)
-
3D reconstructions used in preoperative hip surgery planning
CT Post-Contrast (CT Arthrography):
-
Joint contrast outlines the acetabular labrum, cartilage, and margin
-
Demonstrates labral tears, cartilage defects, and subtle bony abnormalities
-
Alternative to MR arthrography in patients with MRI contraindications
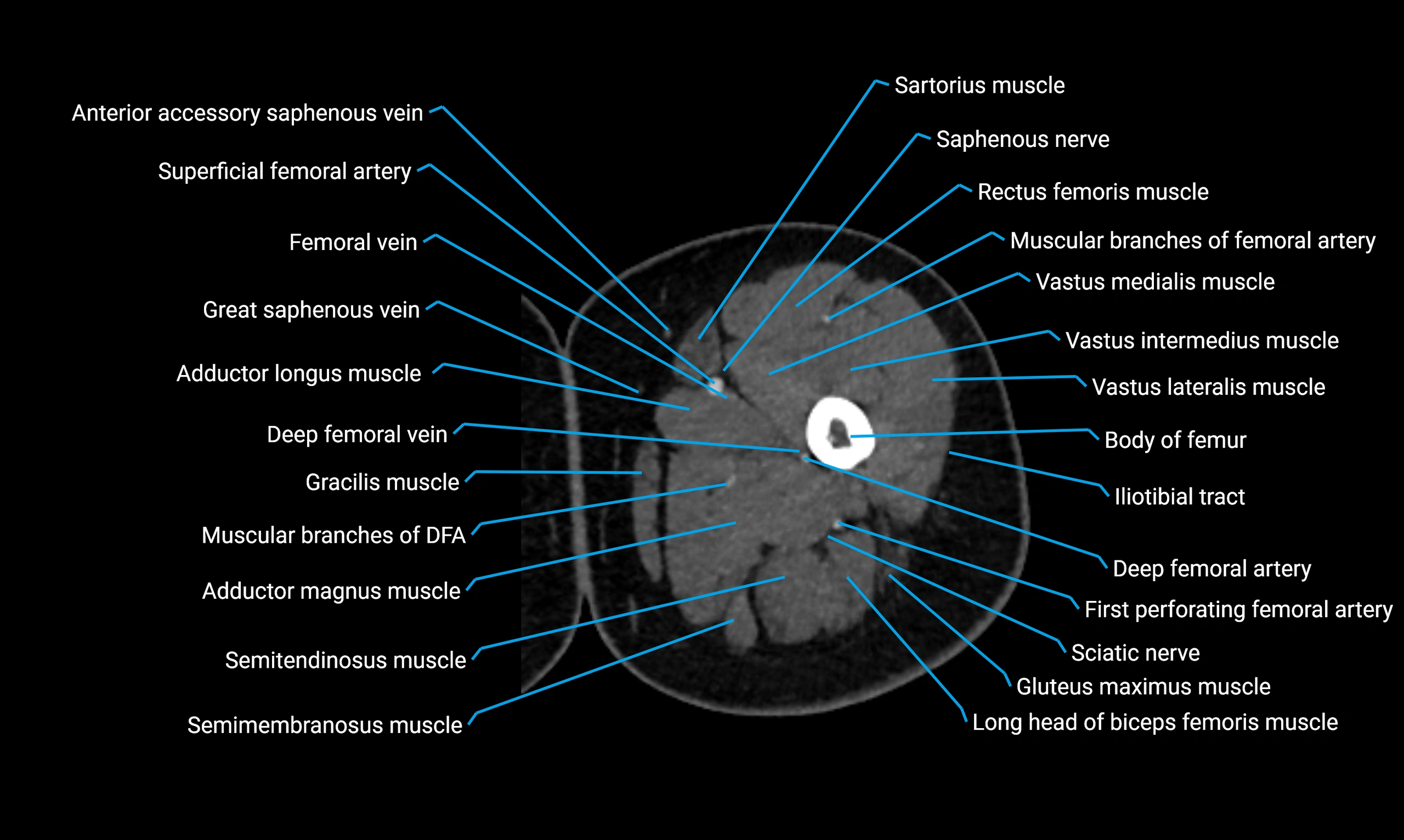
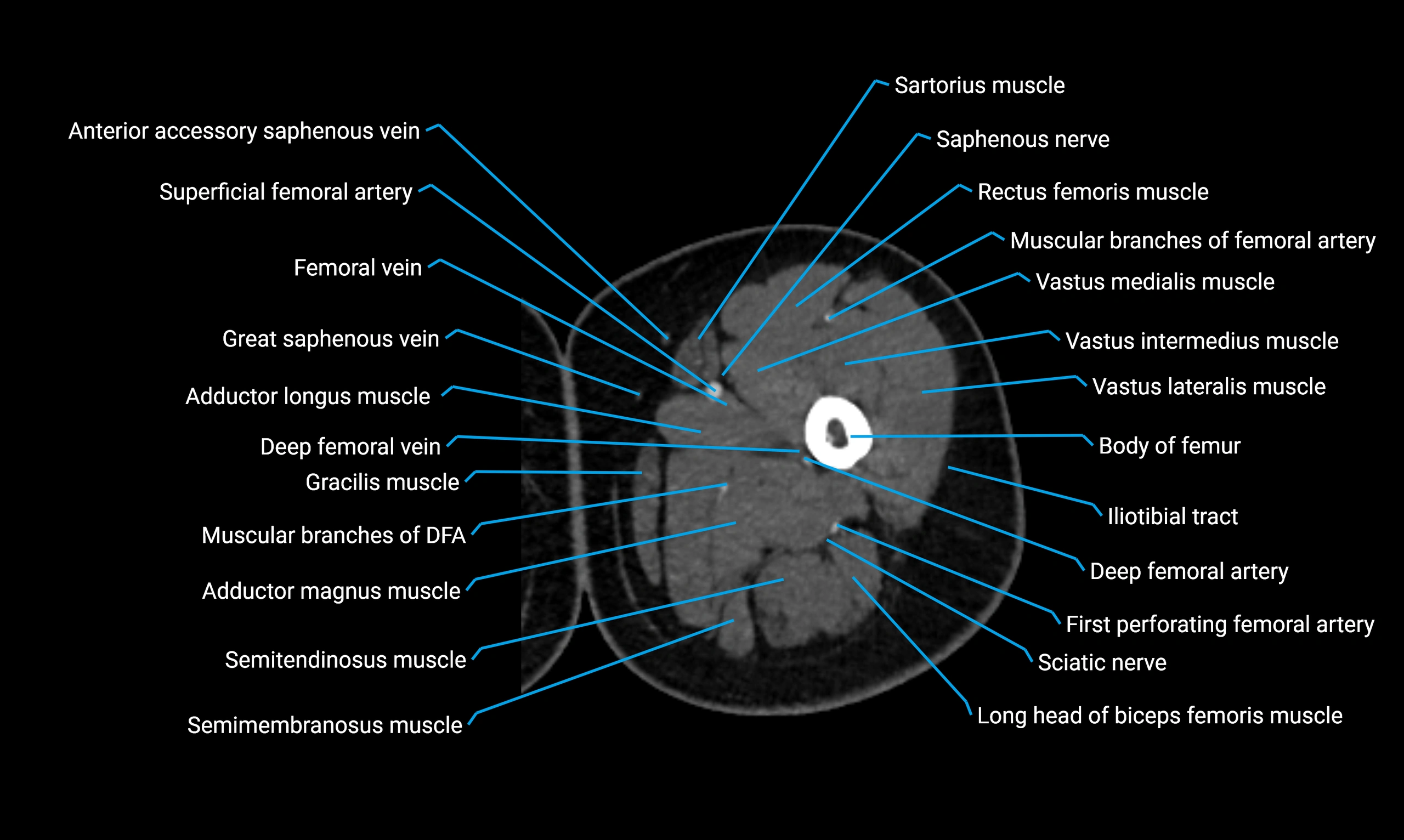
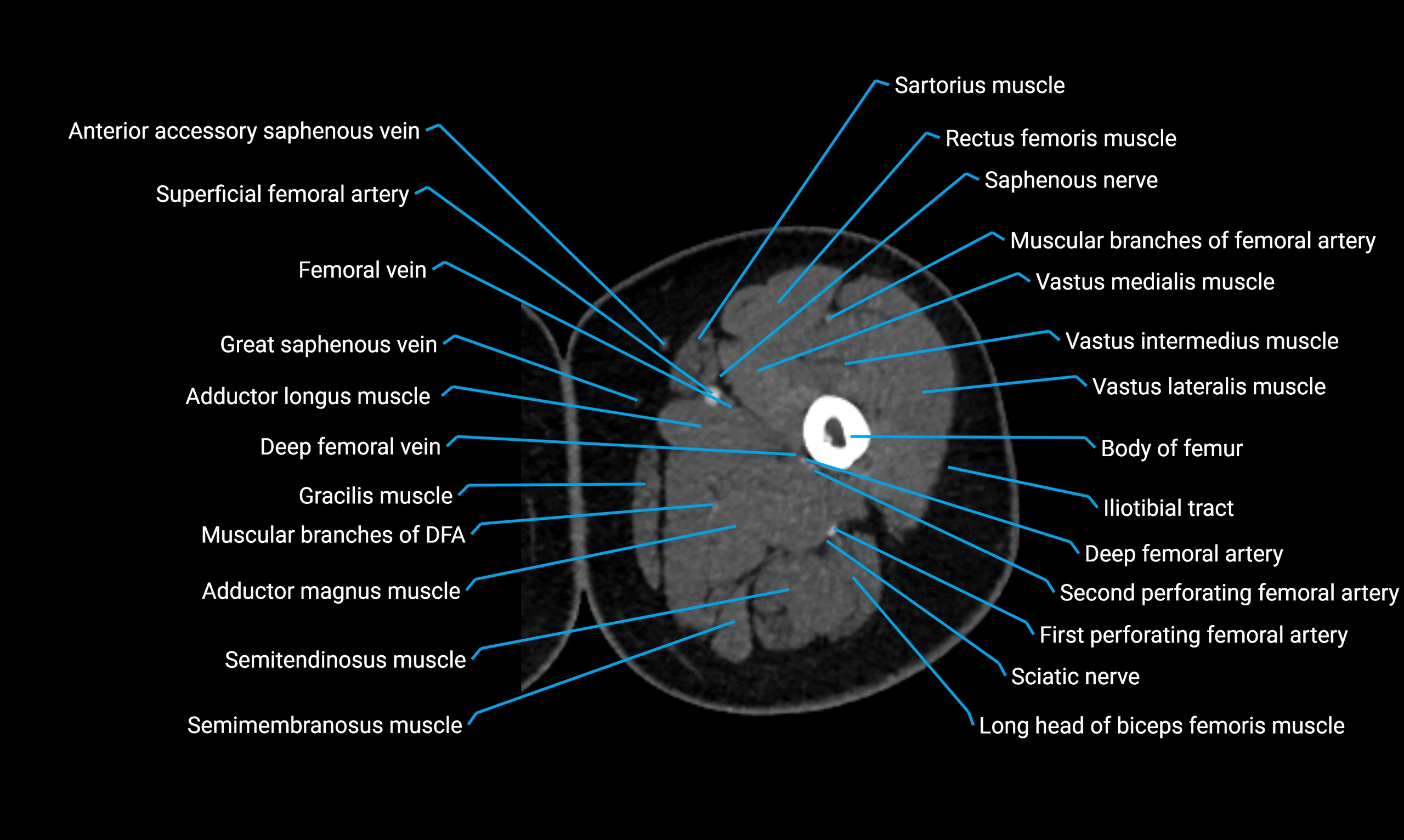
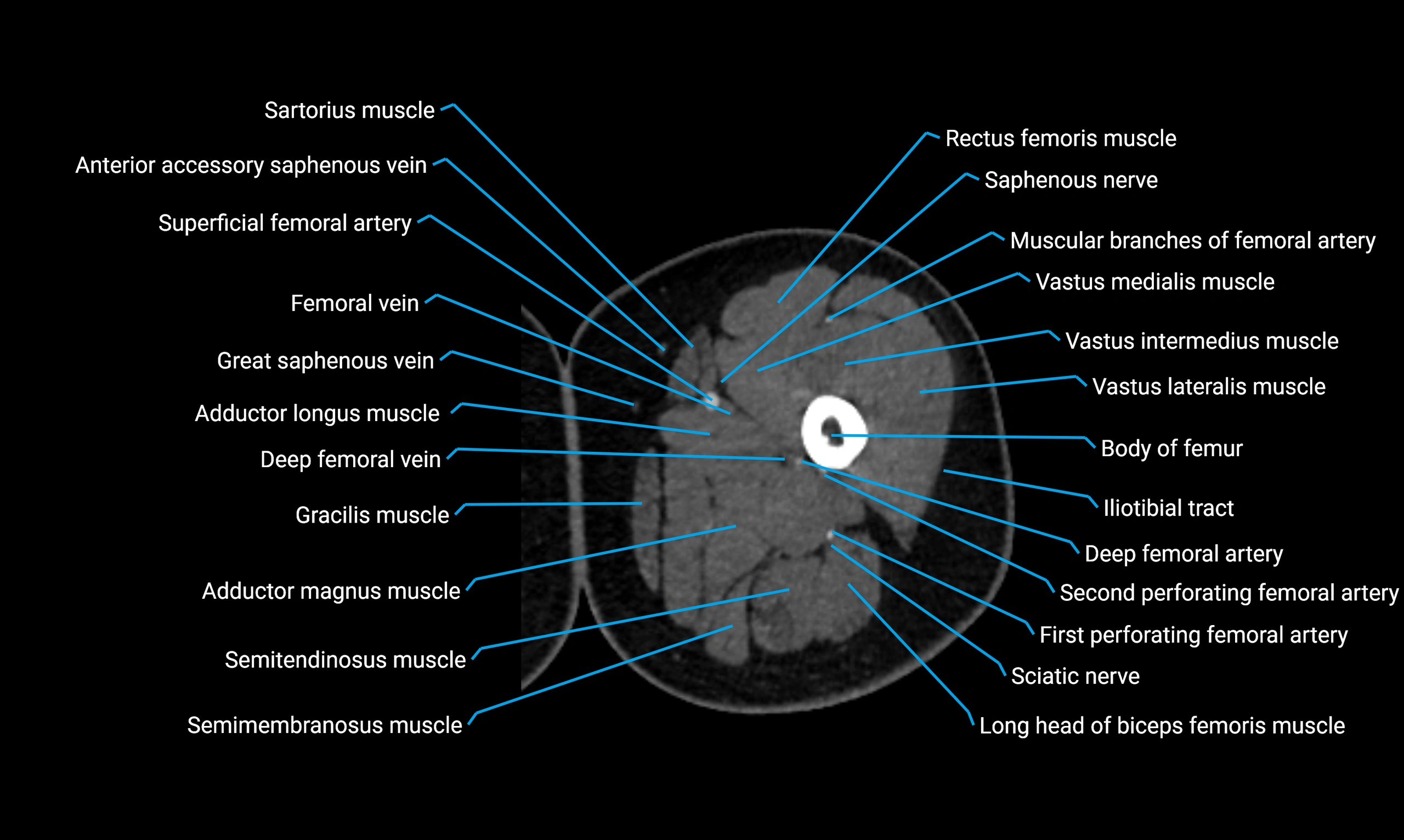
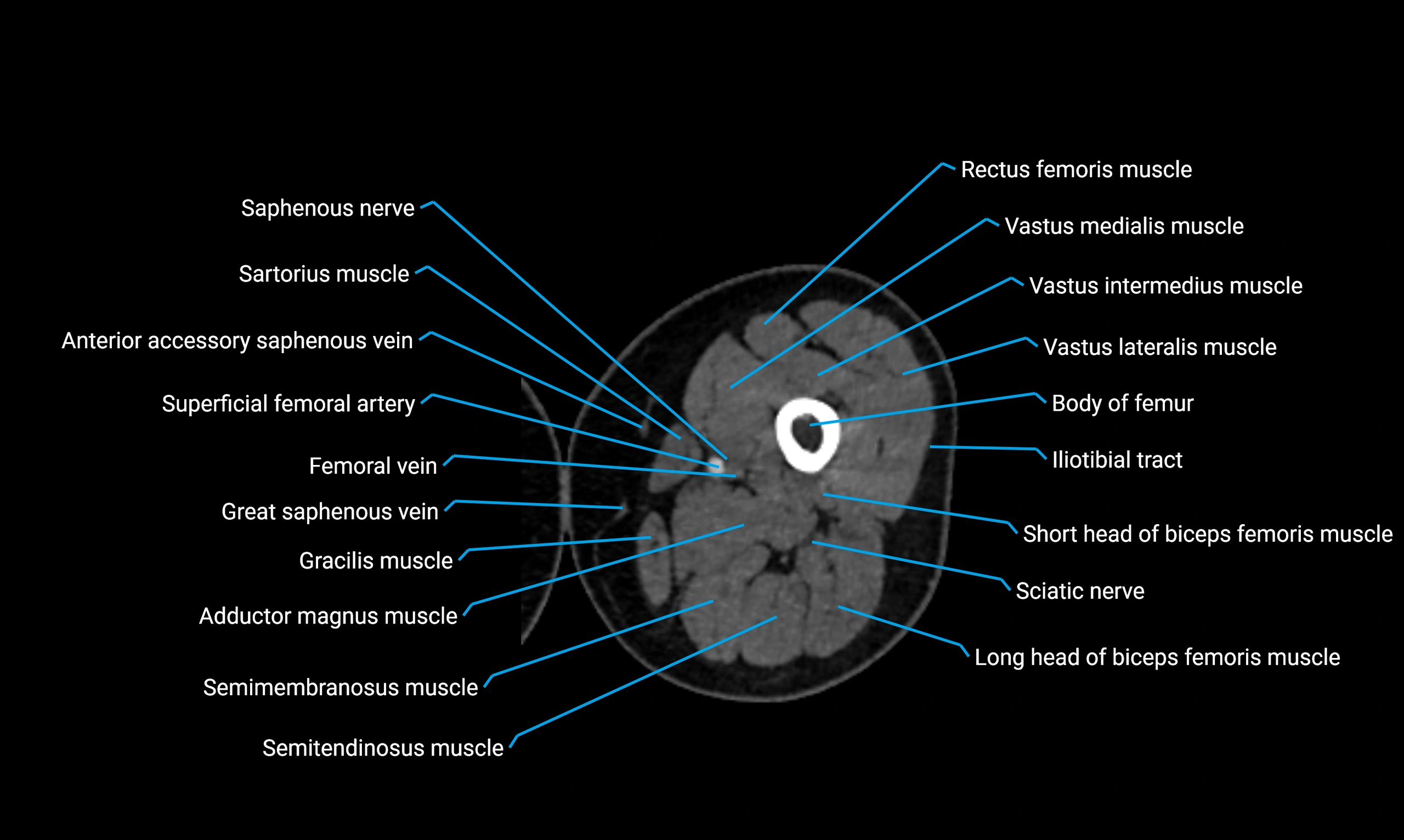
CT VRT 3D image

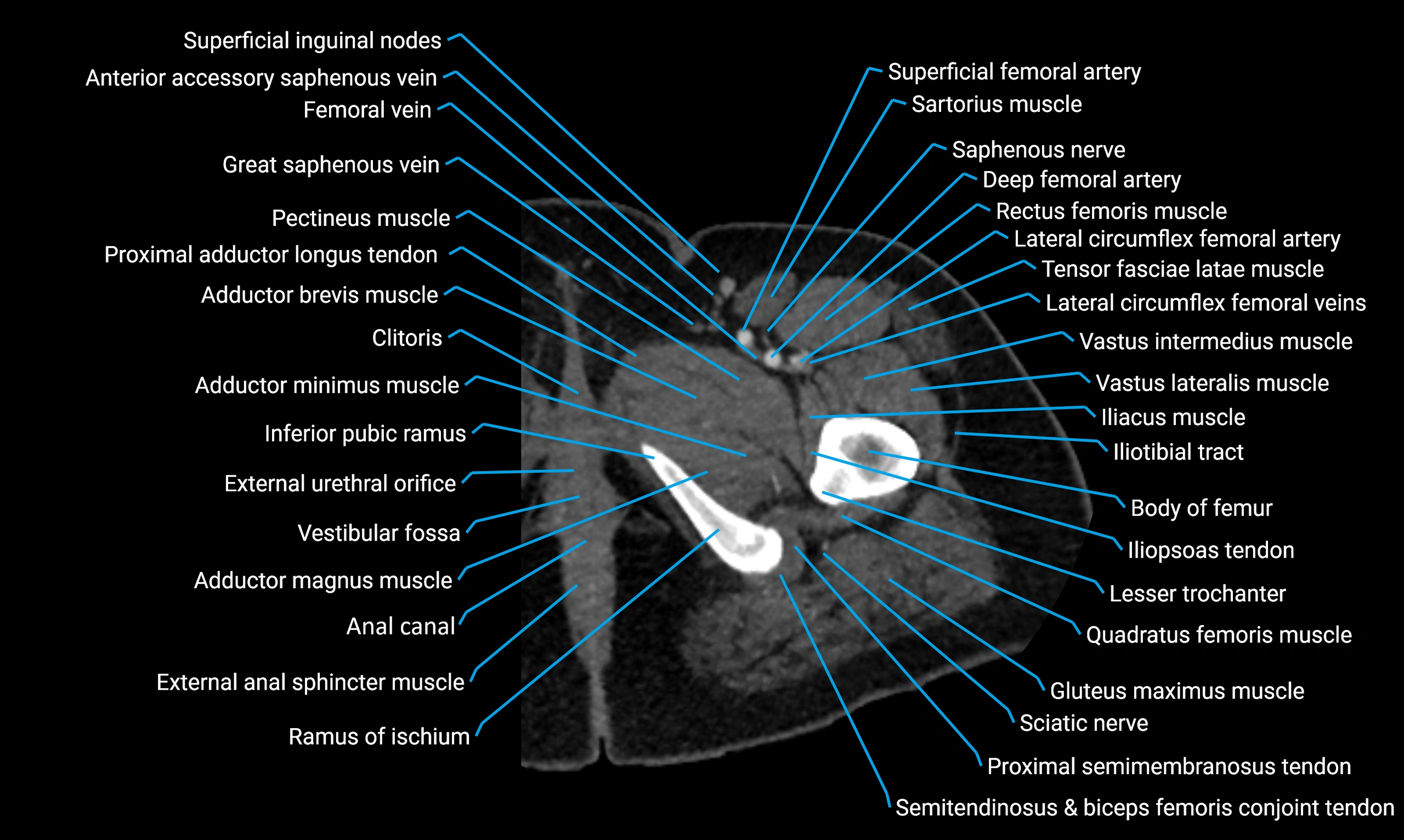
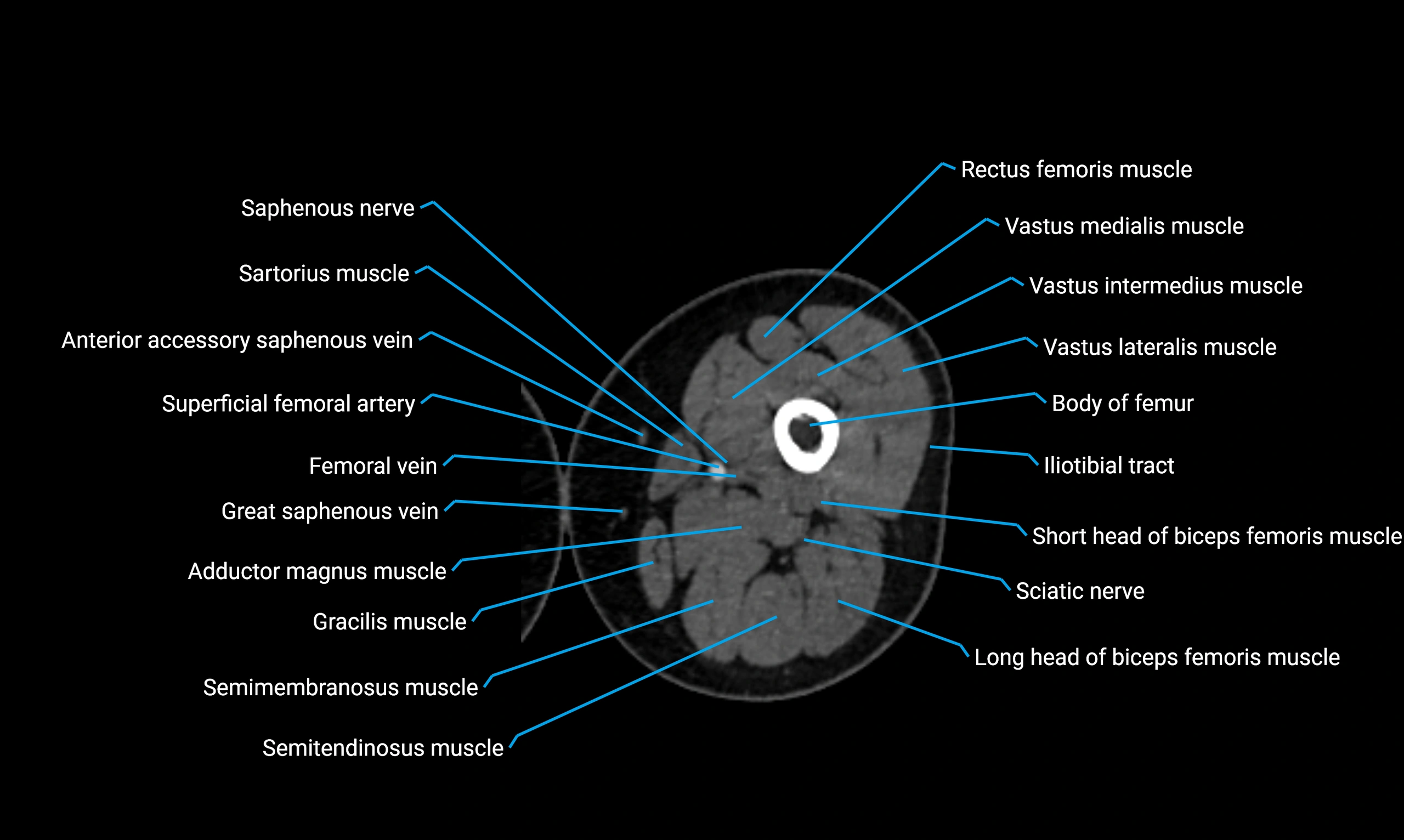
CT image

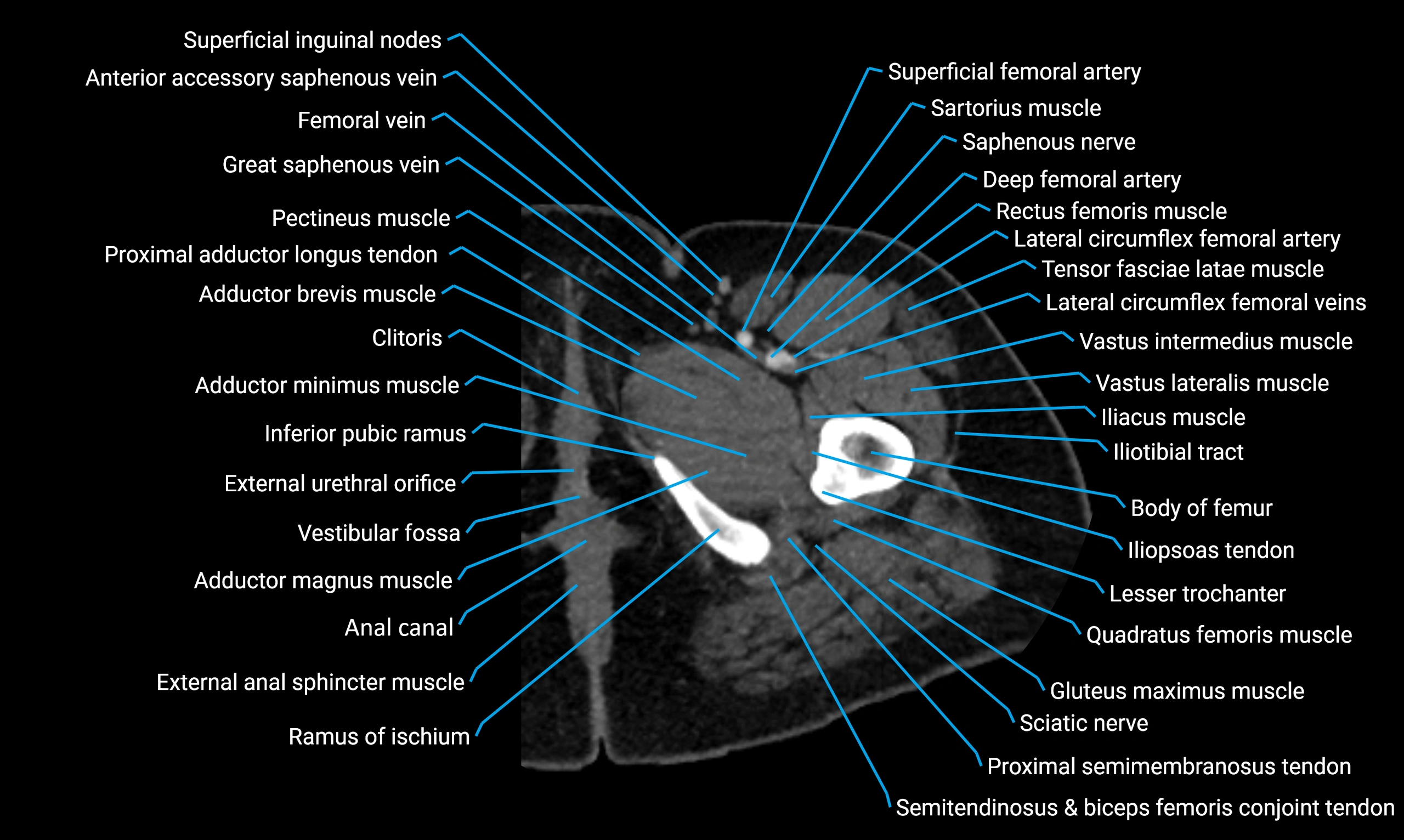
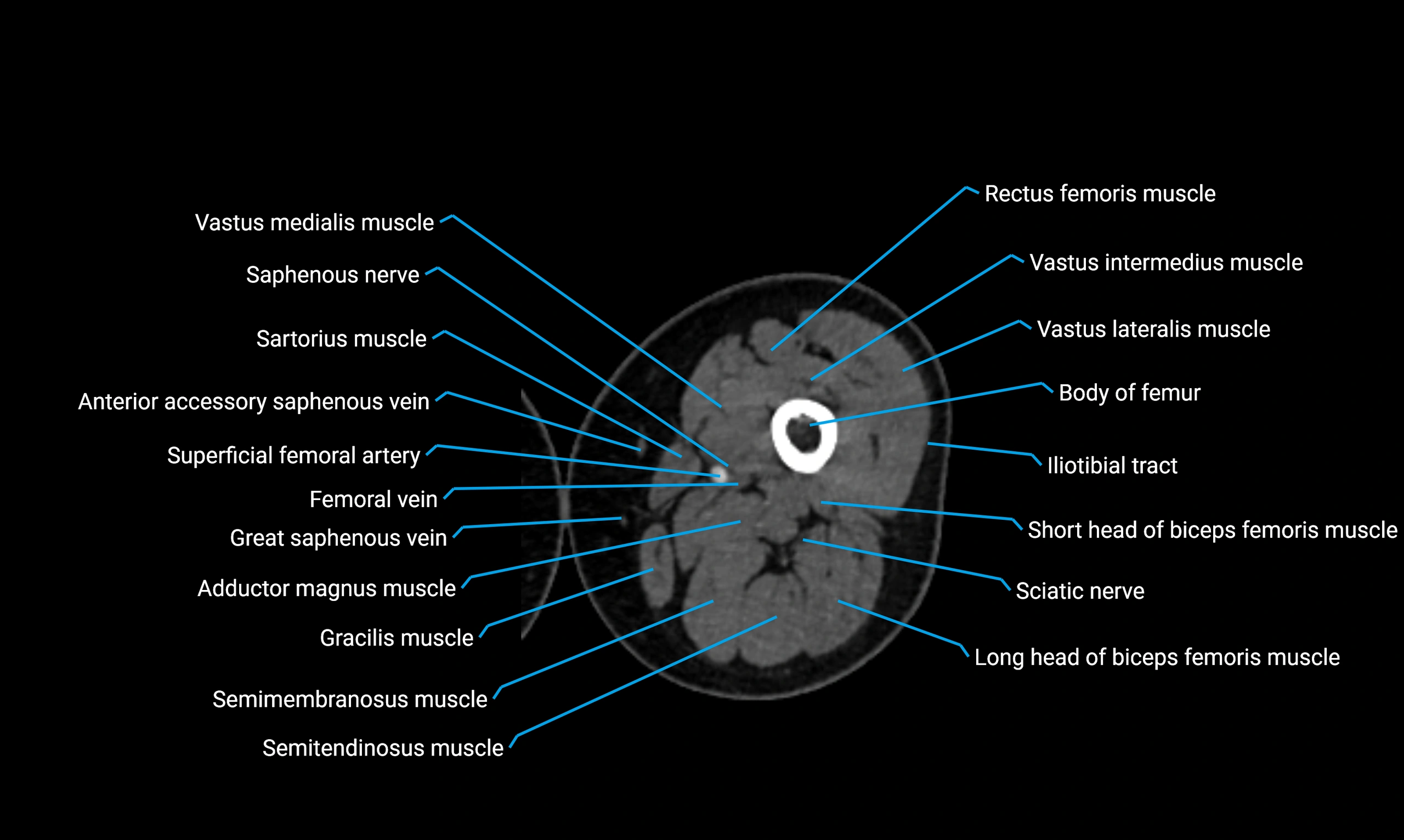
CT image

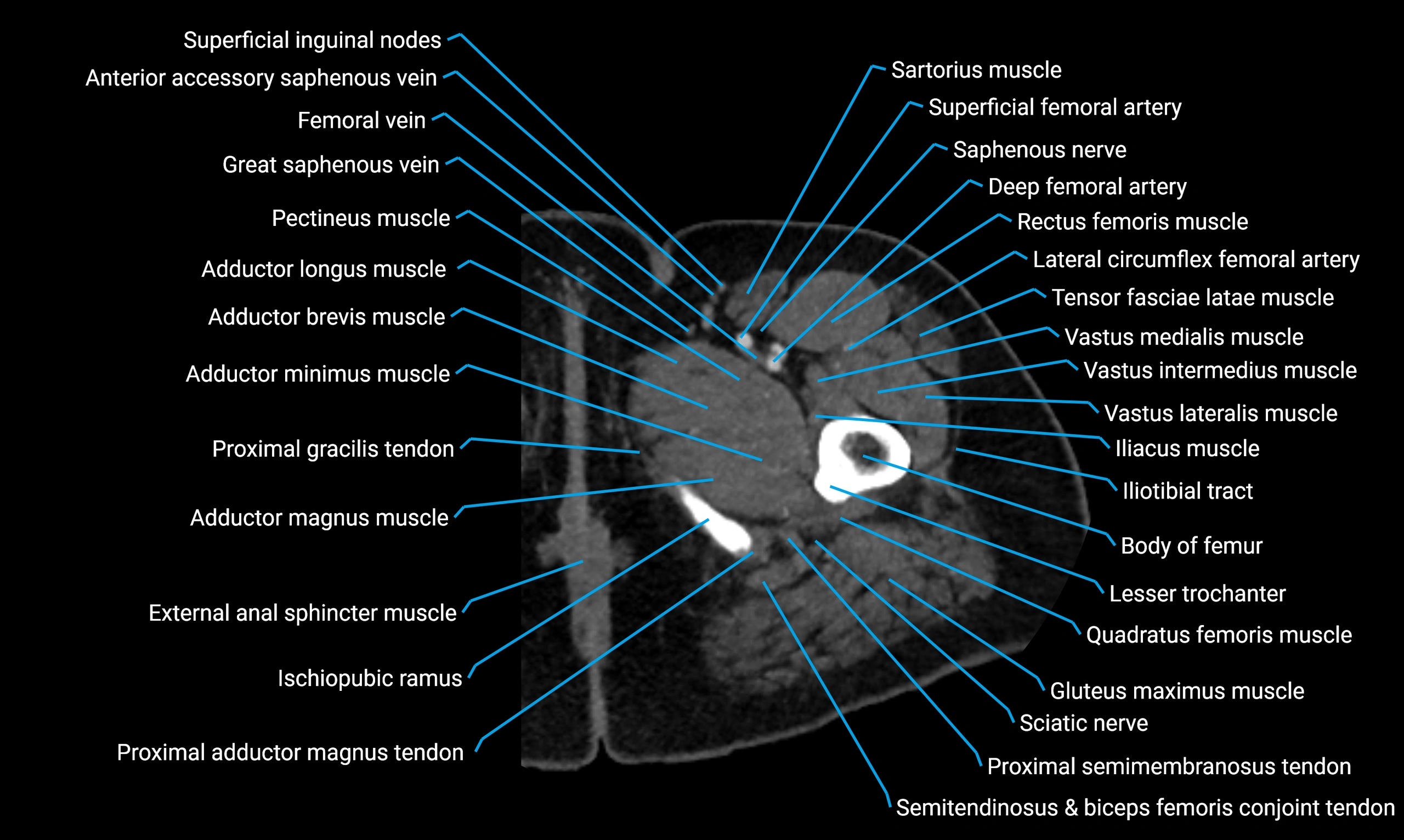
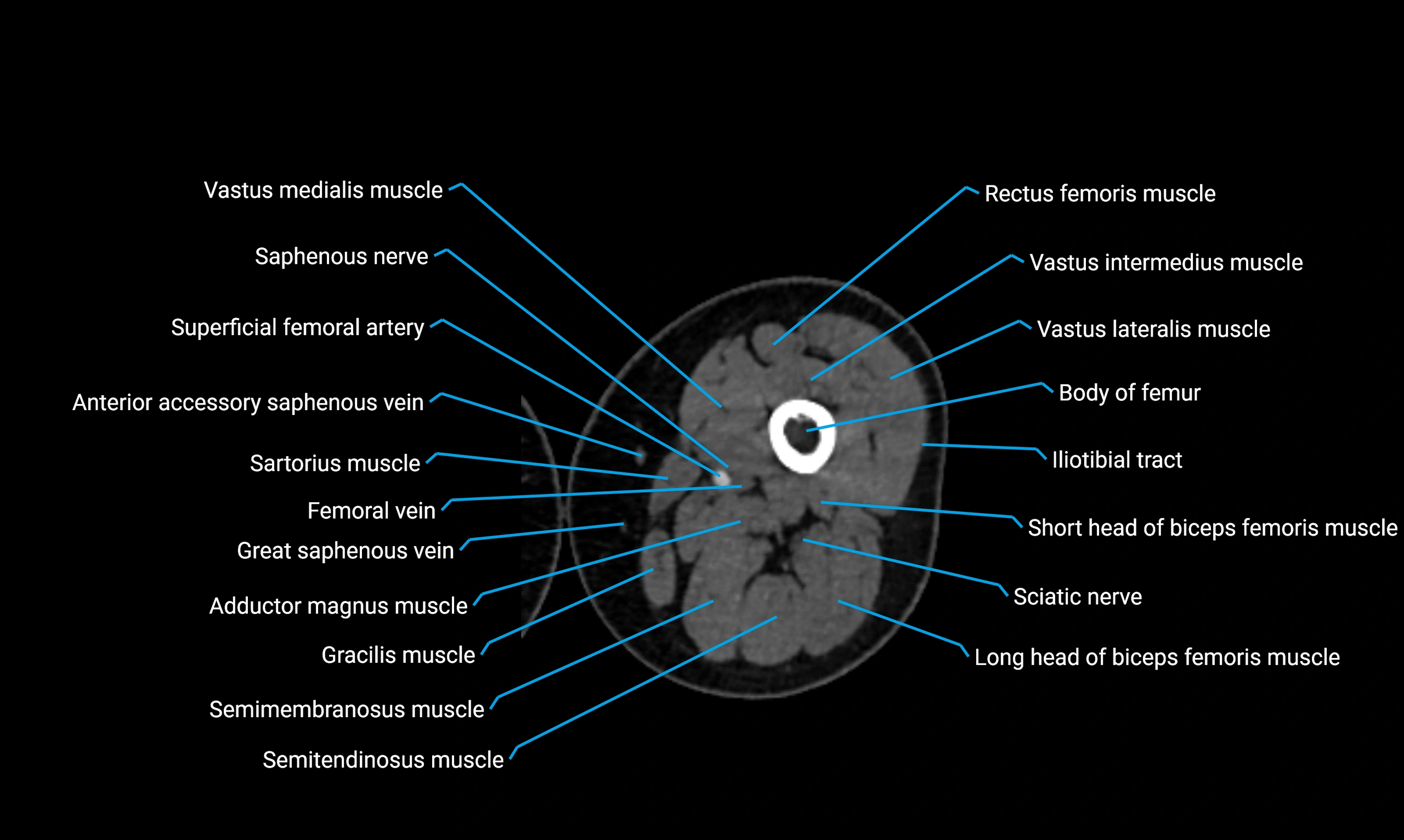
CT image

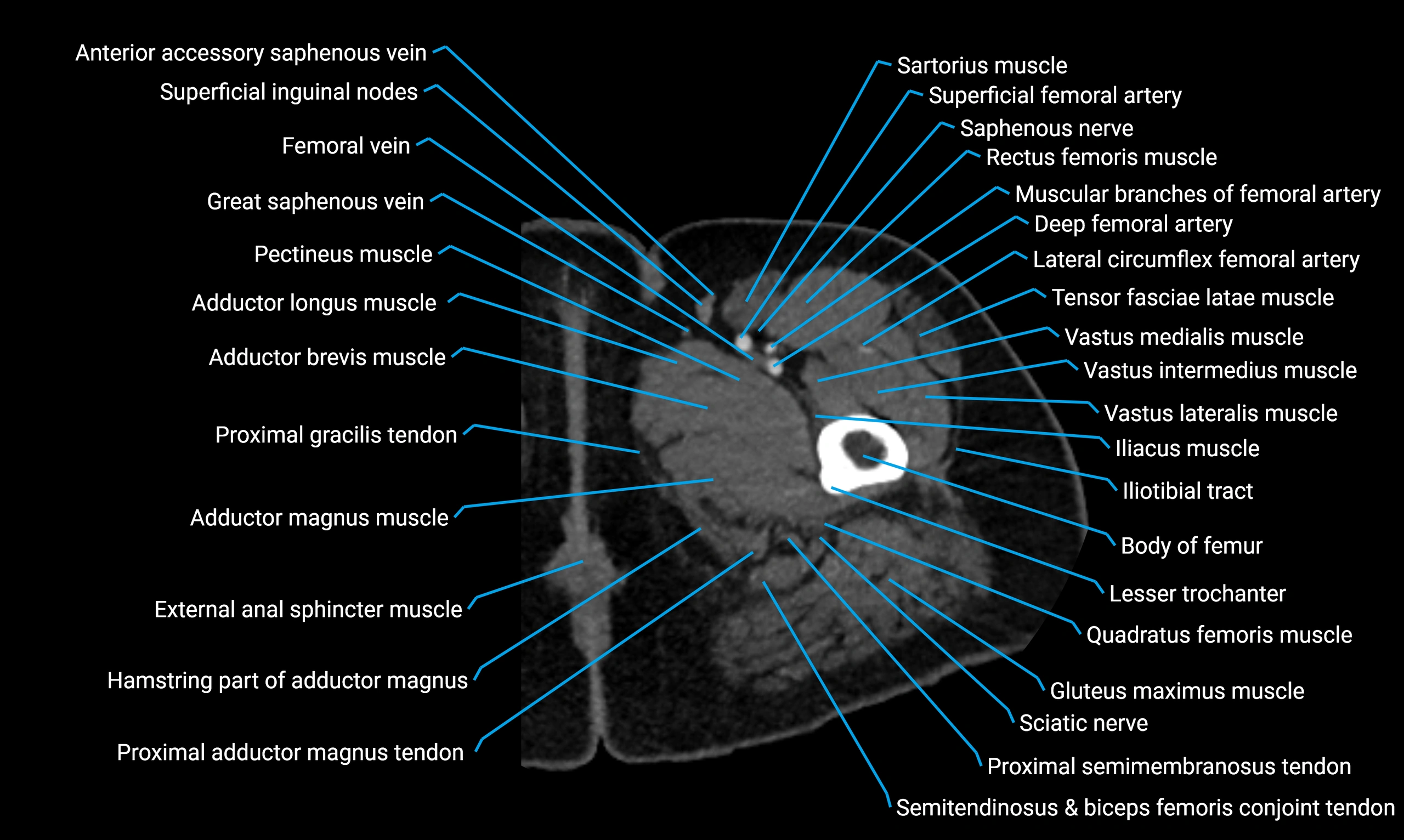
MRI image

MRI image