Topic
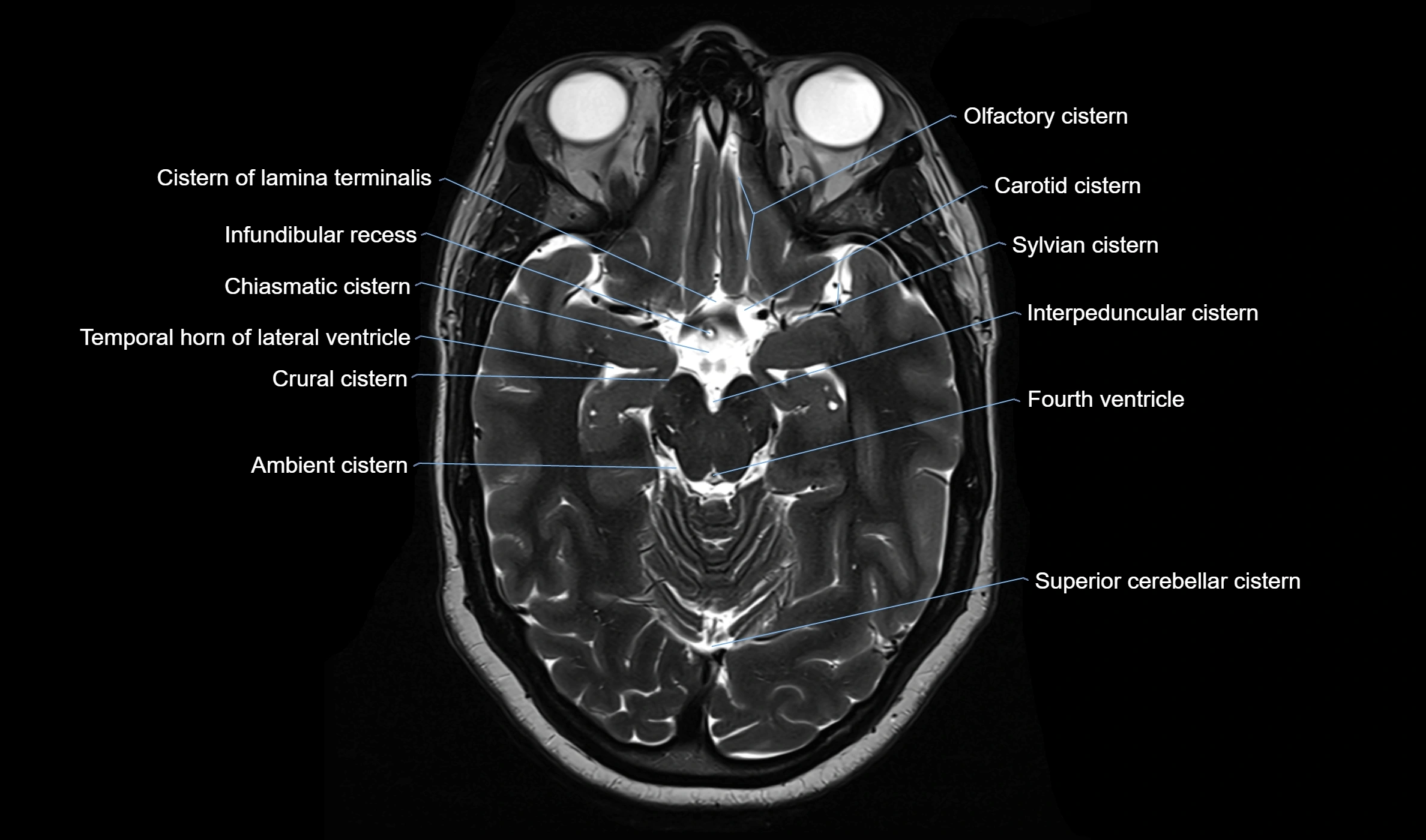
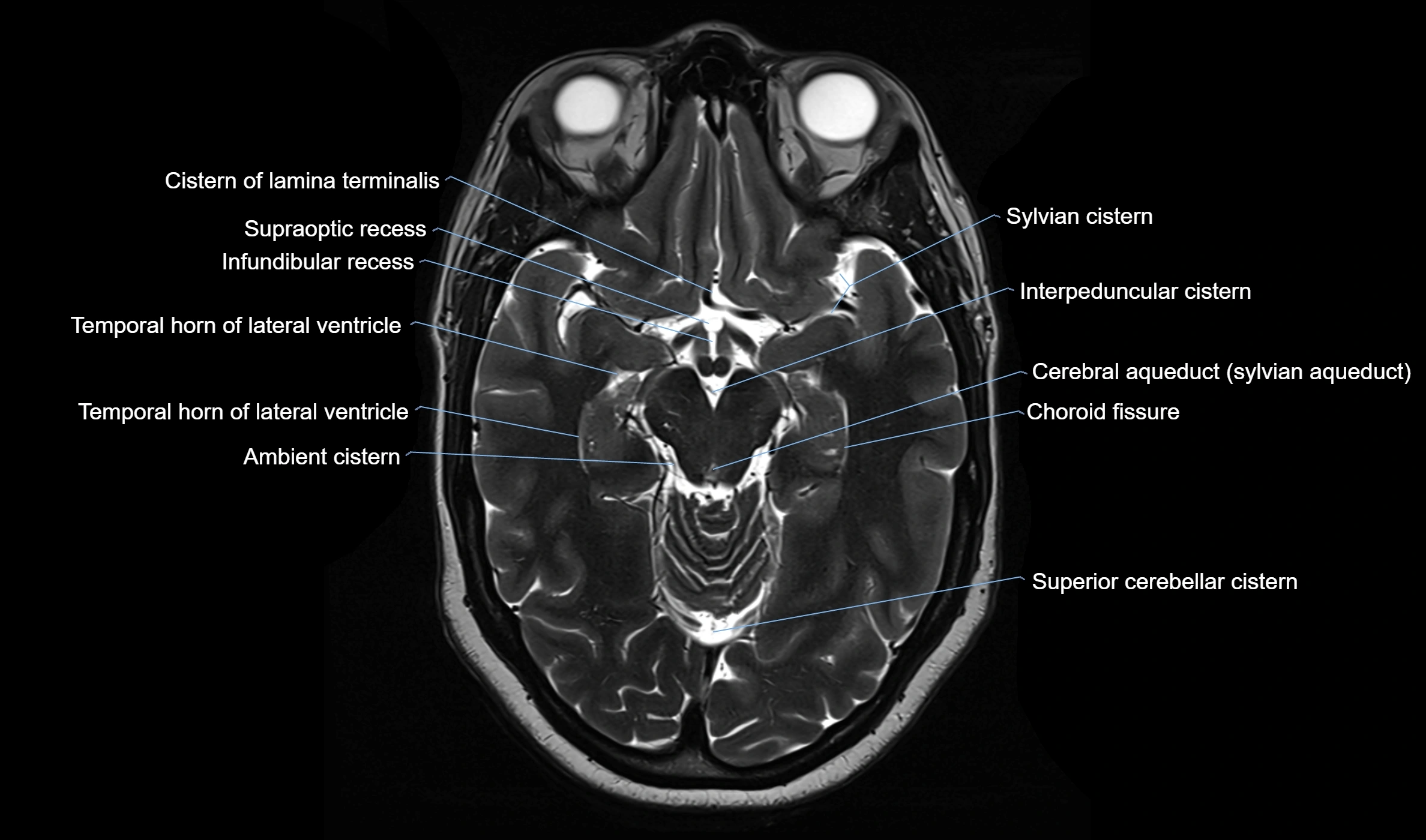
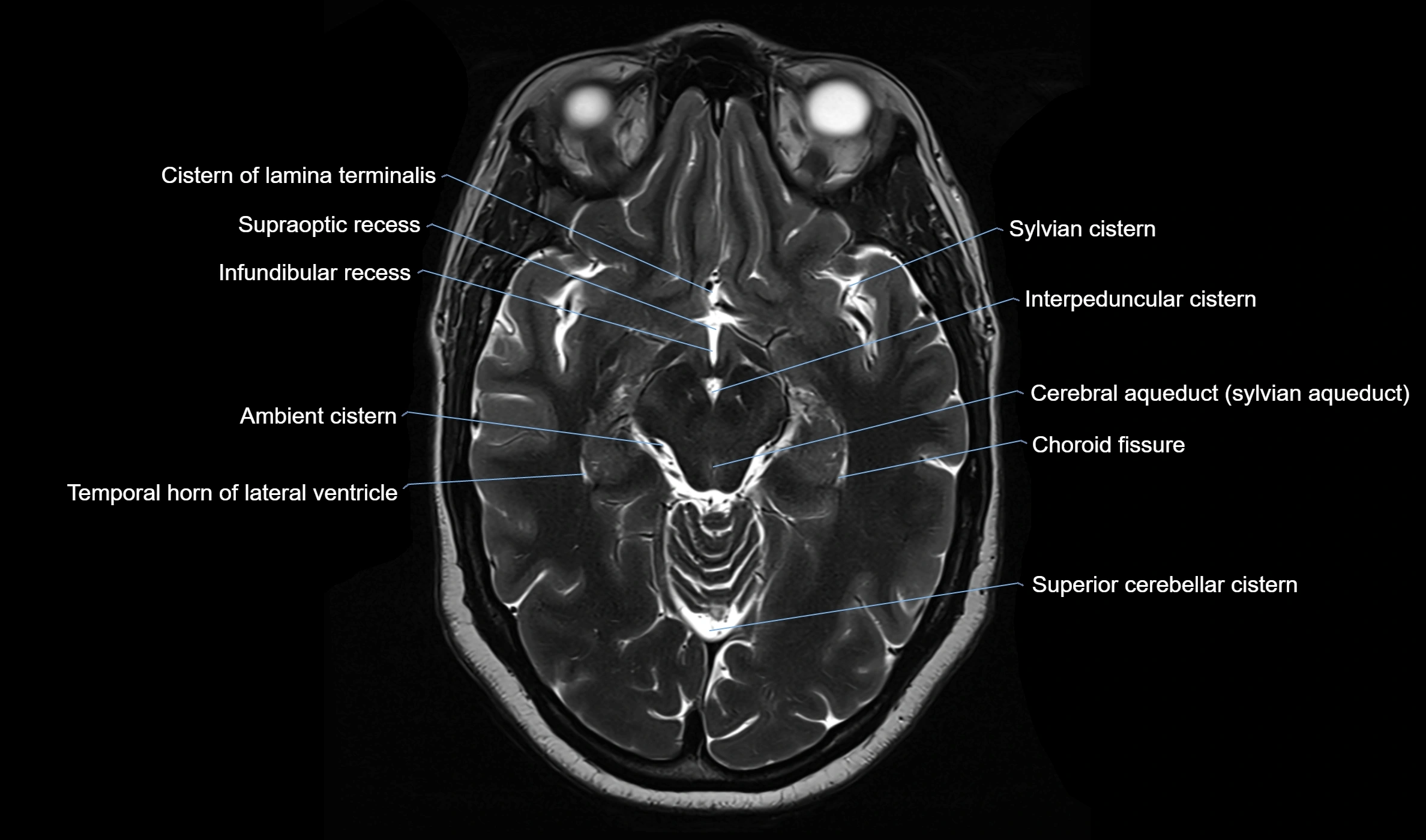
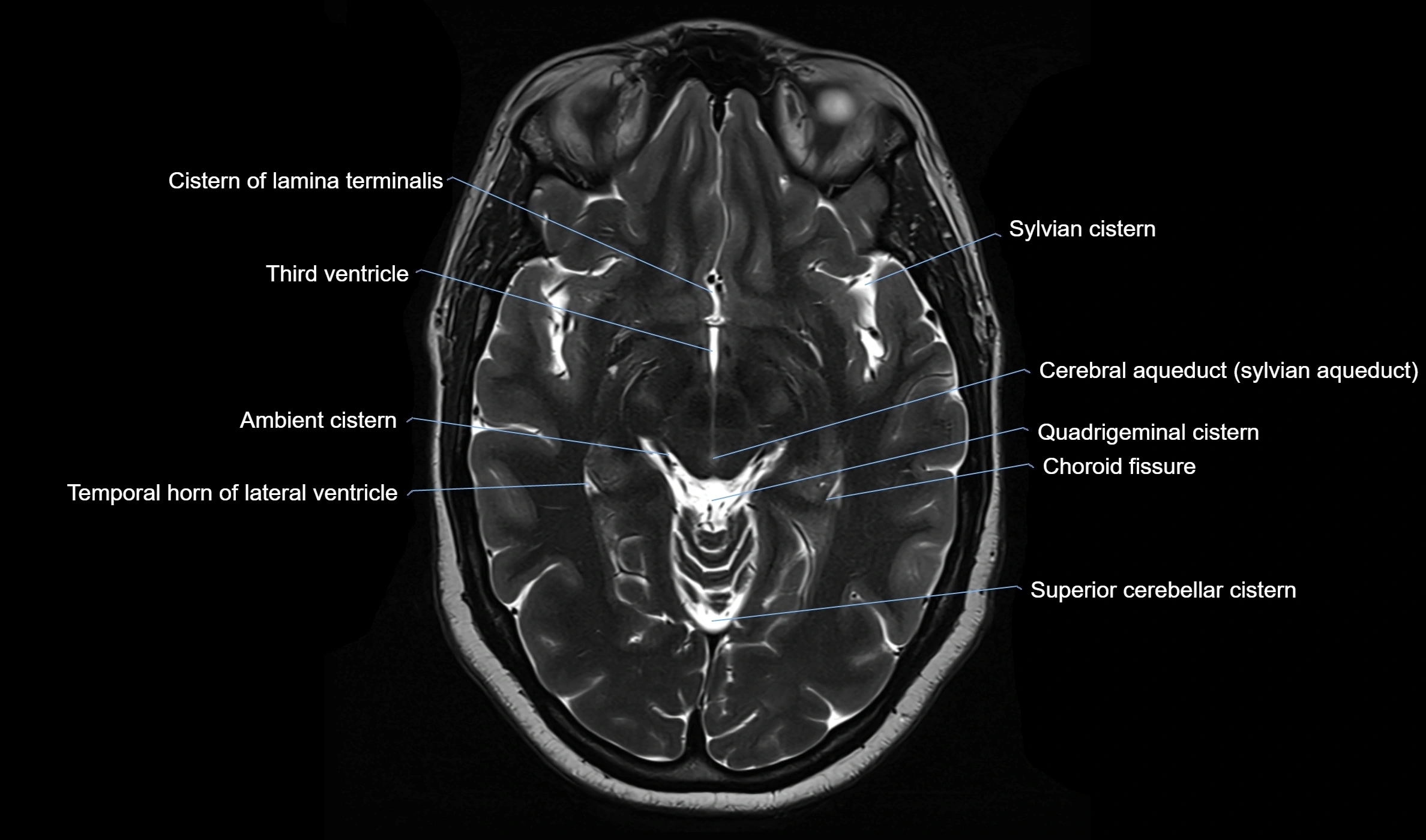
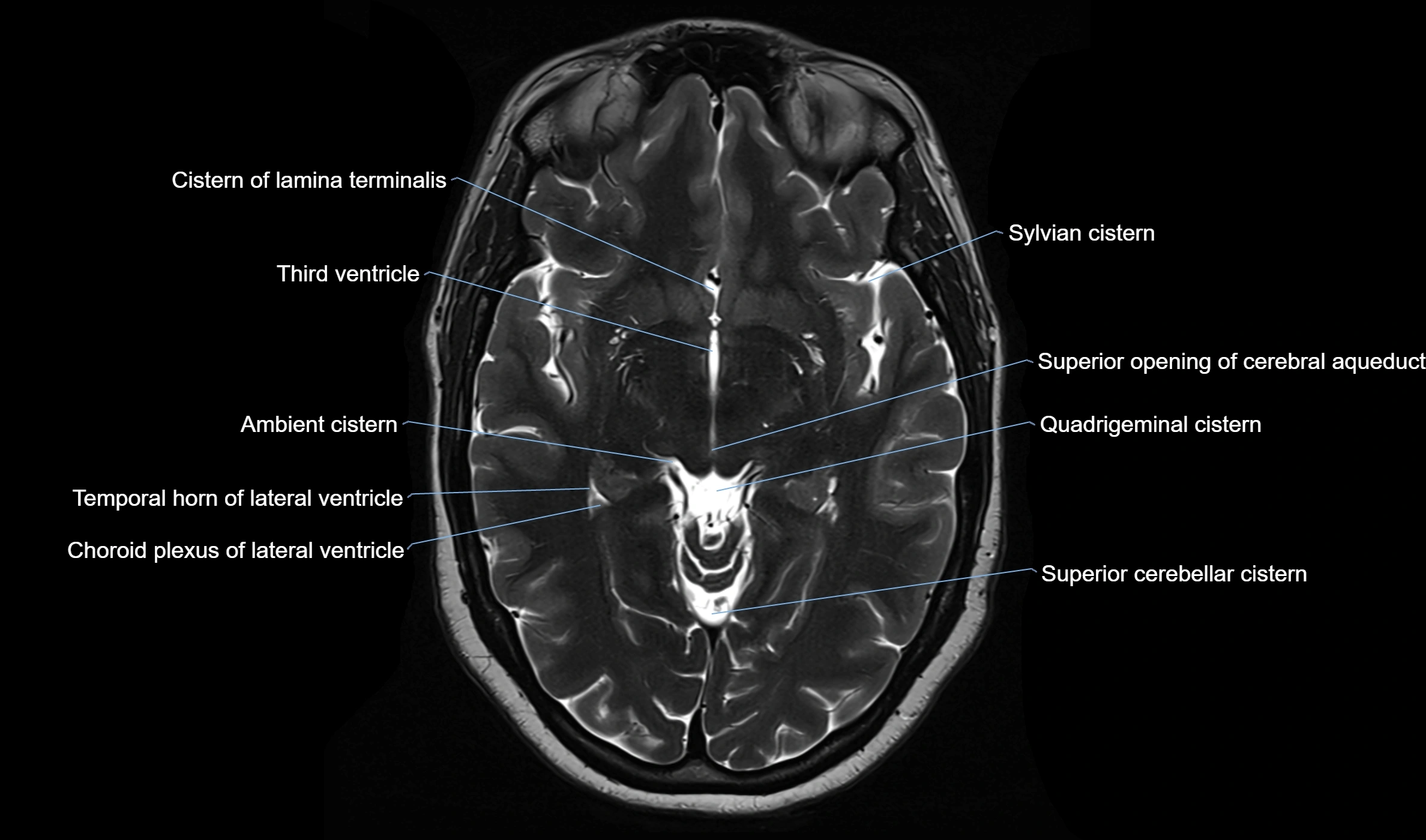
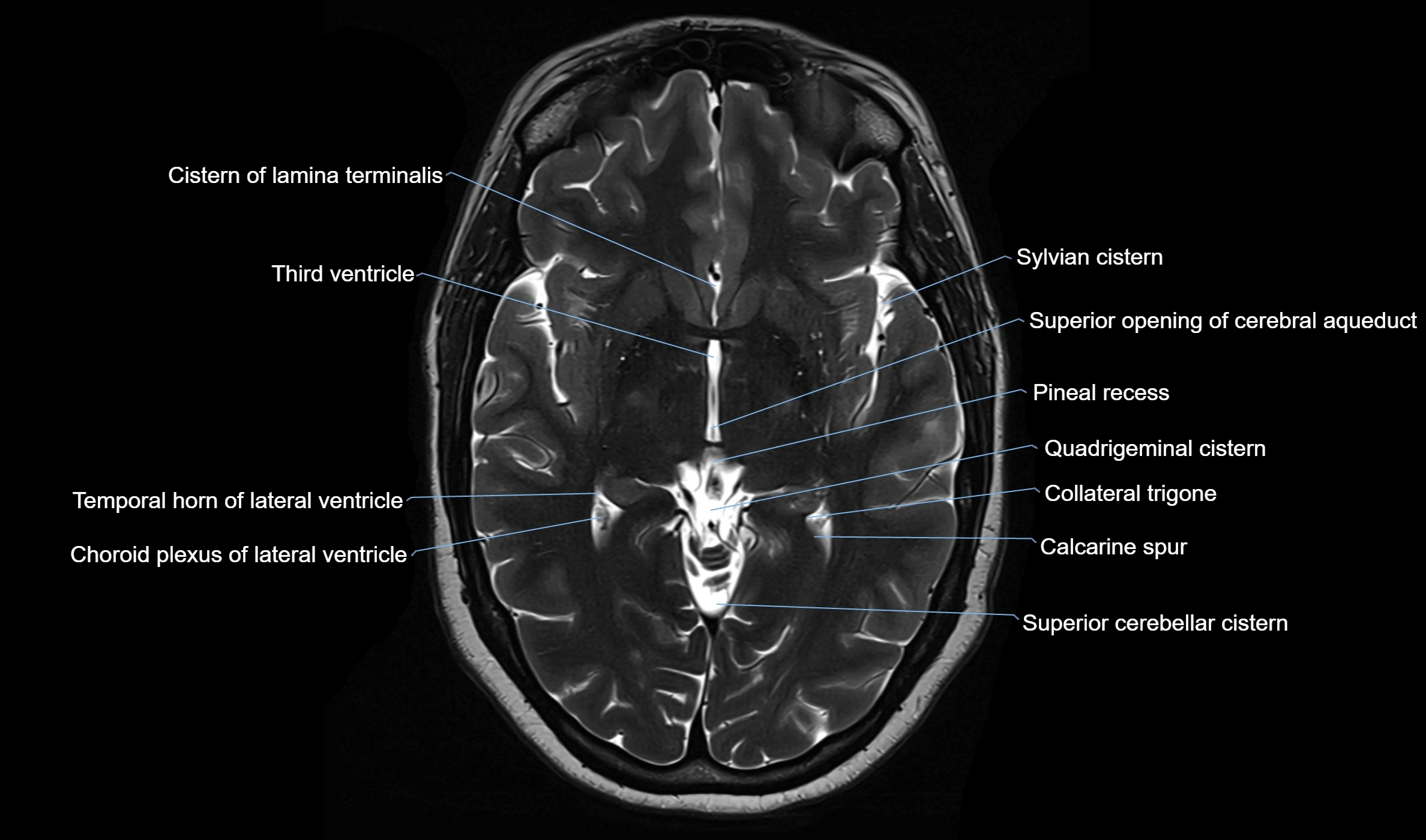
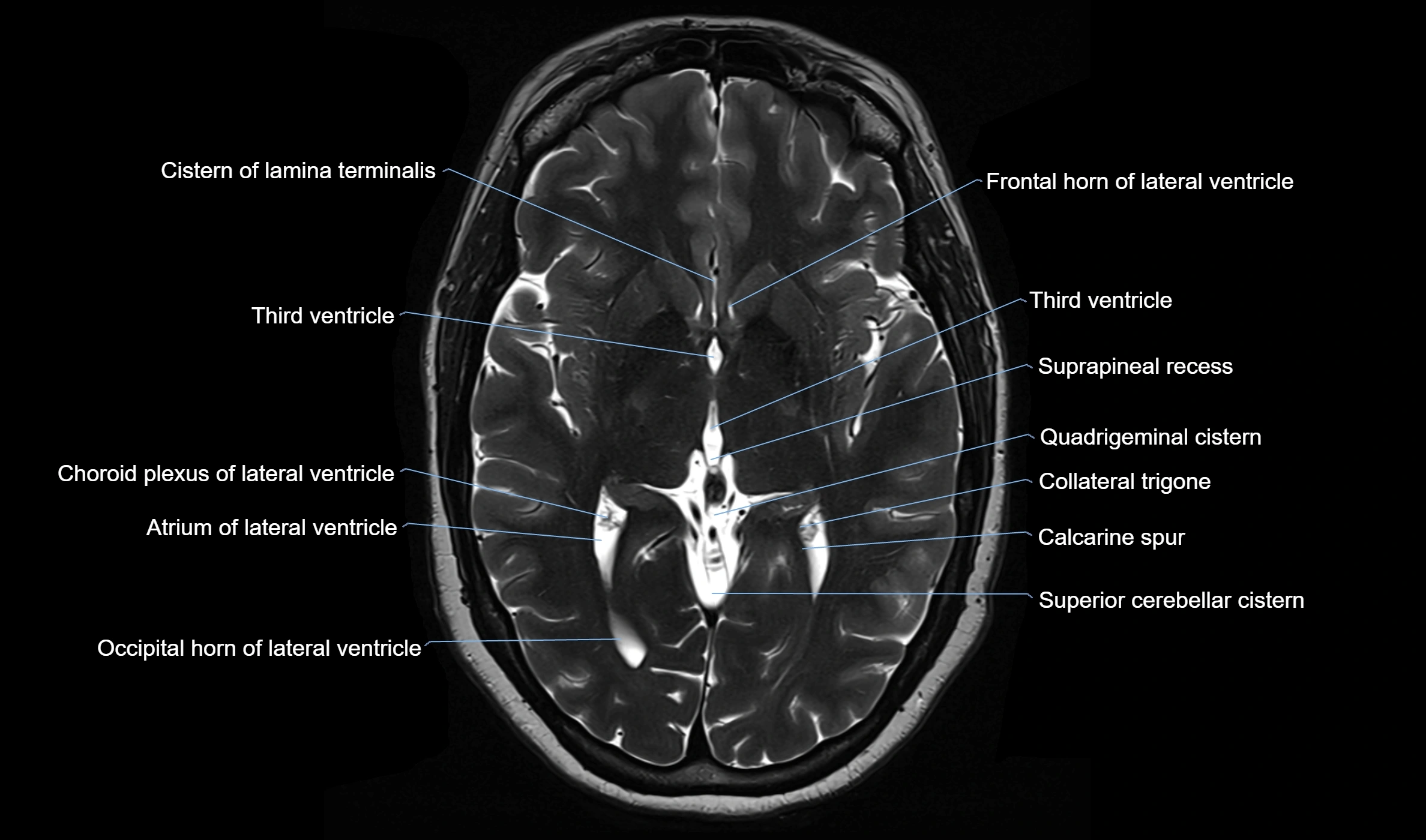
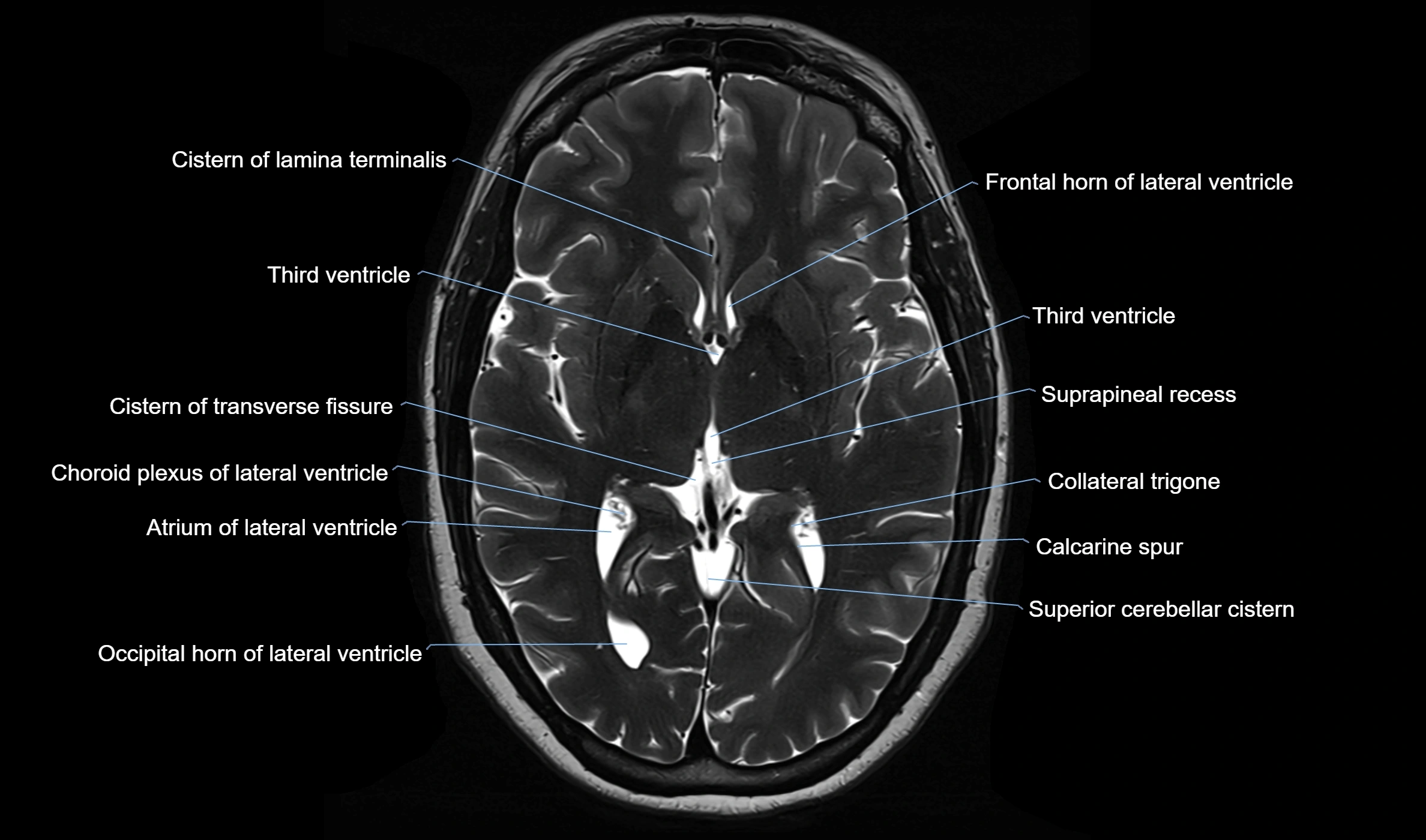
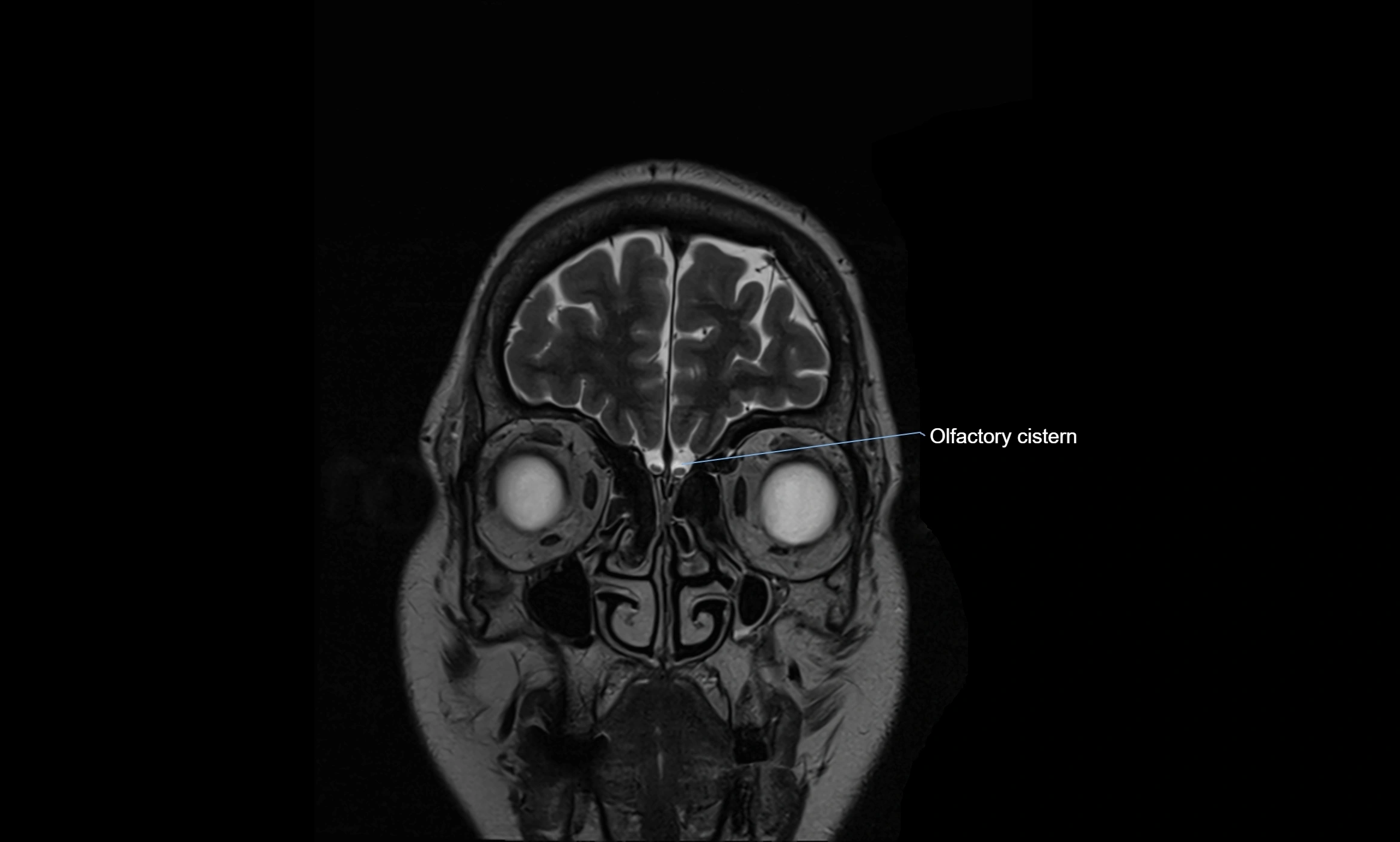
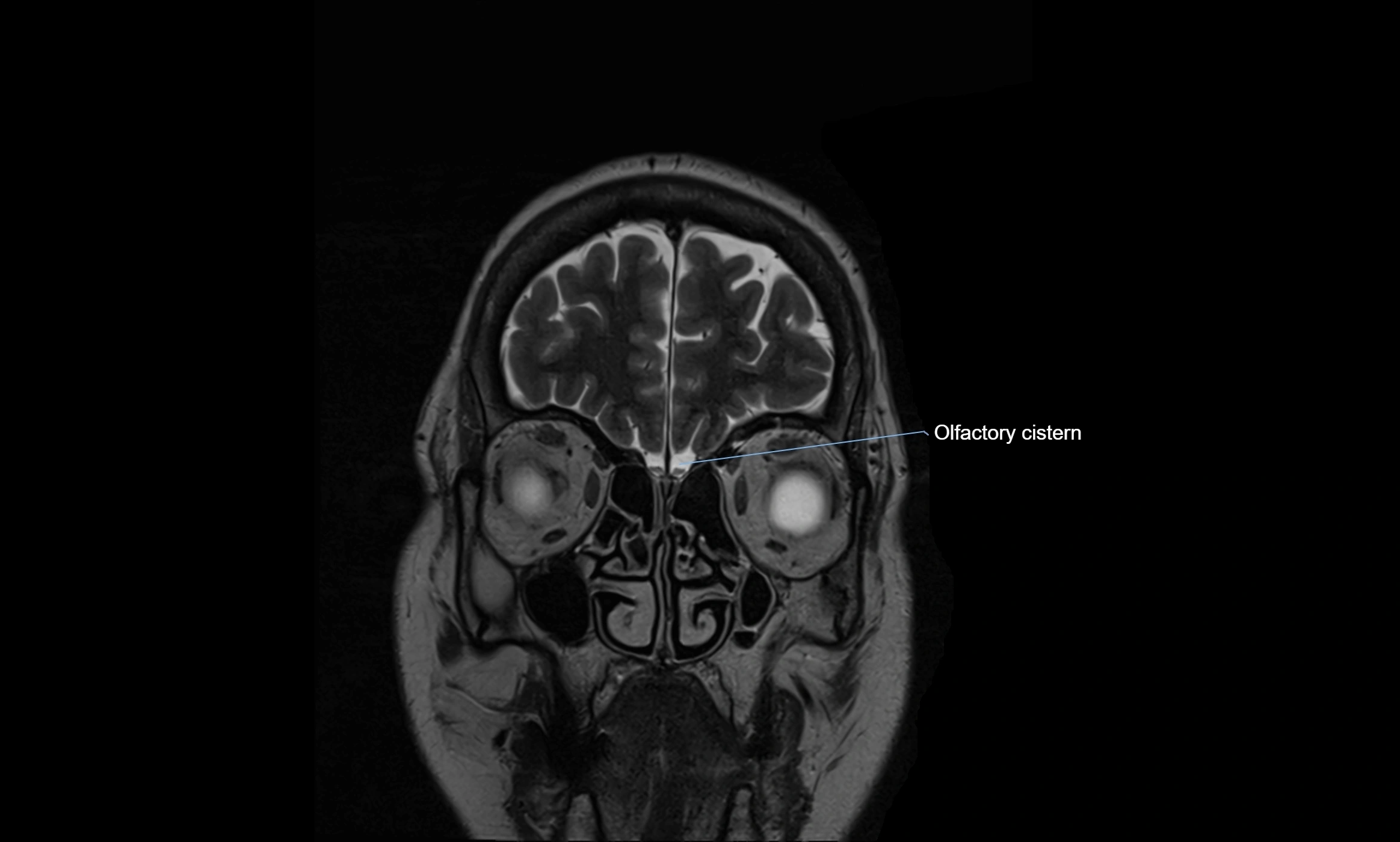
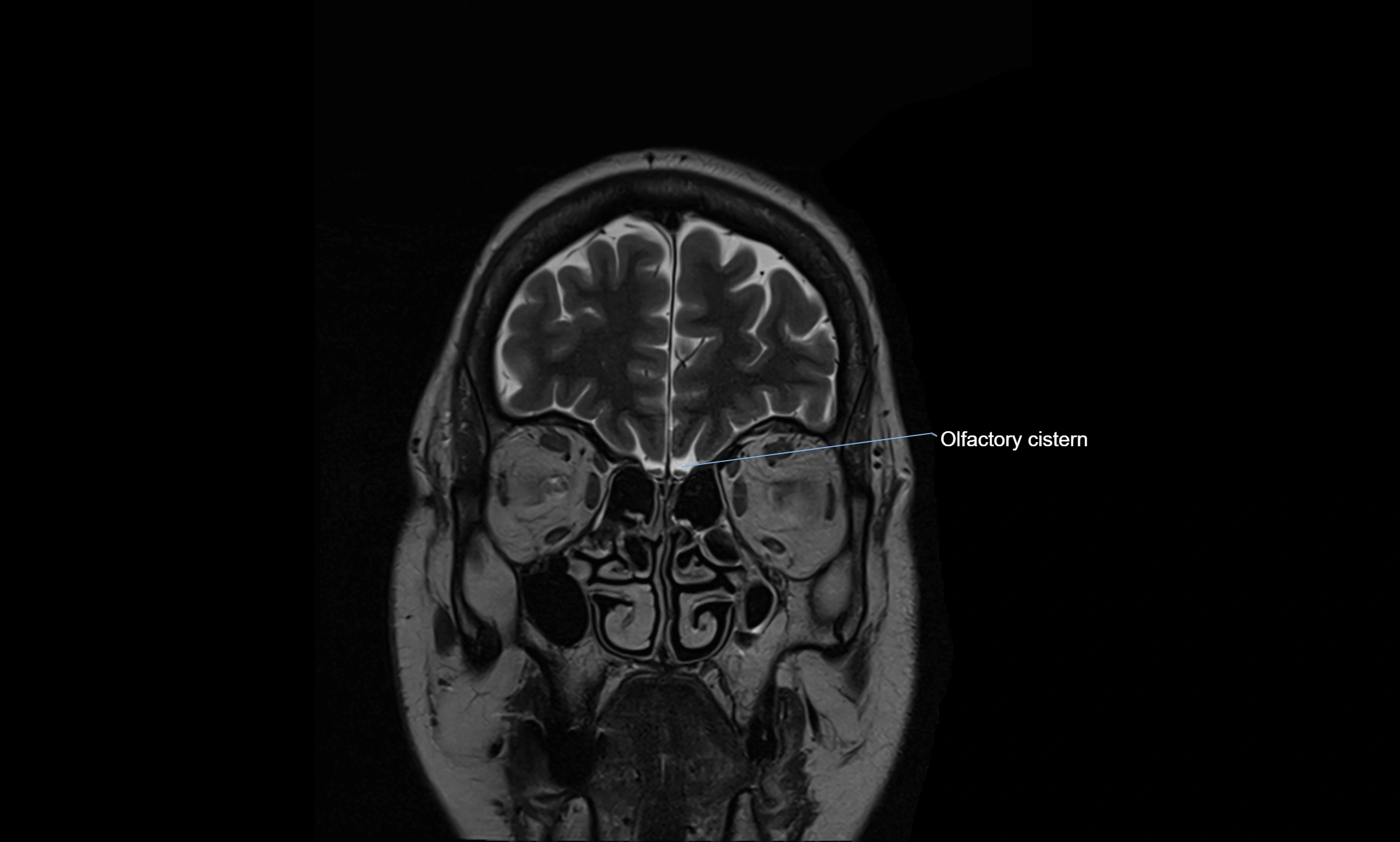
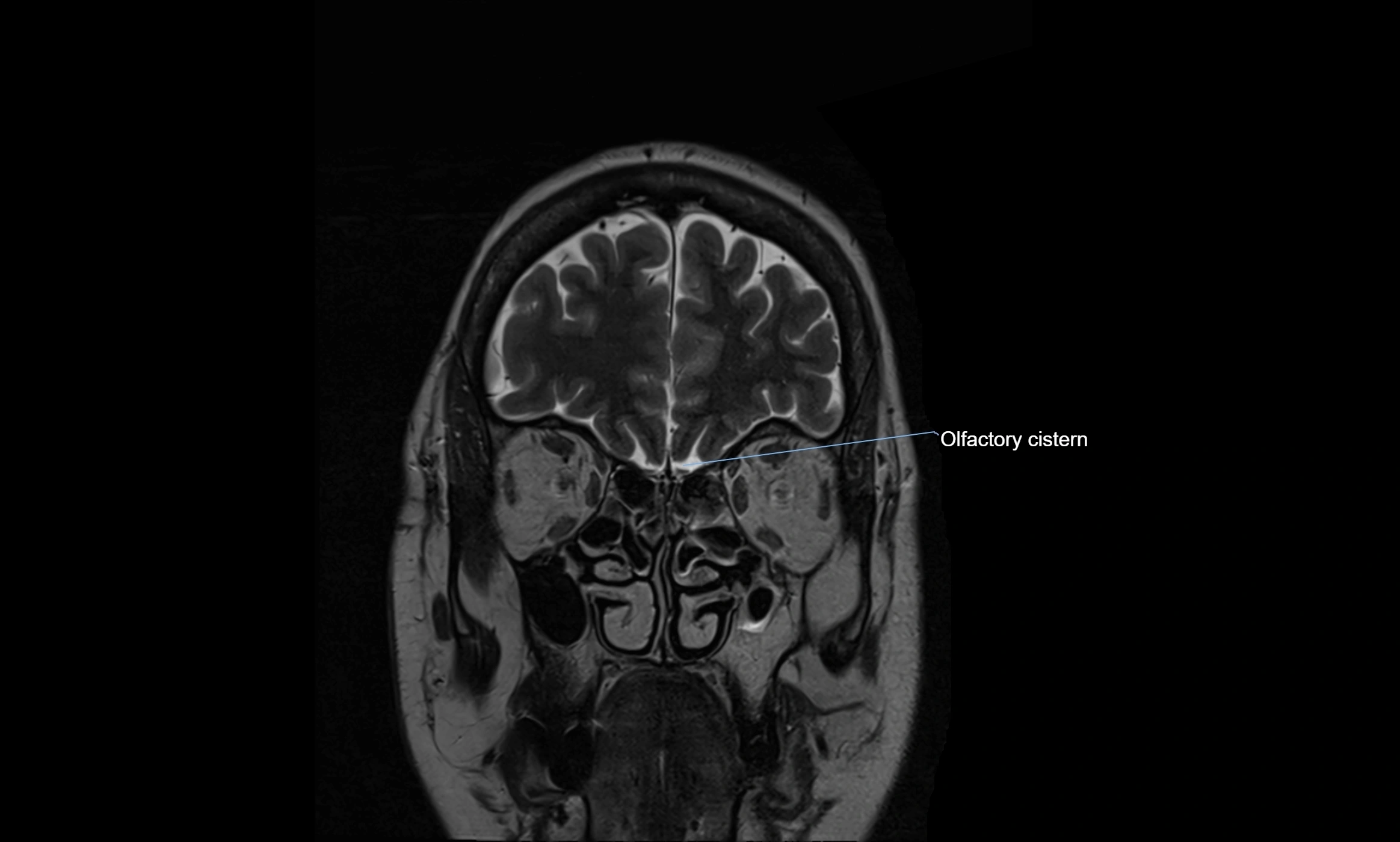
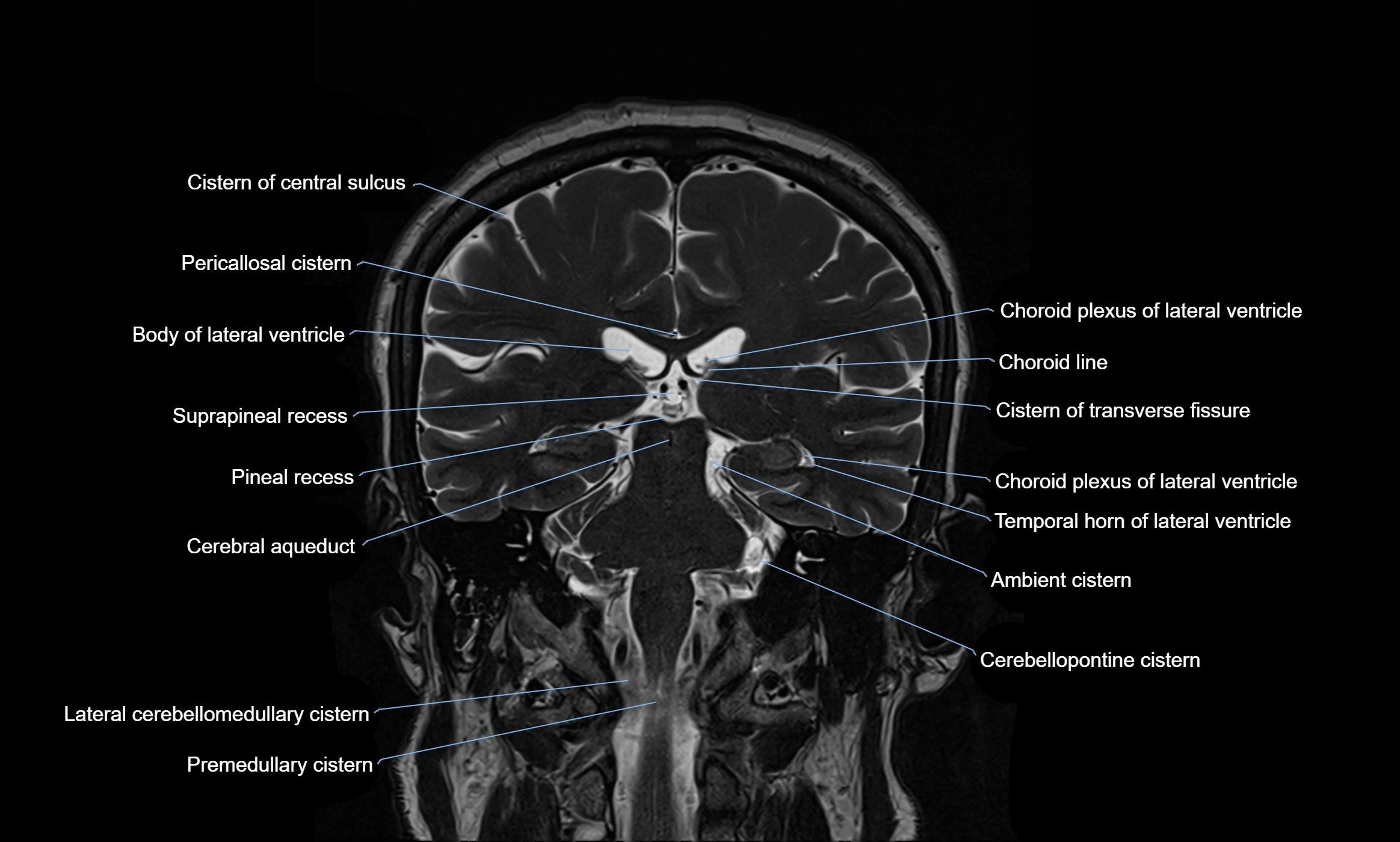
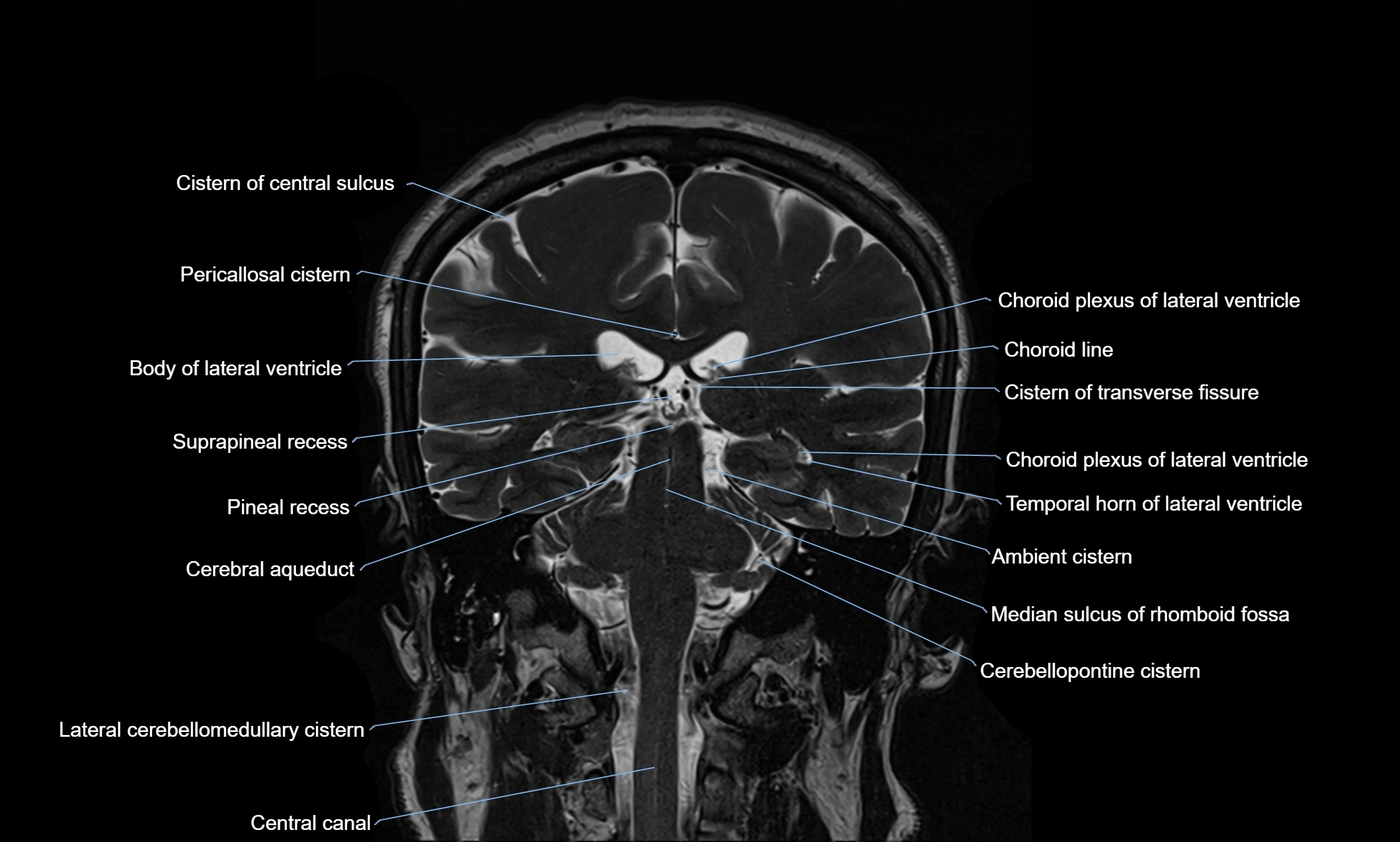
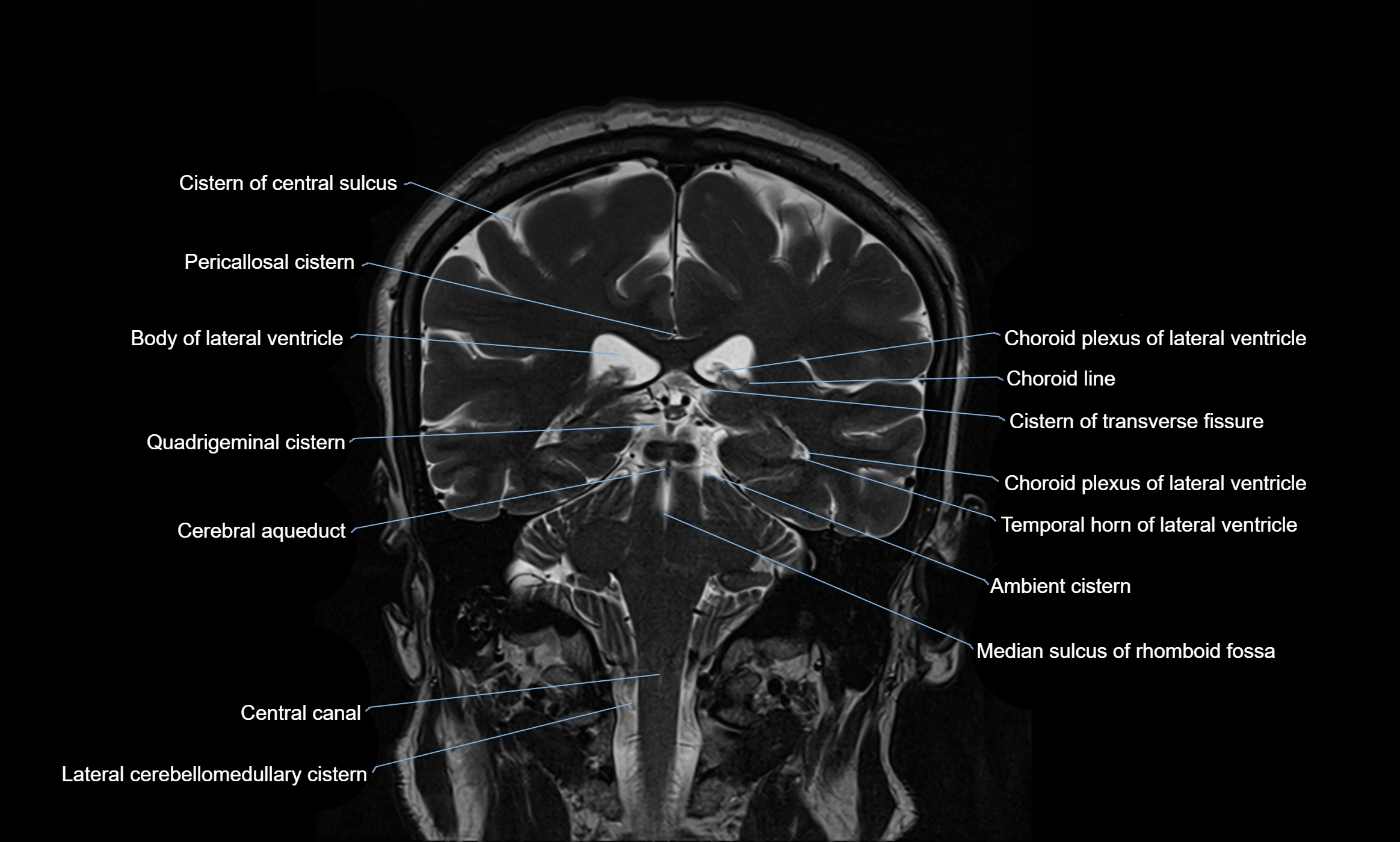
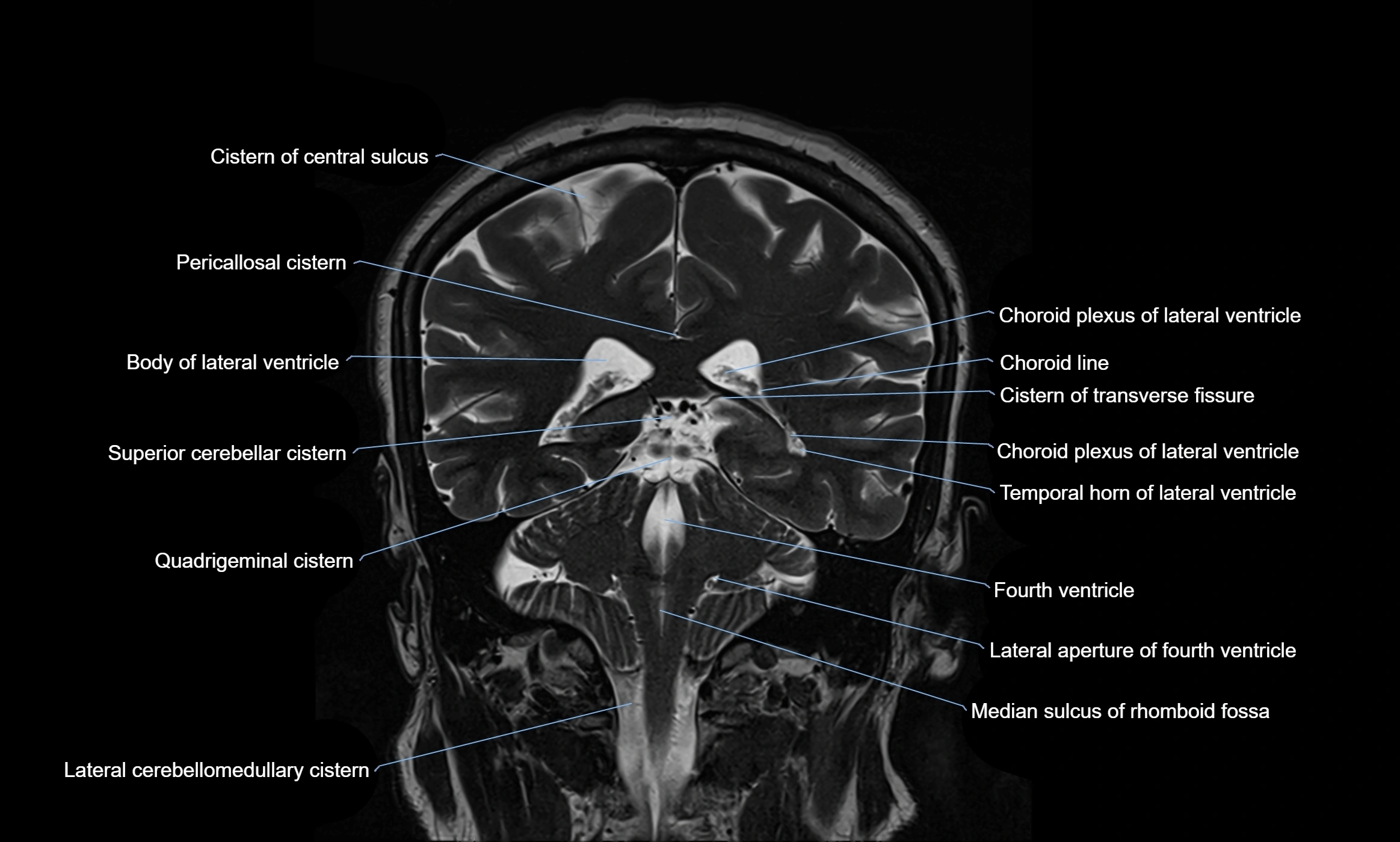
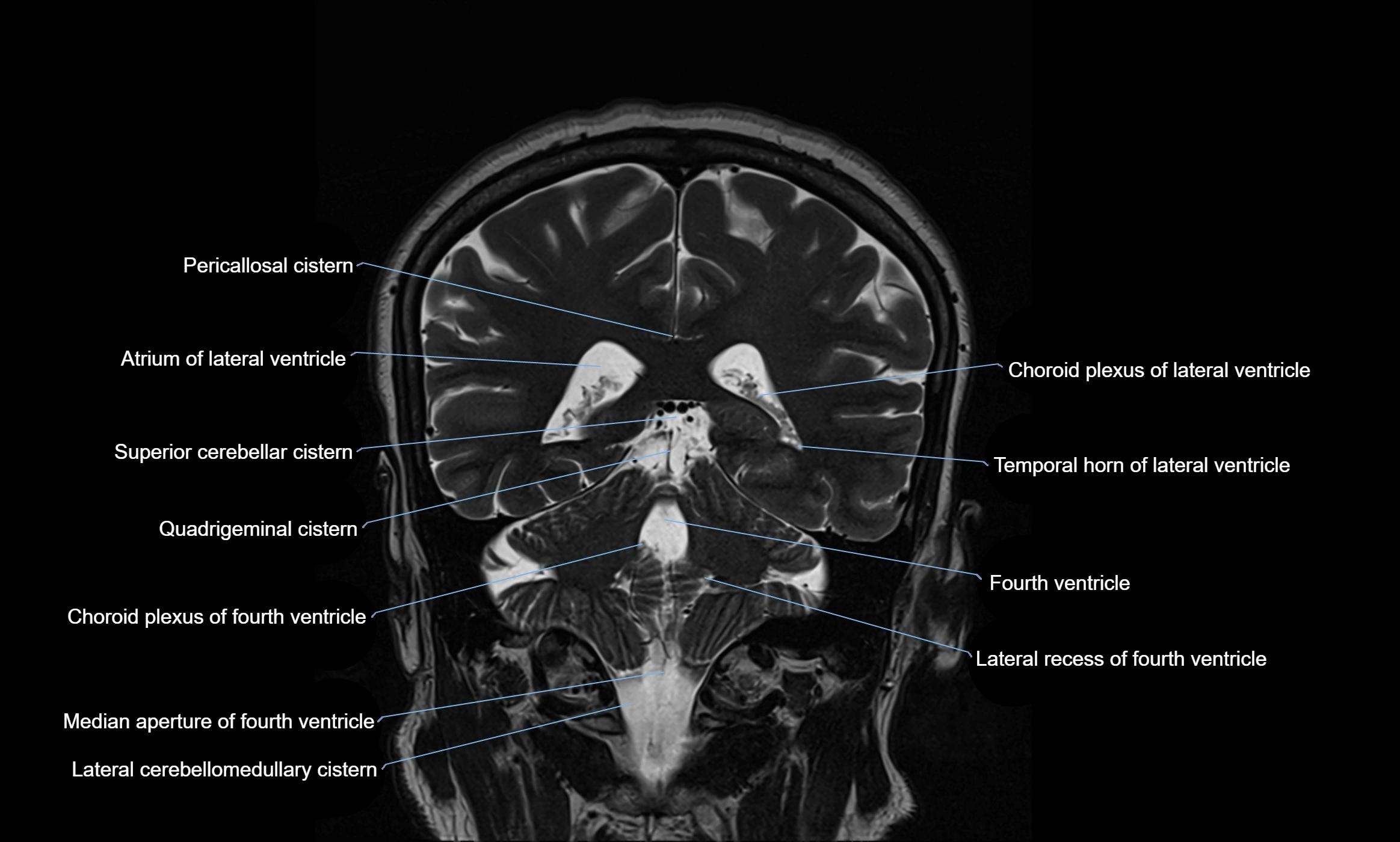
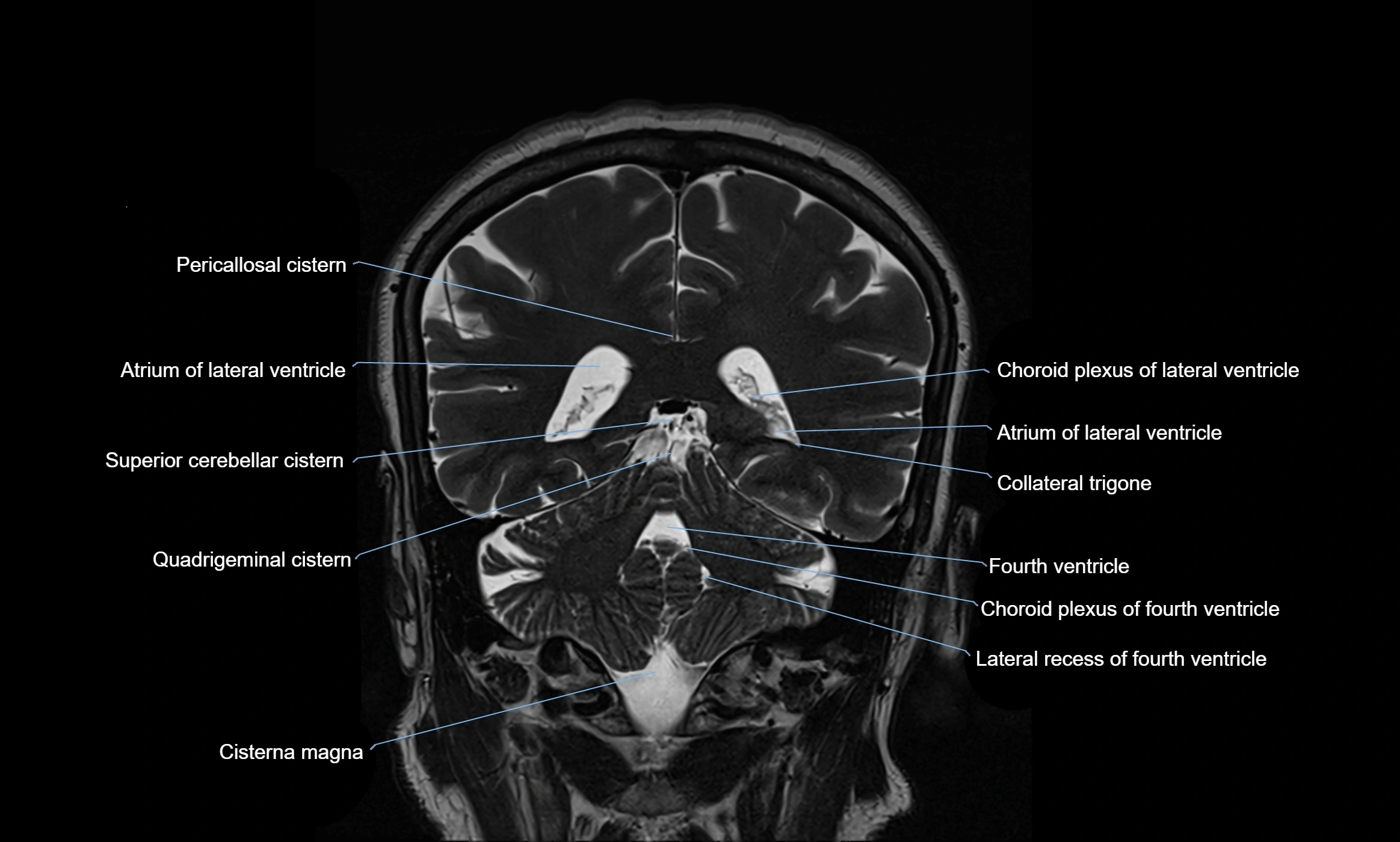
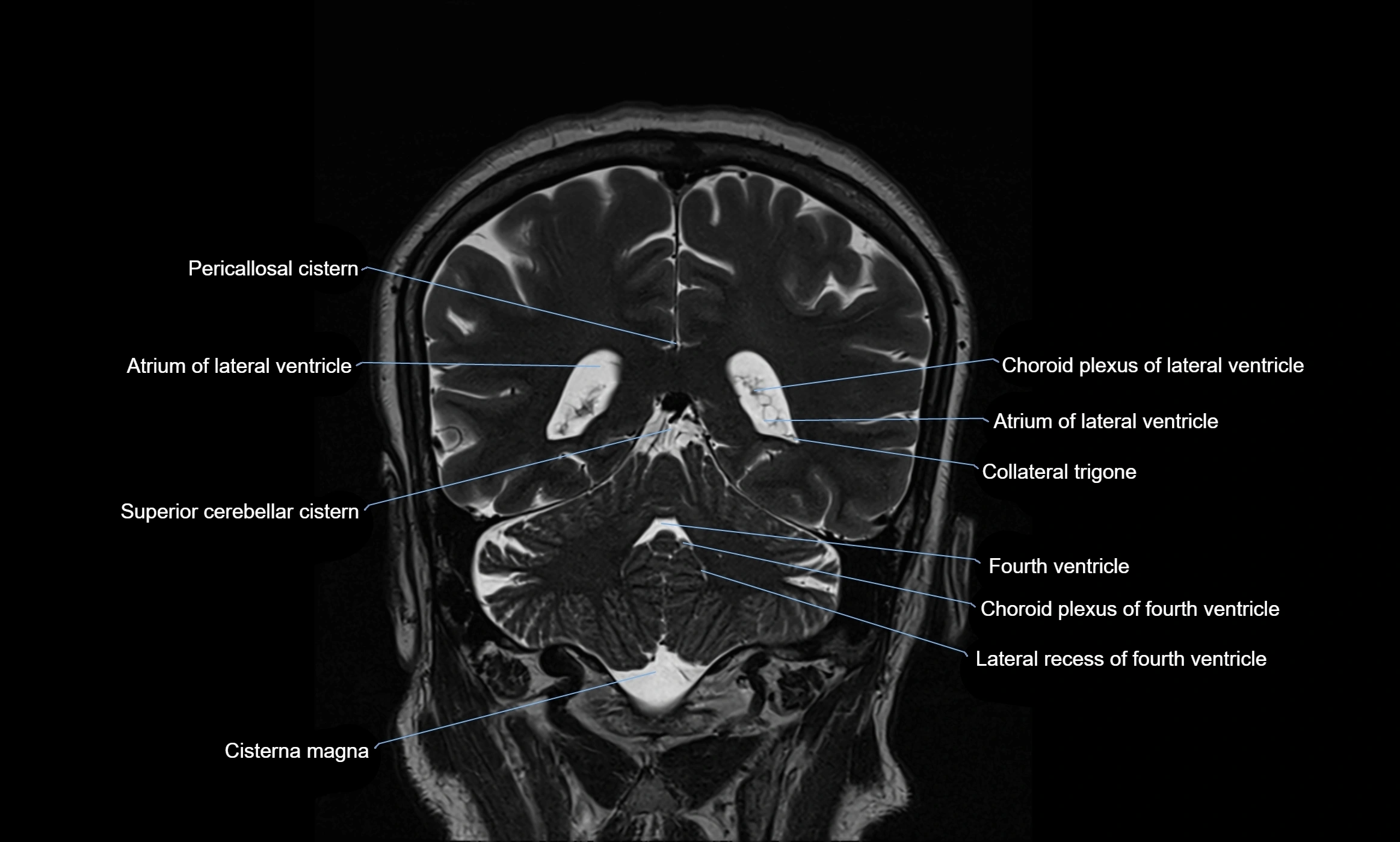
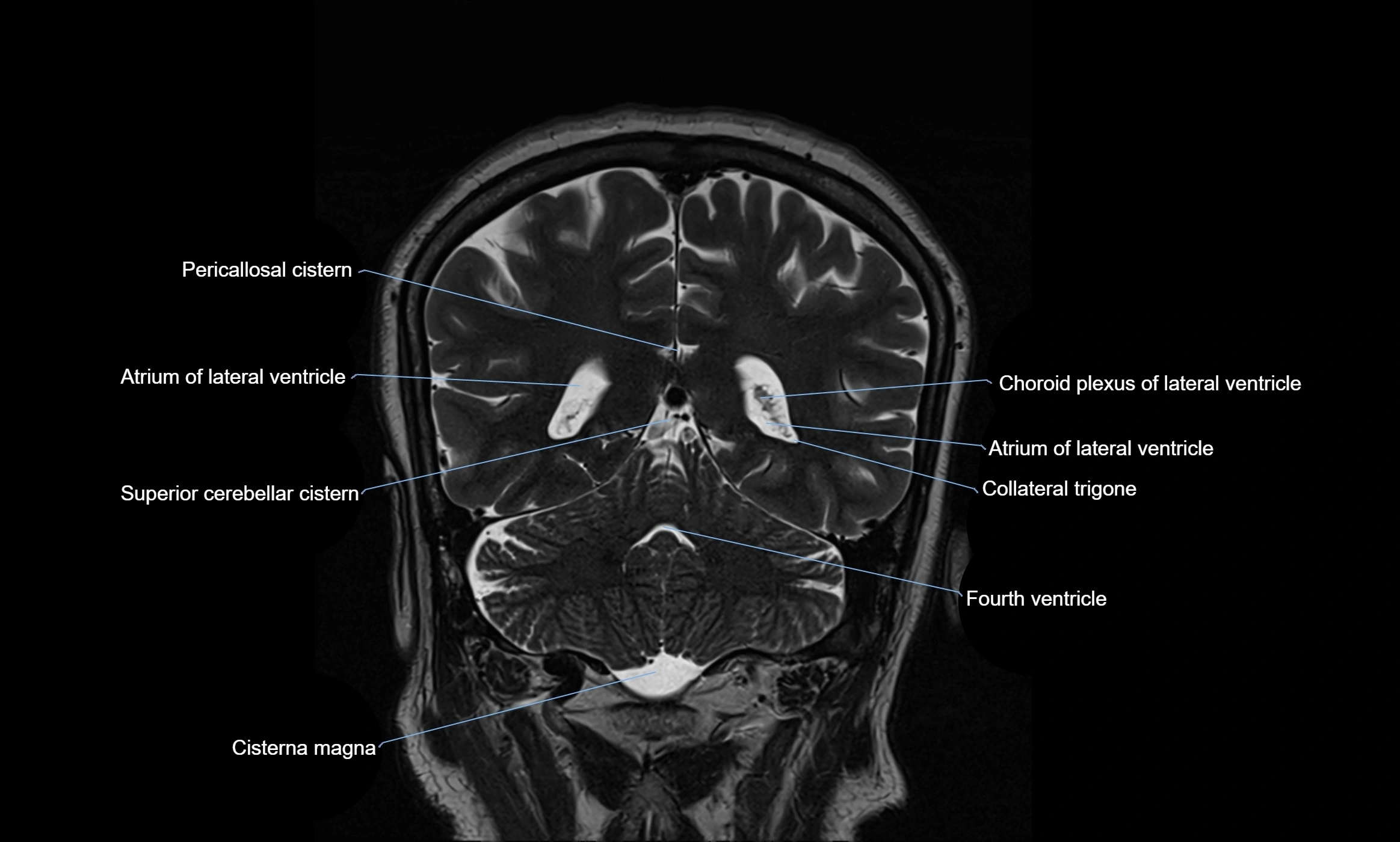
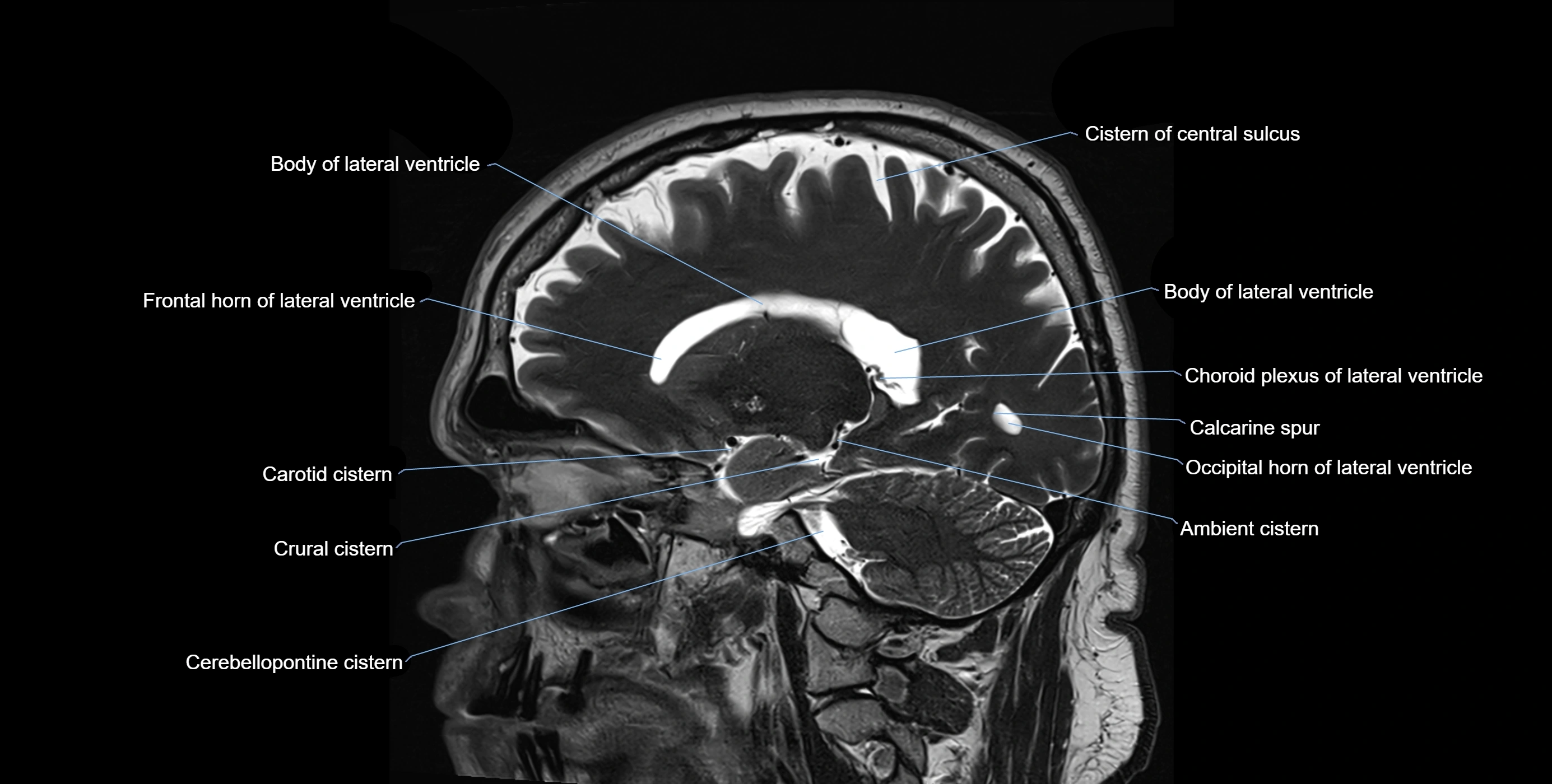
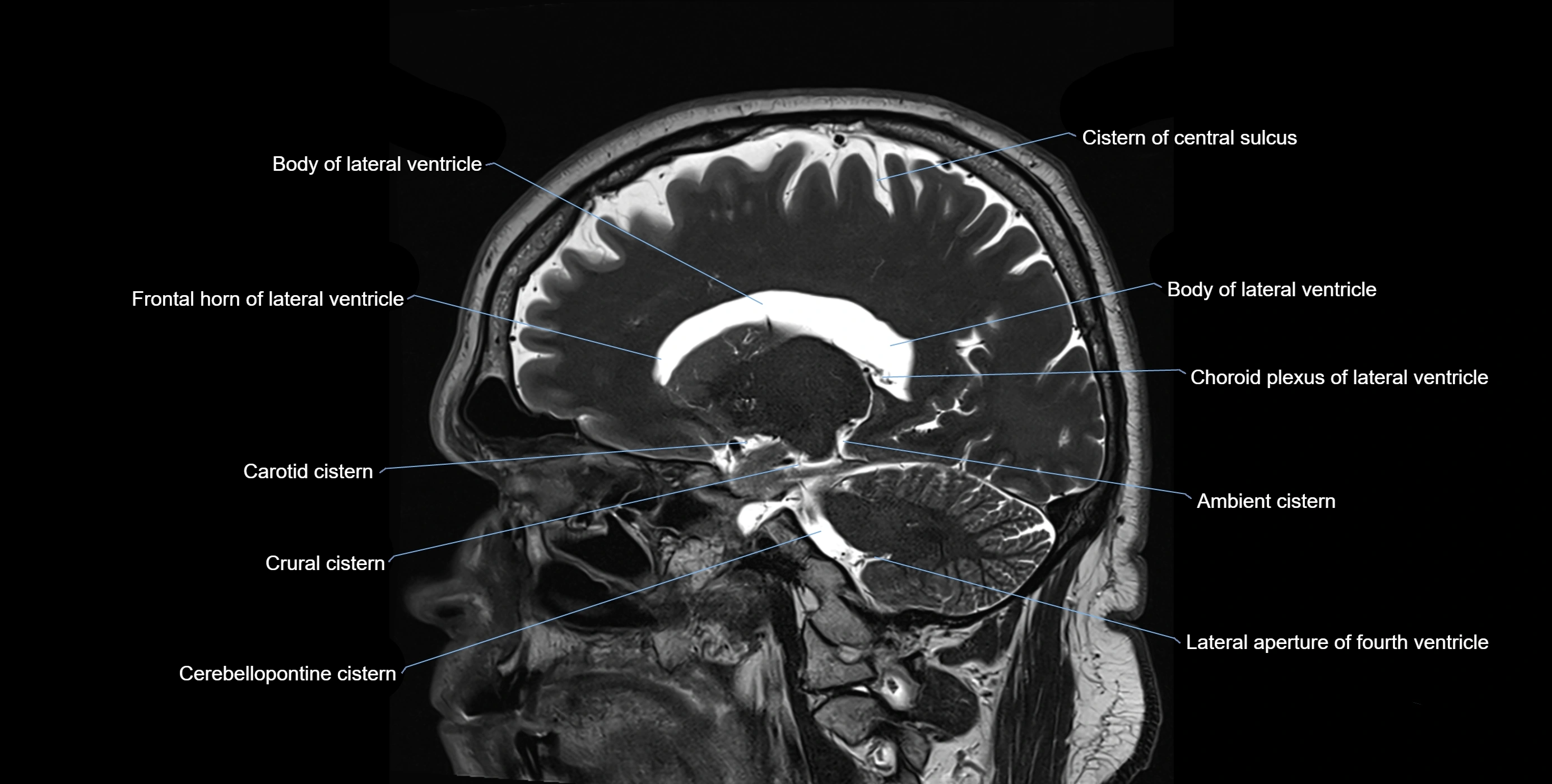
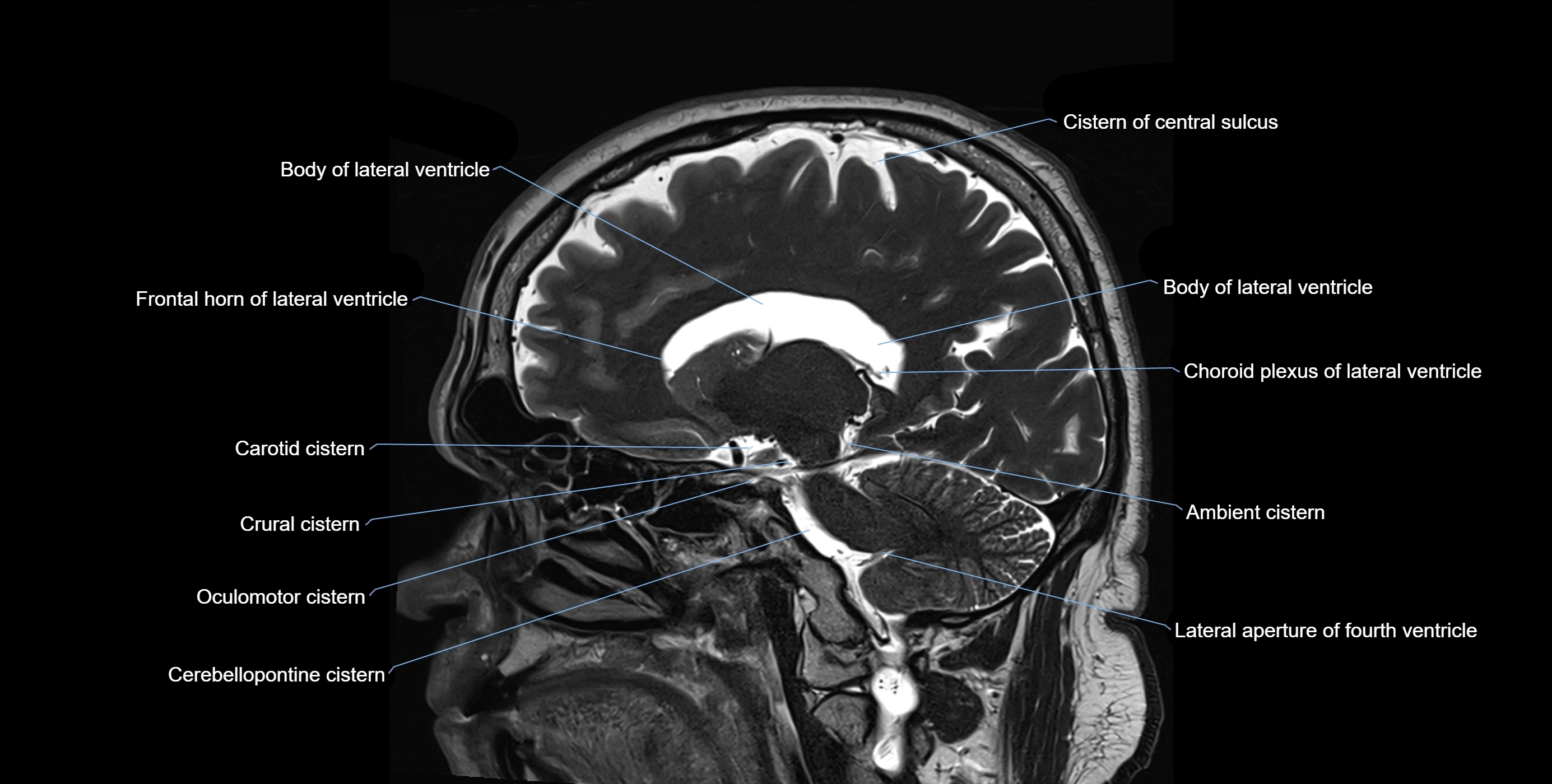
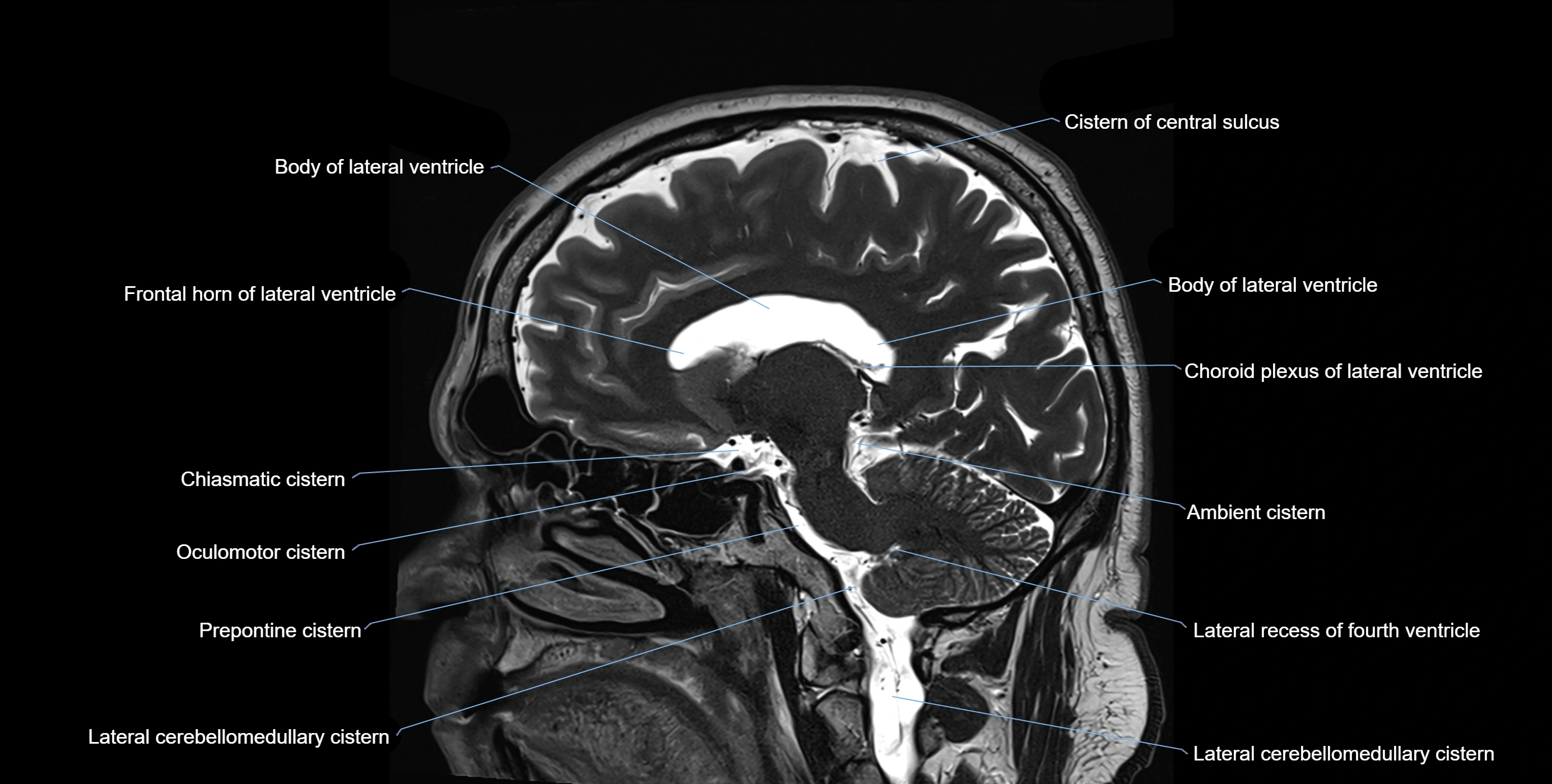
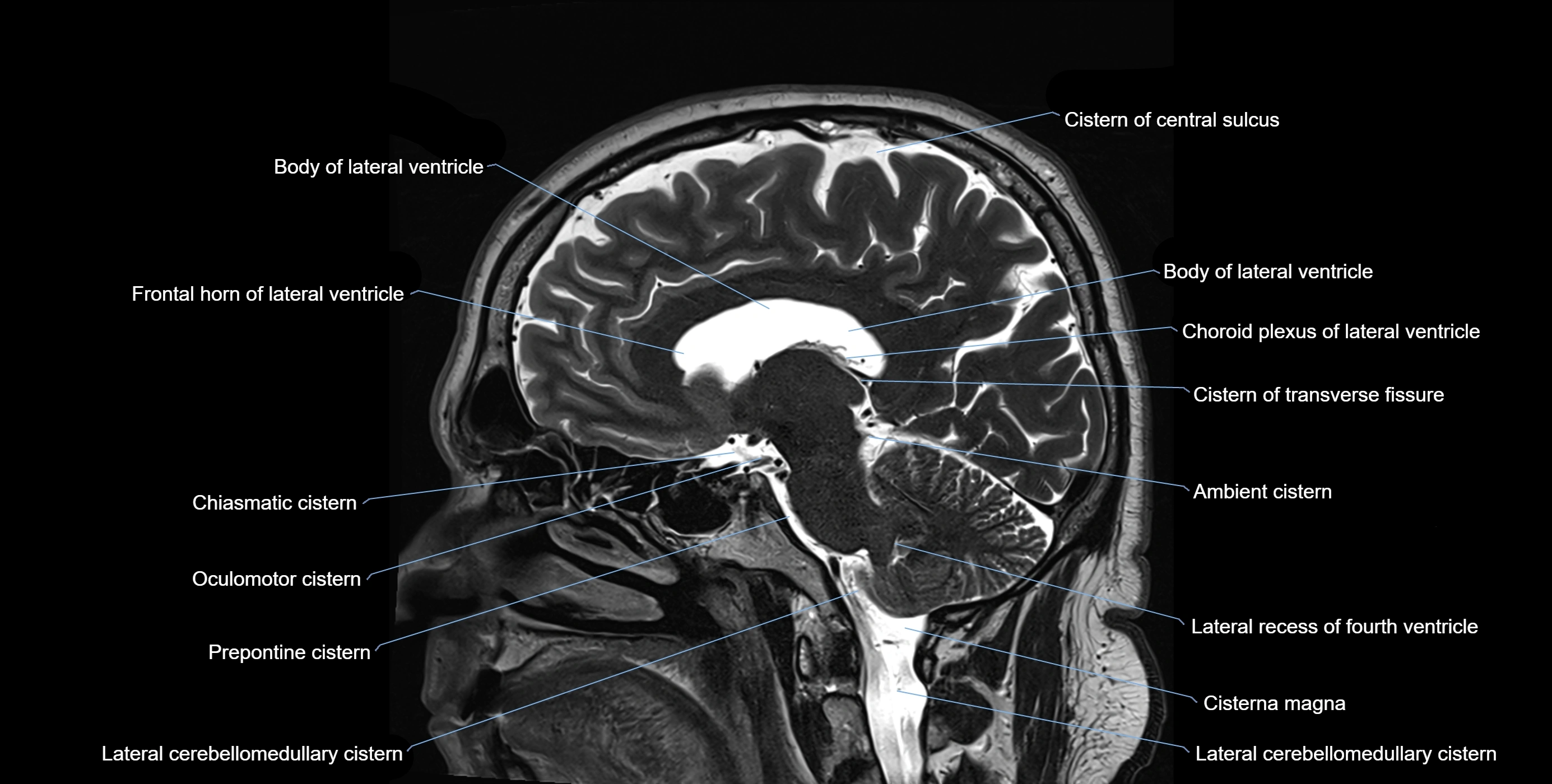
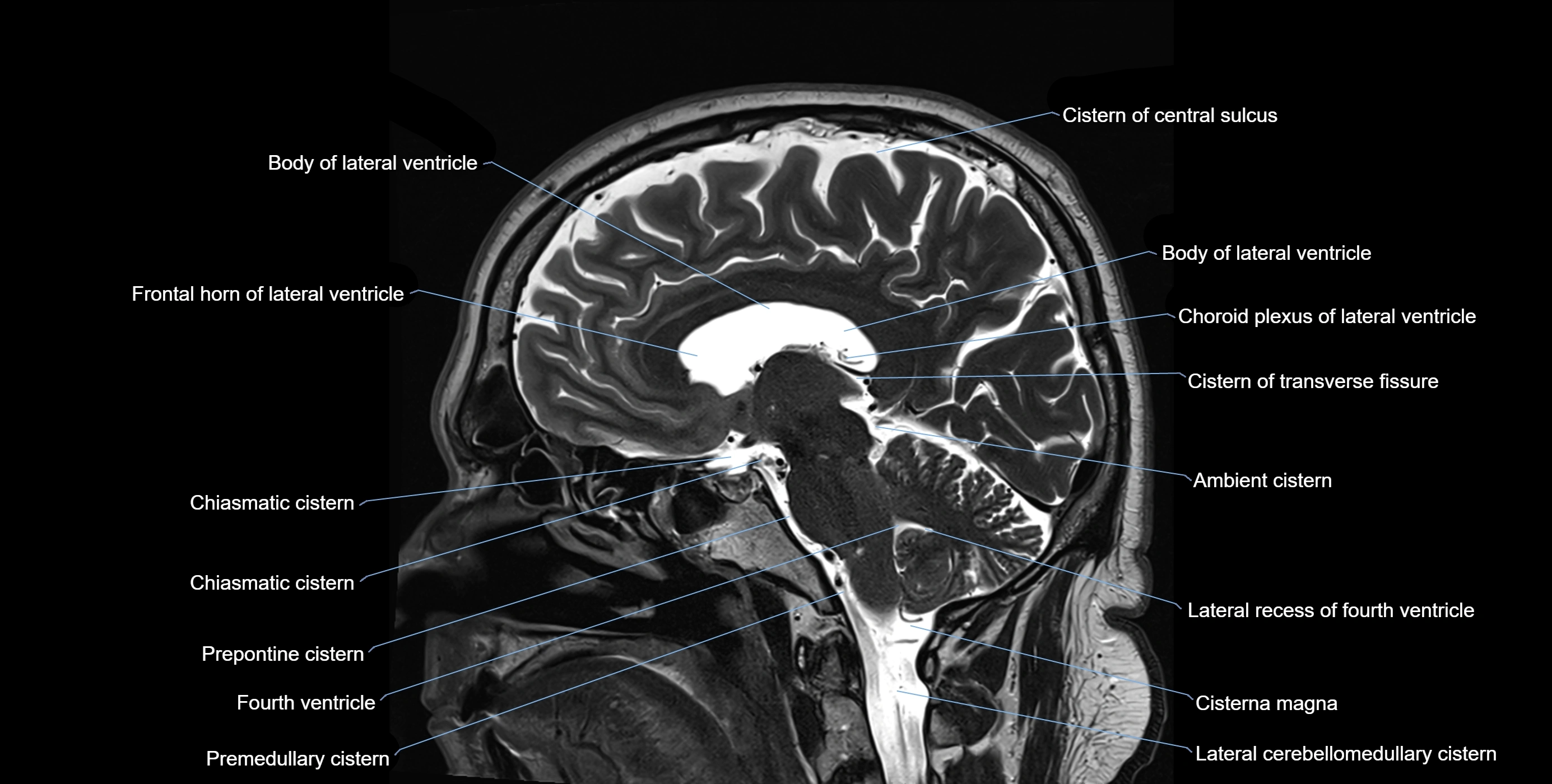
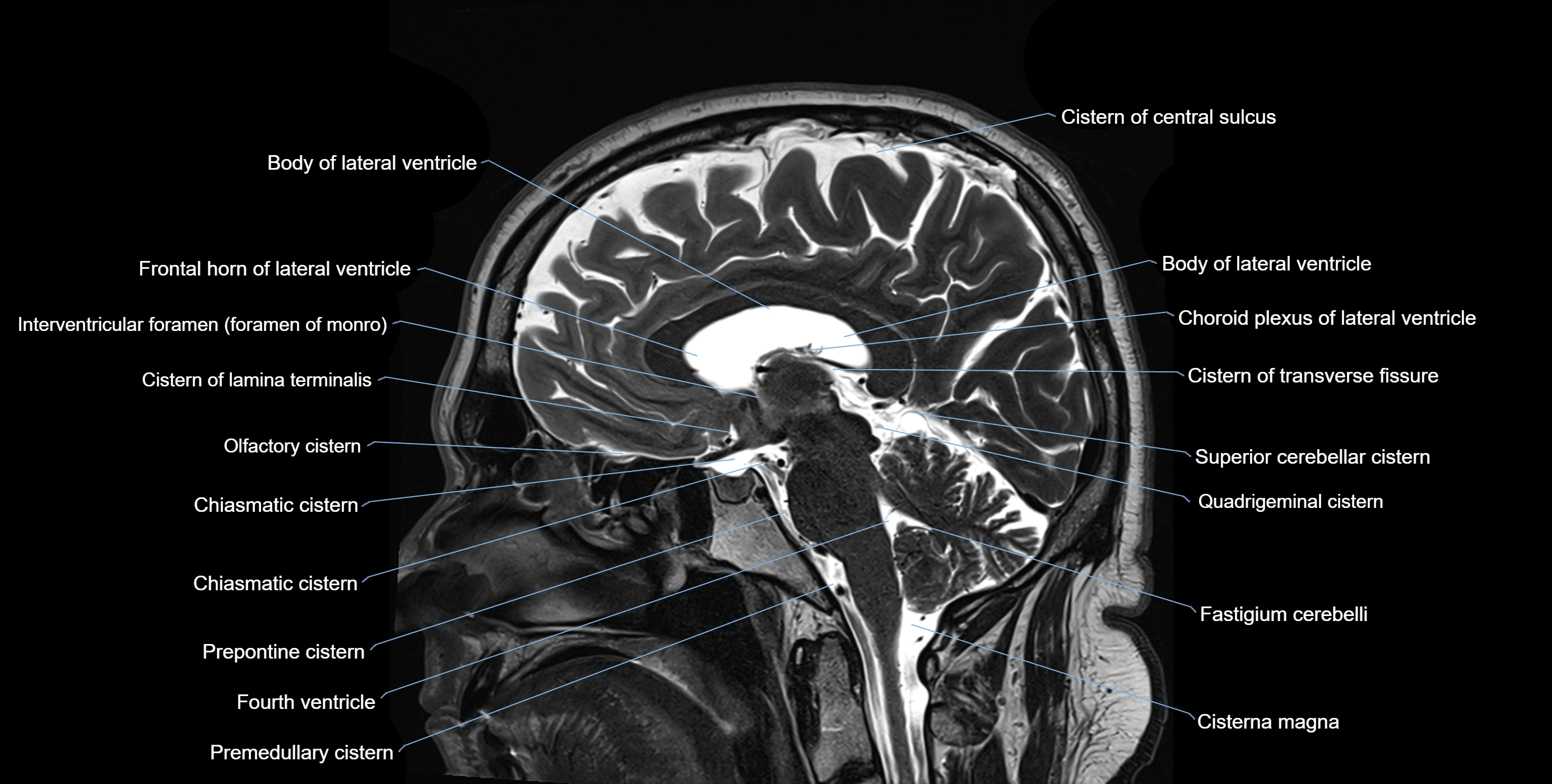
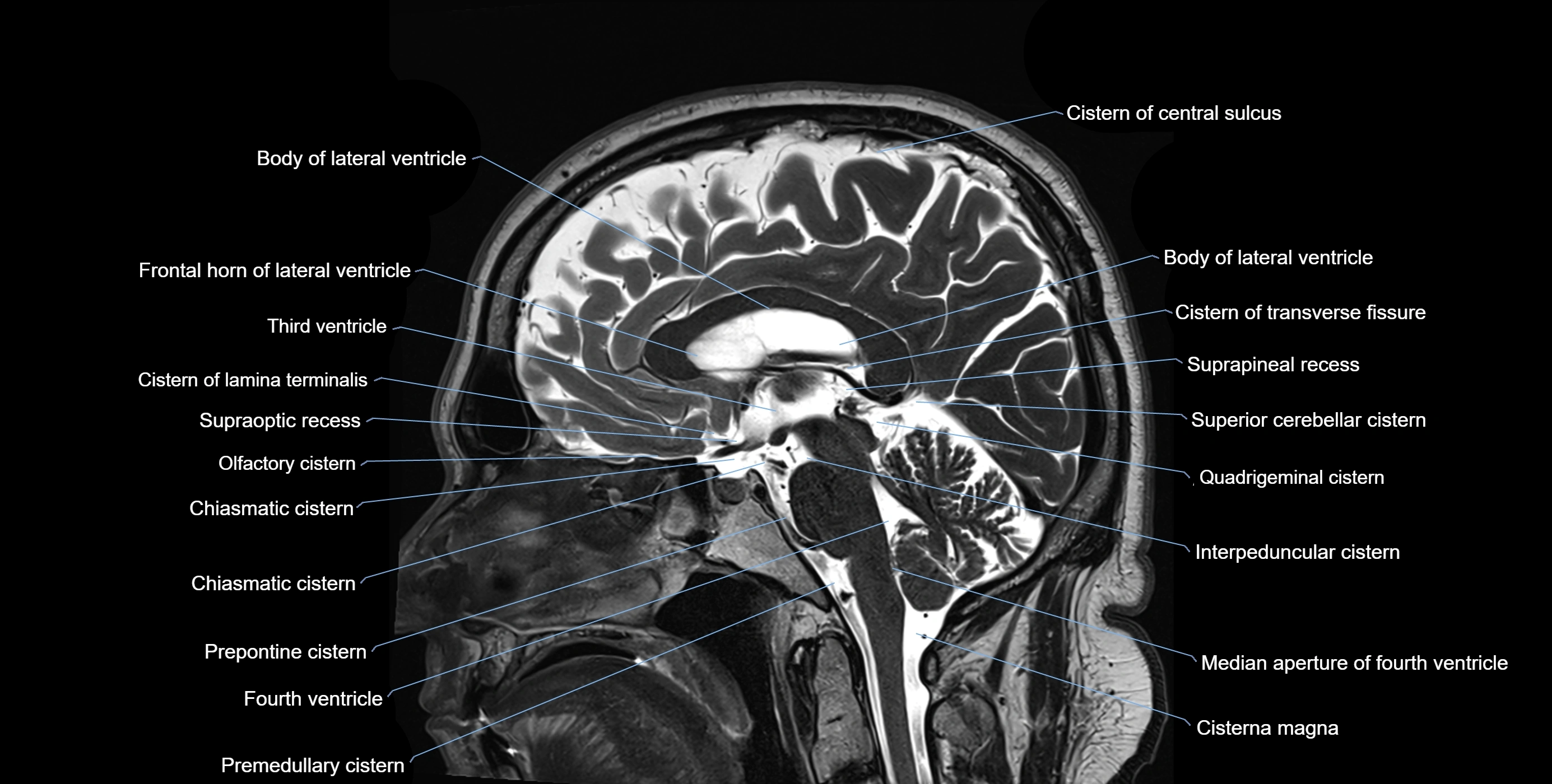
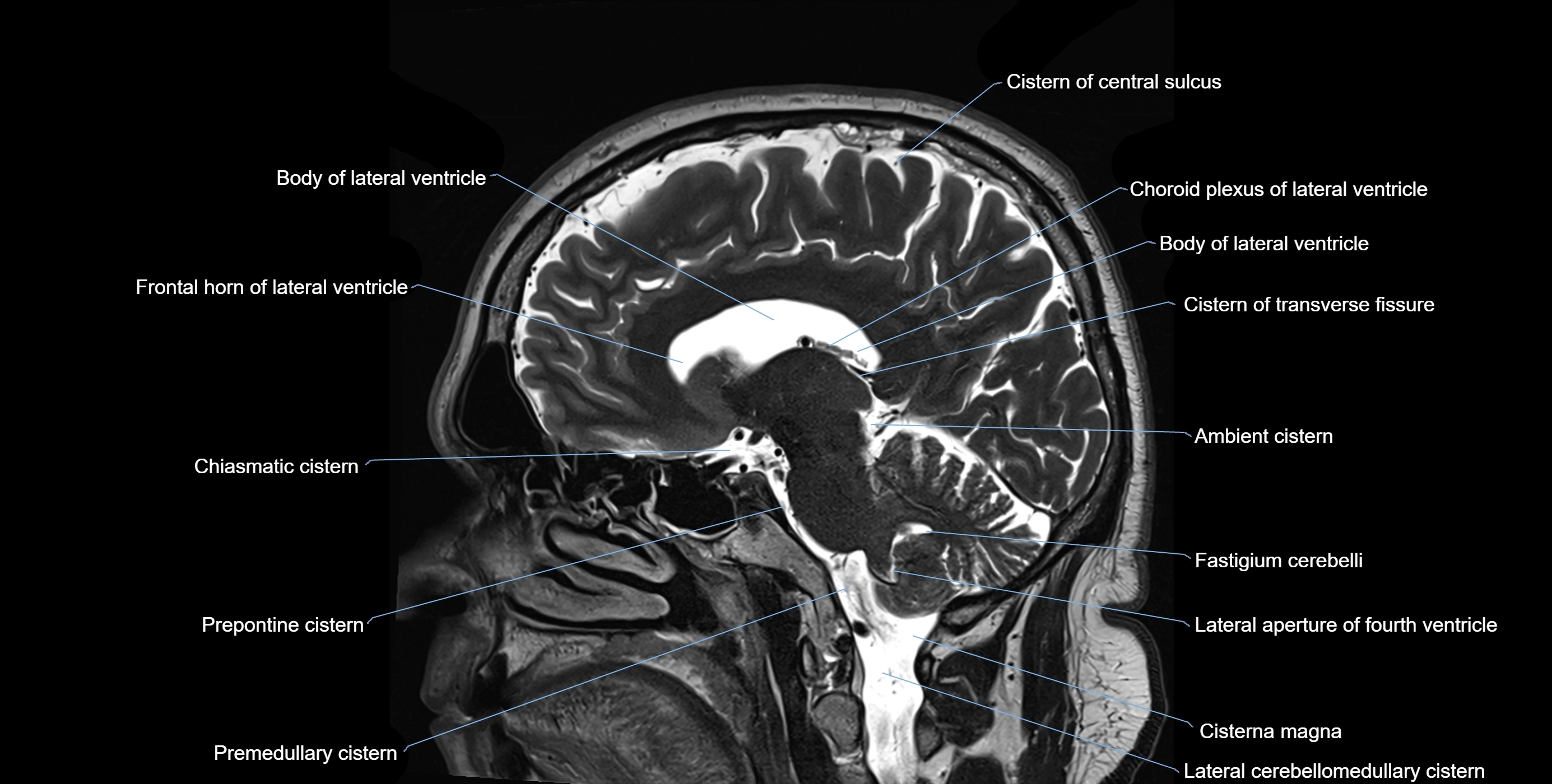
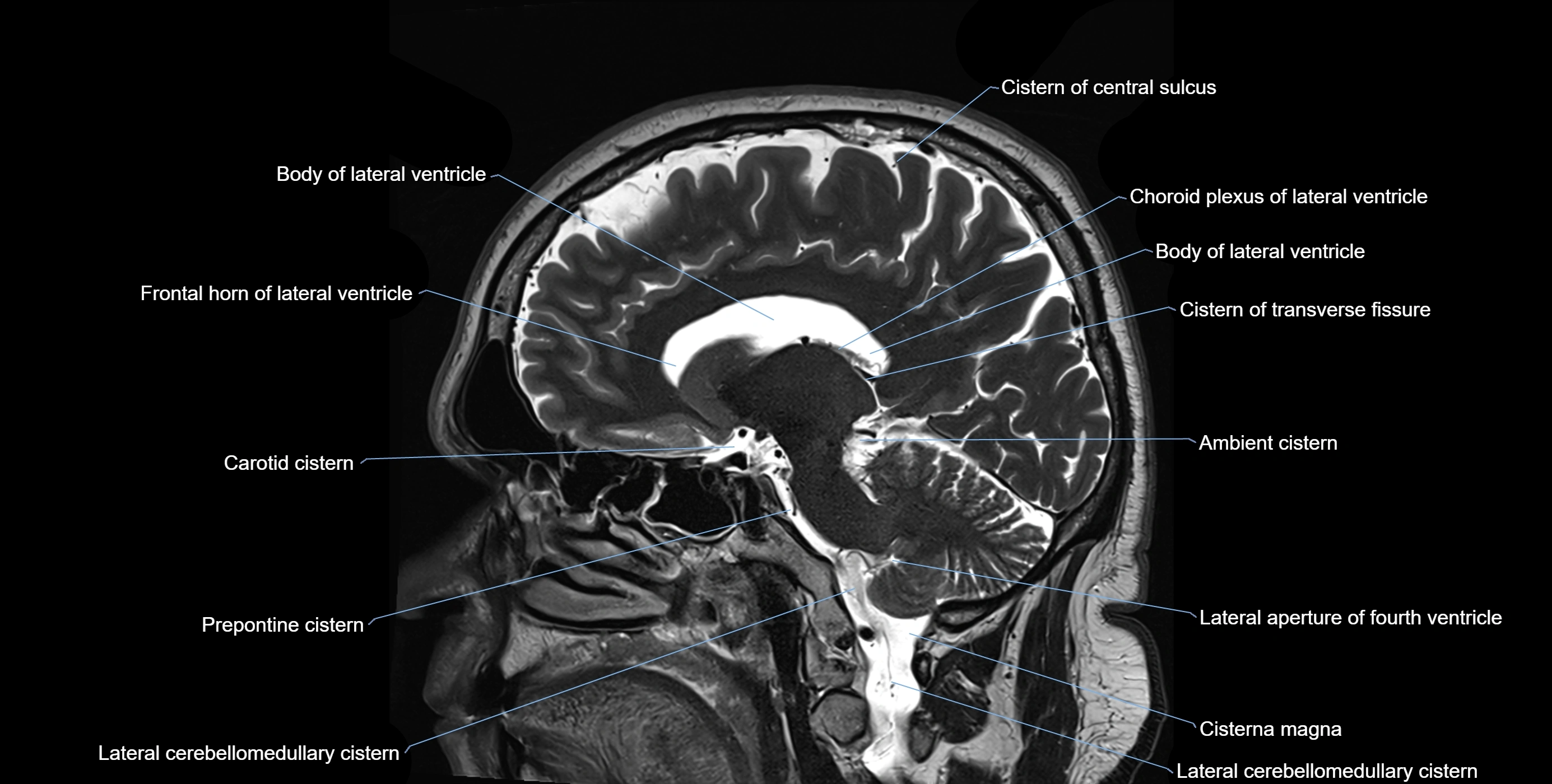
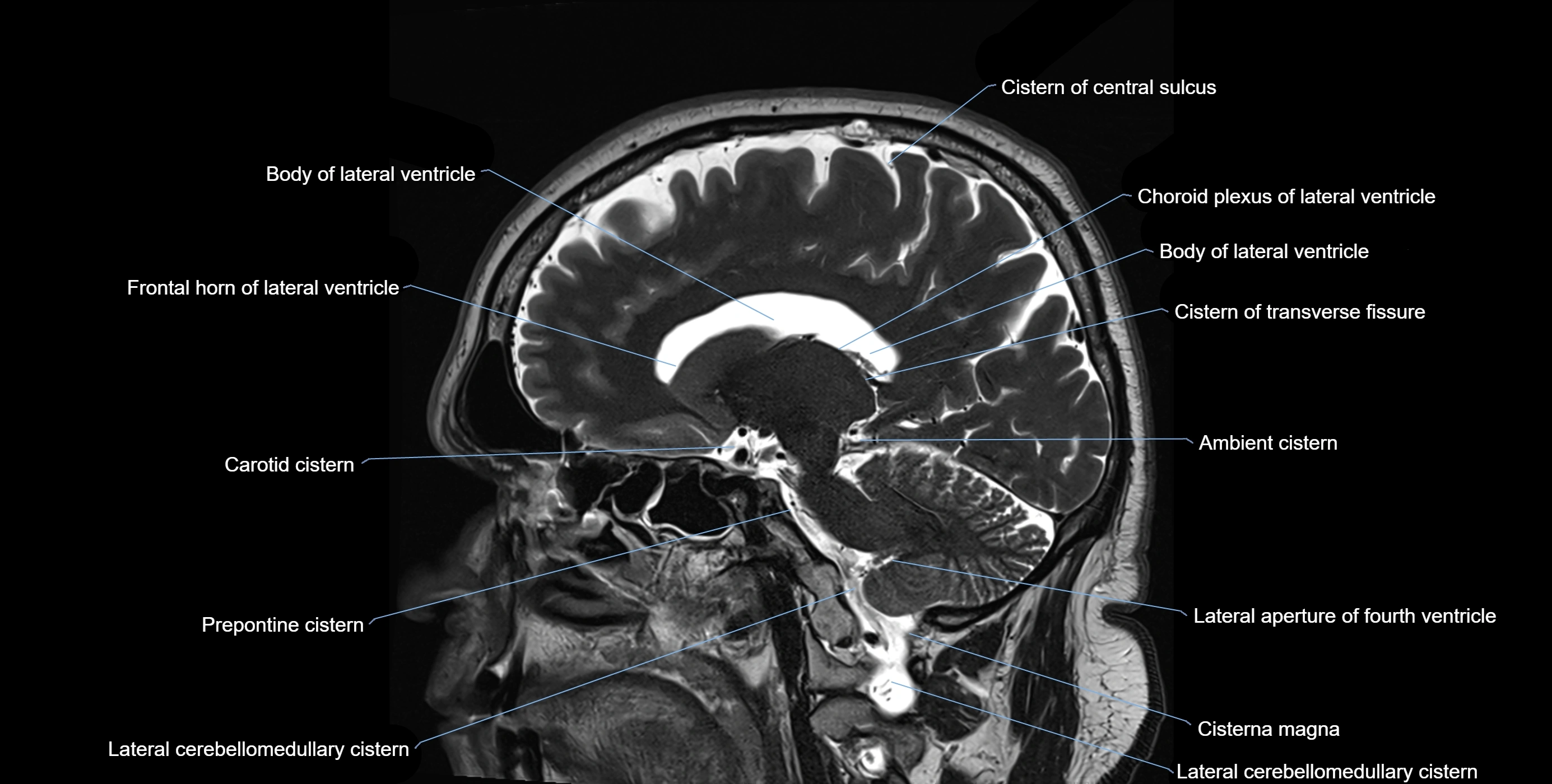
The ambient cistern is a paired, narrow, and elongated subarachnoid space located bilaterally along the lateral aspect of the midbrain. It serves as a conduit between the interpeduncular cistern anteriorly and the quadrigeminal cistern posteriorly. This cistern houses critical neurovascular structures, including parts of the posterior cerebral artery, superior cerebellar artery, trochlear nerve (cranial nerve IV), and the basal vein of Rosenthal. It plays an important role in the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and provides an anatomical corridor for various vessels and nerves passing around the midbrain.
Synonyms
-
Lateral mesencephalic cistern
-
Mesencephalic cistern (less commonly)
-
Perimesencephalic cistern (when describing the complex, which includes the ambient cistern)
Function
-
Contains and cushions neurovascular structures adjacent to the lateral midbrain
-
Acts as a pathway for CSF flow between the interpeduncular and quadrigeminal cisterns
-
Provides a corridor for the passage of arteries, veins, and the trochlear nerve
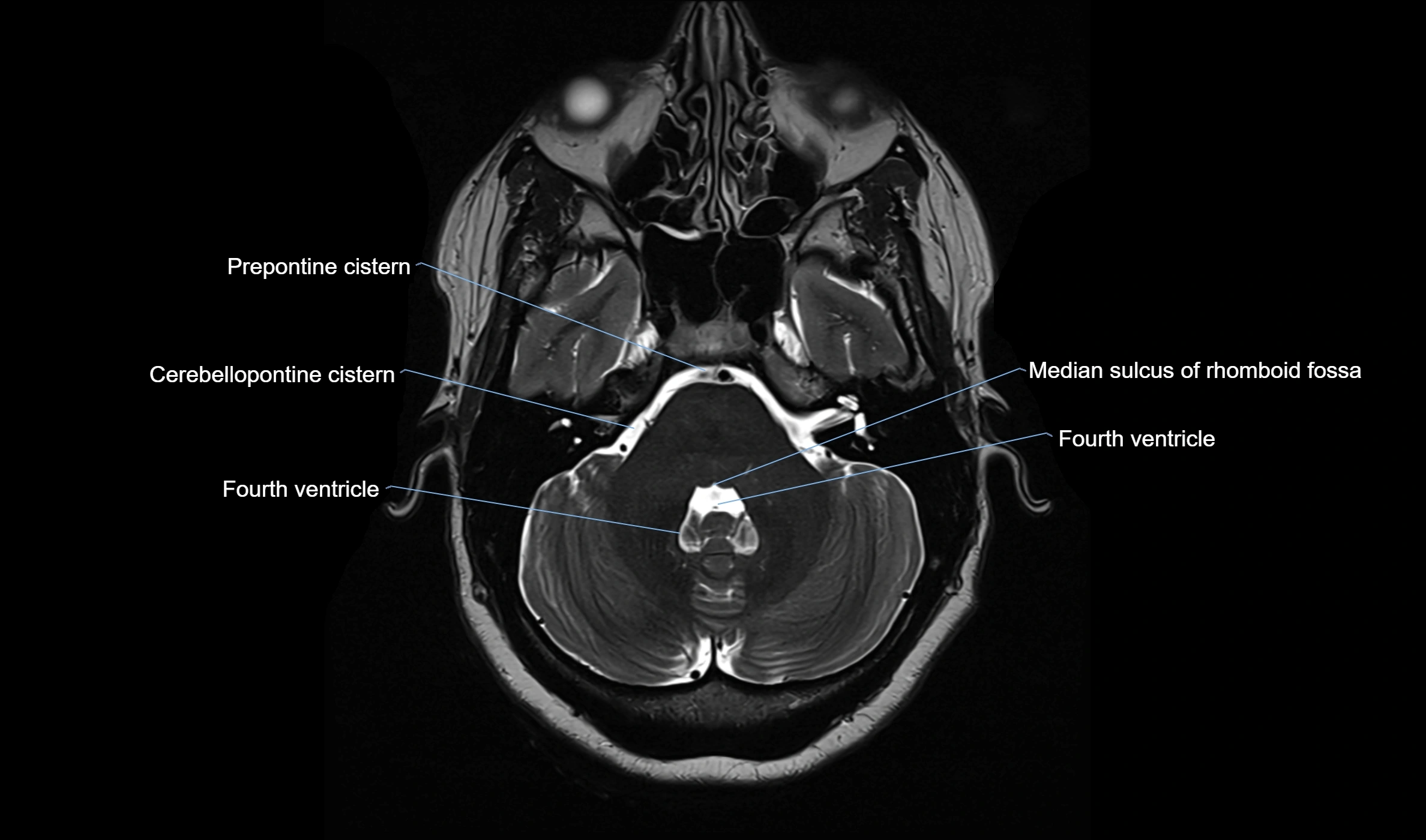
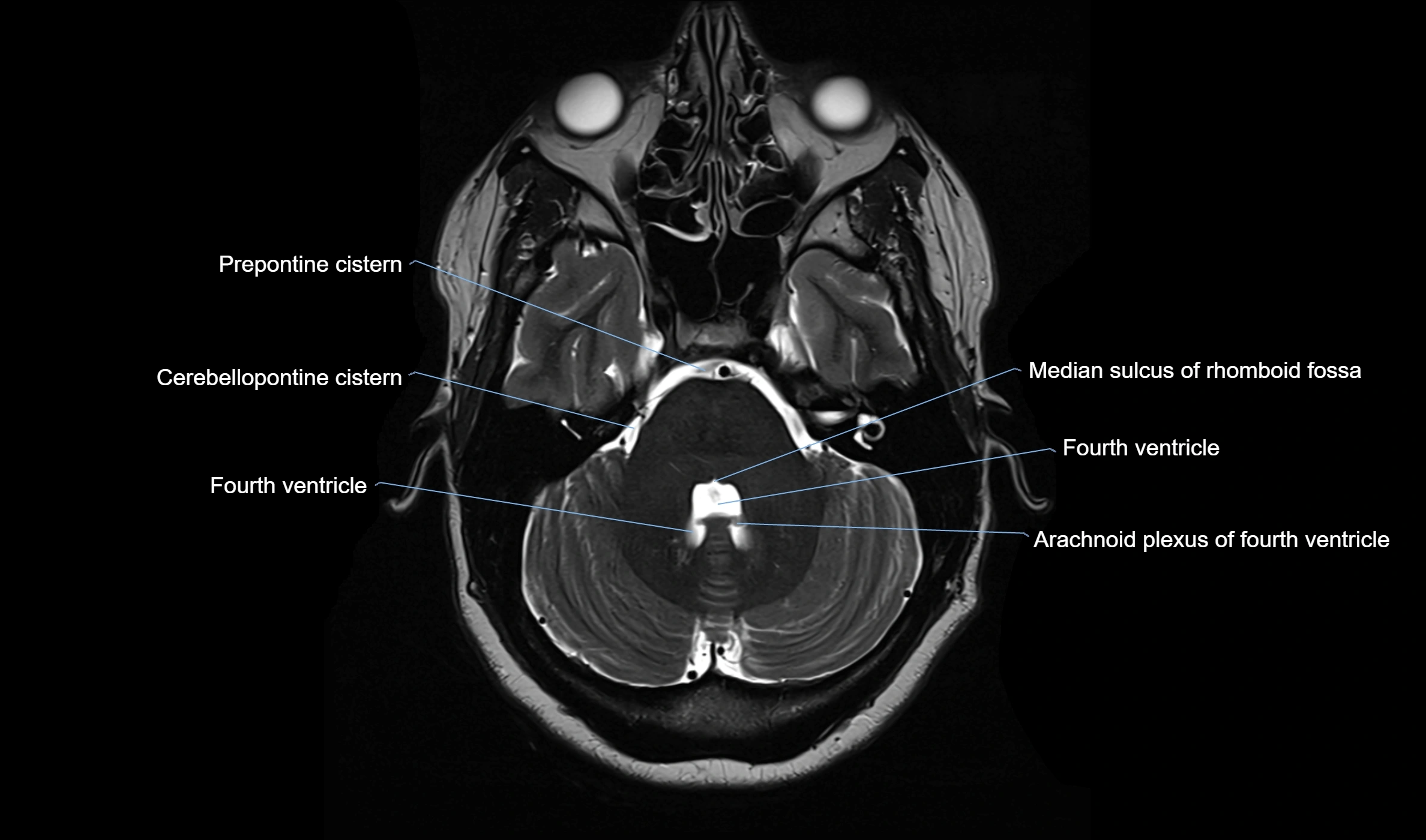
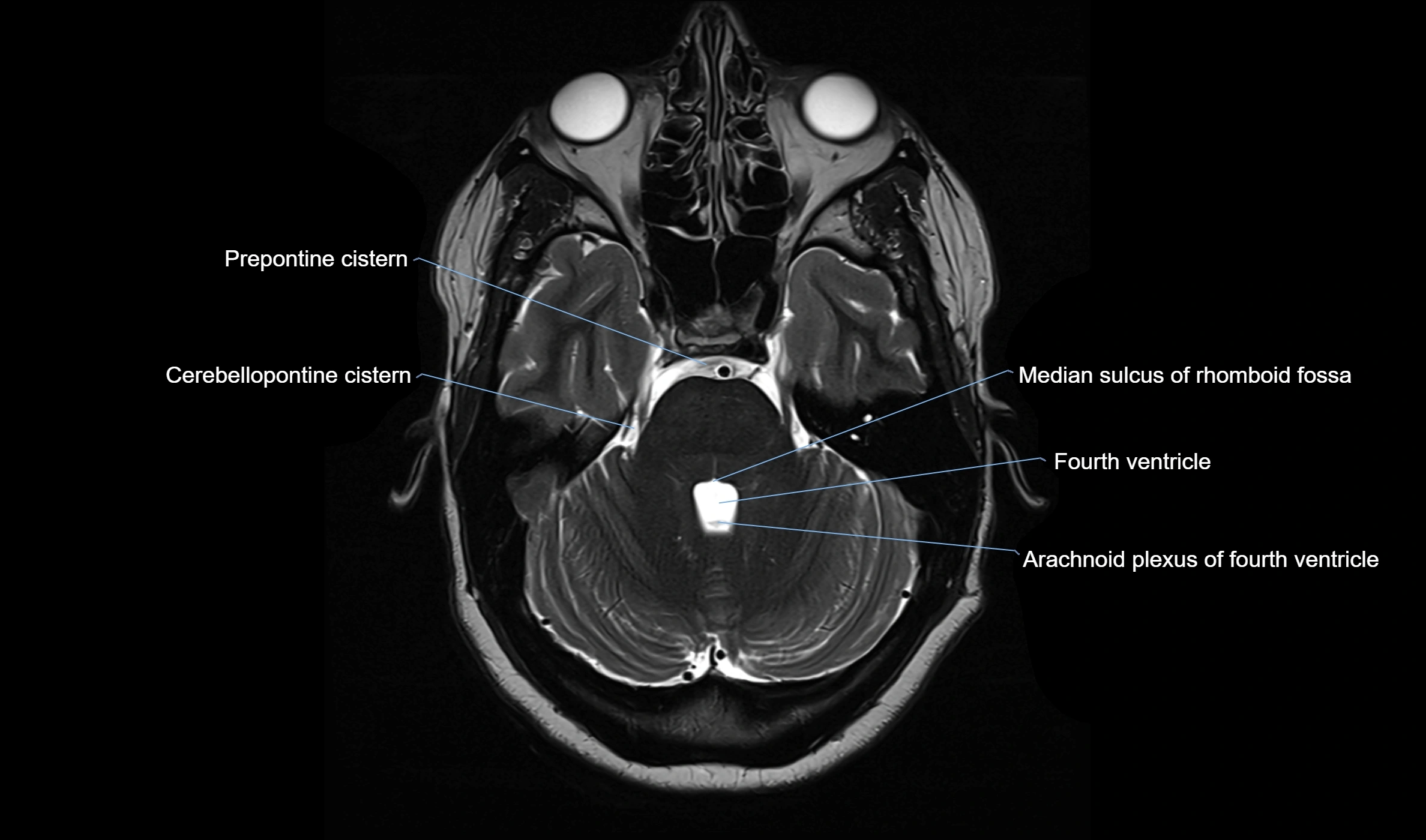
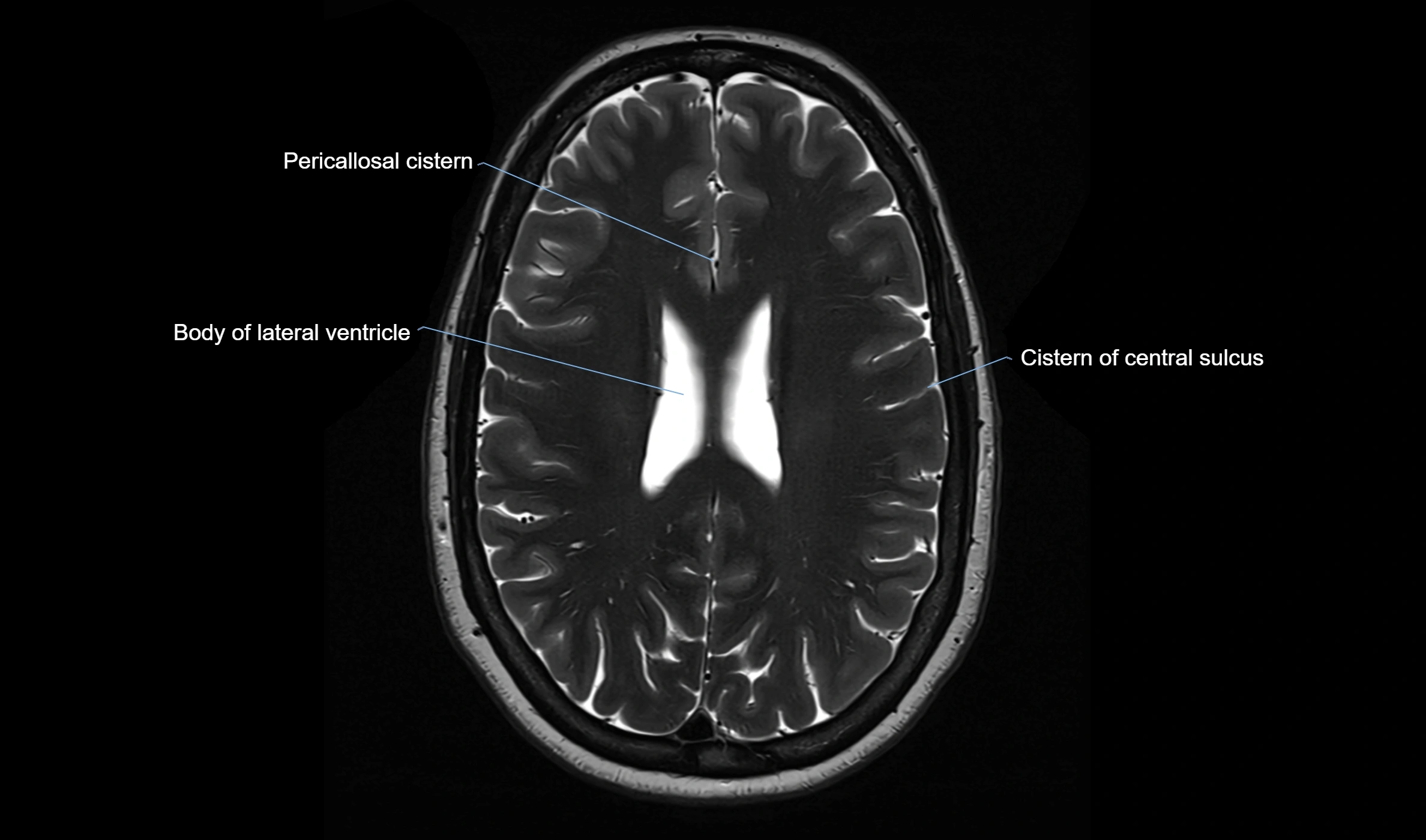
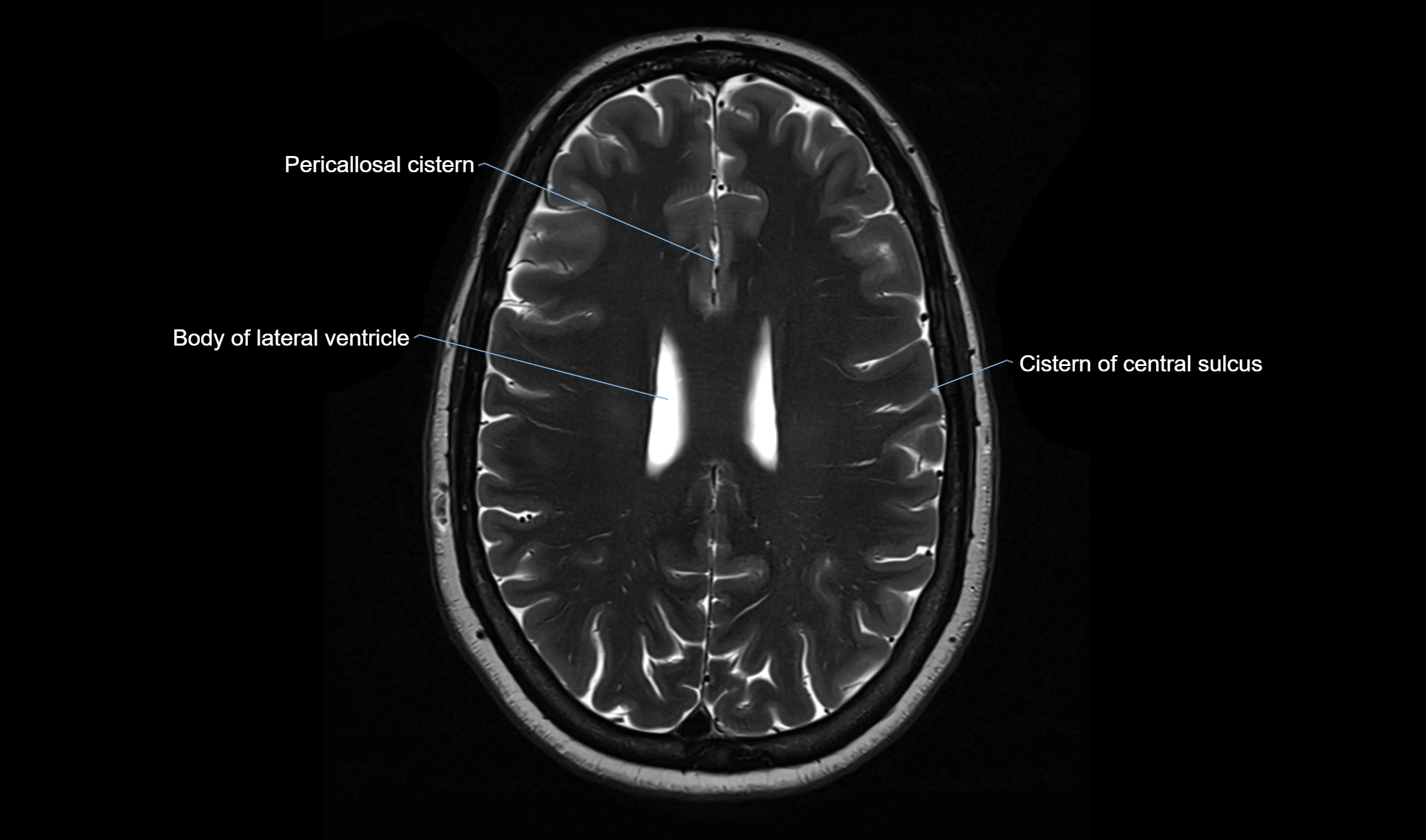
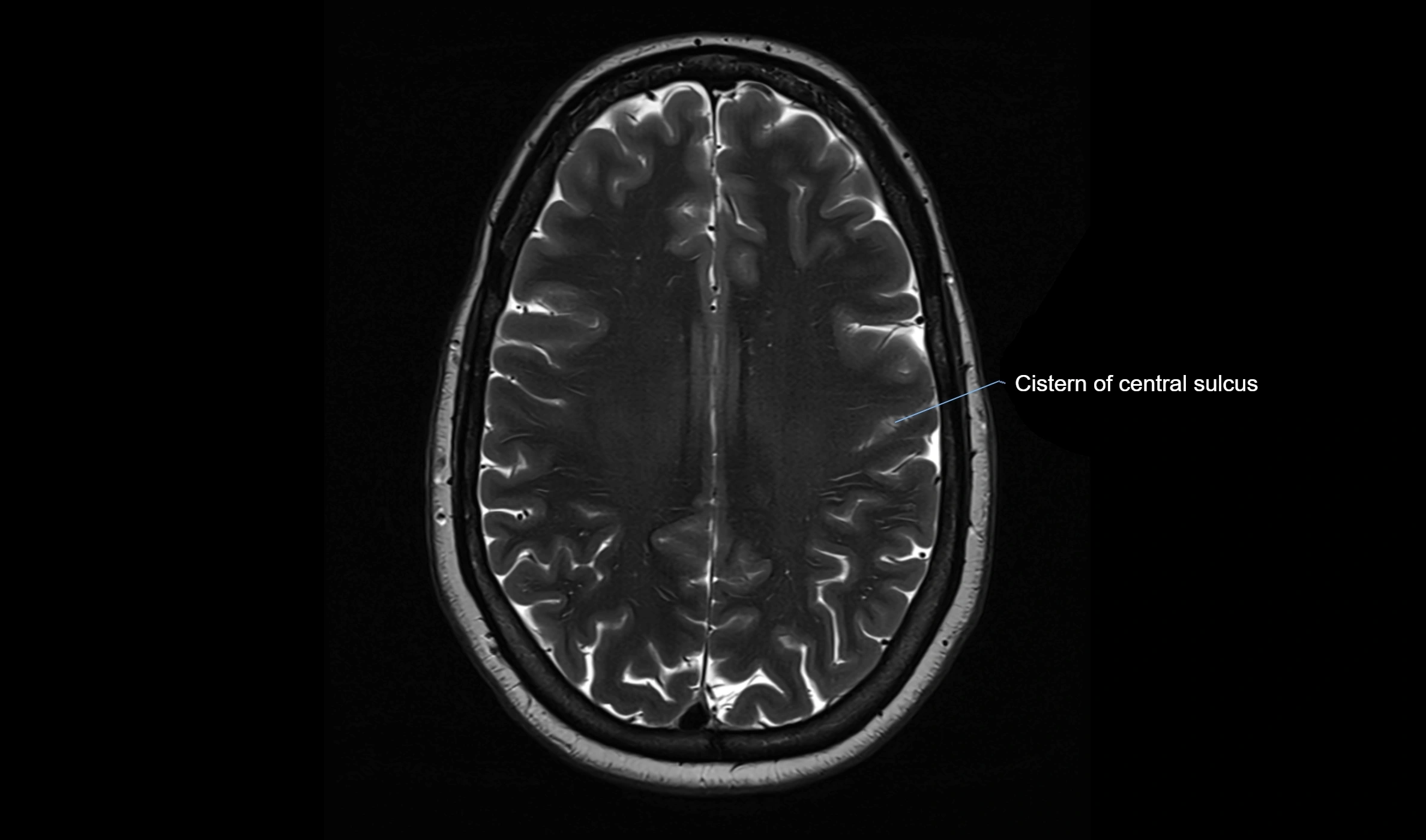
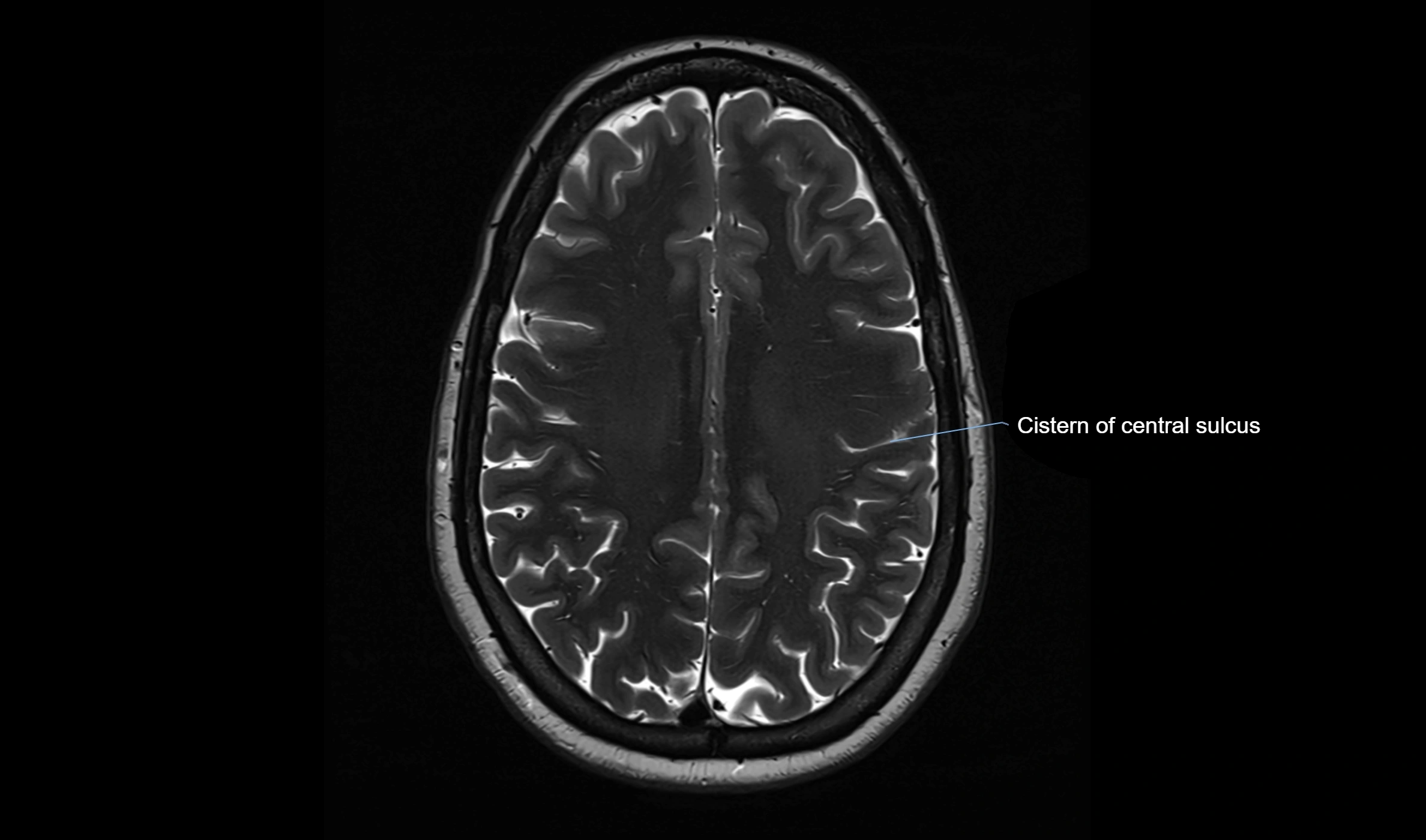
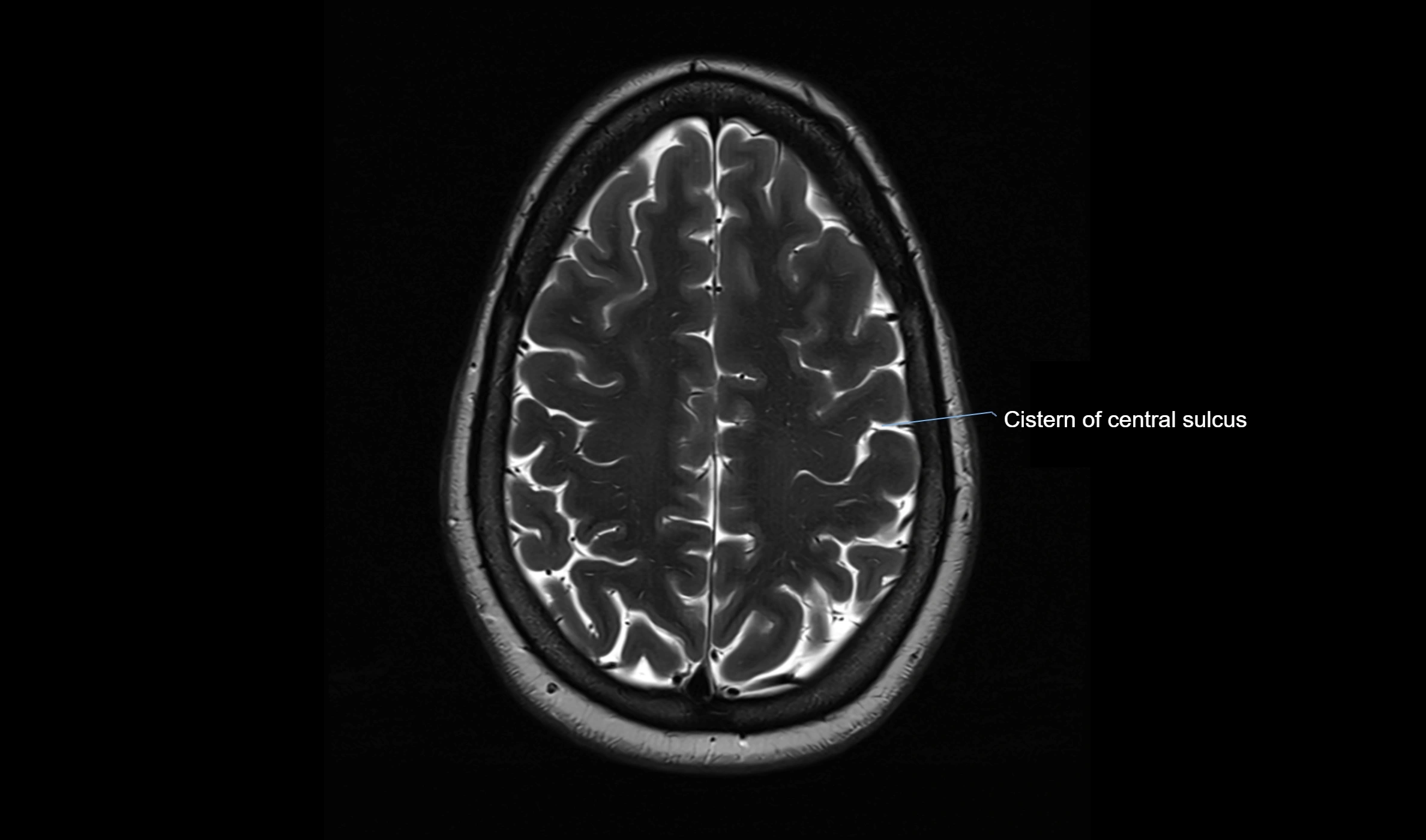
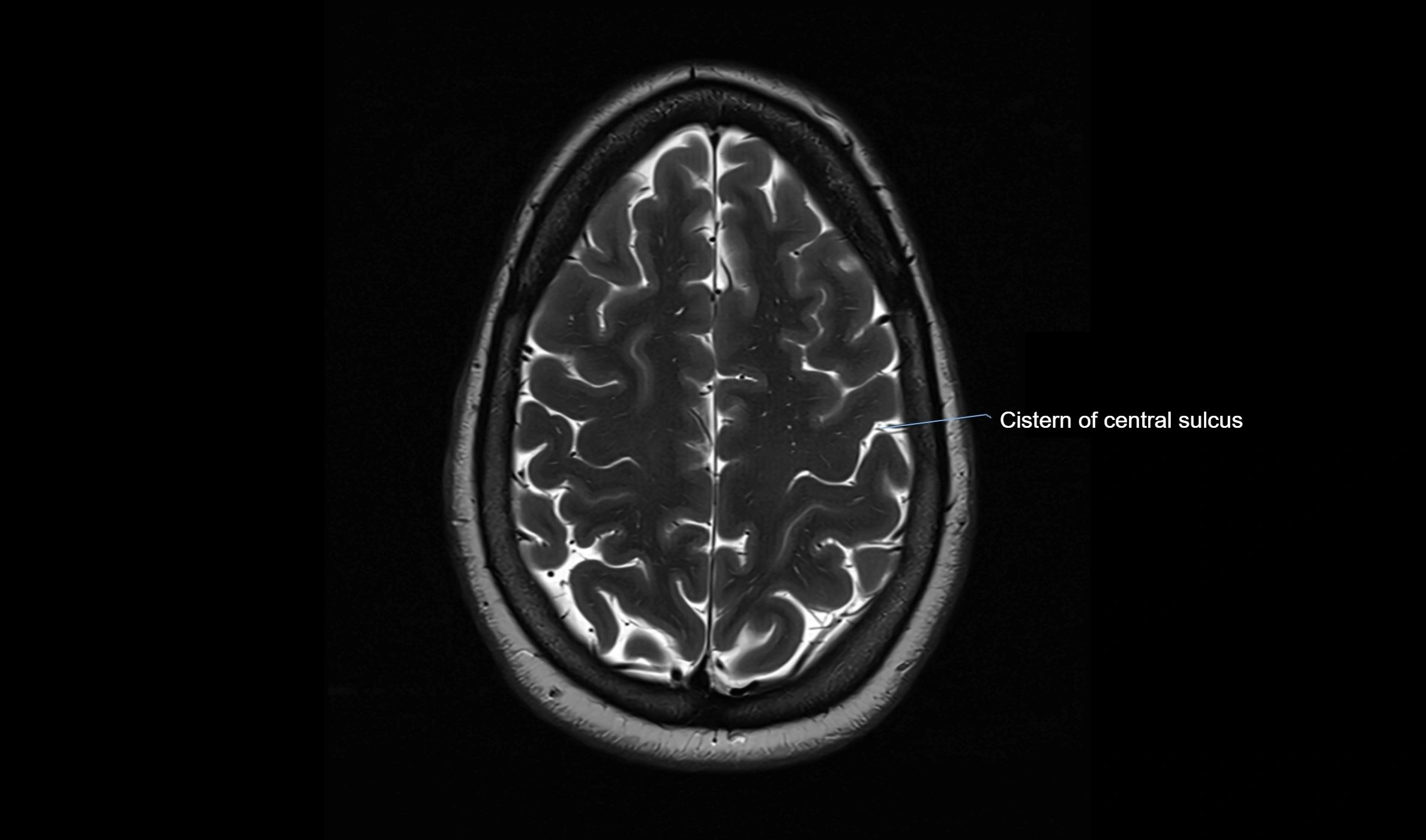
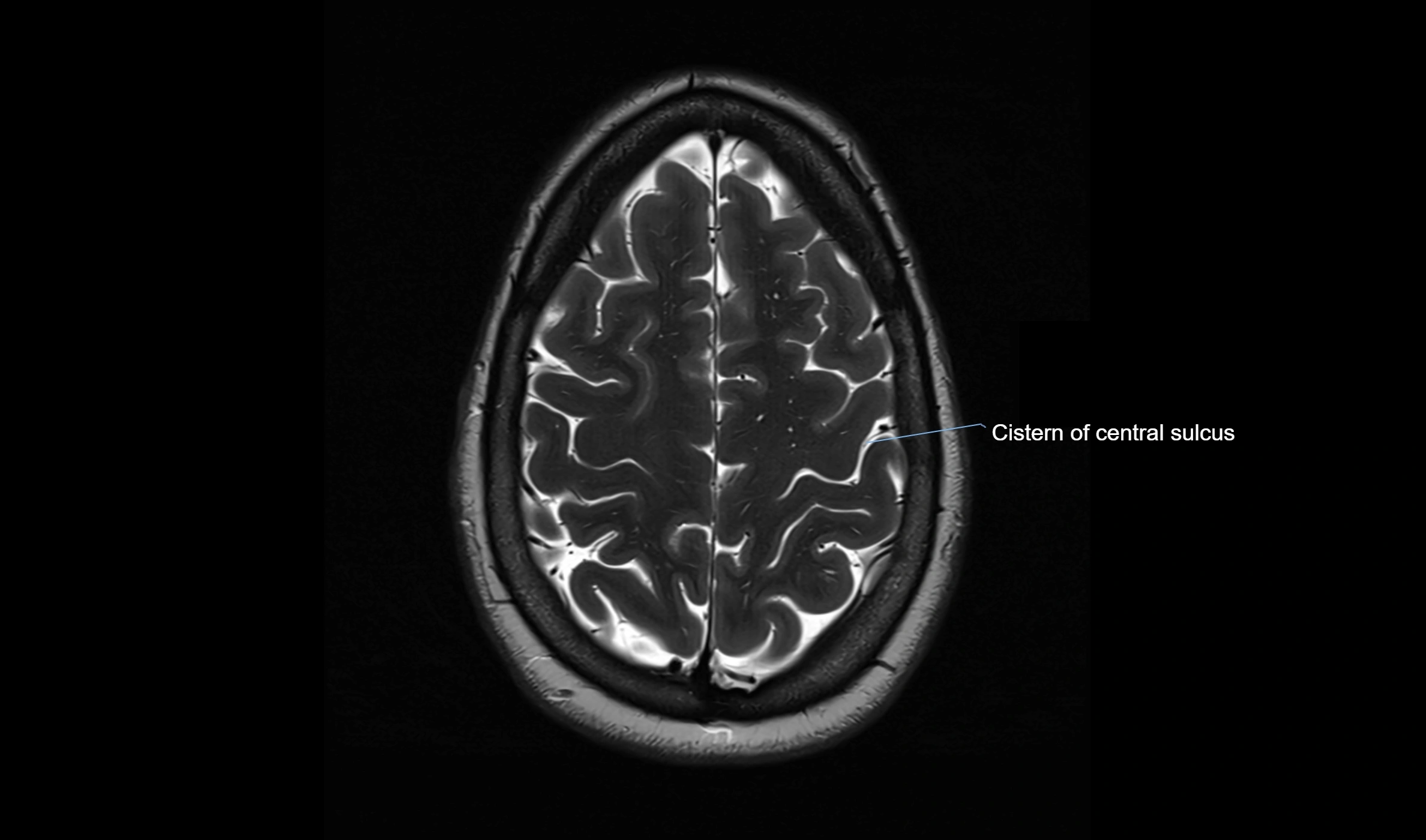
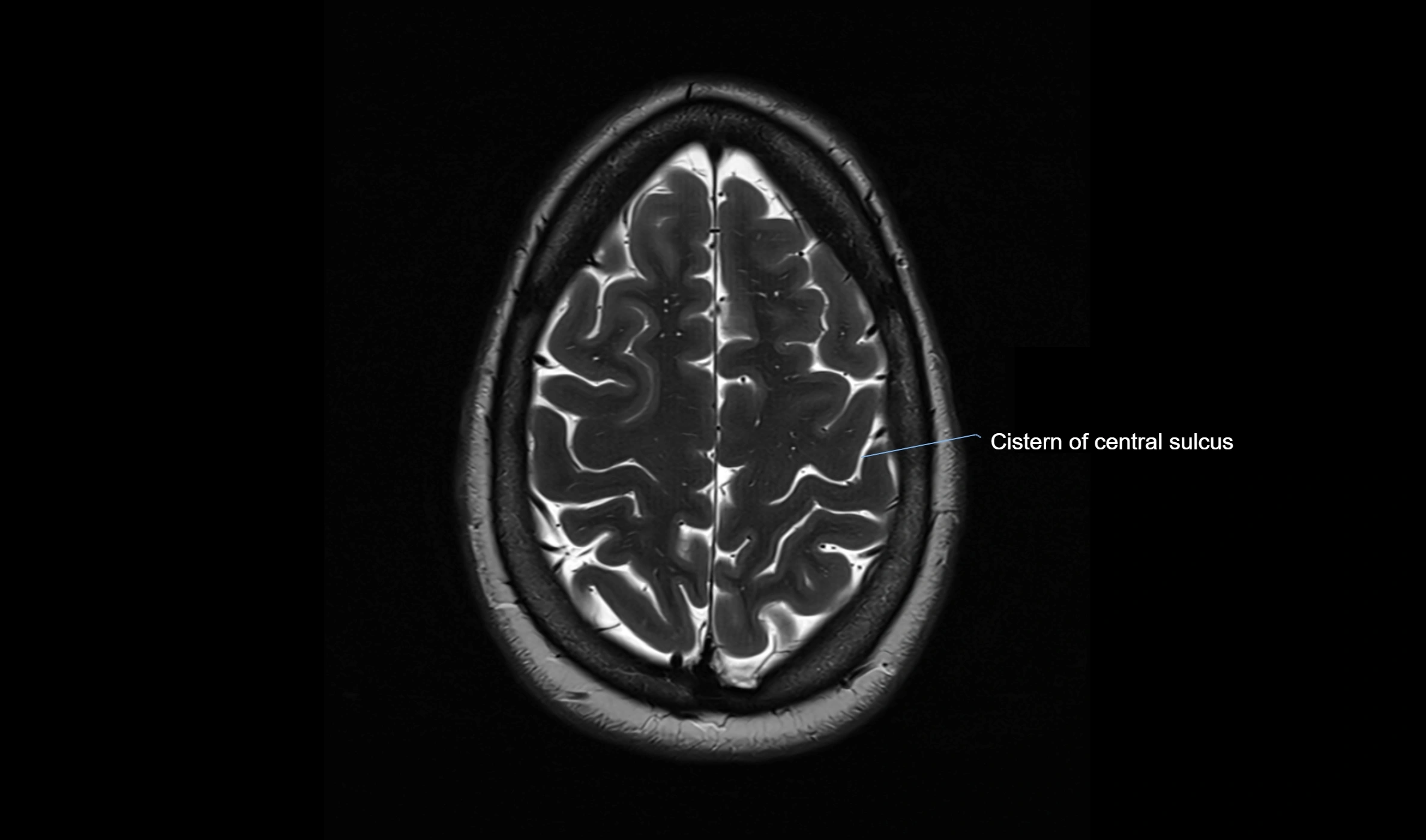
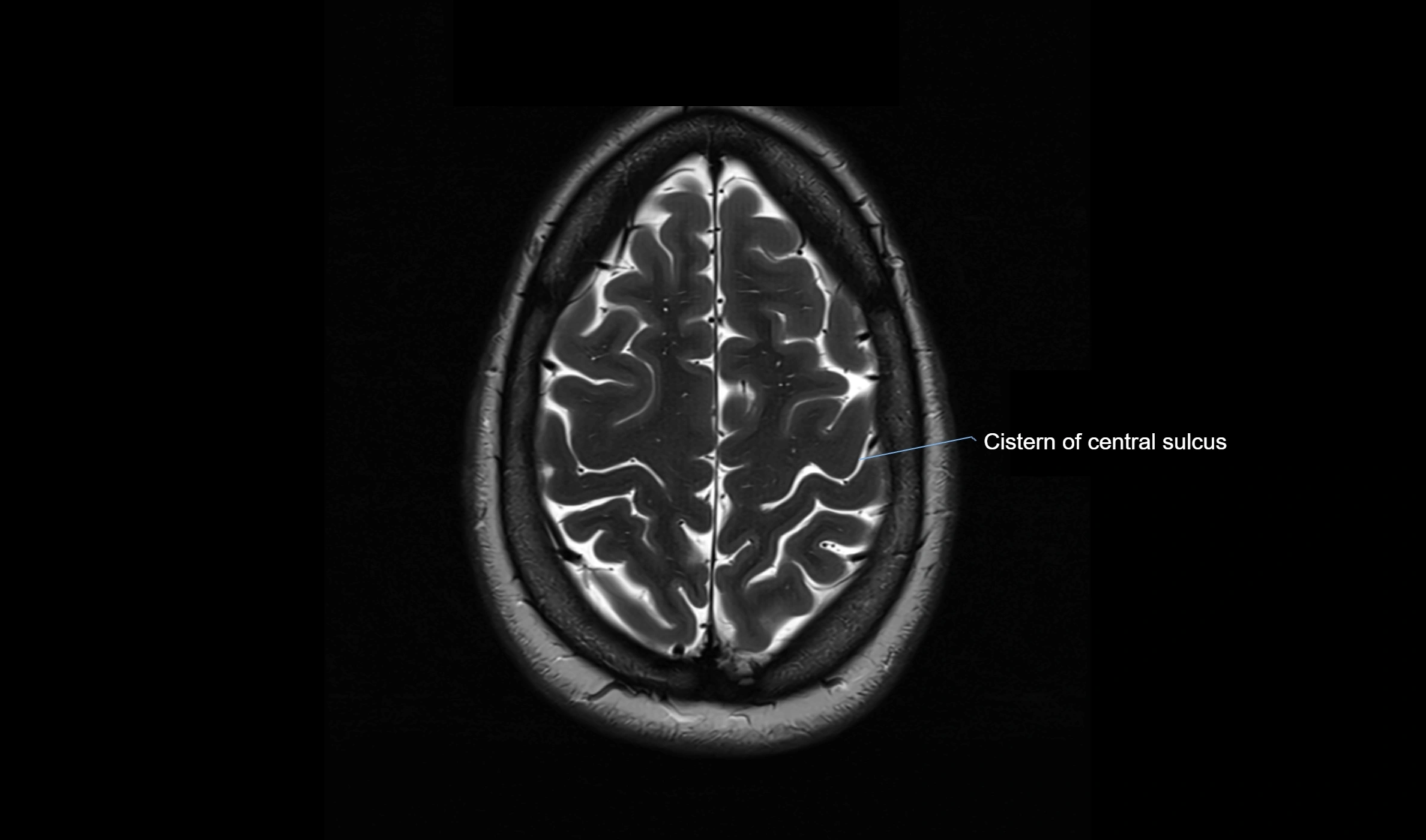
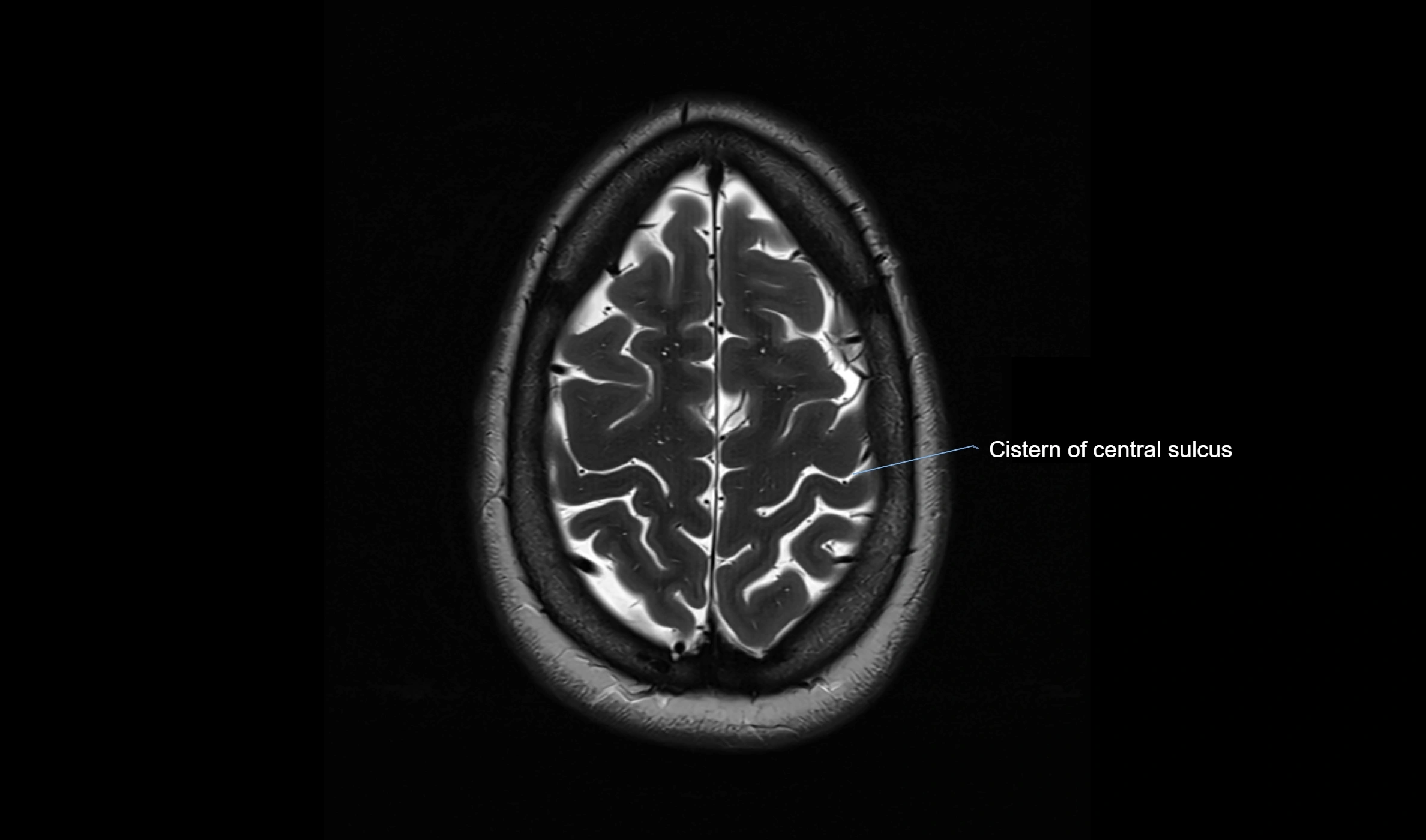
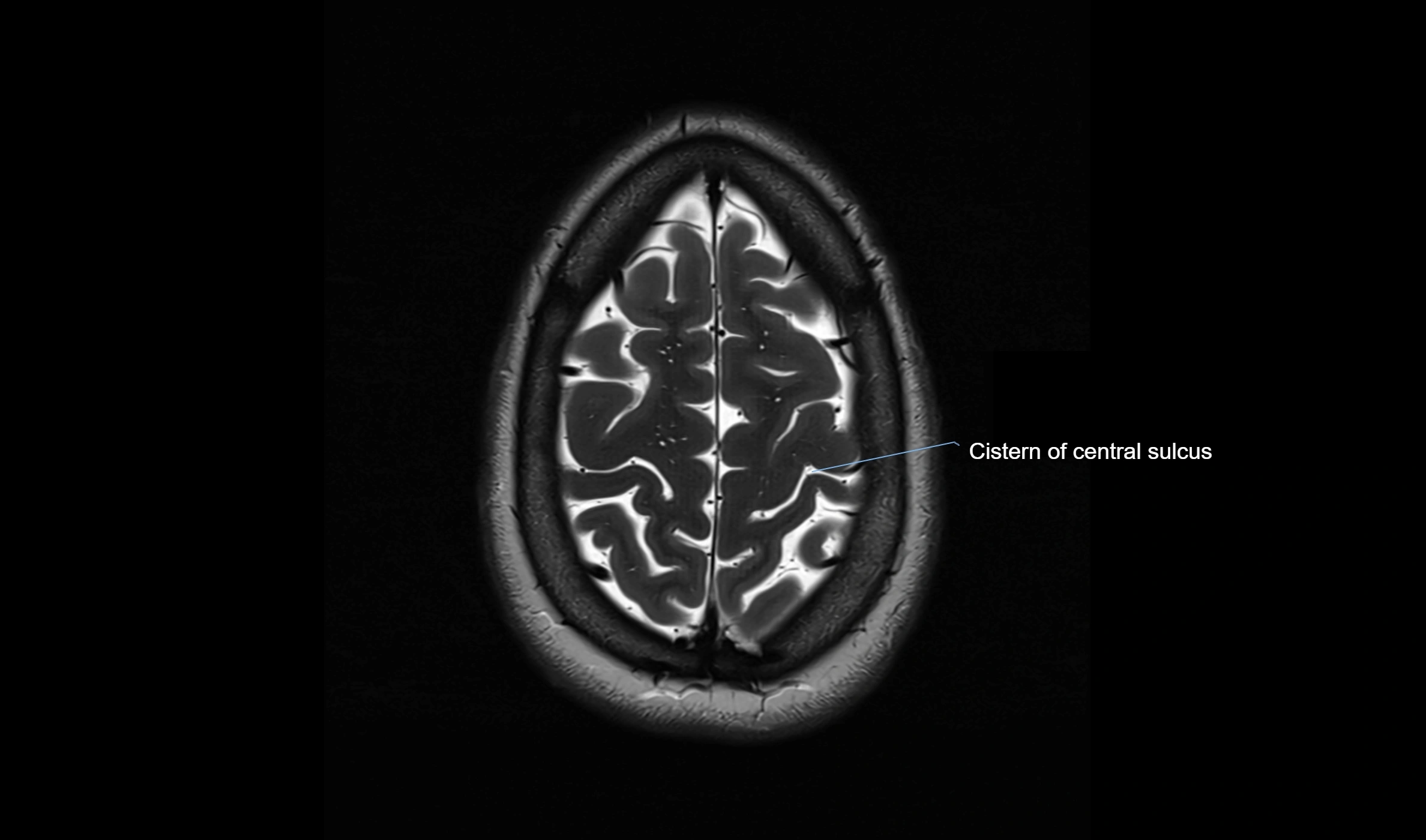
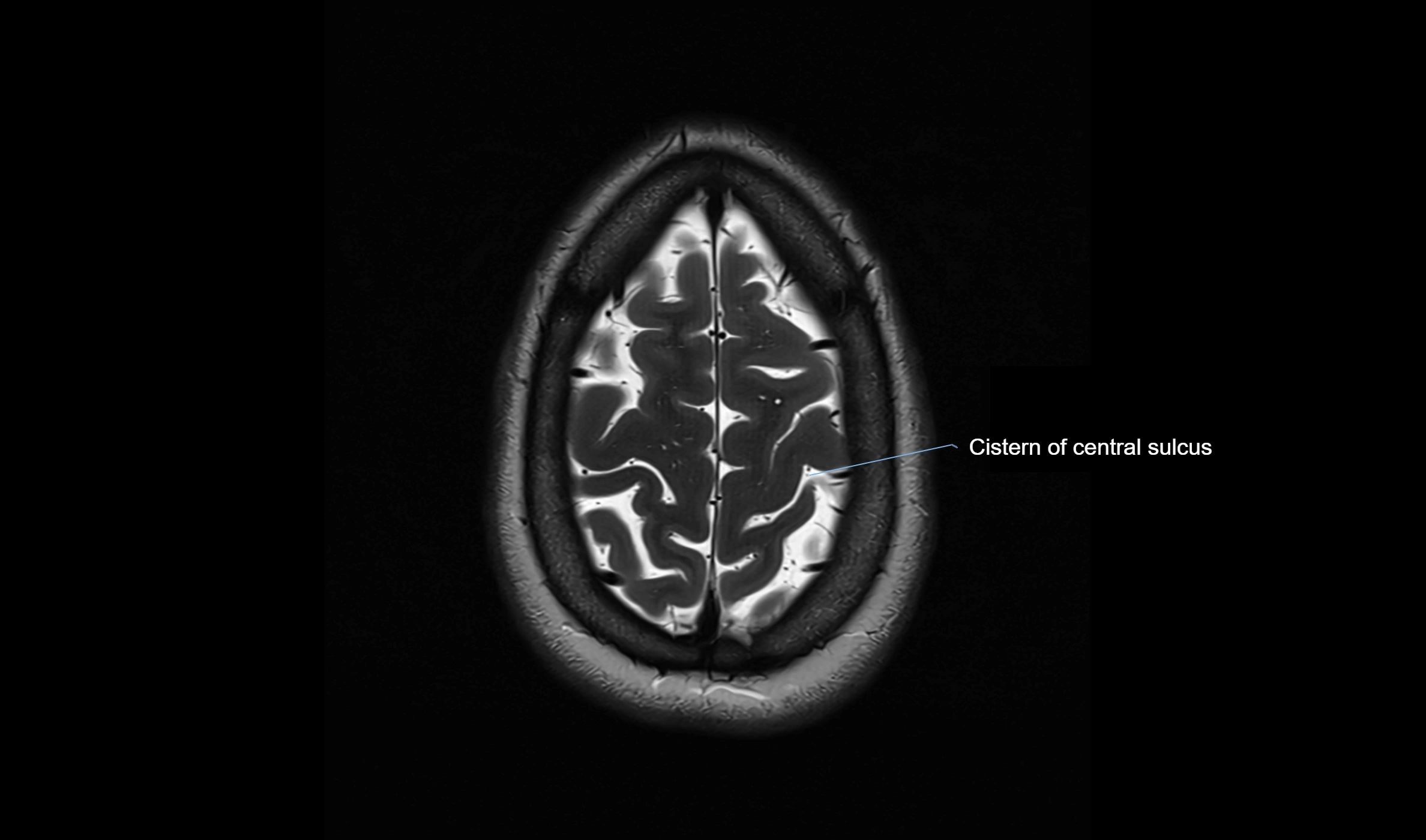
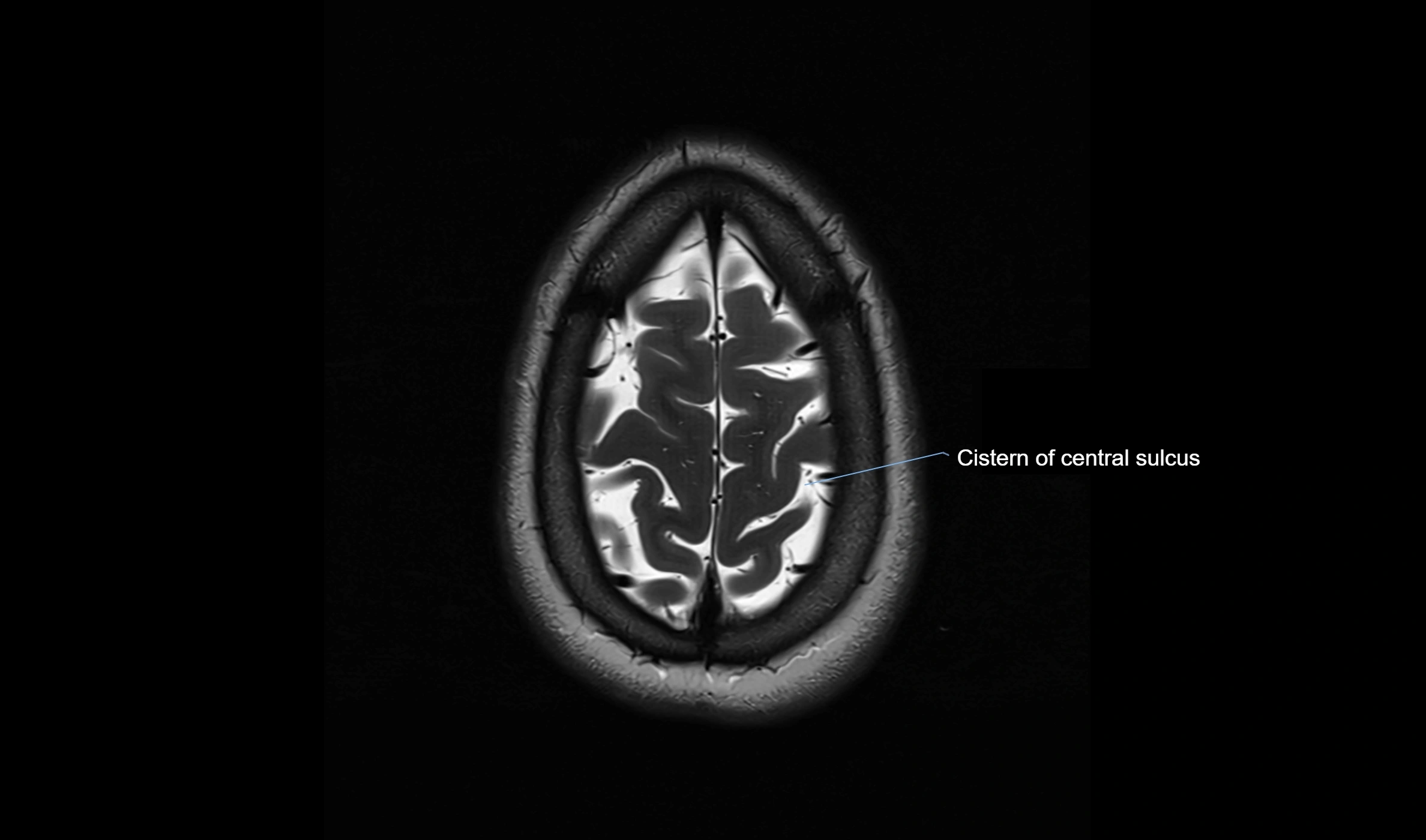
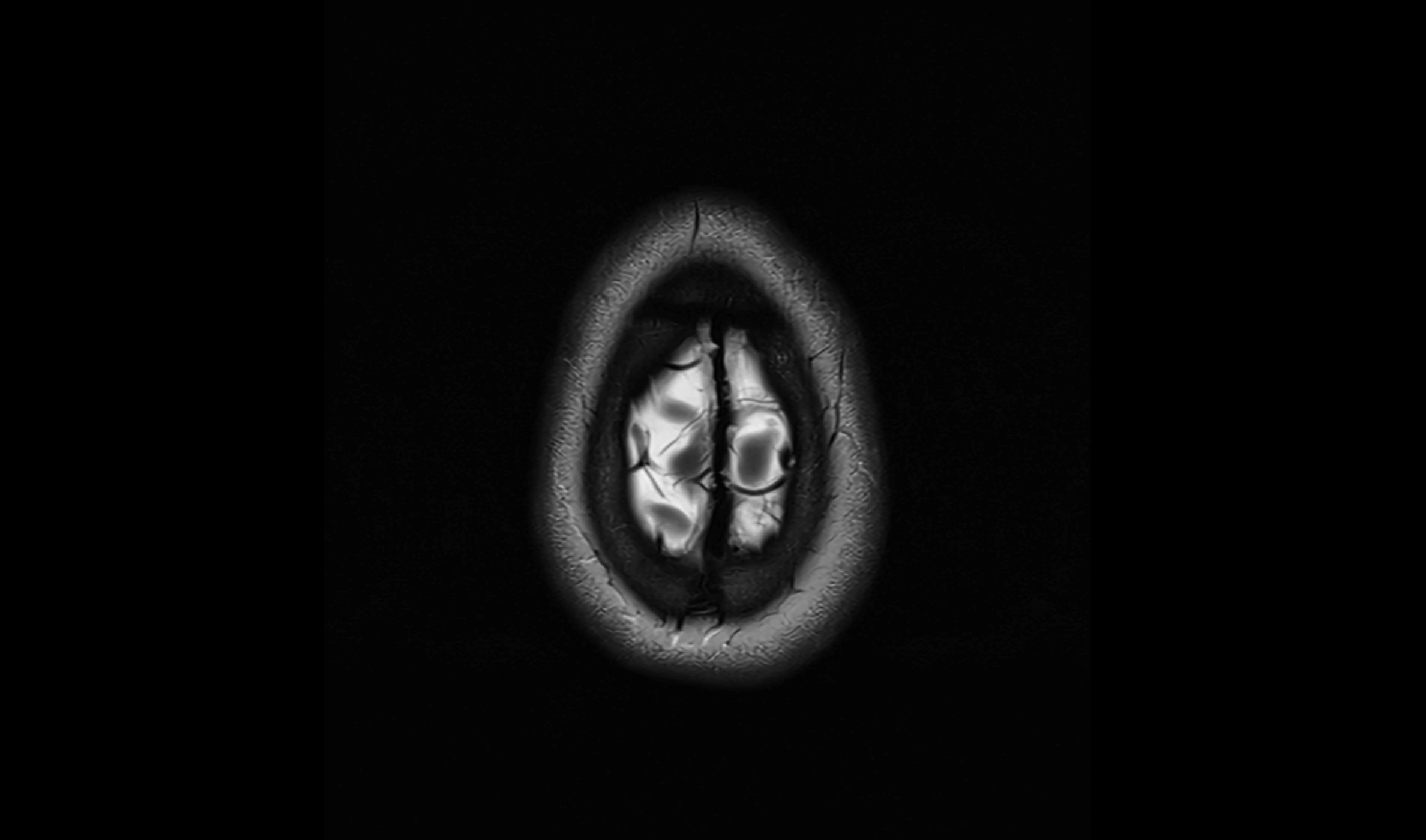
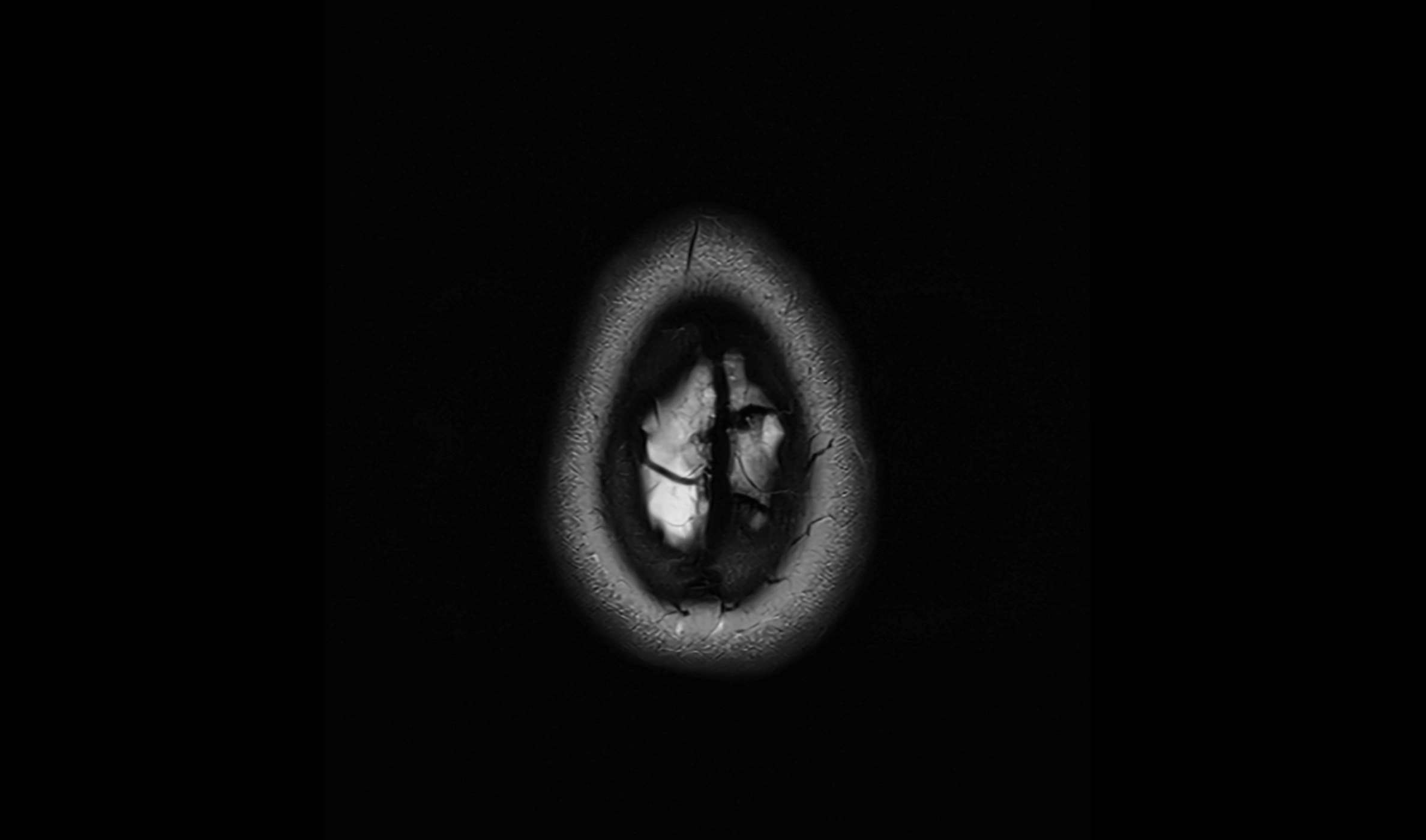
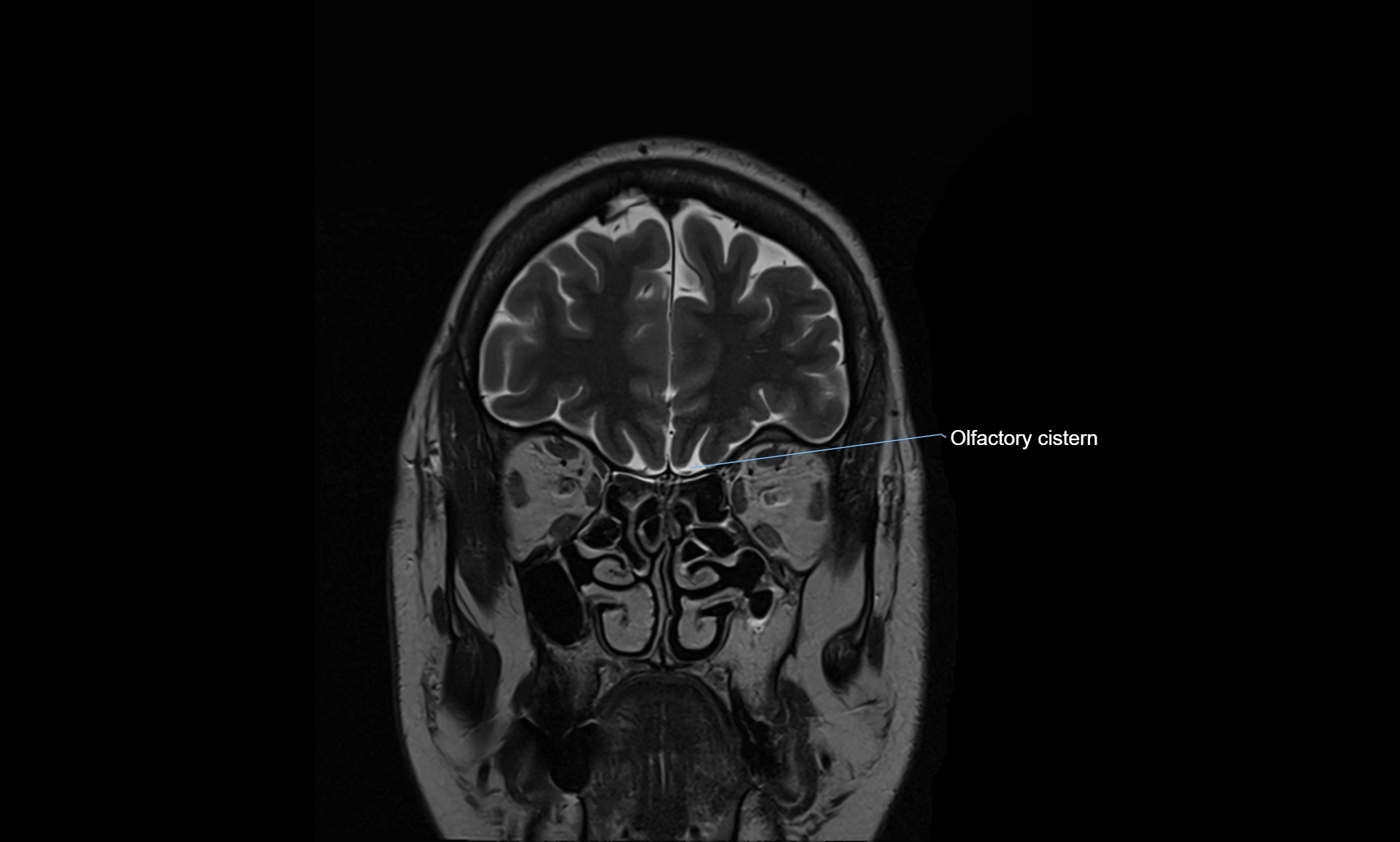
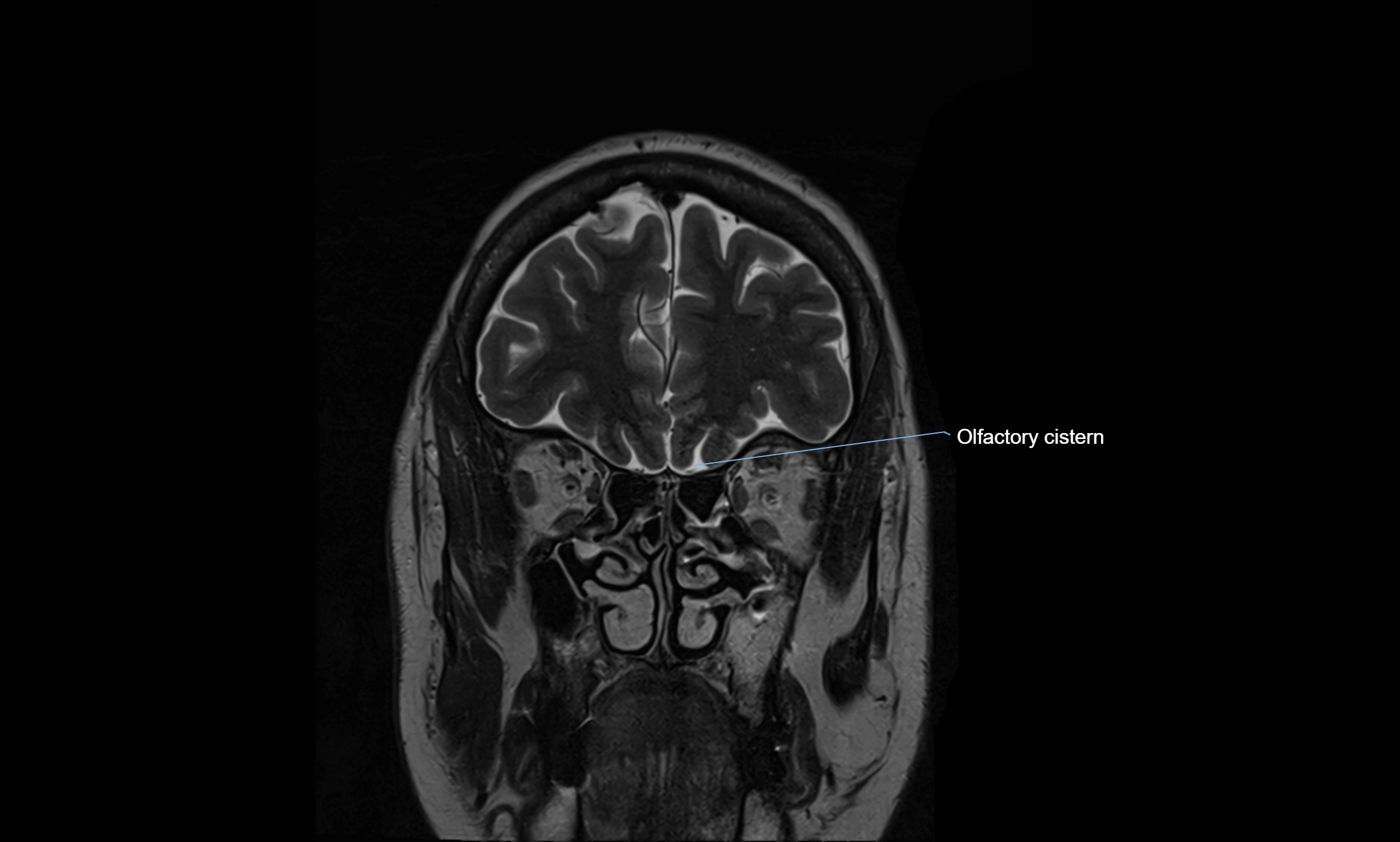
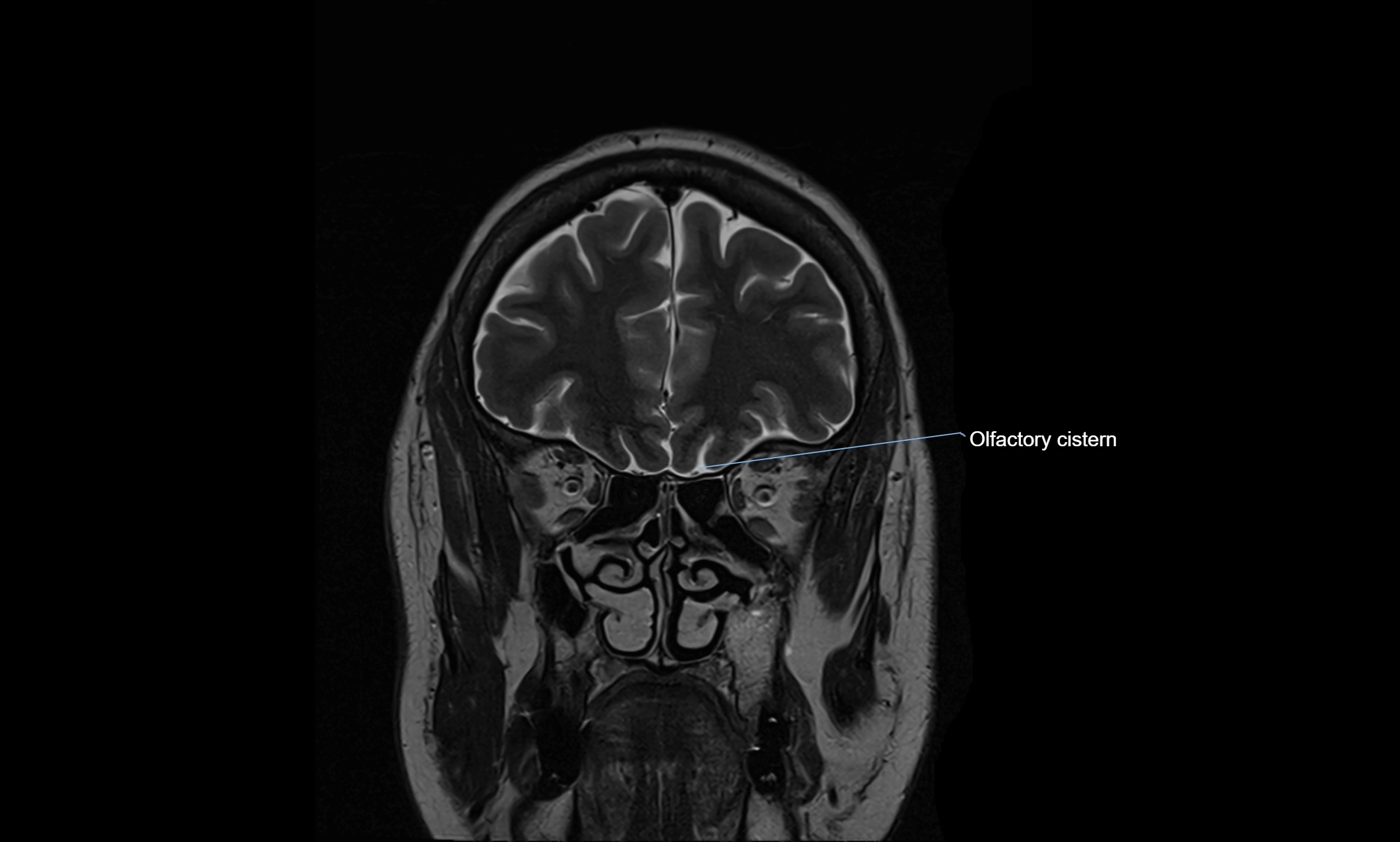
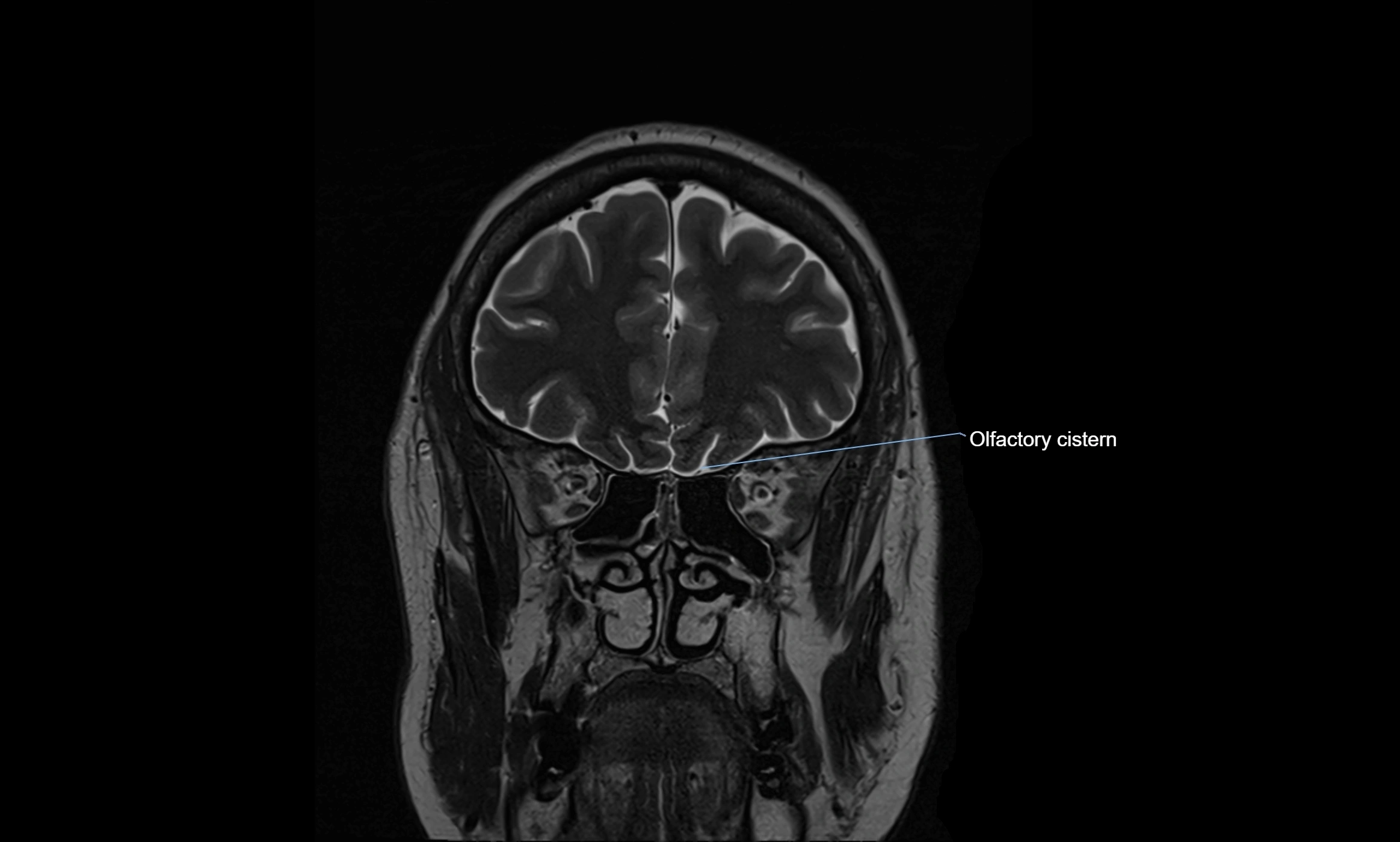
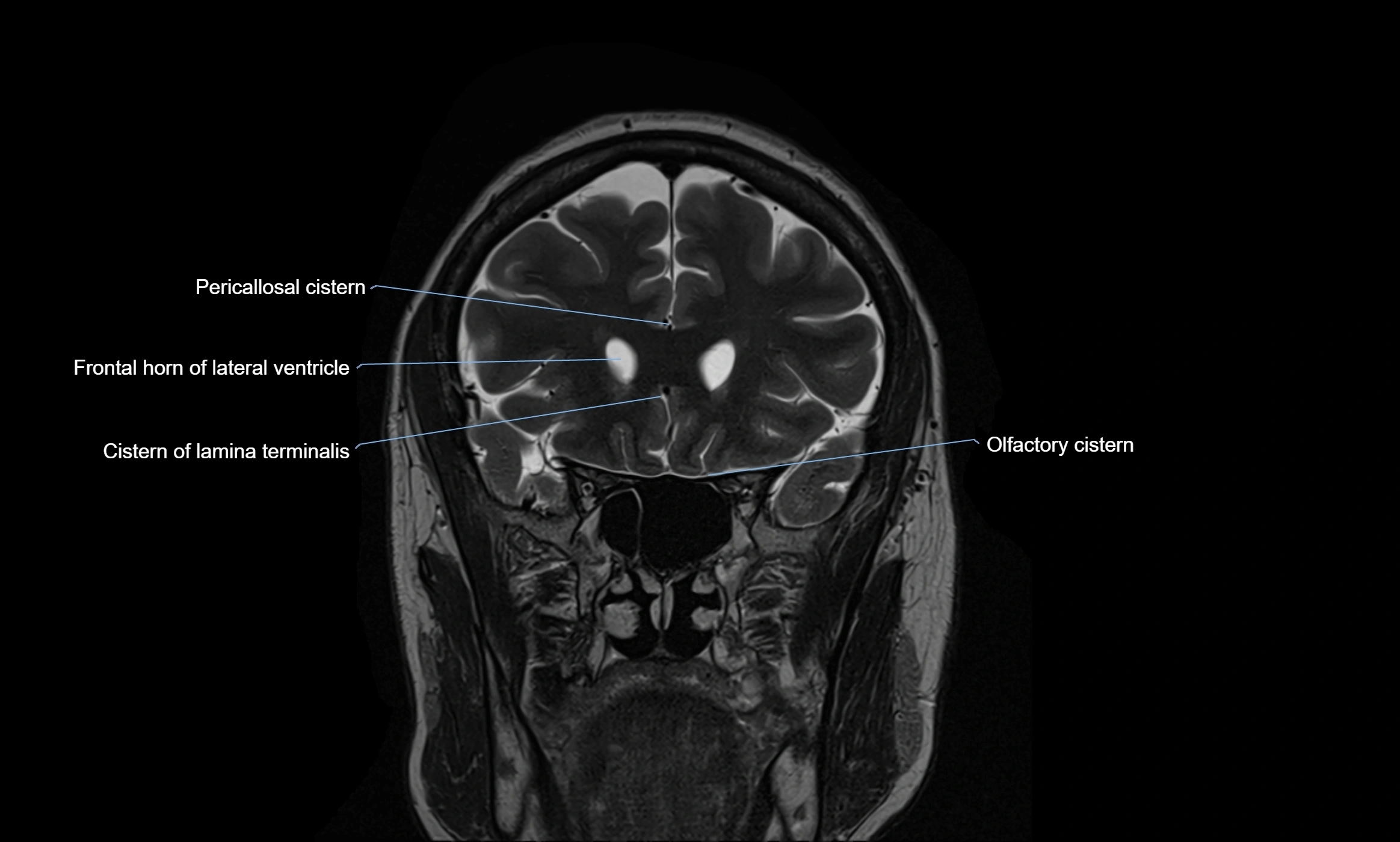
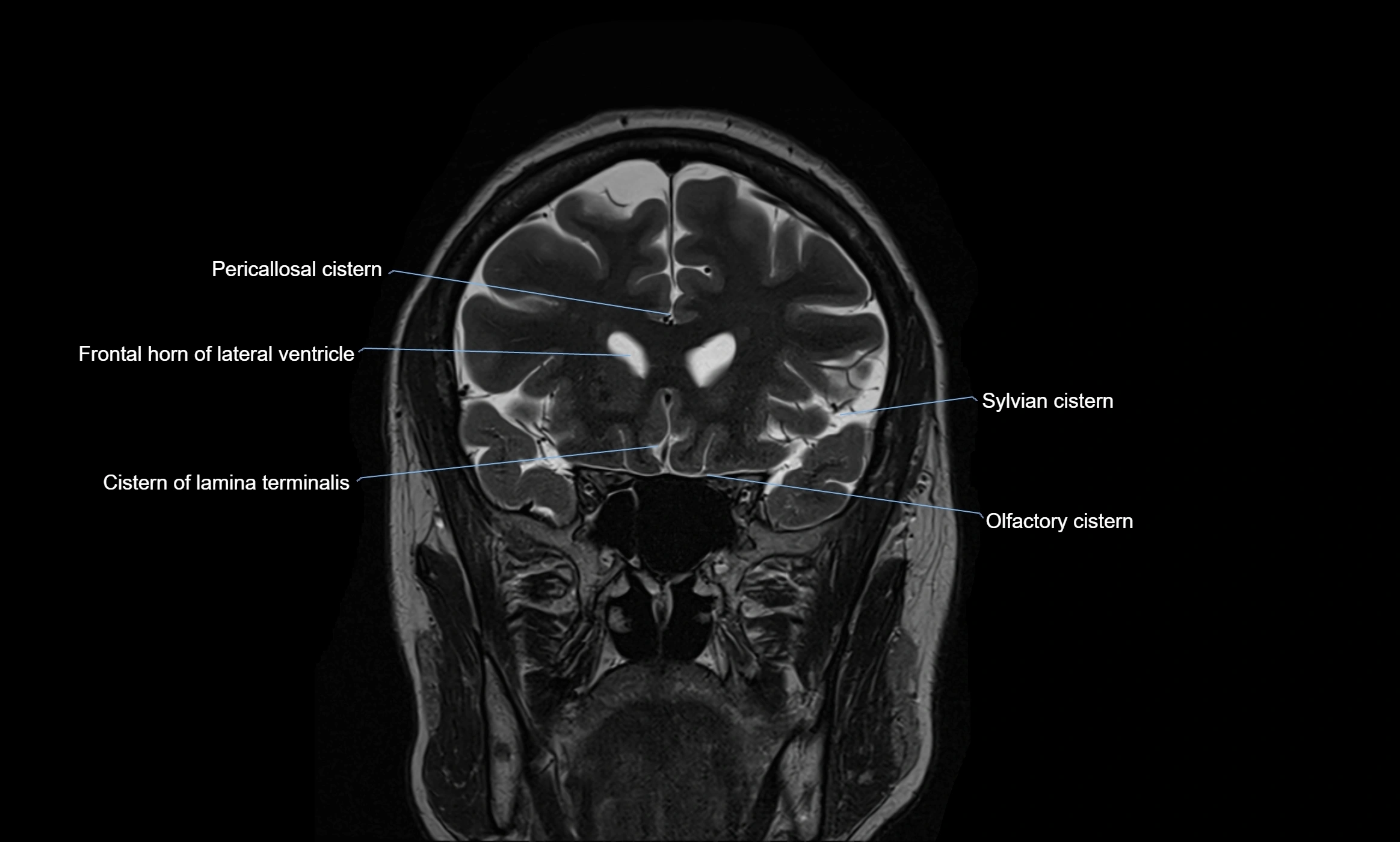
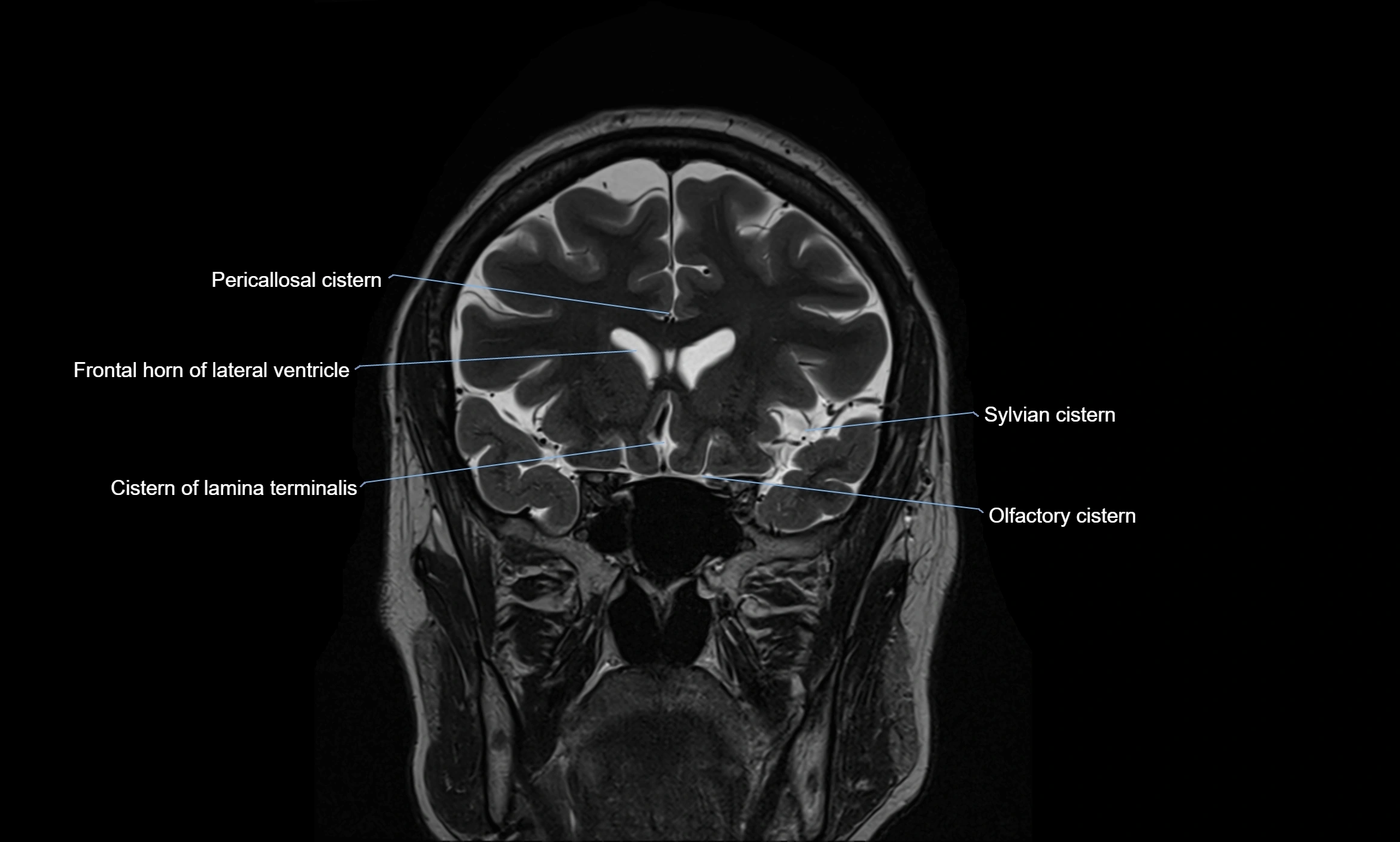
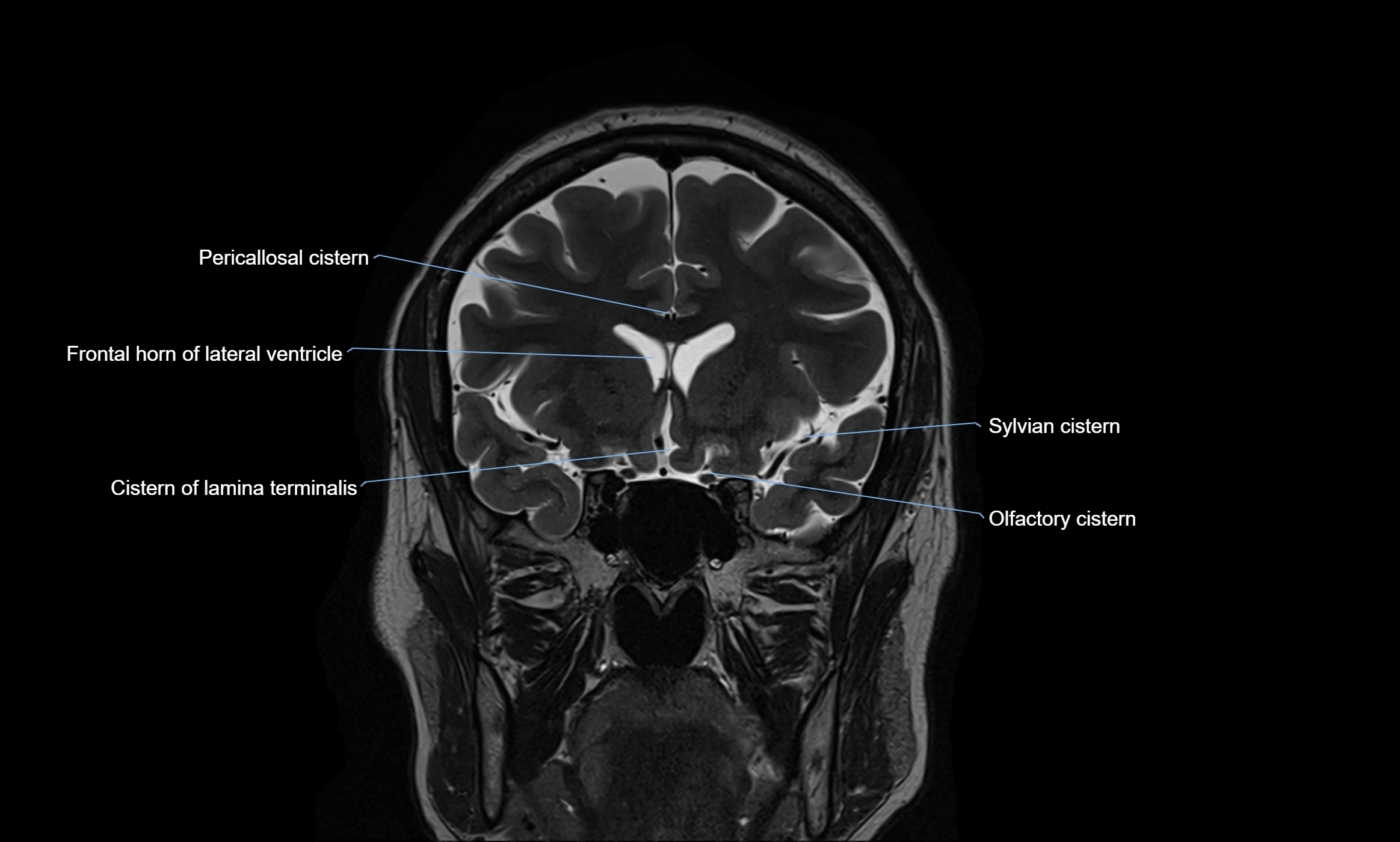
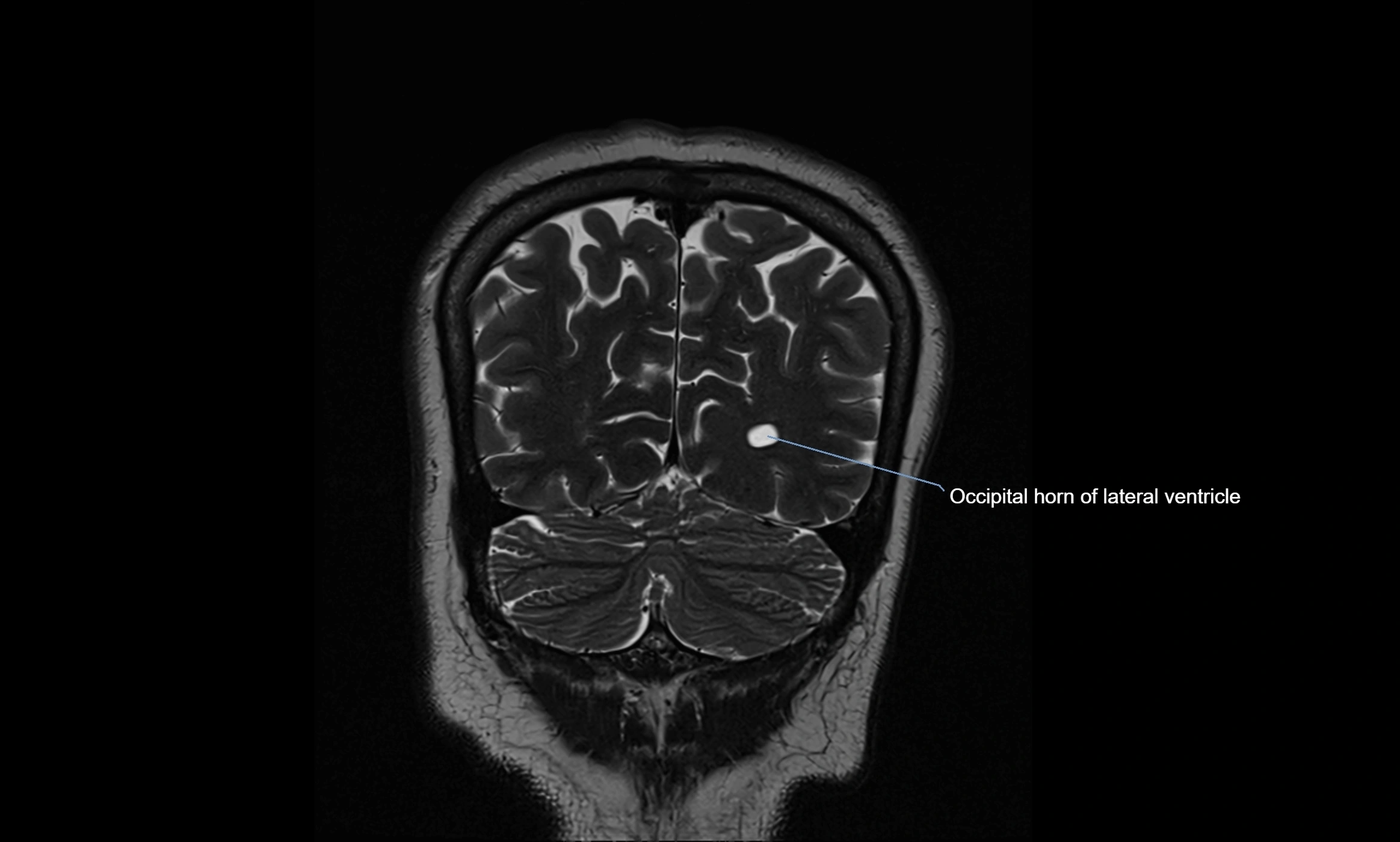
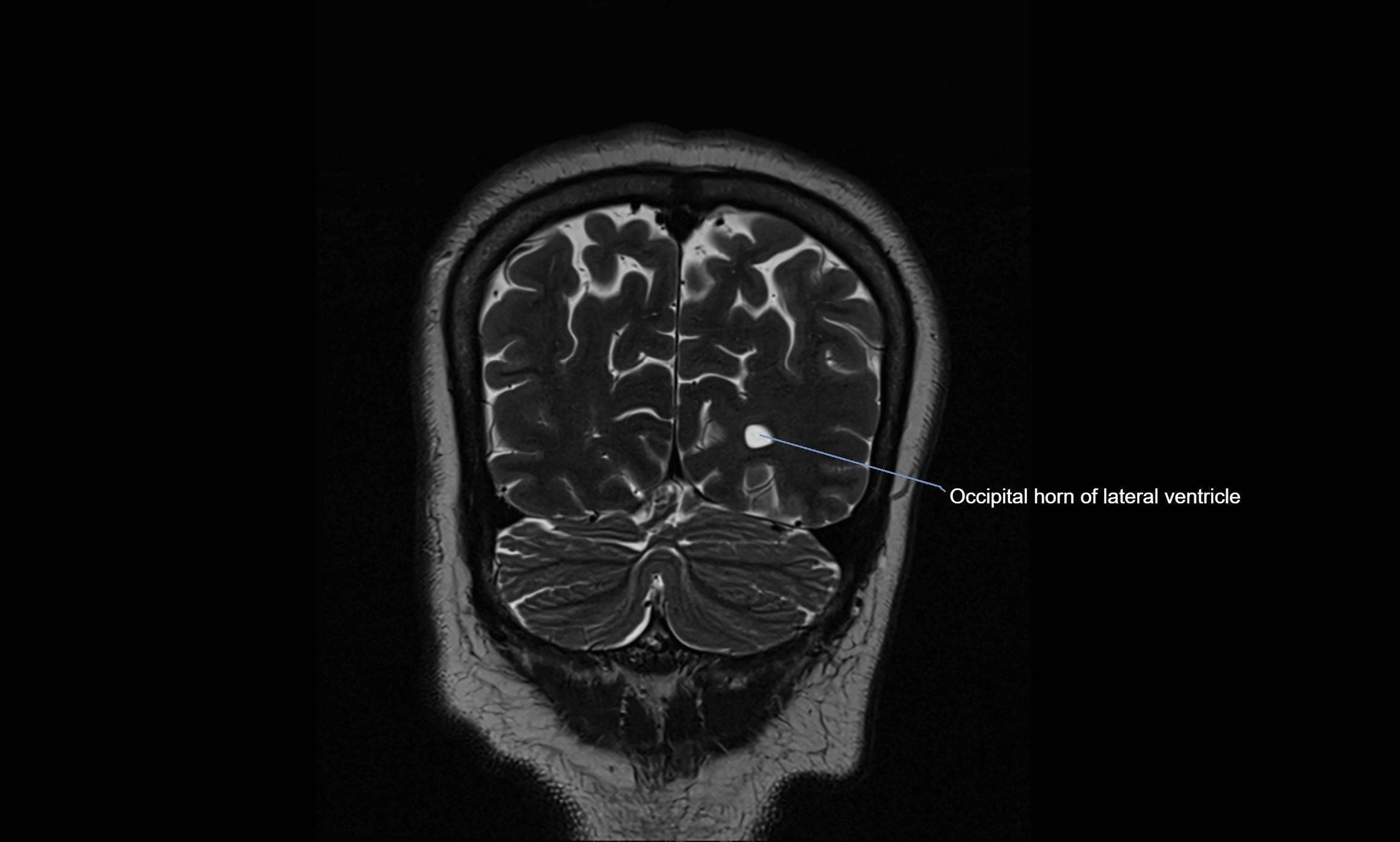
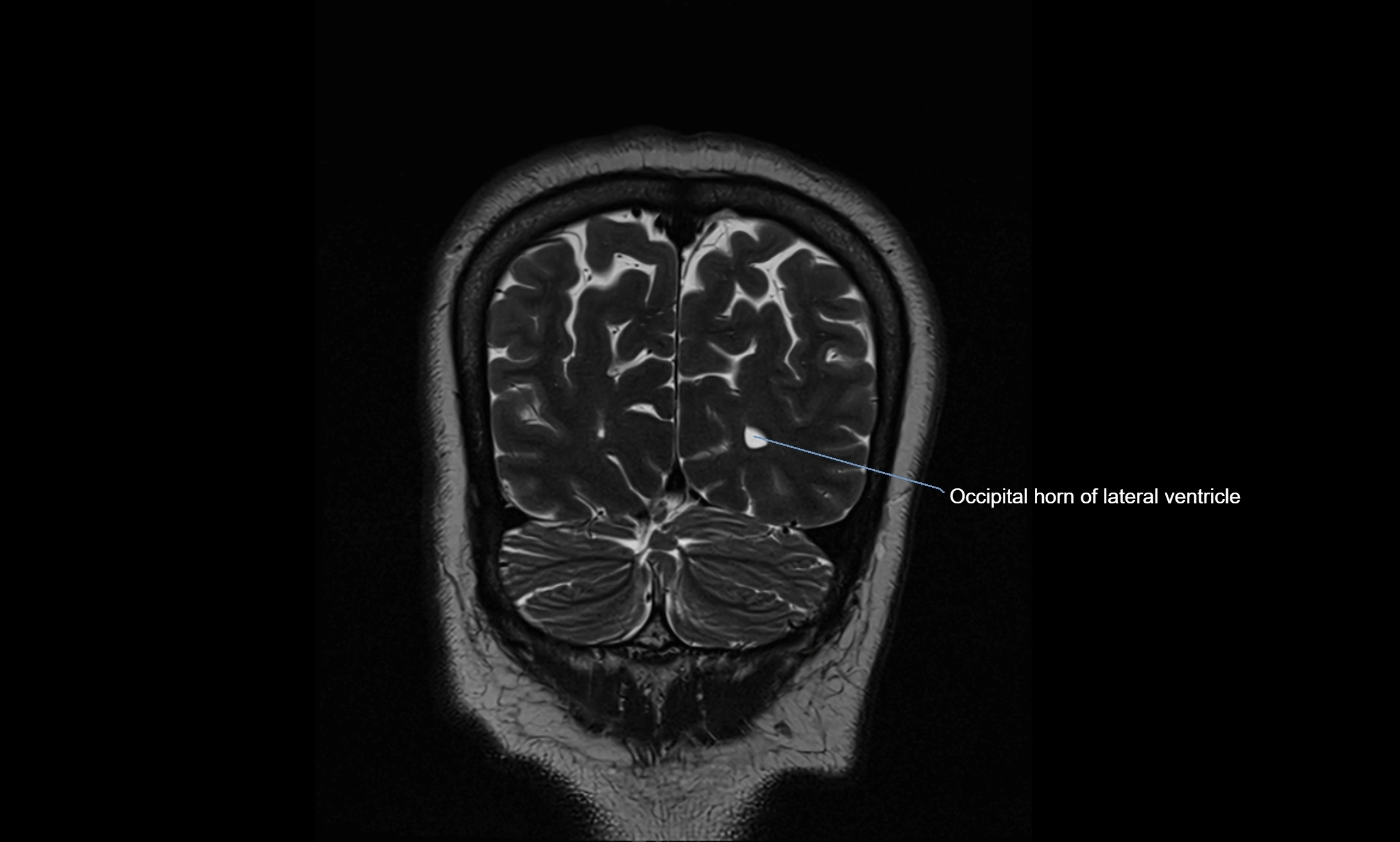
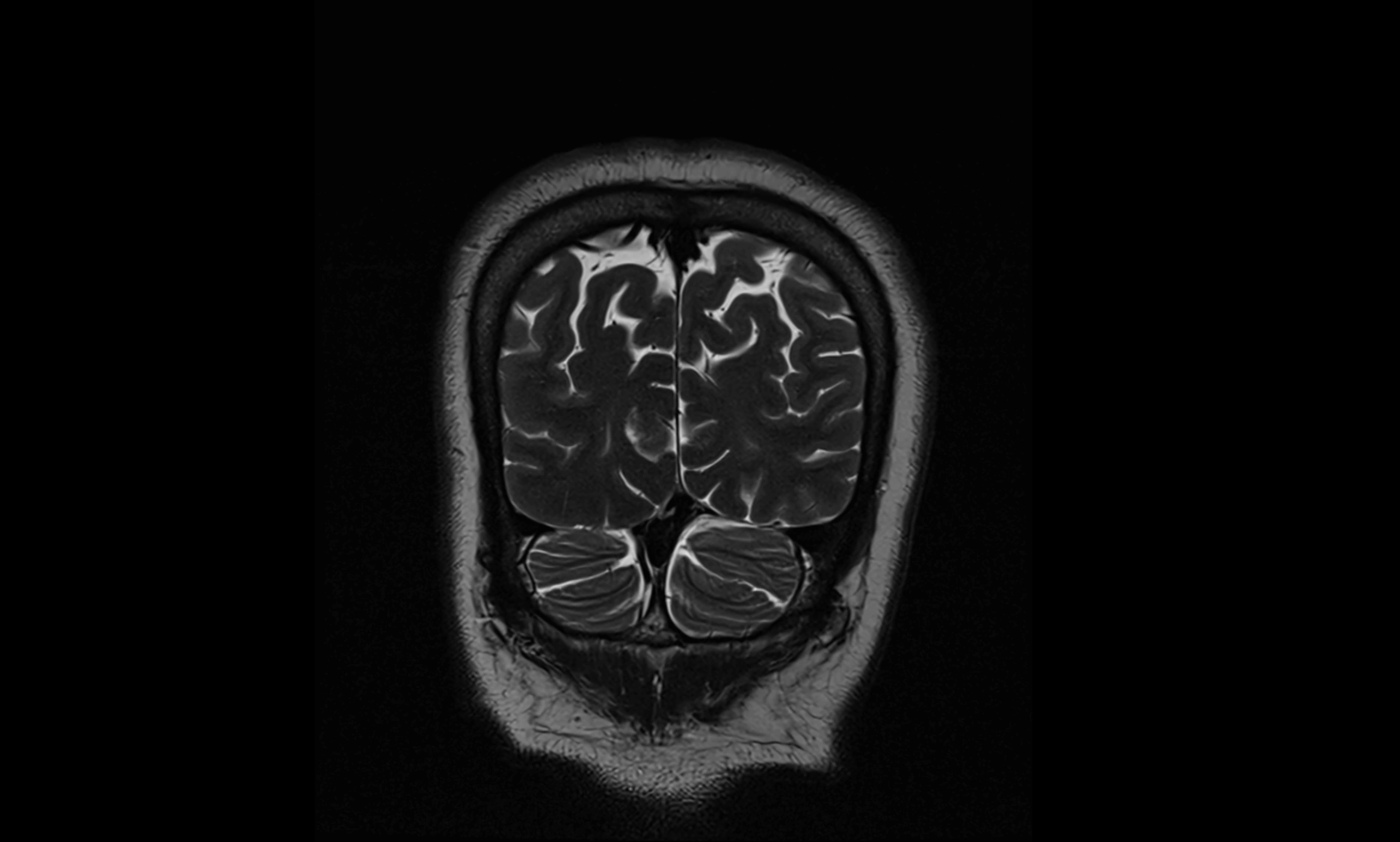
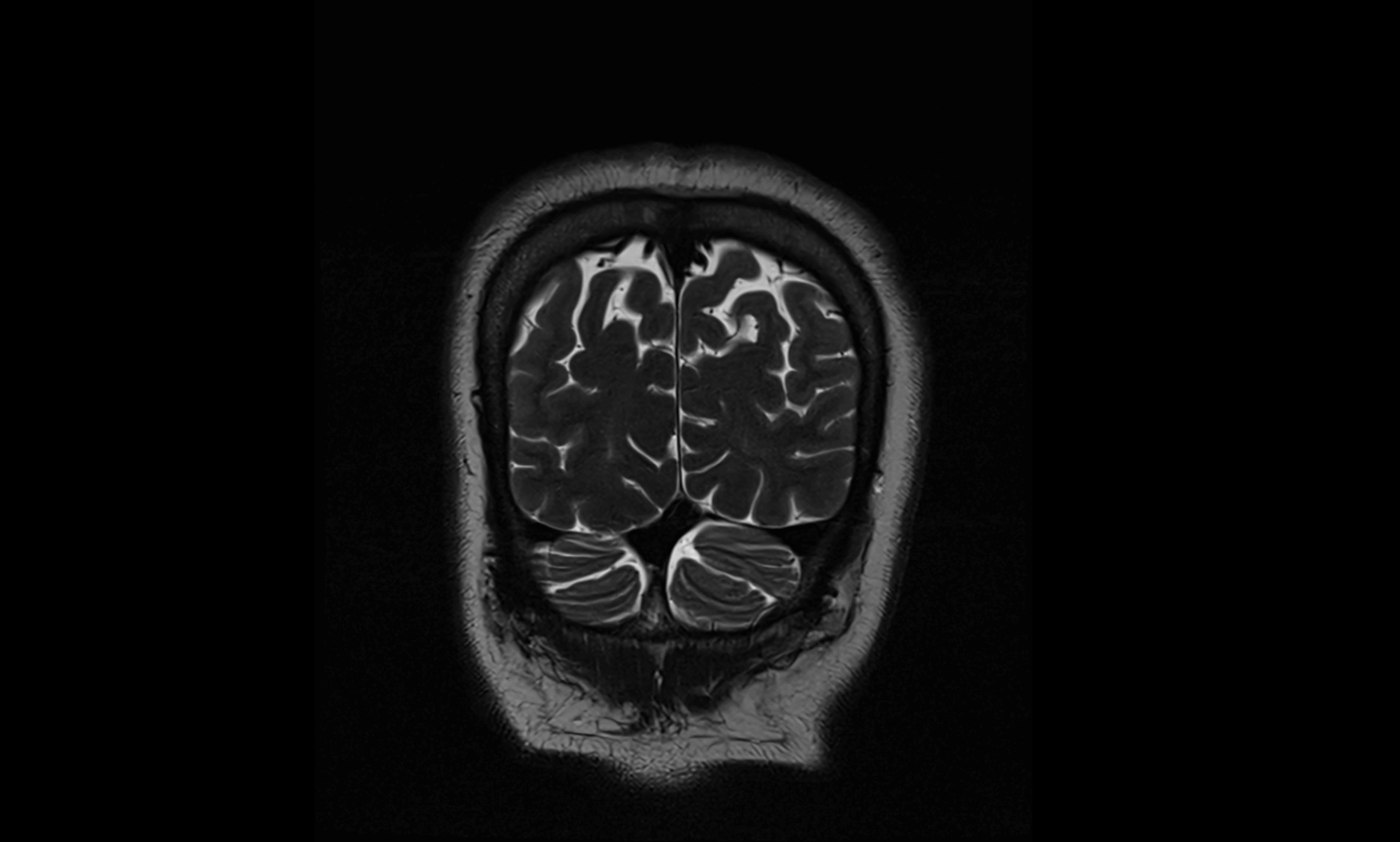
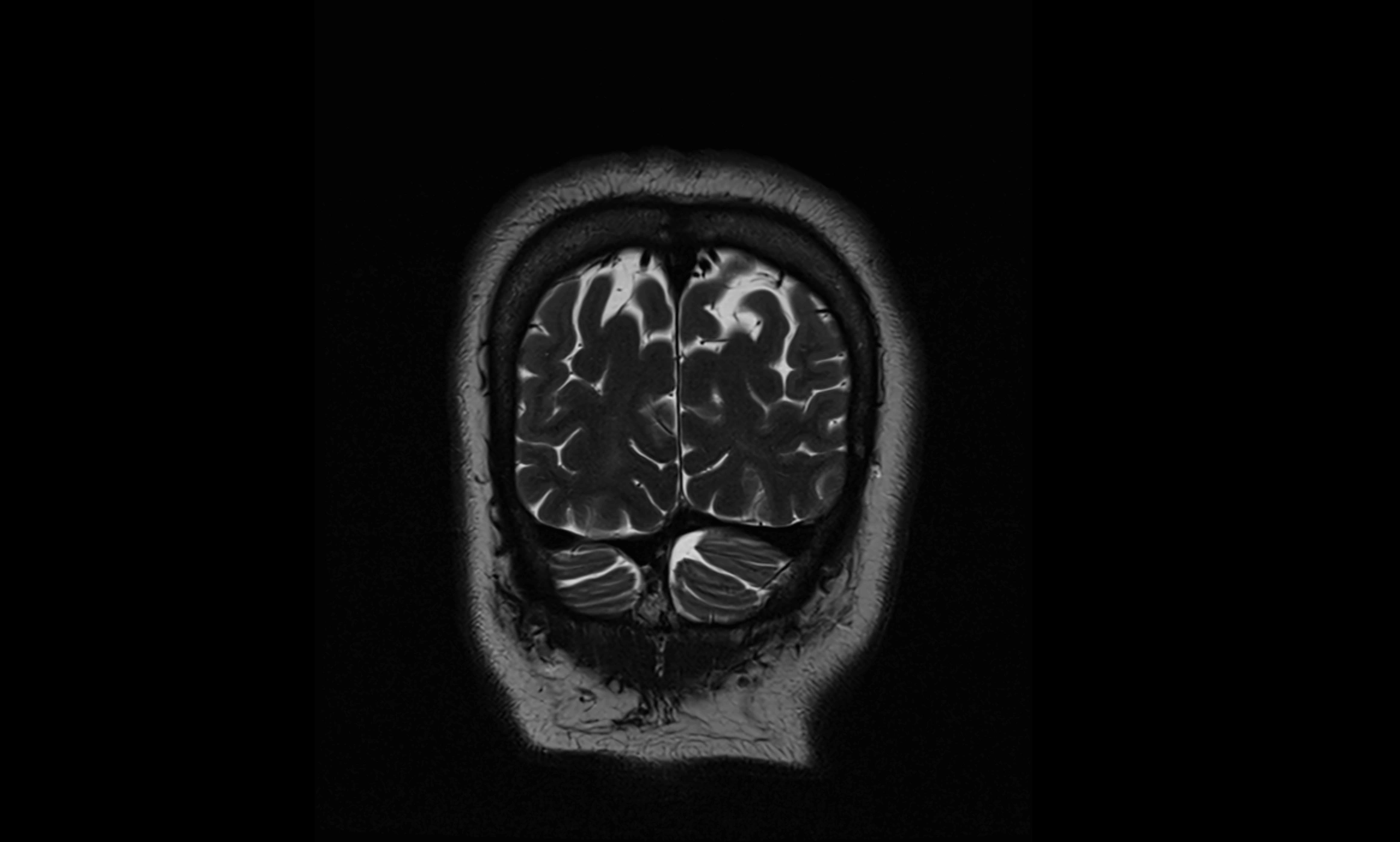
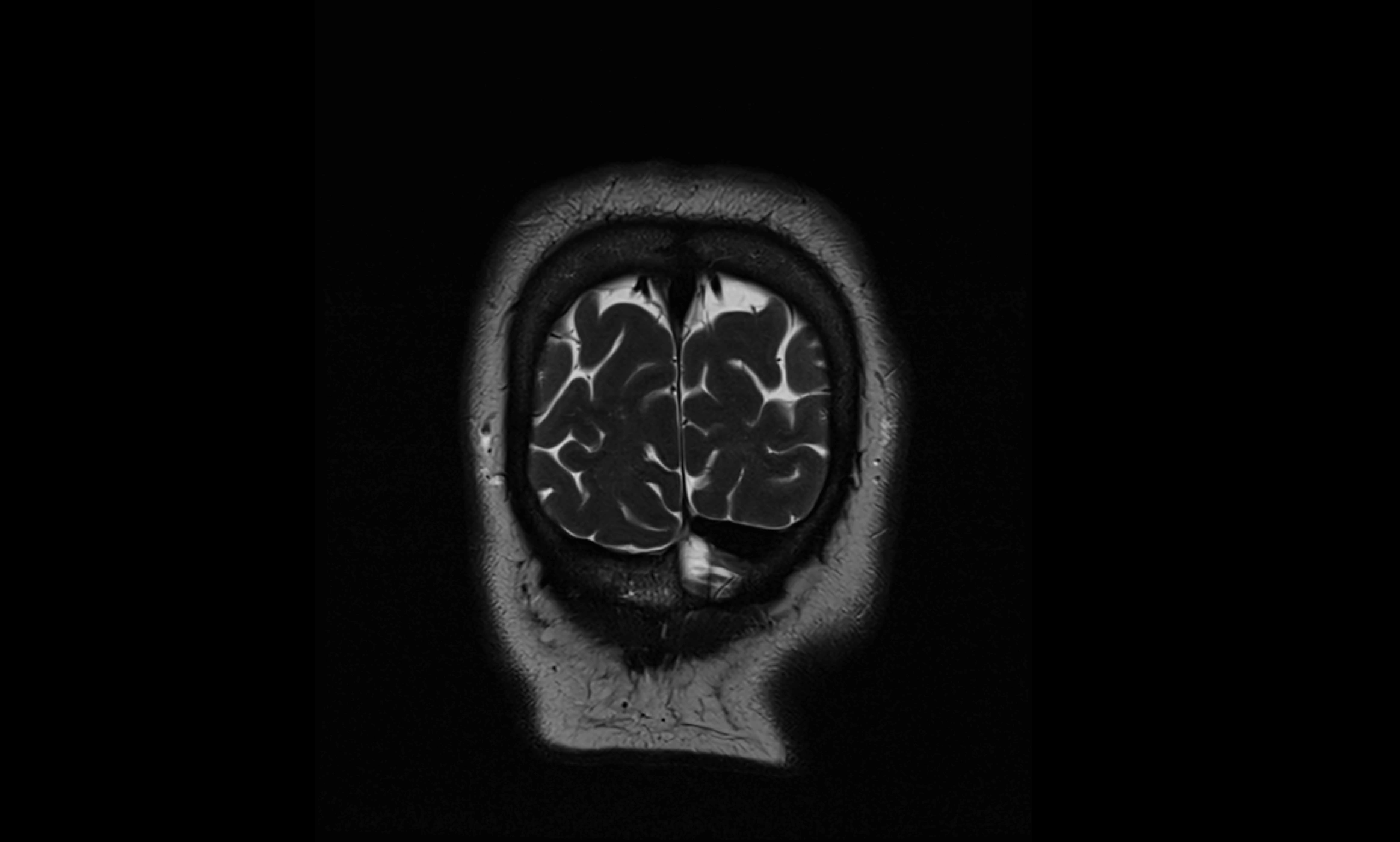
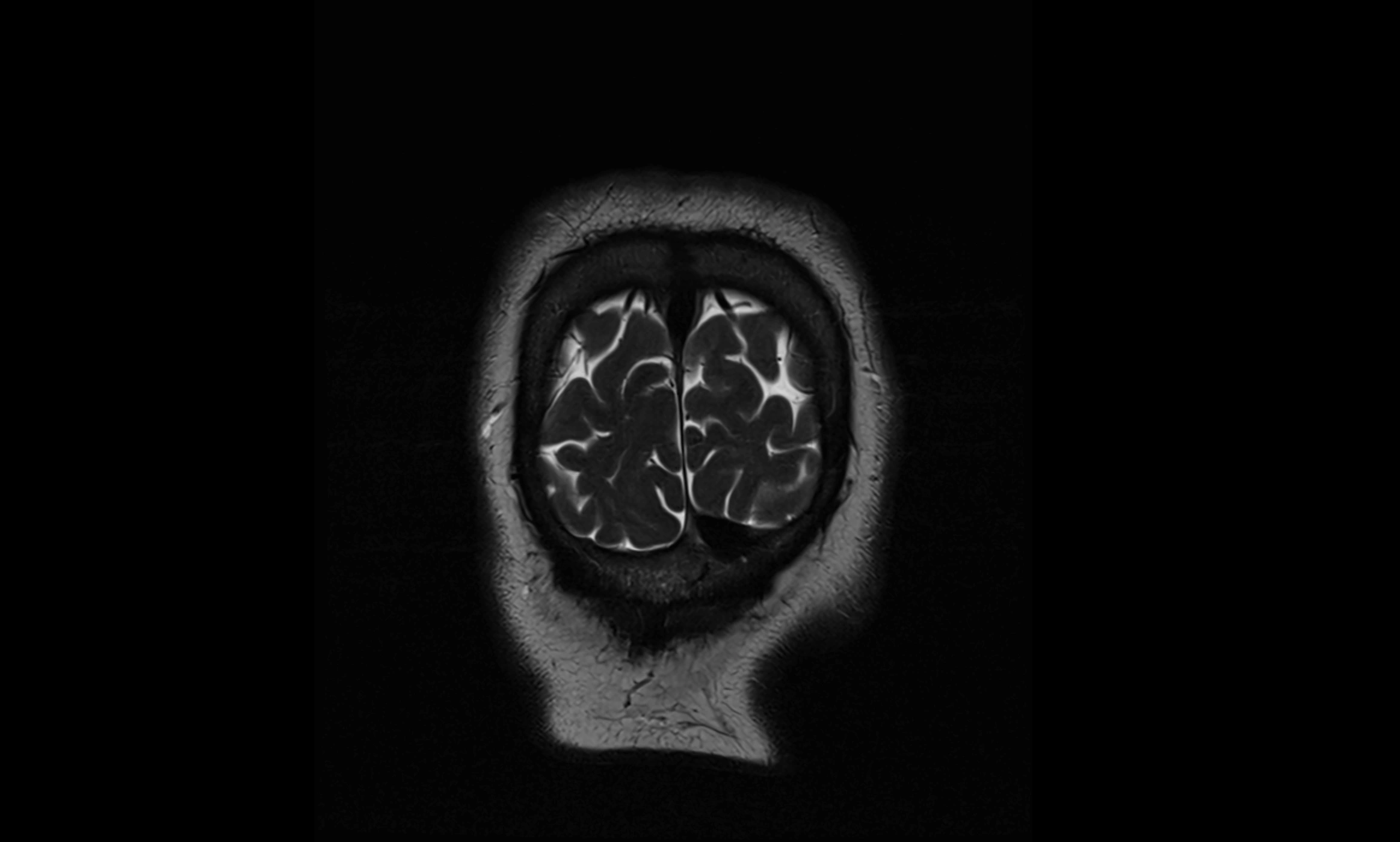
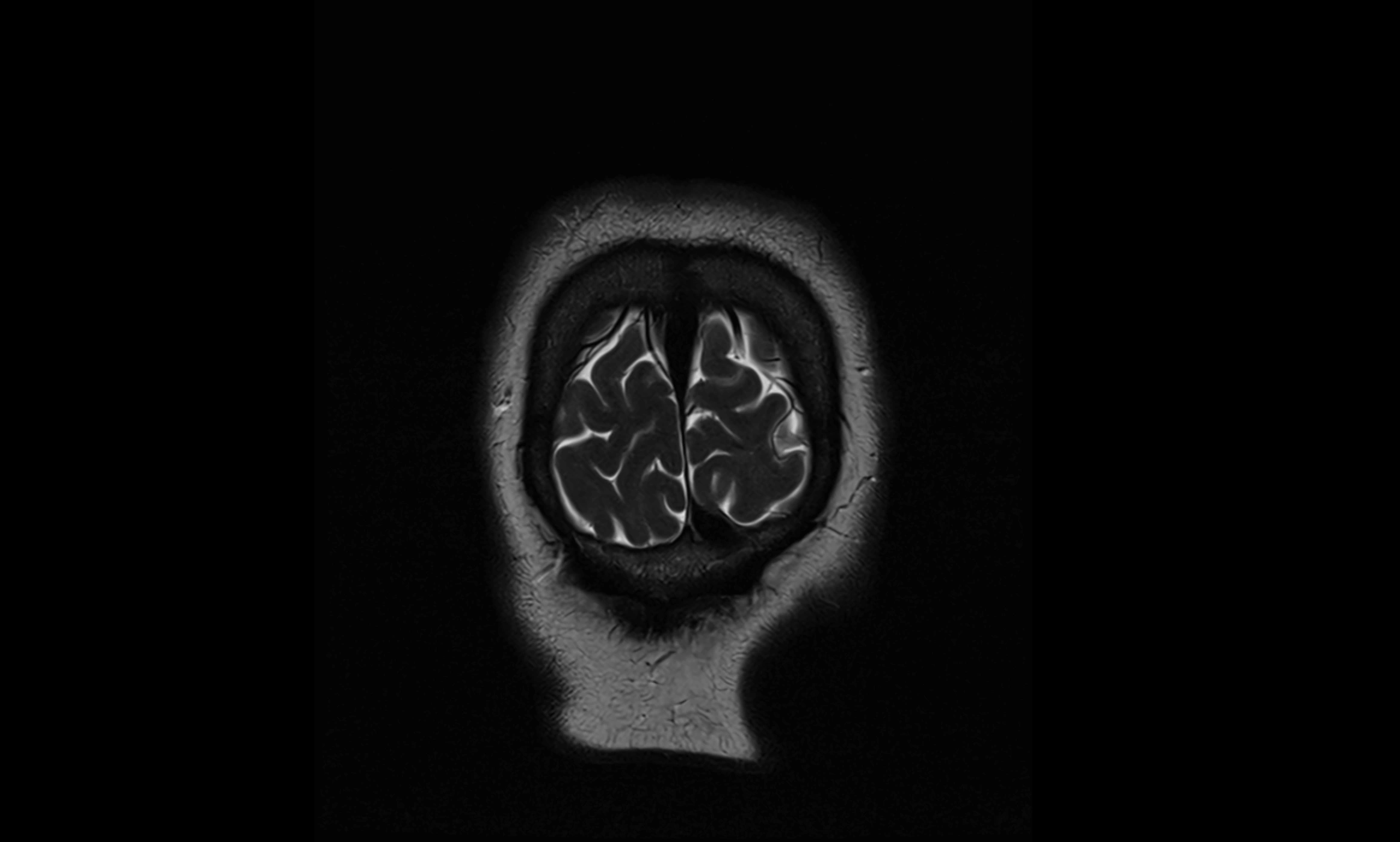
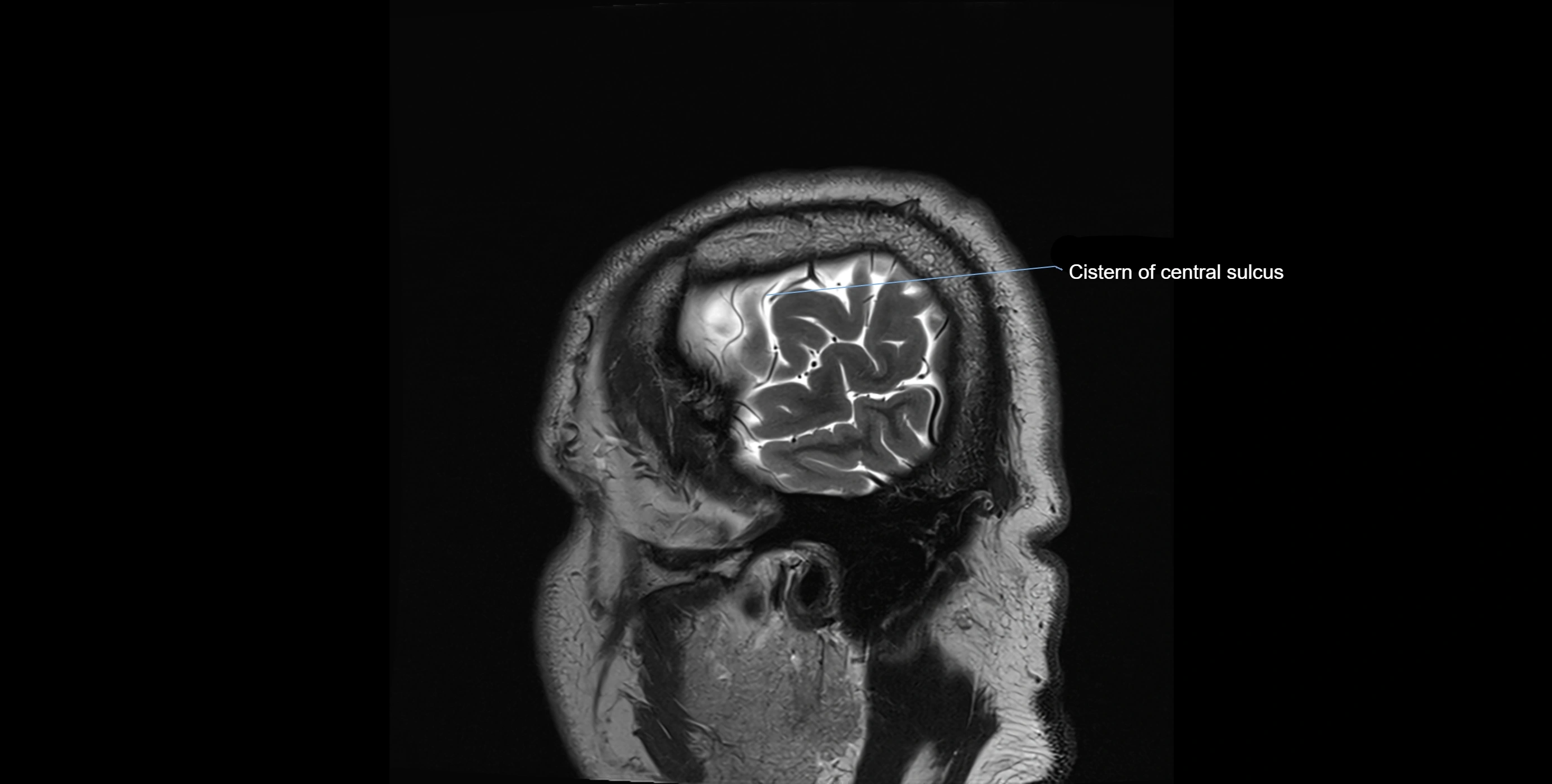
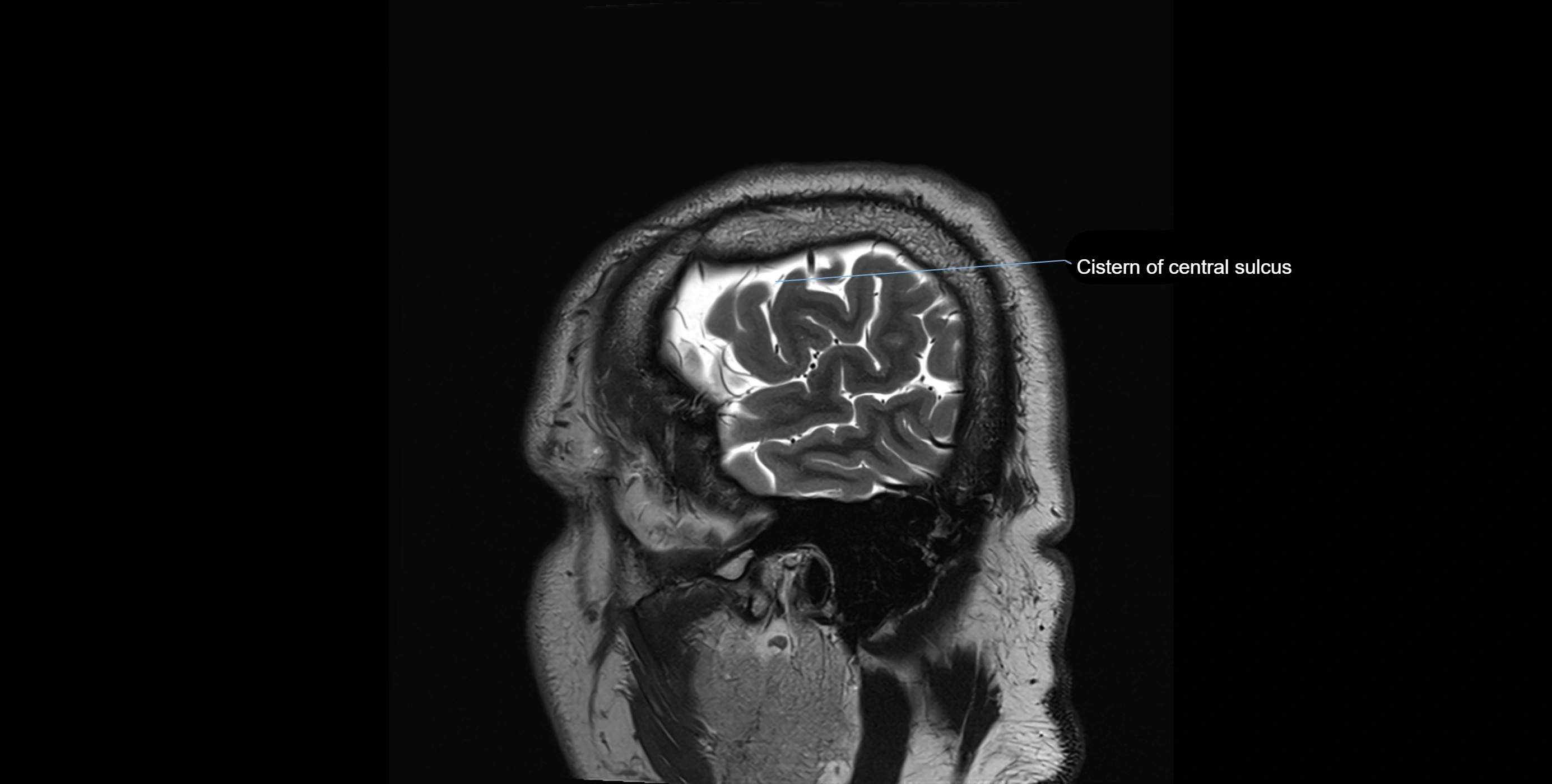
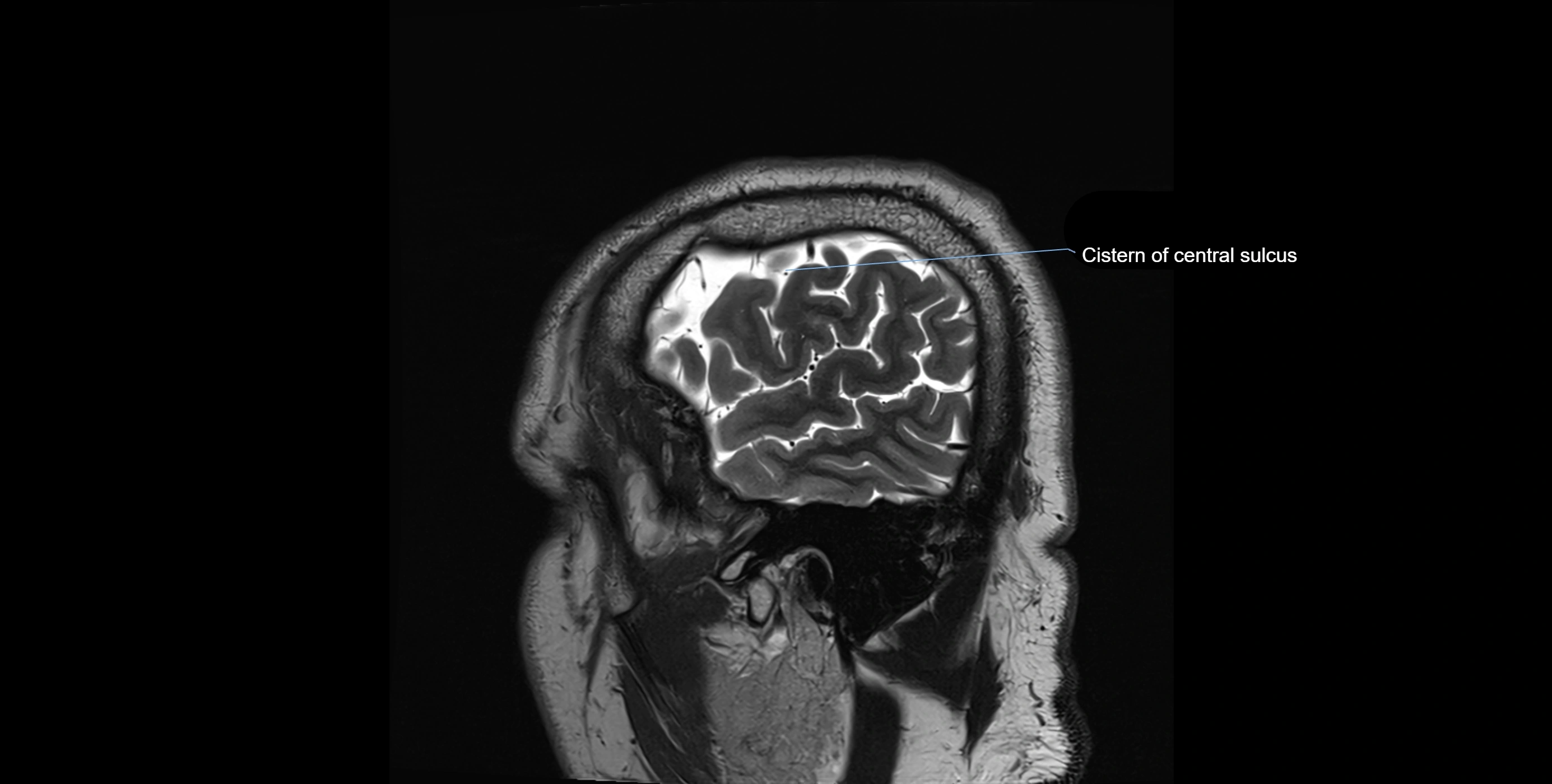
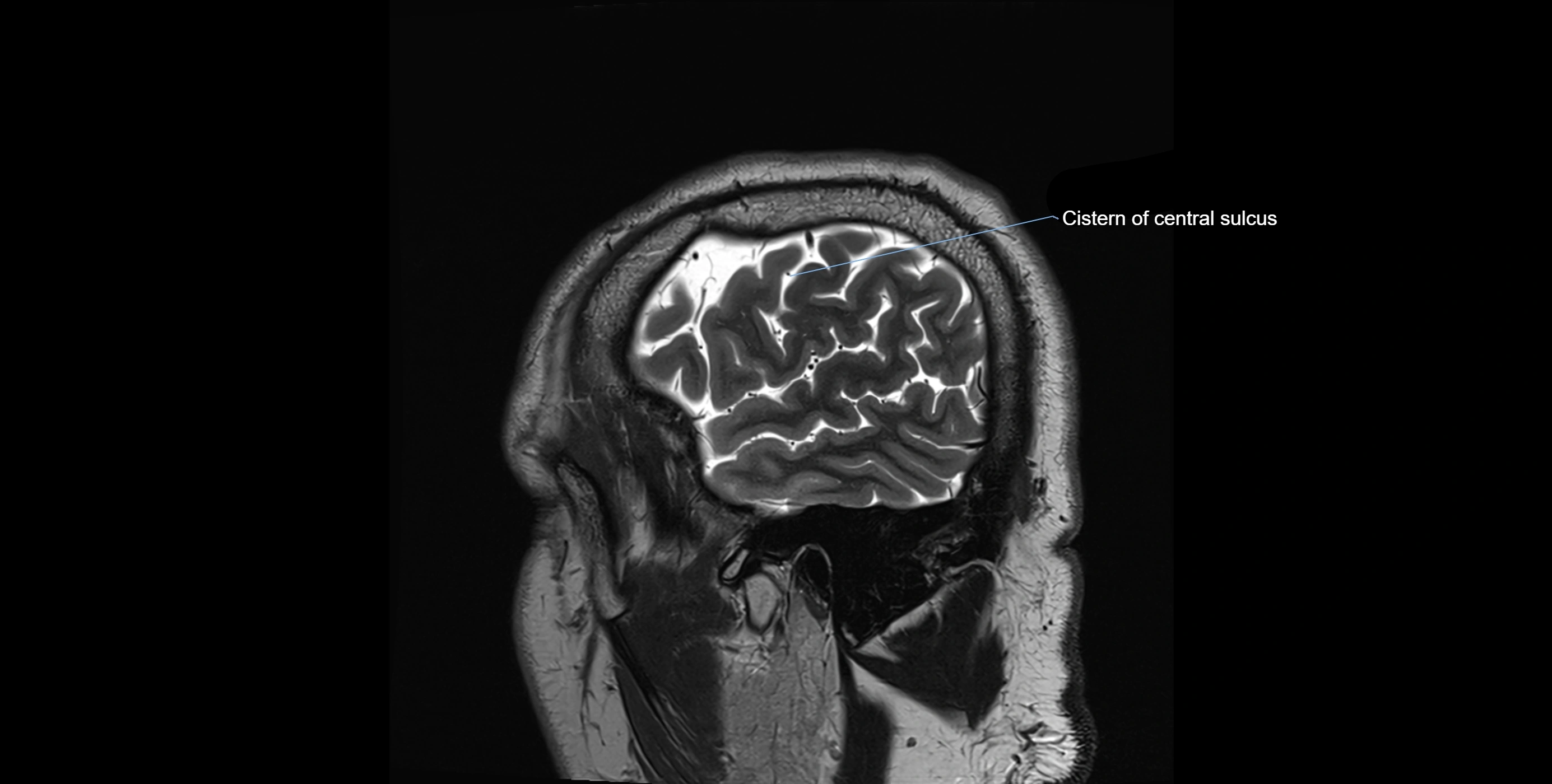
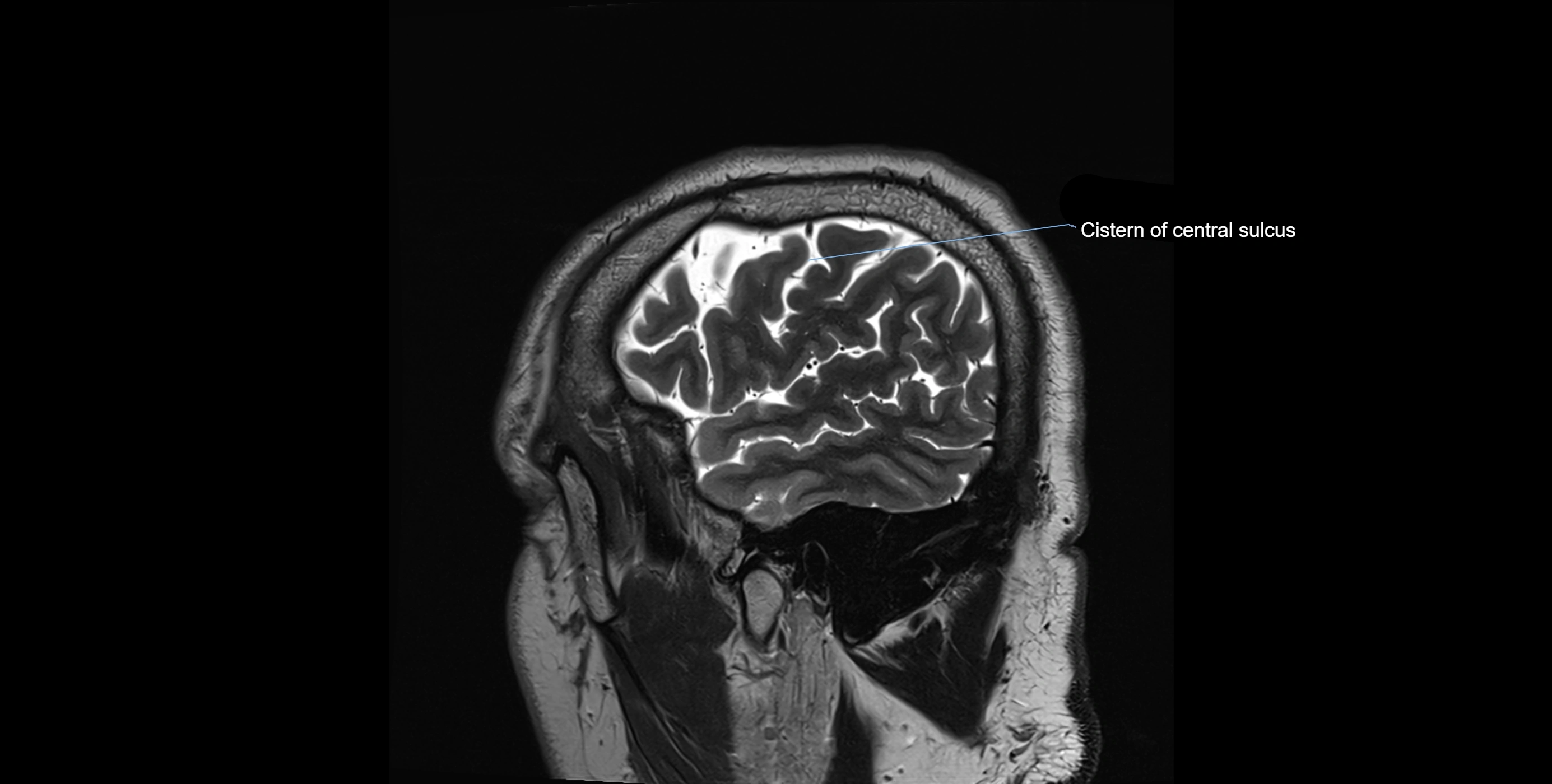
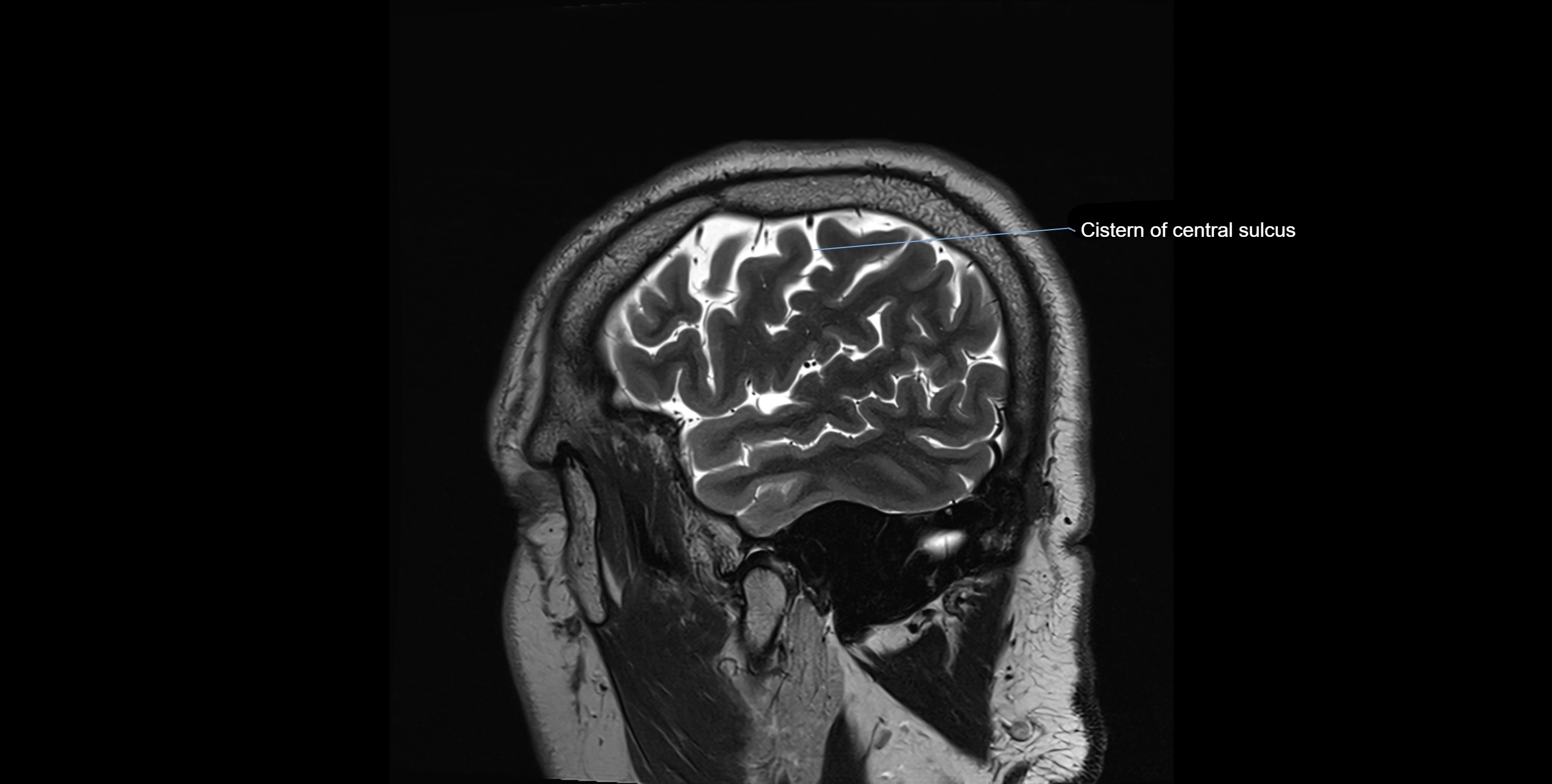
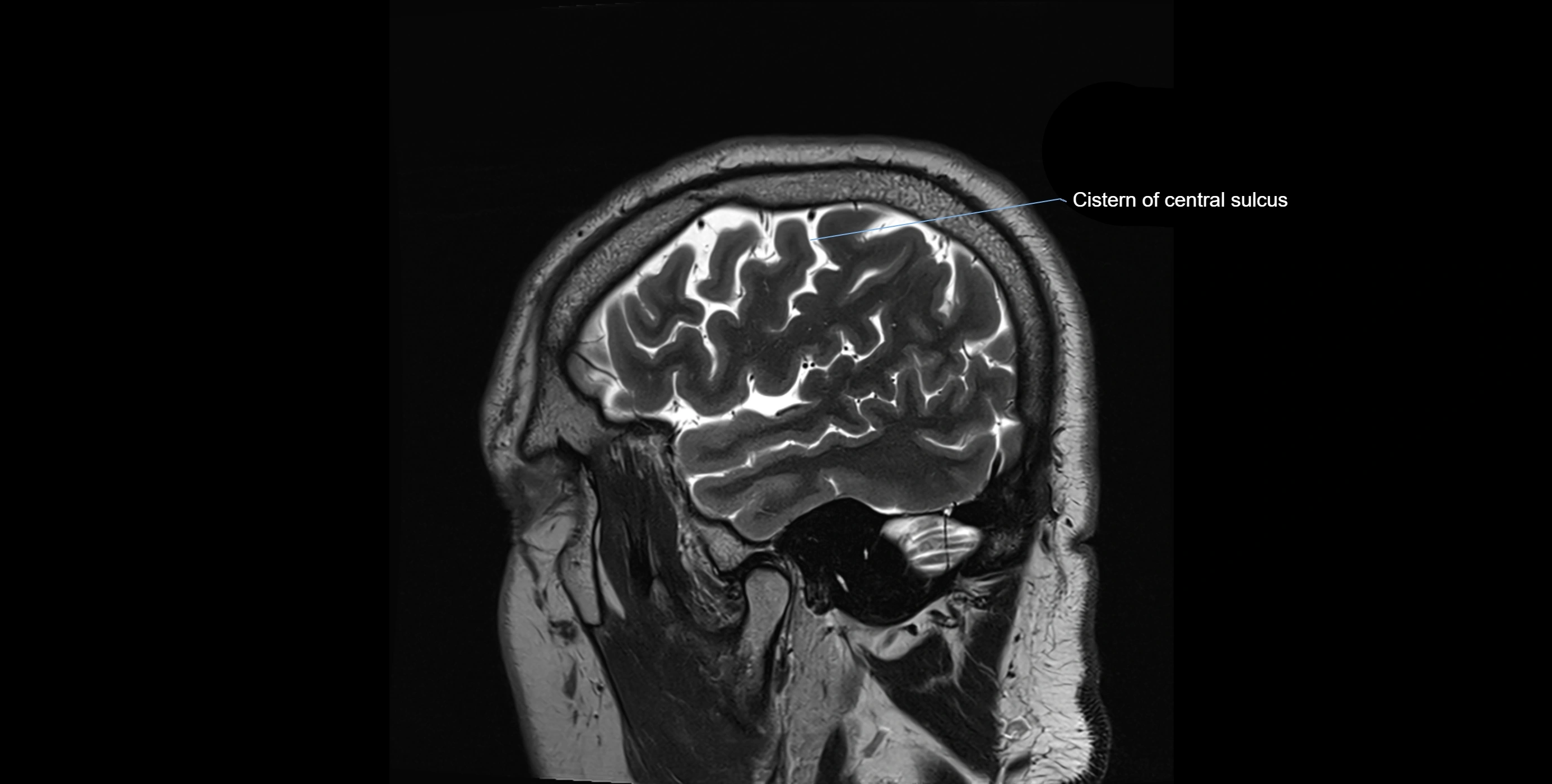
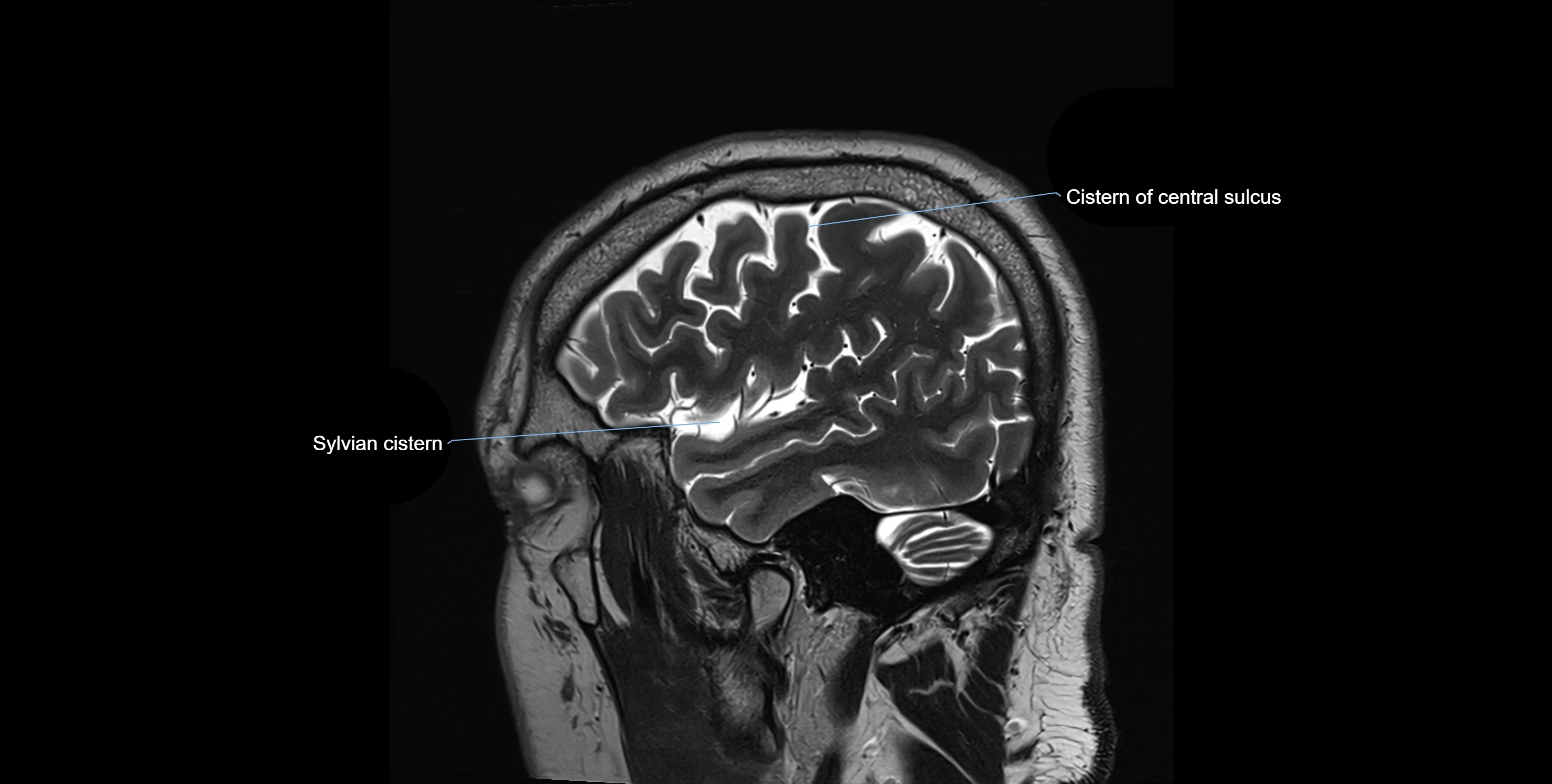
MRI Appearance
-
T1-weighted images:
-
The ambient cistern appears as a region of low signal intensity, matching the dark appearance of CSF.
-
Neurovascular structures within the cistern may appear as flow voids (signal loss from flowing blood) or as small dark linear structures.
-
-
T2-weighted images:
-
The cistern is hyperintense (bright) due to the high water content of CSF.
-
Encapsulated vessels and nerves are seen as flow voids or hypointense lines within the bright background.
-
-
FLAIR (Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery):
-
The cistern normally appears dark because CSF signal is suppressed.
-
Any hyperintensity in this region on FLAIR may indicate pathology (e.g., subarachnoid hemorrhage, infection).
-
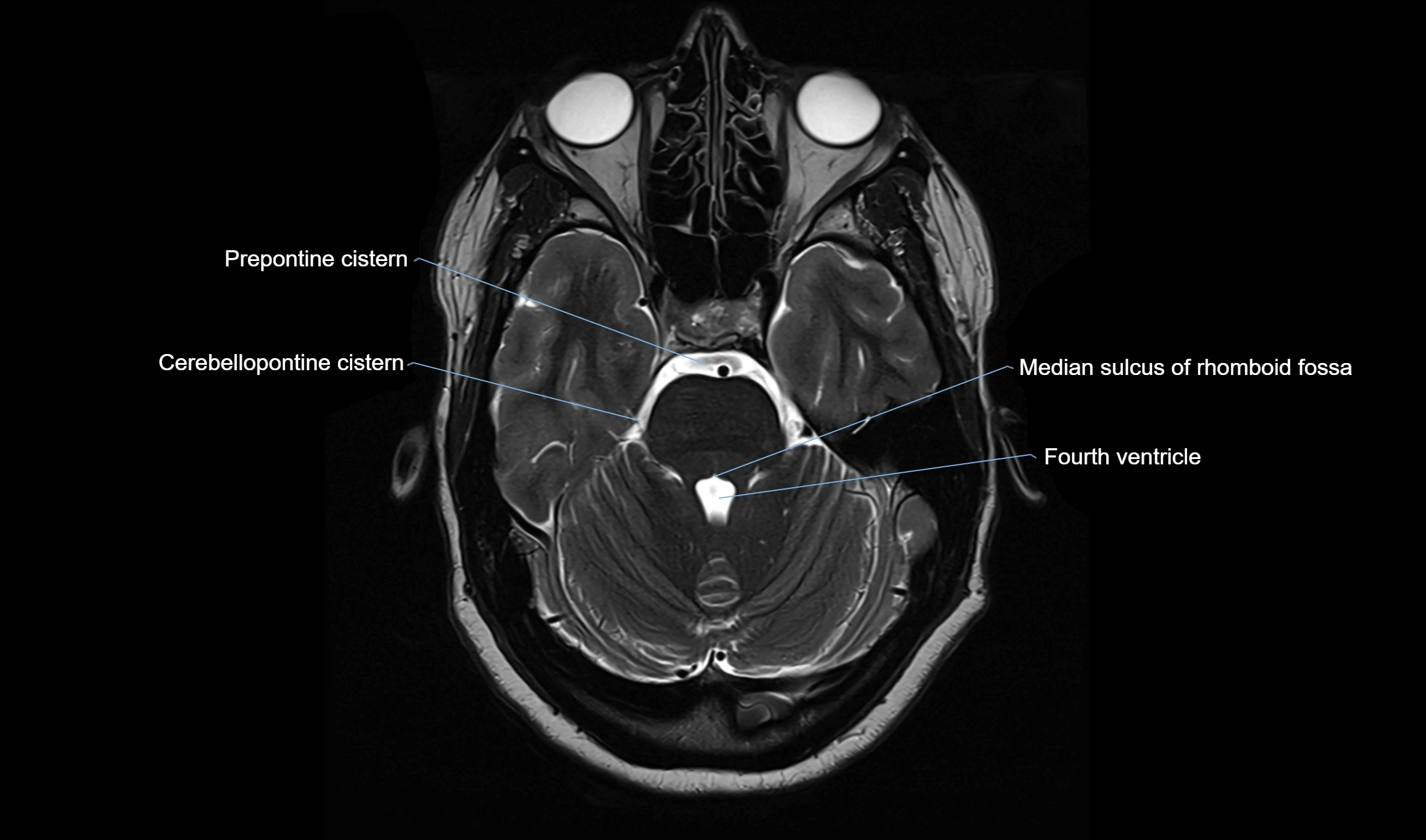
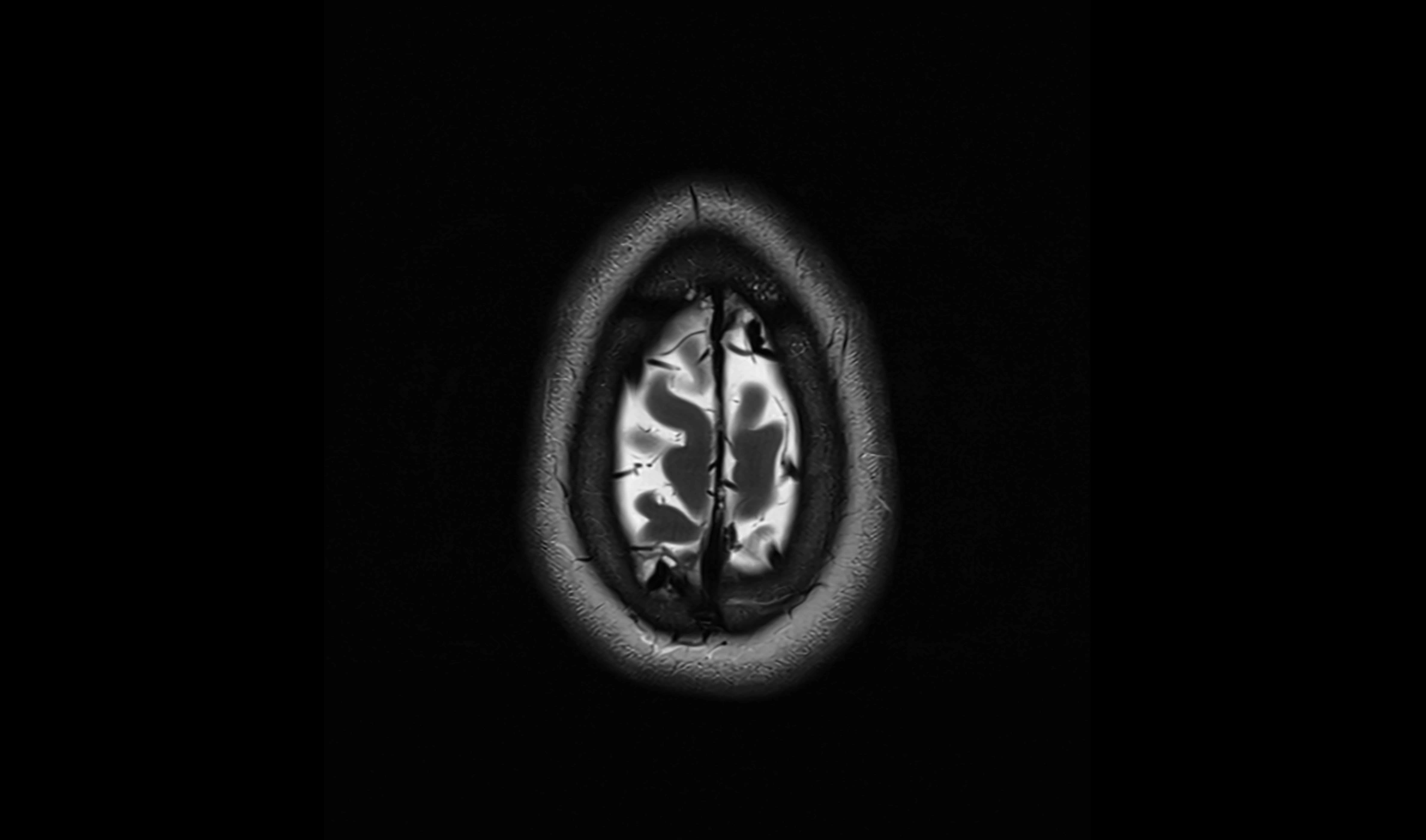
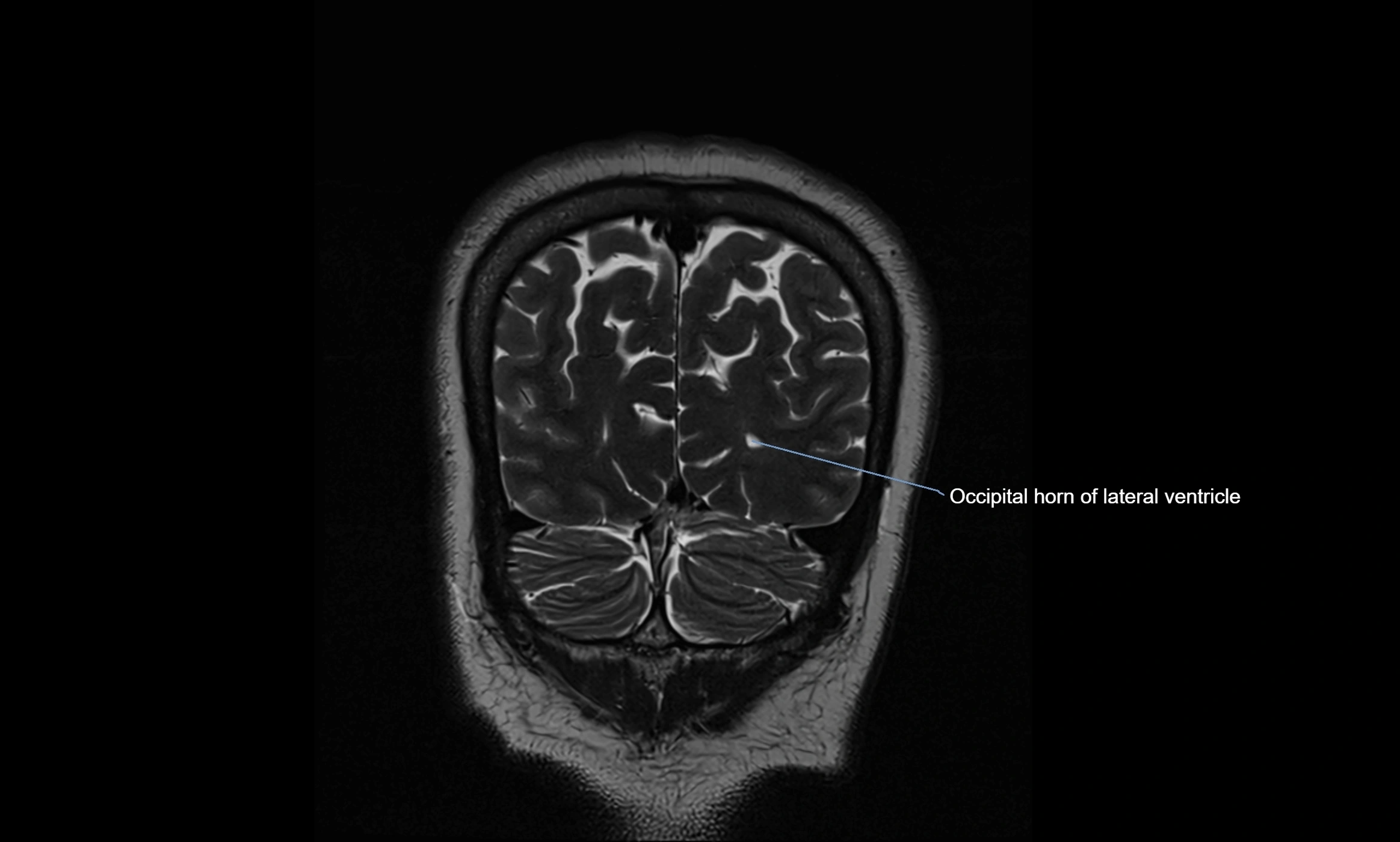
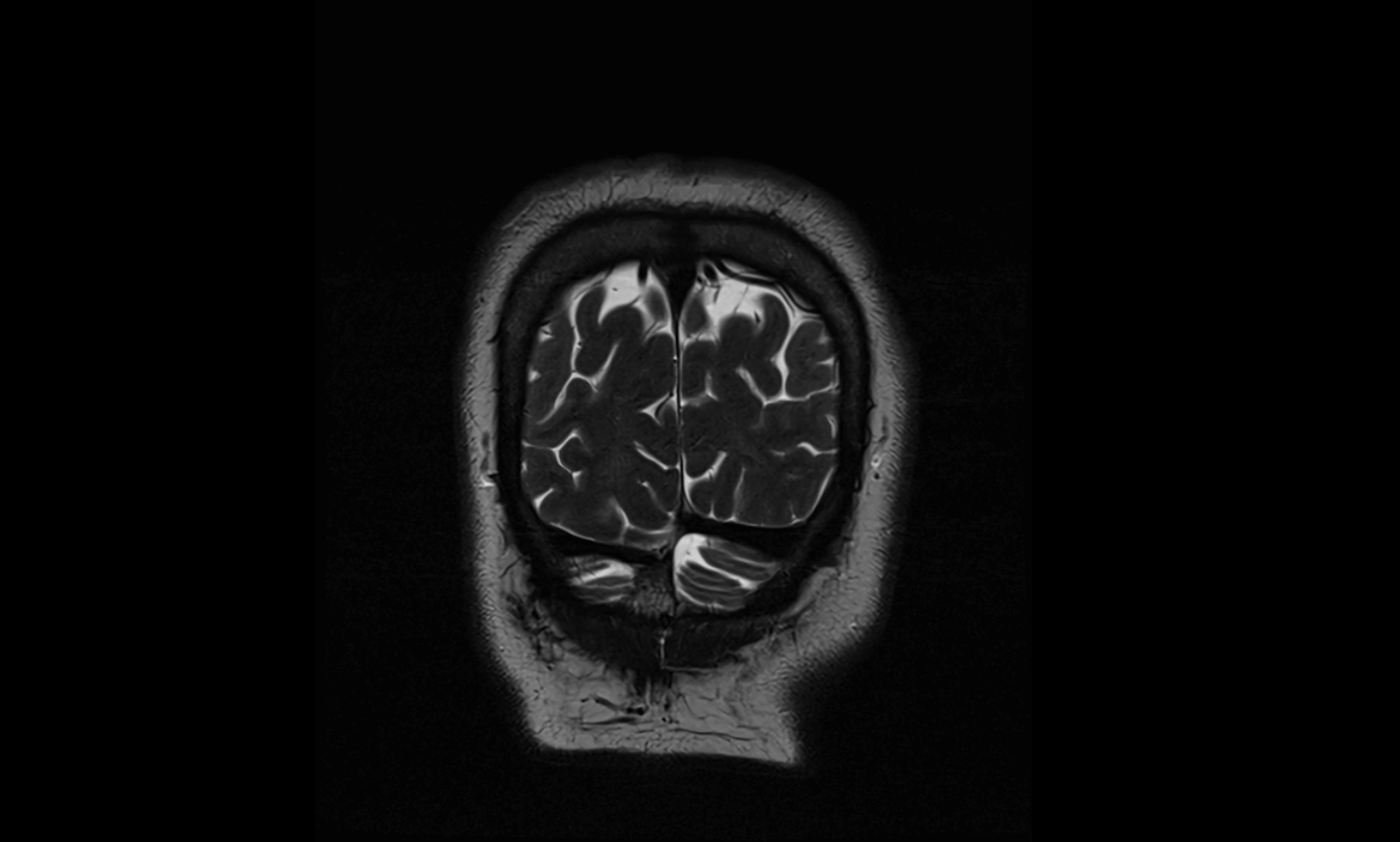
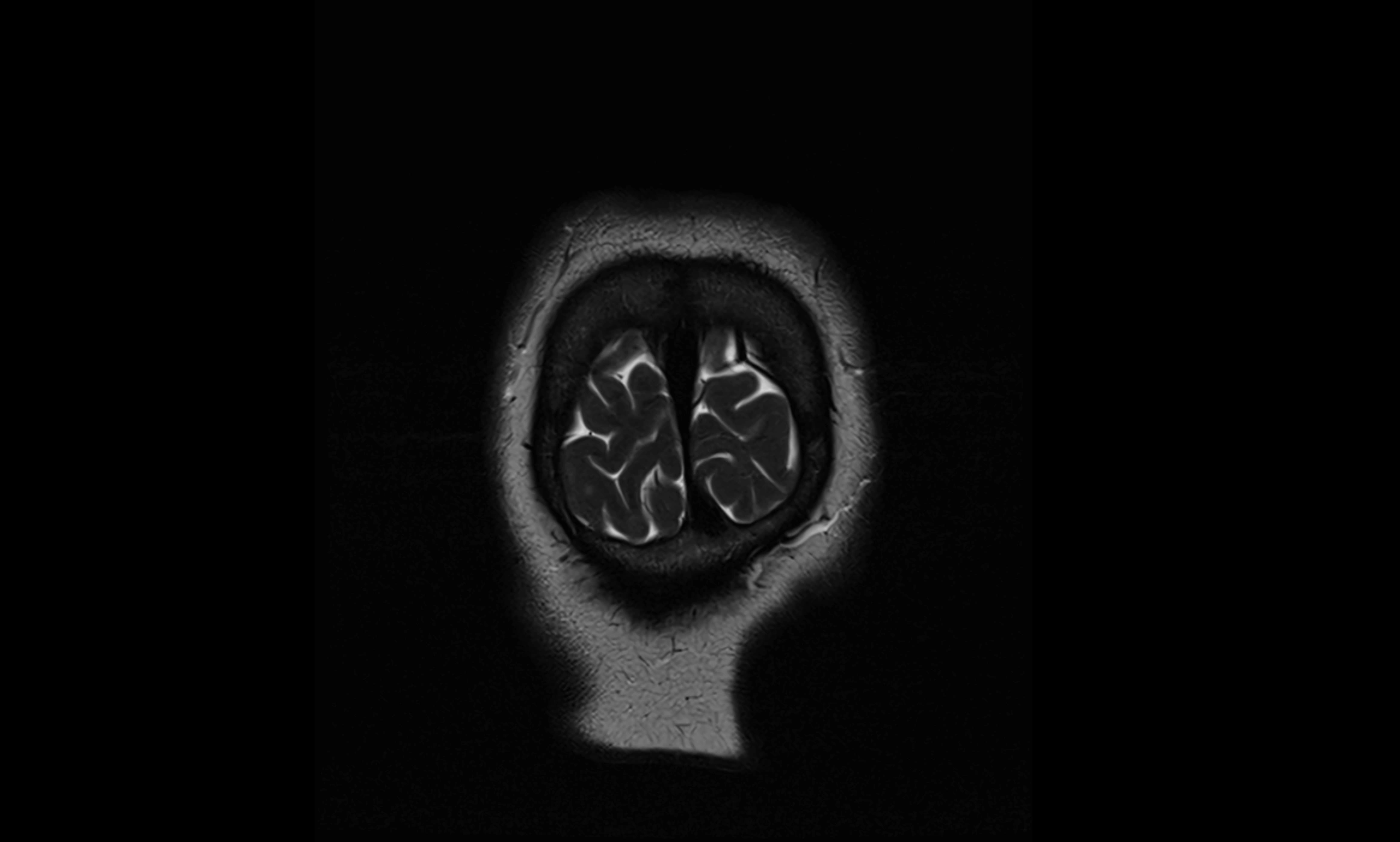
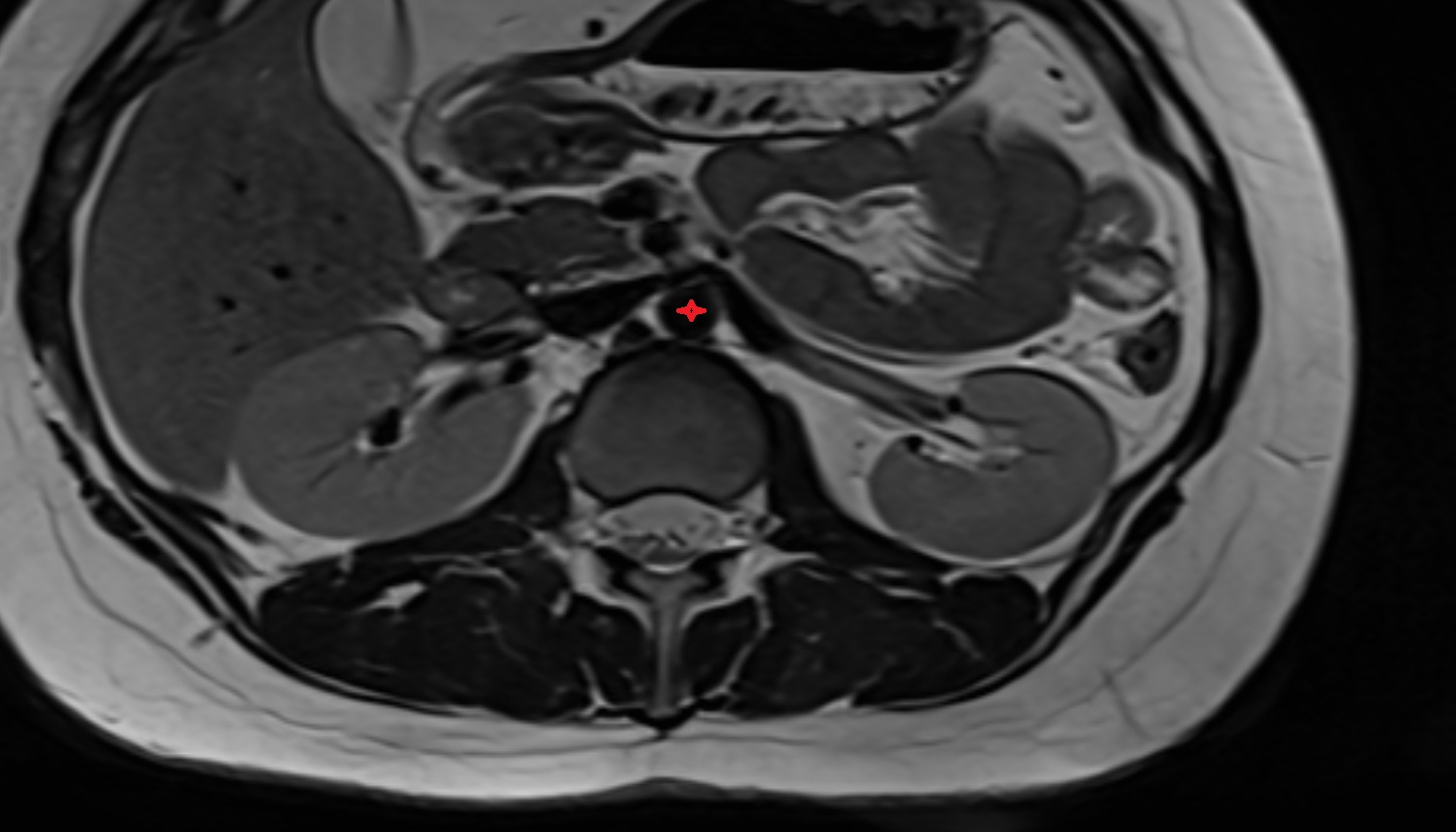
CT Appearance
-
The ambient cistern is visualized as a low-density (hypodense) area, similar to other CSF-filled spaces, lateral to the midbrain.
-
Blood, masses, or increased attenuation in the cistern may suggest pathology (e.g., subarachnoid hemorrhage, mass effect from tumors or edema).
-
Loss of normal cistern outline can indicate mass effect, brain swelling, or herniation.
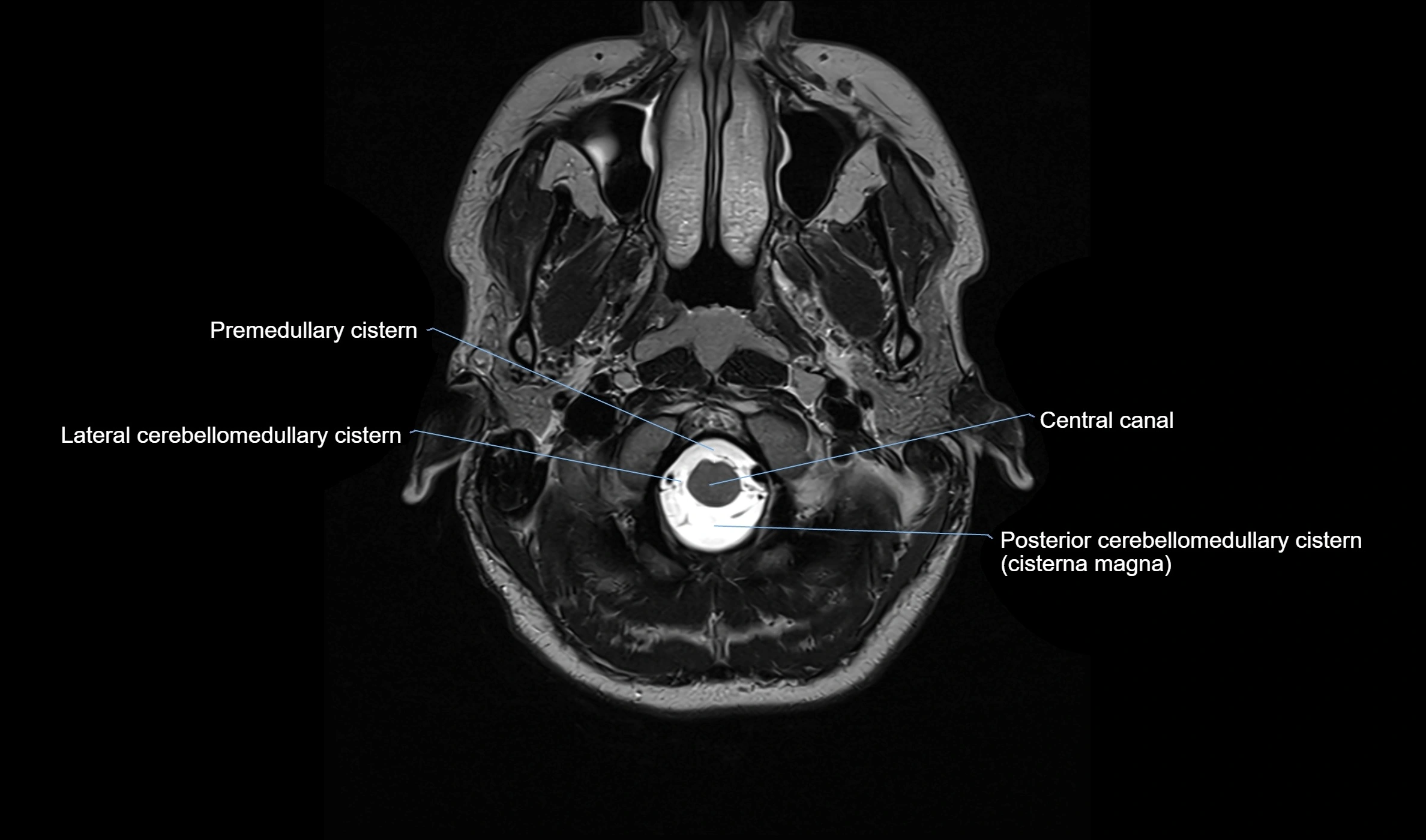
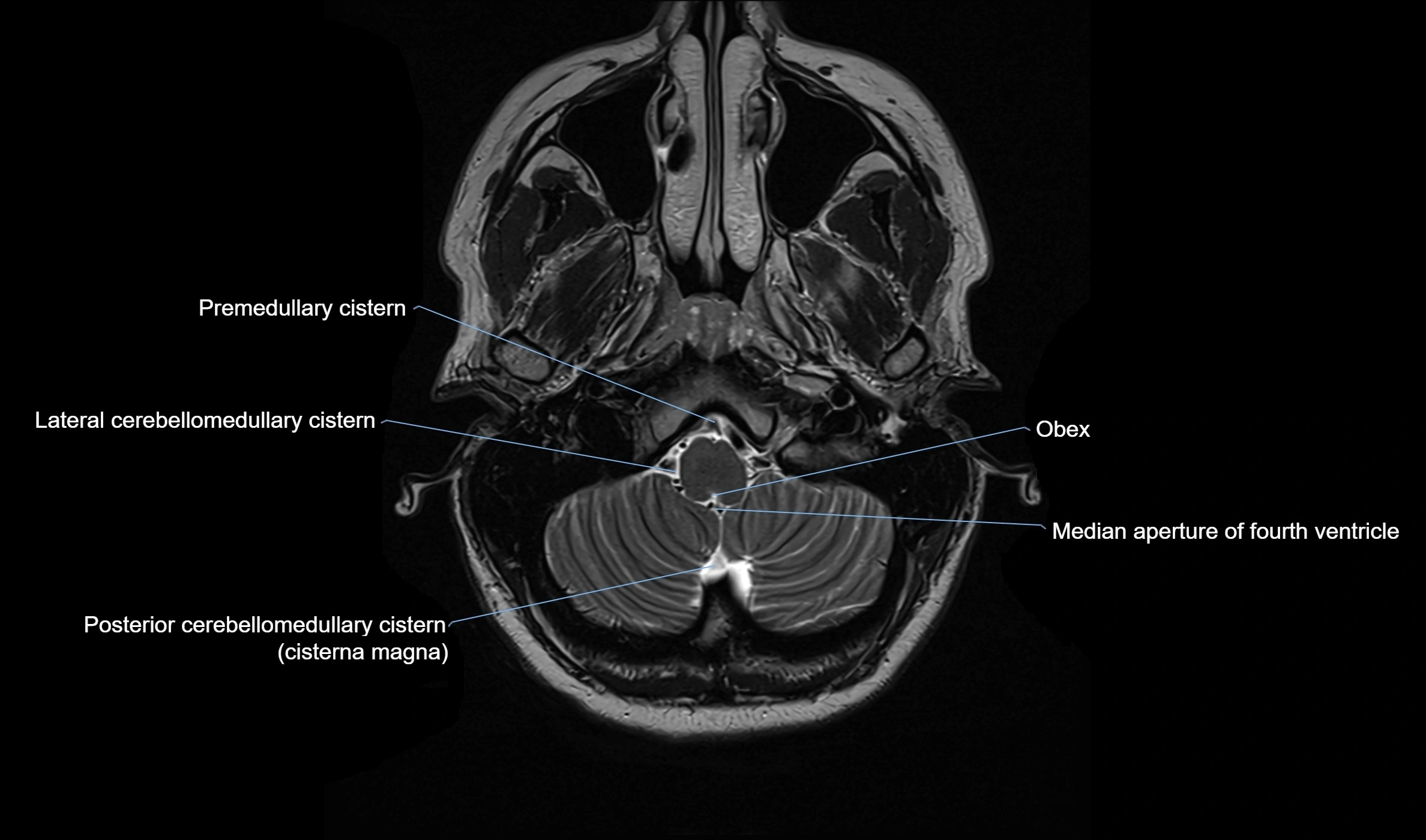
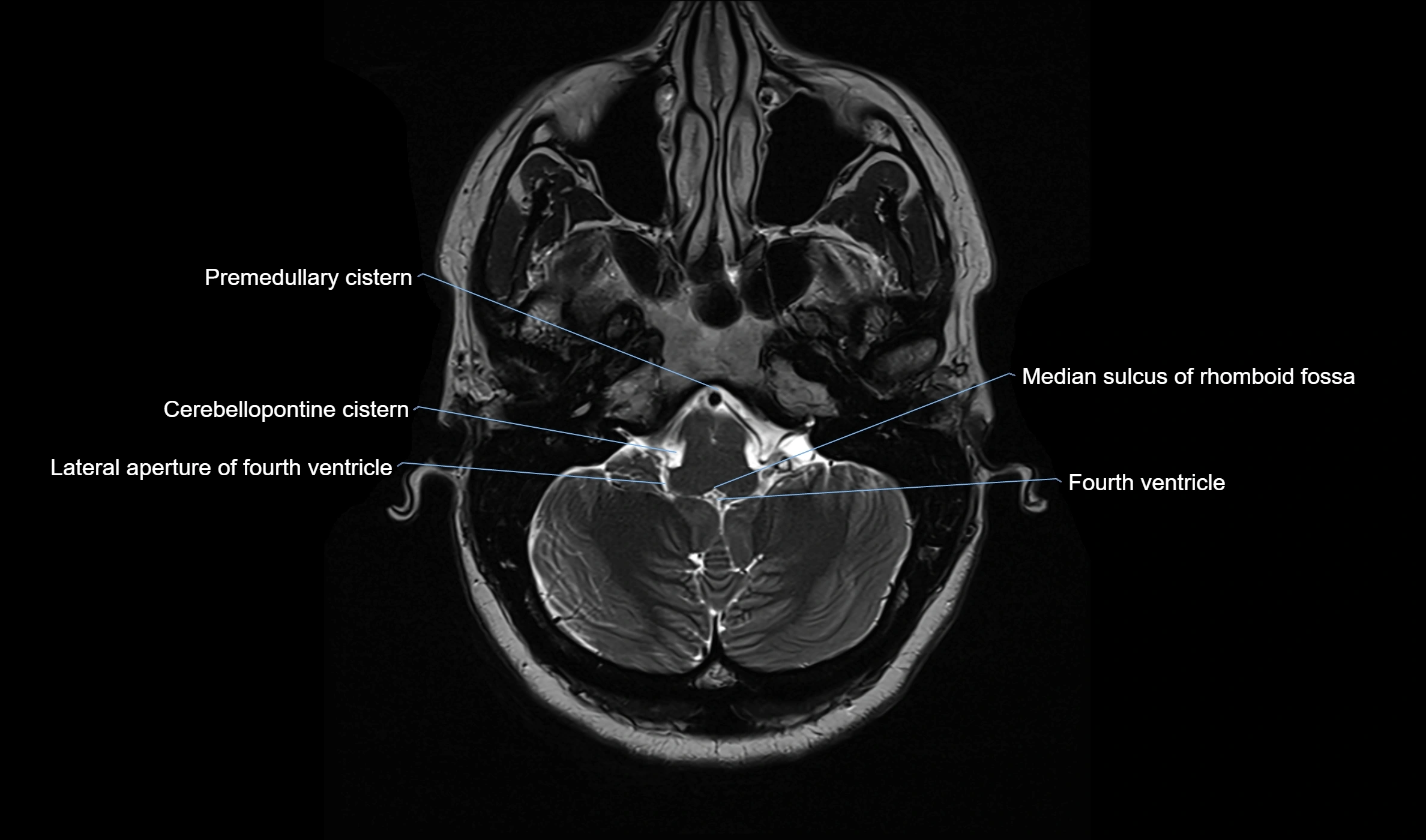
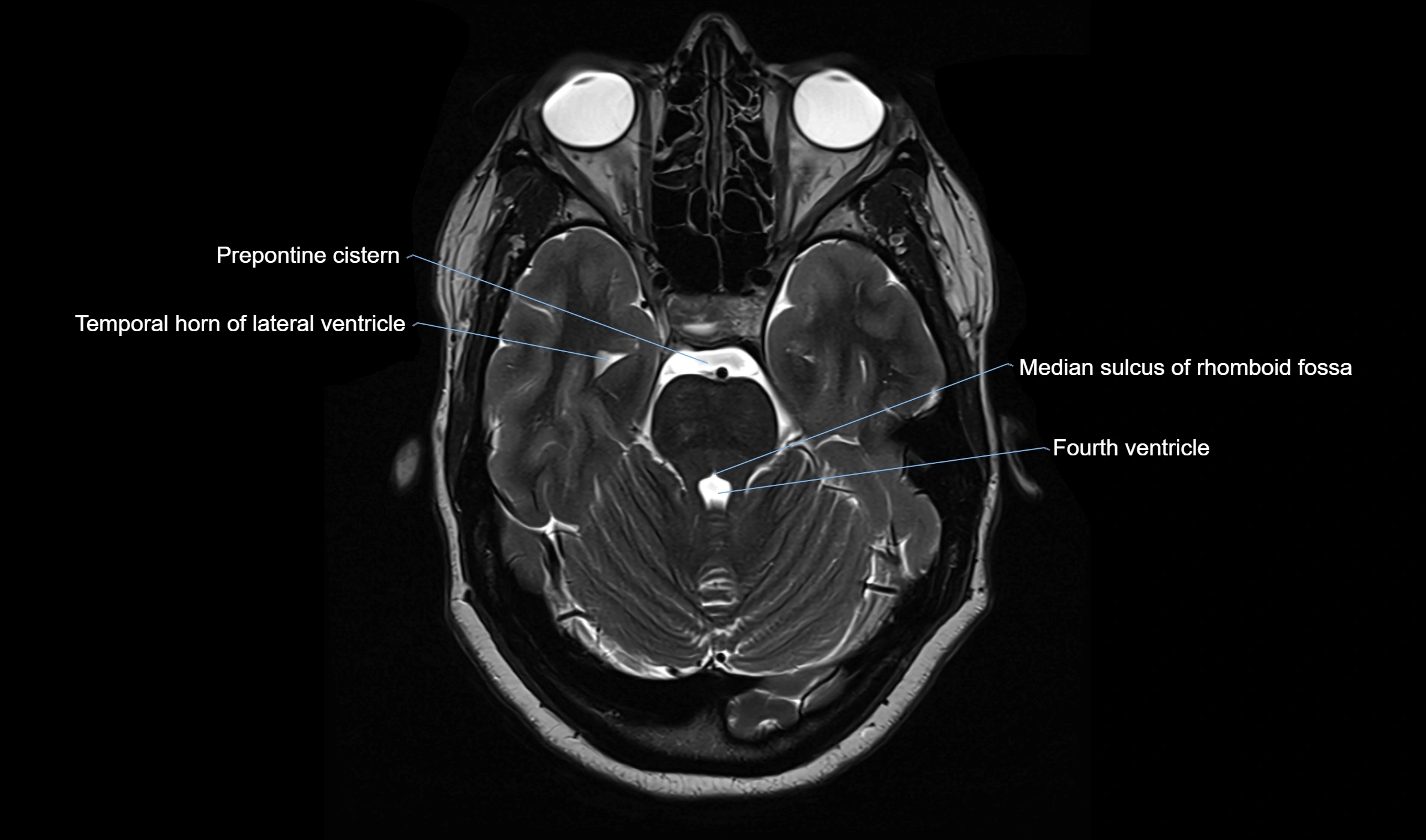
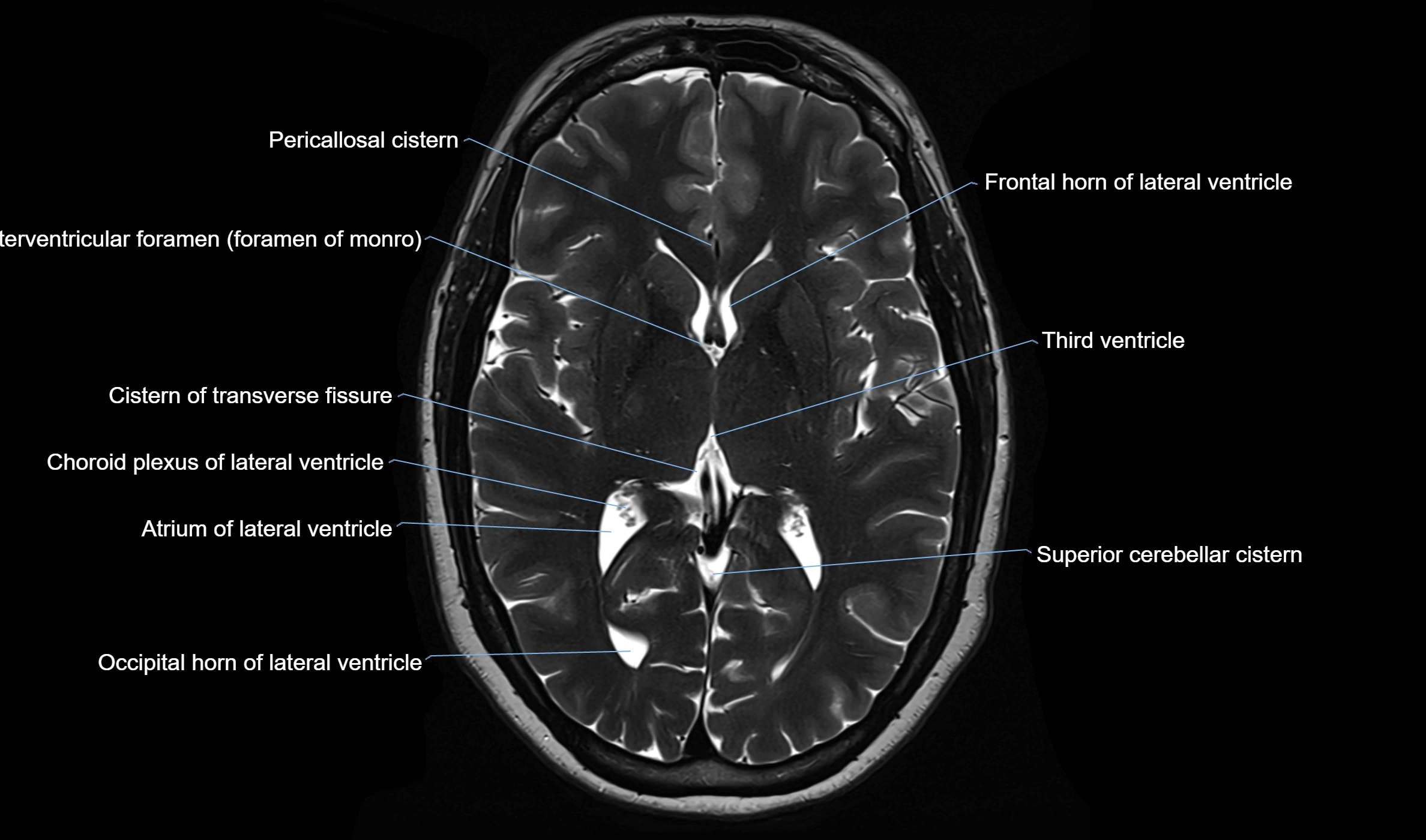
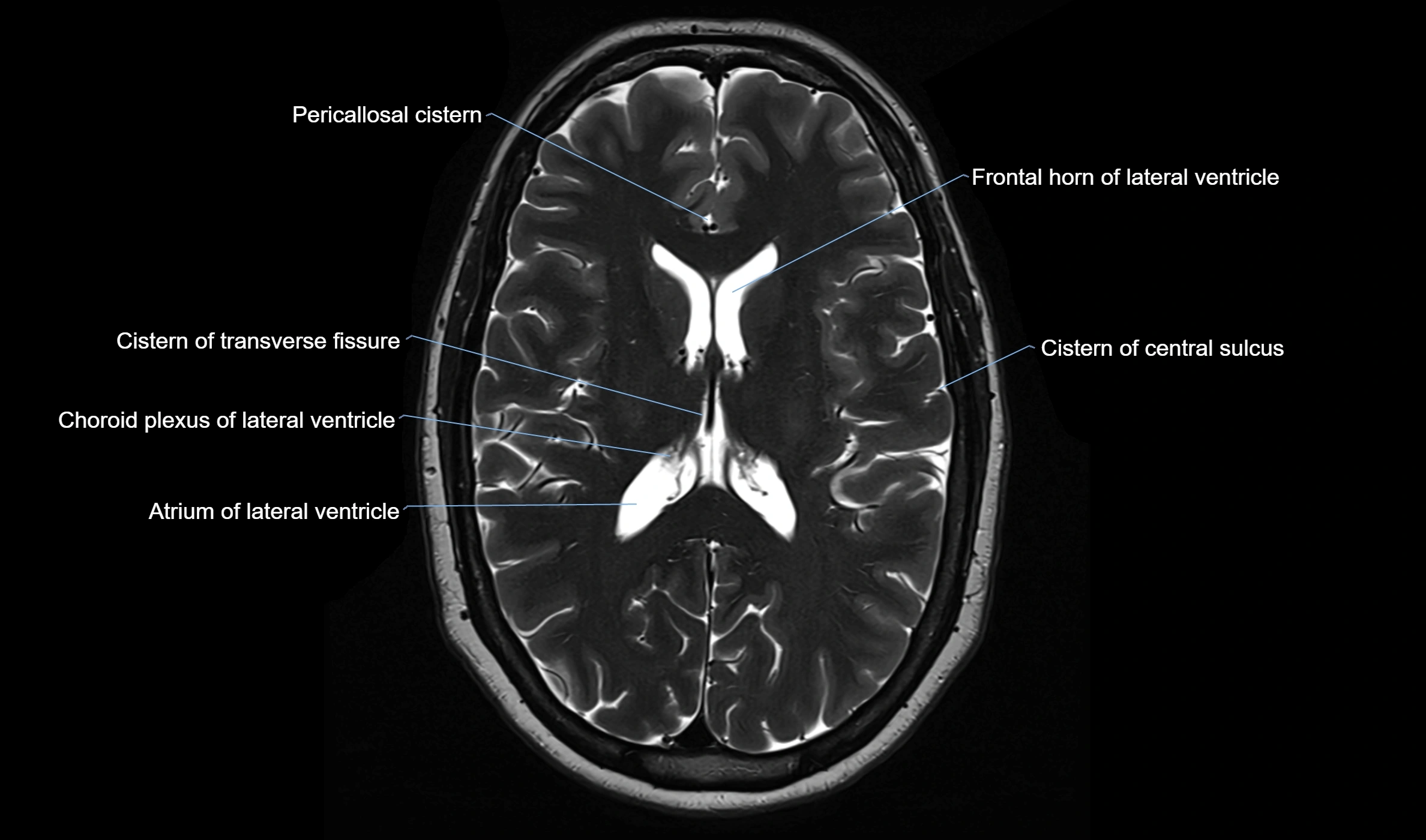
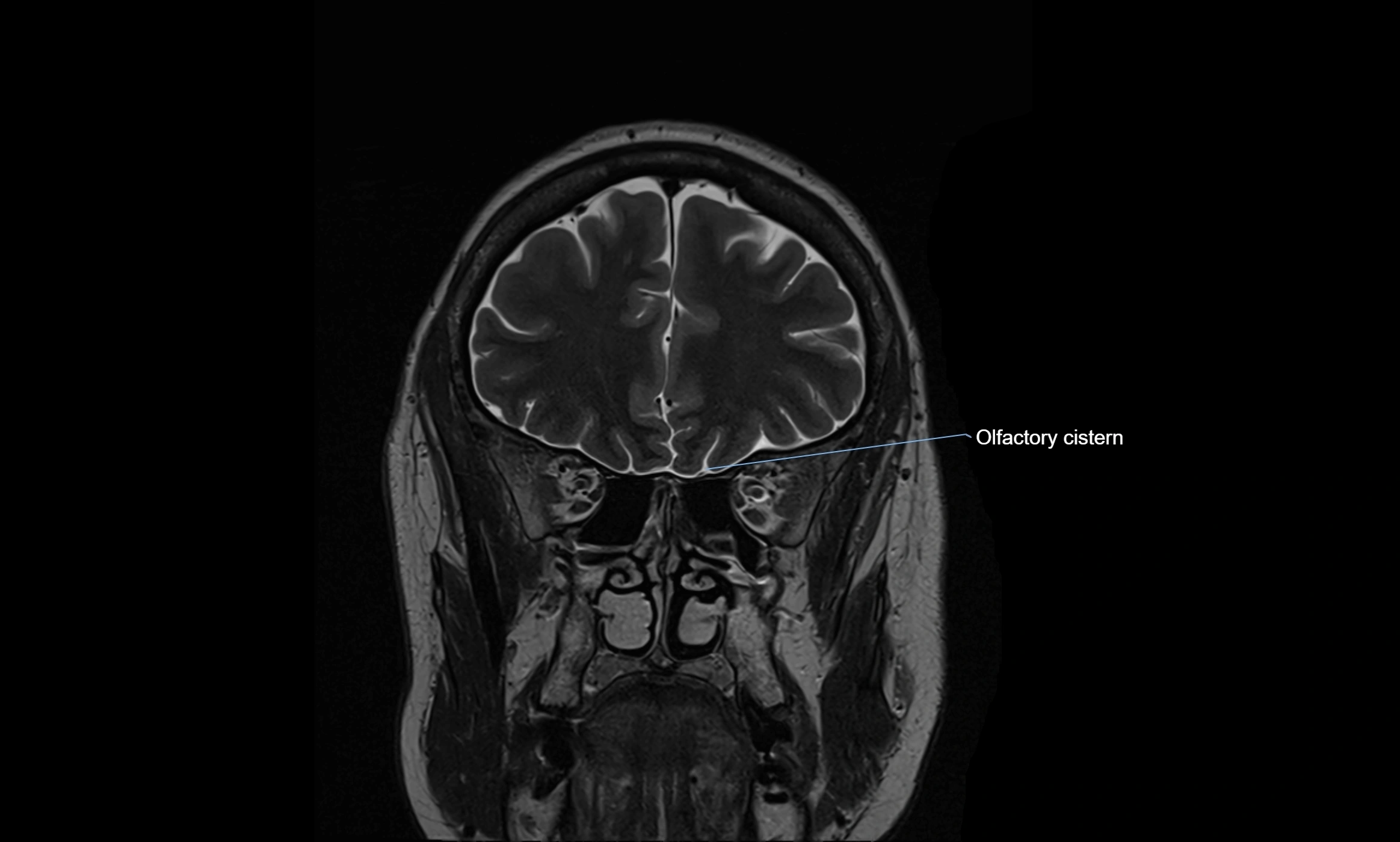
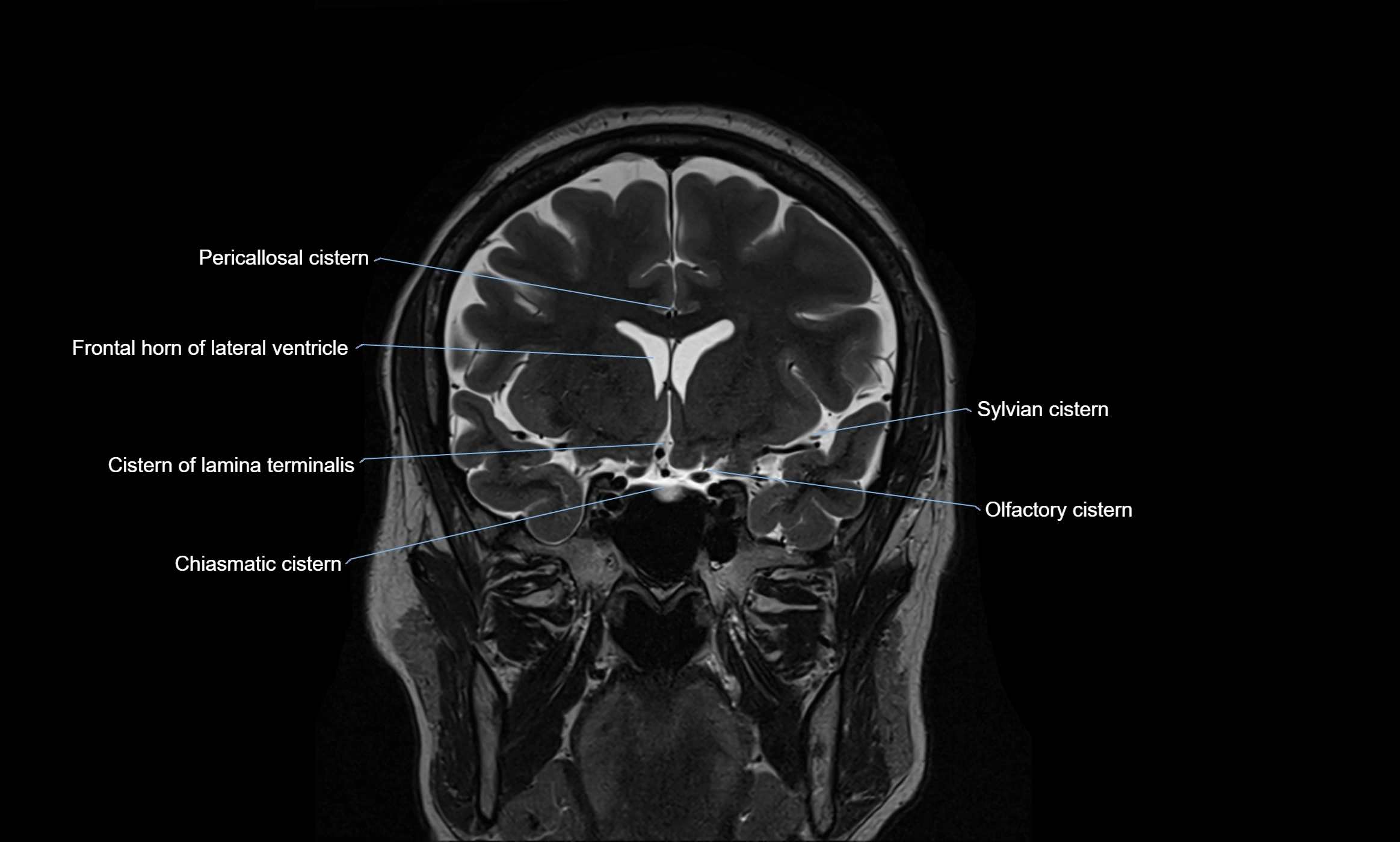
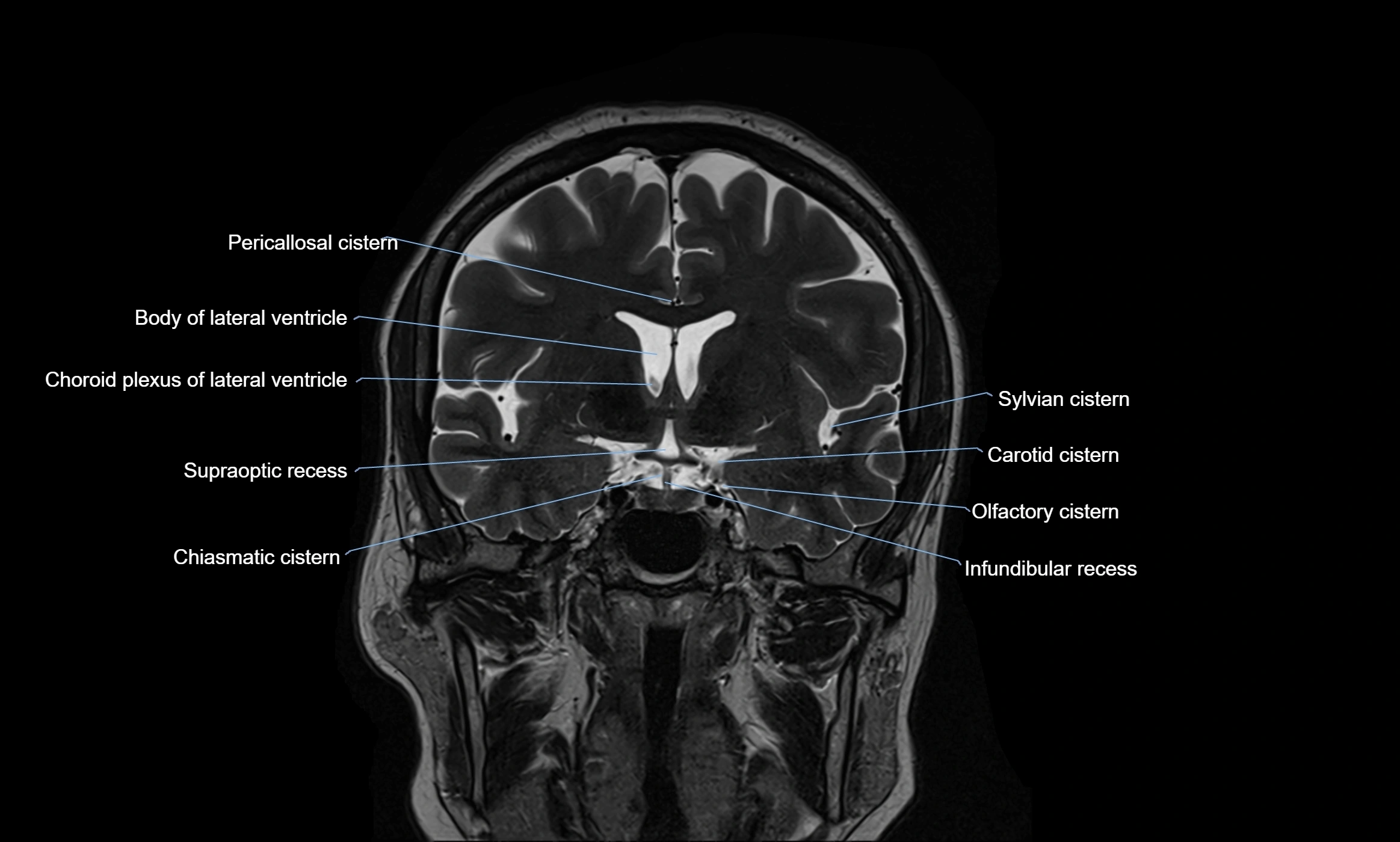
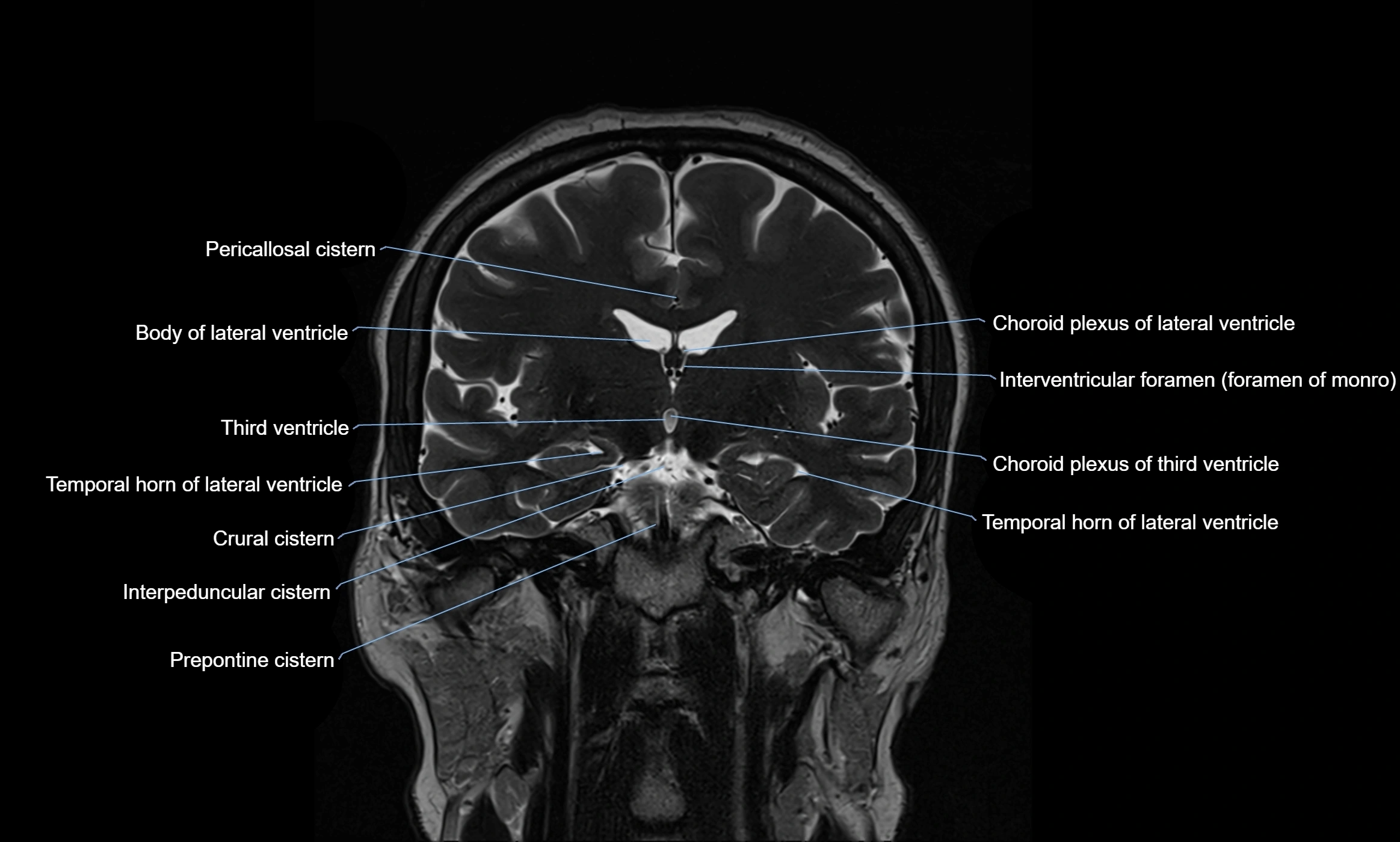
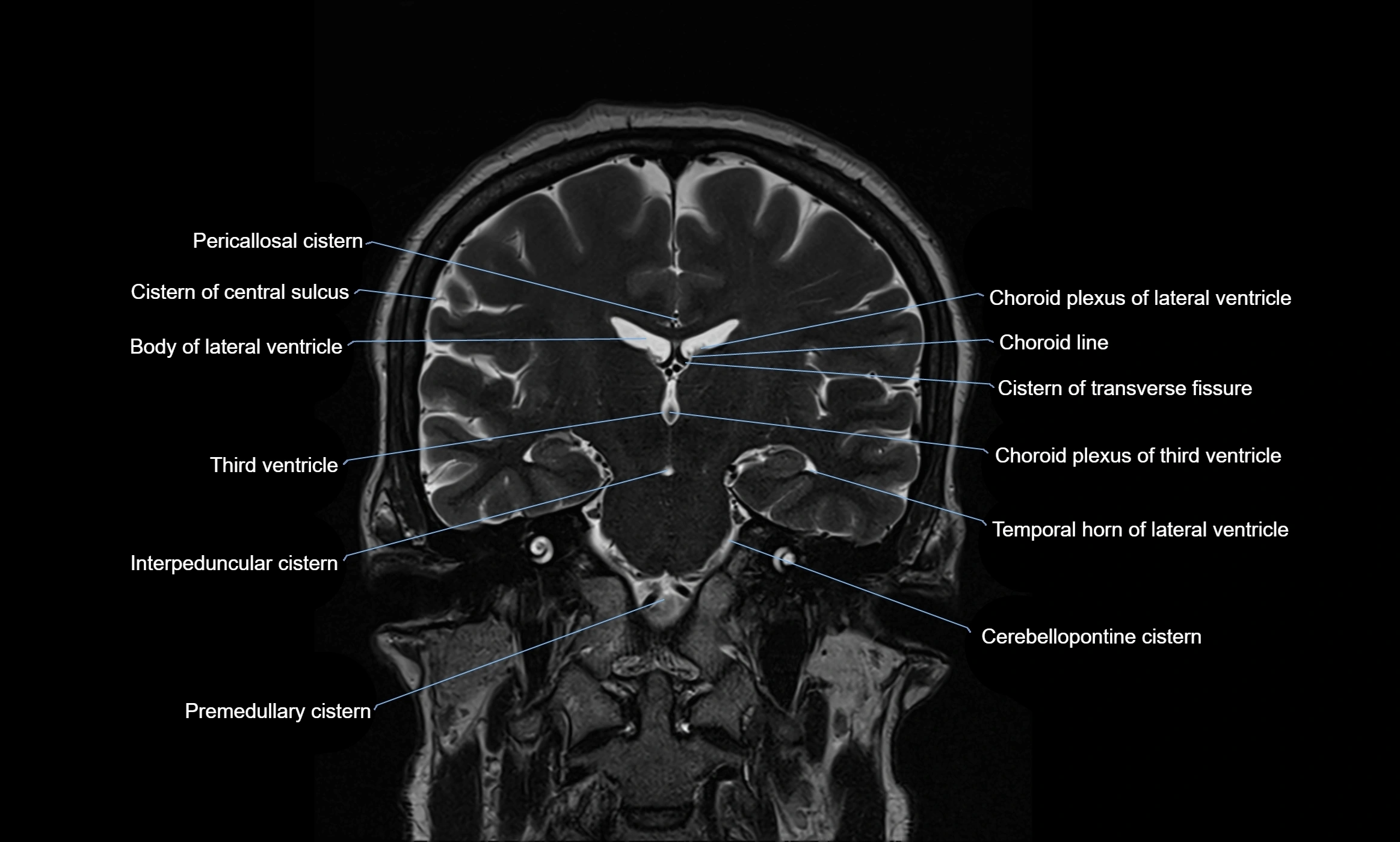
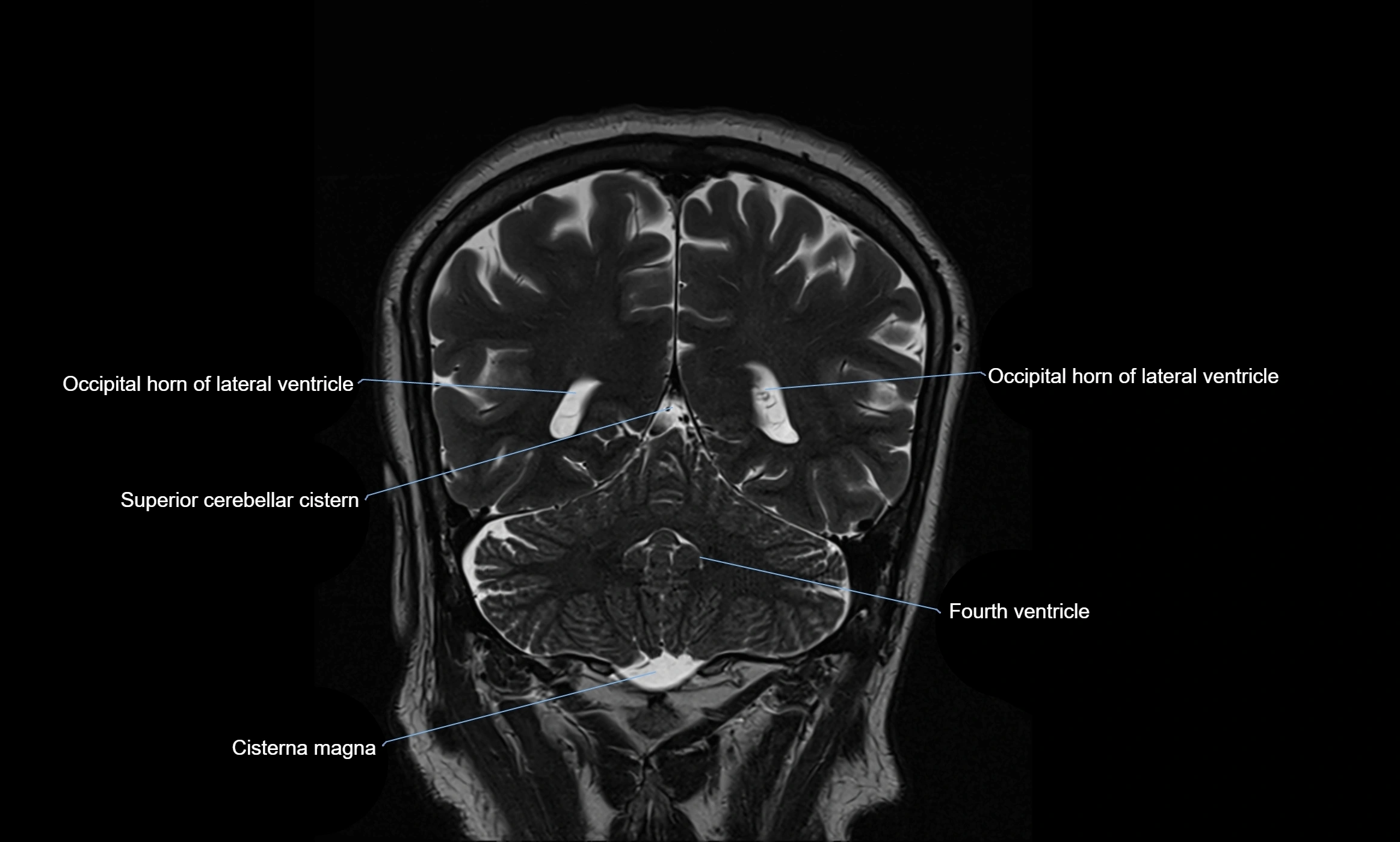
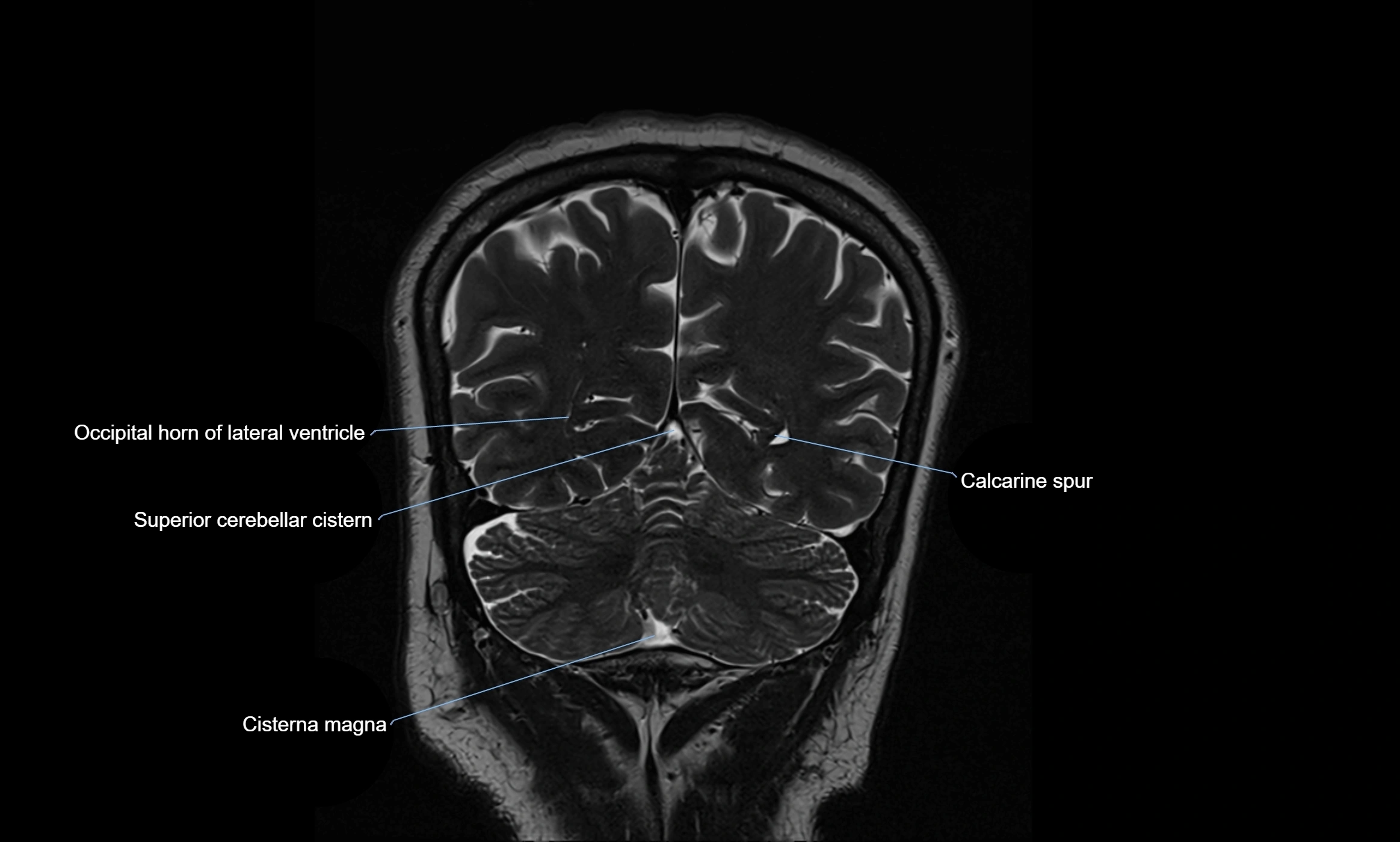
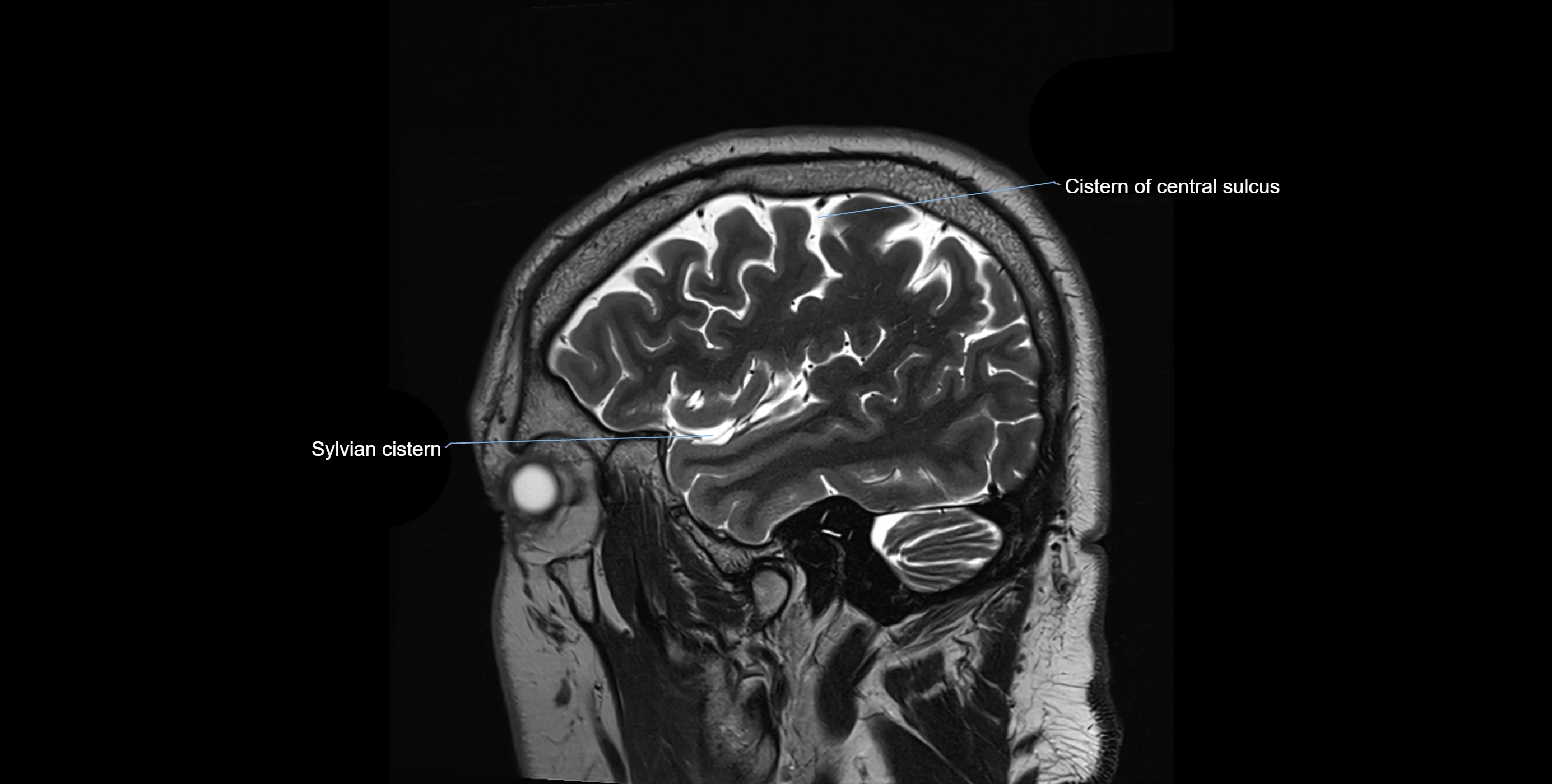
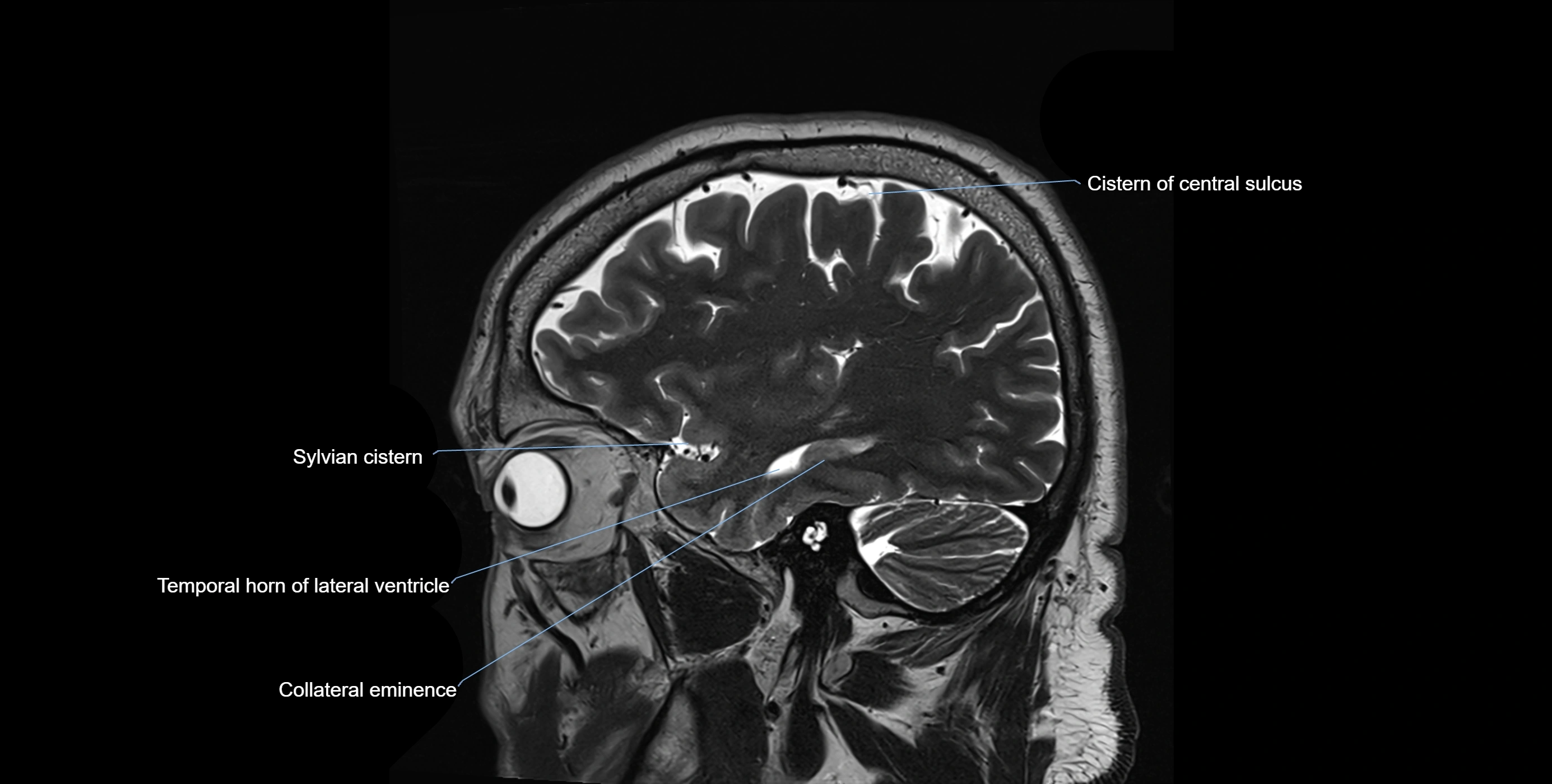
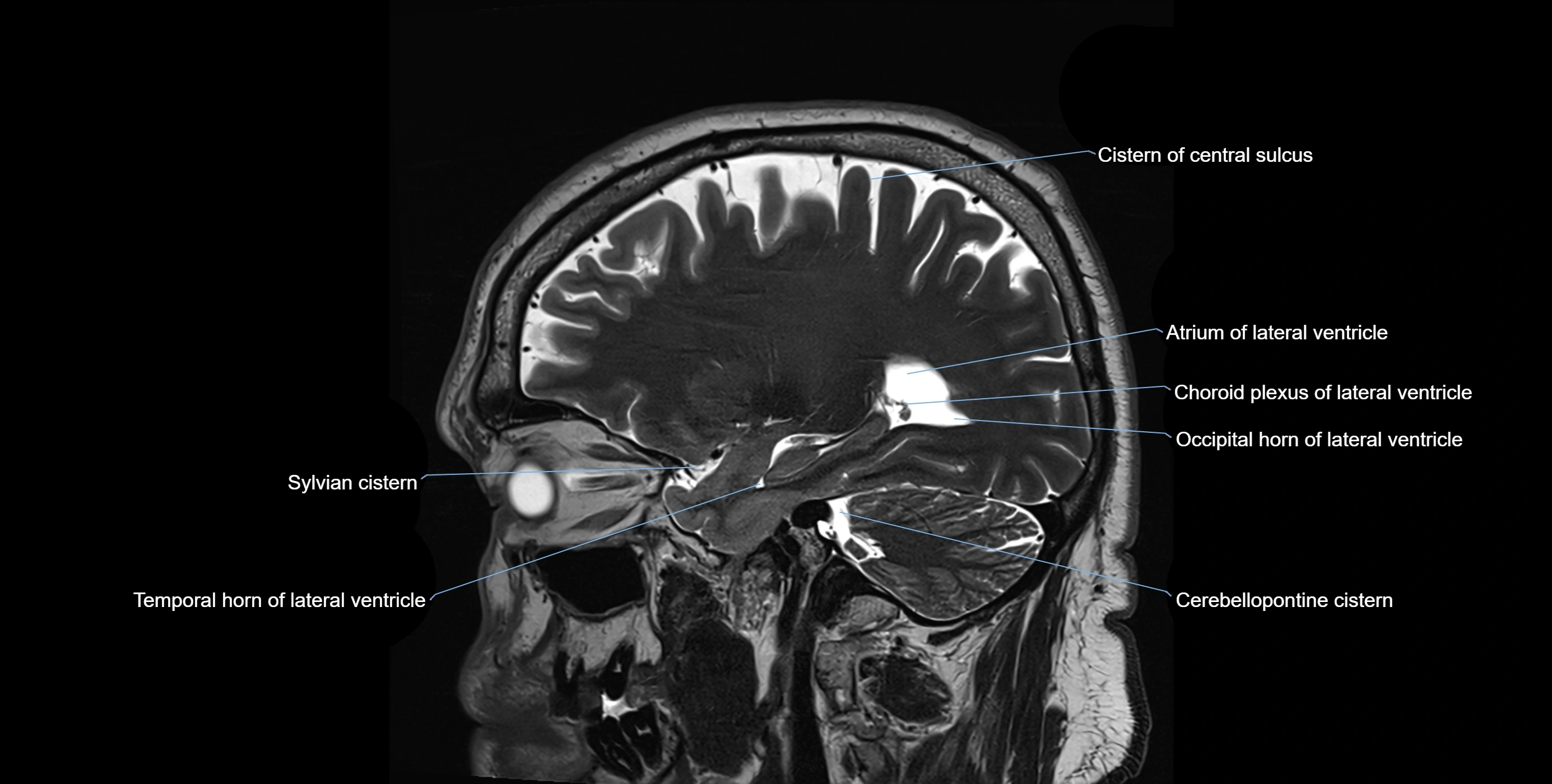
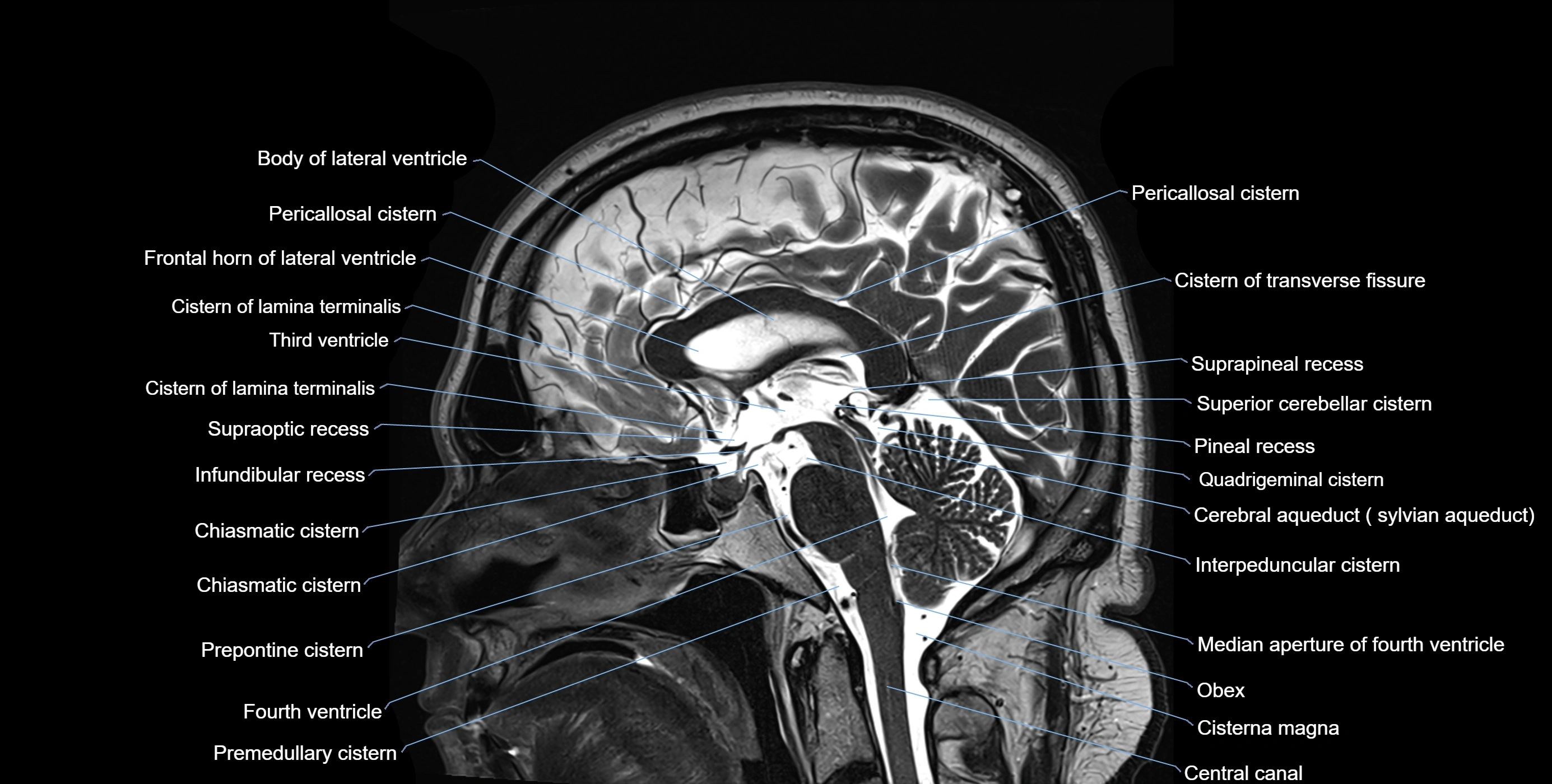
MRI images

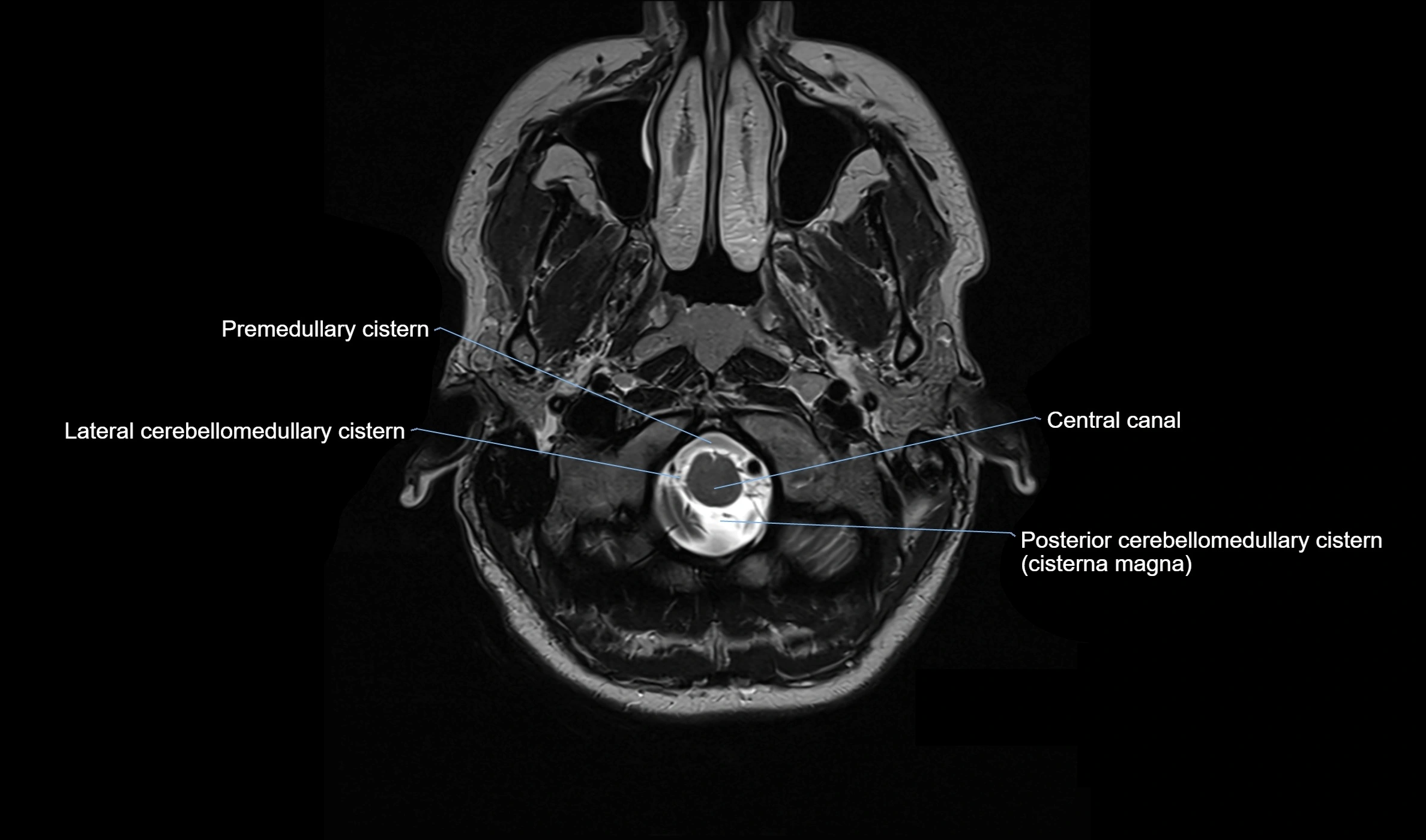
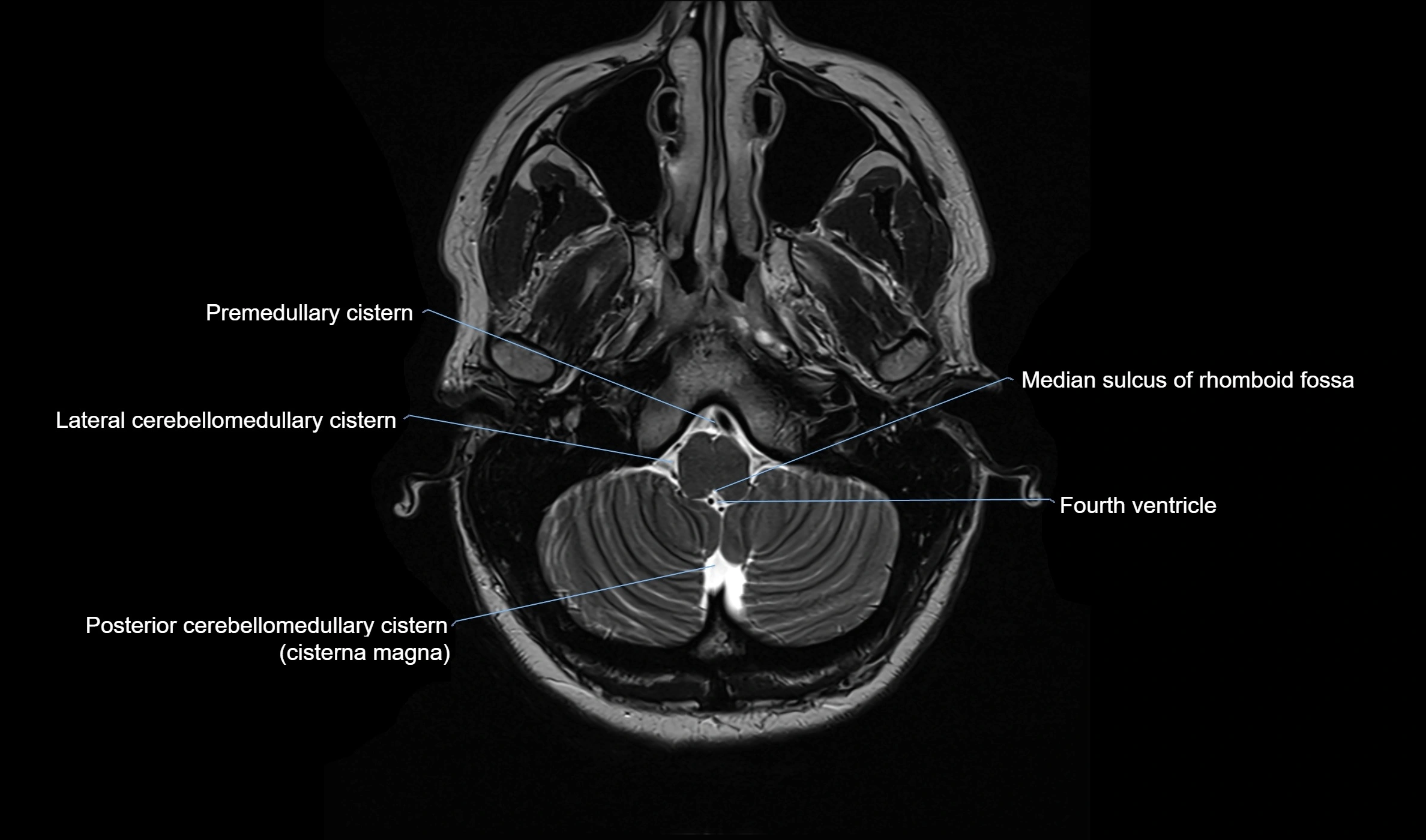
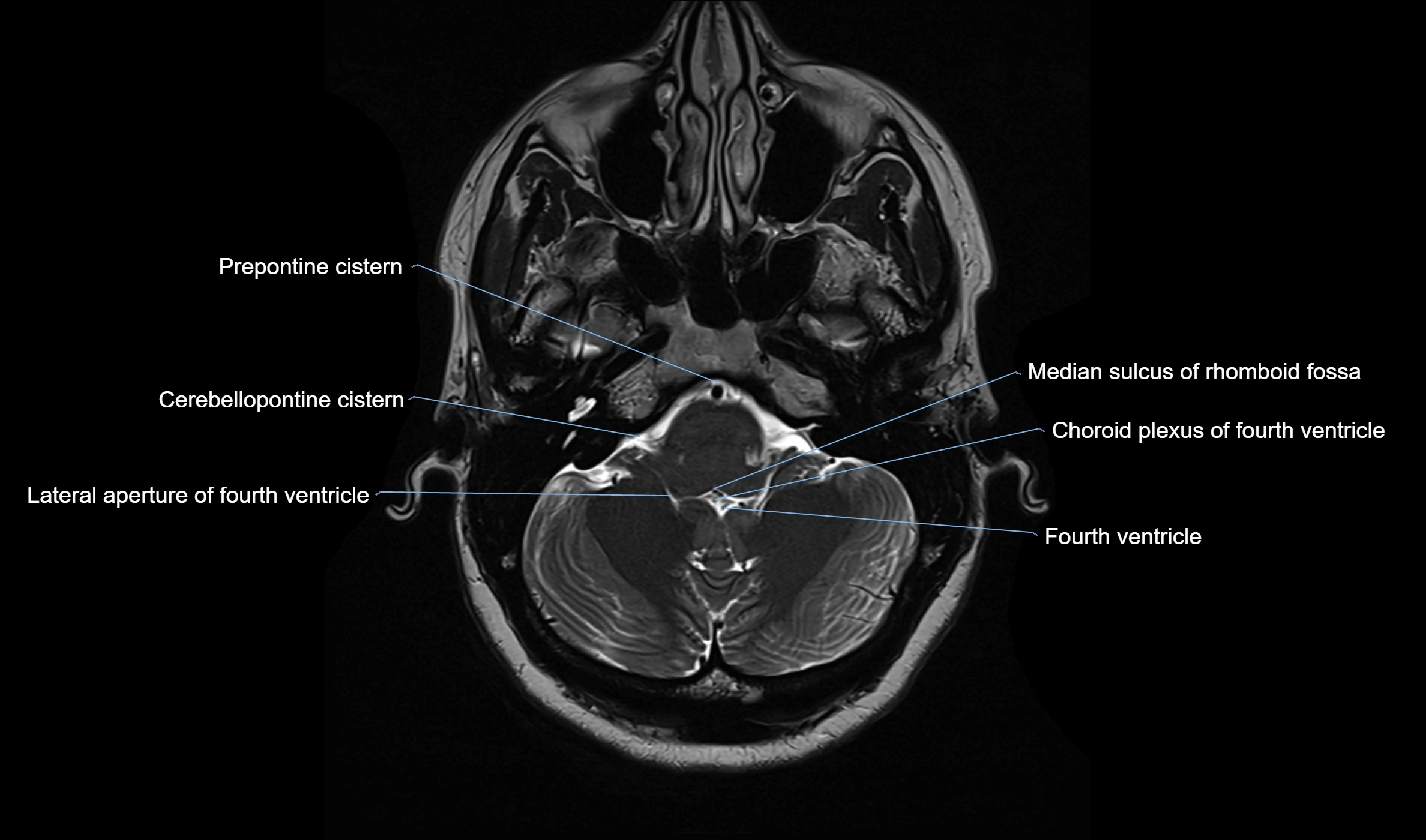
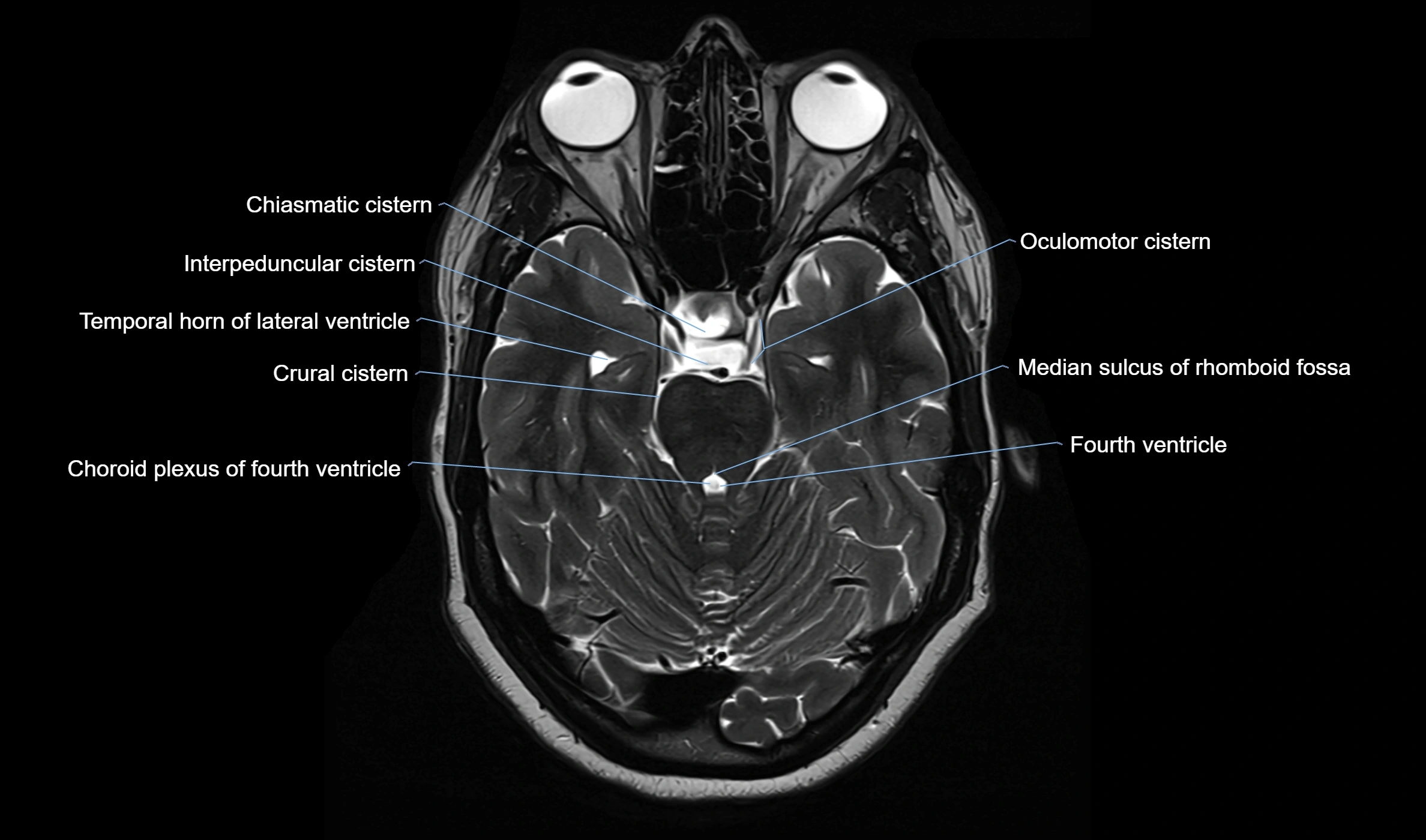
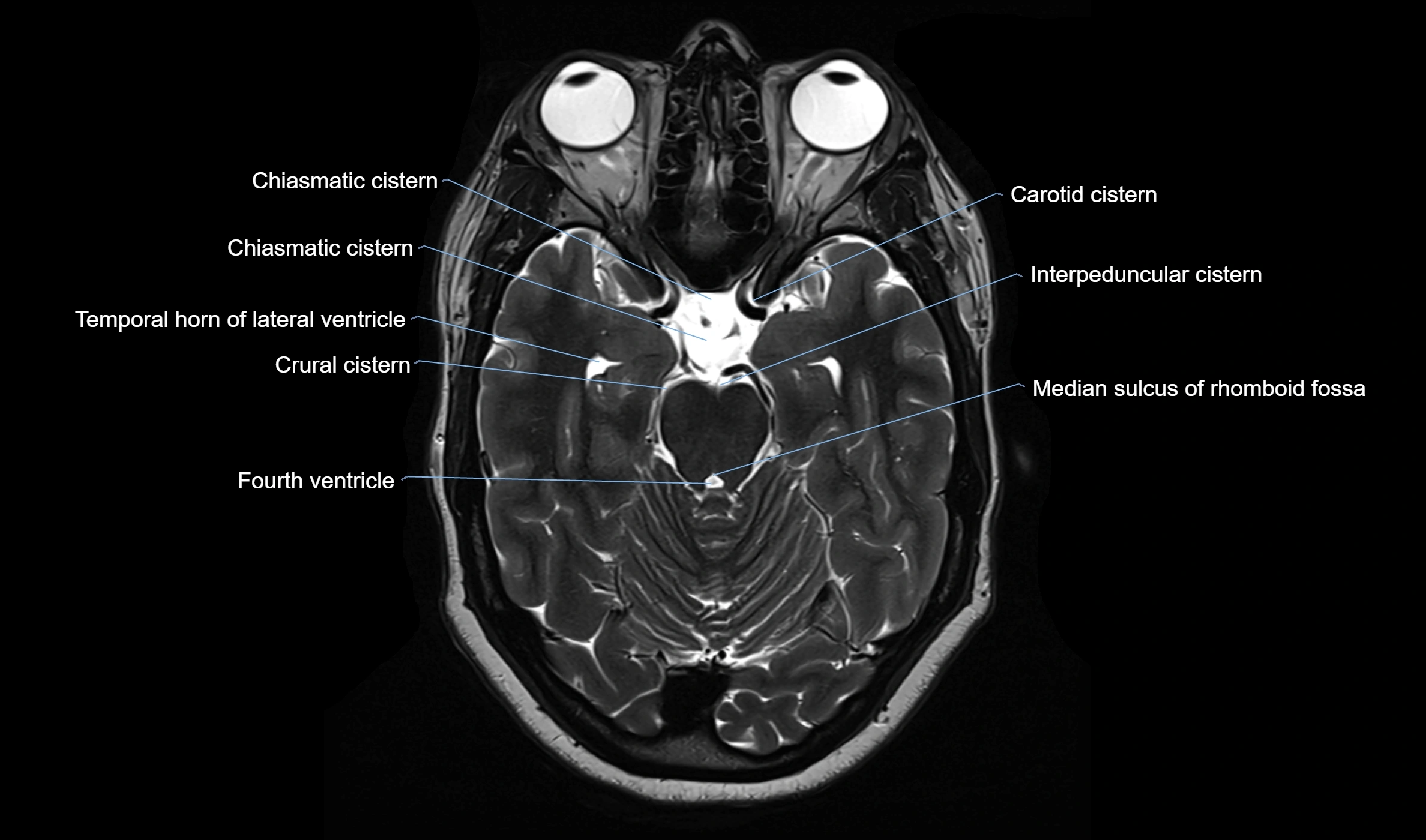
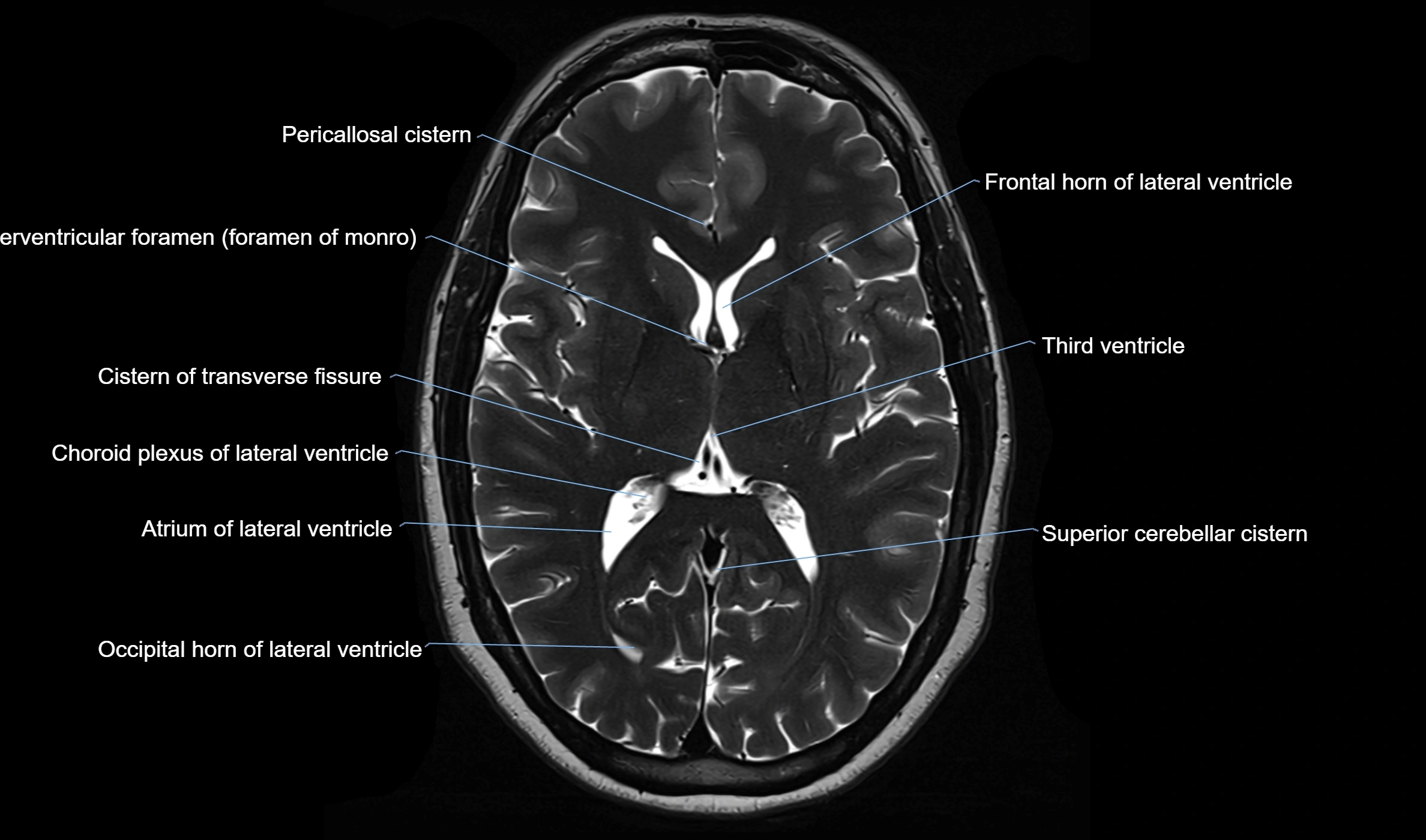
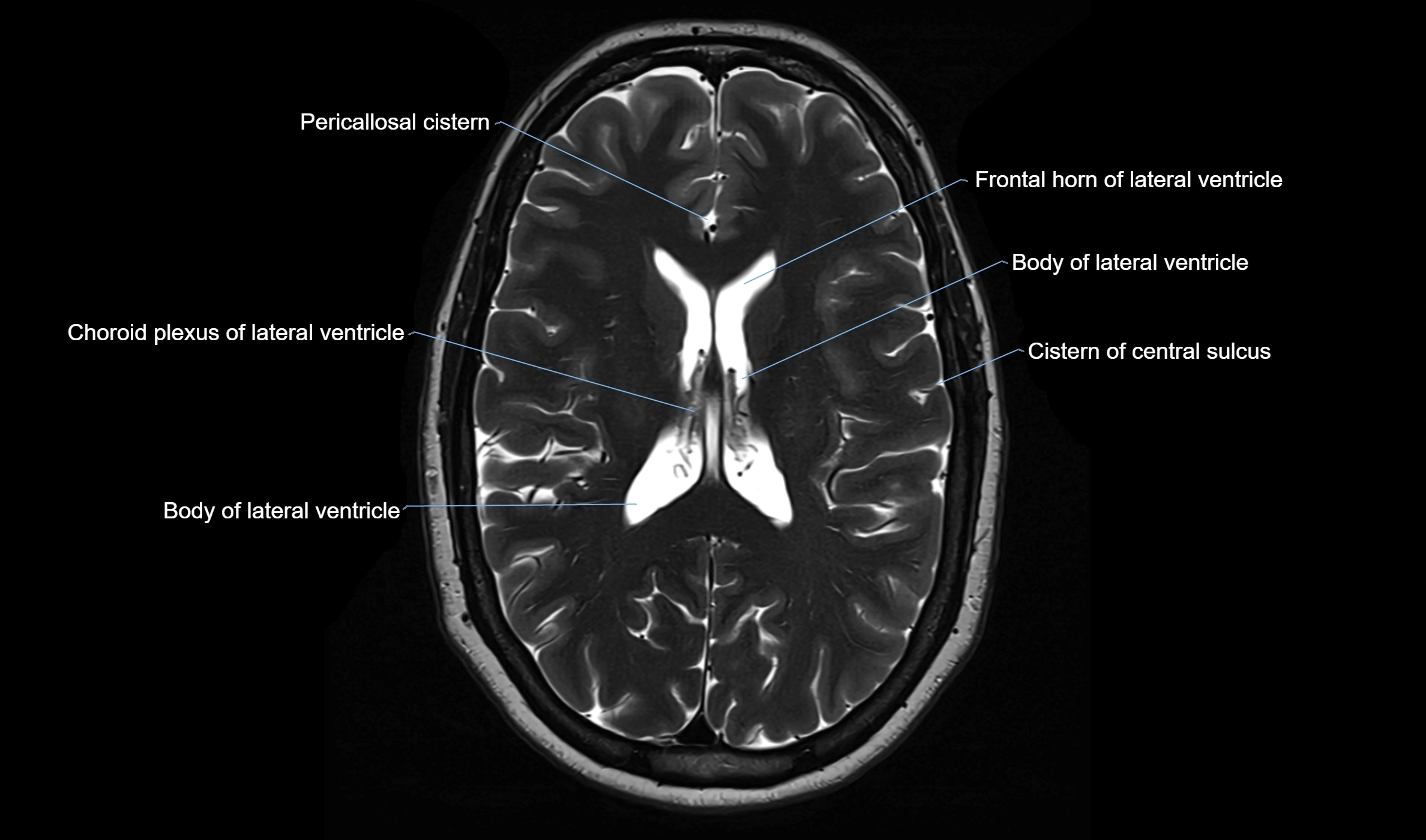
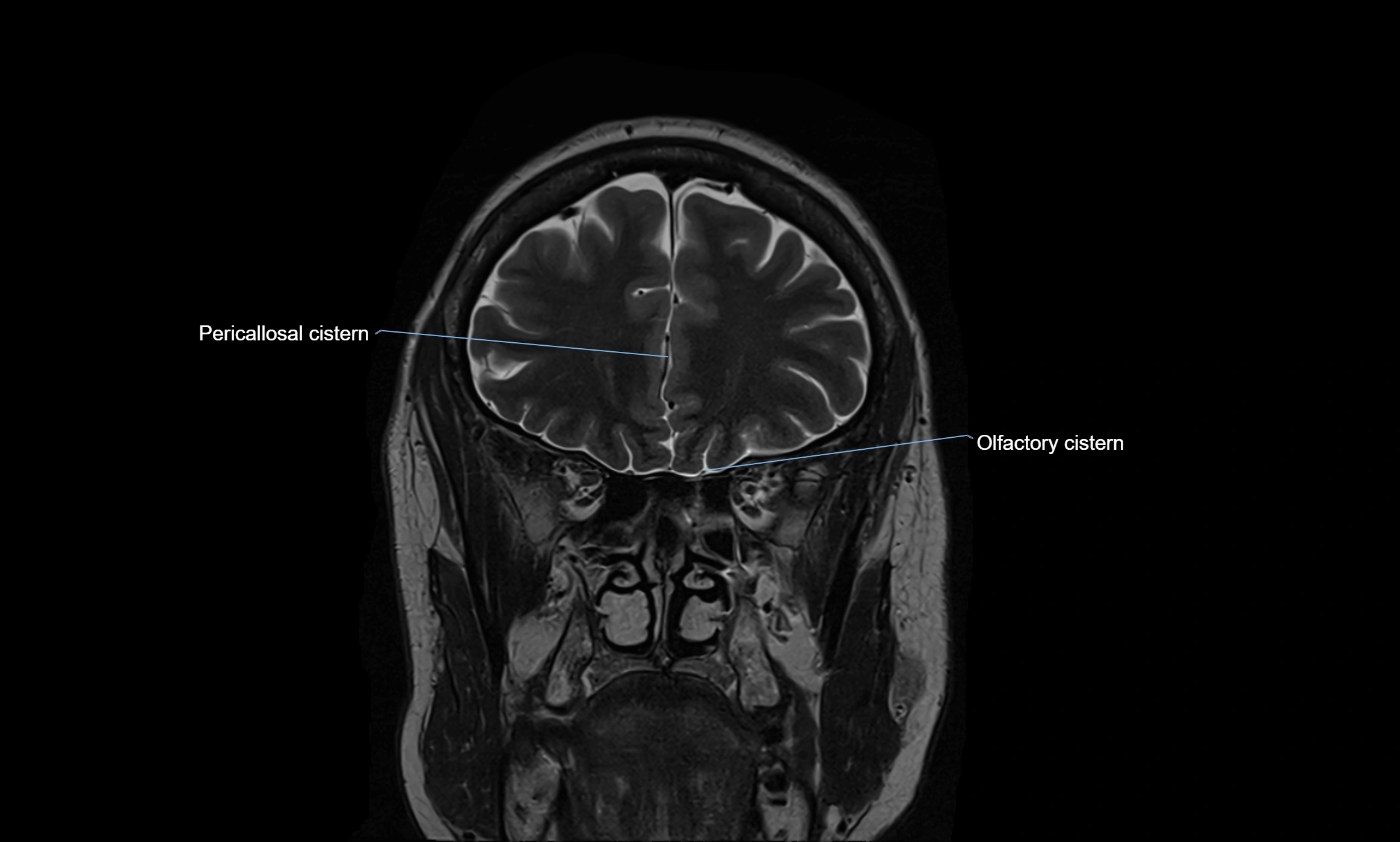
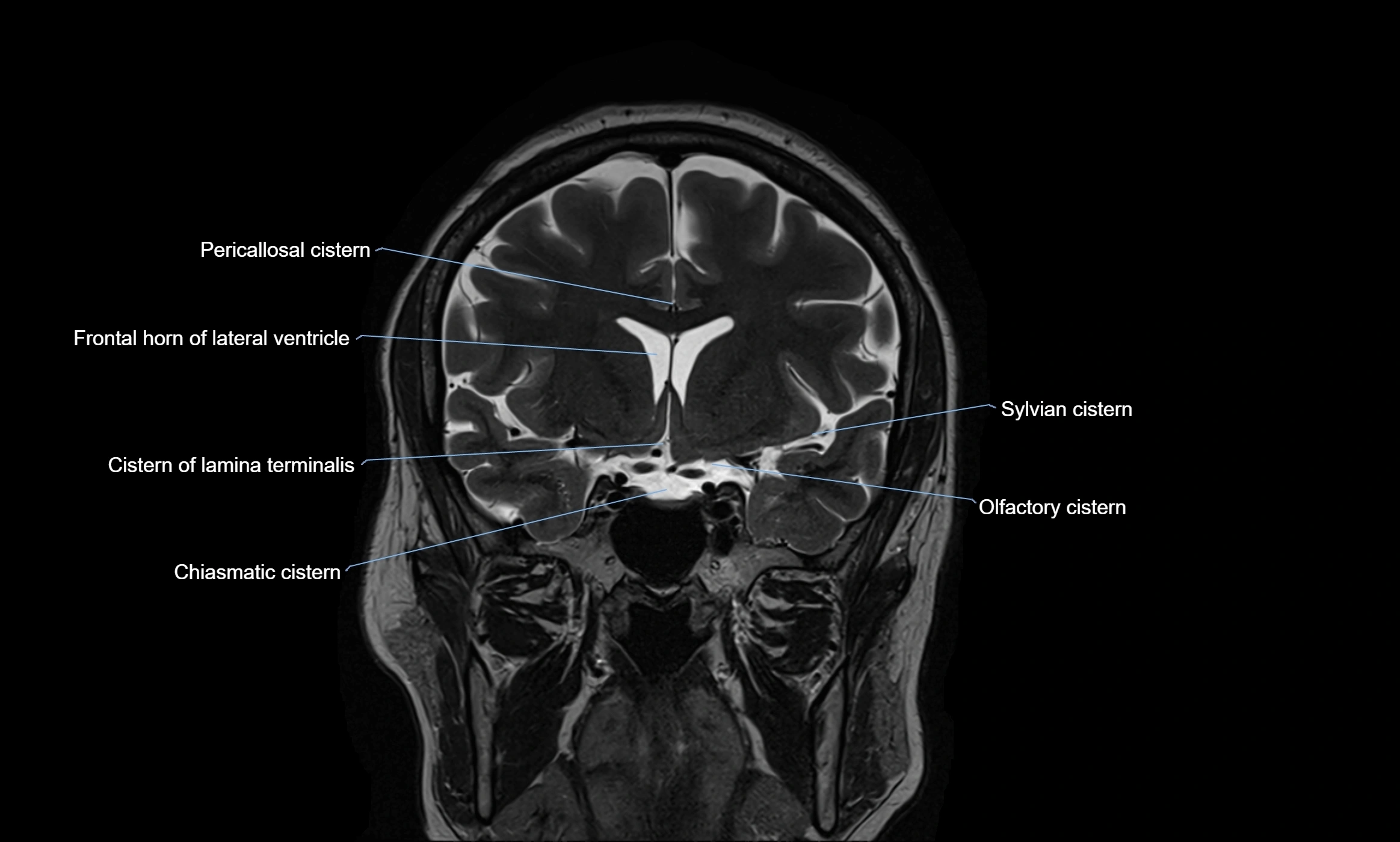
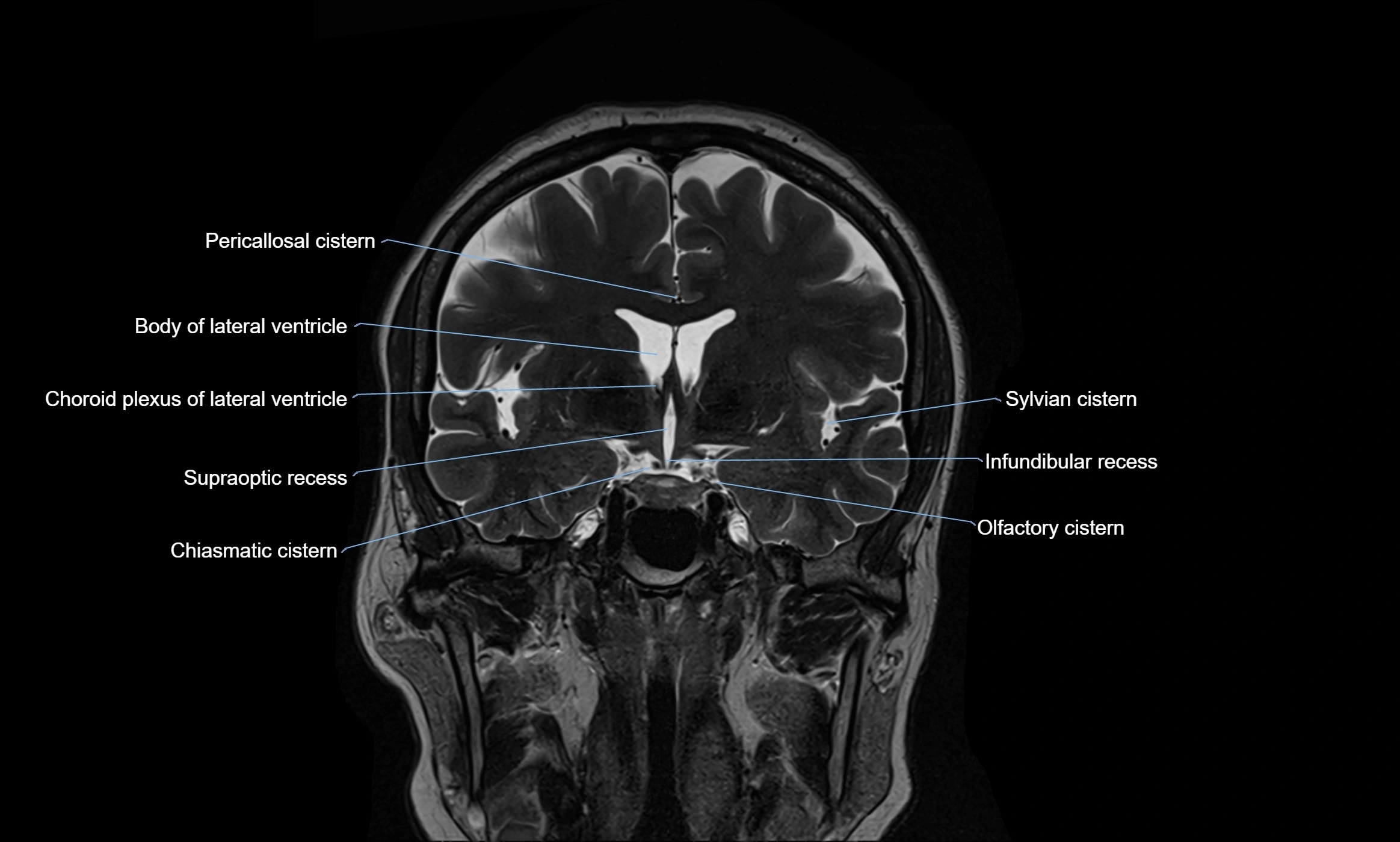
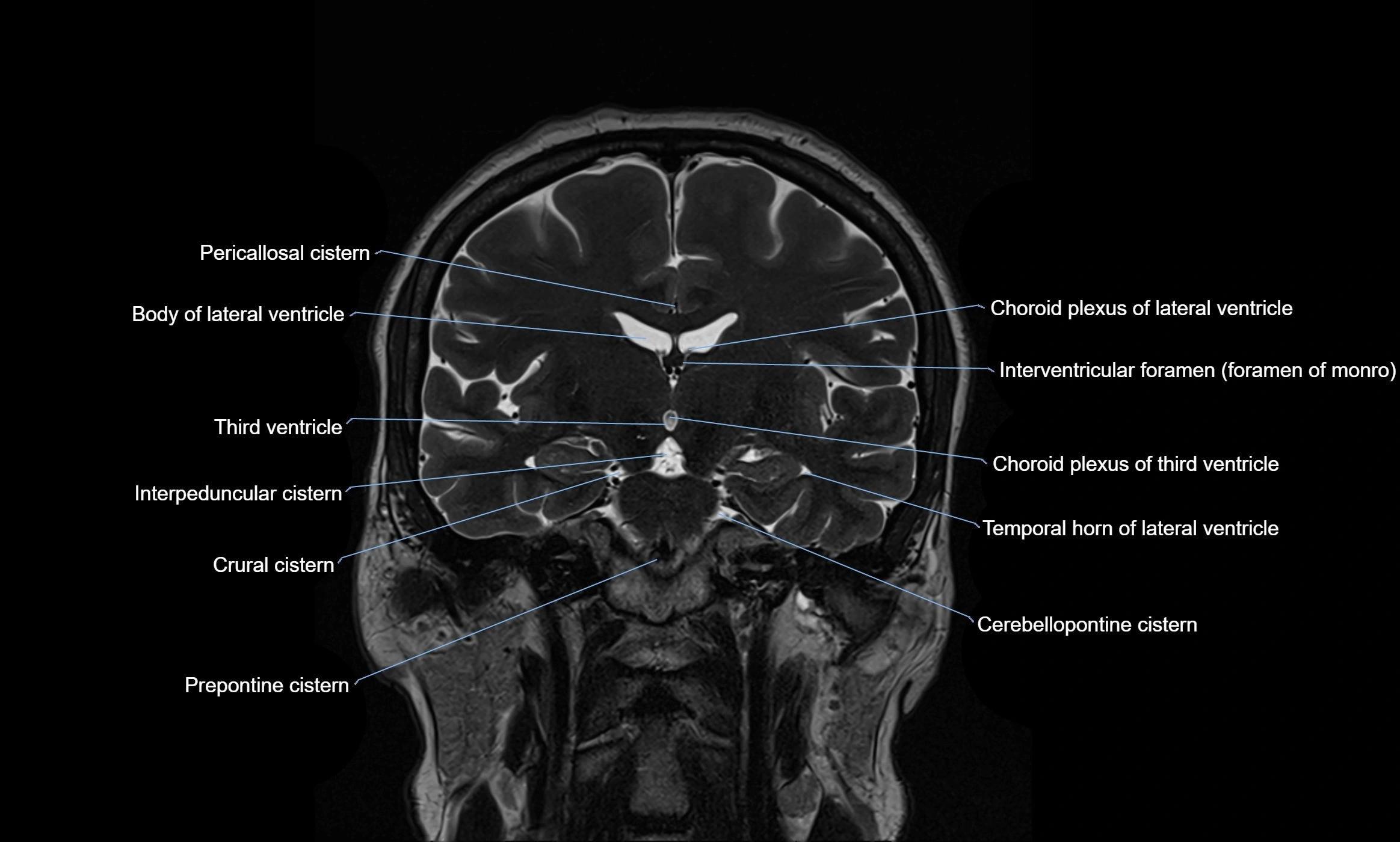
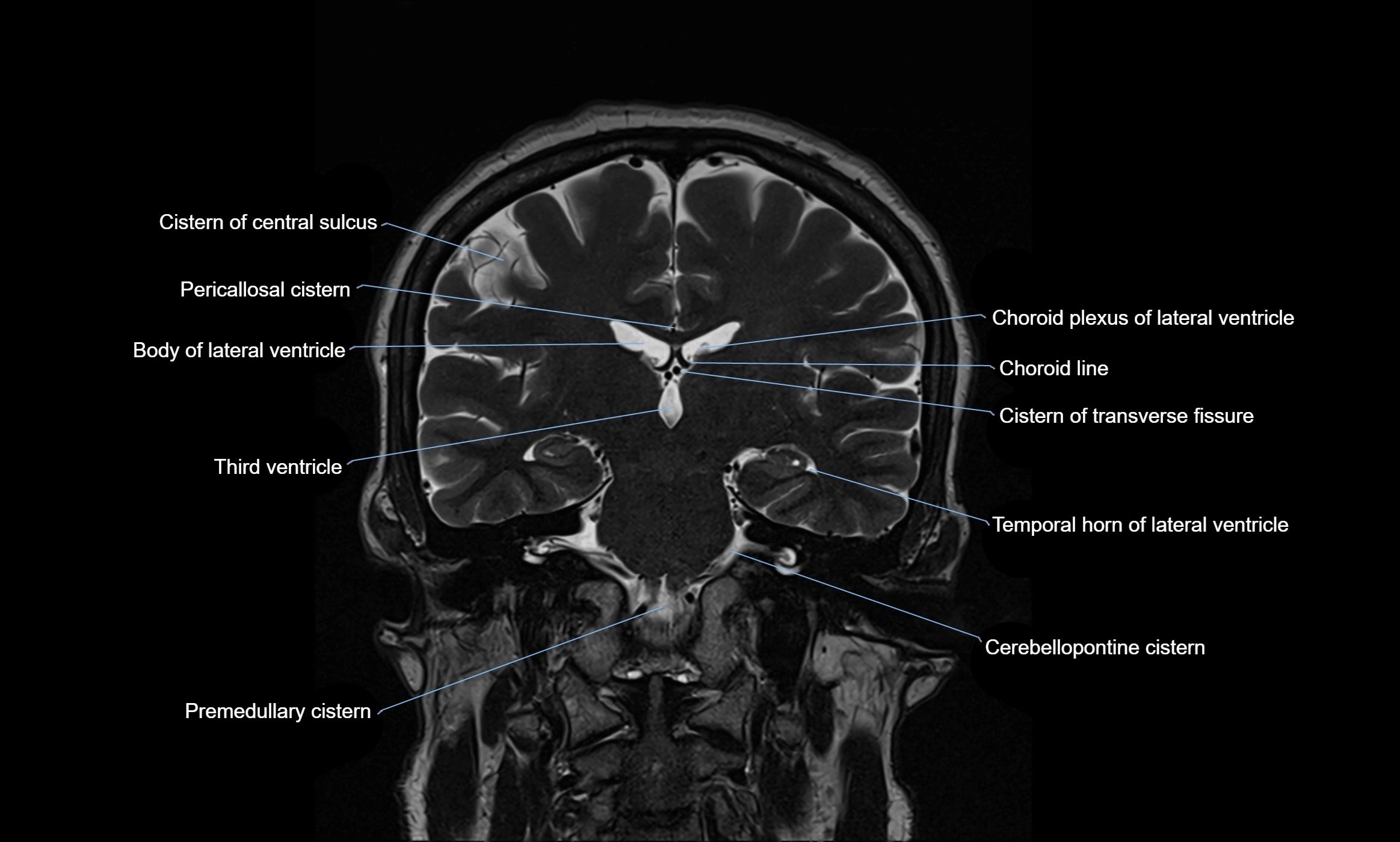
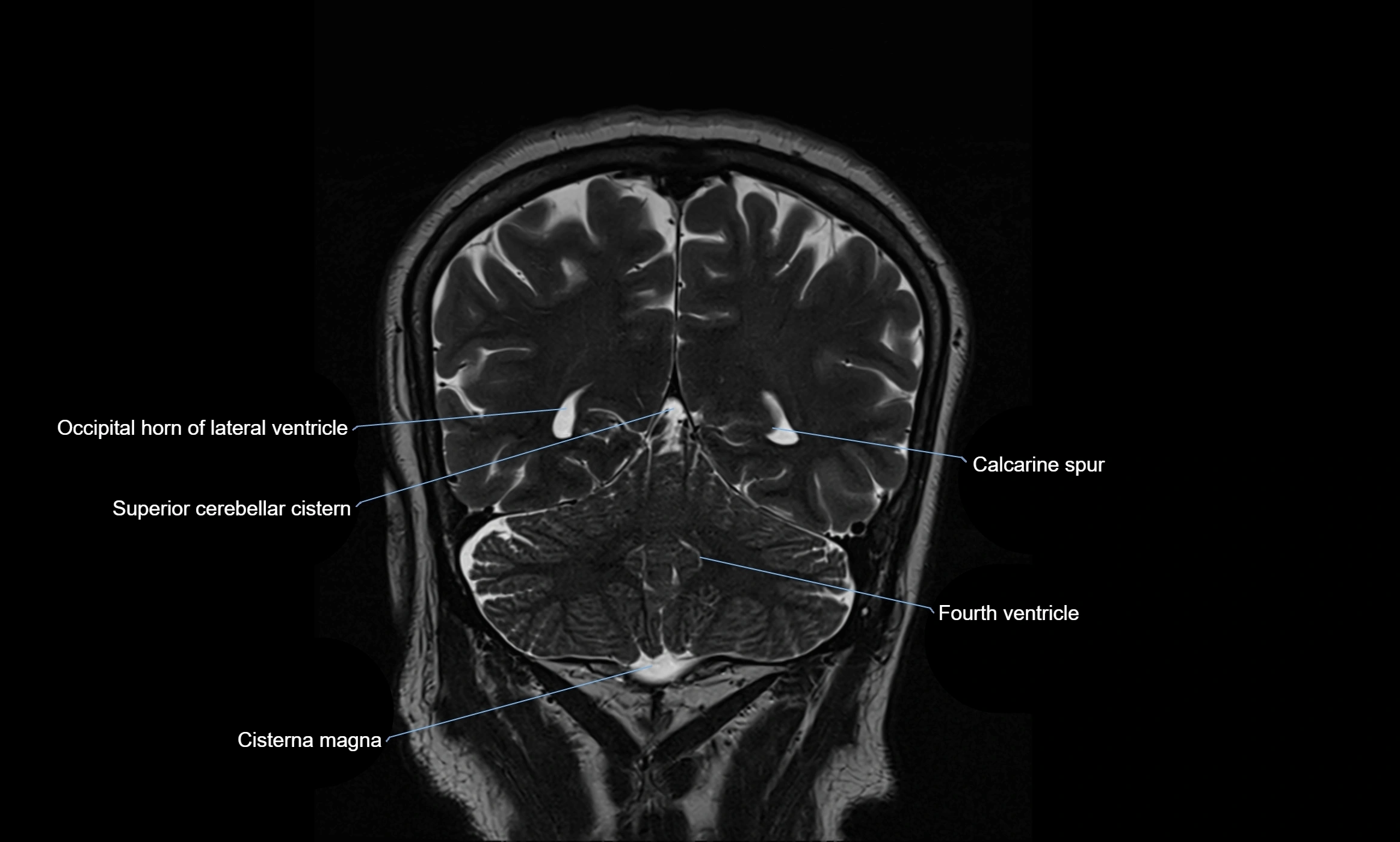
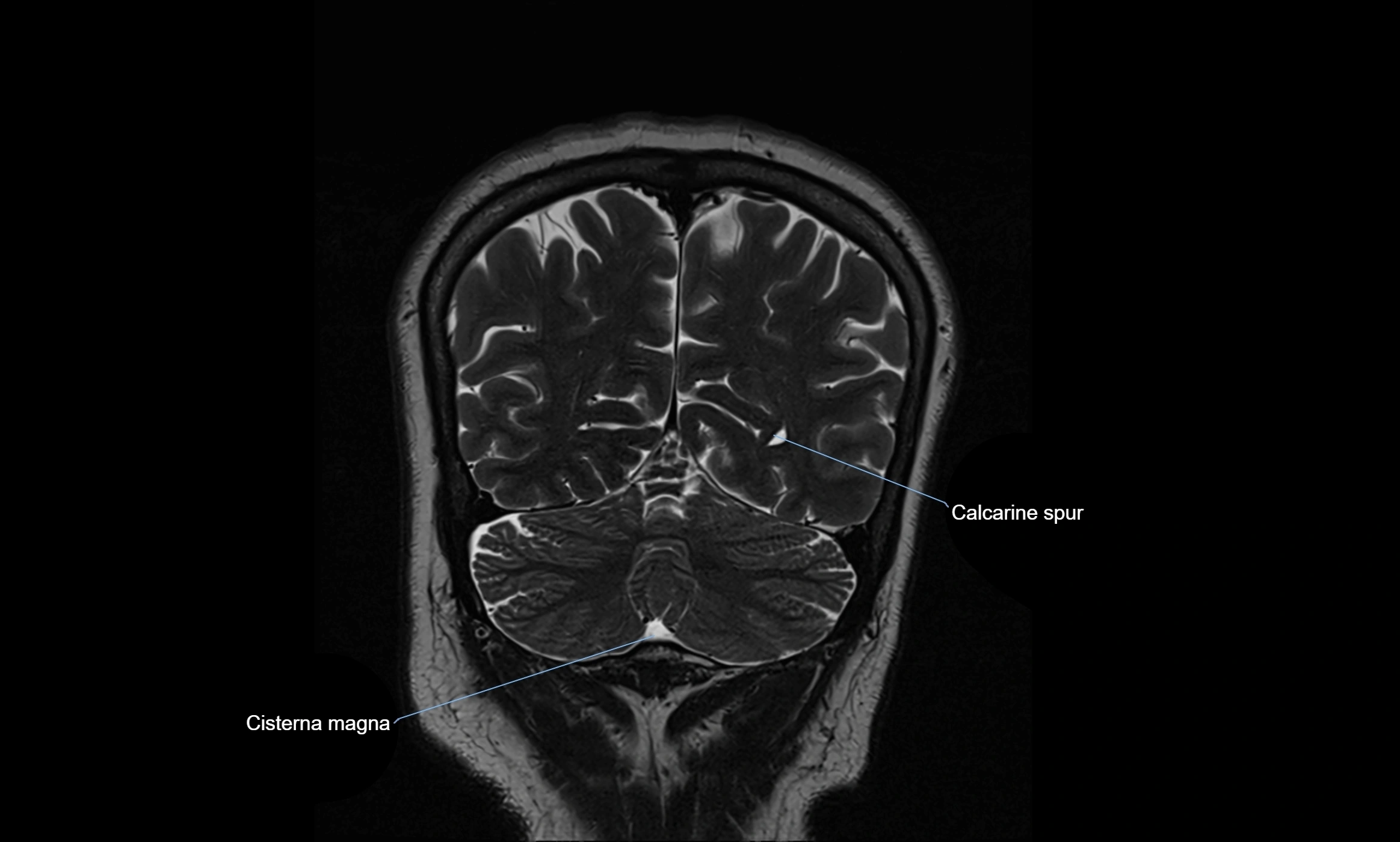
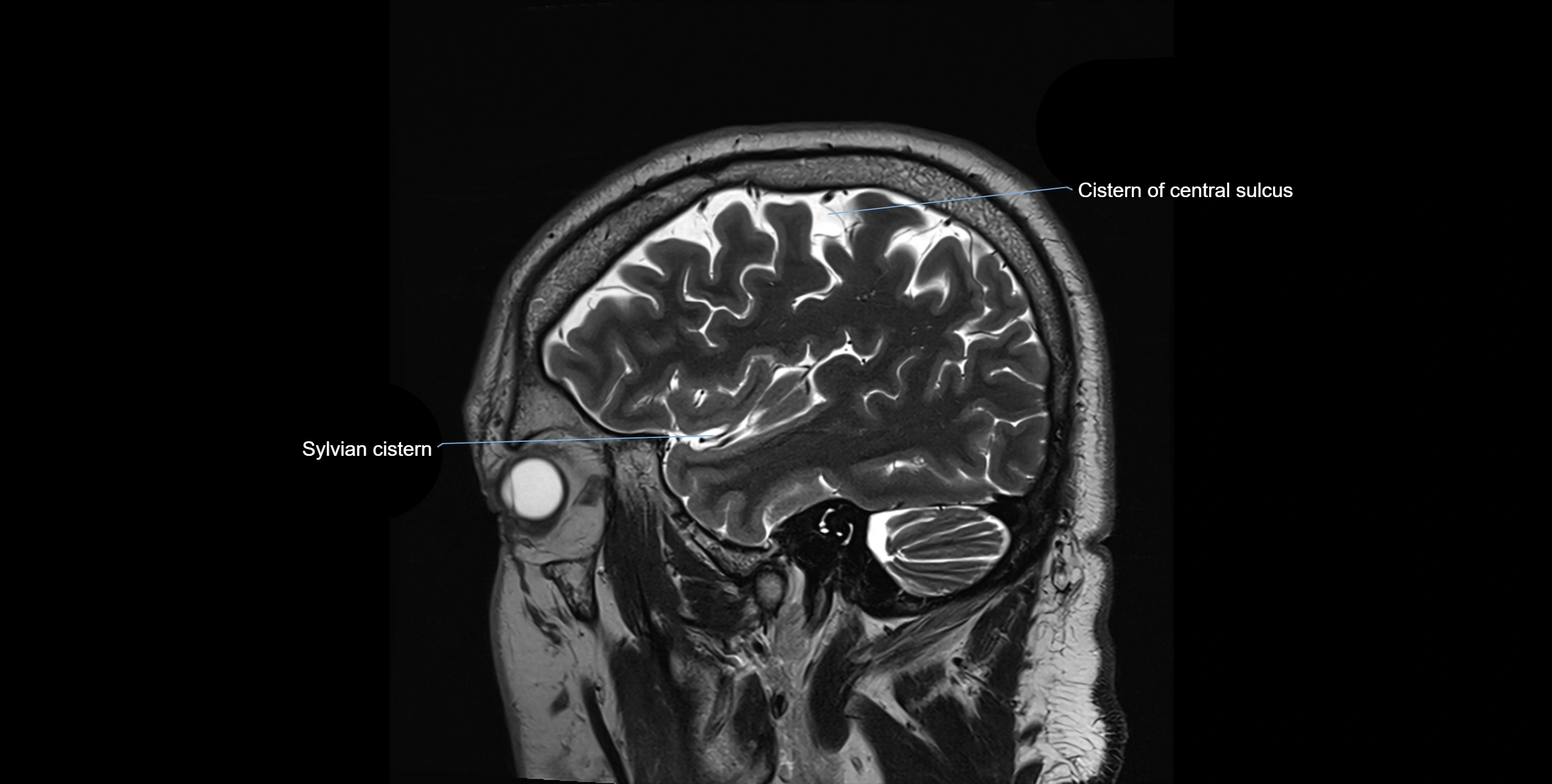
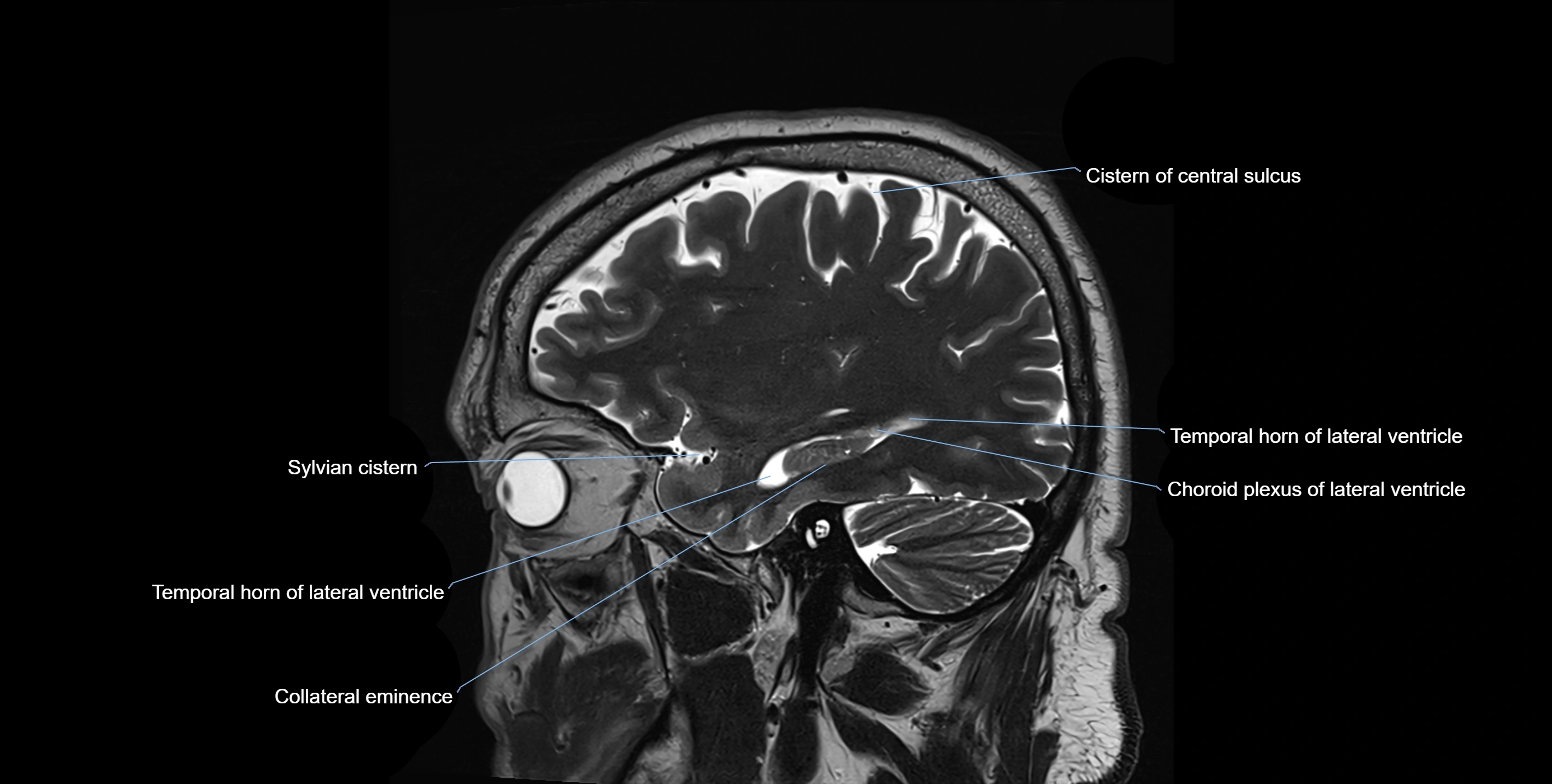
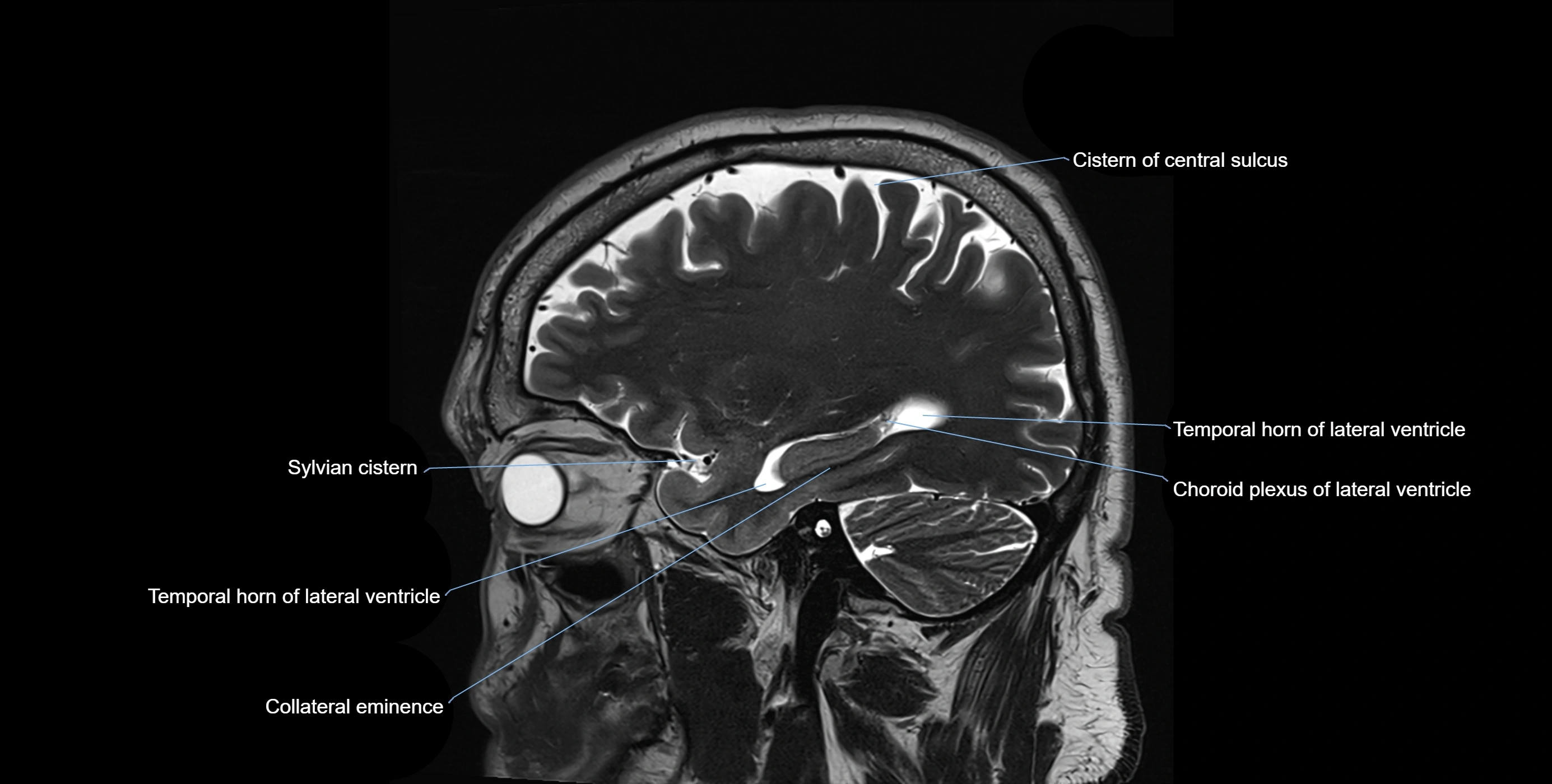
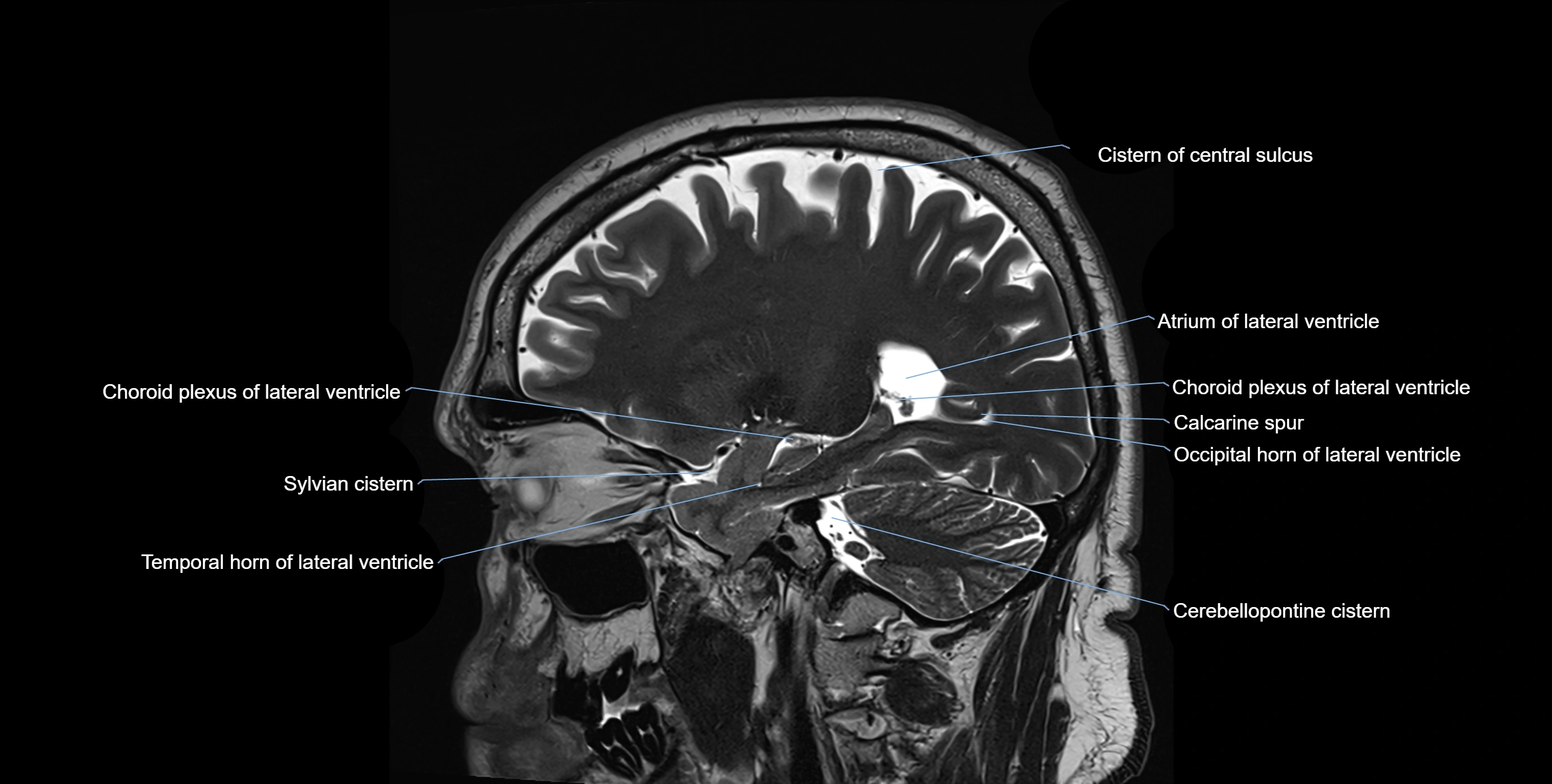
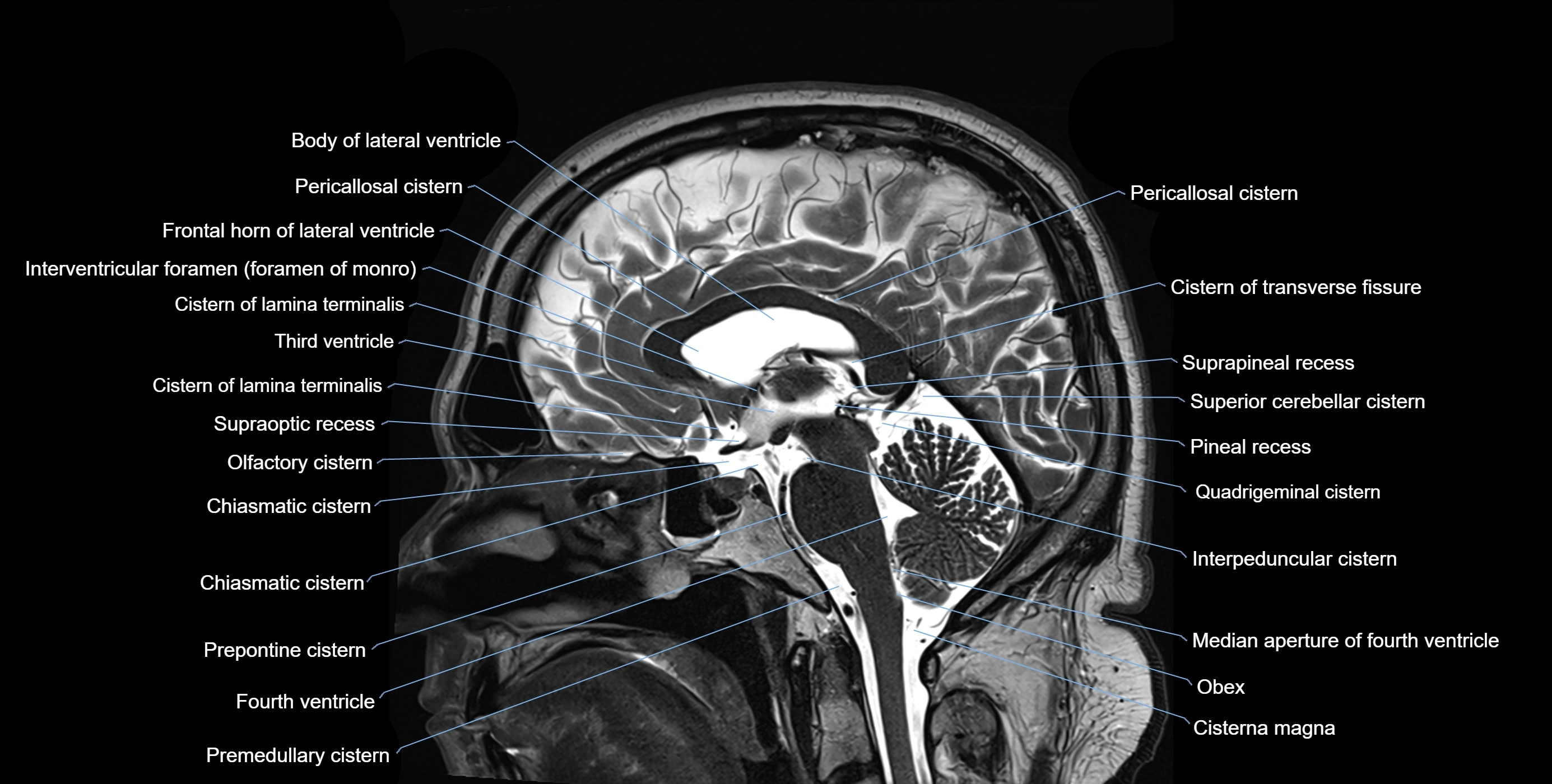
MRI images

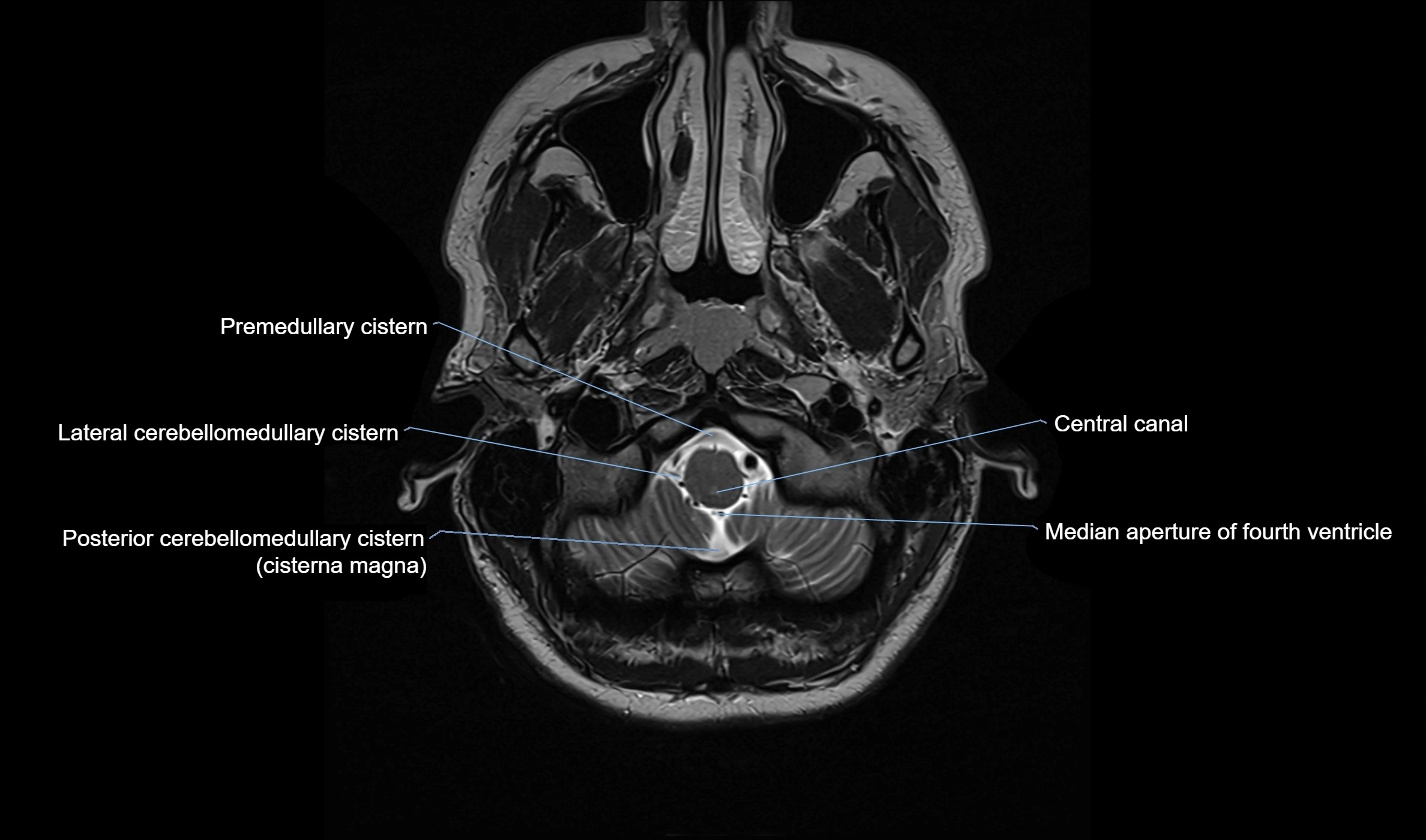
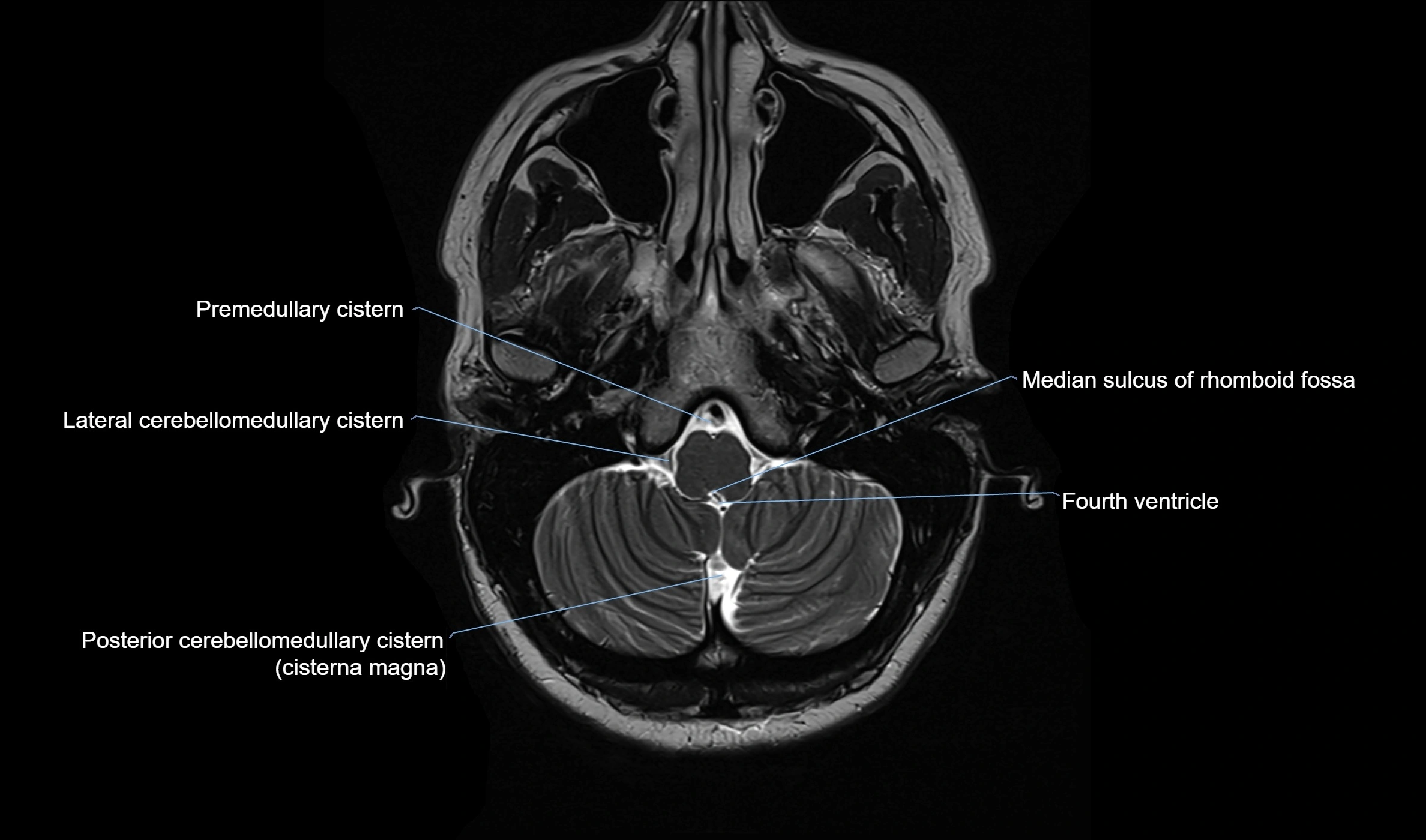
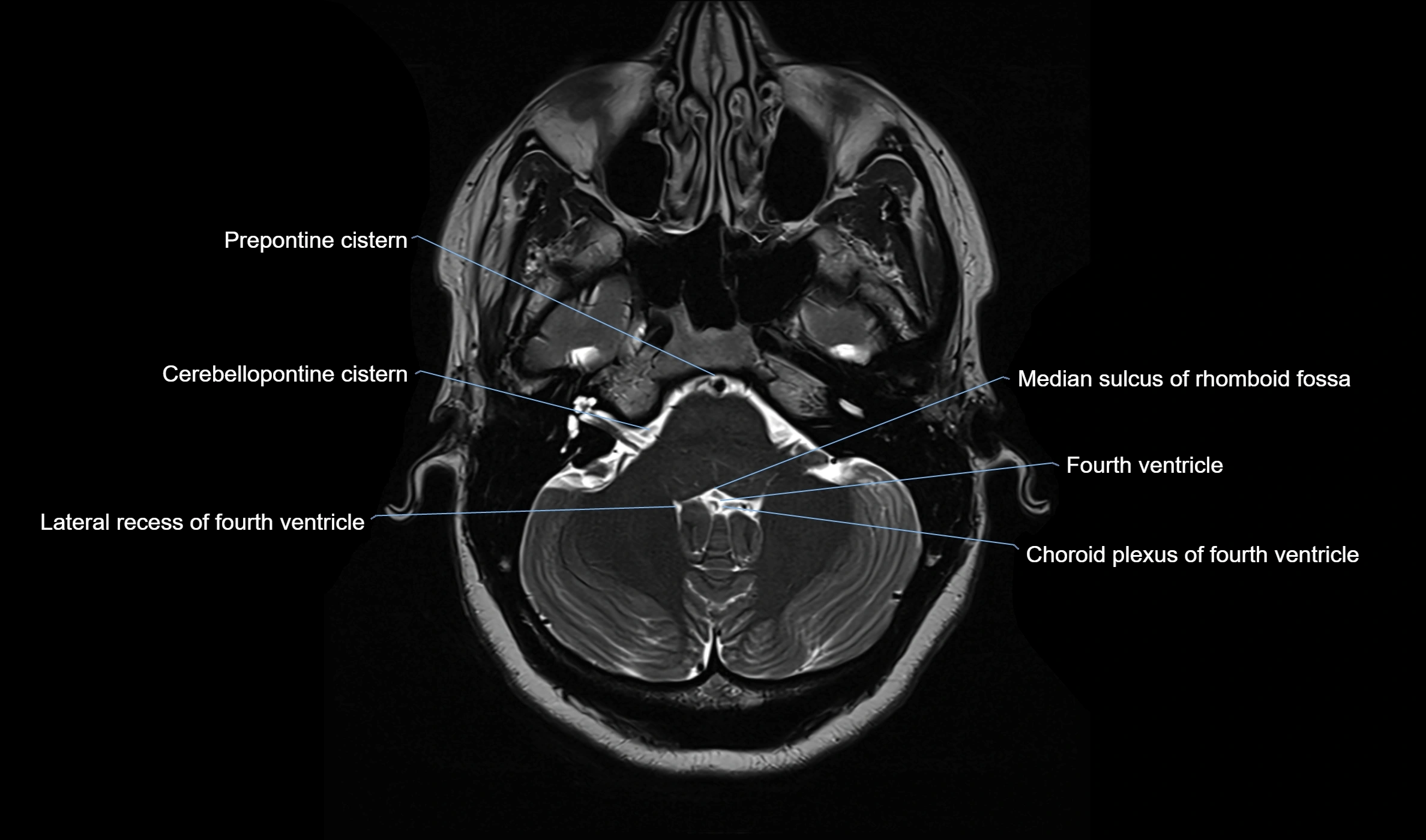
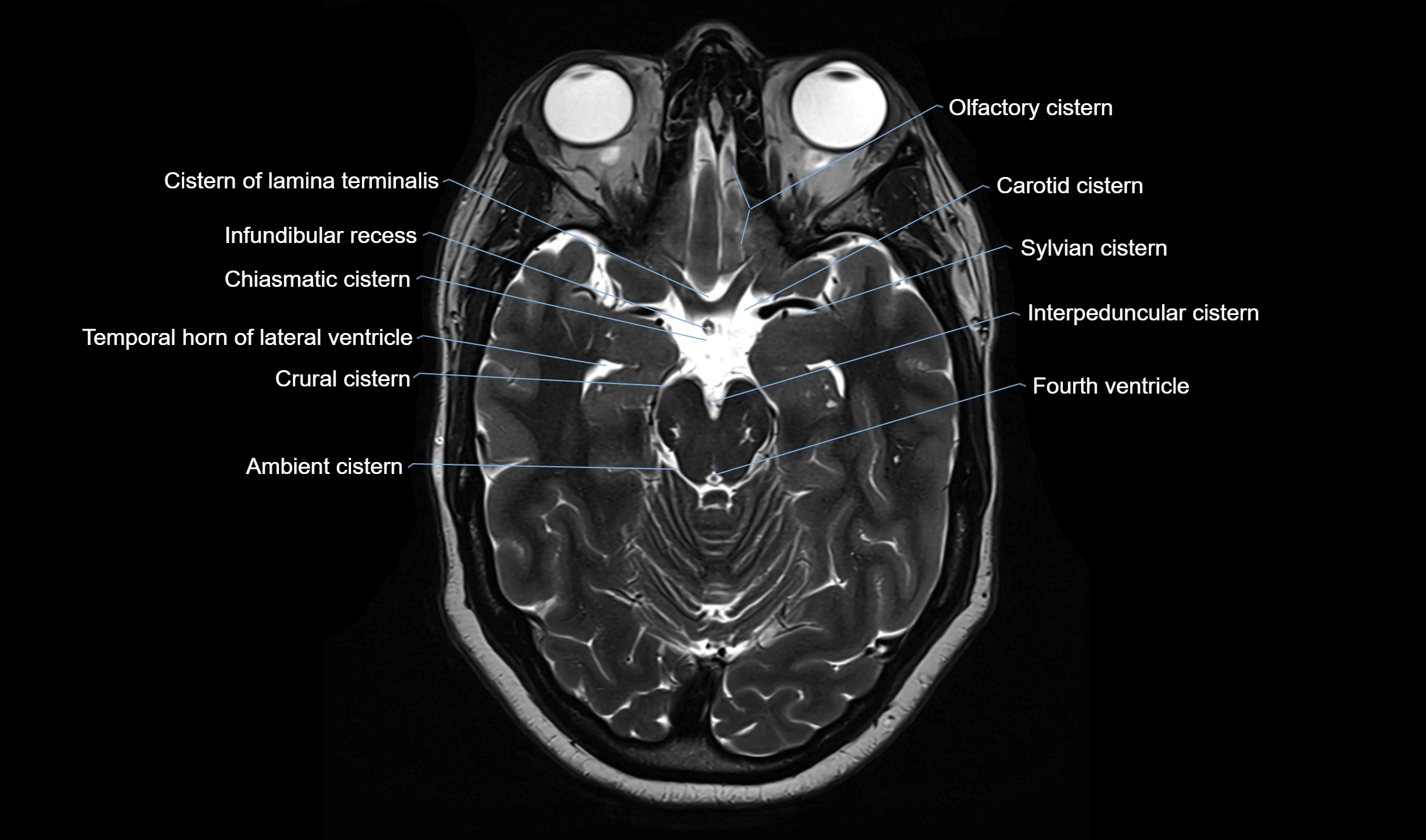
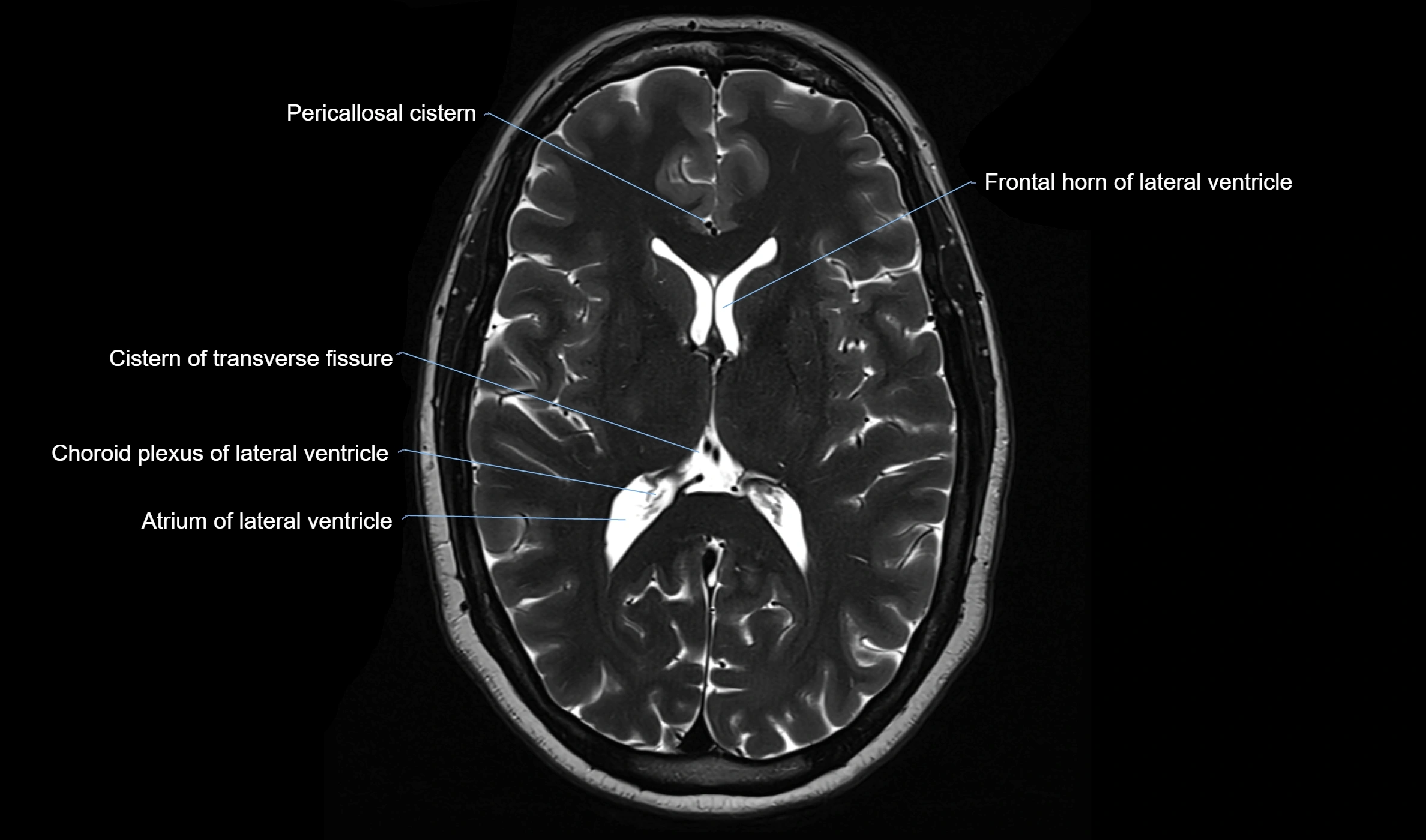
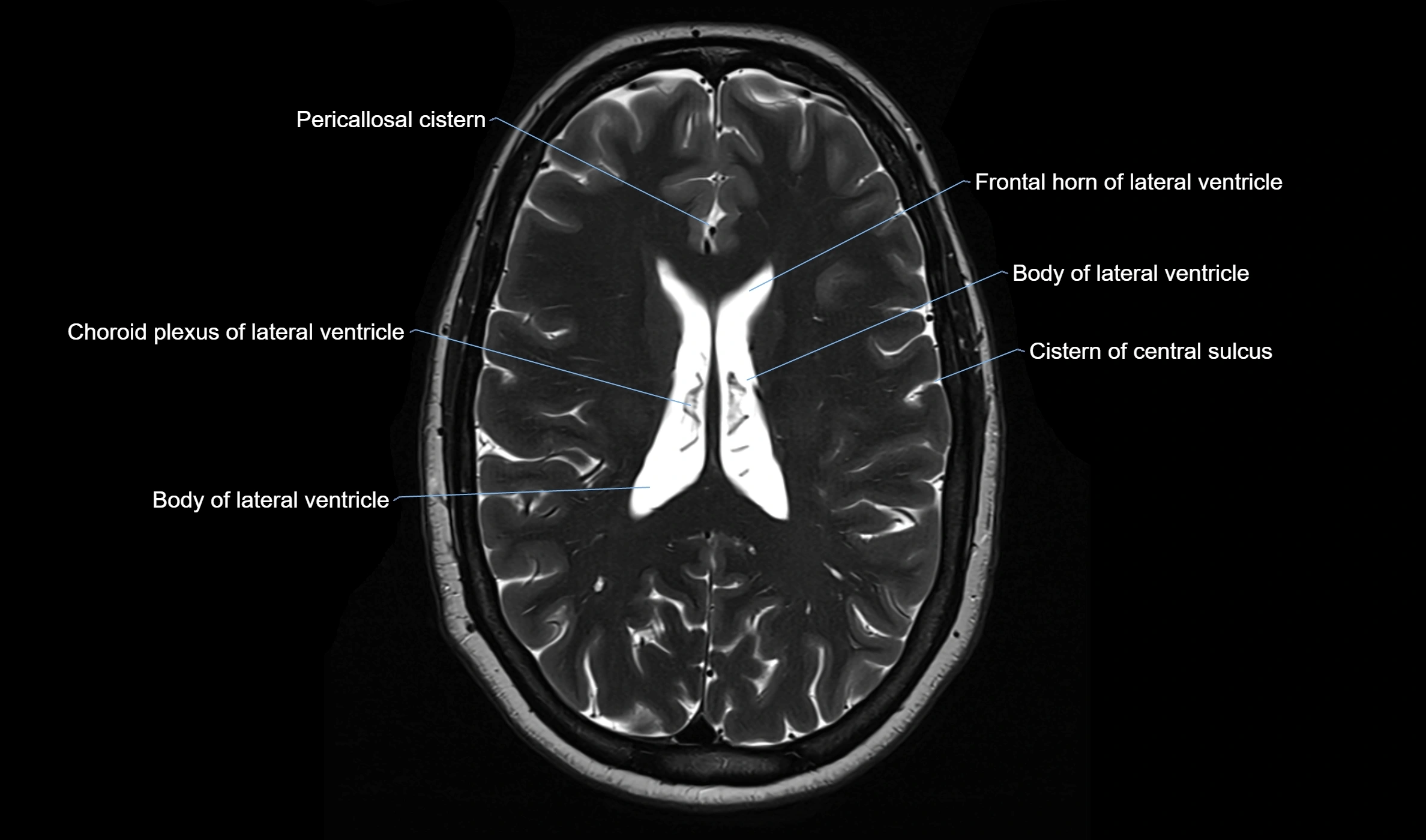
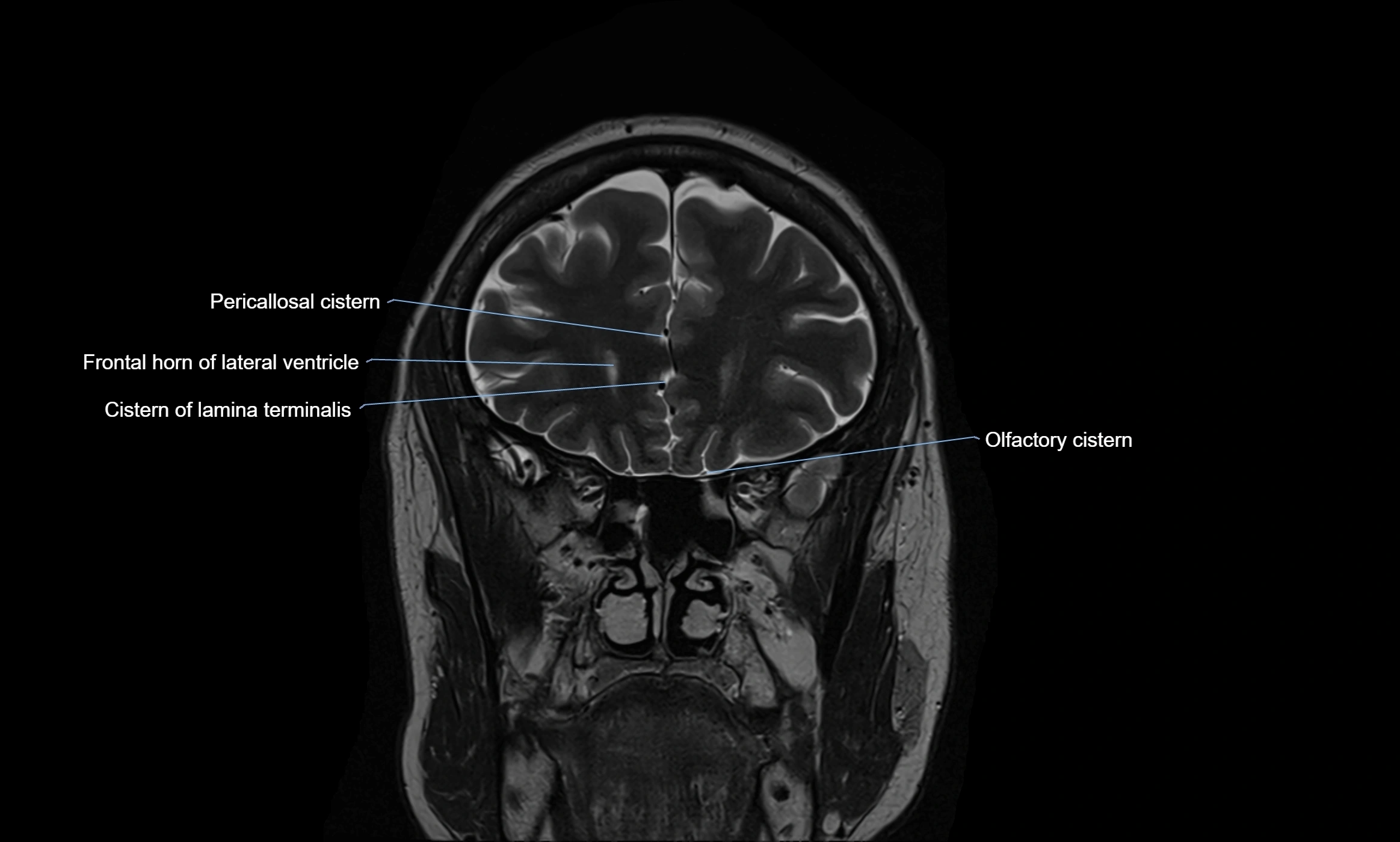
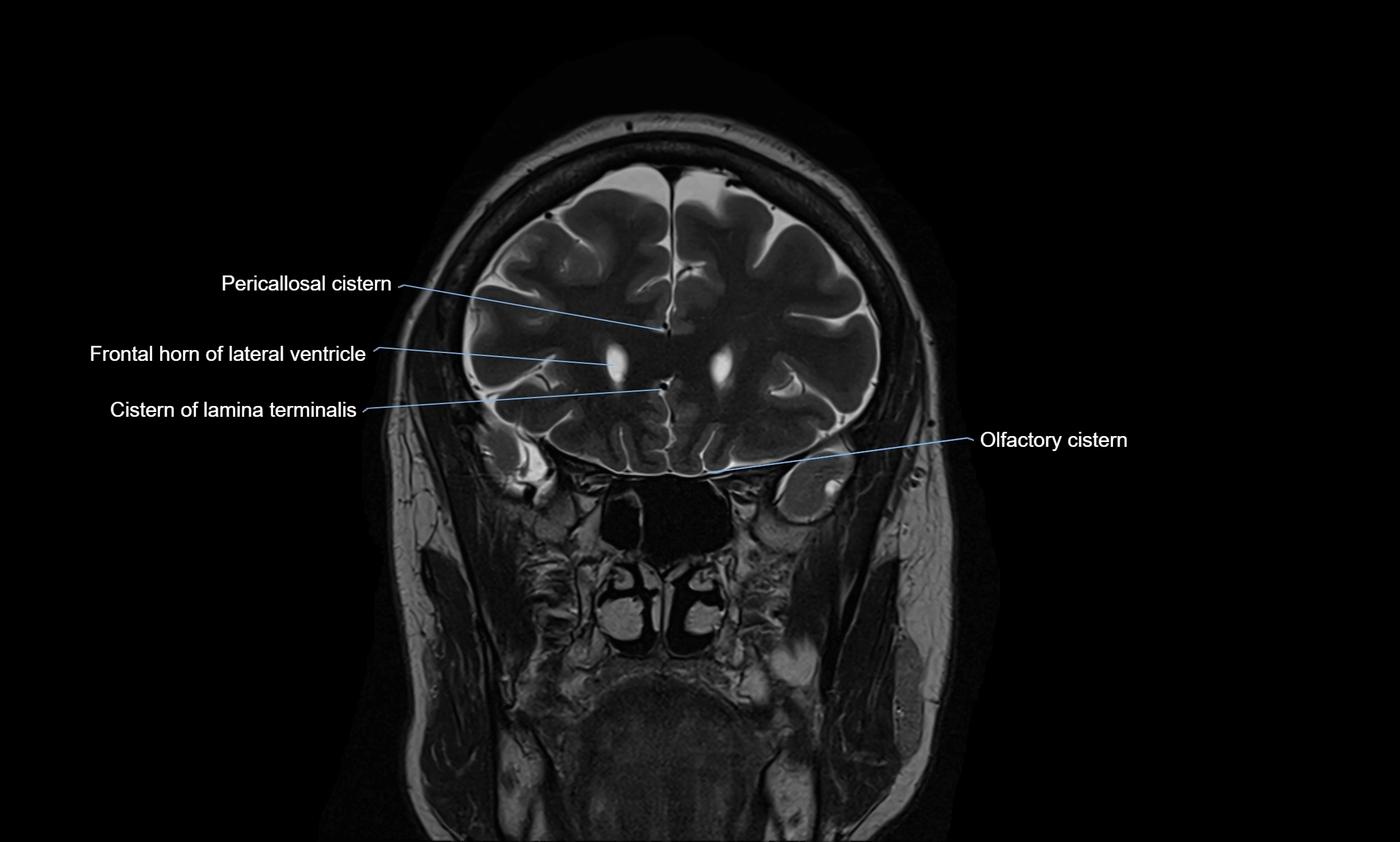
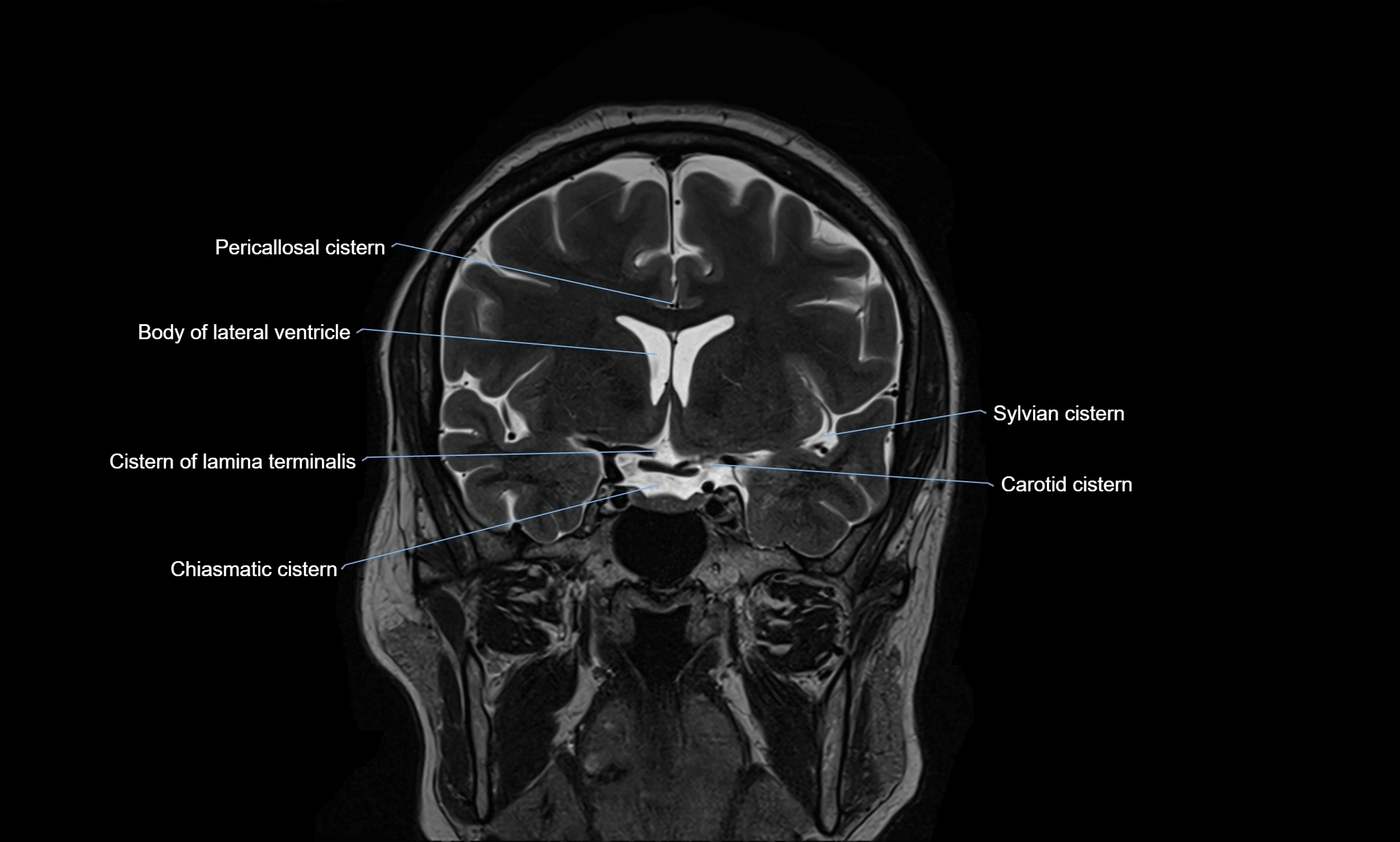
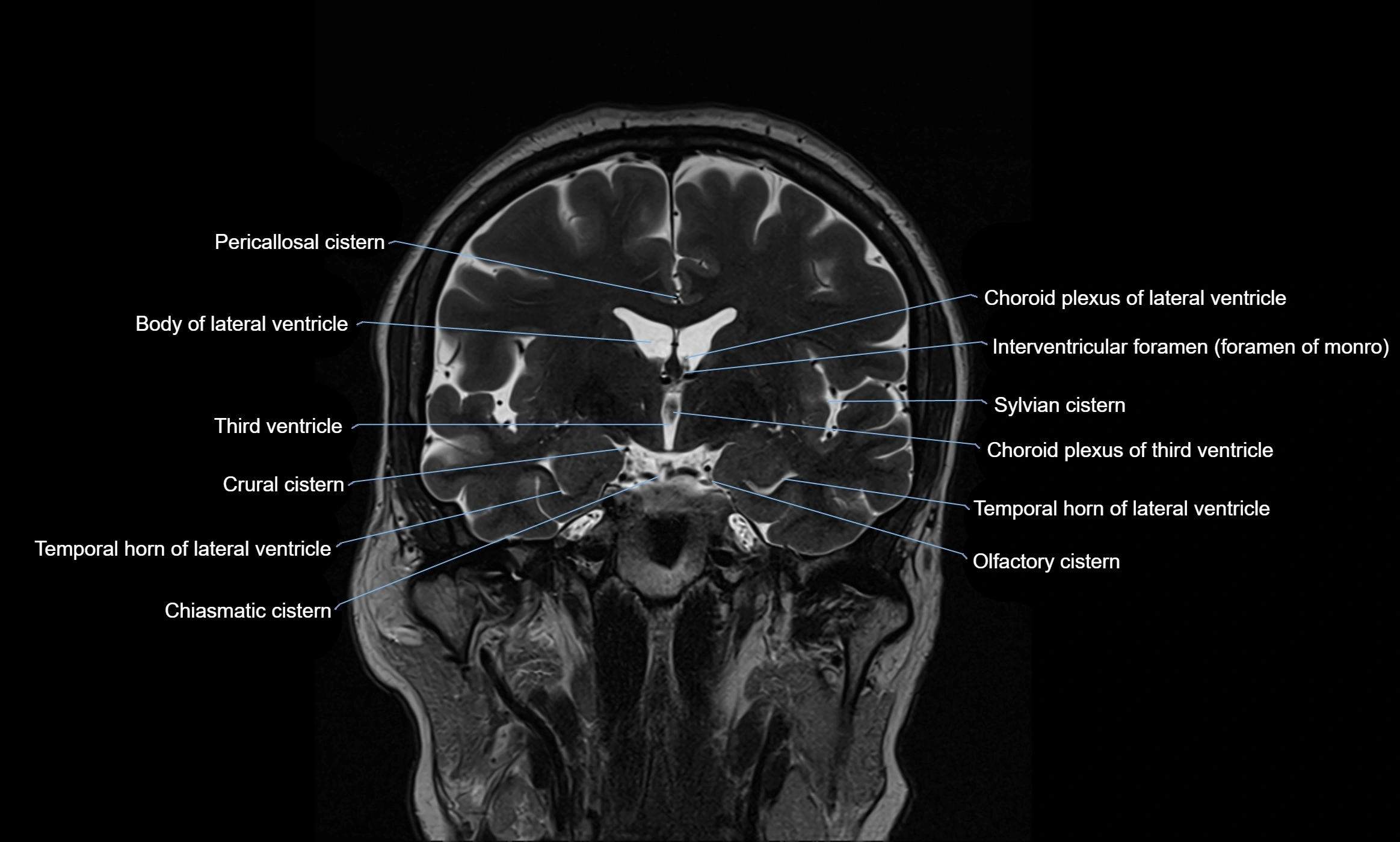
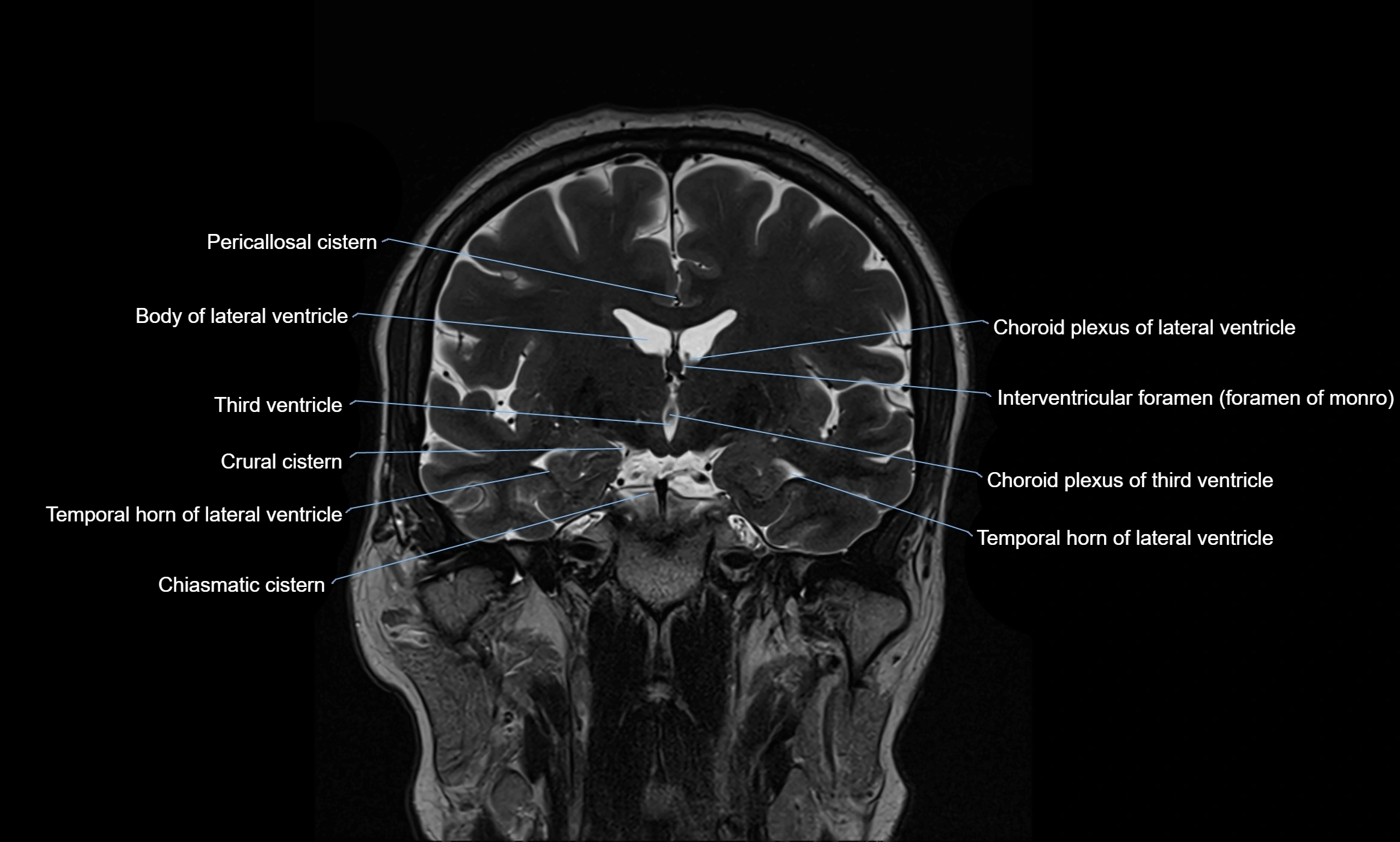
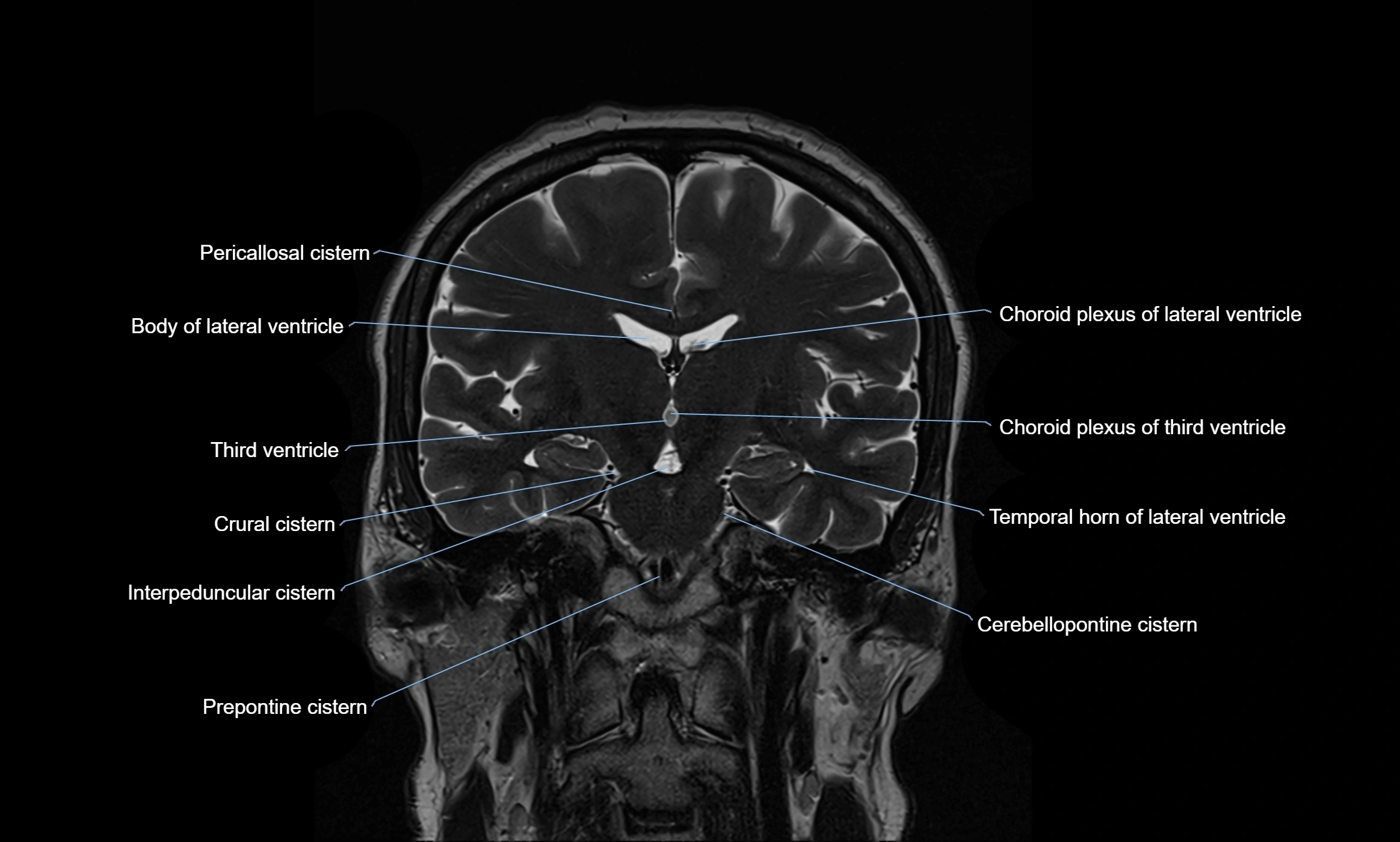
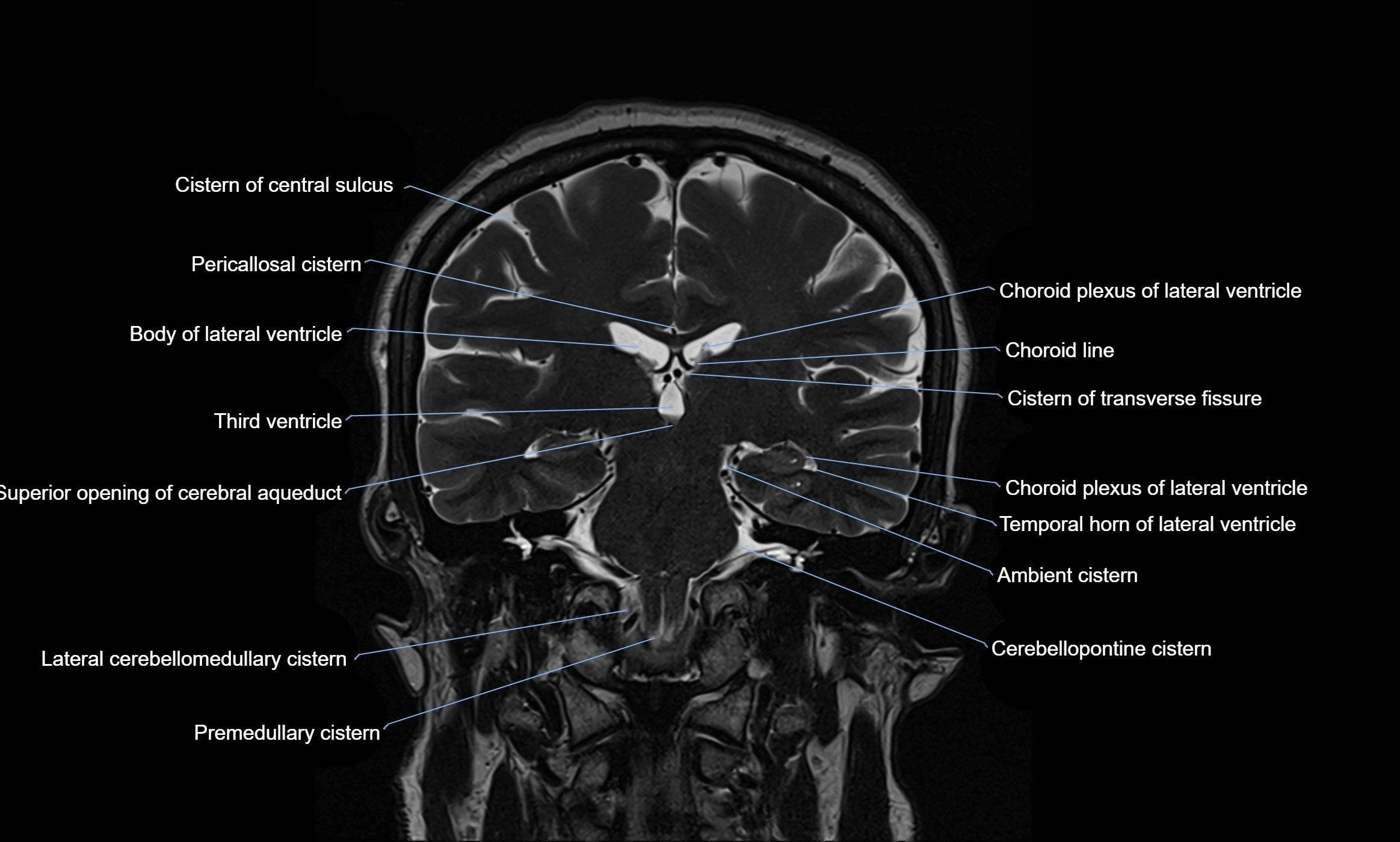
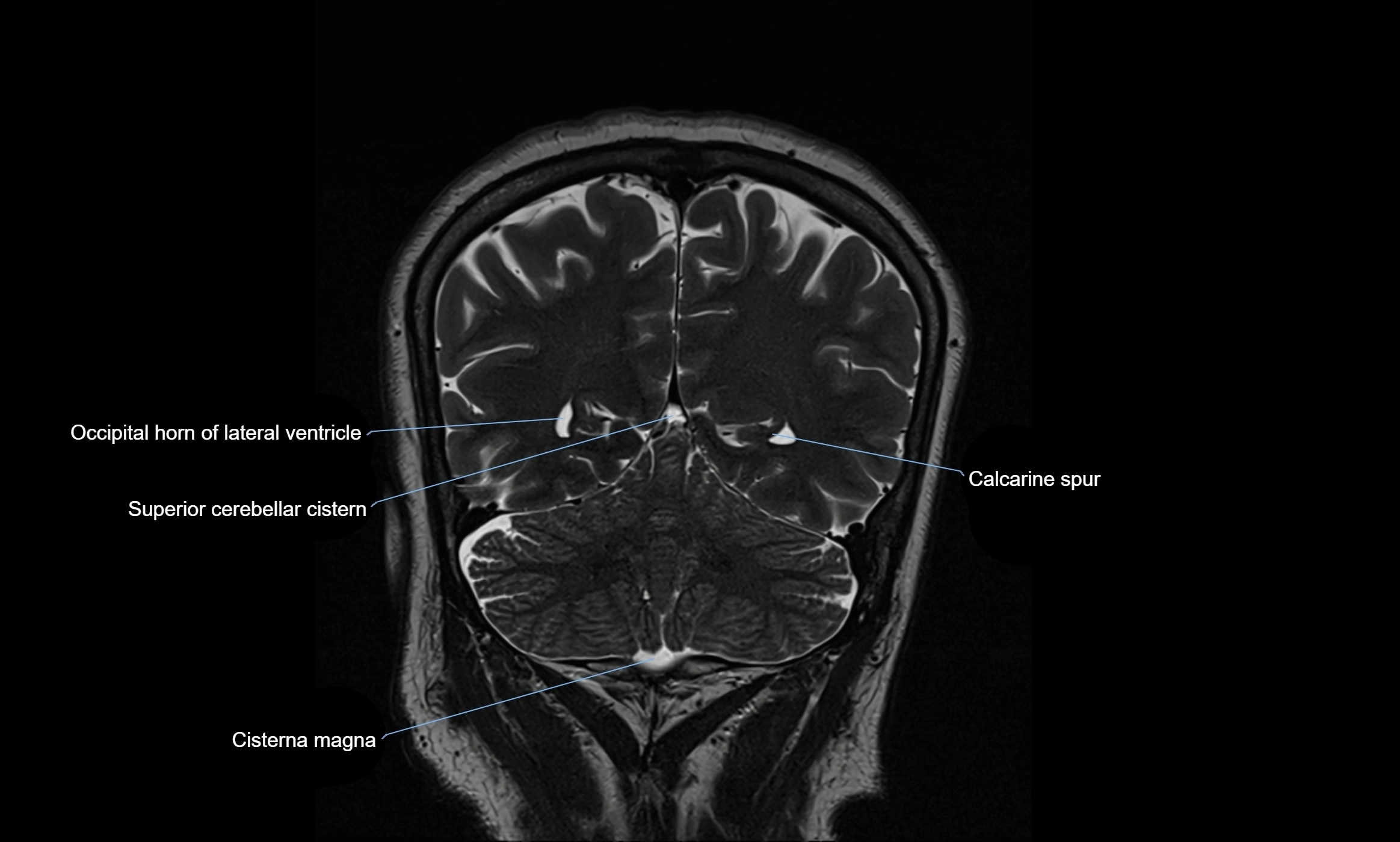
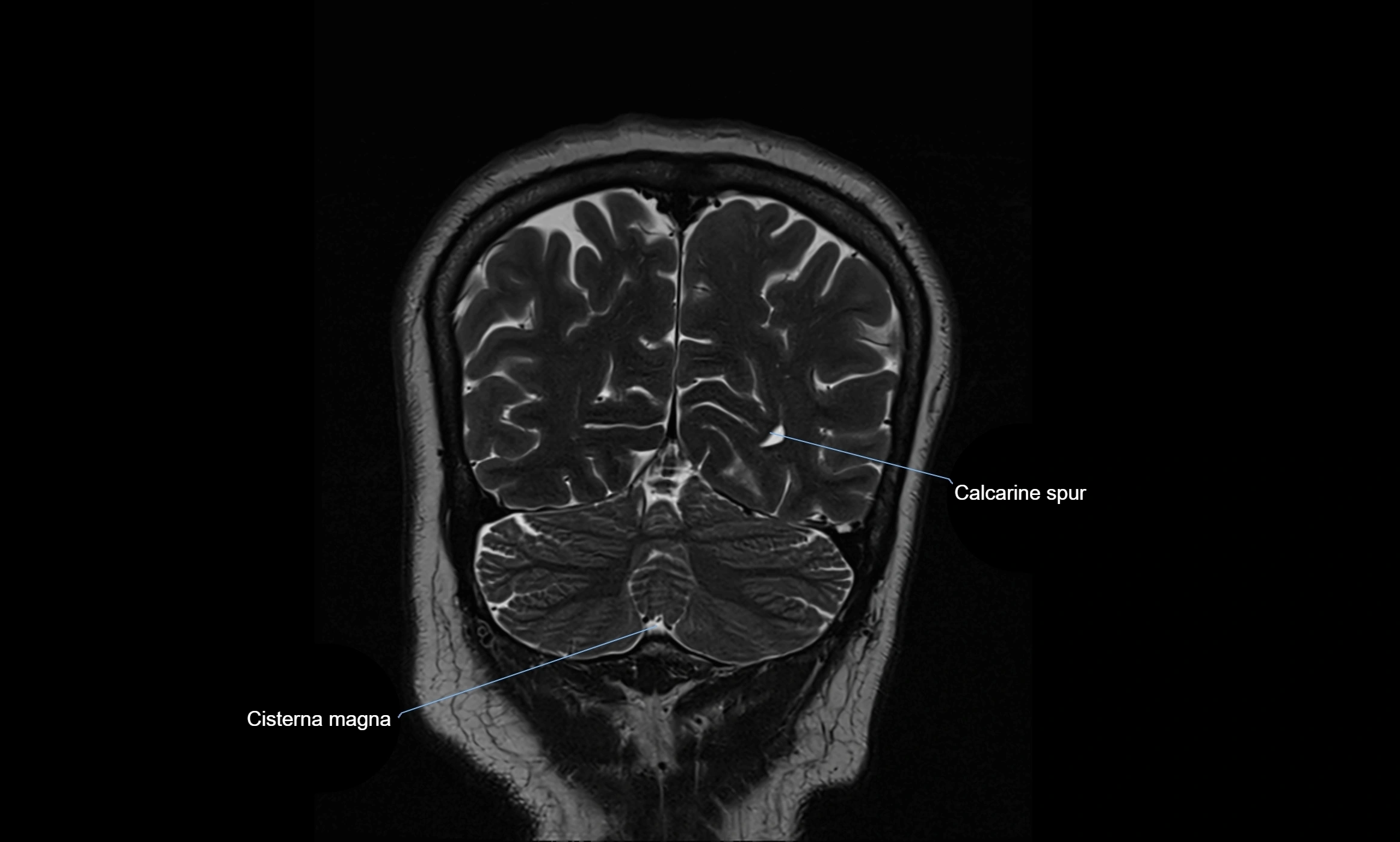
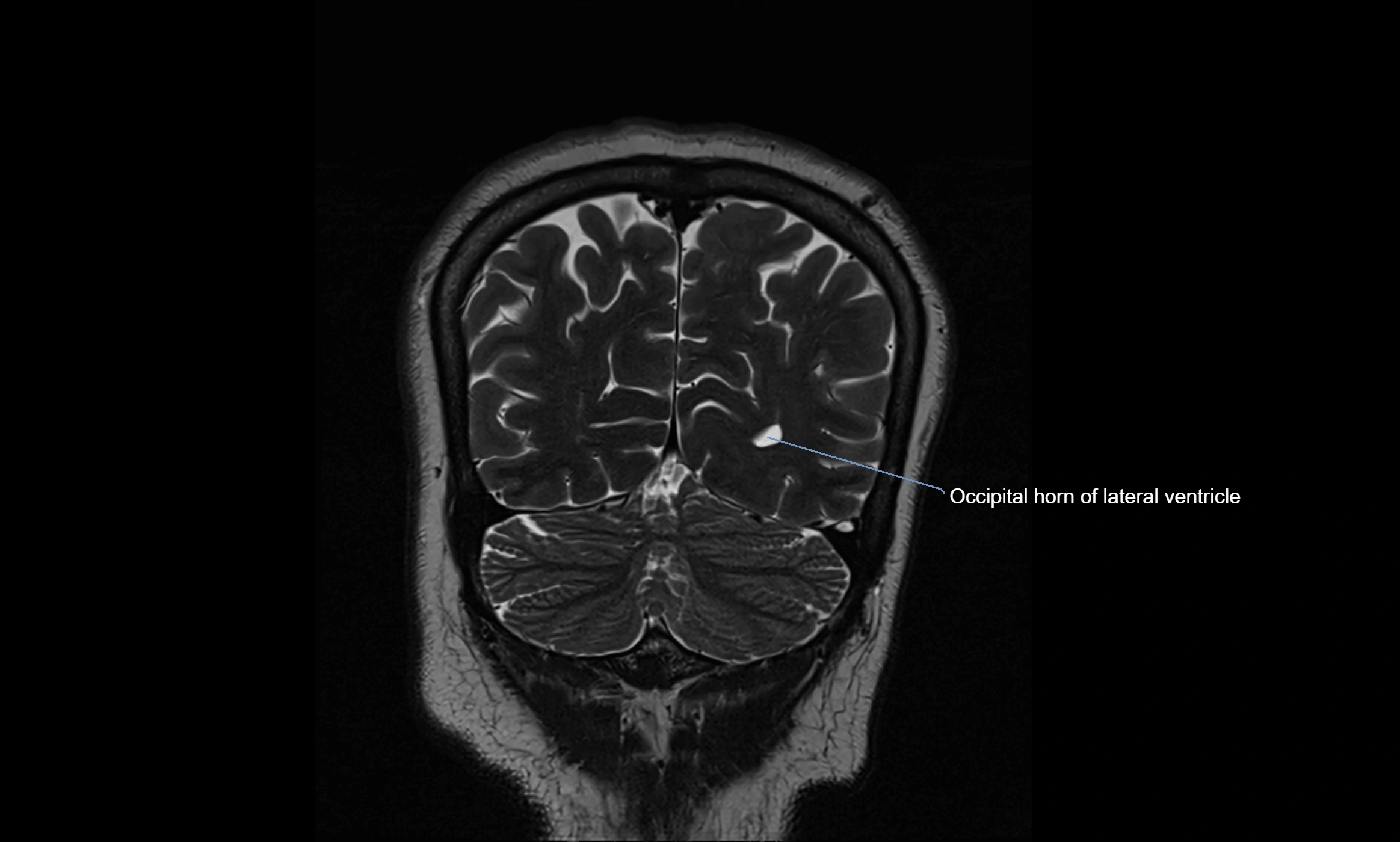
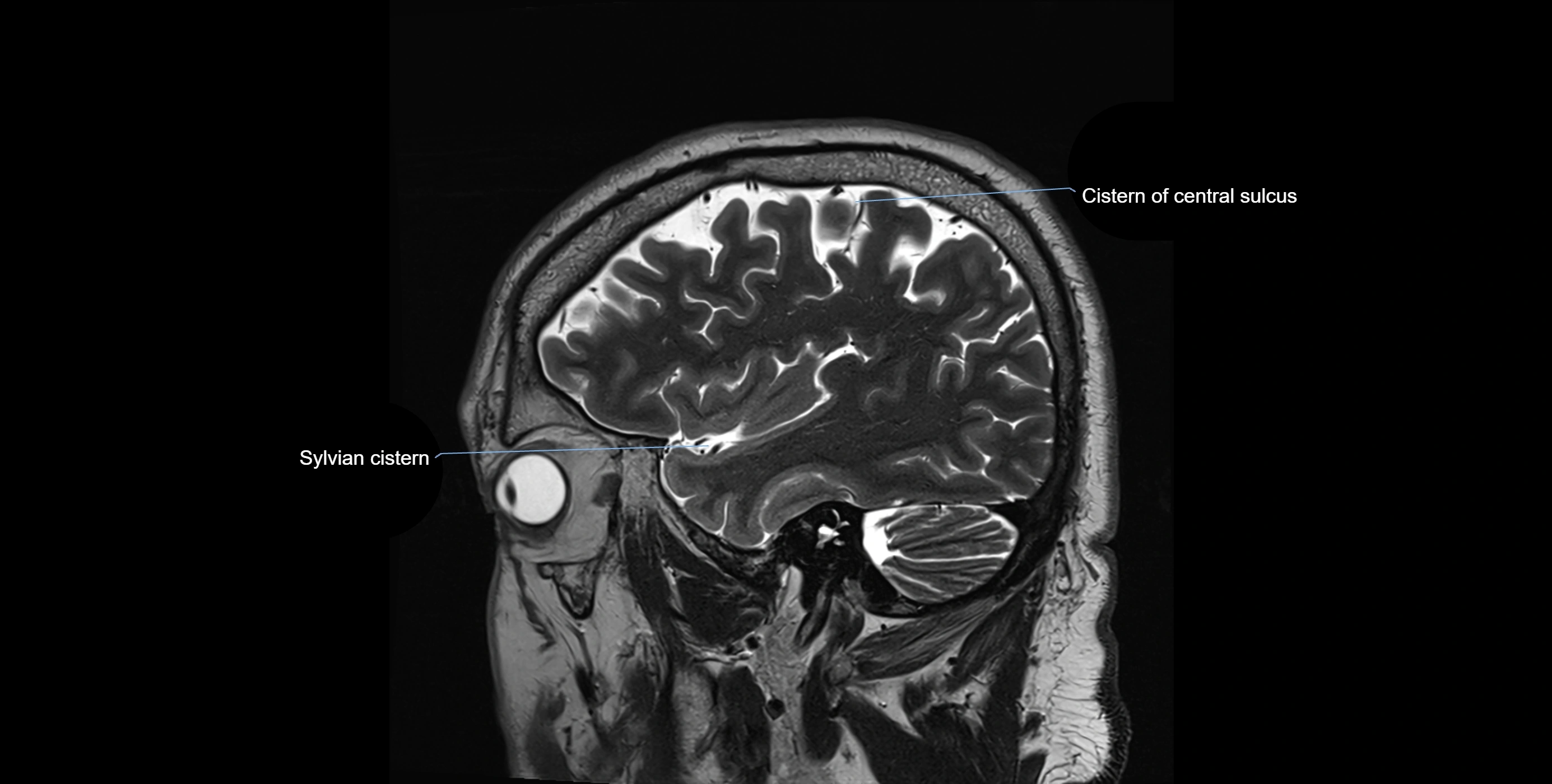
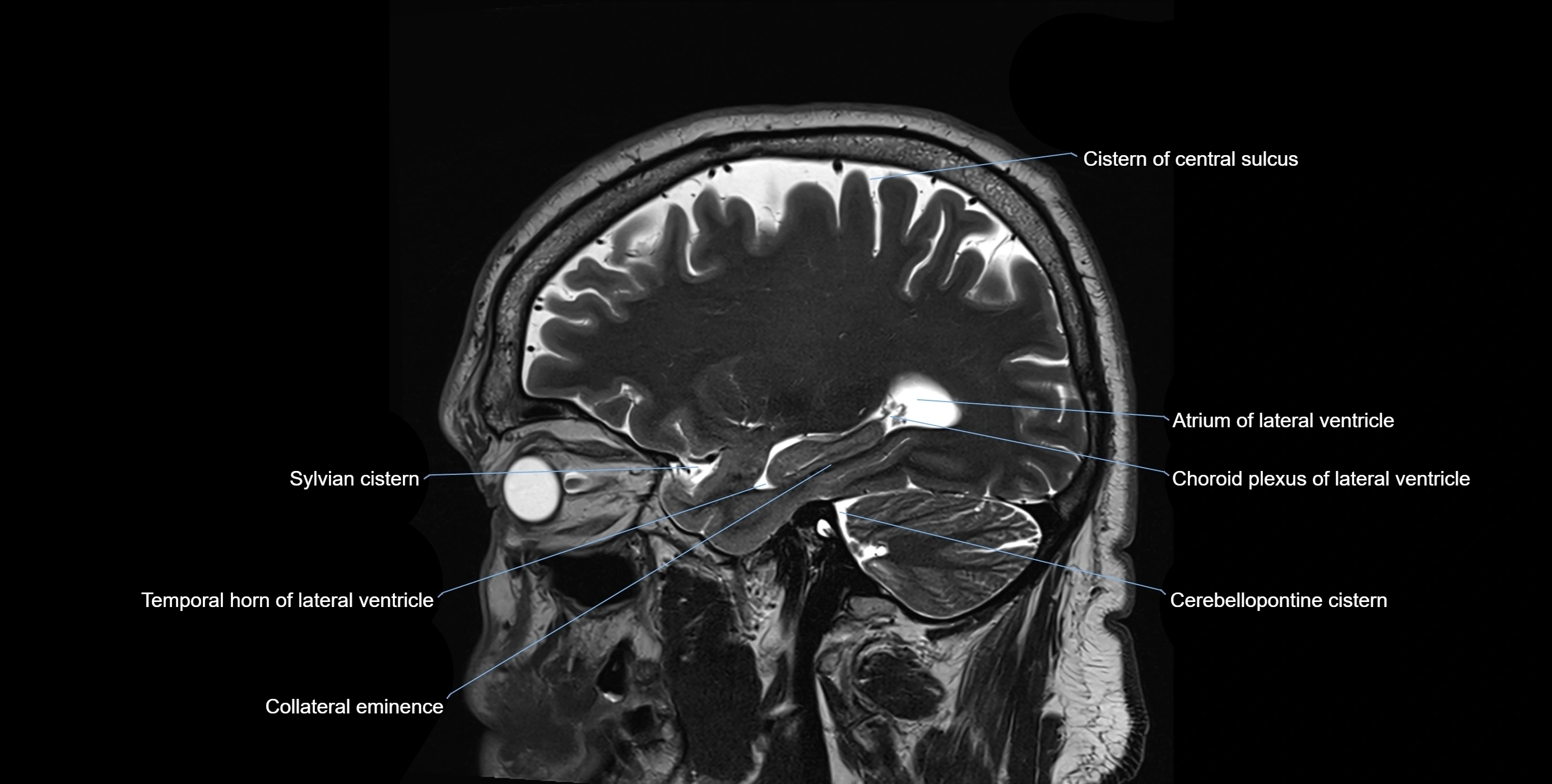
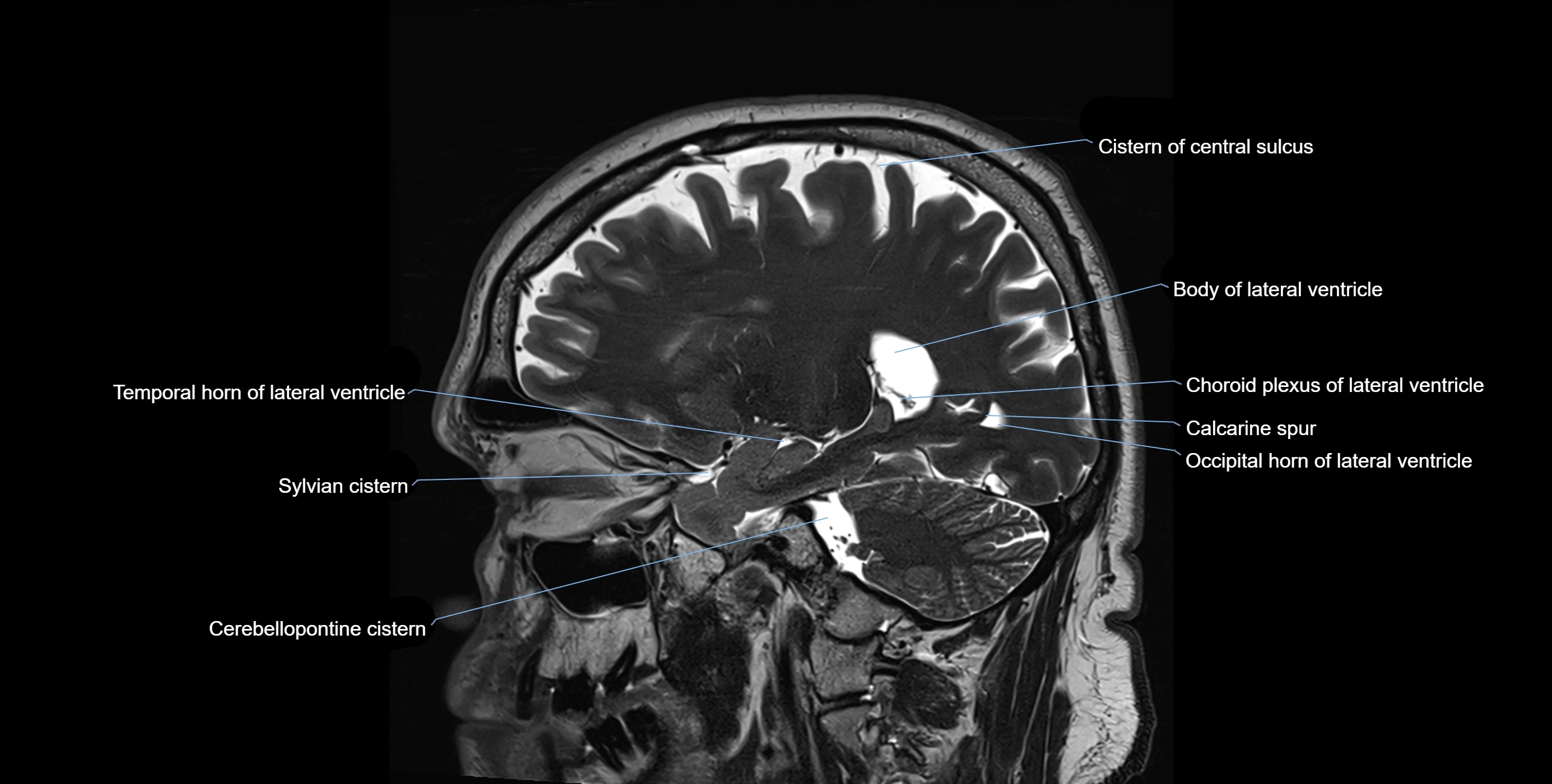
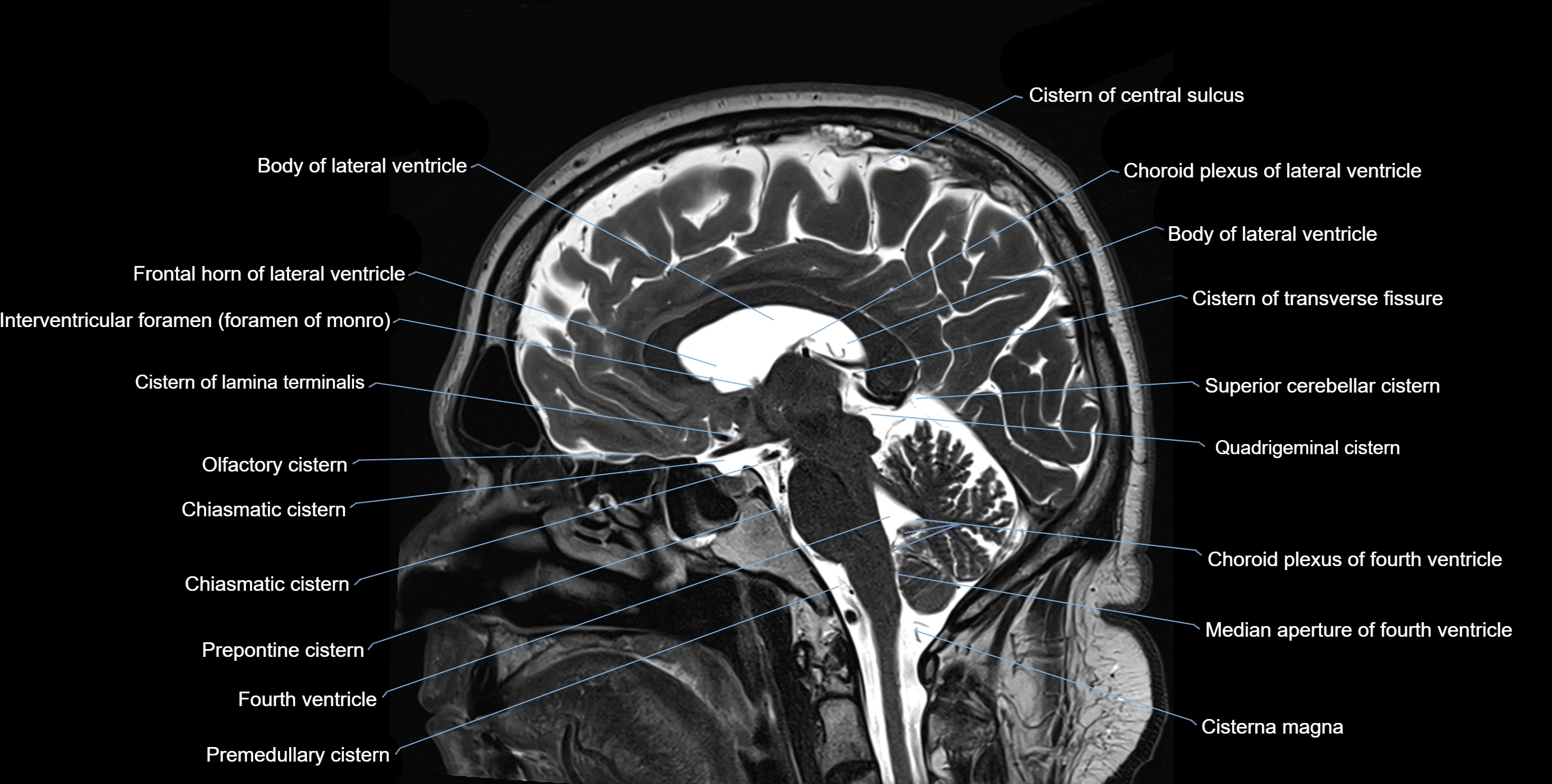
MRI images

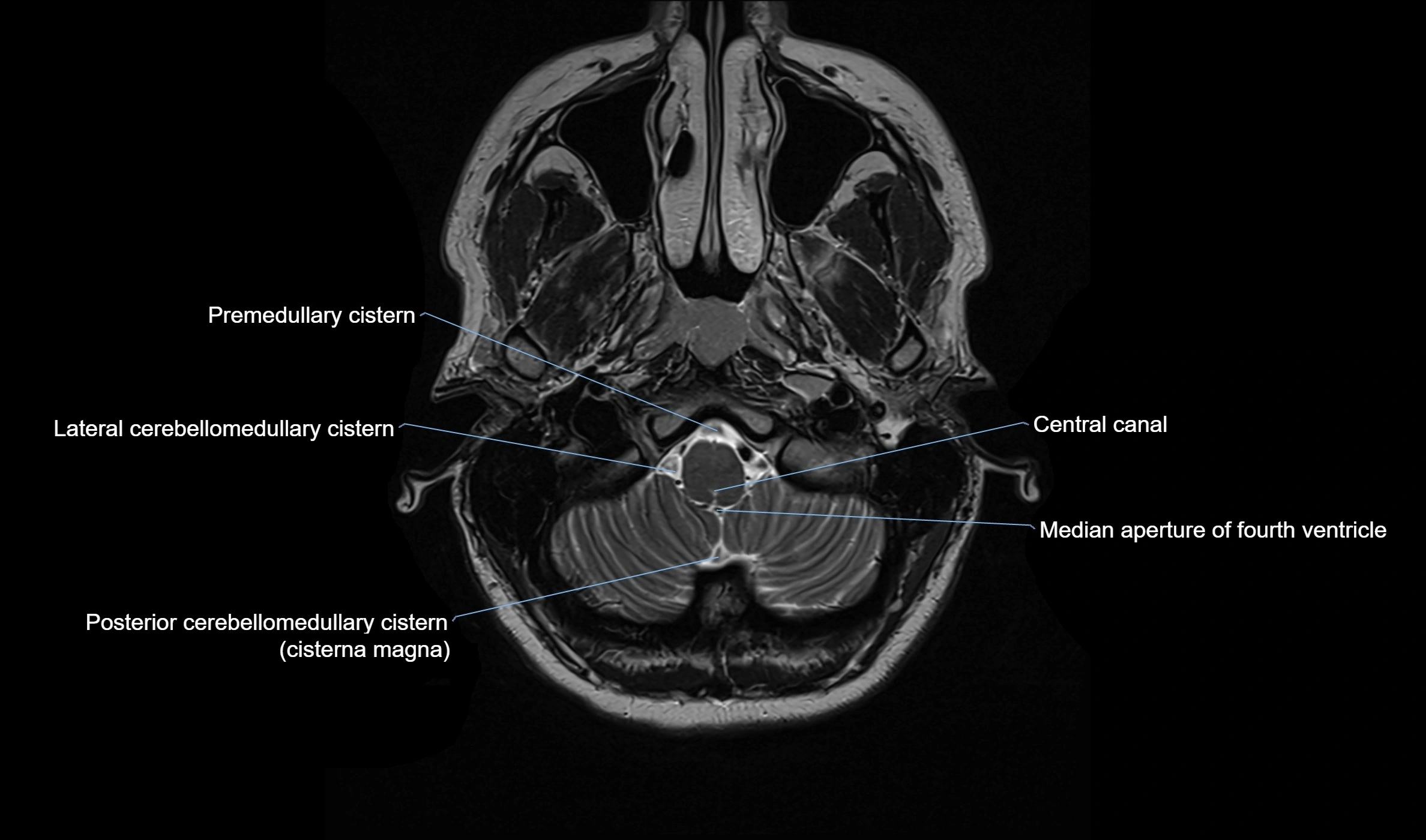
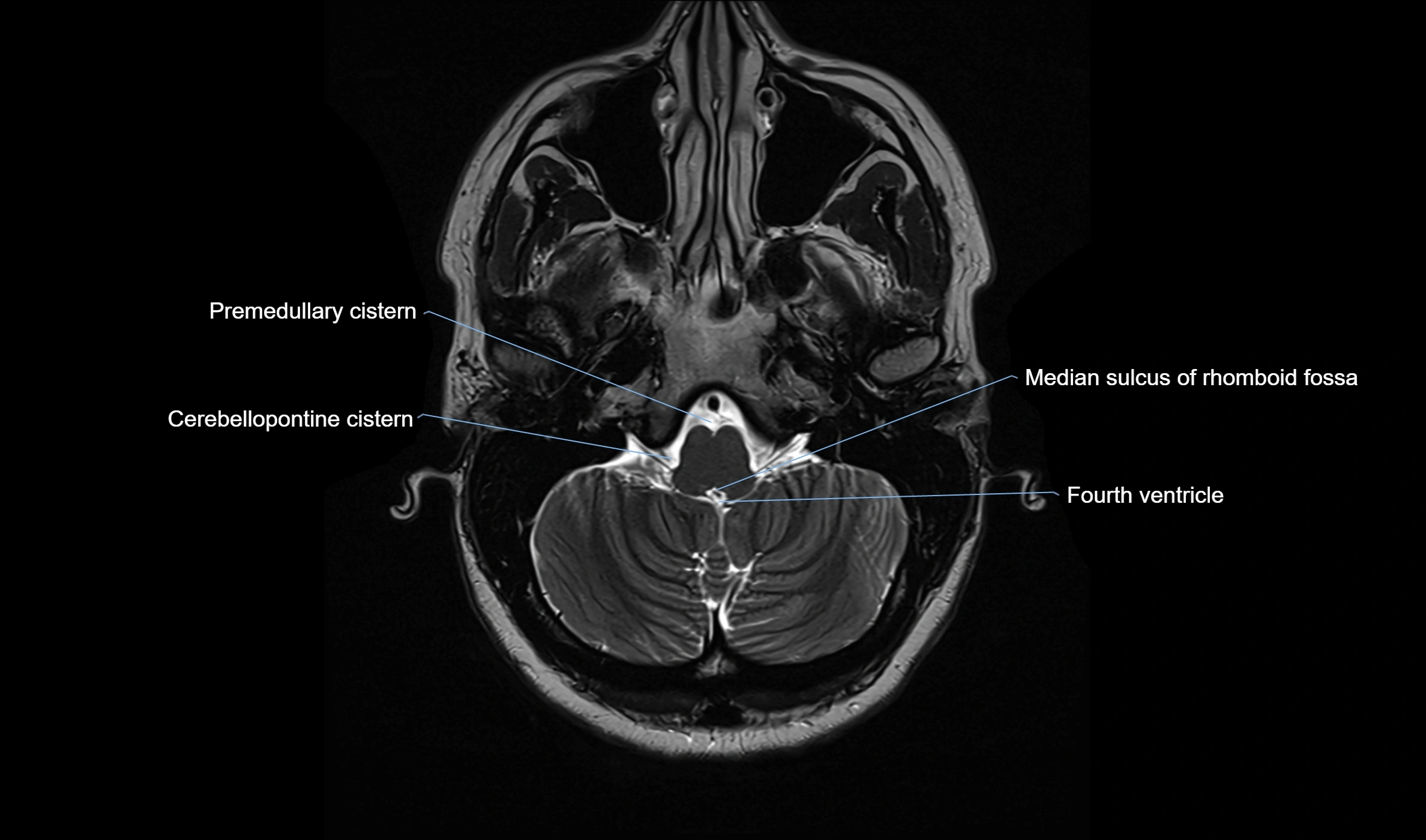
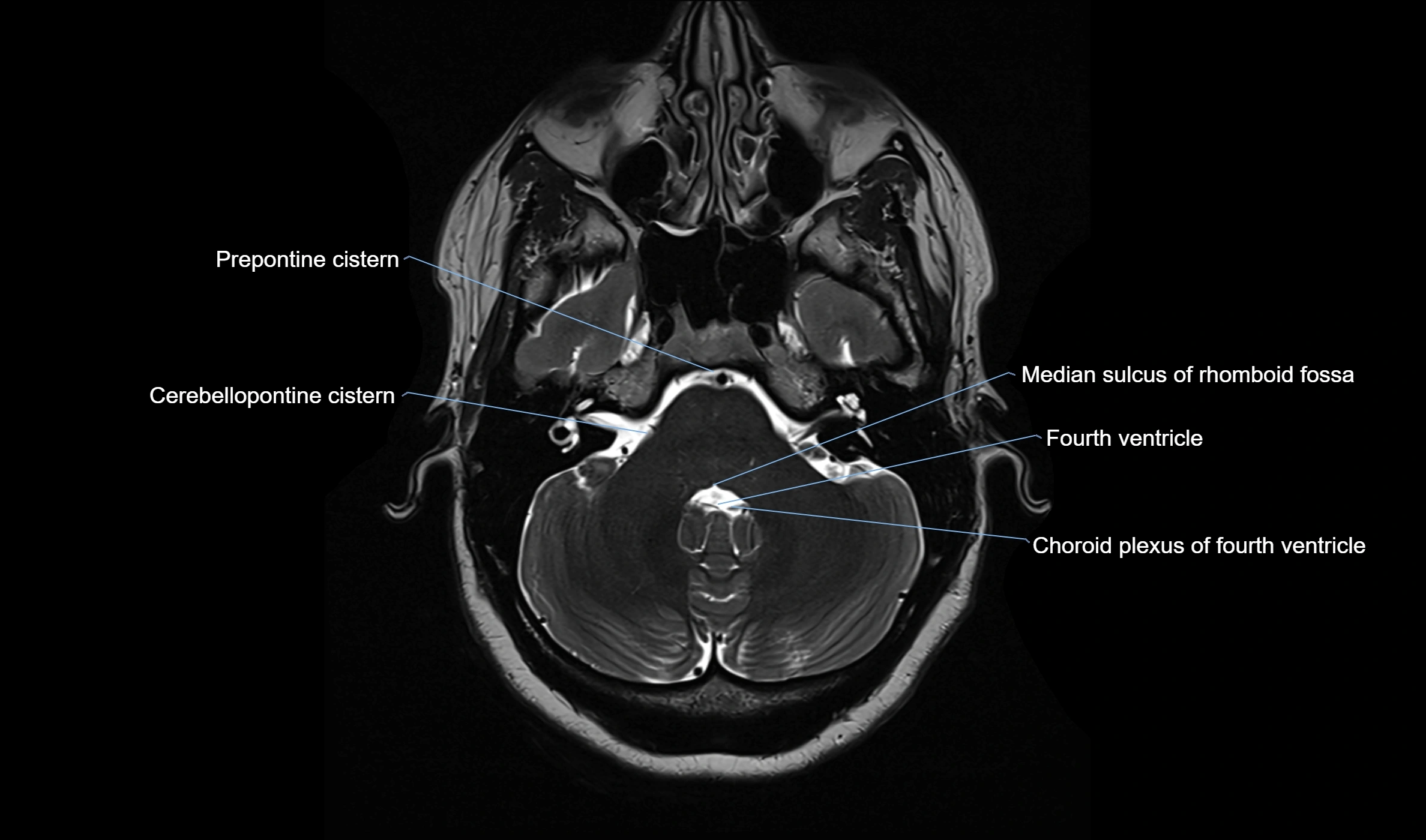
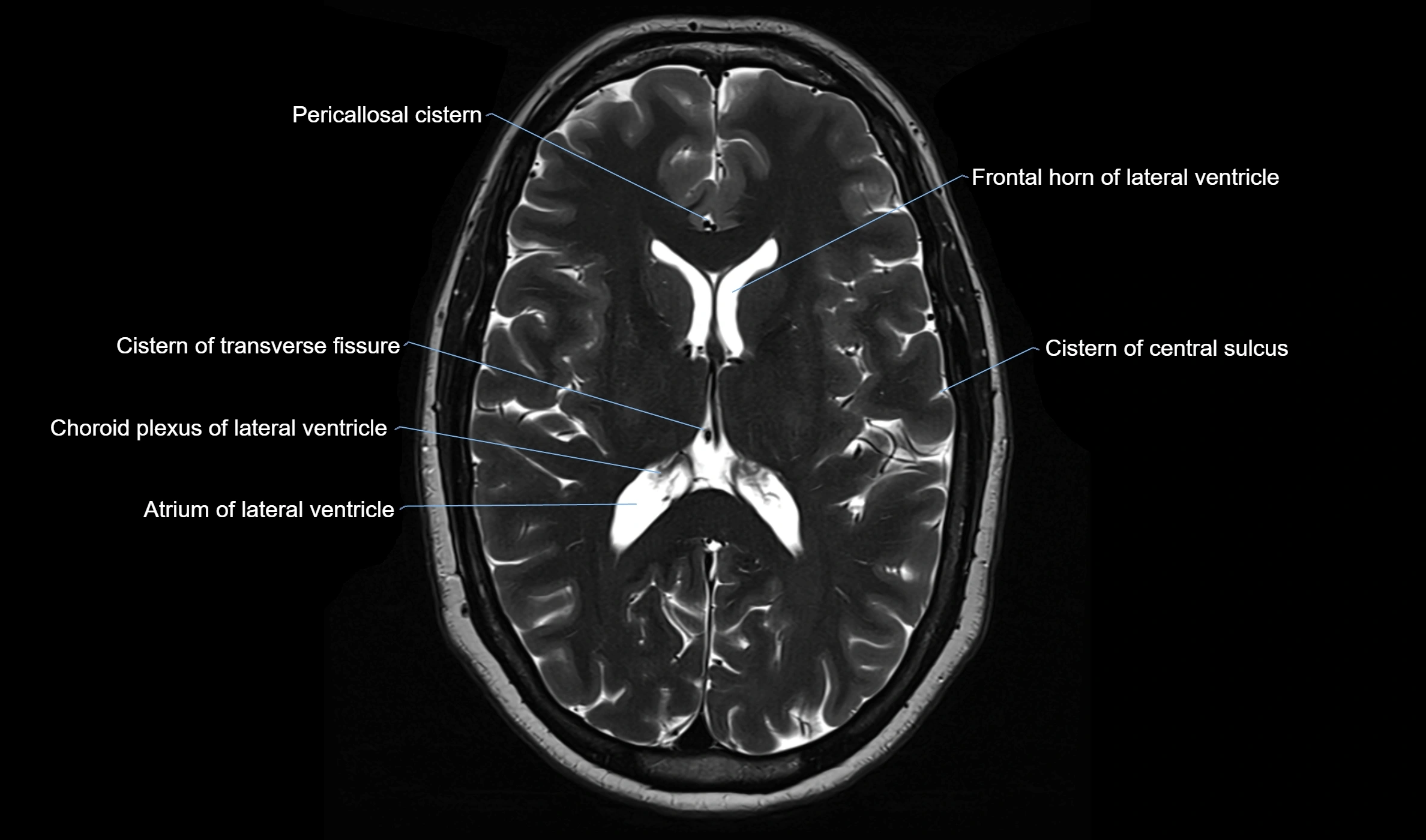
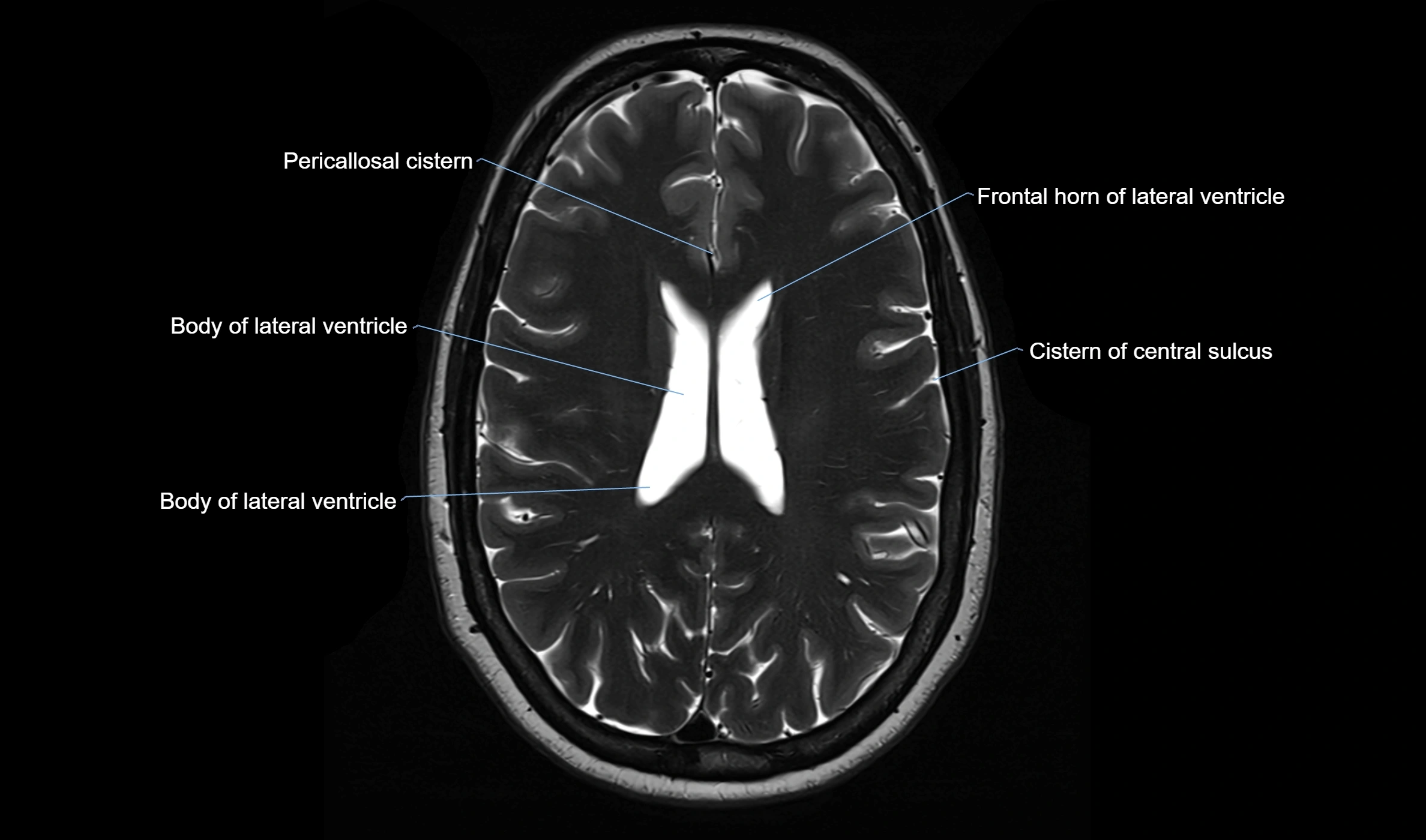
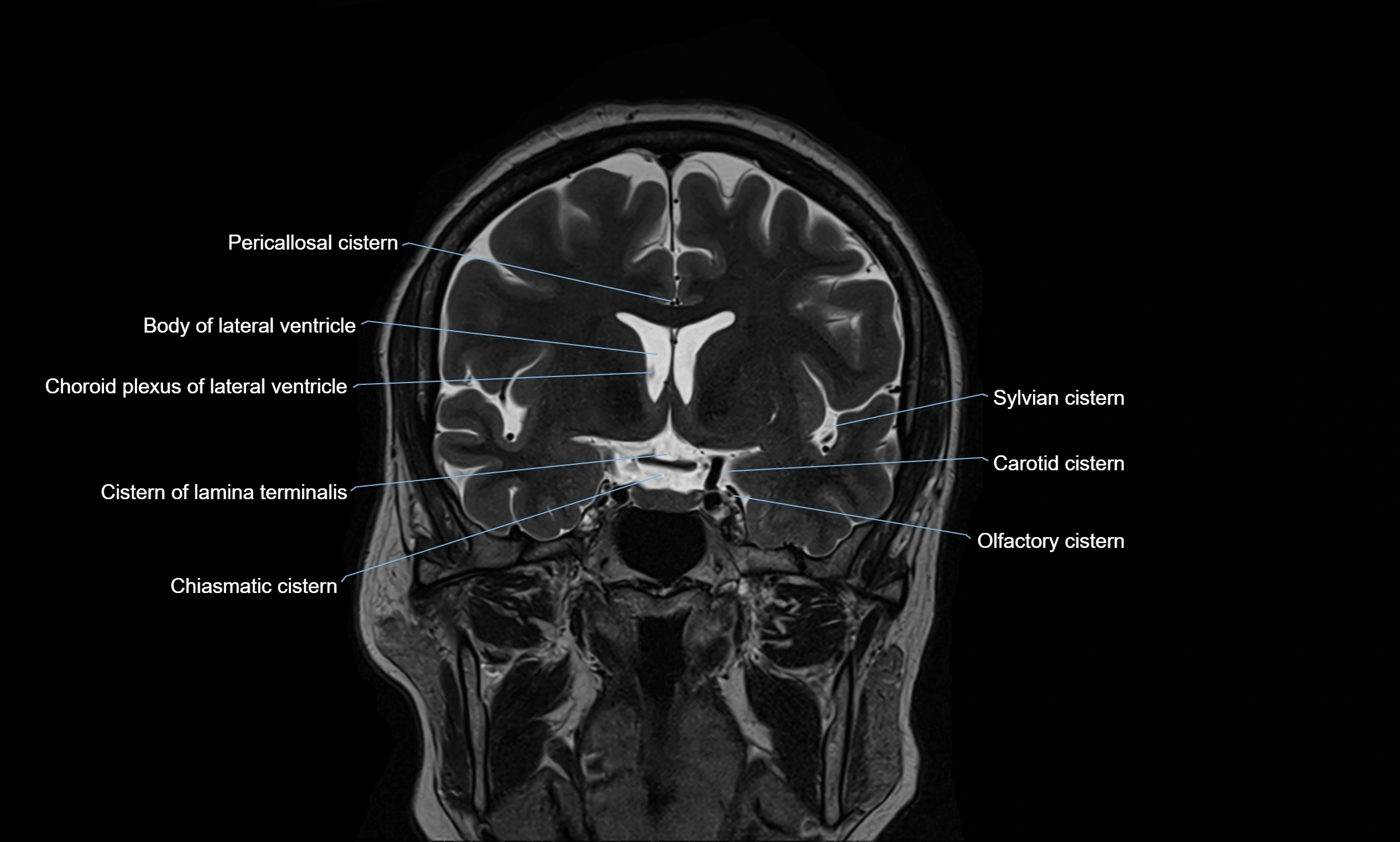
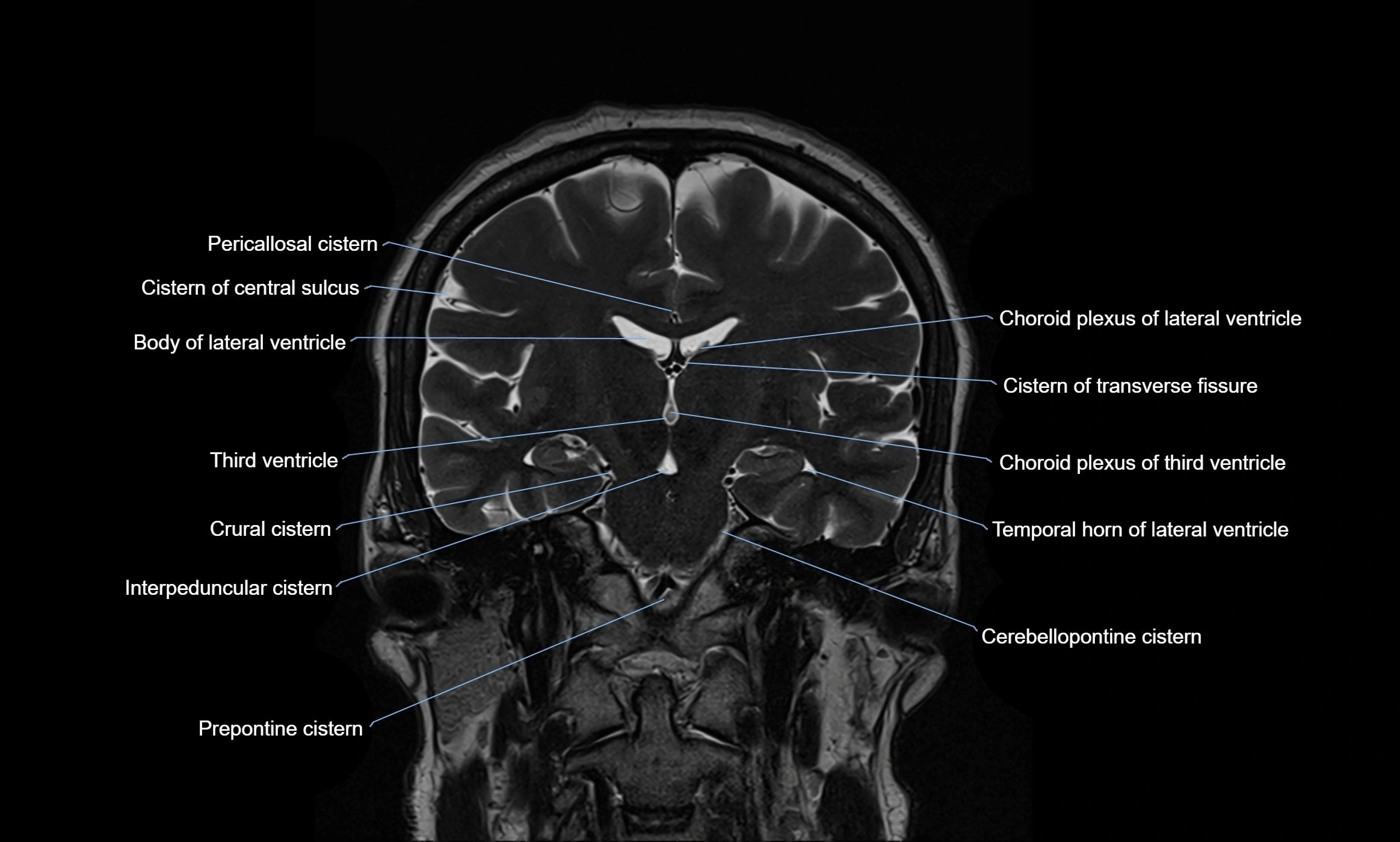
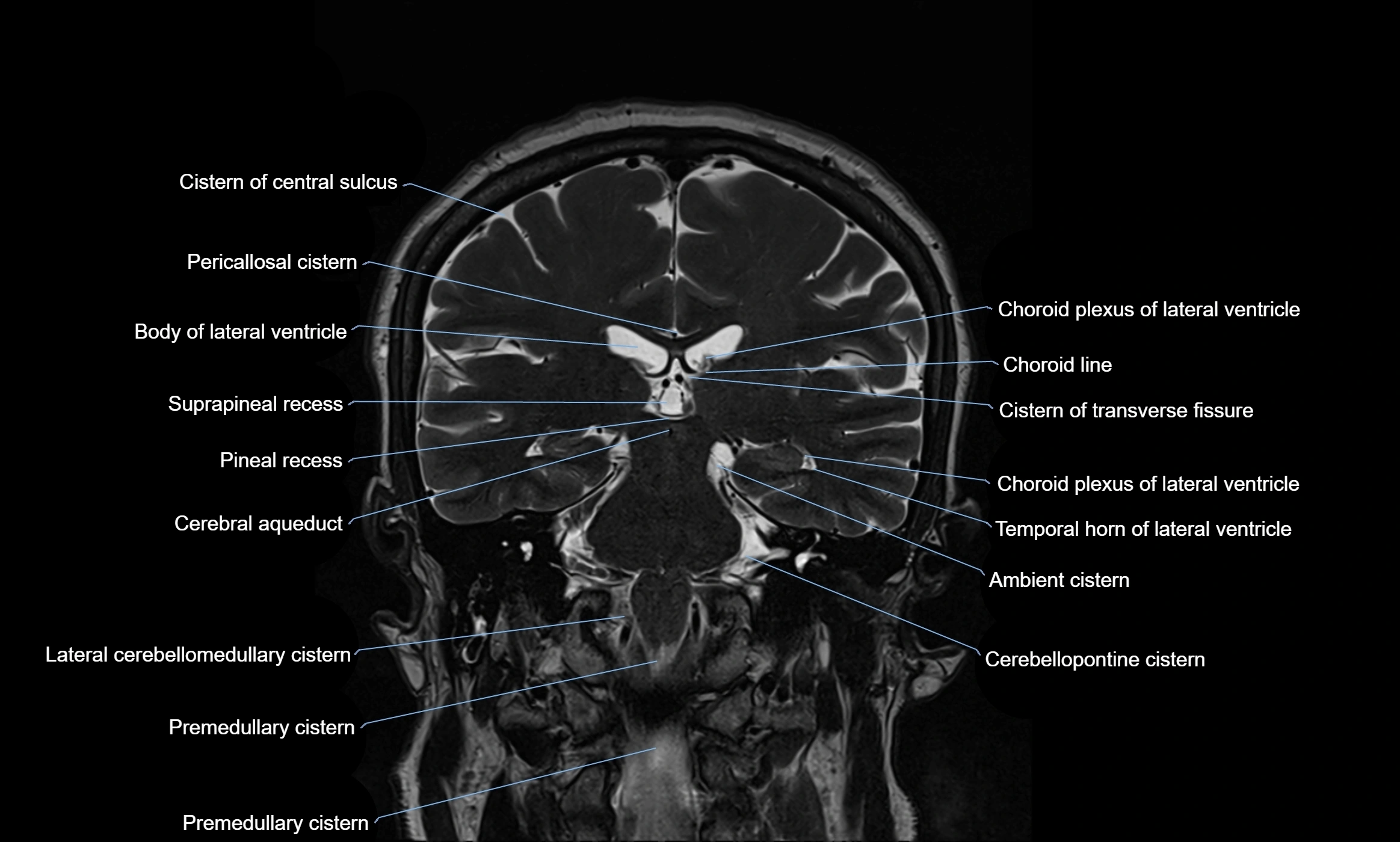
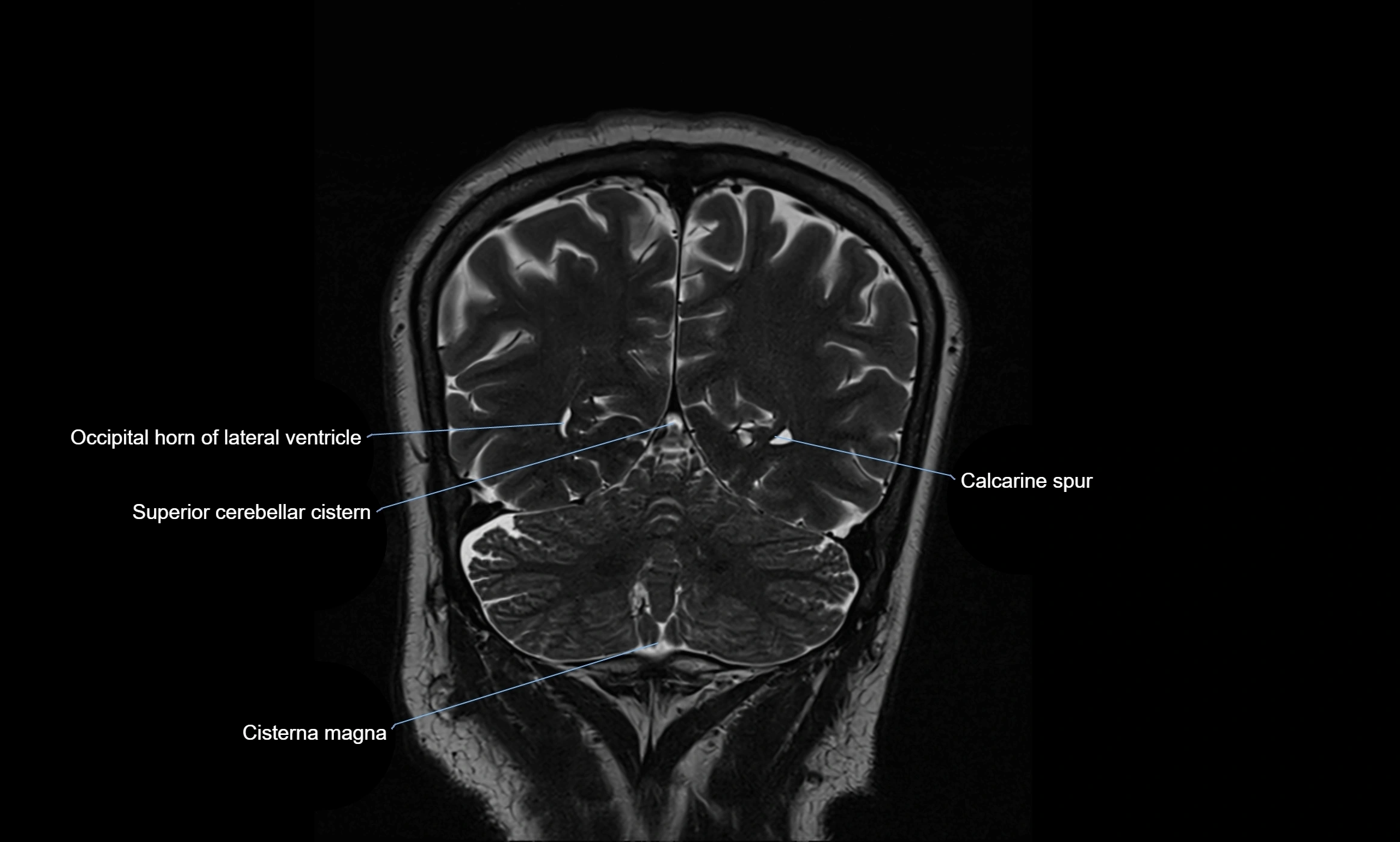
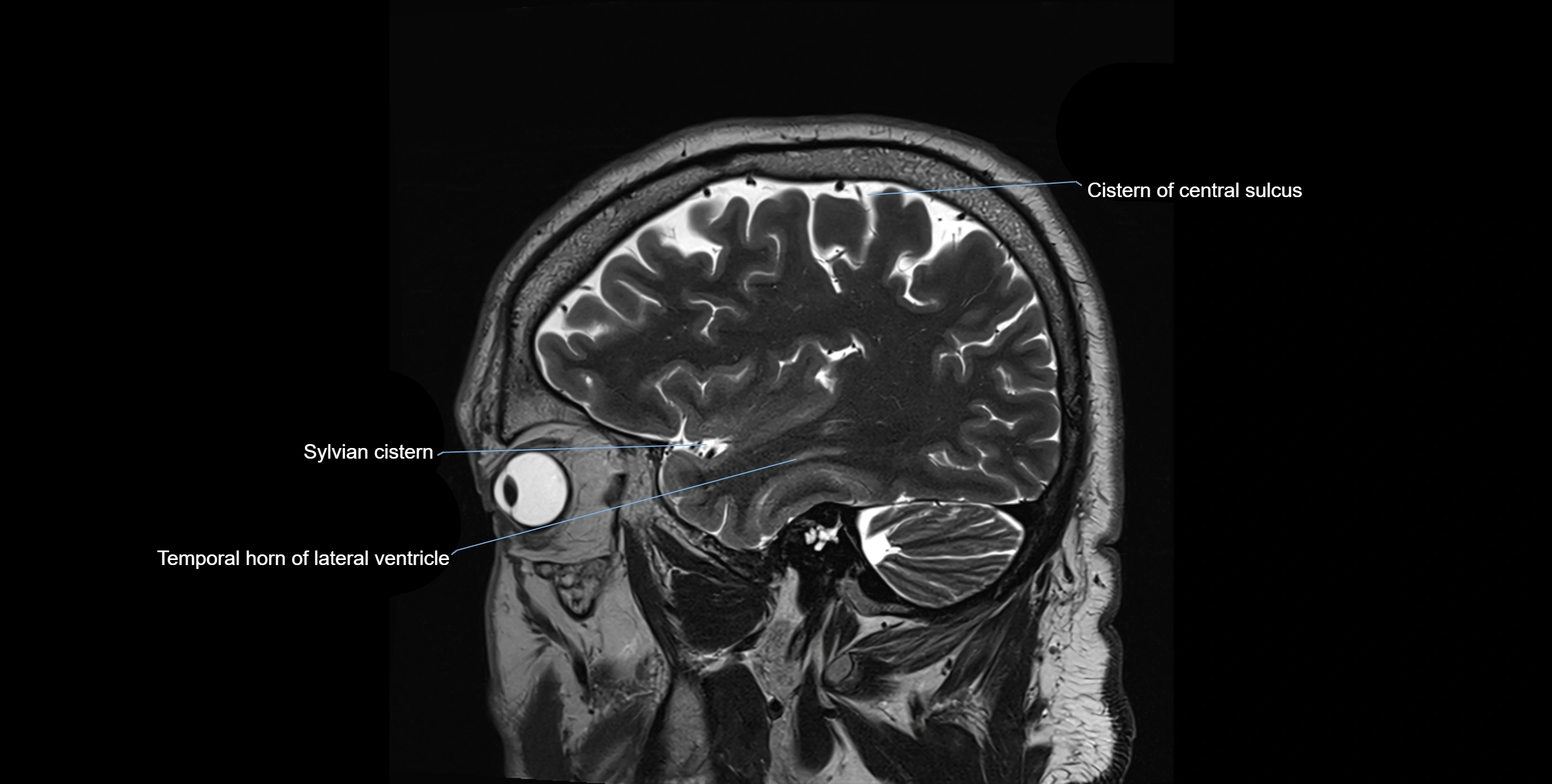
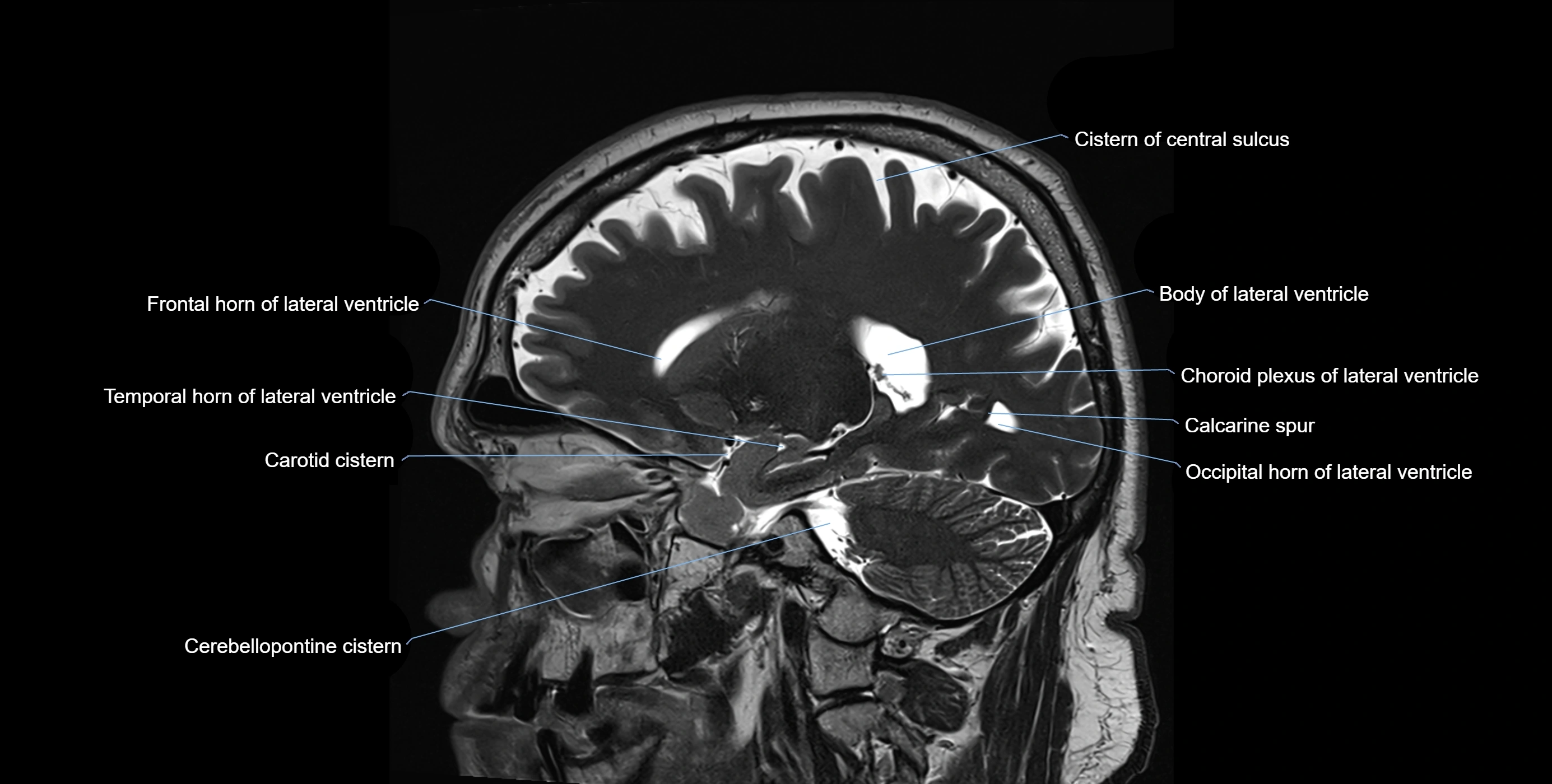
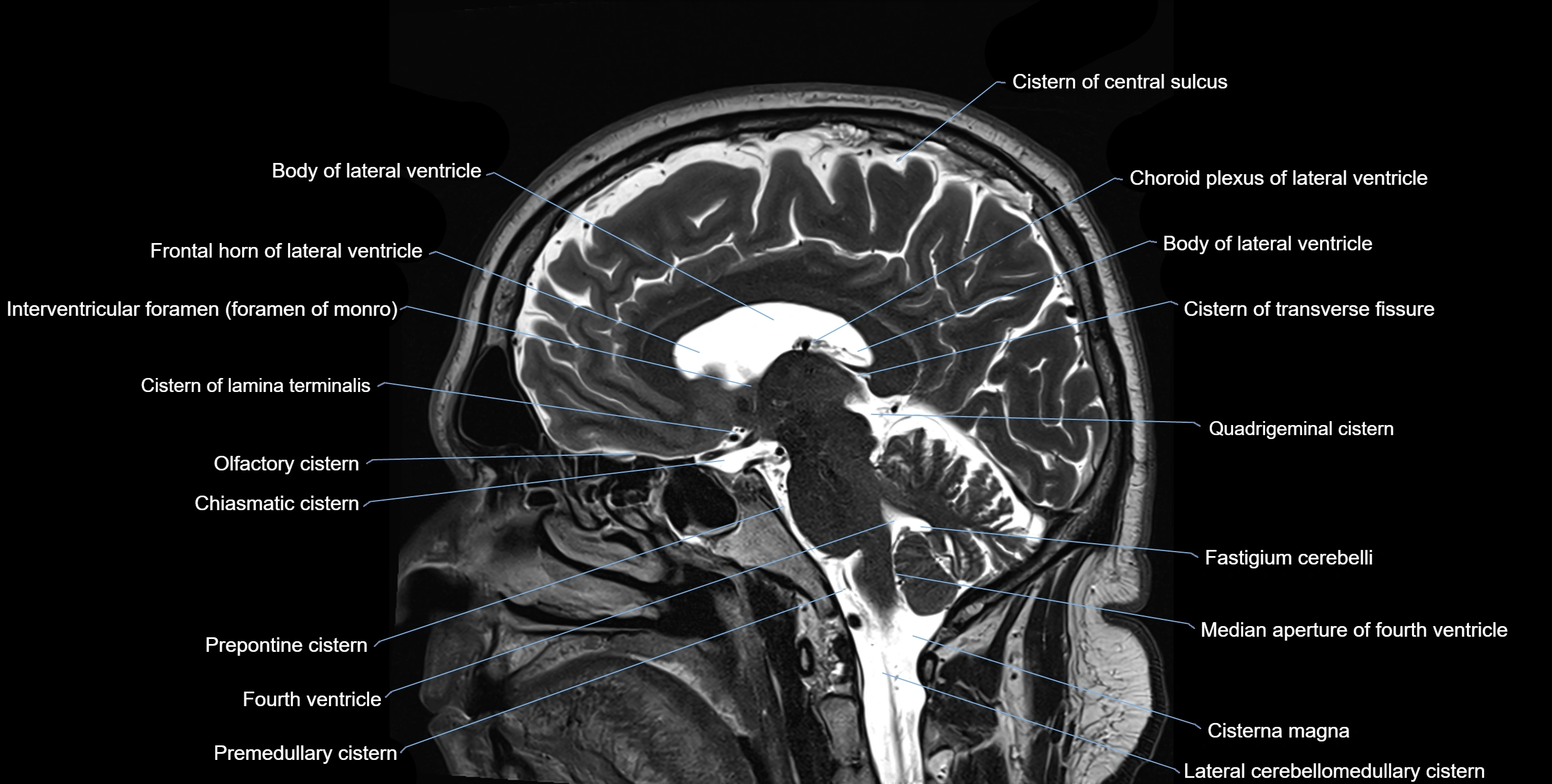
CT image