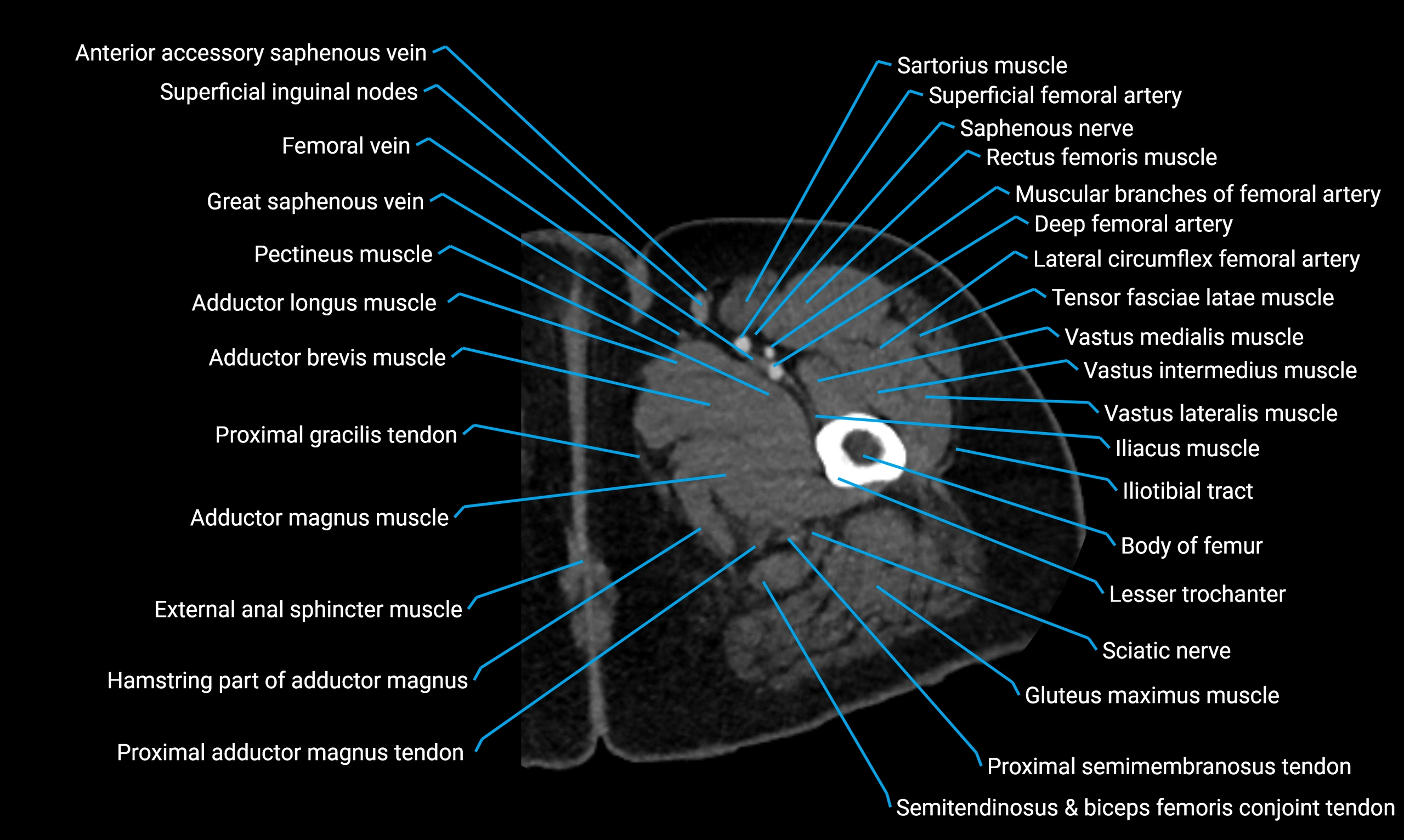
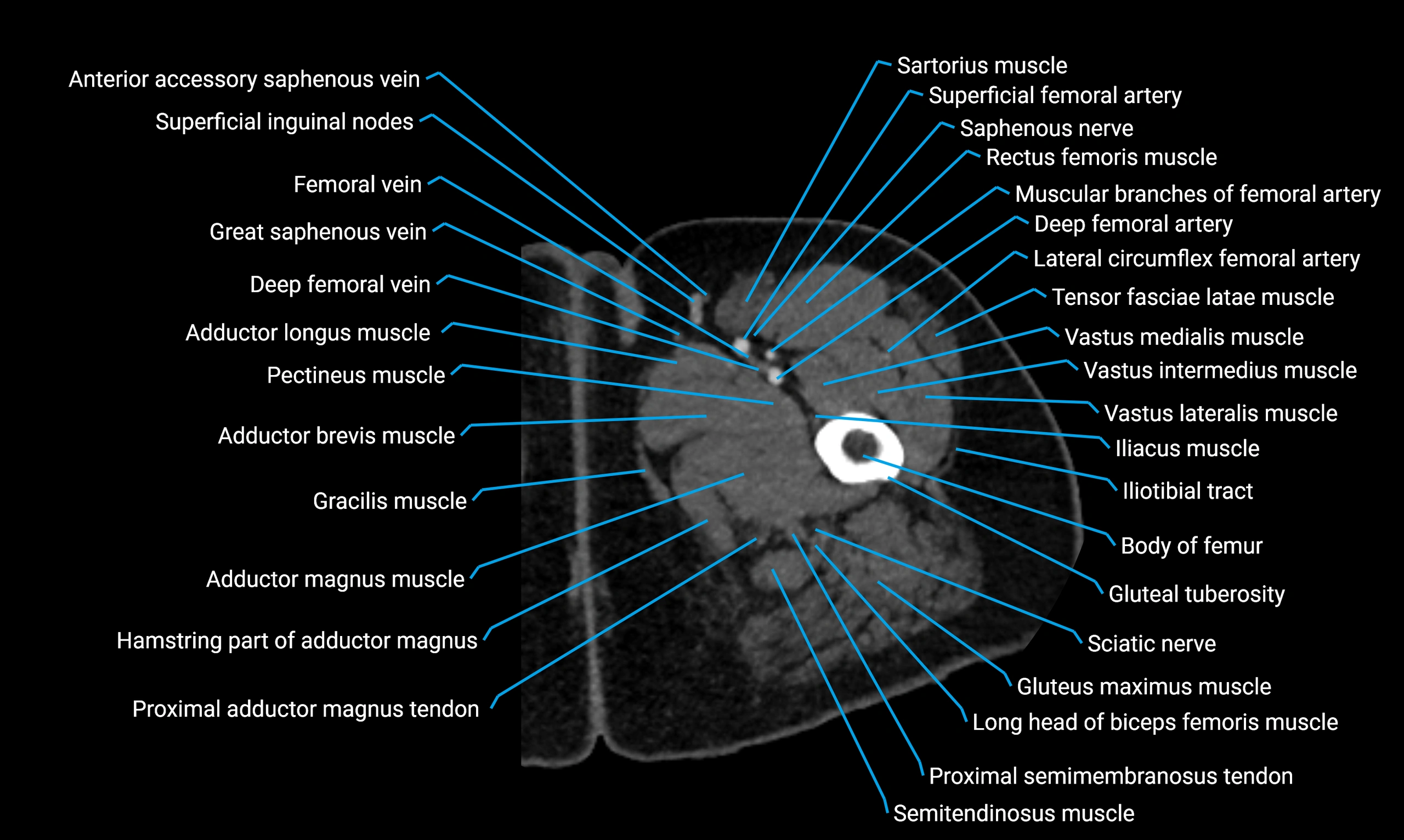
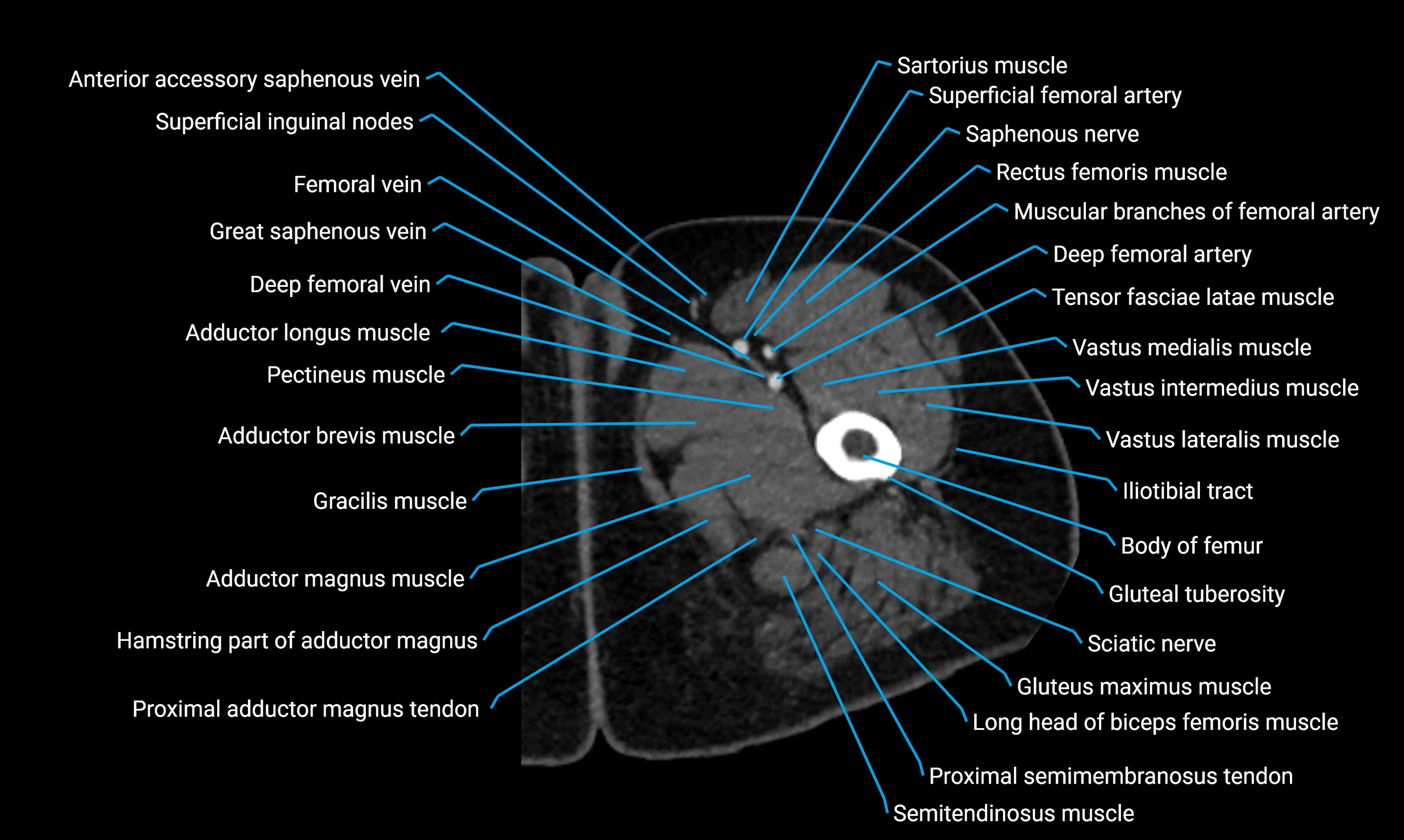
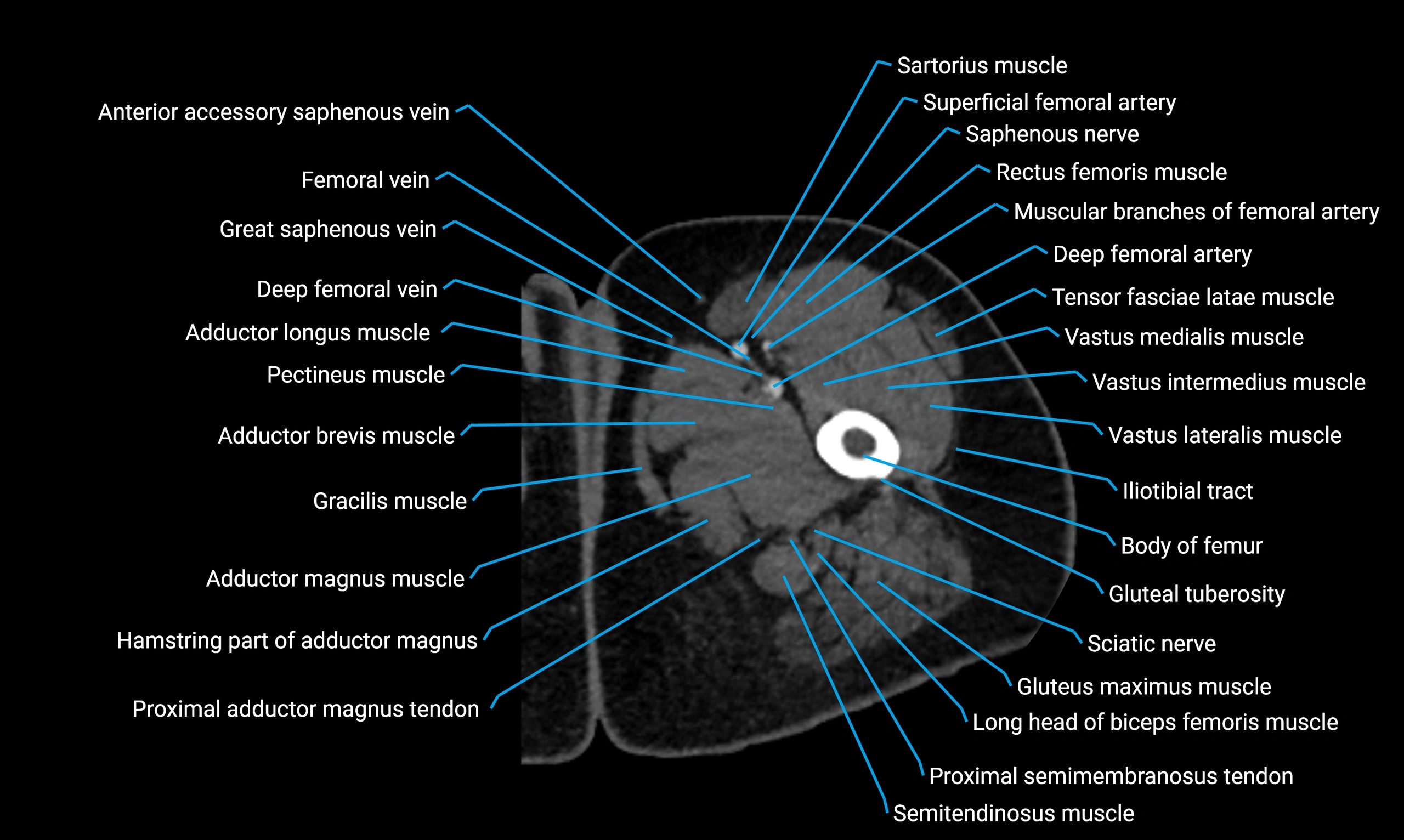
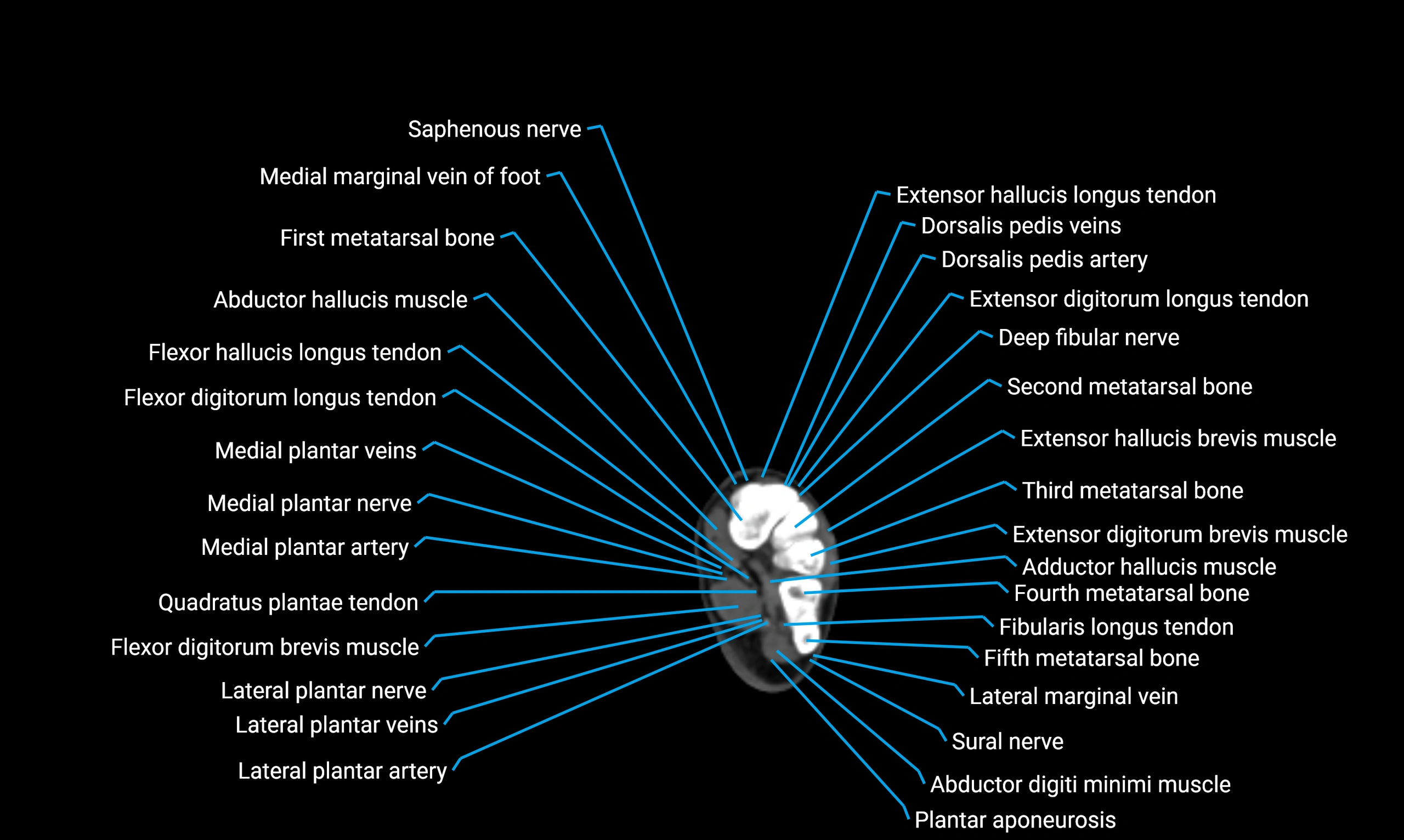
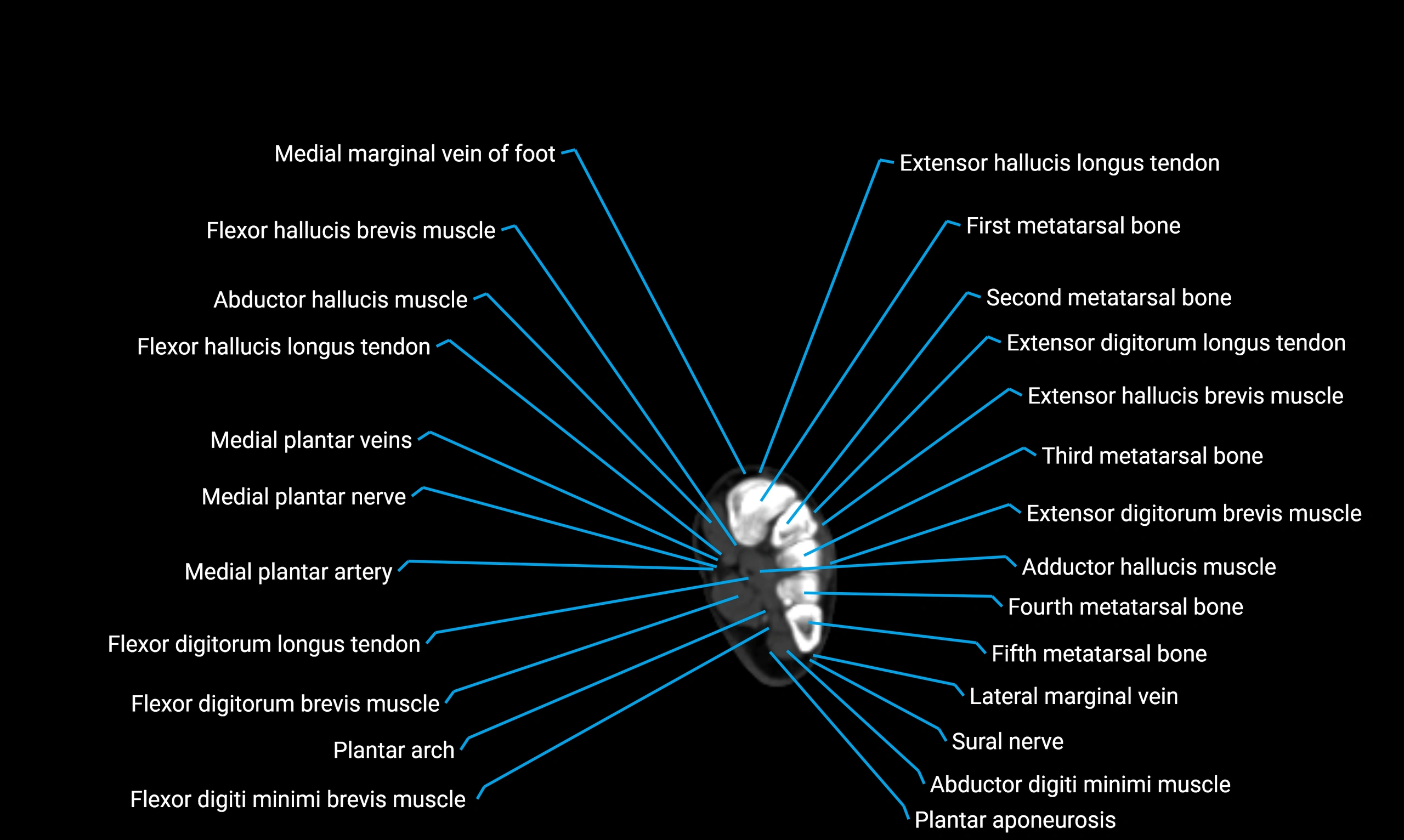
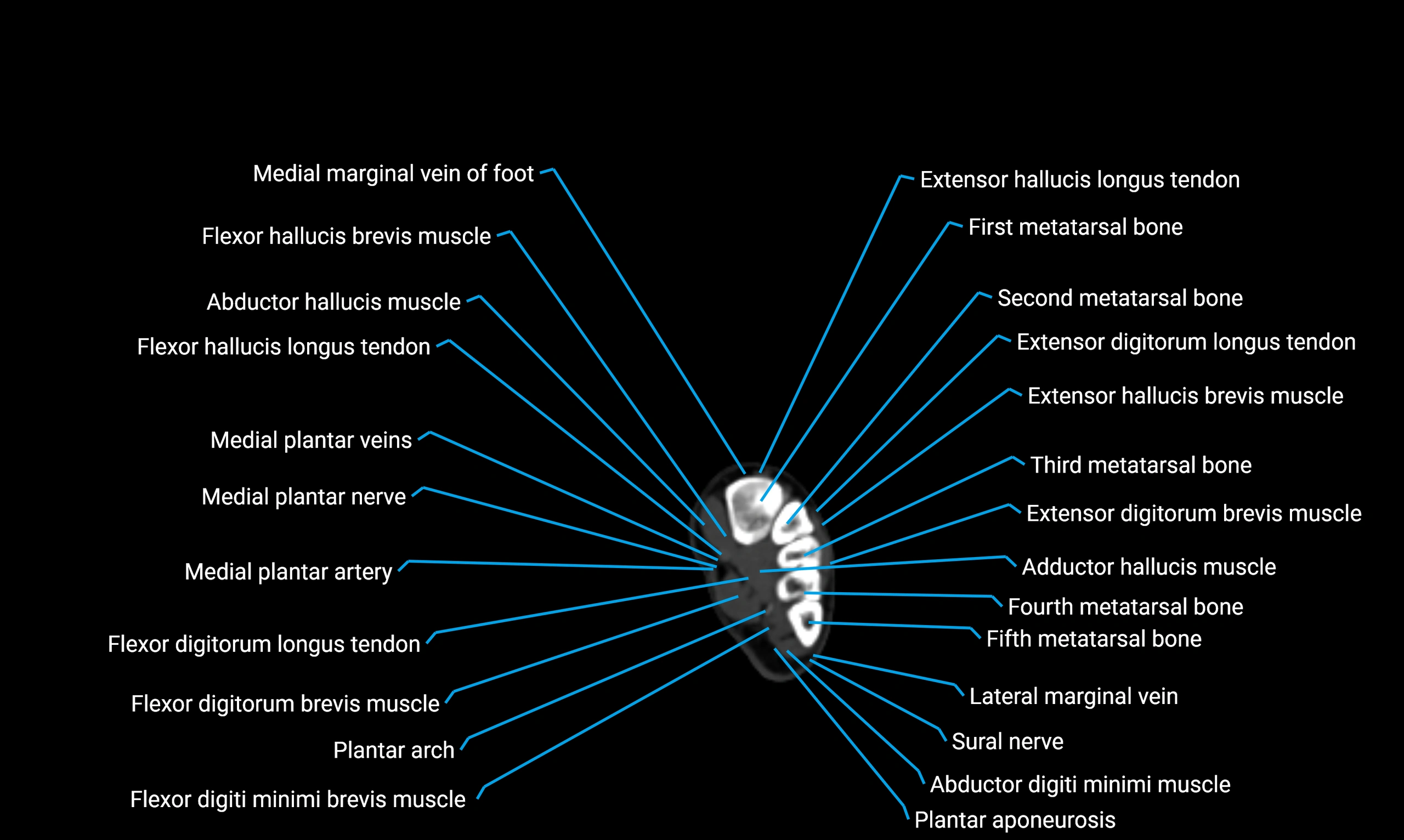
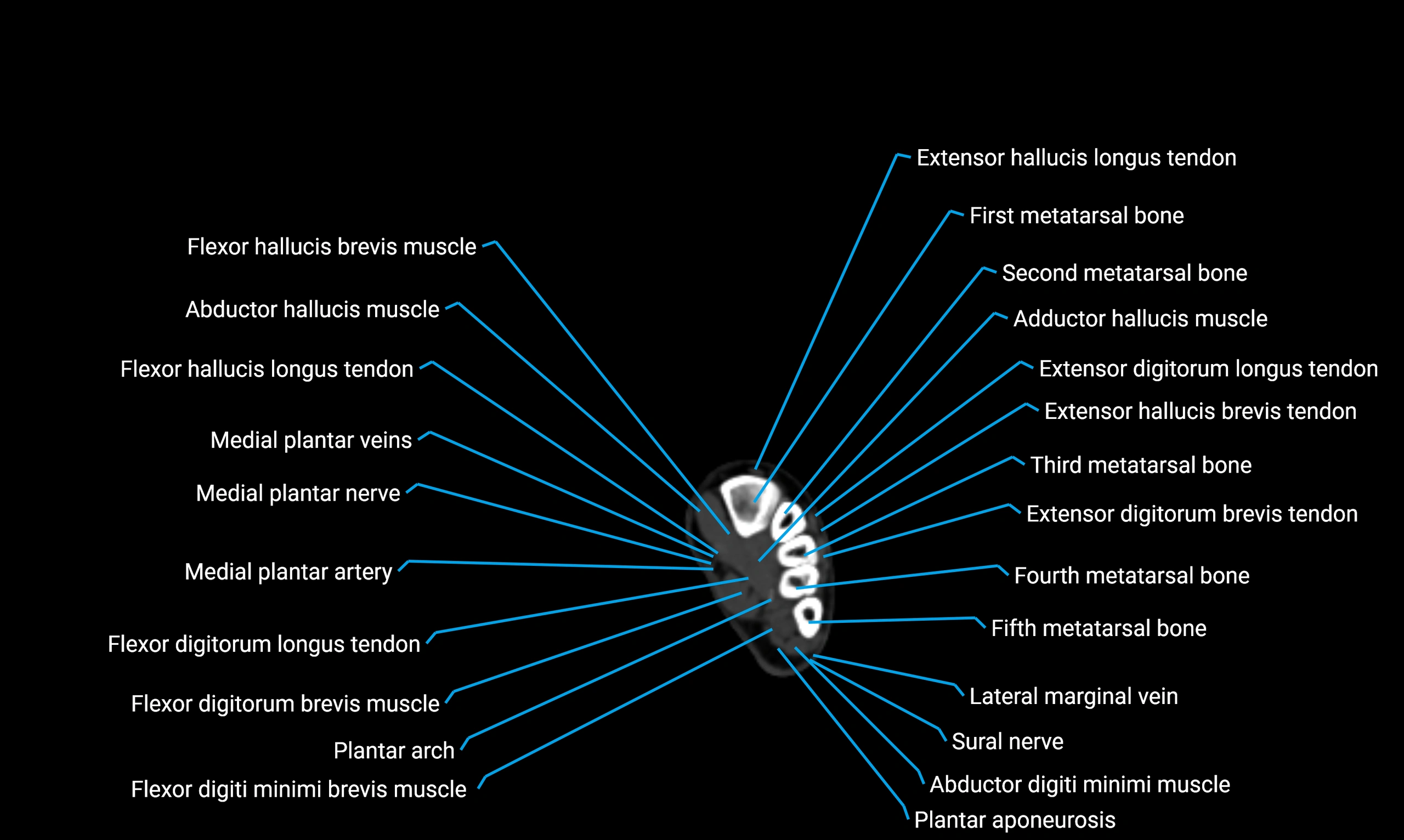
Topic
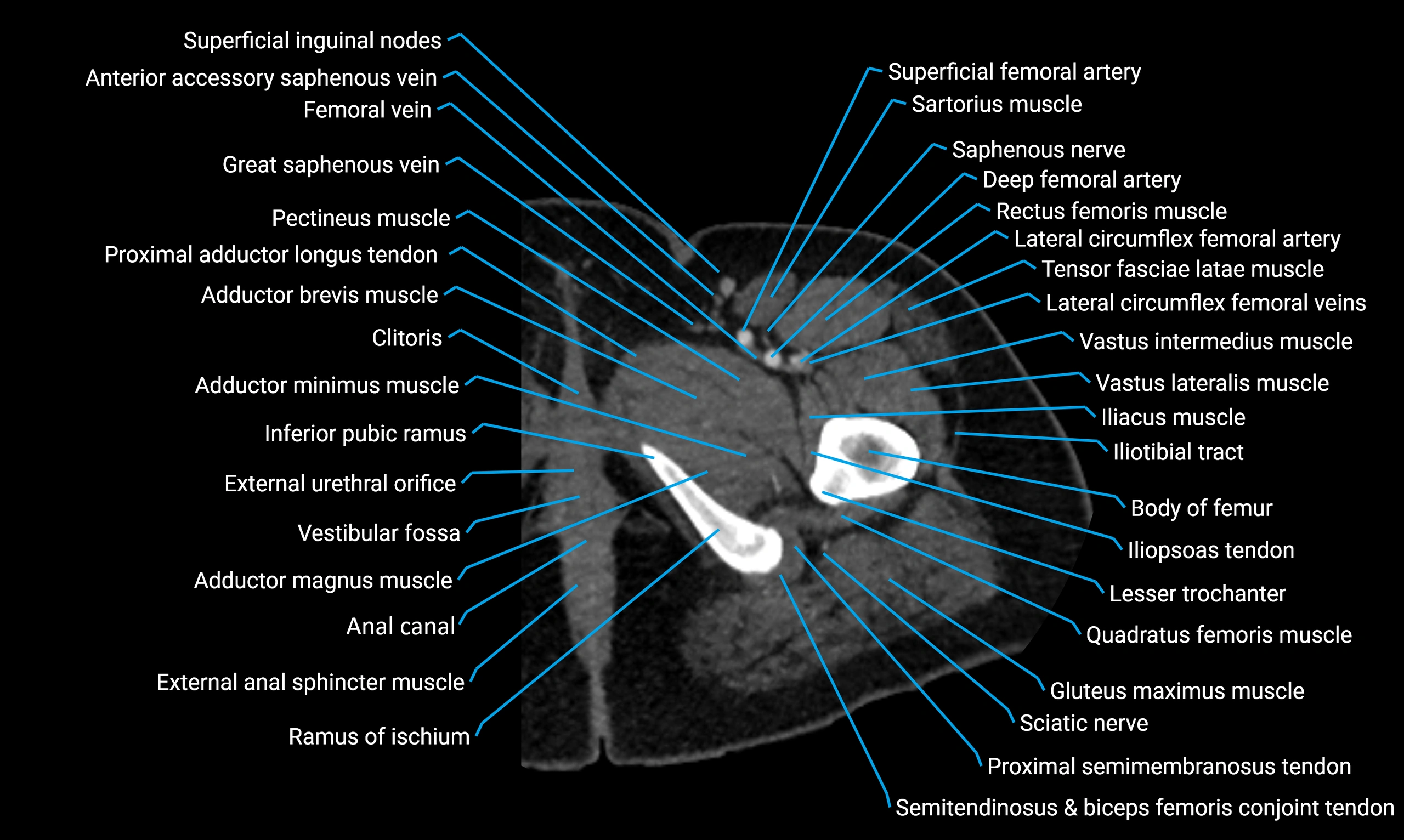
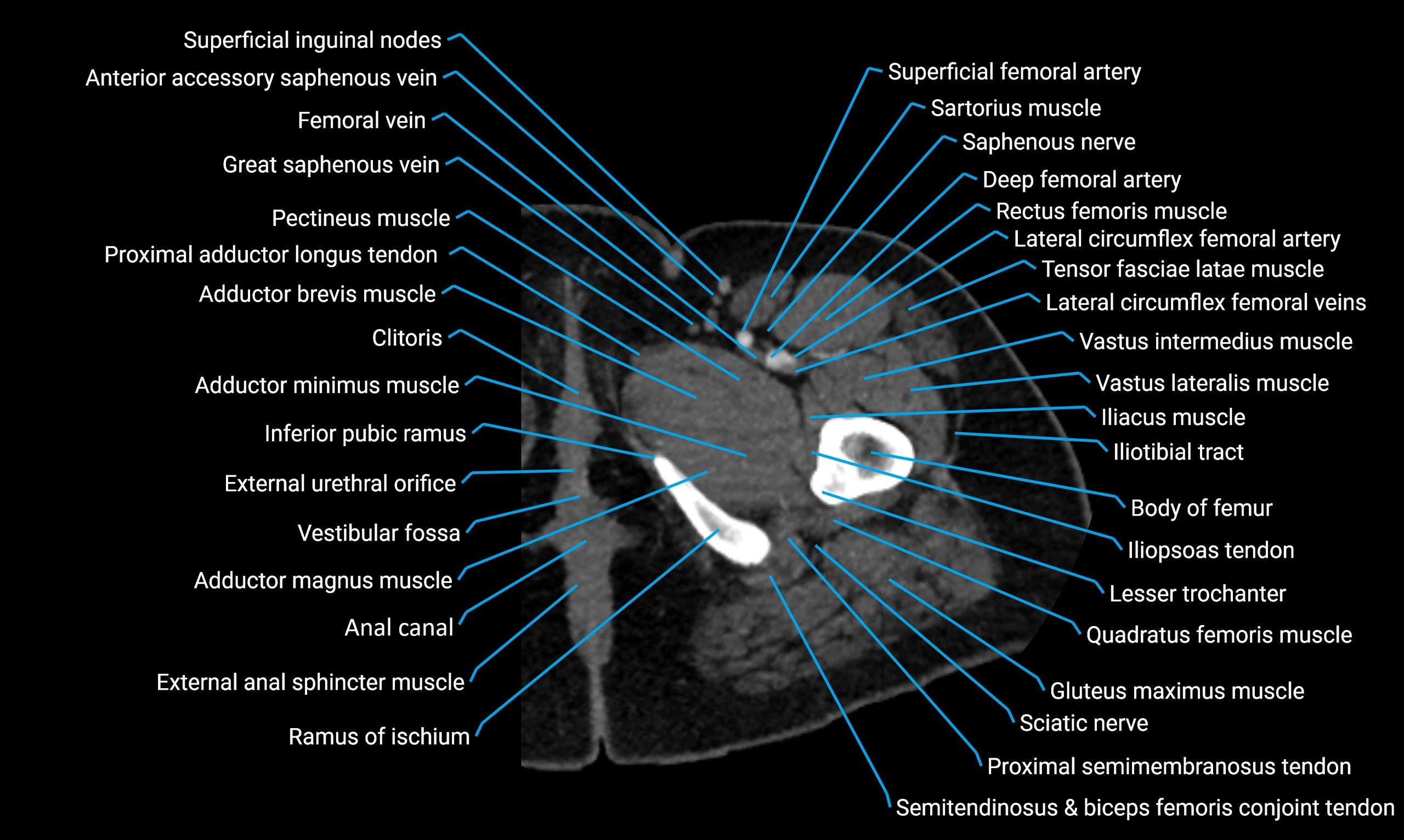
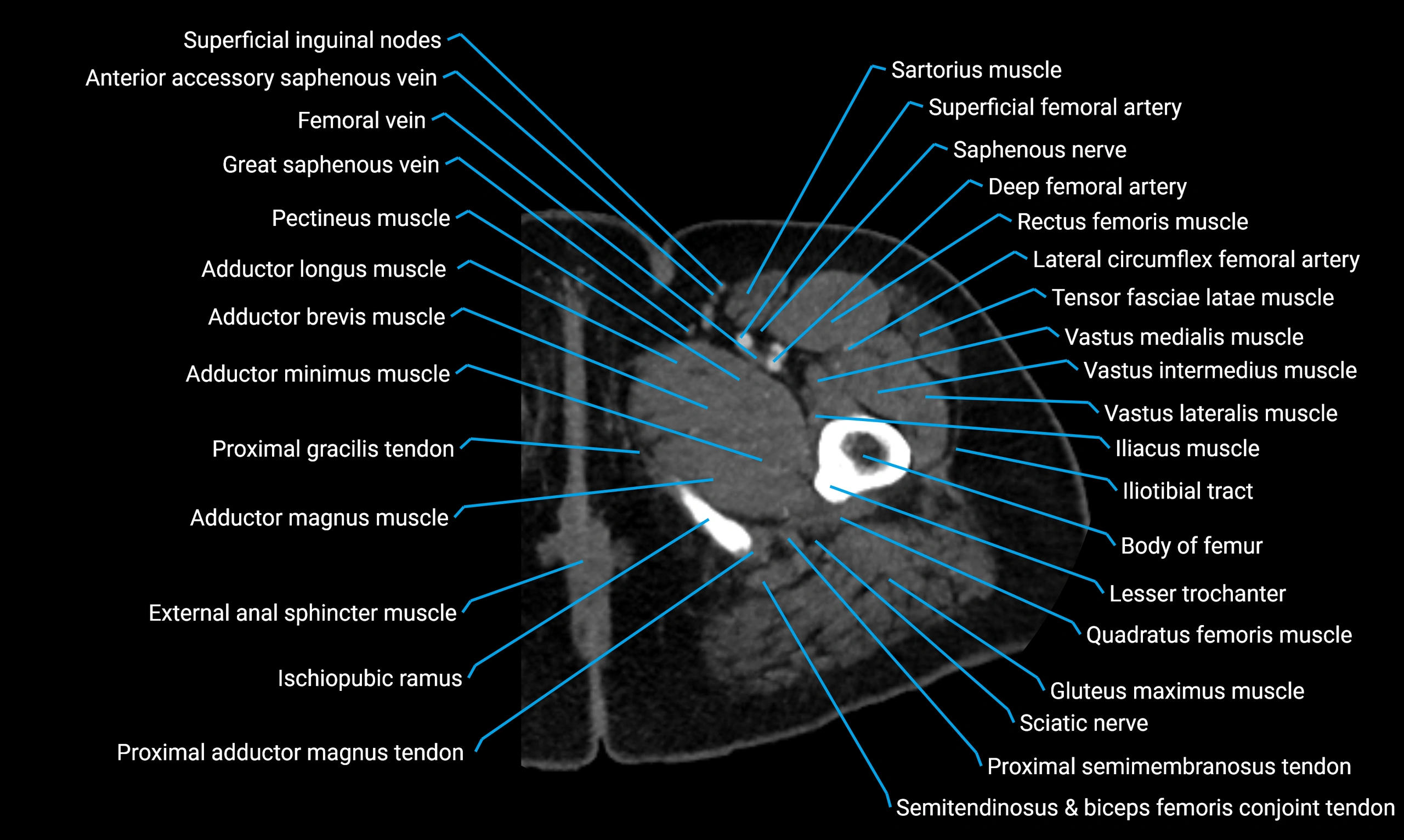
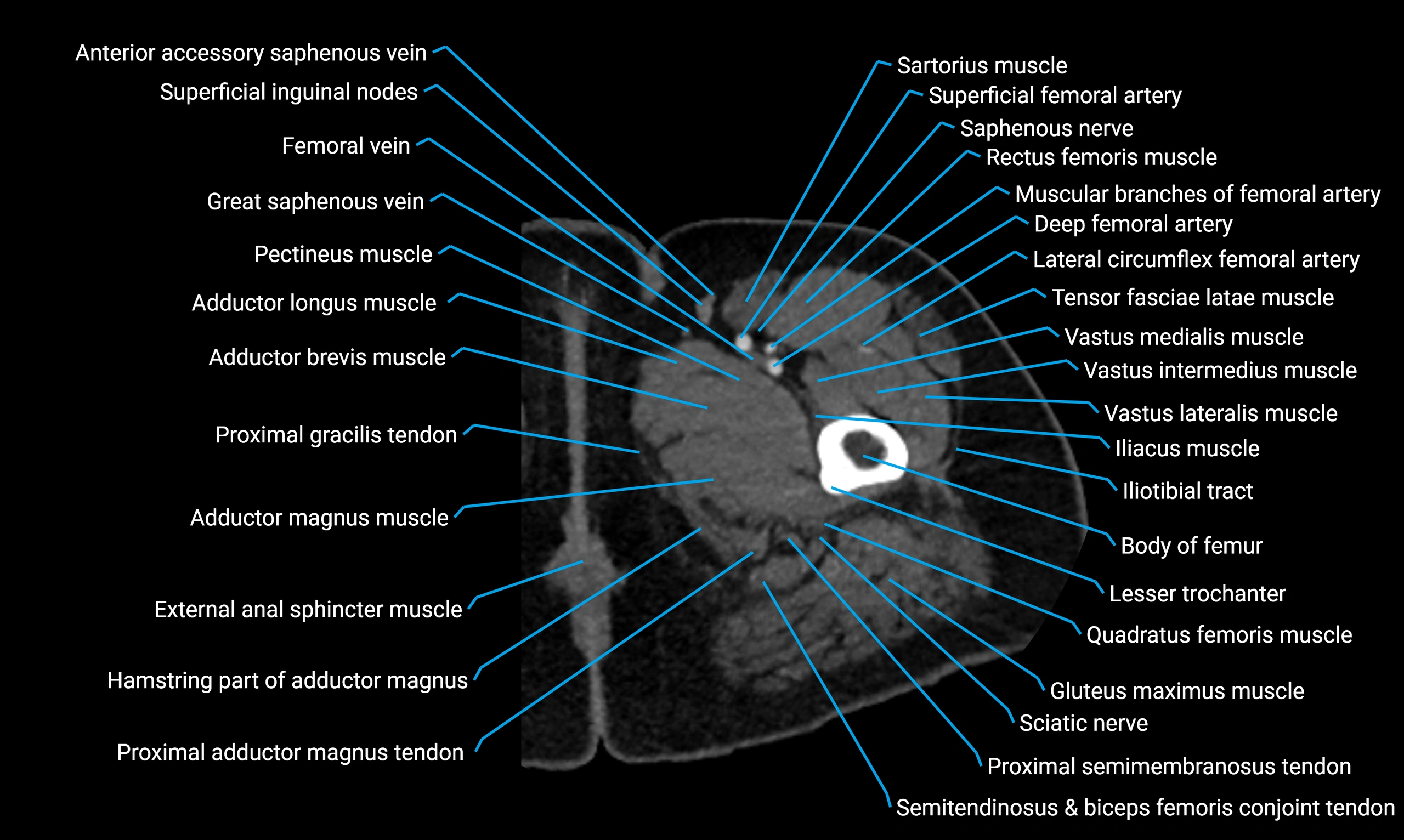
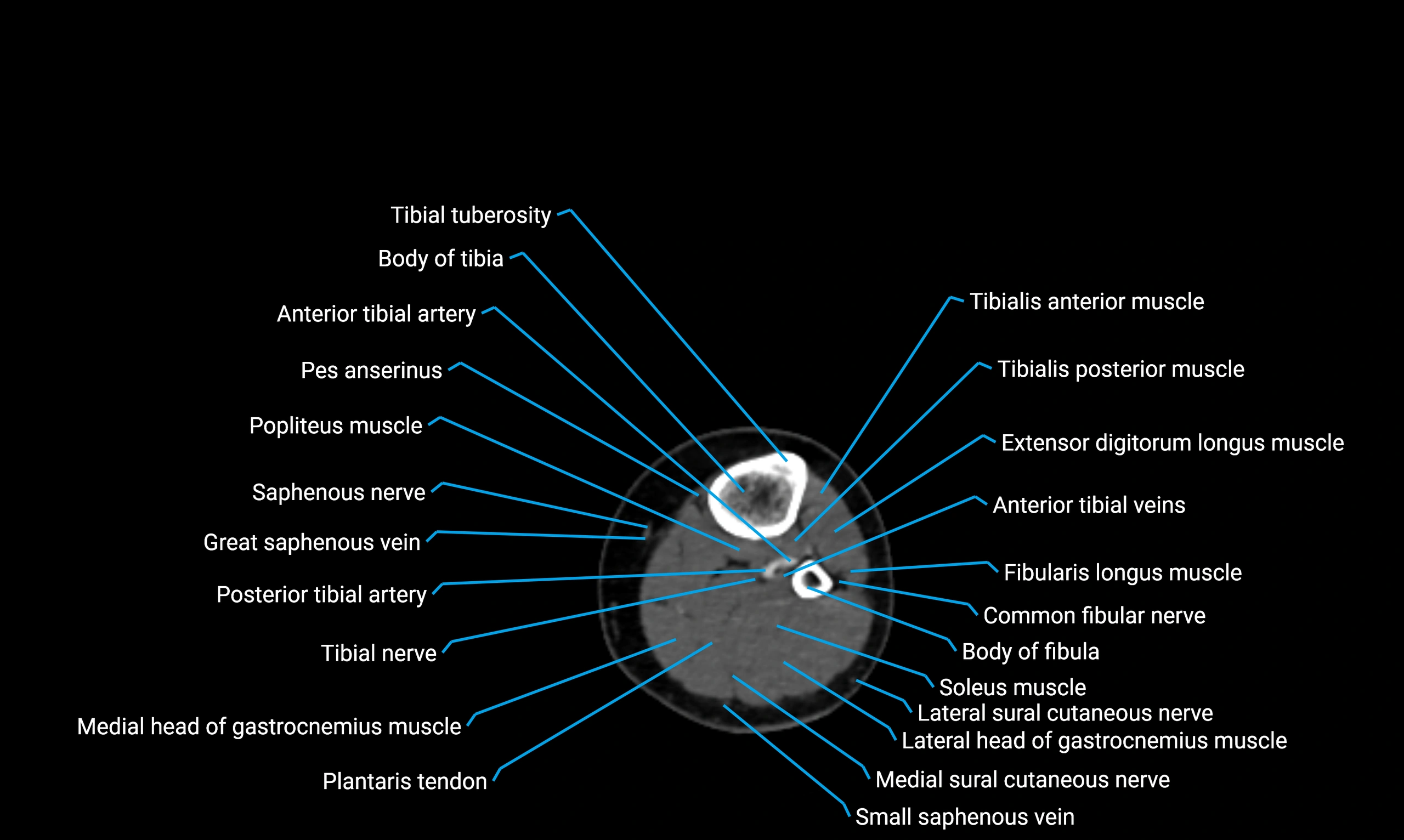
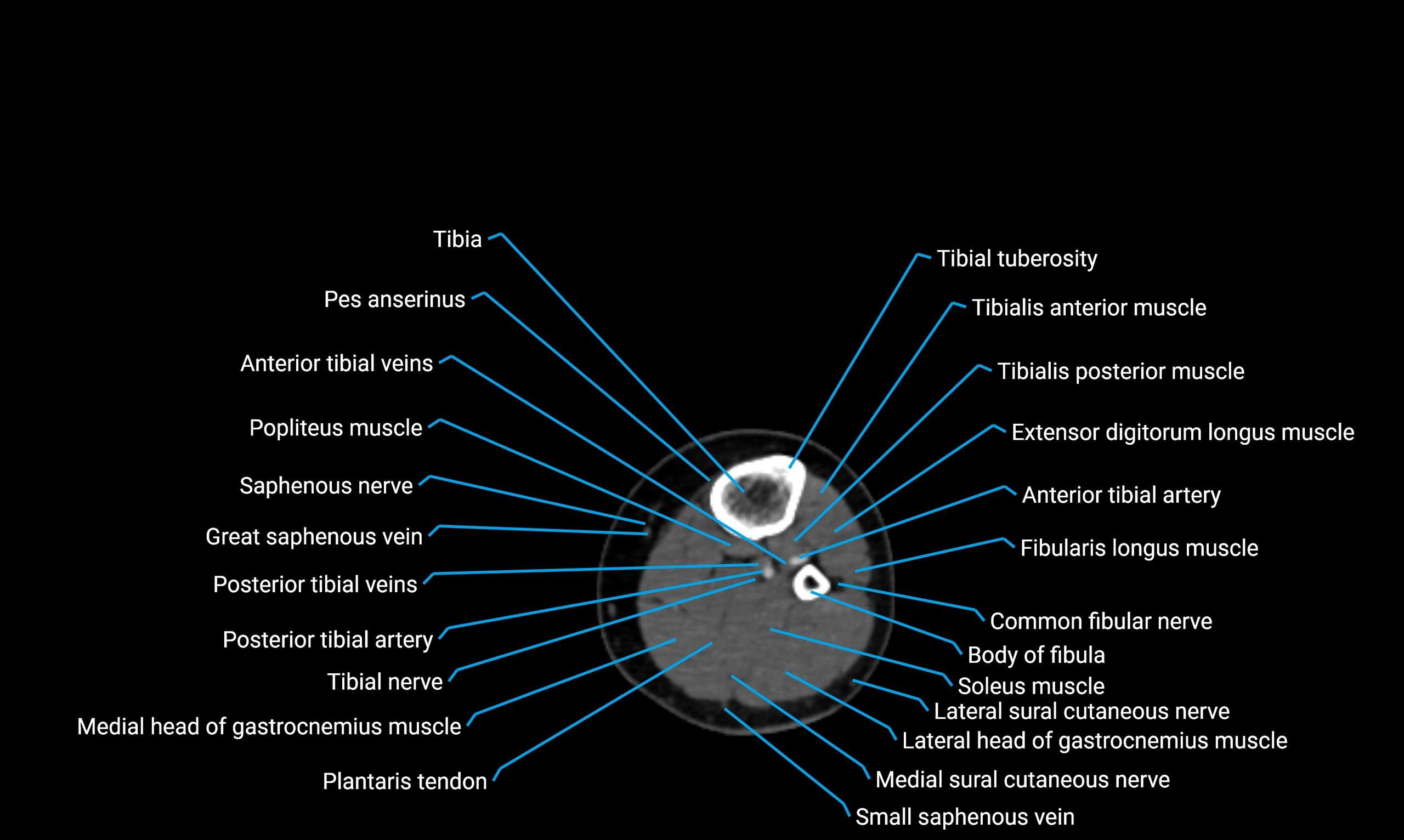
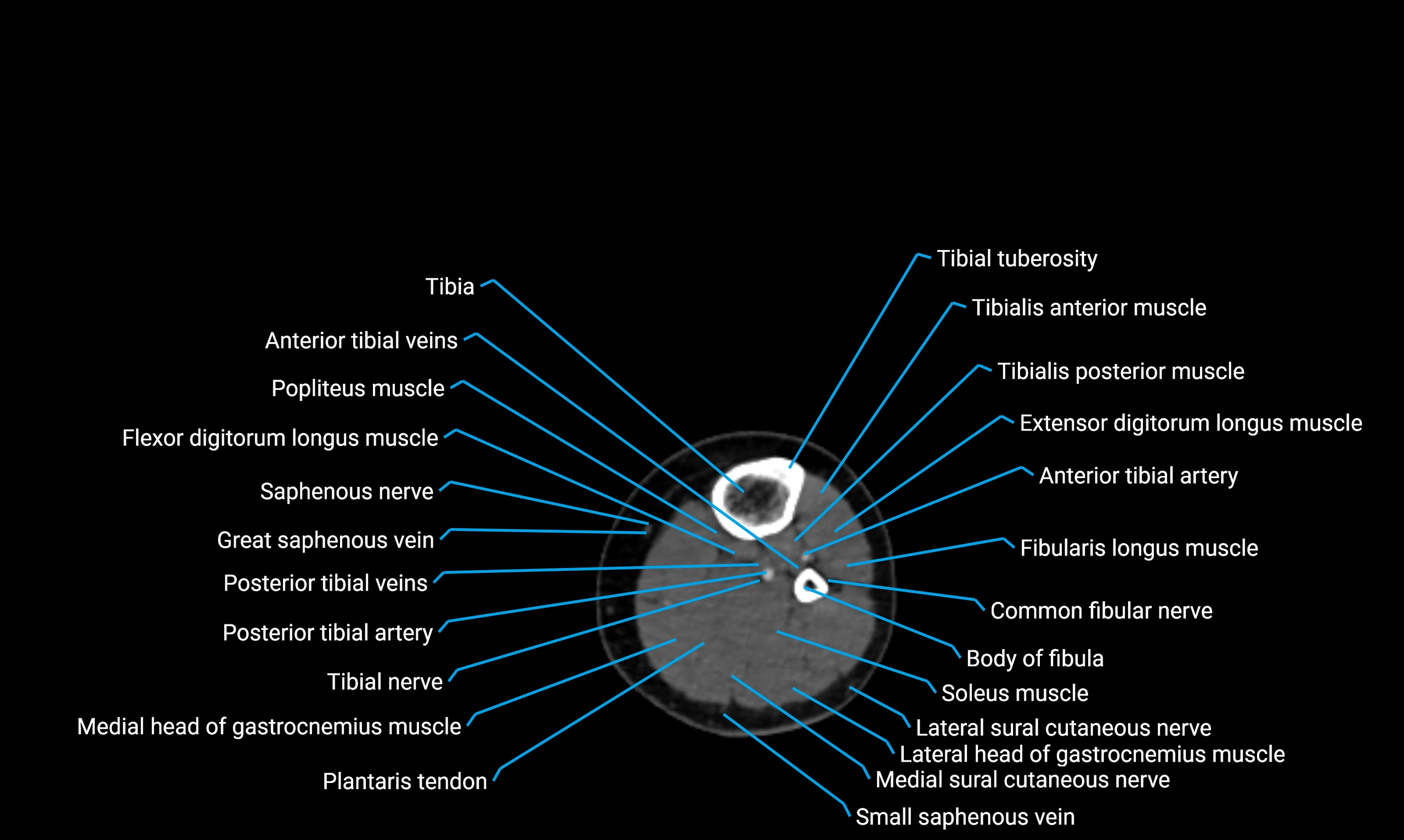
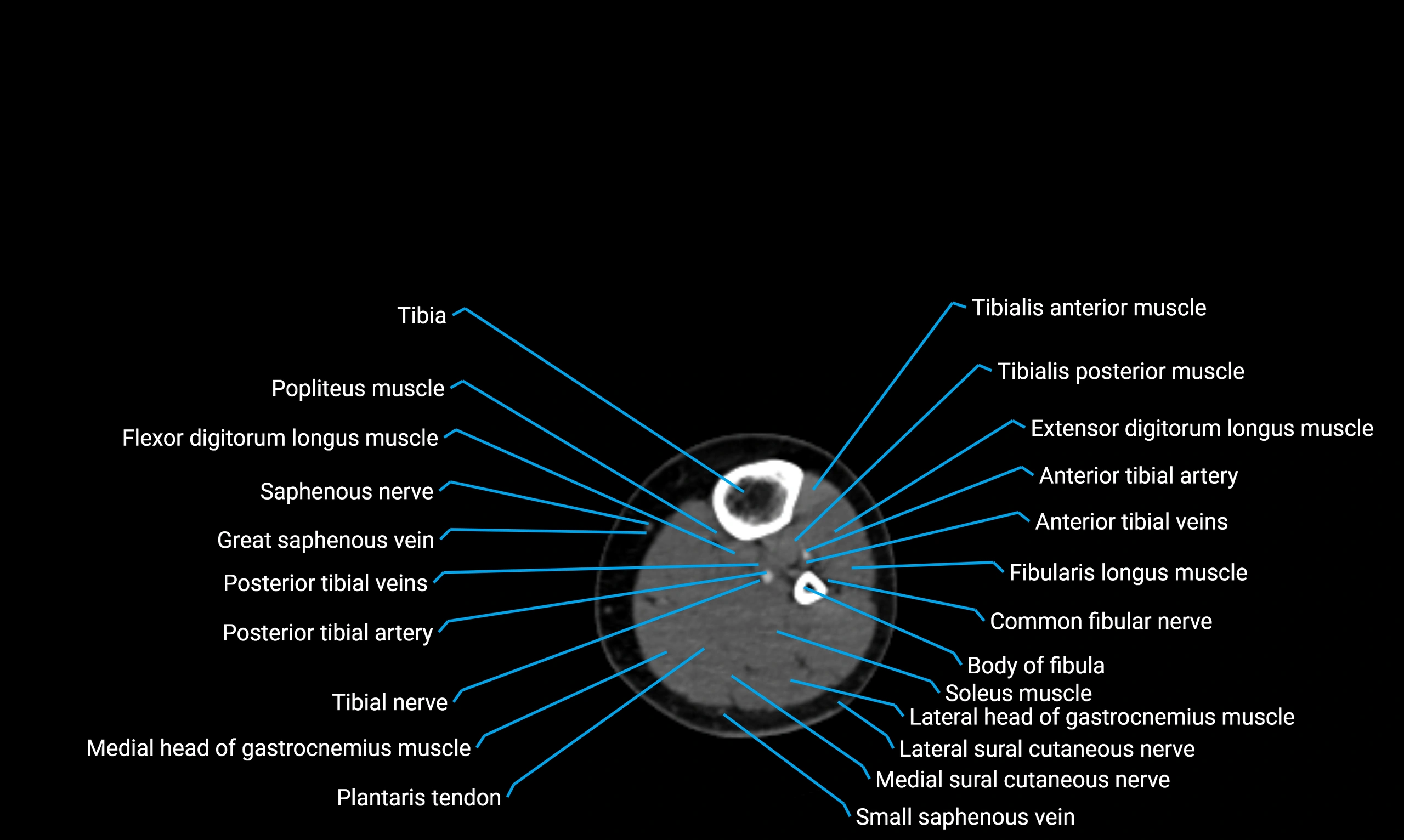
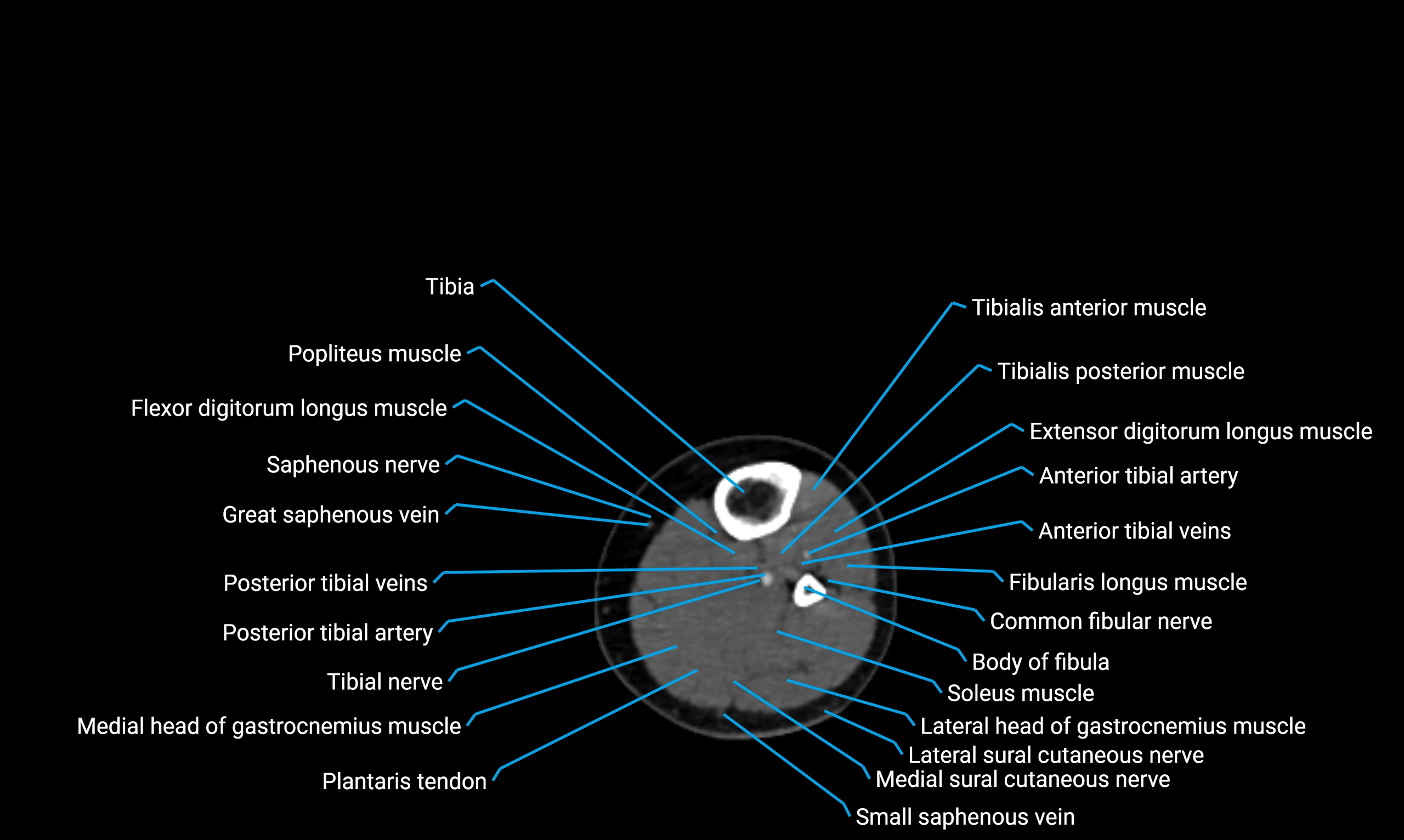
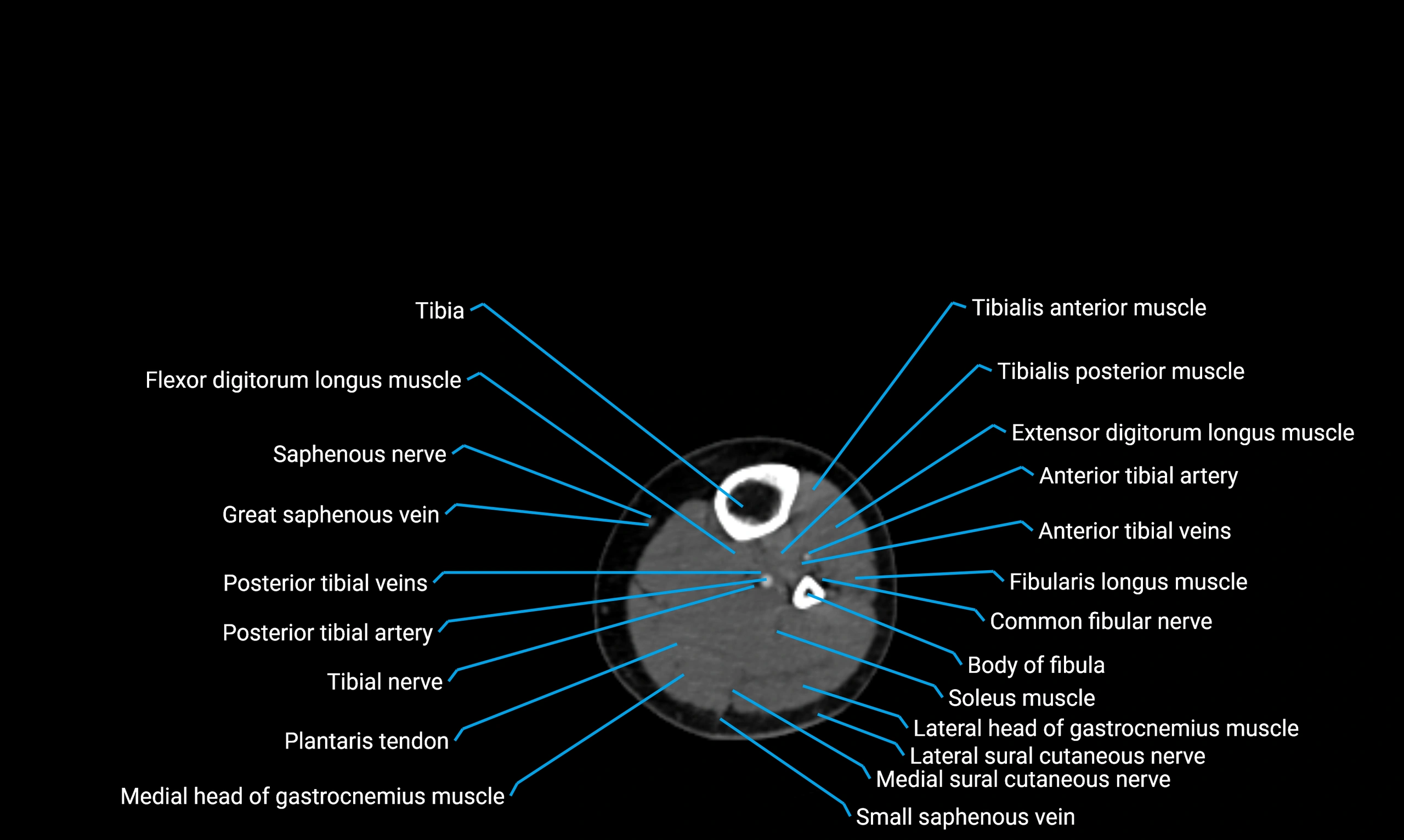
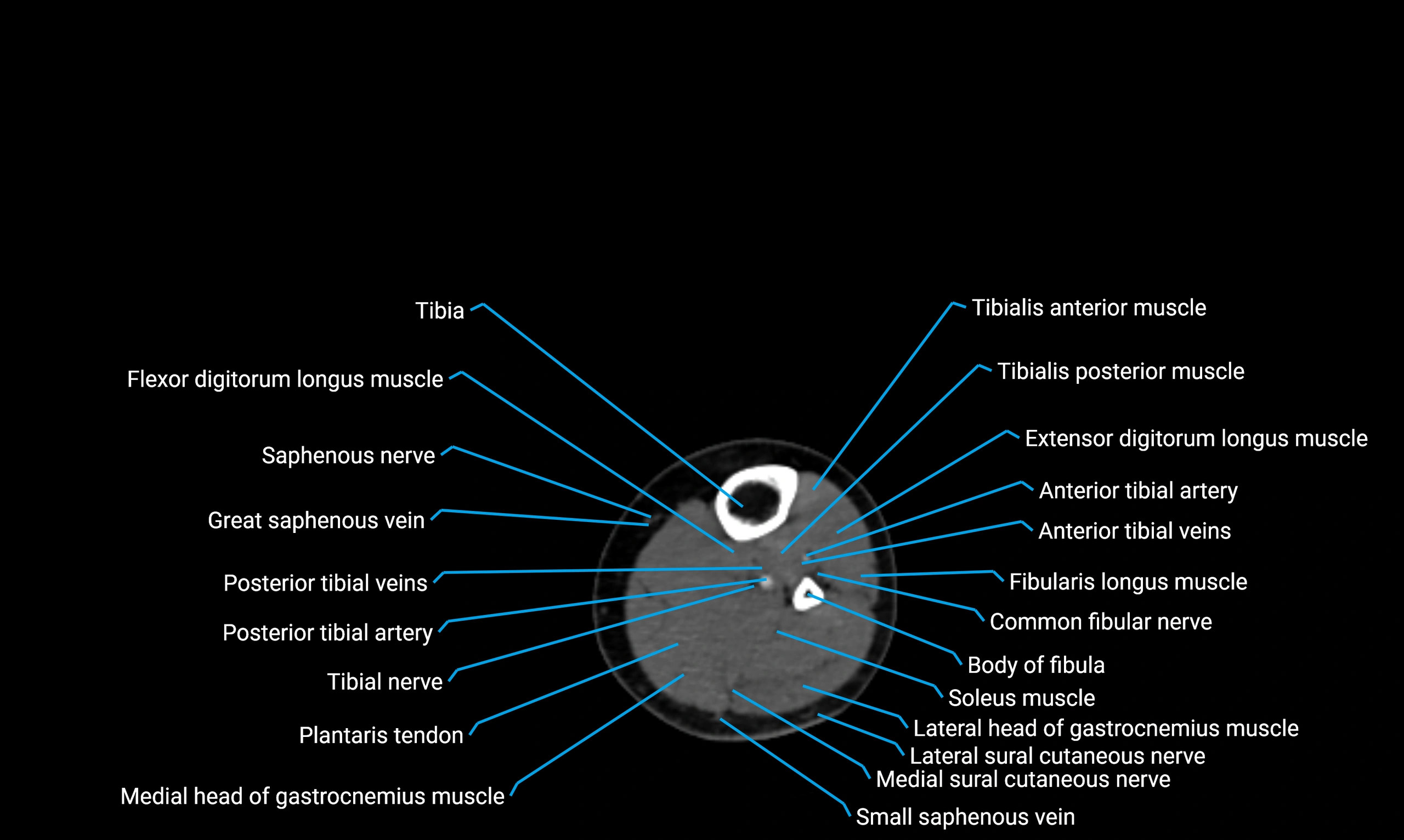
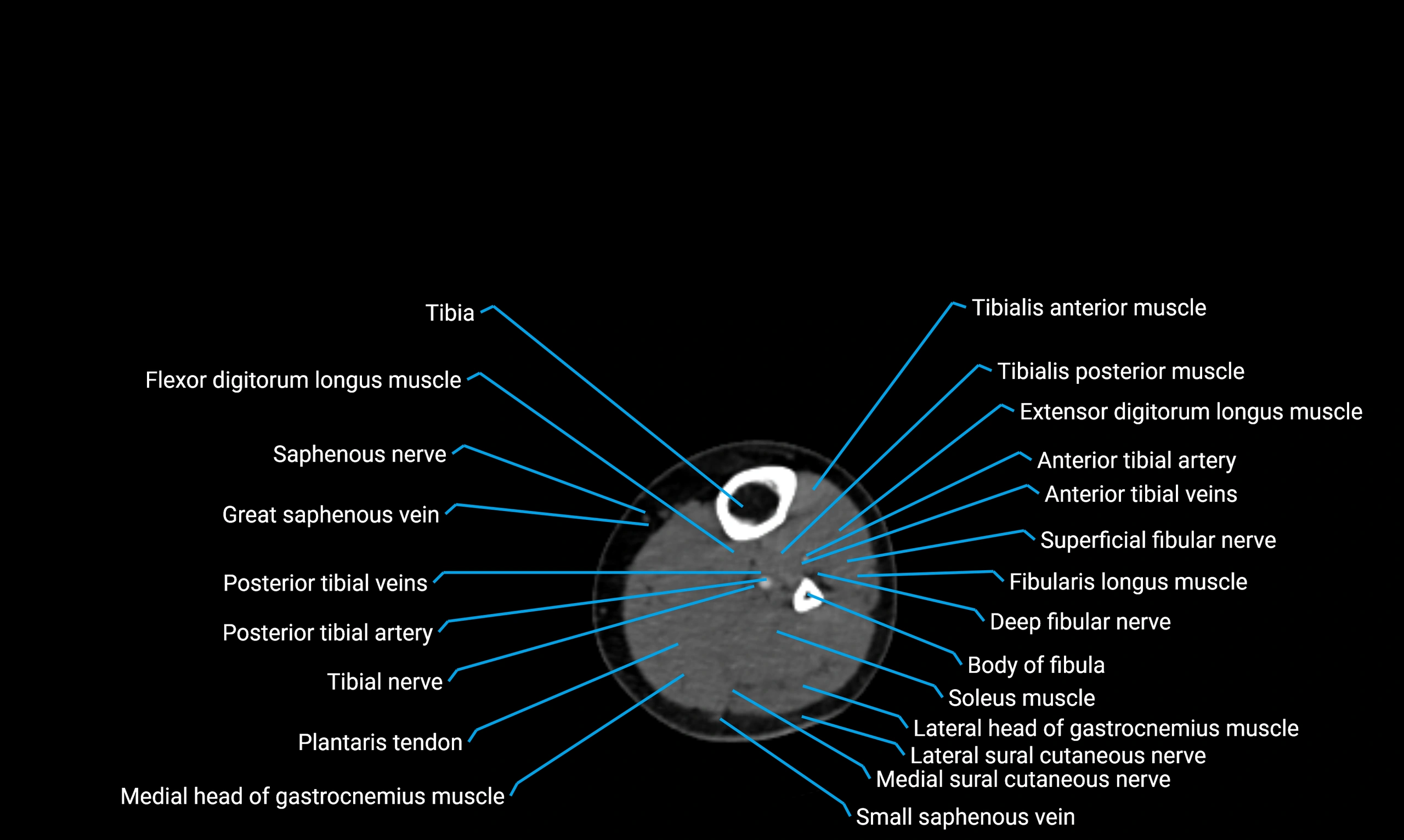
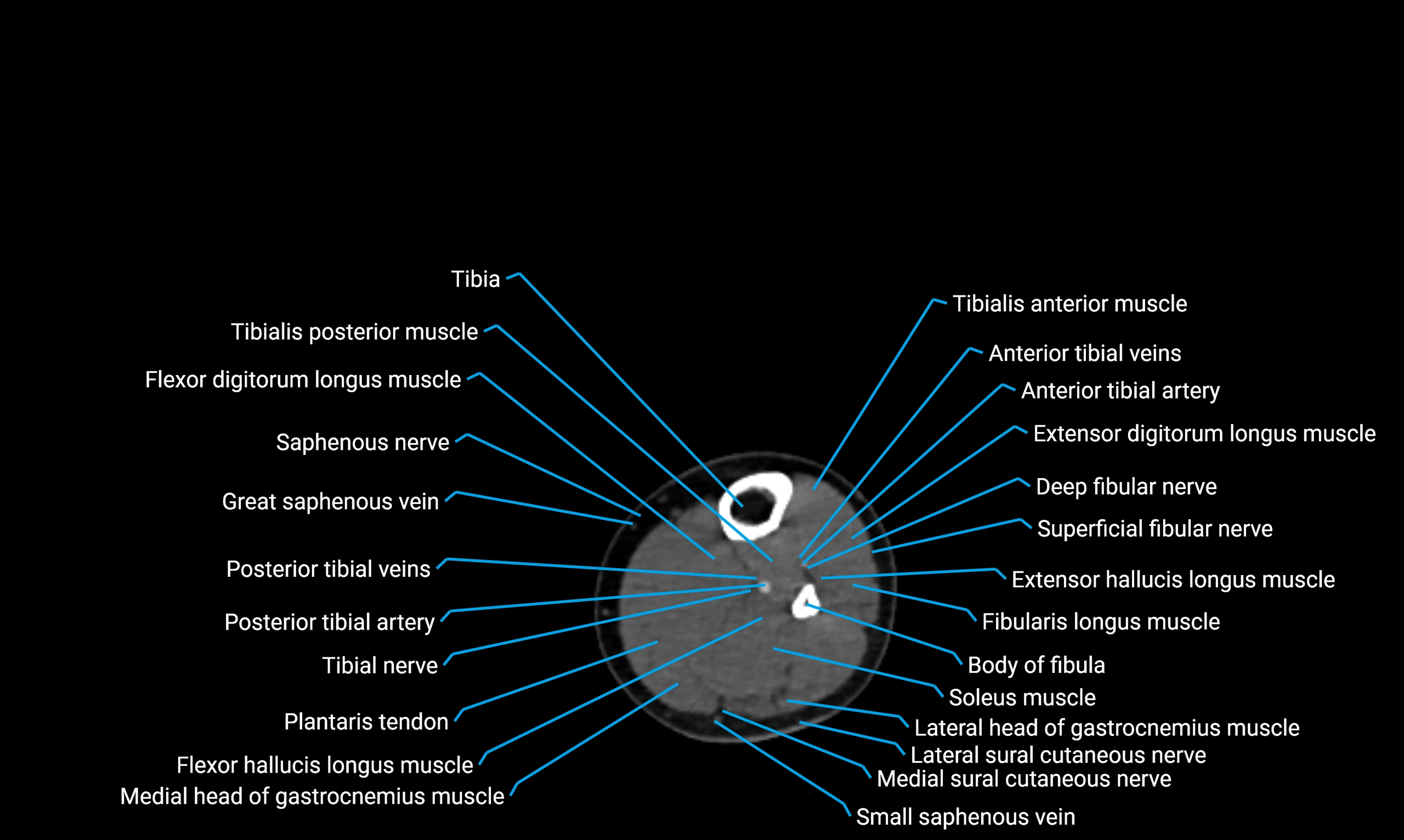
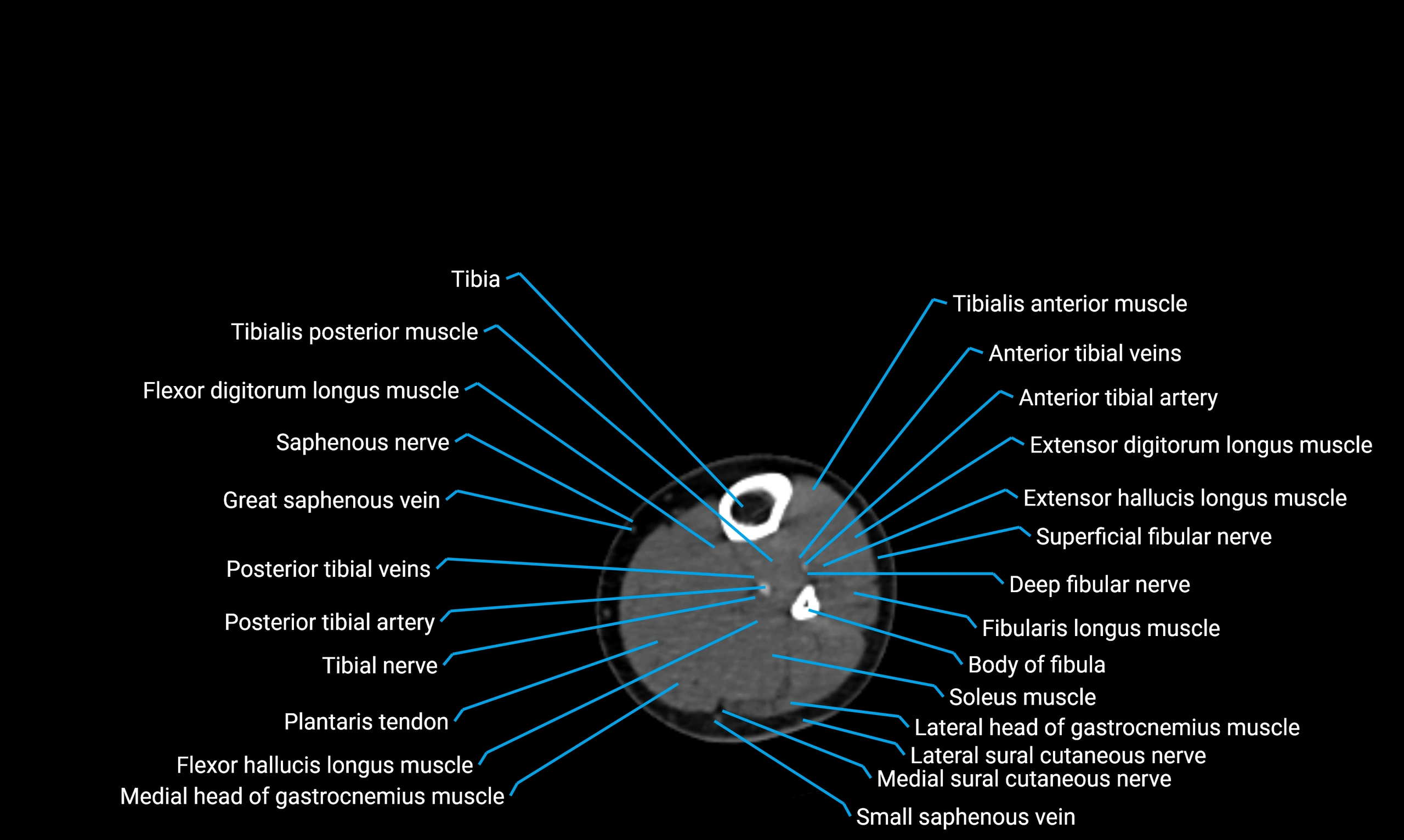
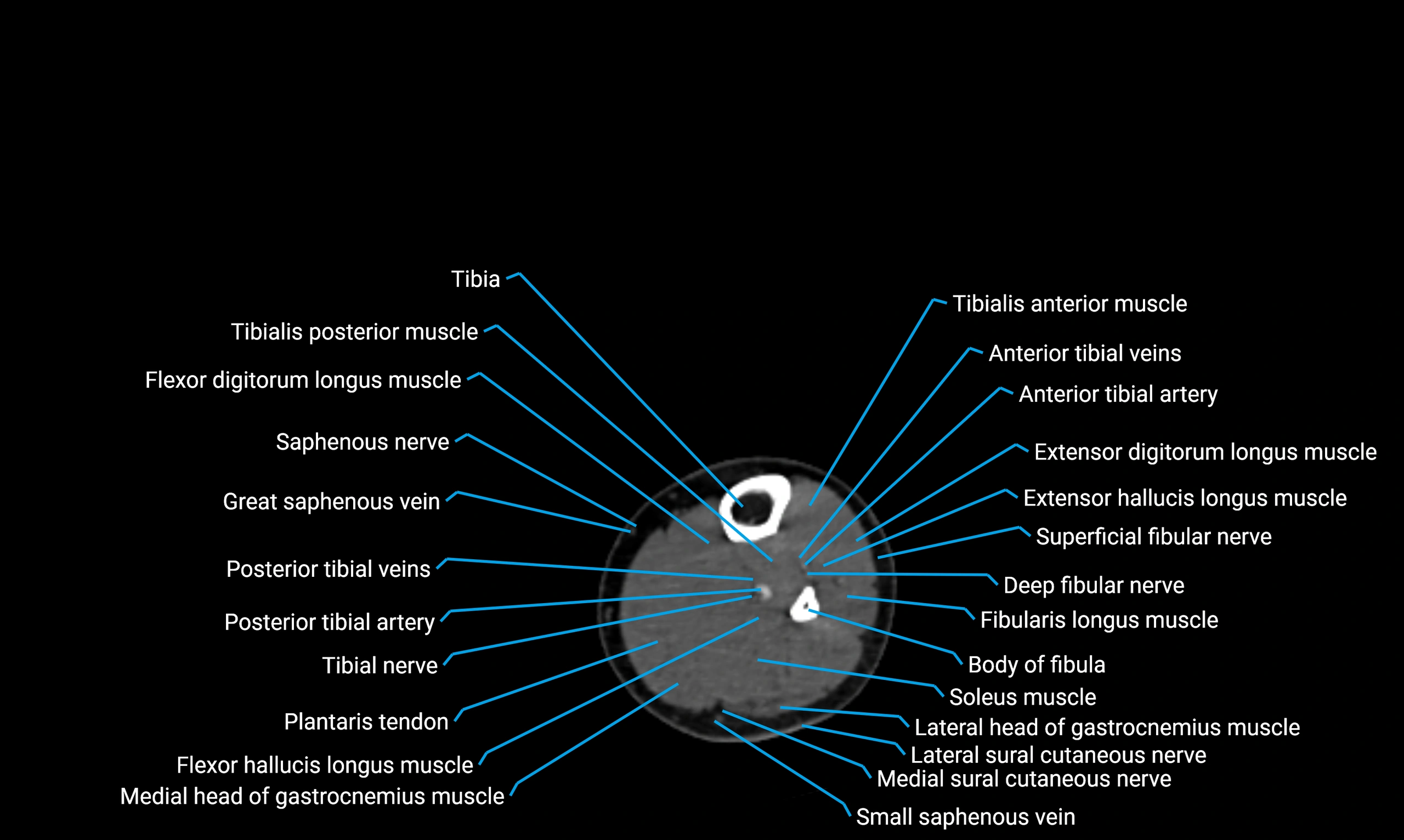
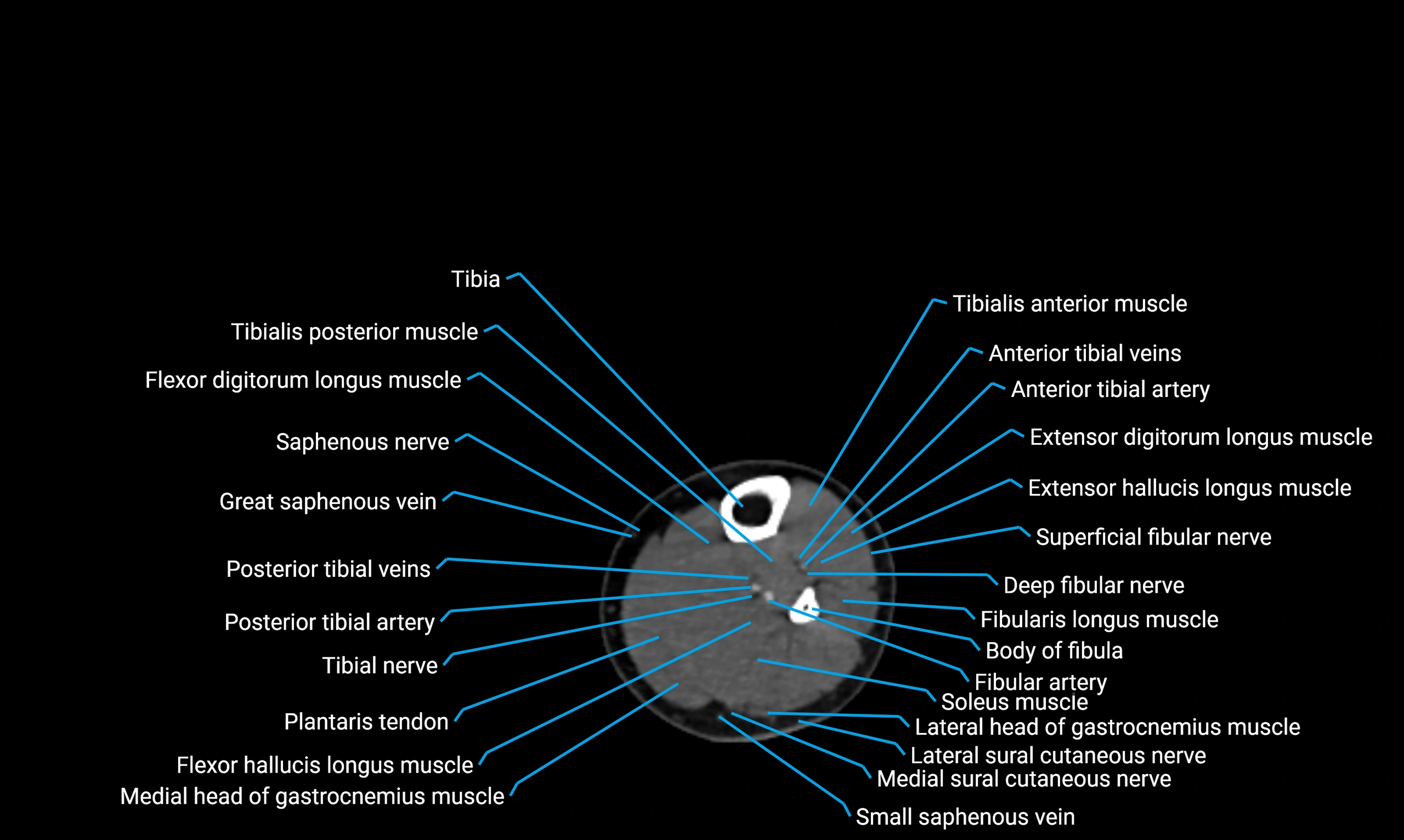
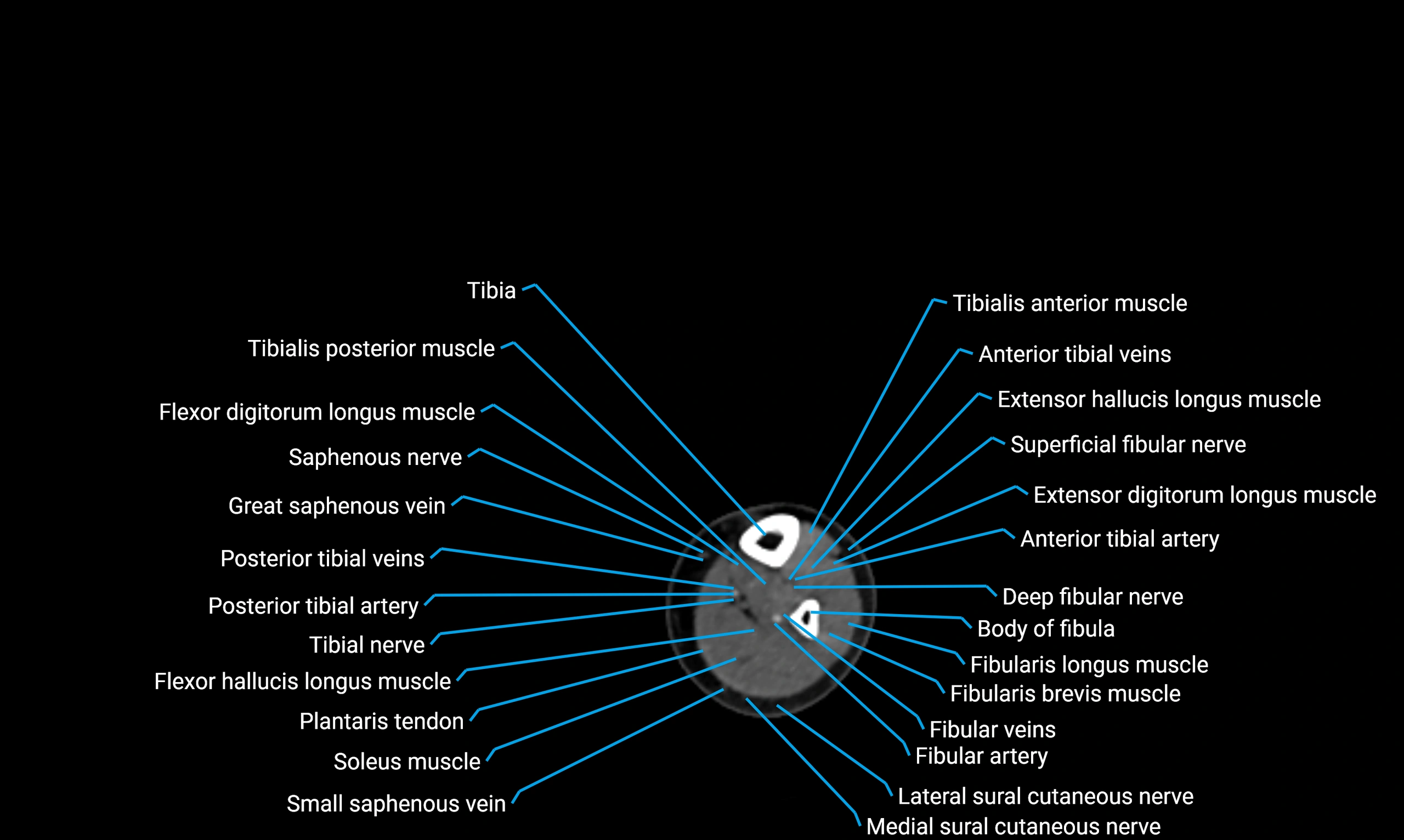
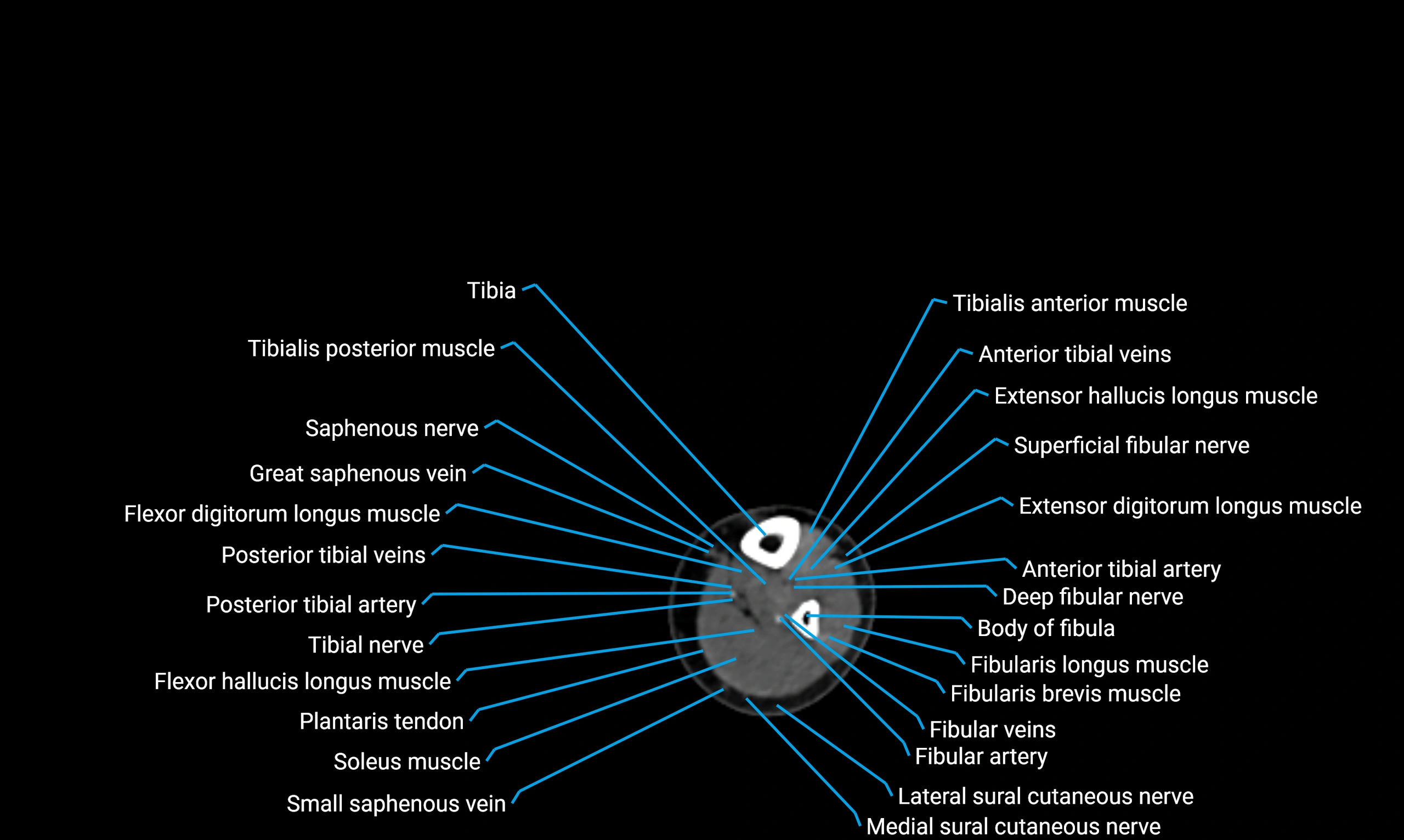
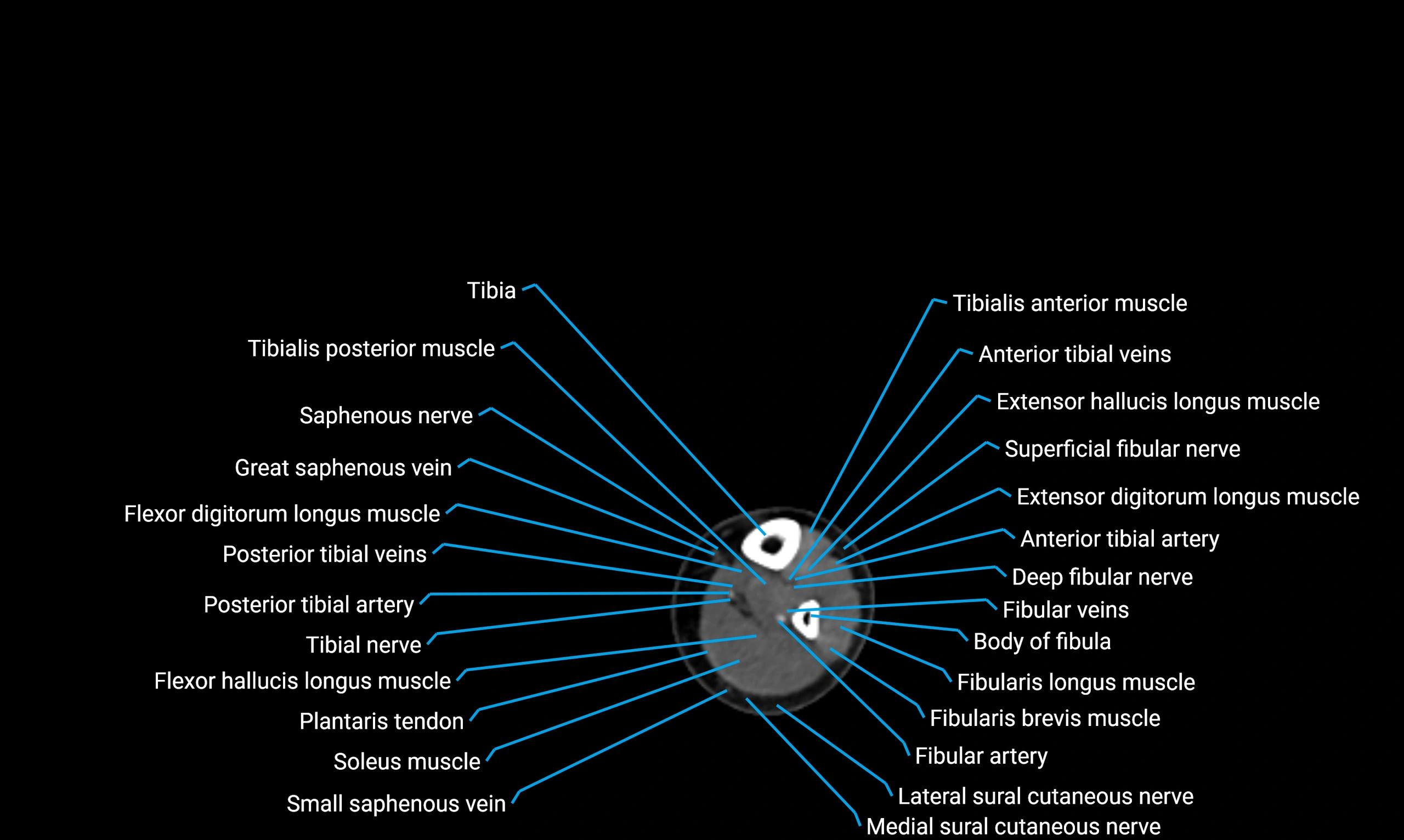
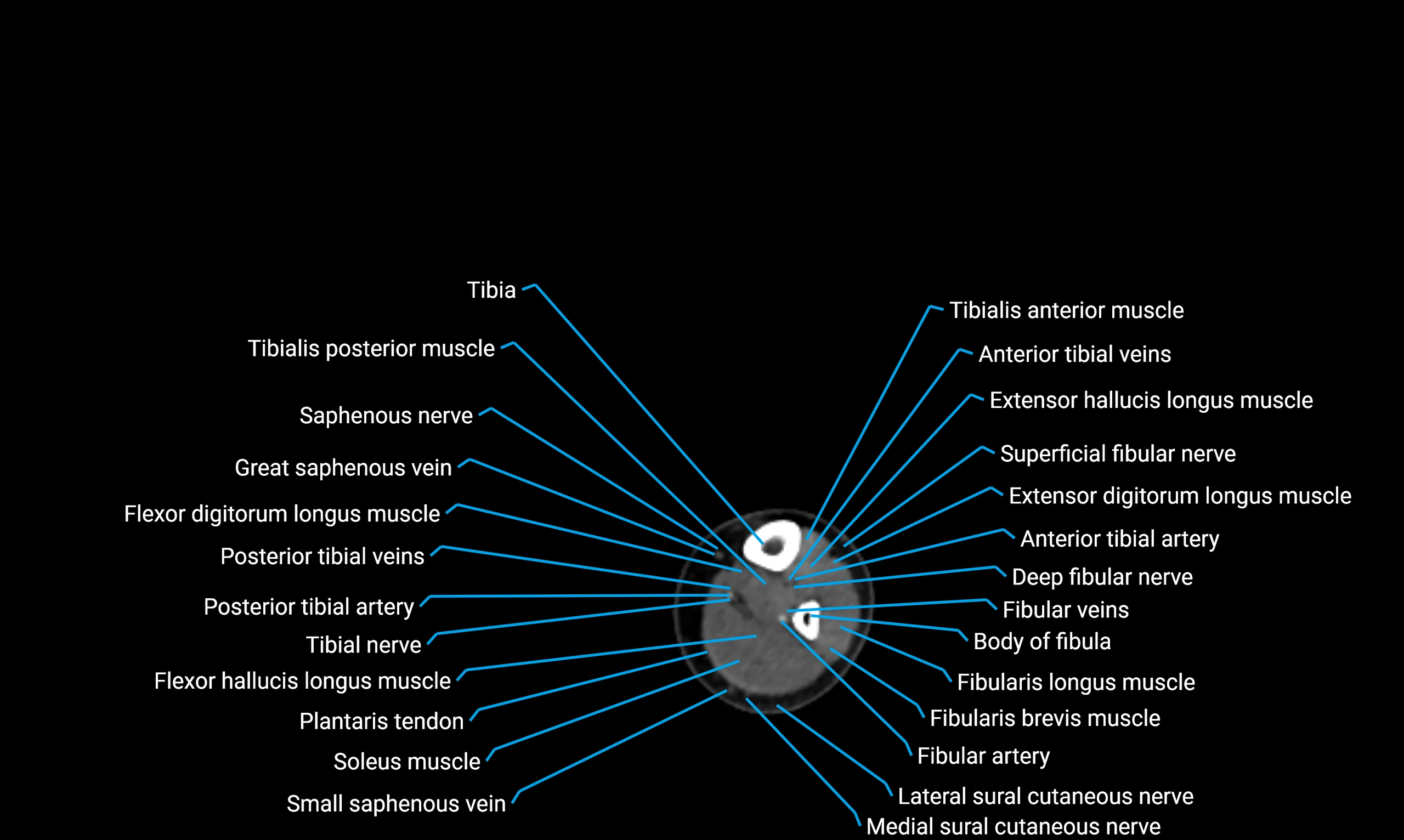
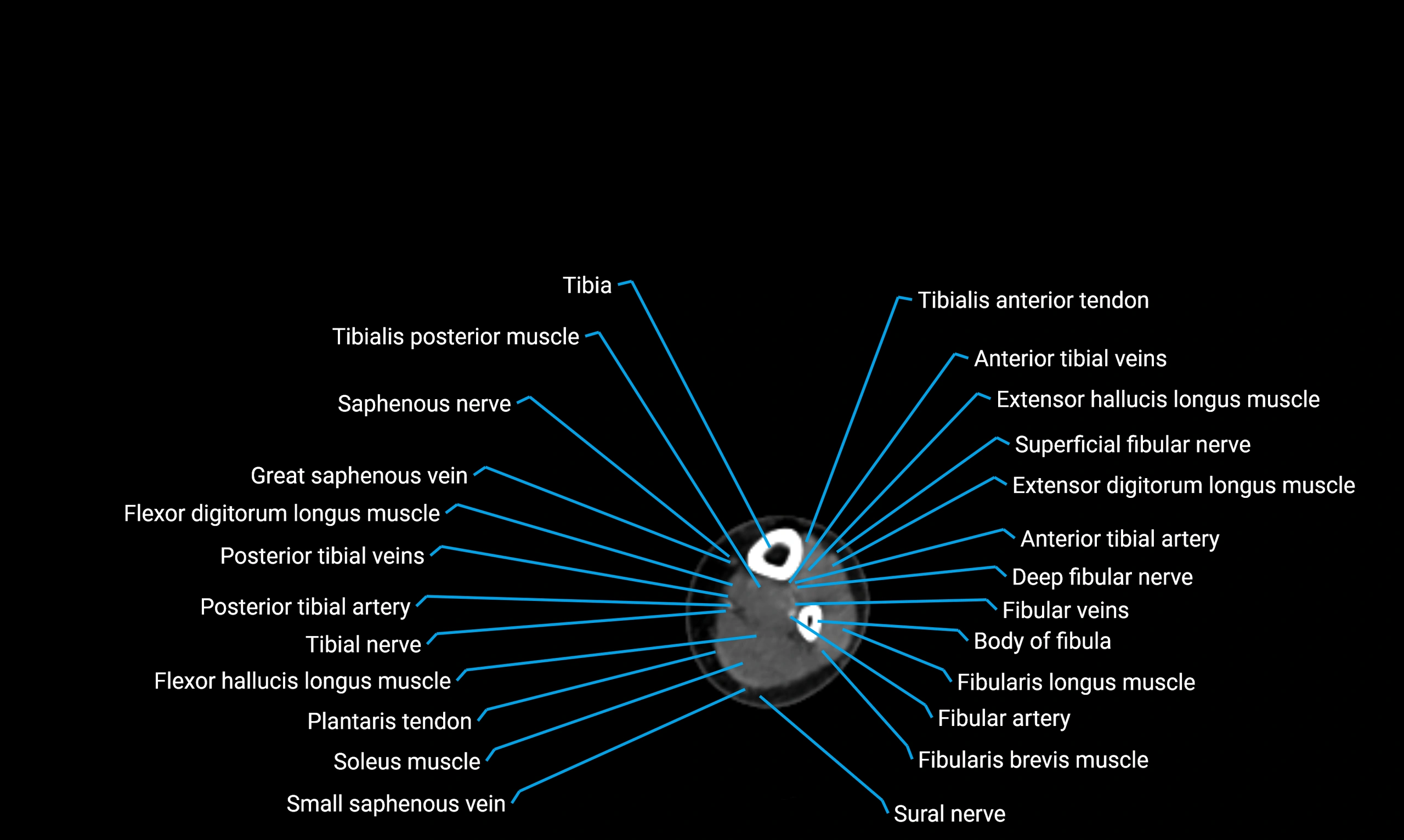
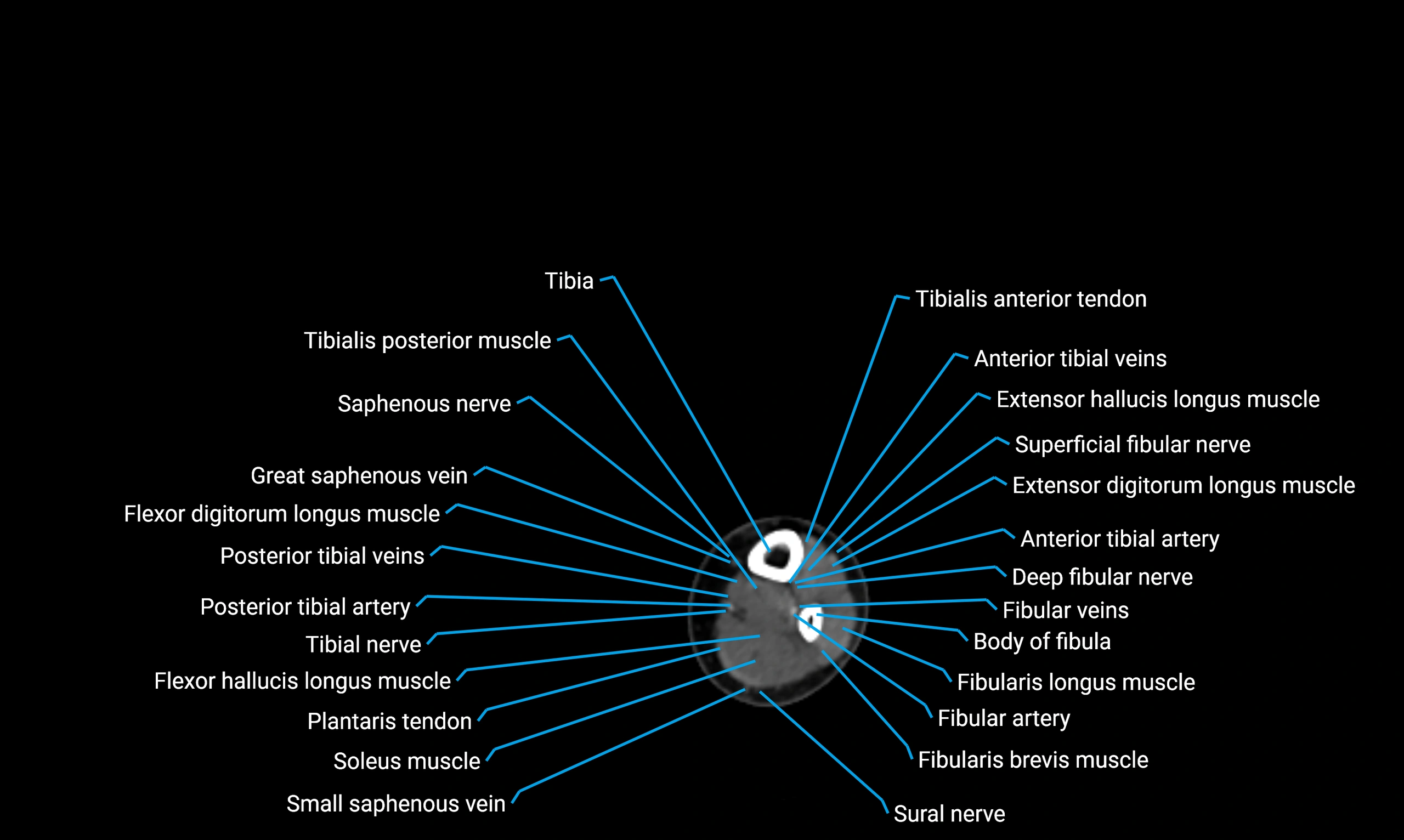
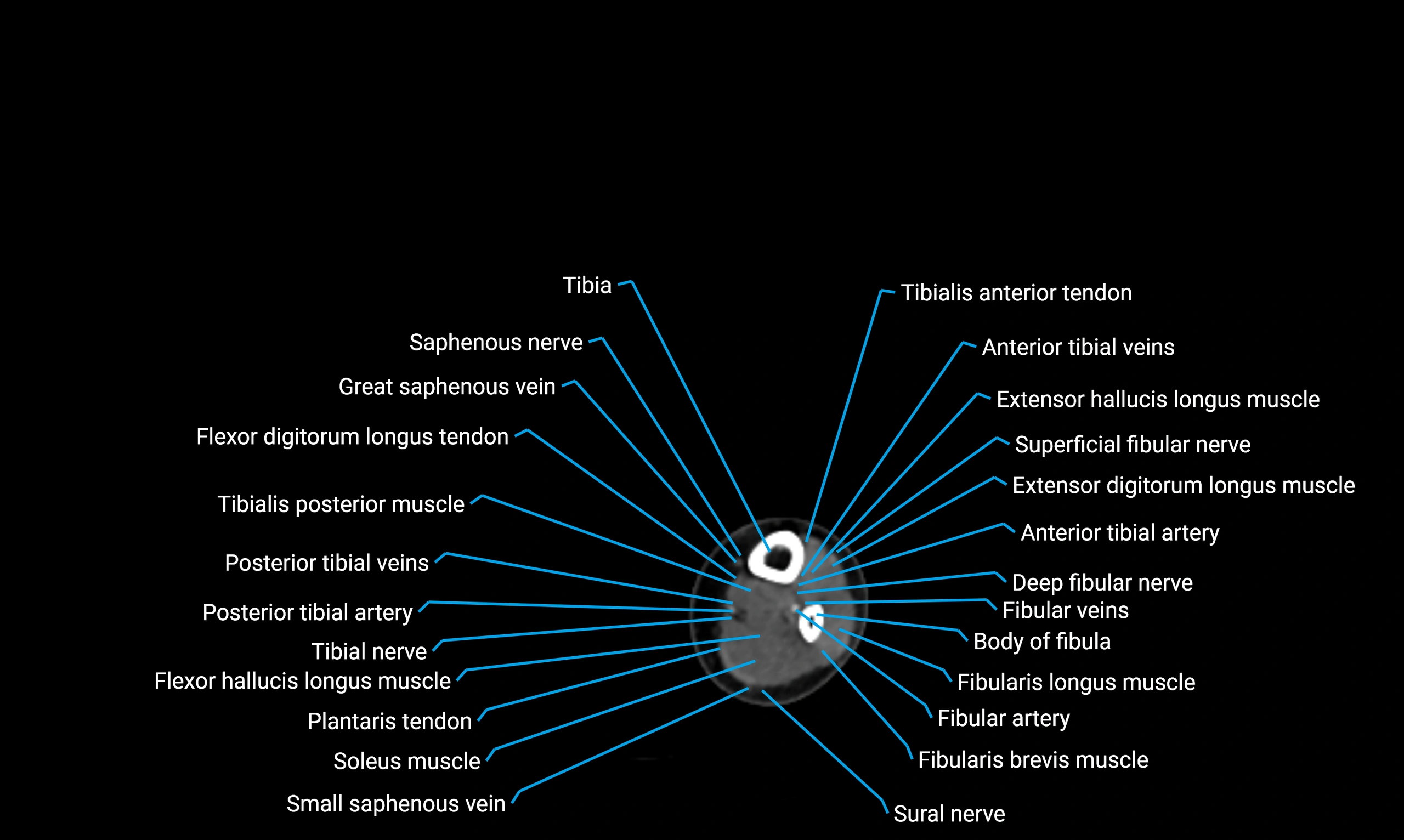
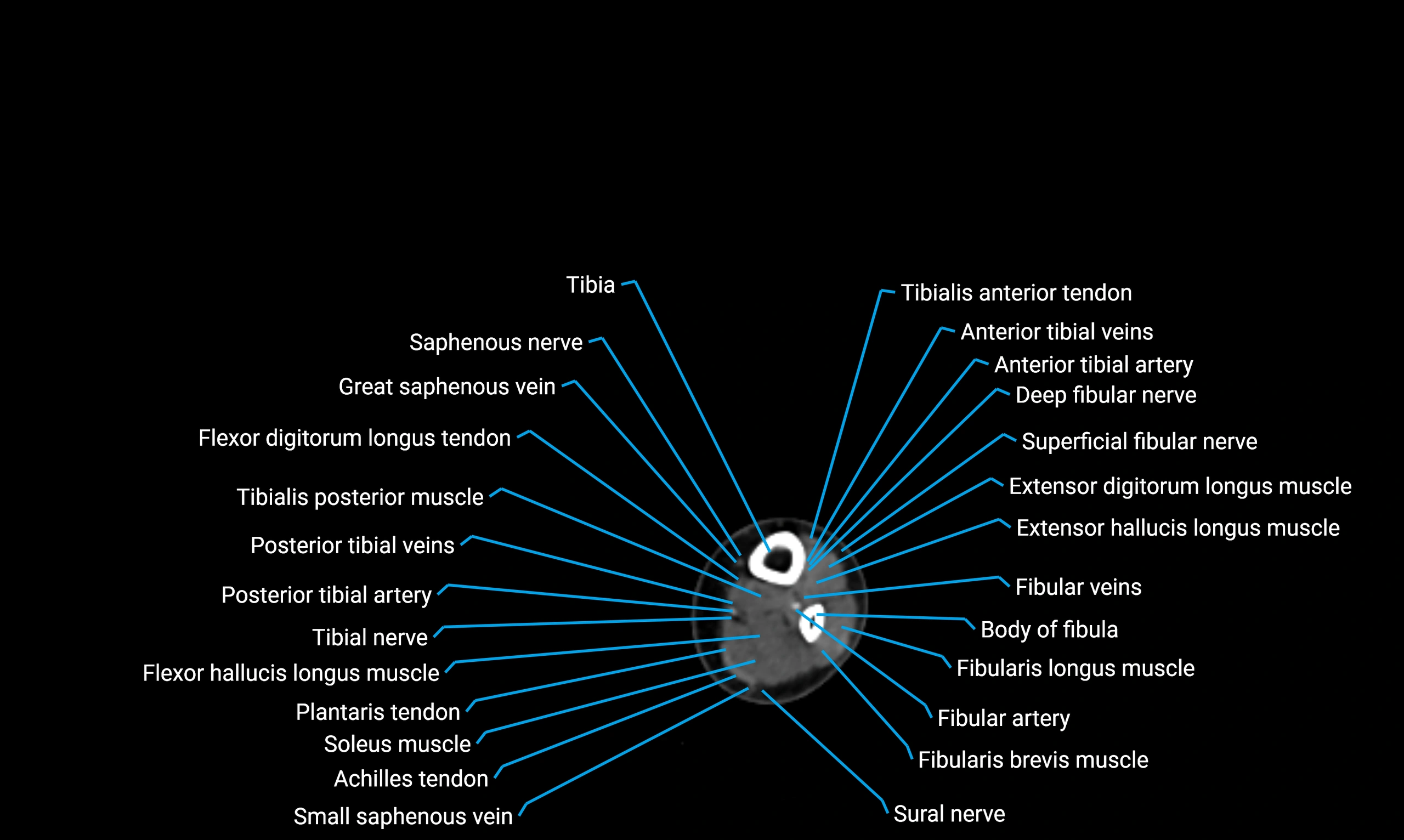
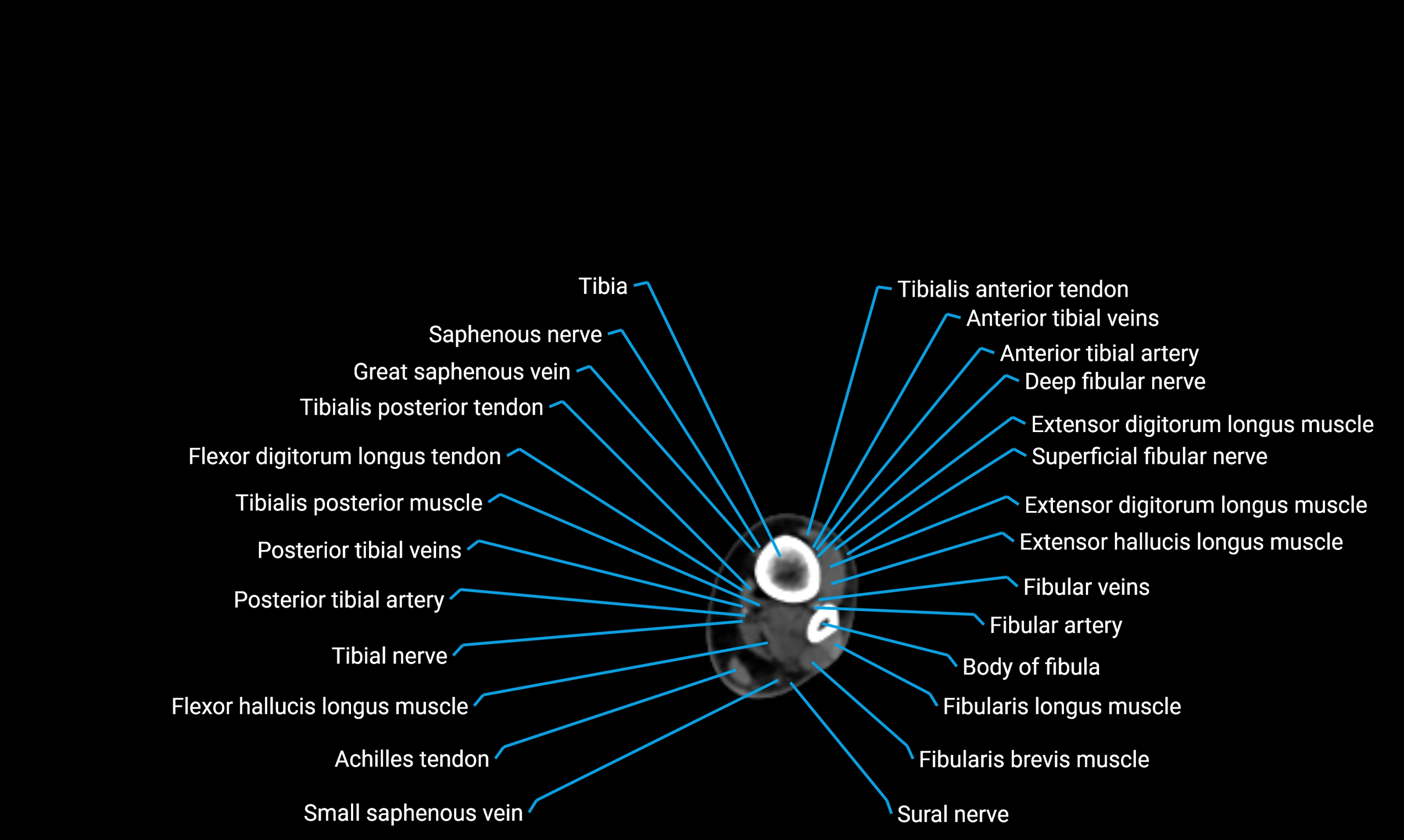
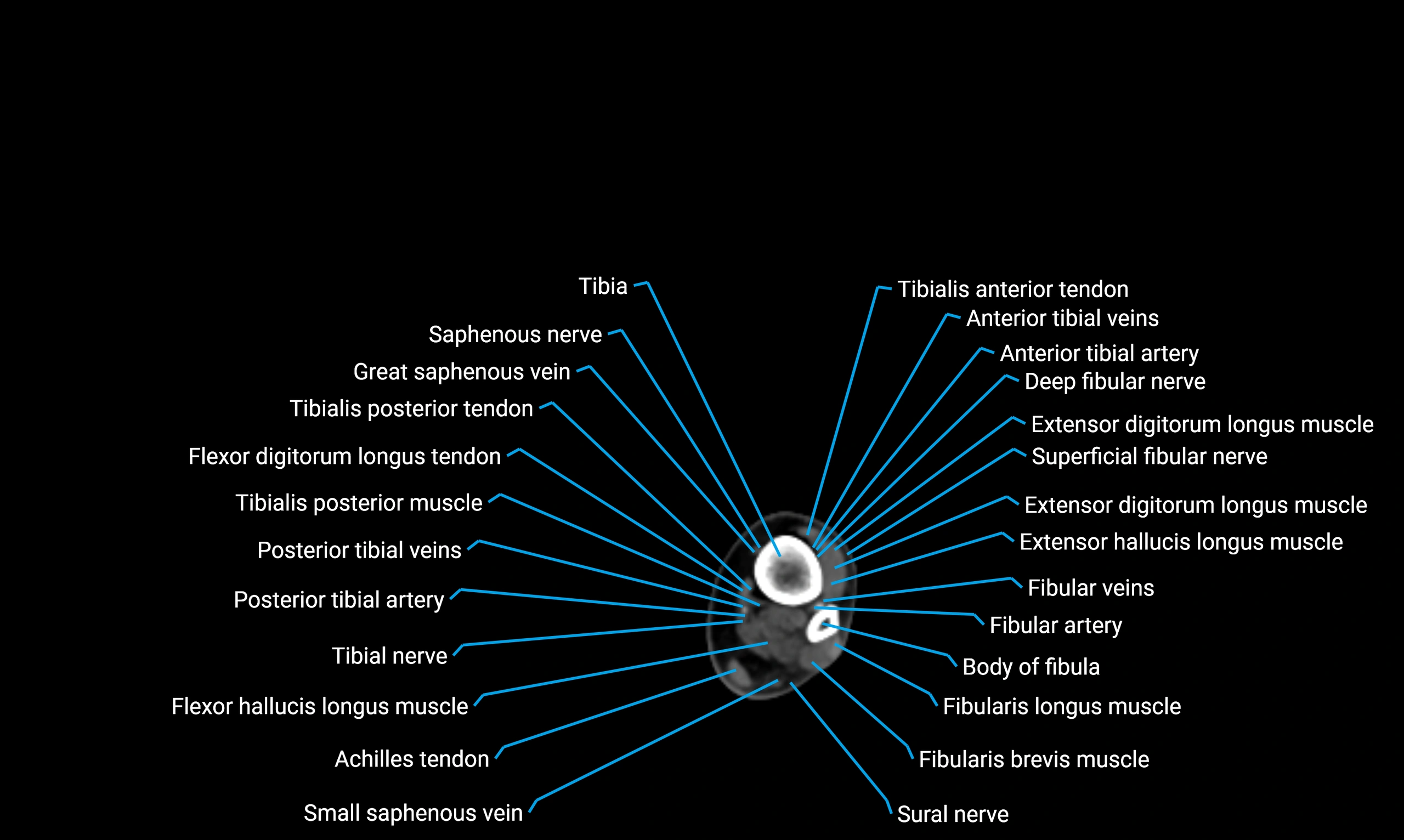
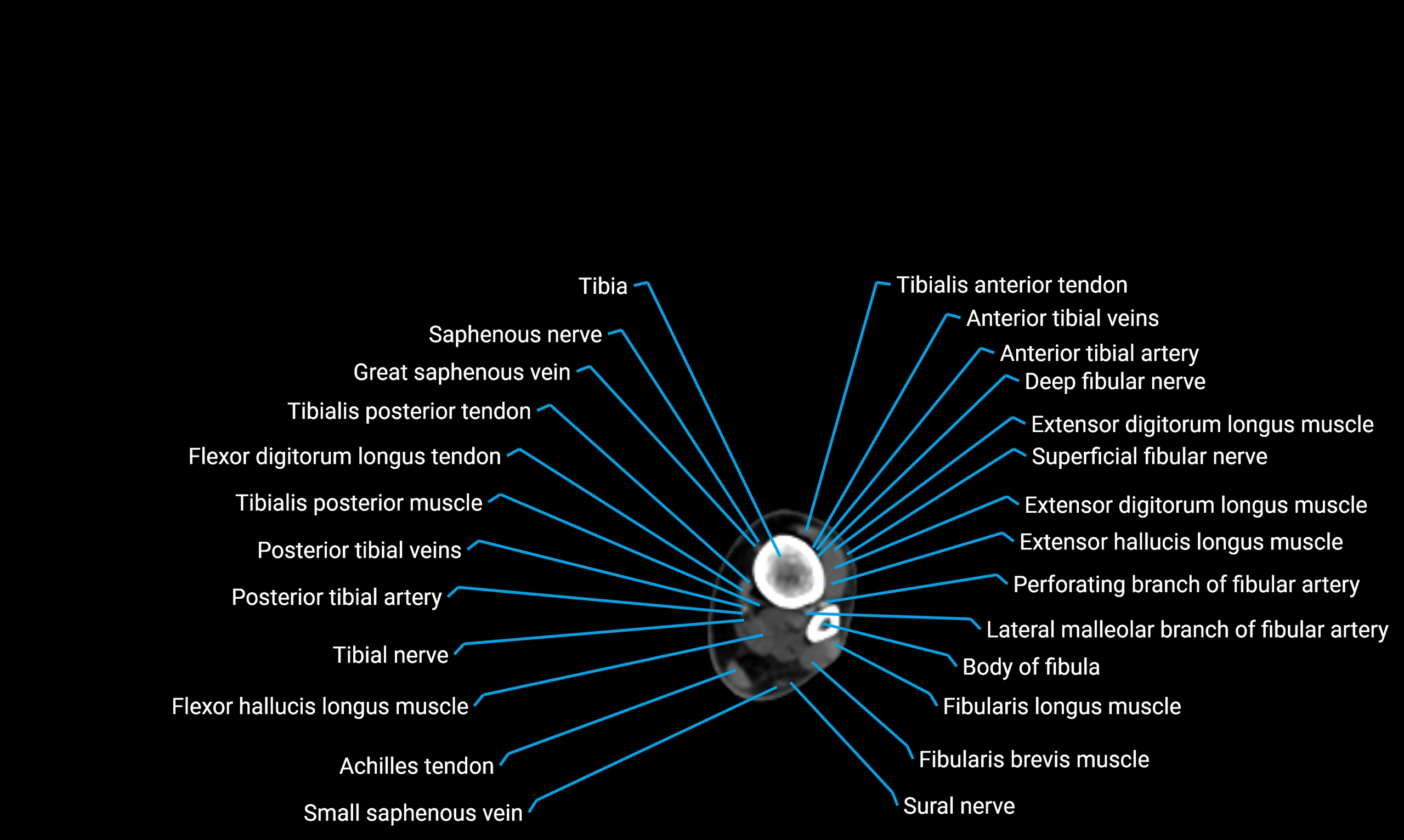
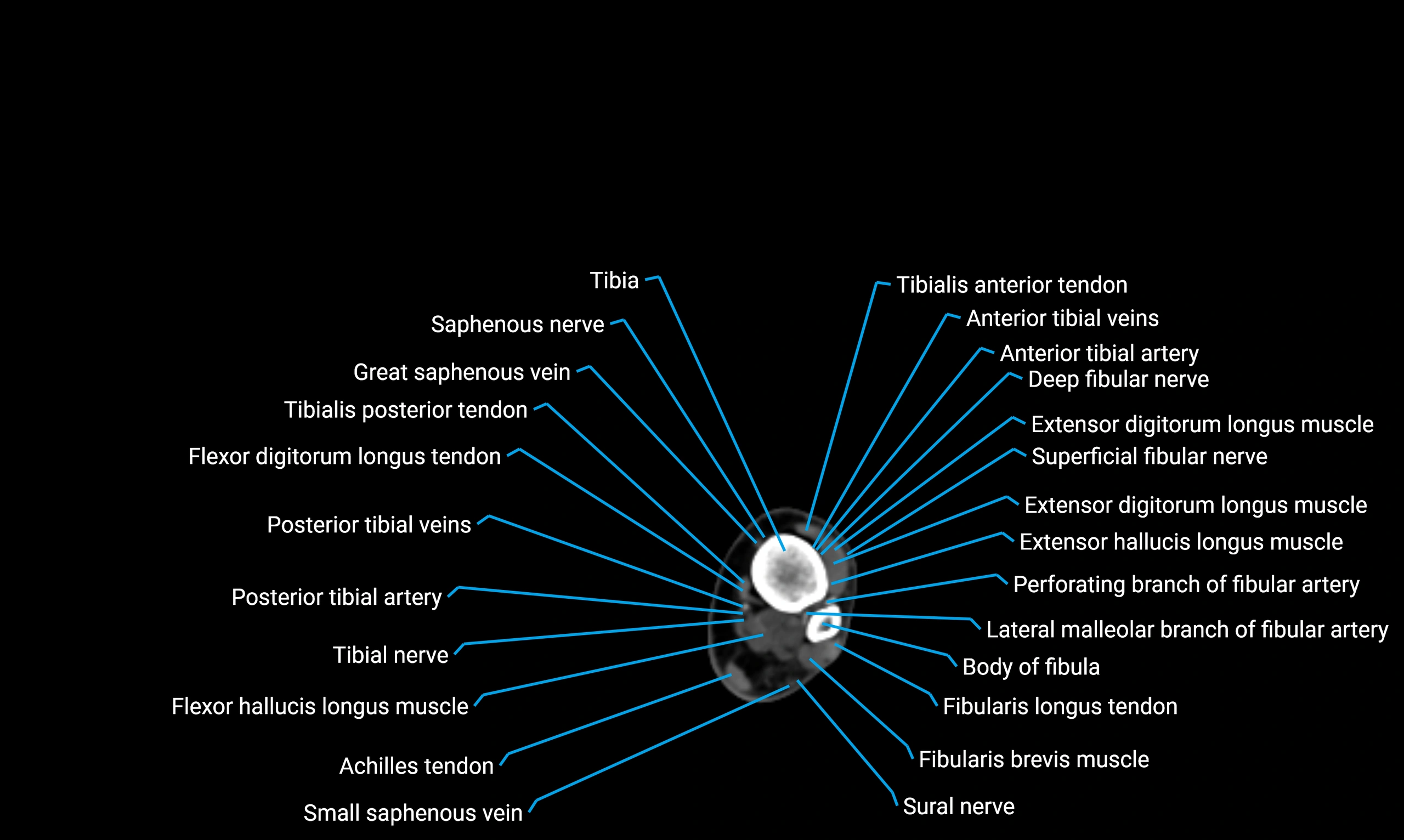
The body of the fibula (shaft of the fibula) is the elongated, slender middle portion of the fibula extending between its proximal and distal ends. It contributes primarily to muscle attachment and ankle stability rather than weight-bearing and plays a vital role in the biomechanics of the leg and ankle.
It is an important anatomical structure in orthopedics, trauma assessment, sports medicine, and musculoskeletal imaging.
Synonyms
-
Shaft of fibula
Location
-
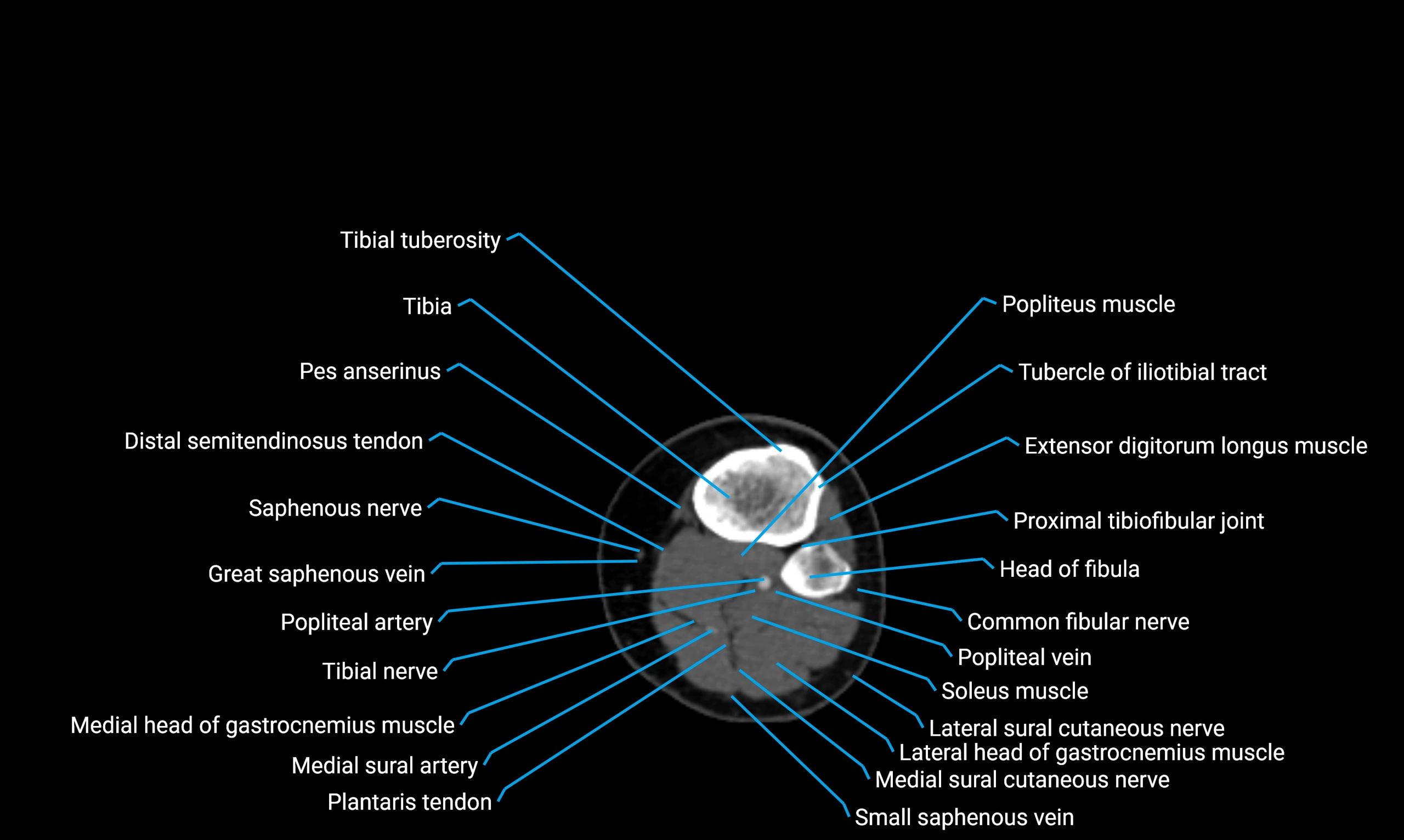
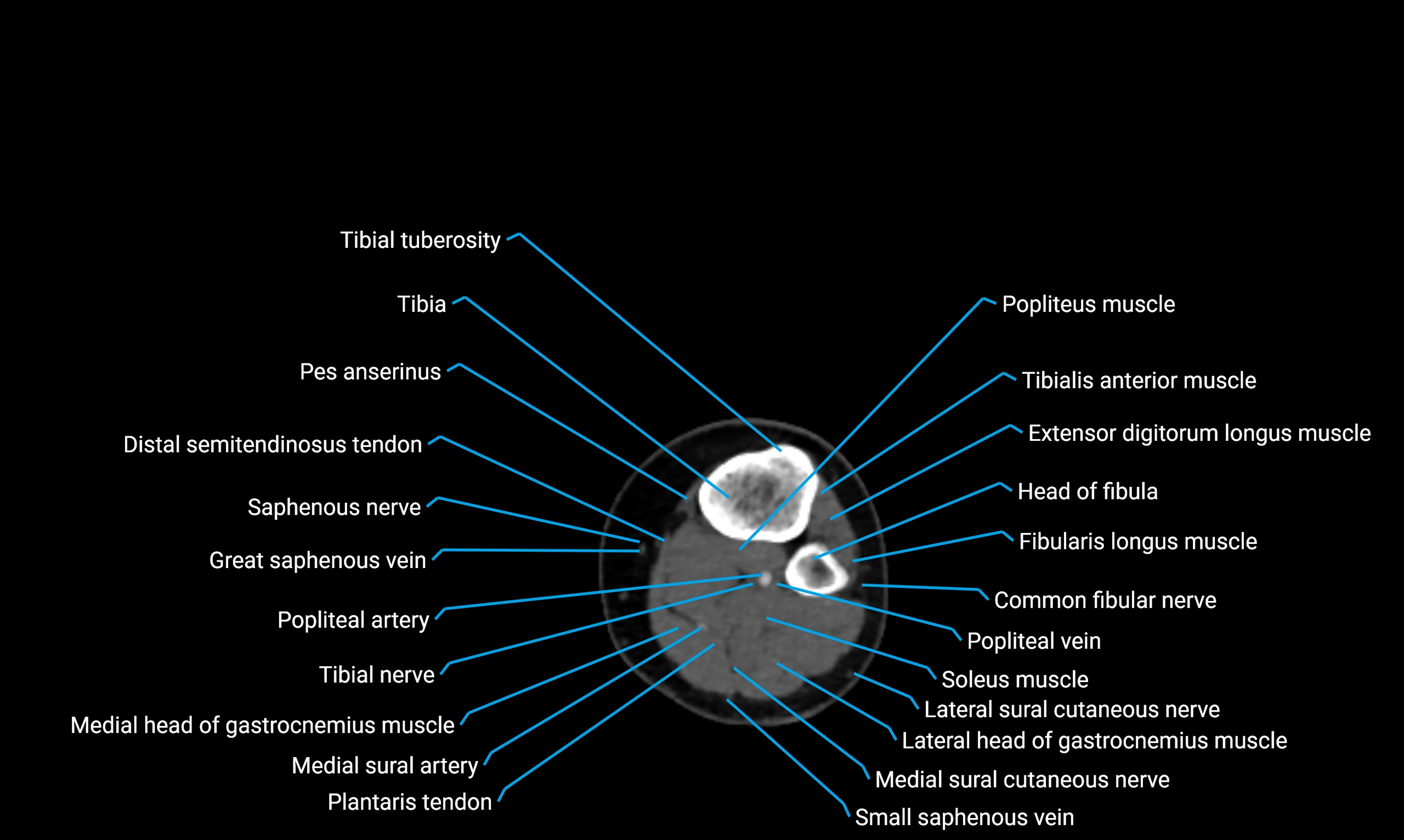
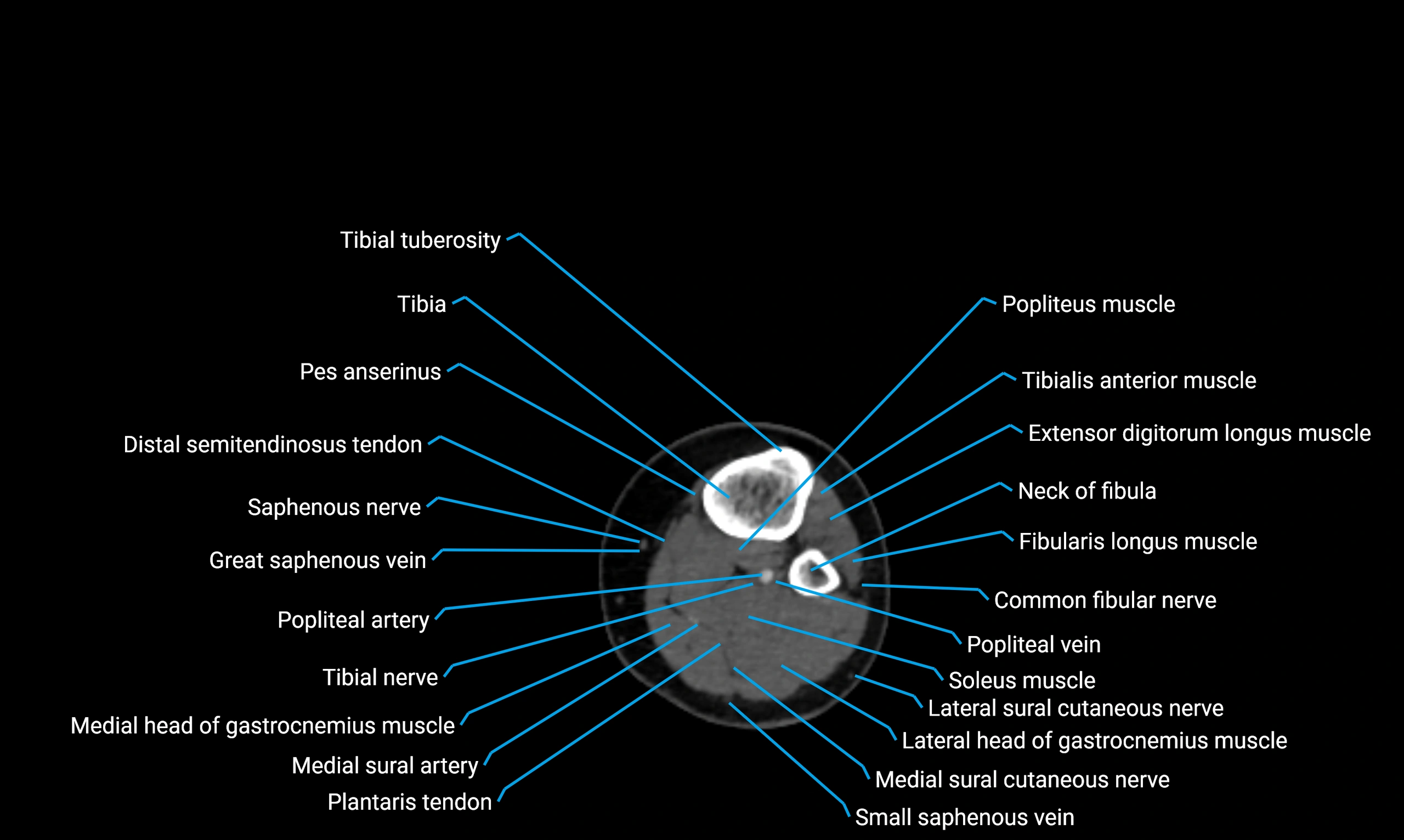
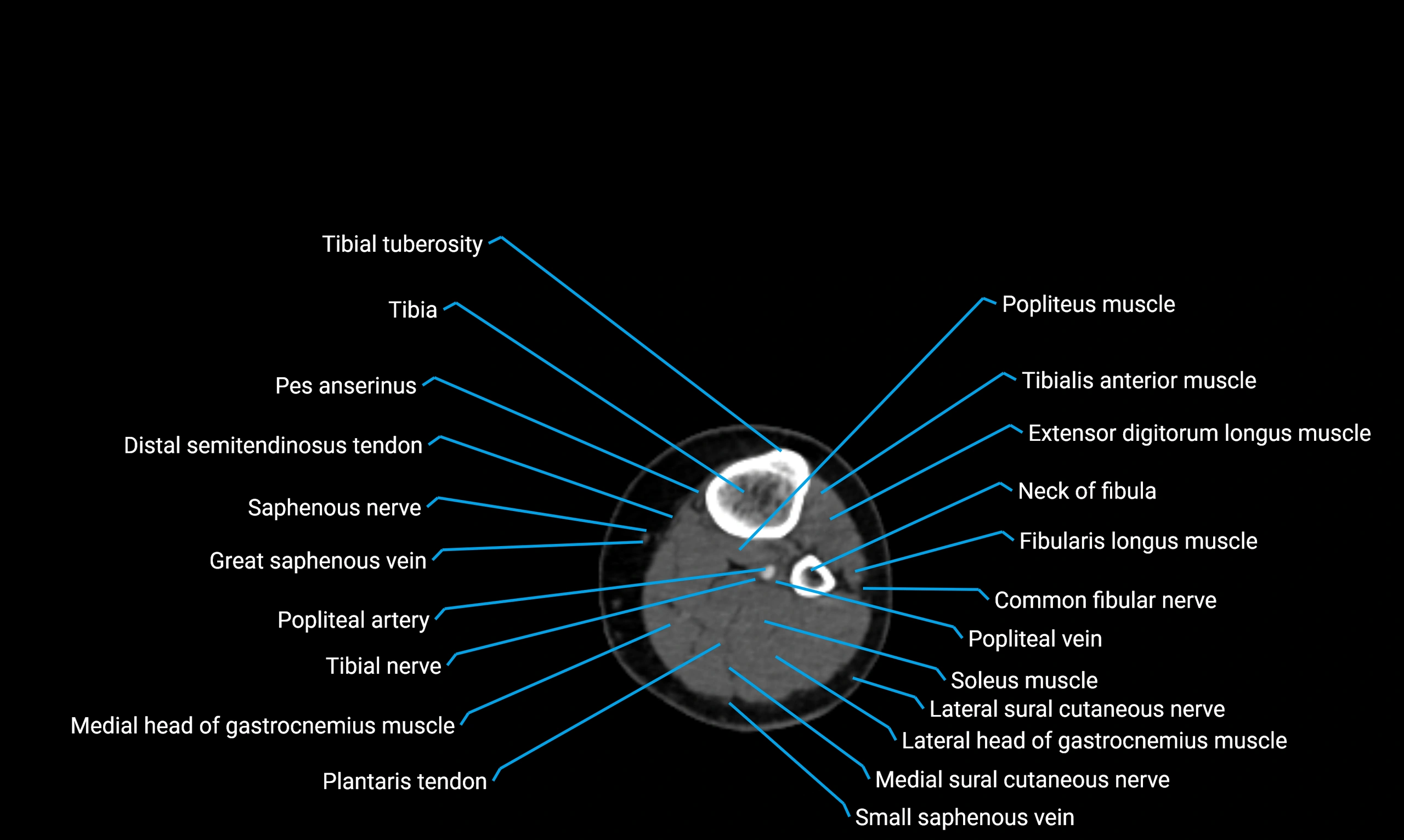
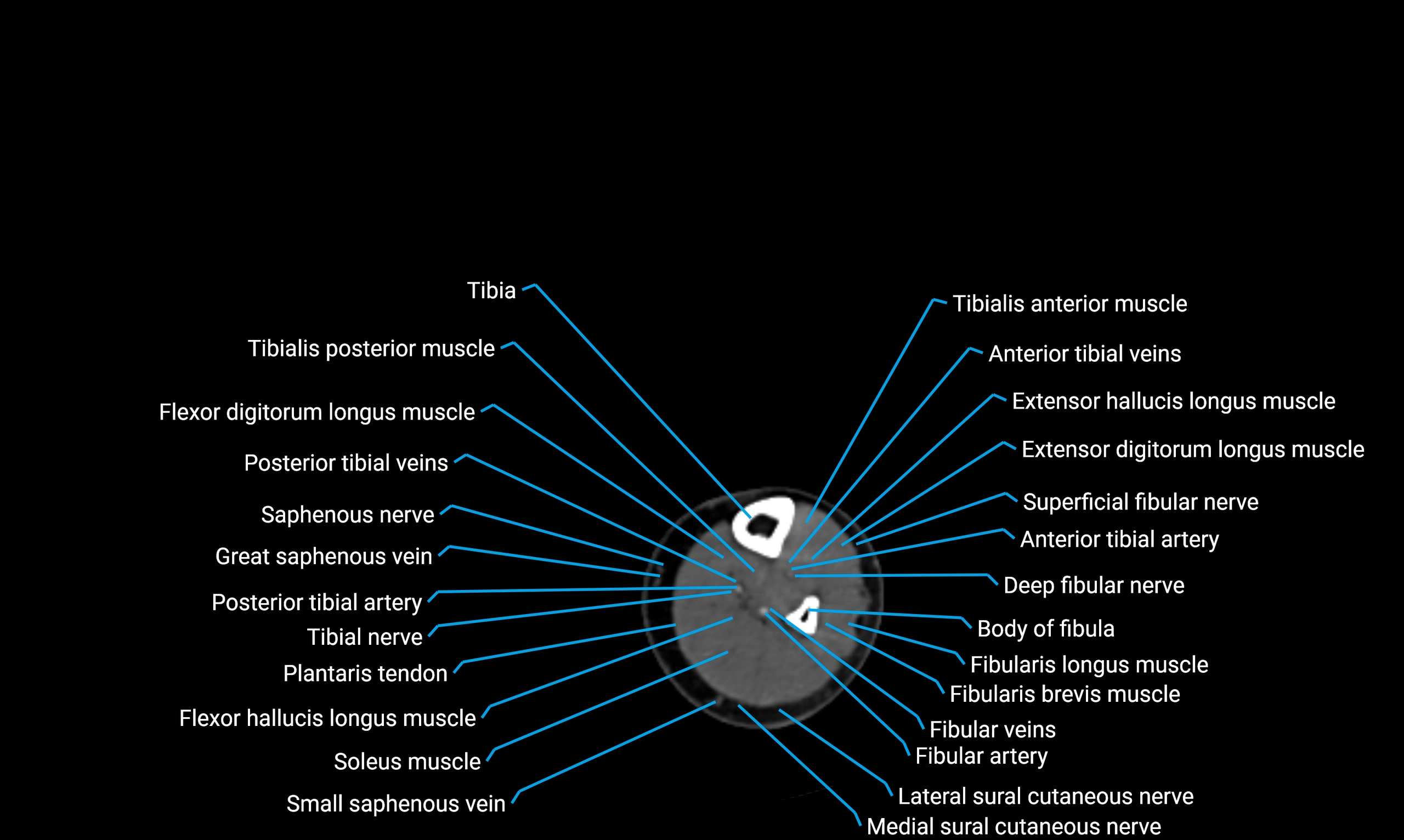
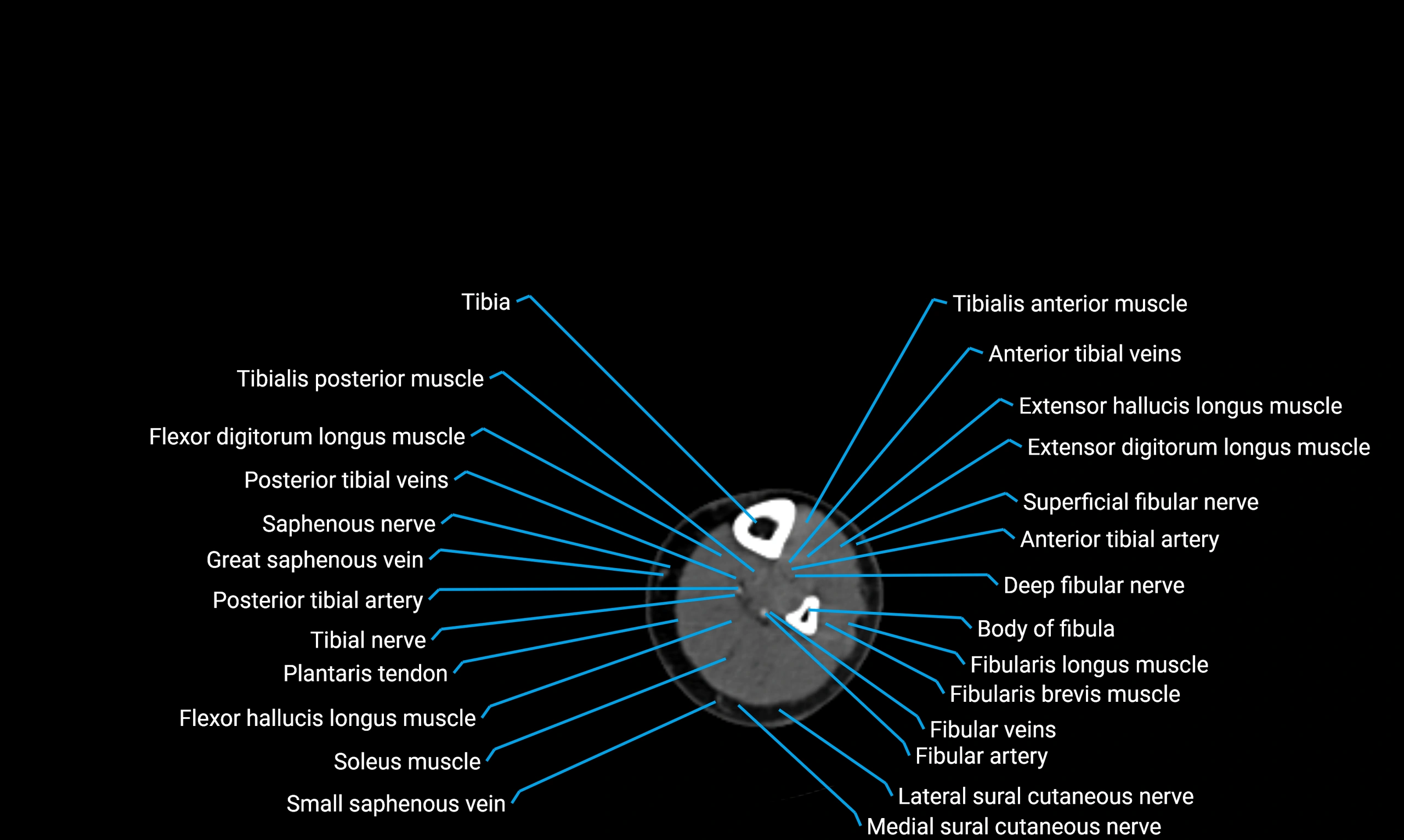
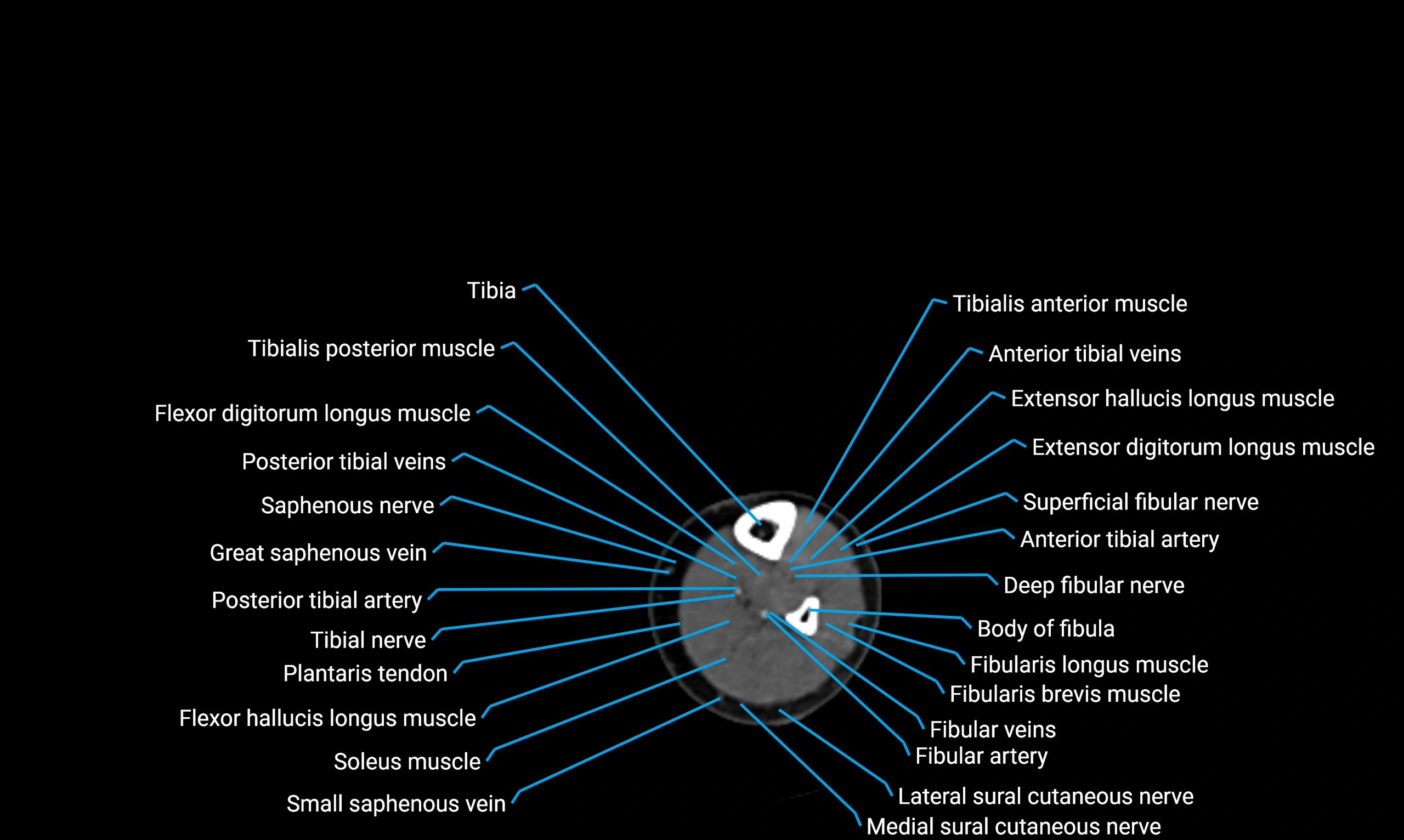
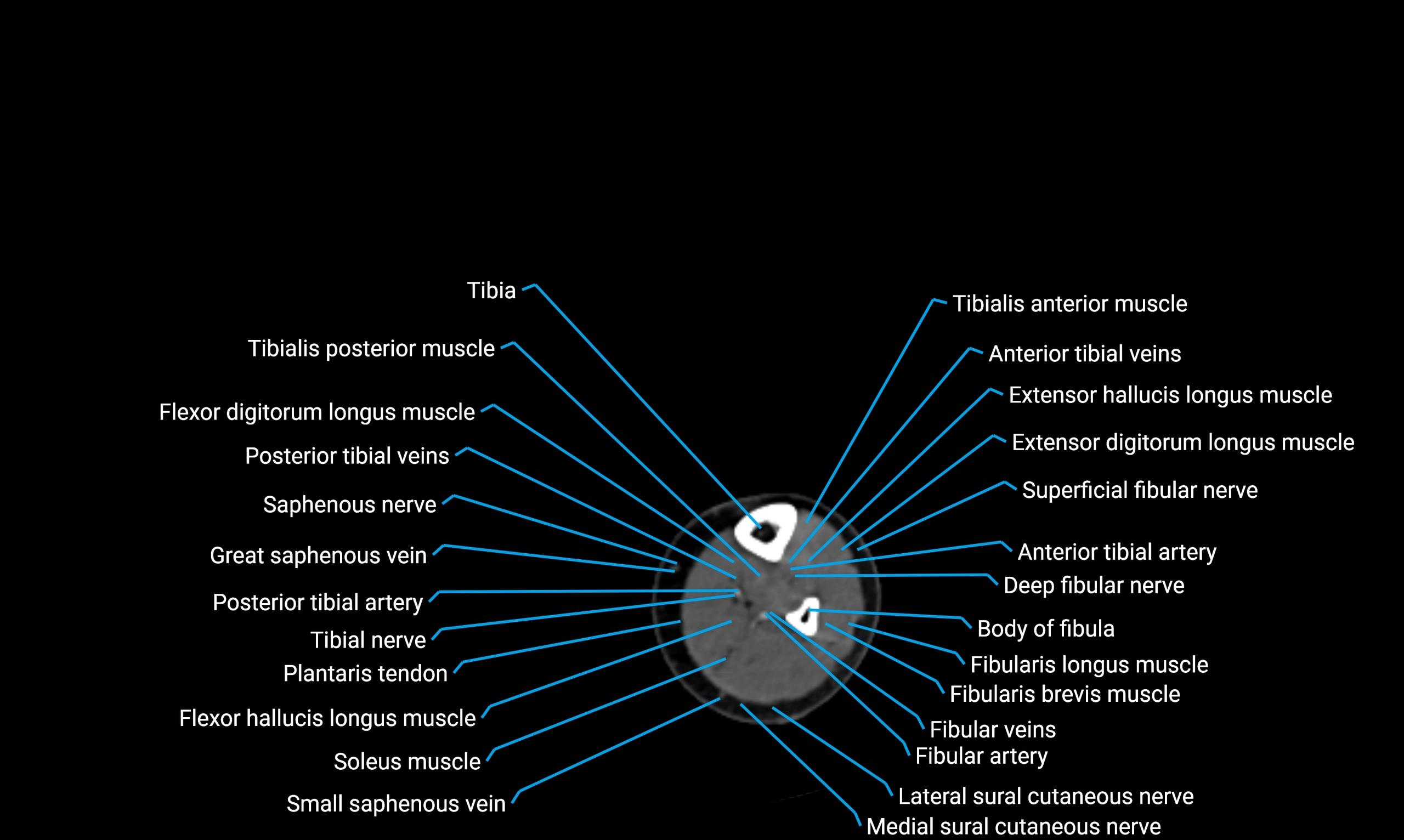
Situated in the lateral aspect of the leg
-
Extends from the fibular head proximally to the lateral malleolus distally
-
Parallel and lateral to the tibial shaft
-
Forms part of the interosseous compartment of the leg
-
Separated from the tibia by the interosseous membrane
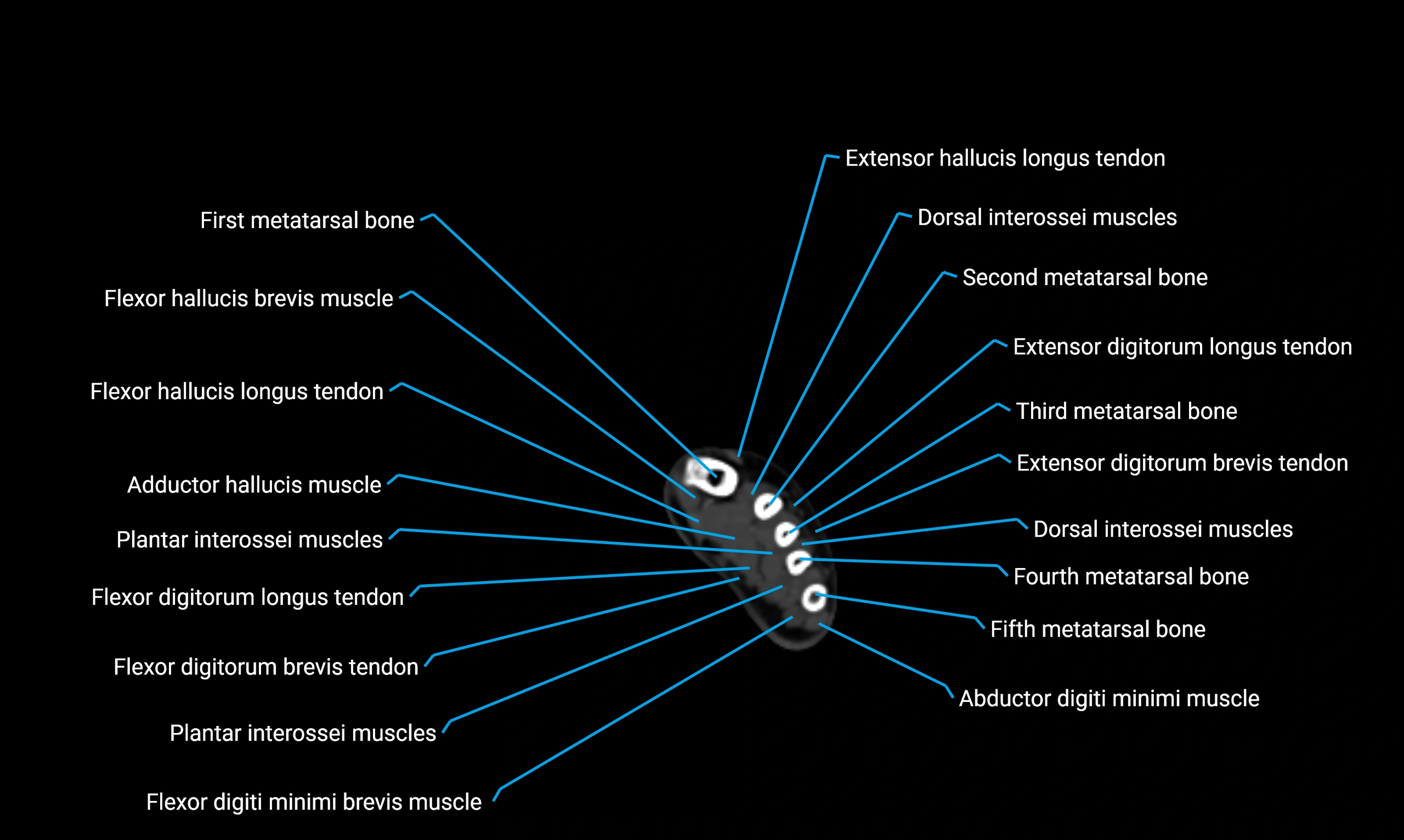
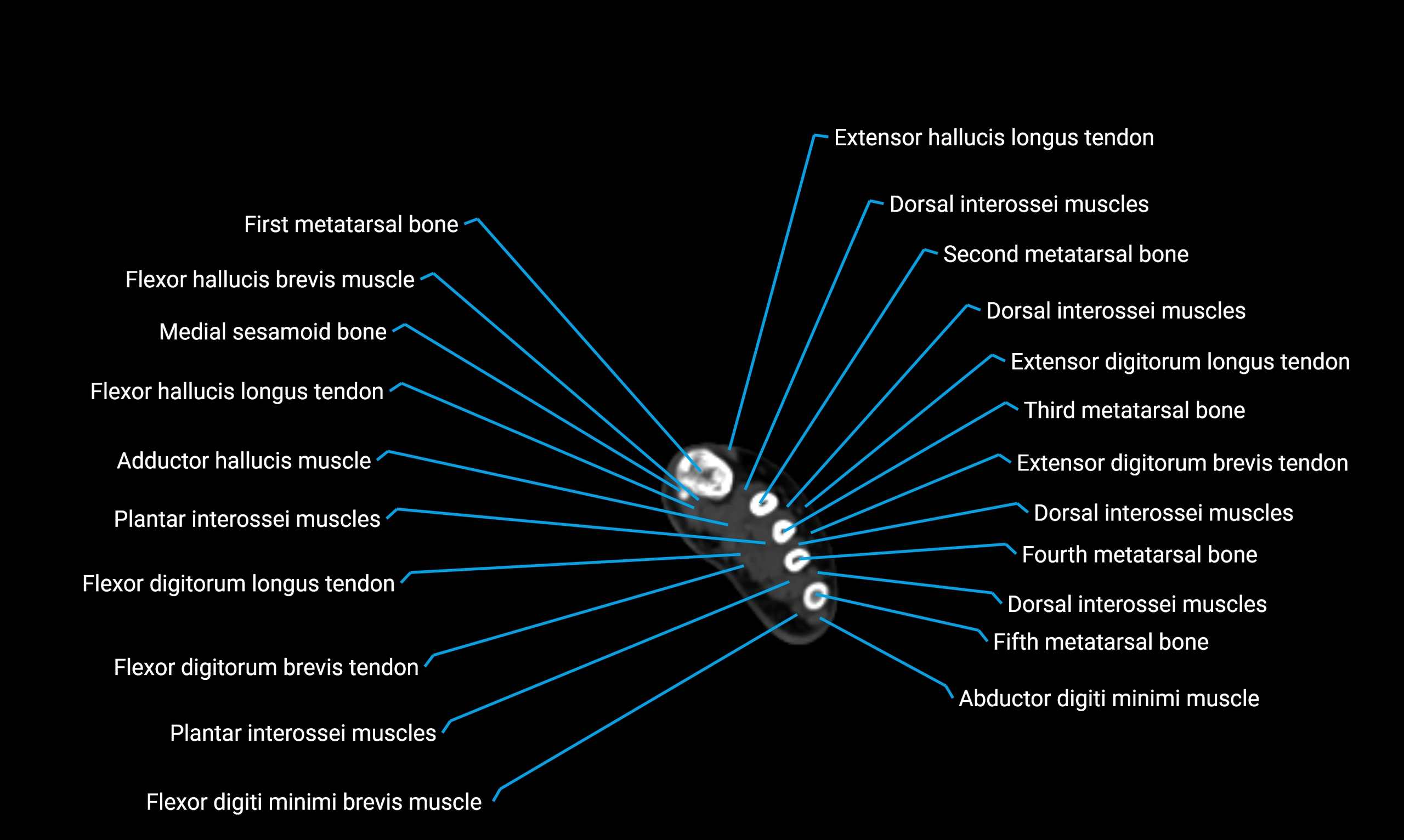
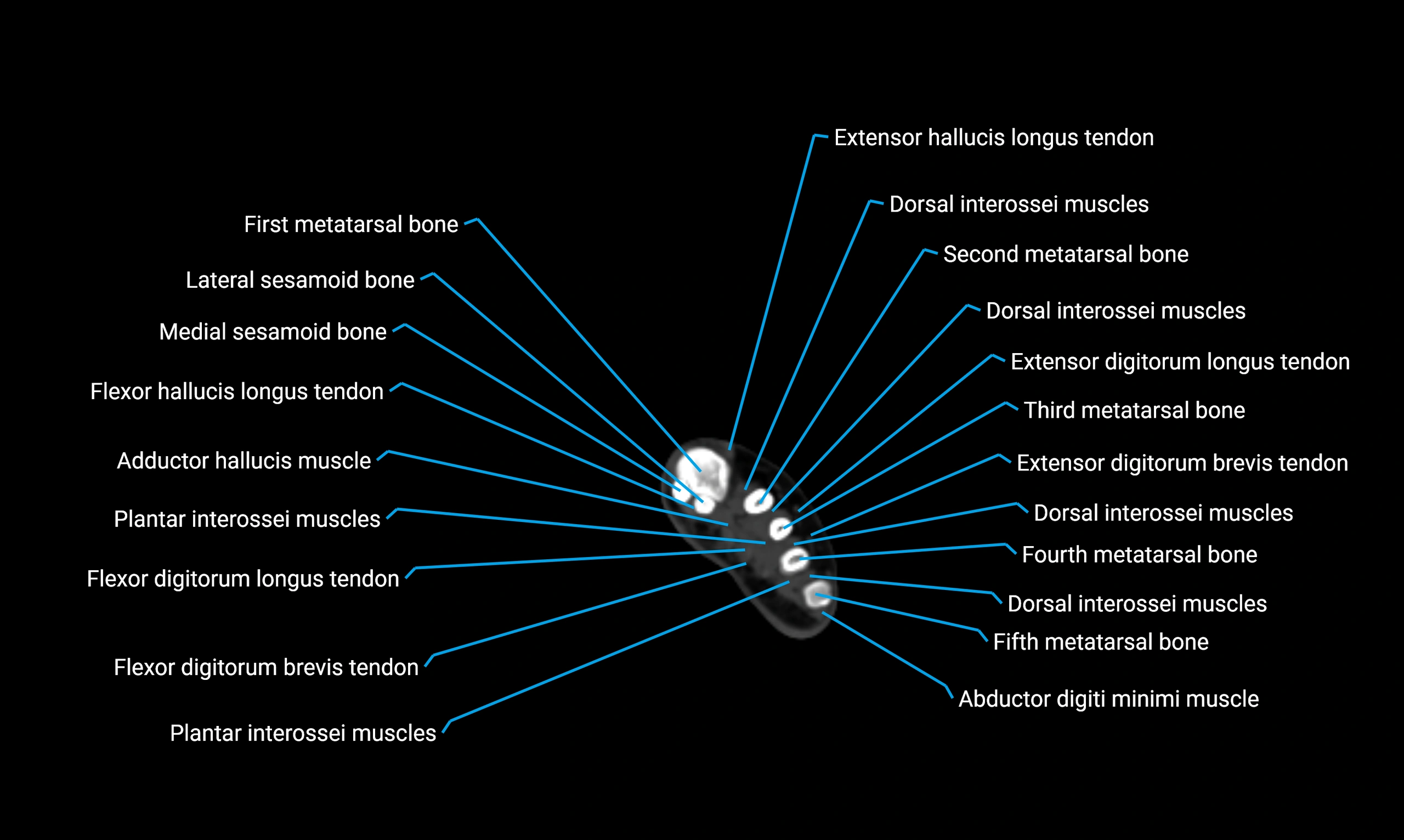
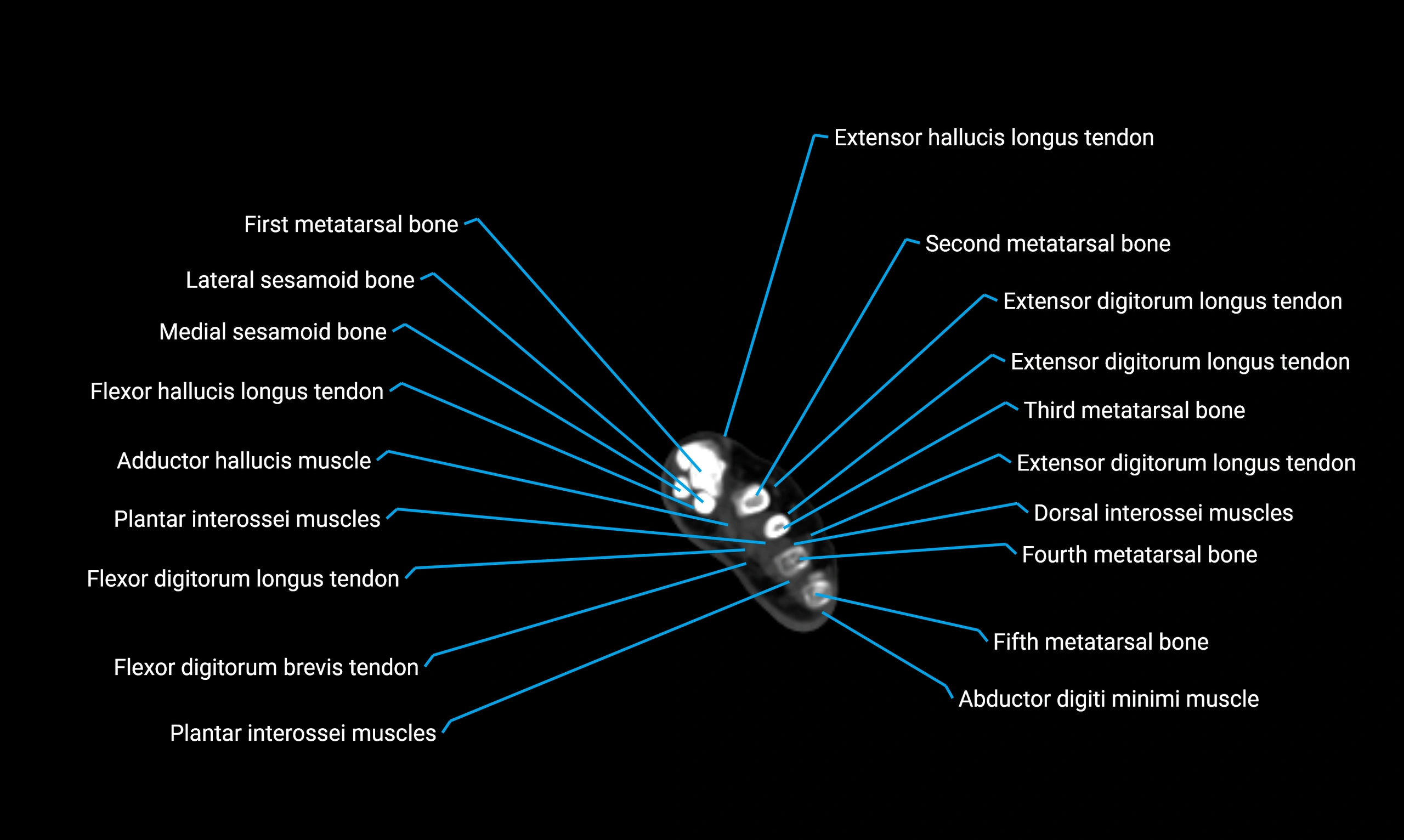
Anatomical components
-
Shaft (diaphysis):
-
Long, slender, slightly twisted structure
-
-
Borders:
-
Anterior border
-
Posterior border
-
Interosseous border (medial)
-
-
Surfaces:
-
Lateral surface
-
Medial surface
-
Posterior surface
-
-
Nutrient foramen:
-
Usually directed proximally
-
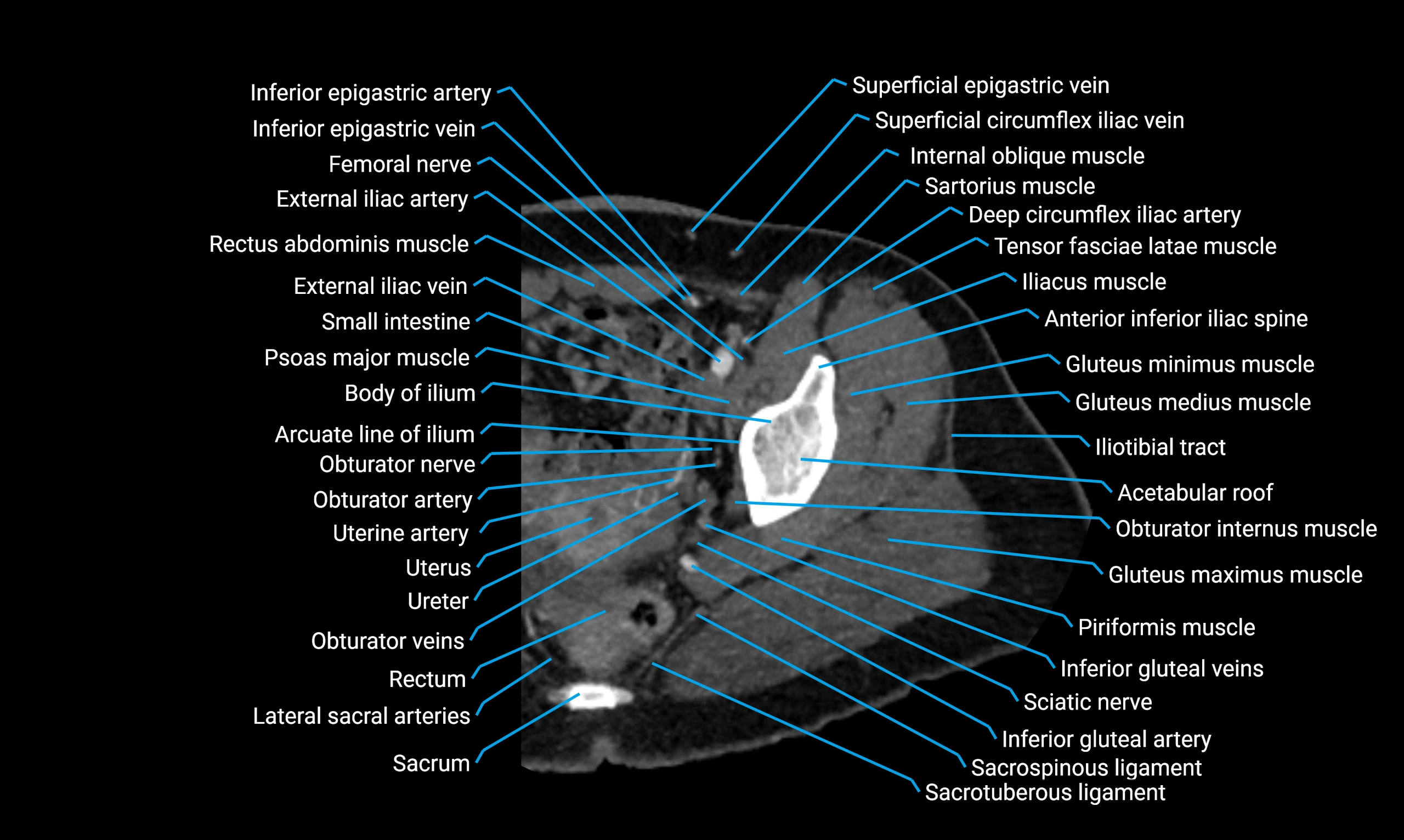
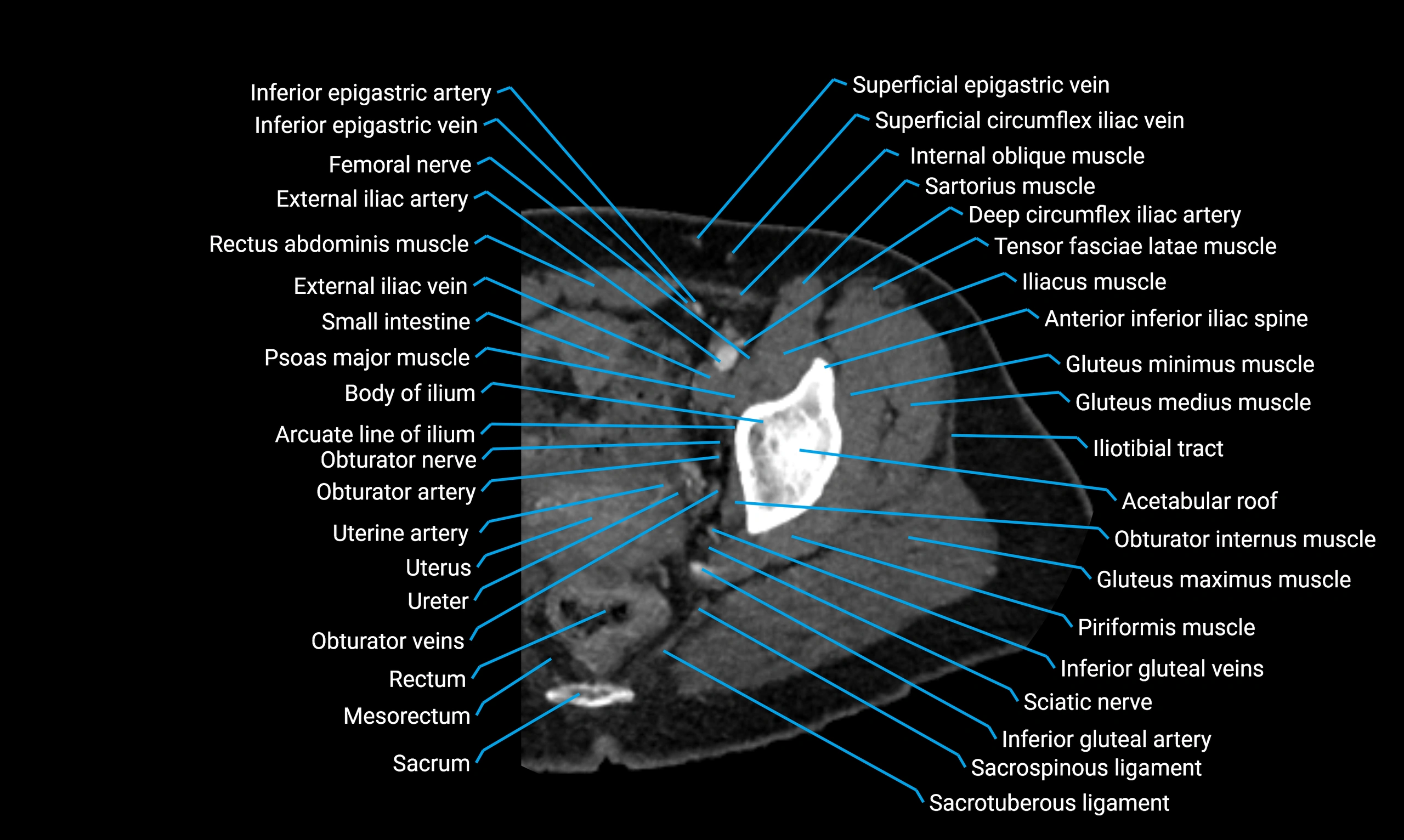
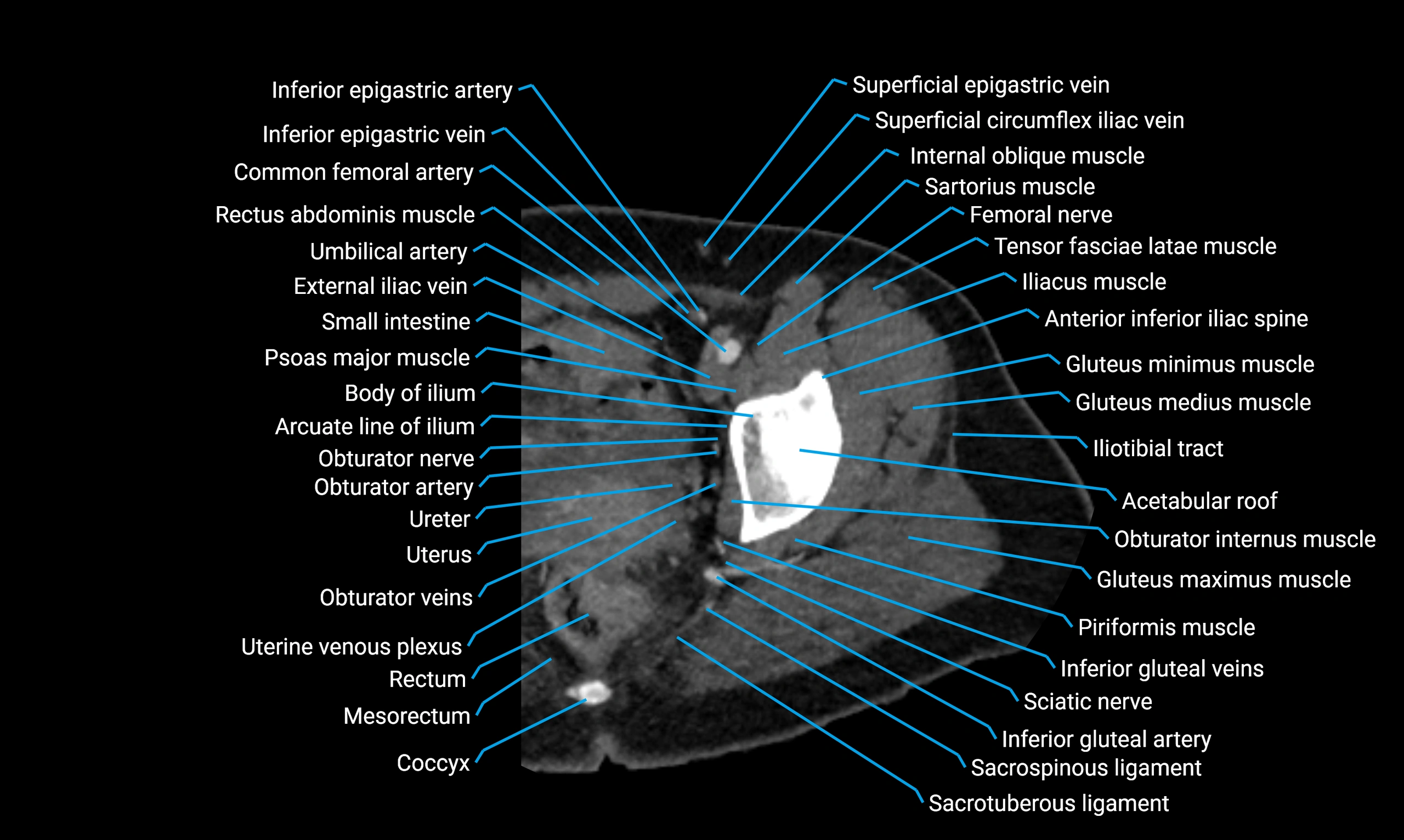
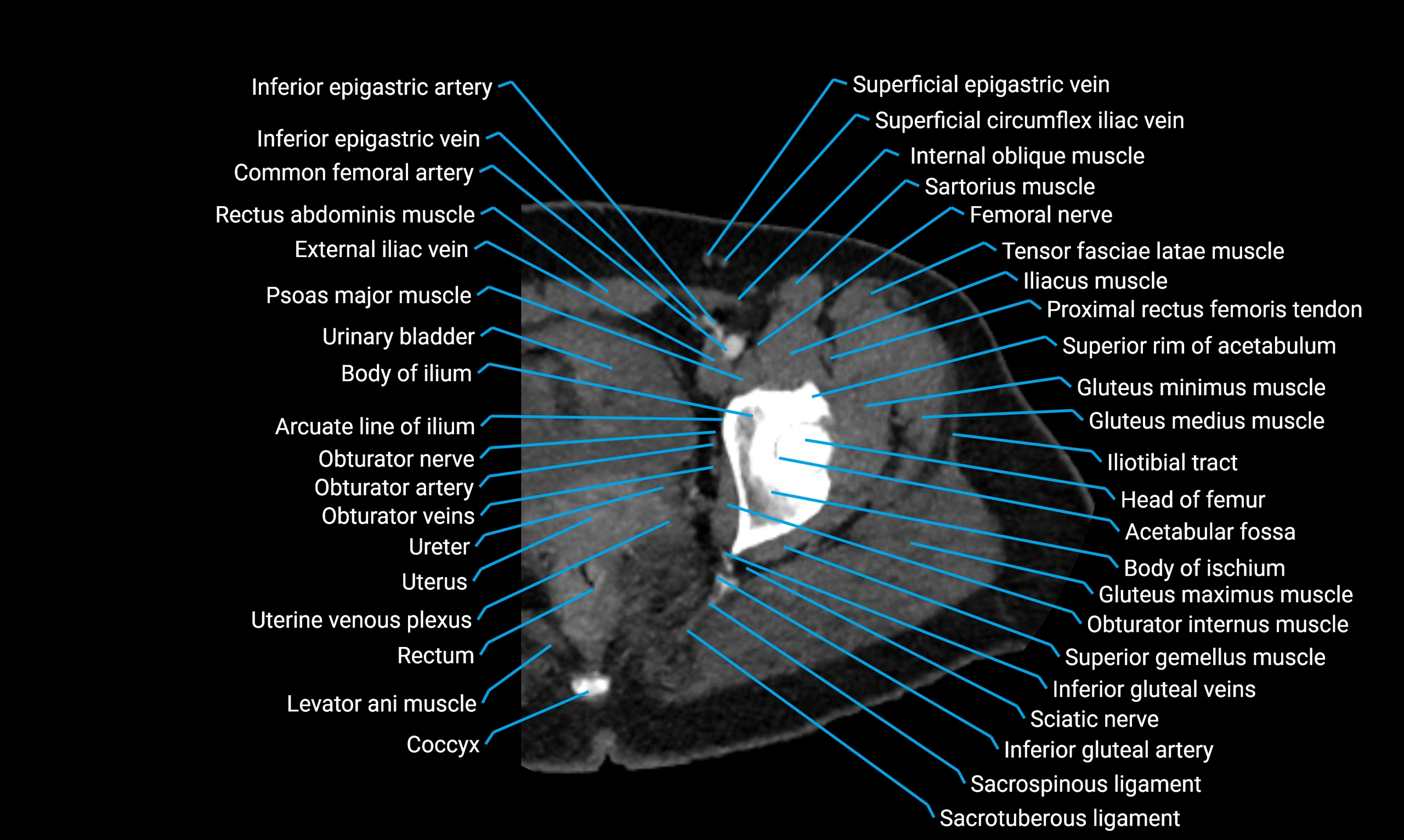
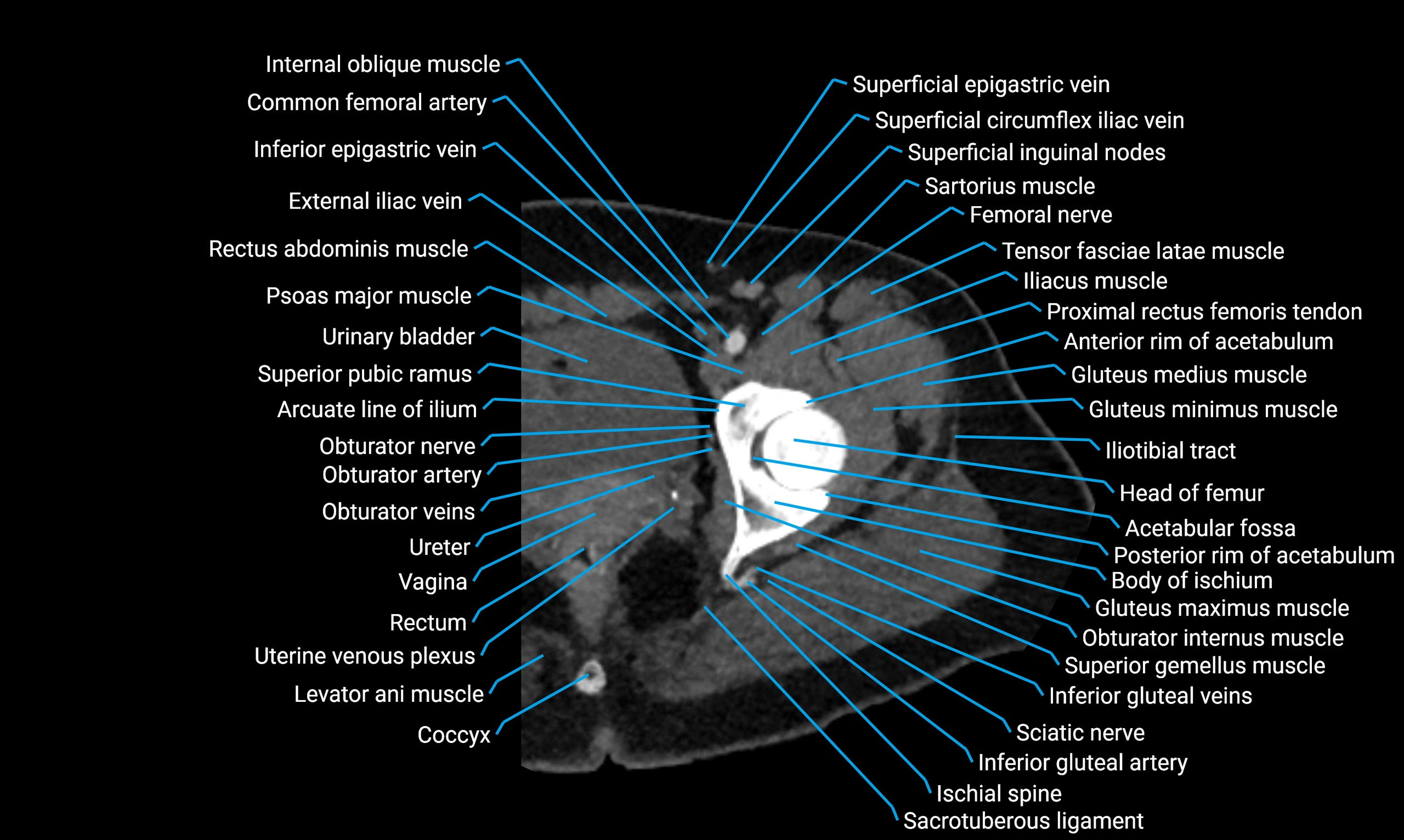
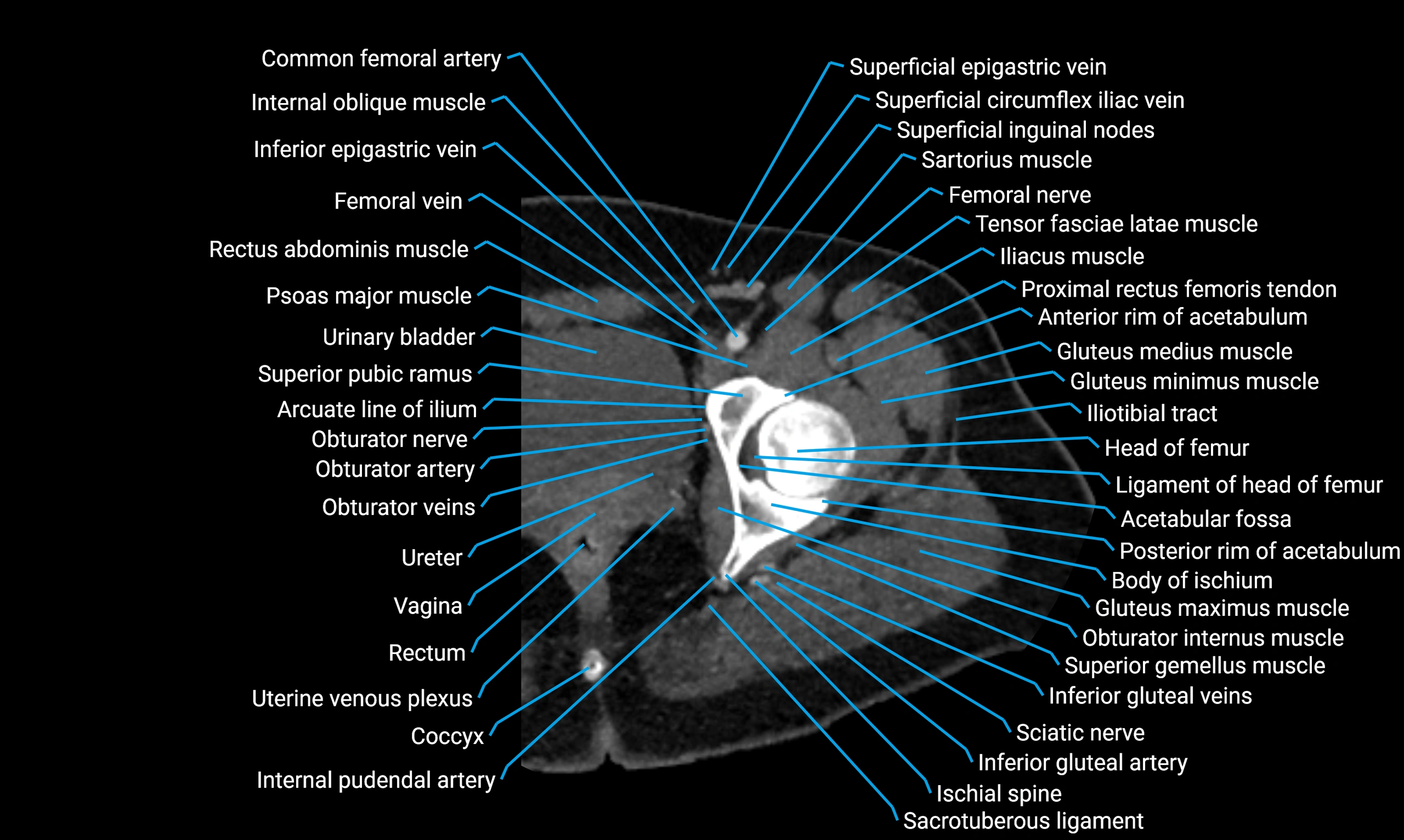
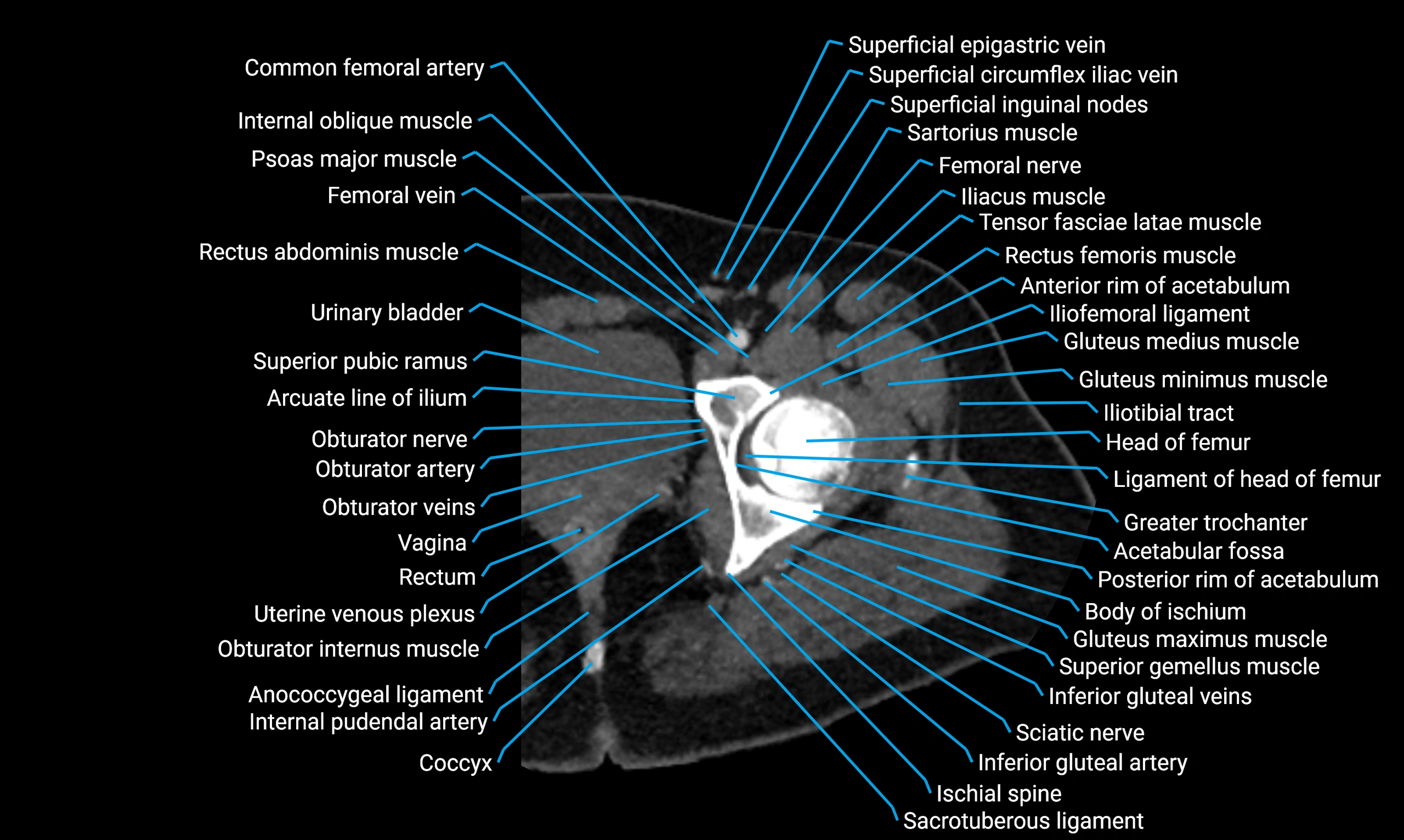
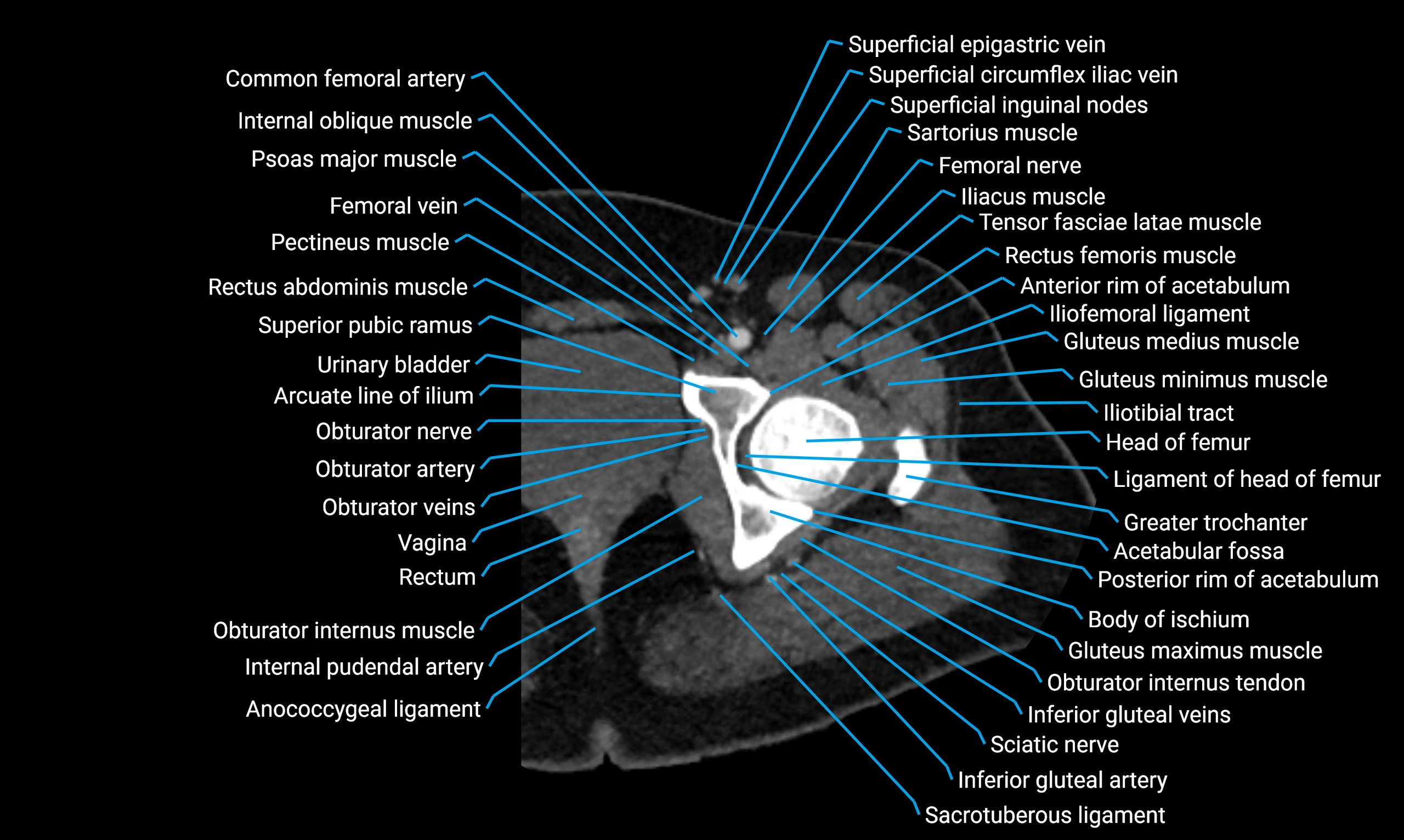
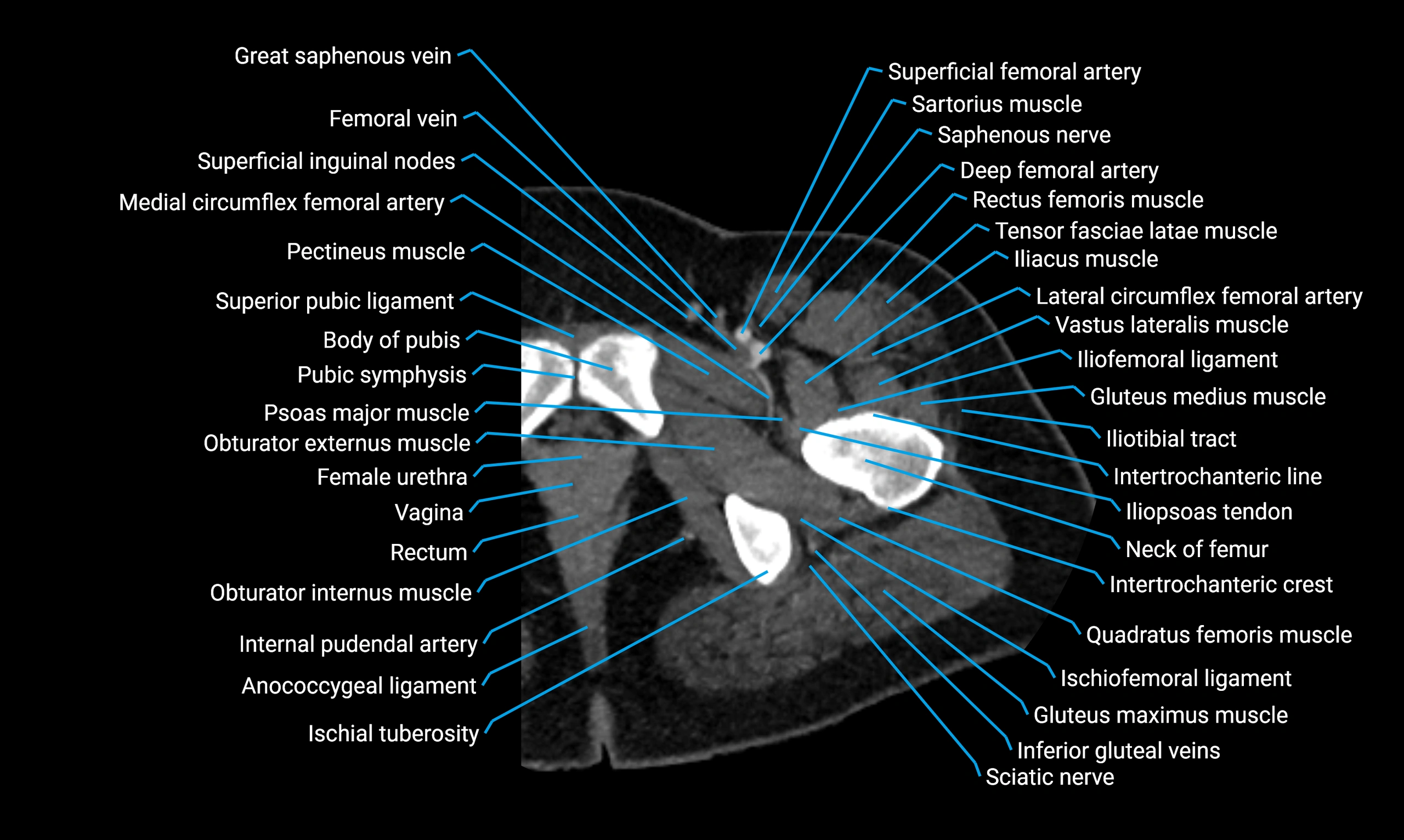
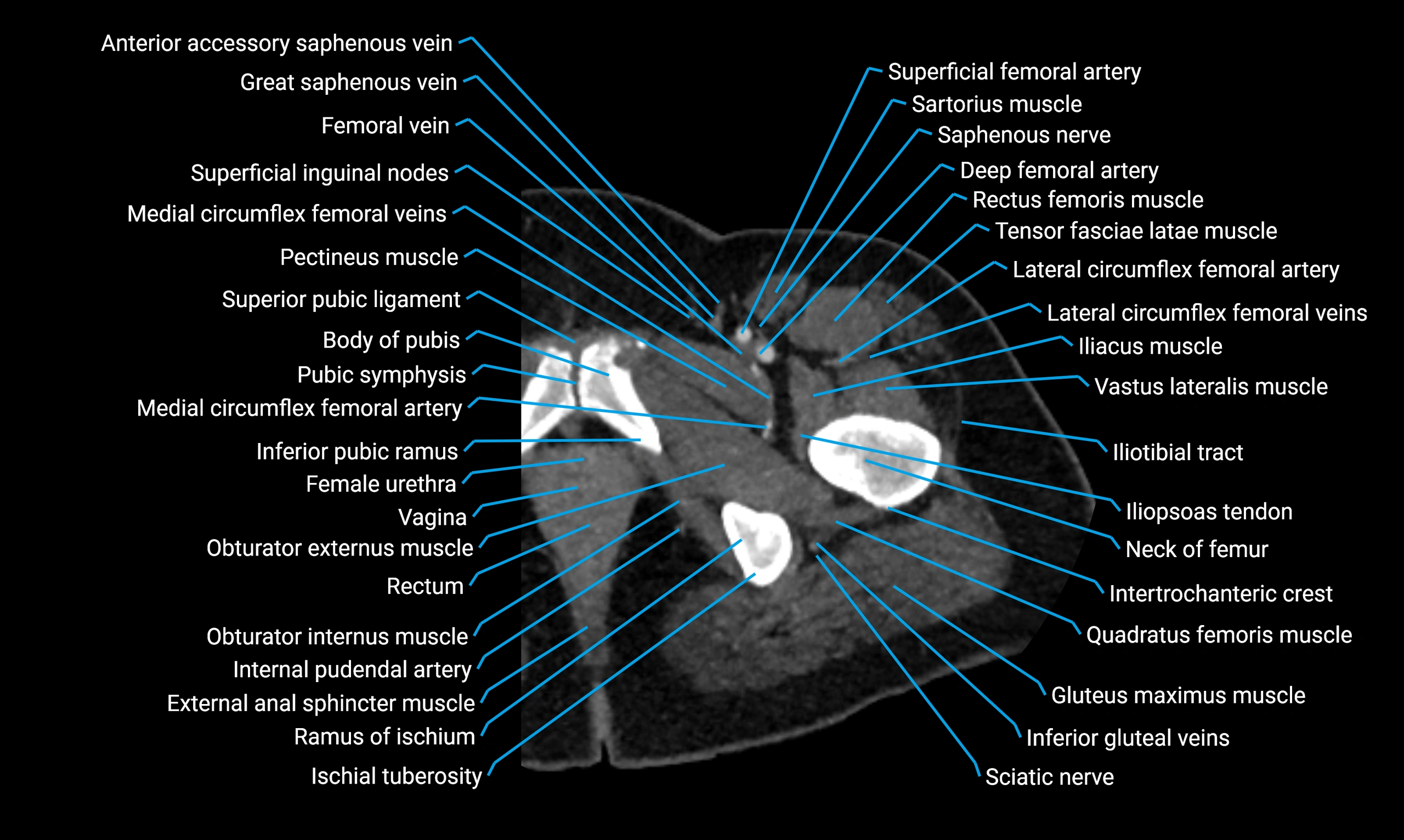
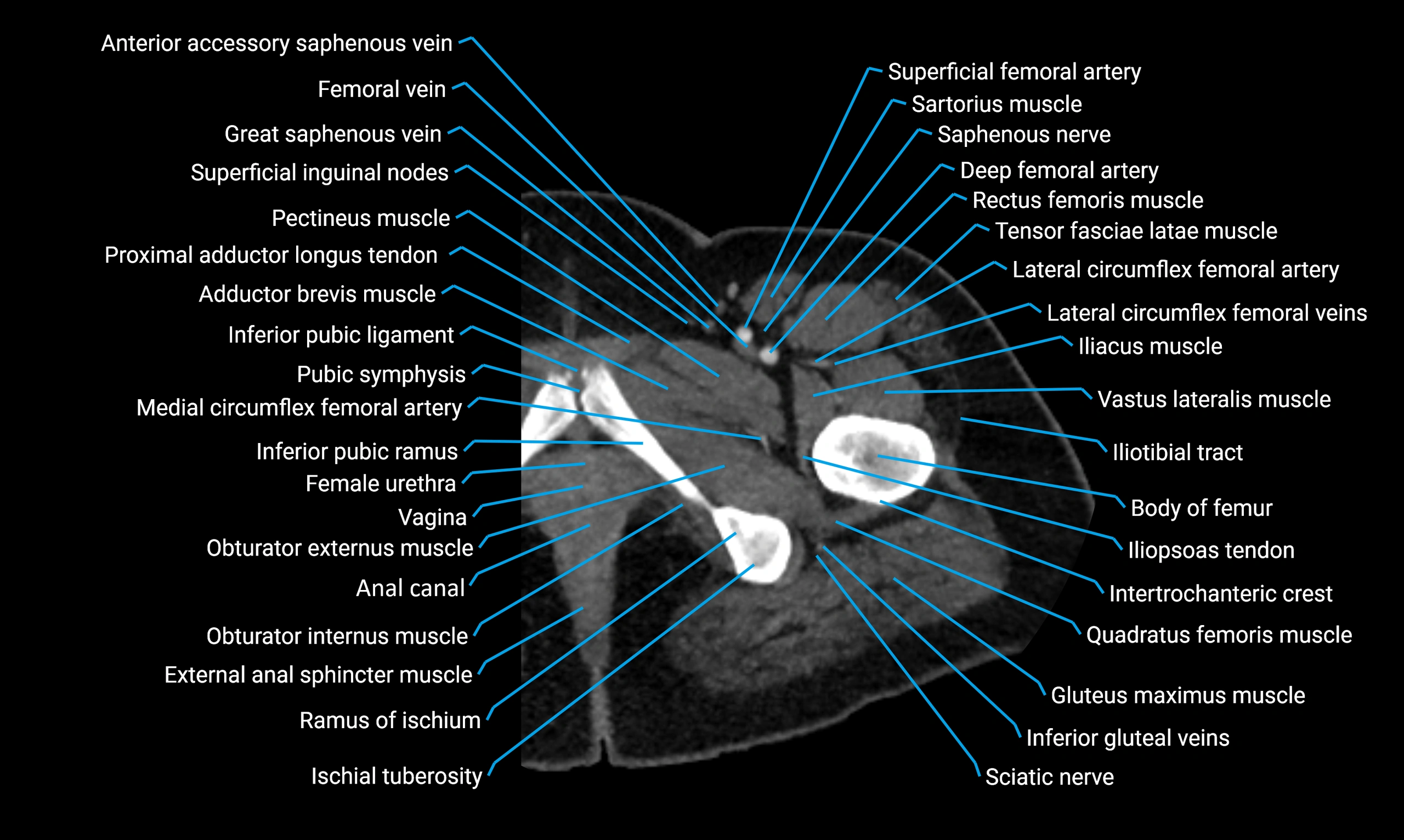
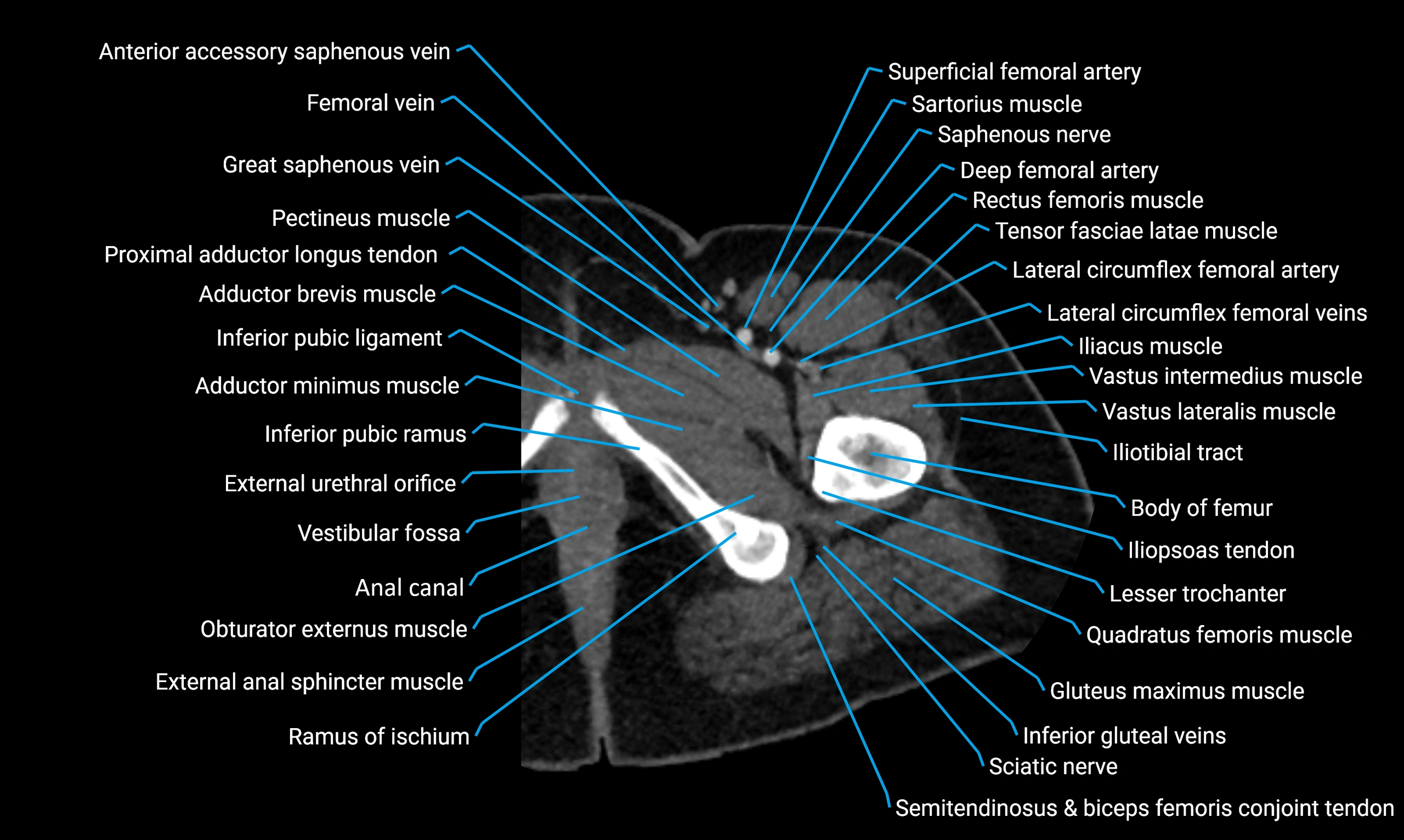
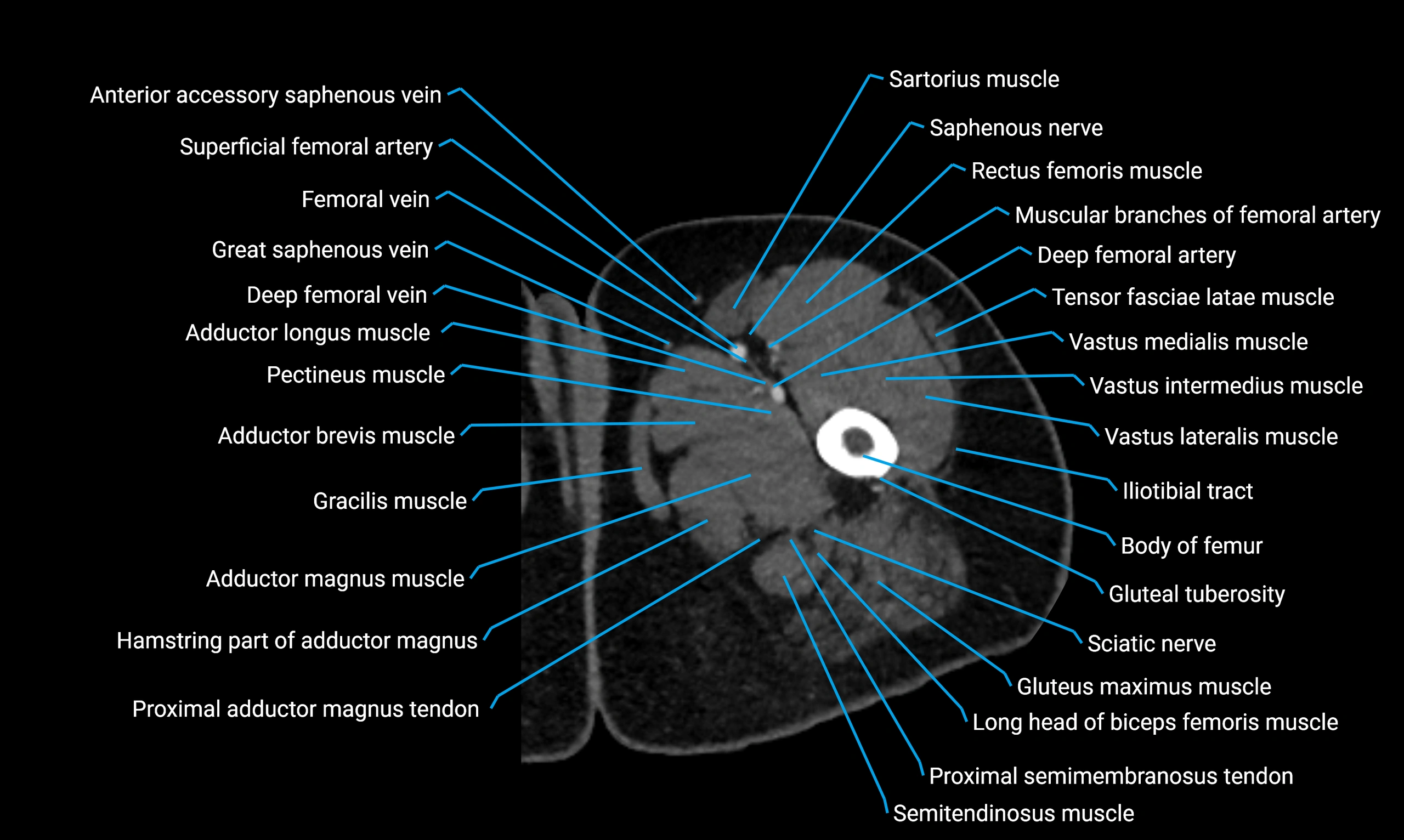
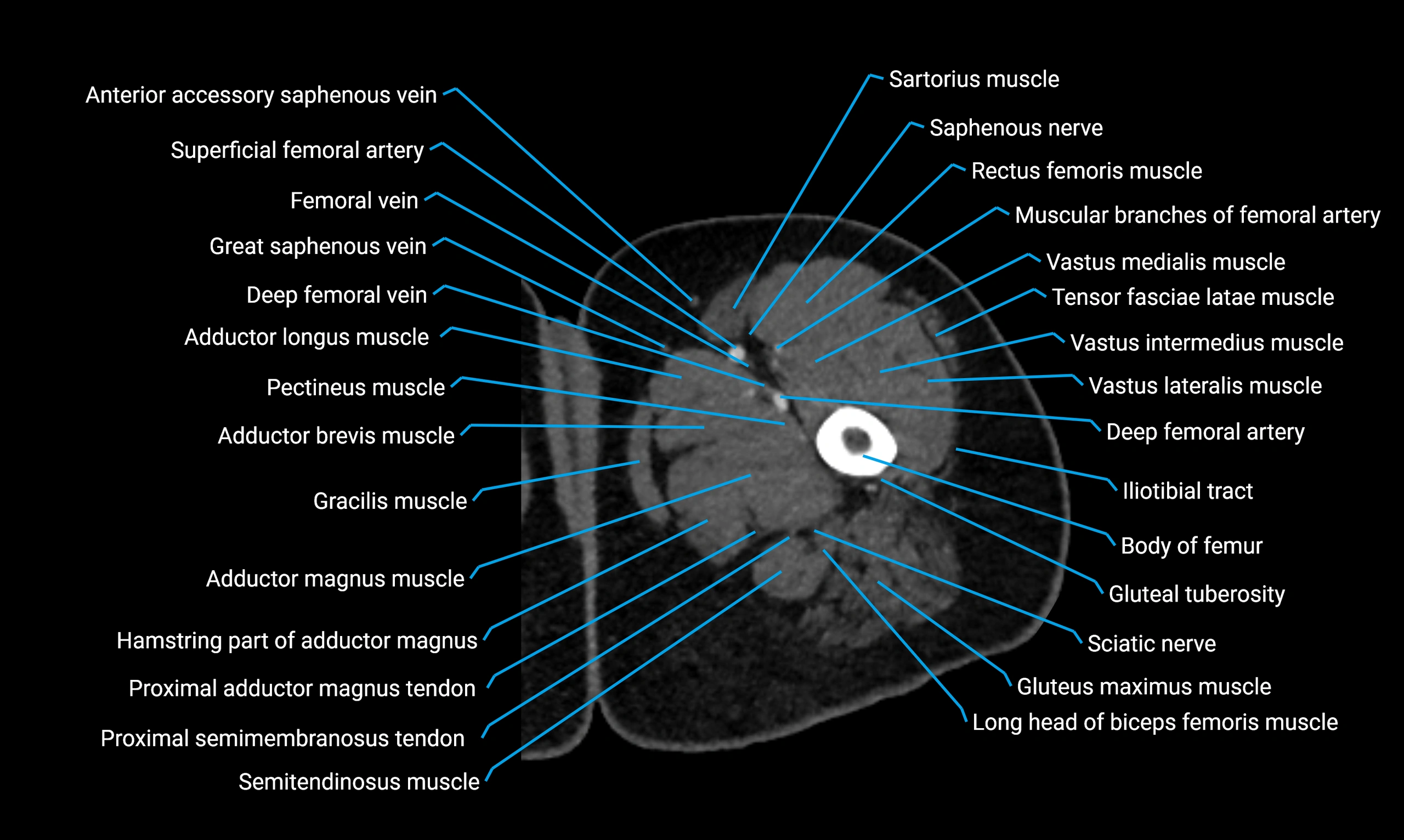
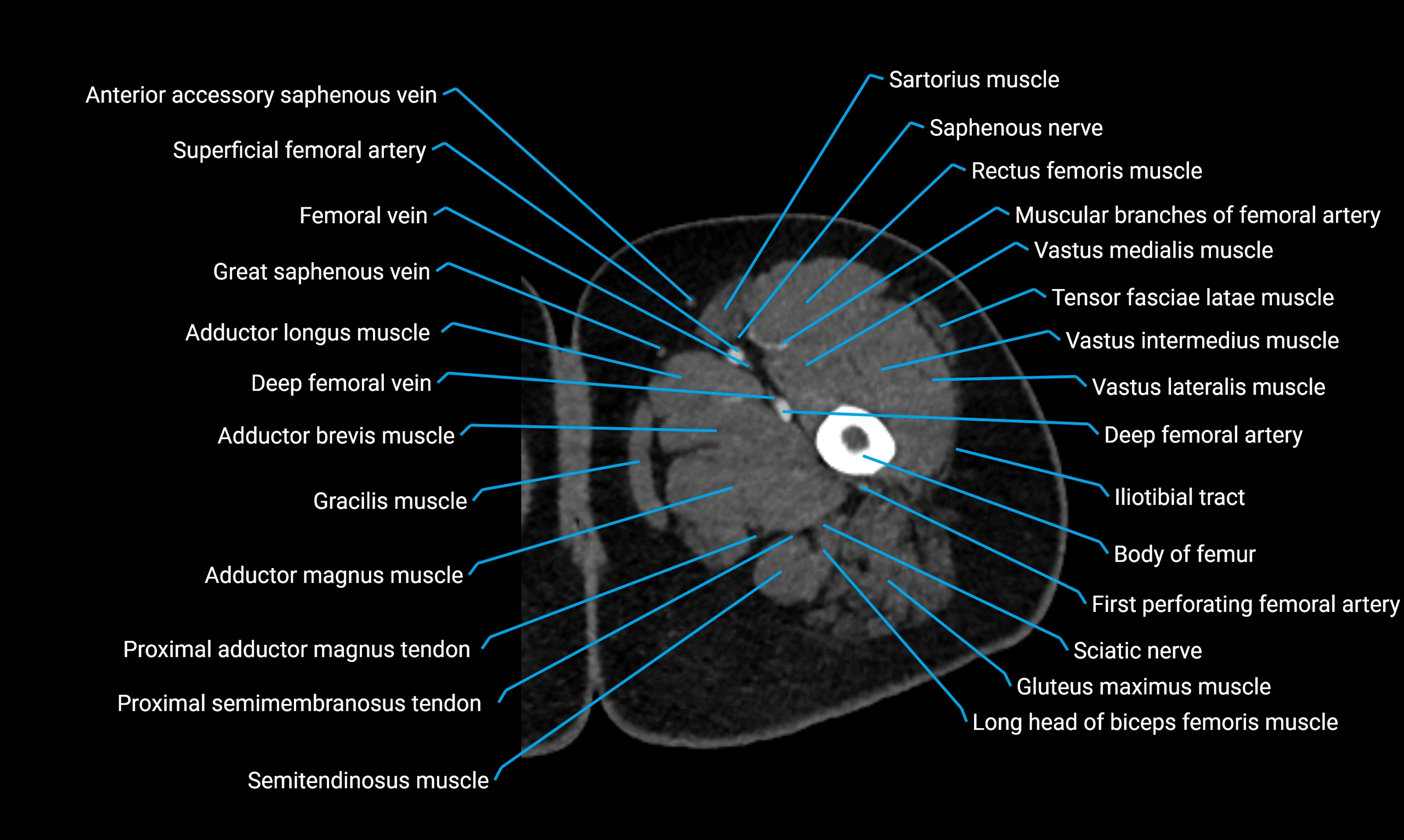
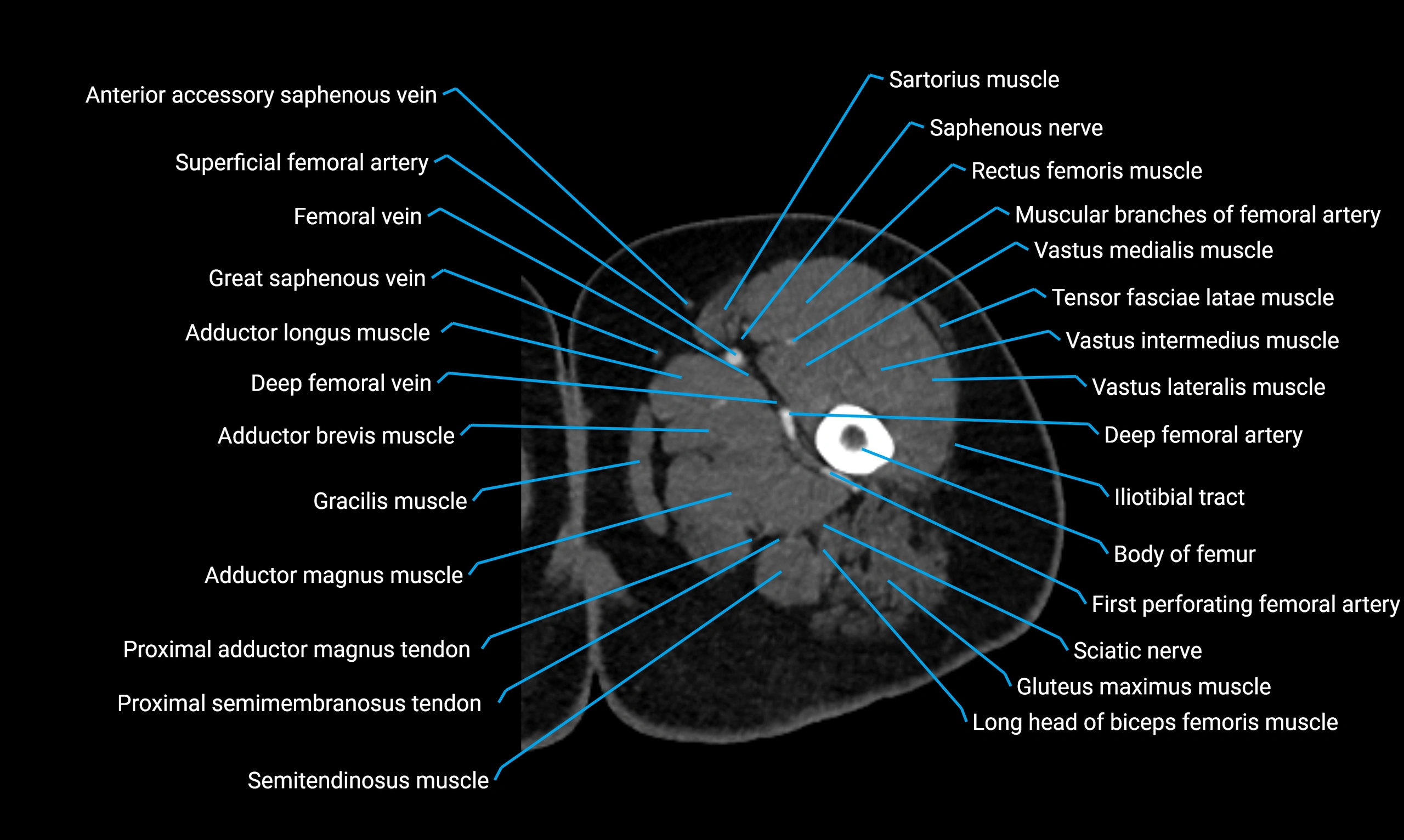
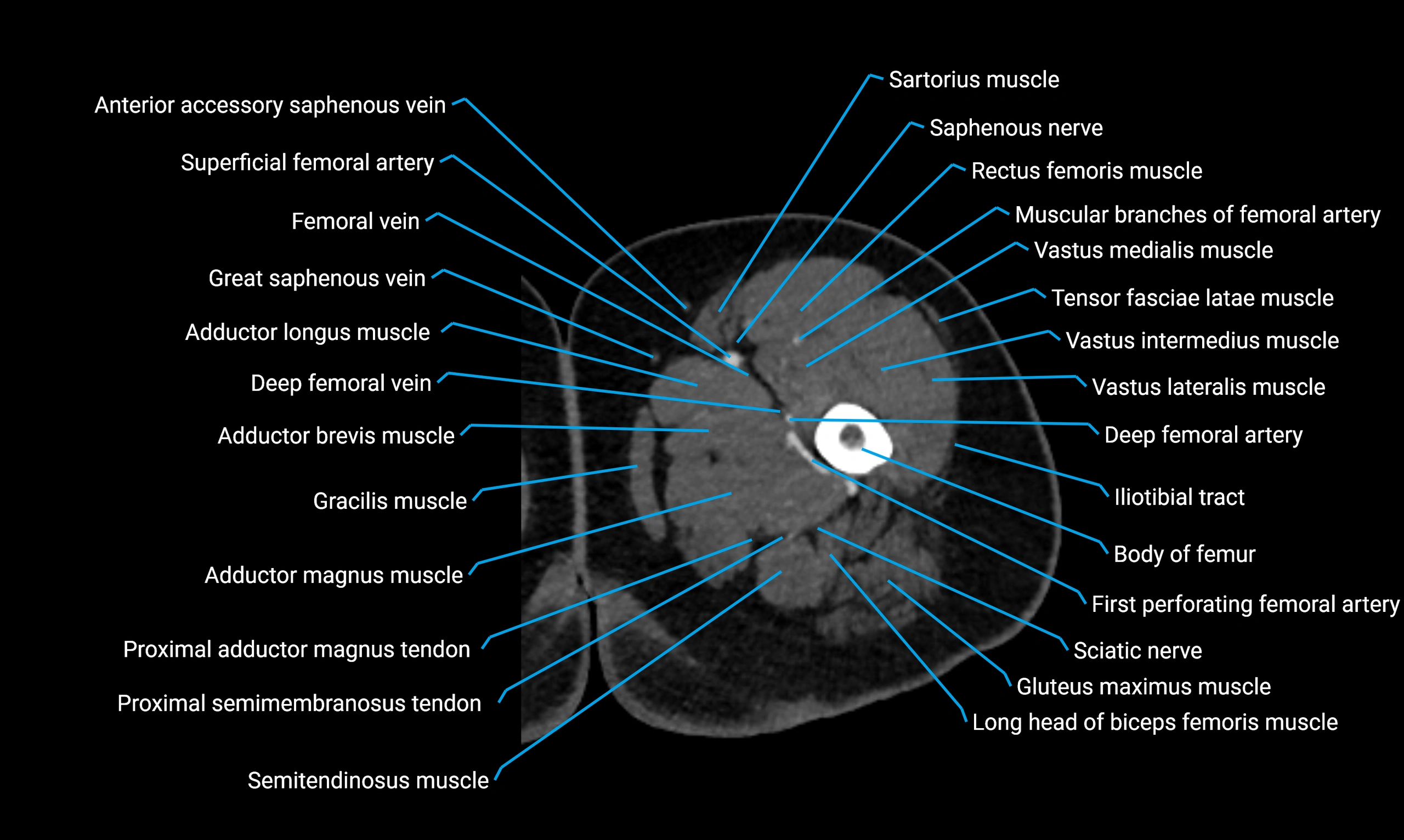
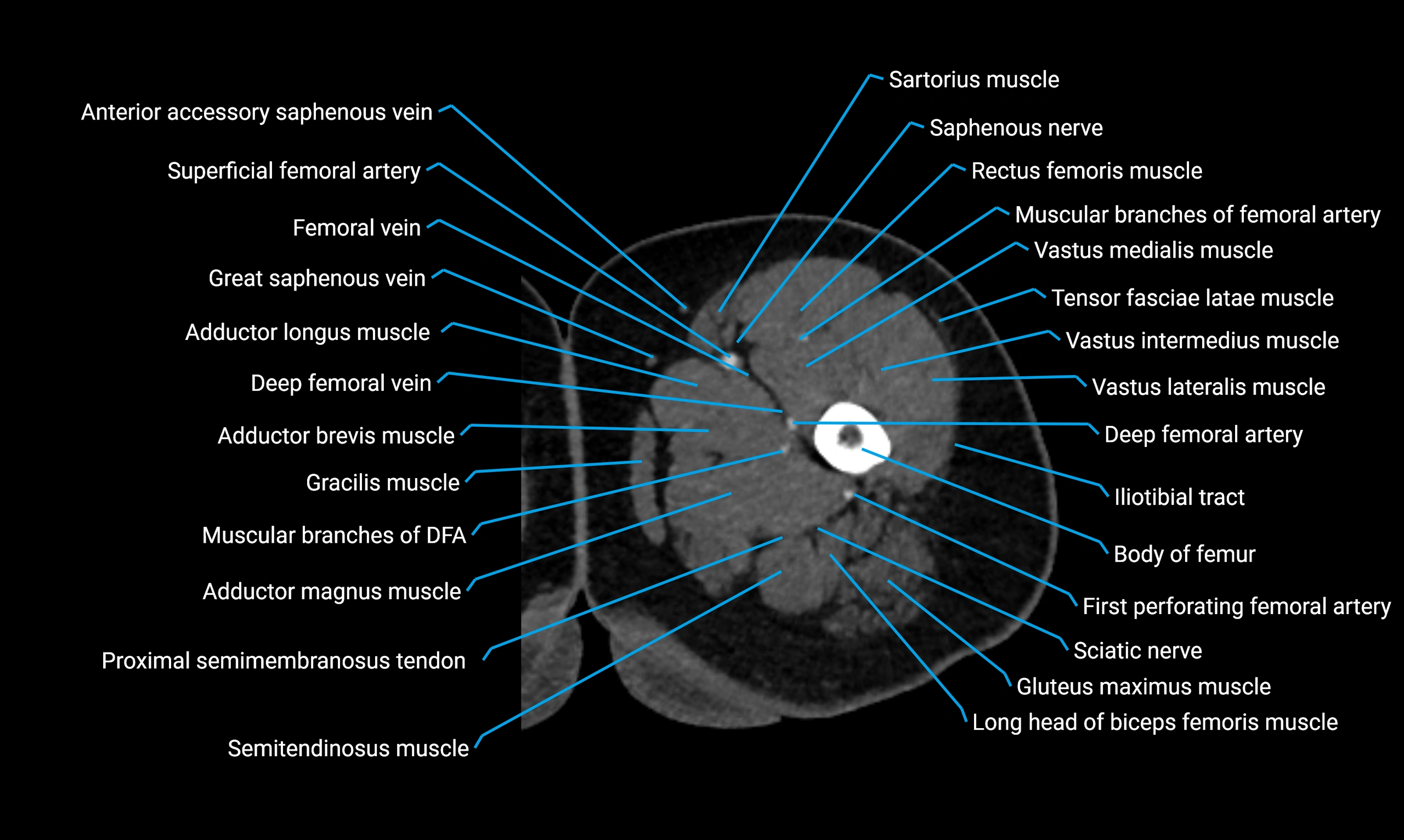
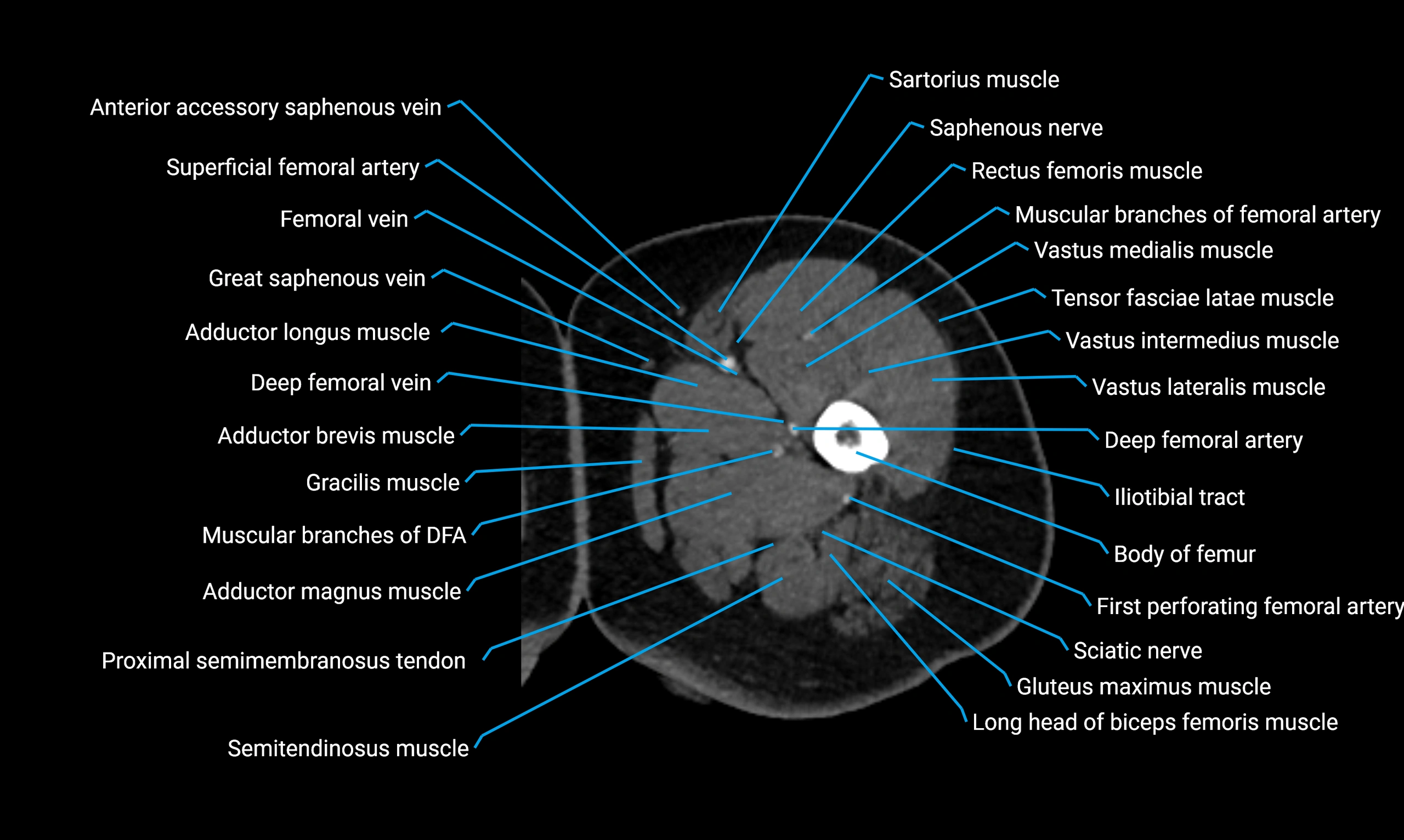
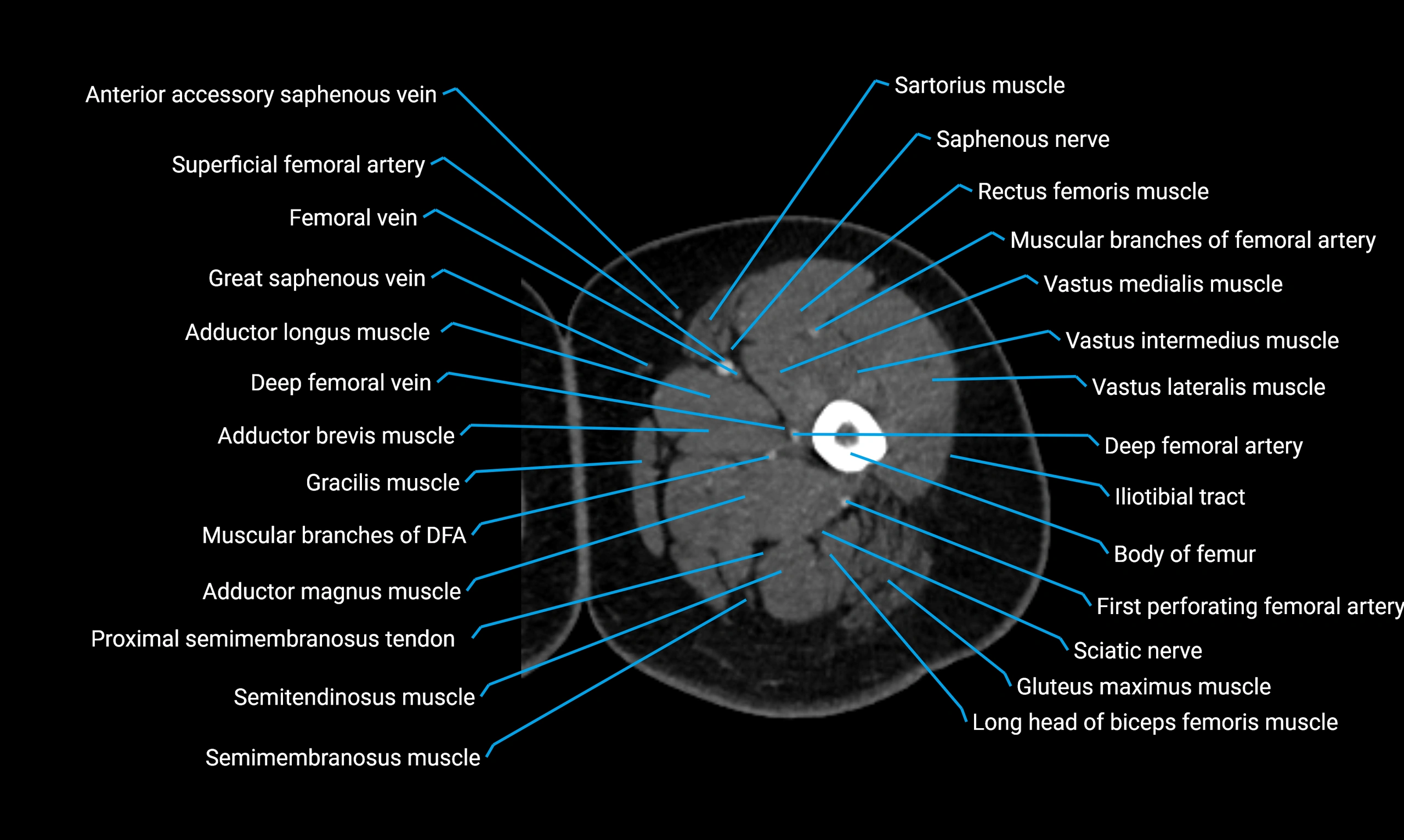
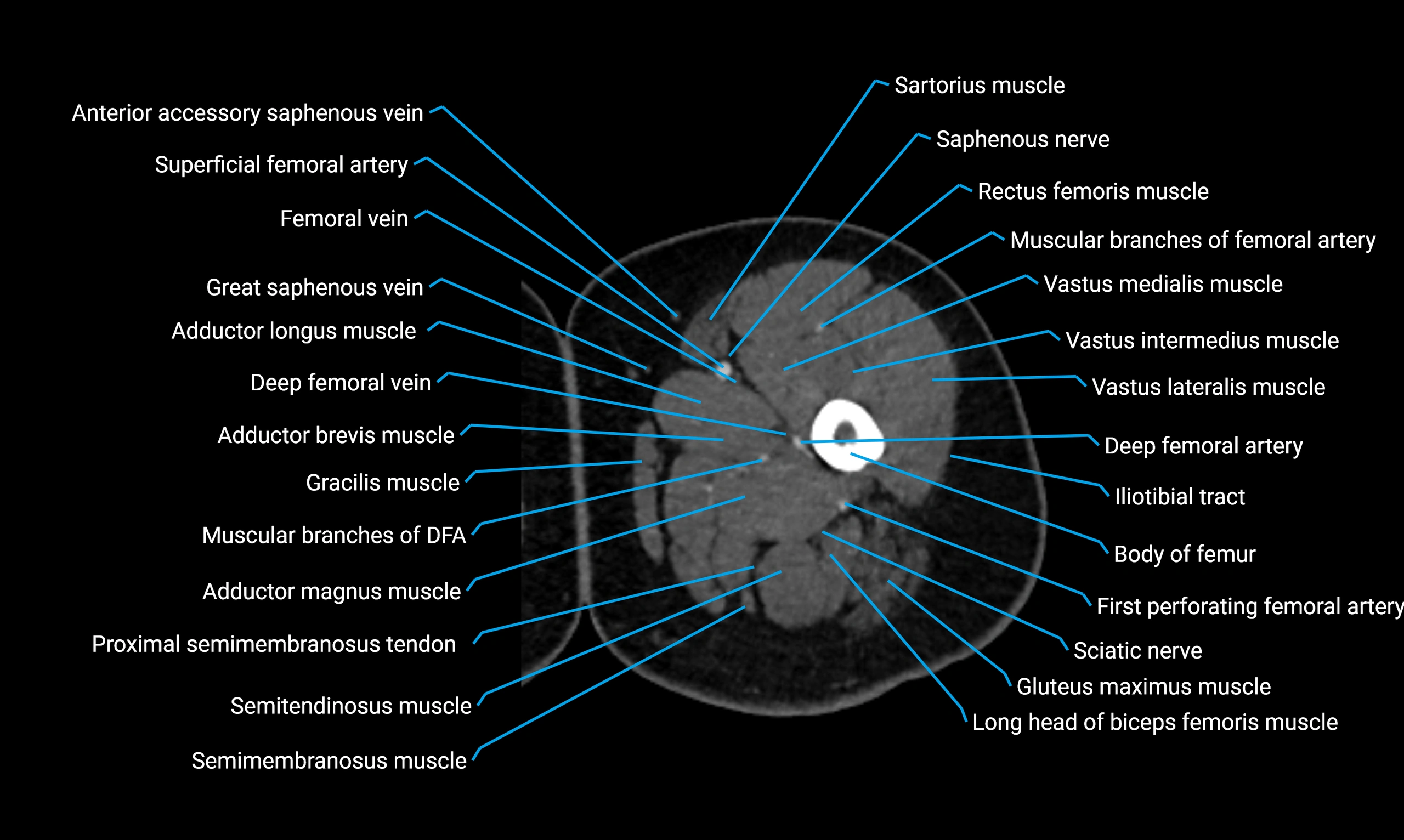
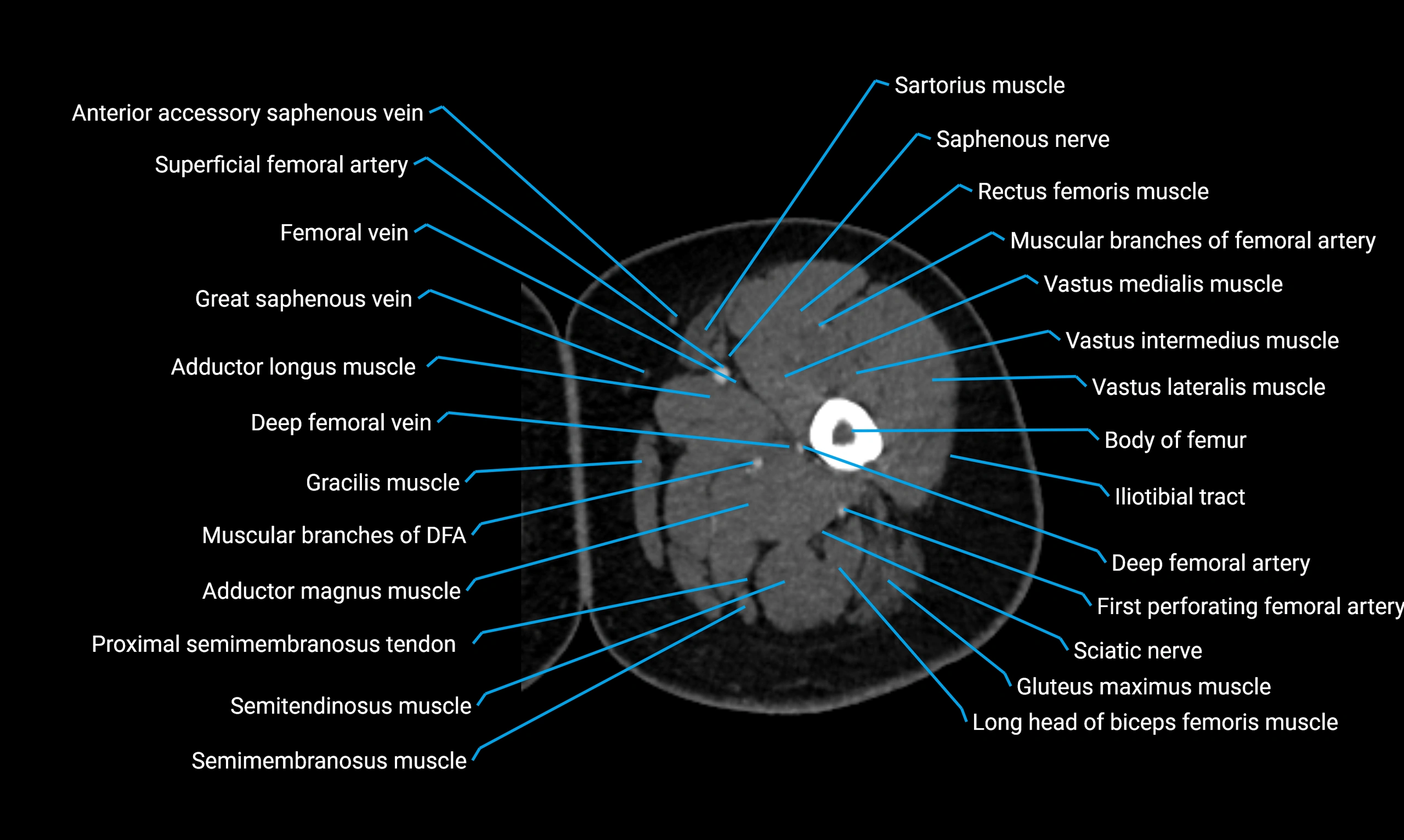
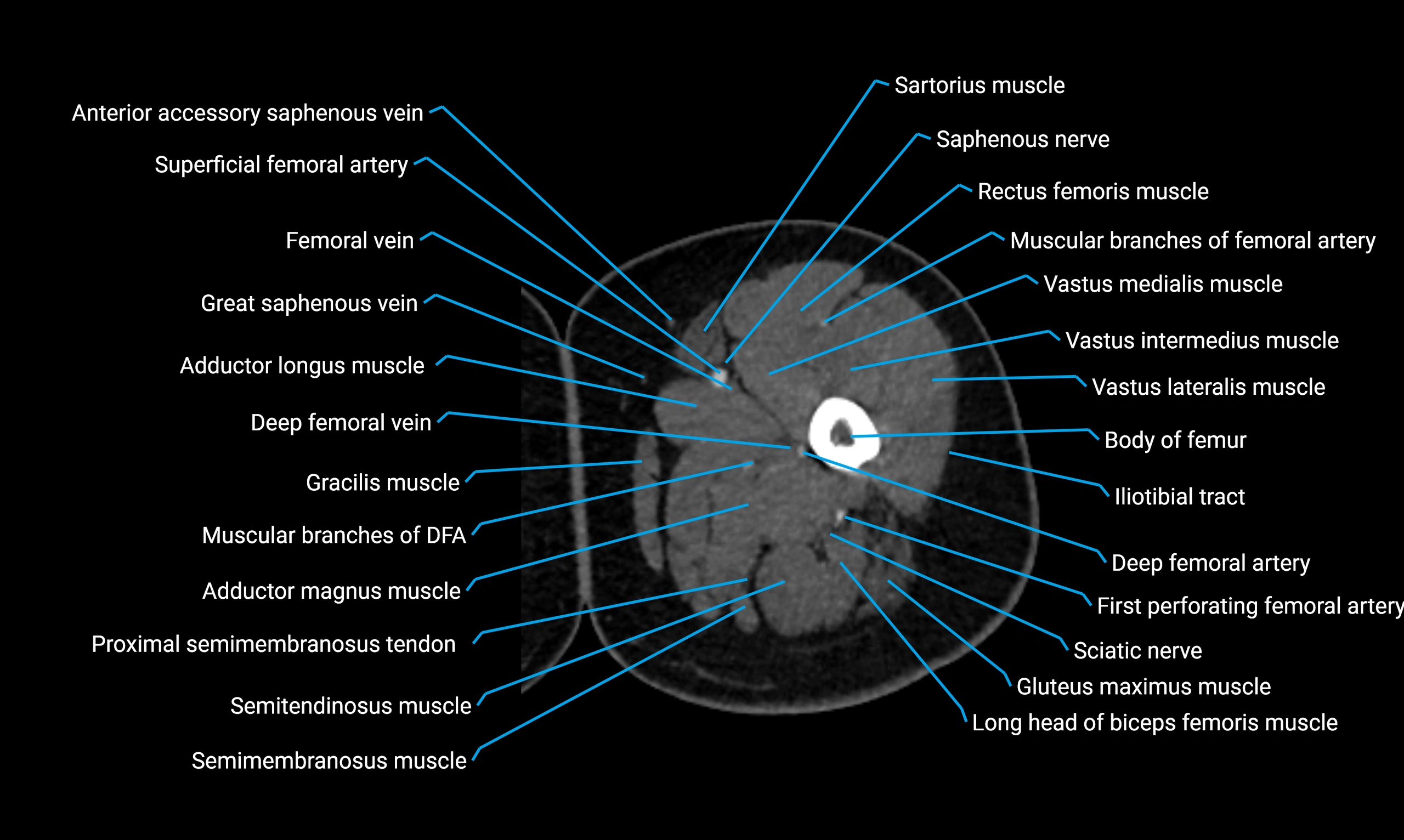
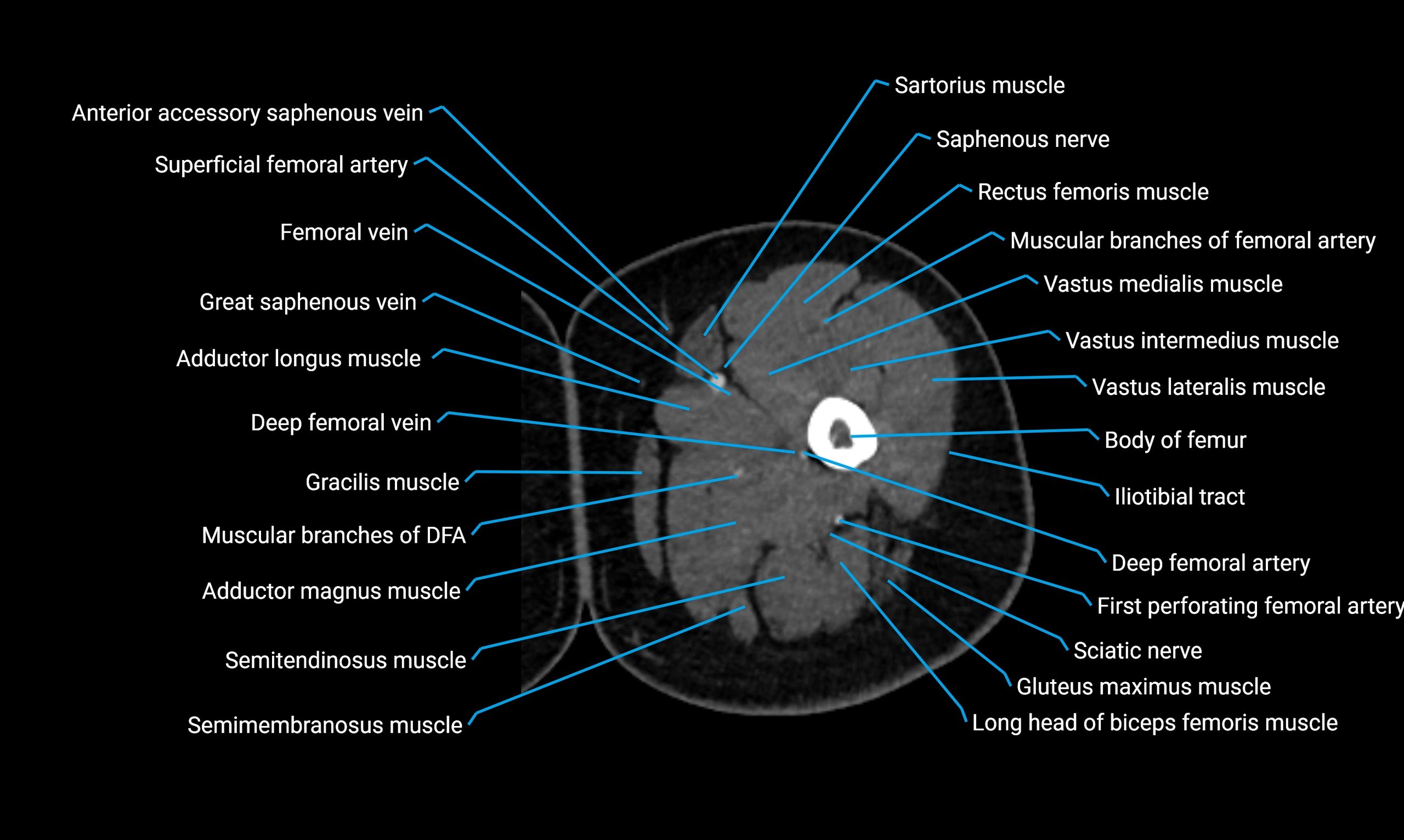
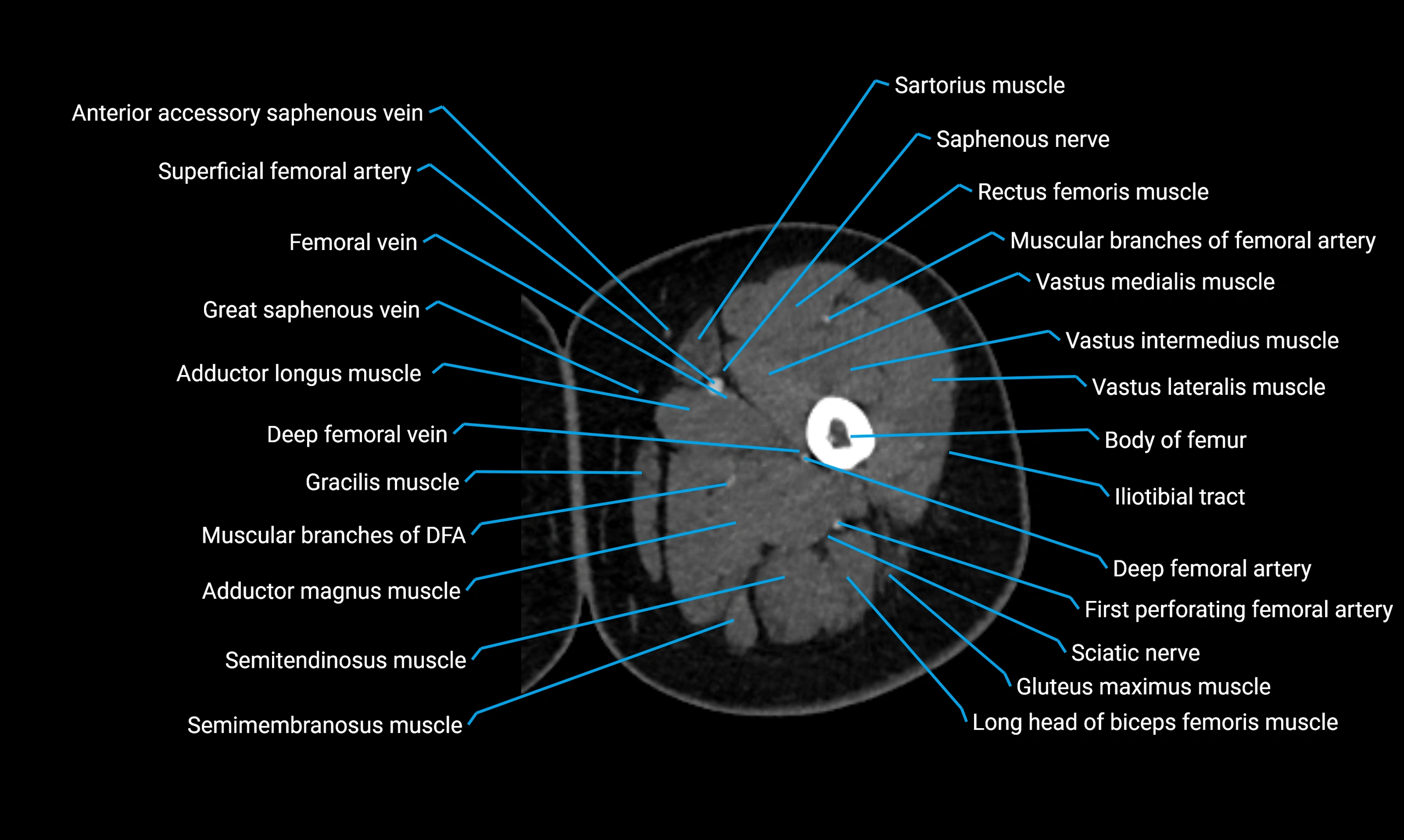
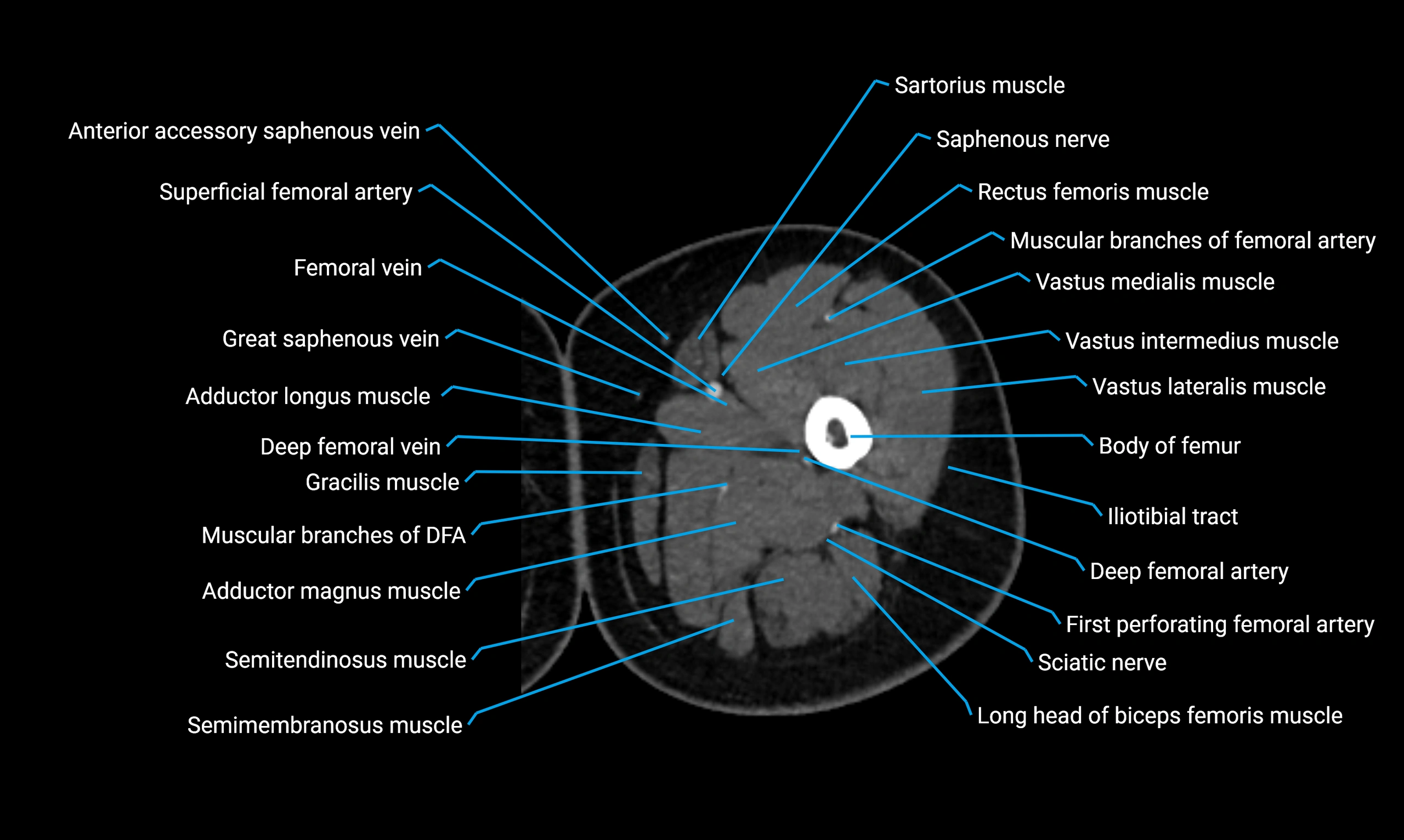
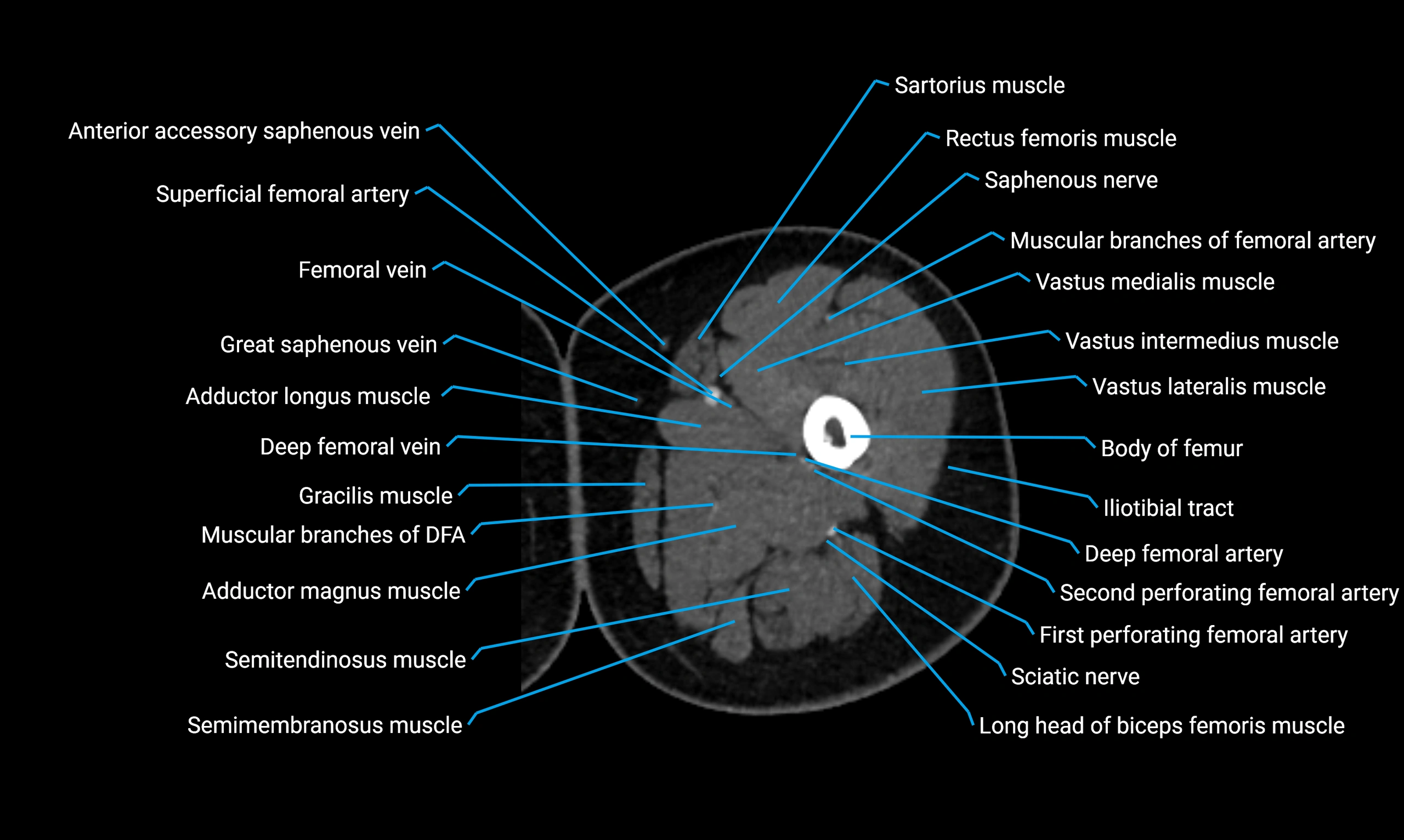
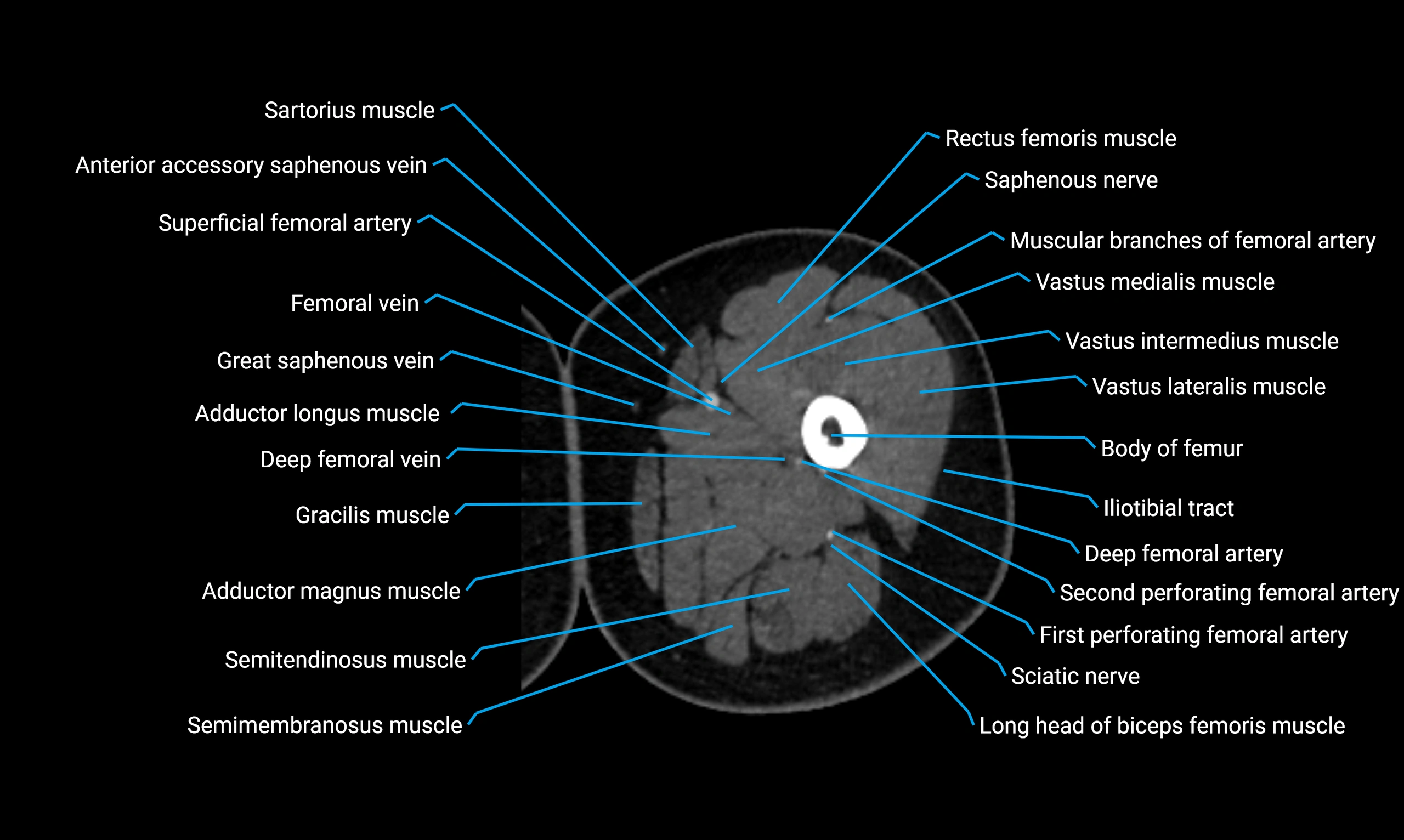
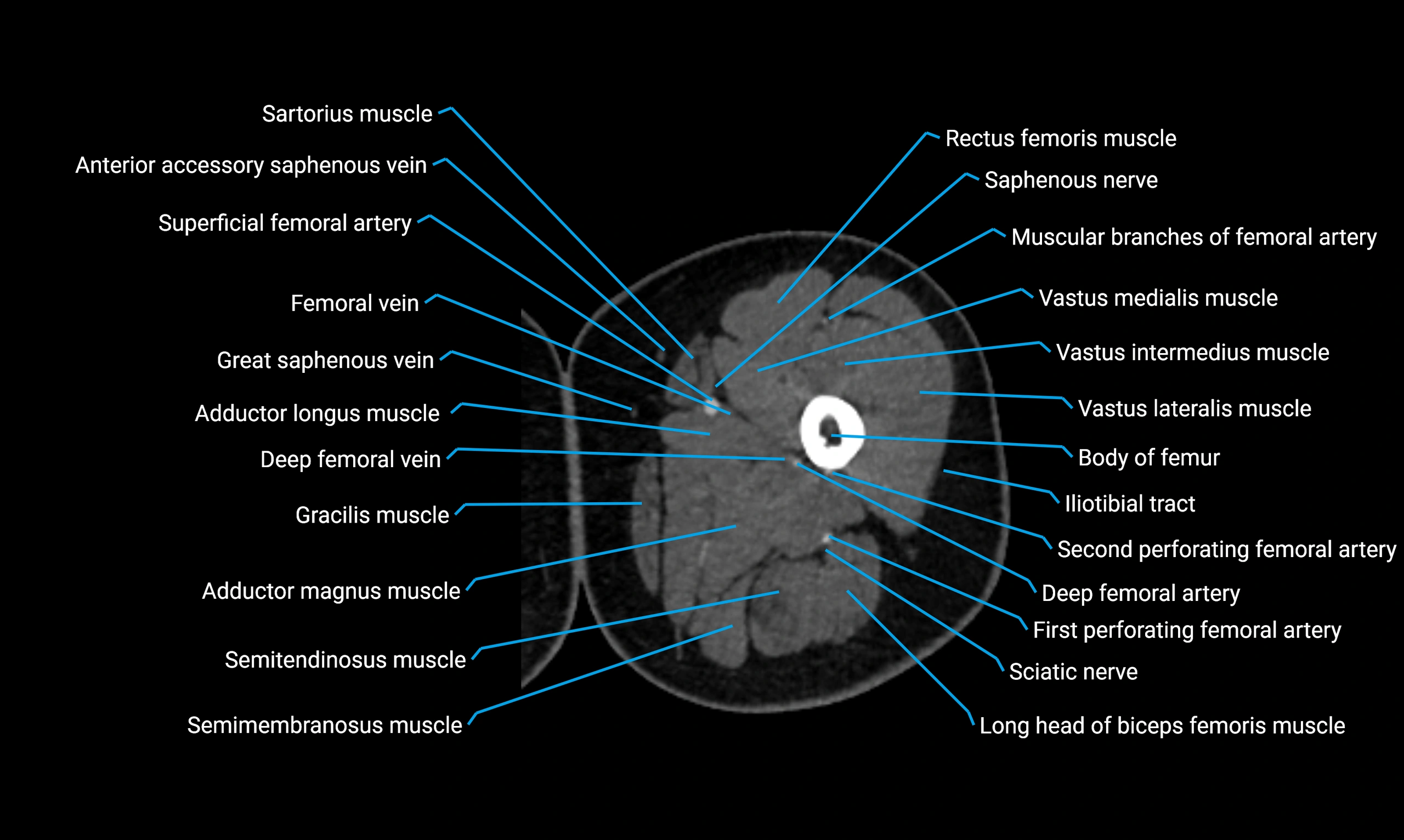
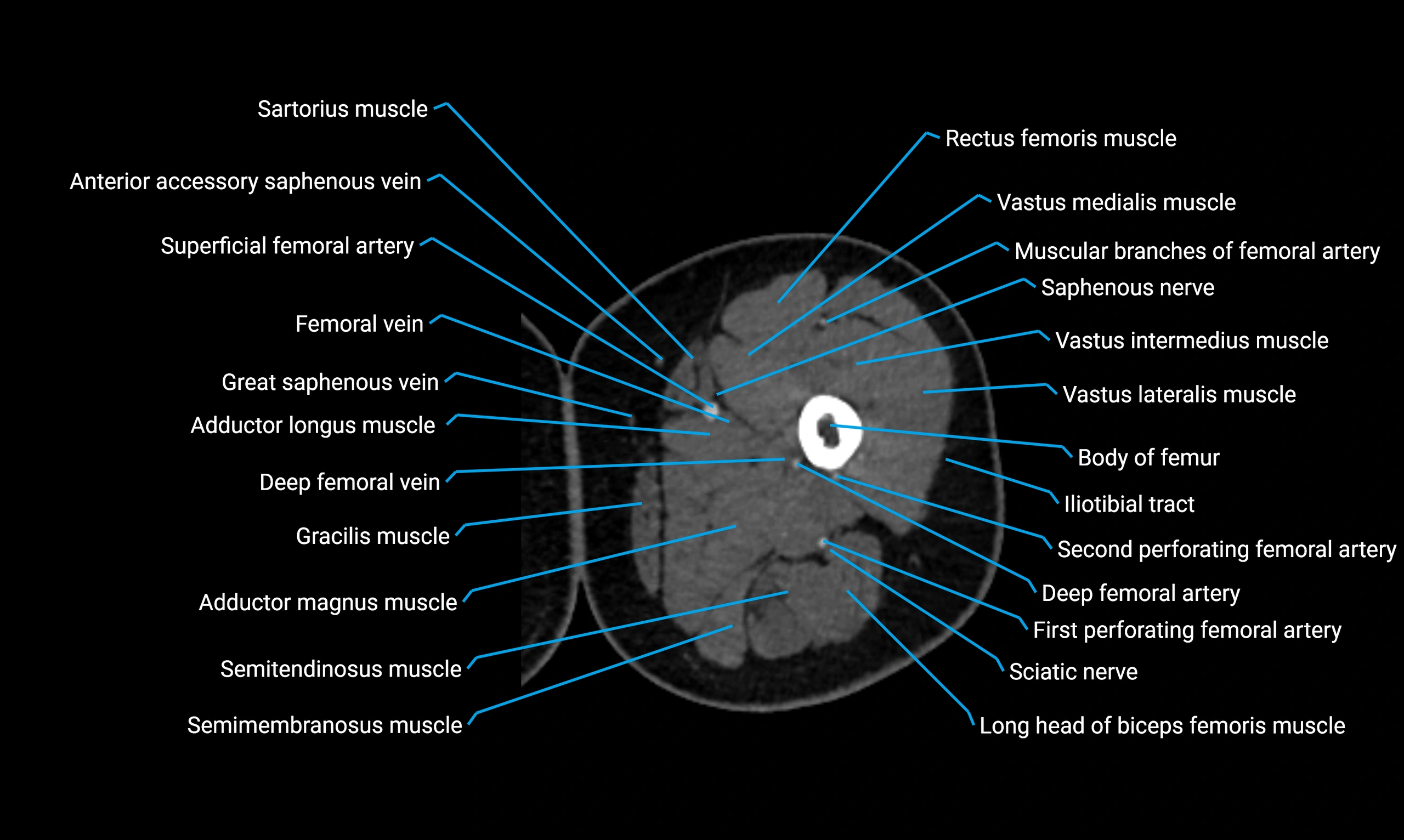
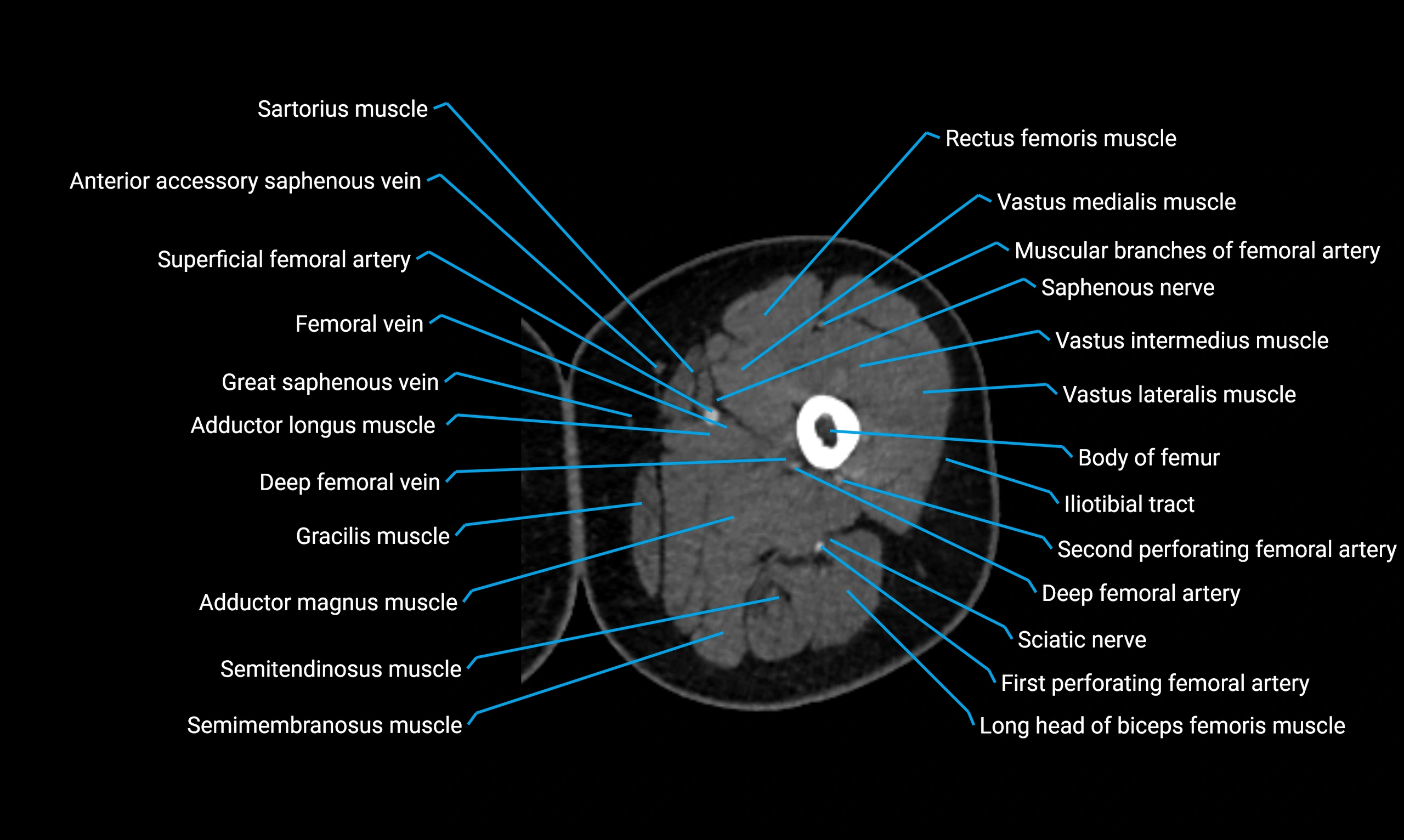
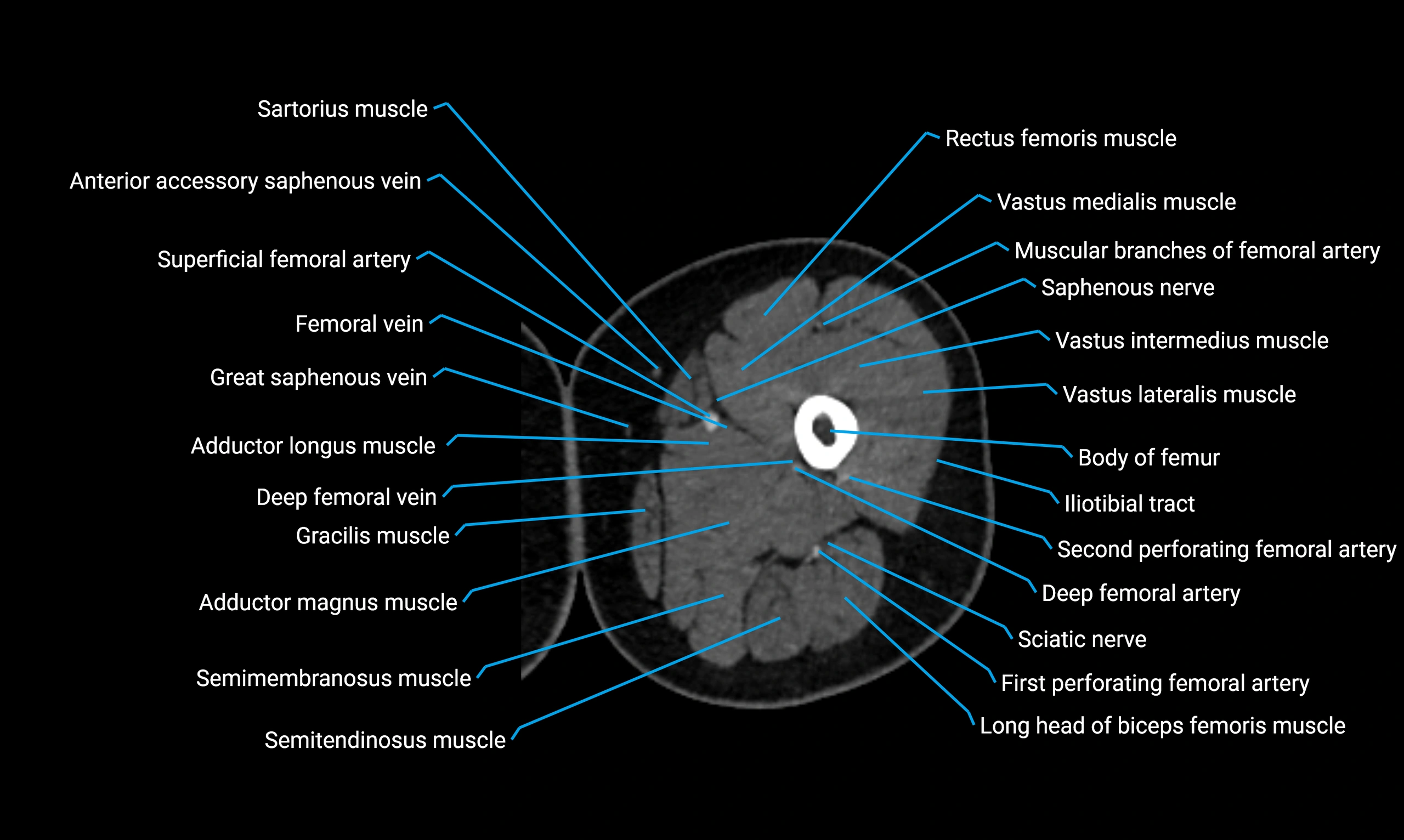
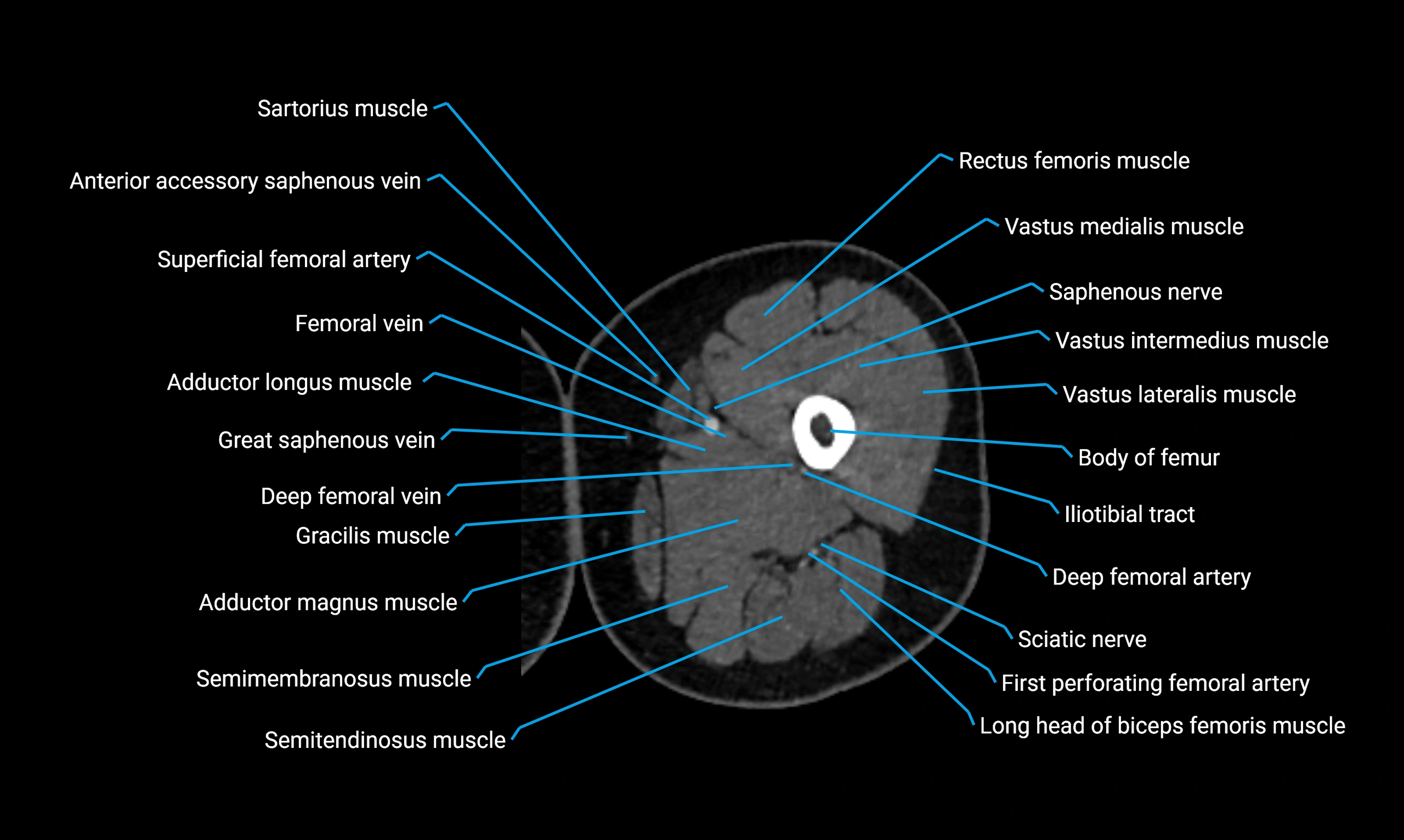
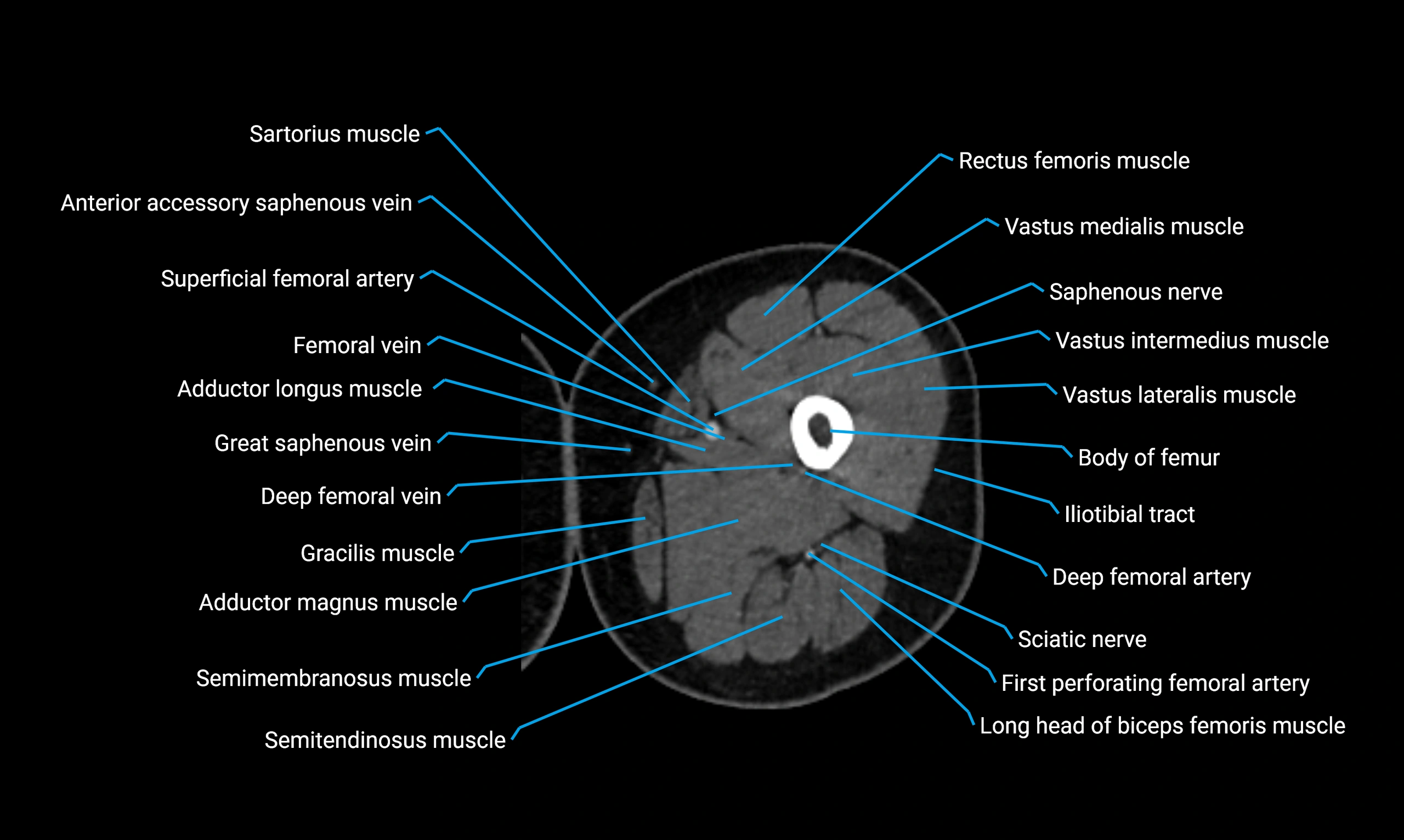
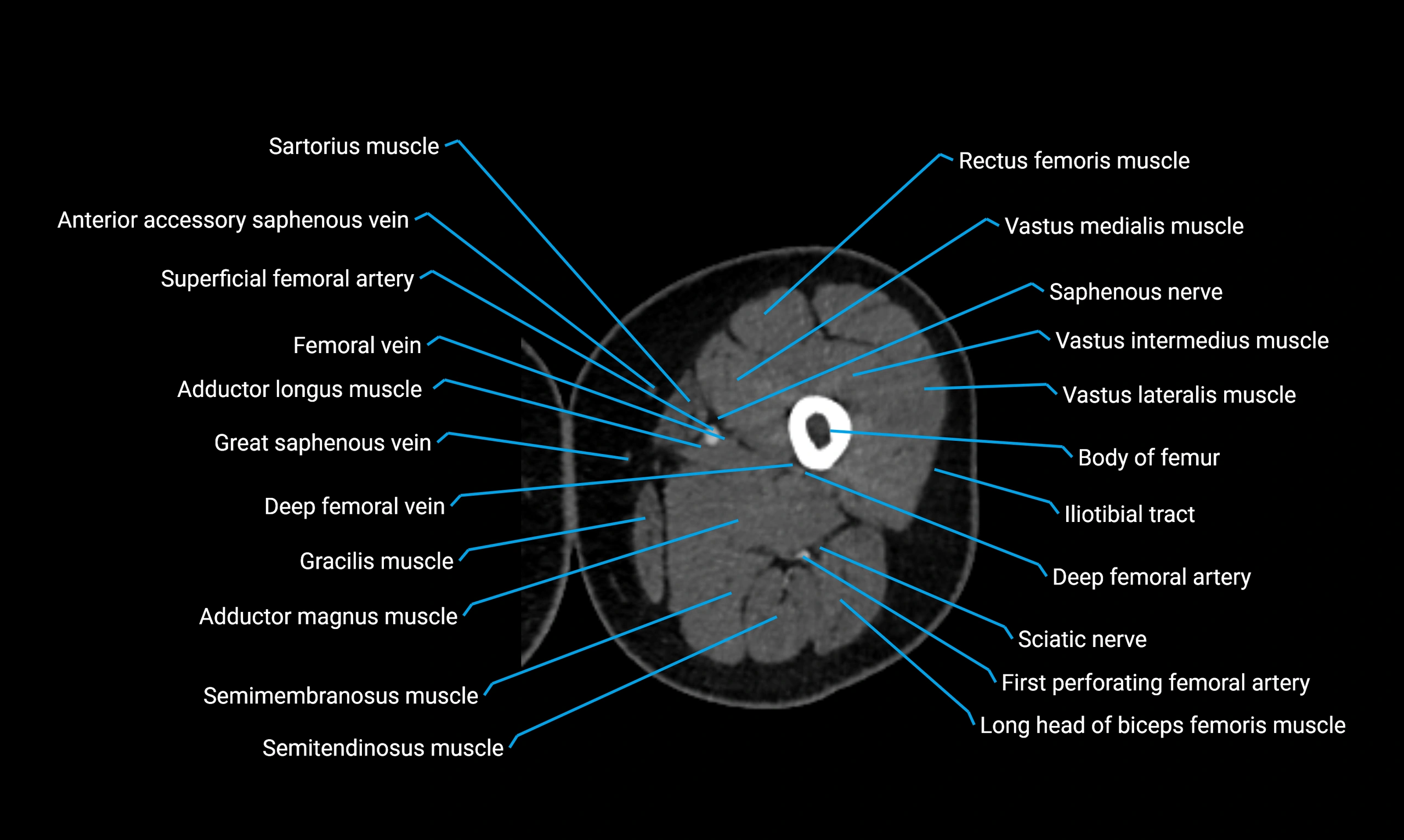
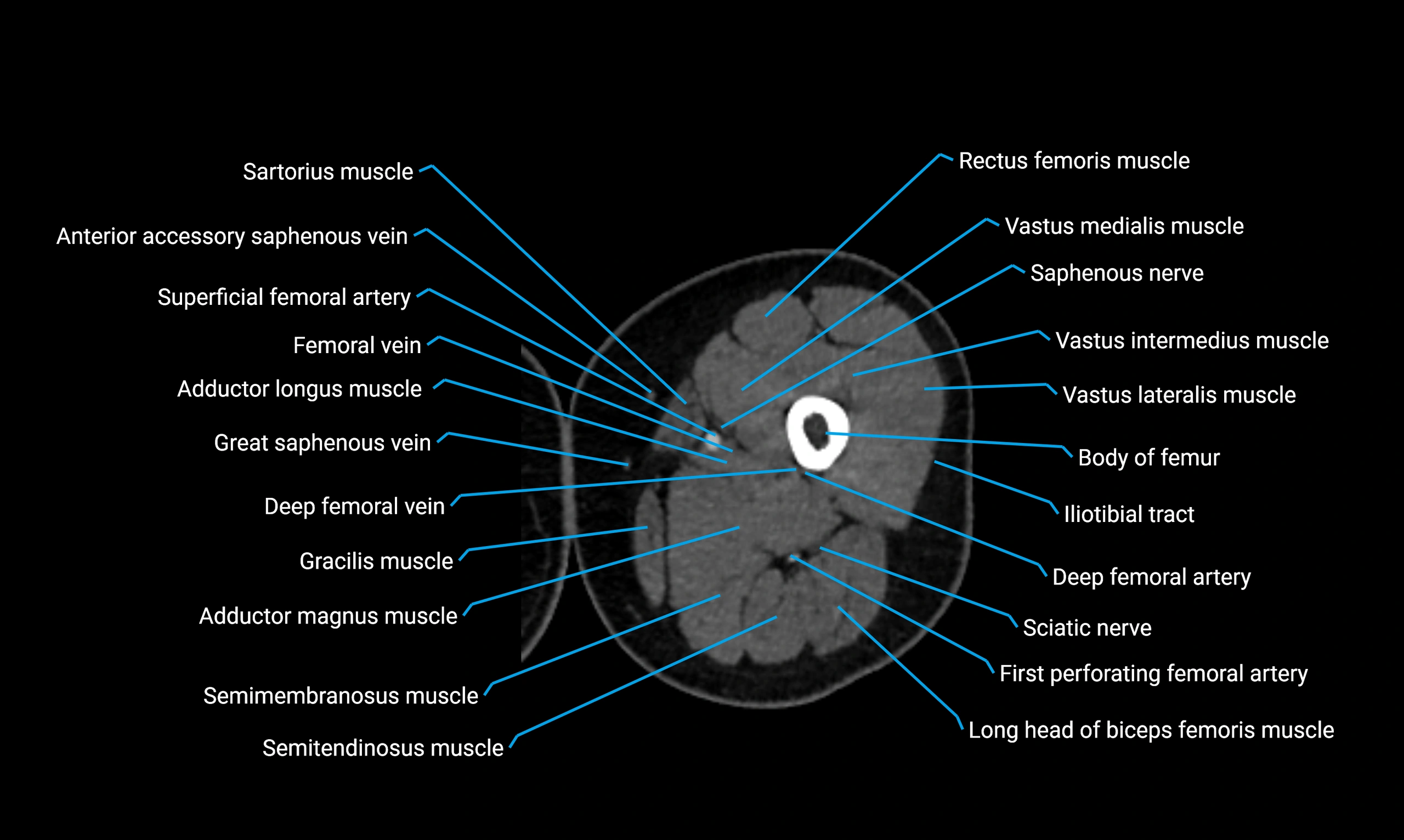
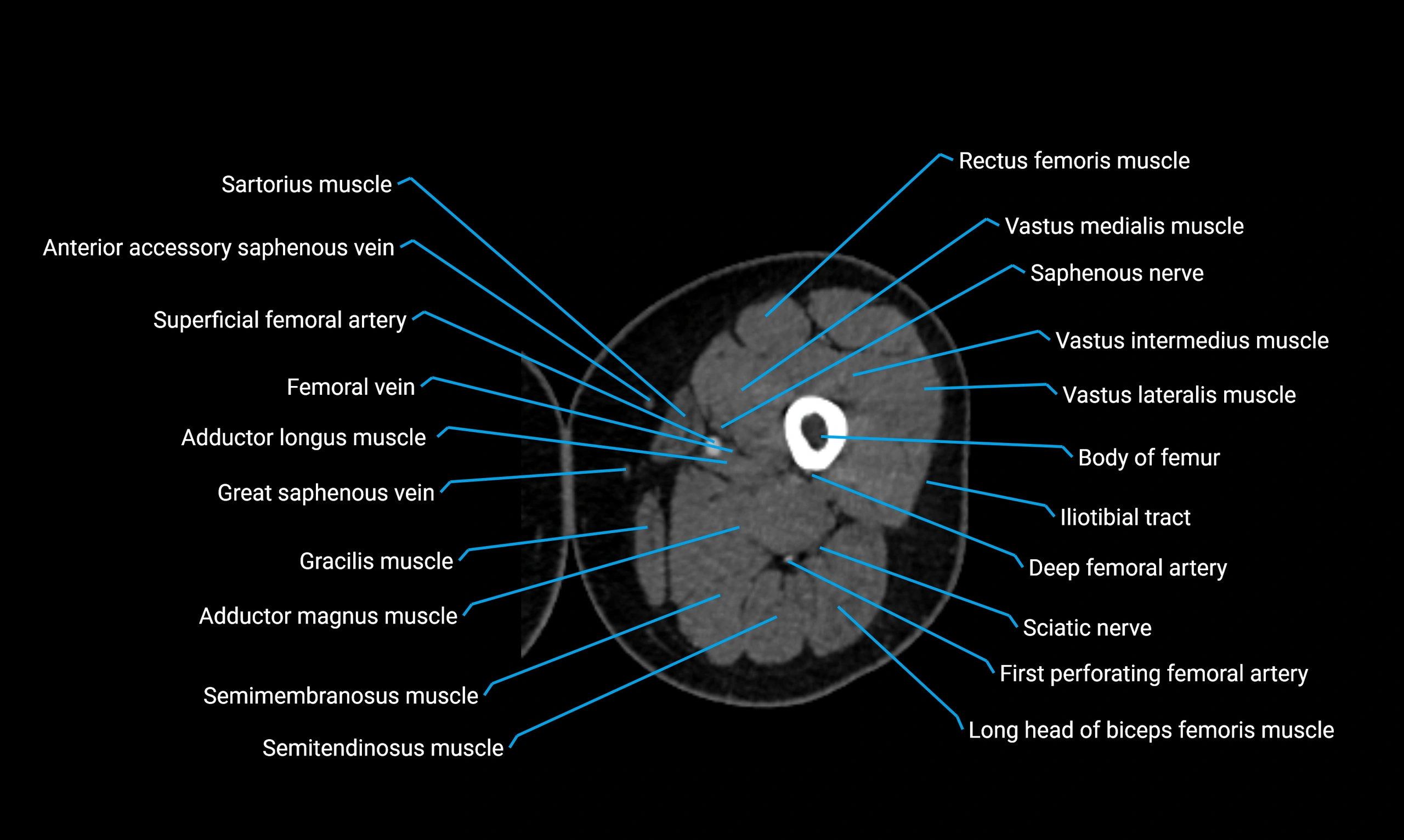
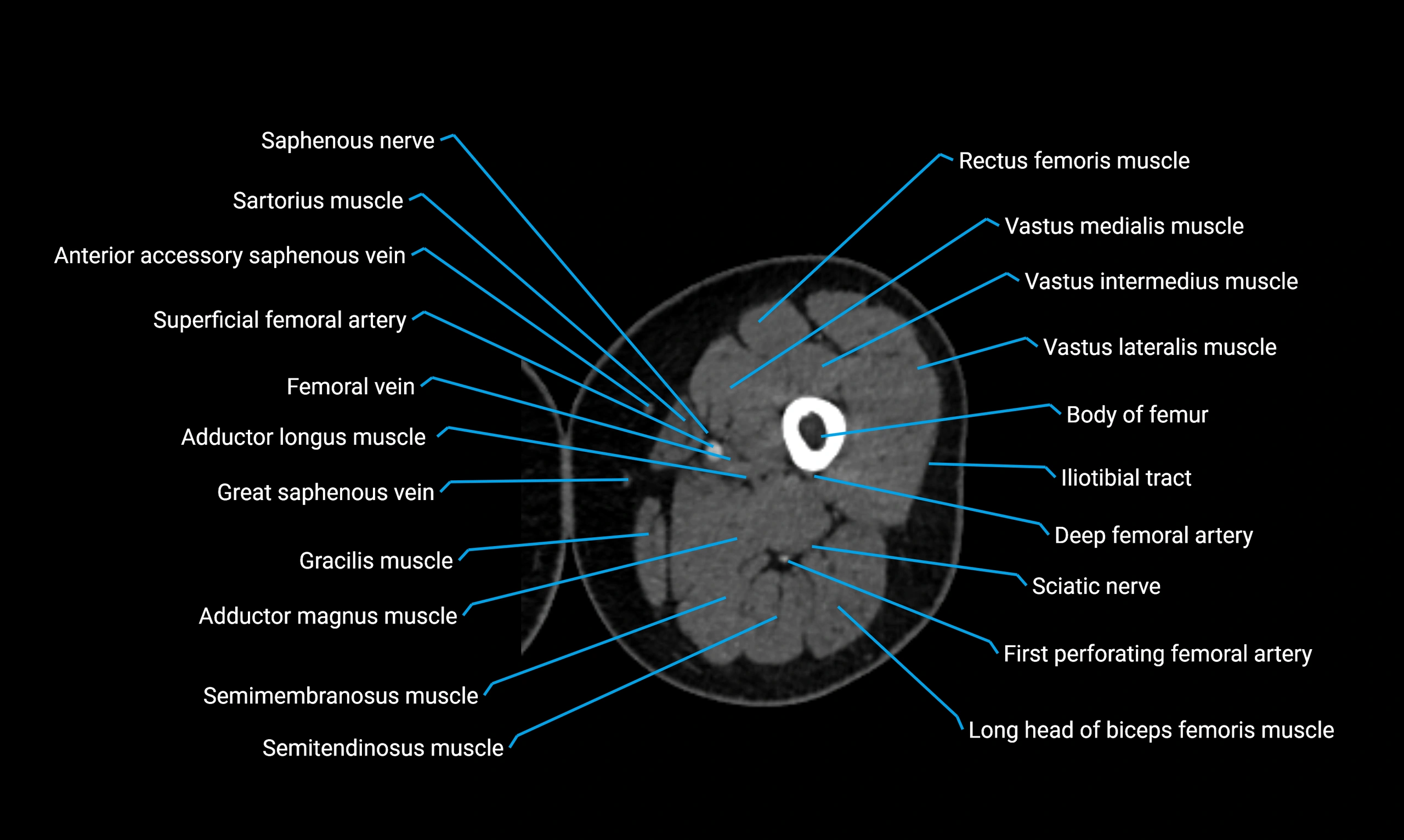
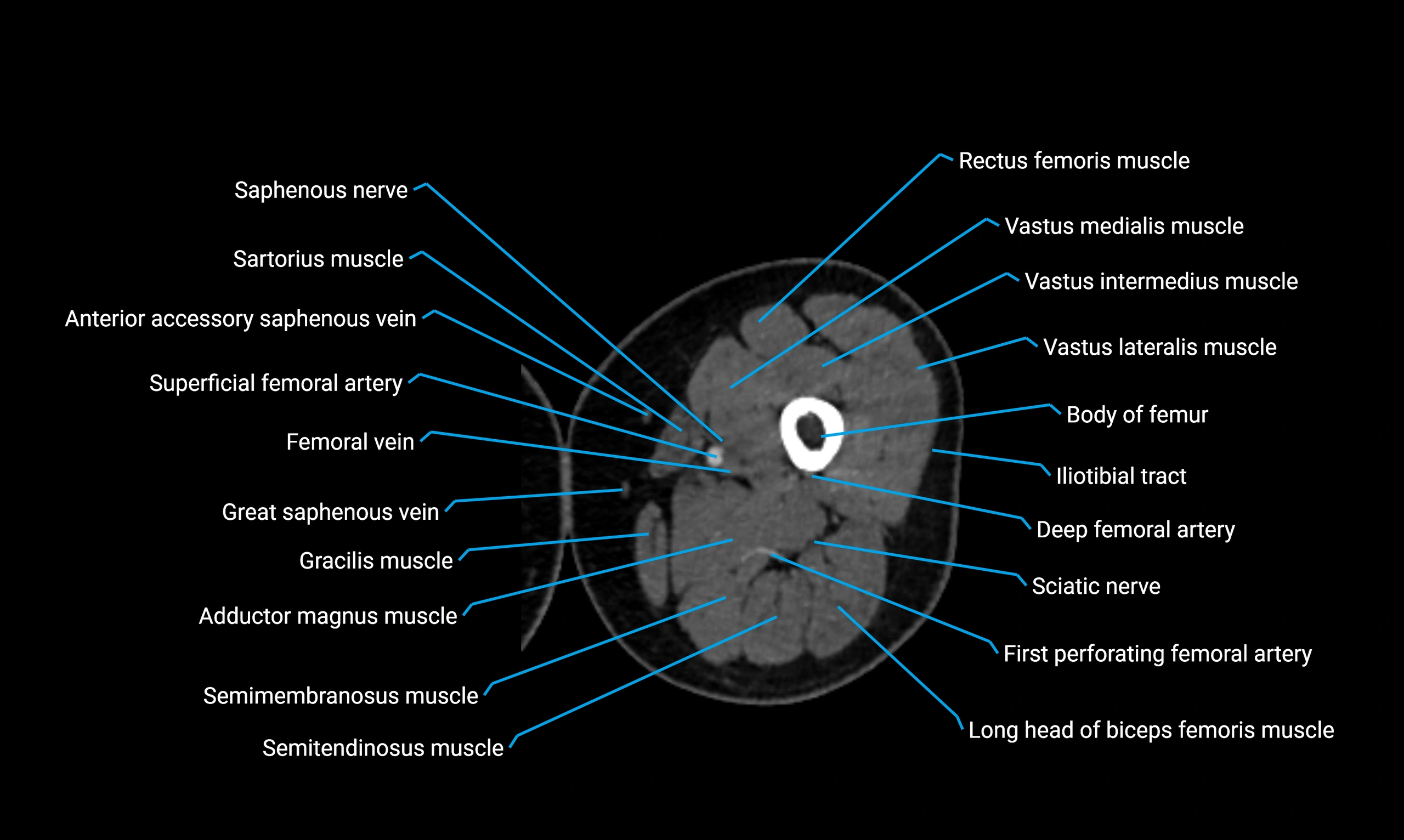
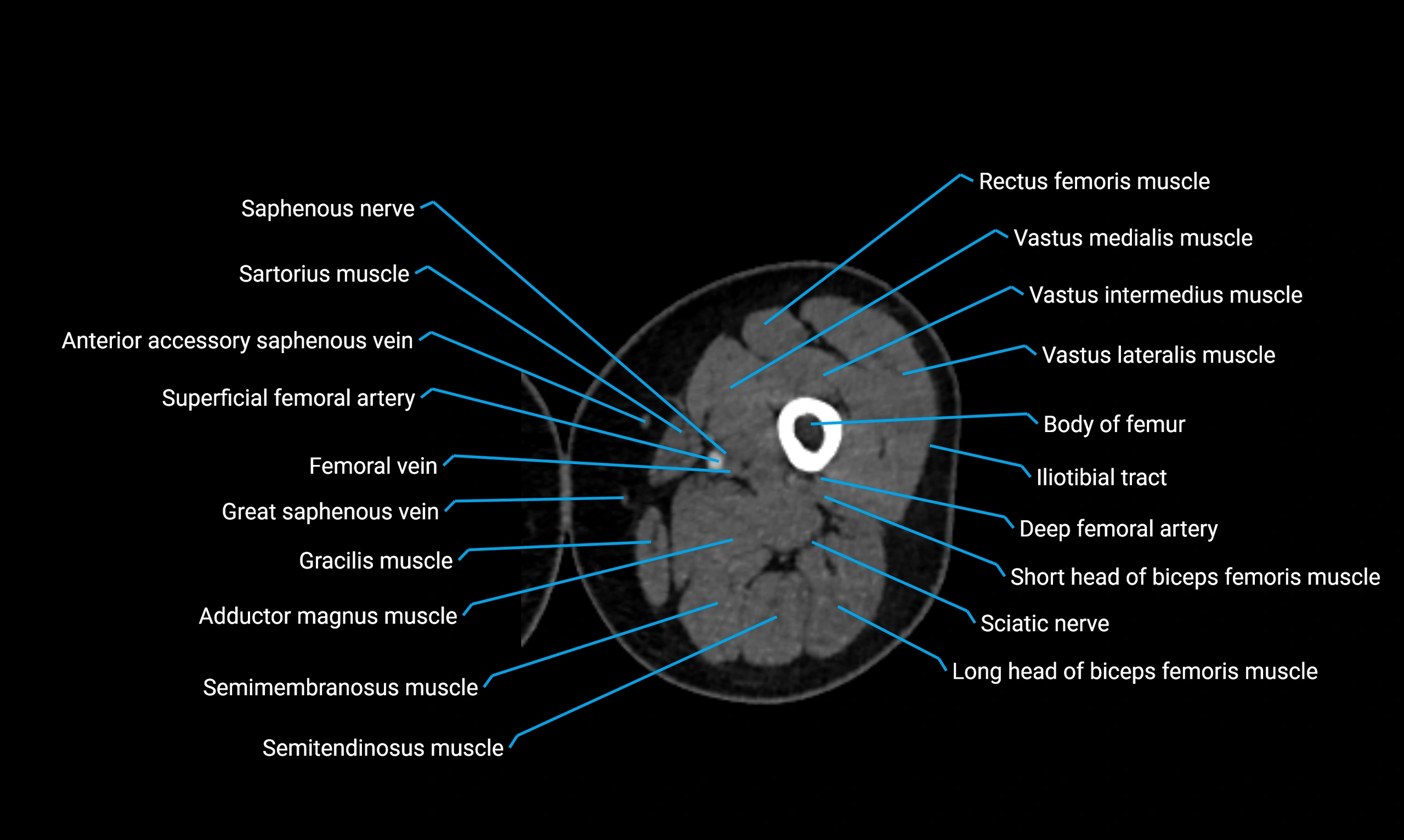
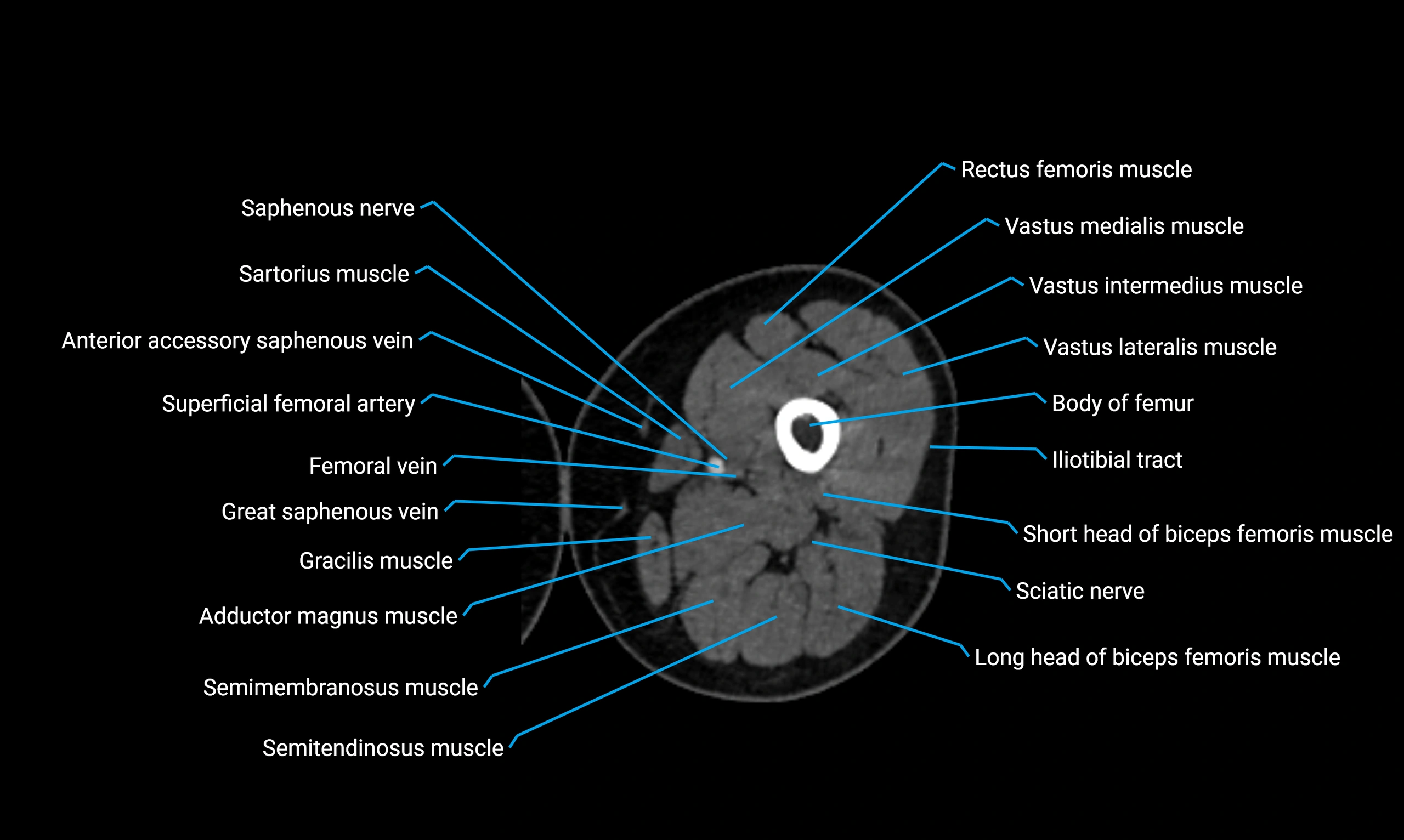
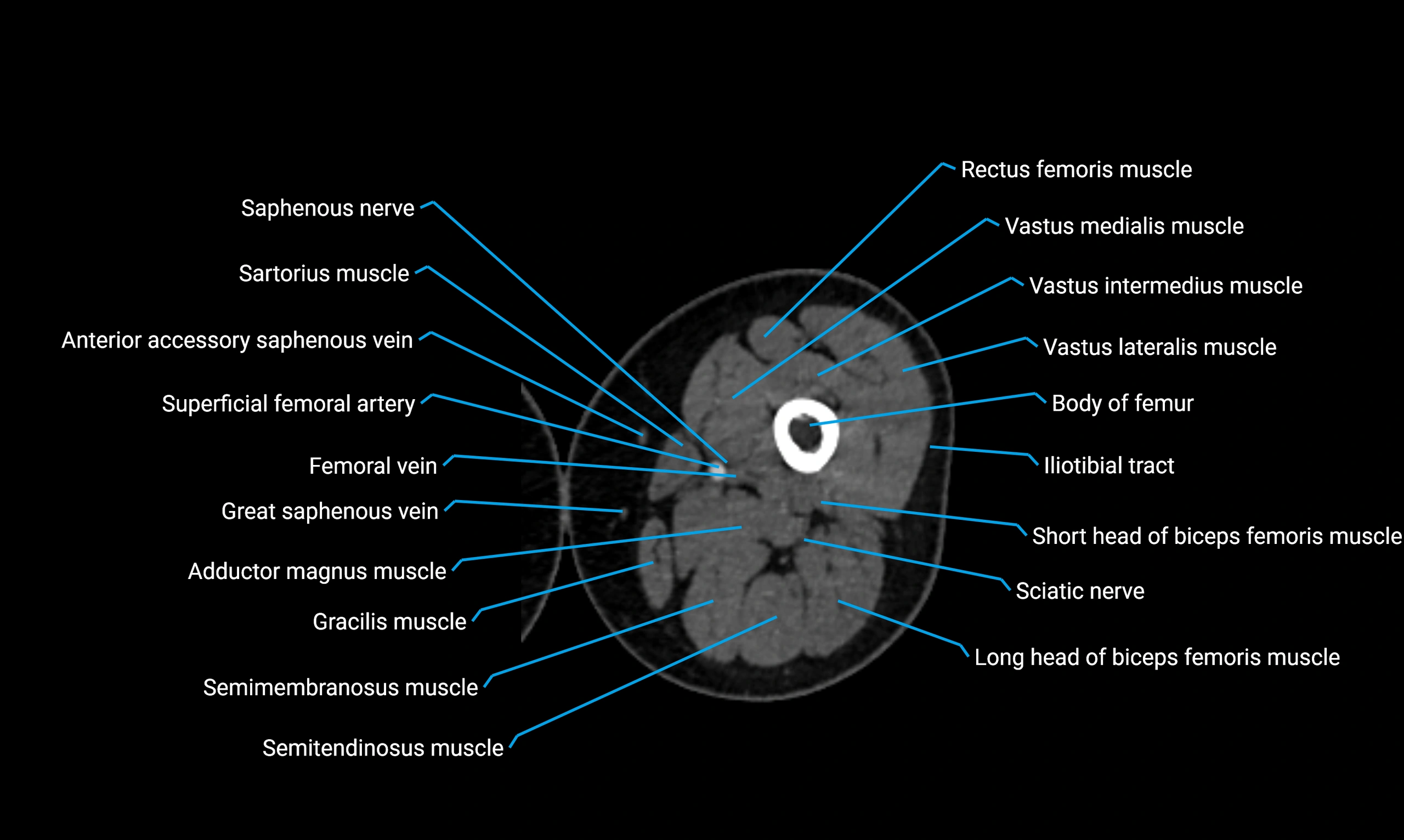
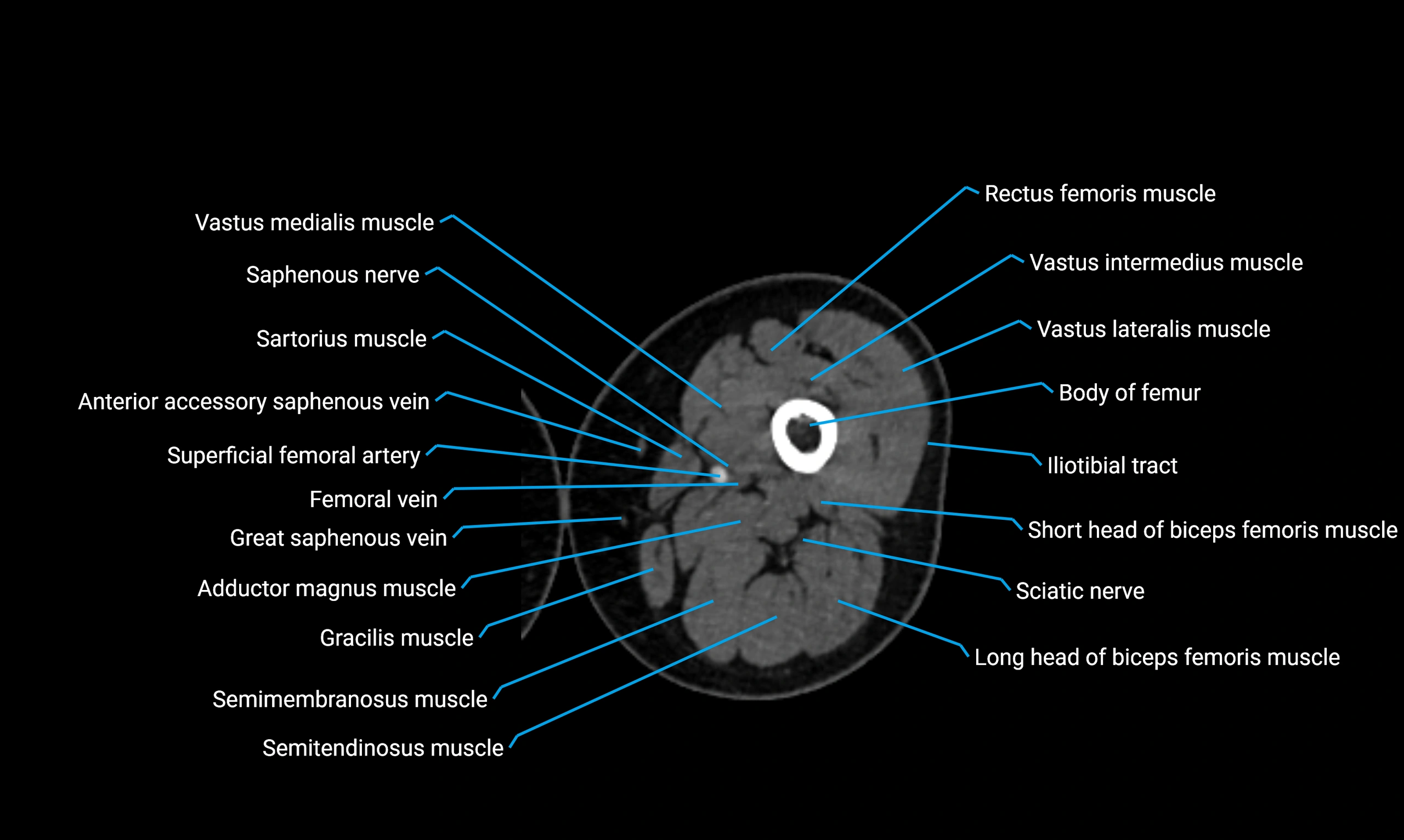
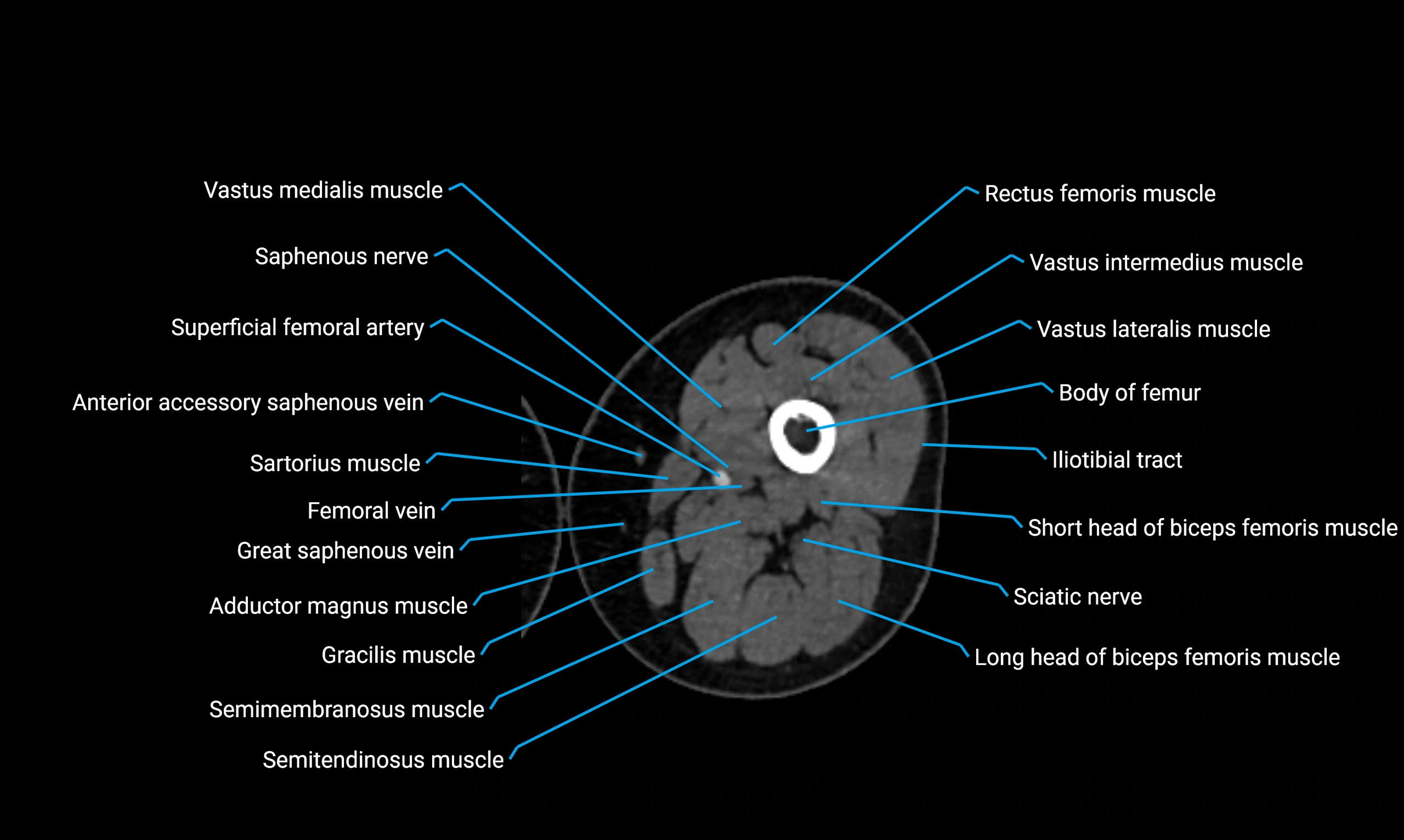
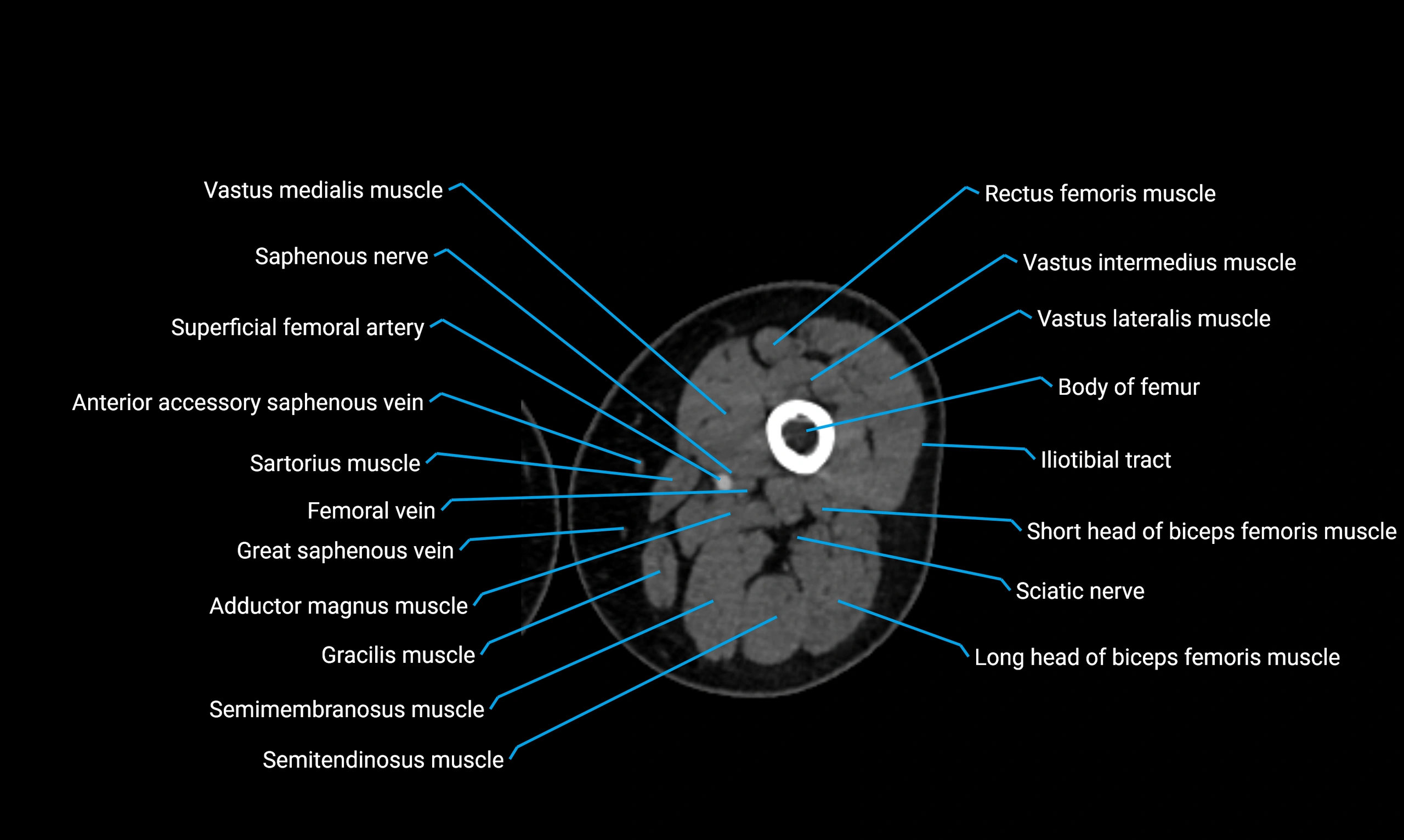
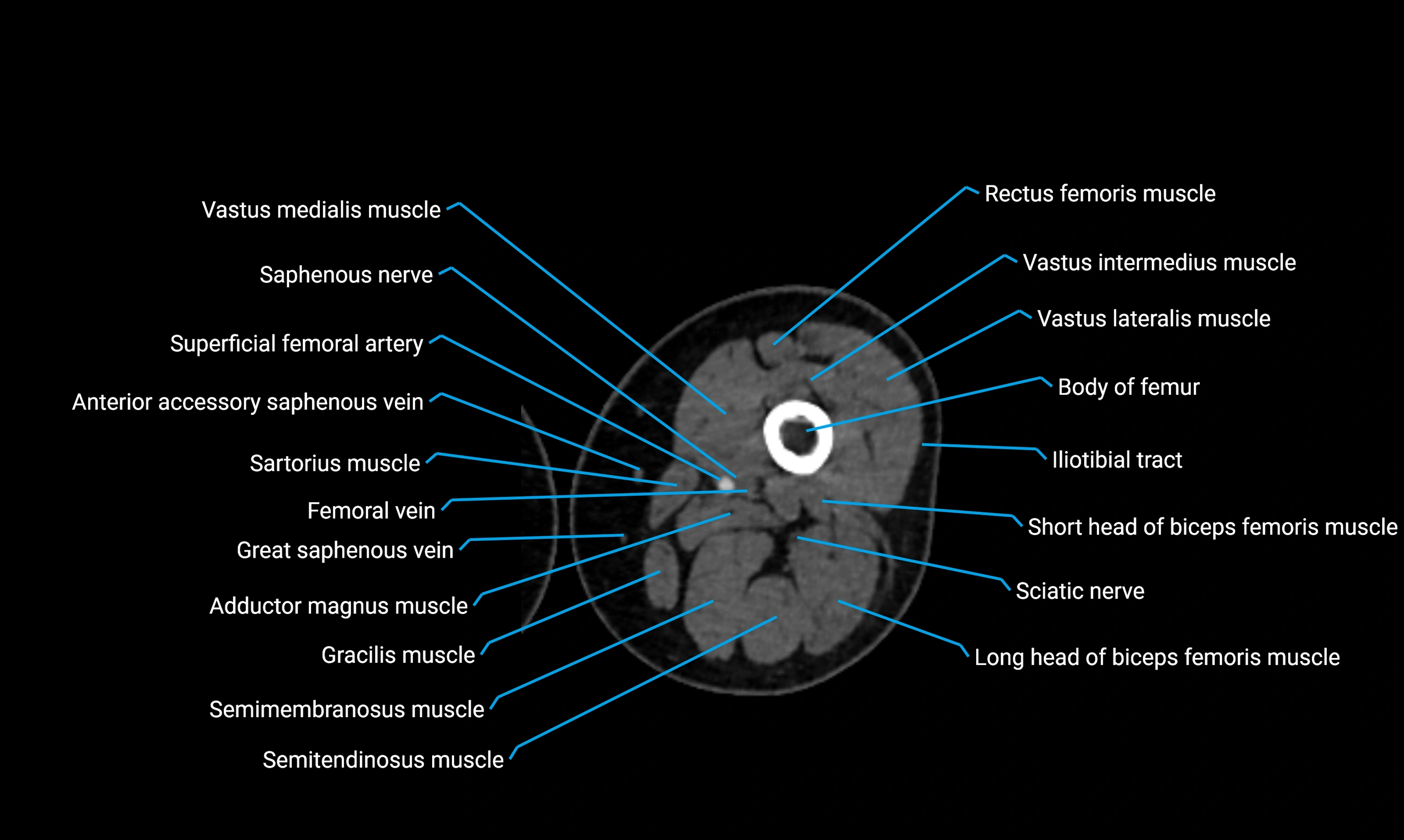
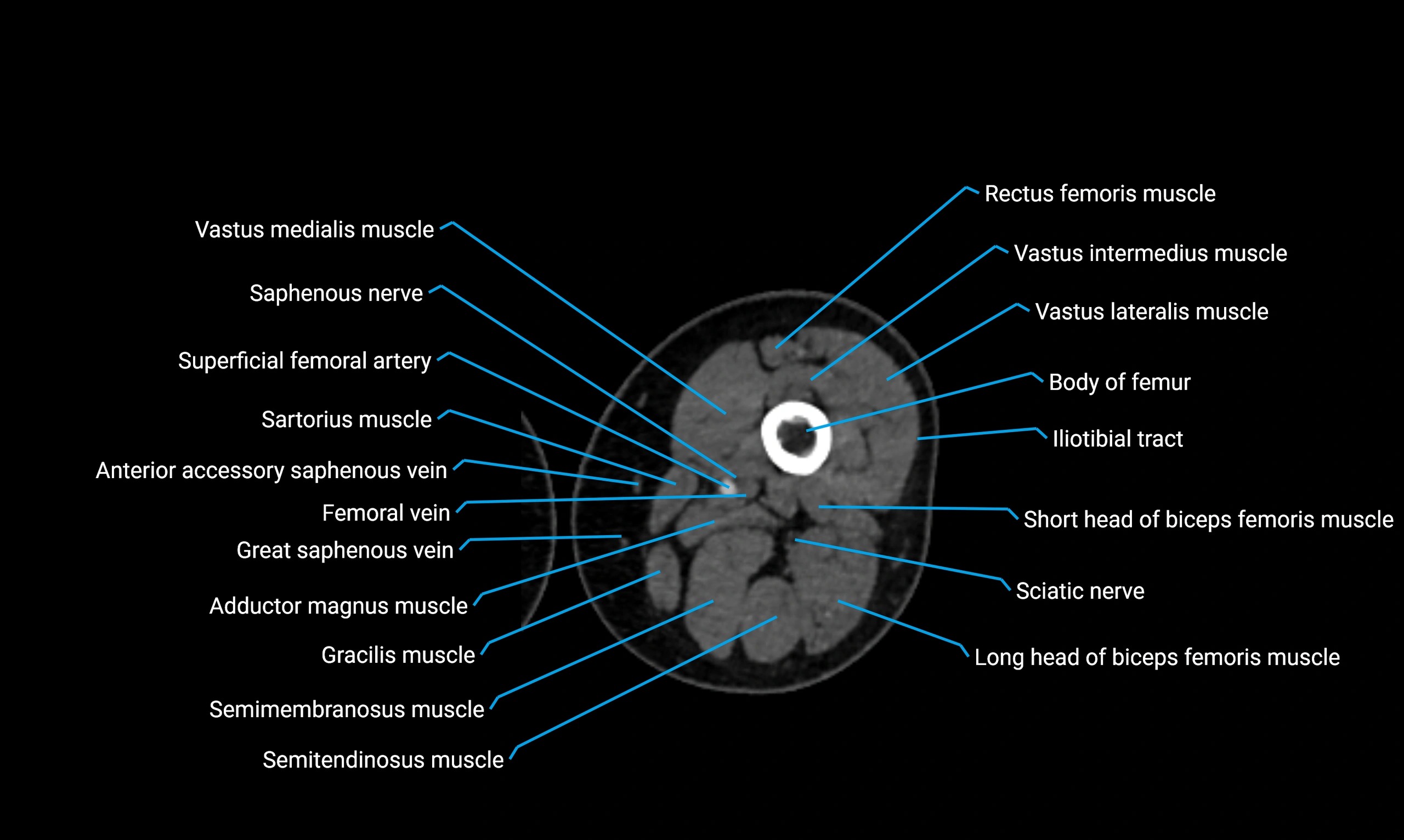
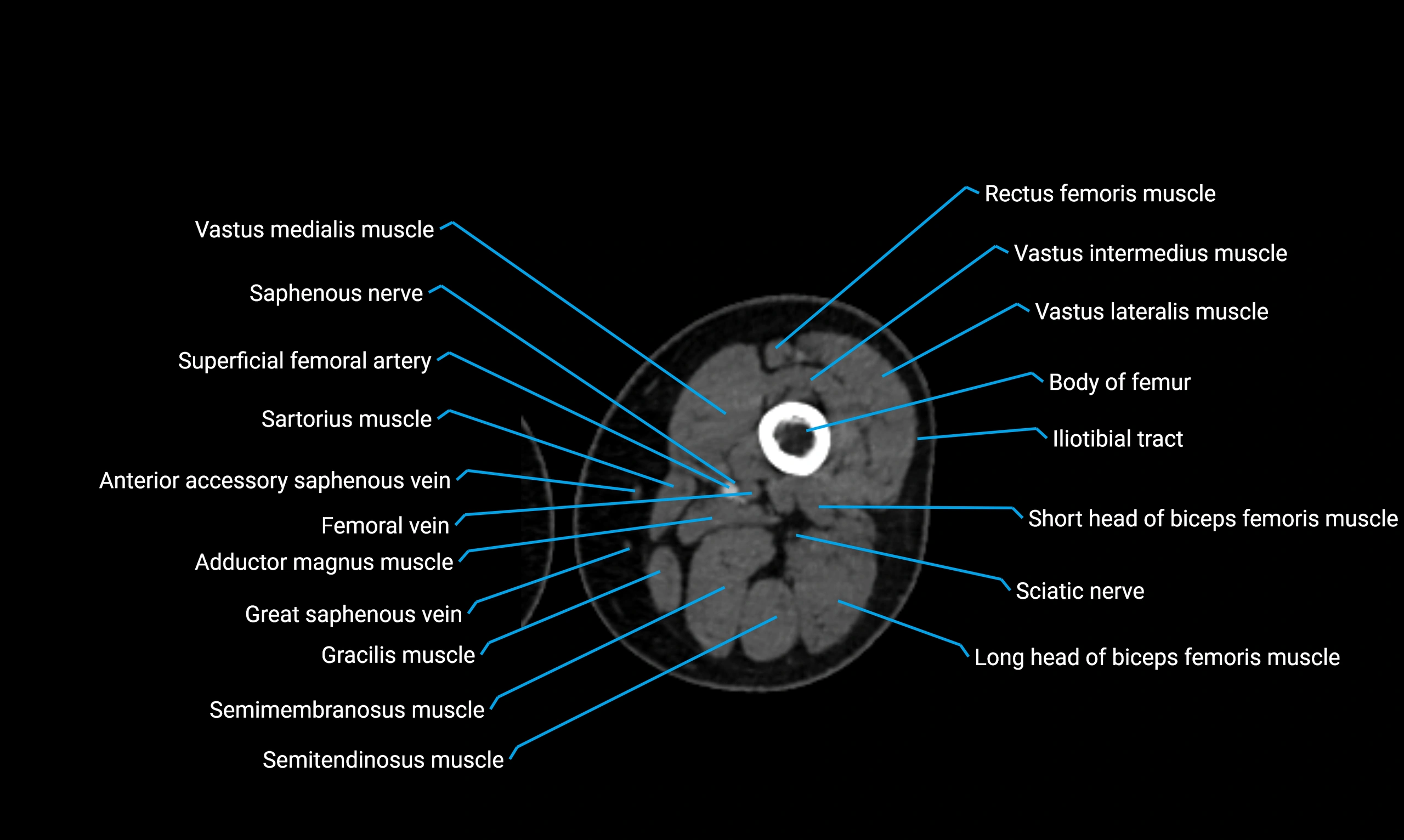
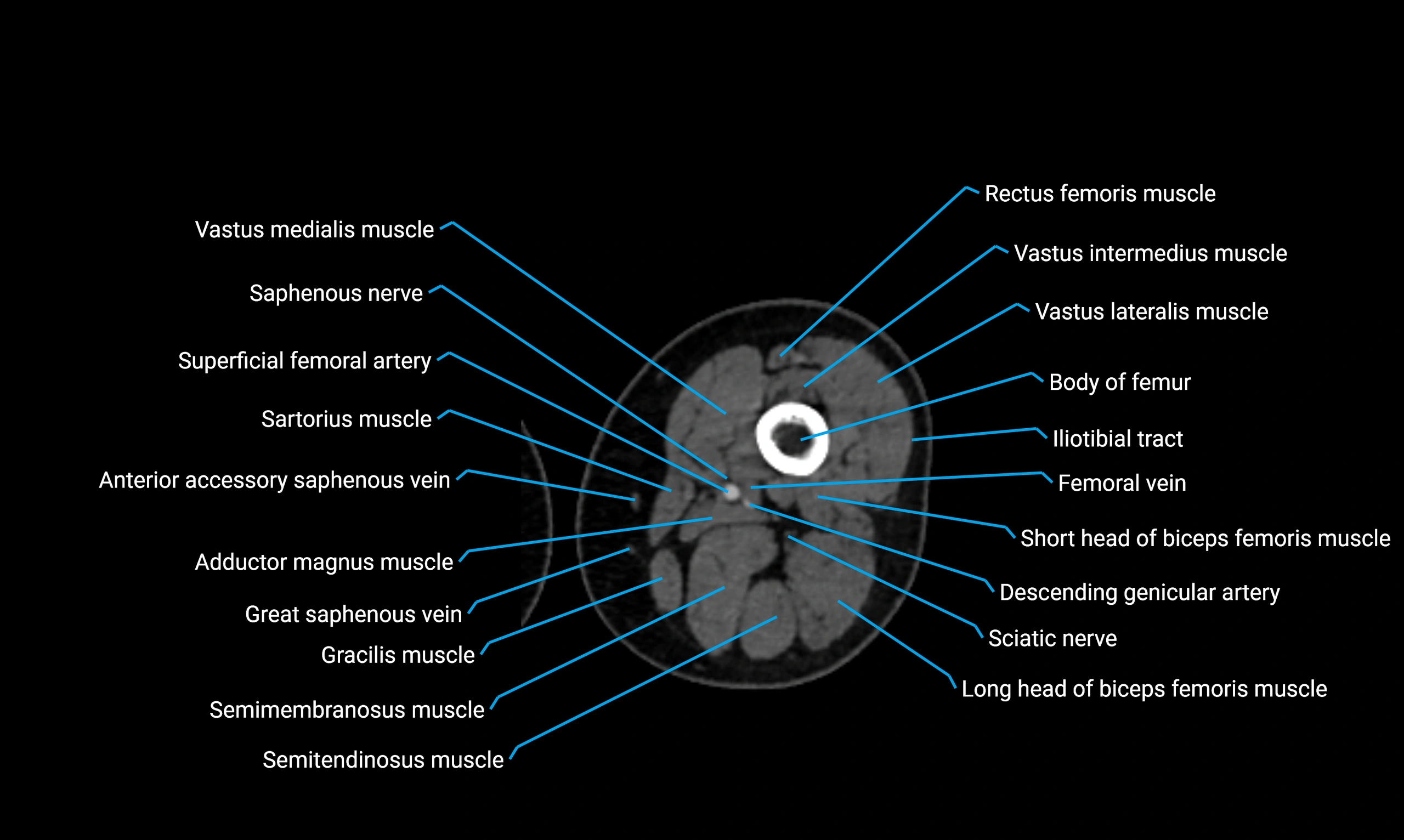
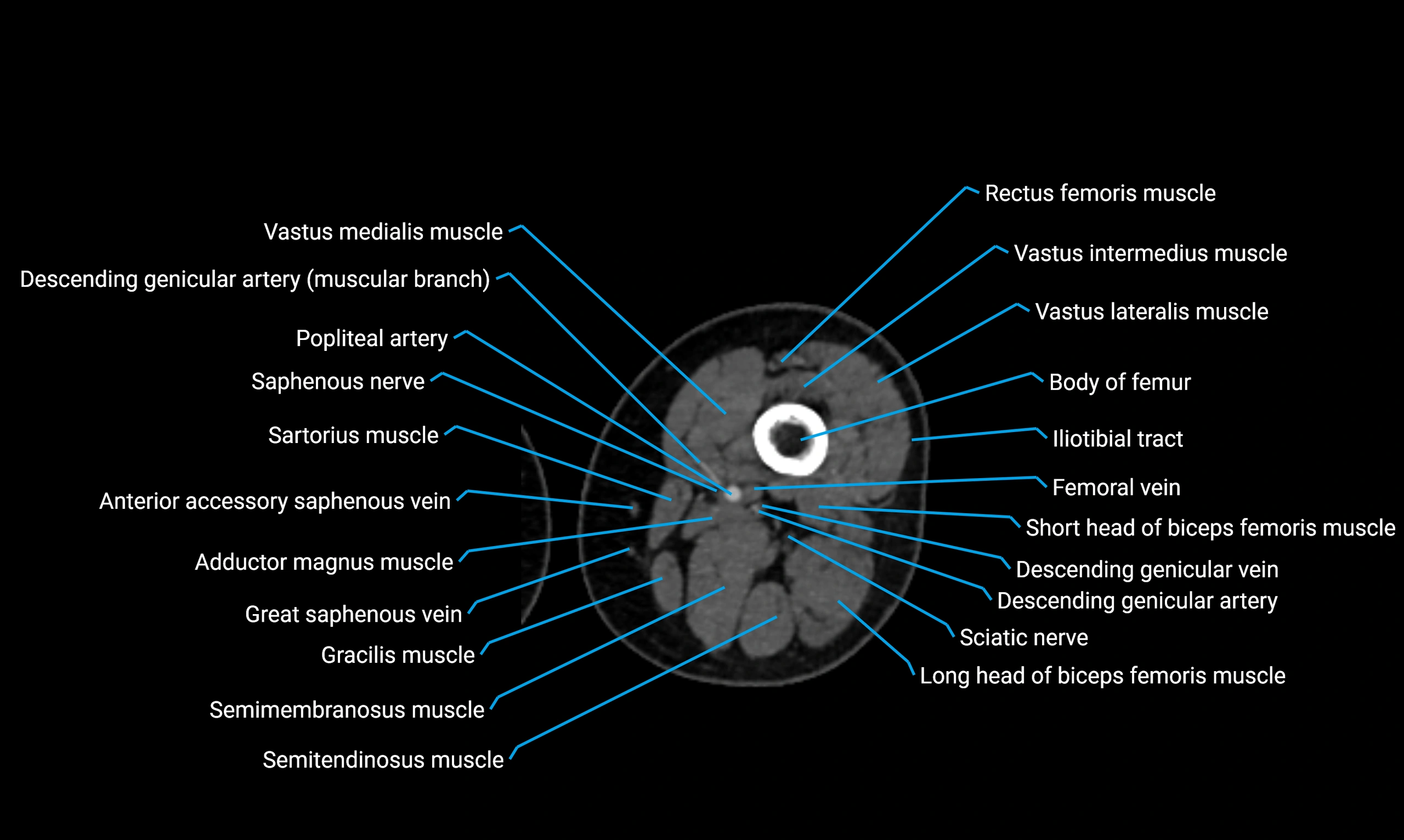
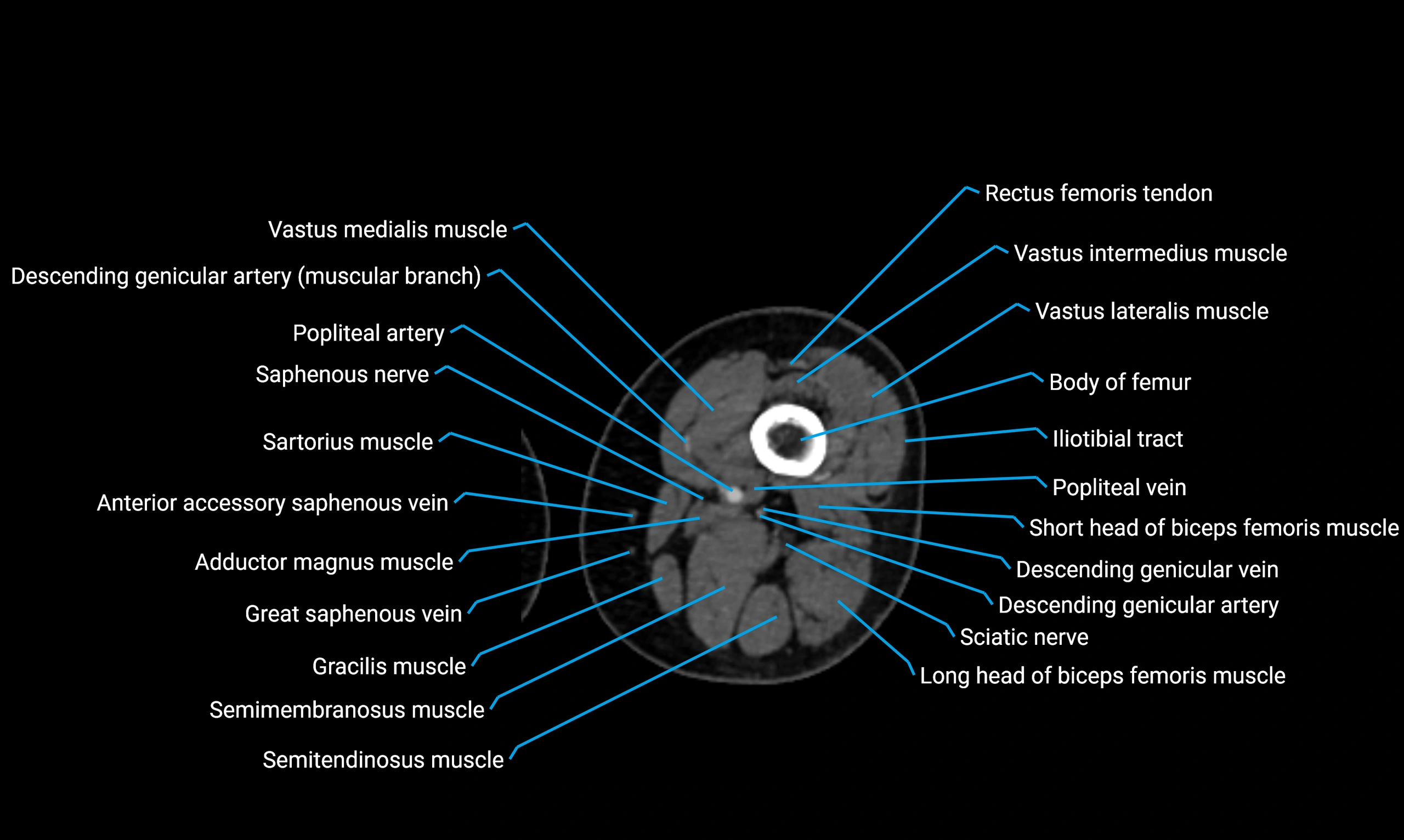
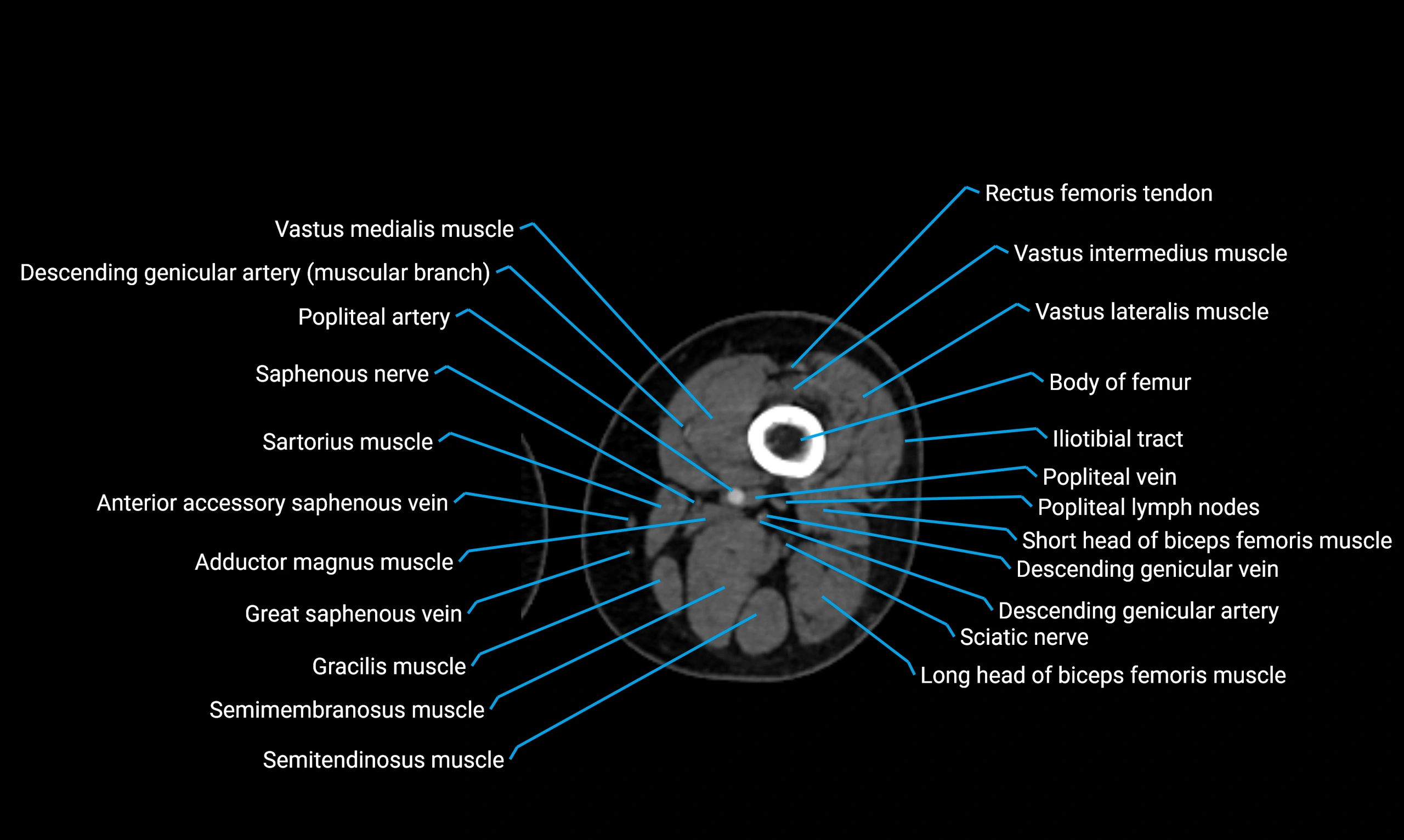
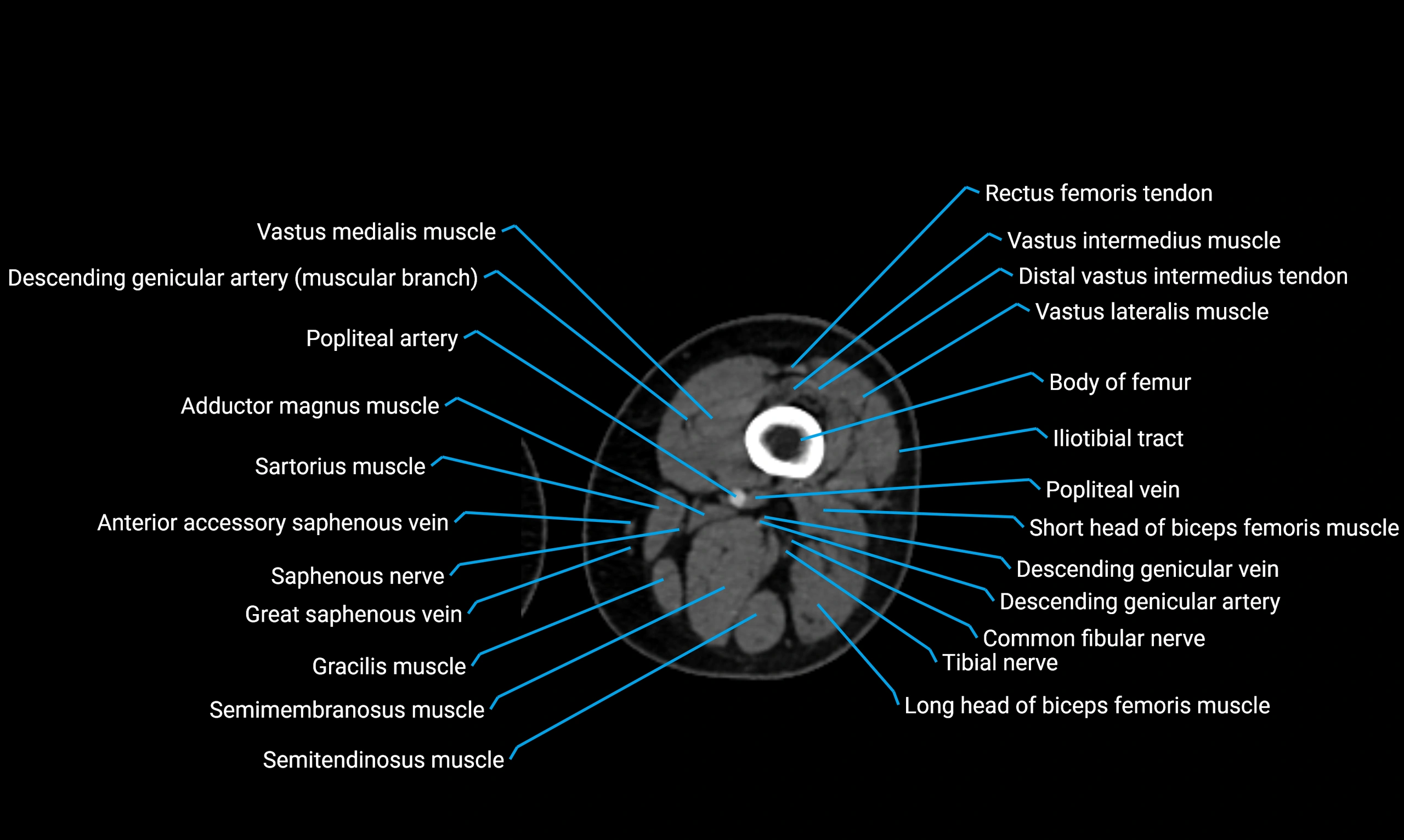
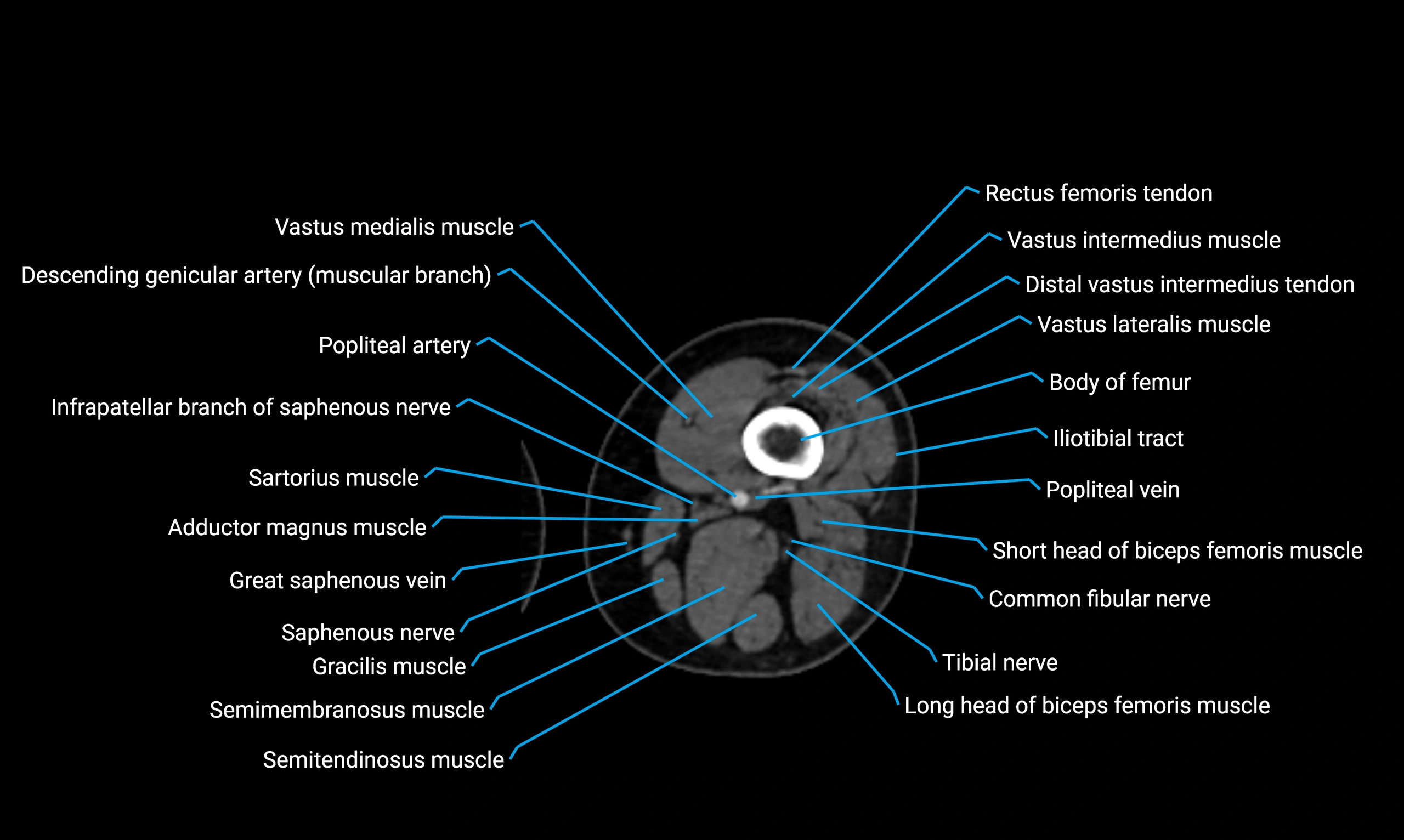
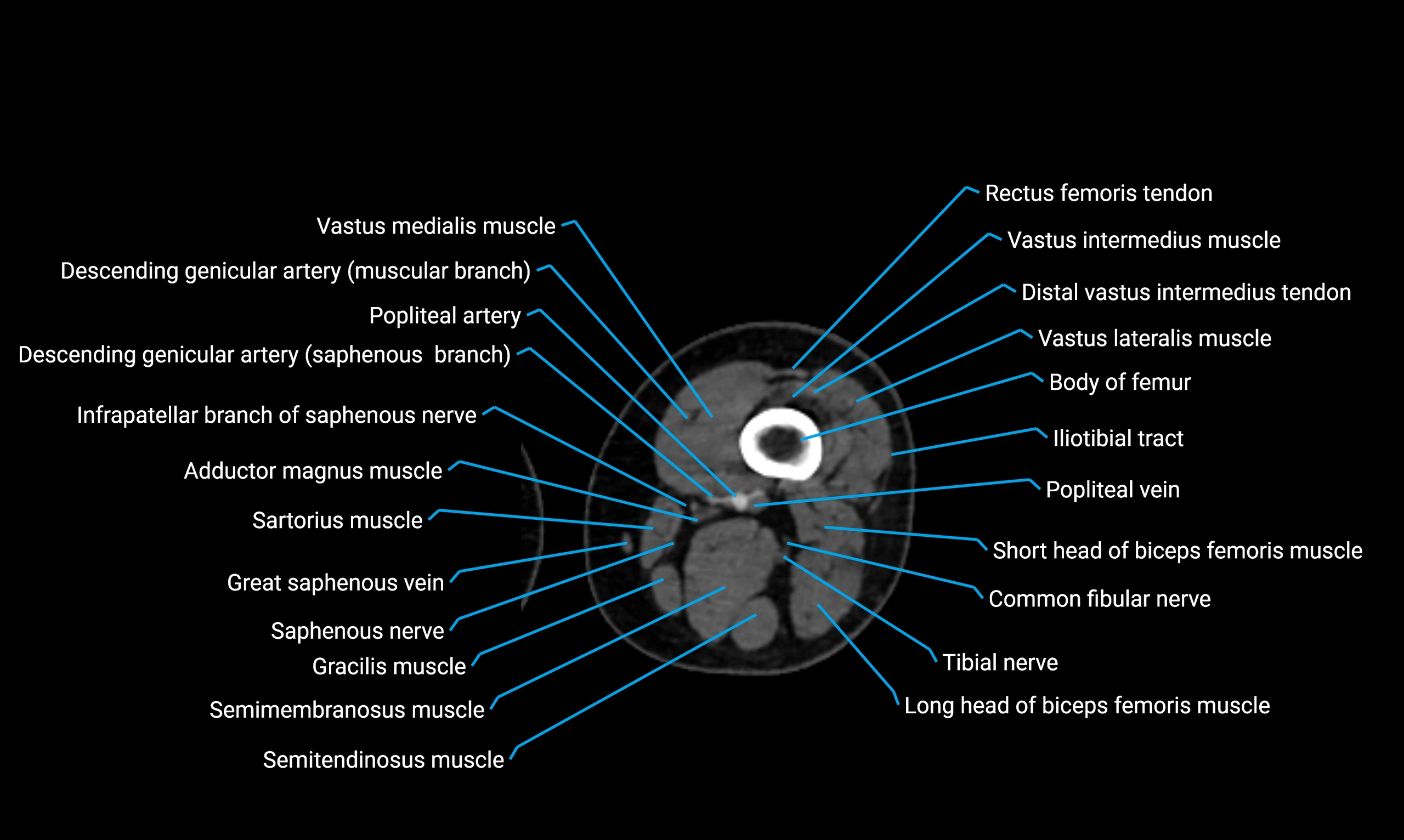
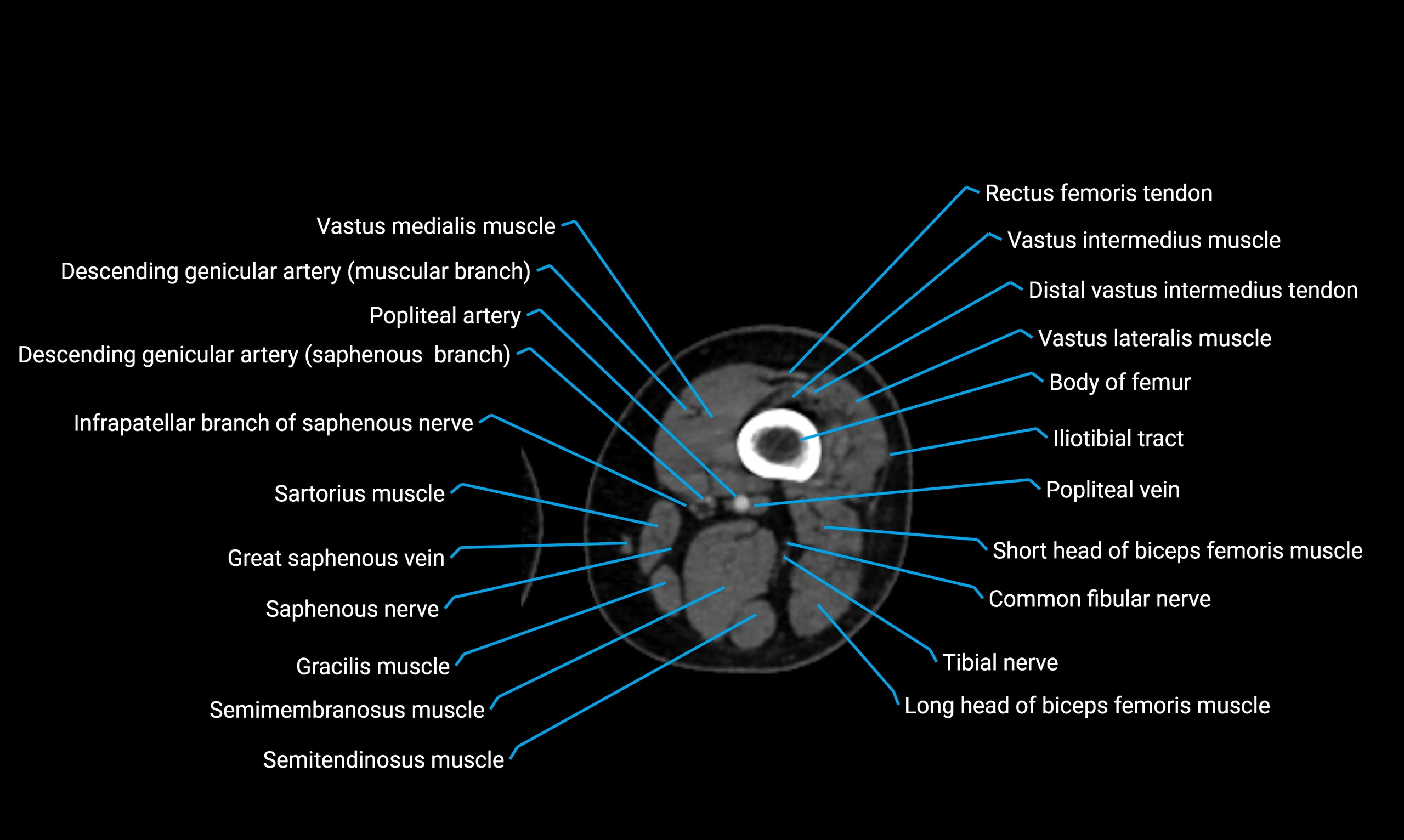
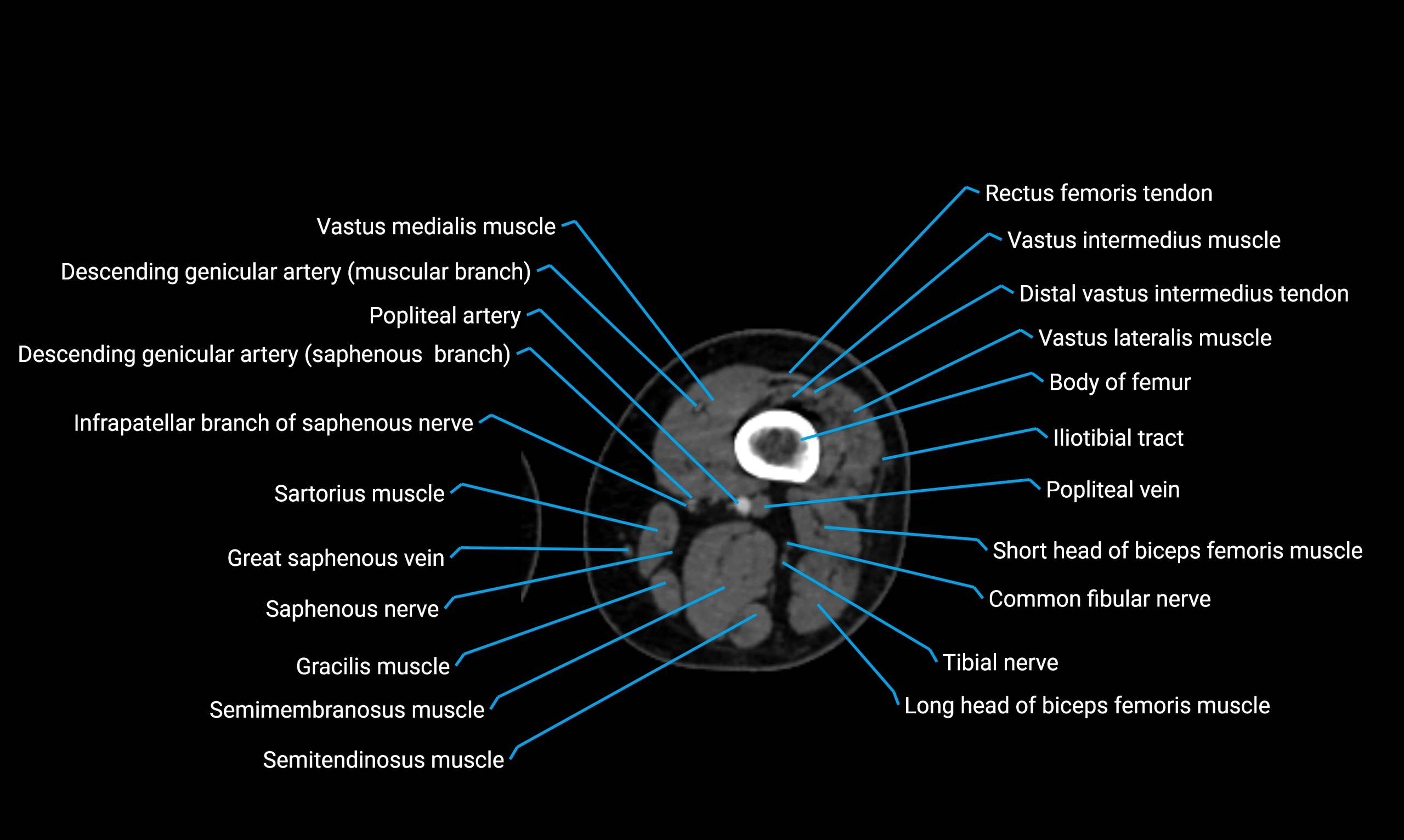
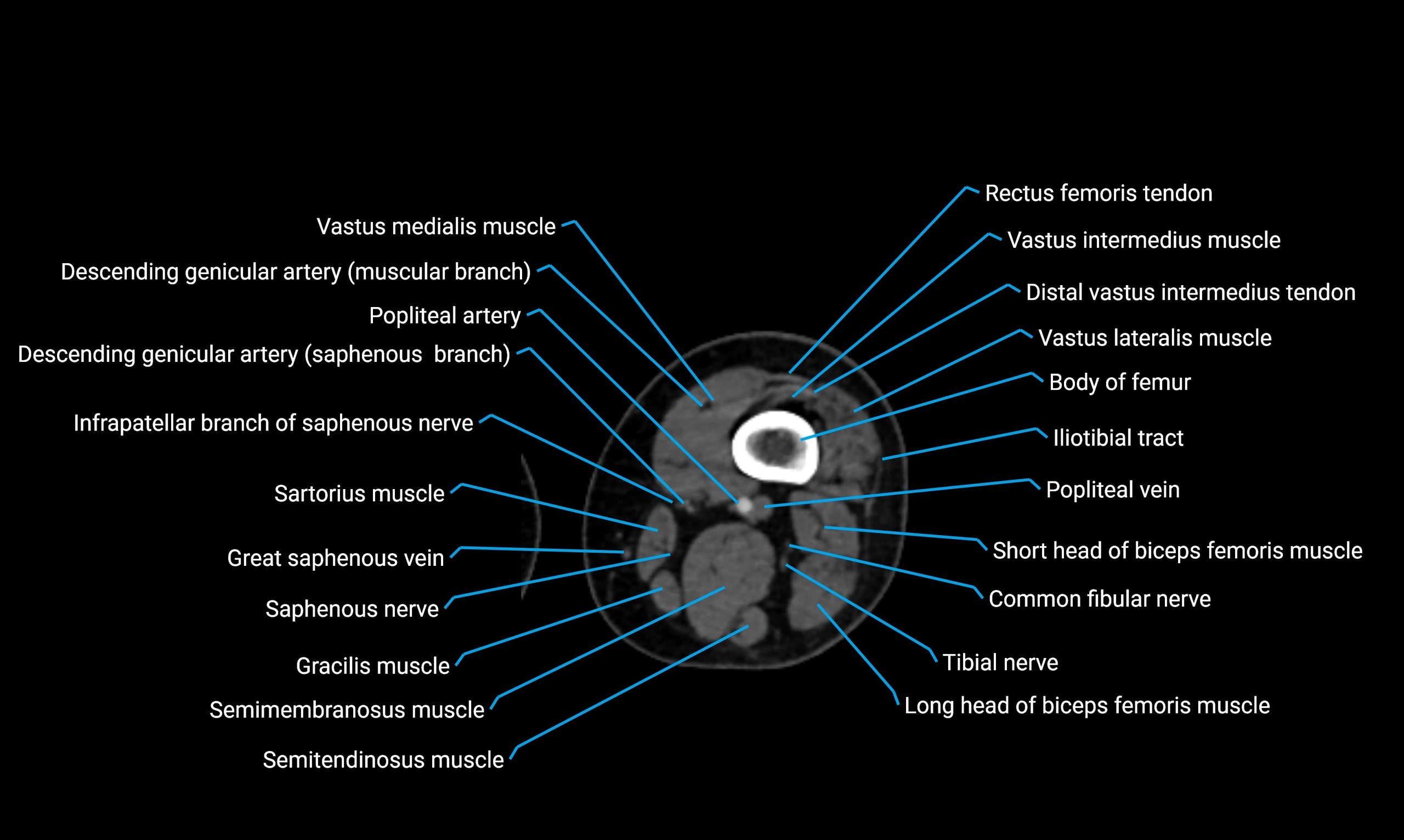
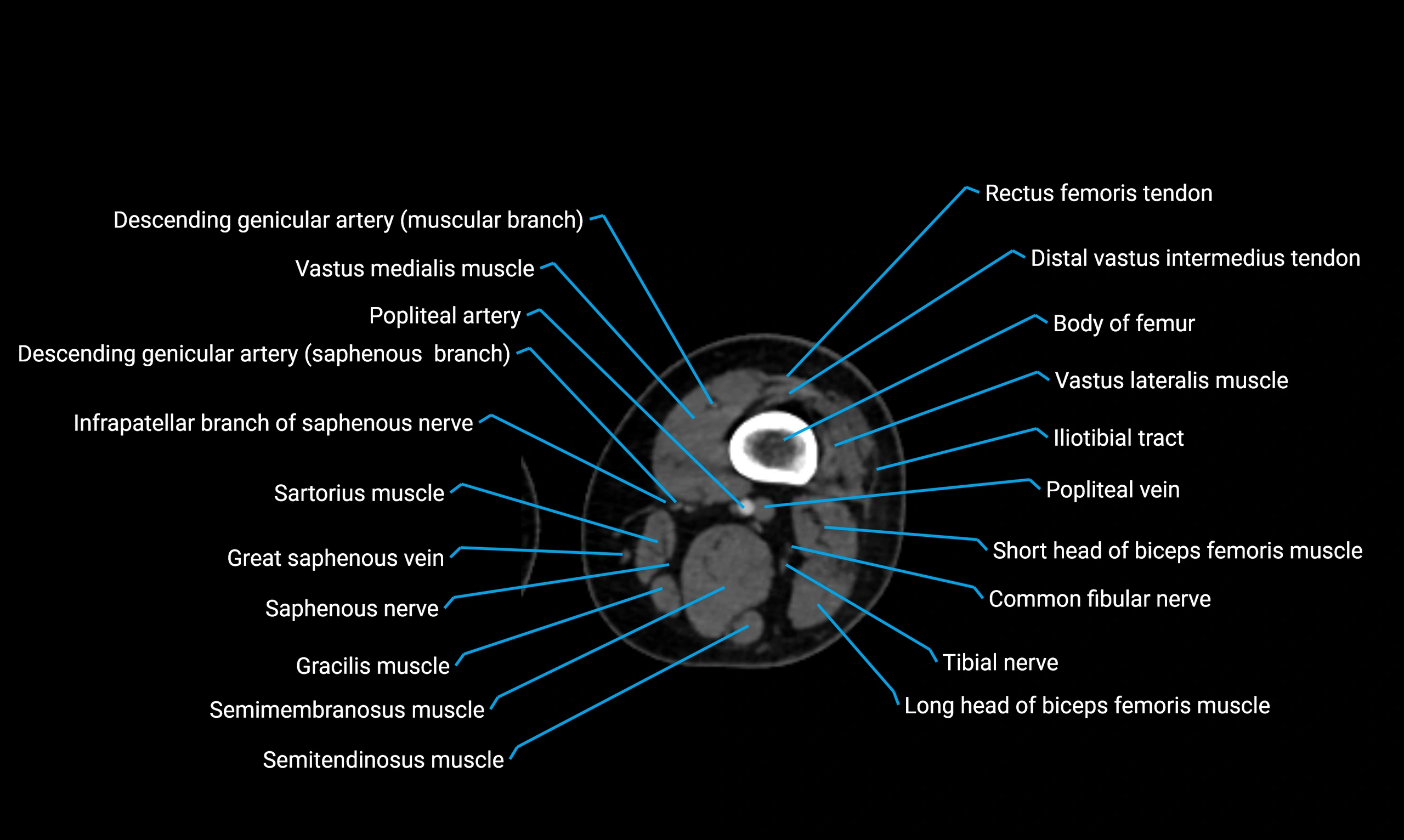
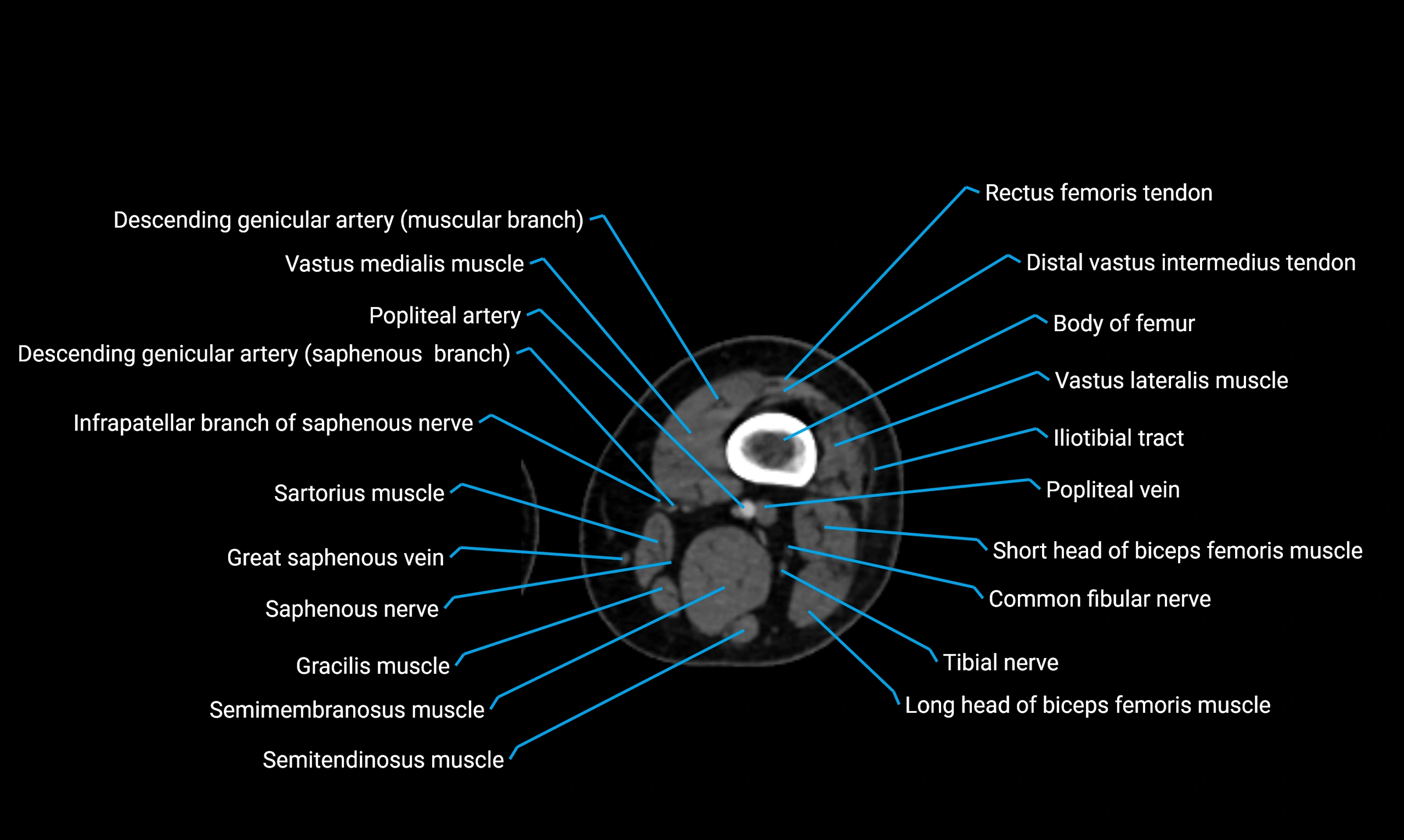
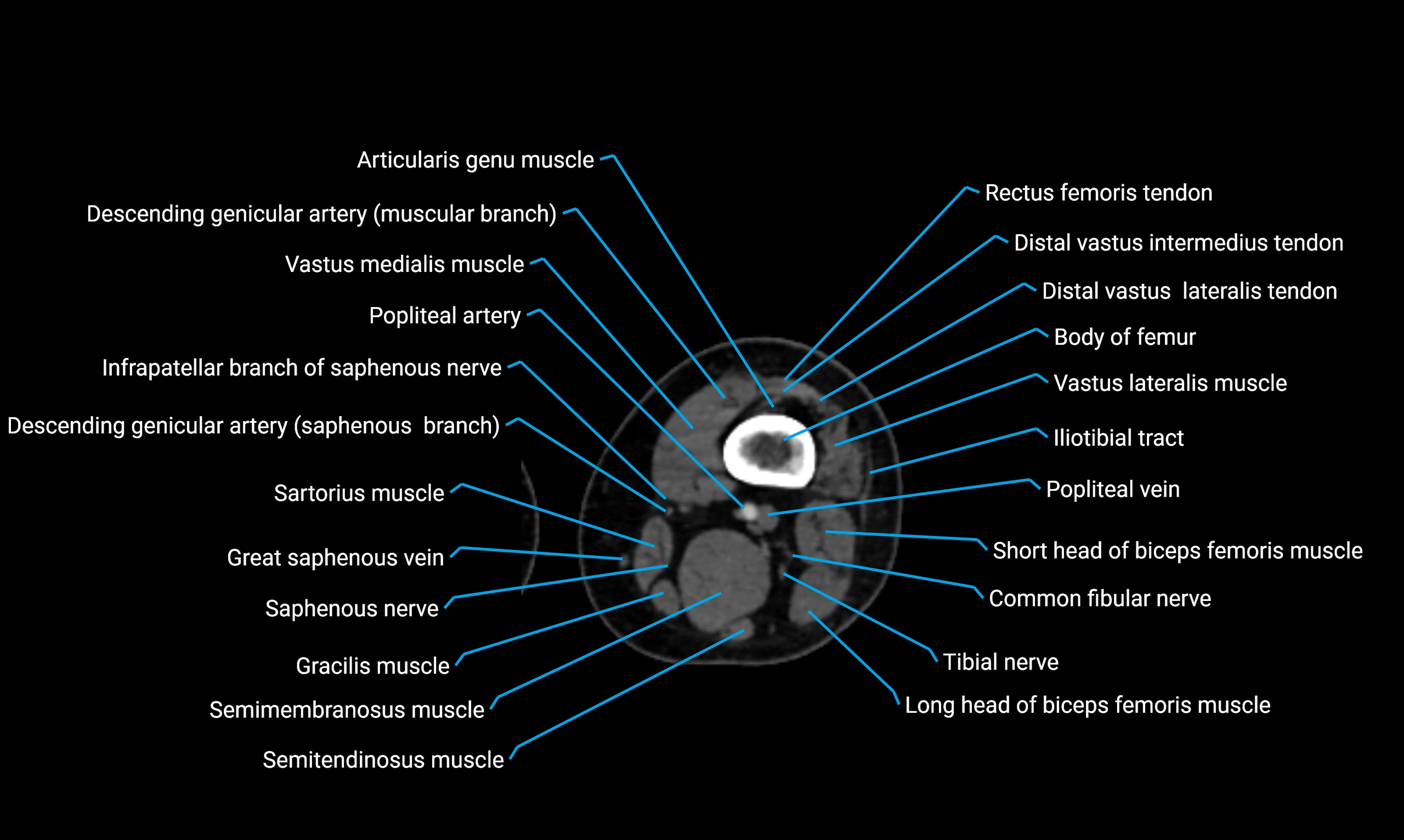
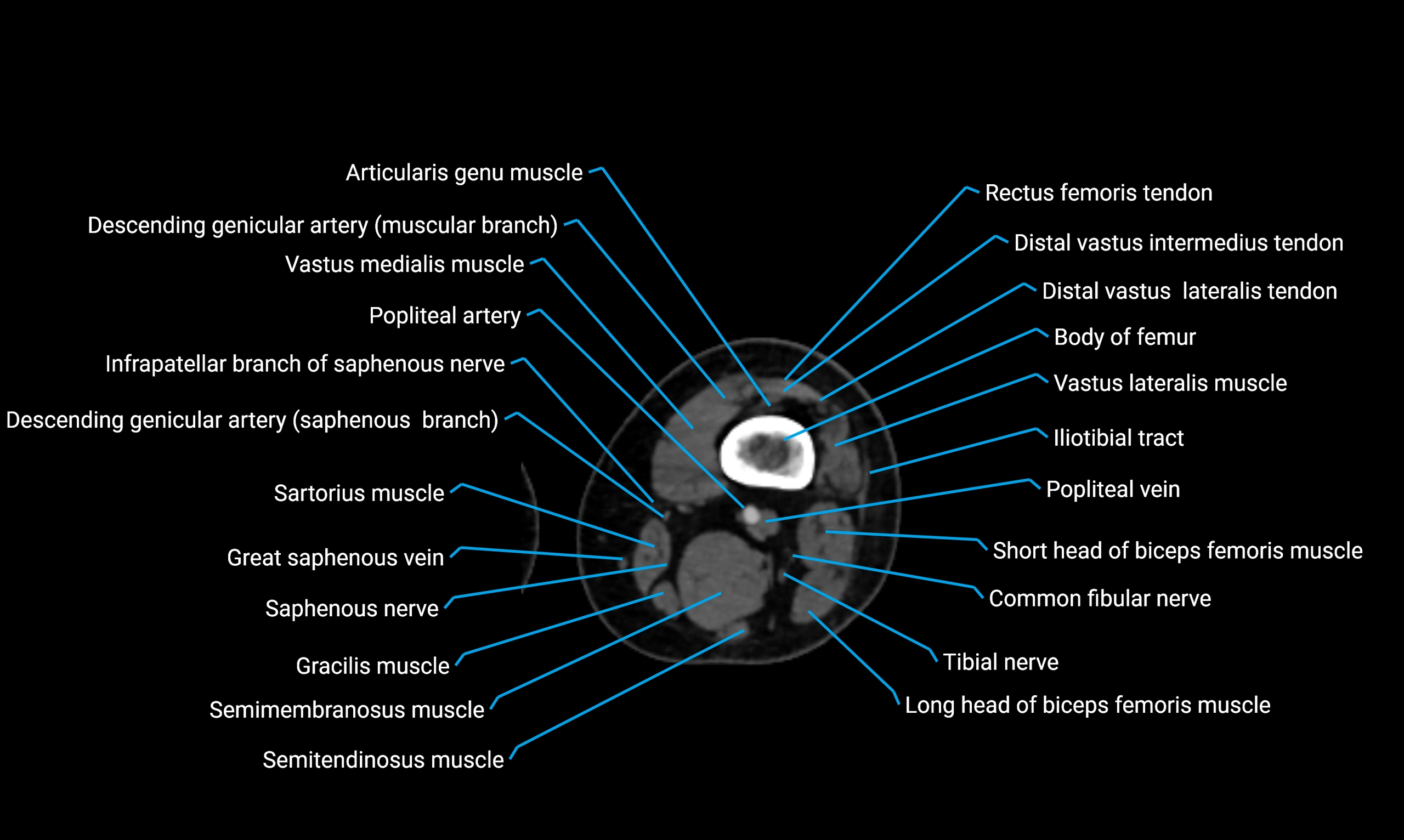
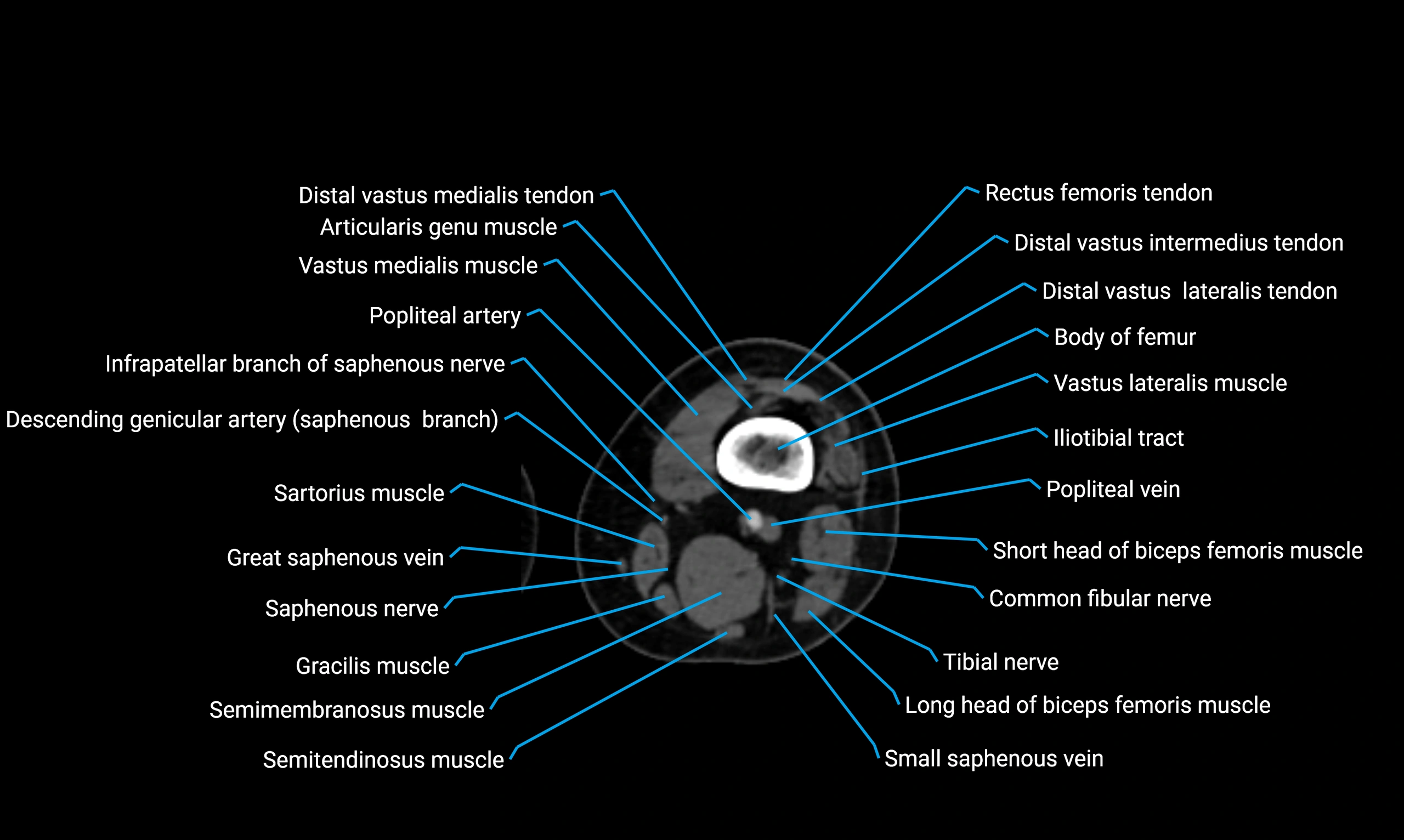
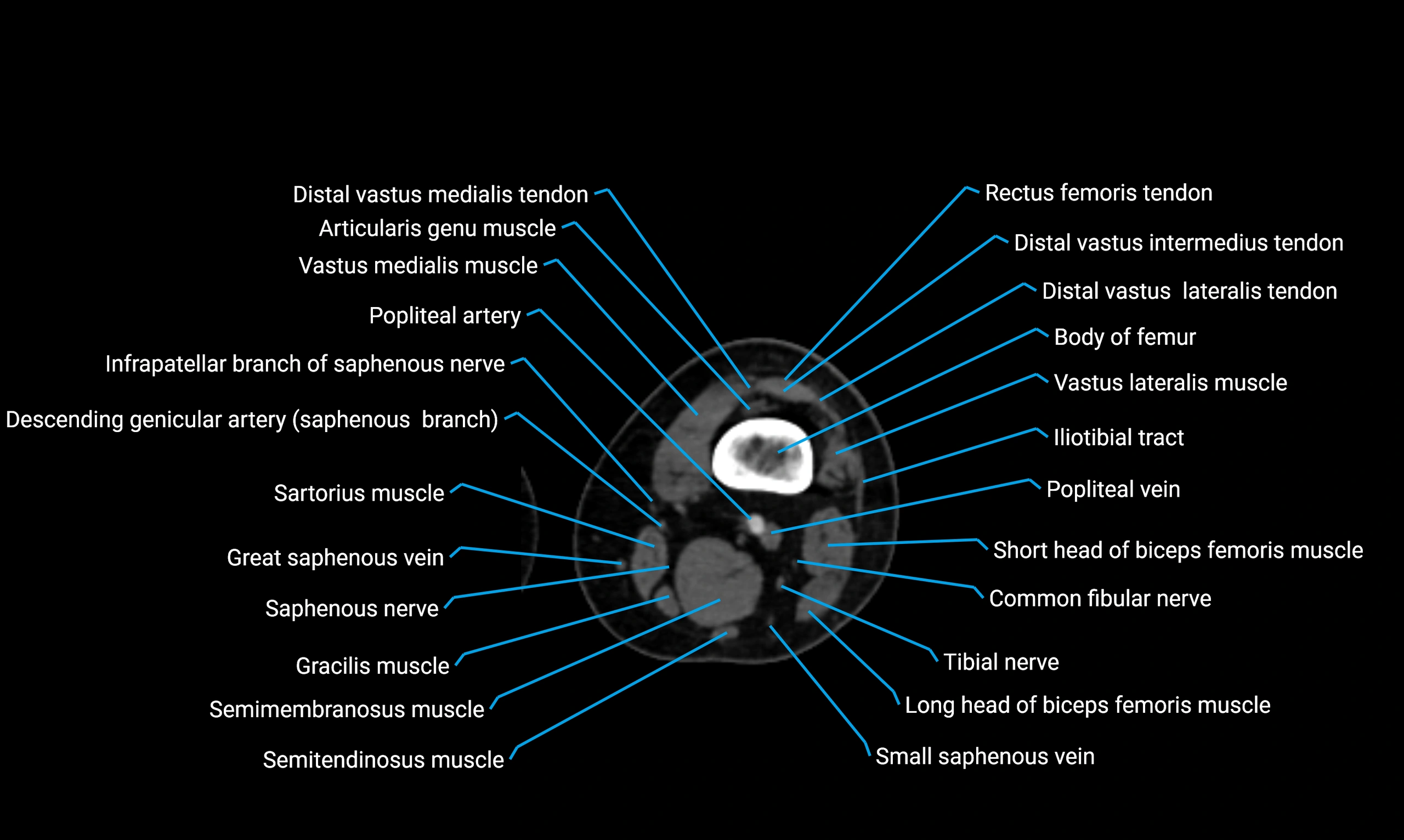
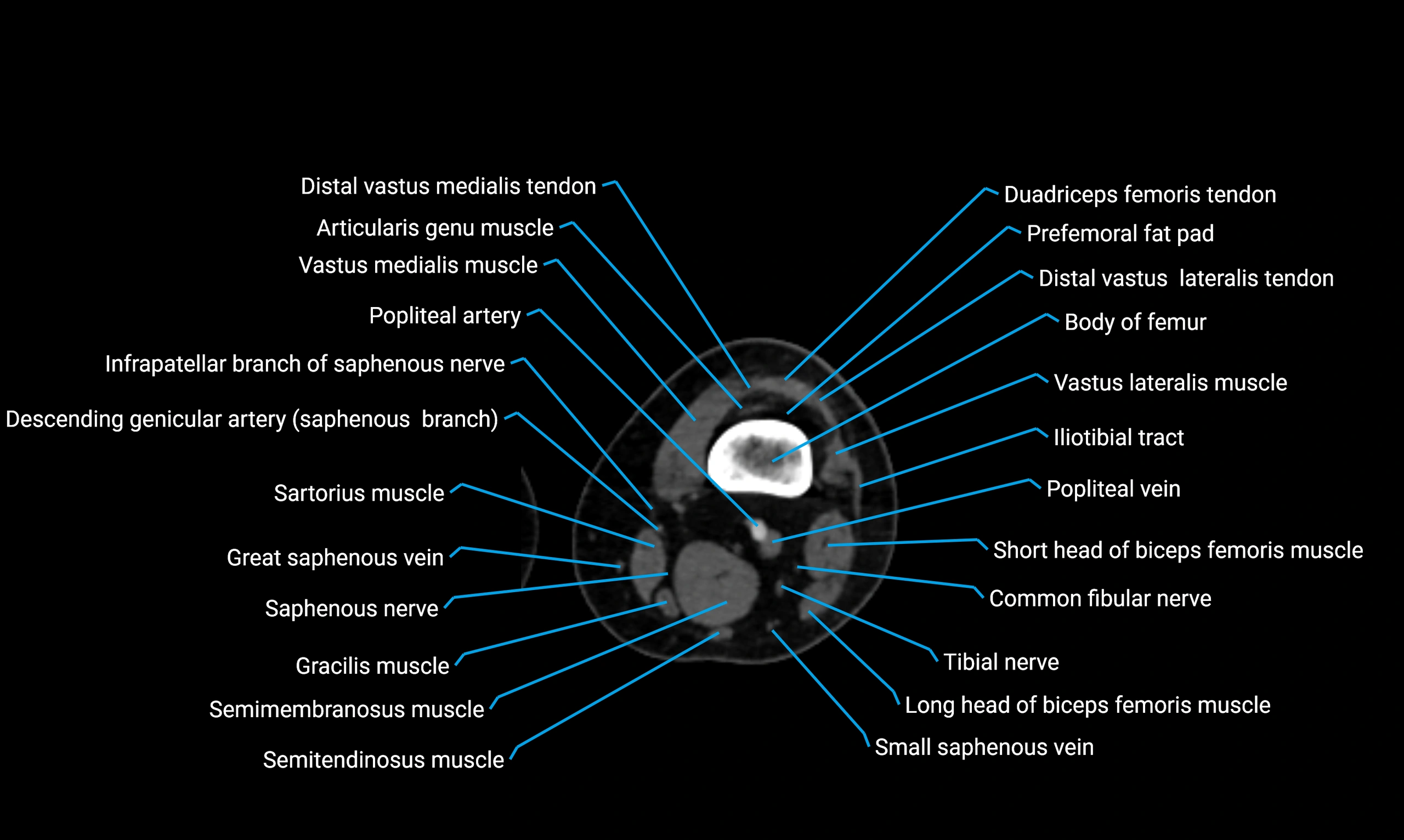
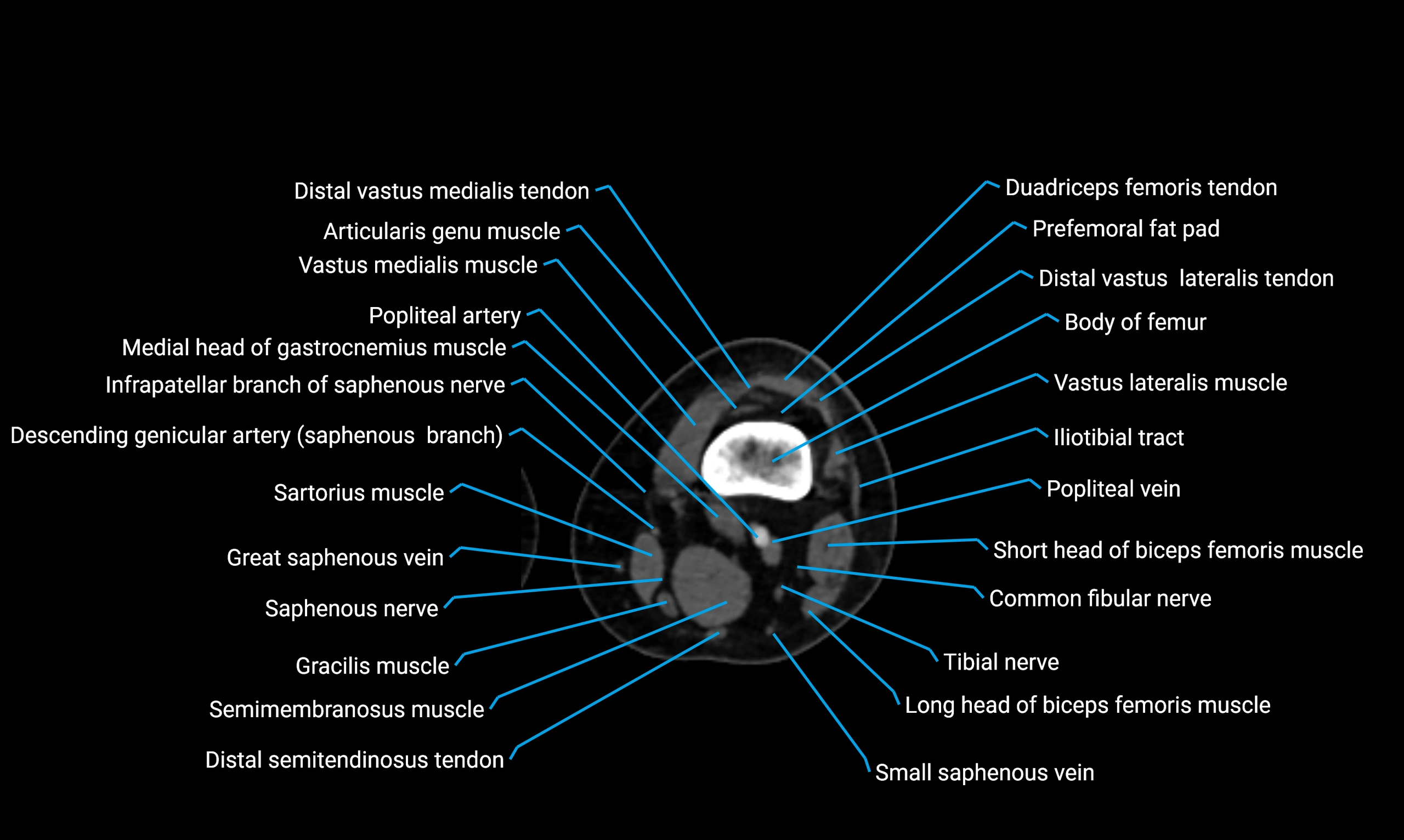
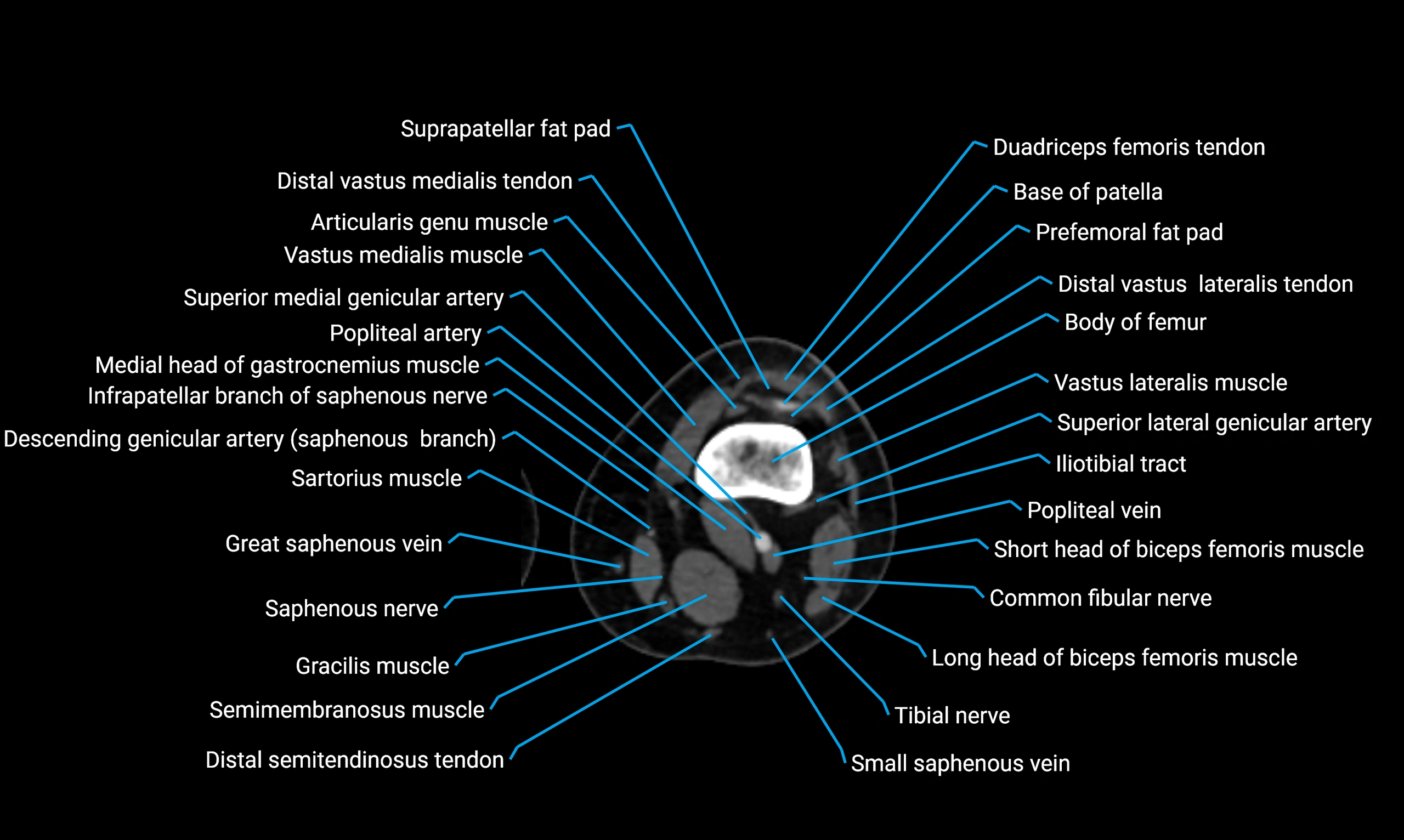
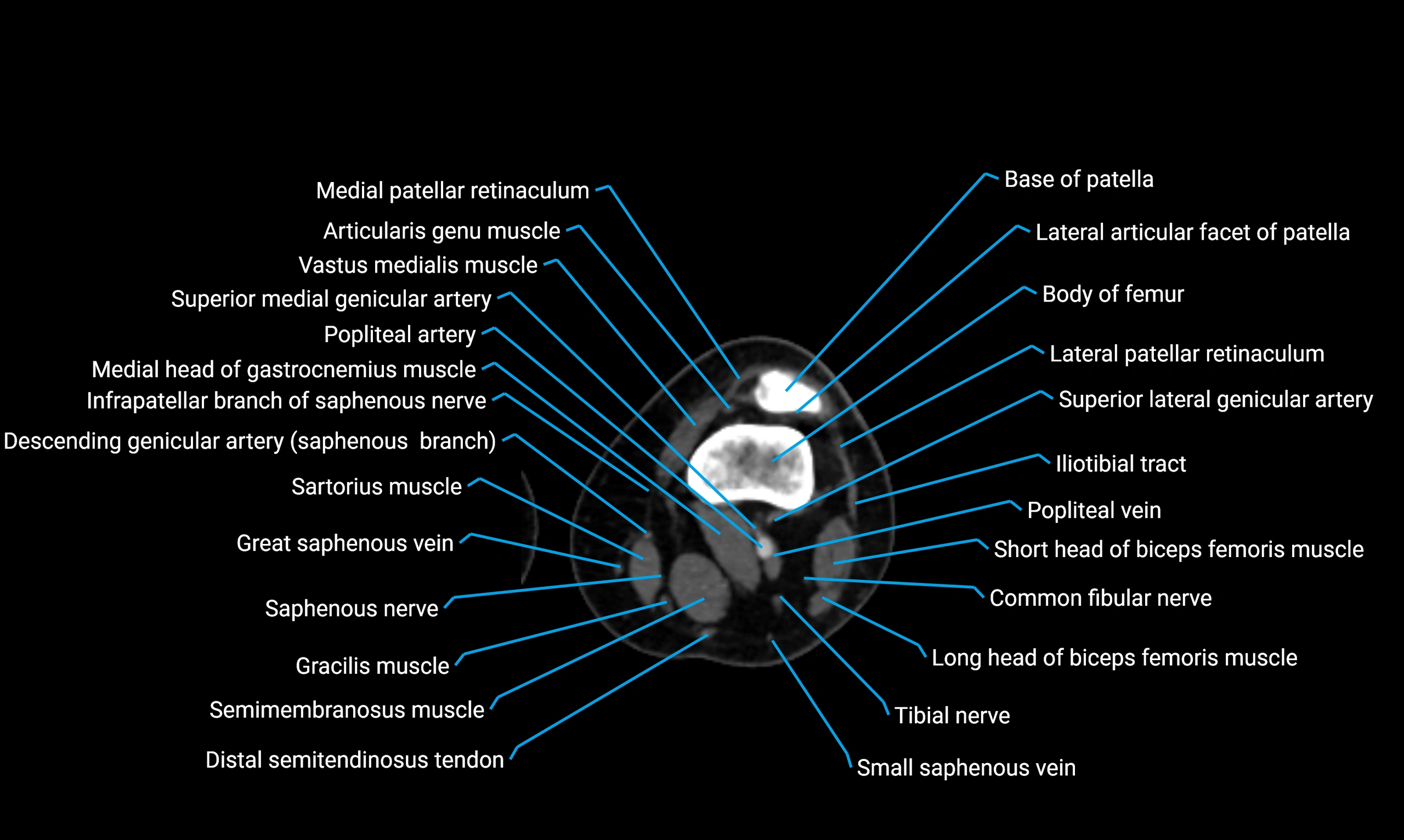
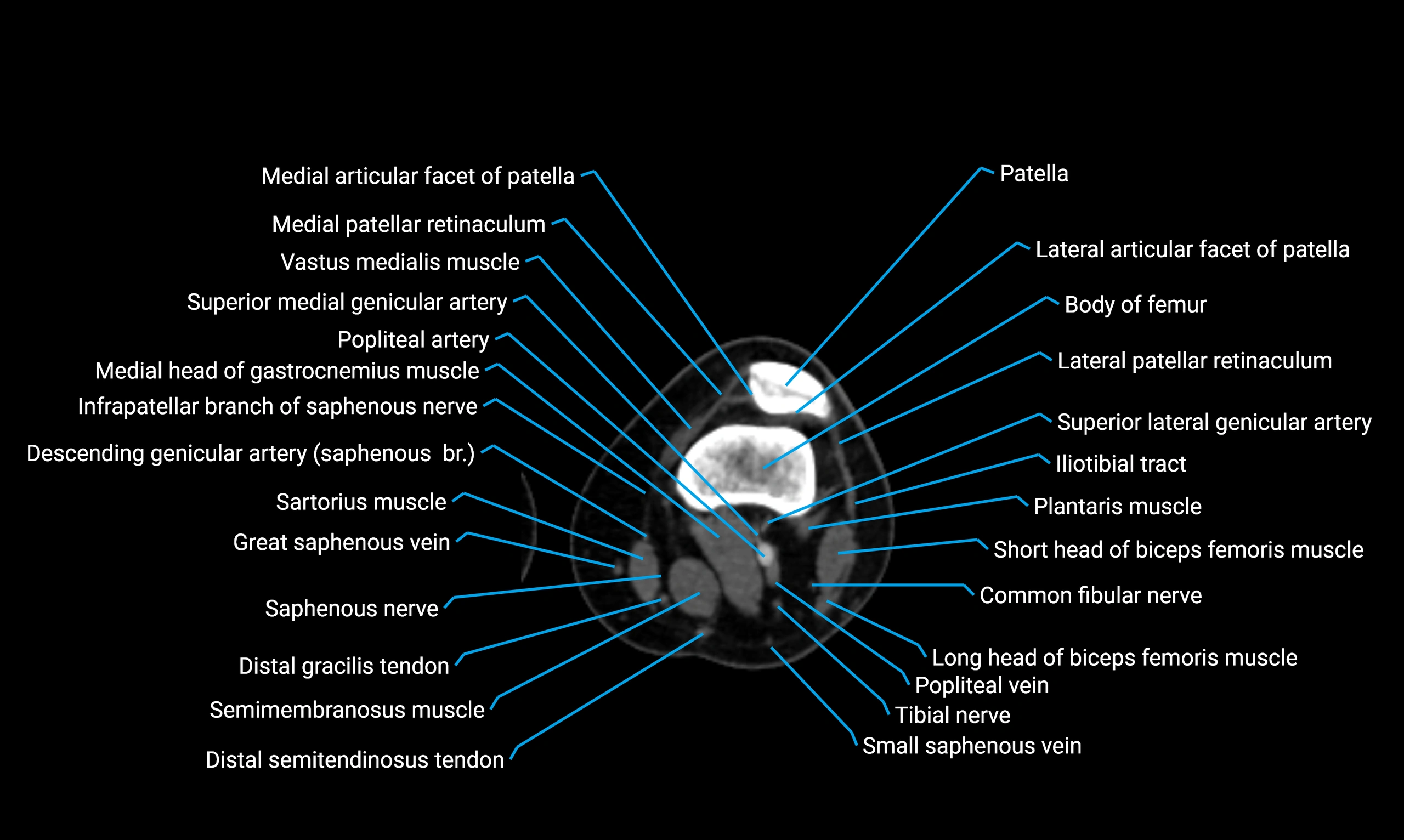
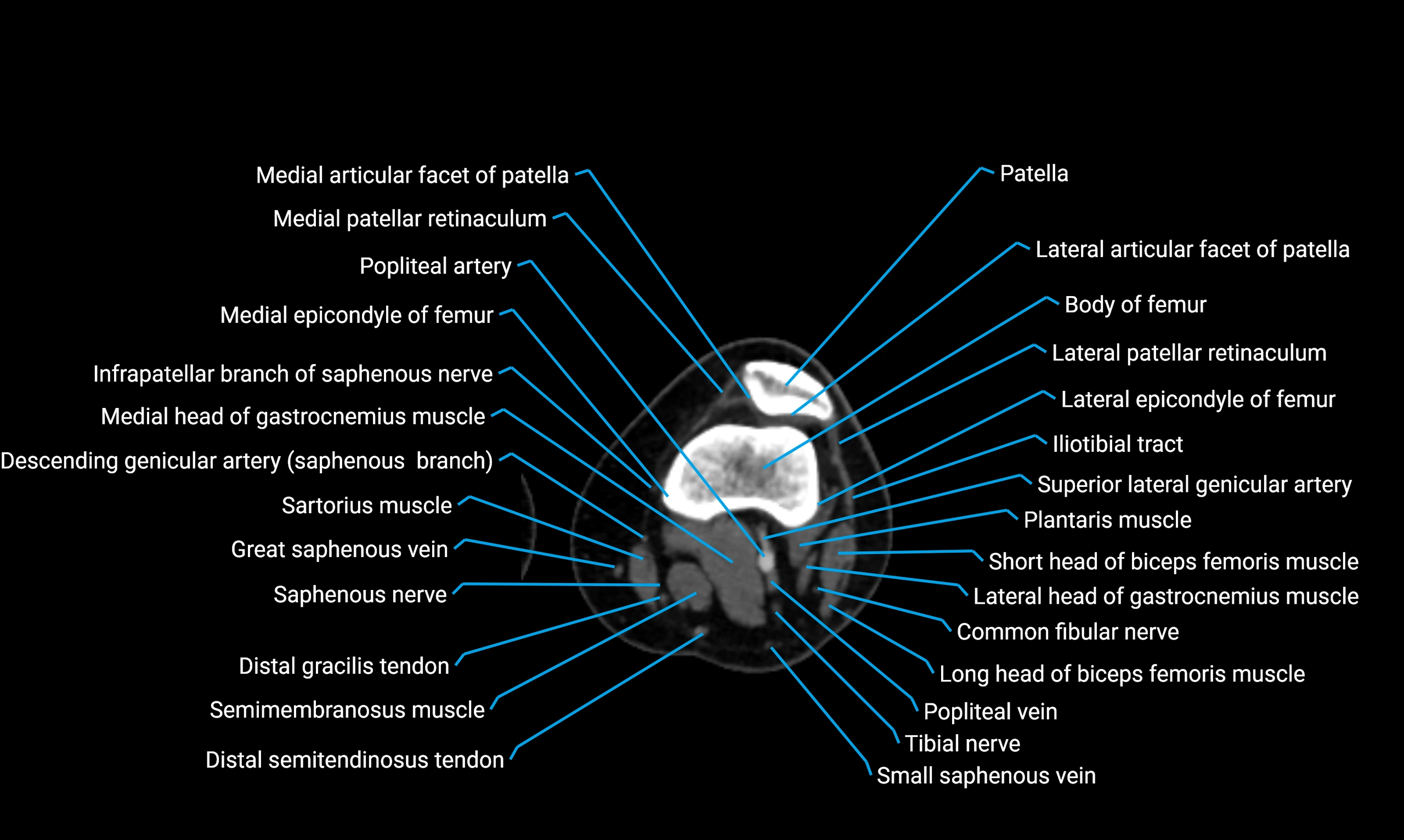
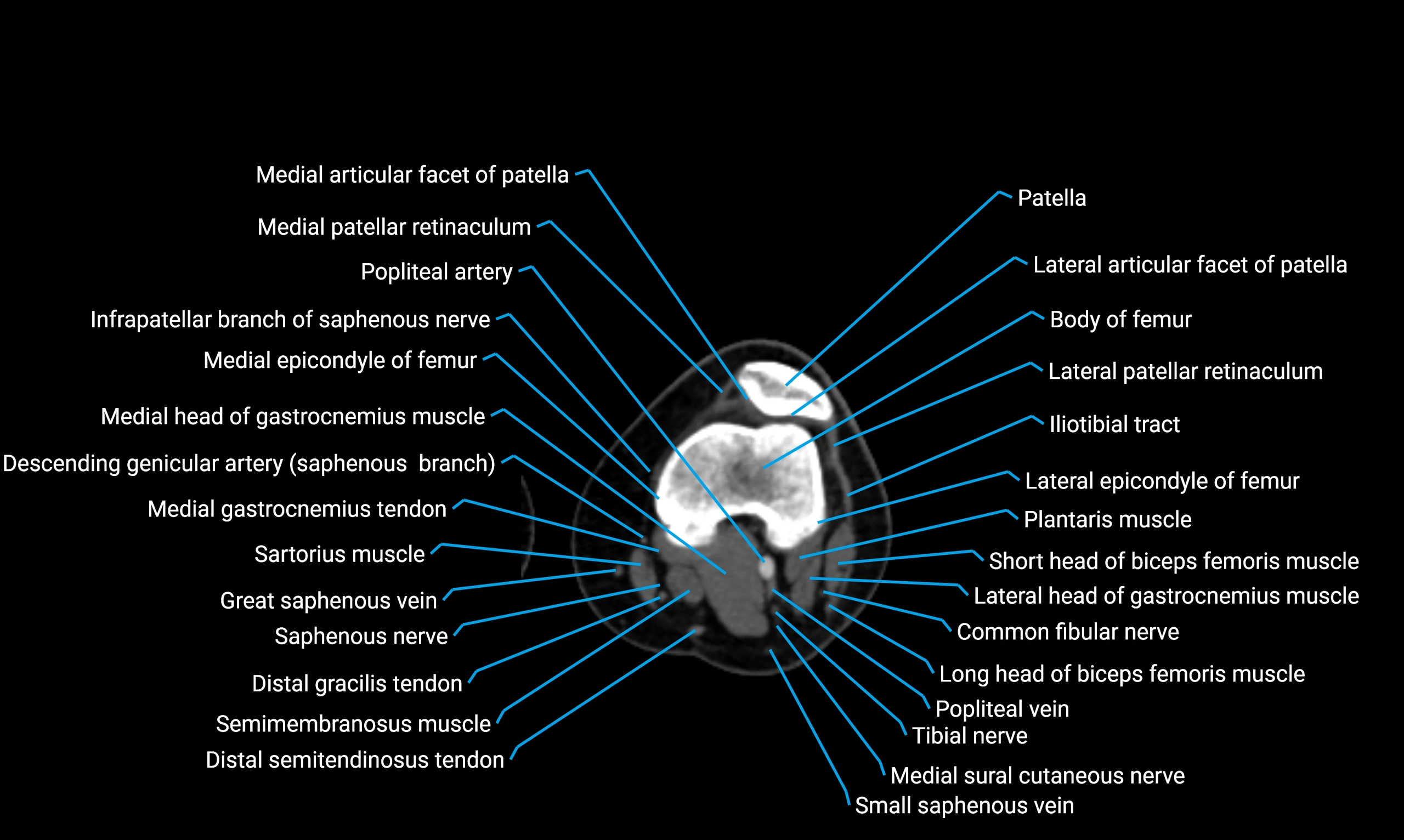
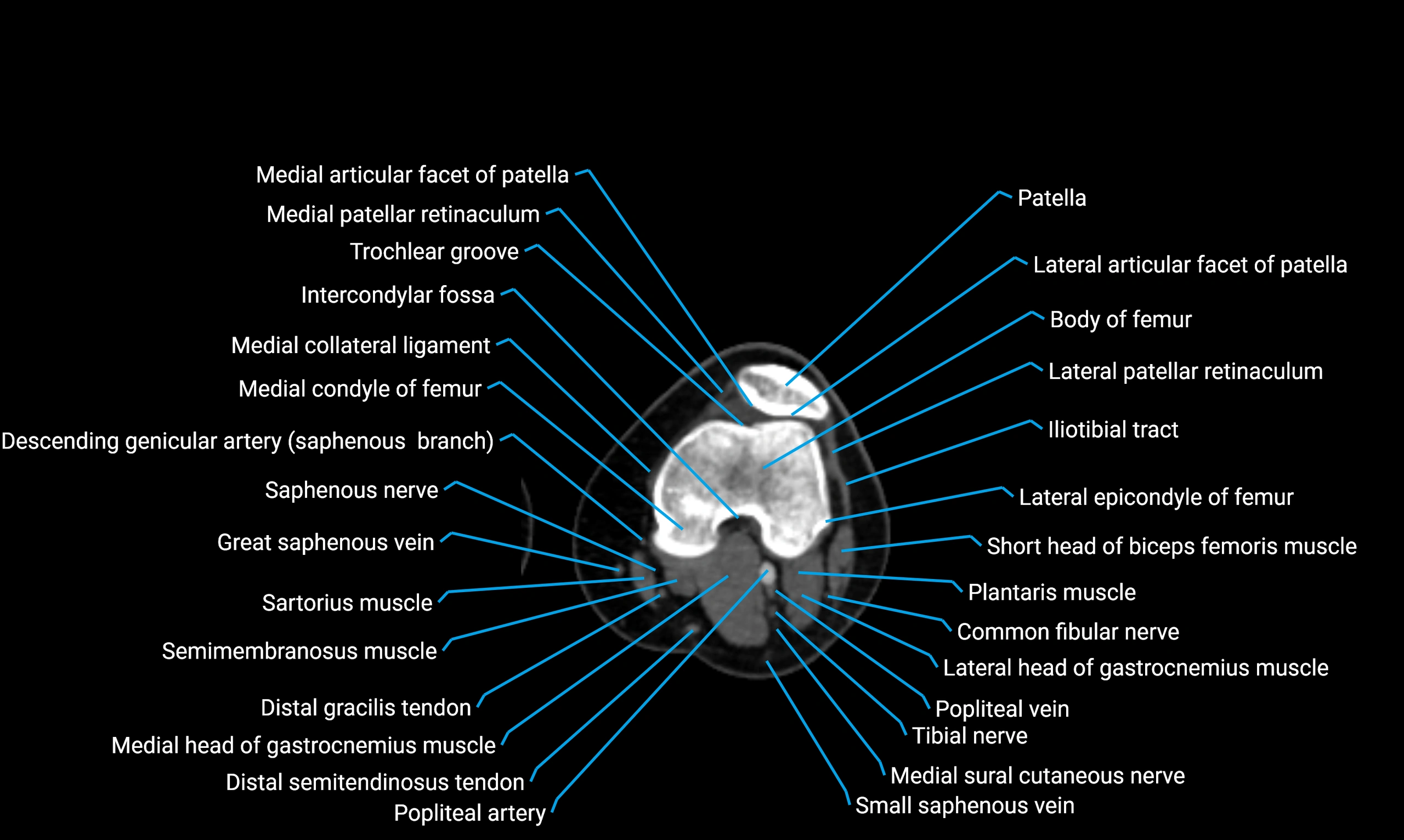
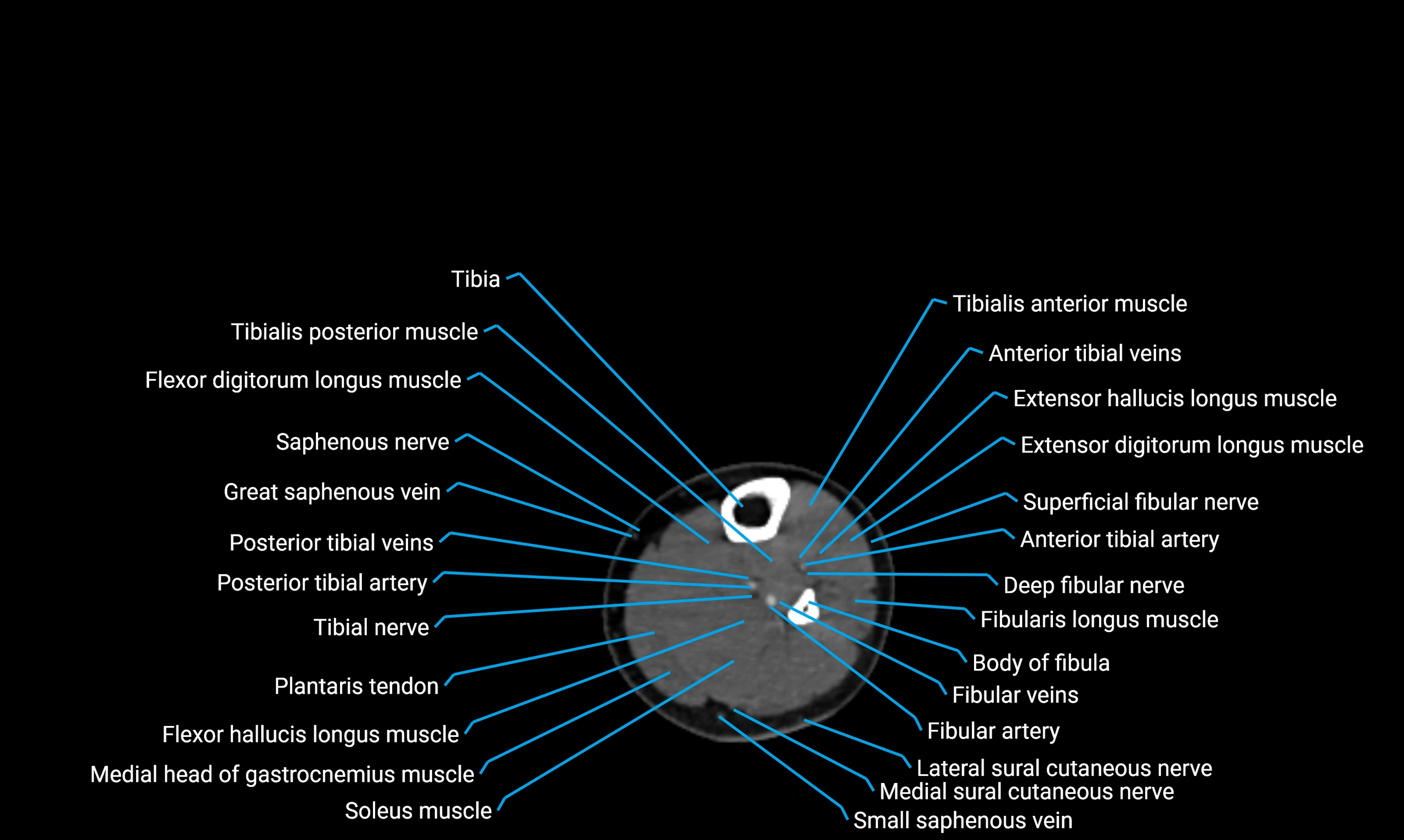
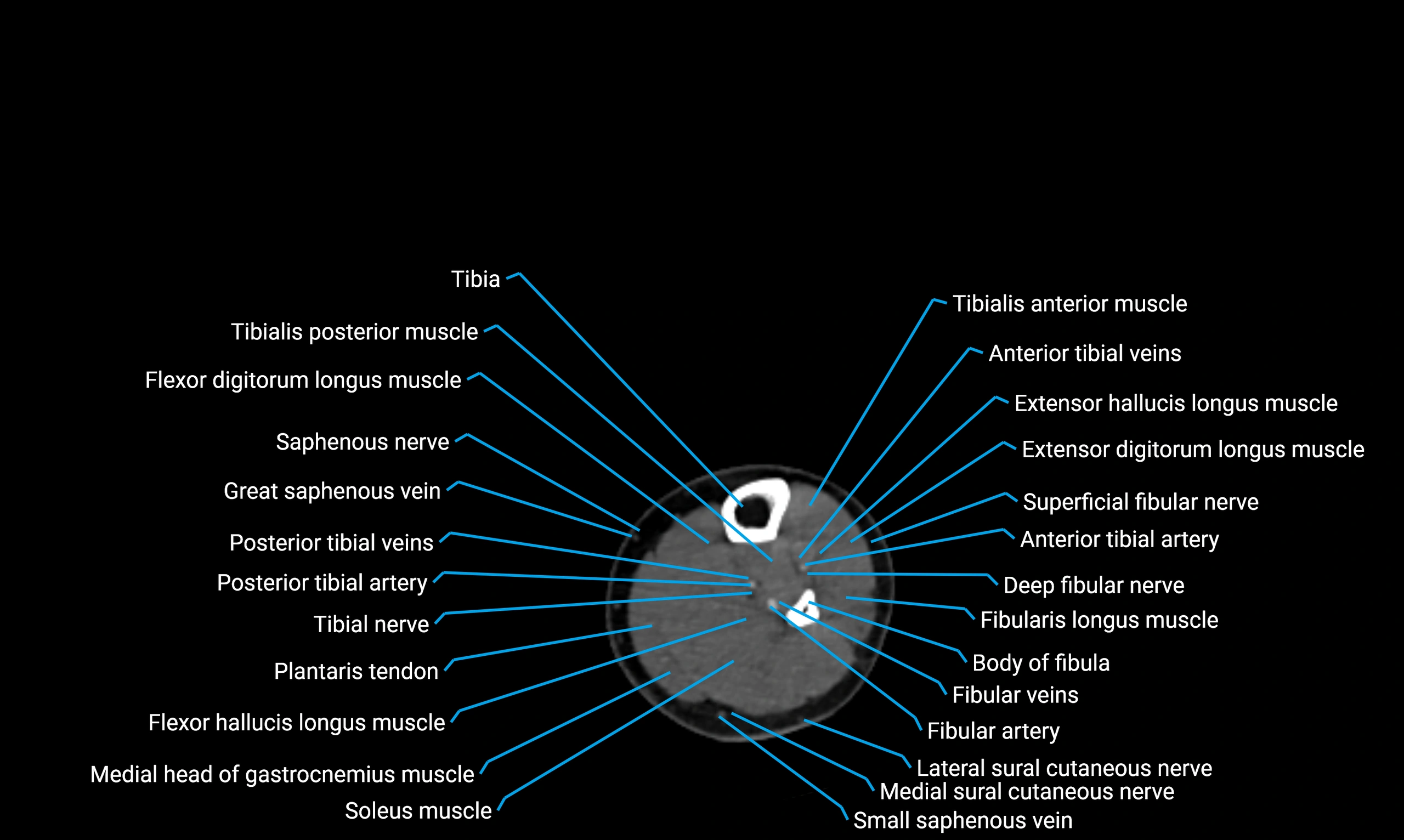
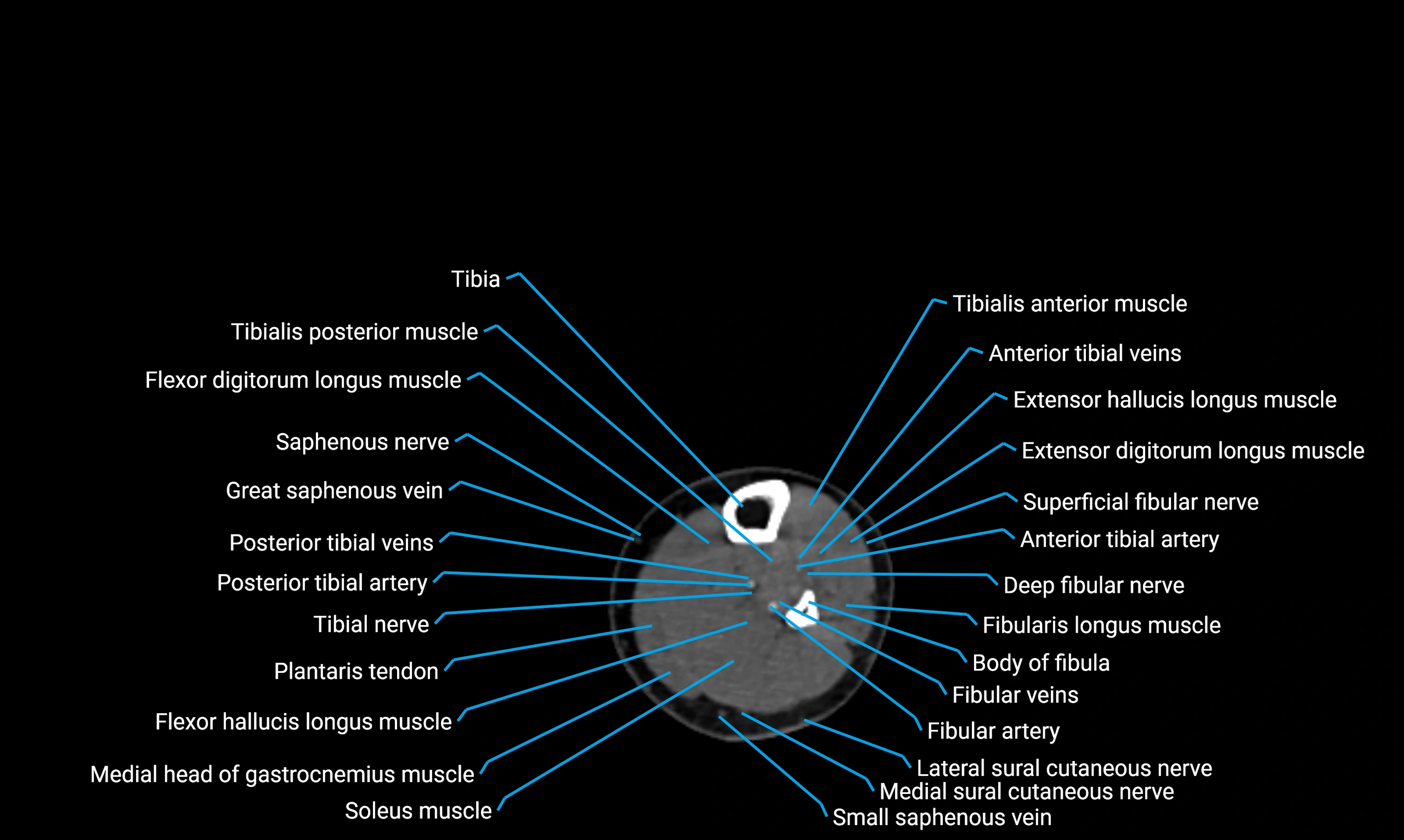
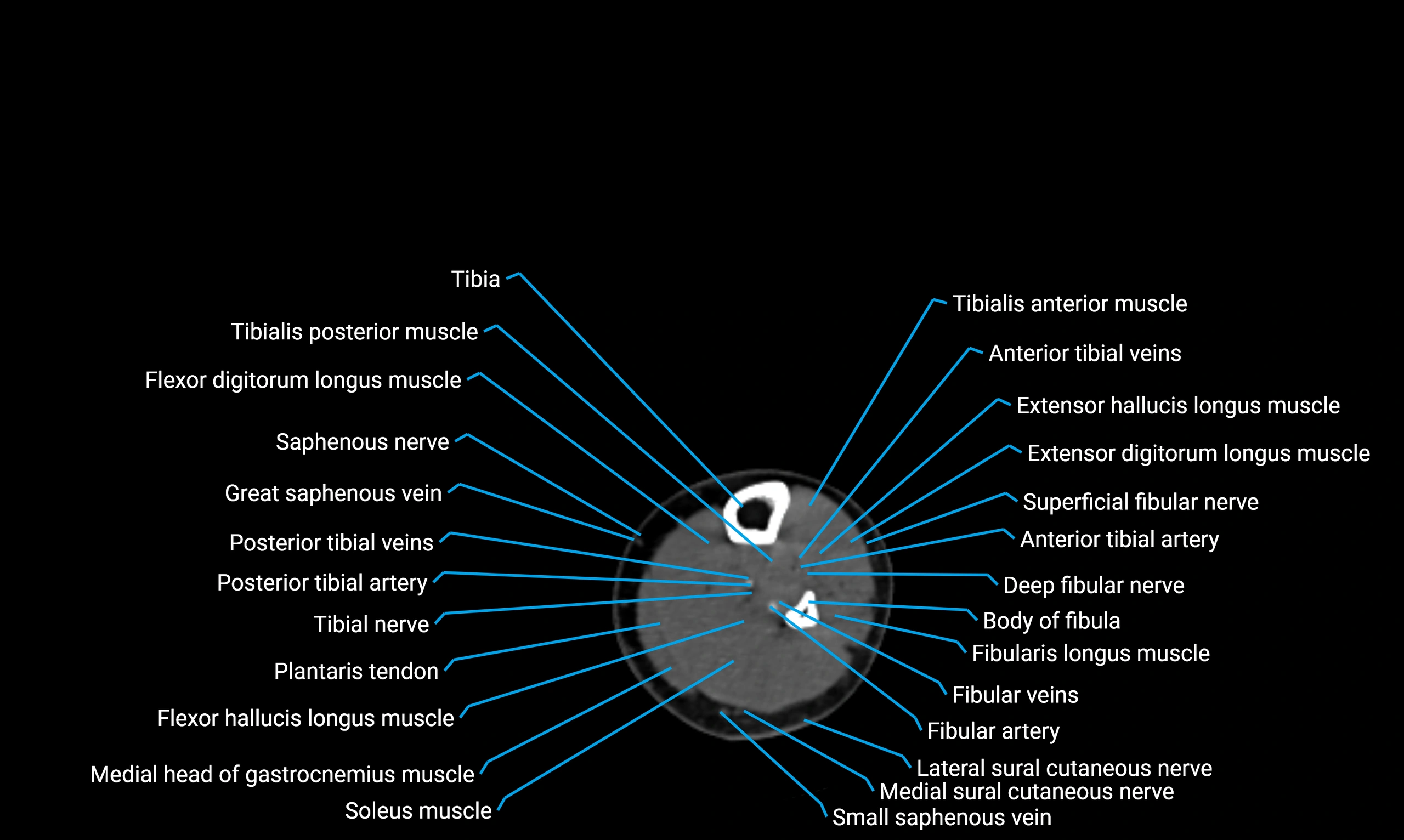
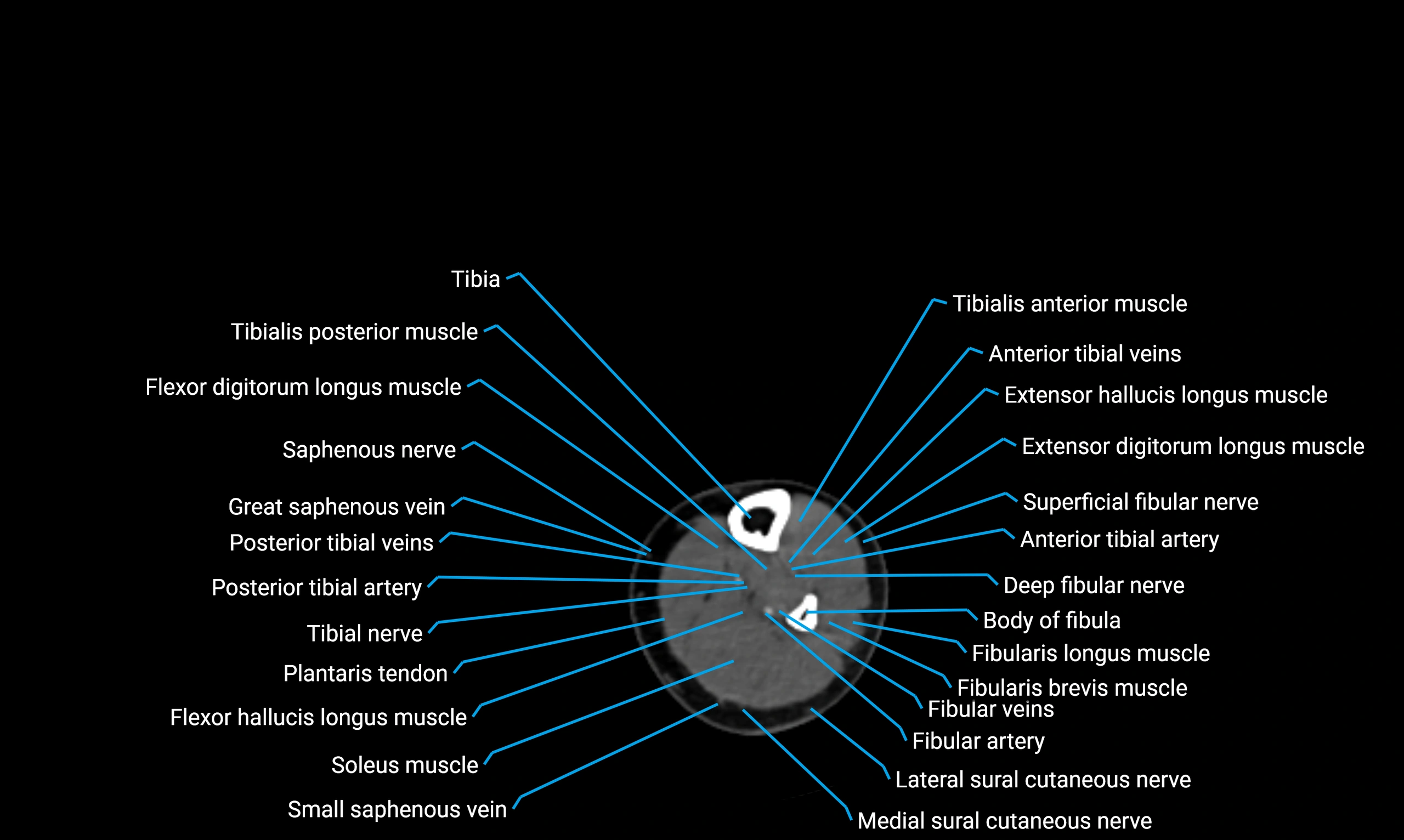
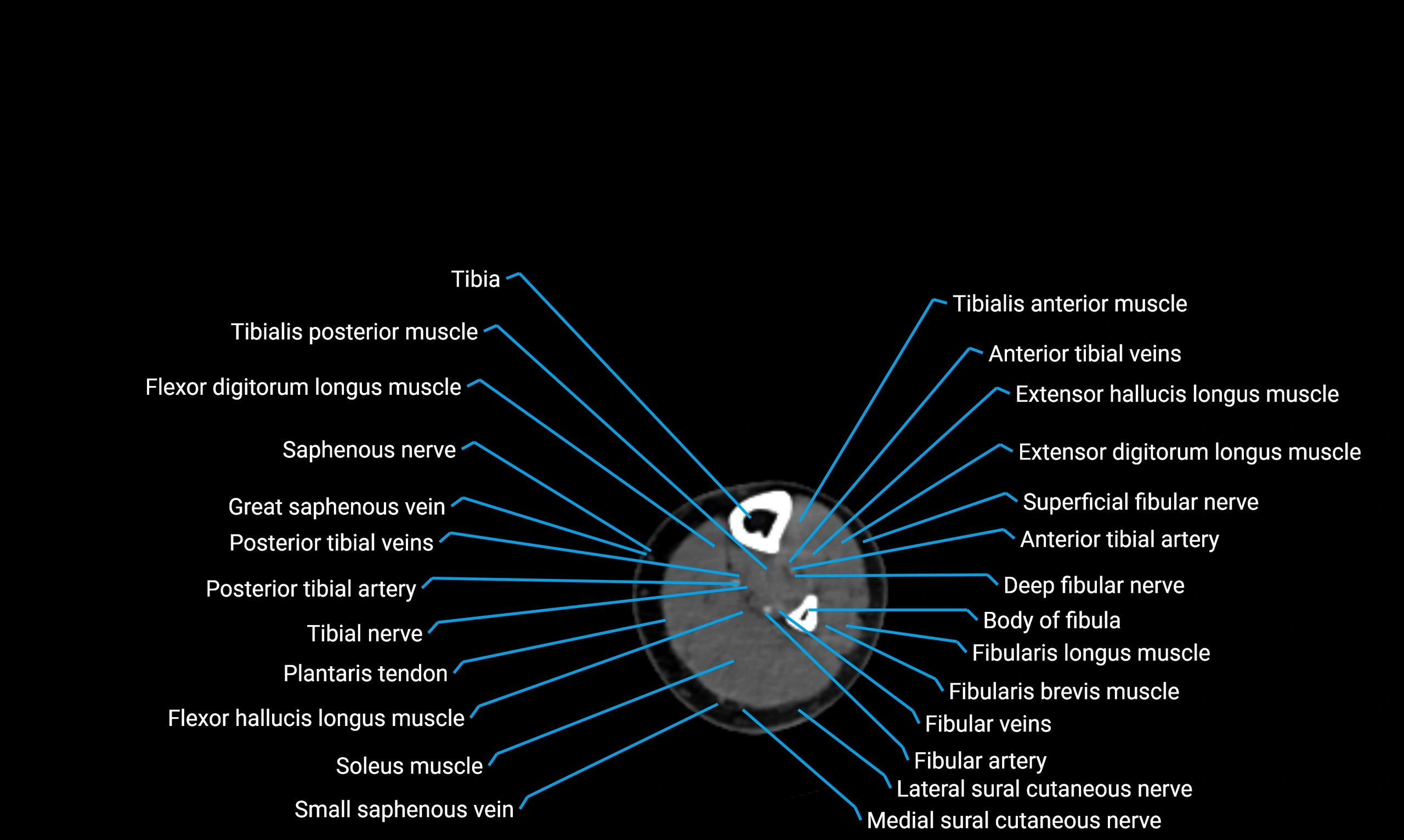
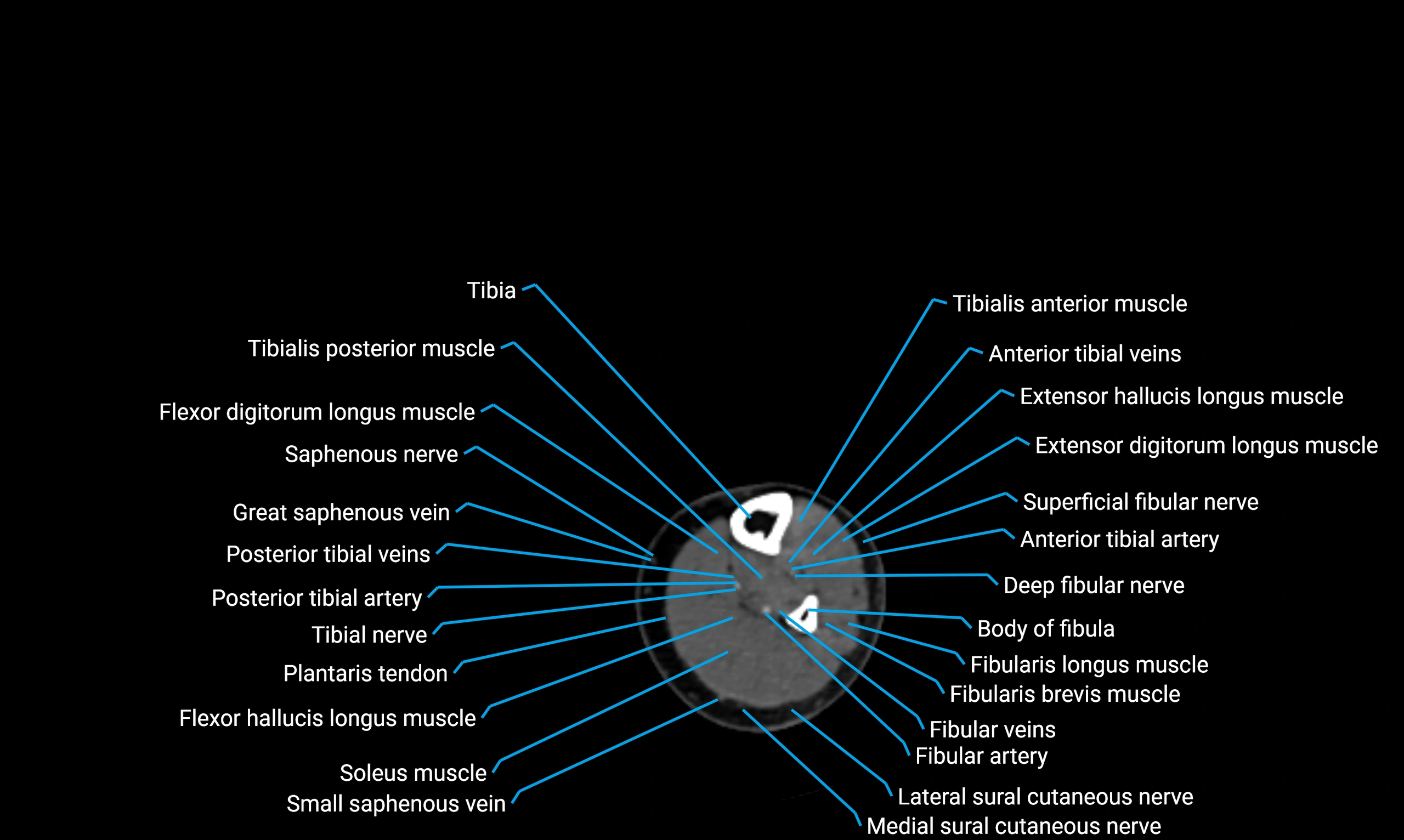
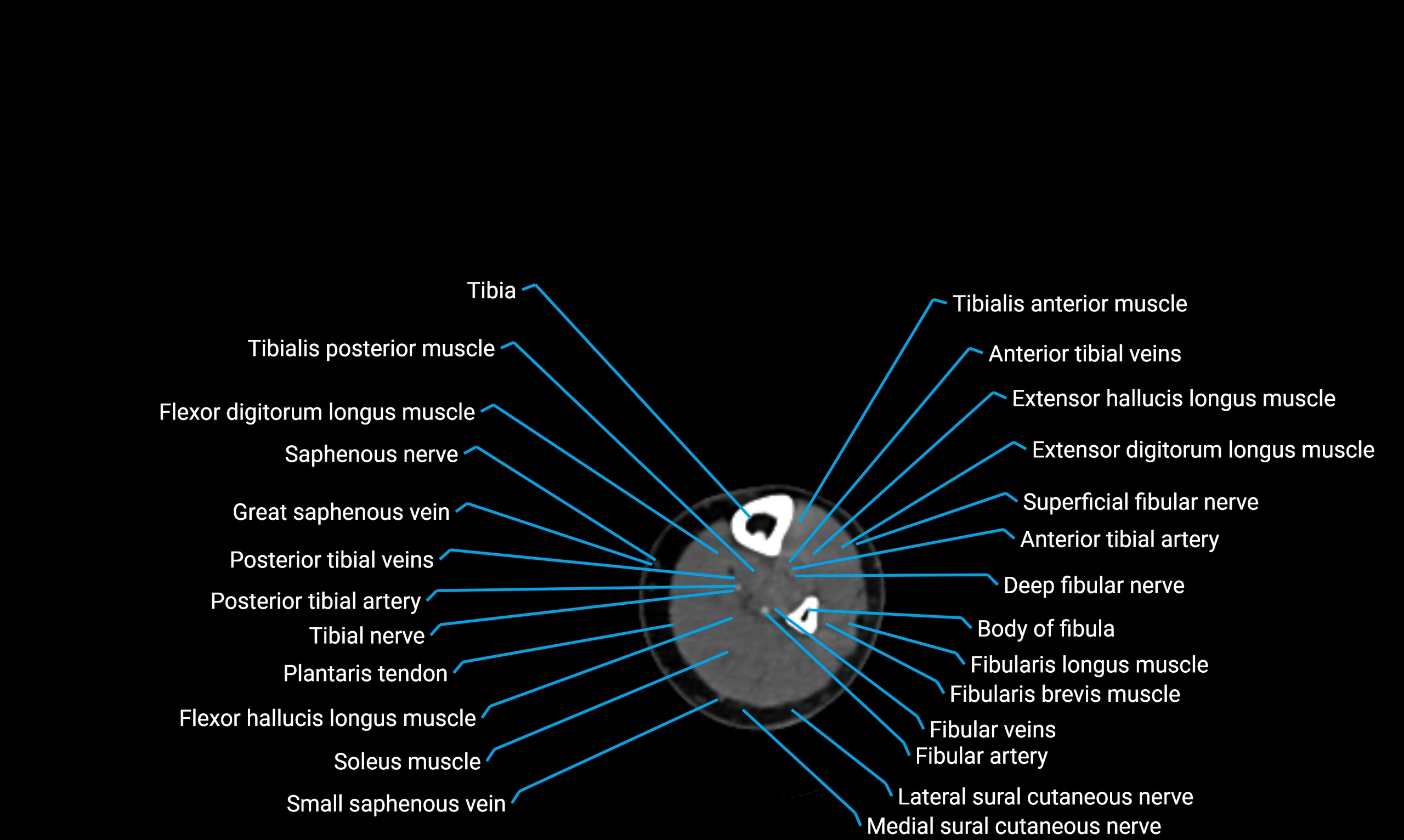
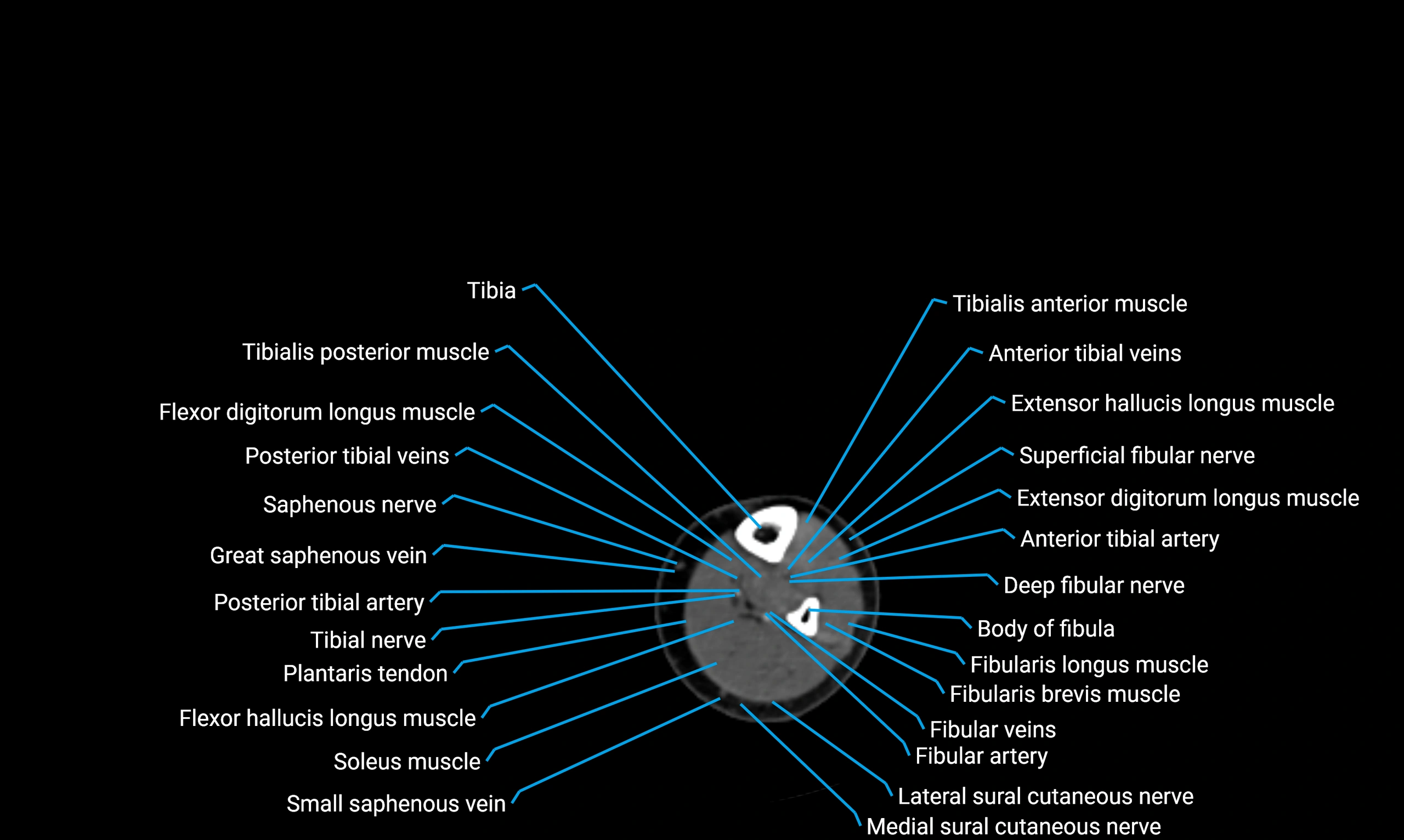
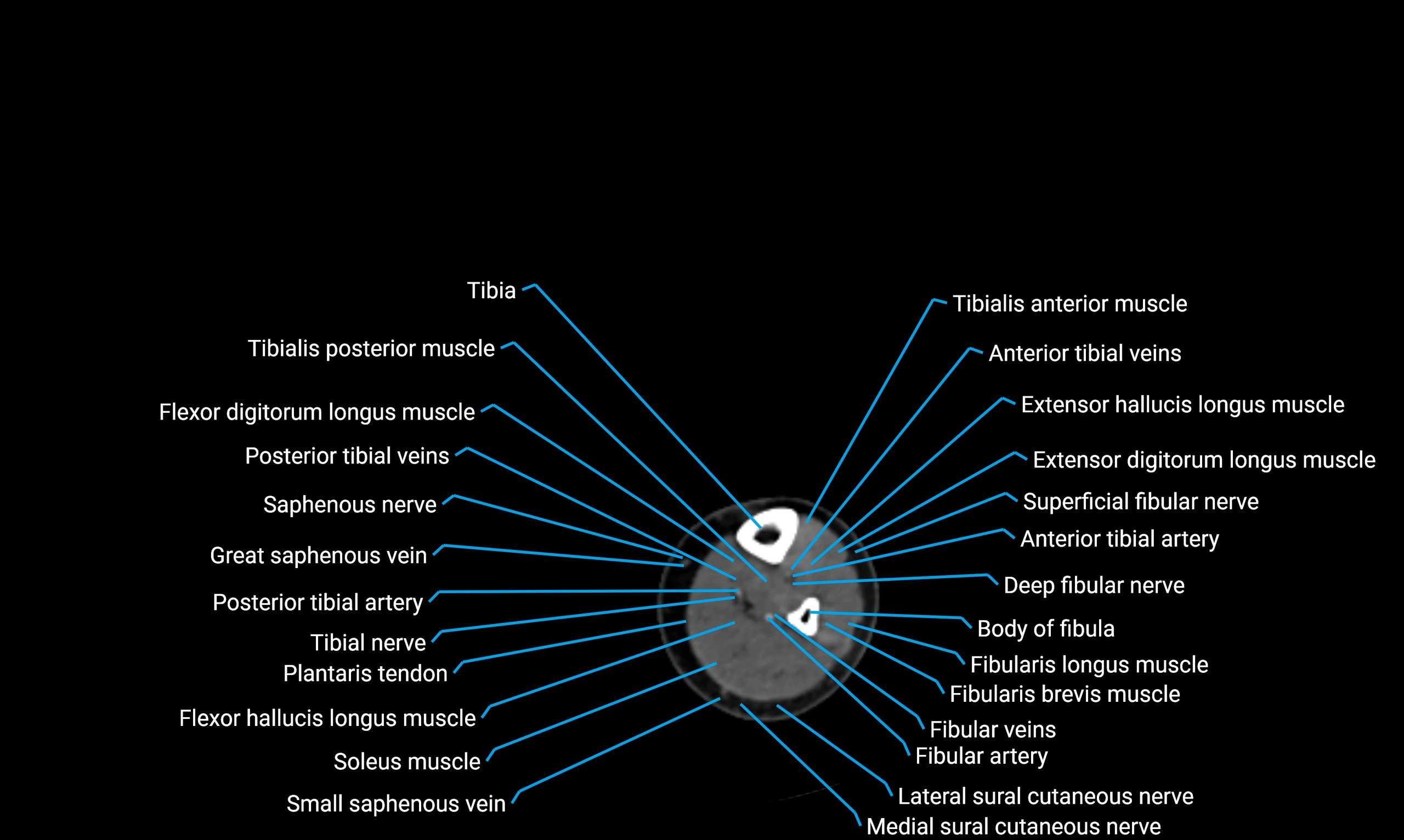
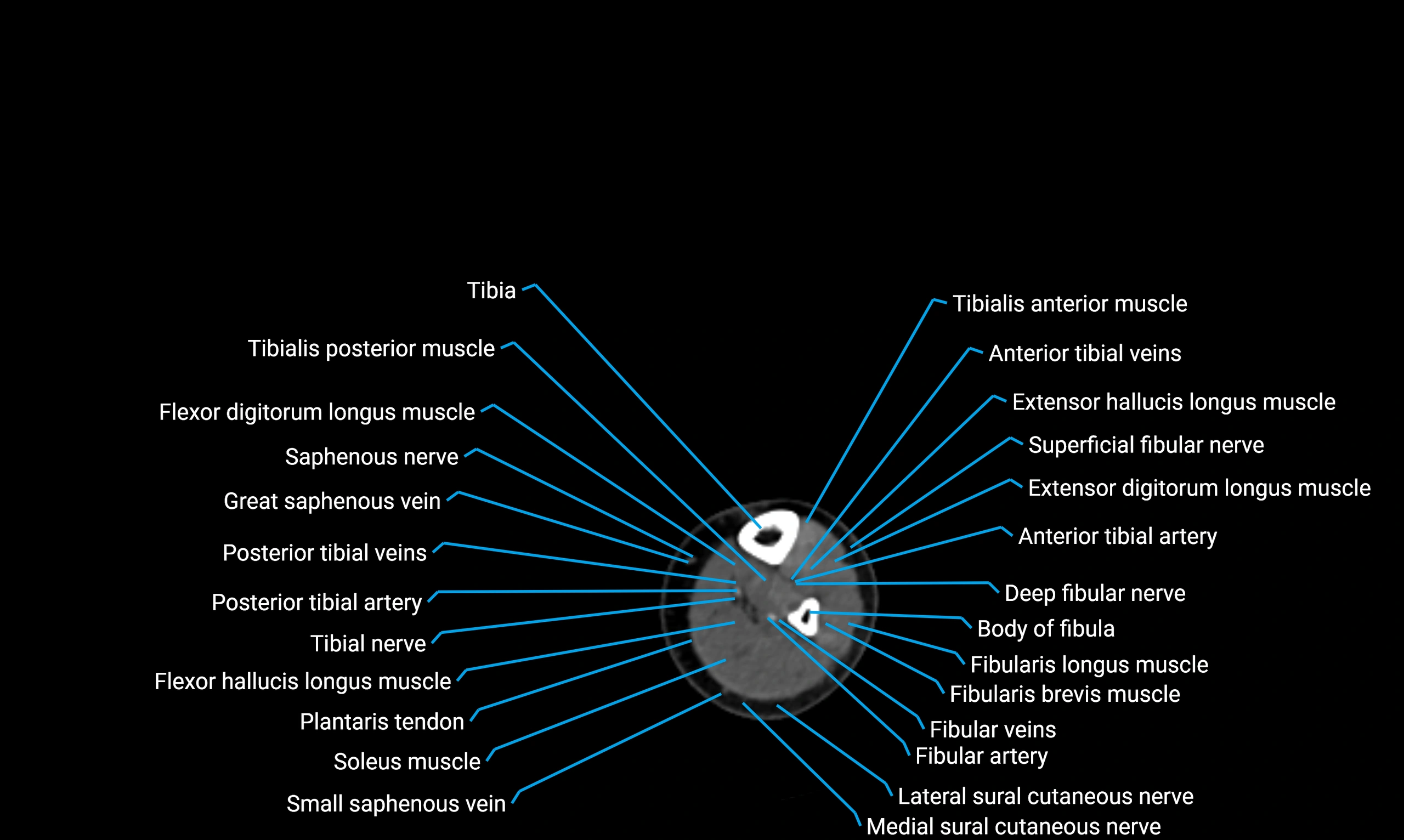
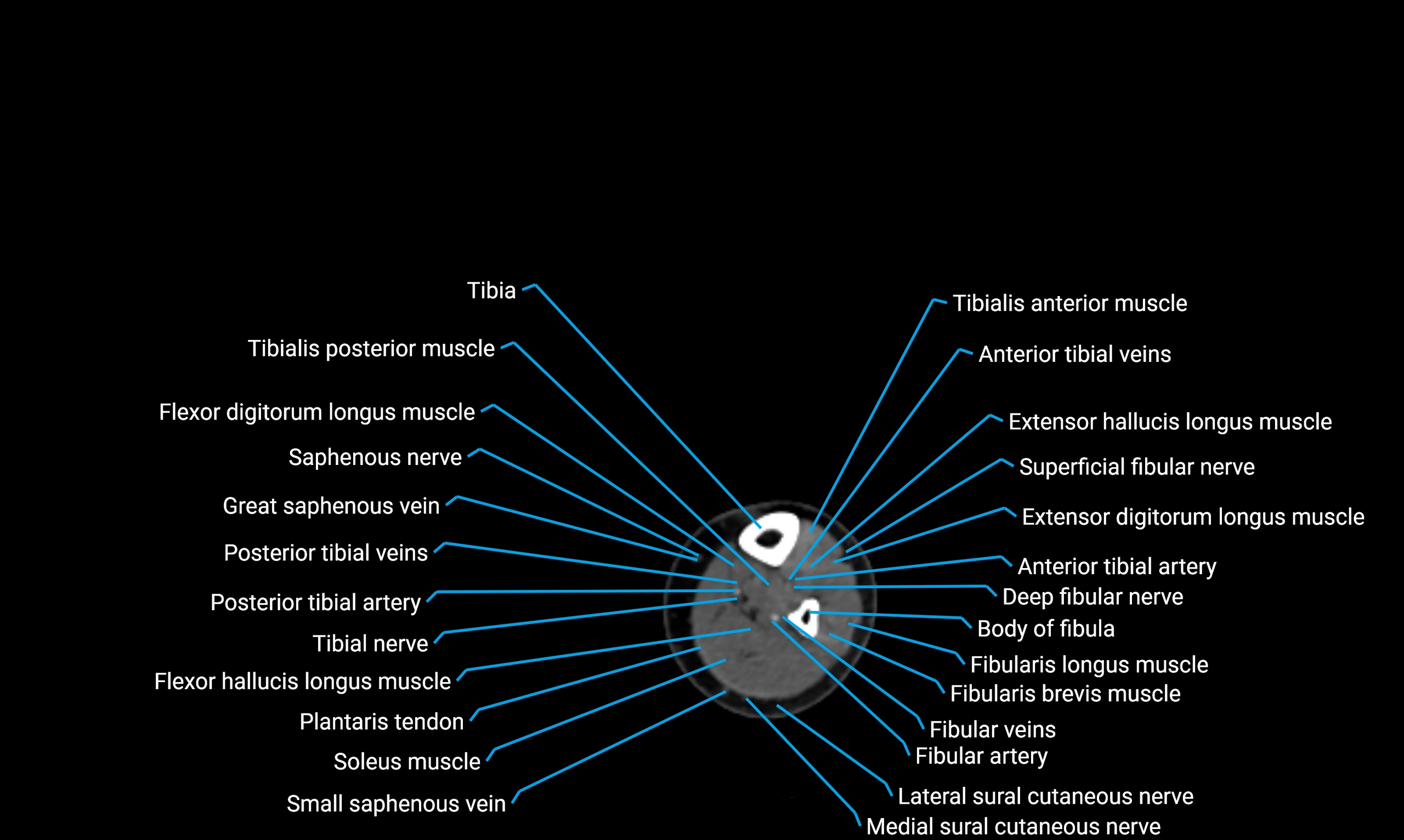
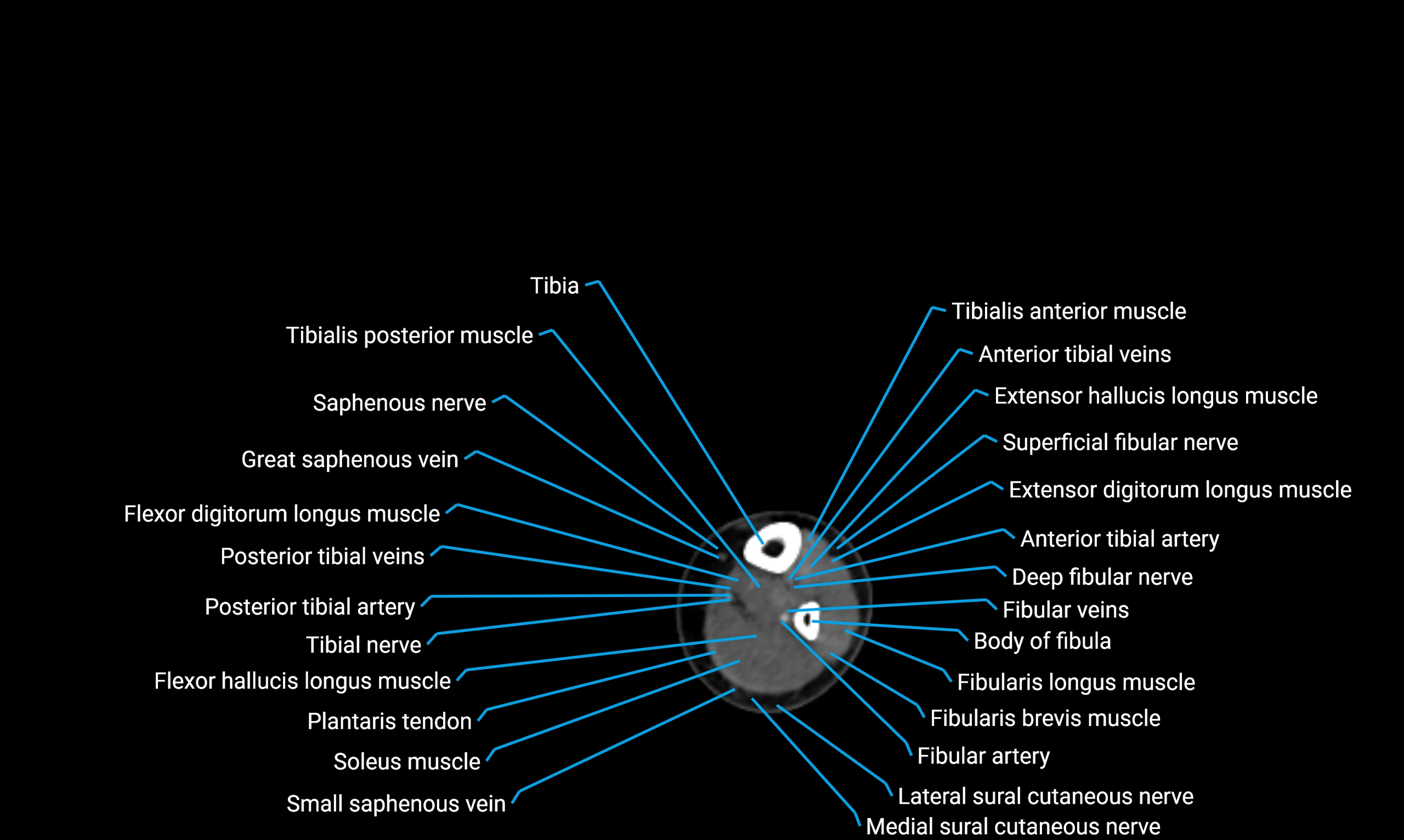
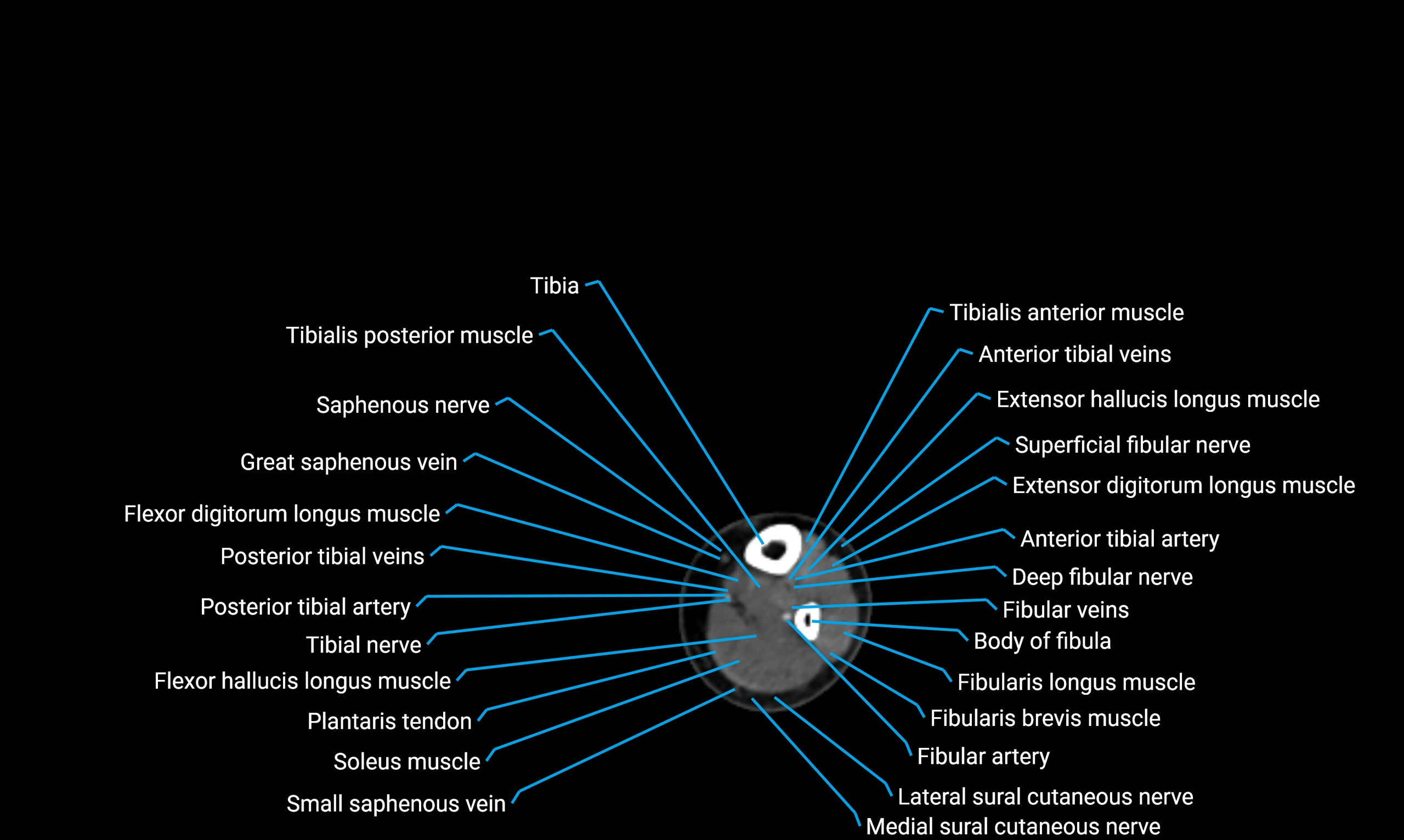
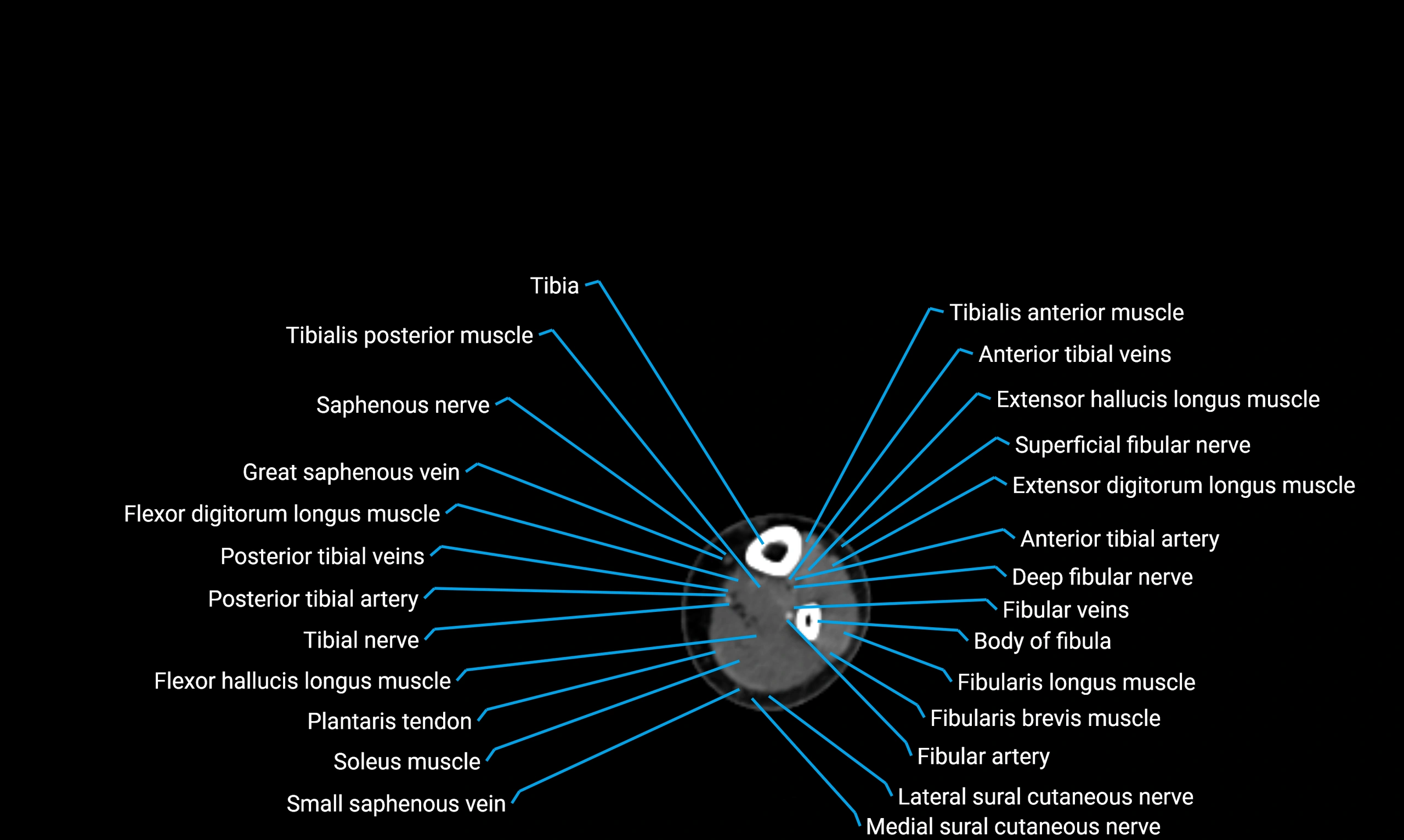
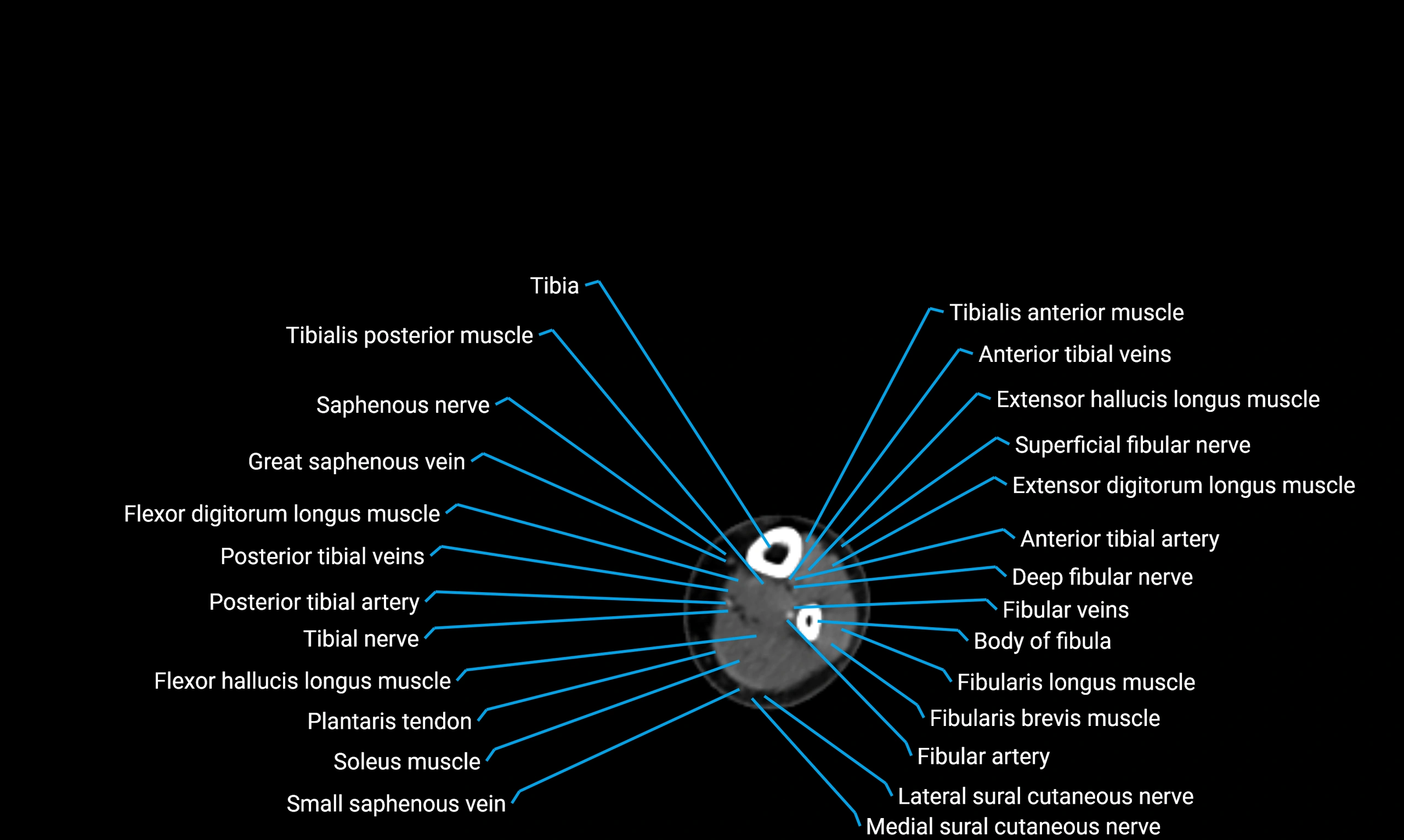
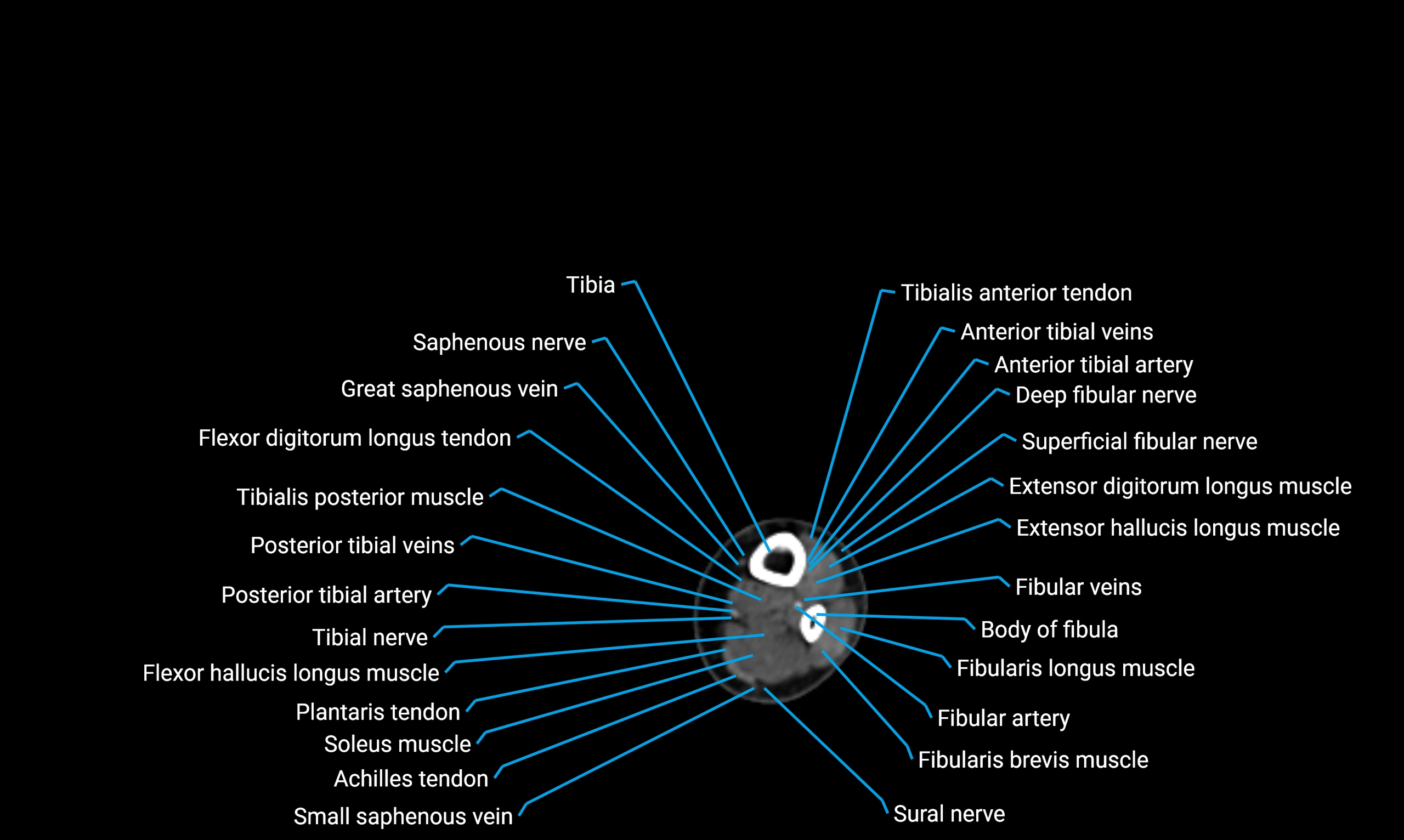
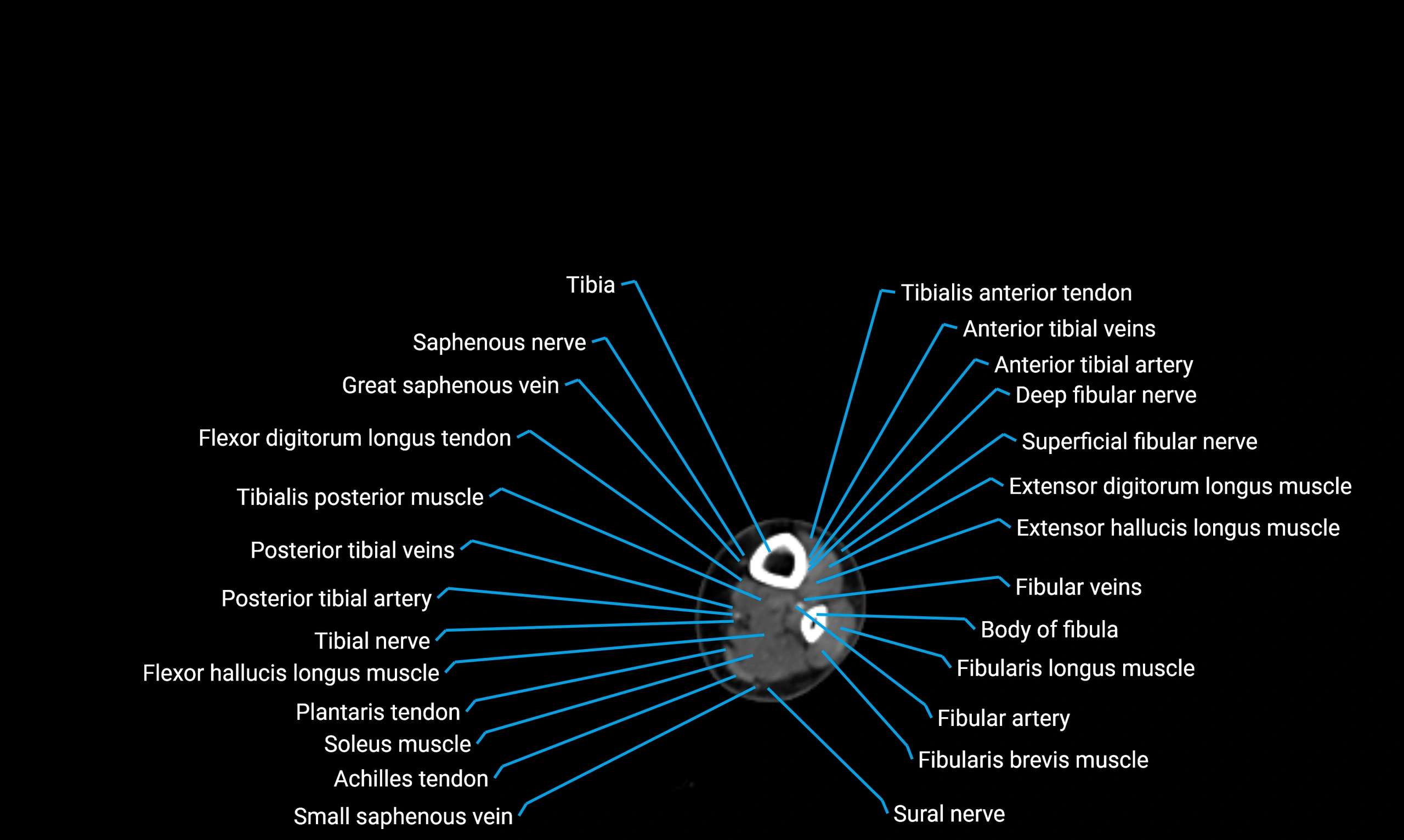
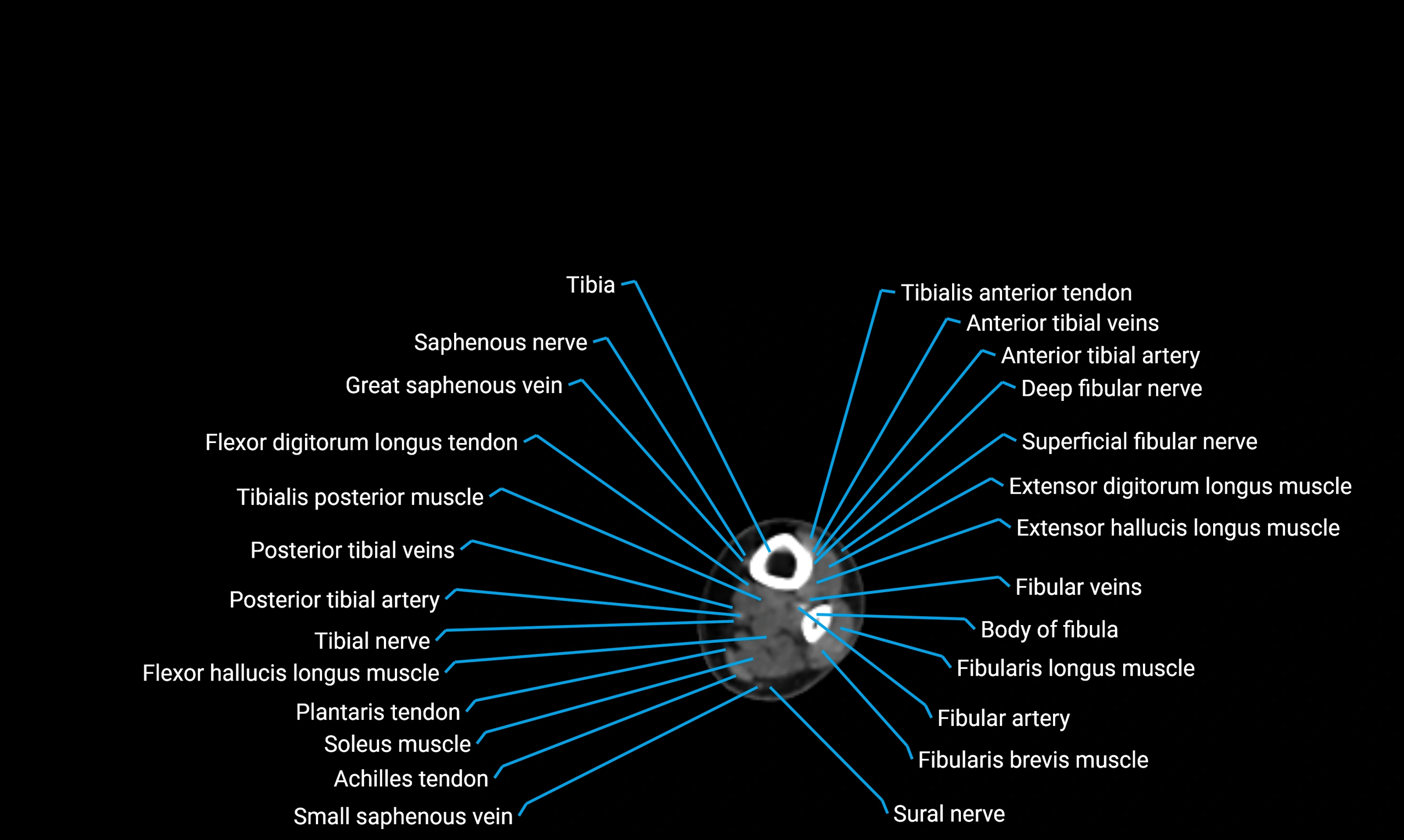
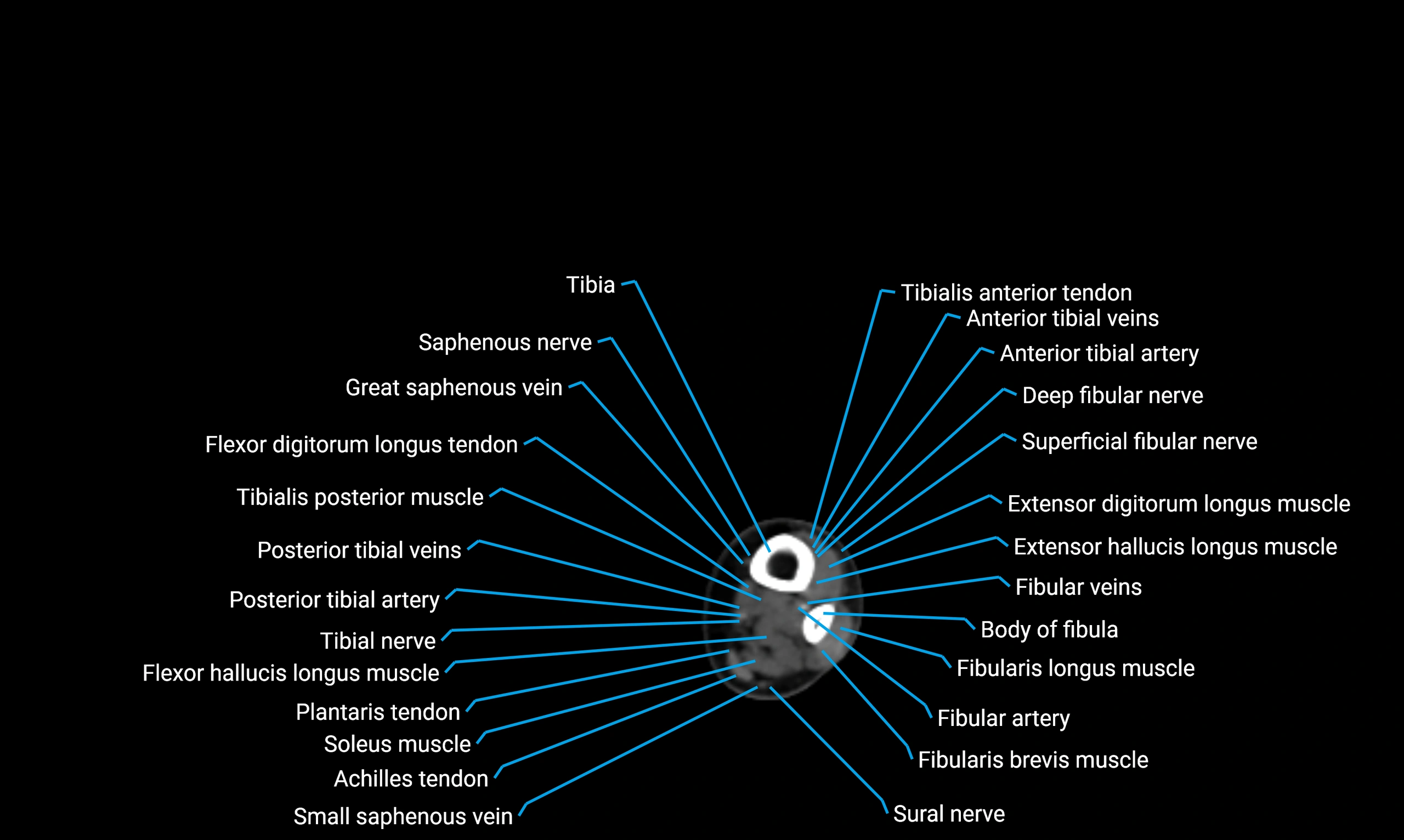
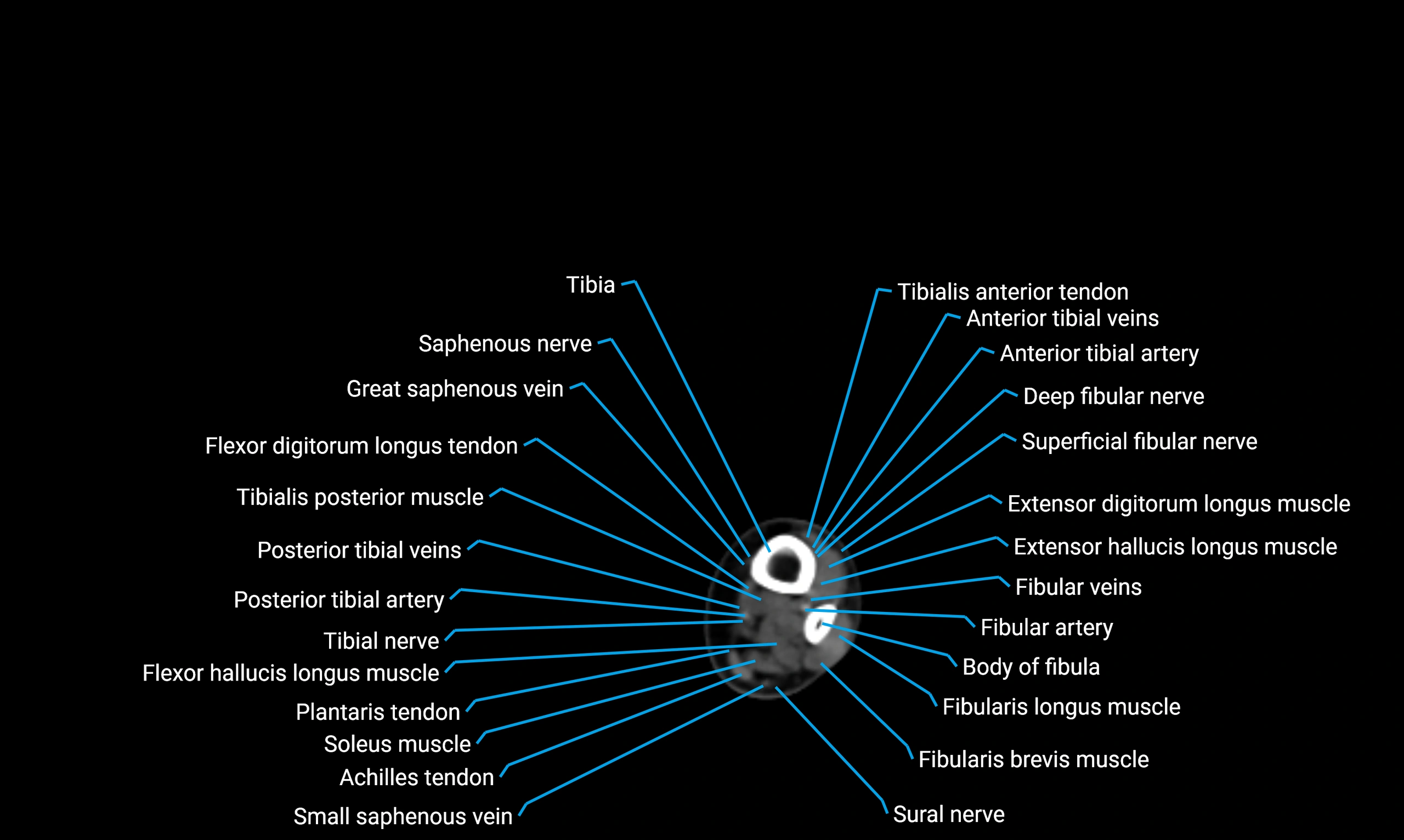
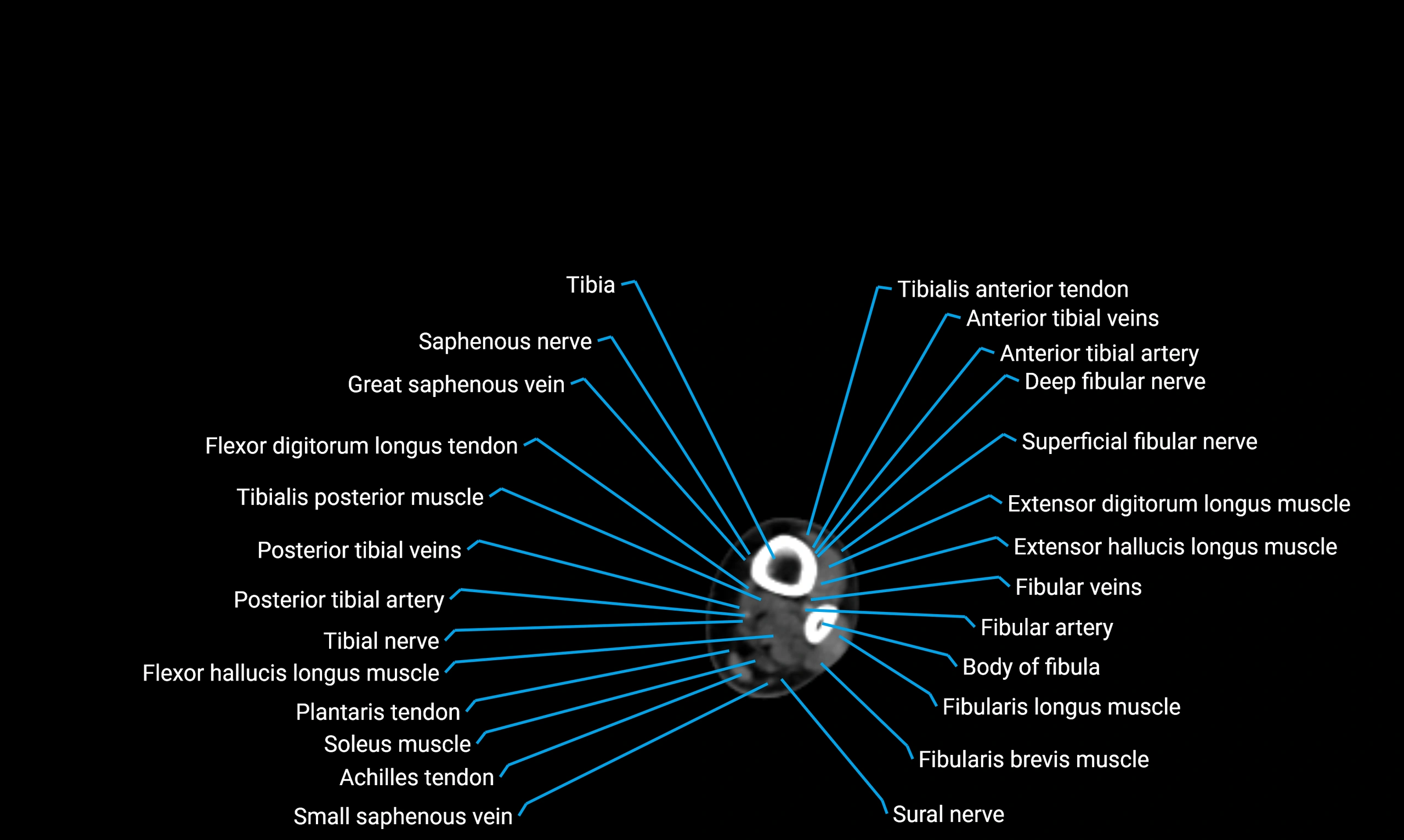
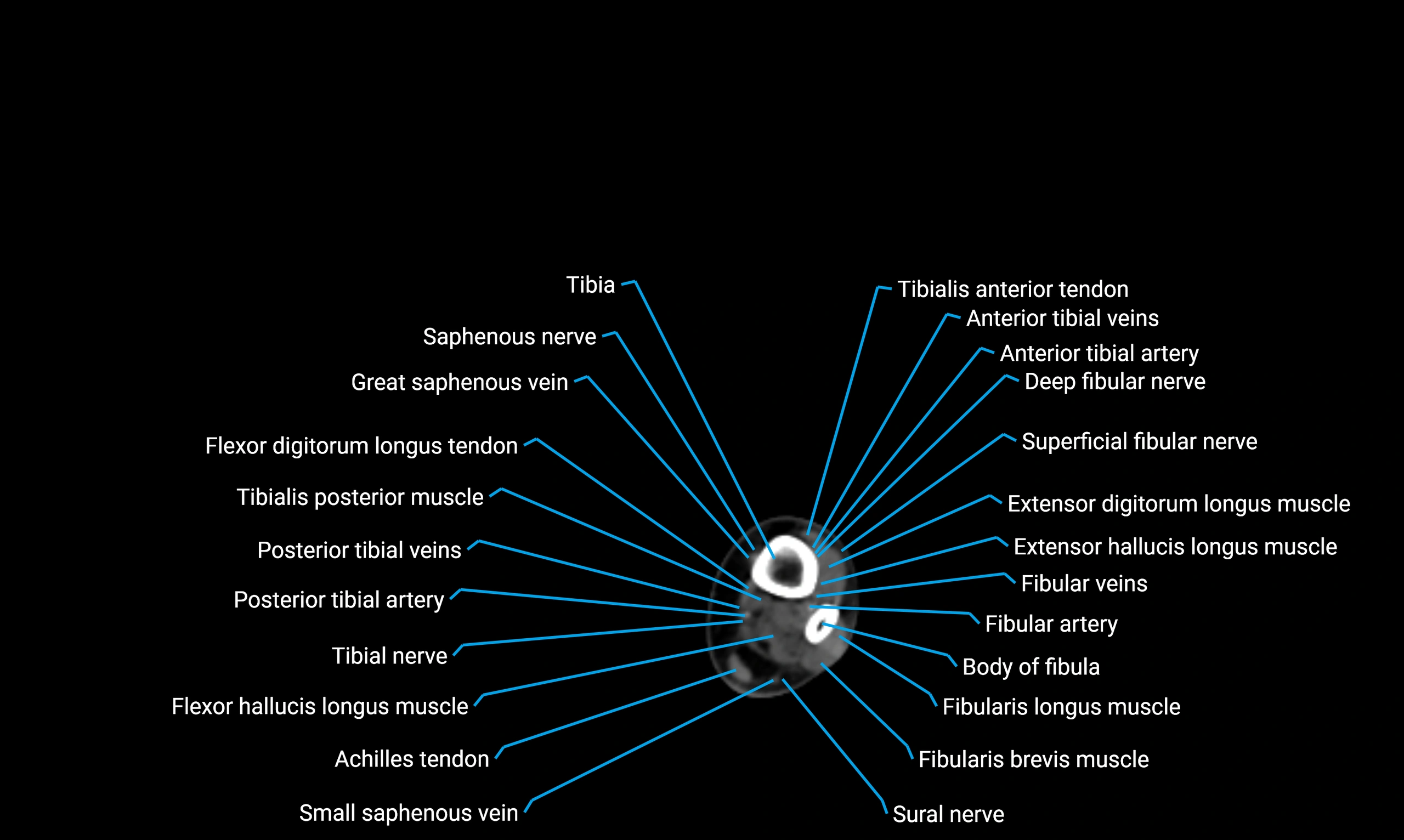
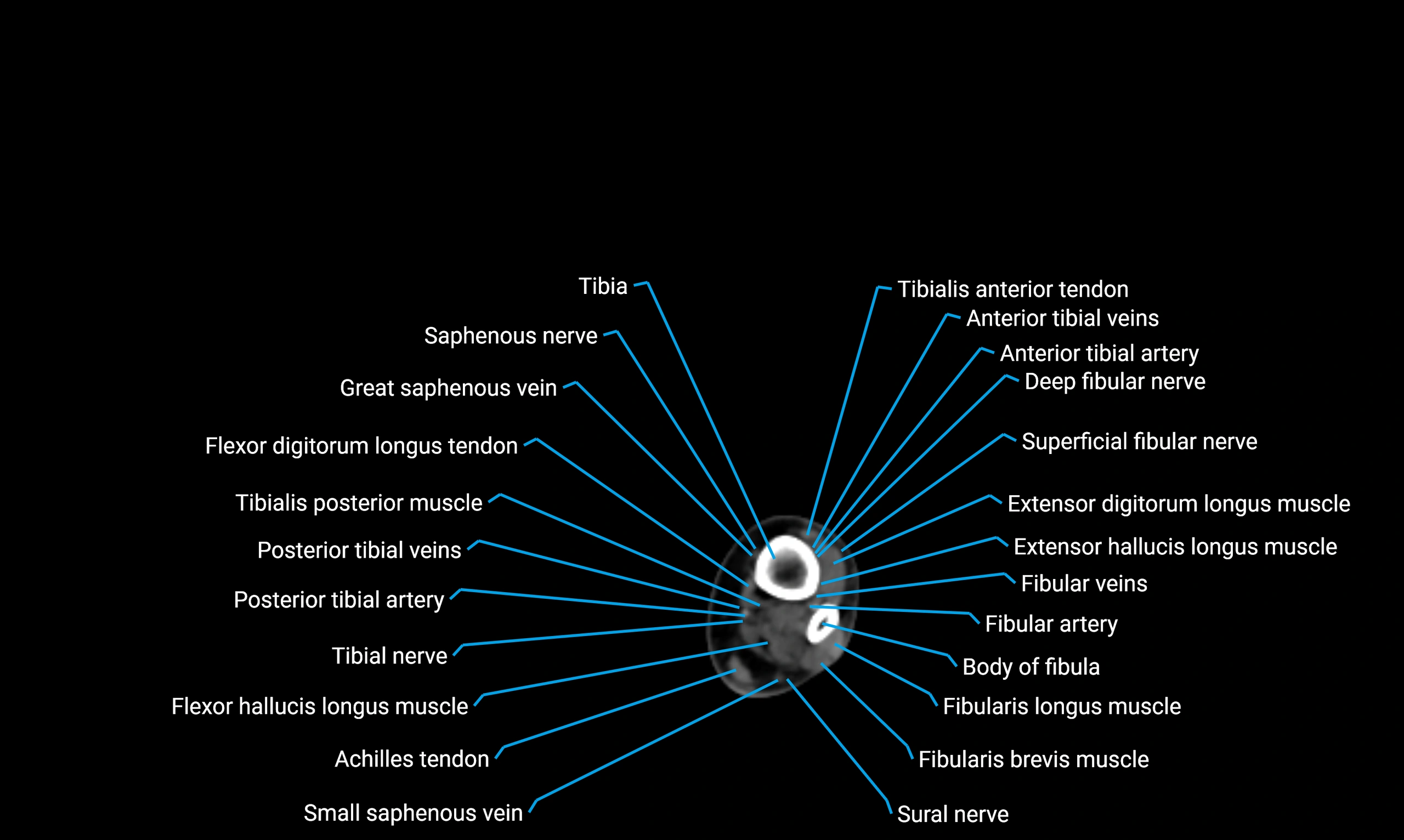
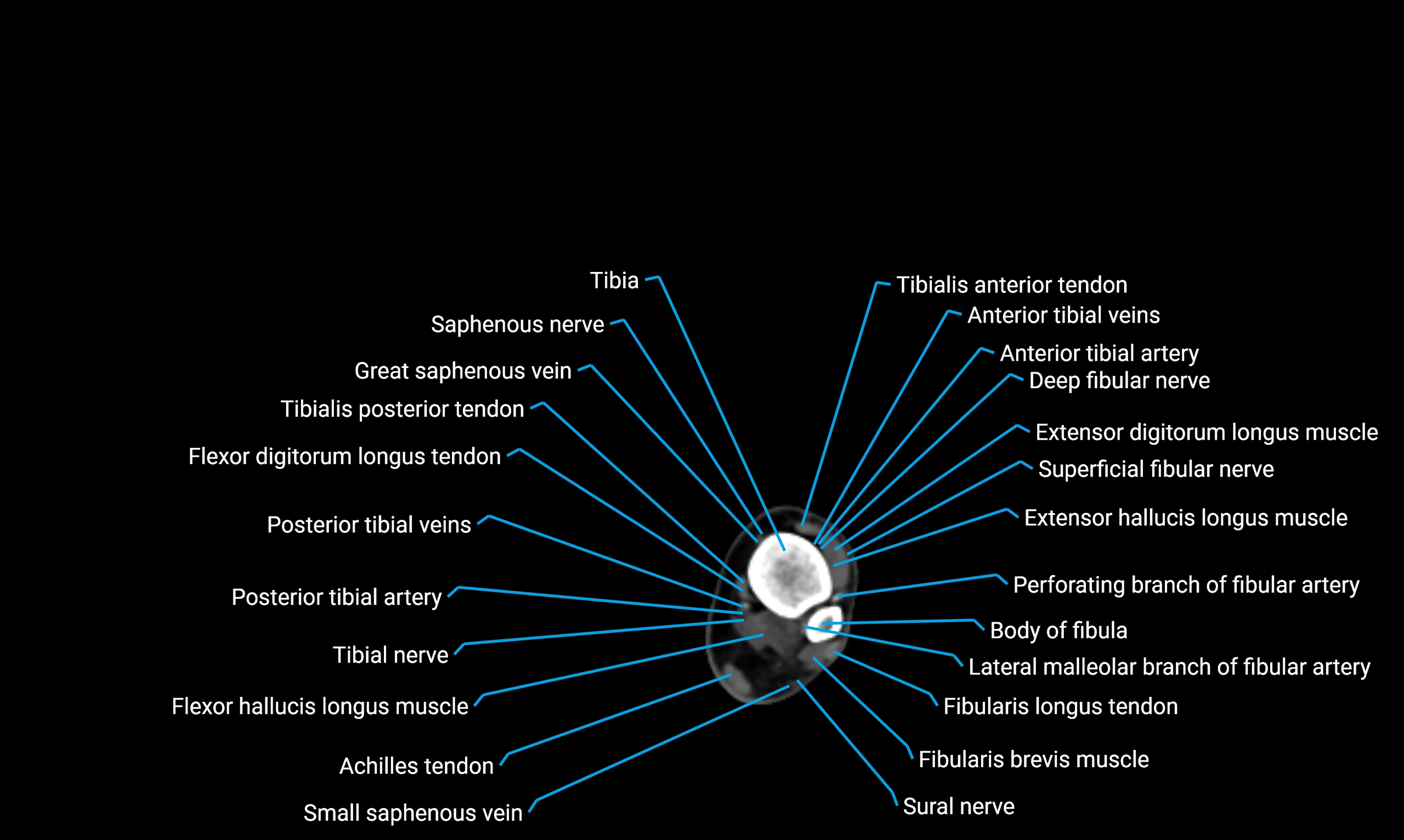
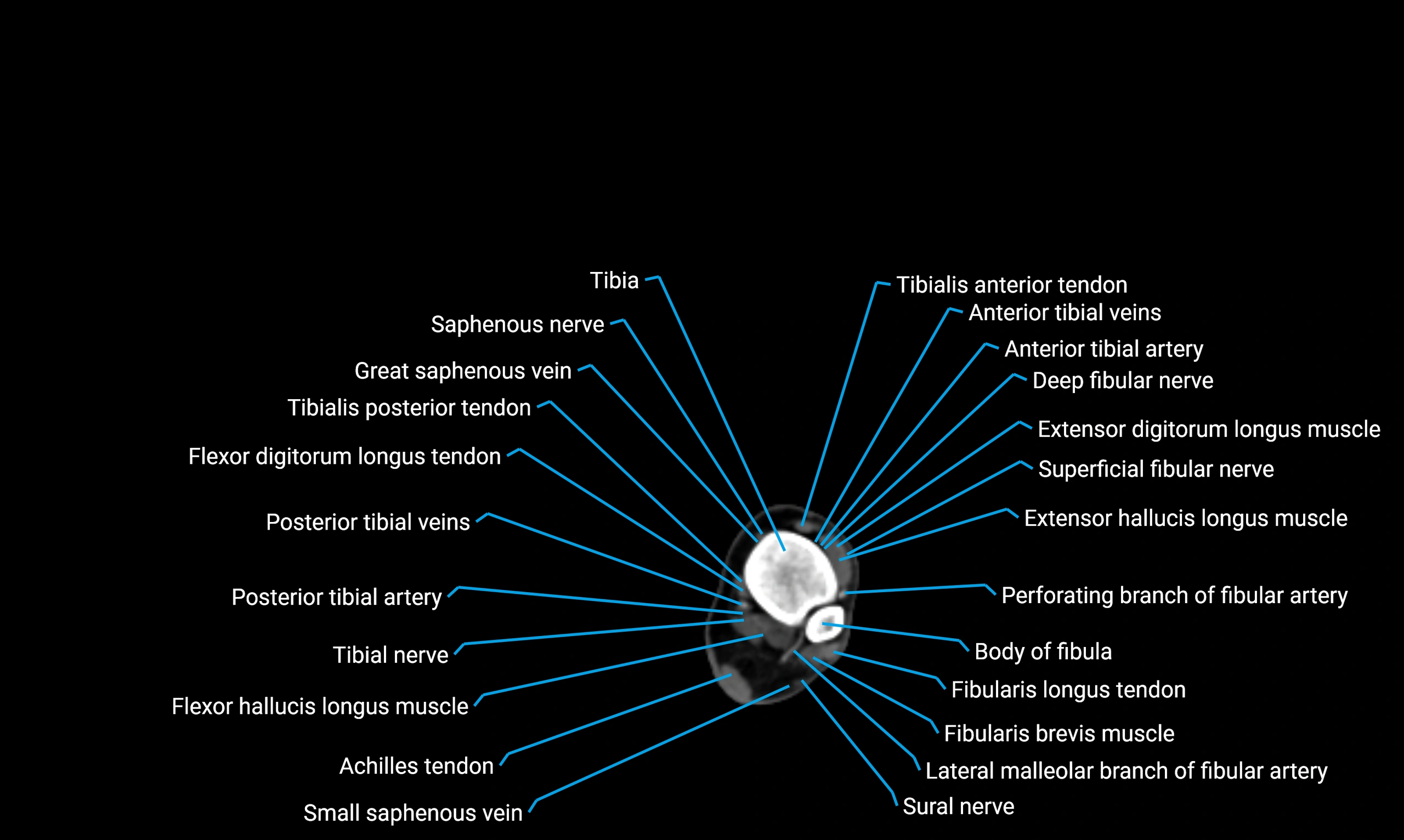
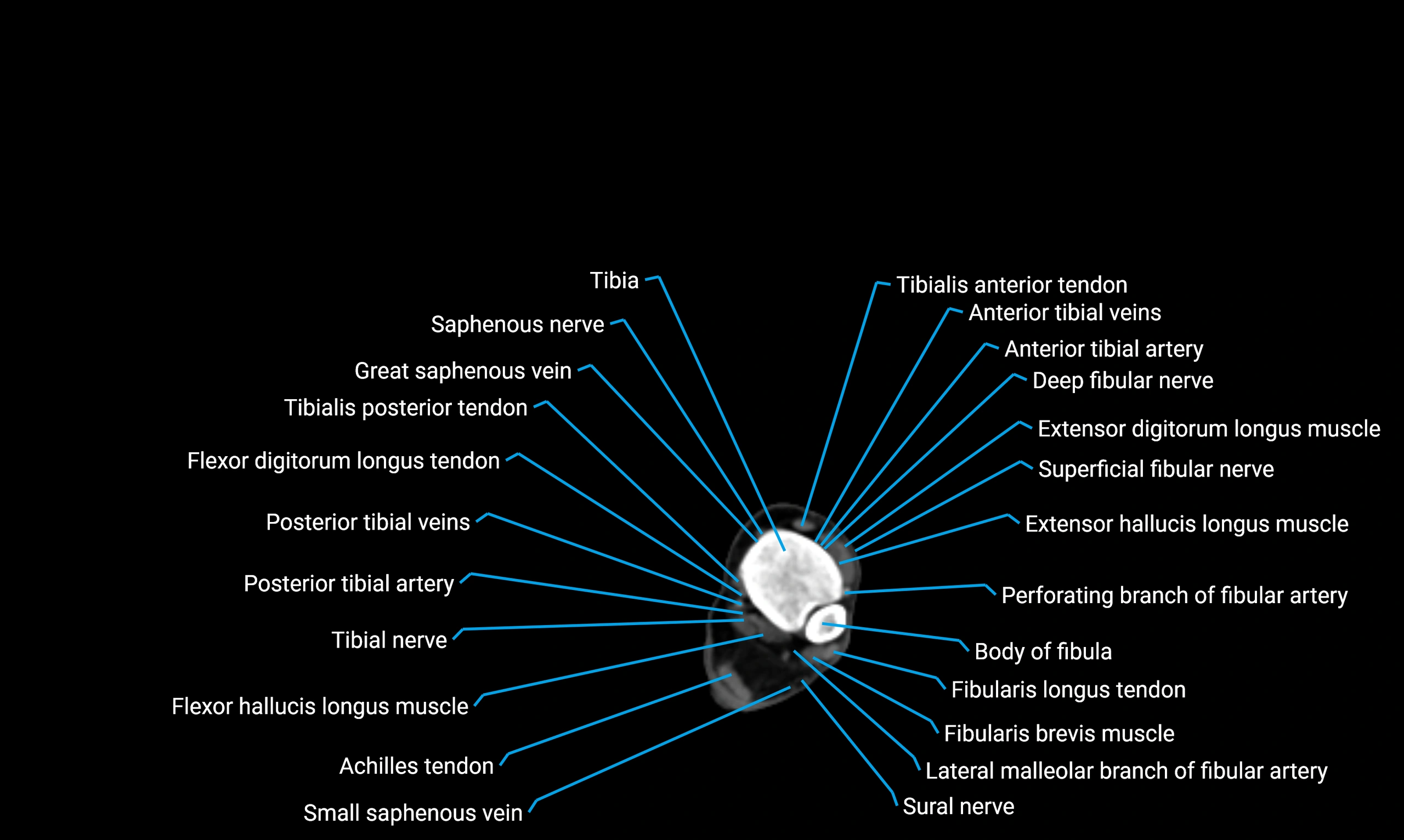
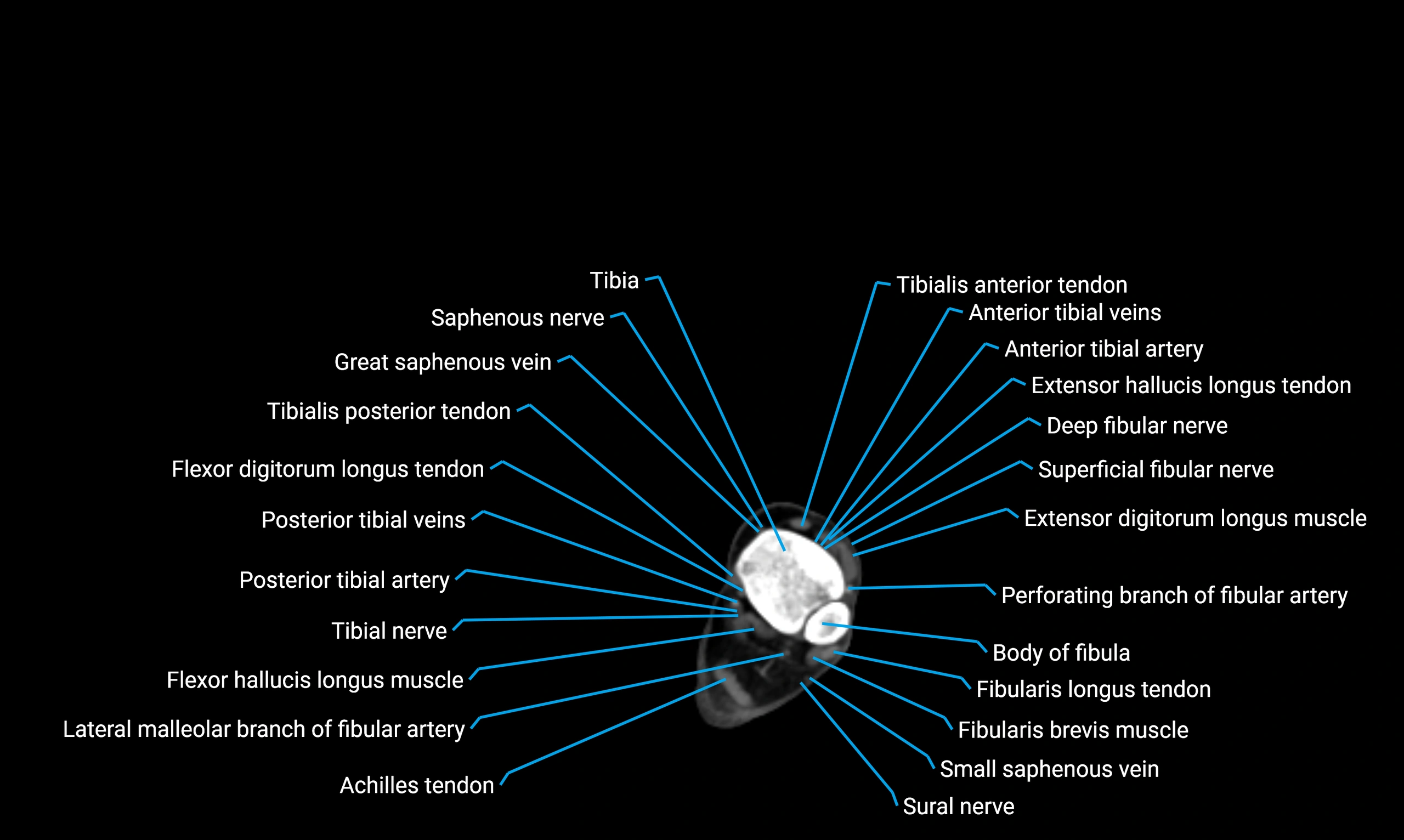
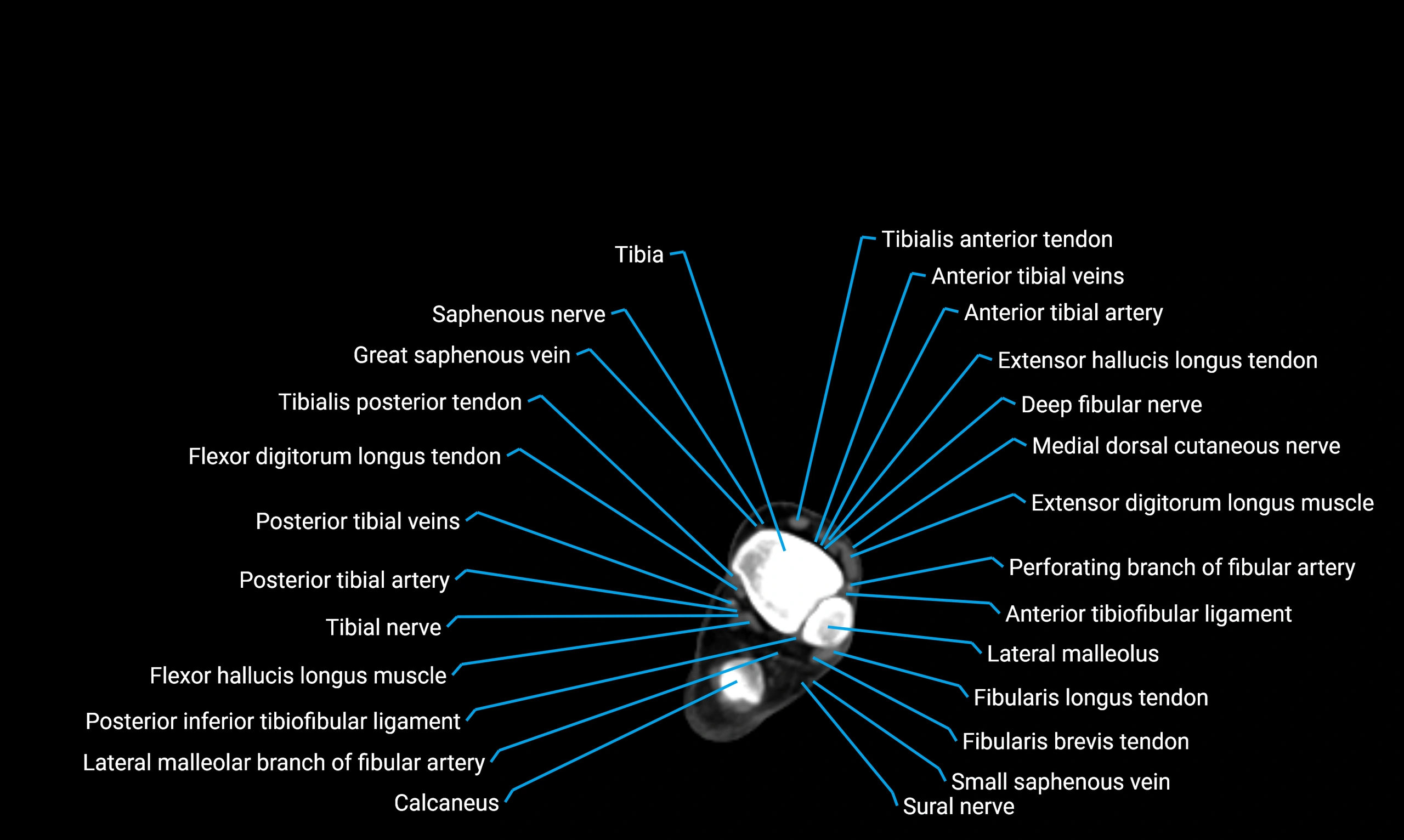
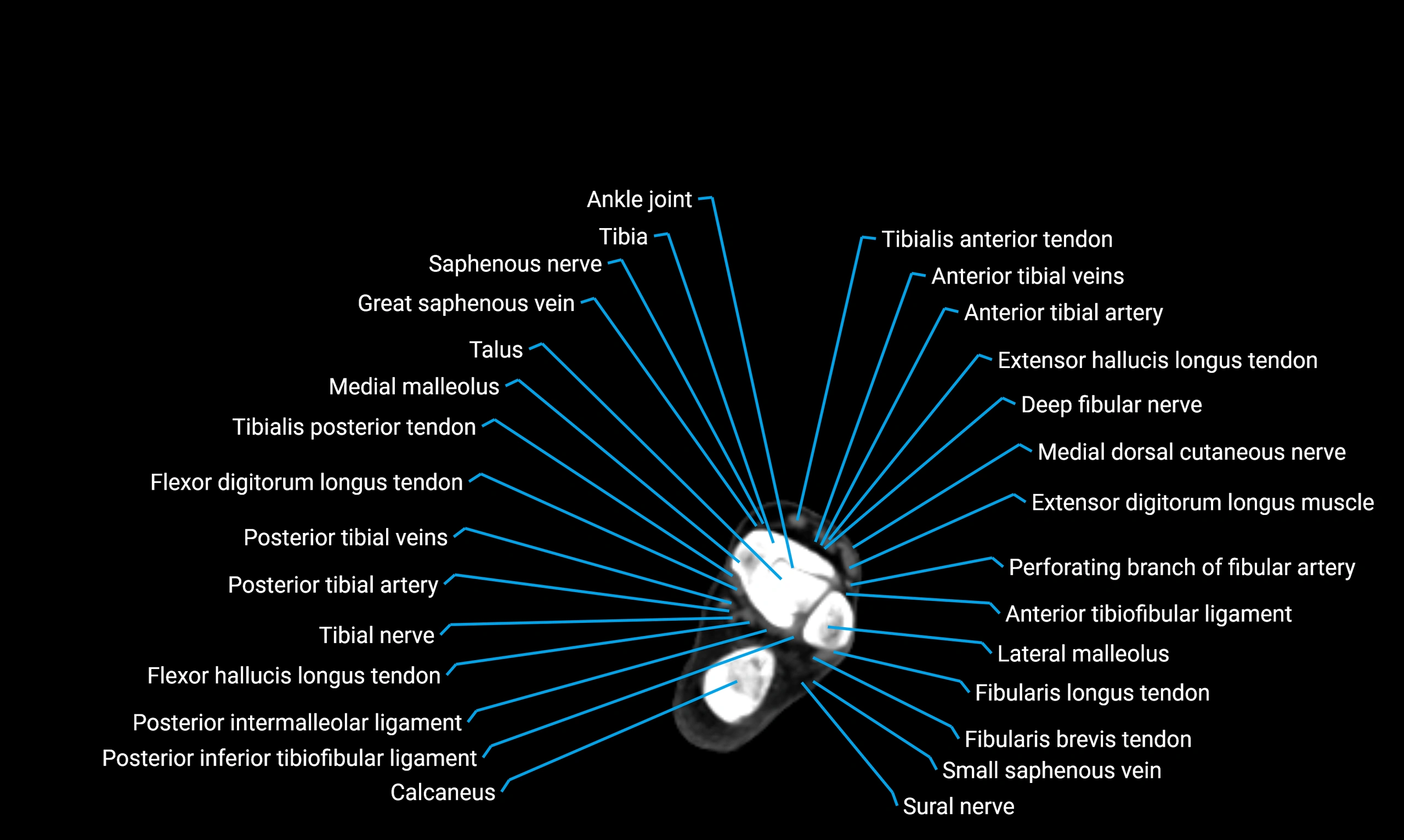
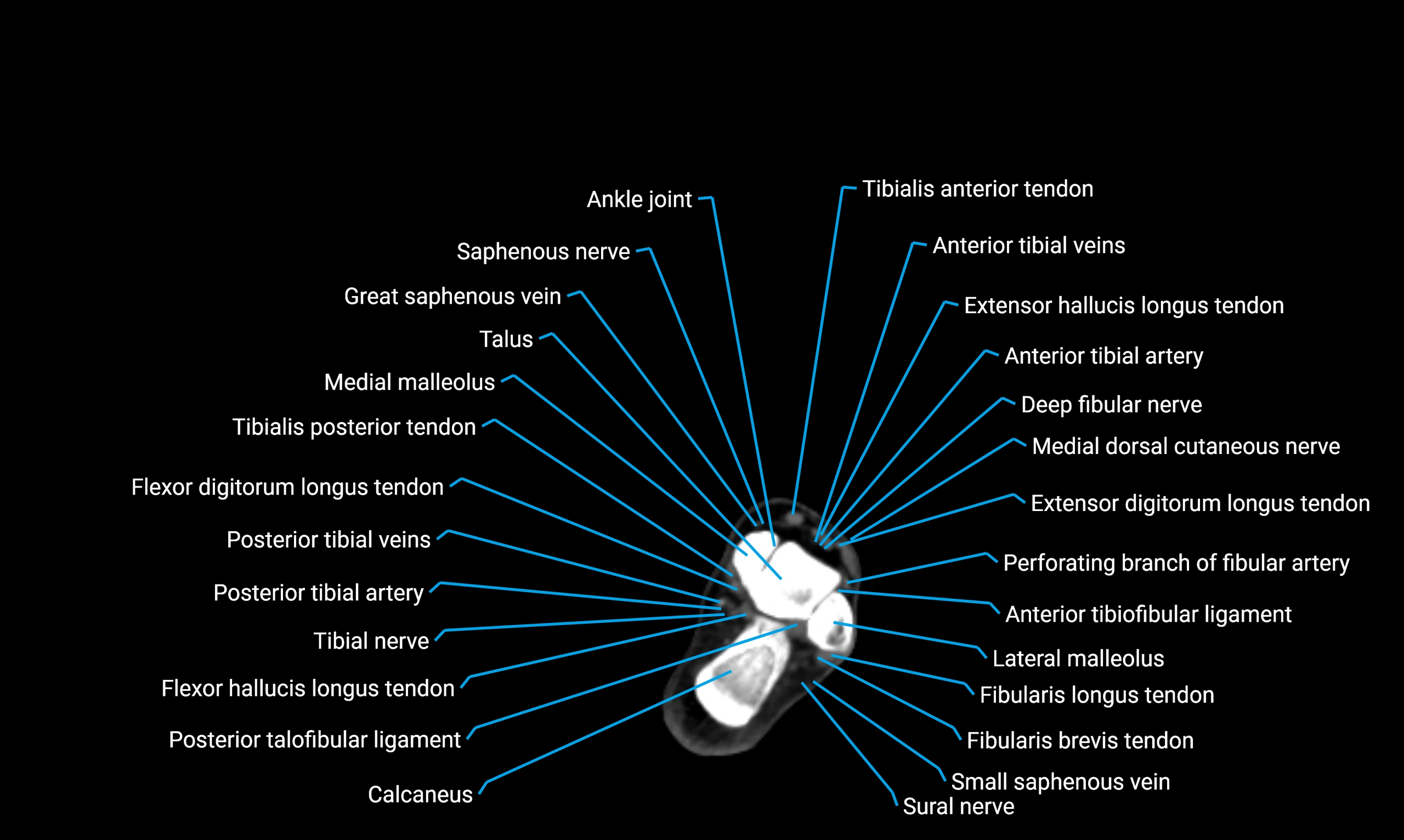
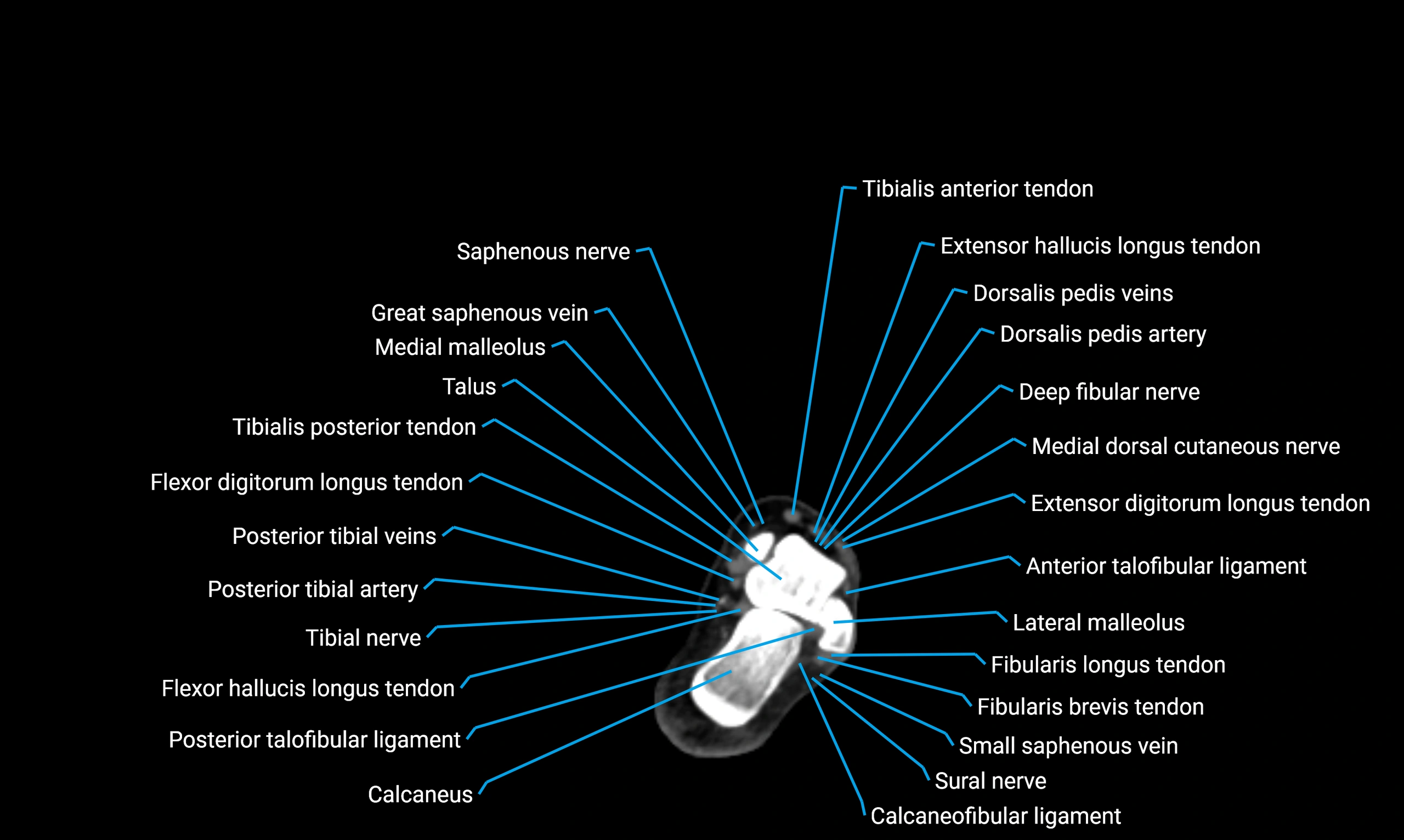
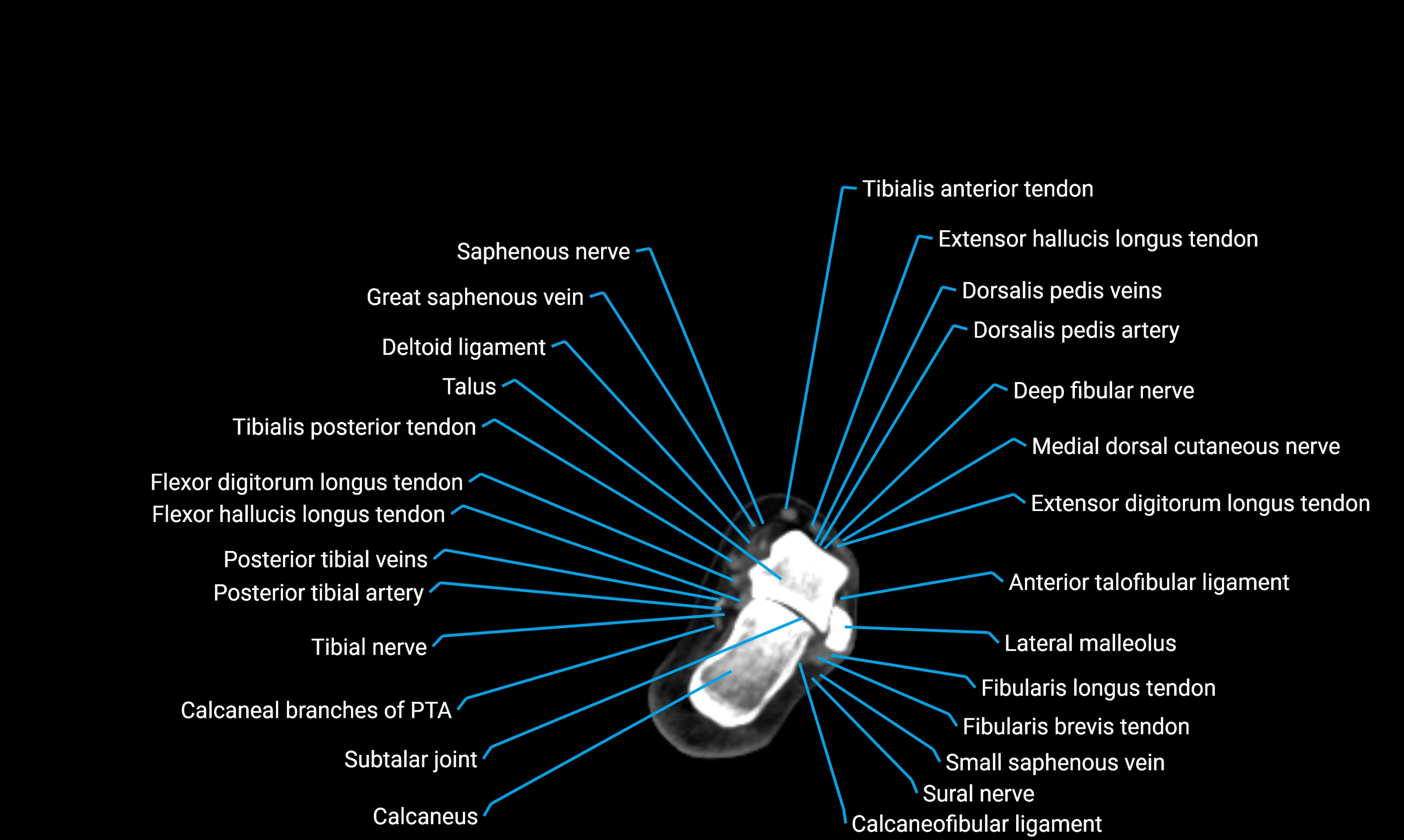
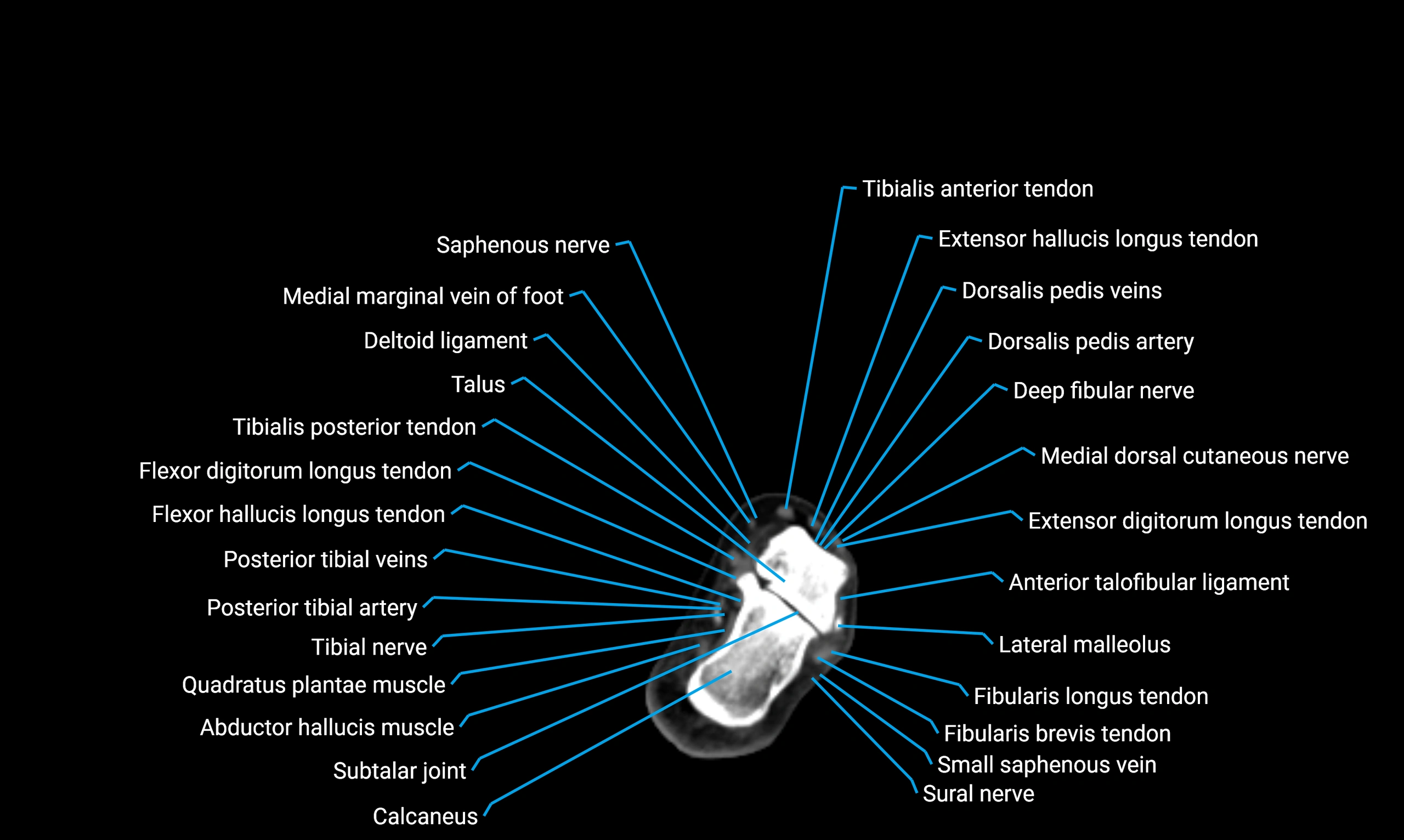
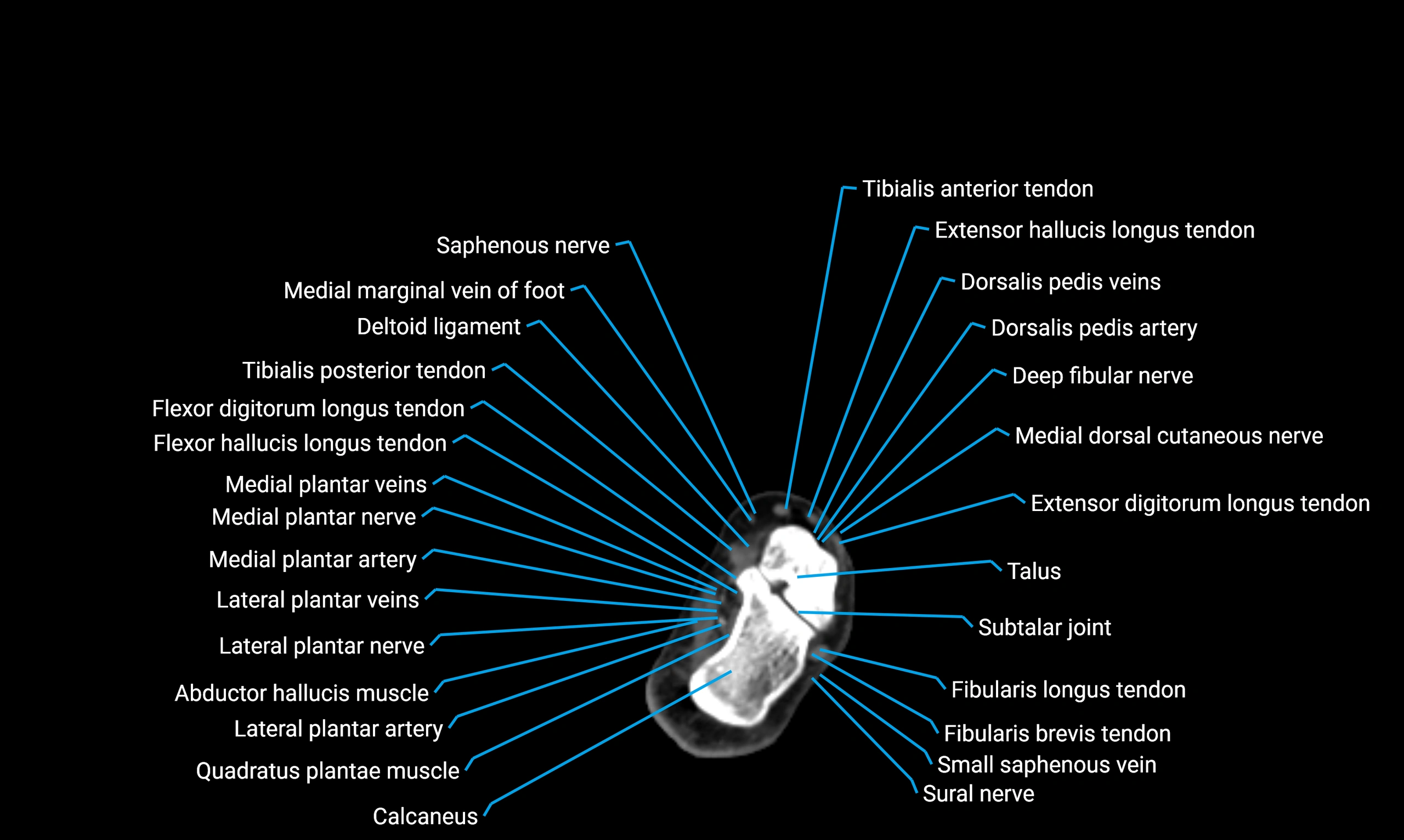
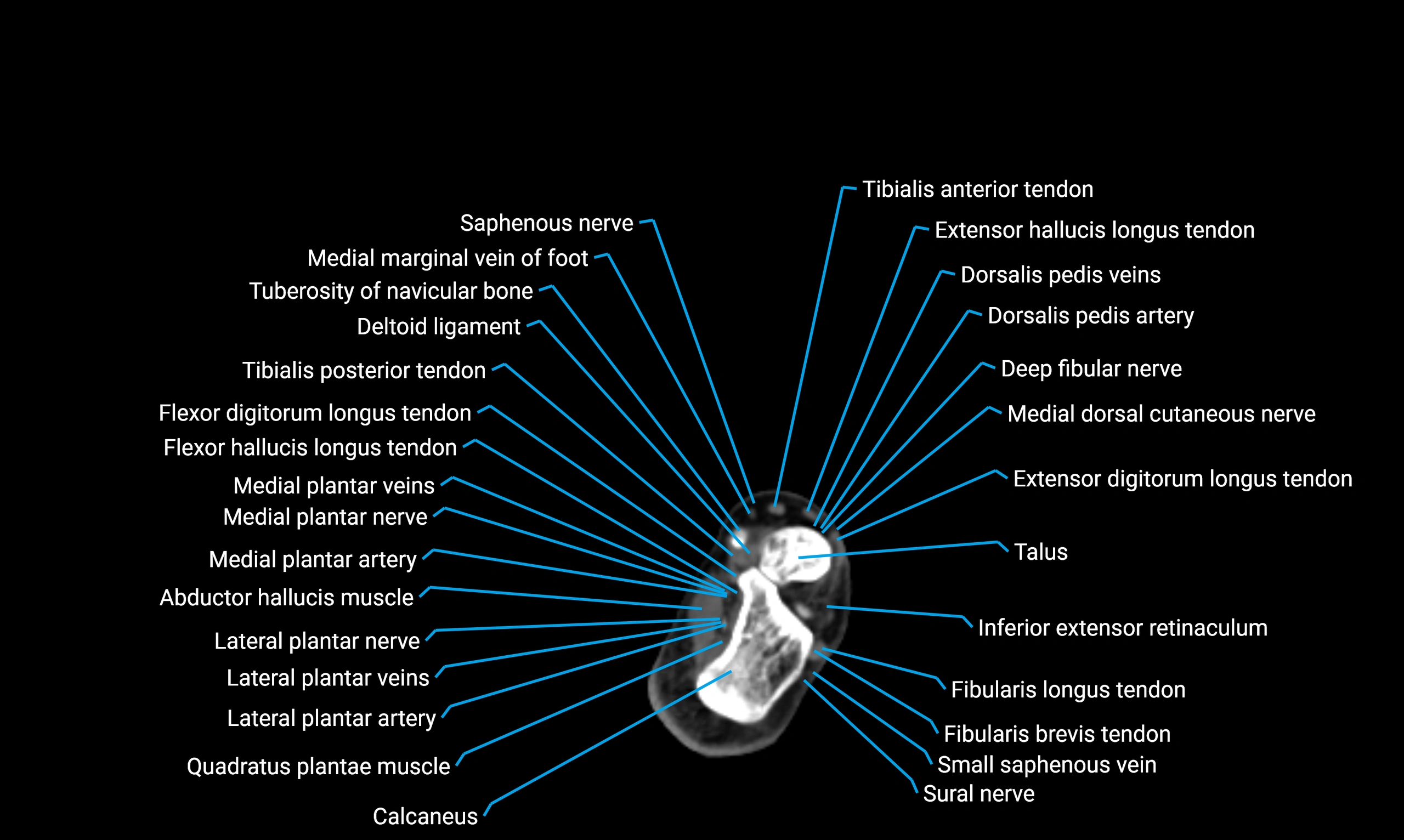
Relations
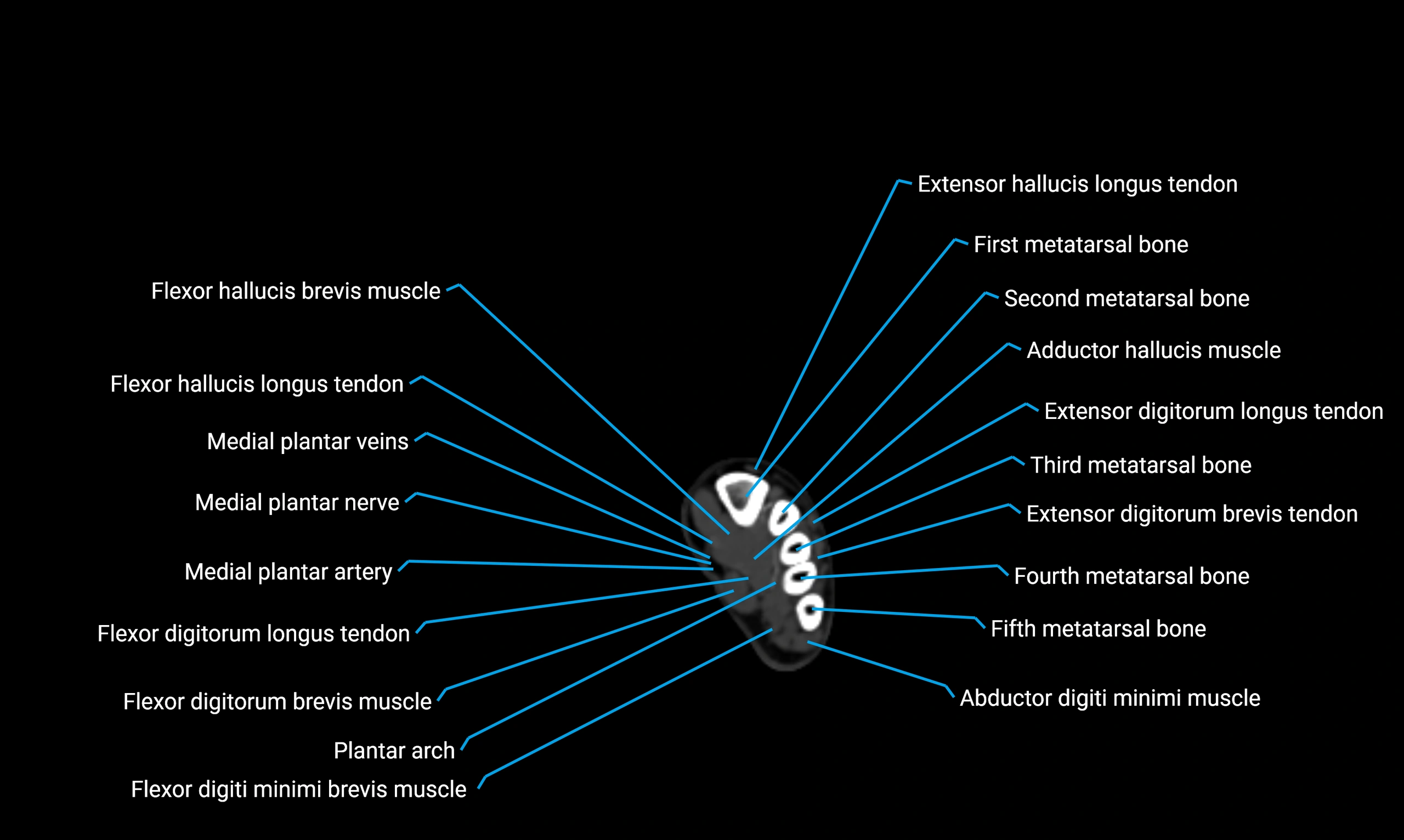
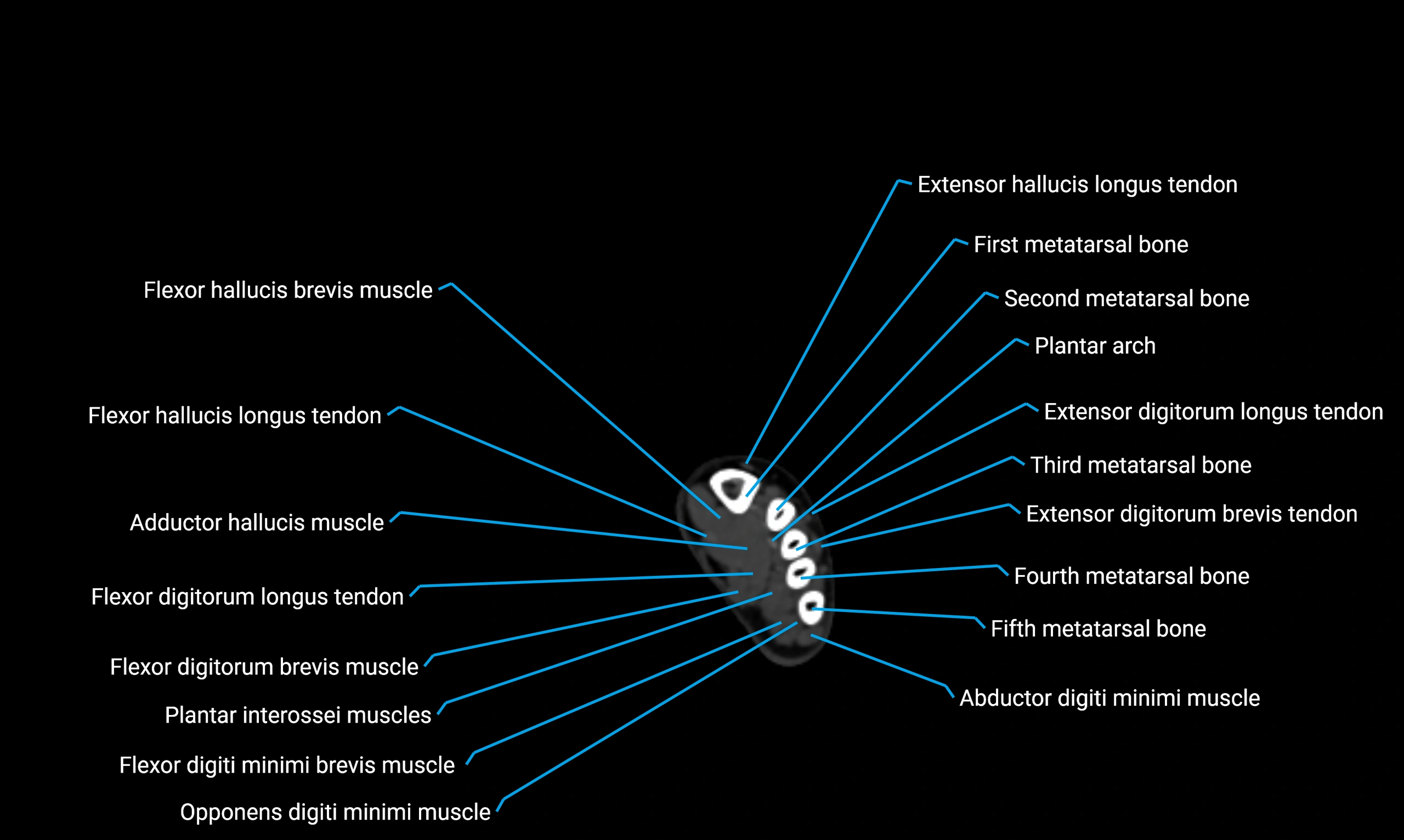
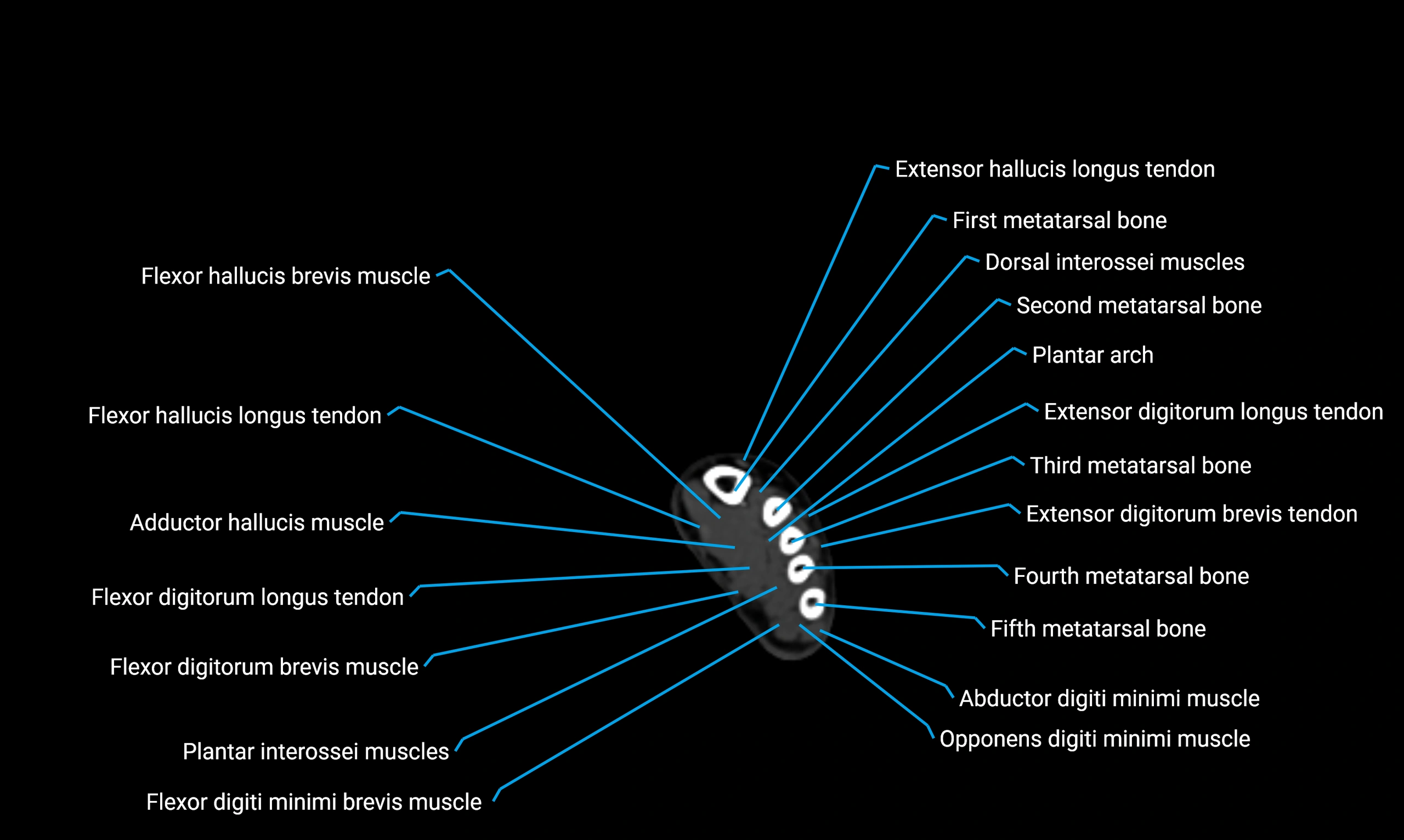
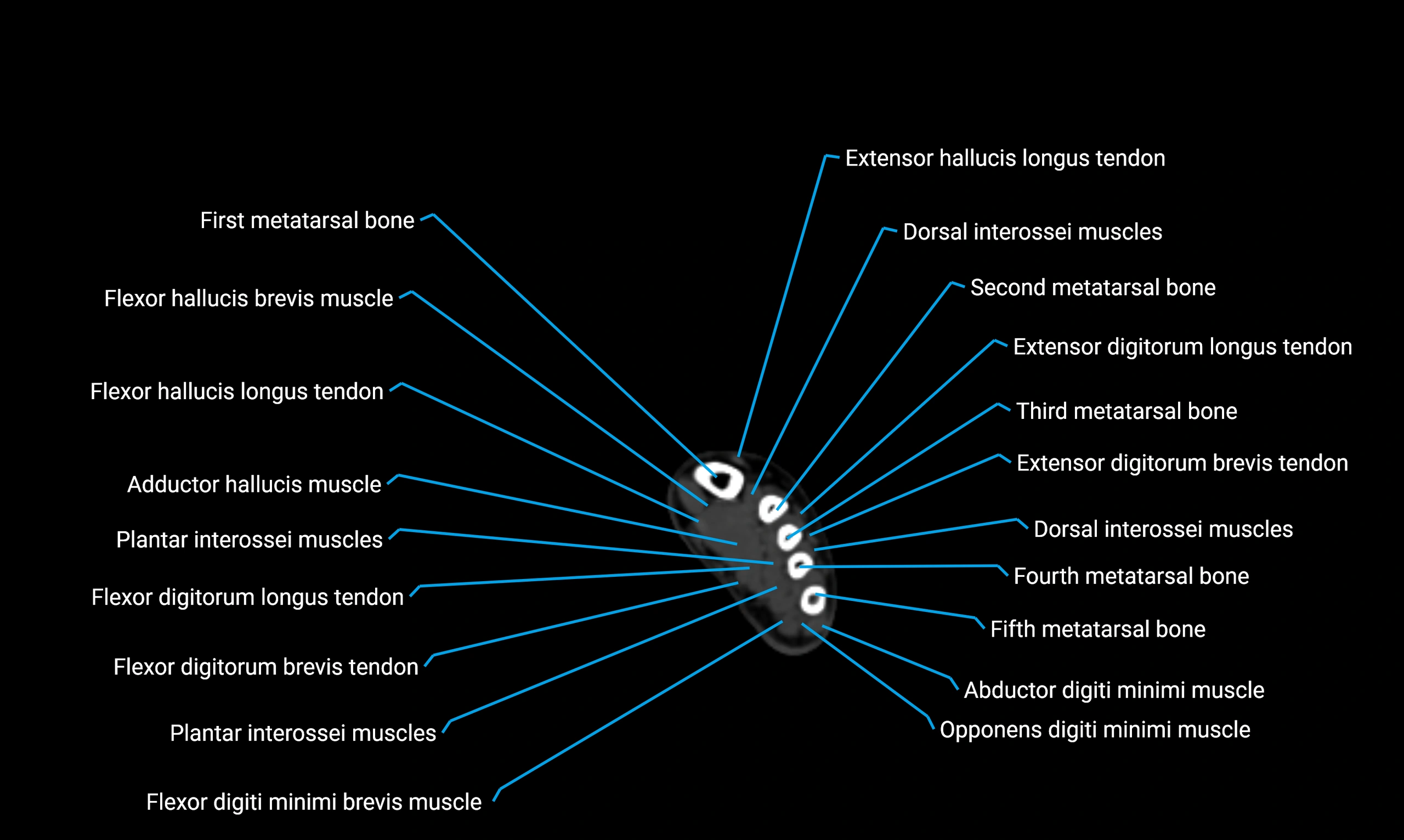
Anteriorly:
-
Extensor muscles of the leg
-
Tibialis anterior
-
Extensor digitorum longus
-
Extensor hallucis longus
-
Posteriorly:
-
Flexor muscles of the leg
-
Soleus
-
Flexor hallucis longus
-
Laterally:
-
Peroneal (fibular) muscles
-
Peroneus longus
-
Peroneus brevis
-
Medially:
-
Interosseous membrane
-
Tibia
Muscle and ligament attachments
-
Peroneus longus and brevis on the lateral surface
-
Soleus and flexor hallucis longus on the posterior surface
-
Extensor muscles on the anterior surface
-
Interosseous membrane along the medial border
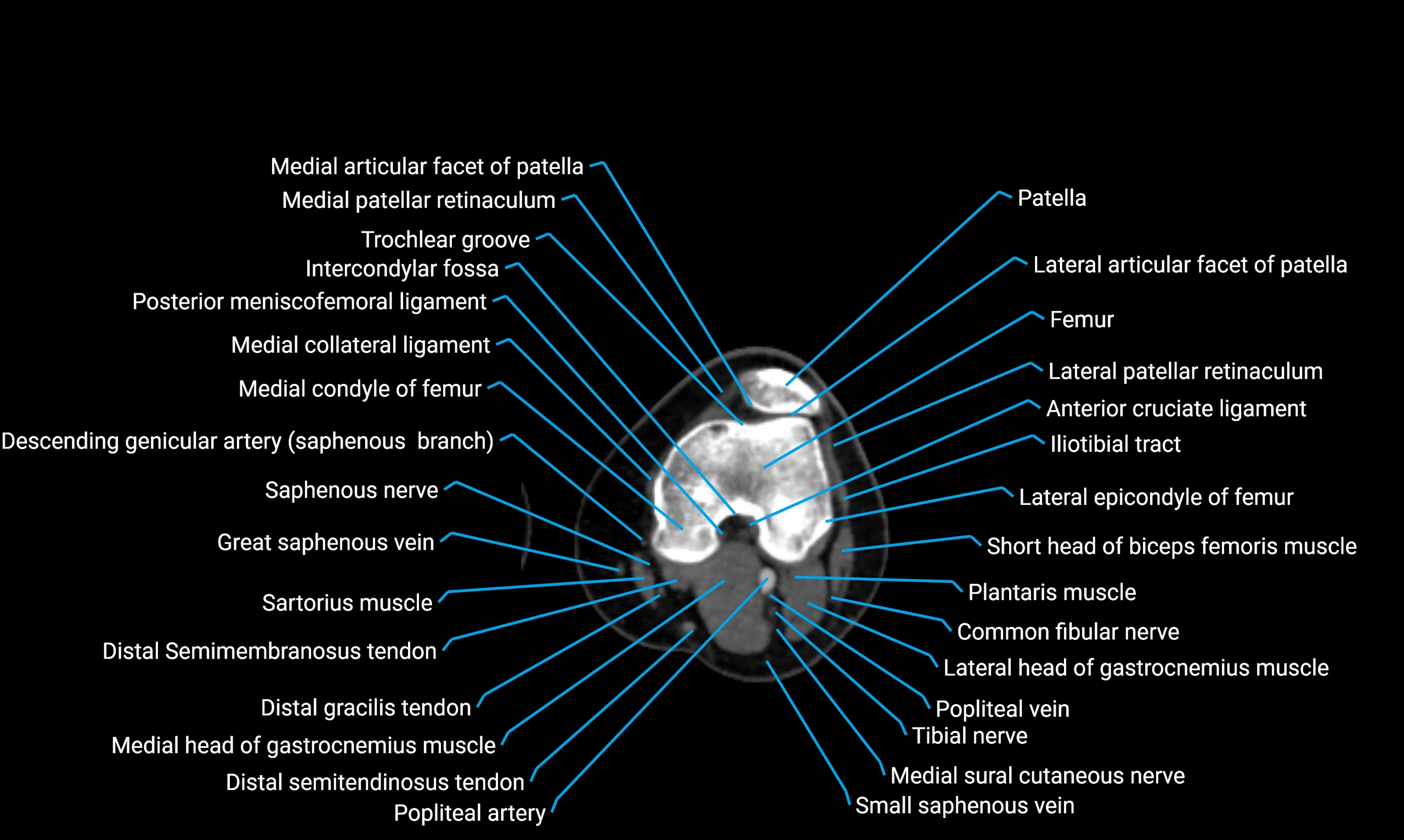
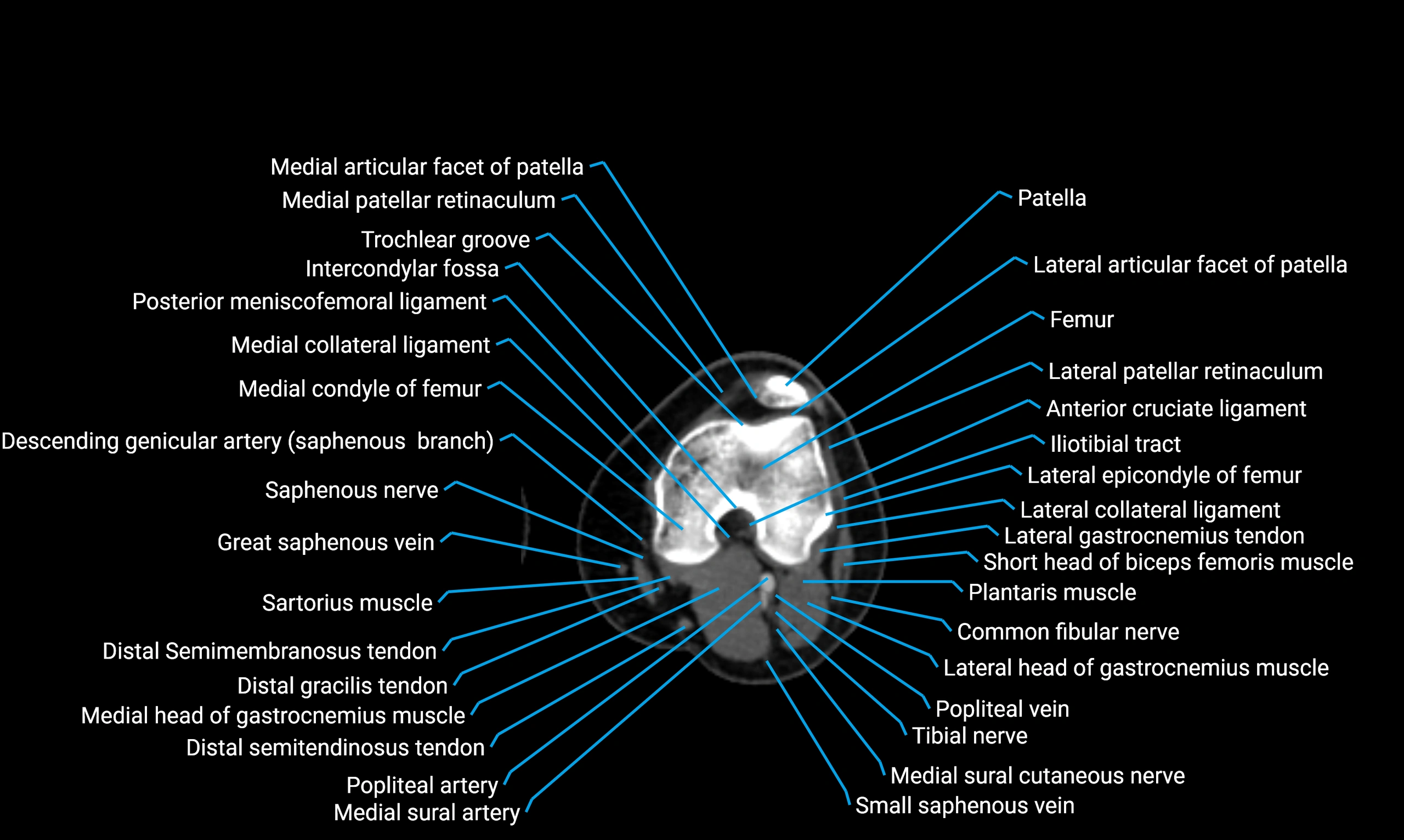
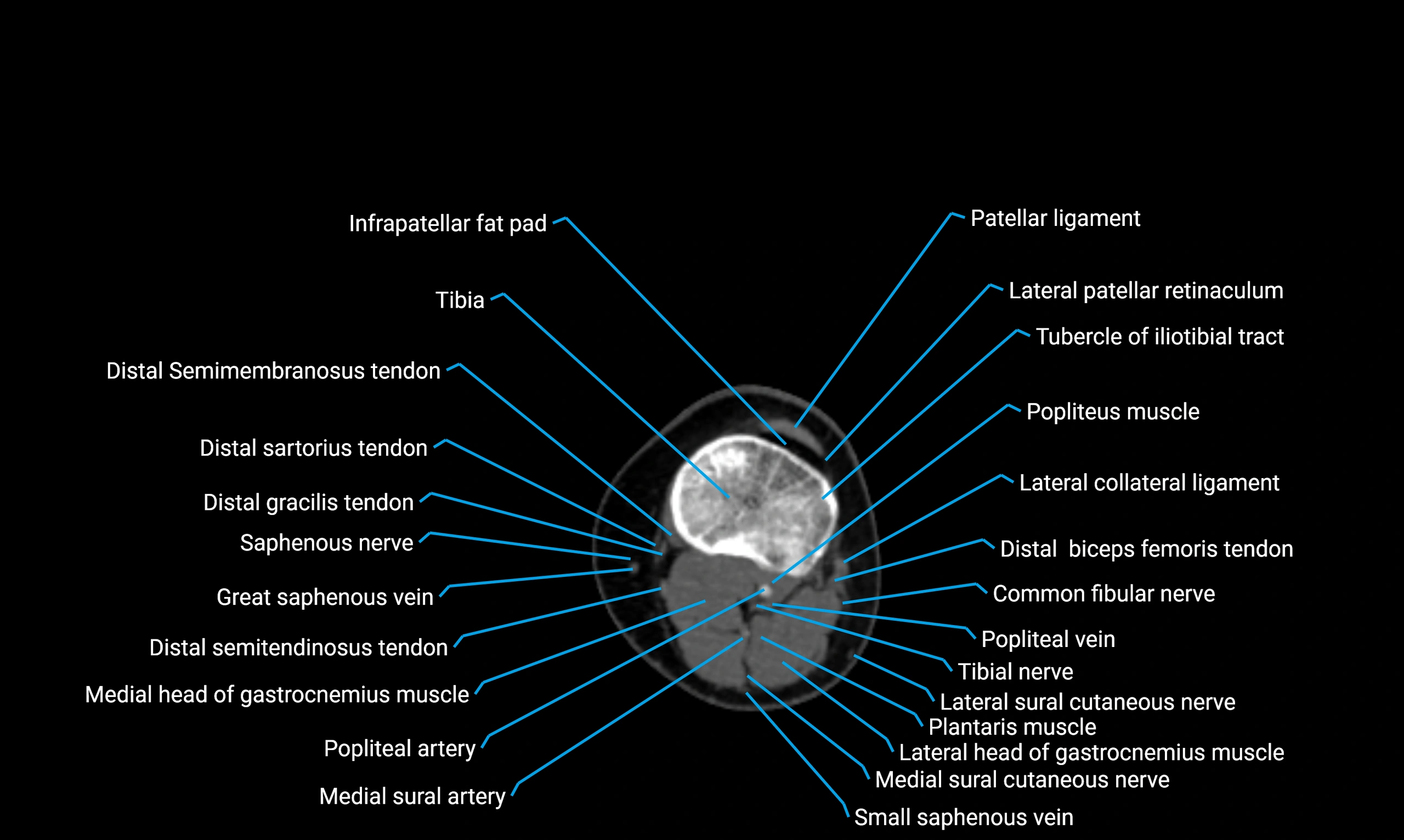
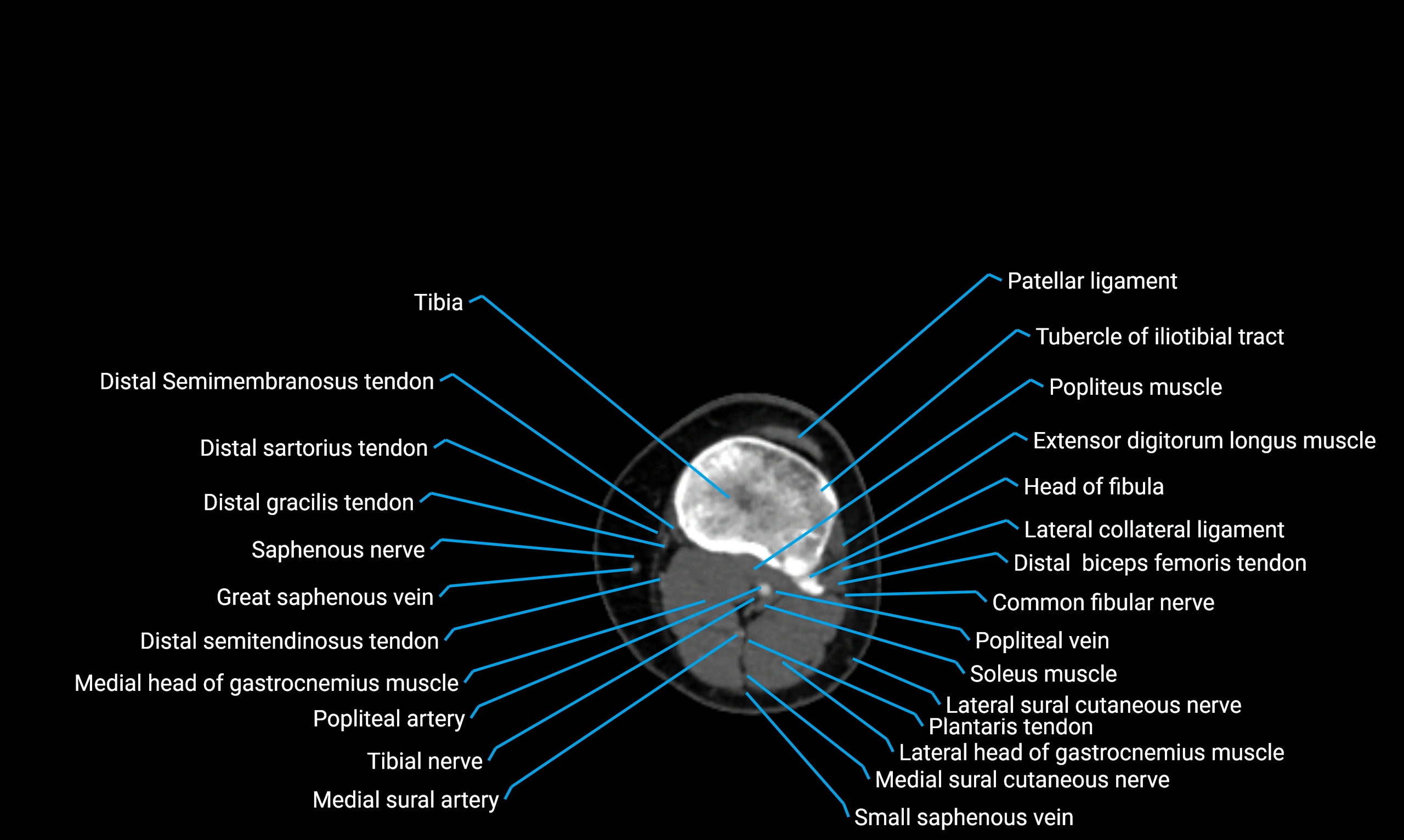
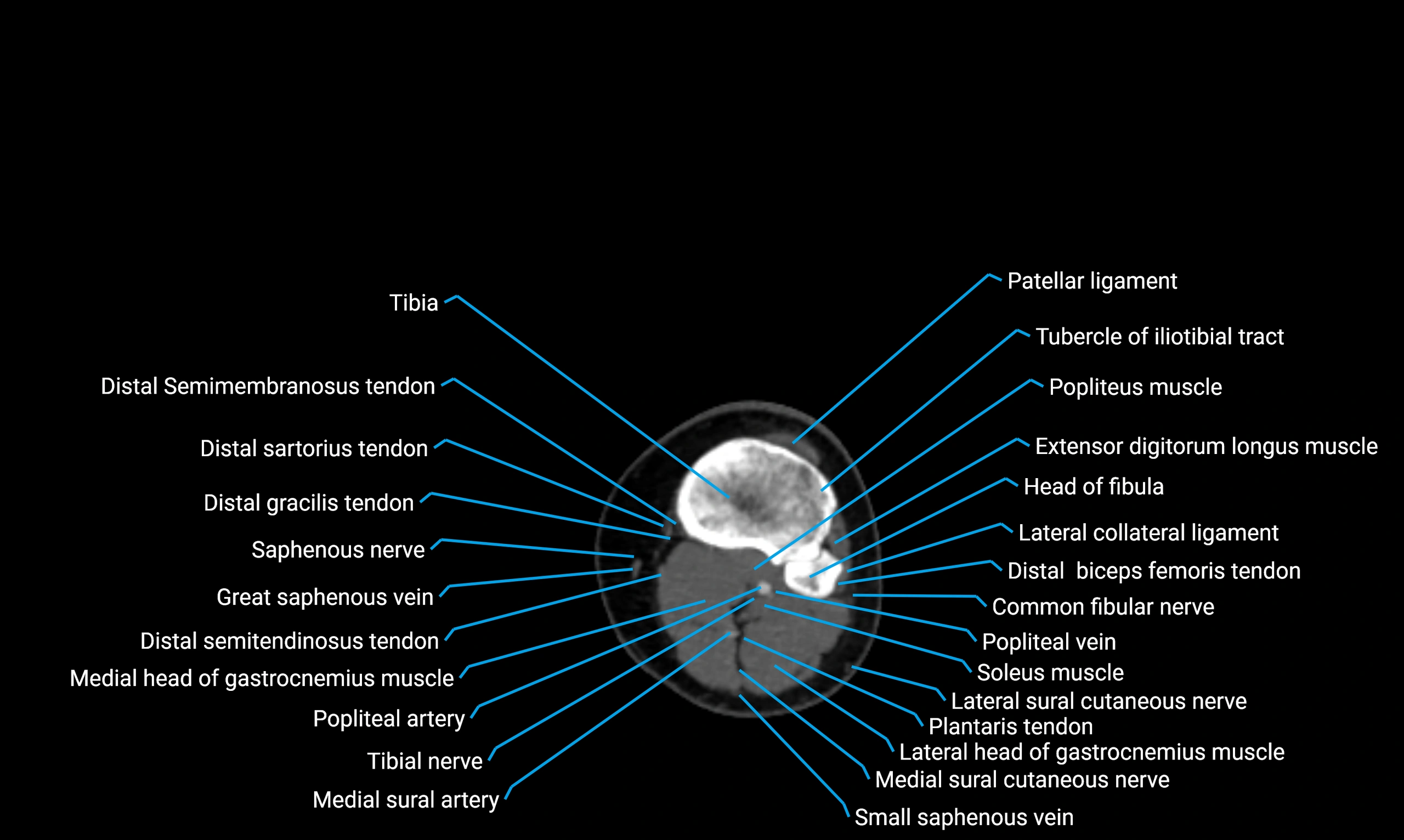
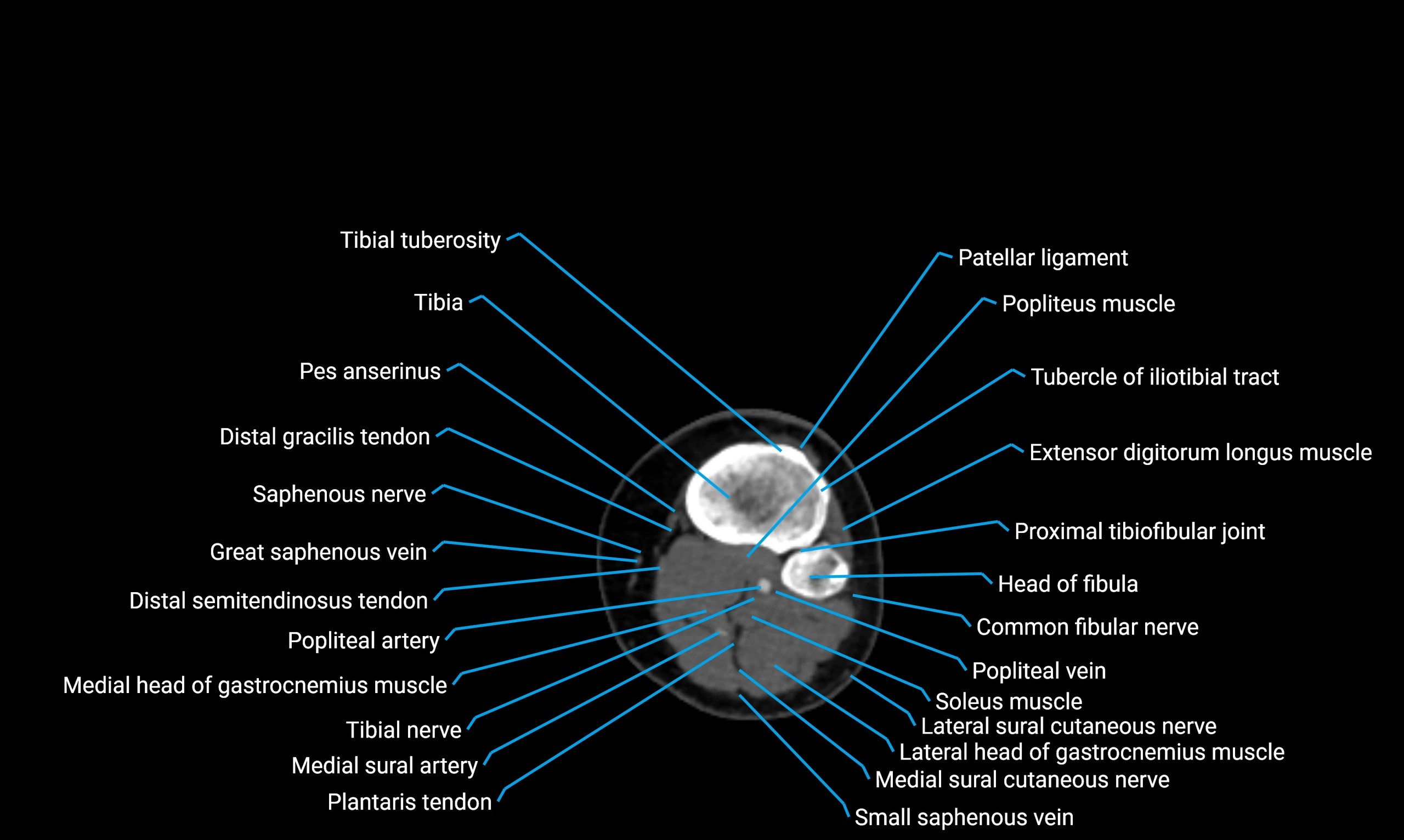
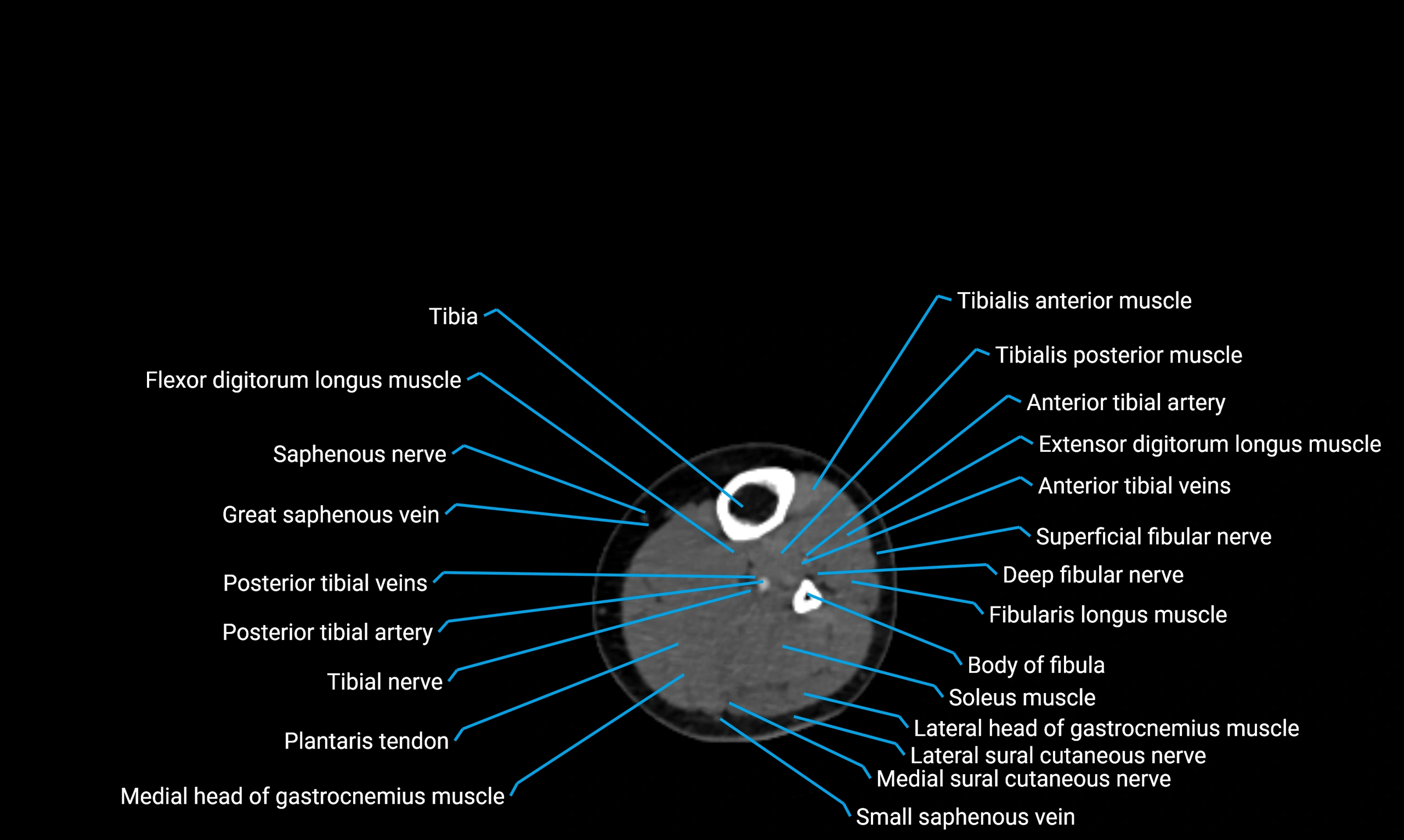
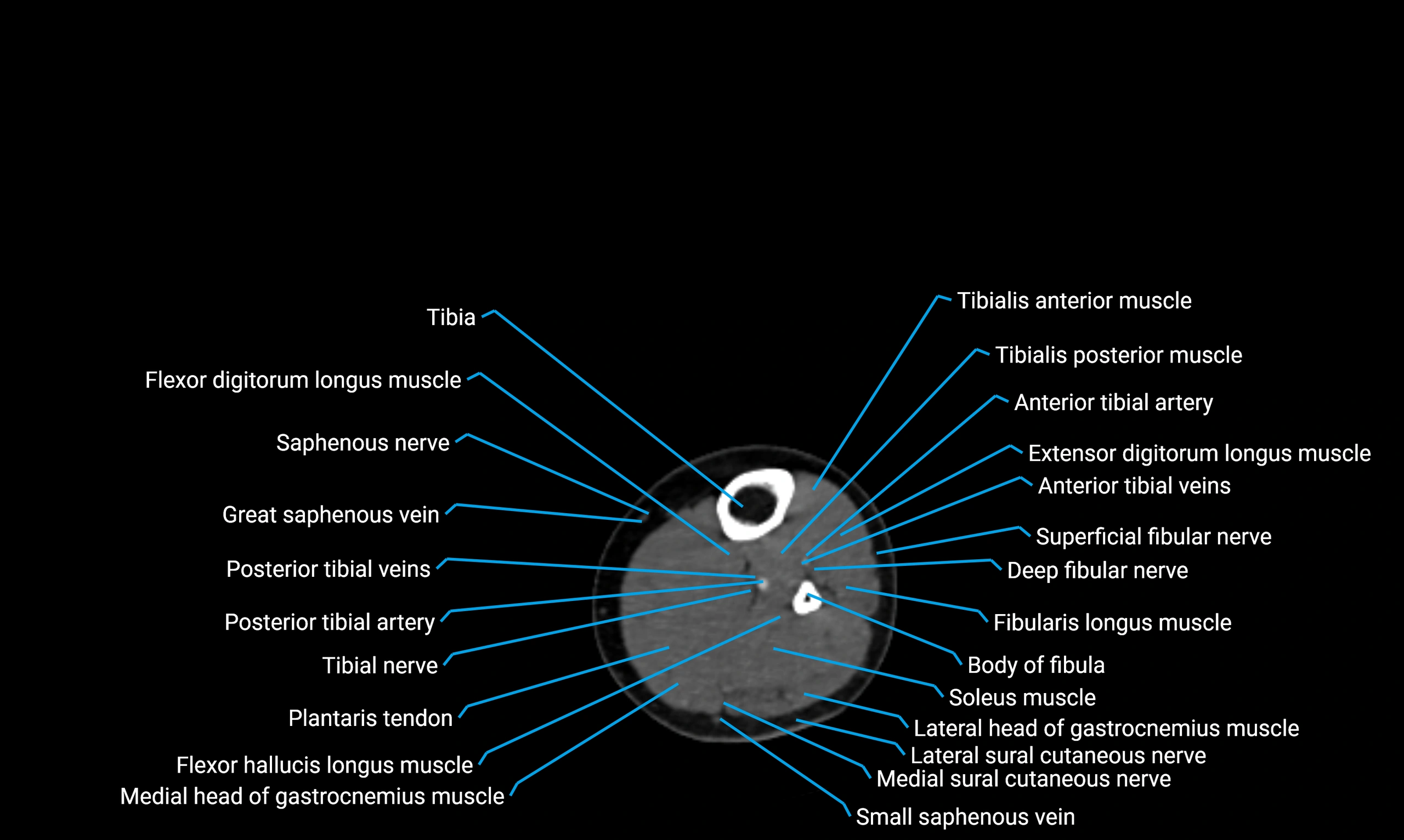
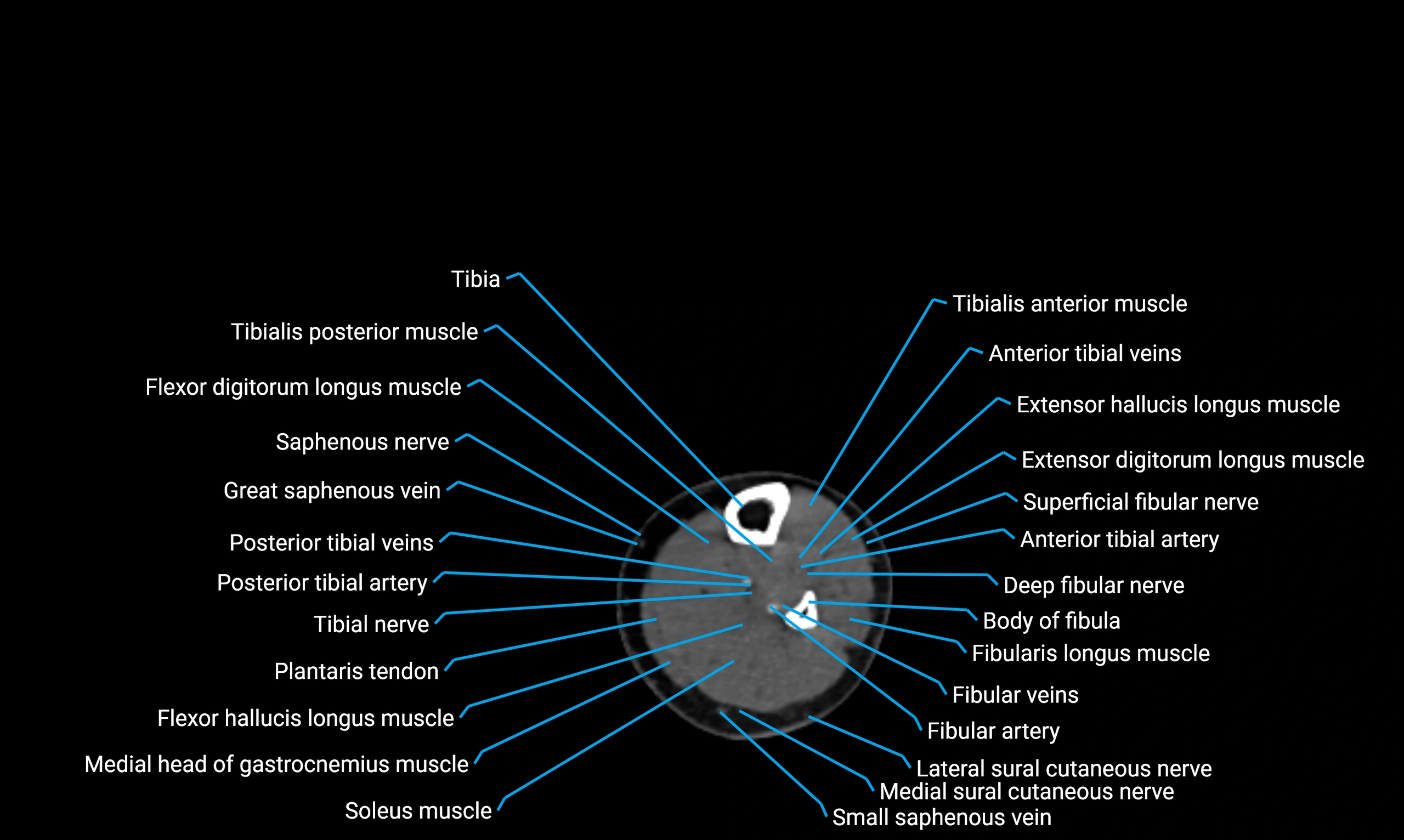
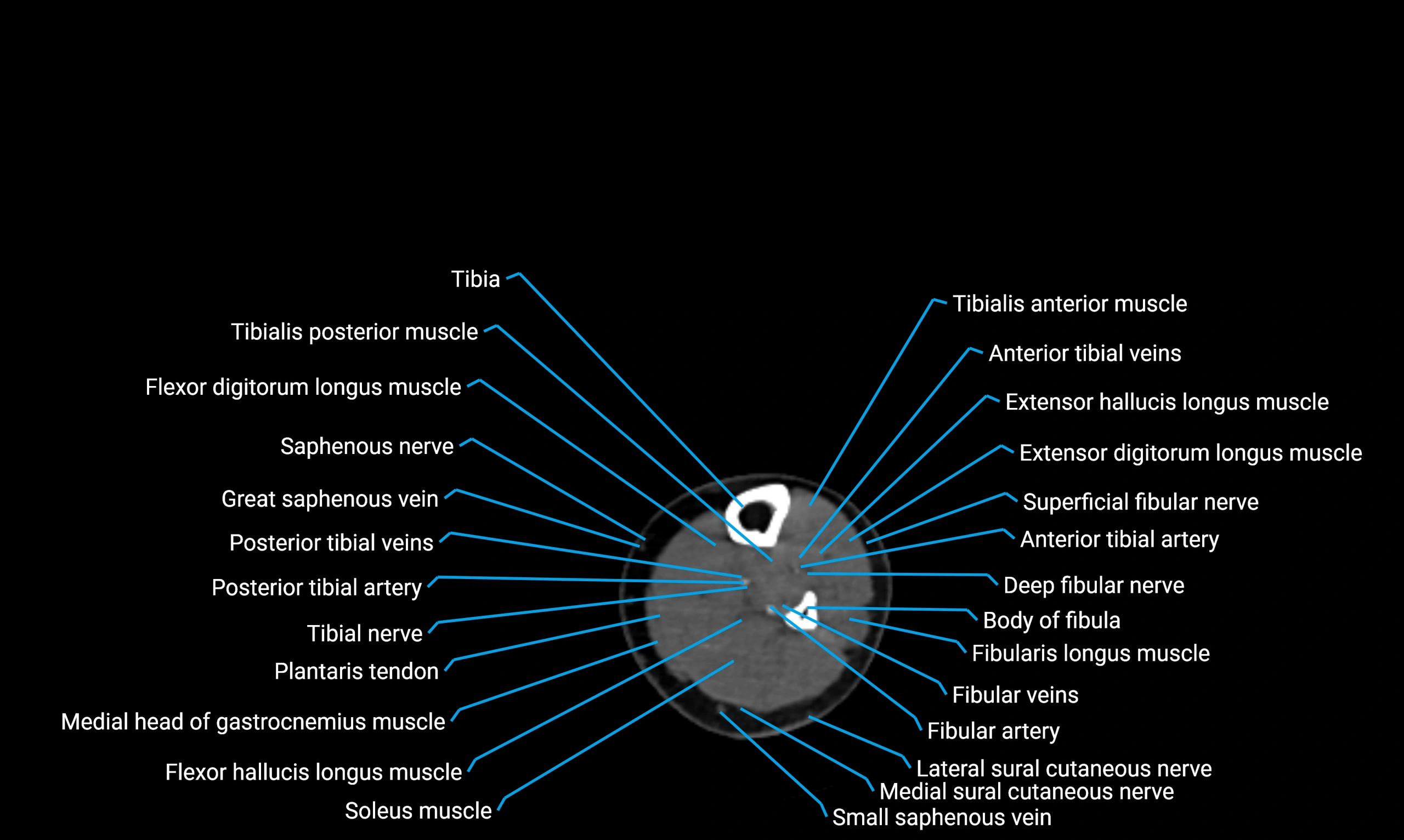
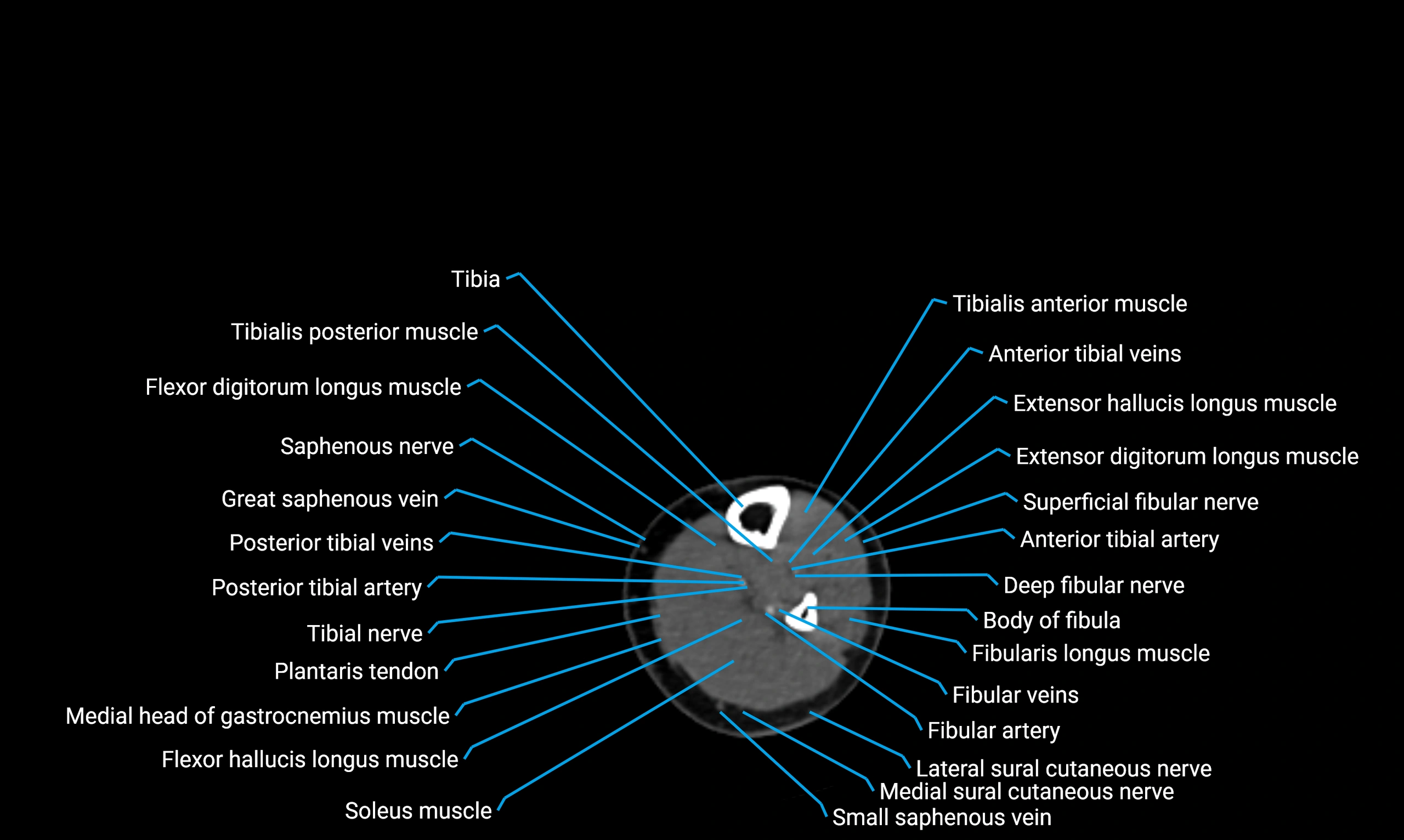
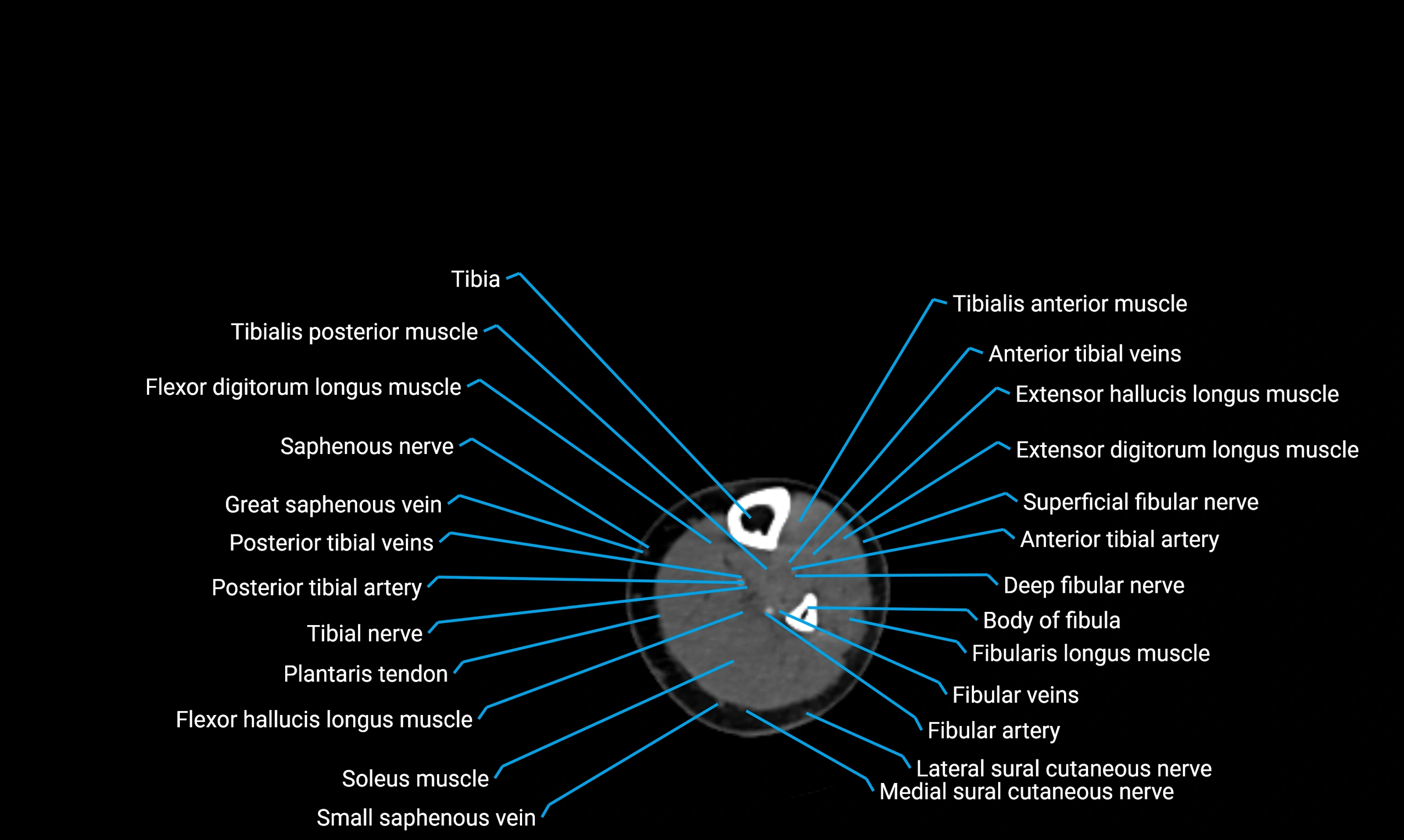
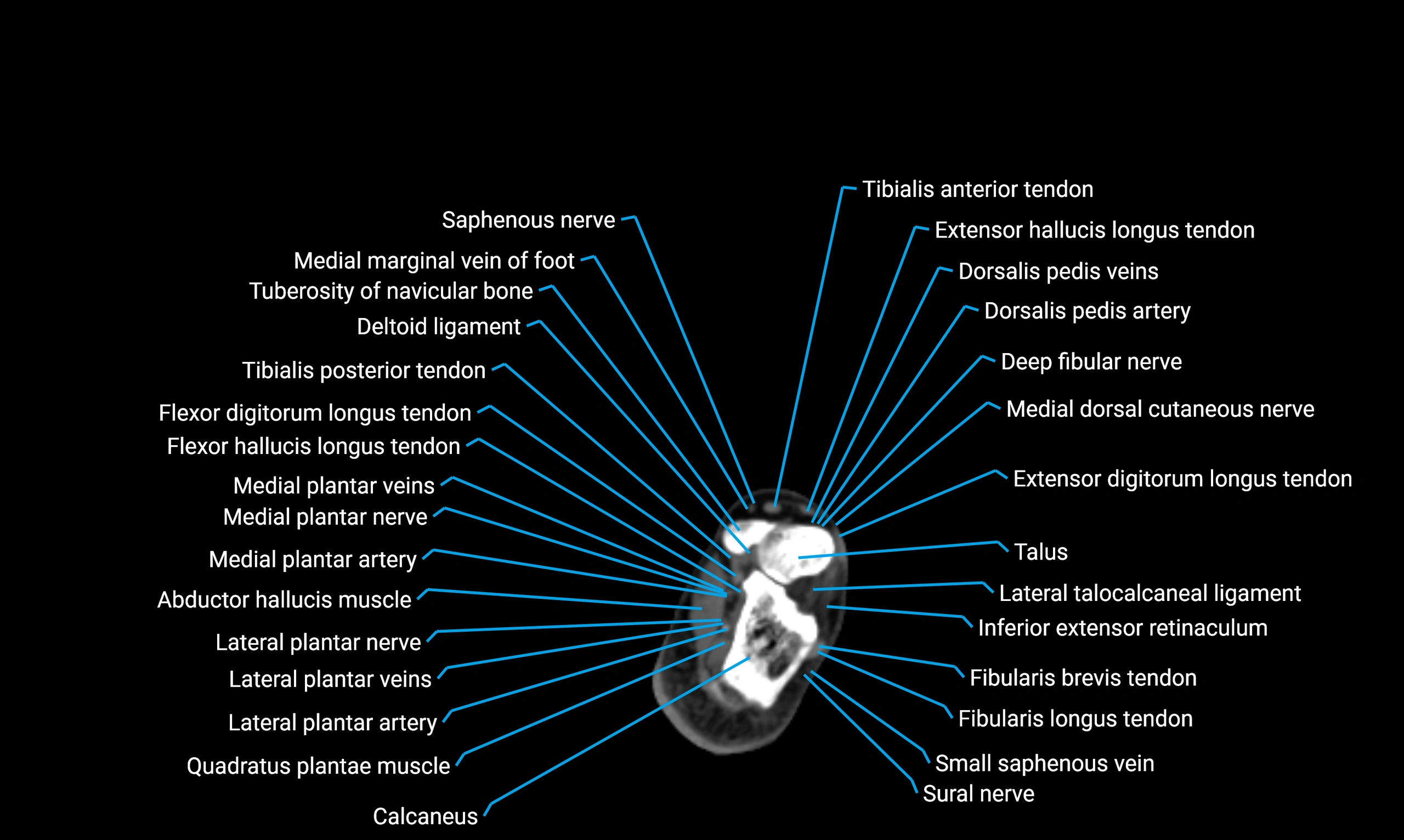
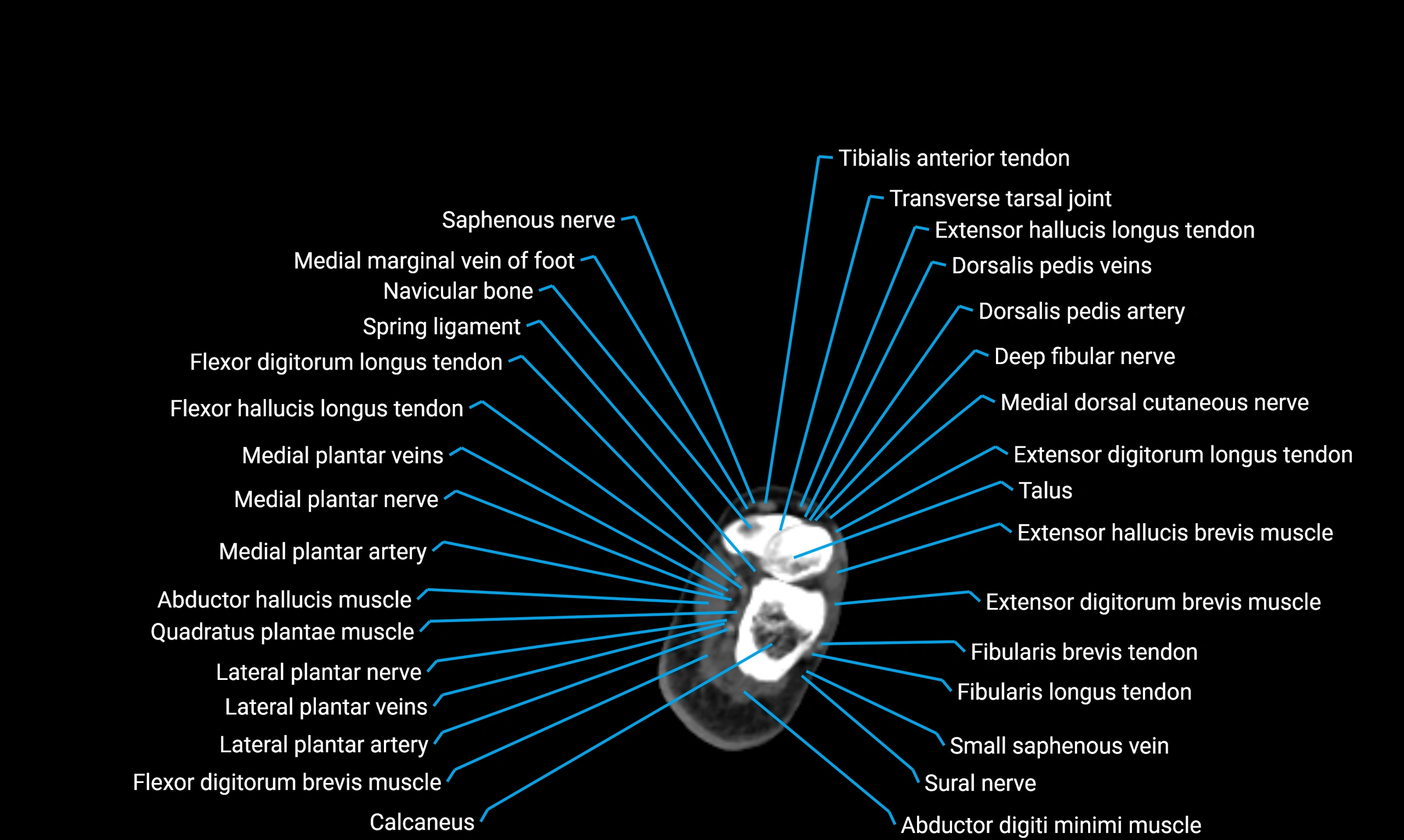
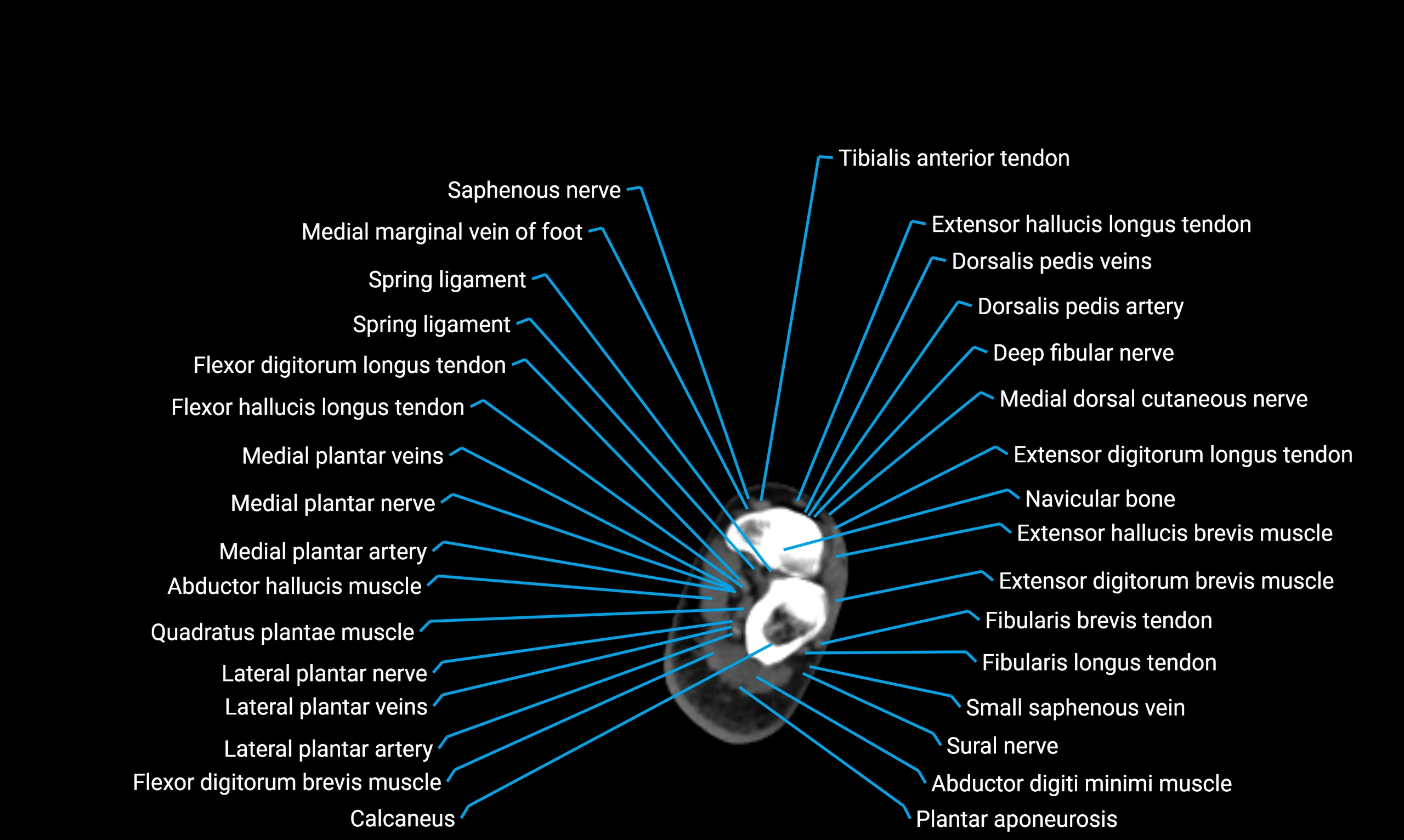
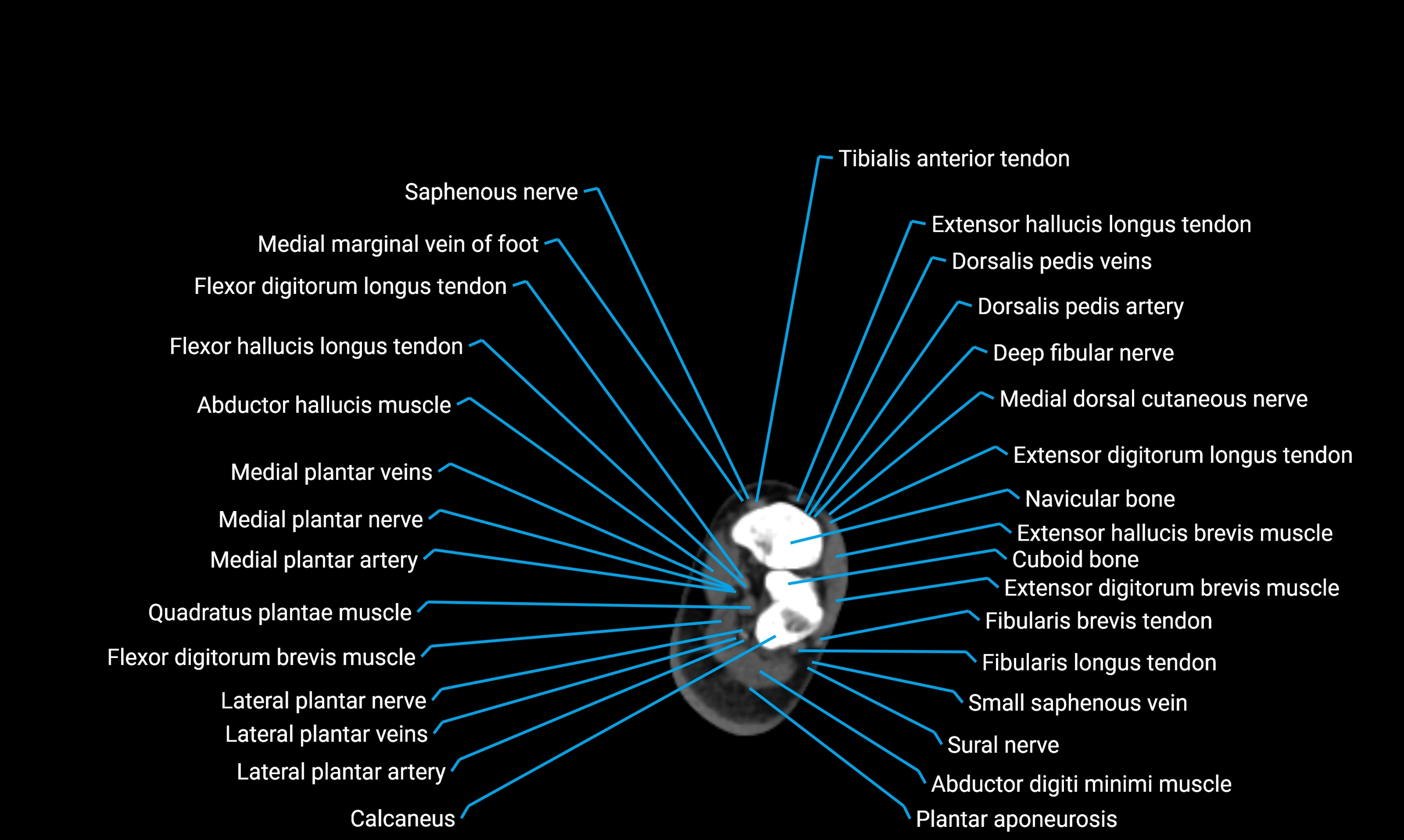
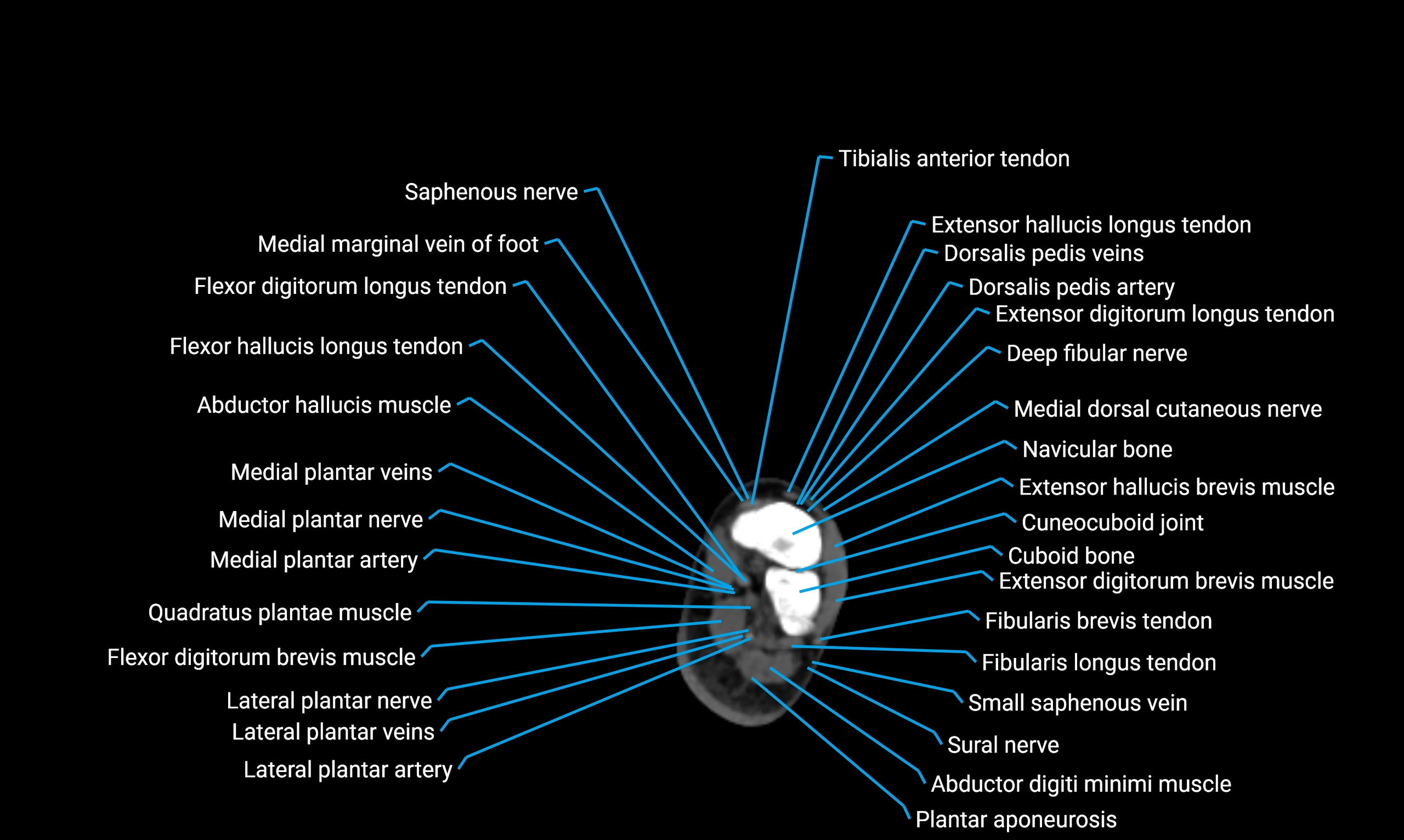
X-ray appearance
Plain radiographs (AP and lateral leg views):
-
Fibular shaft: Thin, tubular radiopaque structure lateral to tibia
-
Cortical margins: Smooth and well-defined
-
Medullary canal: Central radiolucent line
-
Alignment: Parallel to tibial shaft
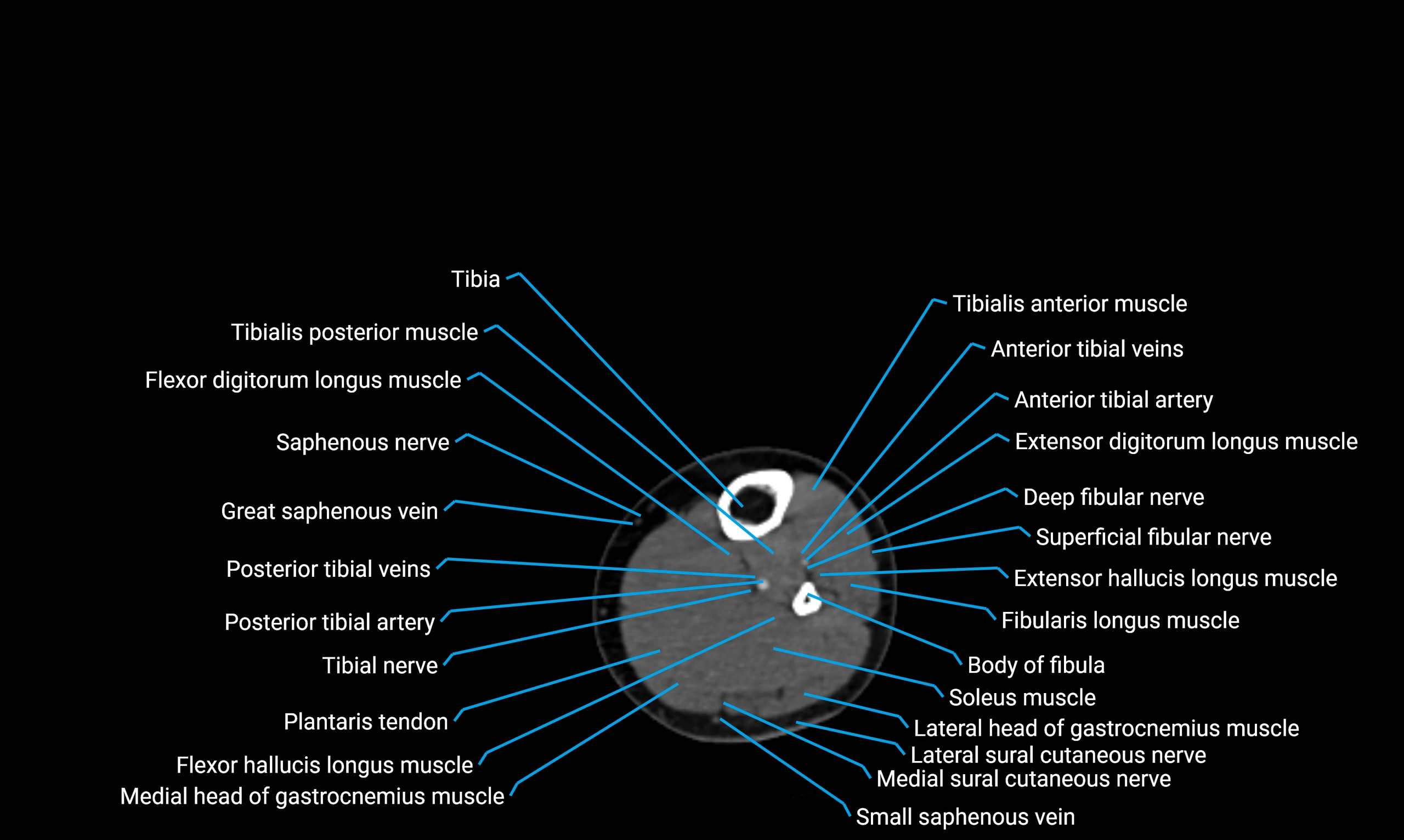
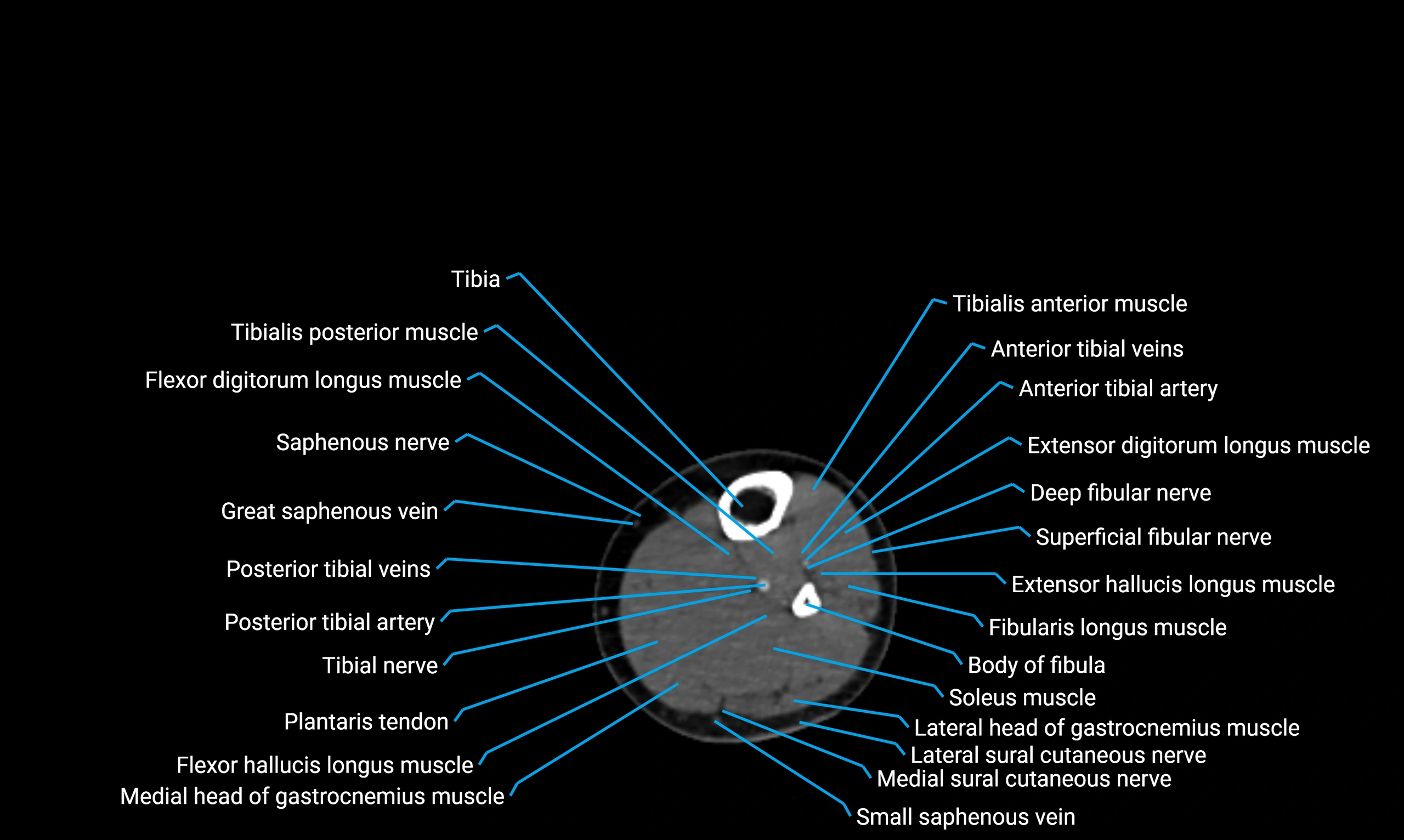
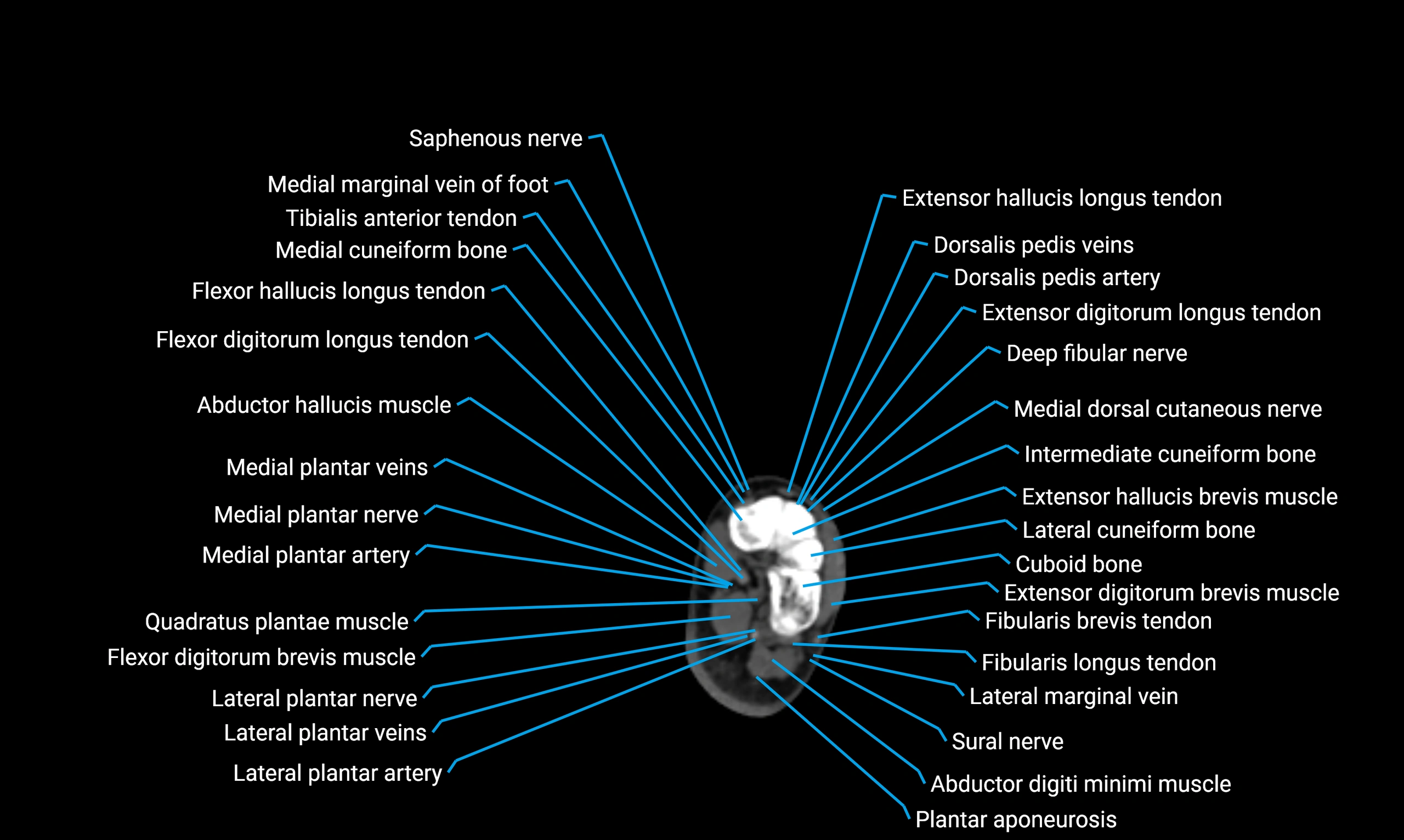
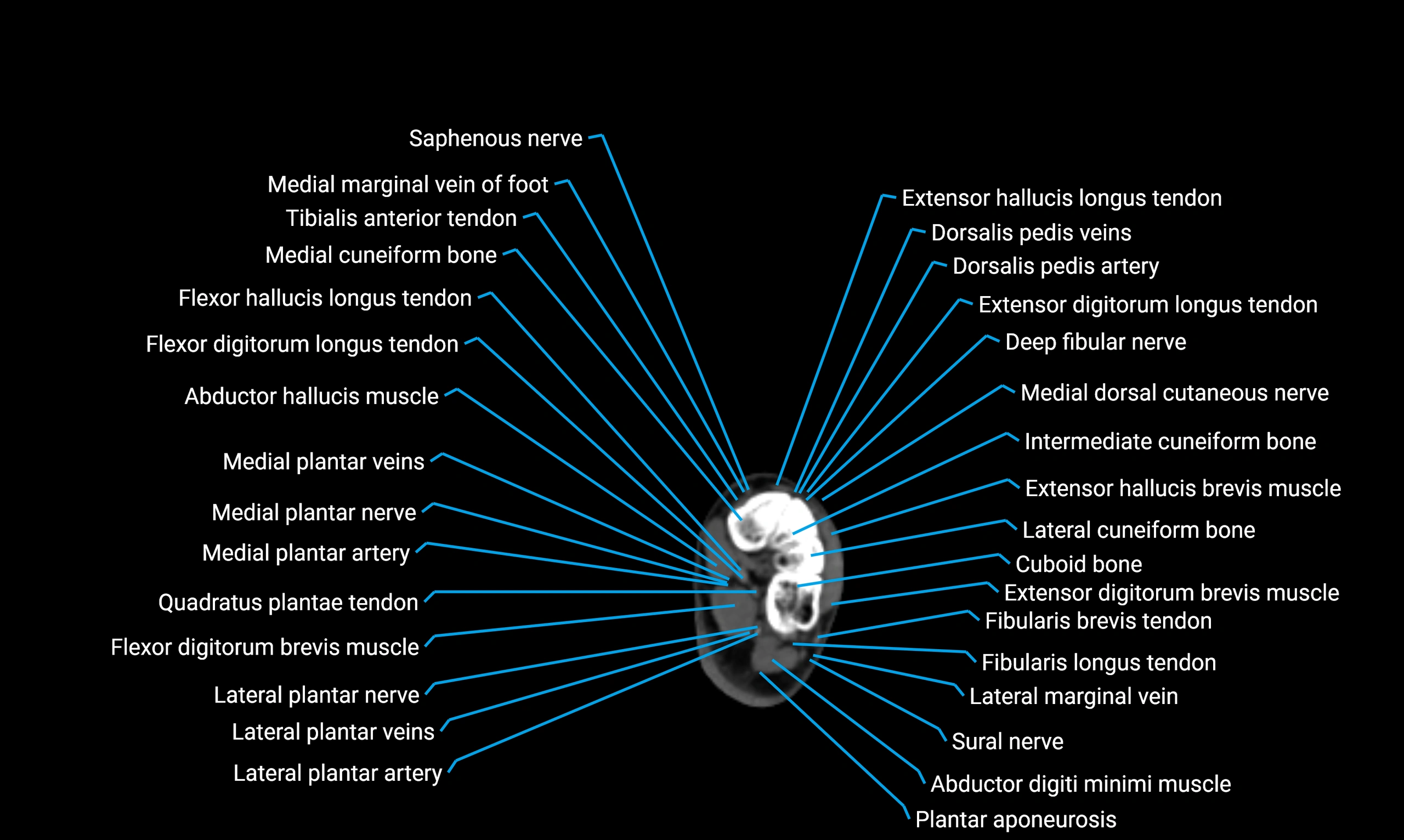
CT appearance
Non-contrast CT:
-
Cortex: Dense outer cortical bone
-
Medulla: Lower-density marrow cavity
-
Shaft contour: Smooth, cylindrical morphology
-
Anatomical detail: Excellent delineation of cortical integrity
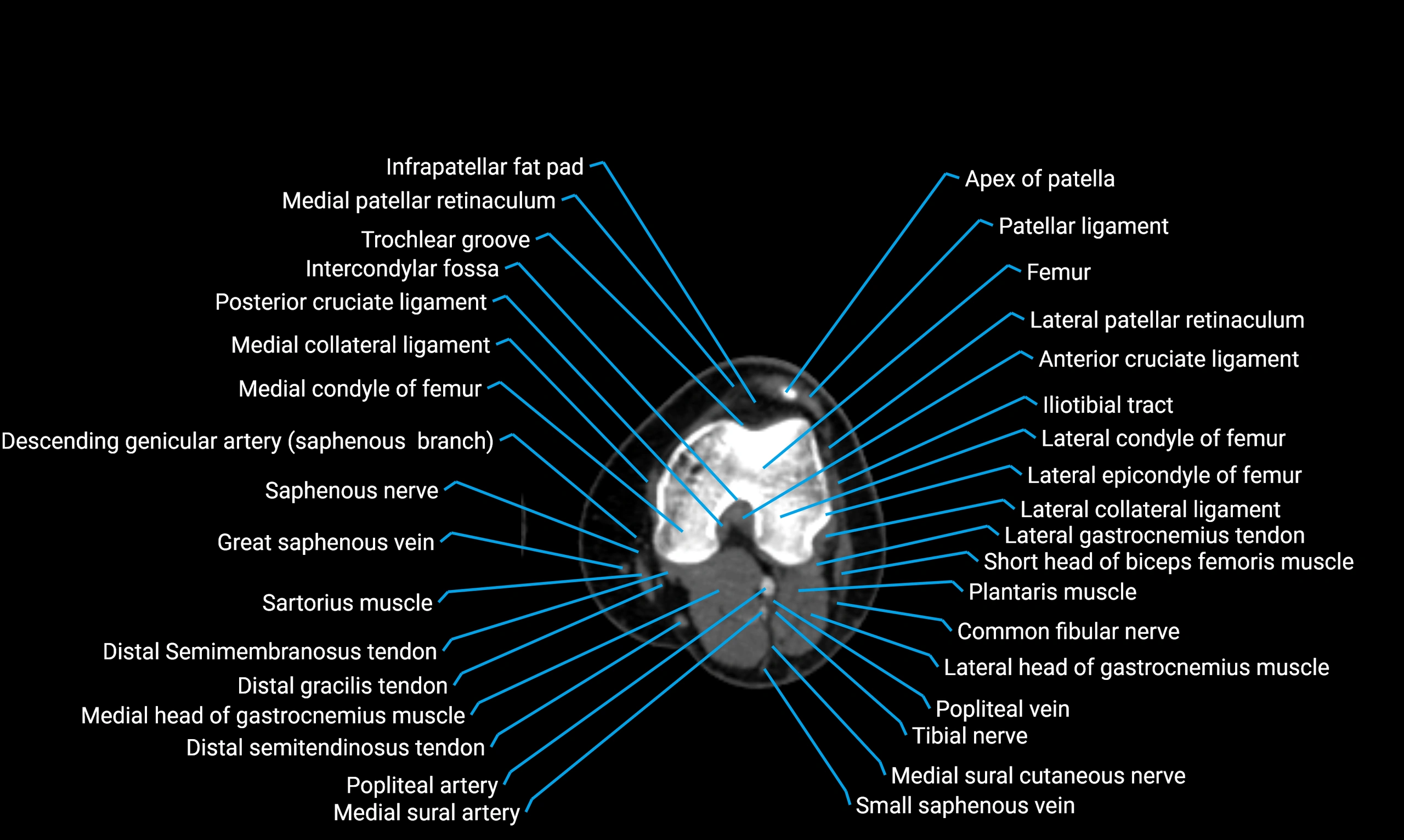
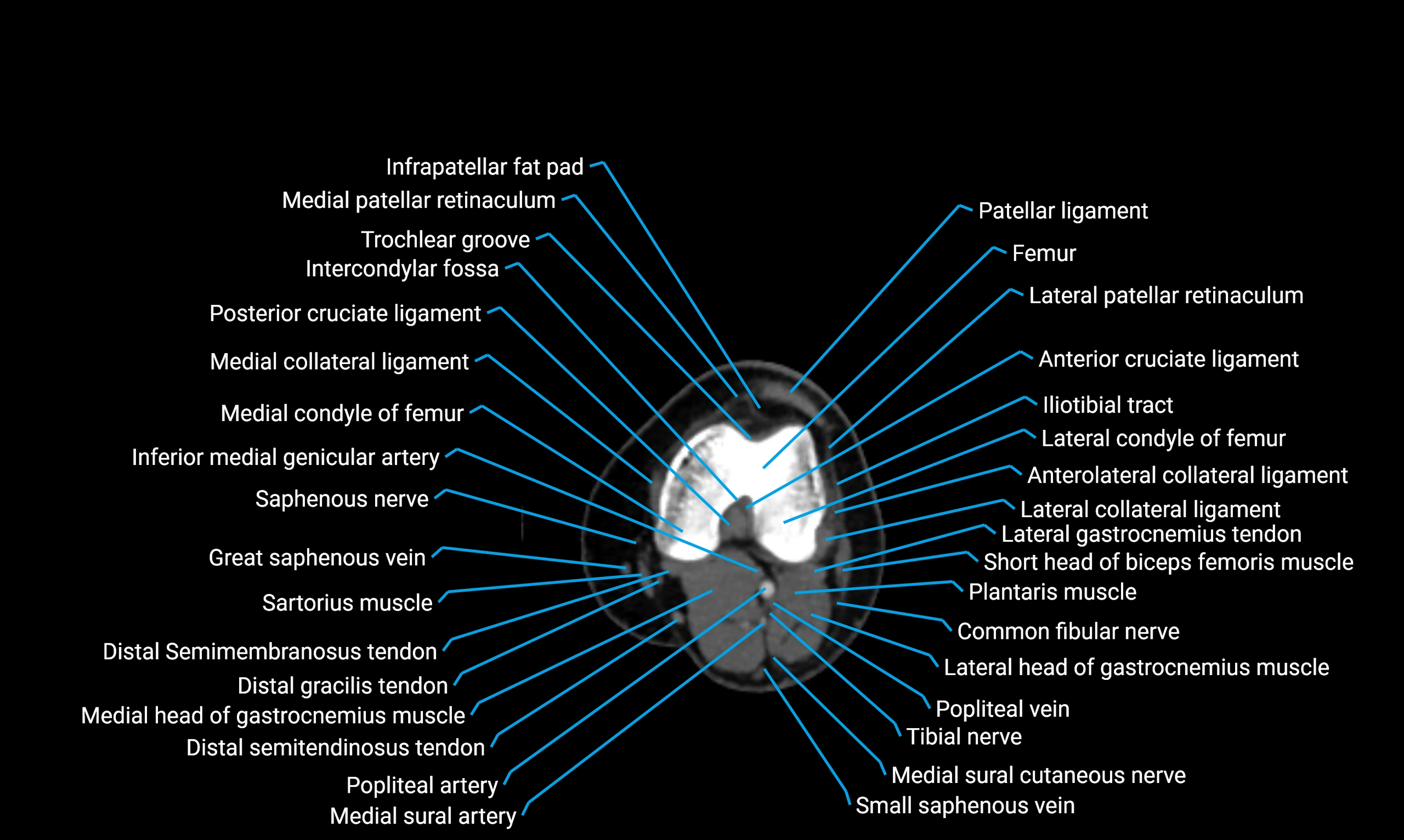
MRI appearance
T1-weighted images:
-
Cortical bone: Low signal intensity
-
Marrow: High signal intensity in adults
-
Surrounding muscles: Intermediate signal
T2-weighted images:
-
Cortex: Low signal
-
Marrow: Intermediate-to-high signal
-
Muscles and soft tissues: Intermediate-to-high signal
STIR:
-
Marrow fat: Suppressed signal
-
Cortex: Remains low signal
-
Soft tissues: High contrast against suppressed fat
Proton density fat-saturated (PD FS):
-
Bone marrow: Fat suppressed
-
Cortical bone: Low signal
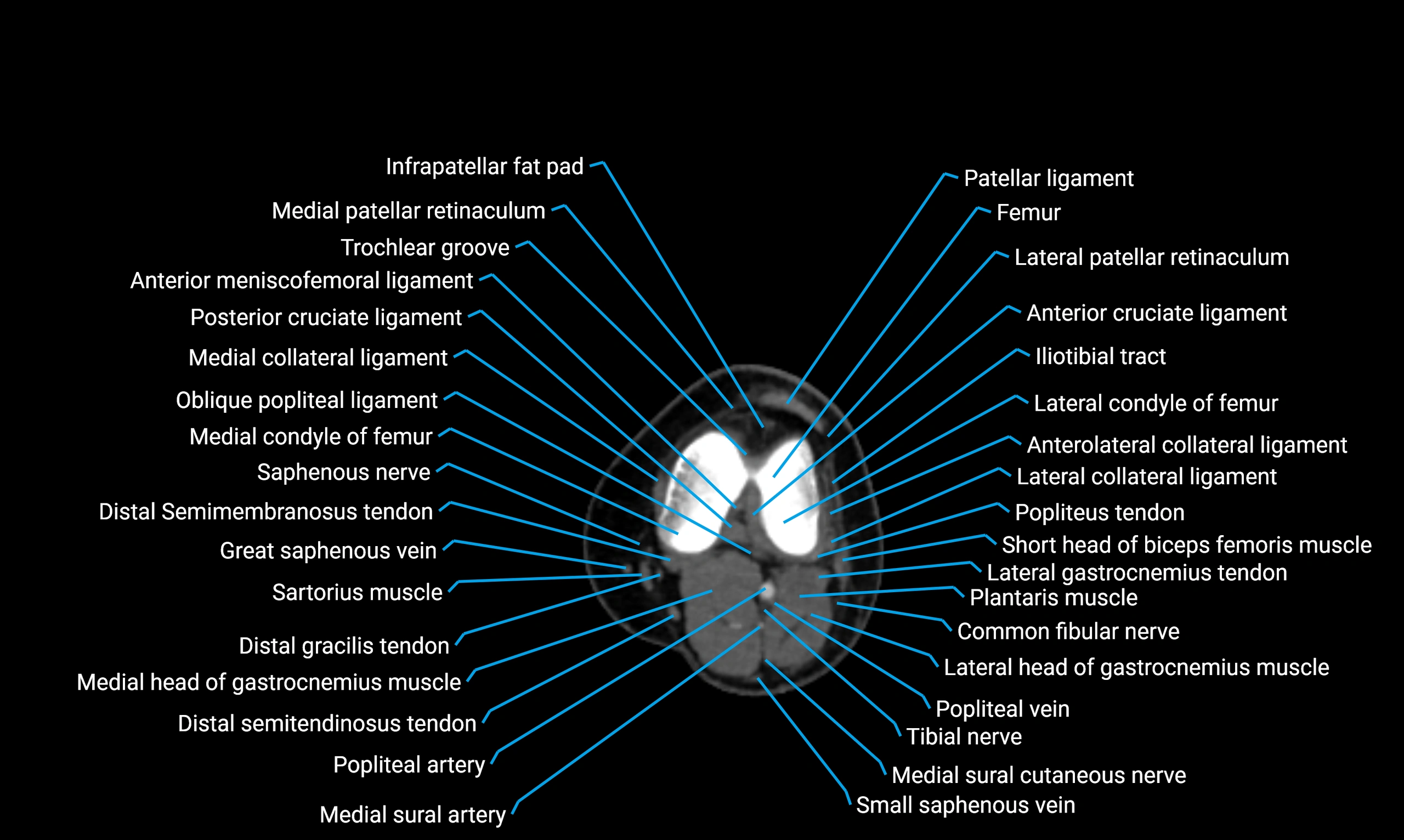
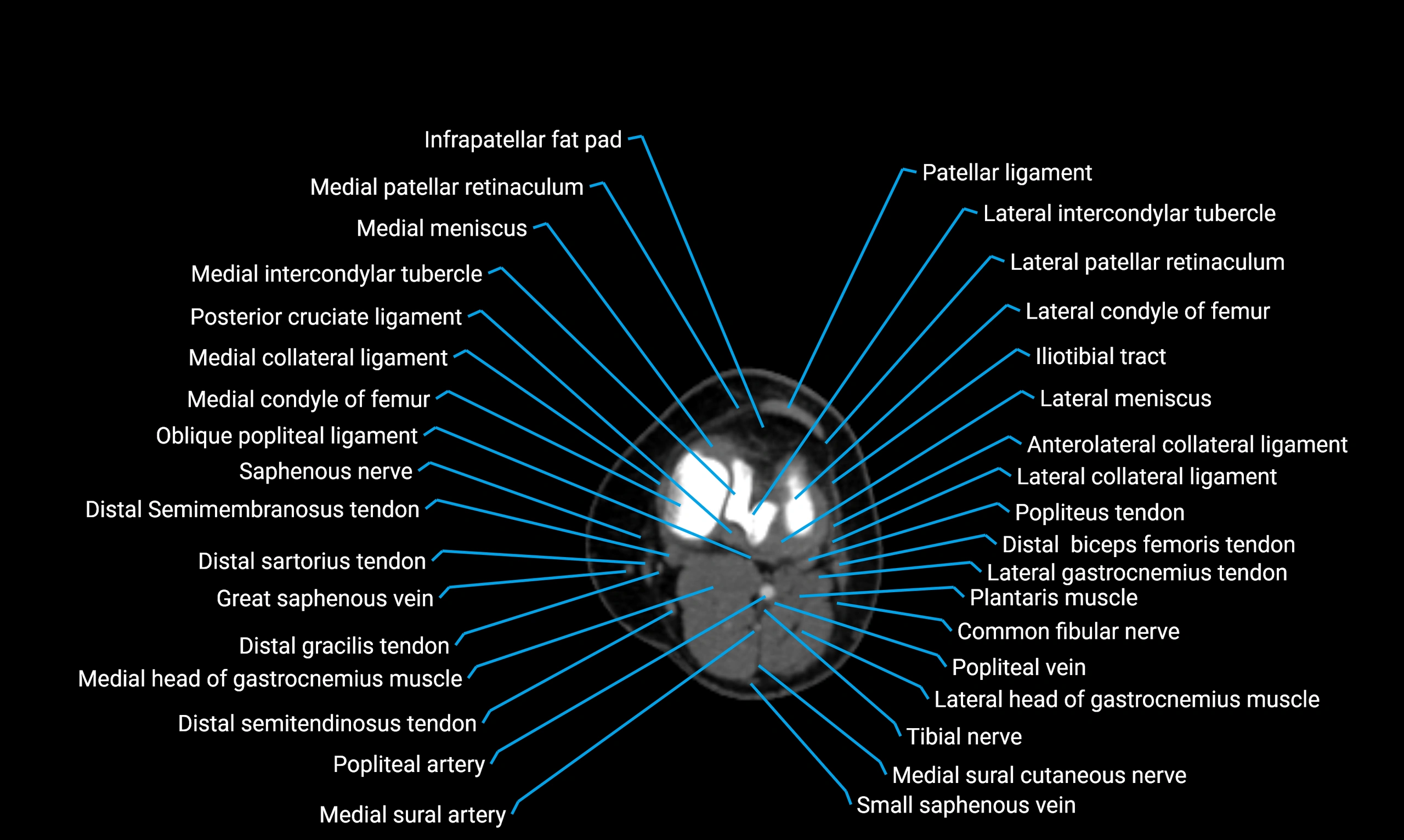
MRI image

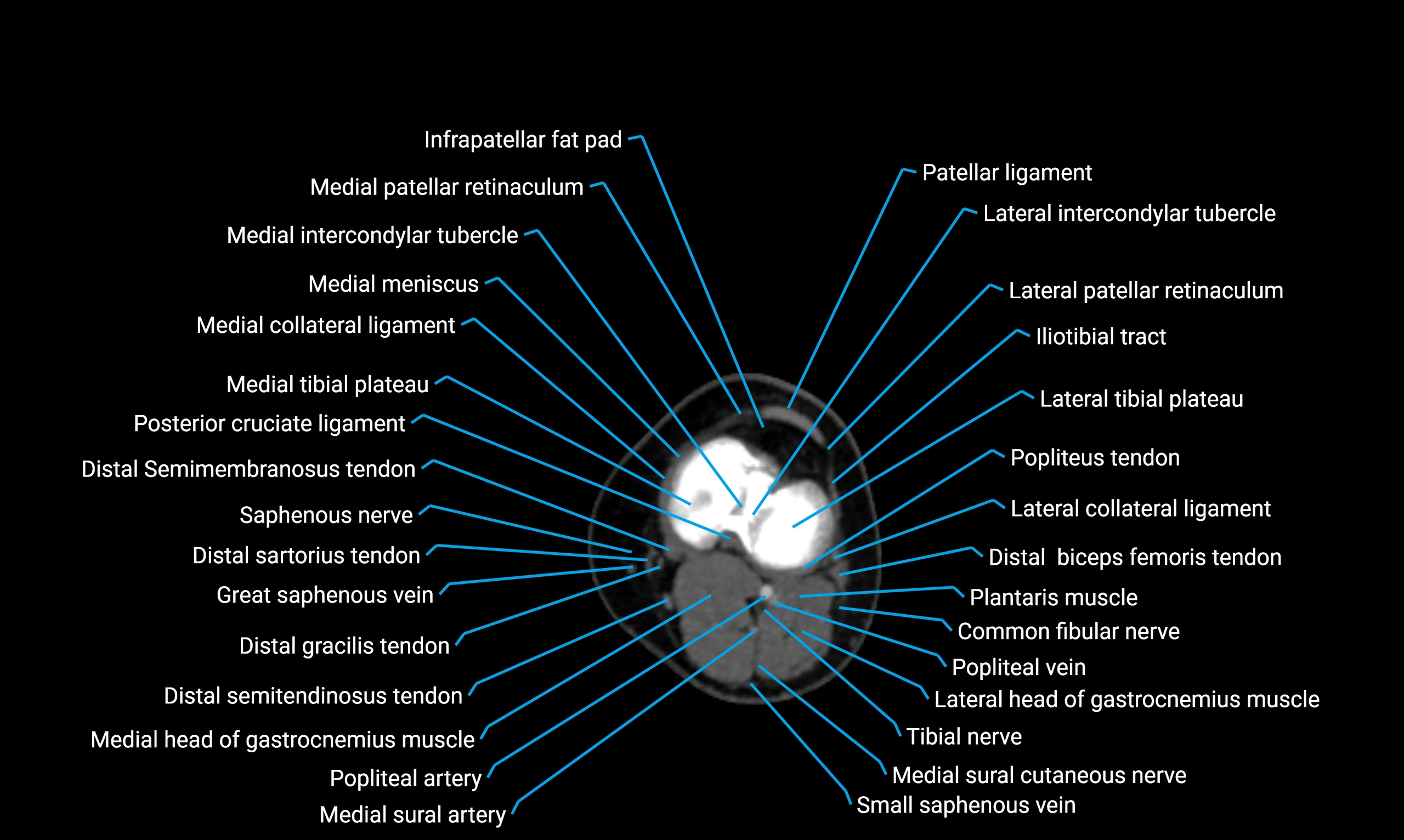
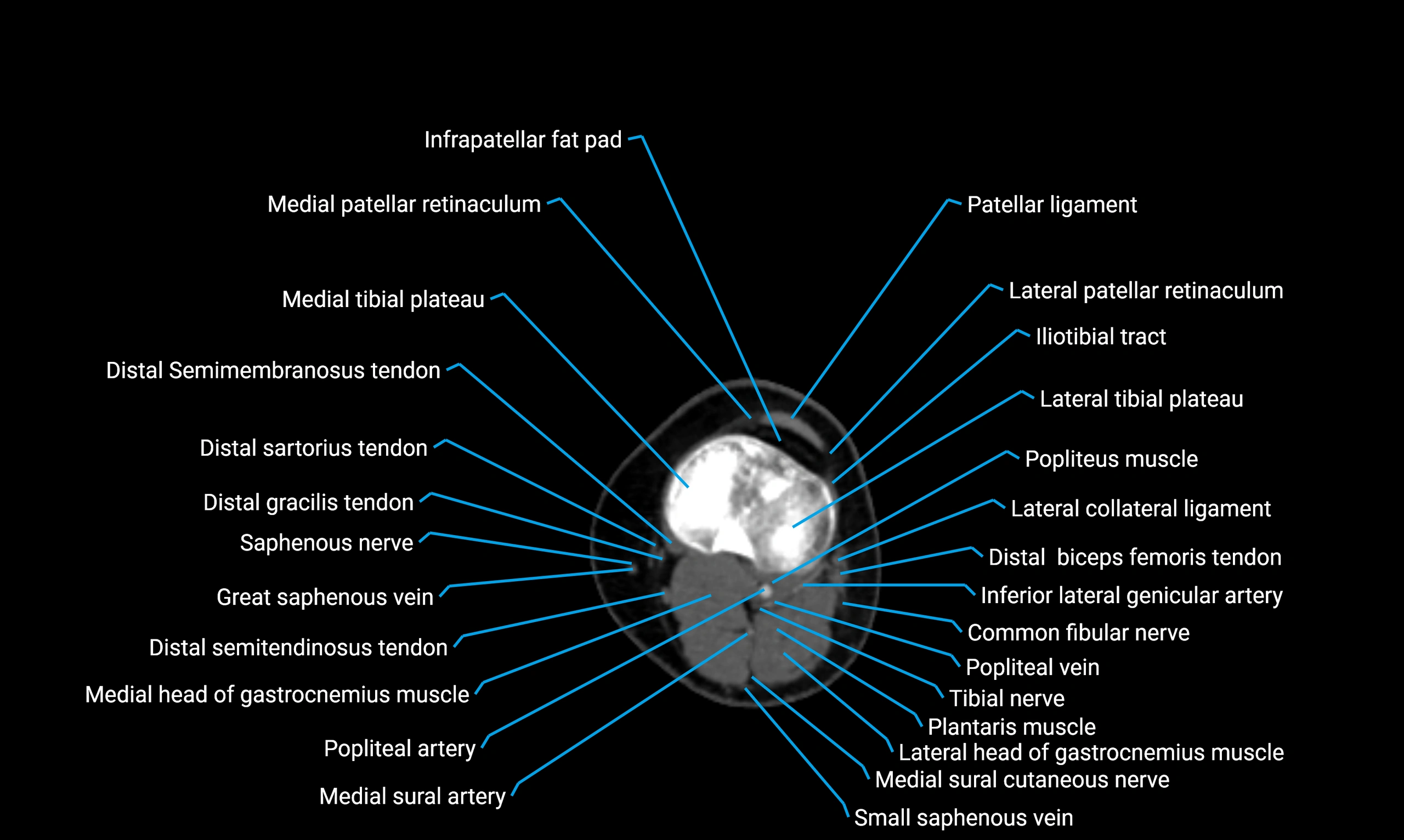
CT image

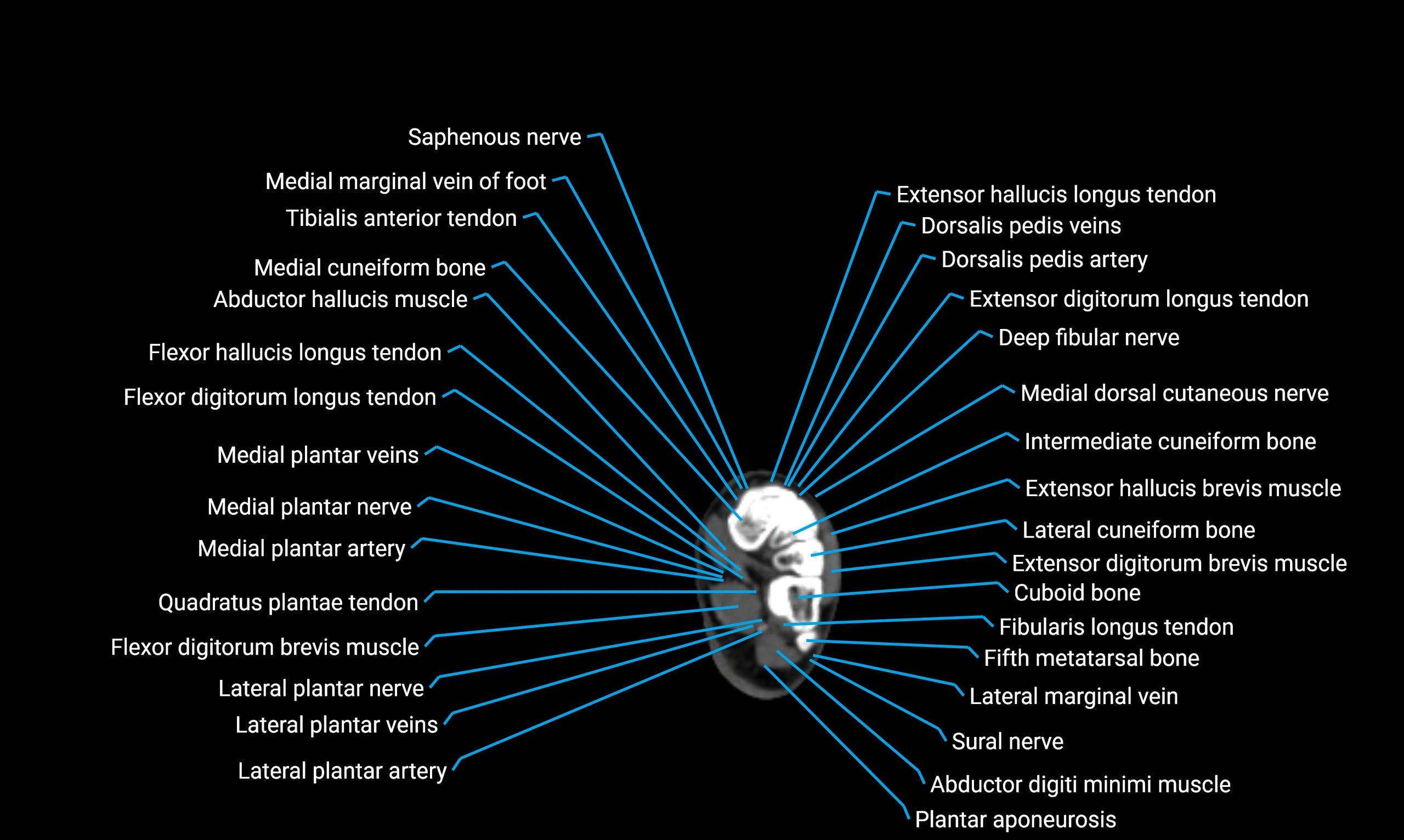
CT VRT 3D image