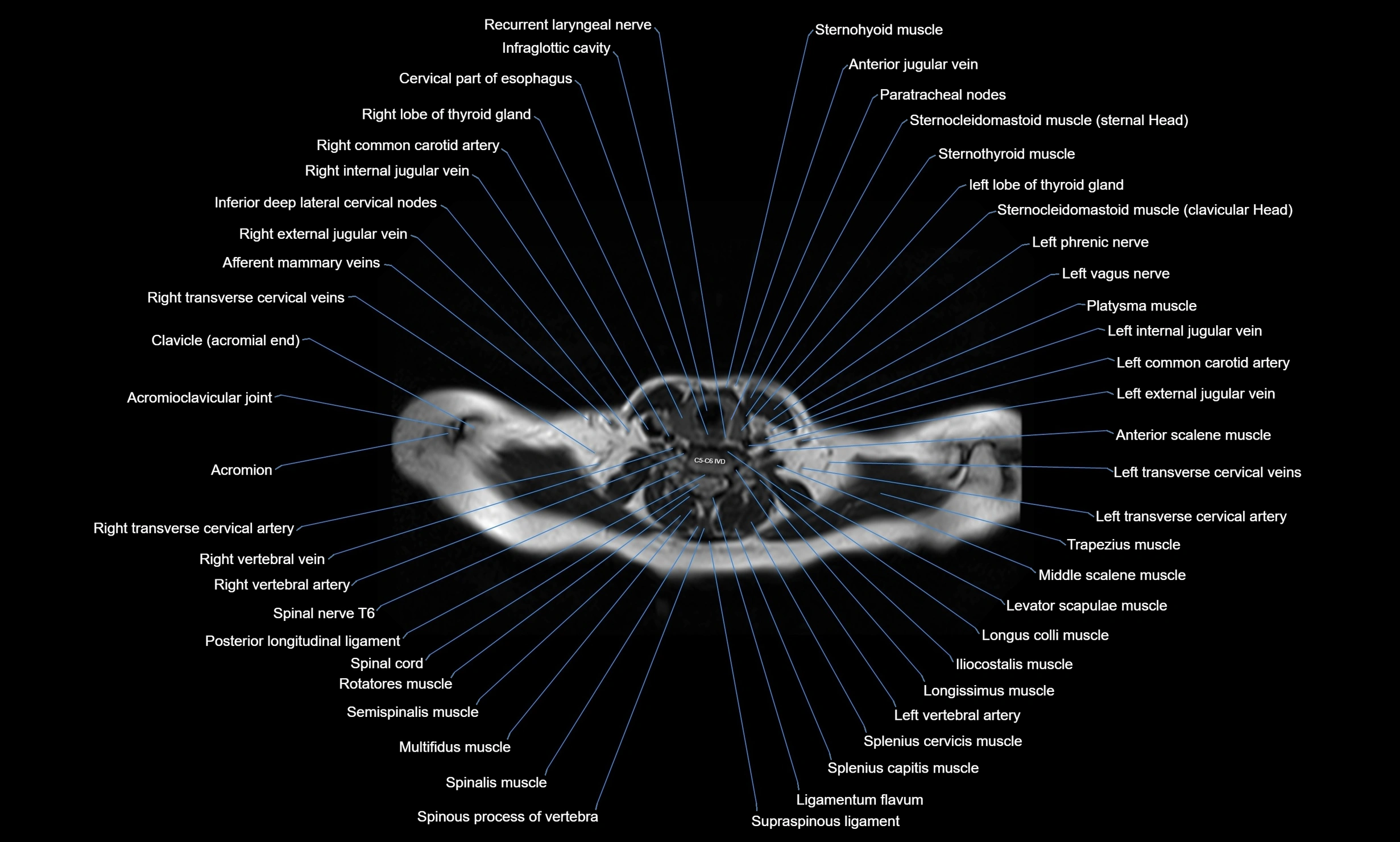
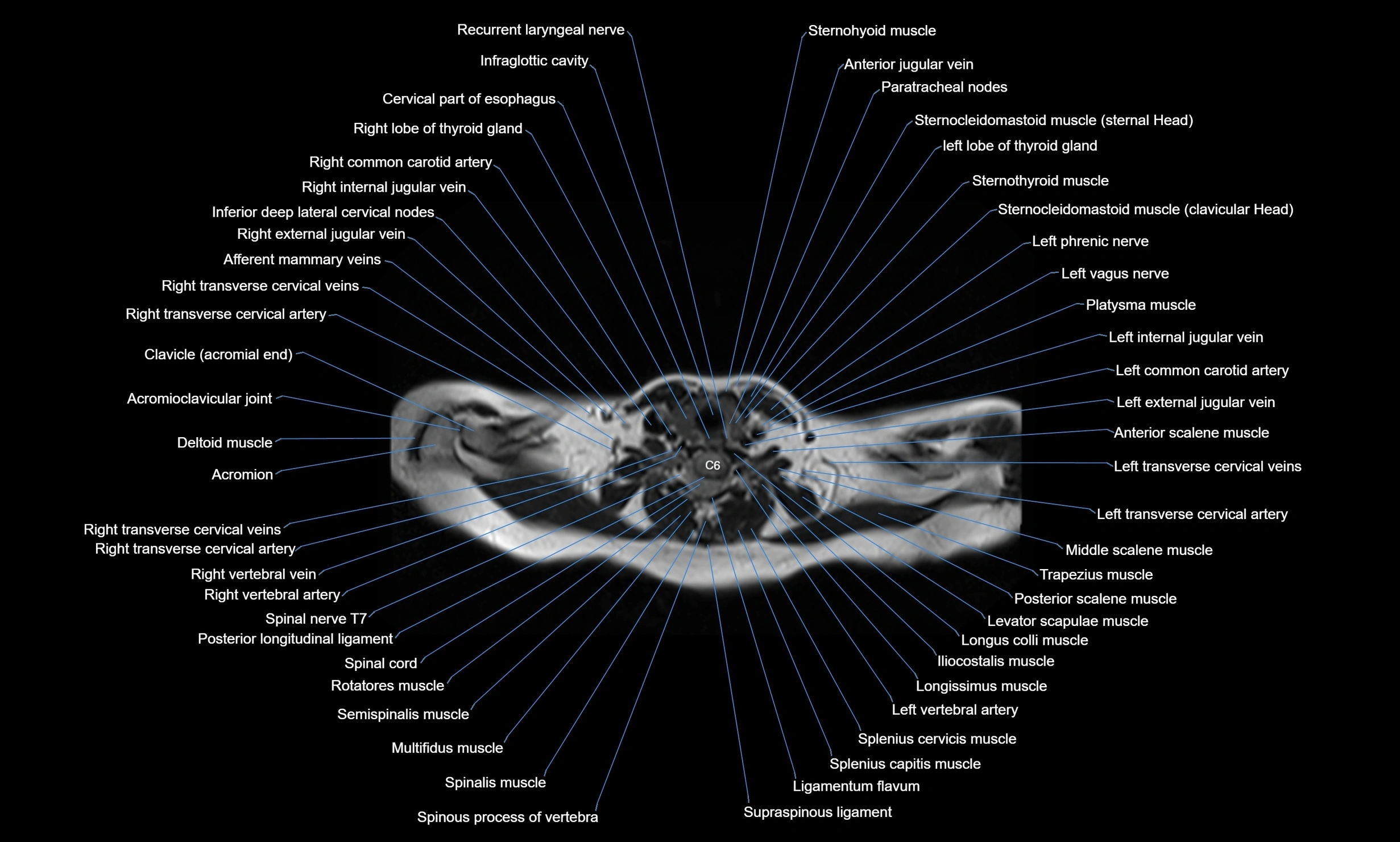
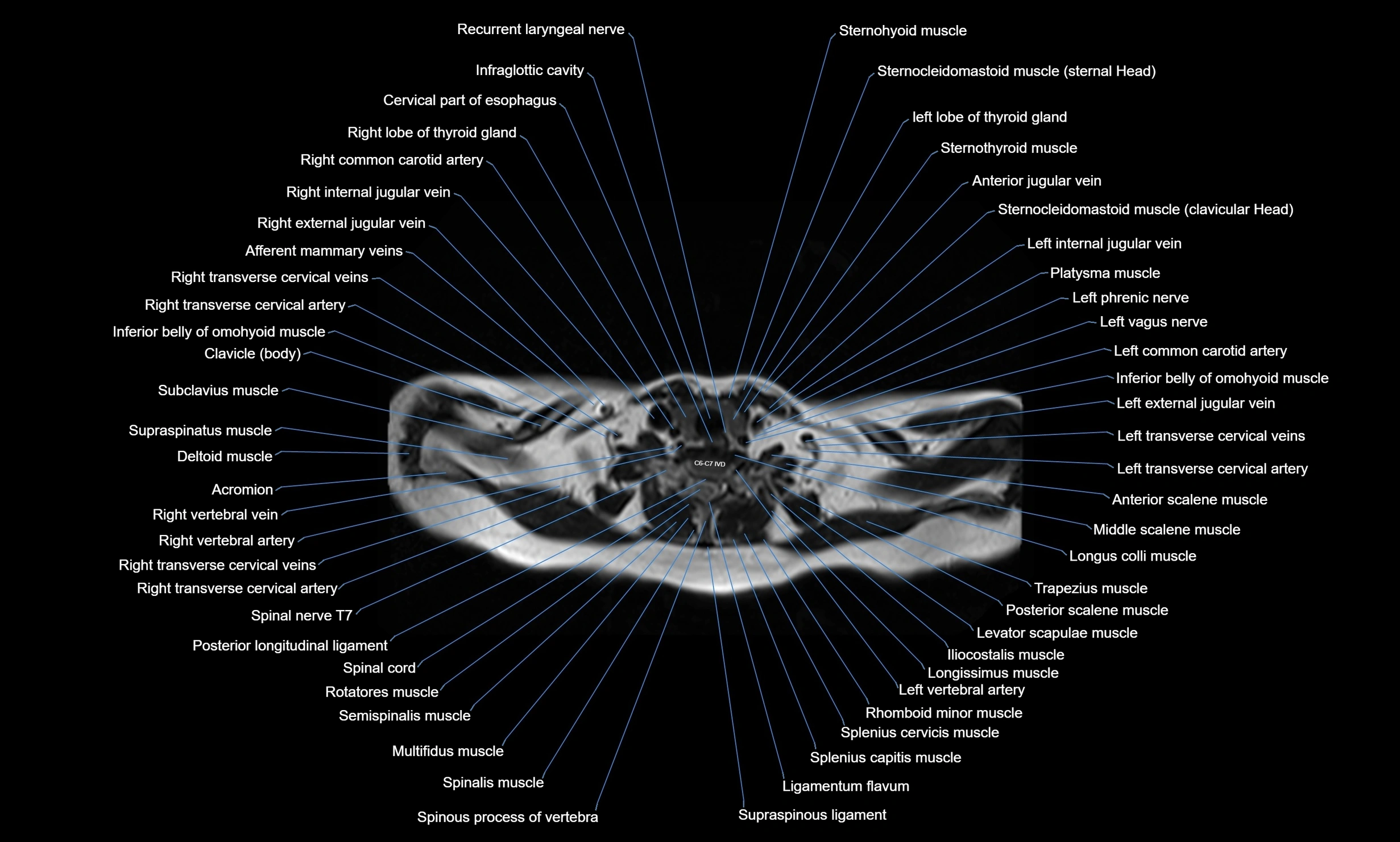
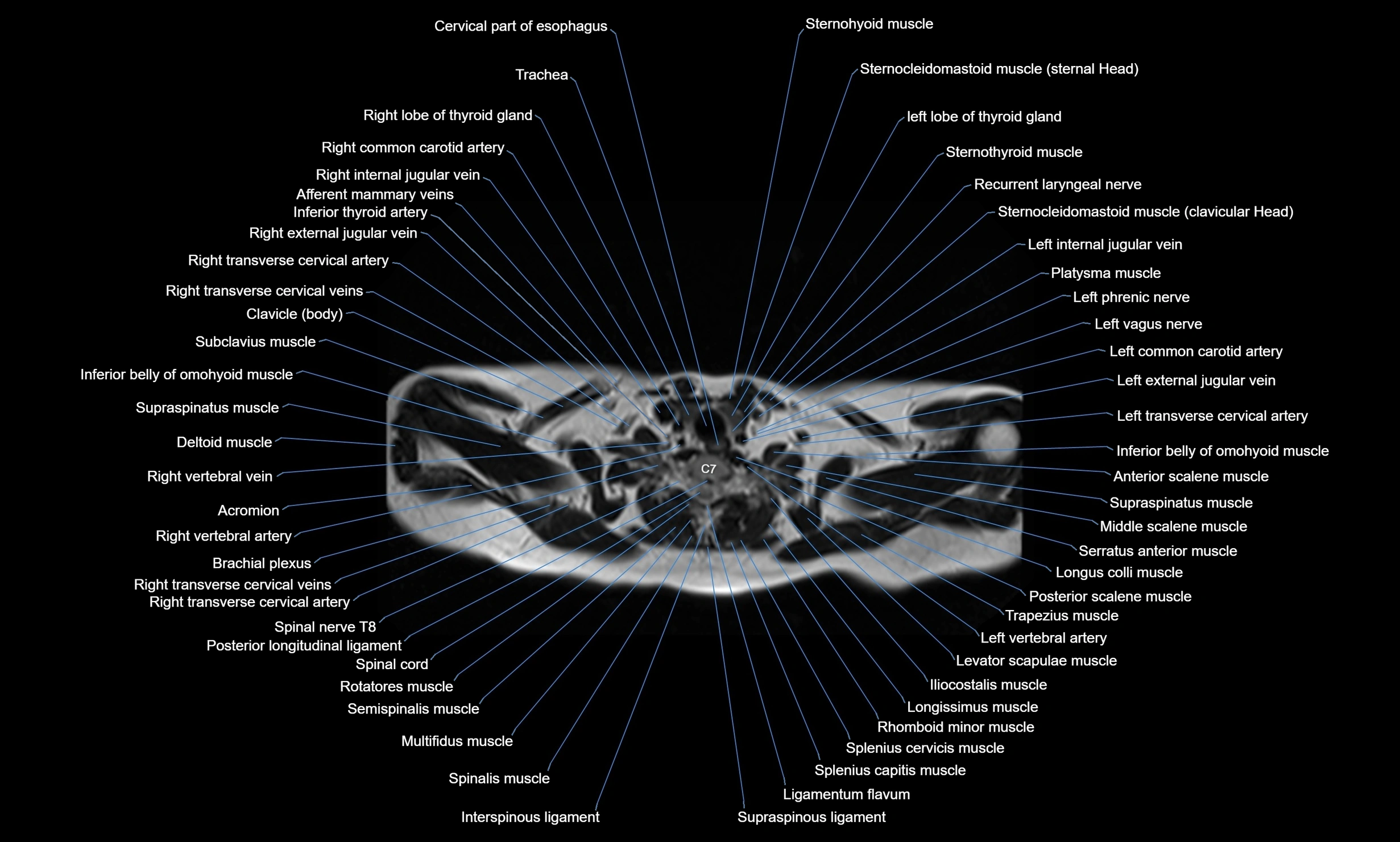
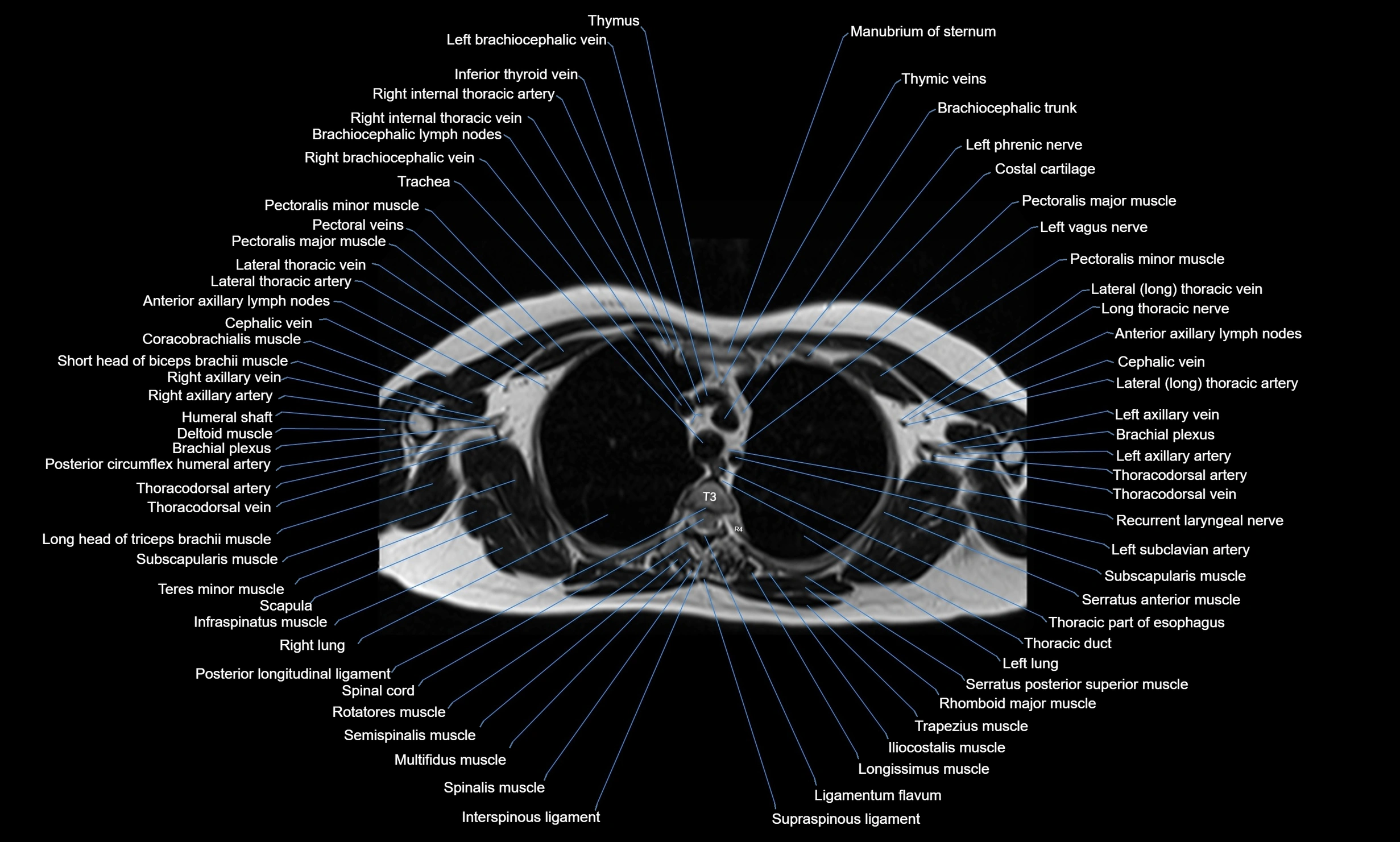
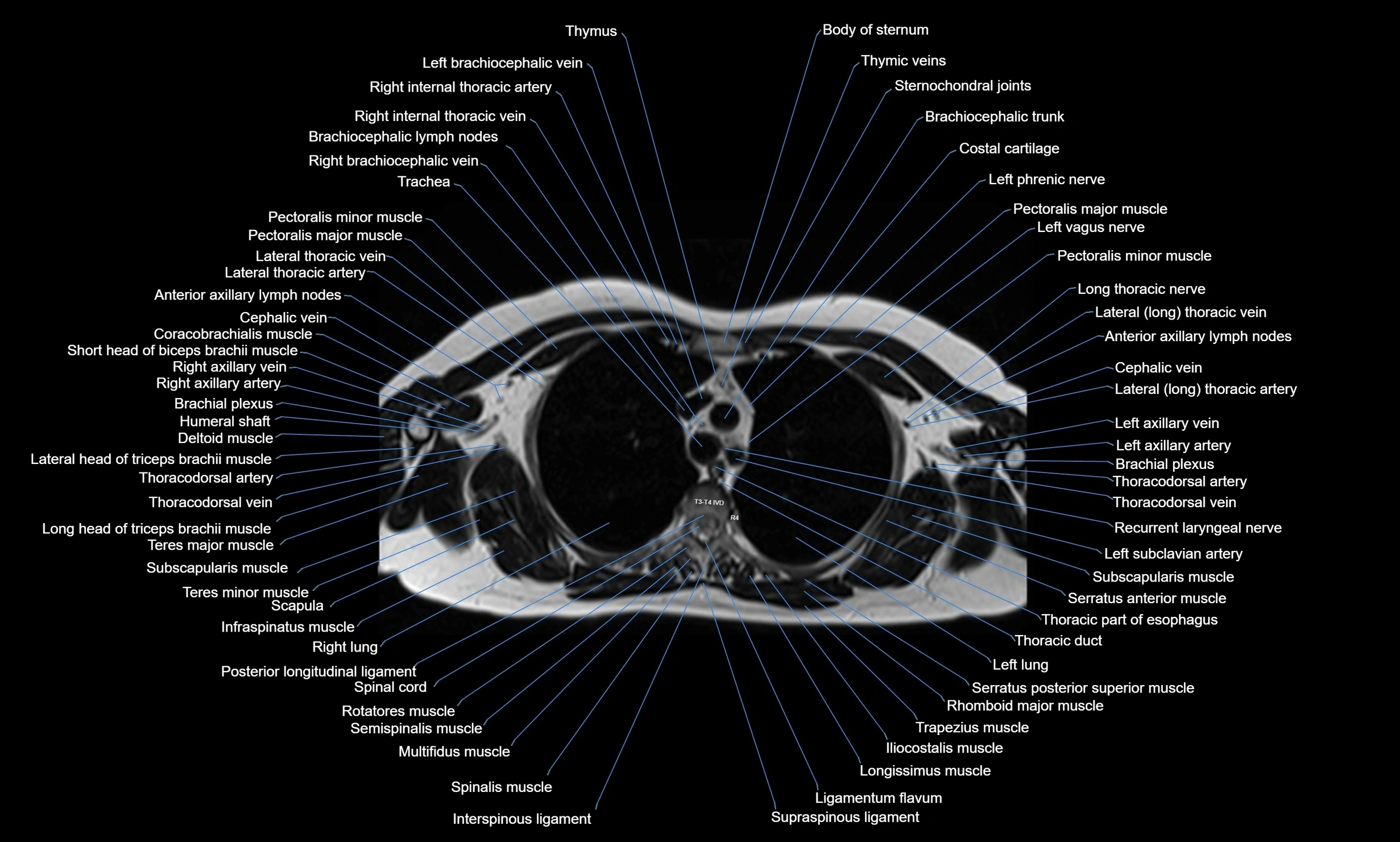
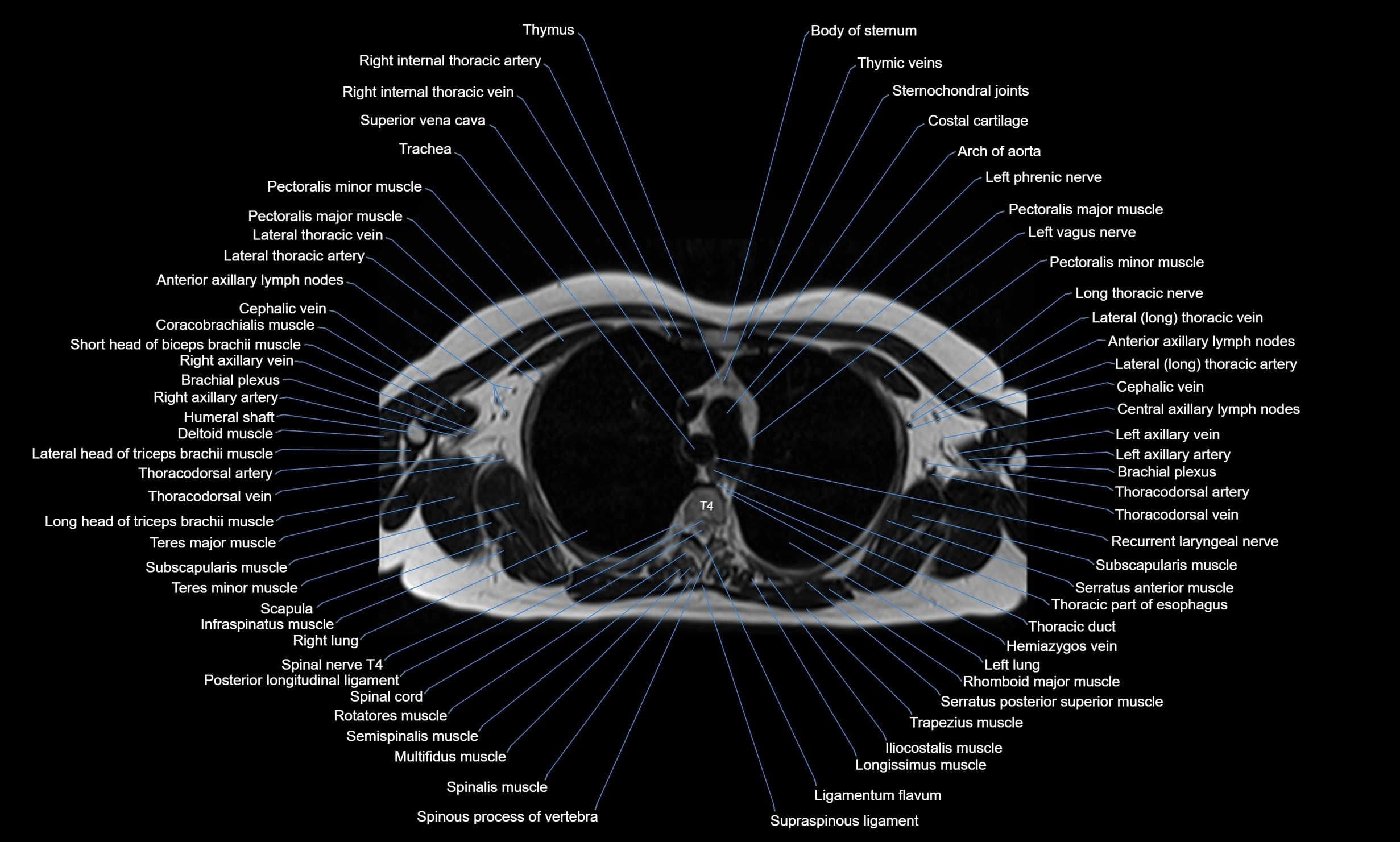
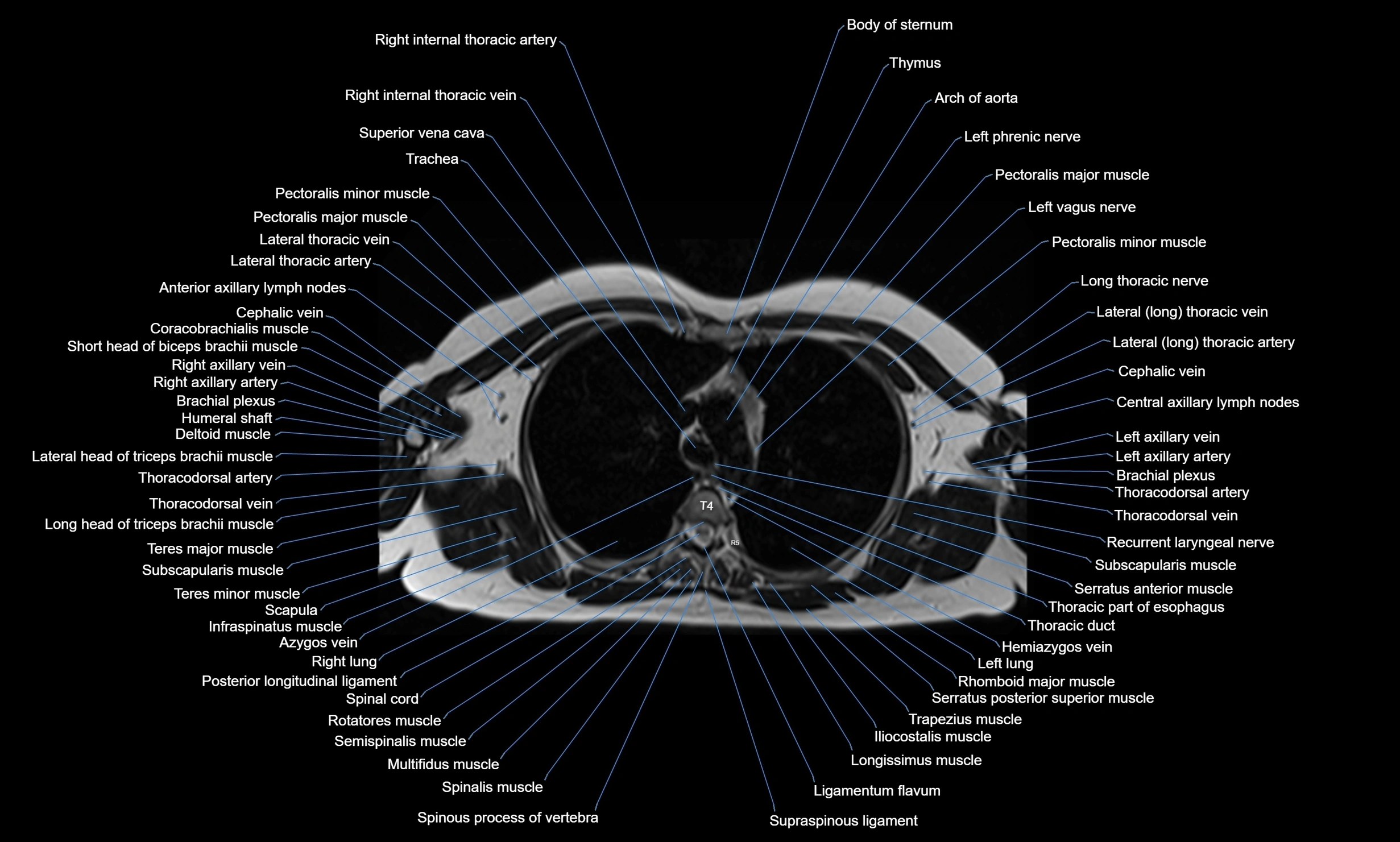
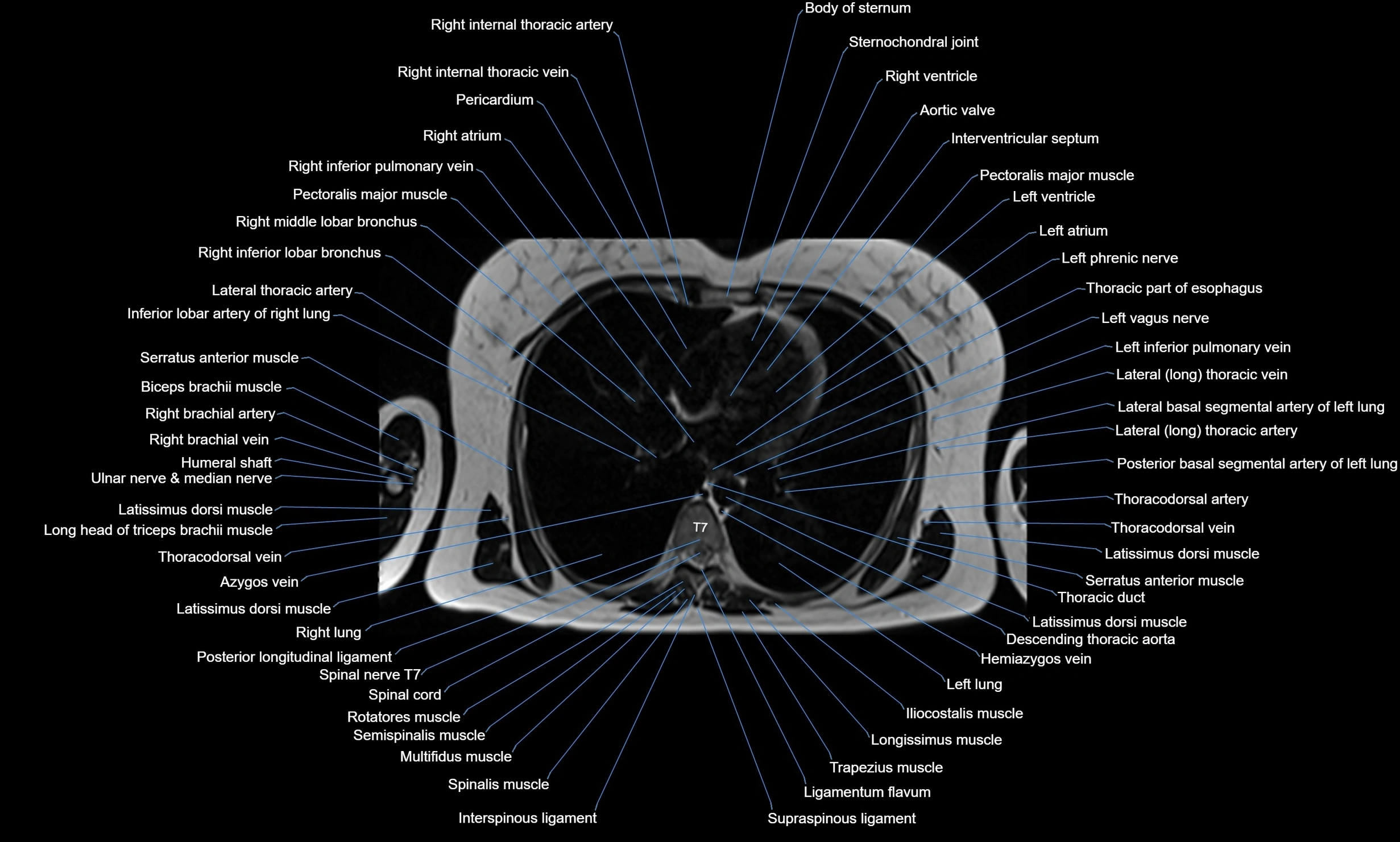
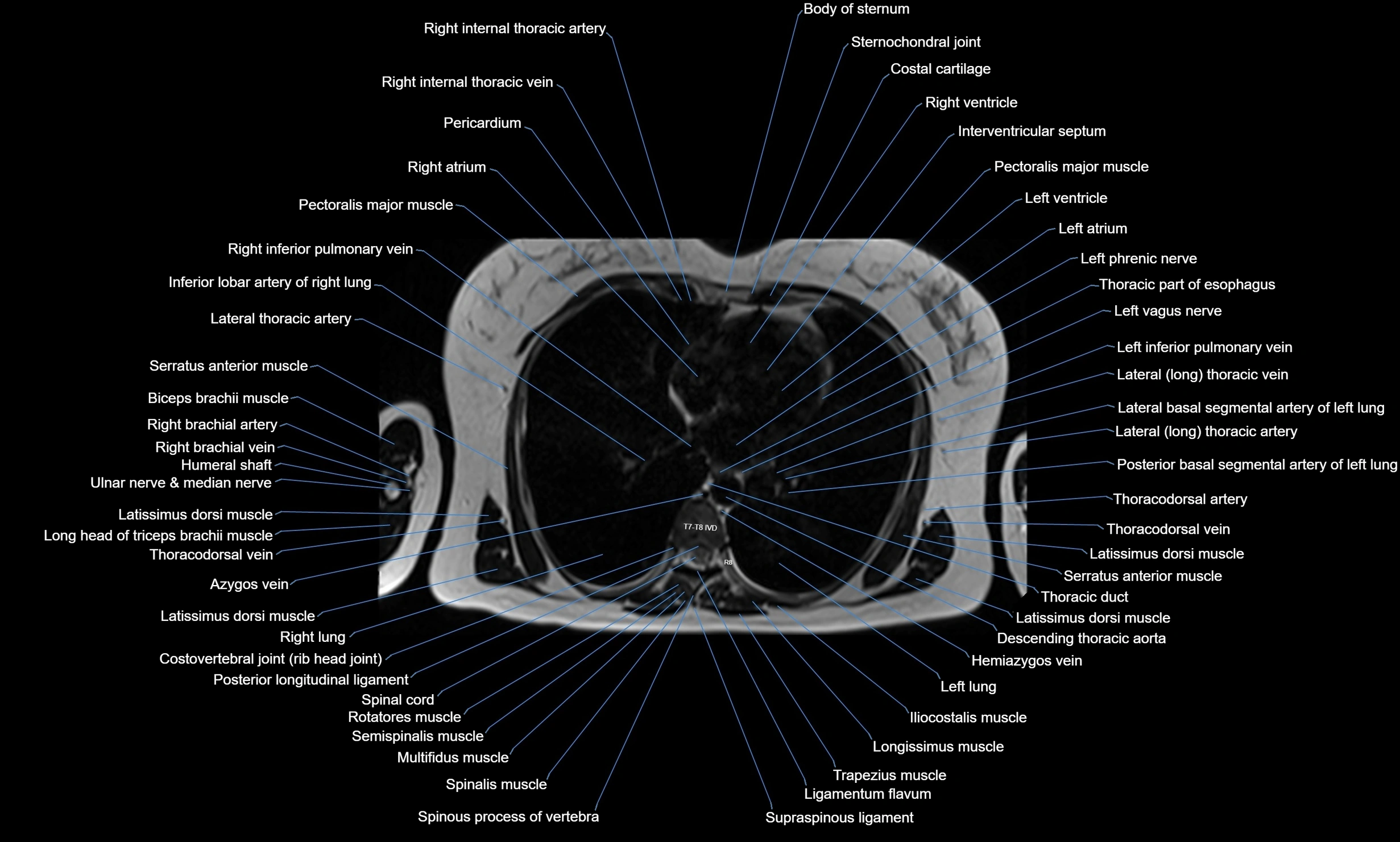
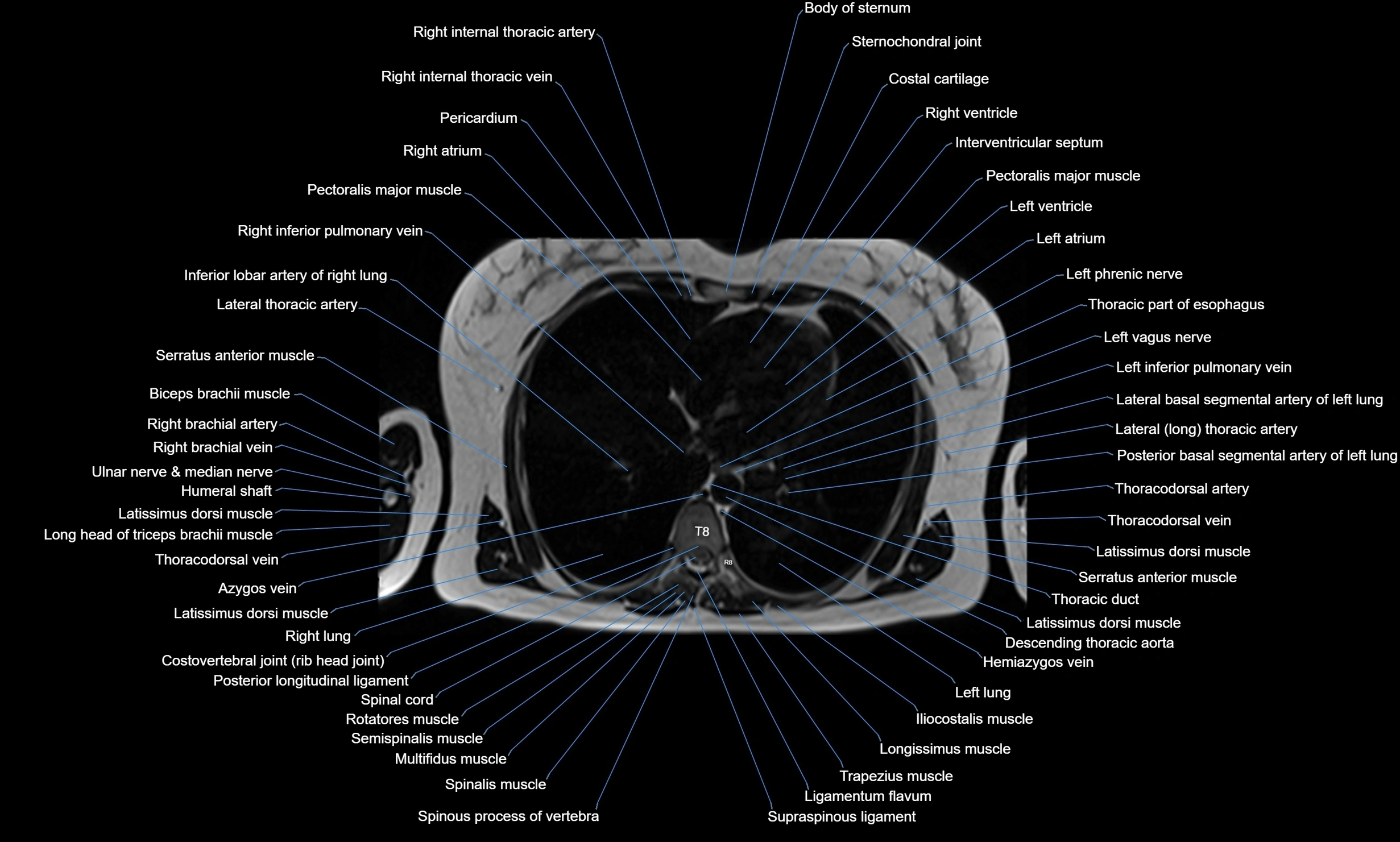
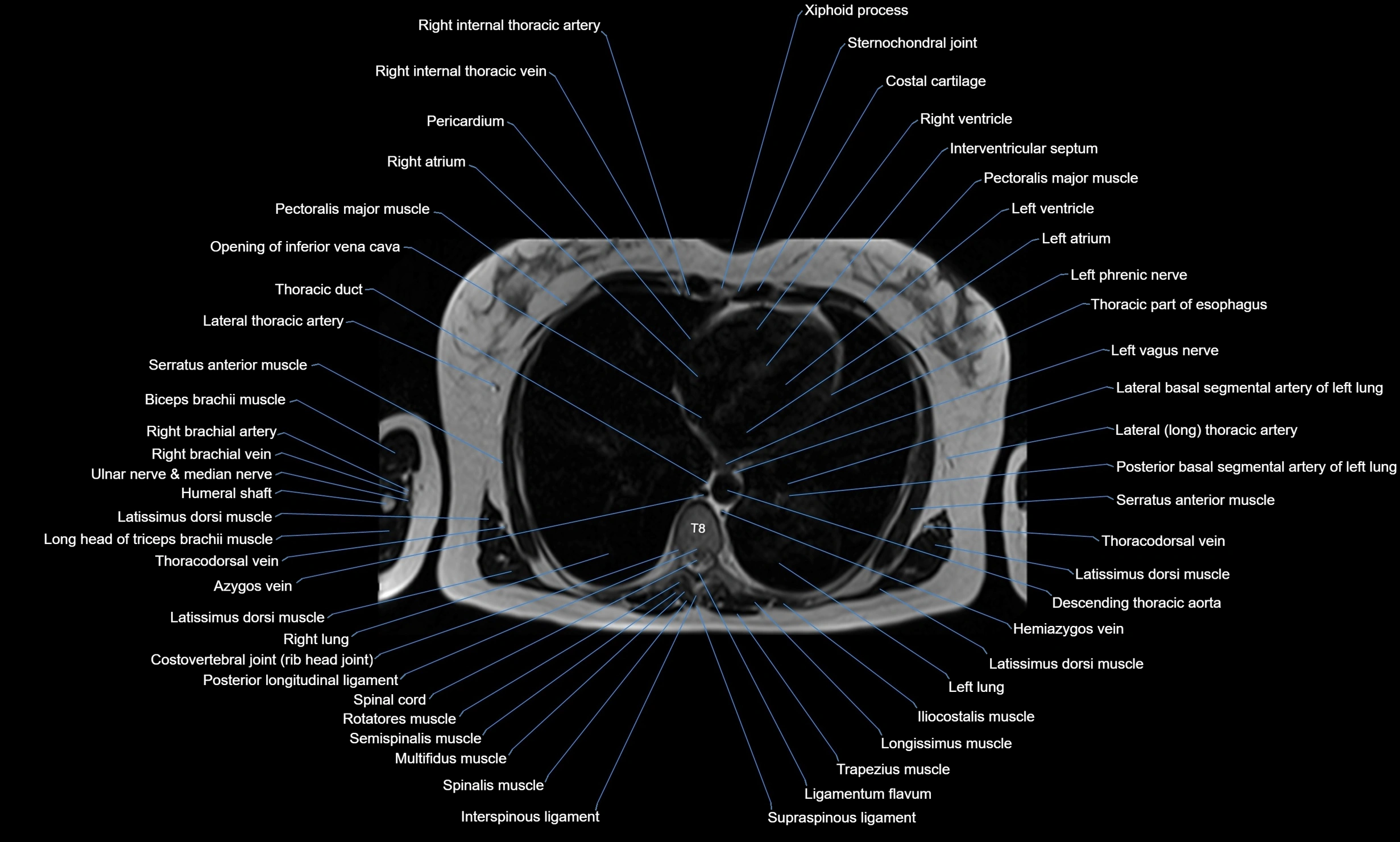
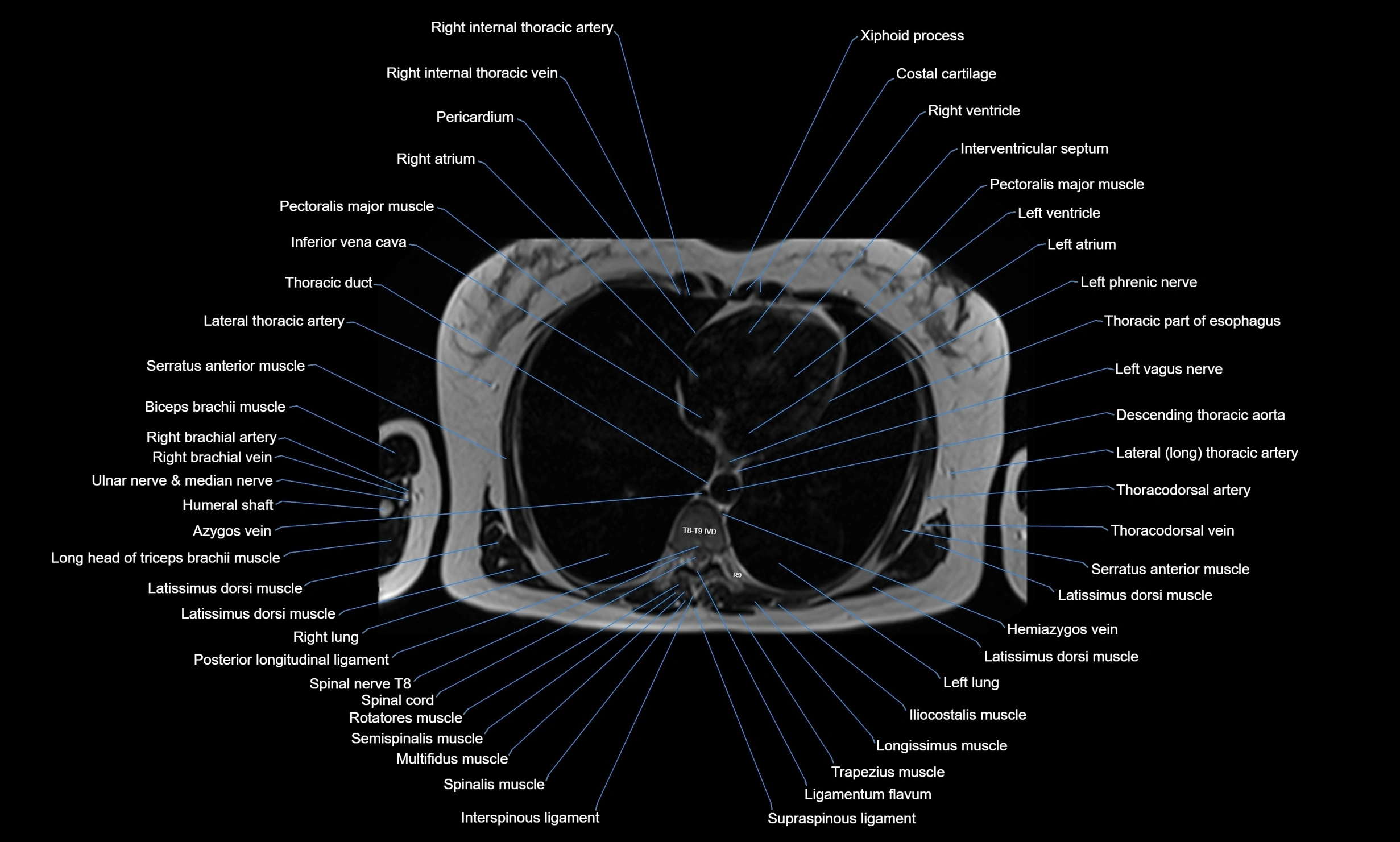
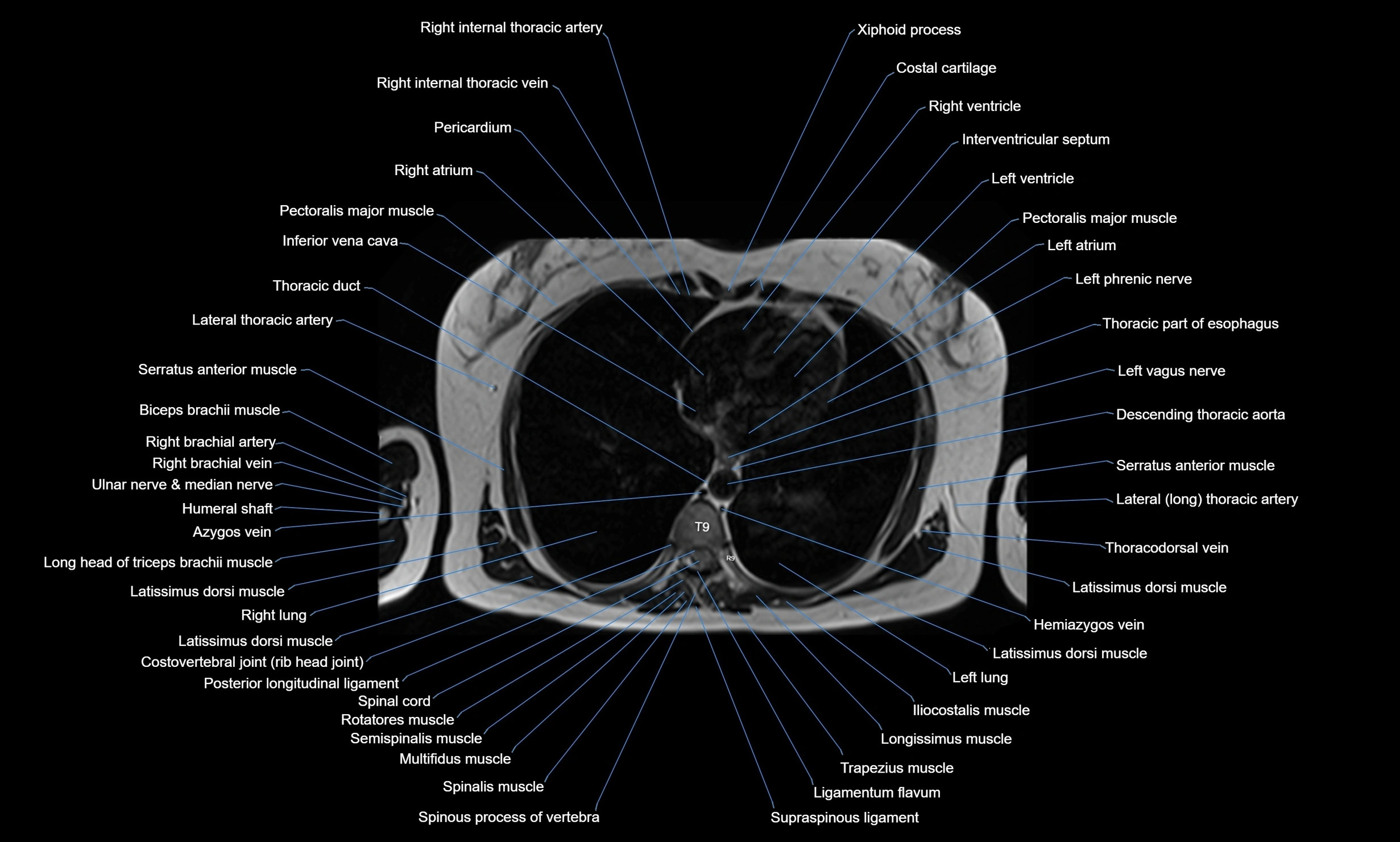
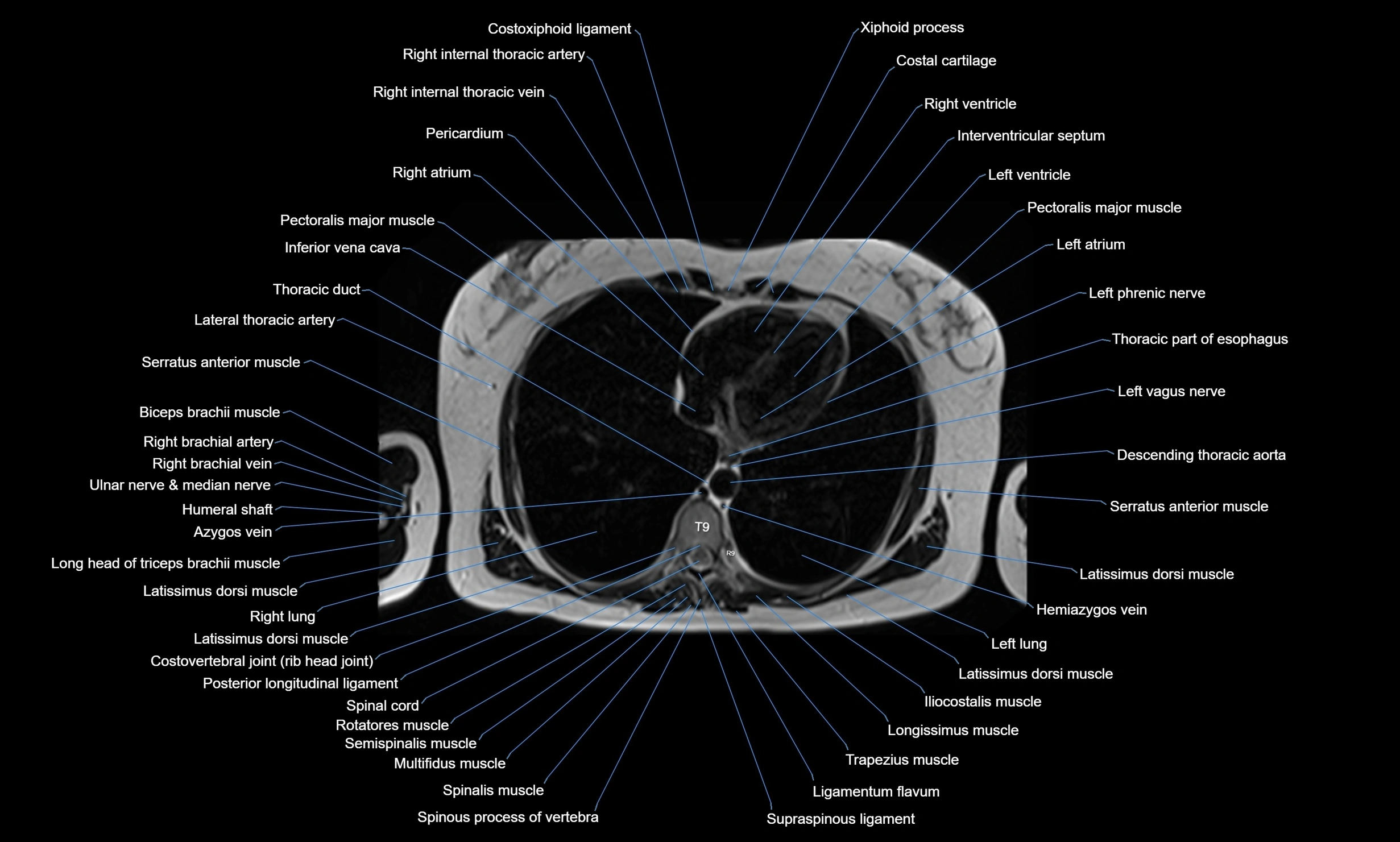
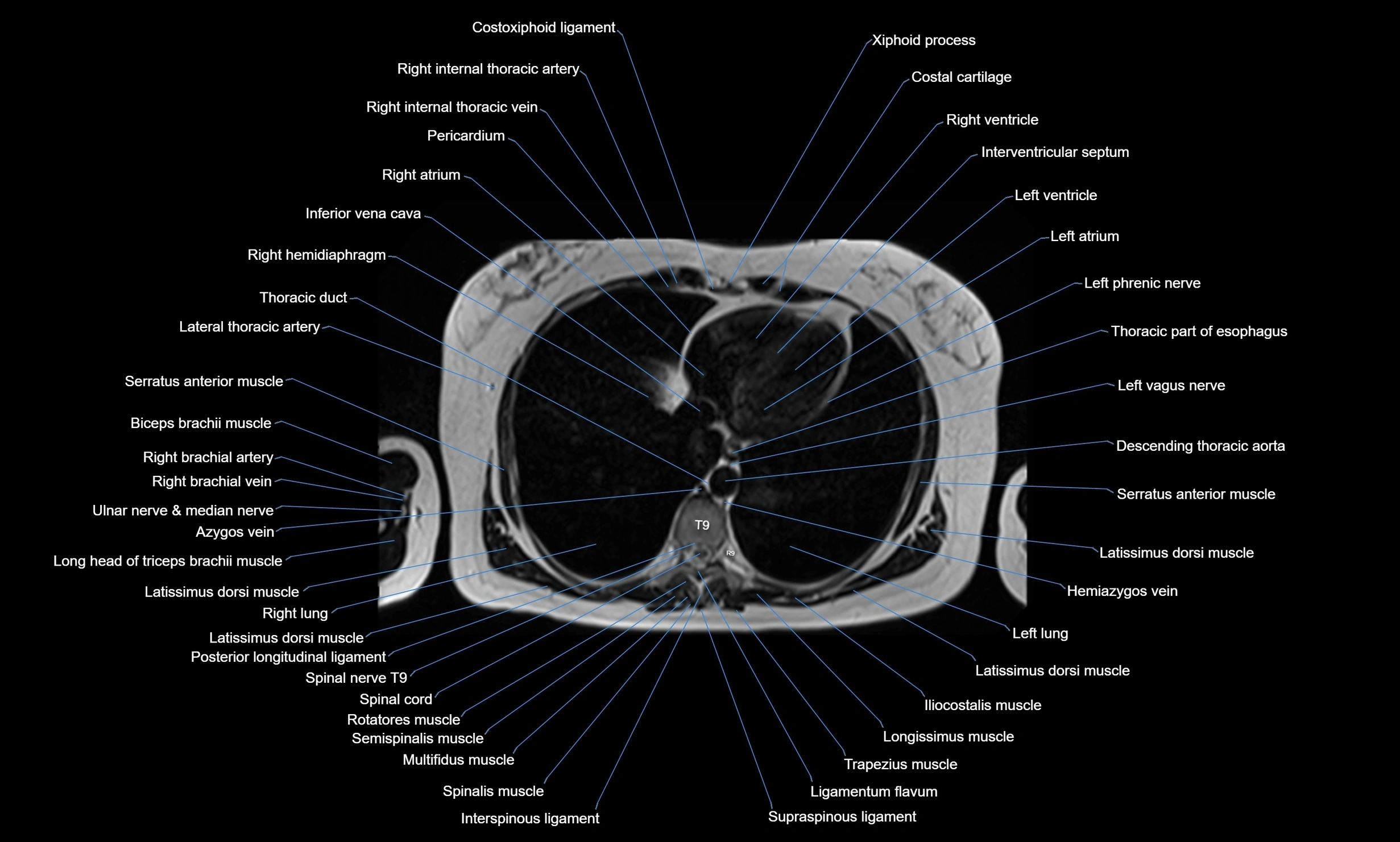
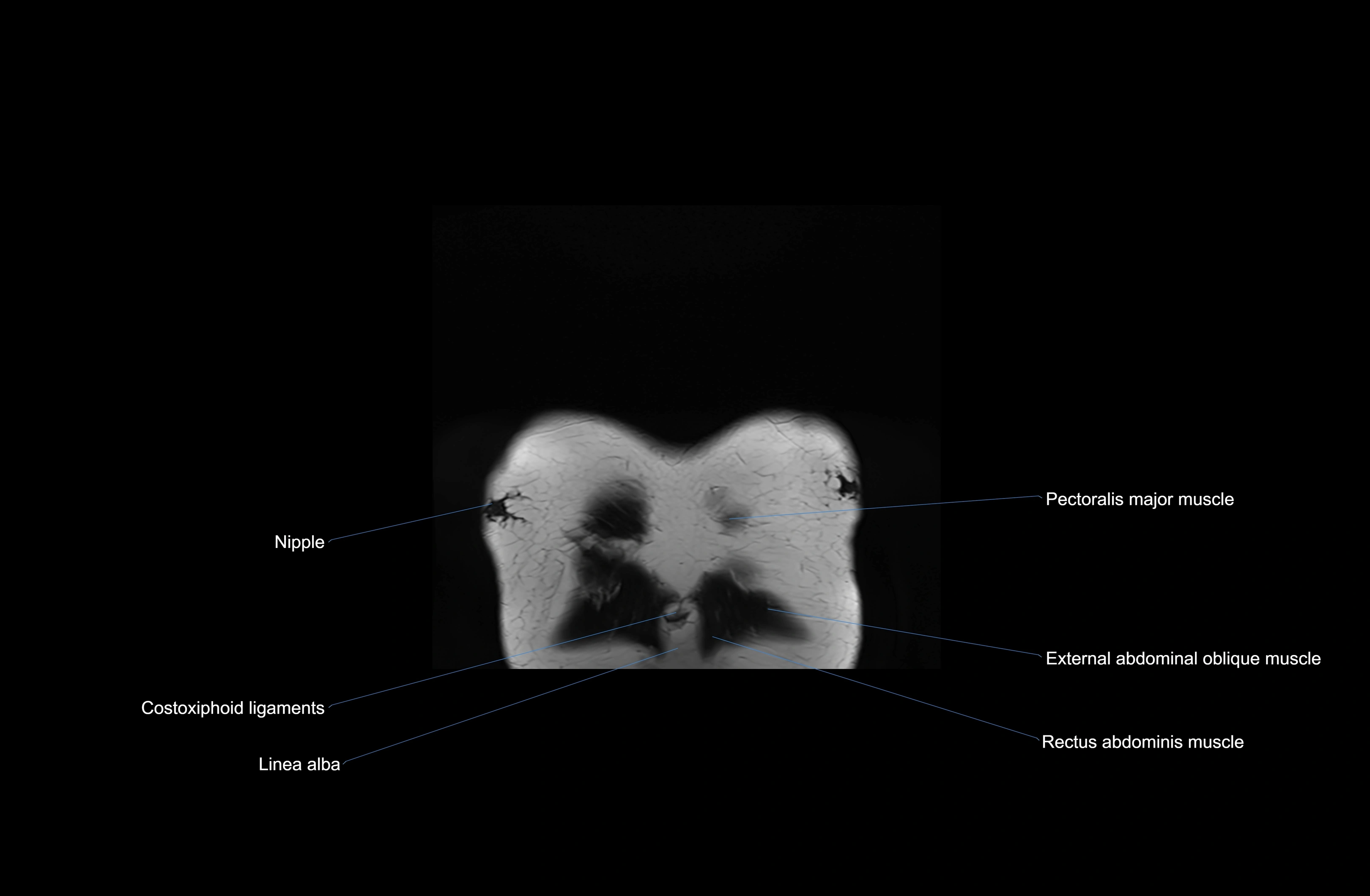
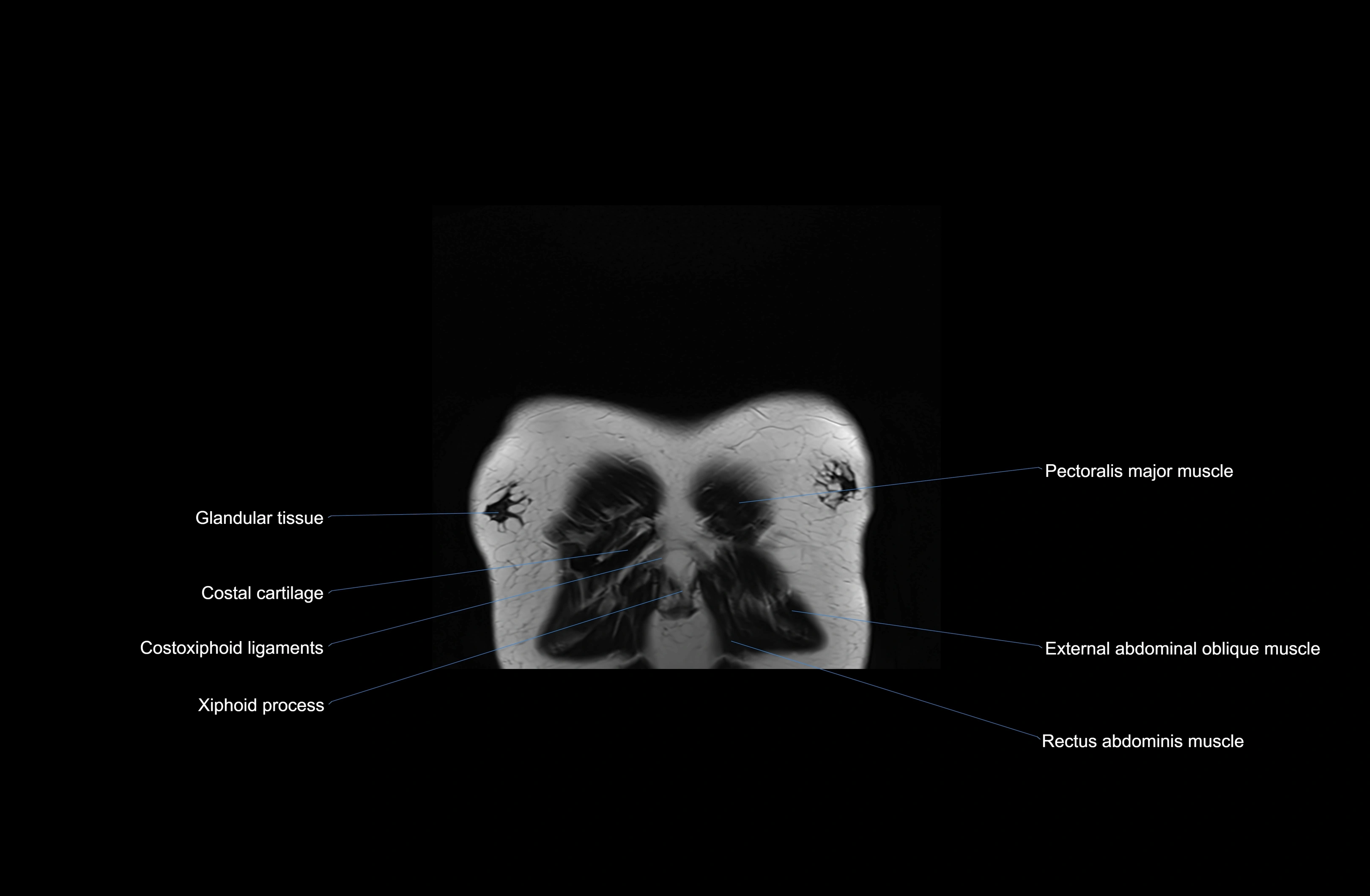
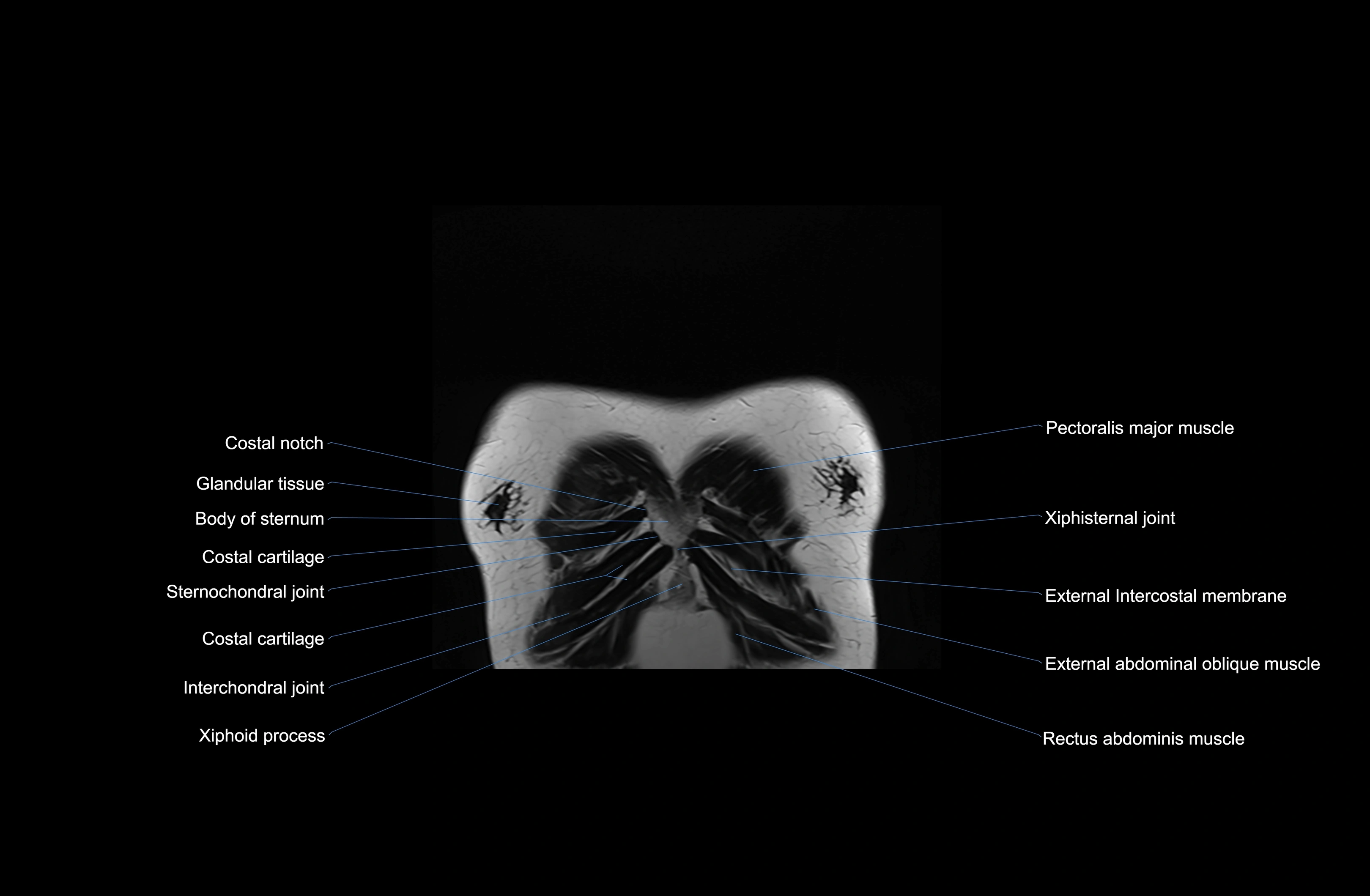
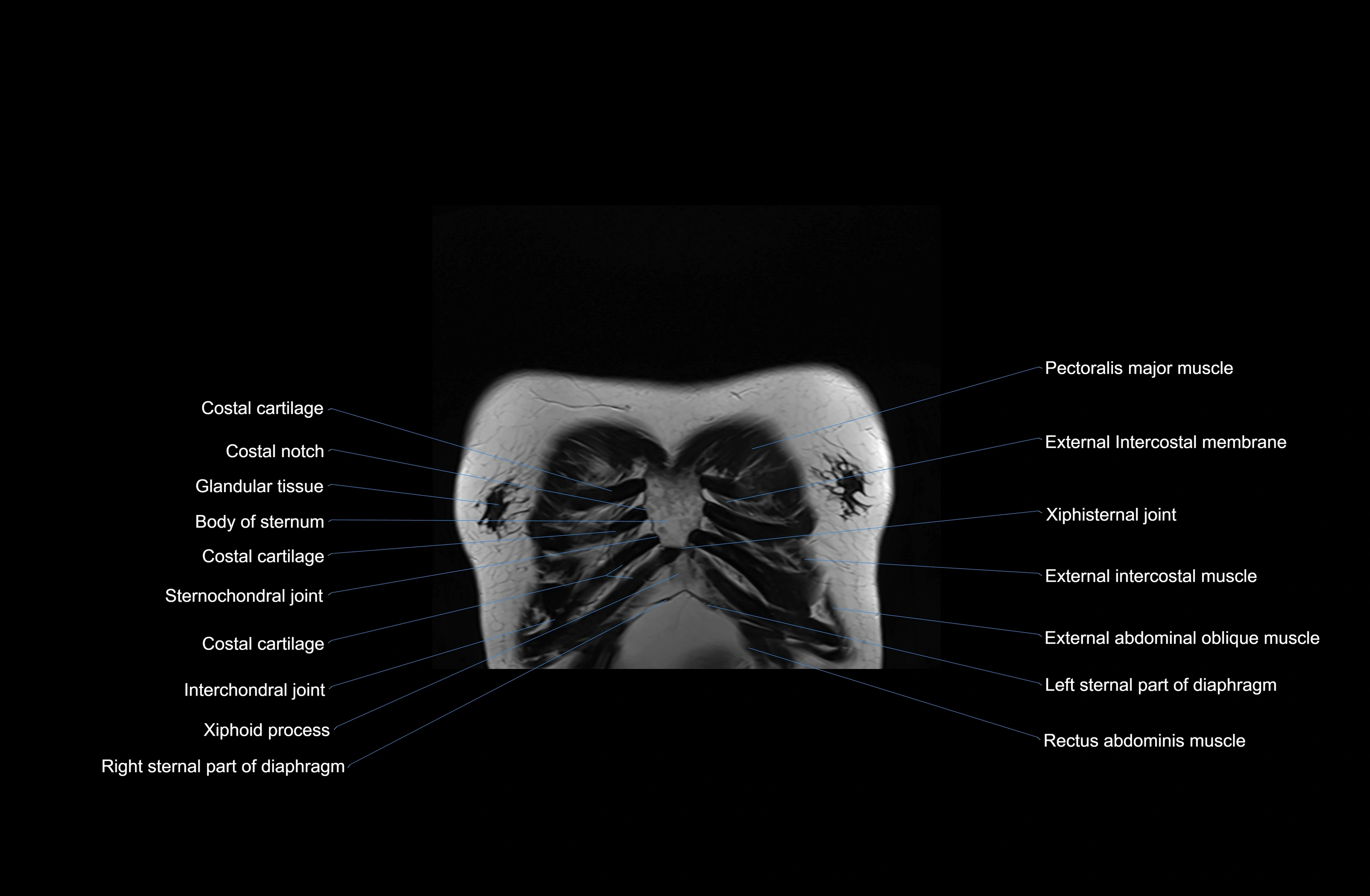
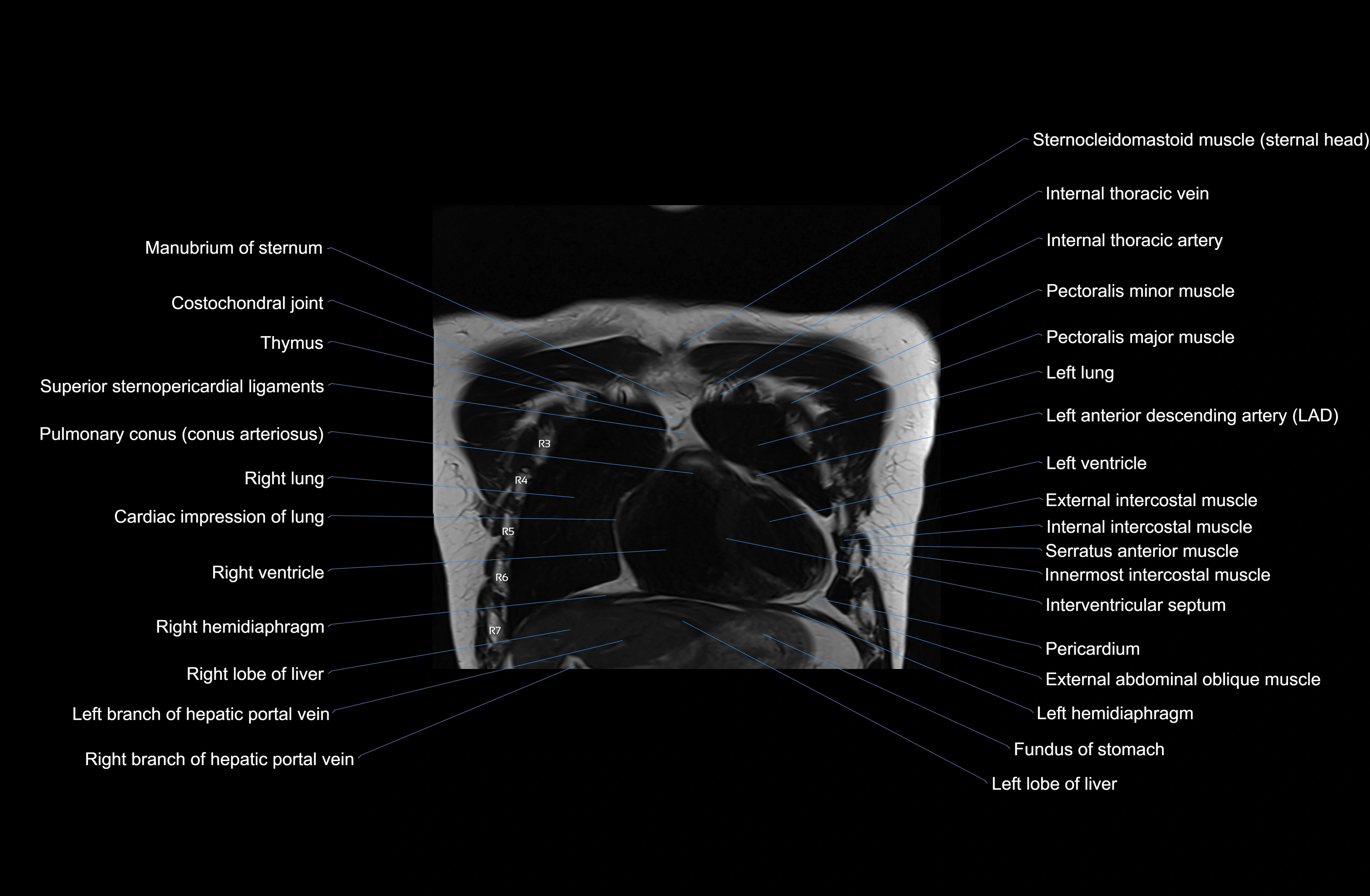
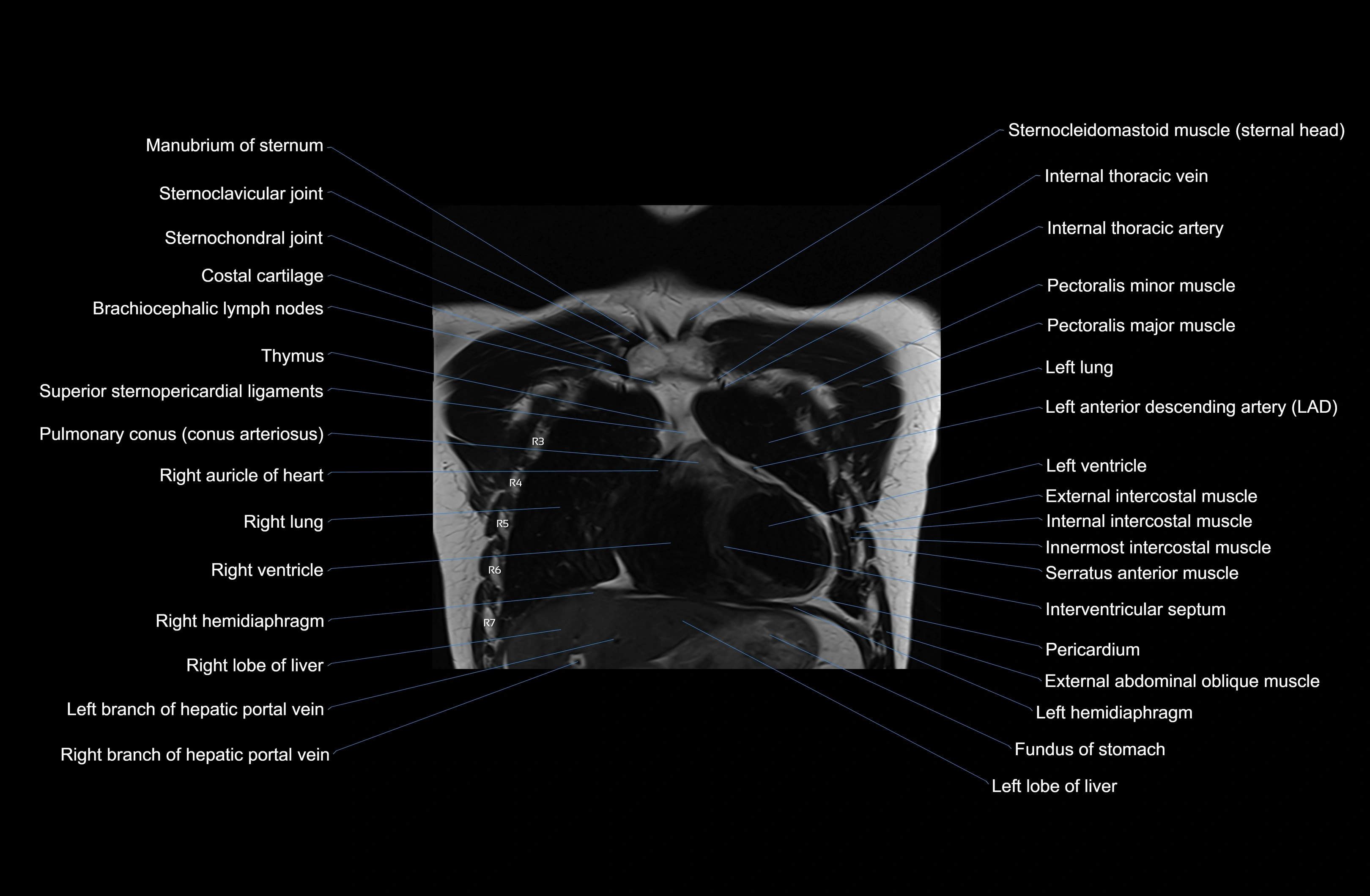
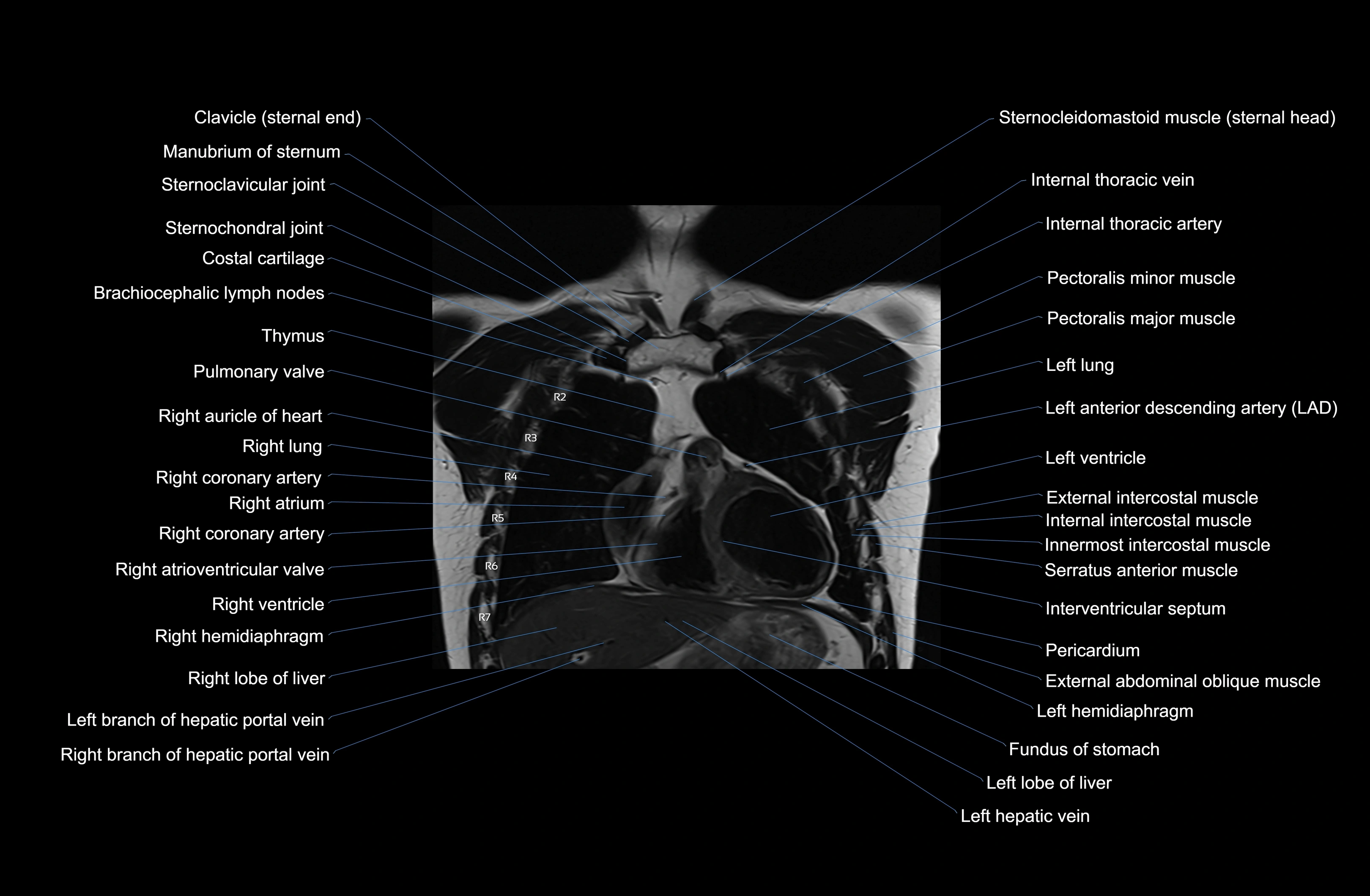
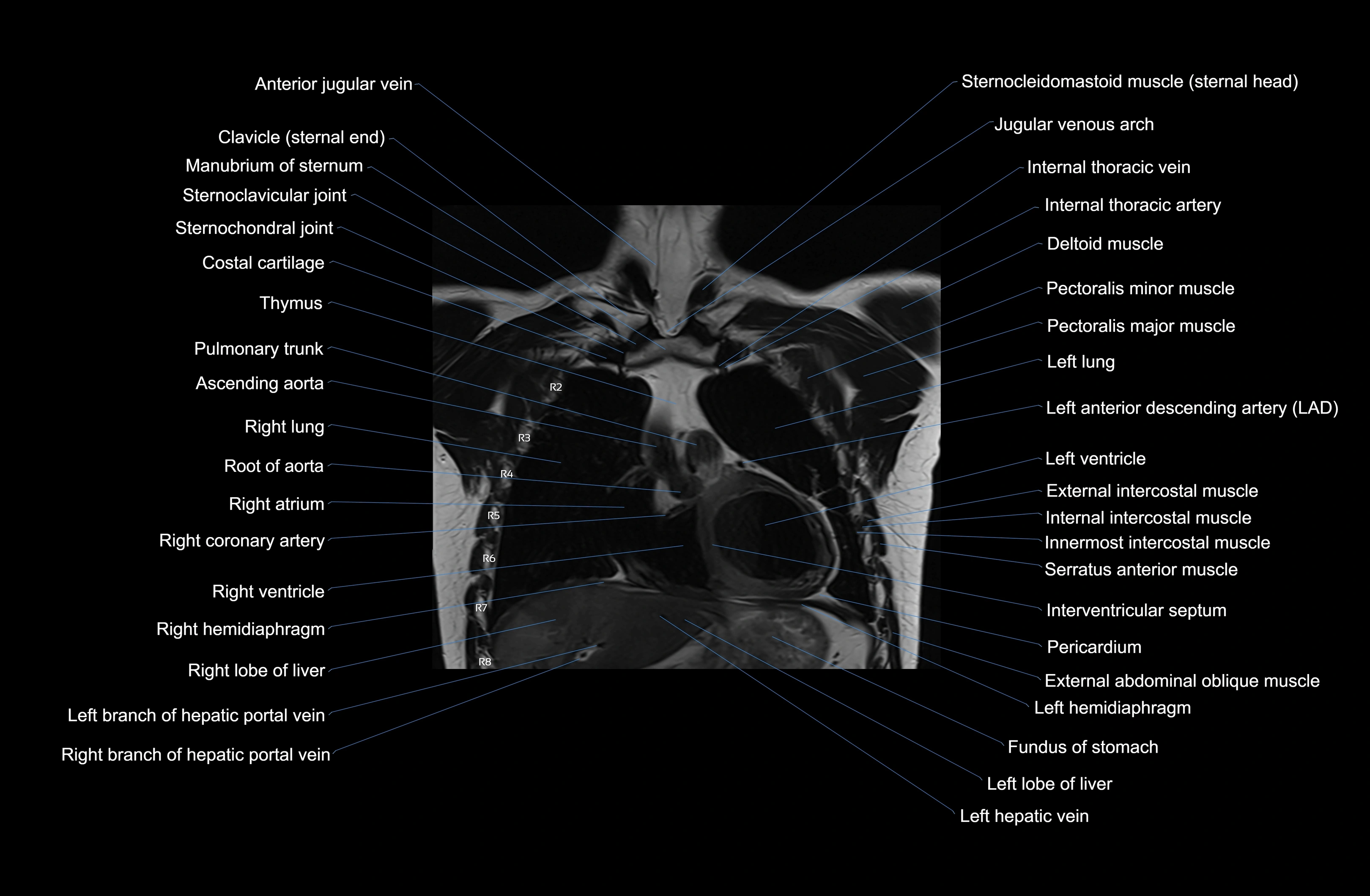
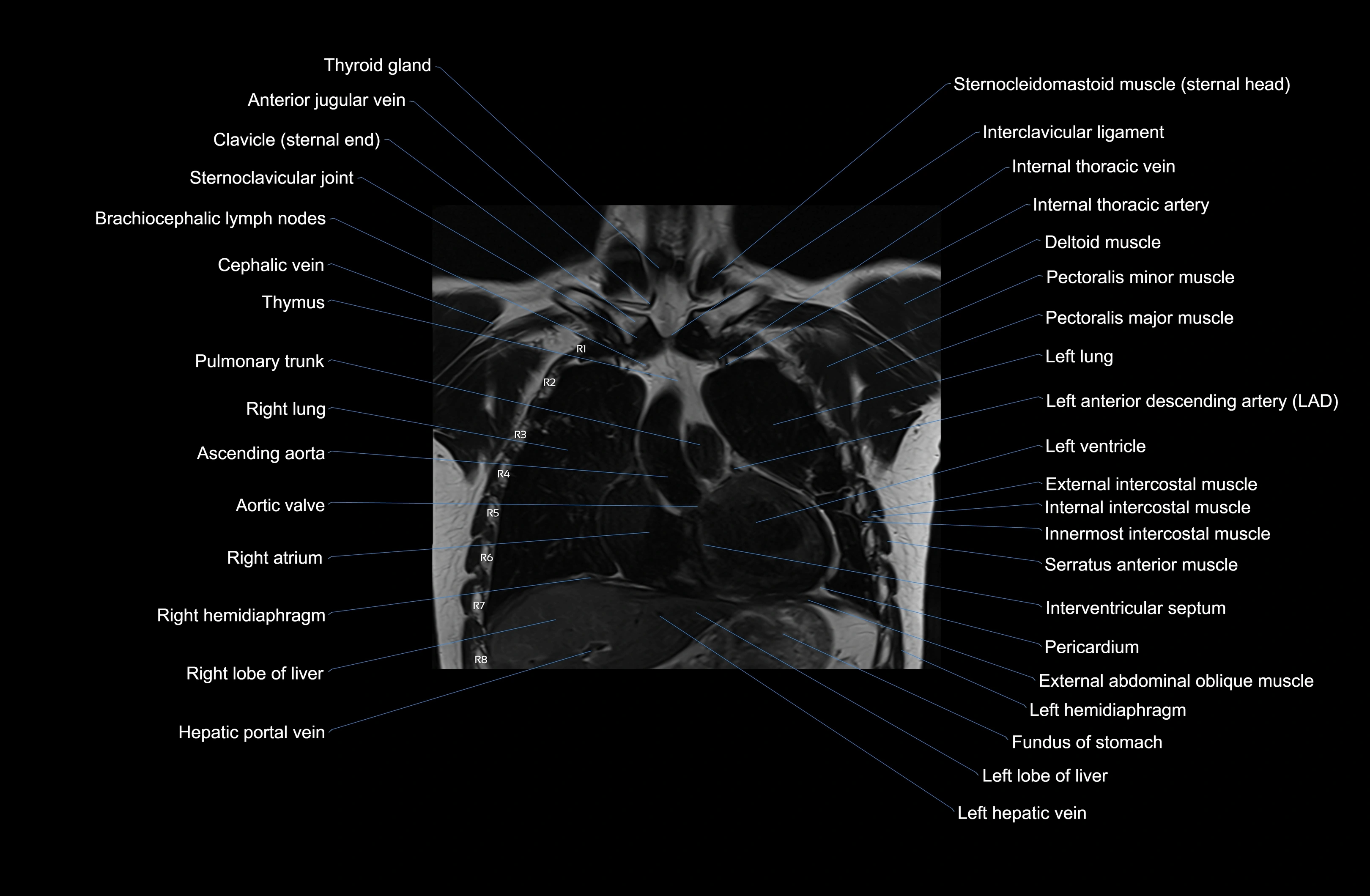
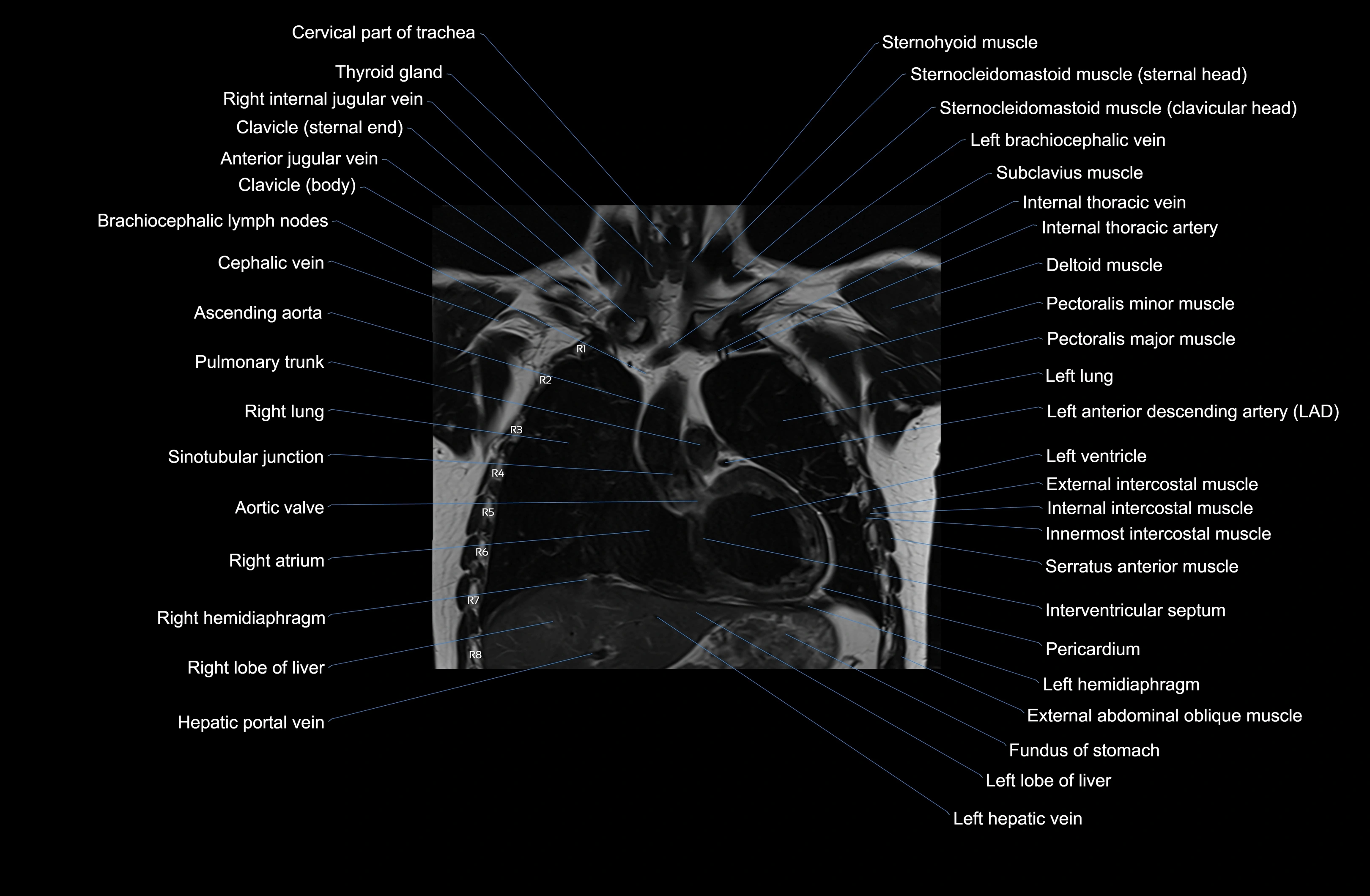
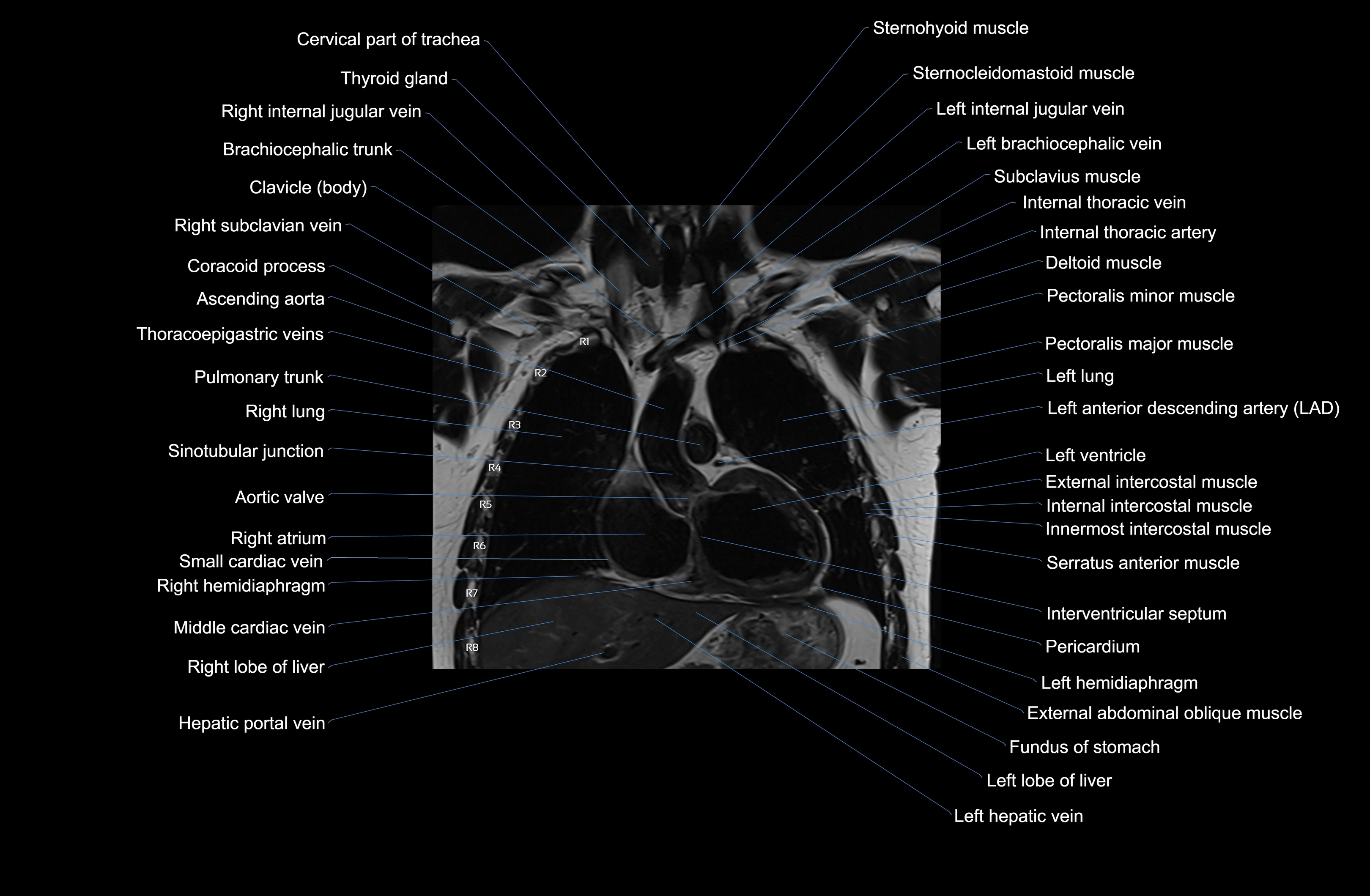
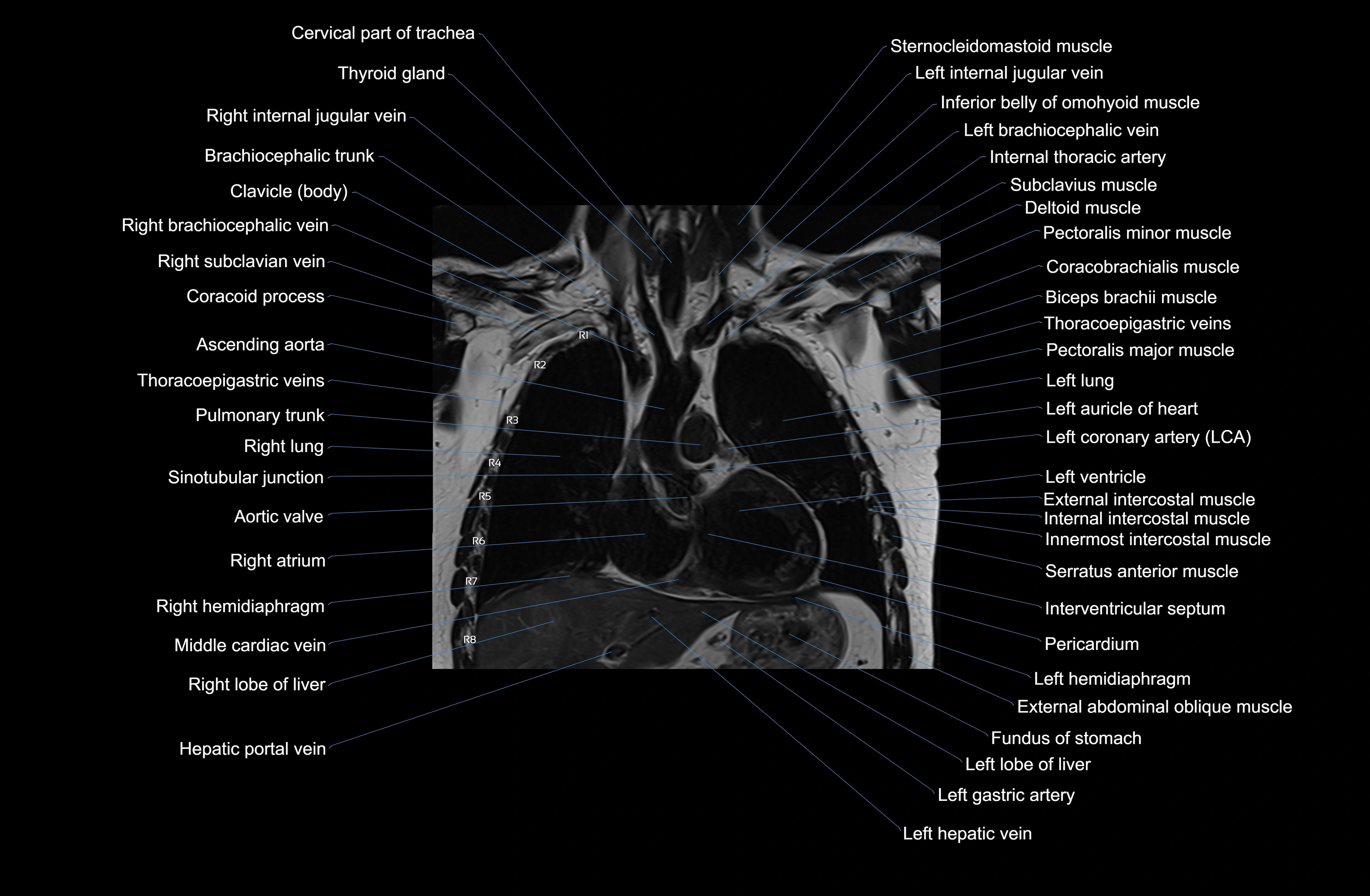
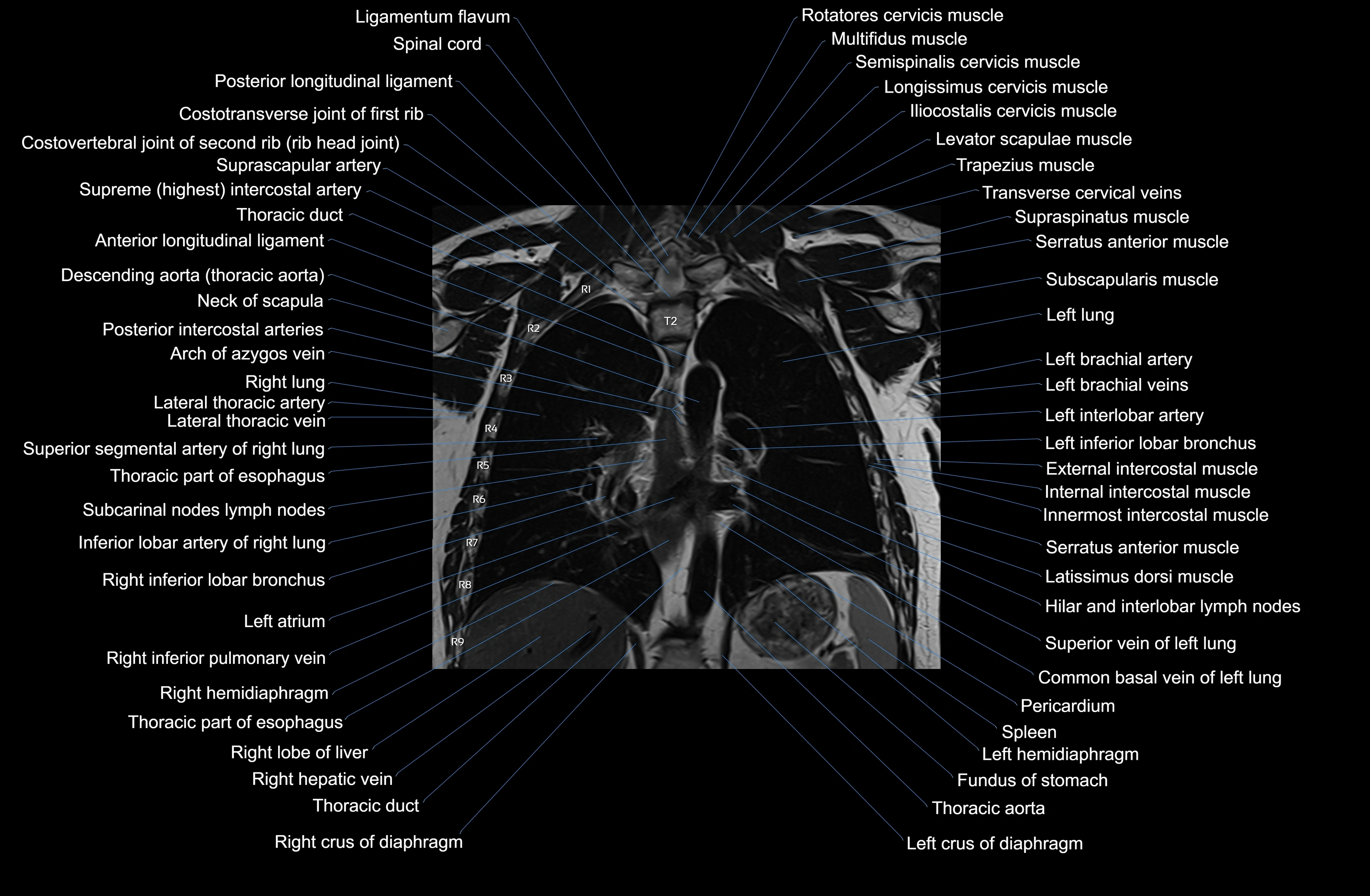
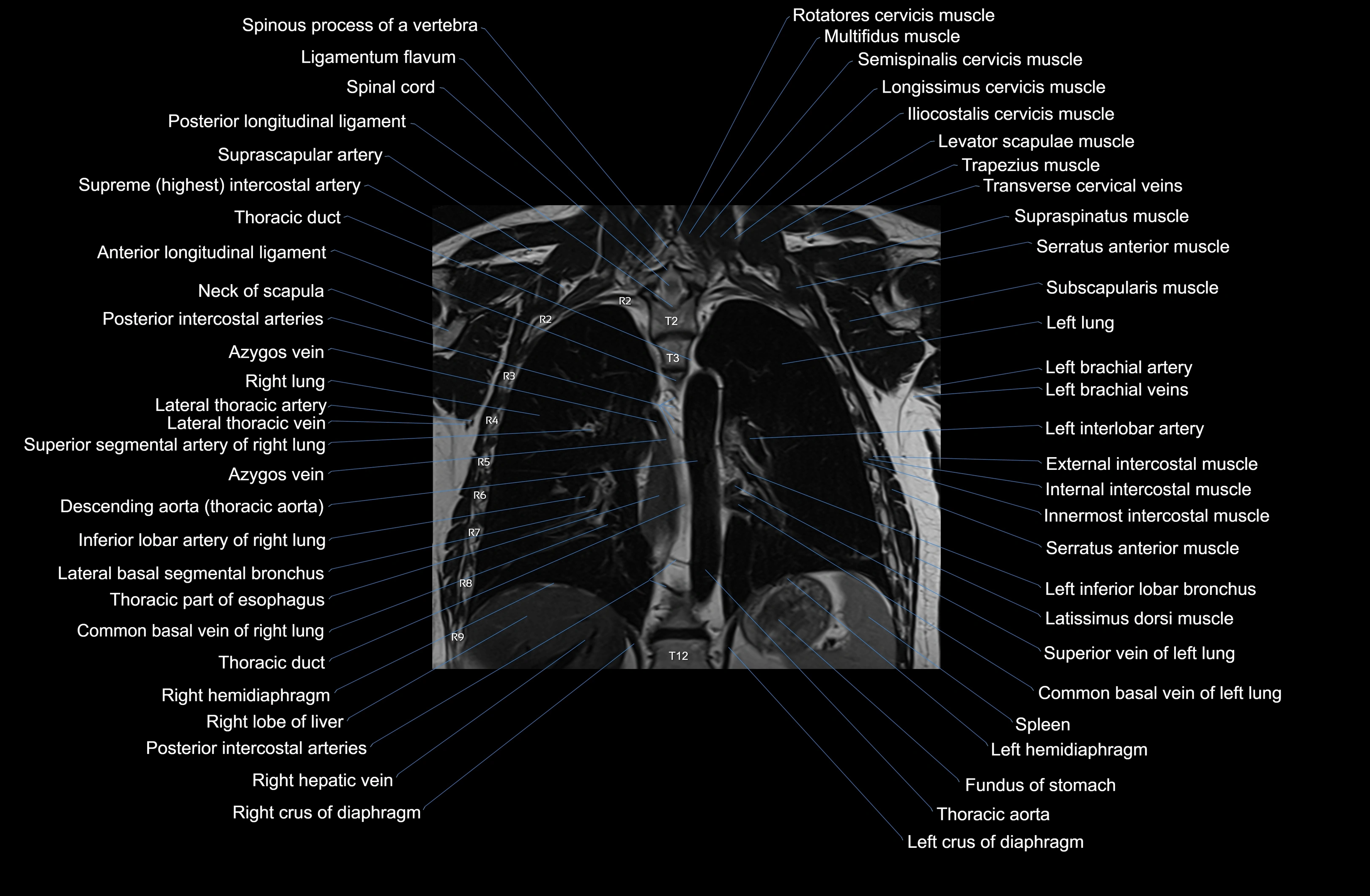
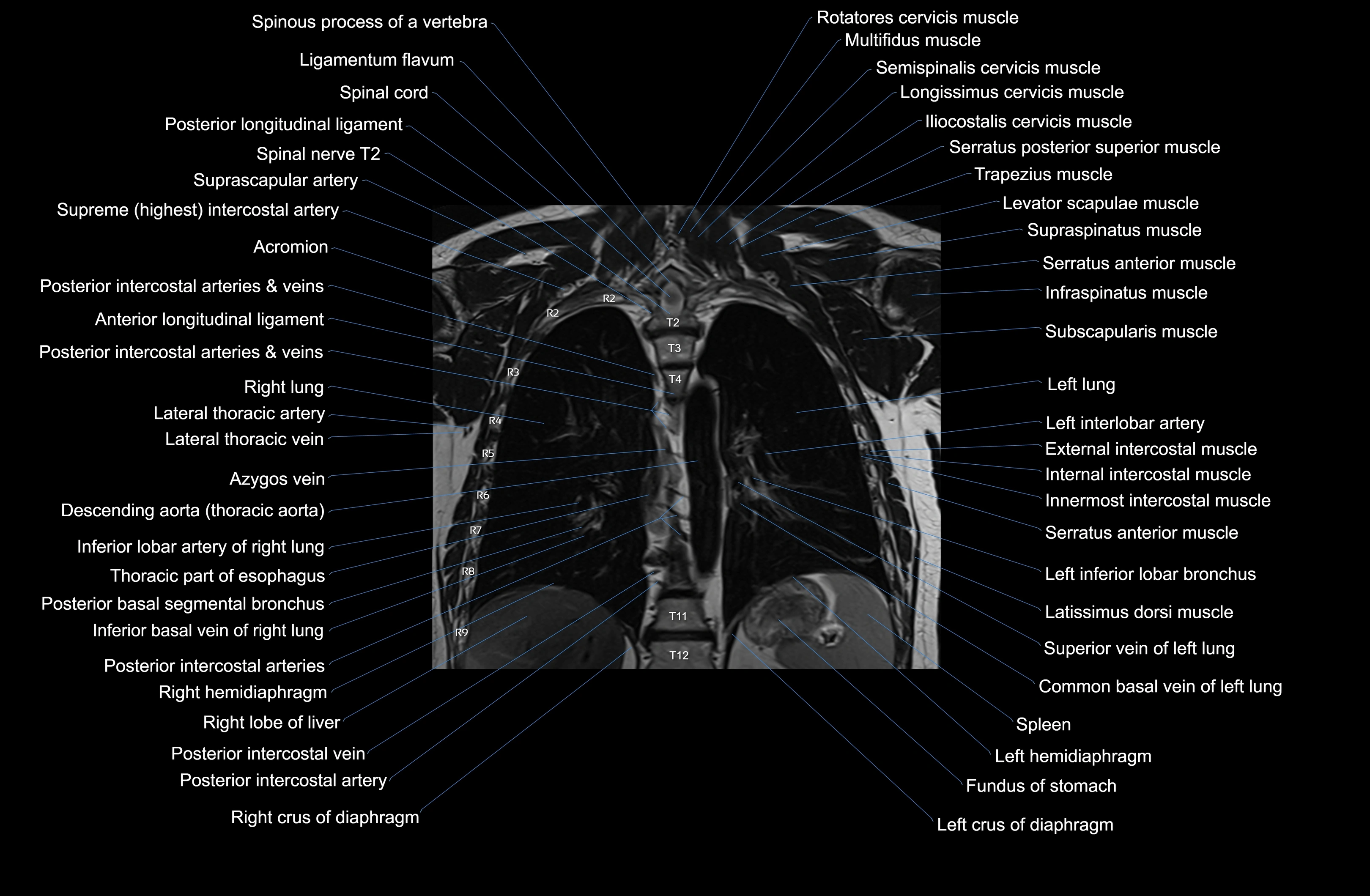
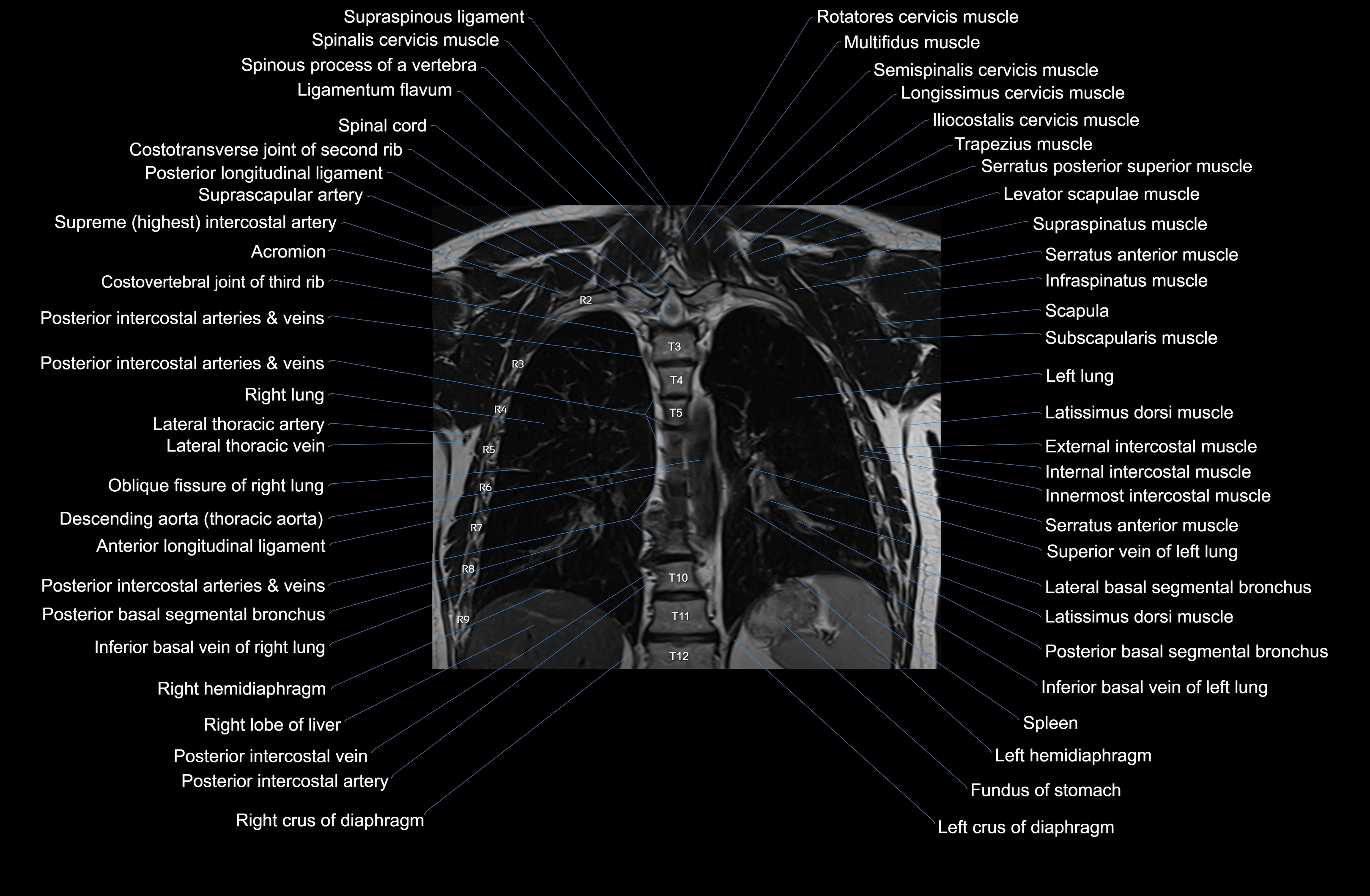
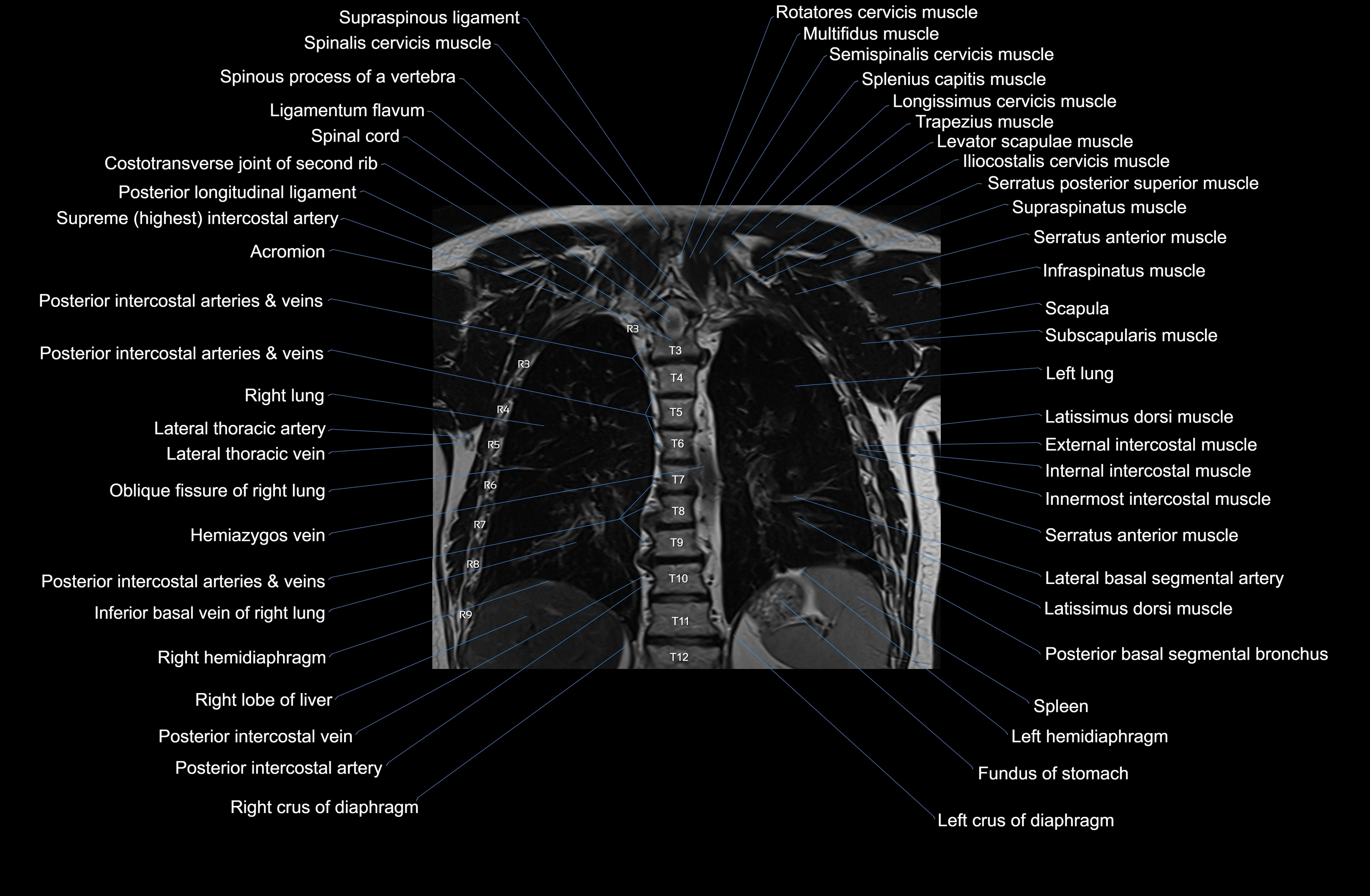
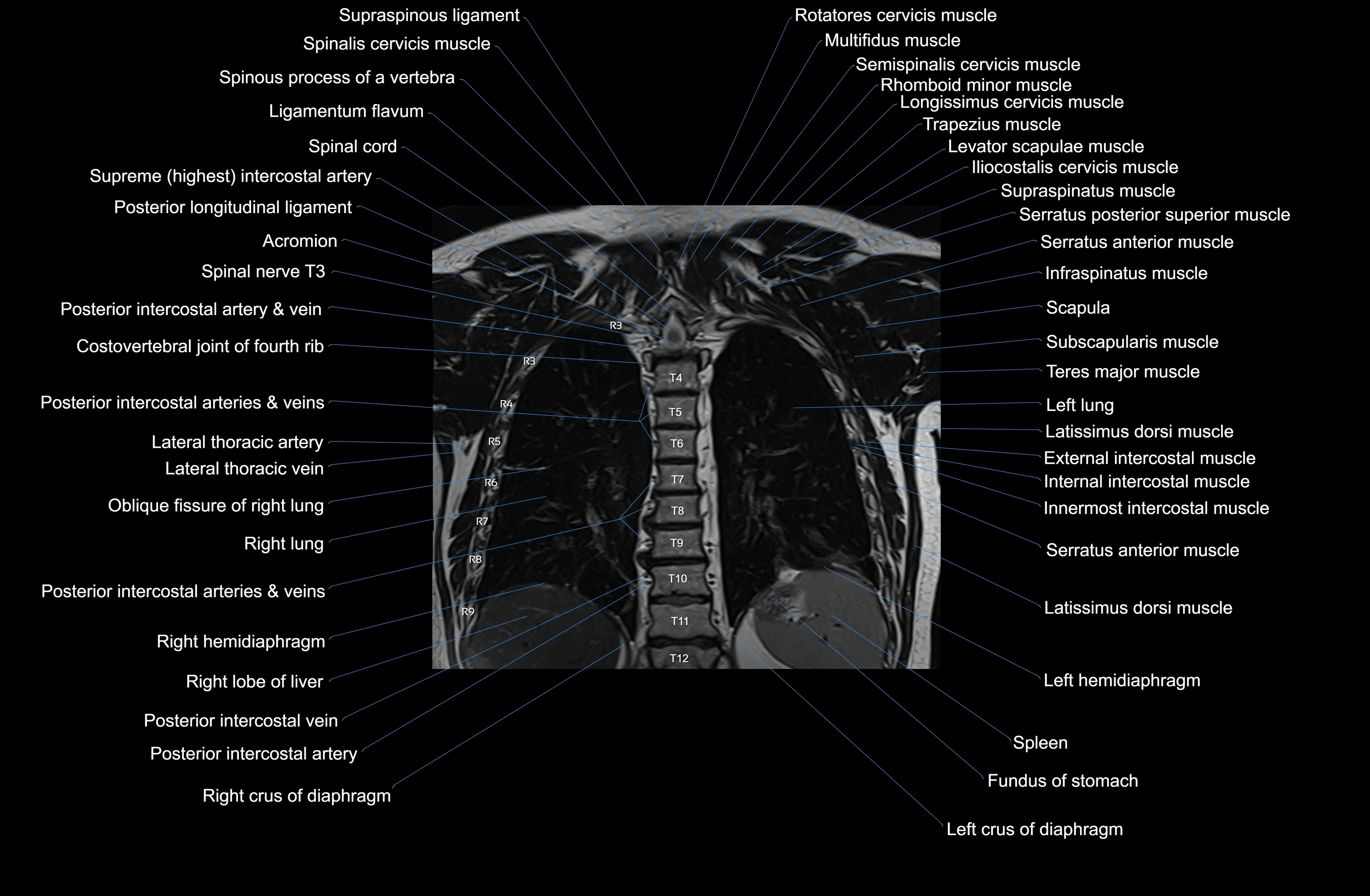
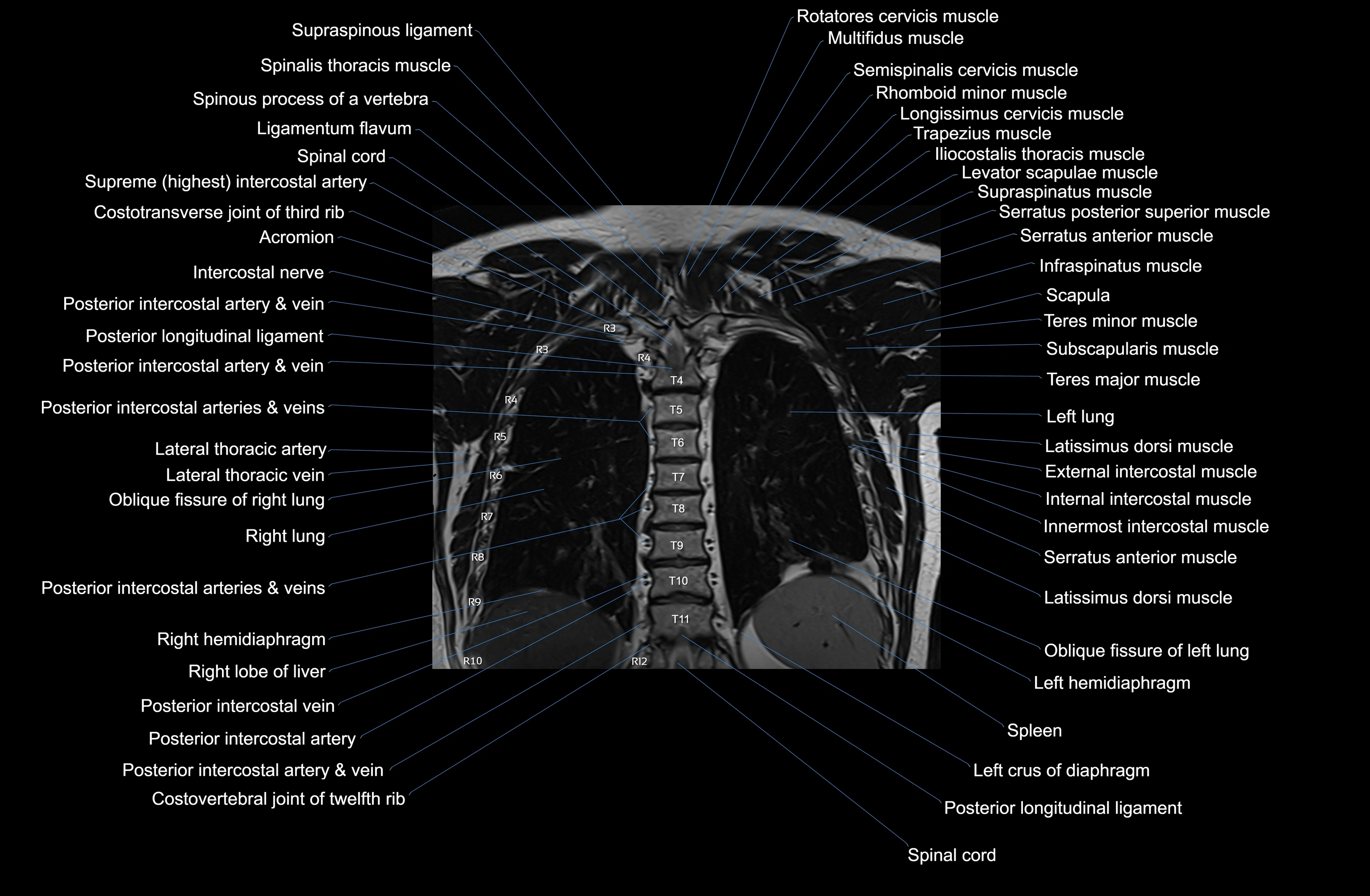
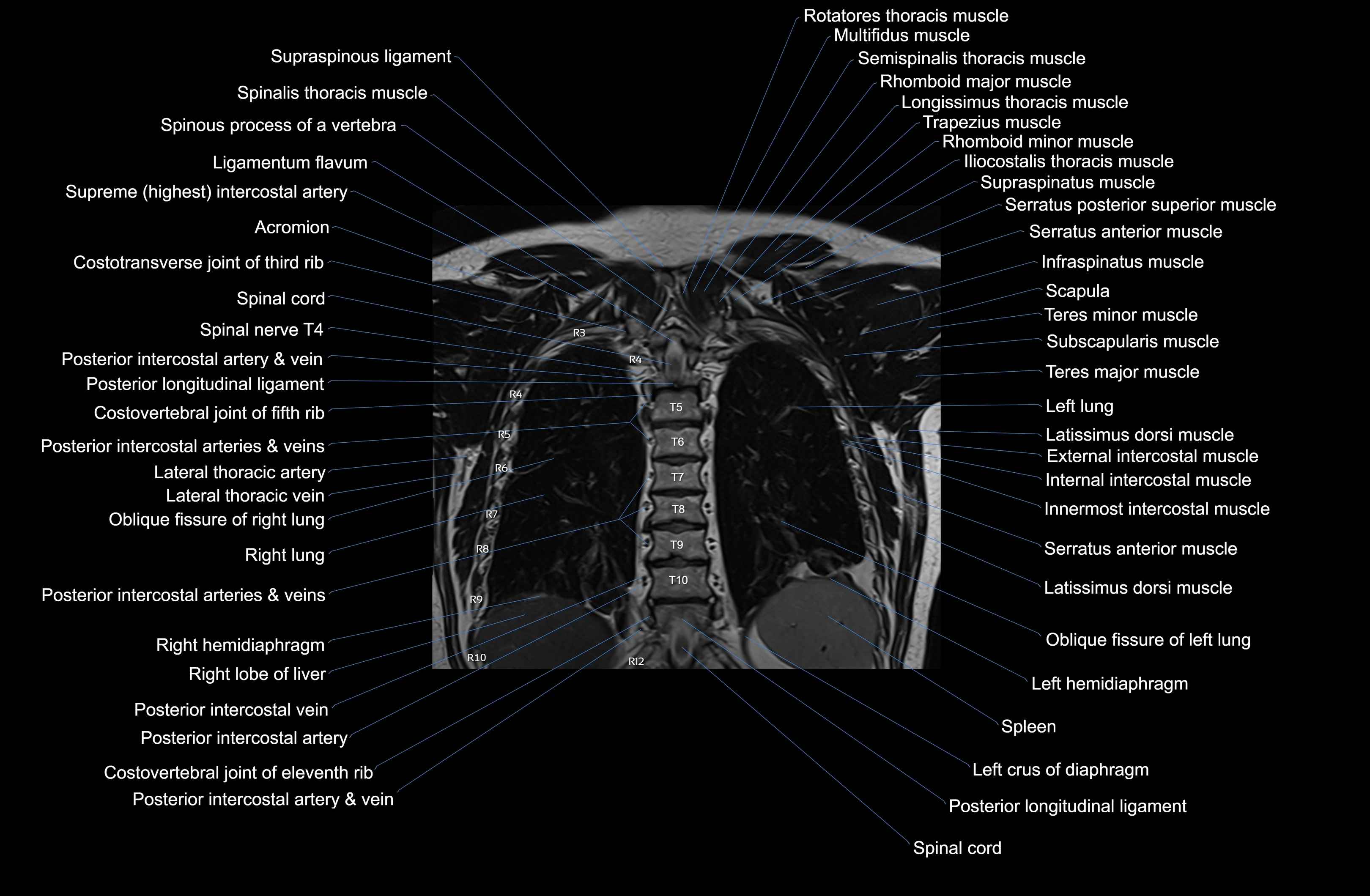
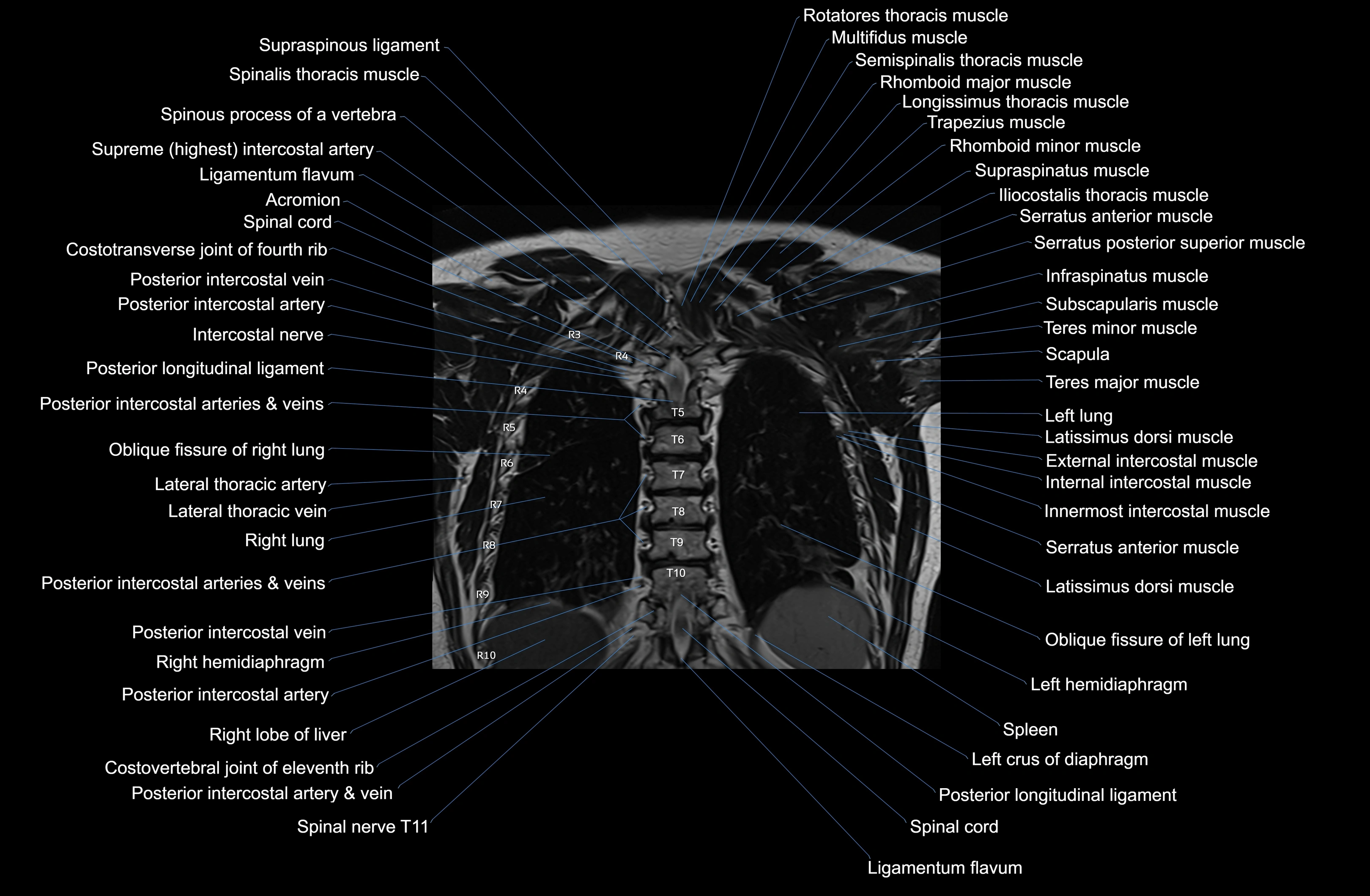
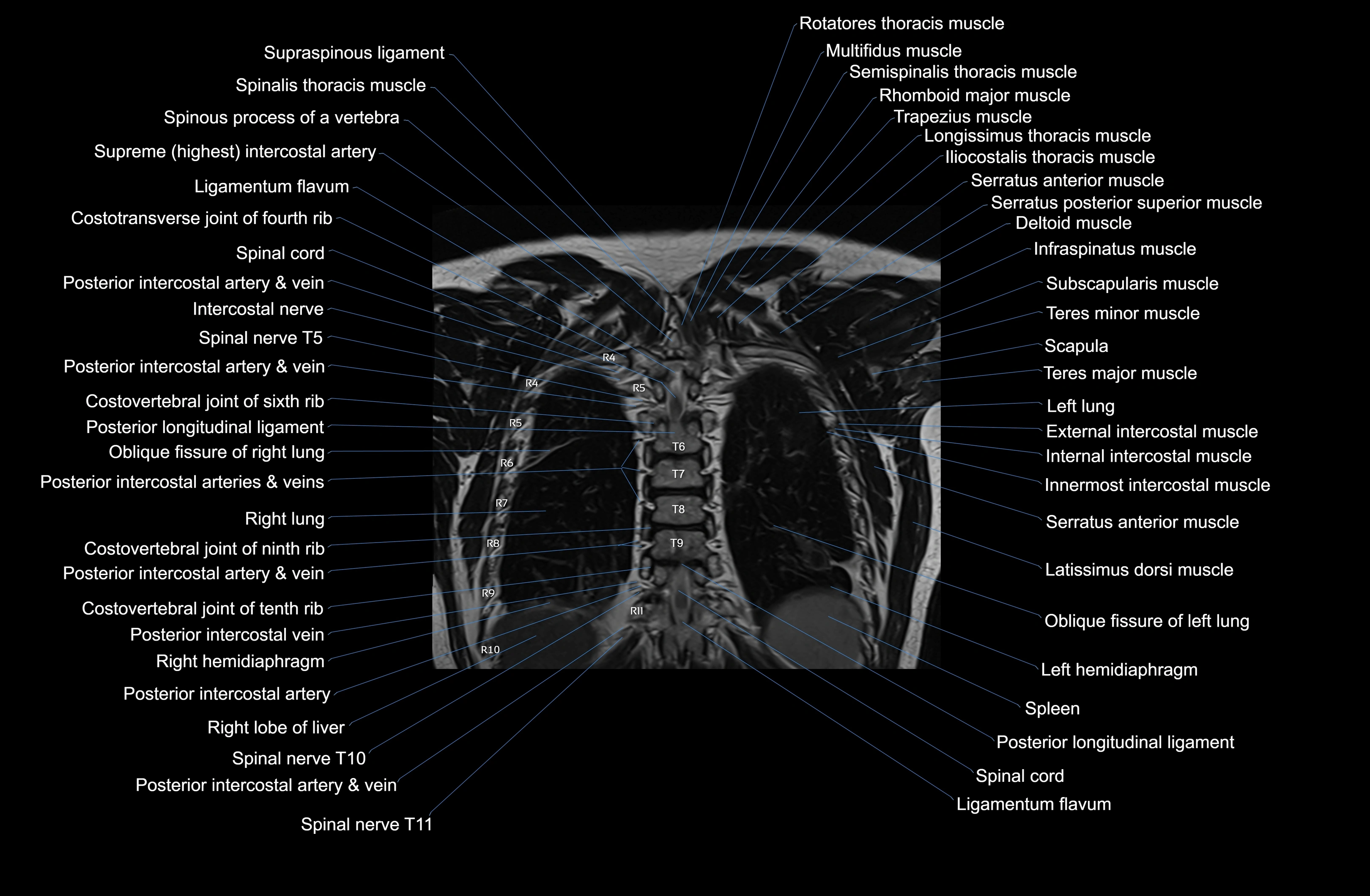
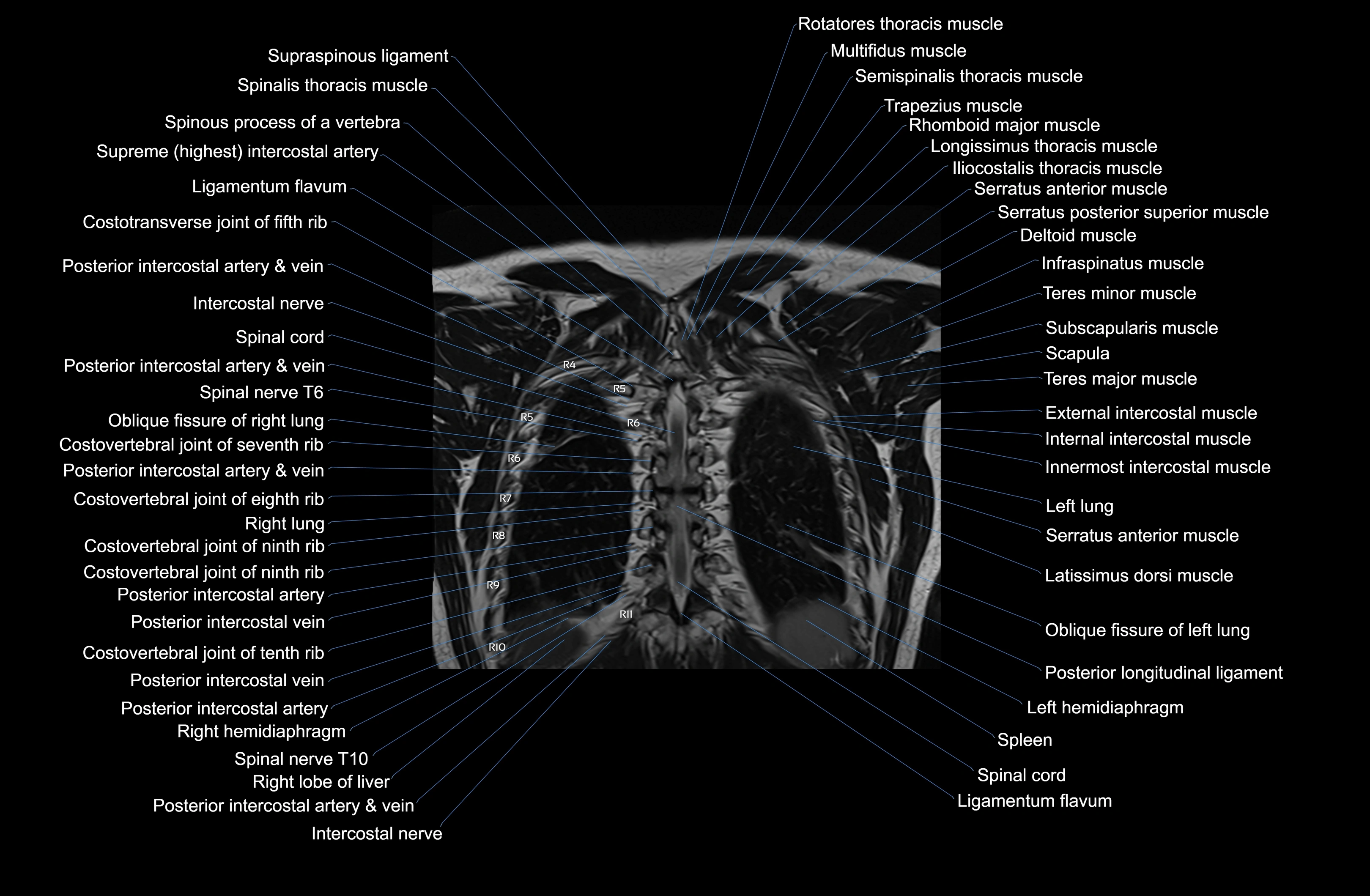
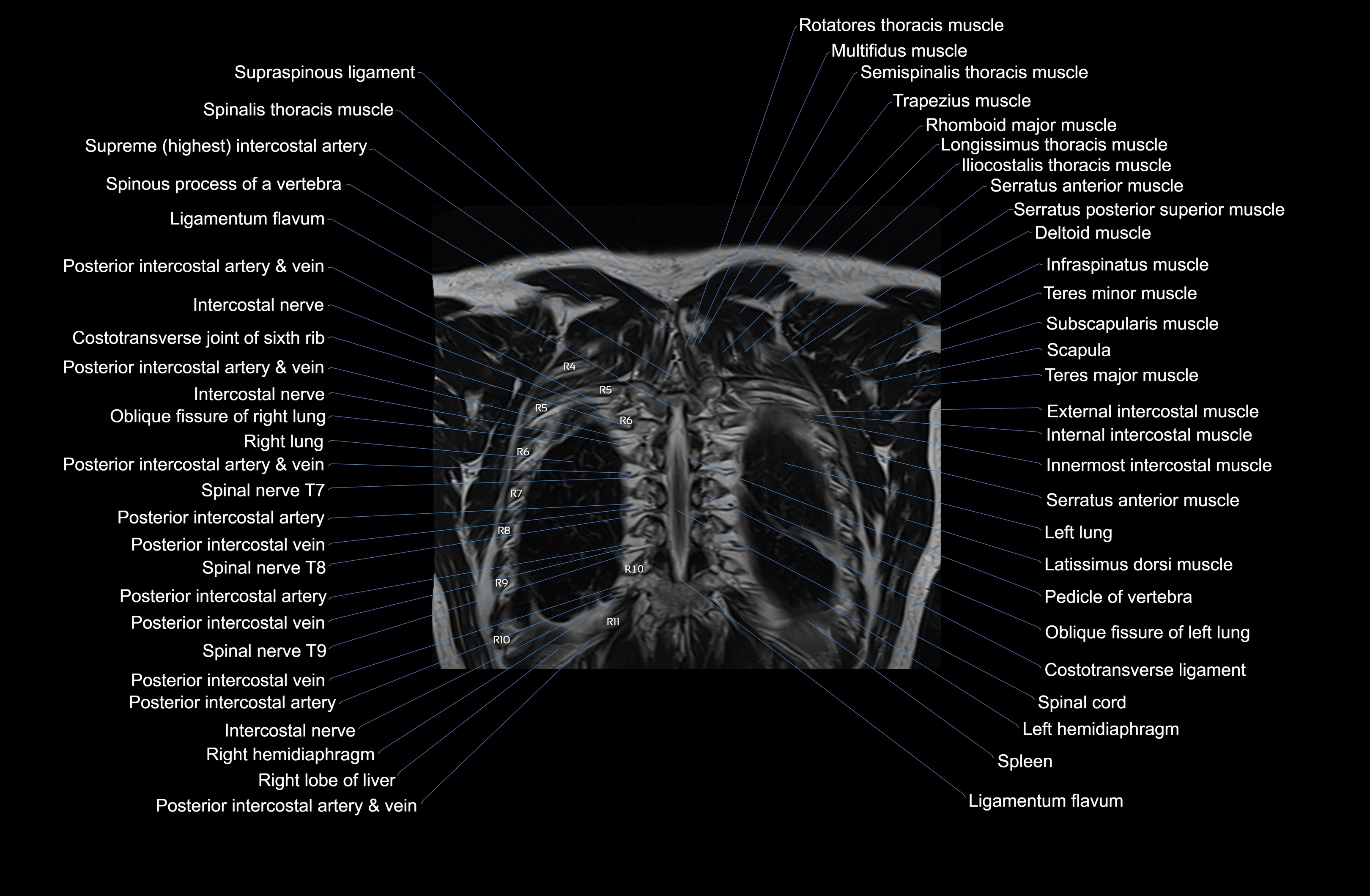
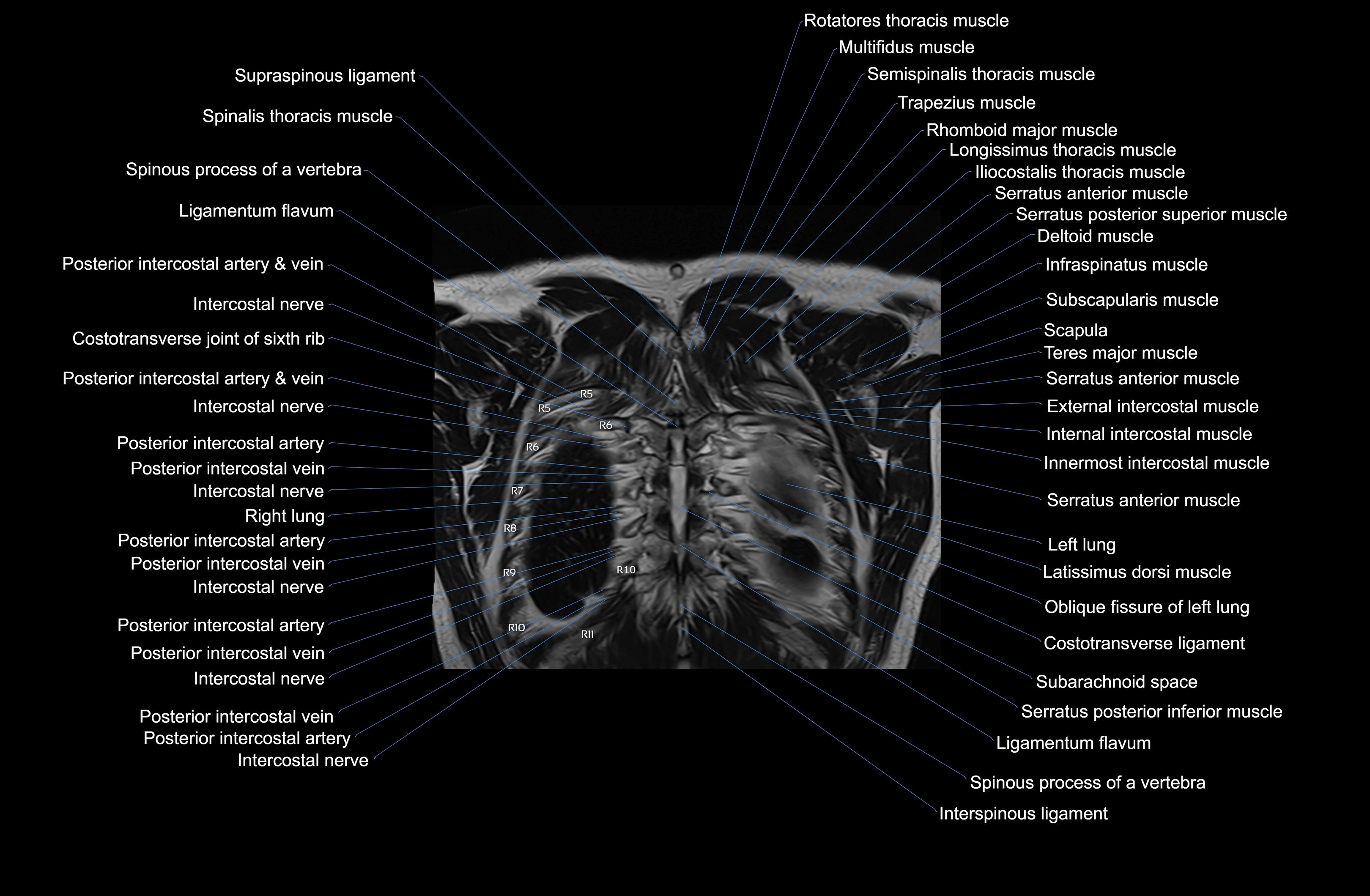
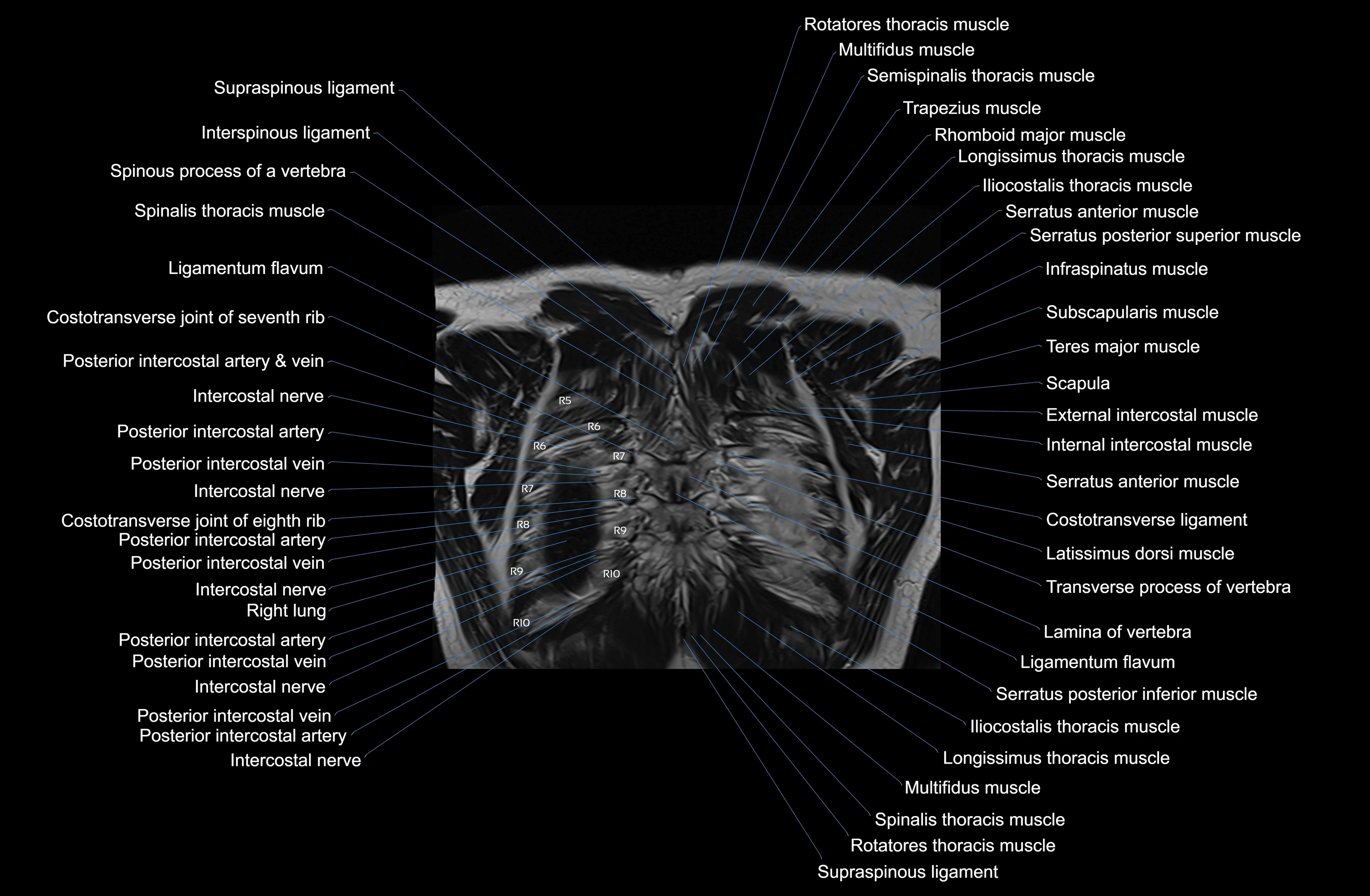
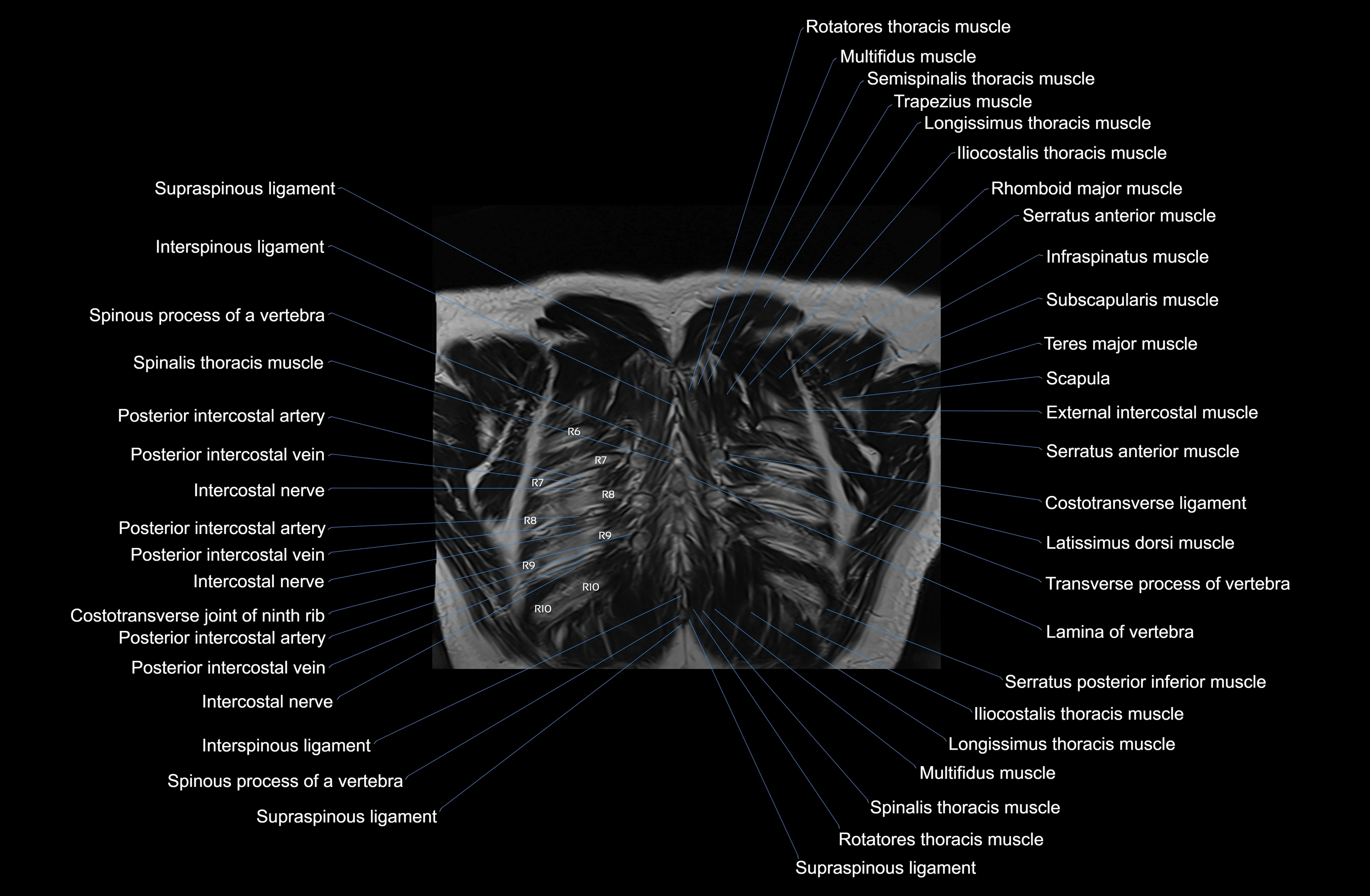
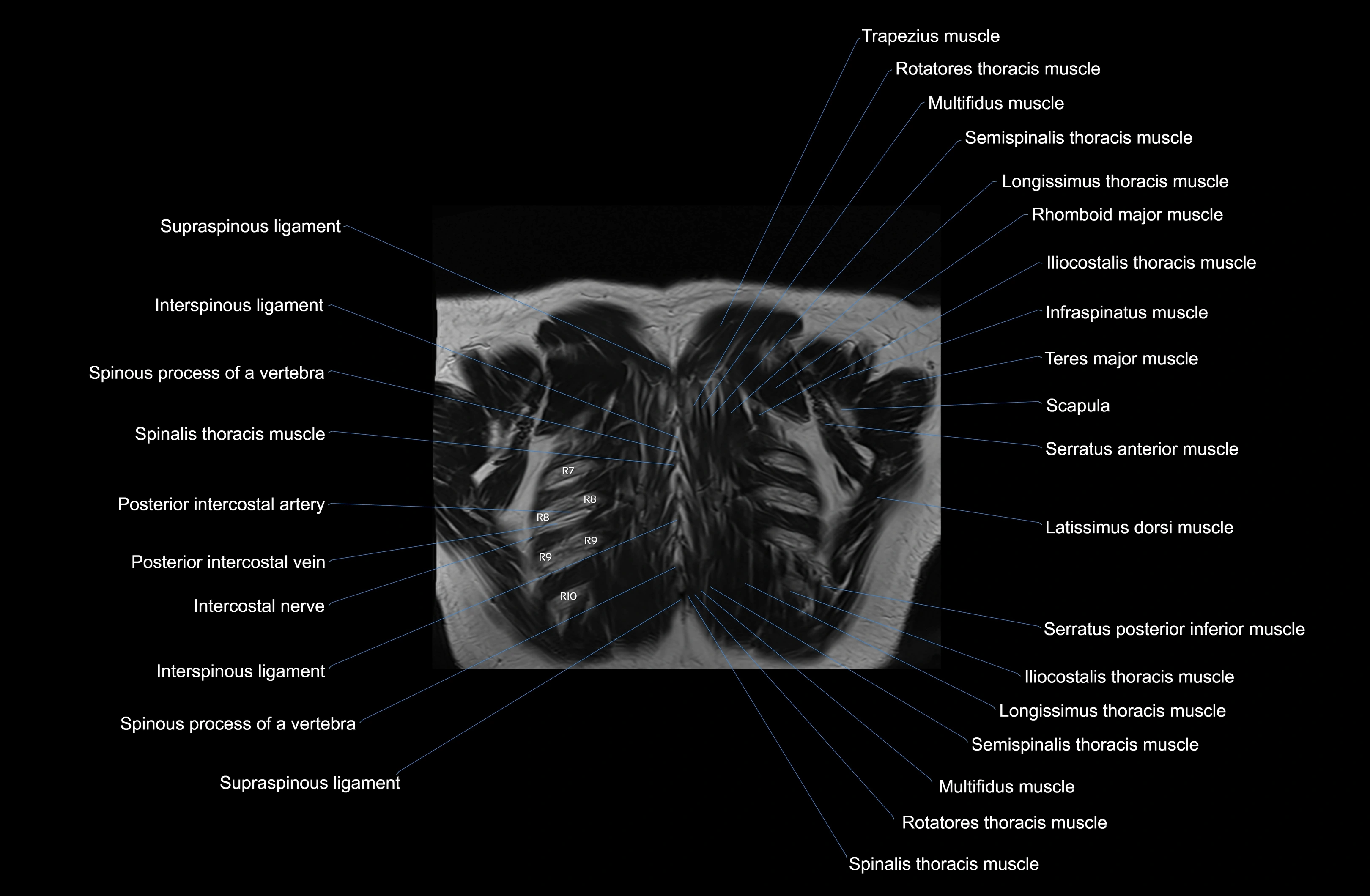
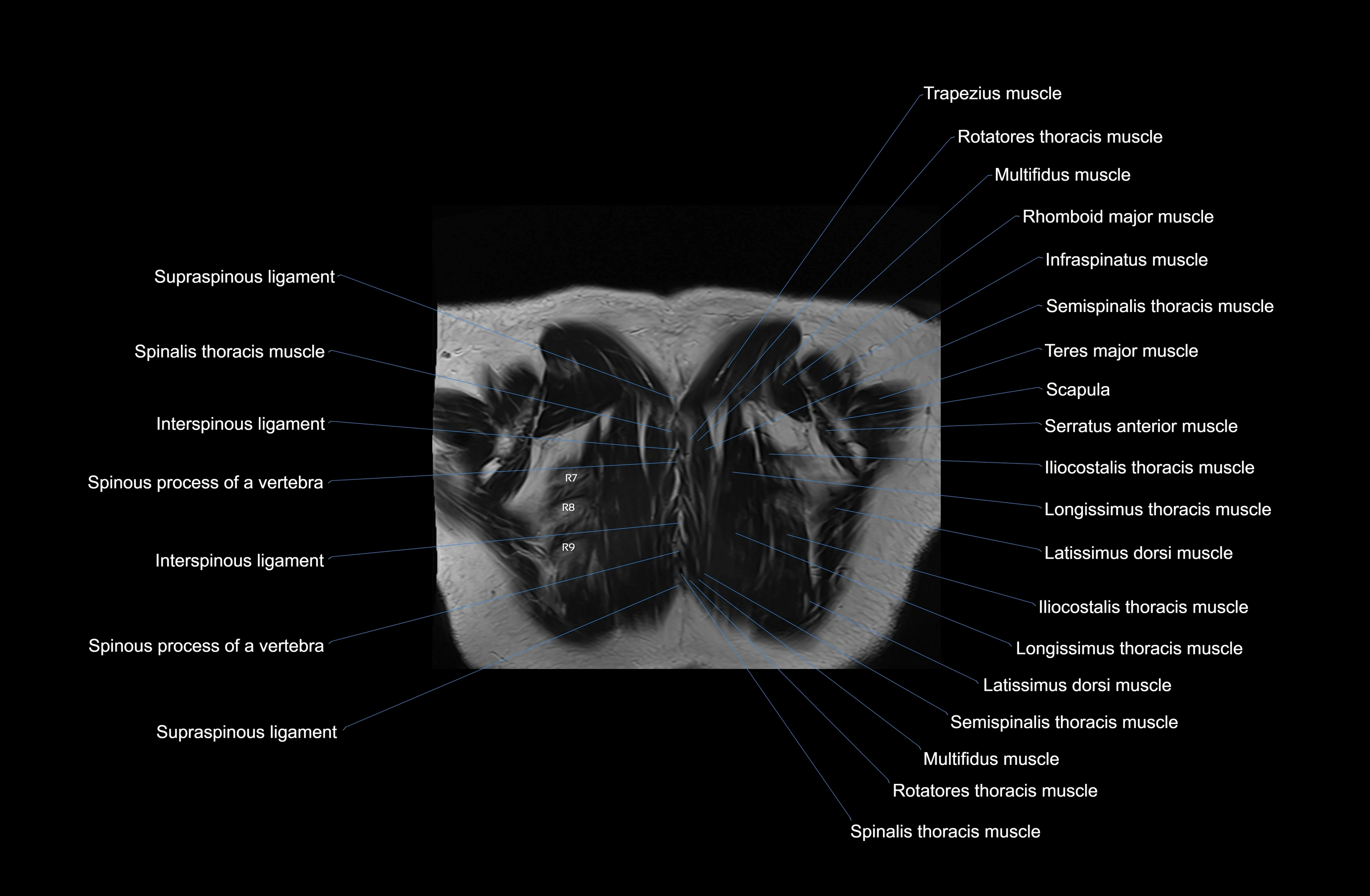
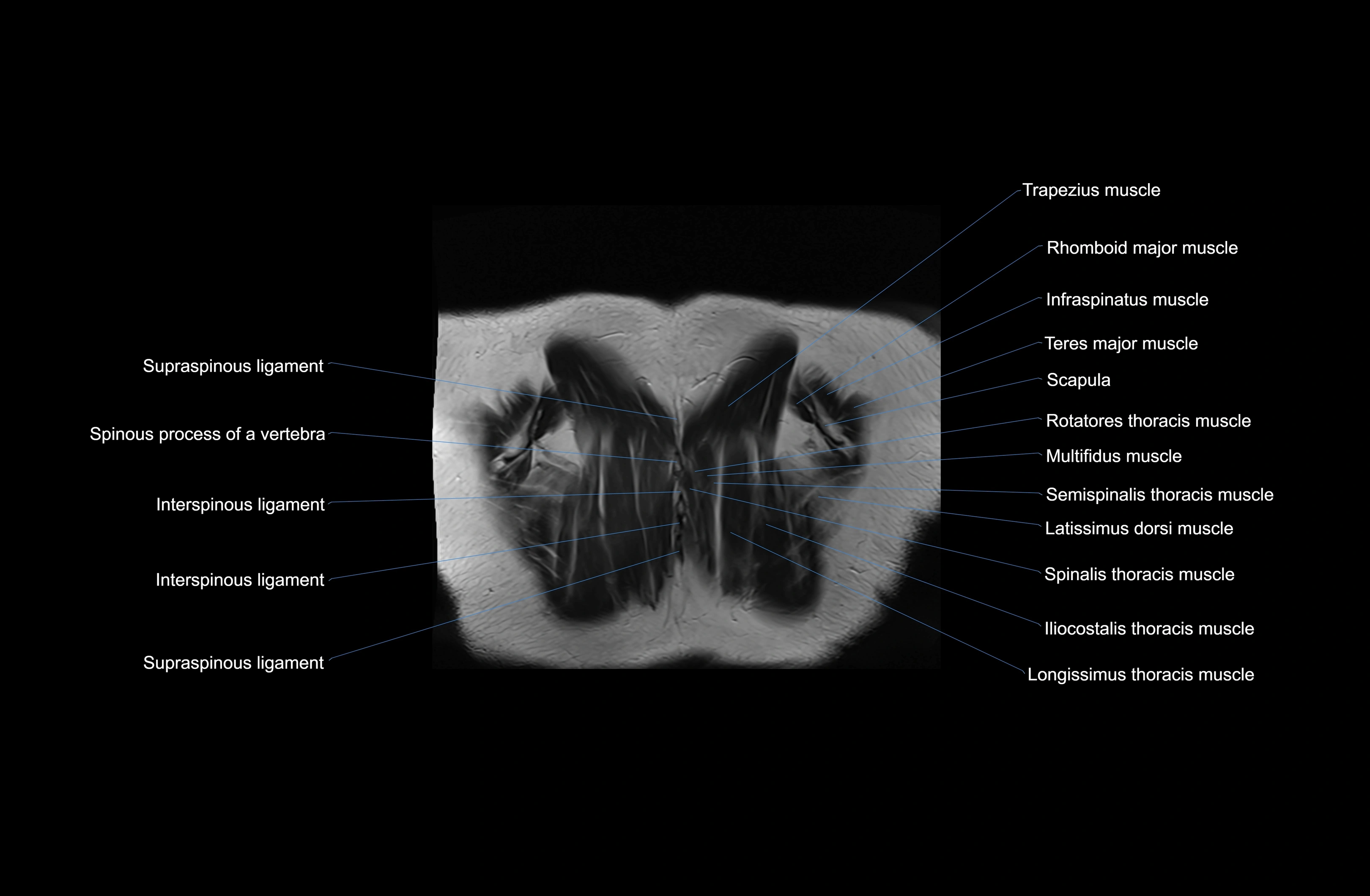
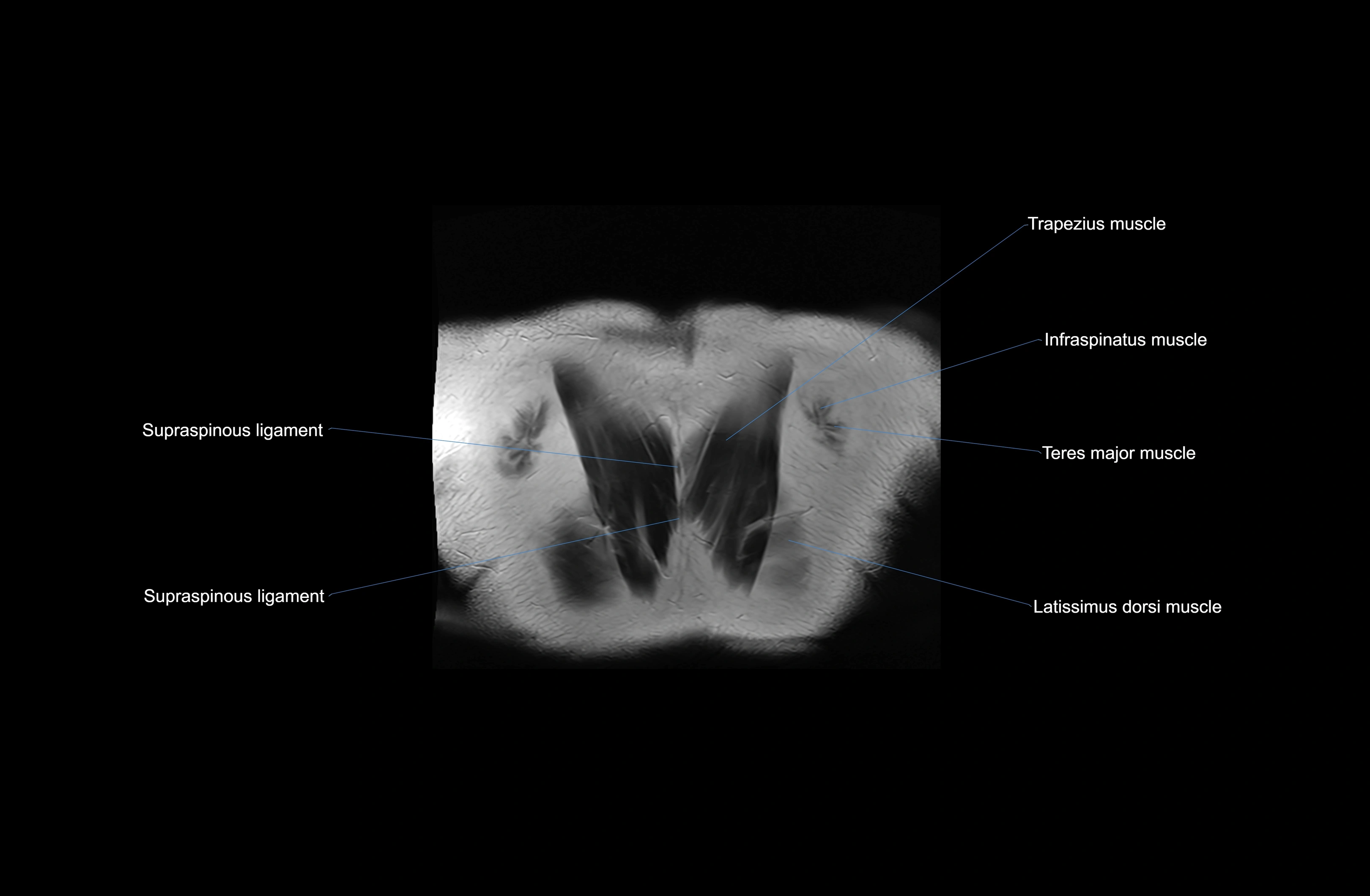
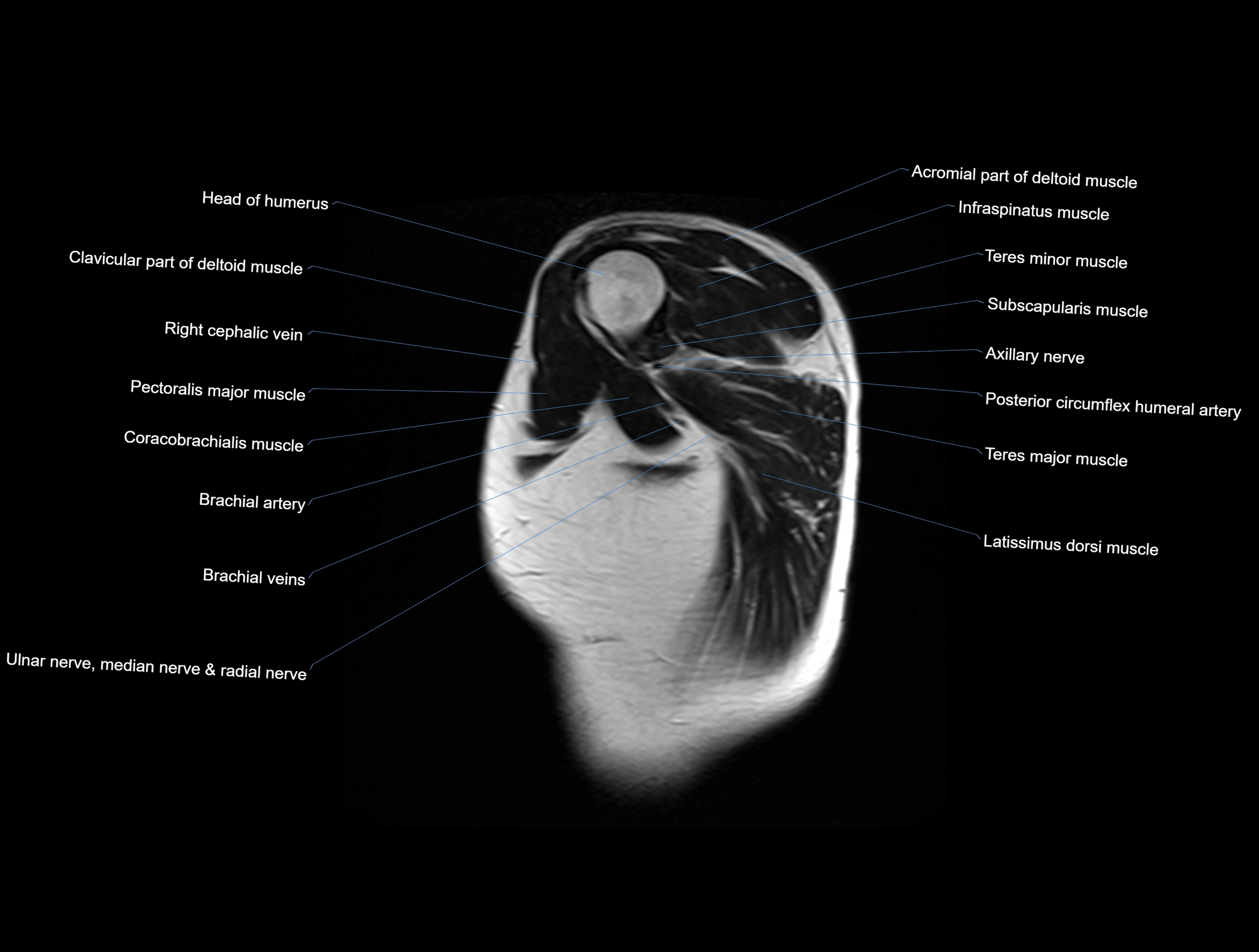
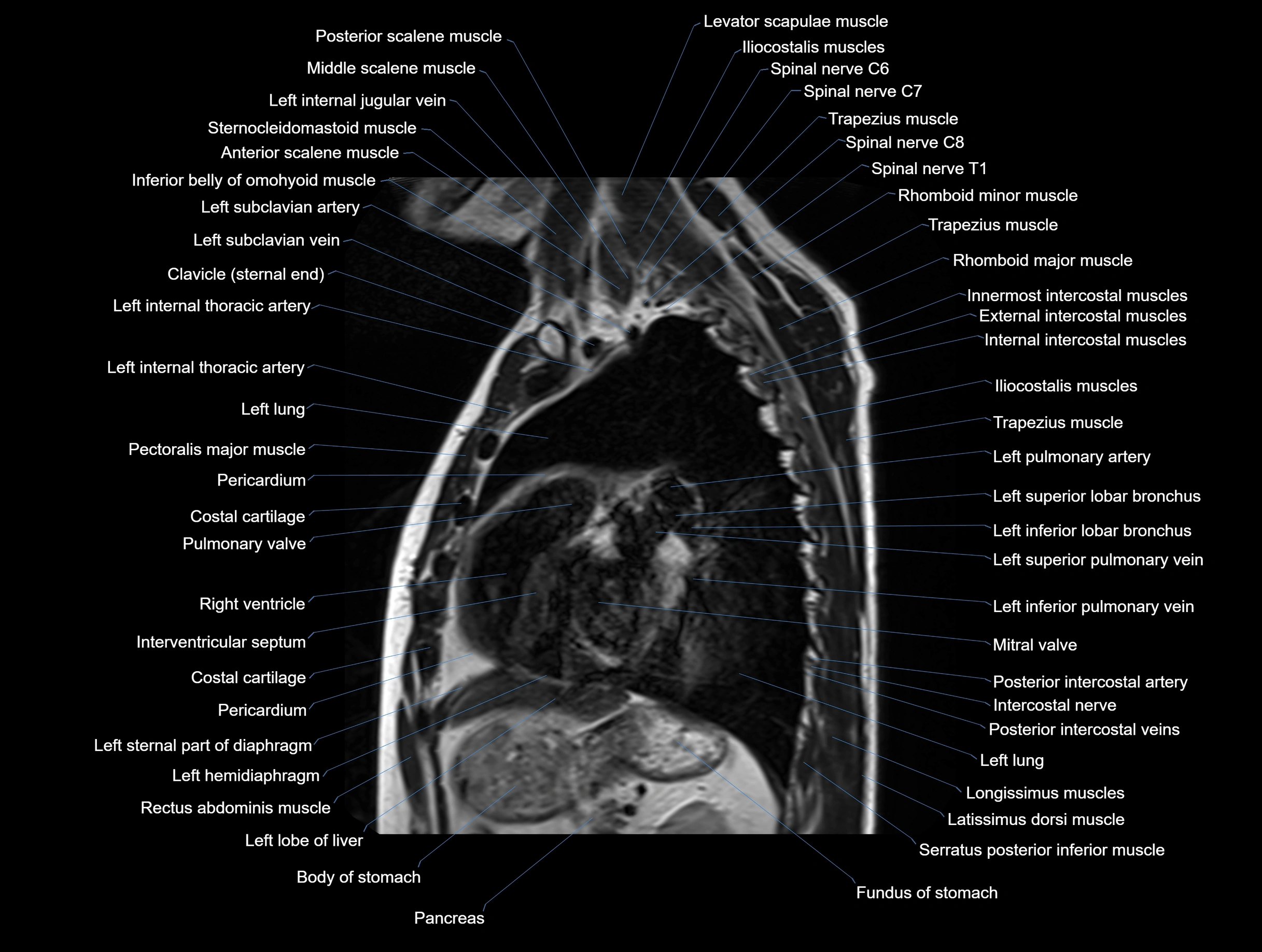
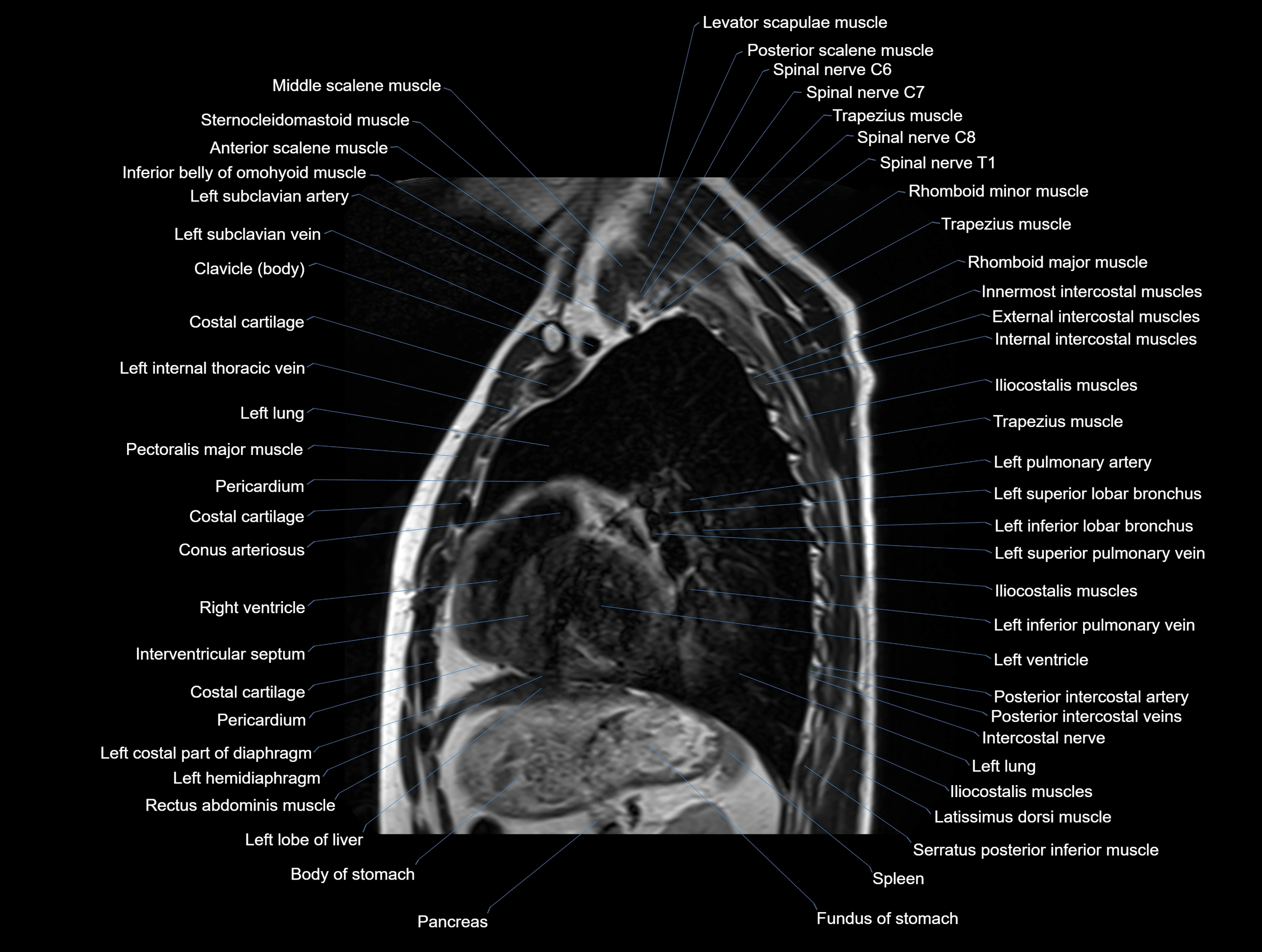
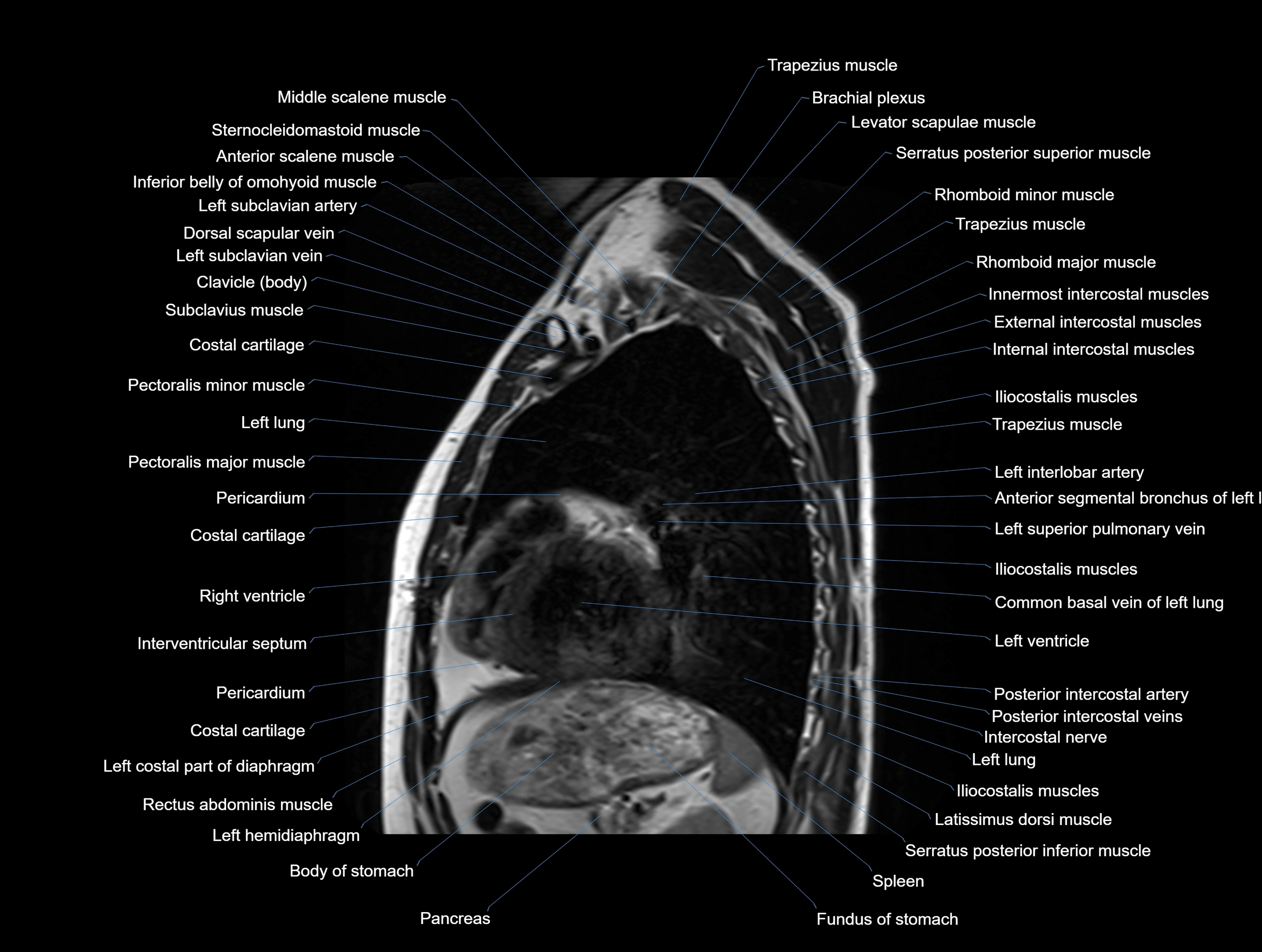
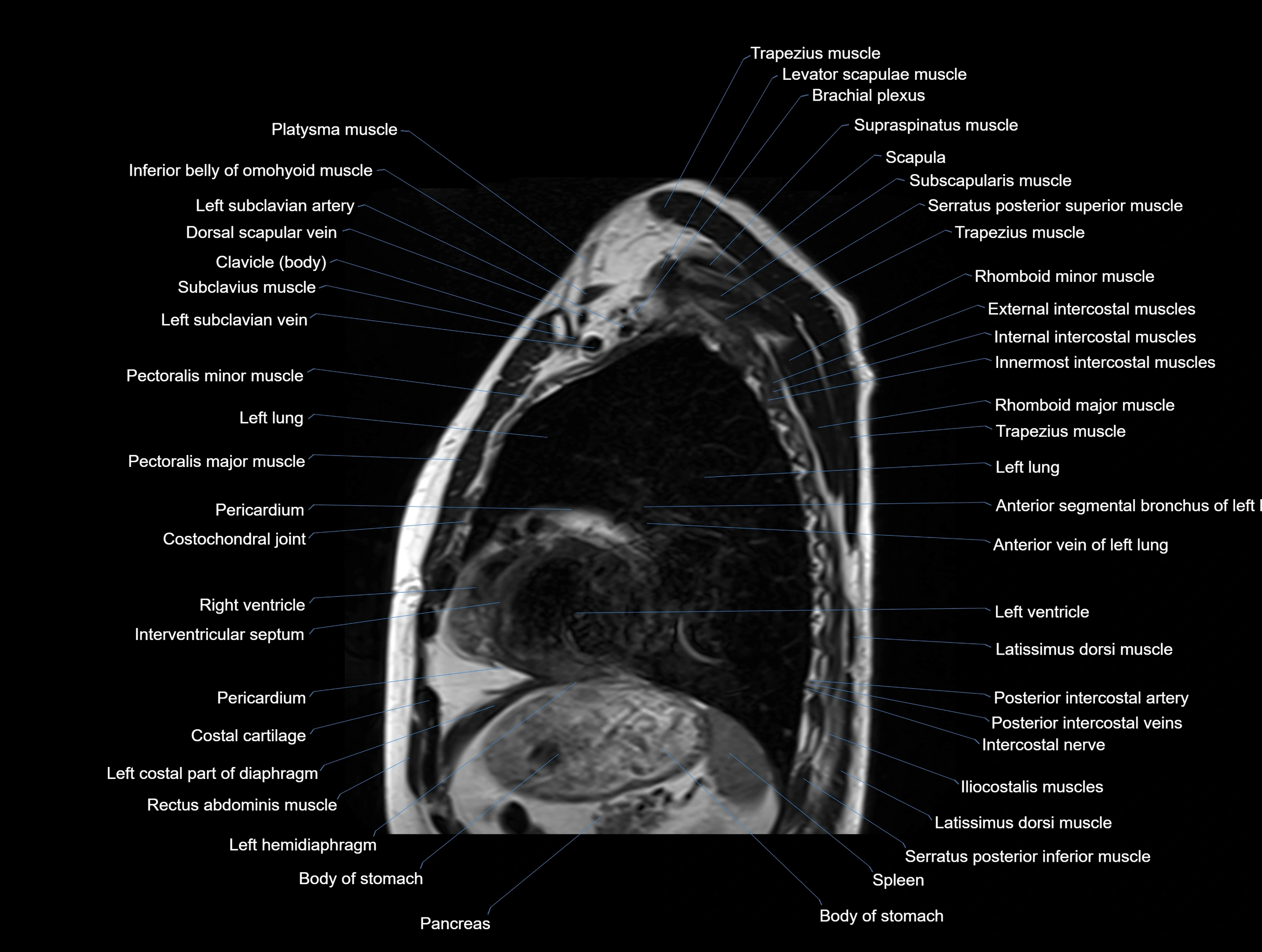
Topic
- Abdominal aorta
- Abdominal part of esophagus
- Acromial part of deltoid muscle
- Acromioclavicular joint
- Adipose tissue (Shoulder)
- Adrenal glands
- Anatomical neck of humerus
- Annular epiphysis
- Anterior basal segmental bronchus of right lung (B7+8, B8)
- Anterior jugular vein
- Anterior longitudinal ligament
- Anterior sternoclavicular ligament
- Anteromedial basal bronchus of left lung (B7+8)
- Aortic arch
- Aortic knob
- Aortic root
- Aortic sinus
- Apex of left lung
- Apex of right lung
- Apex of the heart
- Arch of aorta
- Articular cartilage of glenoid fossa
- Ascending aorta
- Ascending colon
- Axilla
- Axillary artery
- Axillary lymph nodes
- Axillary nerve
- Azygos vein
- Base of right lung
- Basivertebral veins
- Biceps brachii muscle
- Bicipital groove
- Body of rib
- Body of scapula
- Body of sternum
- Body of vertebra
- Brachial plexus
- Brachiocephalic trunk
- Cardia of stomach
- Cecum
- Celiac trunk
- Central axillary lymph nodes
- Cephalic vein
- Circumflex artery (LCx)
- Circumflex scapular artery
- Circumflex subscapular artery
- Clavicle
- Clavicular notch
- Clavicular part of deltoid muscle
- Common carotid artery
- Conoid tubercle
- Conus arteriosus
- Conus artery
- Coracobrachialis muscle
- Coronary sinus
- Costal cartilages
- Costal notches
- Costal part of diaphragm
- Costochondral joints
- Costotransverse joint
- Costotransverse ligament
- Costovertebral joint
- Costoxiphoid ligaments
- Crura of diaphragm
- Crural part of diaphragm
- Deltoid Tendon (Proximal)
- Deltoid muscle
- Deltoid tendon (Distal)
- Descending colon
- Descending thoracic aorta
- Diaphragm
- Dorsal scapular artery
- Dorsal scapular nerve
- Duodenum – Superior part (D1)
- Erector spinae muscles
- External oblique muscle
- Facet joint of vertebra (Zygapophyseal joints)
- Falciform ligament (liver)
- First diagonal branch (D1) of LAD
- Fissure for ligamentum teres
- Fissure for ligamentum venosum
- Gallbladder
- Gastroduodenal artery
- Glenohumeral joint
- Greater tubercle of humerus
- Head of humerus
- Head of rib
- Heart
- Hemiazygos vein
- Hilum of lung
- Horizontal fissure of right lung
- Humerus
- Iliocostalis cervicis muscle
- Inferior belly of omohyoid muscle
- Inferior lingular bronchus of left lung (B5)
- Inferior lobe of left lung
- Inferior lobe of right lung
- Inferior thyroid artery
- Inferior vena cava
- Infraclavicular lymph nodes
- Infraspinatus muscle
- Infraspinatus tendon
- Infraspinous fossa
- Intercostal muscles
- Intercostal space
- Internal thoracic artery
- Internal thoracic veins
- Interspinales muscles
- Interspinous ligament
- Intertransversarii muscle
- Intertransverse ligament
- Interventricular Septum
- Intervertebral foramen
- Intra-articular ligament of head of rib
- Jugular notch
- L (Lumbar spine)
- Lamina of vertebra
- Lateral basal segmental bronchus of left lung (B9)
- Lateral basal segmental bronchus of right lung (B9)
- Lateral head of triceps brachii muscle
- Lateral thoracic artery
- Latissimus dorsi muscle
- Latissimus dorsi tendon
- Left Lung (Superior Lobe)
- Left adrenal gland
- Left anterior descending artery (LAD)
- Left anterior segmental bronchus (B3a, B3b, B3c)
- Left apicoposterior bronchus (B1+2a, B1+2b)
- Left atrioventricular valve (mitral or bicuspid valve)
- Left atrium
- Left auricle
- Left cardiophrenic angle
- Left common carotid artery
- Left costophrenic angle
- Left hemidiaphragm
- Left hepatic artery
- Left inferior lobar bronchus
- Left inferior pulmonary vein
- Left internal thoracic artery
- Left internal thoracic veins
- Left lobe of liver
- Left lobe of thyroid gland
- Left lung
- Left lung (inferior lobe)
- Left main bronchus
- Left main coronary artery (LMCA)
- Left phrenic nerve
- Left recurrent laryngeal nerve
- Left subclavian artery
- Left superior lobar bronchus
- Left superior pulmonary vein
- Left ventricle
- Lesser tubercle of humerus
- Levator scapulae muscle
- Ligamentum teres (round ligament of the liver)
- Ligamentum venosum
- Lingular bronchus of left lung
- Liver
- Long head of biceps brachii muscle
- Long head of biceps tendon
- Long head of triceps brachii muscle
- Long thoracic nerve
- Lumbar part of diaphragm
- Manubriosternal joint
- Manubrium of sternum
- Medial cutaneous nerve of forearm
- Medial head of triceps brachii muscle
- Medial segmental bronchus of right lung (B5)
- Median arcuate ligament
- Median nerve
- Mediastinum
- Middle lobe of right lung
- Neck of rib
- Oblique fissure of left lung
- Oblique fissure of right lung
- Pancreas
- Pectoralis major muscle
- Pectoralis minor muscle
- Pedicle of vertebra
- Pericardium
- Phrenicomediastinal recess
- Phrenoesophageal ligament
- Platysma muscle
- Pleura
- Posterior basal segmental bronchus of left lung (B10)
- Posterior basal segmental bronchus of right lung (B10)
- Posterior circumflex humeral artery
- Posterior circumflex humeral vein
- Posterior cutaneous nerve of arm
- Posterior intercostal arteries
- Posterior intercostal veins
- Posterior sternoclavicular ligament
- Proper hepatic artery
- Pulmonary trunk
- Pulmonary valve
- Radiate sternocostal ligament
- Rectus abdominis muscle
- Retrosternal space
- Rhomboid major muscle
- Rhomboid minor muscle
- Right adrenal gland
- Right anterior segmental bronchus (B3)
- Right apical segmental bronchus (B1)
- Right atrioventricular valve (tricuspid valve)
- Right atrium
- Right cardiophrenic angle
- Right coronary artery (RCA)
- Right costophrenic angle
- Right crus of diaphragm
- Right hemidiaphragm
- Right hepatic artery
- Right inferior pulmonary vein
- Right intermediate bronchus
- Right internal thoracic artery
- Right internal thoracic veins
- Right lobe of liver
- Right lobe of thyroid gland
- Right lung
- Right lung (inferior lobe)
- Right lung (middle lobe)
- Right lung (superior lobe)
- Right main bronchus
- Right middle lobe bronchus
- Right ovarian vein
- Right posterior segmental bronchus (B2, B2a, B2b)
- Right subclavian artery
- Right superior pulmonary vein
- Right ventricle
- Risorius muscle
- Rotatores cervicis muscle
- Rotatores muscle
- Scalenus anterior muscle (Anterior scalene muscle)
- Scalenus medius muscle (middle scalene muscle)
- Scalenus posterior muscle (Posterior scalene muscle)
- Scapula
- Scapular spinal part of deltoid muscle
- Second diagonal branch (D2) of LAD
- Semispinalis capitis muscle
- Semispinalis cervicis muscle
- Serratus anterior muscle
- Serratus posterior inferior muscle
- Serratus posterior superior muscle
- Shaft of humerus
- Short gastric arteries
- Short head of biceps brachii muscle
- Short head of the biceps brachii tendon
- Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint)
- Sigmoid veins
- Sinoatrial nodal artery
- Spinal nerves
- Spinalis cervicis muscle
- Spinous process of vertebra
- Spleen
- Splenic artery
- Splenius capitis muscle
- Splenius cervicis muscle
- Sternal angle
- Sternal end of the clavicle
- Sternal part of diaphragm
- Sternoclavicular joint
- Sternocleidomastoid muscle
- Sternocostal joint
- Sternocostal synchondrosis of first rib
- Sternohyoid muscle
- Sternothyroid muscle
- Sternum
- Stomach
- Subclavian artery
- Subclavius muscle
- Subscapular artery
- Subscapularis muscle
- Subscapularis tendon
- Superior articular process of vertebra
- Superior epigastric artery
- Superior epigastric veins
- Superior intercostal artery
- Superior lingular bronchus of left lung (B4)
- Superior lobe of left lung
- Superior lobe of right lung
- Superior mesenteric artery (SMA)
- Superior mesenteric vein (SMV)
- Superior phrenic artery
- Superior rectal vein
- Superior segmental bronchus of right lung (B6)
- Superior vena cava
- Suprascapular artery
- Supraspinatus muscle
- Supraspinatus tendon
- Surgical neck of humerus
- T (Thoracic spine)
- Teres major muscle
- Teres major tendon (Distal)
- Teres minor muscle
- Teres minor tendon (Distal)
- Third diagonal branch (D3) of LAD
- Thoracic duct
- Thoracic part of esophagus
- Thoracodorsal artery
- Thyrocervical trunk
- Thyroid gland
- Trachea
- Transverse abdominal muscle
- Transverse cervical artery
- Transverse colon
- Transverse processes
- Transversus thoracis muscle
- Trapezius muscle
- Triceps brachii muscle
- Umbilical vein
- Vasa recta (kidney)
- Xiphisternal joint
- Xiphoid process of sternum
- left gastro-omental artery (left gastroepiploic artery)
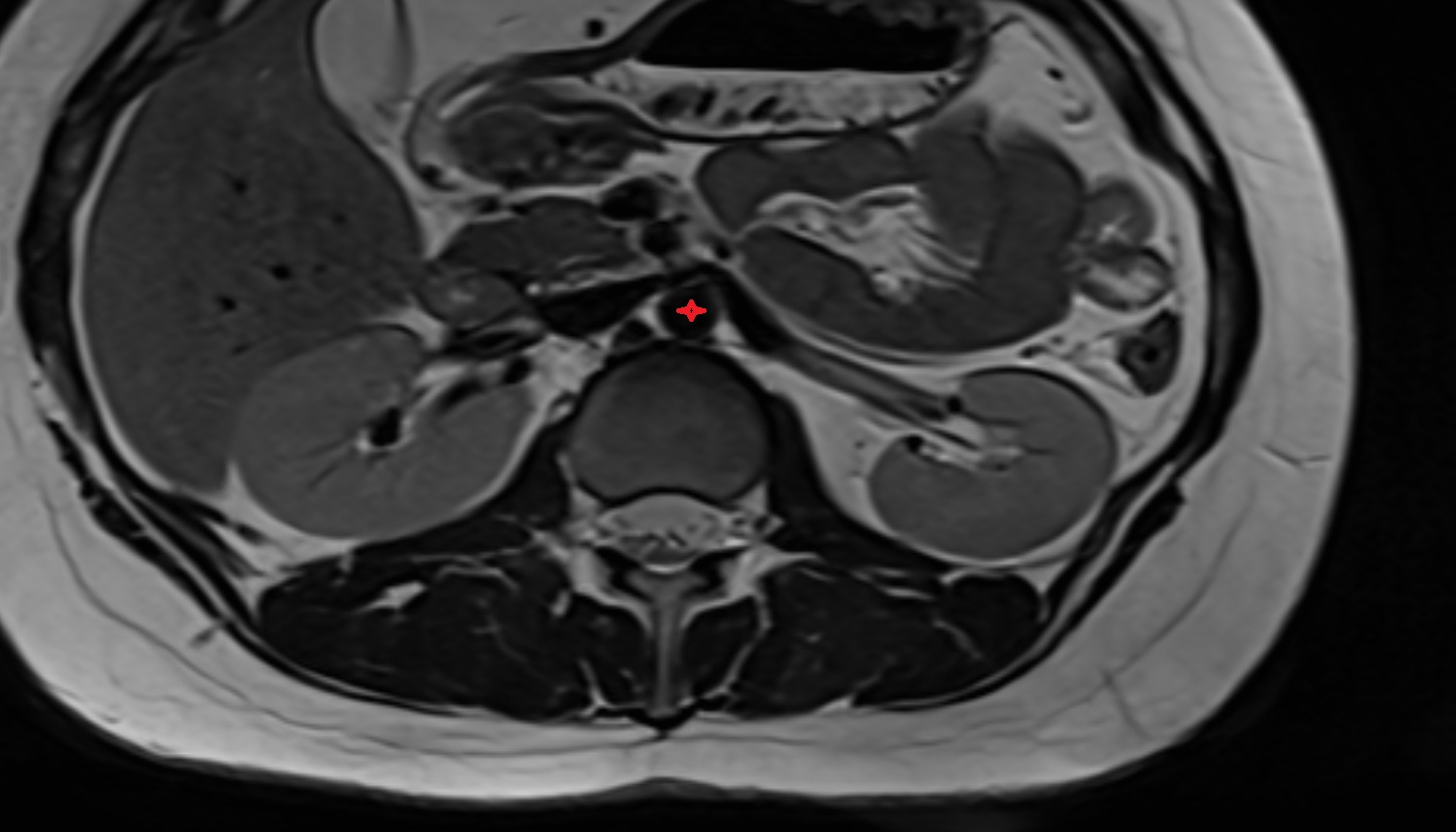
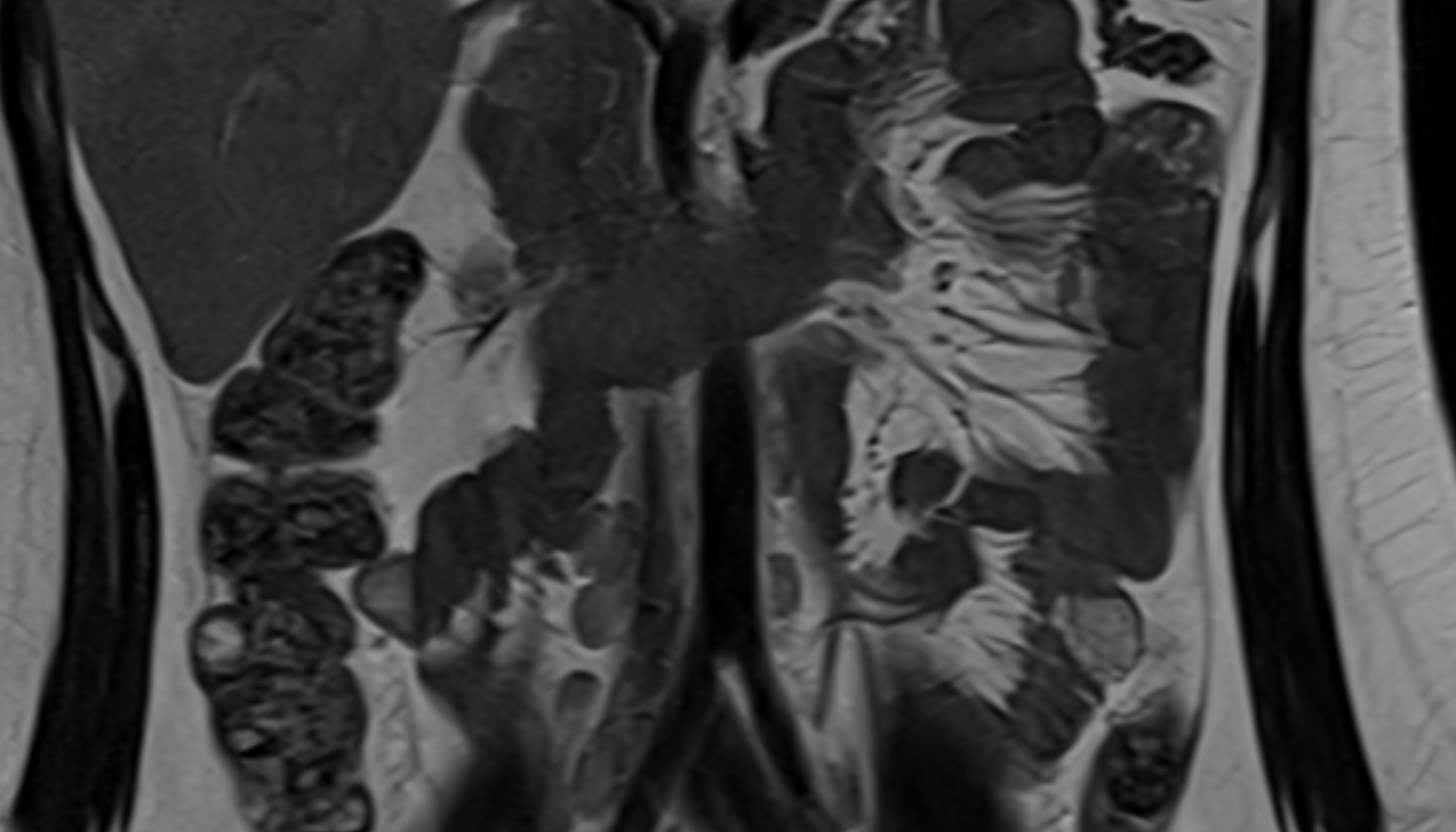
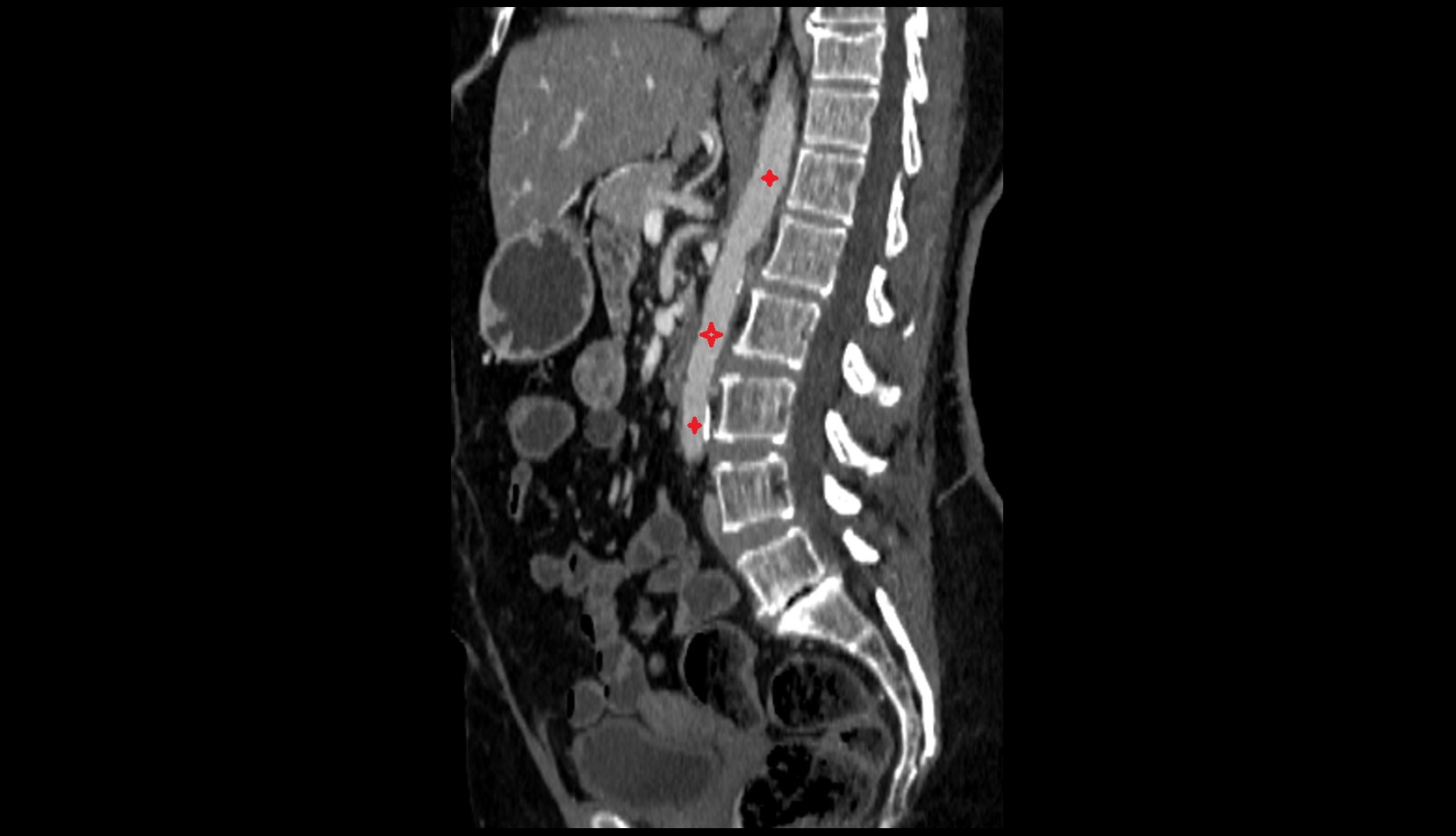
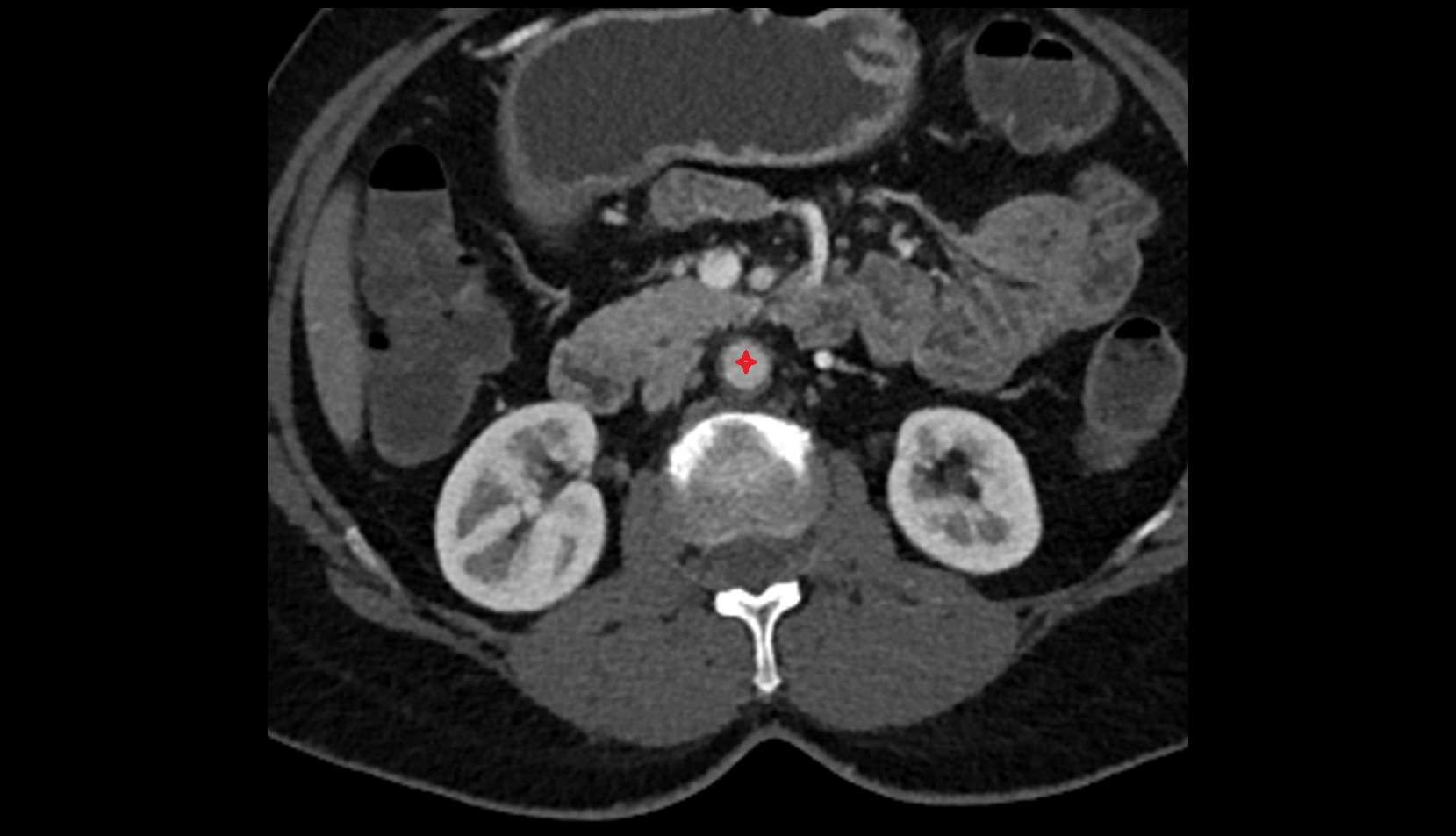
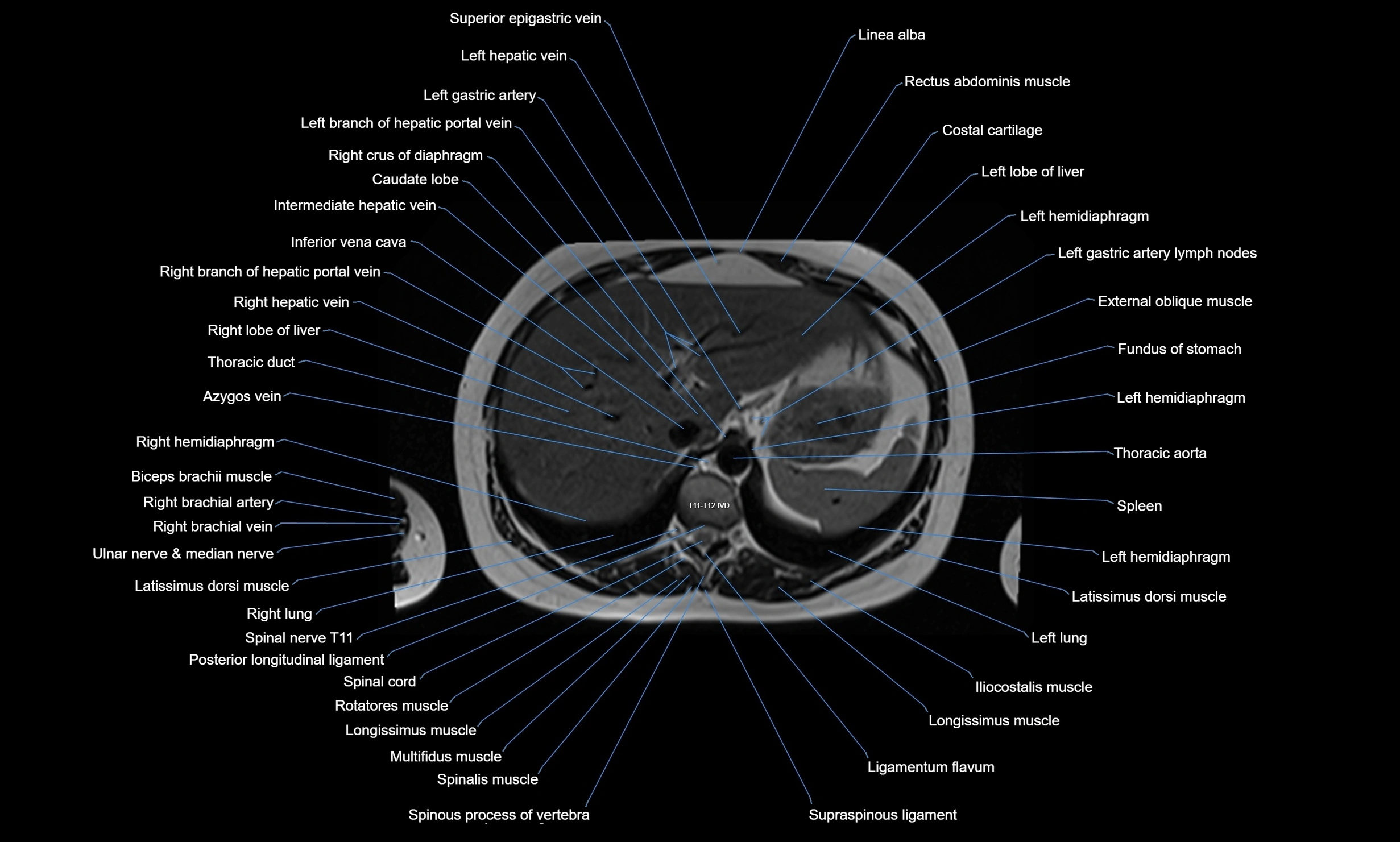
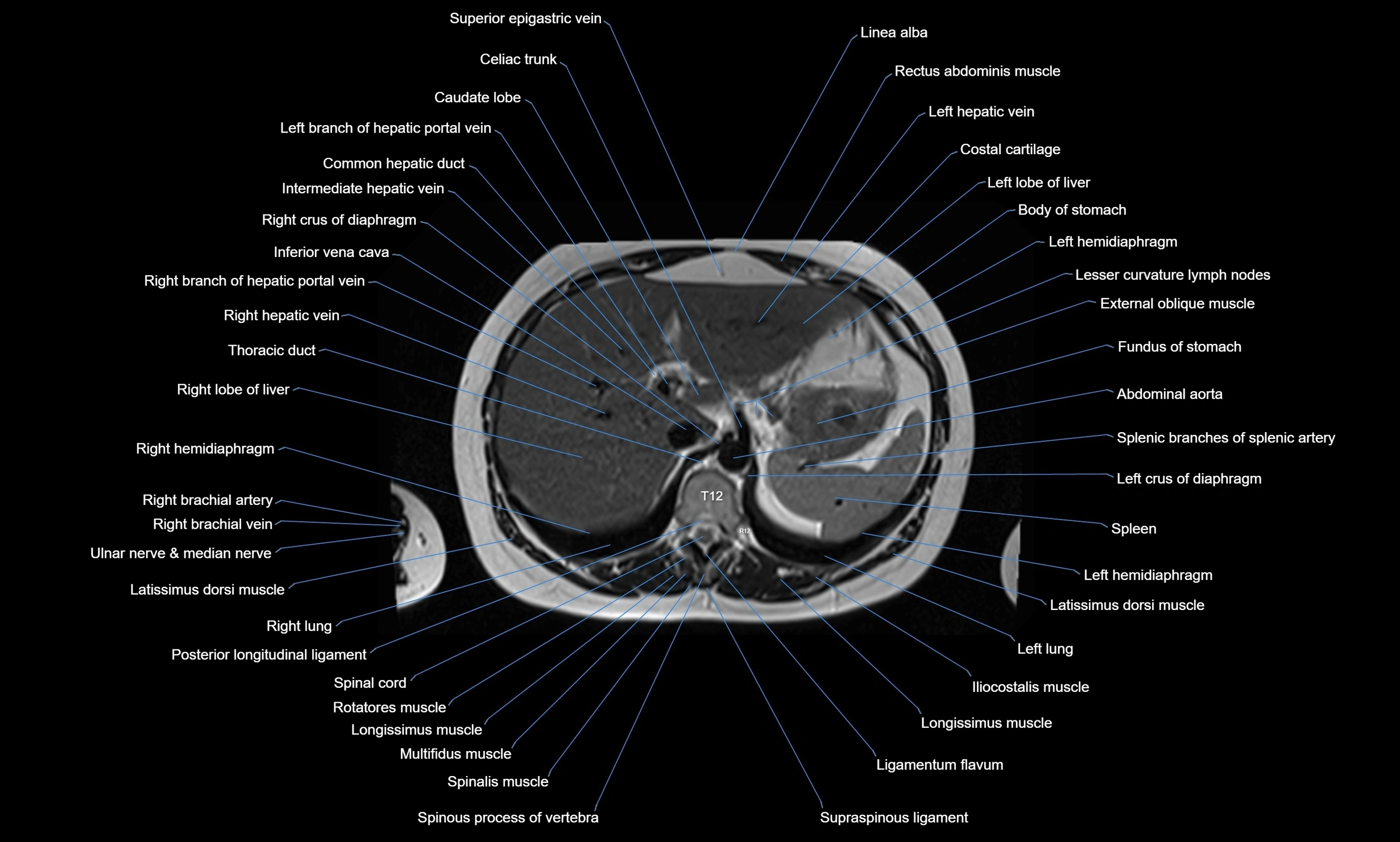
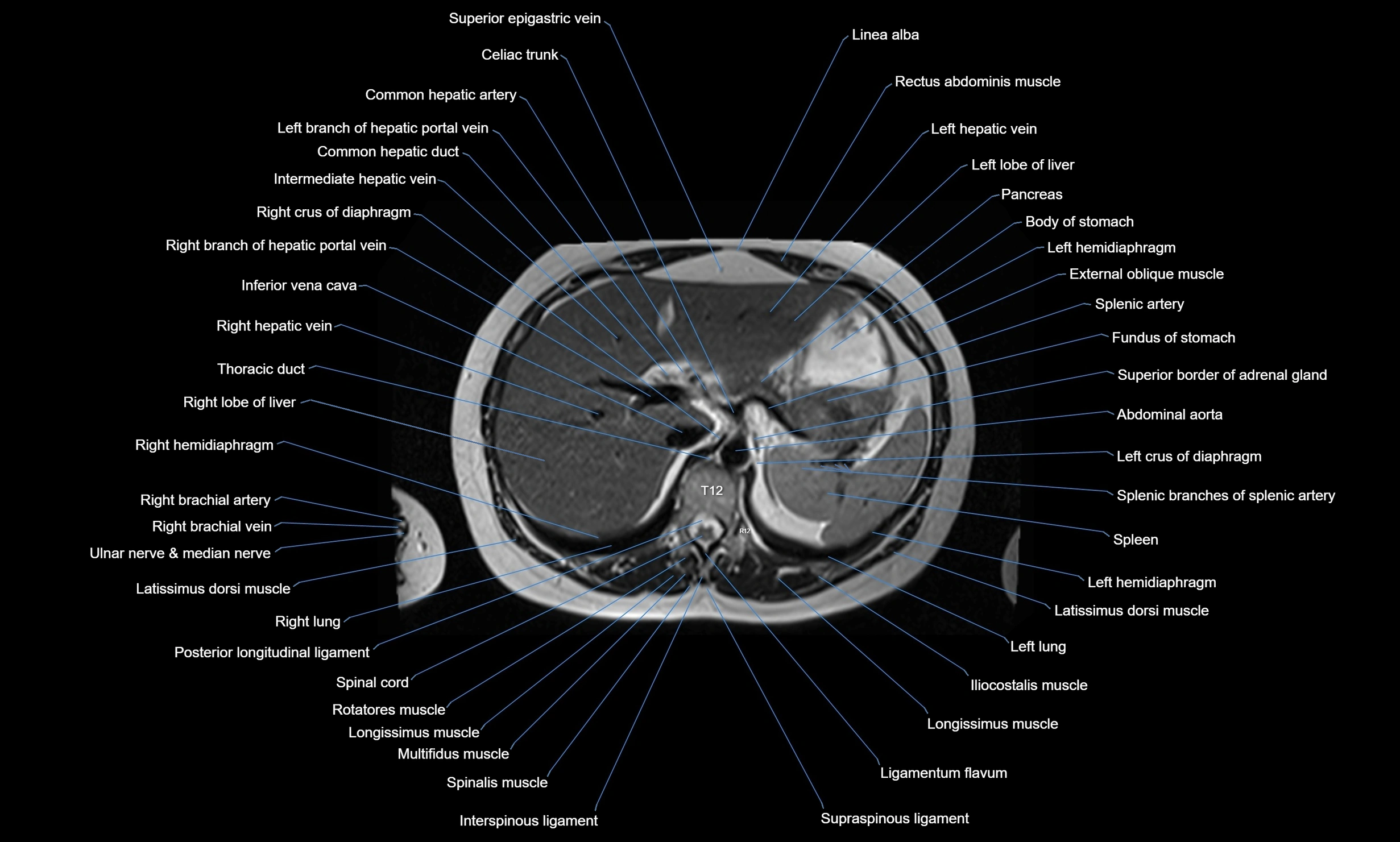
The abdominal aorta is the continuation of the thoracic aorta, beginning at the level of the aortic hiatus of the diaphragm (T12 vertebra) and terminating at the level of the L4 vertebra where it bifurcates into the right and left common iliac arteries. It lies slightly to the left of the midline and courses anterior to the vertebral bodies, surrounded by the retroperitoneal structures of the abdomen.
The abdominal aorta gives off numerous visceral and parietal branches, supplying the abdominal organs, pelvic structures, and lower limbs. It is the main conduit of oxygenated blood from the heart to the abdomen and lower body. The aorta is clinically significant as the common site of aneurysm, dissection, atherosclerosis, and traumatic injury.
Synonyms
-
Aorta abdominalis
-
Infradiaphragmatic aorta
-
Abdominal portion of aorta
Function
-
Conducts oxygenated blood from the thoracic aorta to abdominal, pelvic, and lower limb structures
-
Provides direct arterial supply to major abdominal organs (liver, spleen, kidneys, intestines)
-
Maintains systemic blood flow and hemodynamic regulation
-
Plays a central role in surgical and interventional procedures (aneurysm repair, stent grafts)
Branches
-
Unpaired visceral branches: celiac trunk, superior mesenteric artery (SMA), inferior mesenteric artery (IMA)
-
Paired visceral branches: middle suprarenal arteries, renal arteries, gonadal arteries (testicular or ovarian)
-
Parietal branches: inferior phrenic arteries, lumbar arteries, median sacral artery
-
Terminal branches: right and left common iliac arteries
MRI Appearance
T1-weighted images:
-
Flowing blood appears as a signal void (black lumen)
-
Vessel wall appears as a thin hypointense rim; retroperitoneal fat enhances contrast
T2-weighted images:
-
Lumen remains a signal void due to flow
-
Adjacent edema, hematoma, or aneurysm wall thrombus may appear hyperintense
STIR (Short Tau Inversion Recovery):
-
Fat suppression improves visualization of the aortic wall and periaortic tissues
-
Wall edema, inflammation, or periaortic hematoma appears hyperintense
-
Useful in vasculitis, dissection, or trauma
T1 Post-Contrast (Gadolinium-enhanced):
-
Aortic lumen enhances brightly and homogeneously
-
Clearly demonstrates aneurysm, stenosis, dissection, mural thrombus, or aortic wall enhancement in vasculitis
MRA (Magnetic Resonance Angiography):
-
Contrast-enhanced MRA provides high-resolution imaging of the aorta and its branches
-
Allows 3D reconstruction of visceral, parietal, and terminal branches
-
Excellent for evaluating aneurysm size, dissection flap, stenosis, or preoperative planning
-
Non-invasive alternative to conventional angiography
CT Appearance
Non-contrast CT:
-
Appears as a tubular soft tissue structure anterior to vertebral bodies
-
Calcified atherosclerotic plaques appear as hyperdense foci along the wall
-
Useful for screening abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) size and mural calcification
Contrast-enhanced CT (CTA):
-
Gold standard for abdominal aortic imaging
-
Provides excellent detail of lumen, wall, aneurysm, thrombus, and branch vessels
-
Multiplanar and 3D reconstructions help in aneurysm measurement, stent graft planning, and dissection evaluation
-
Detects acute rupture, traumatic injury, or occlusion with high sensitivity
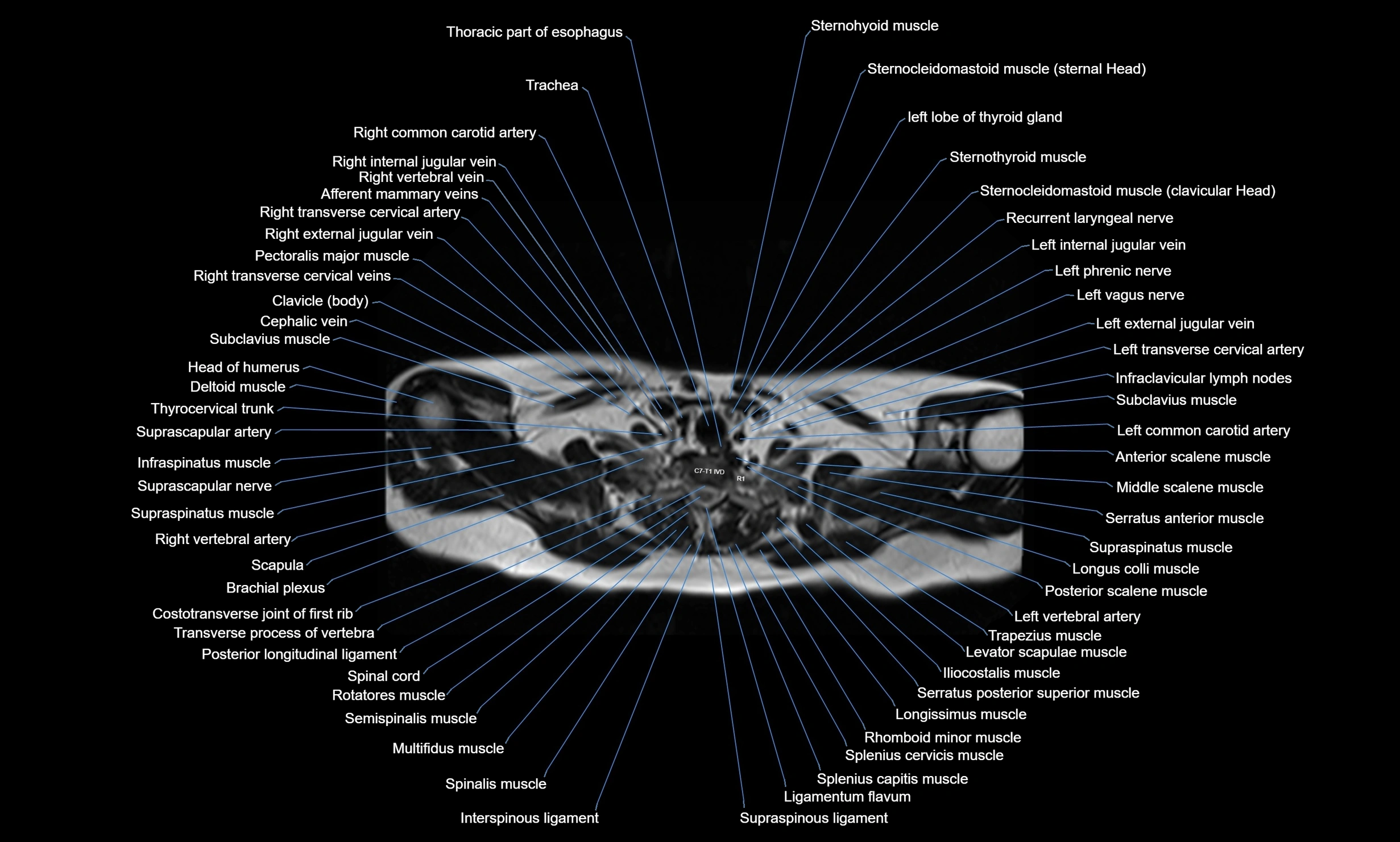
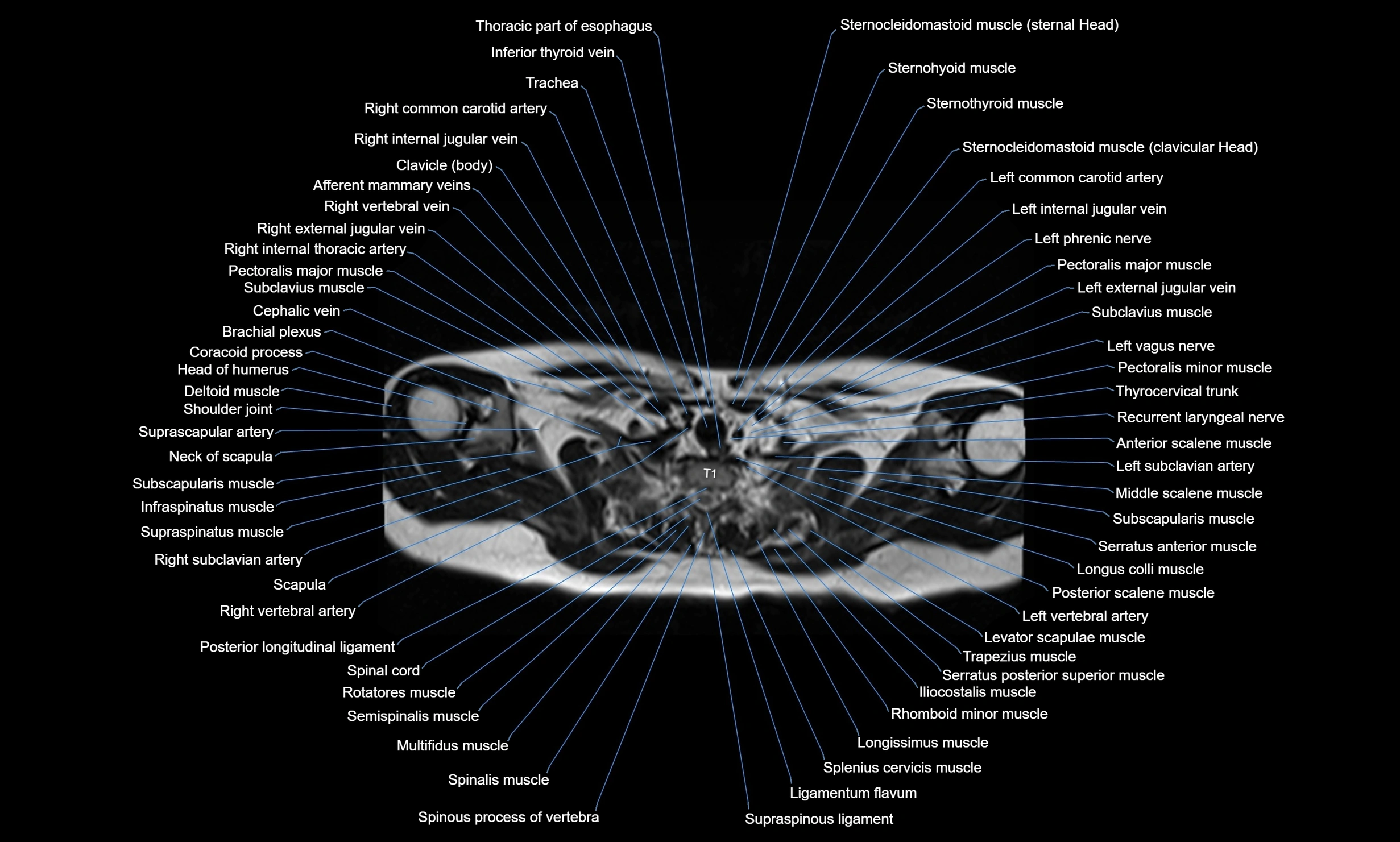
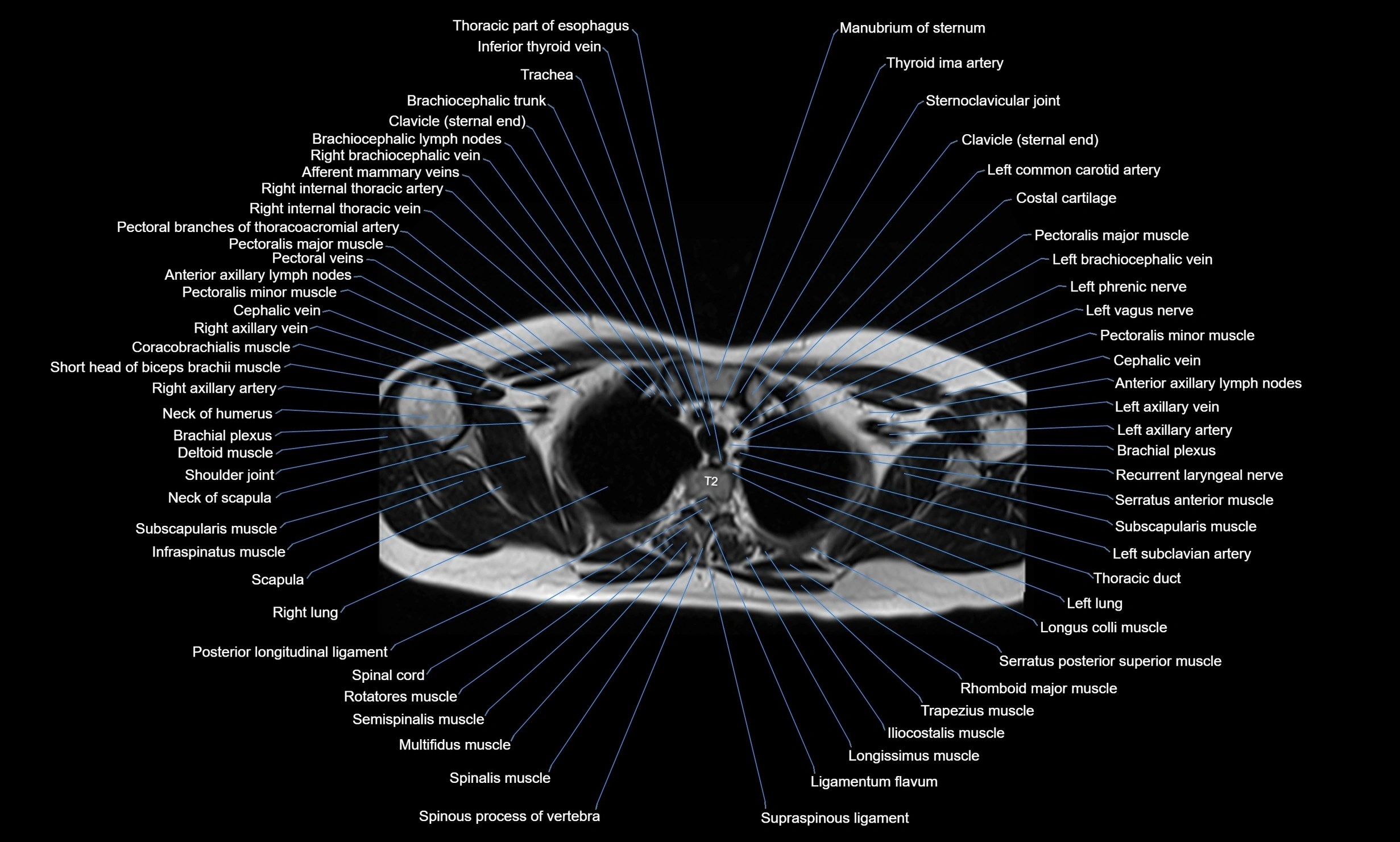
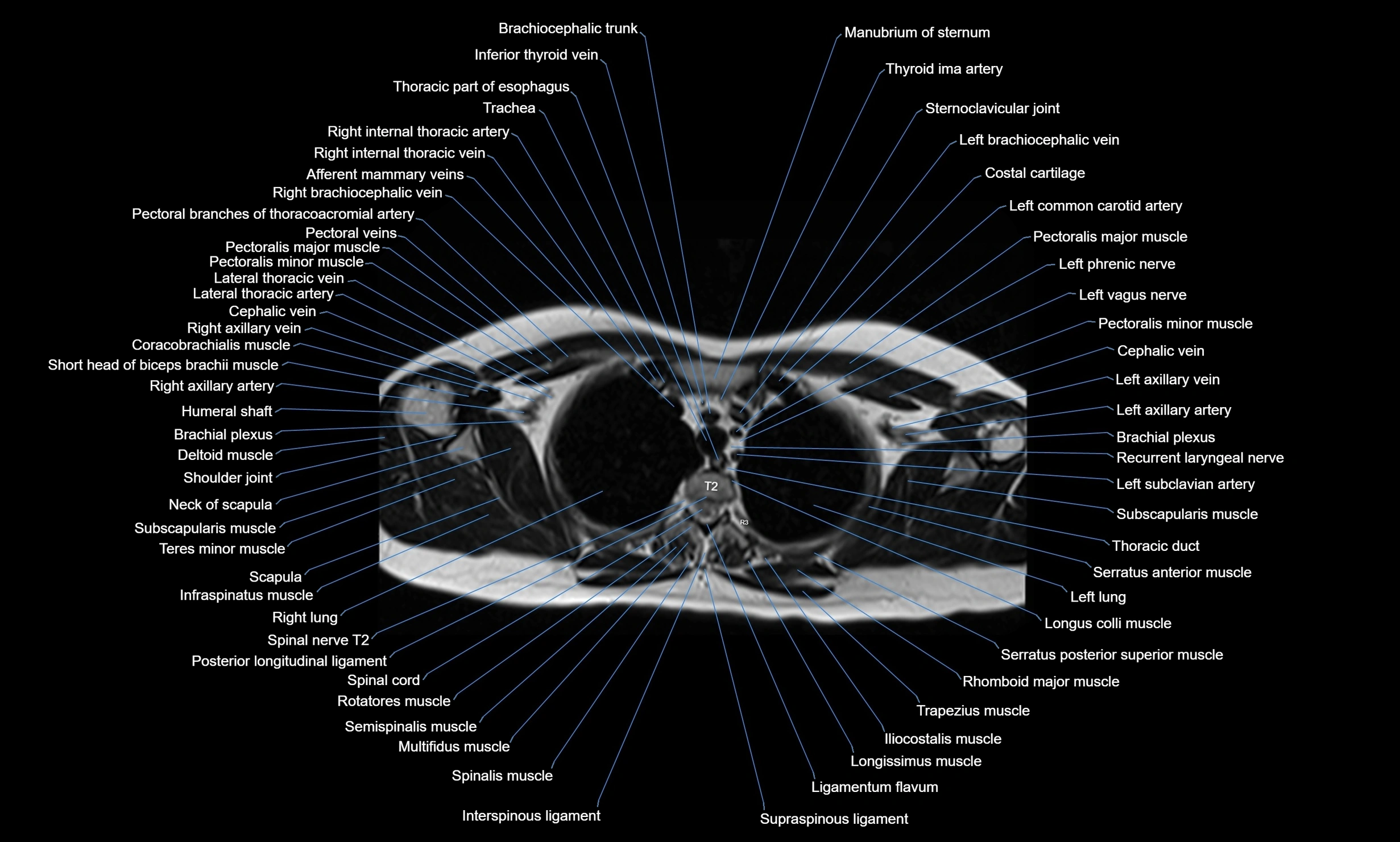
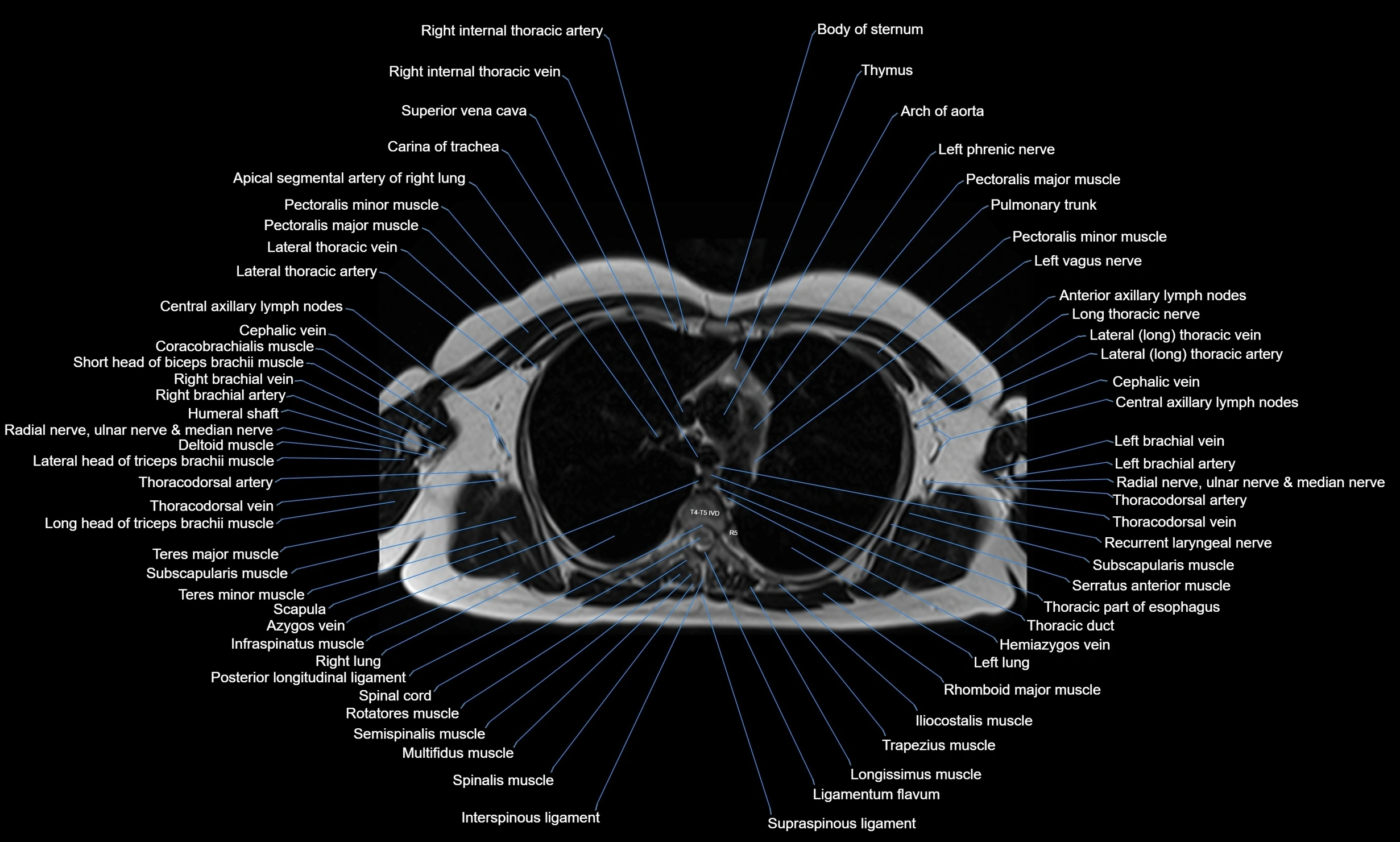
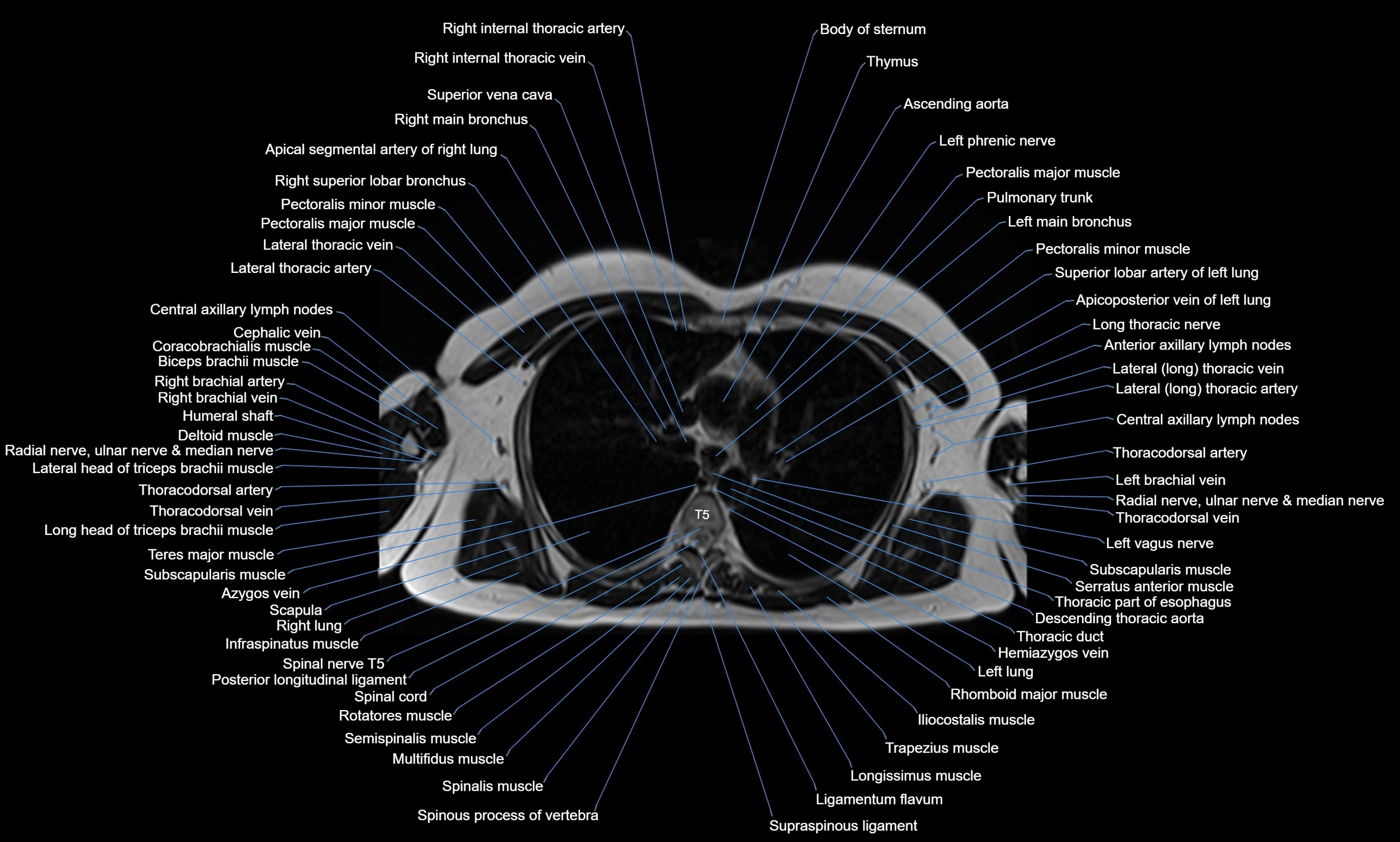
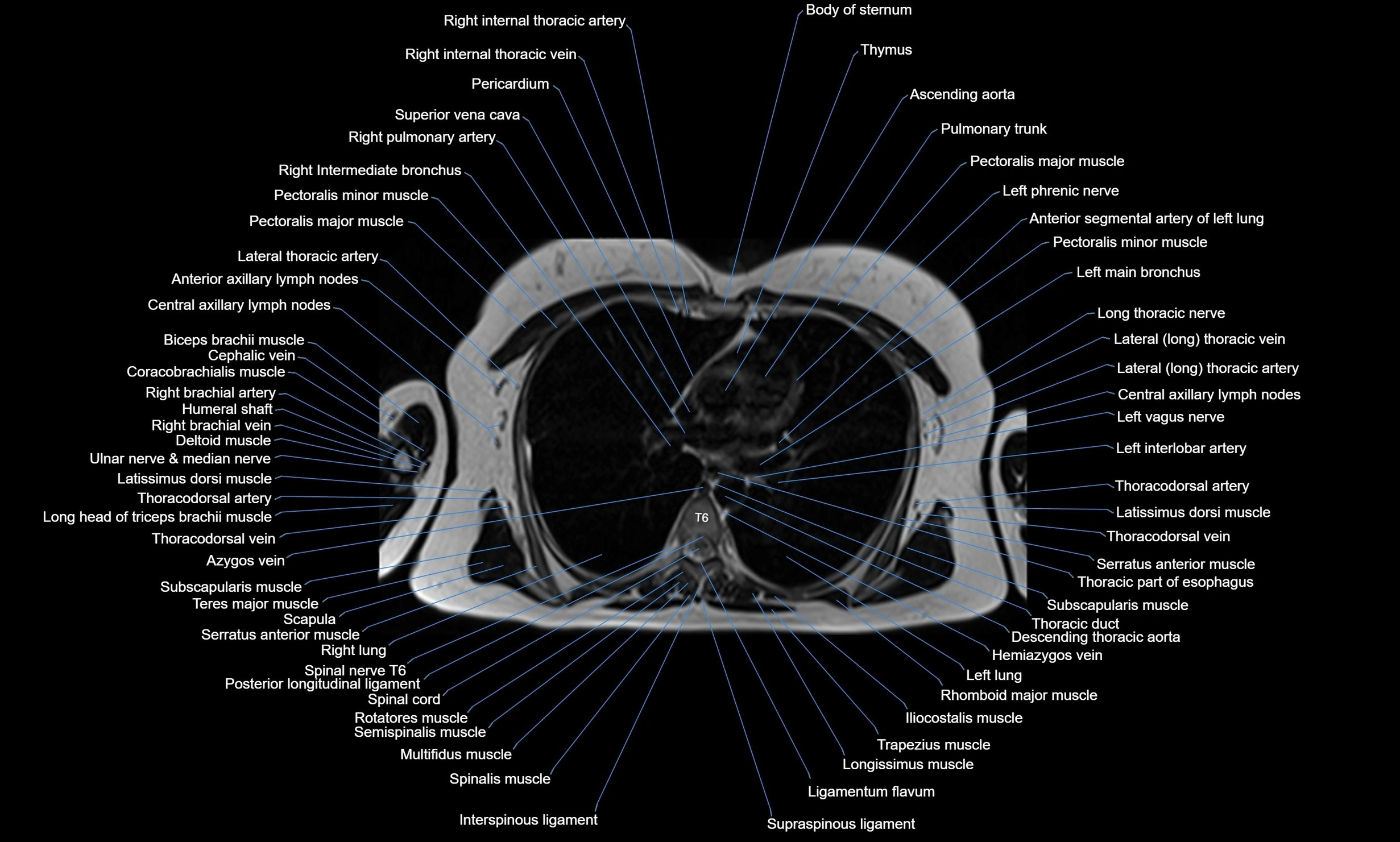
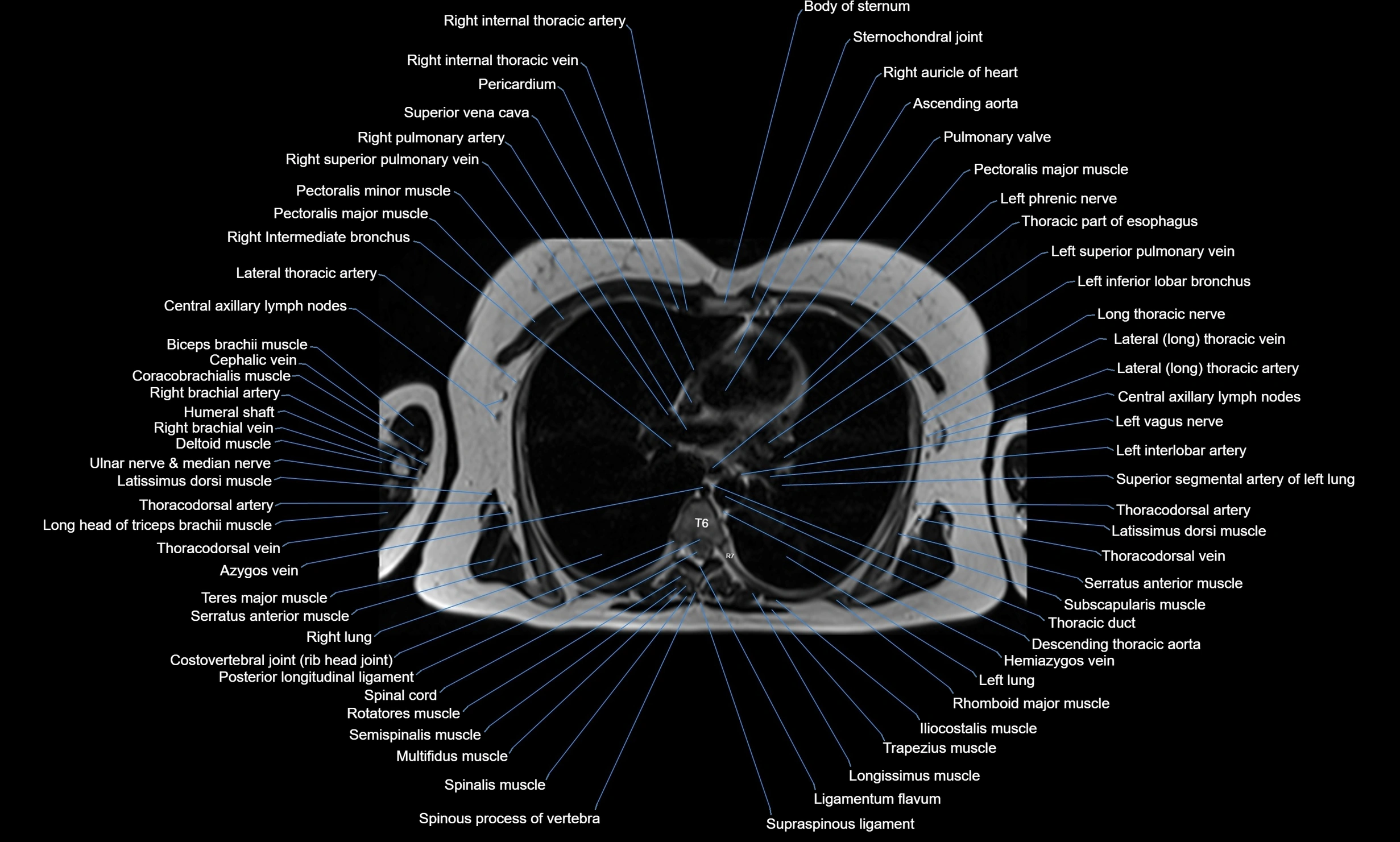
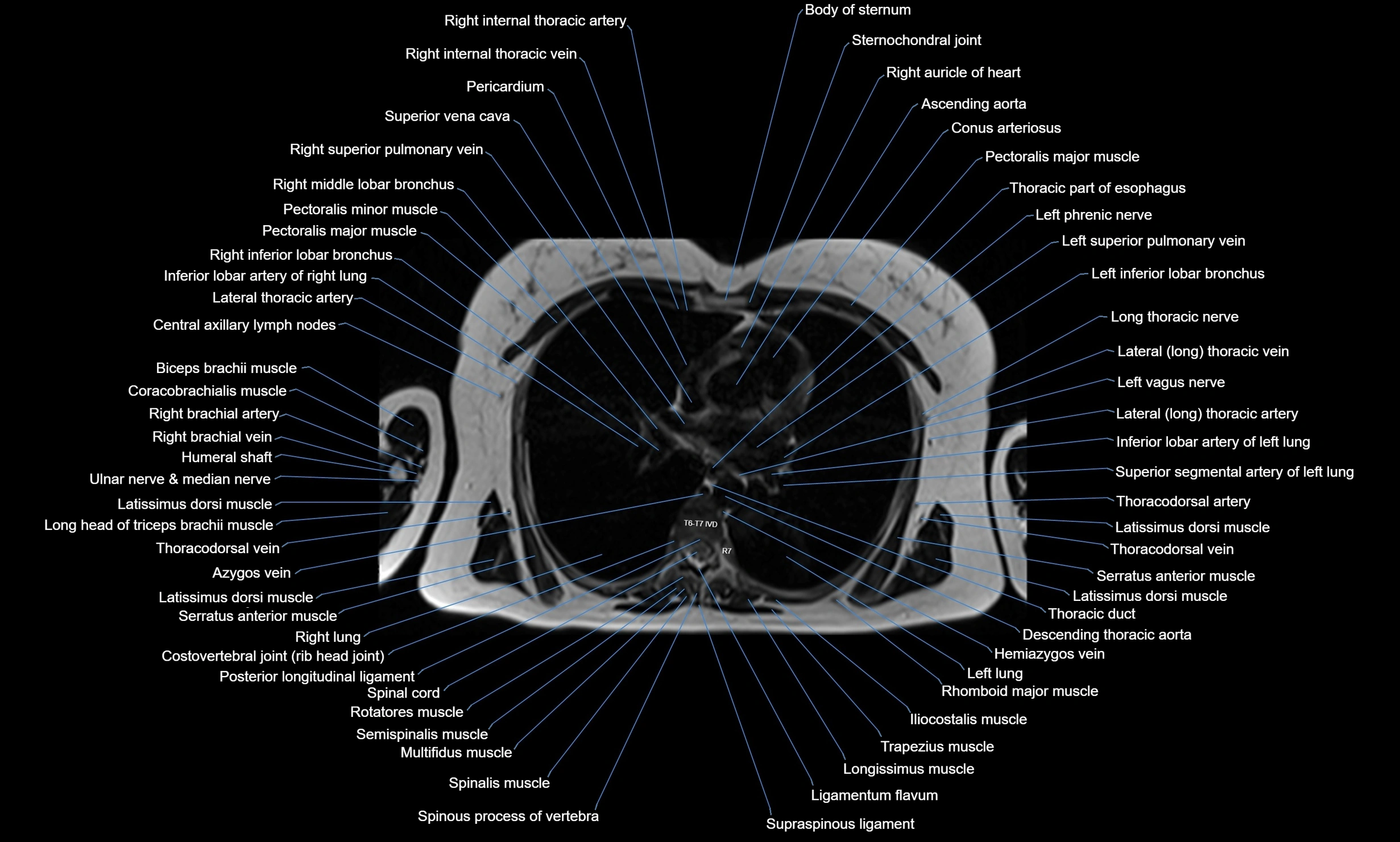
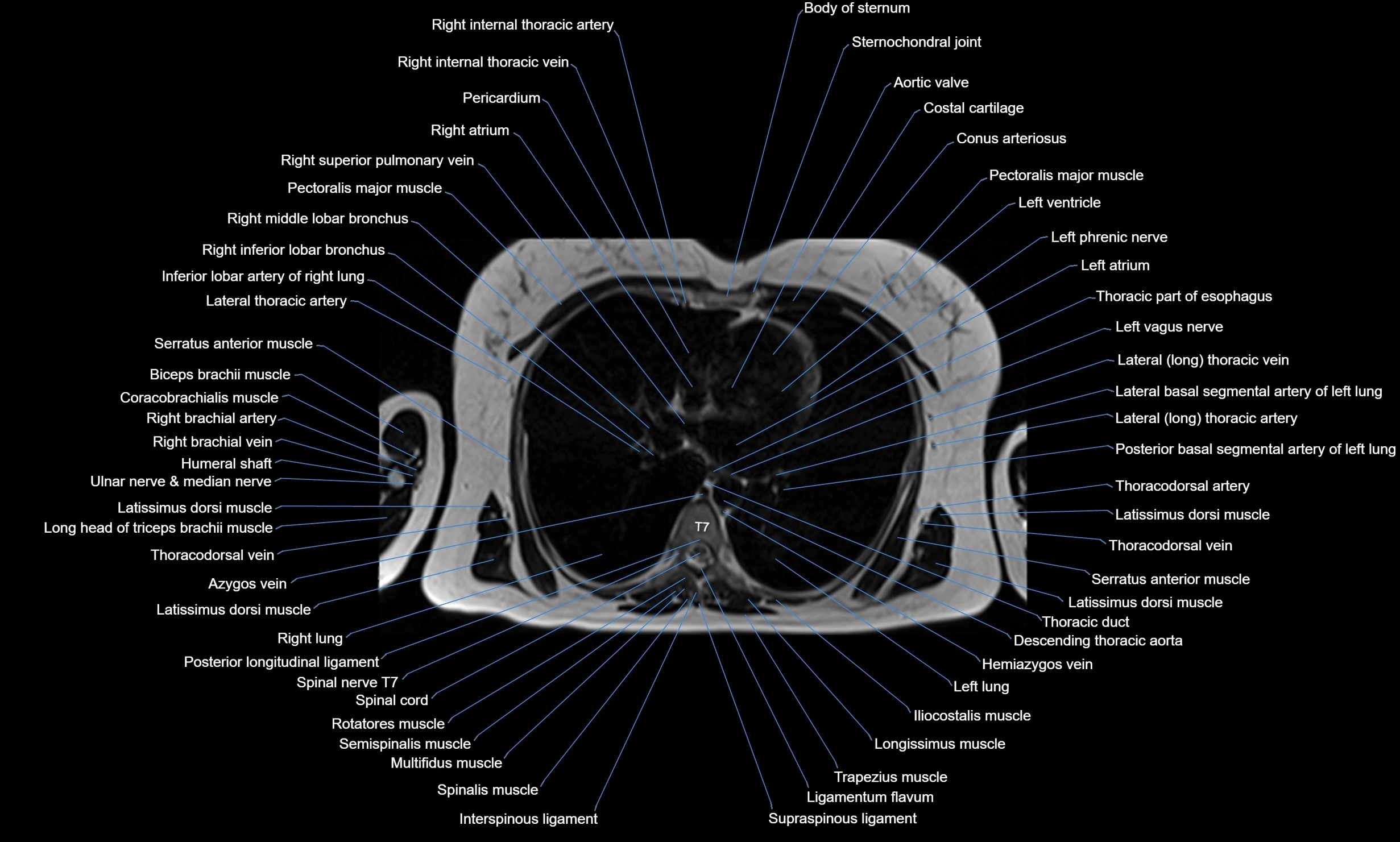
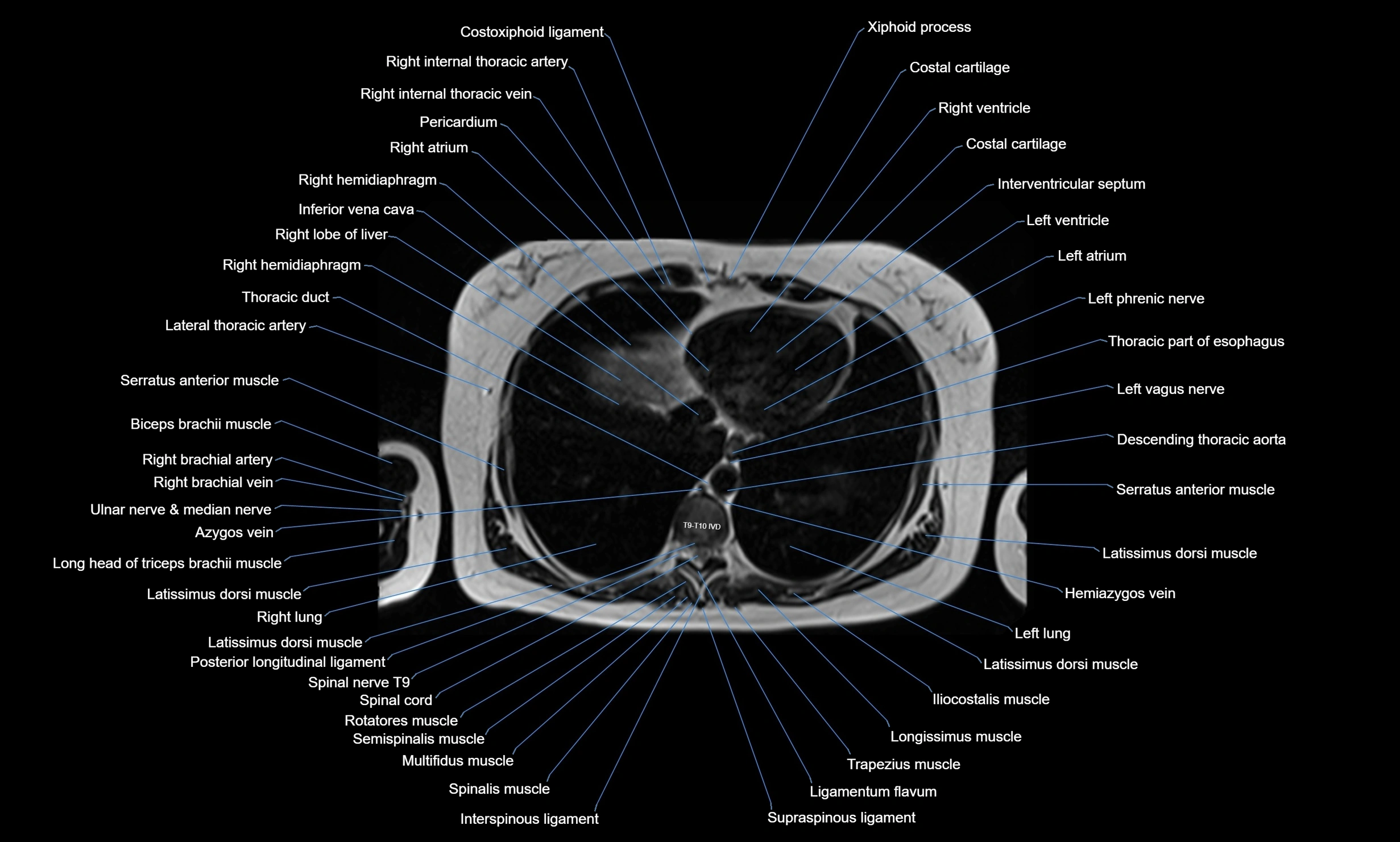
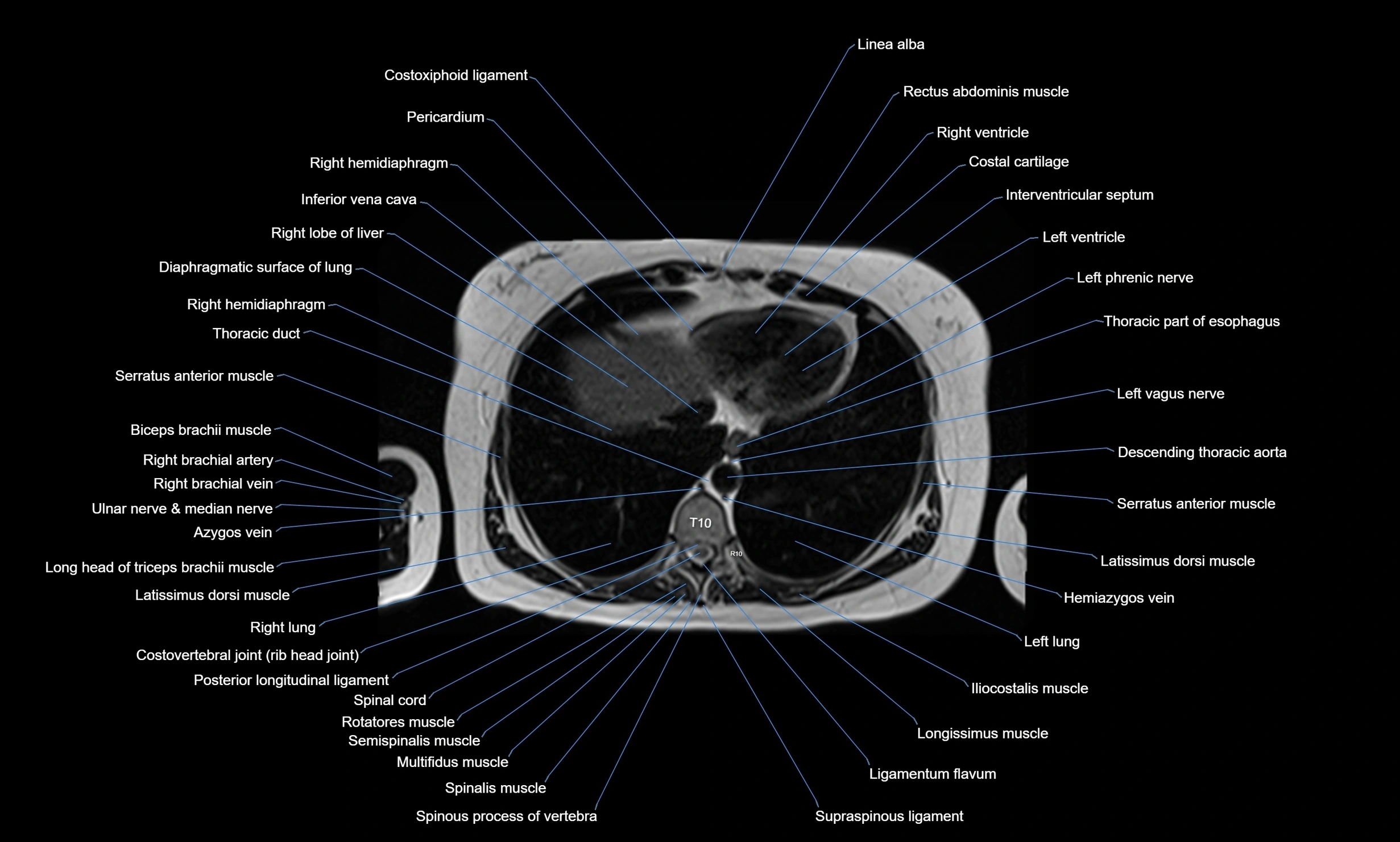
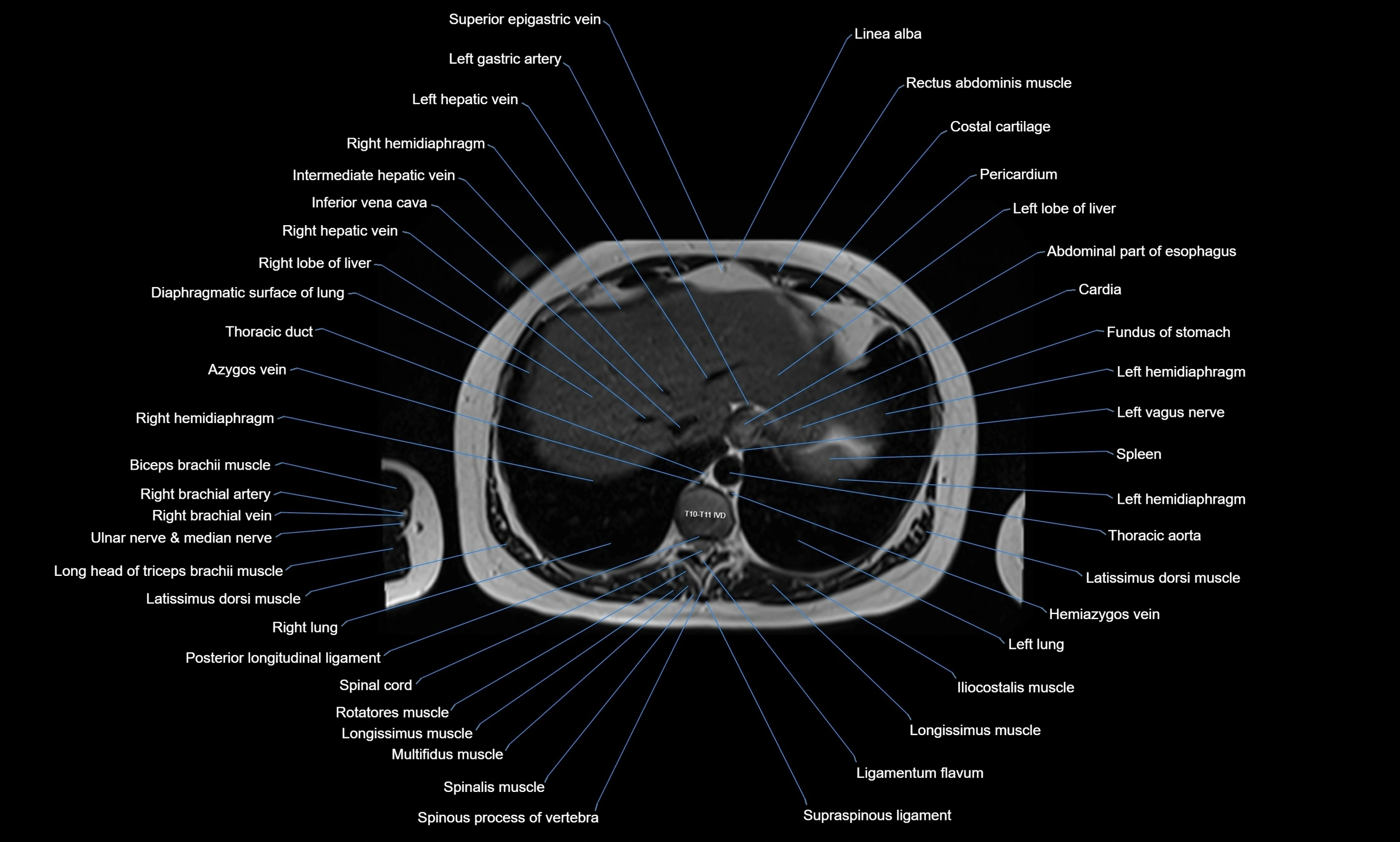
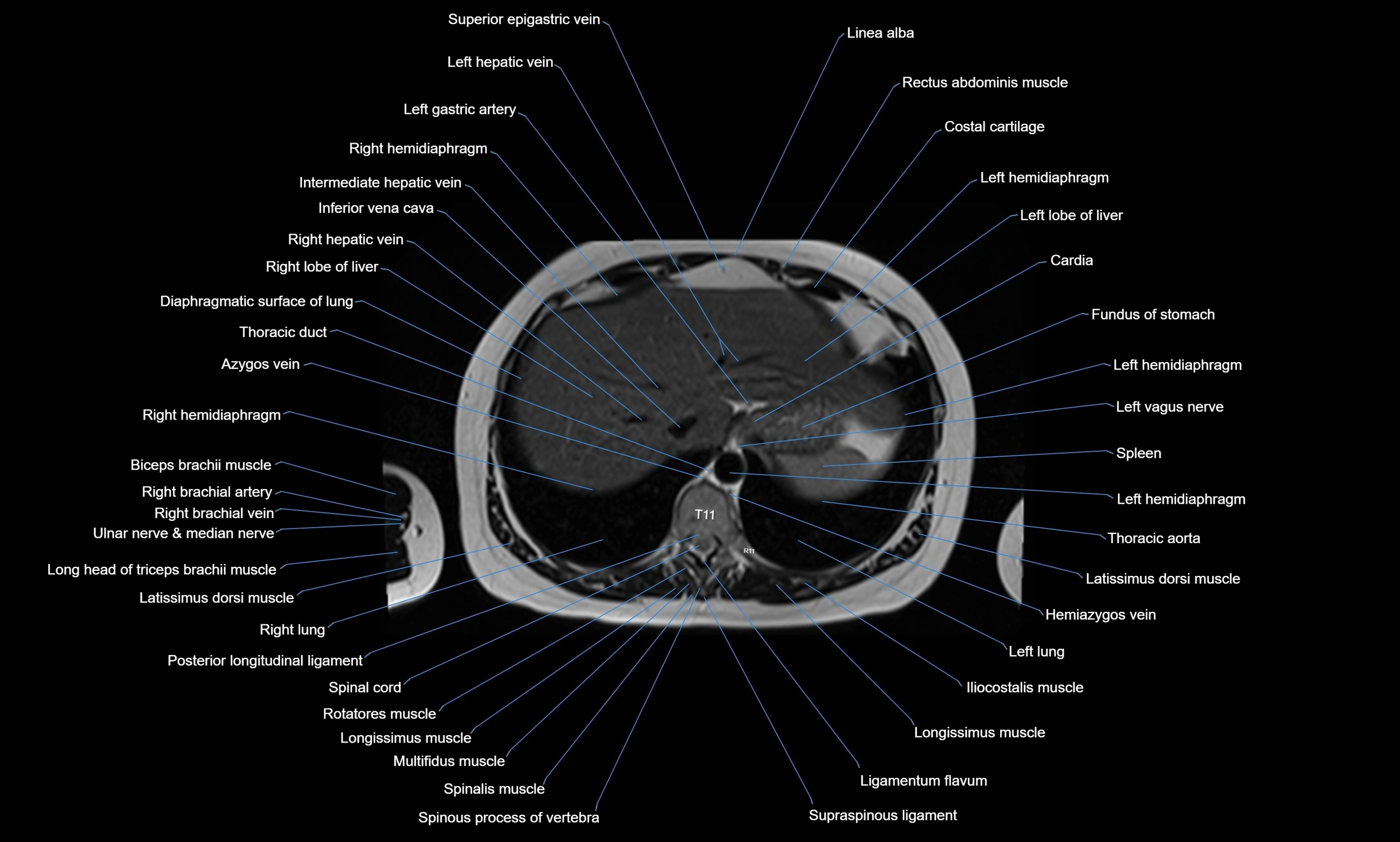
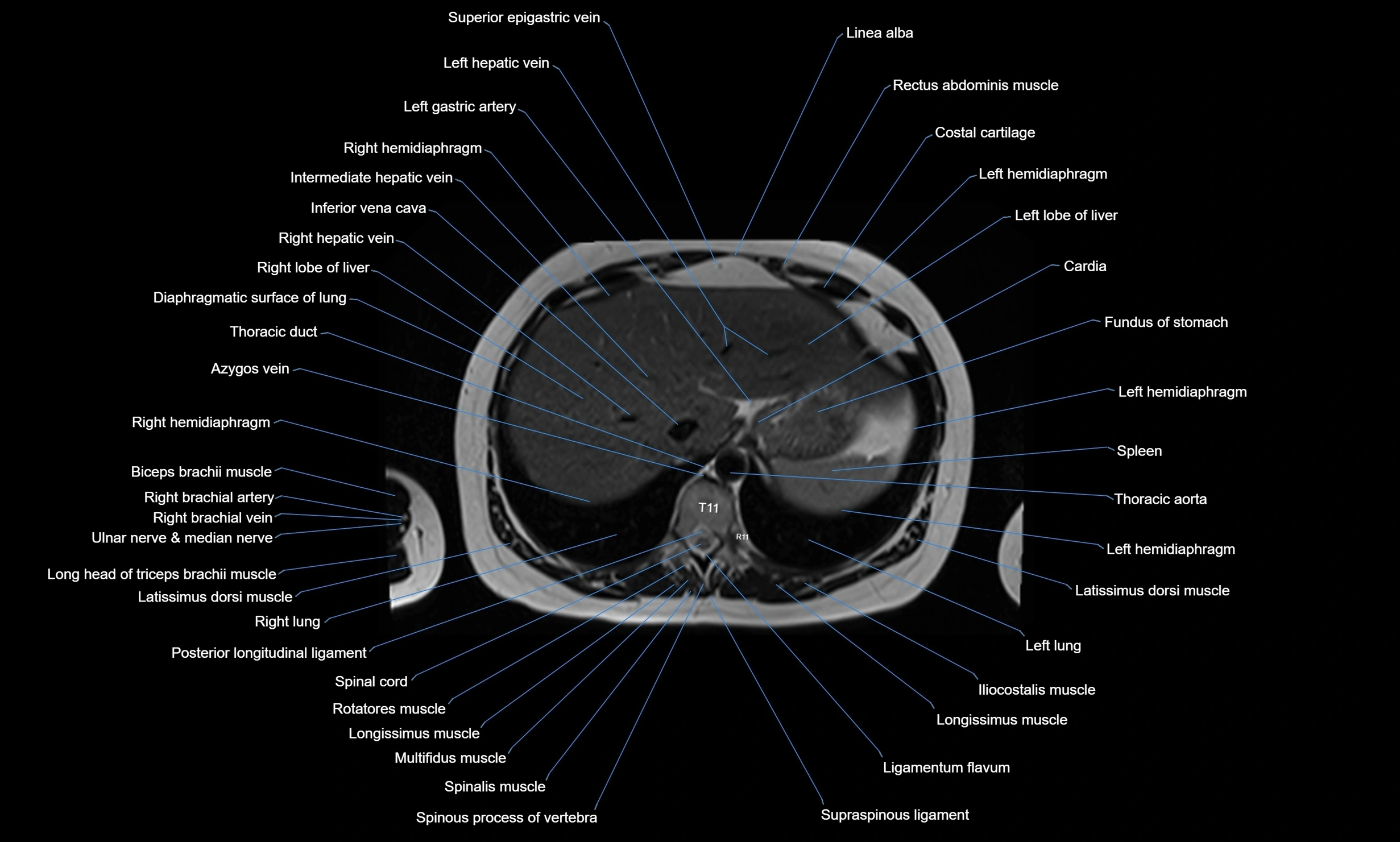
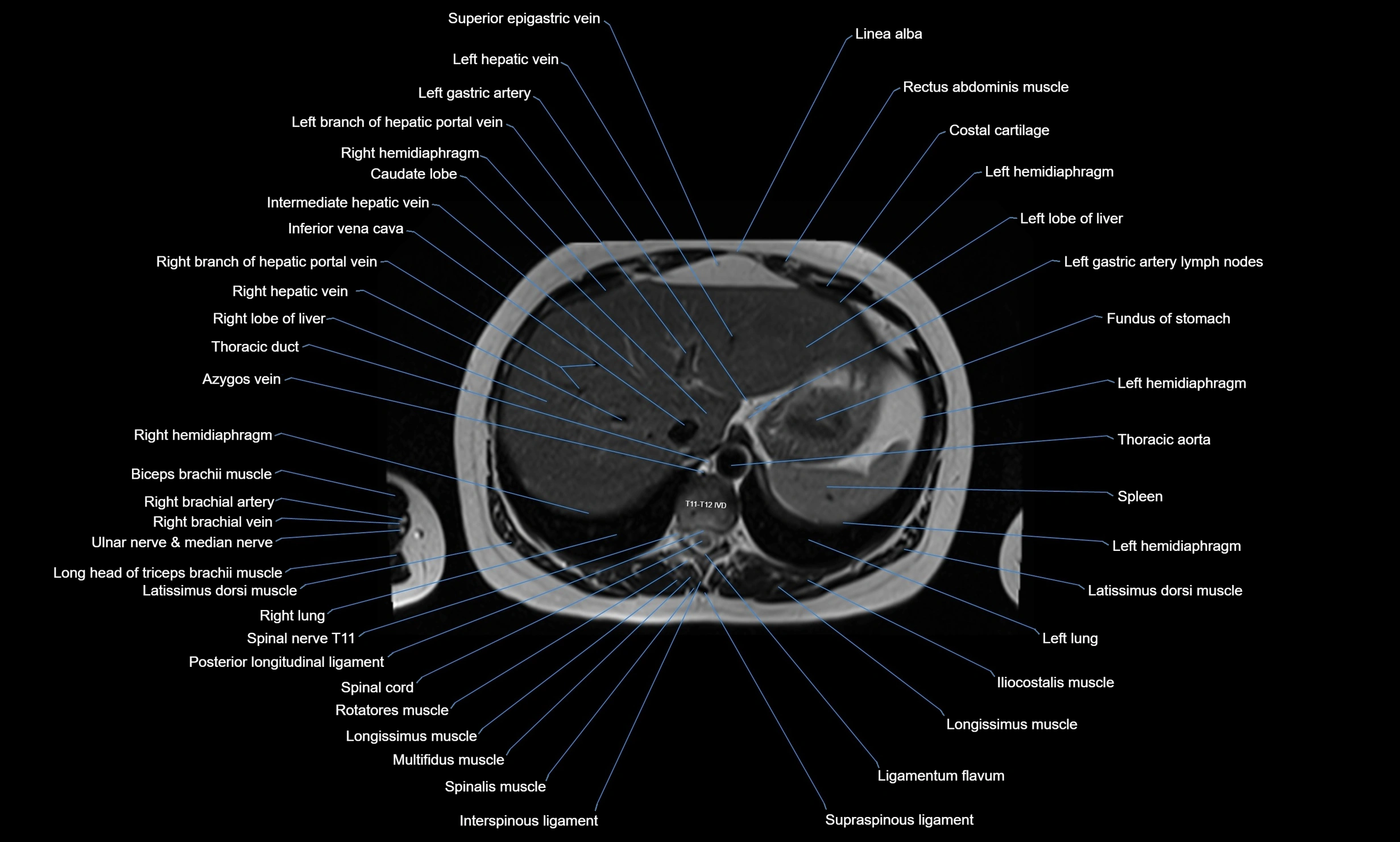
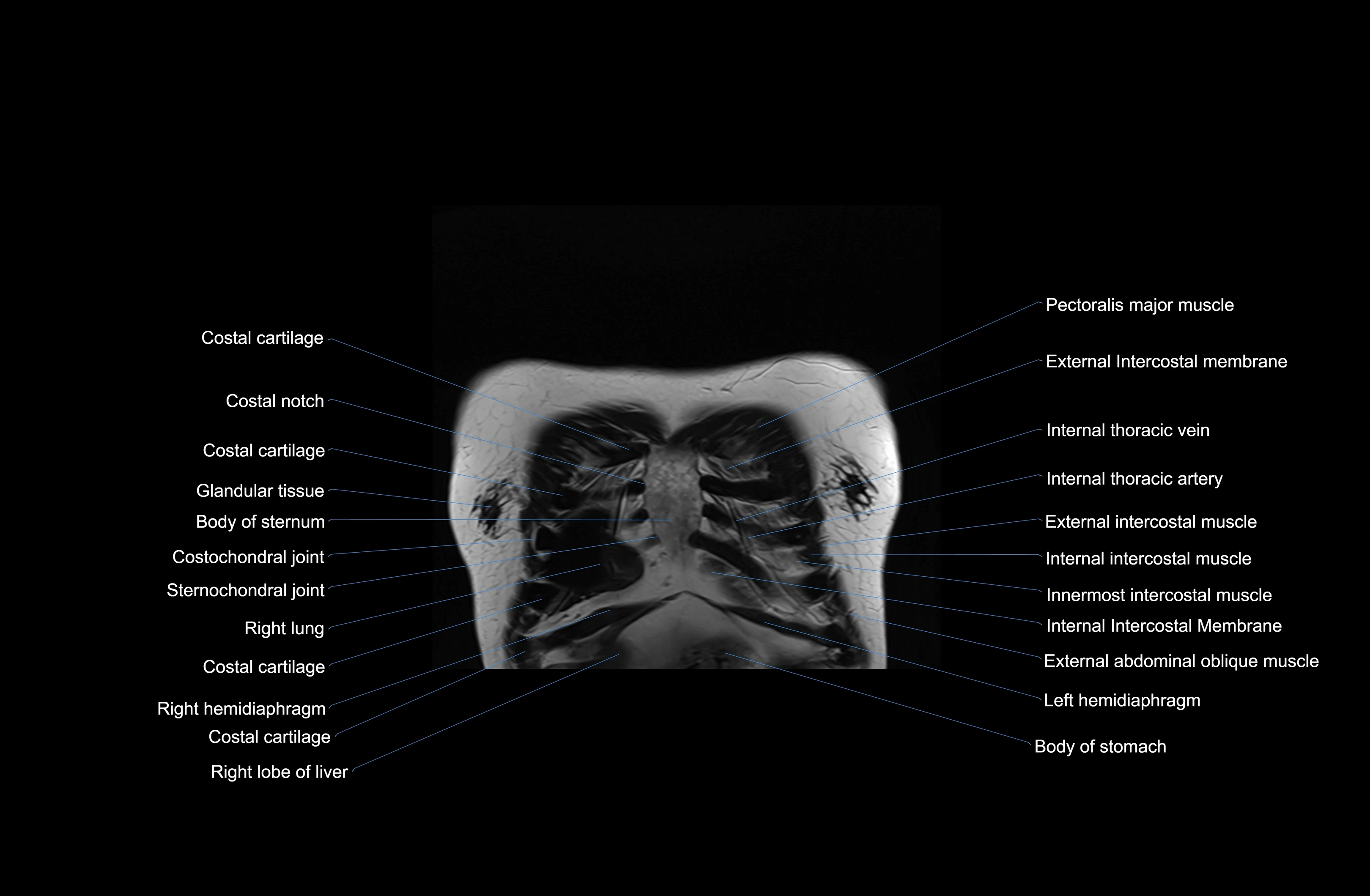
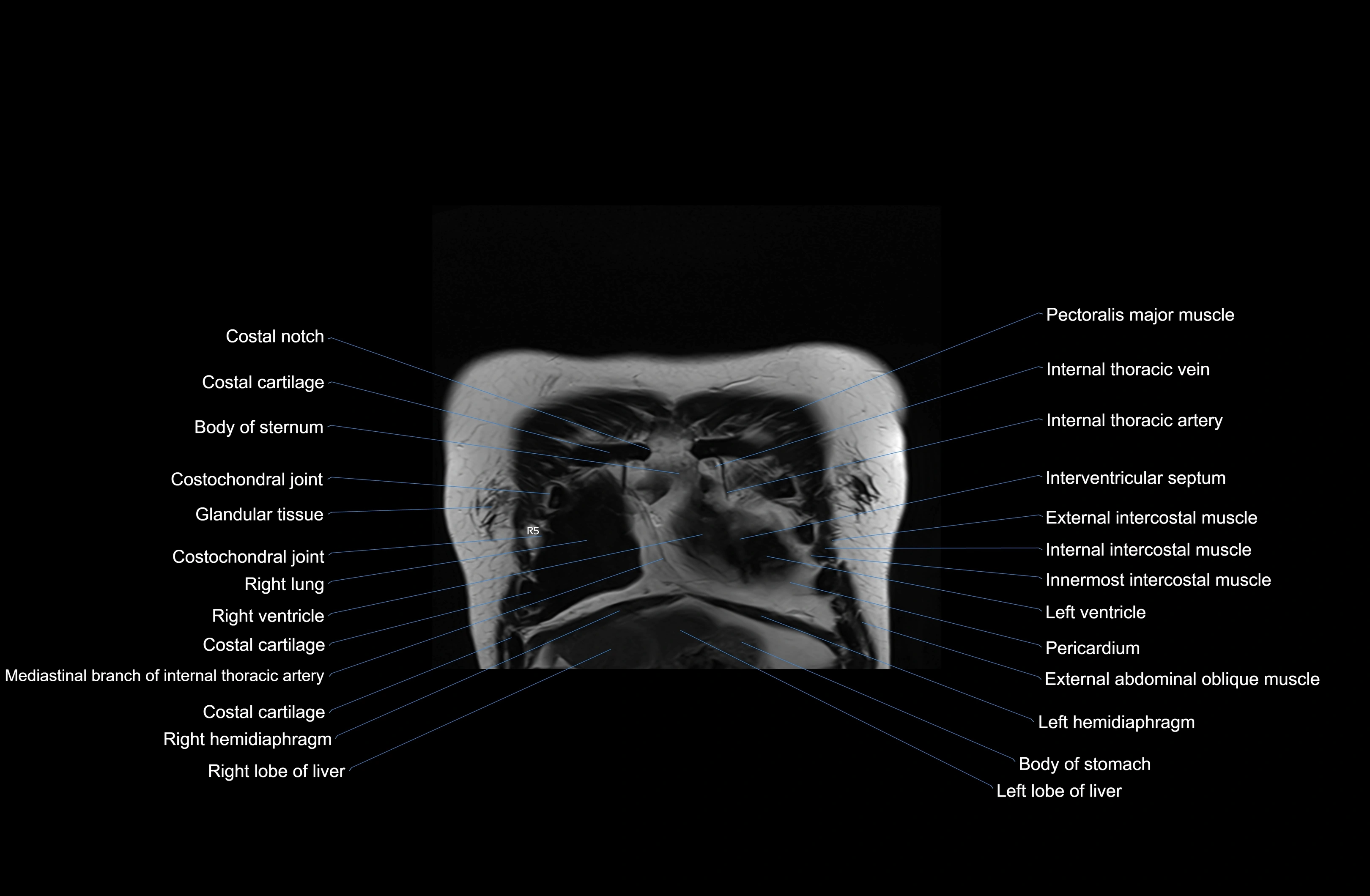
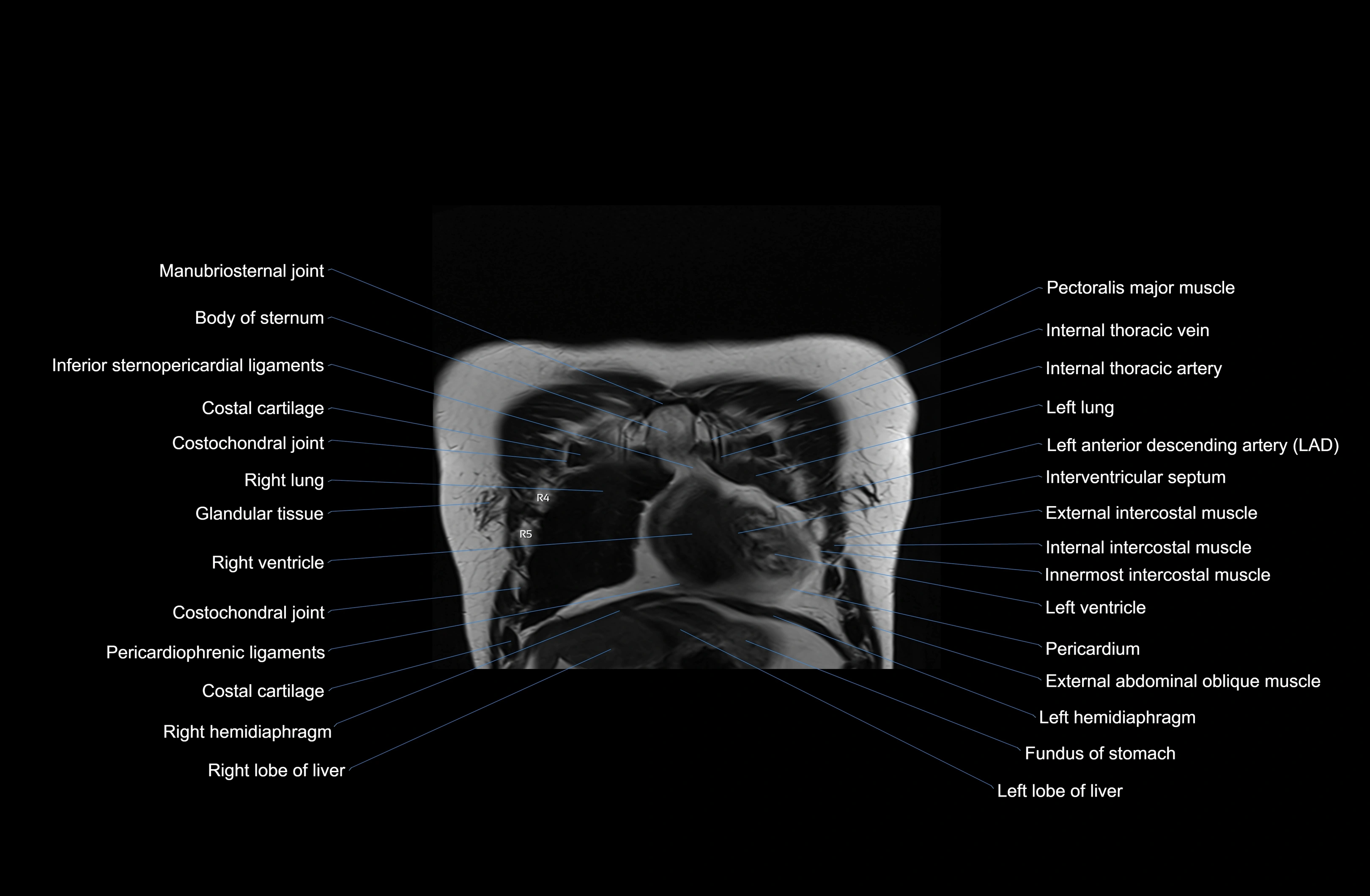
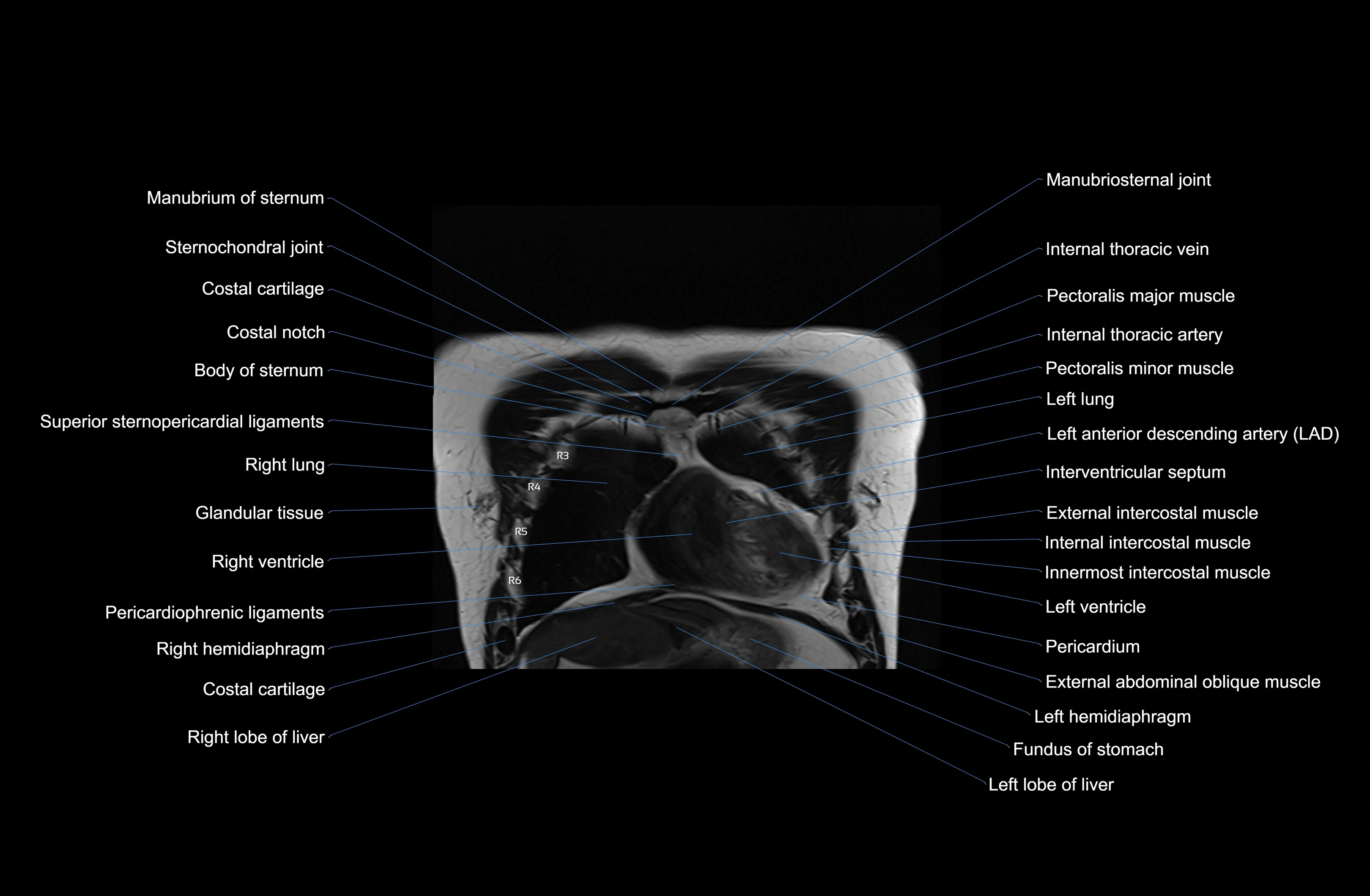
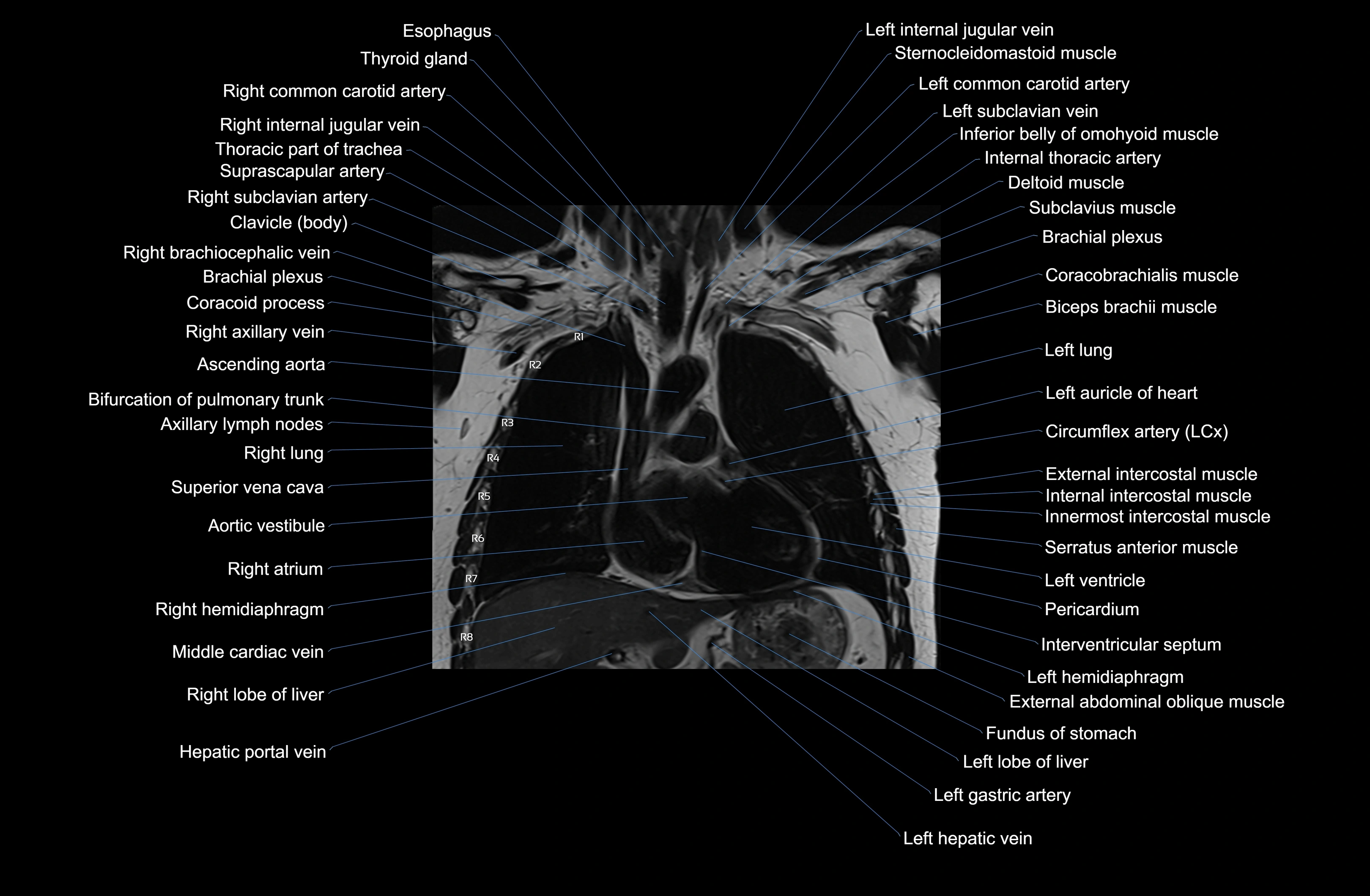
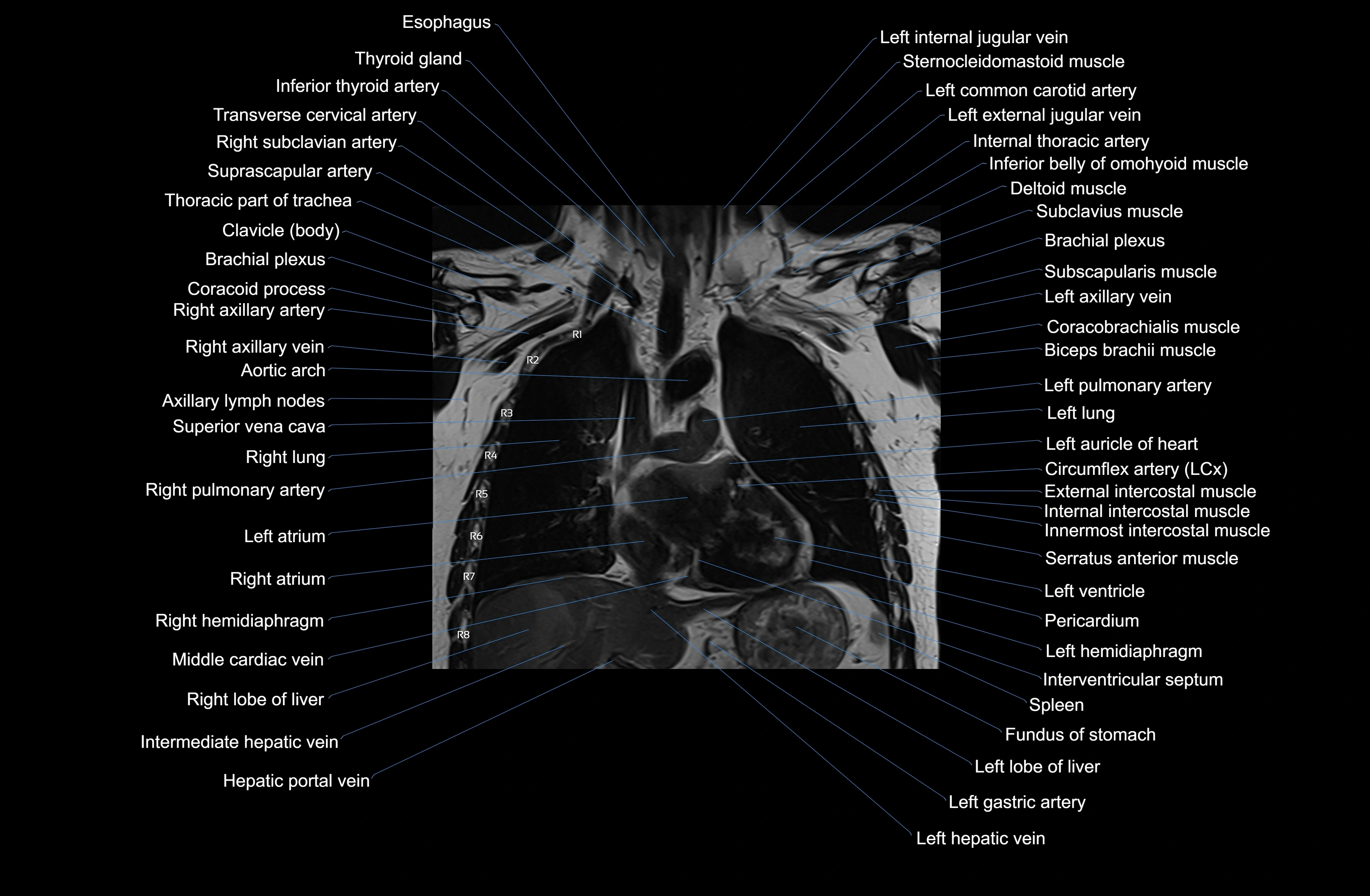
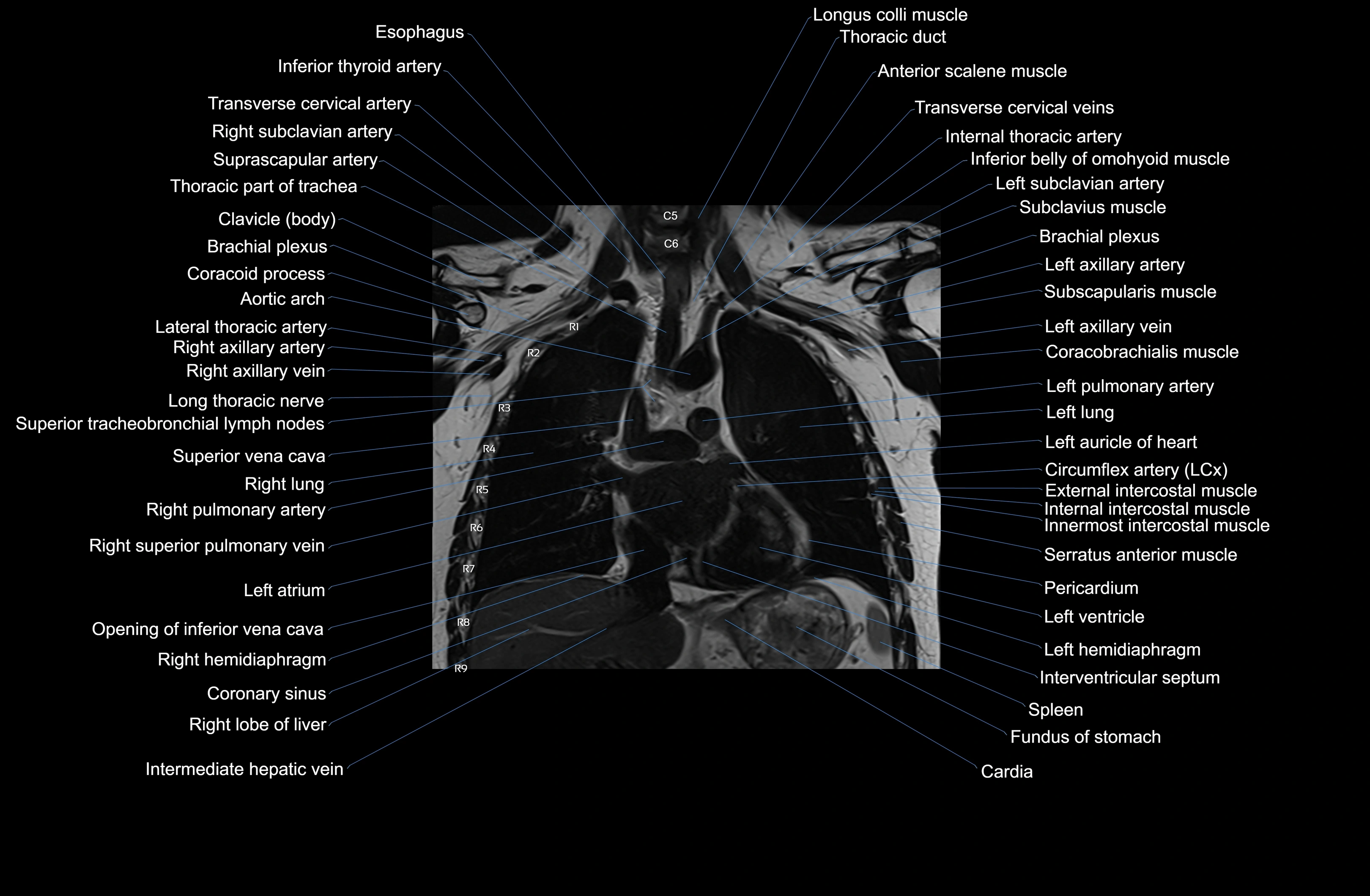
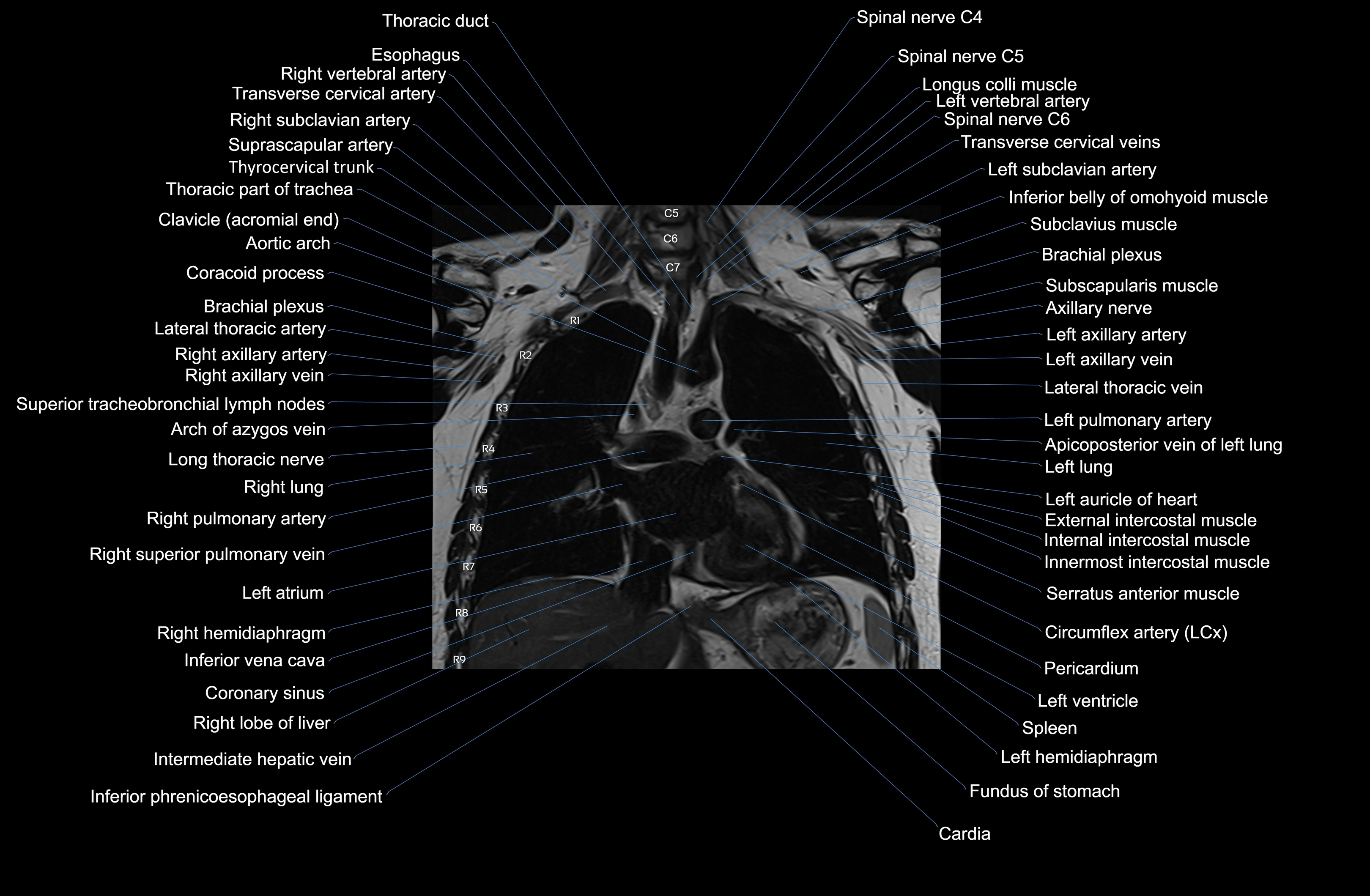
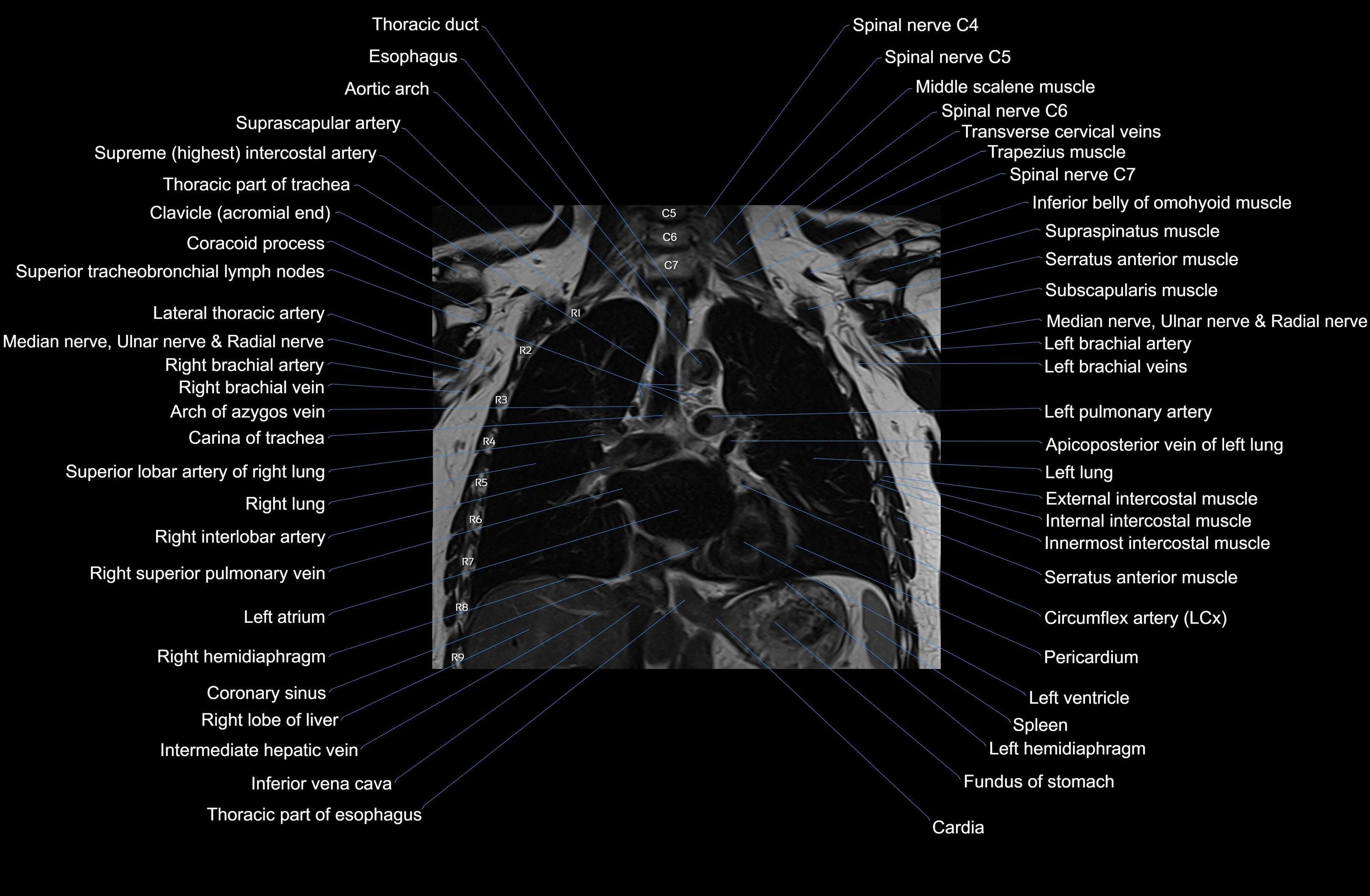
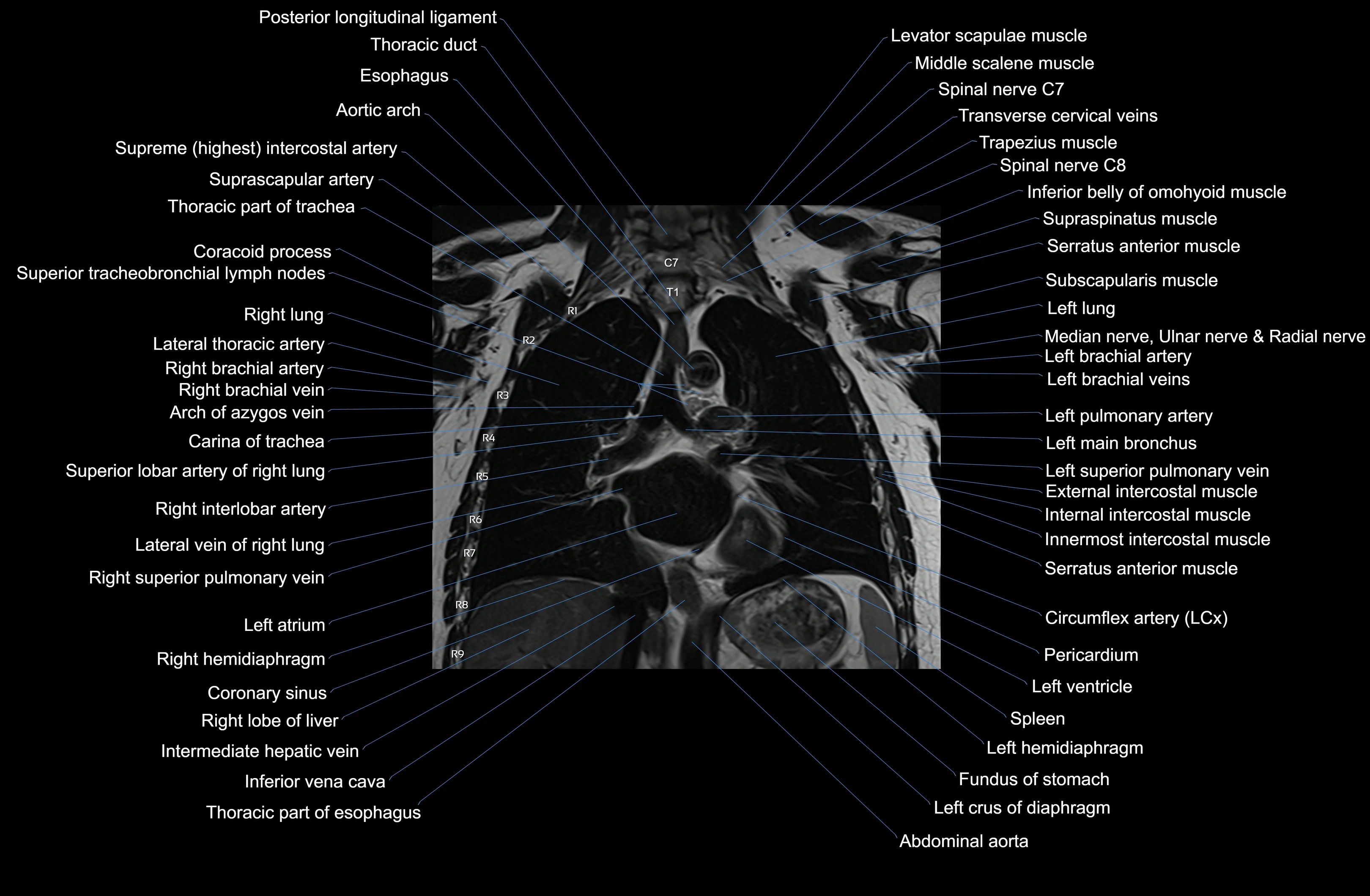
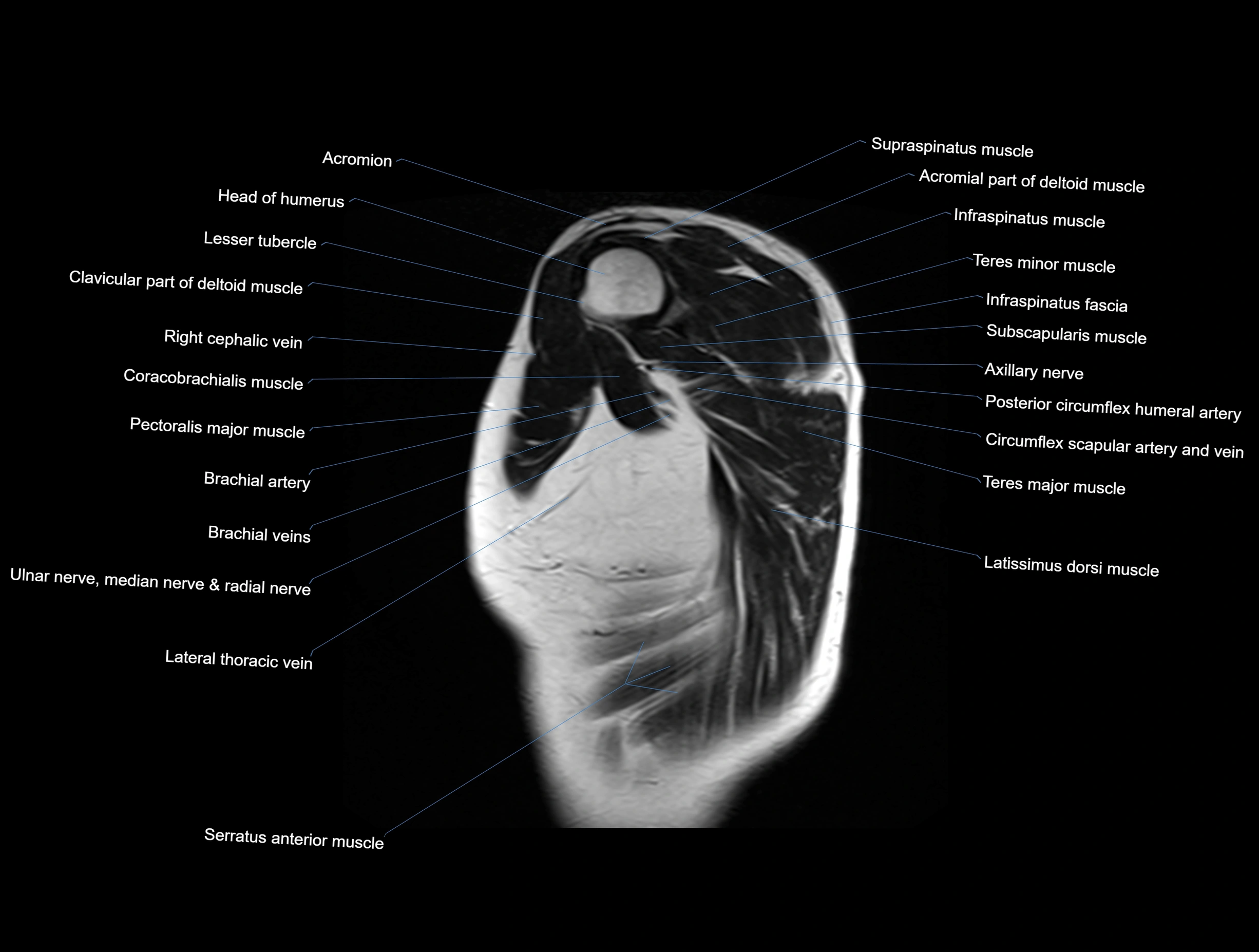
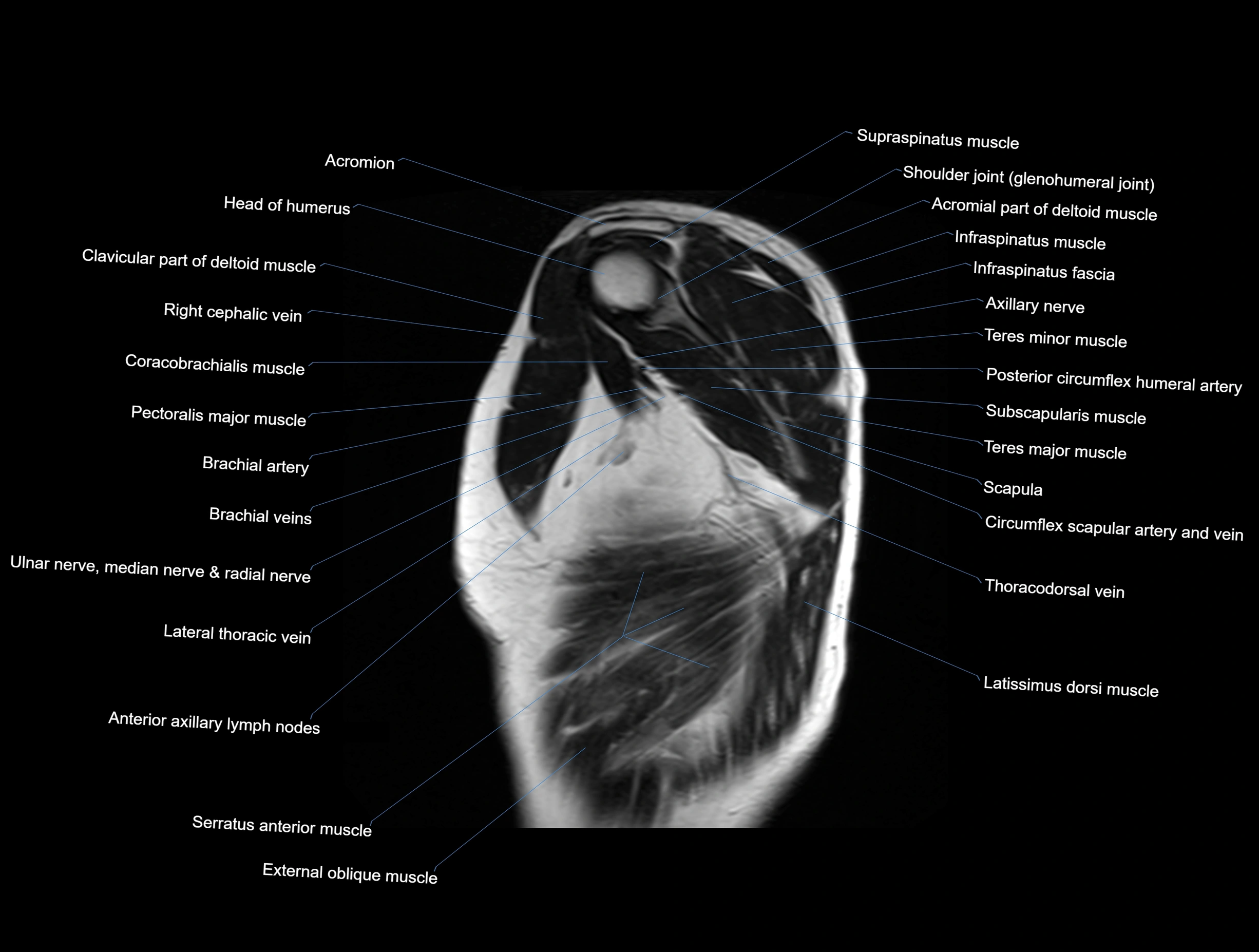
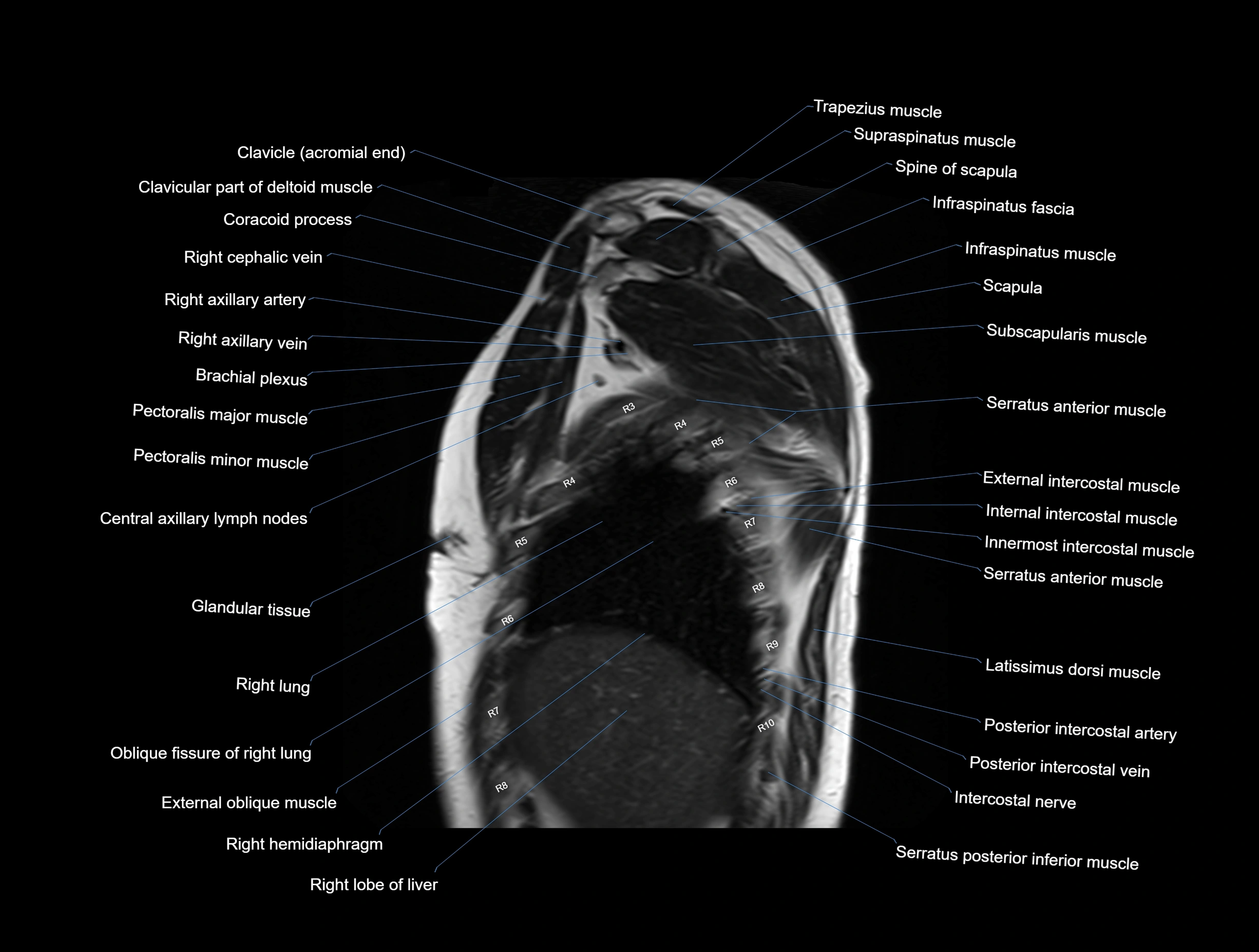
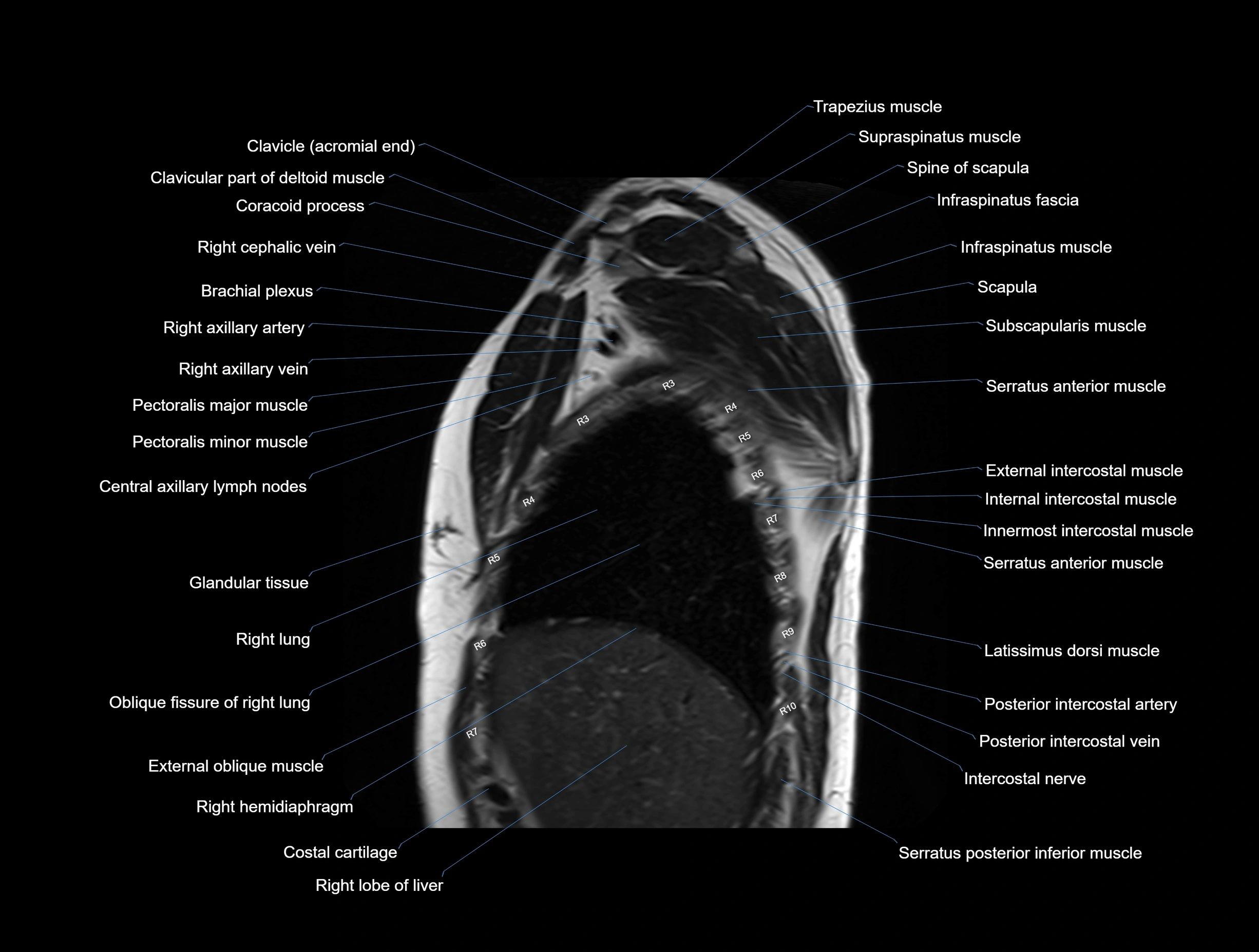
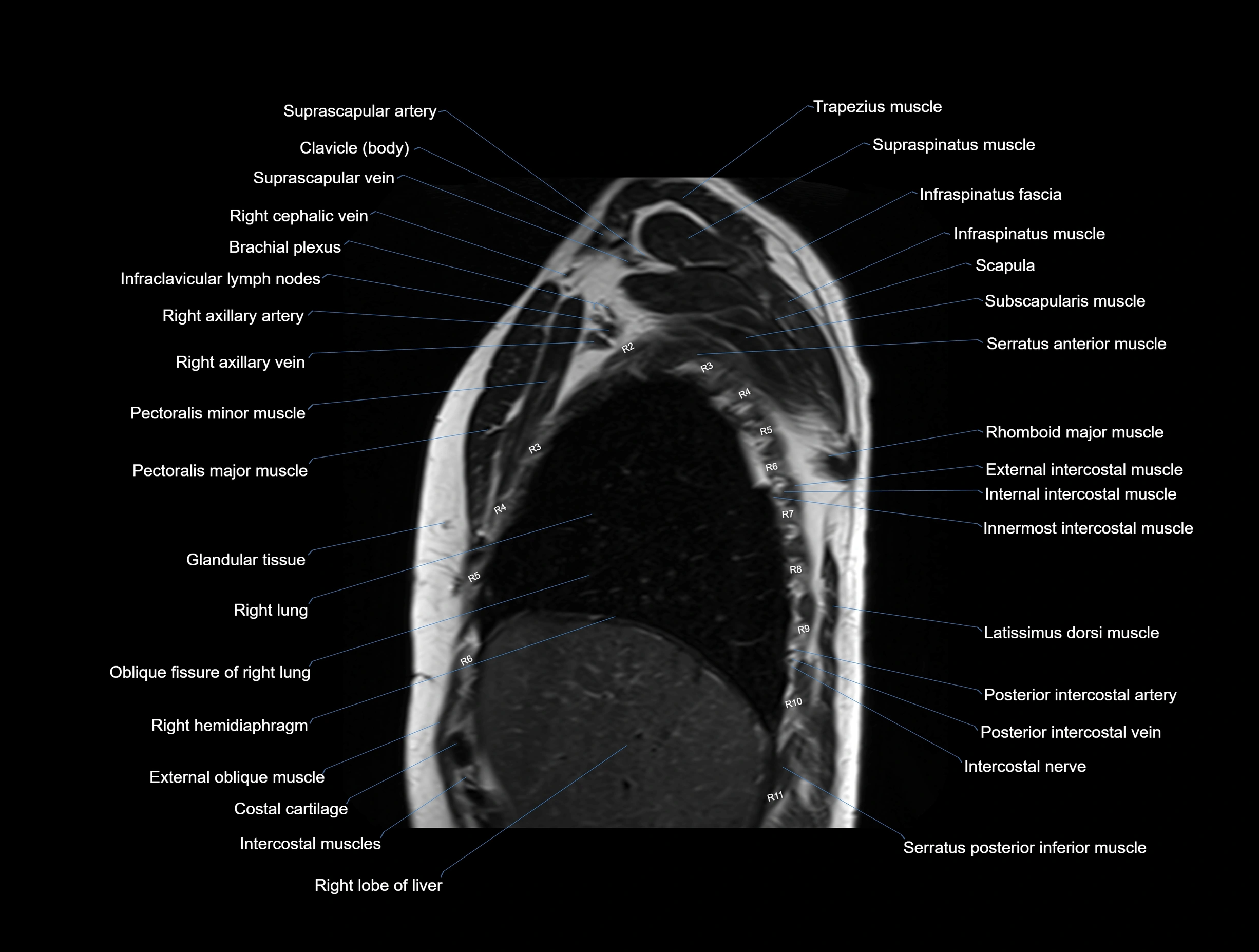
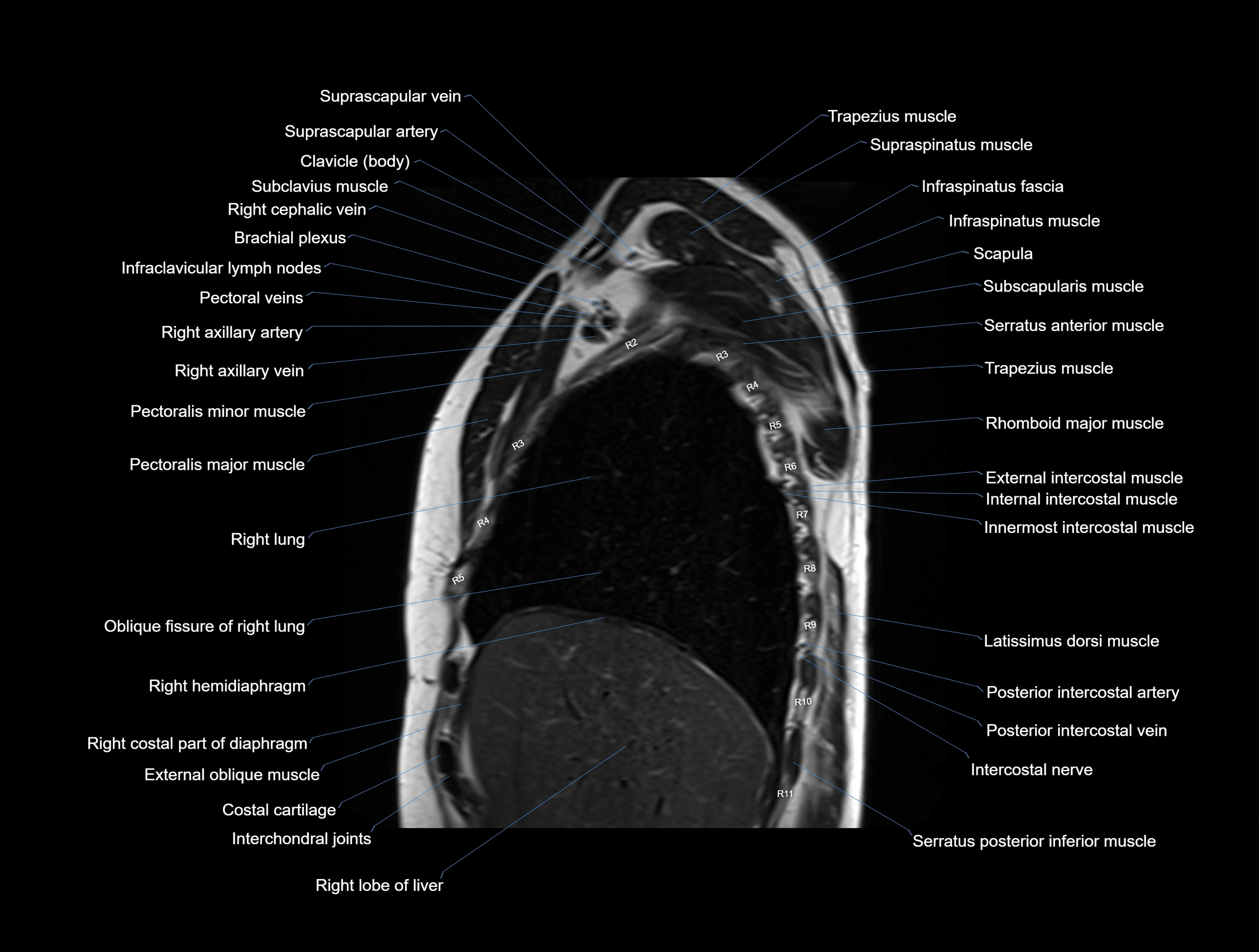
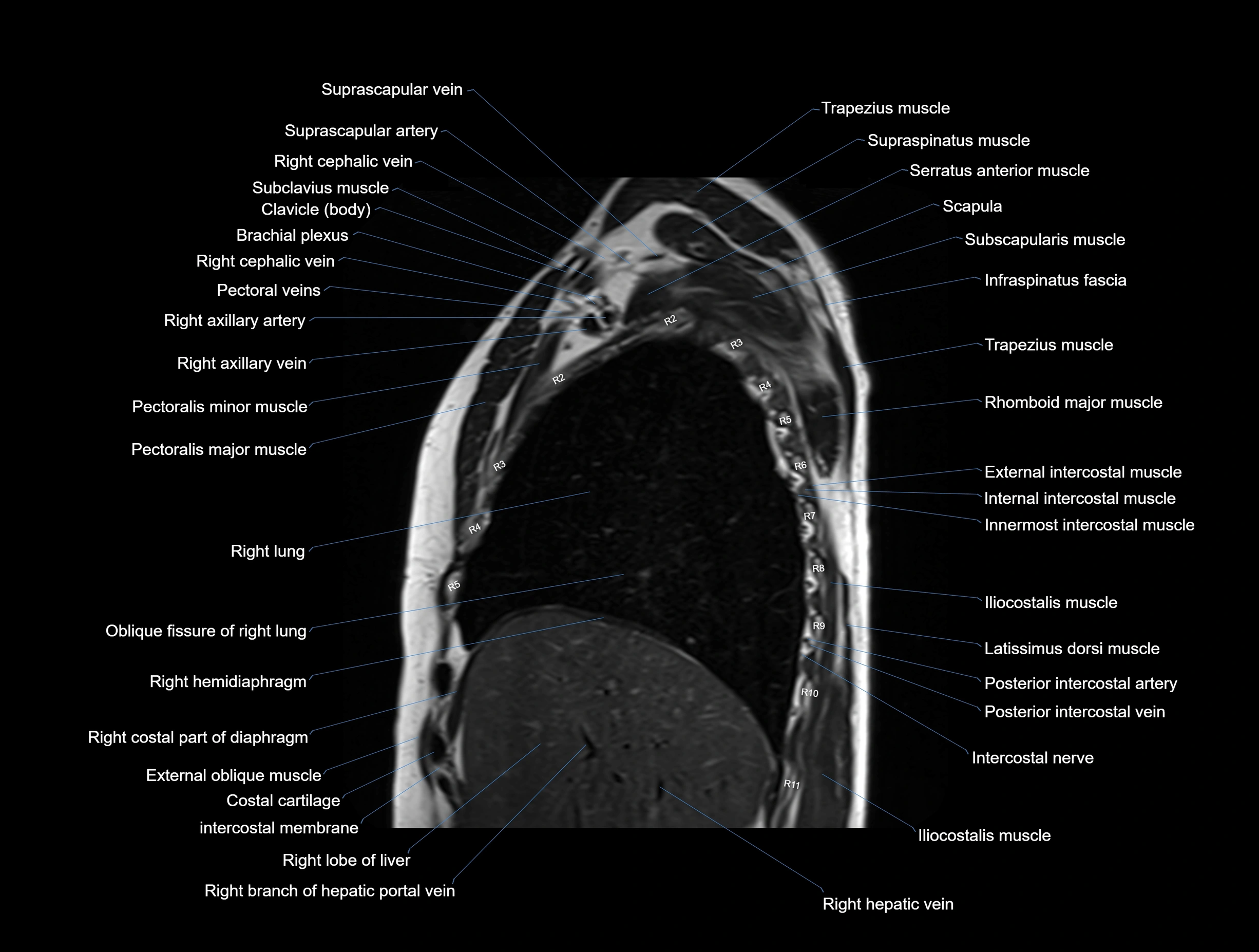
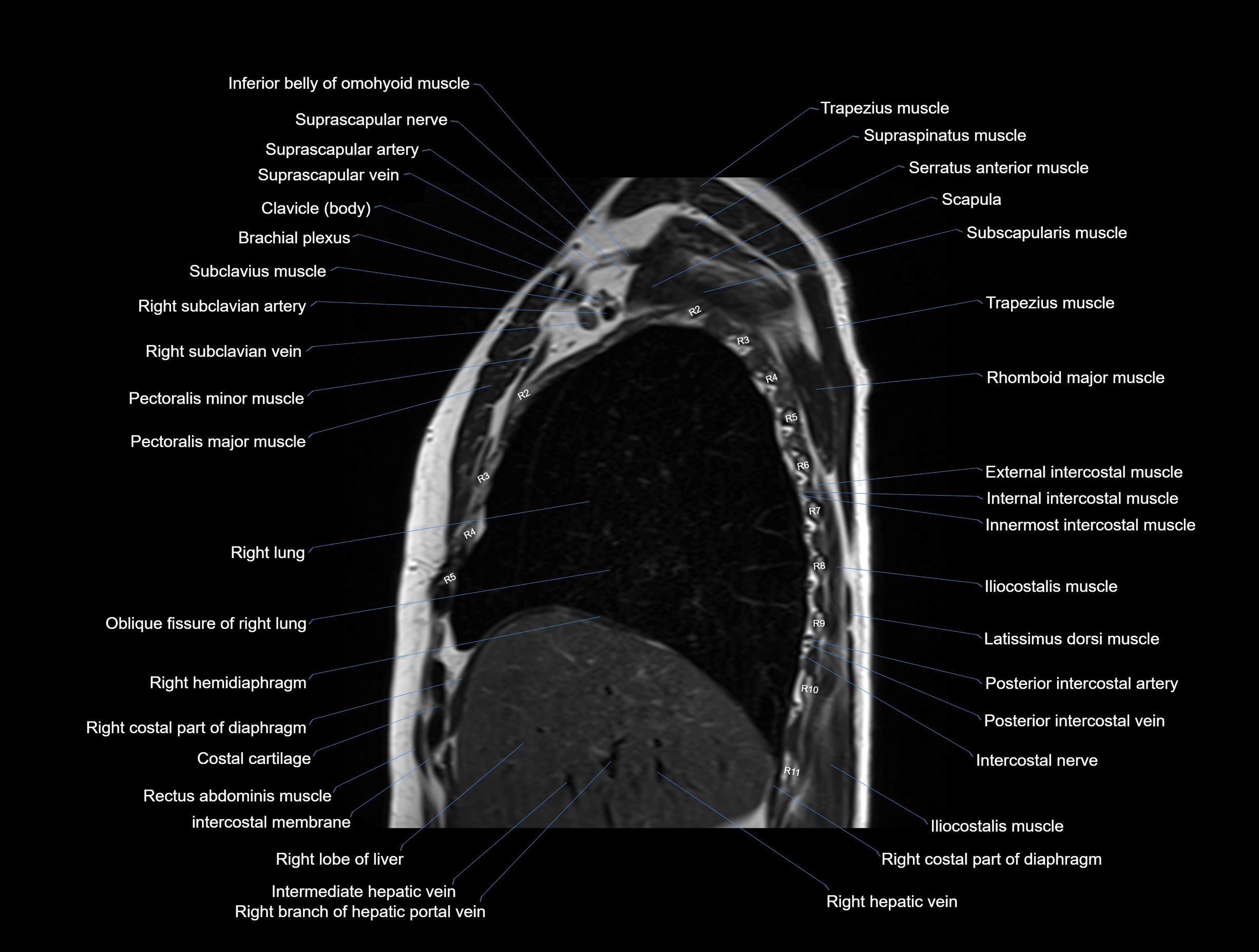
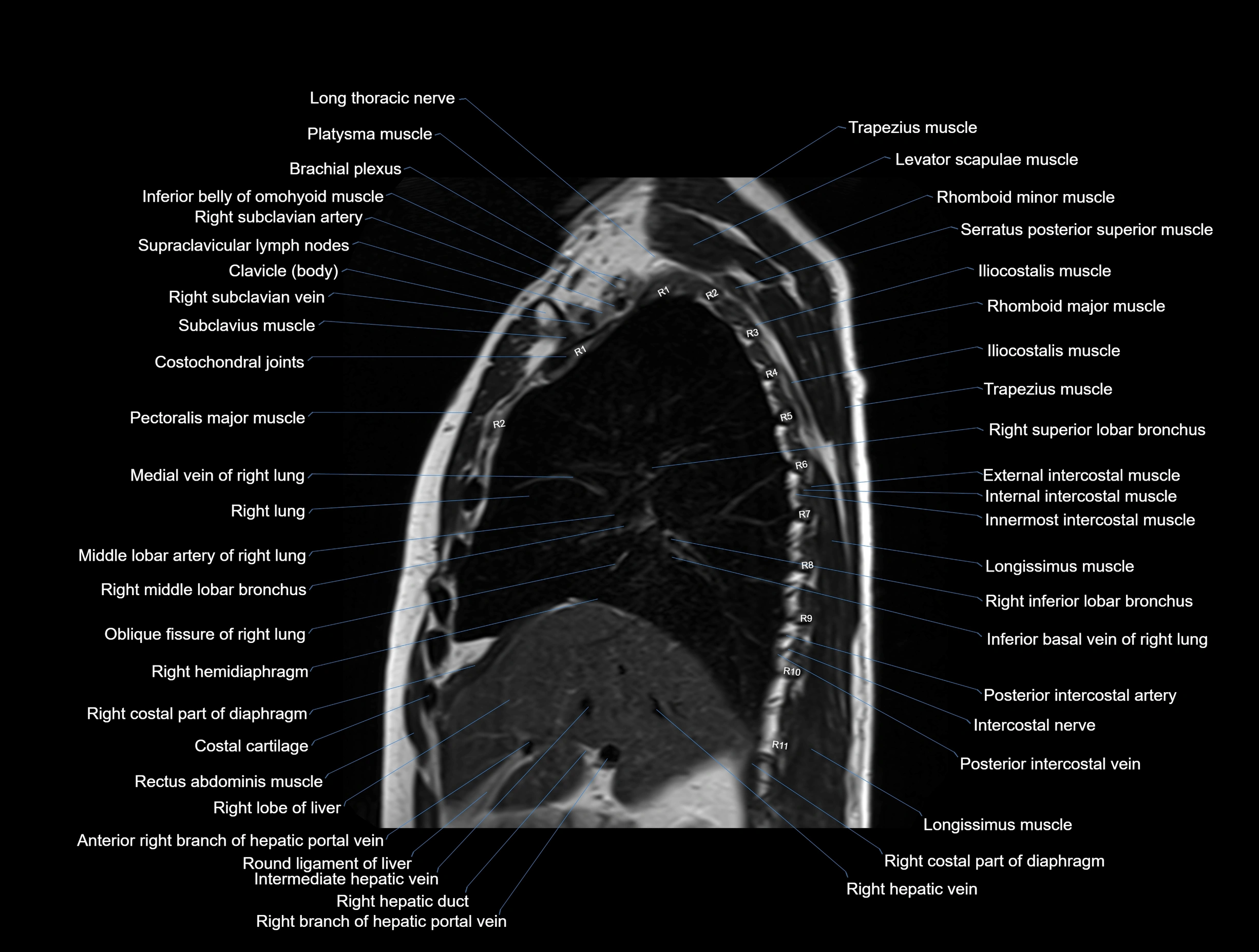
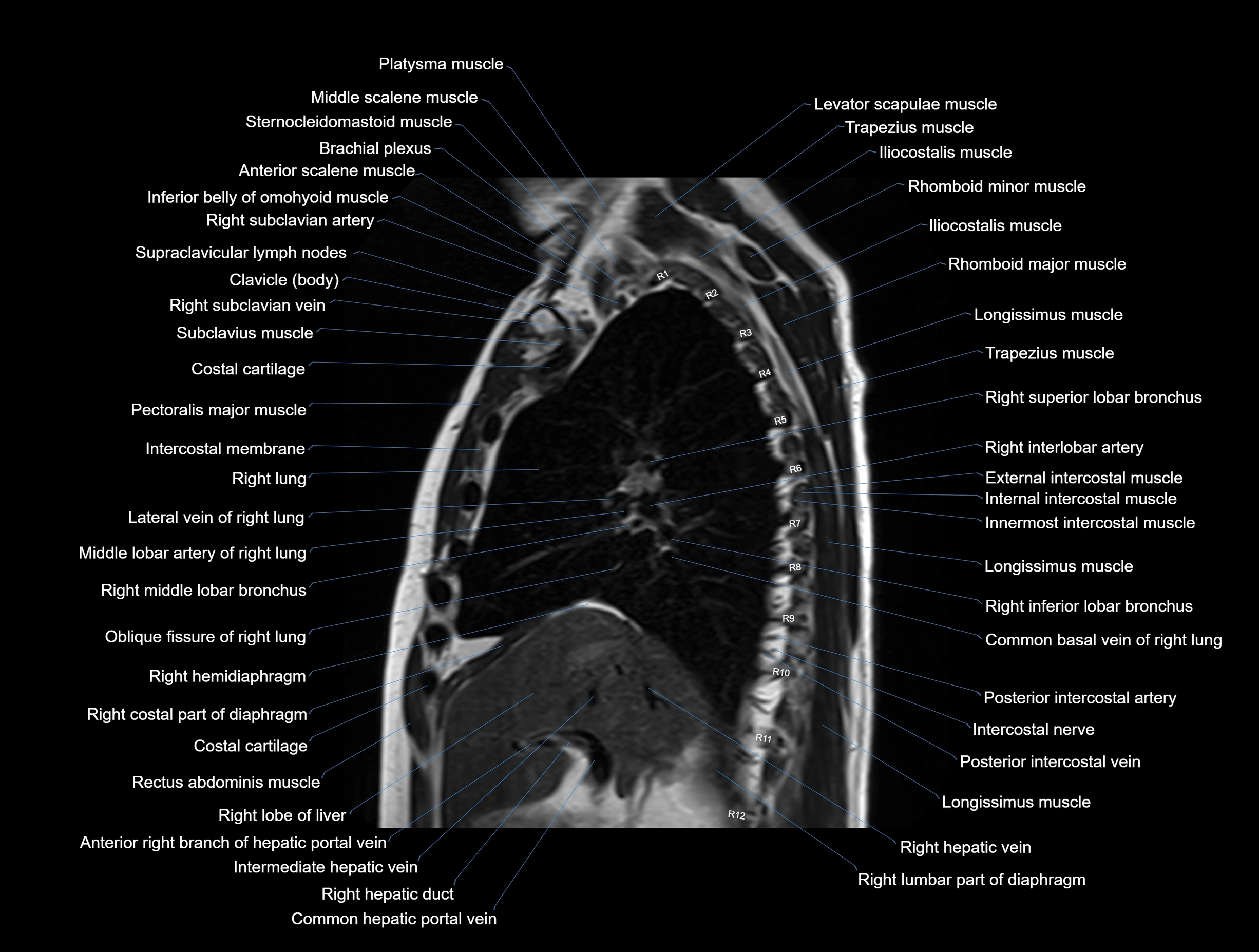
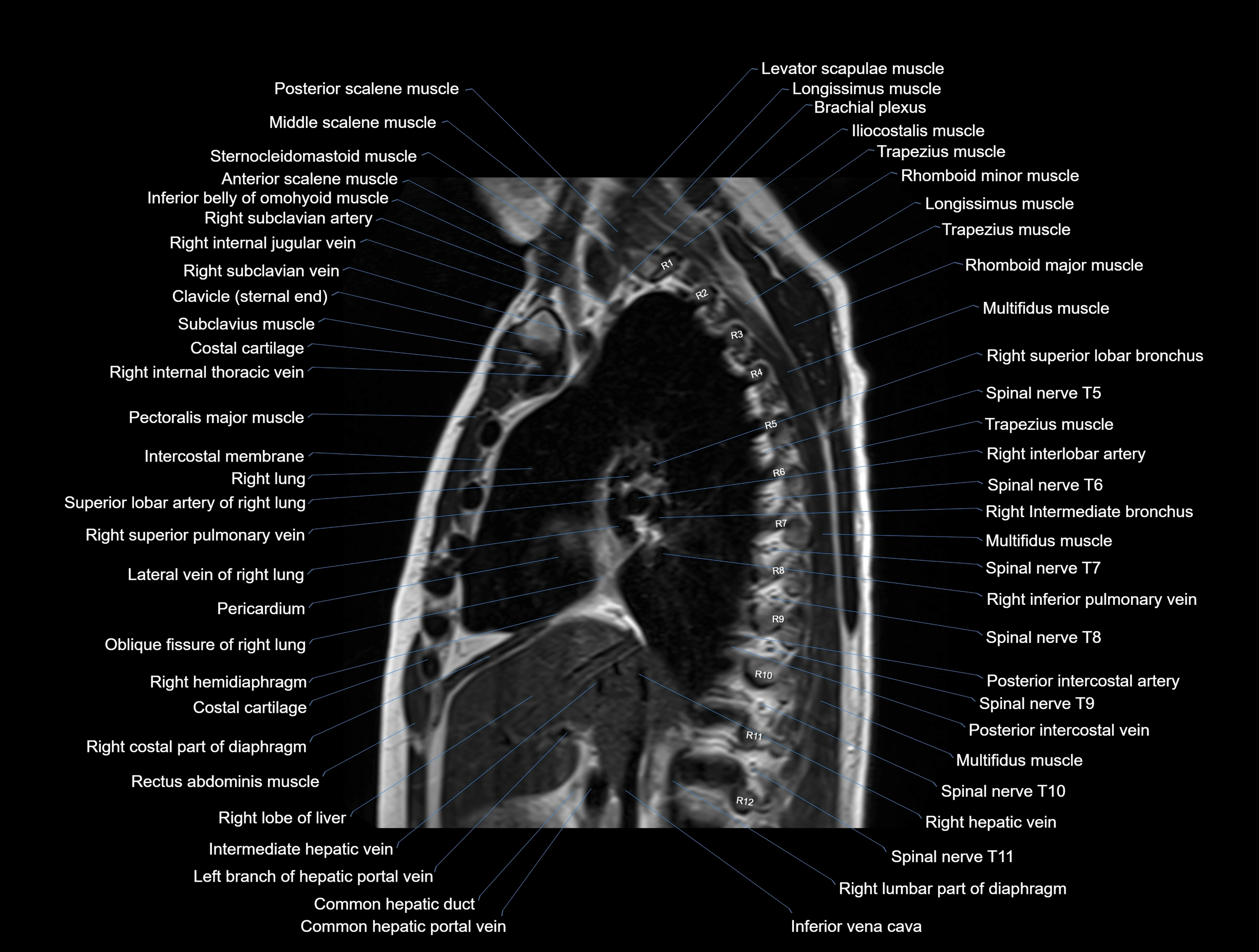
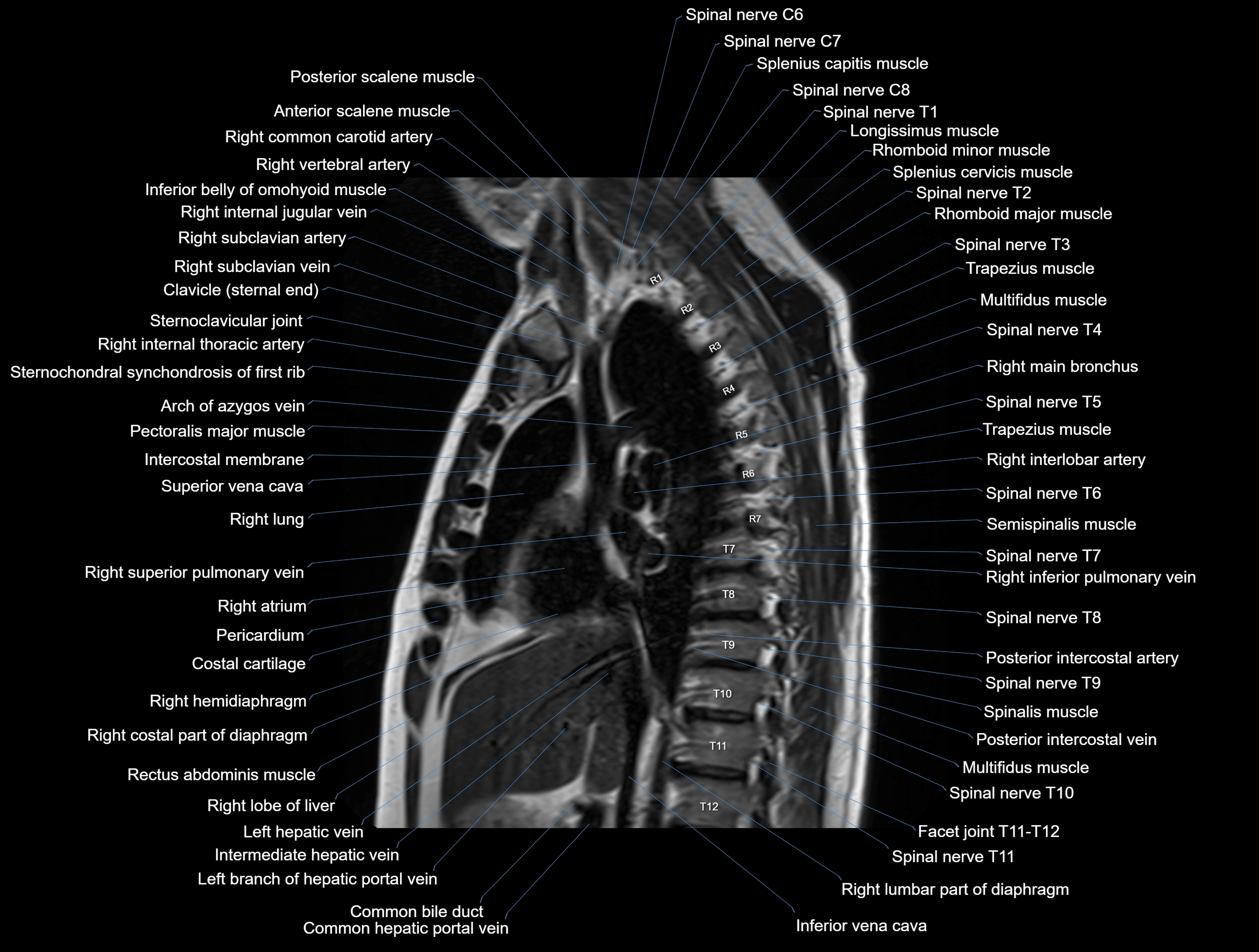
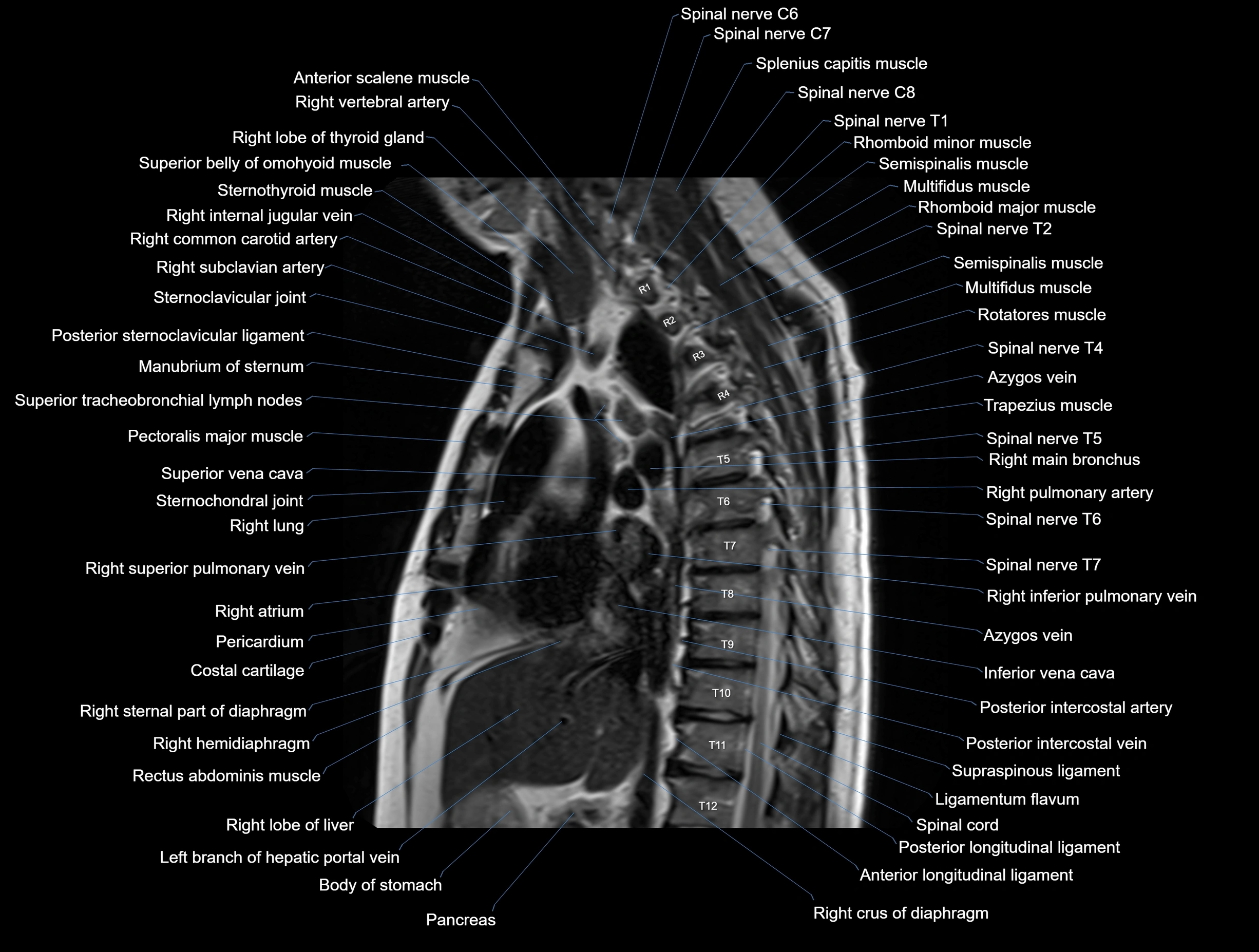
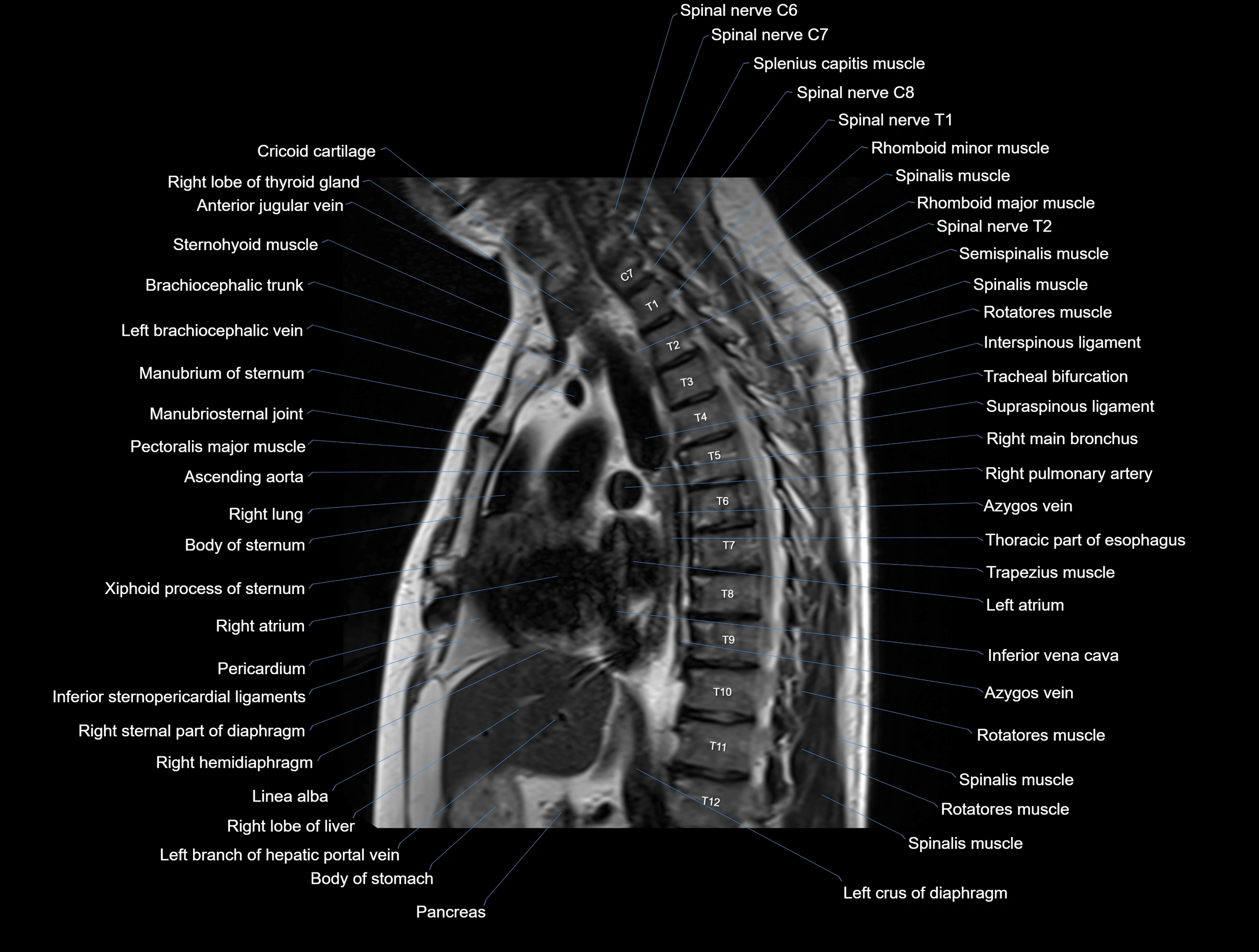
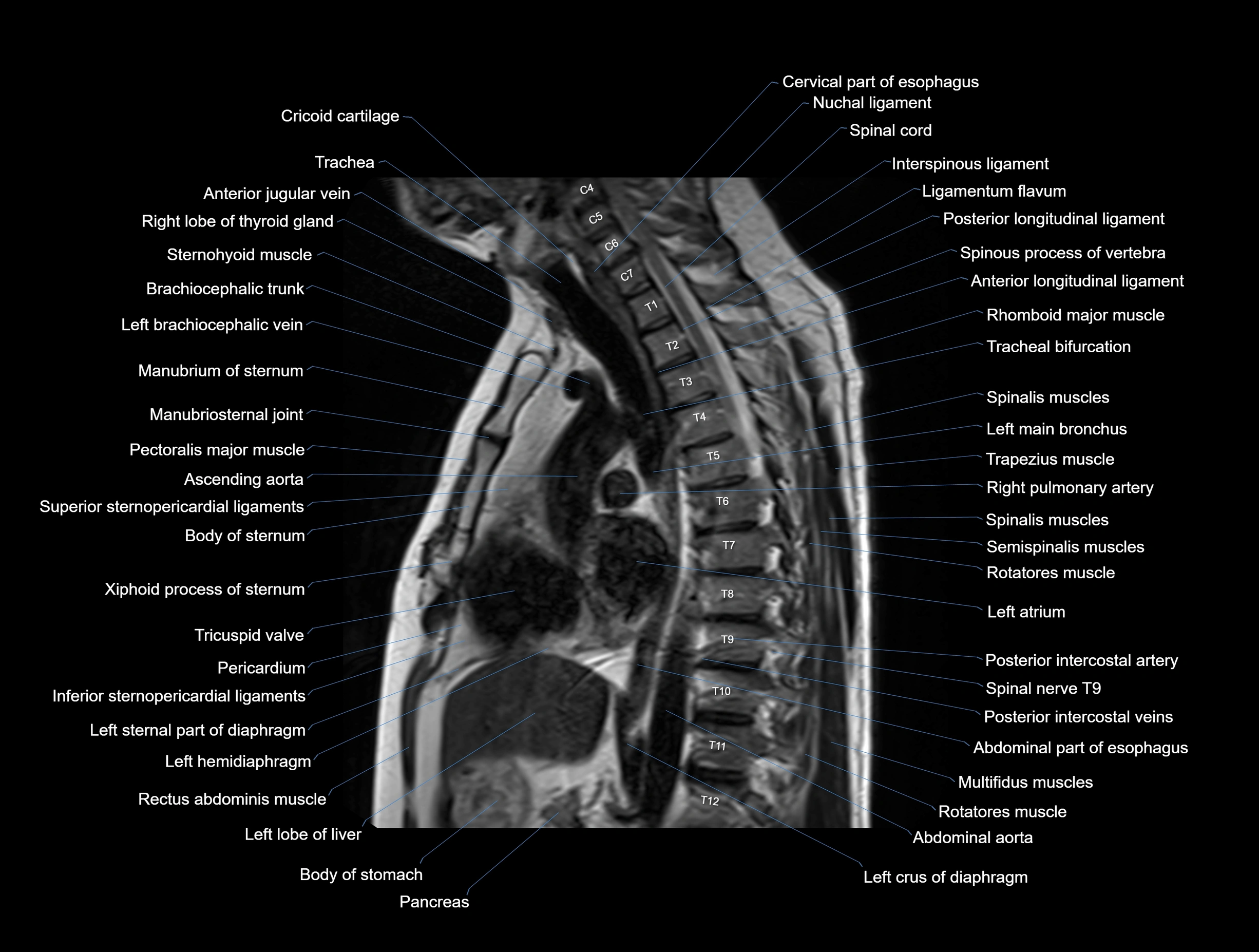
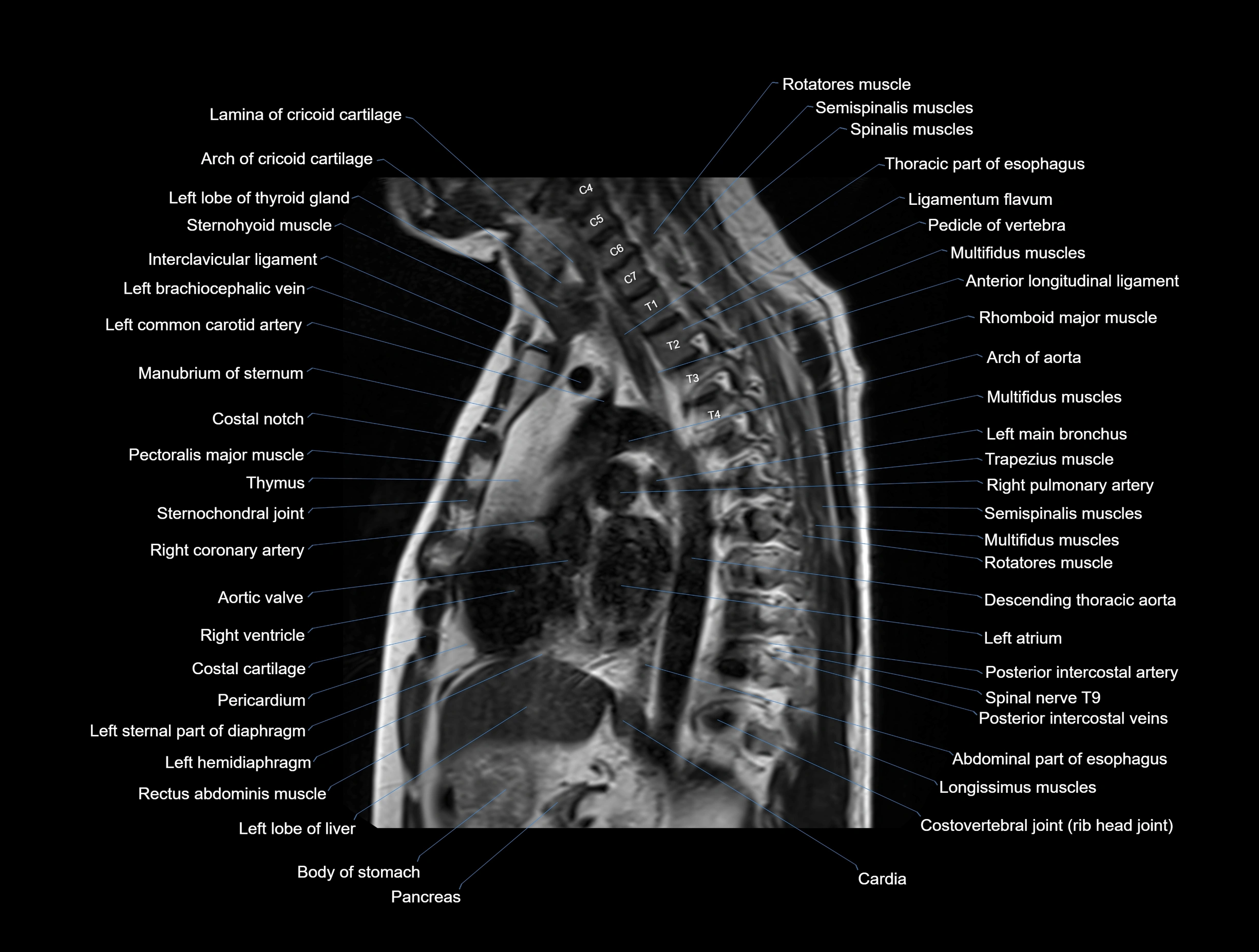
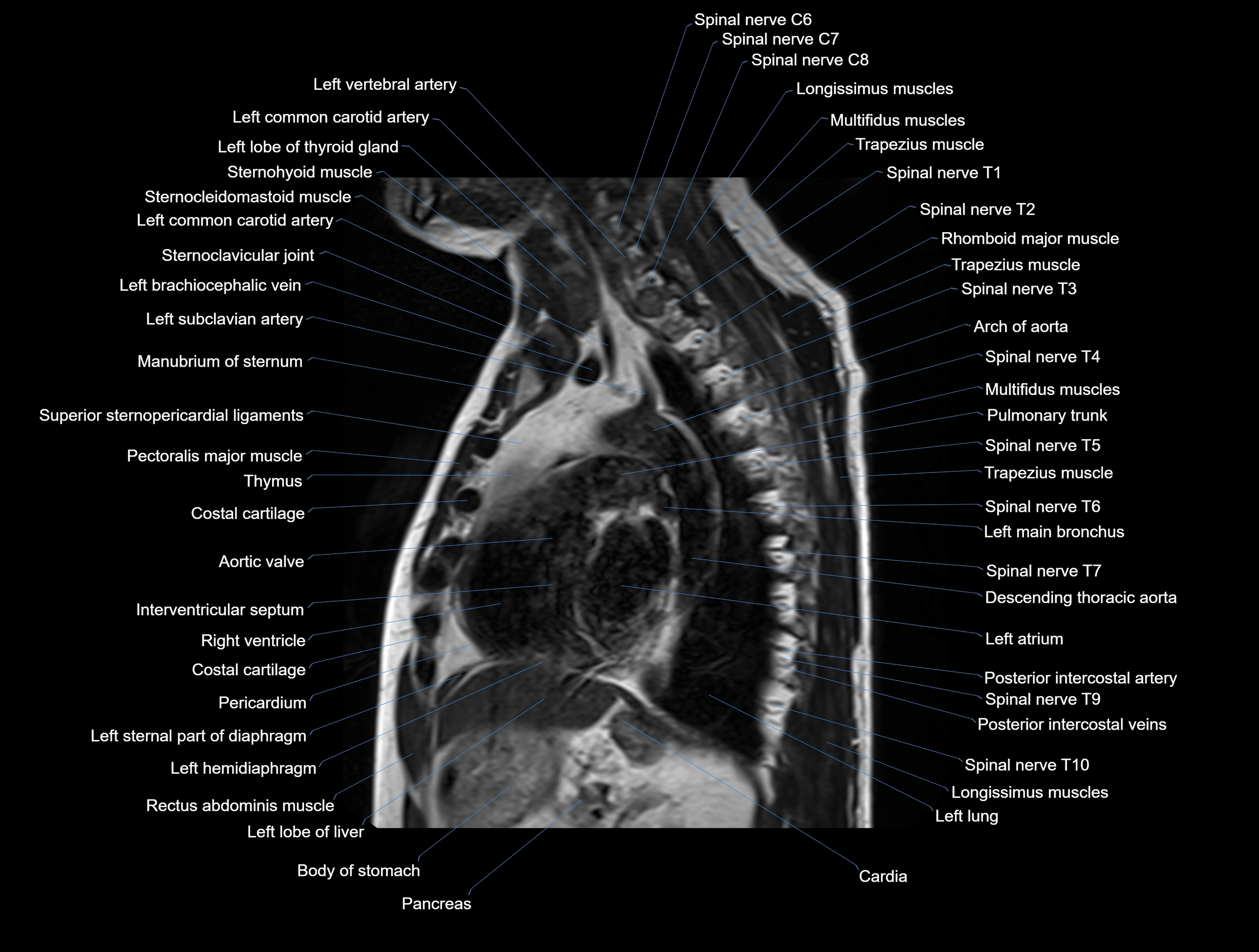
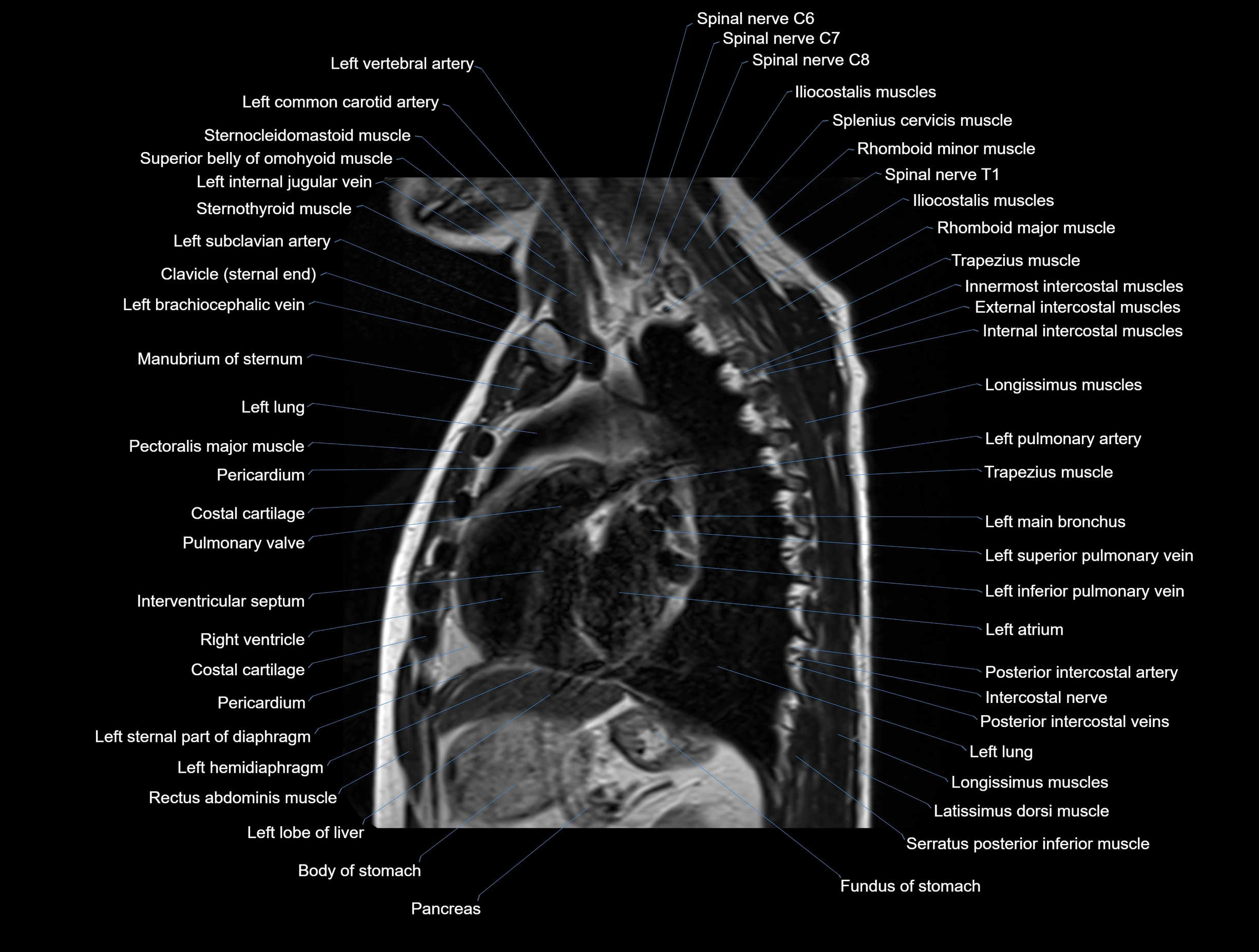
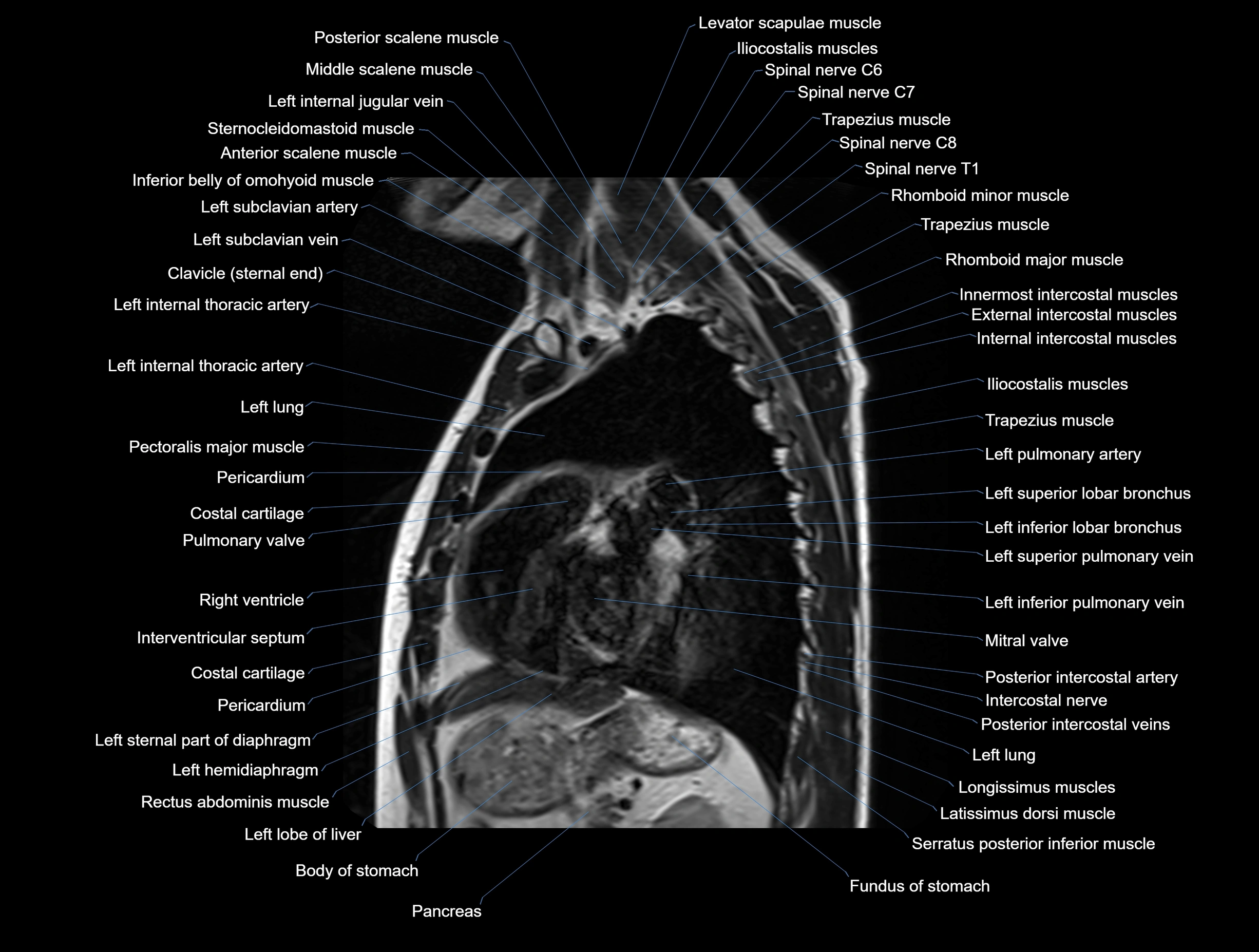
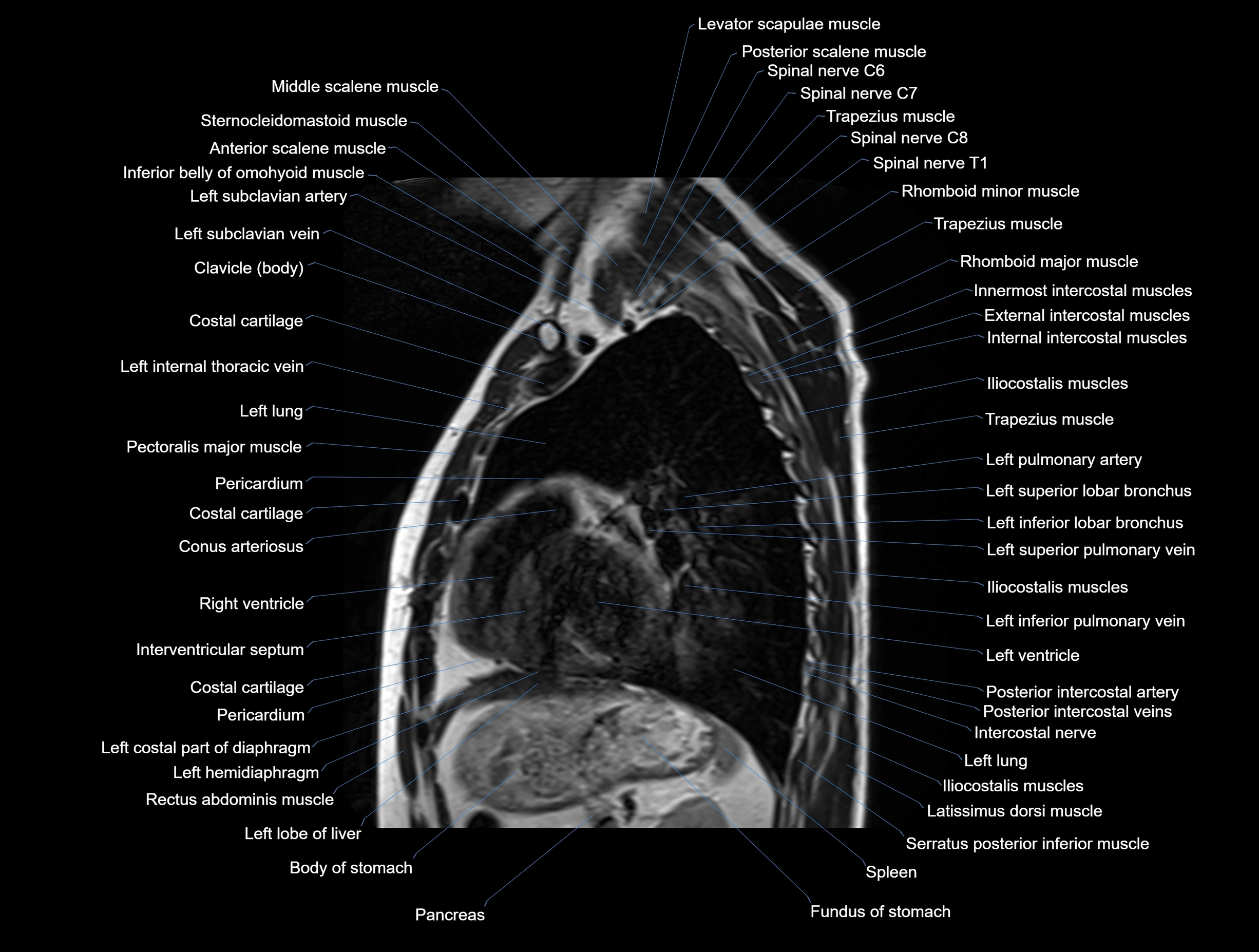
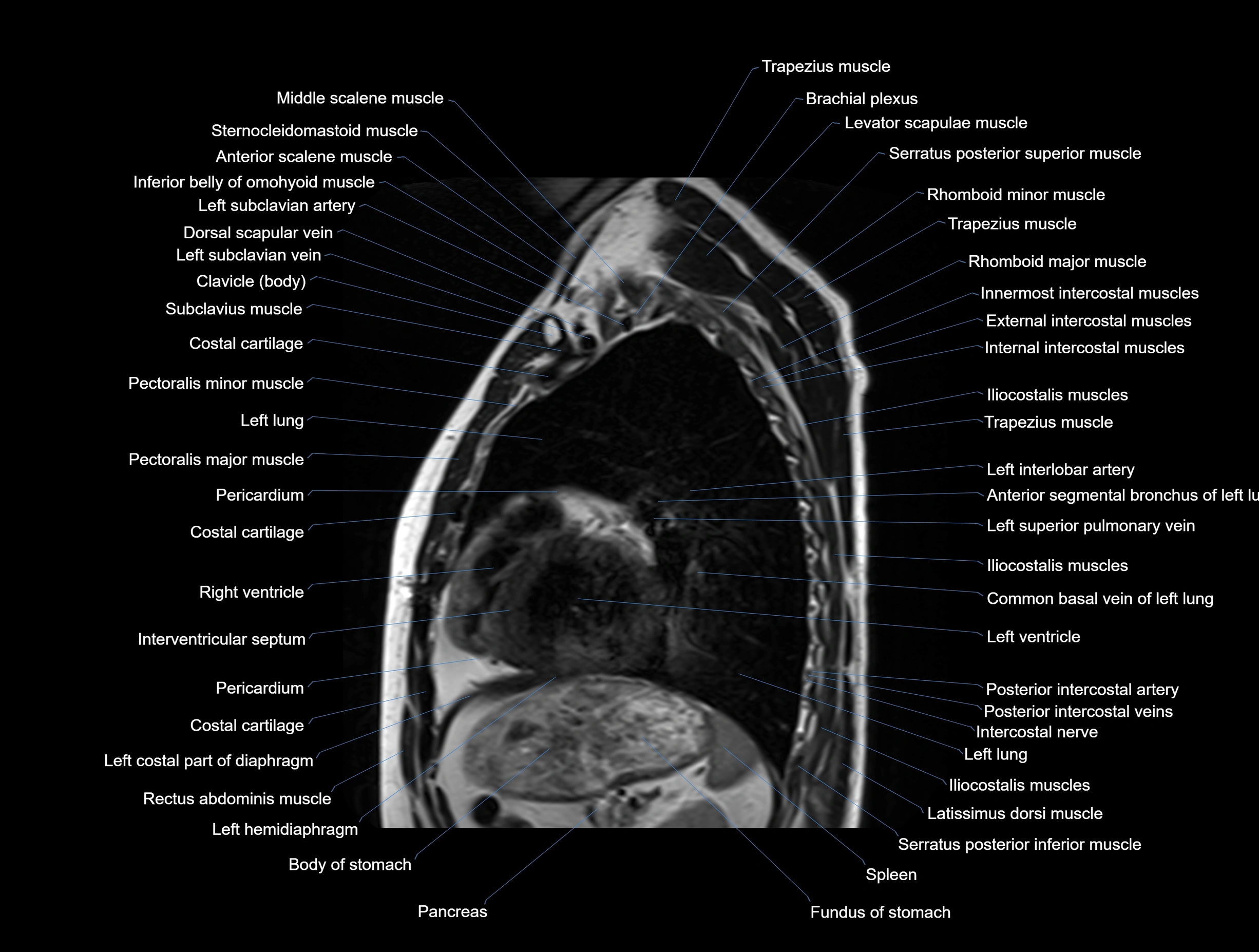
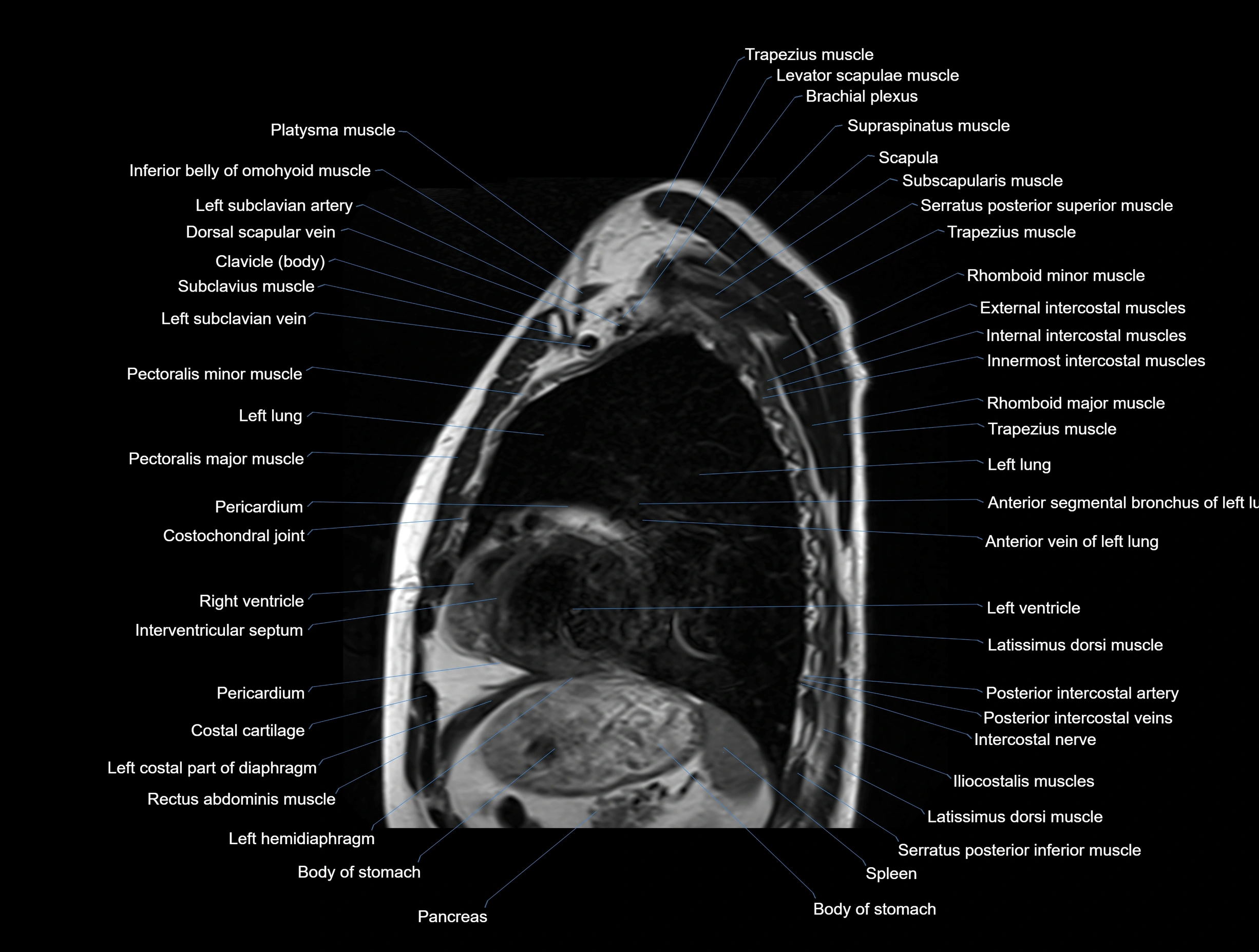
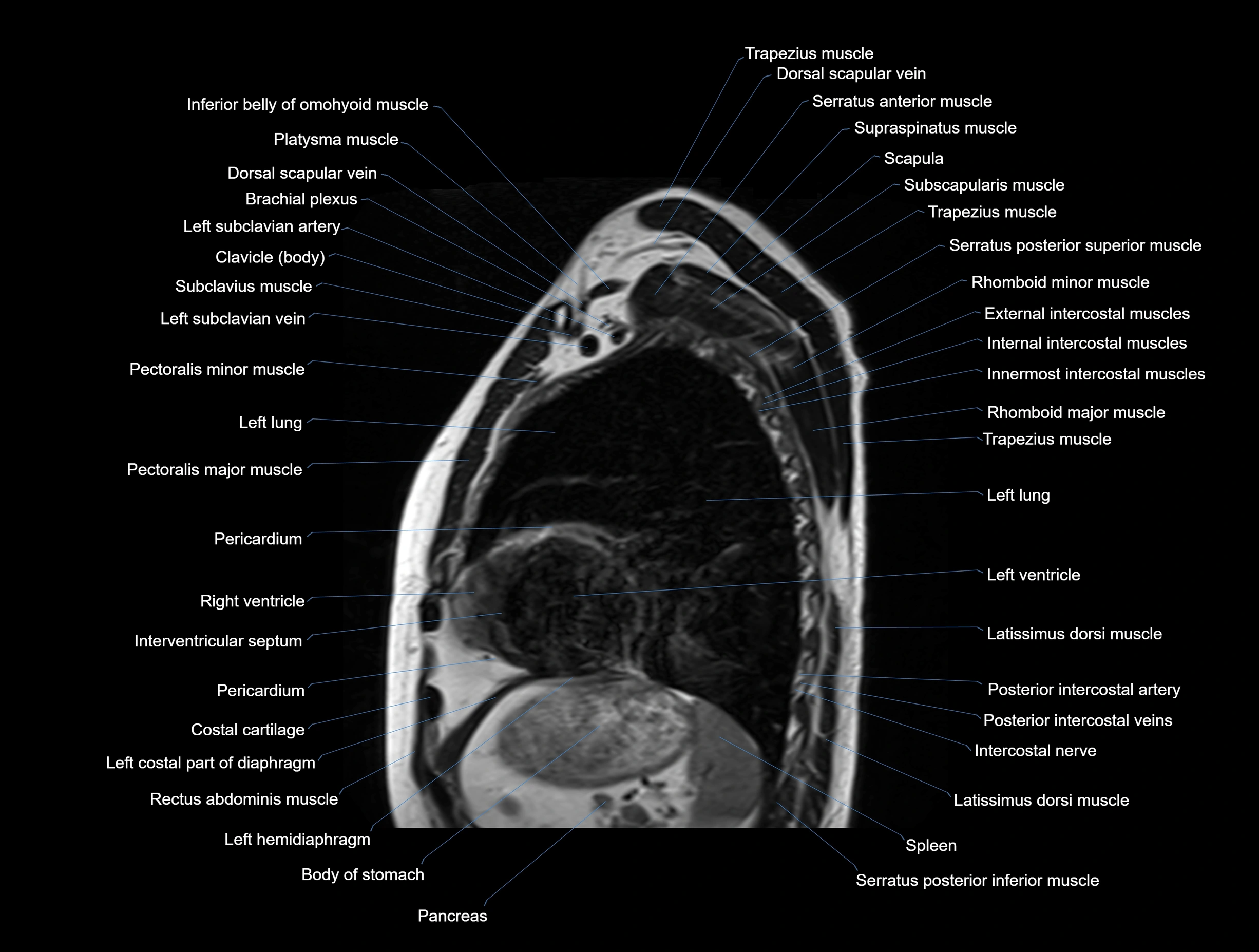
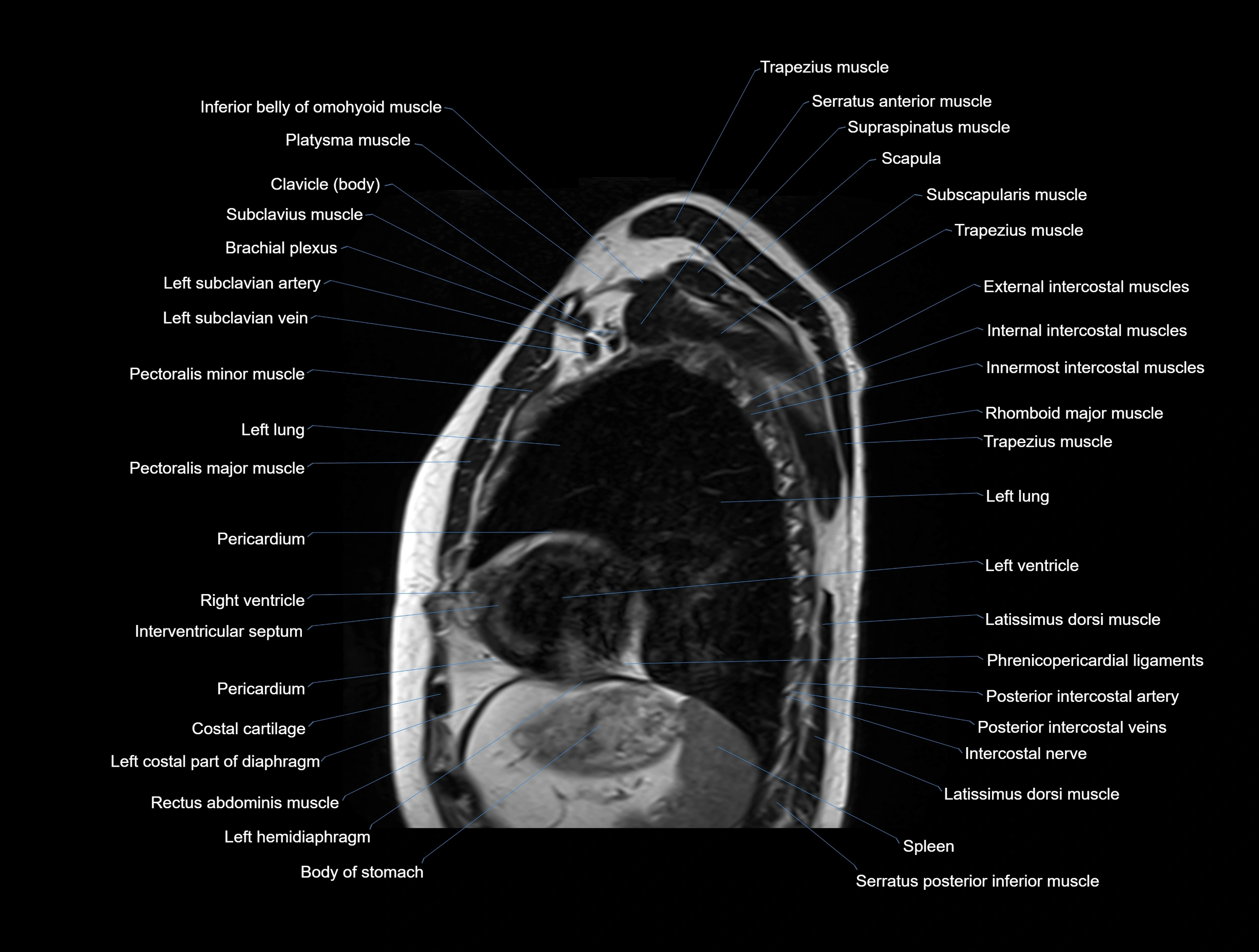
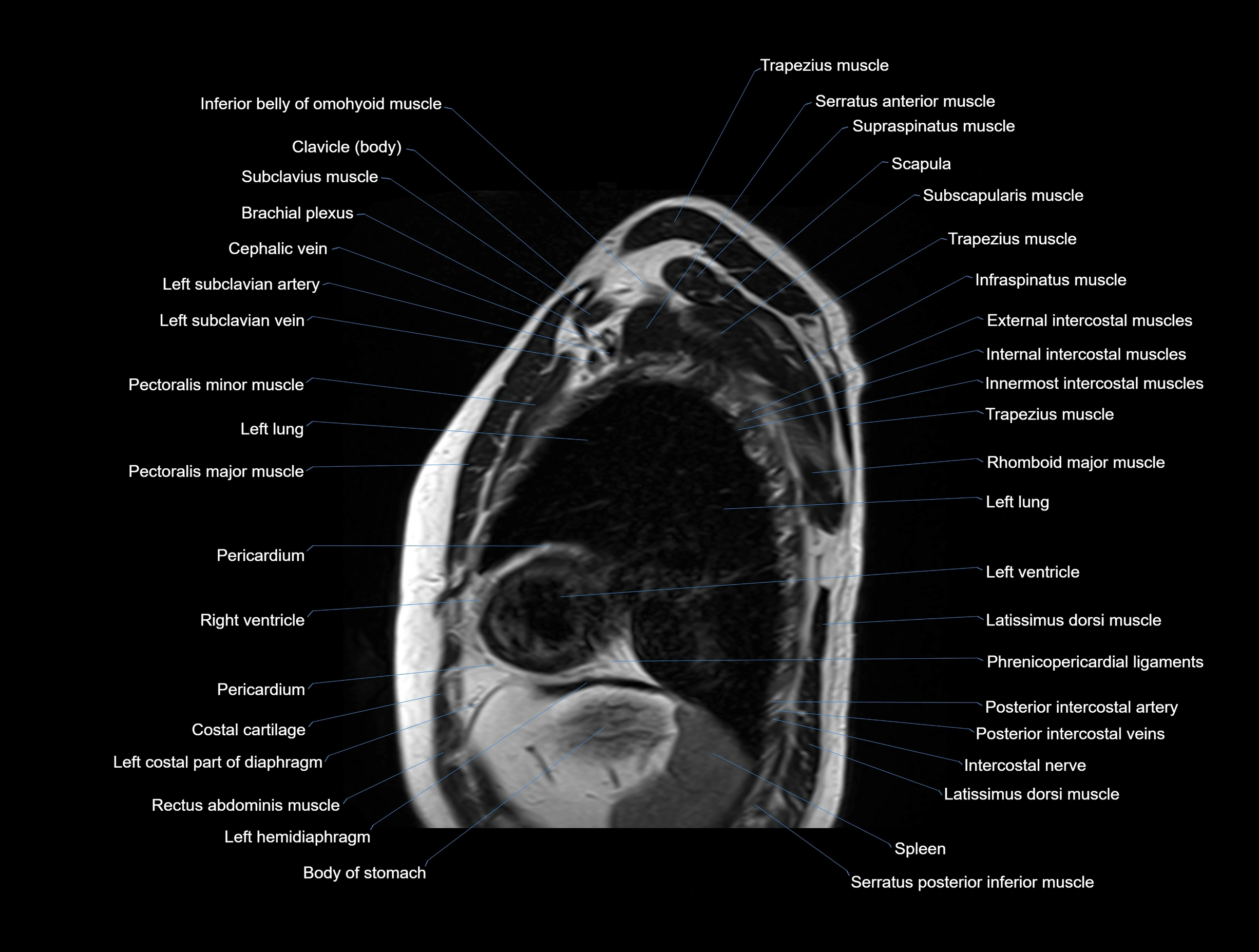
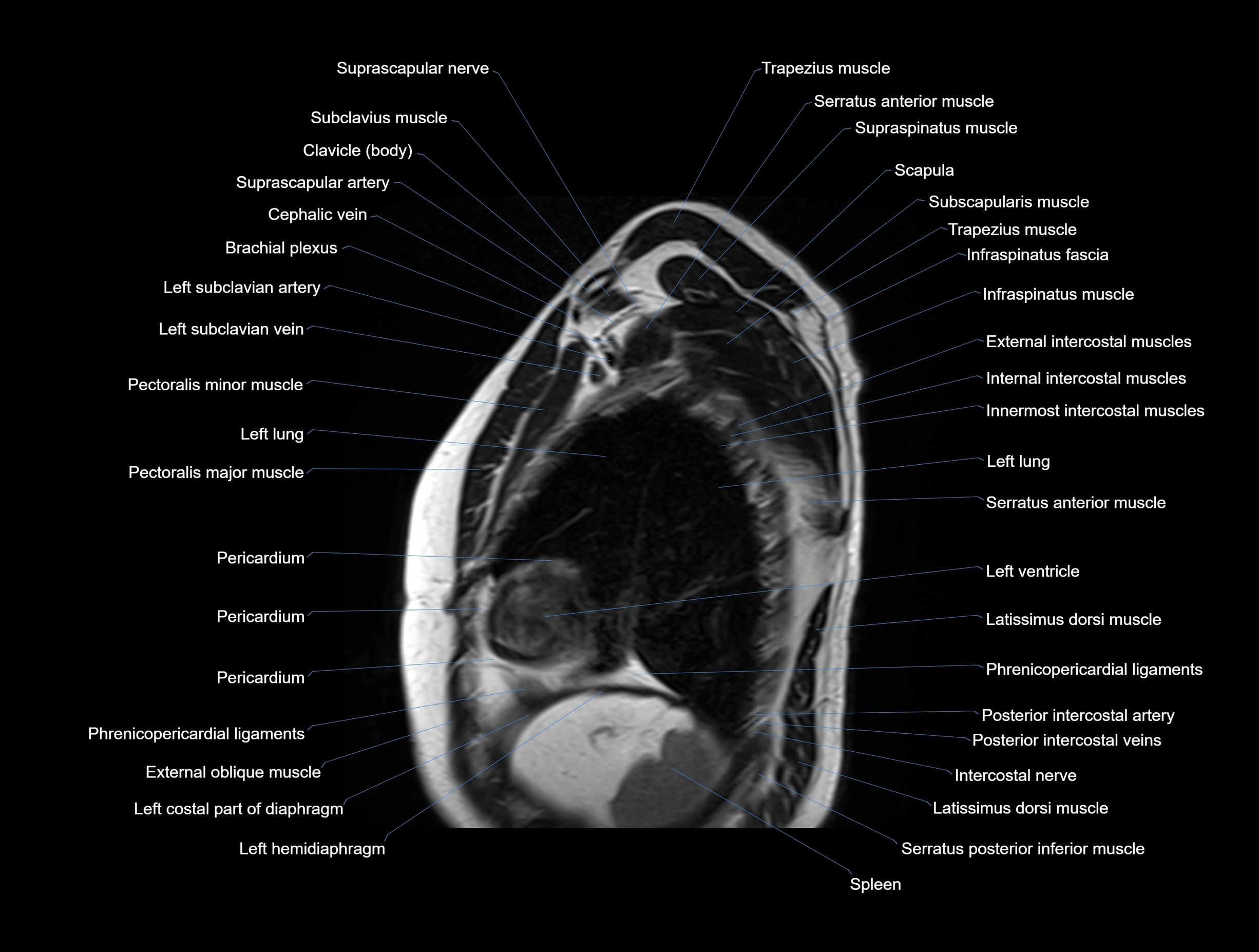
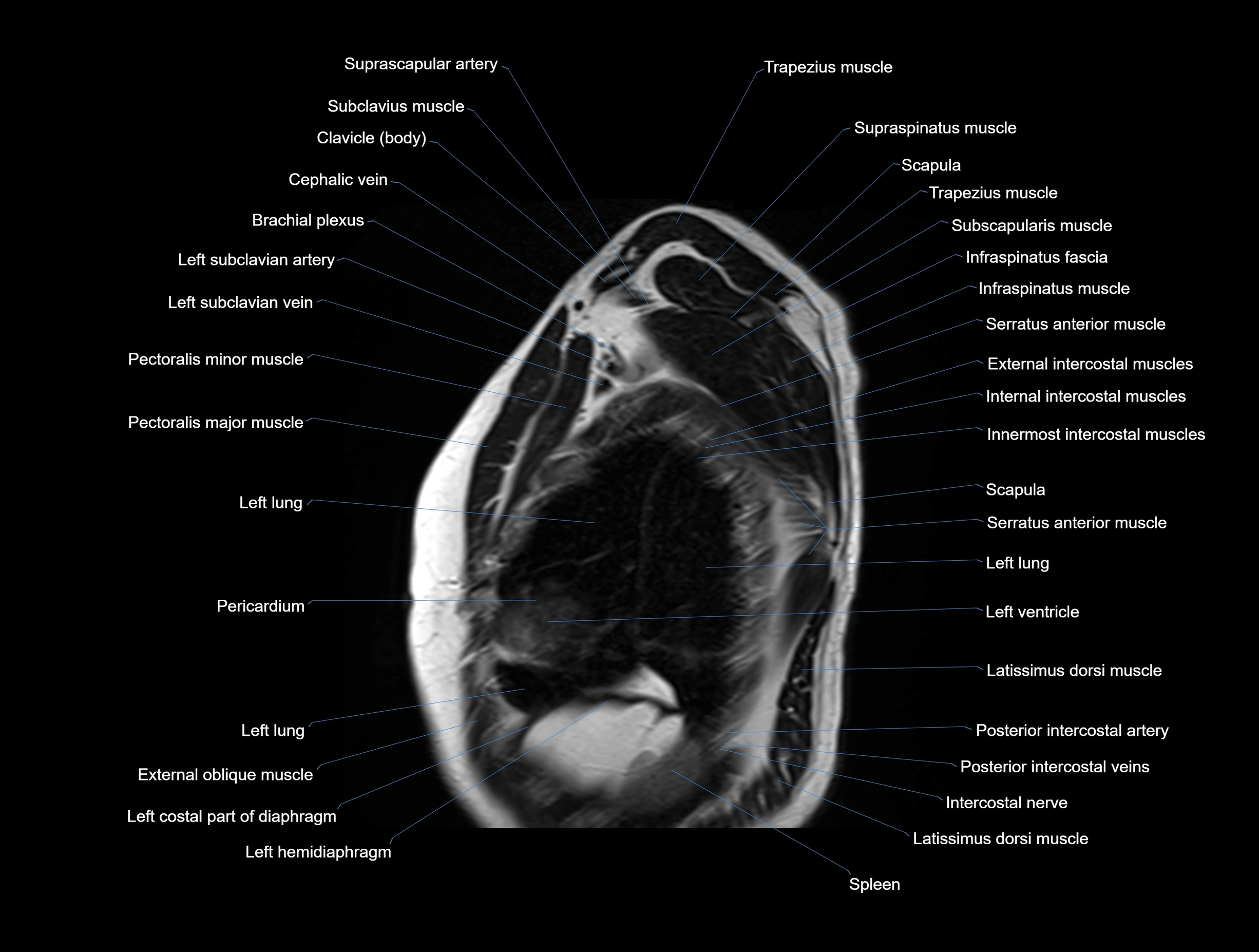
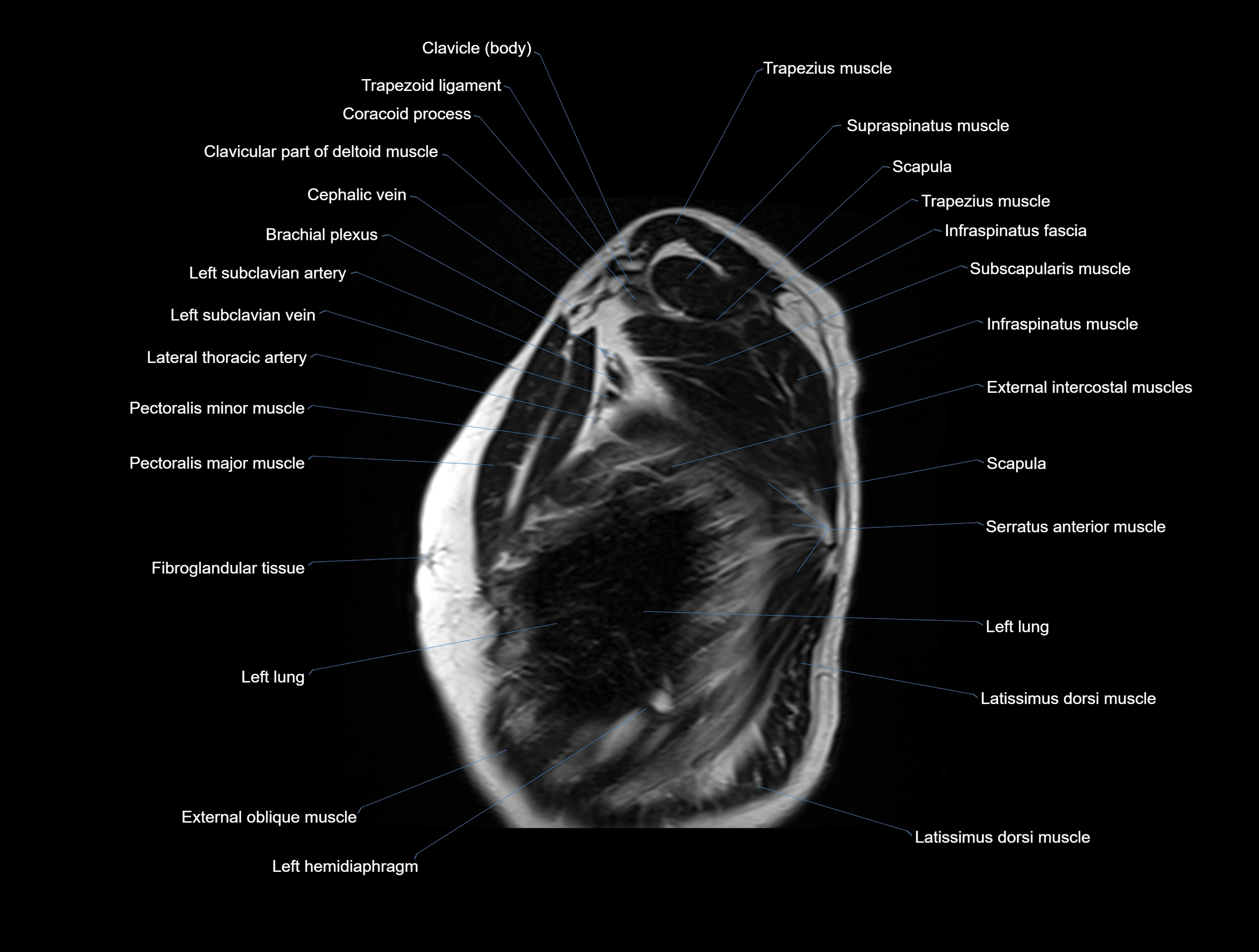
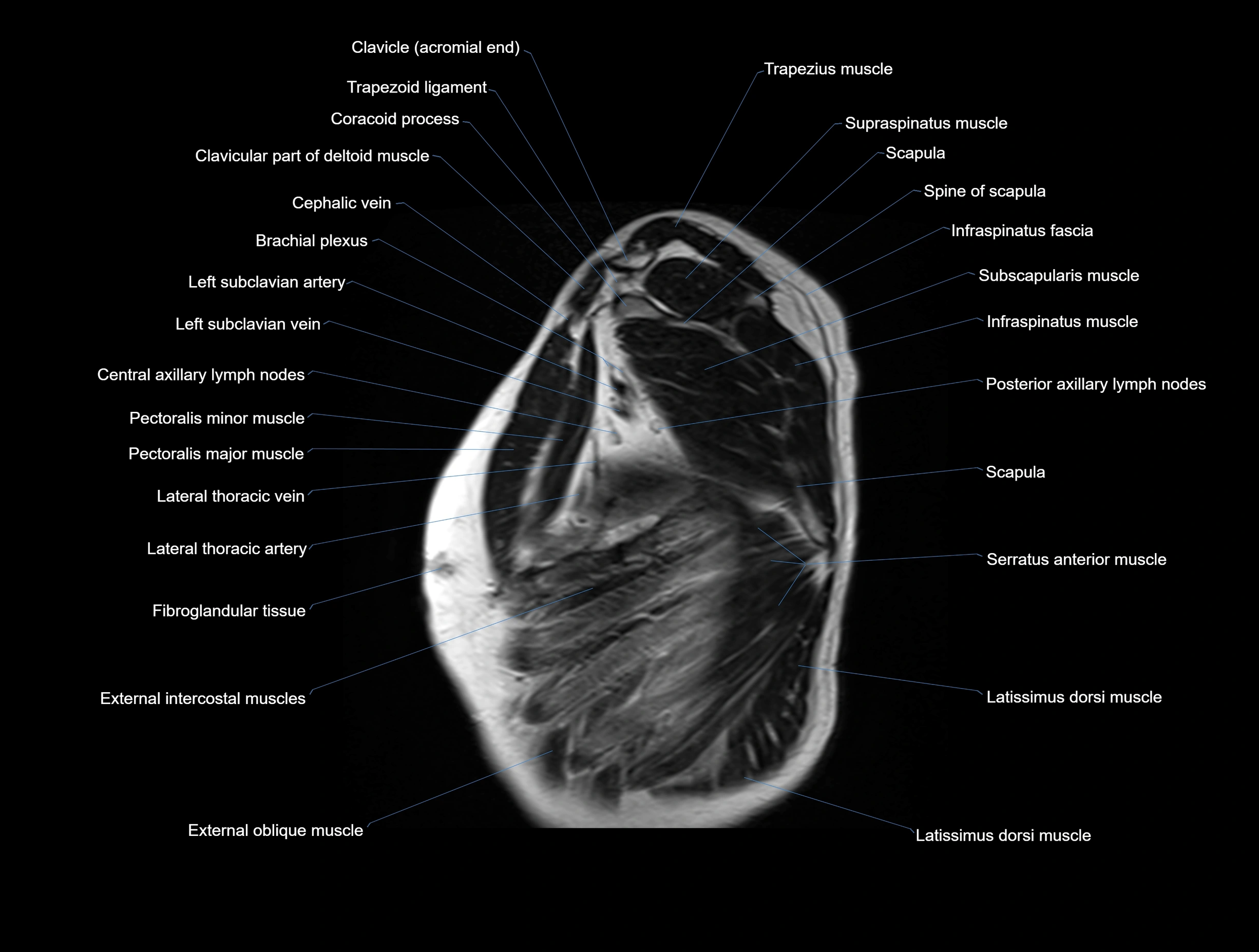
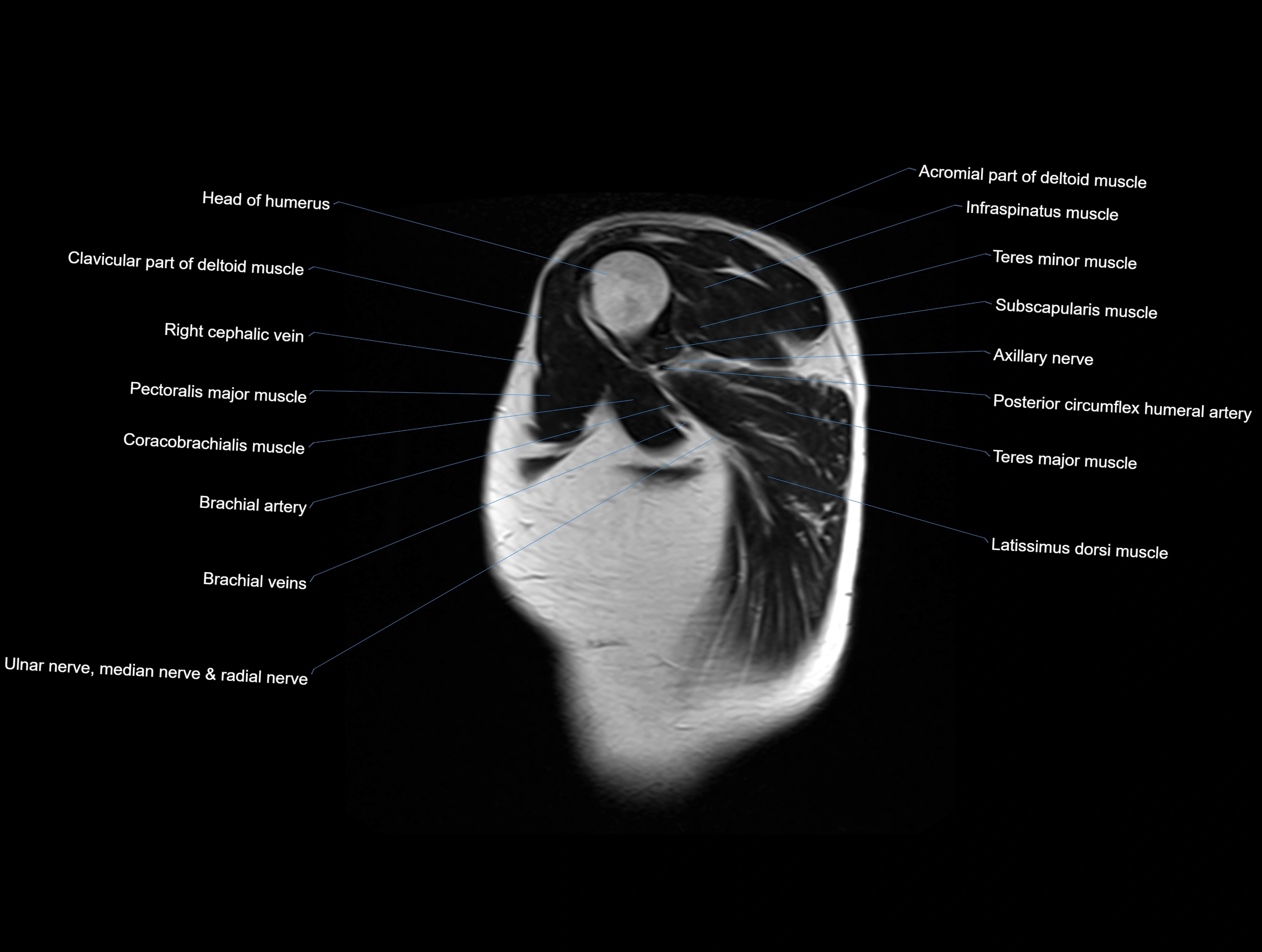
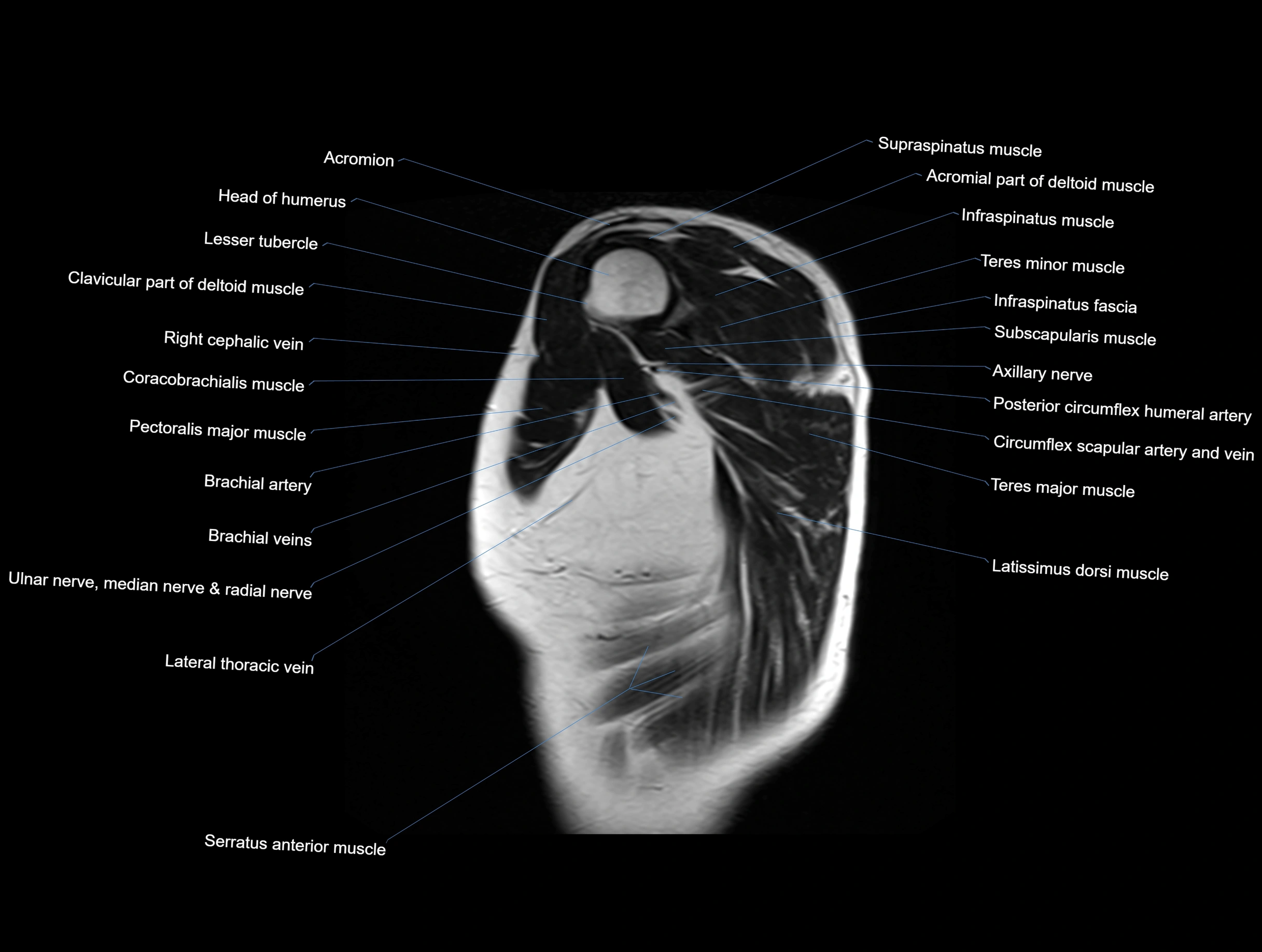
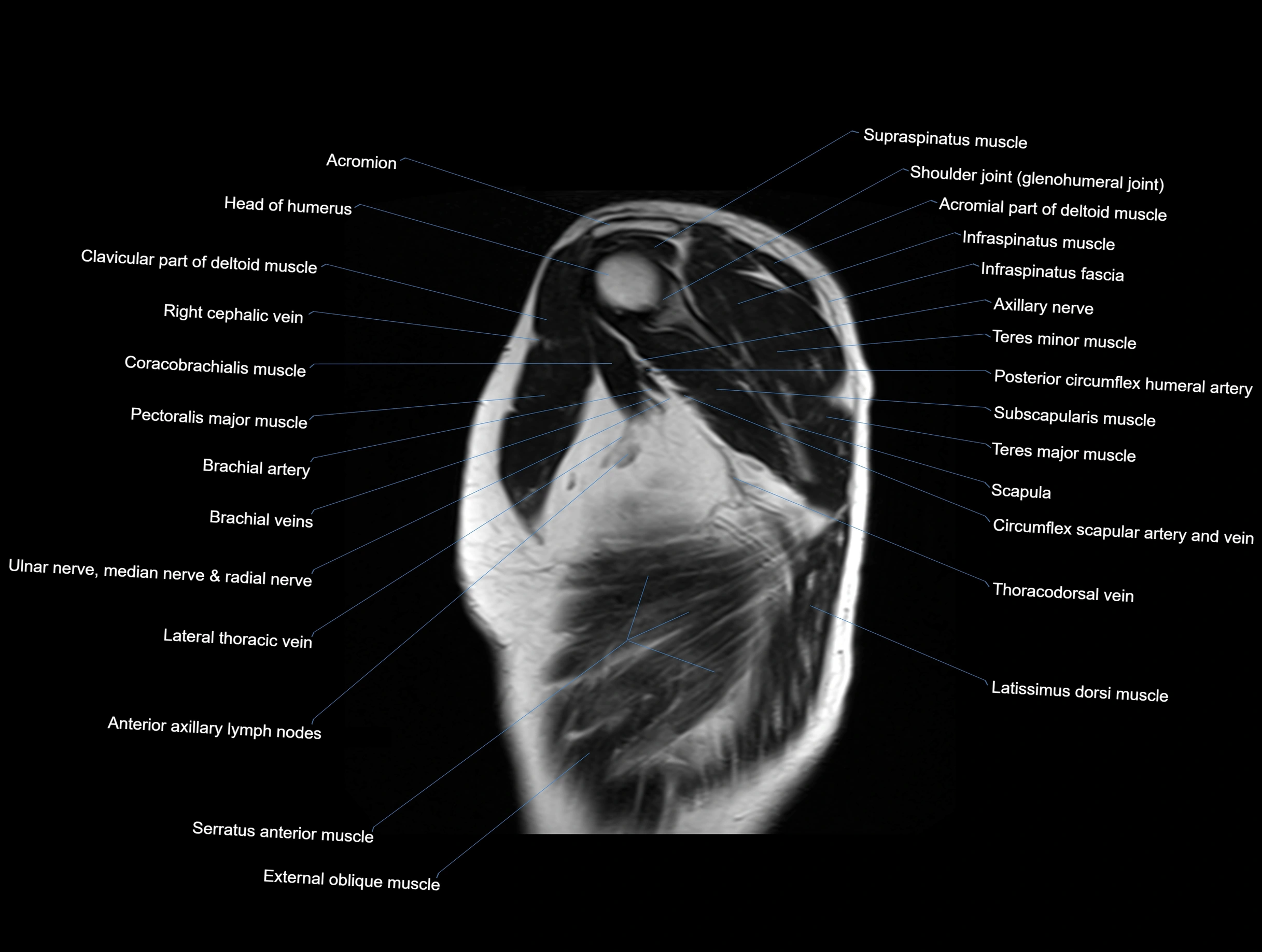
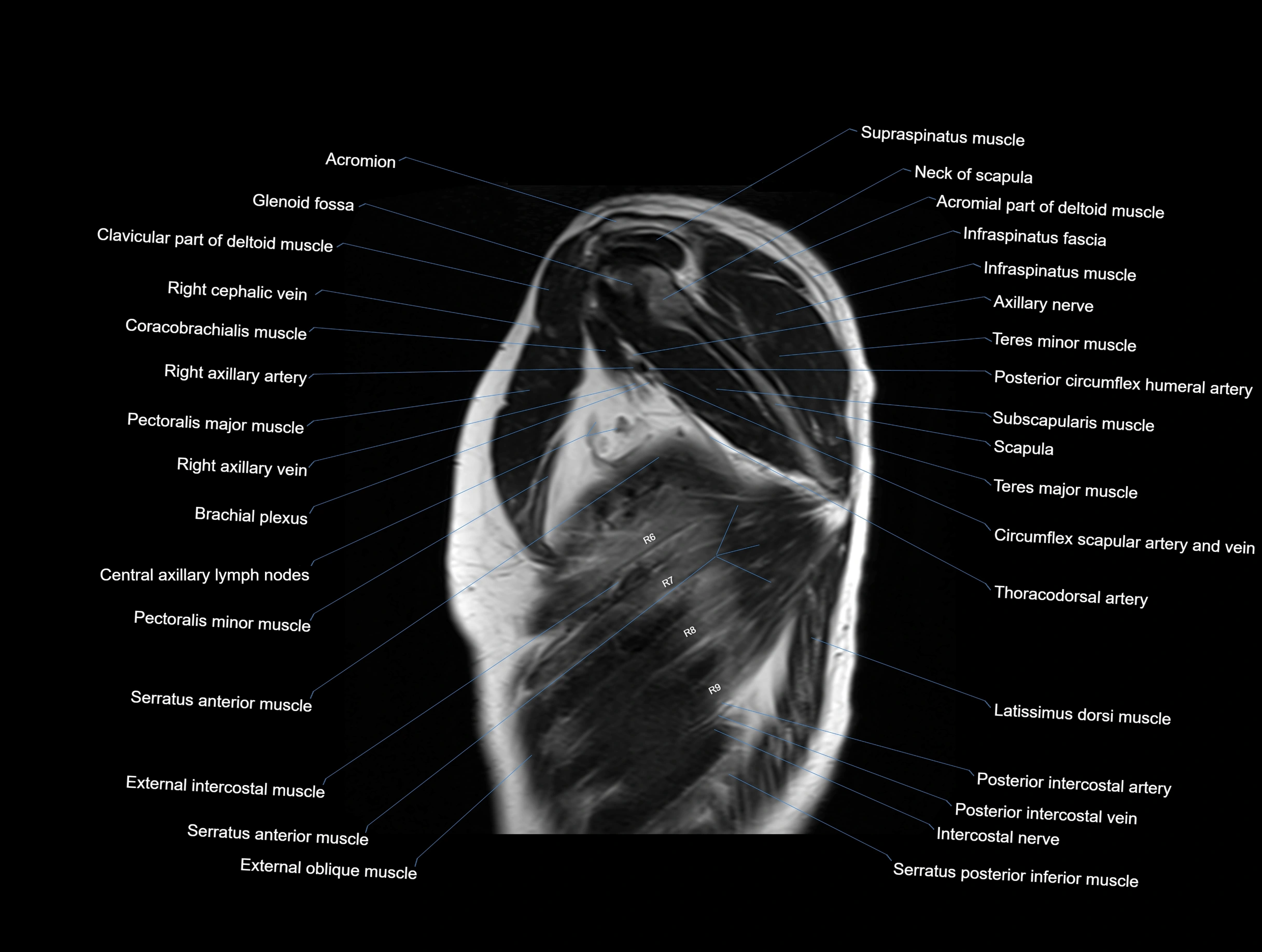
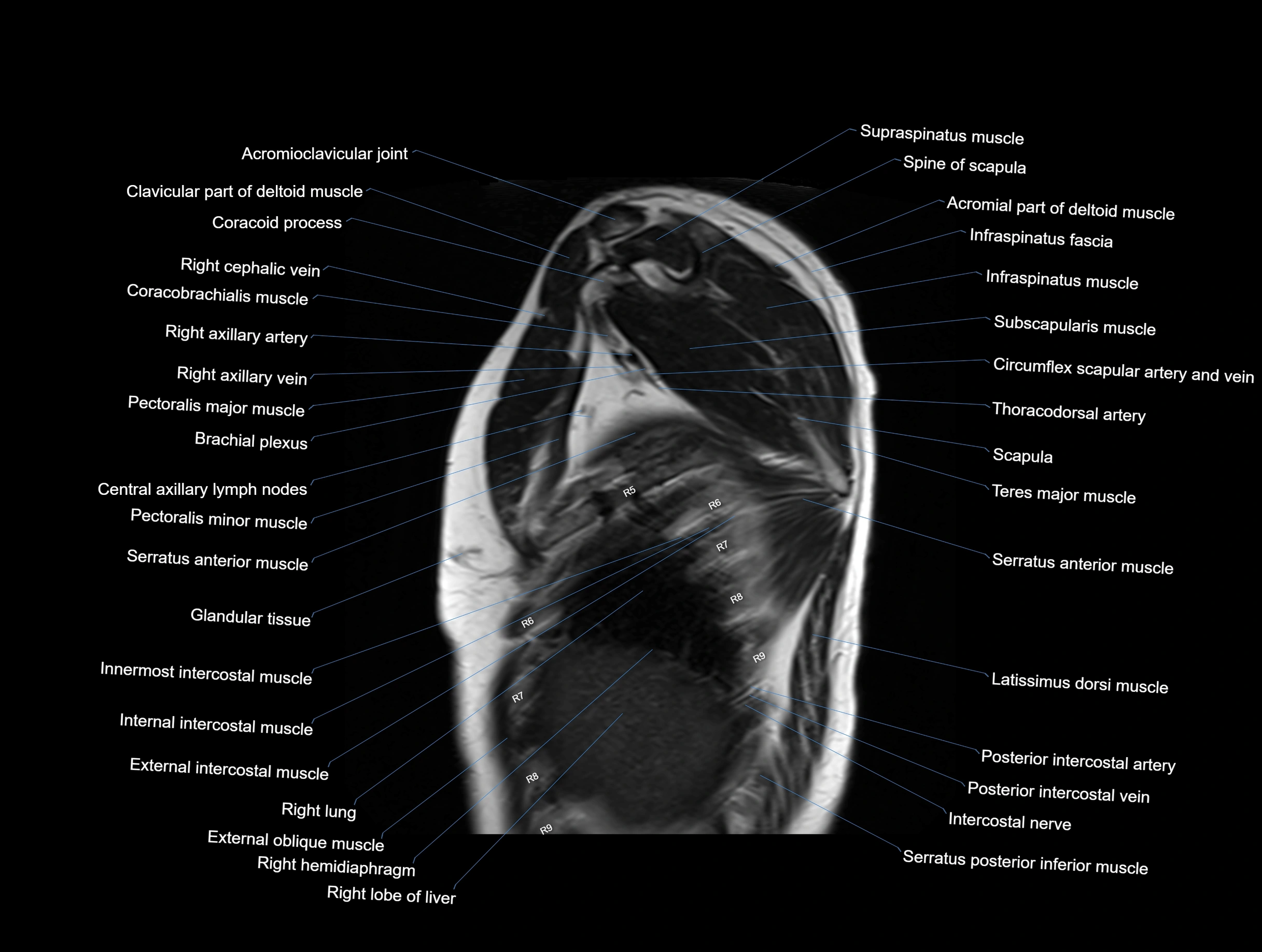
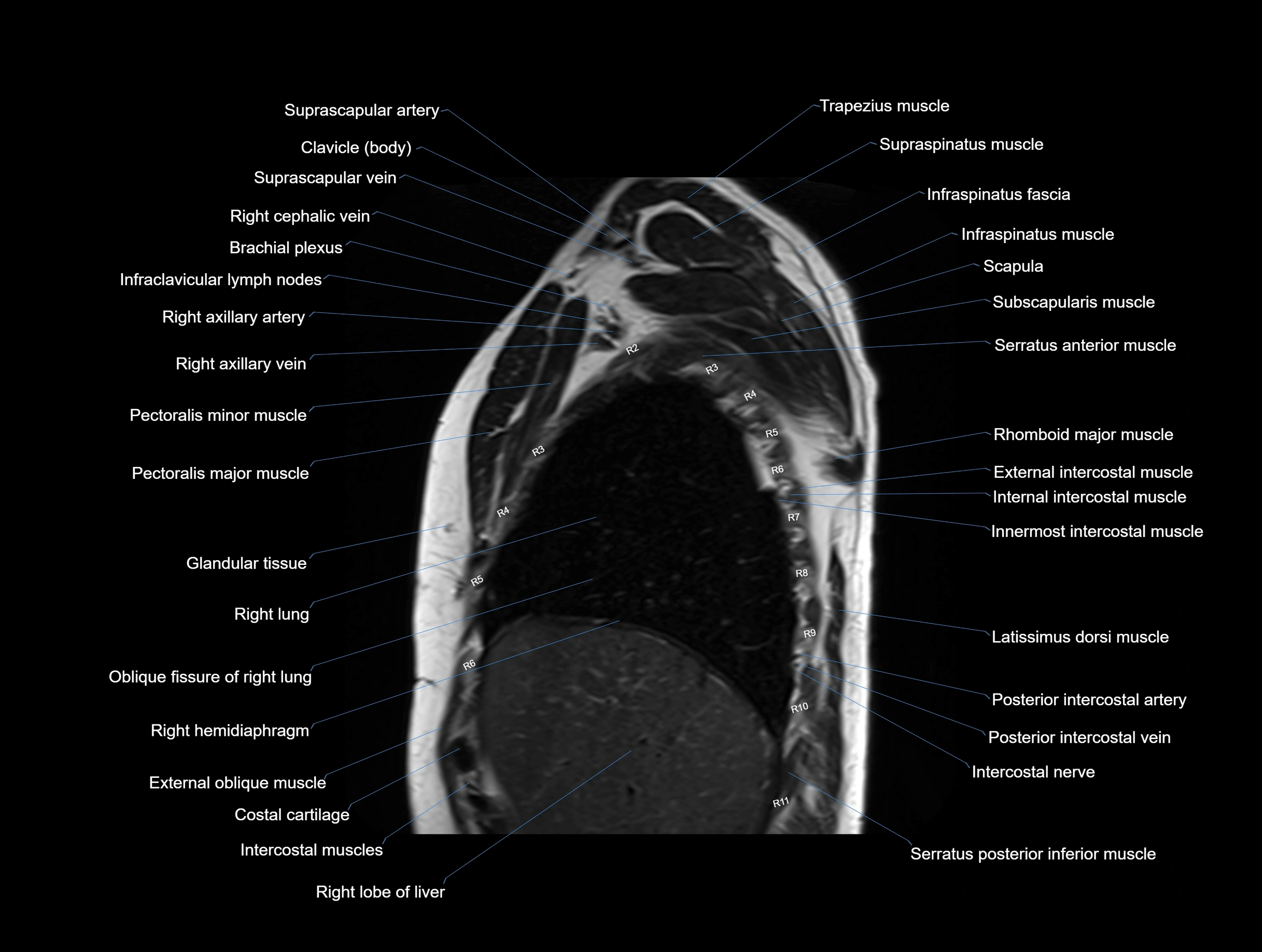
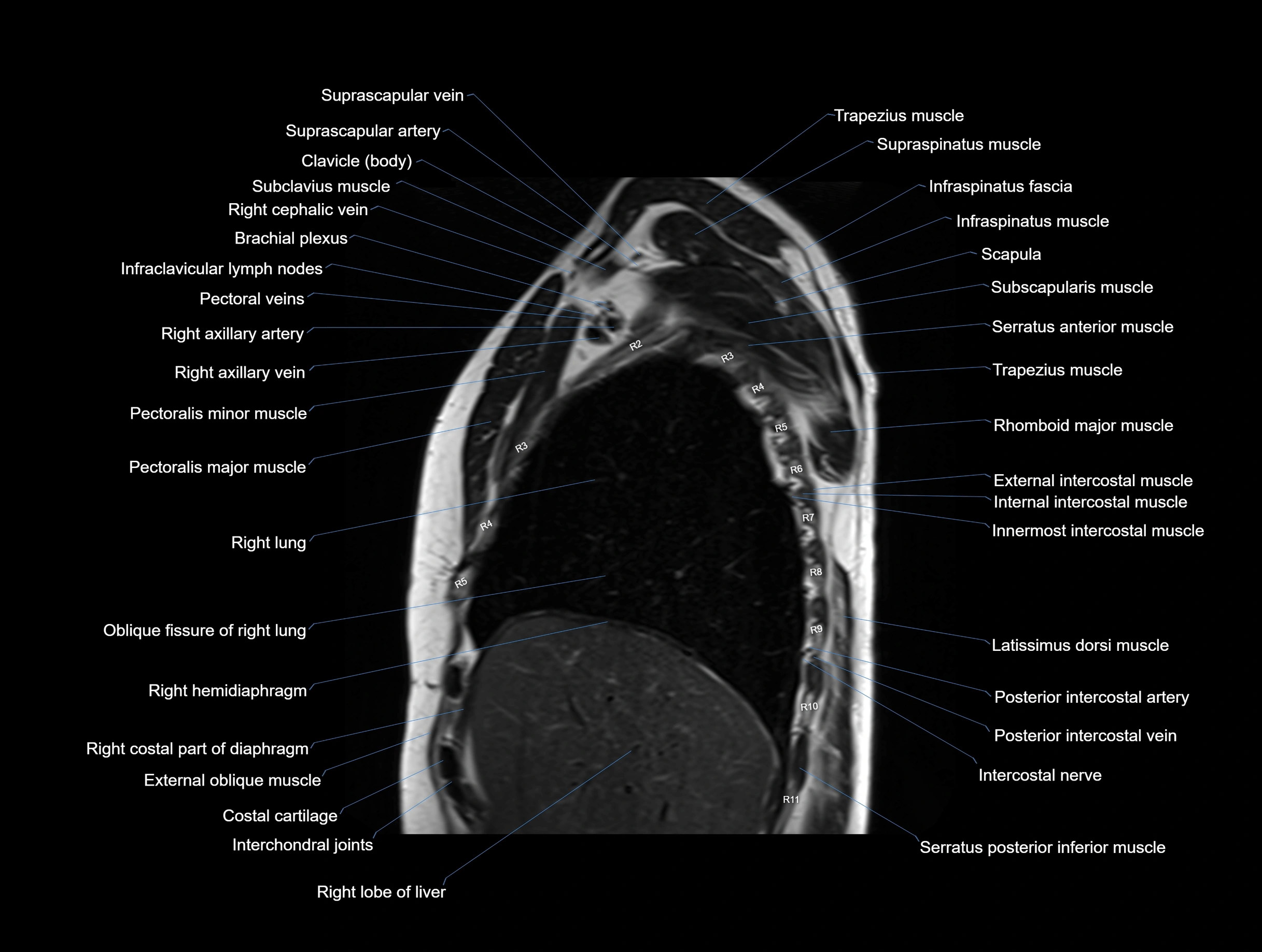
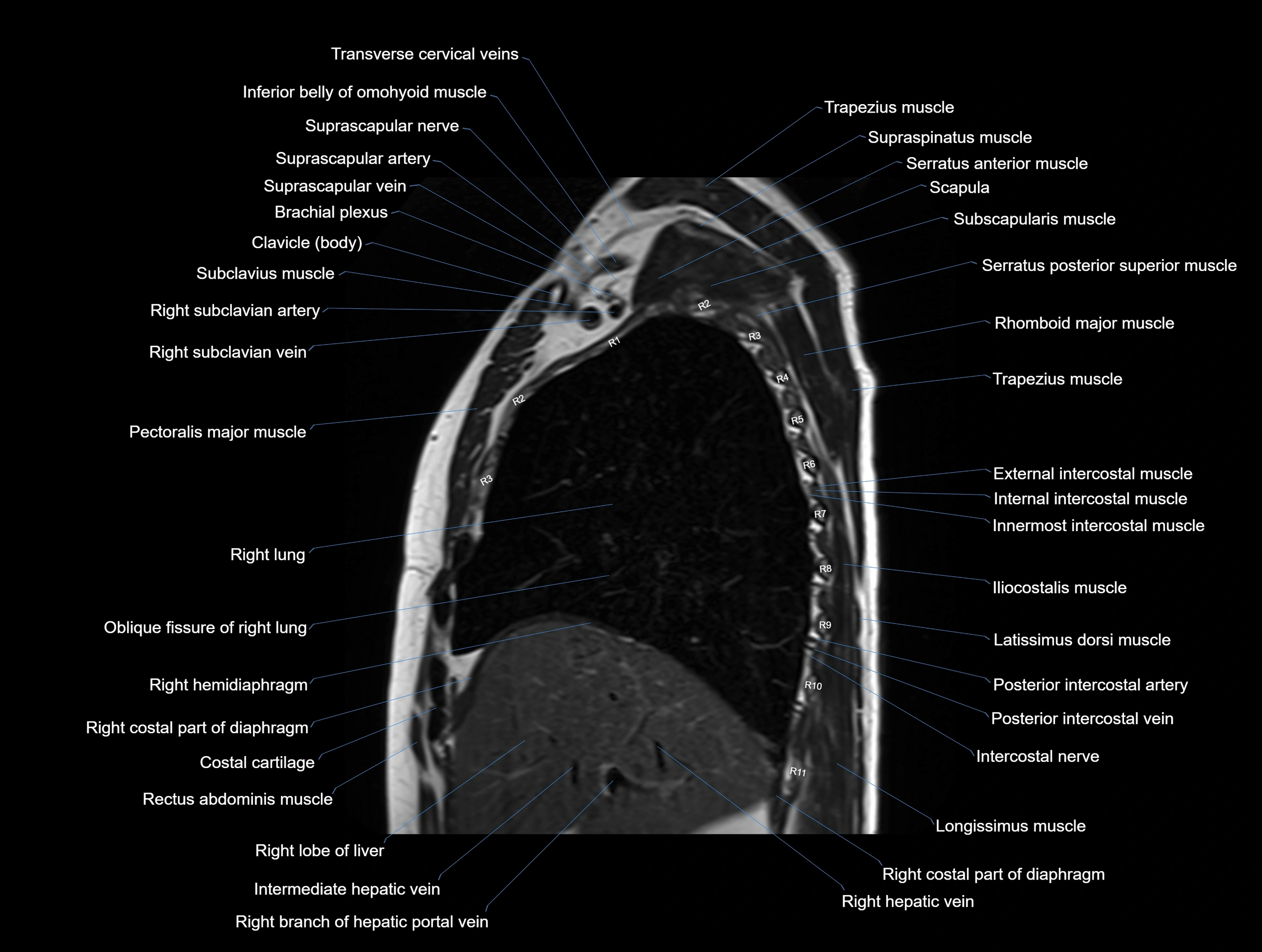
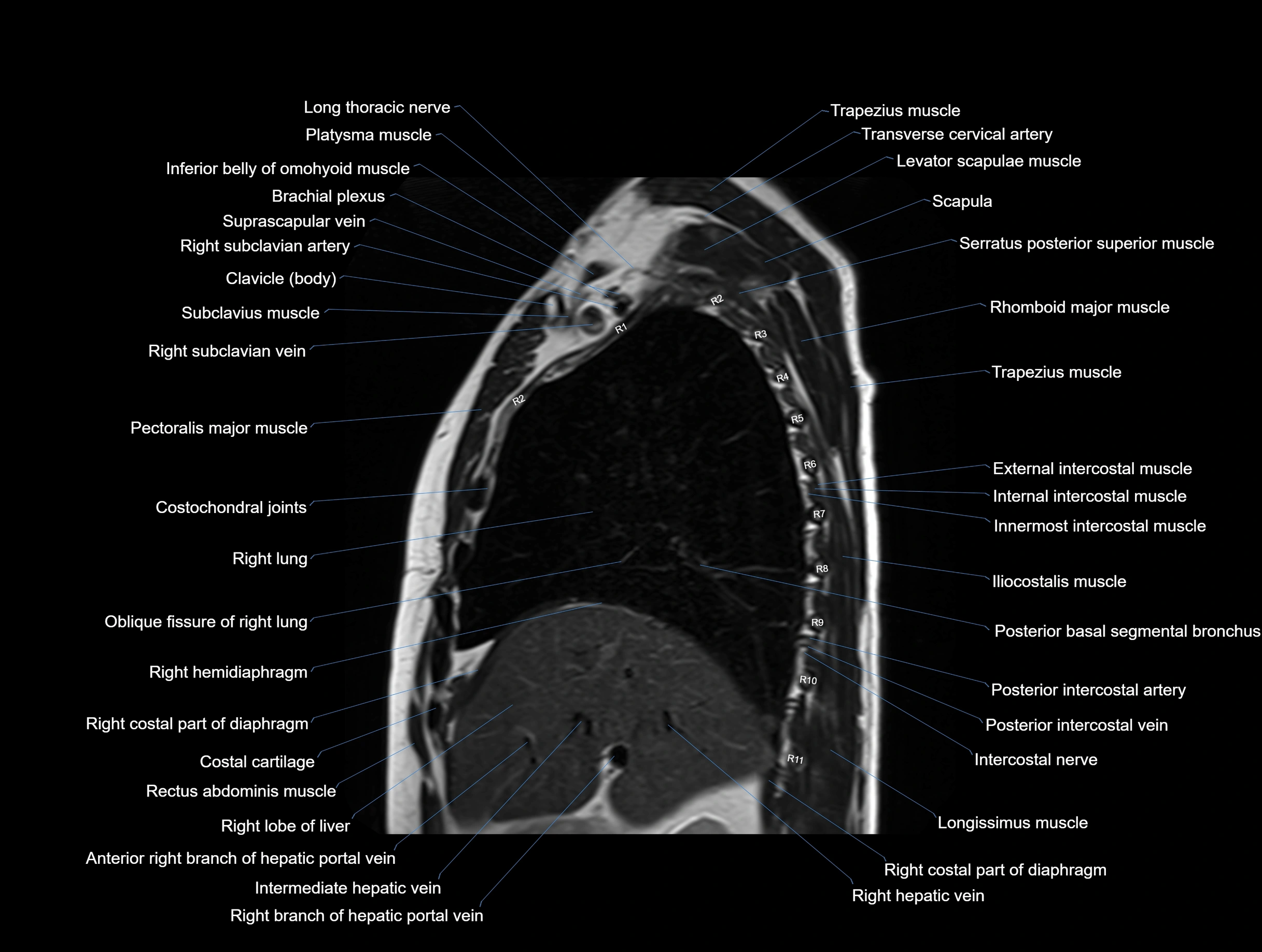
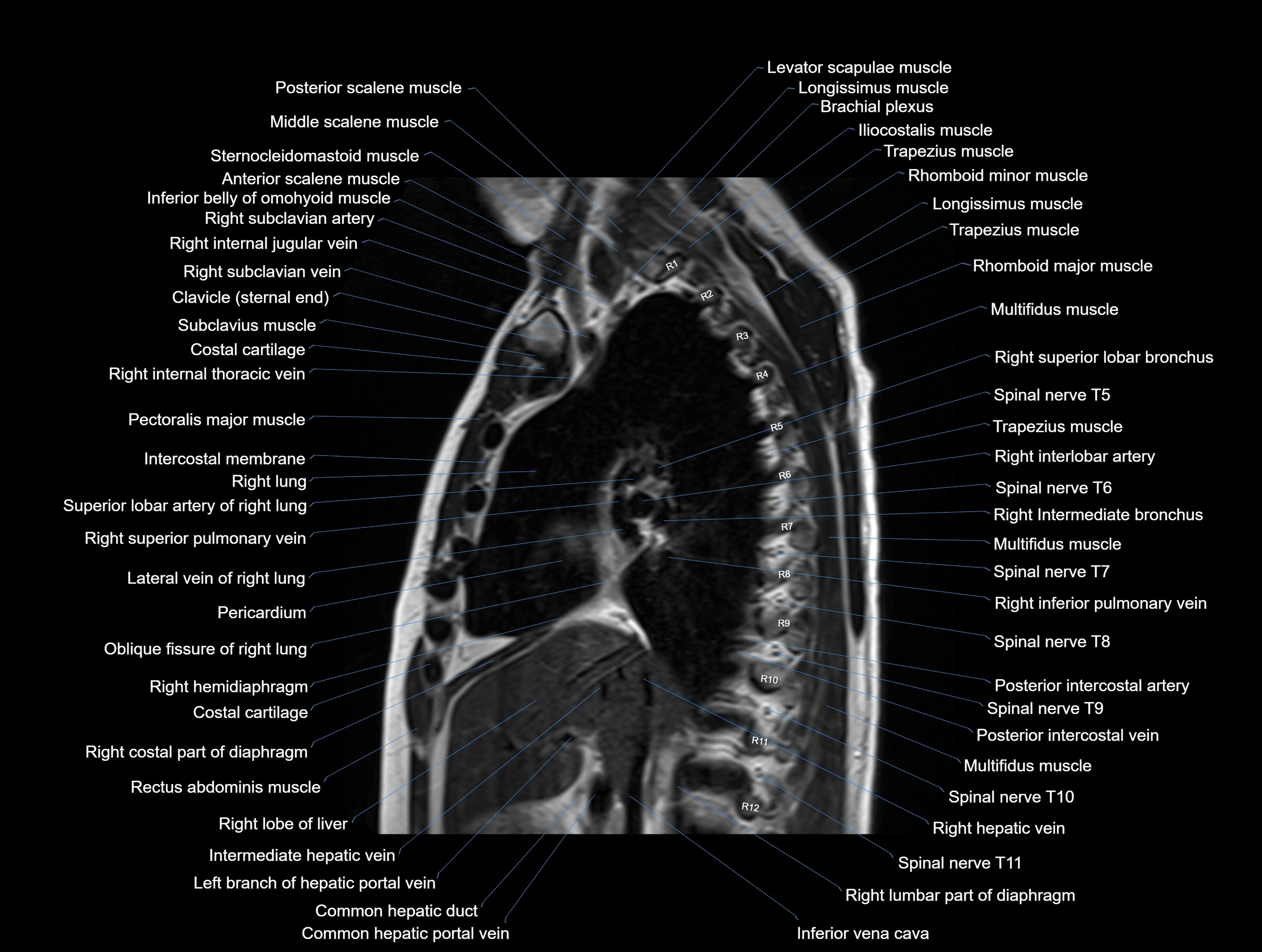
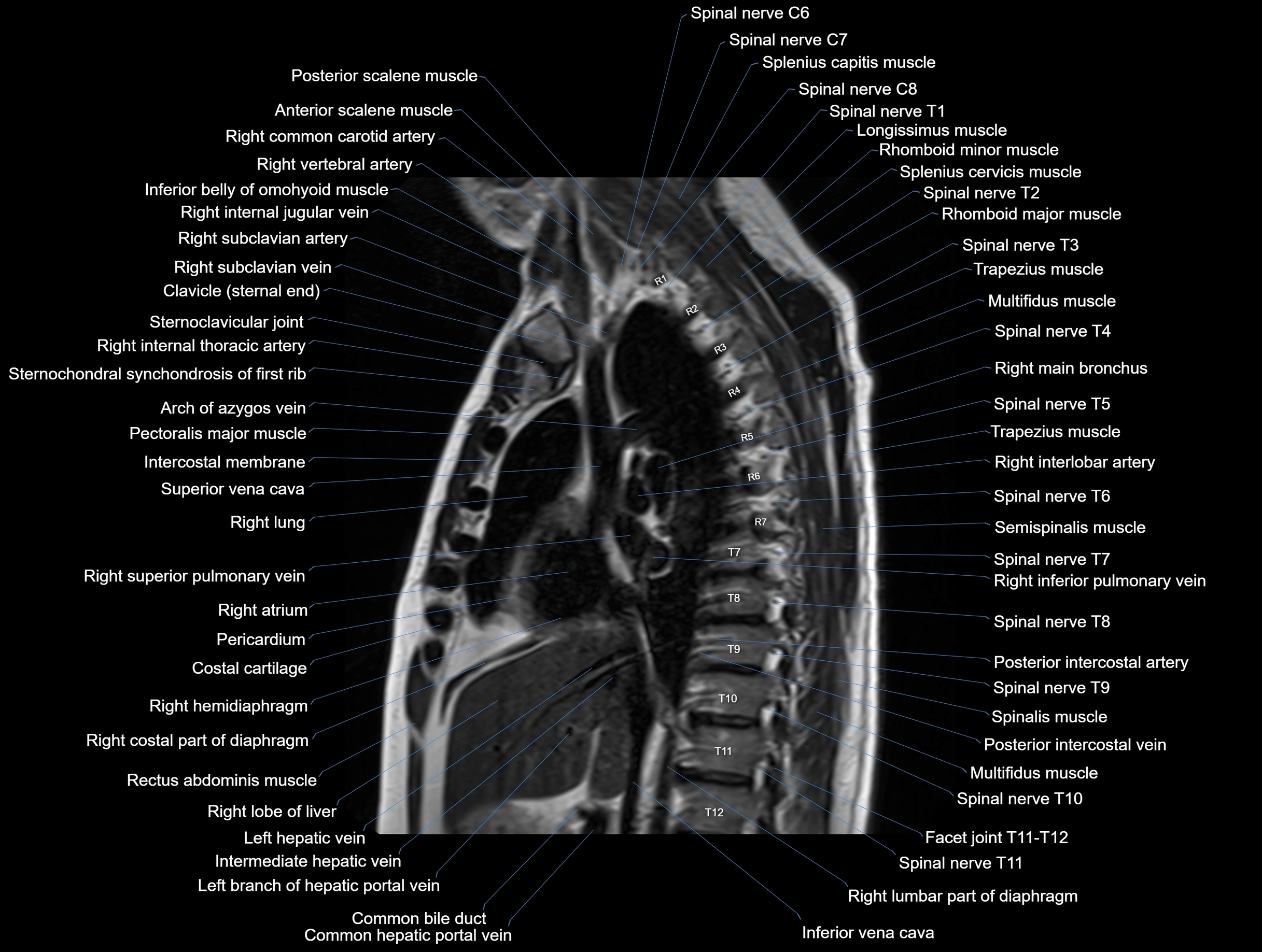
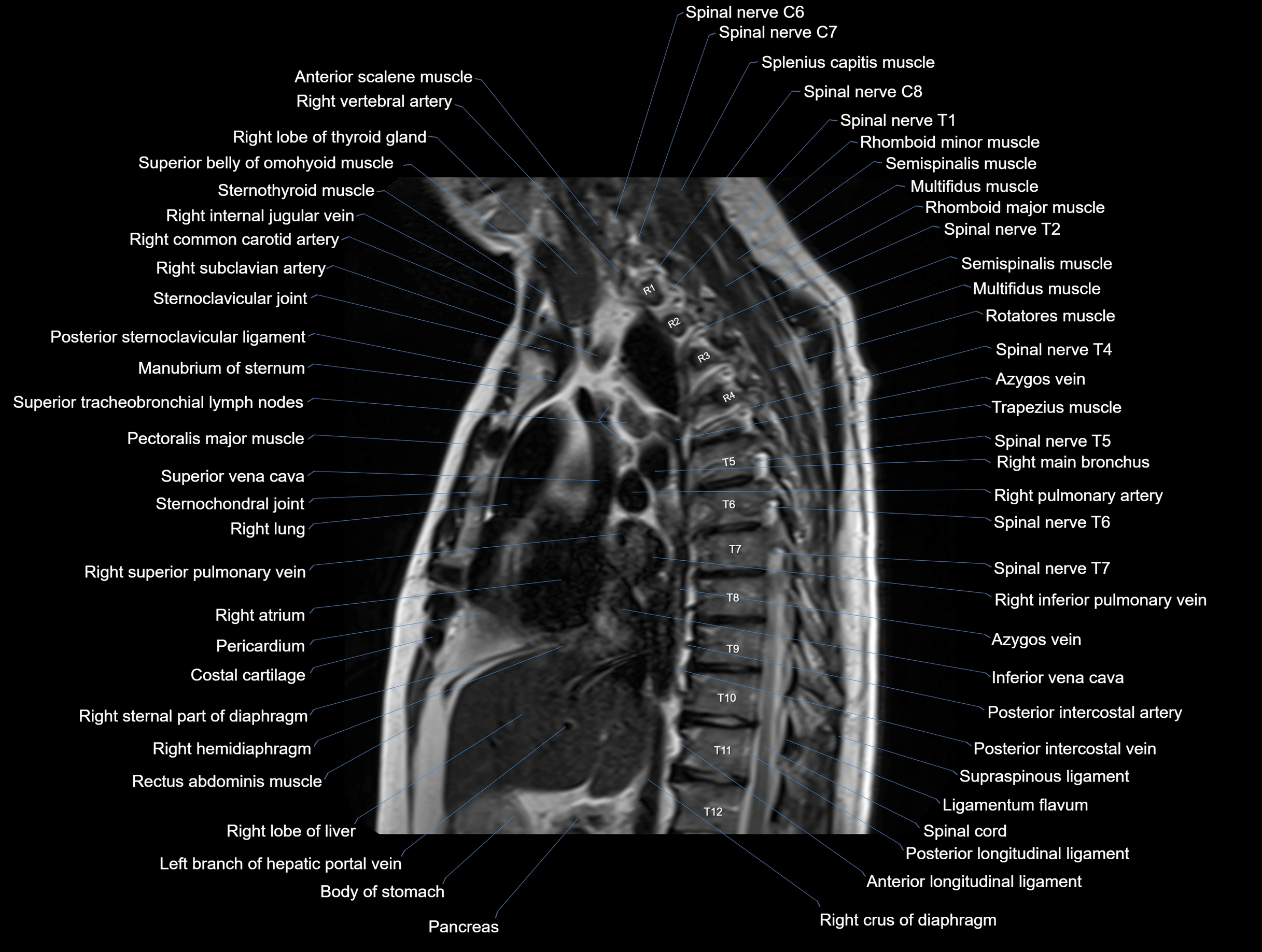
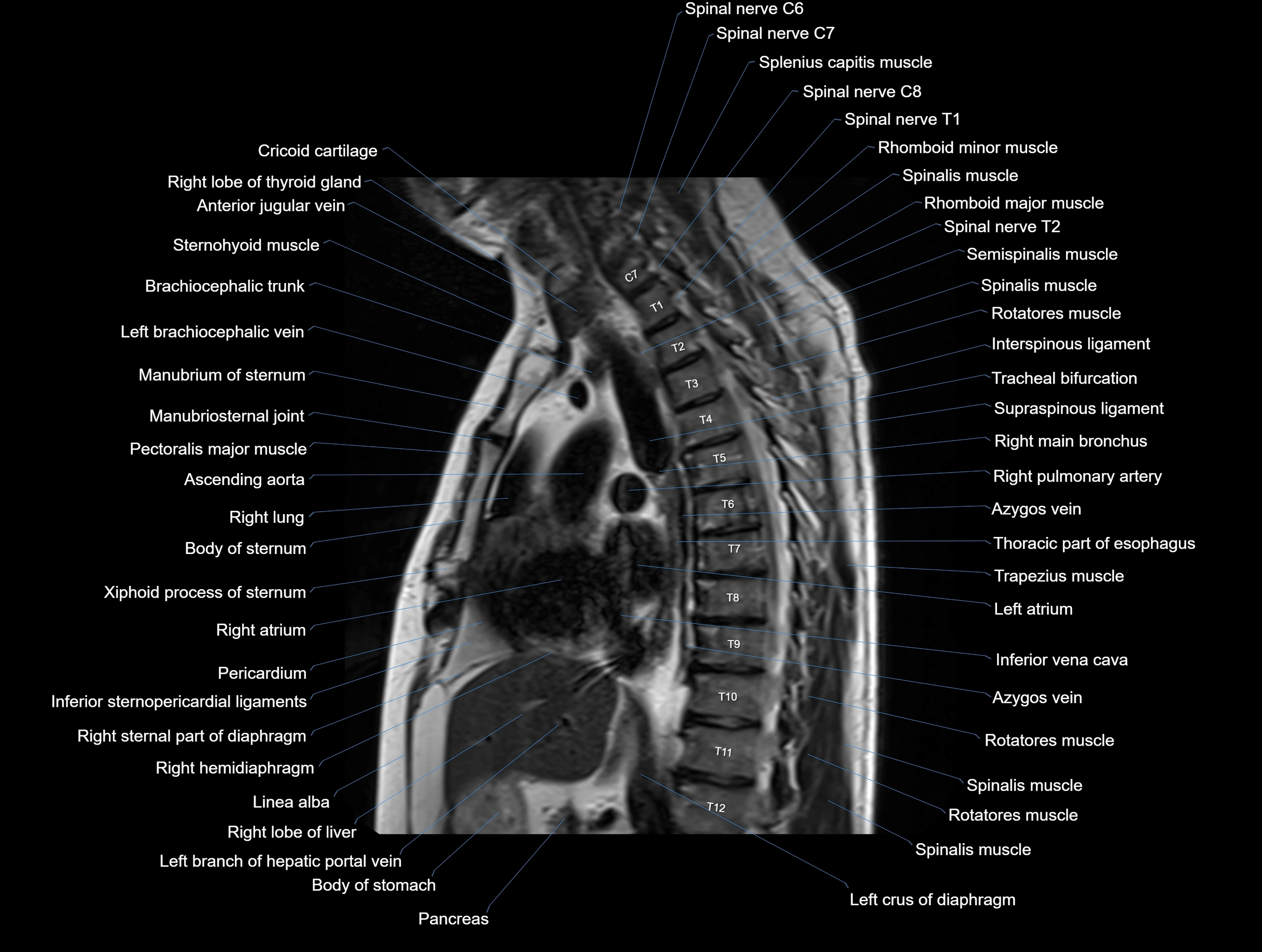
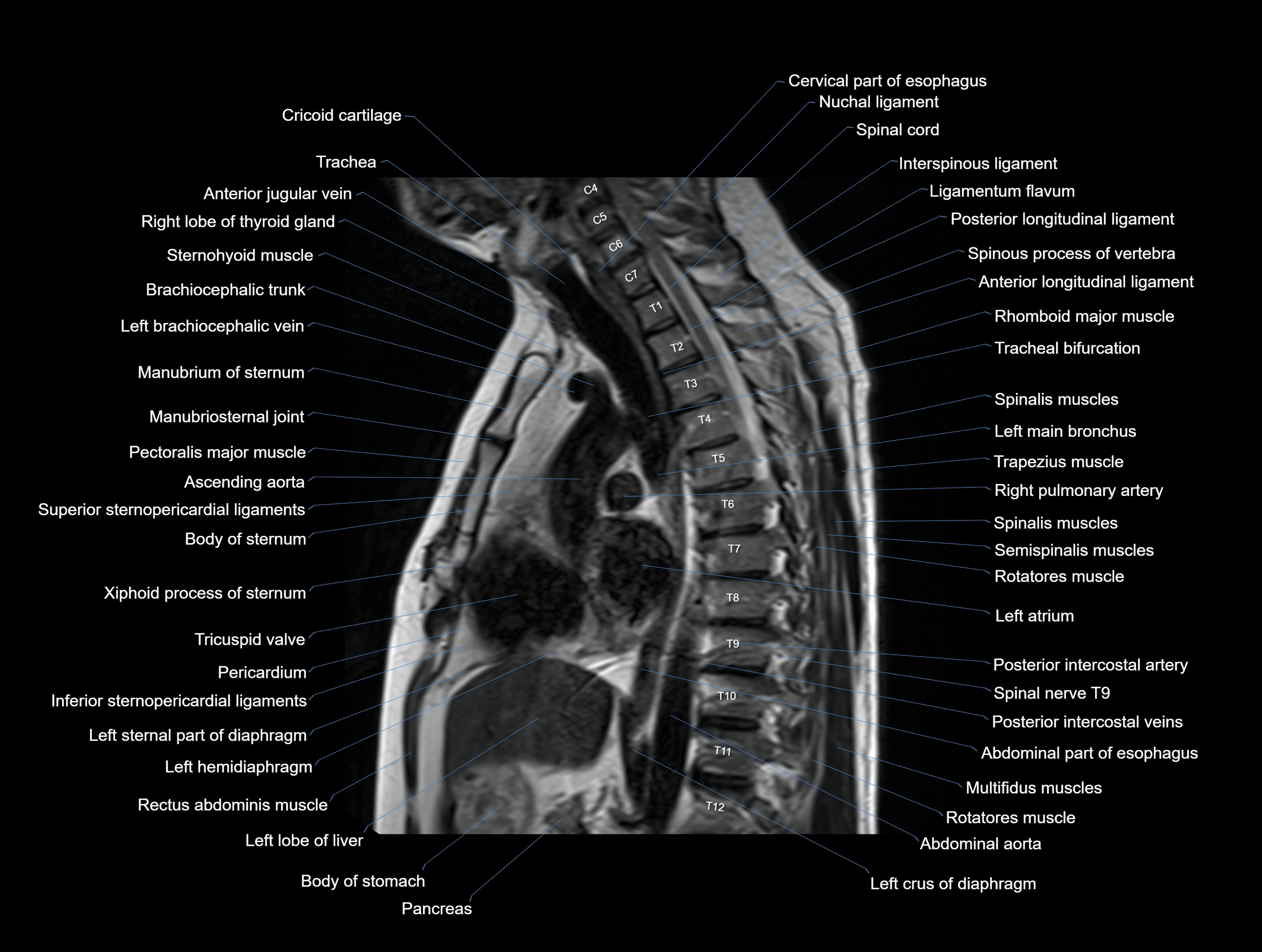
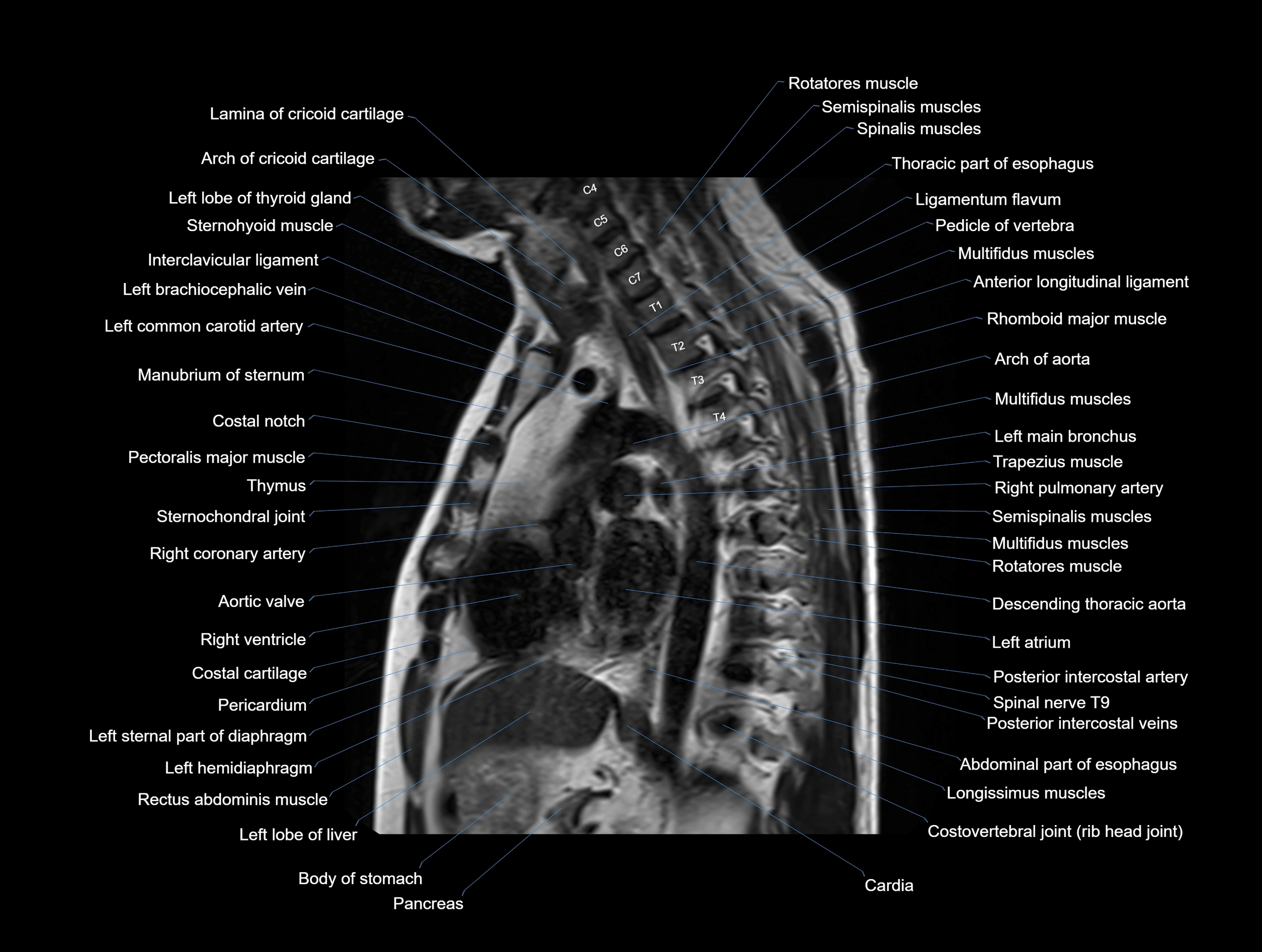
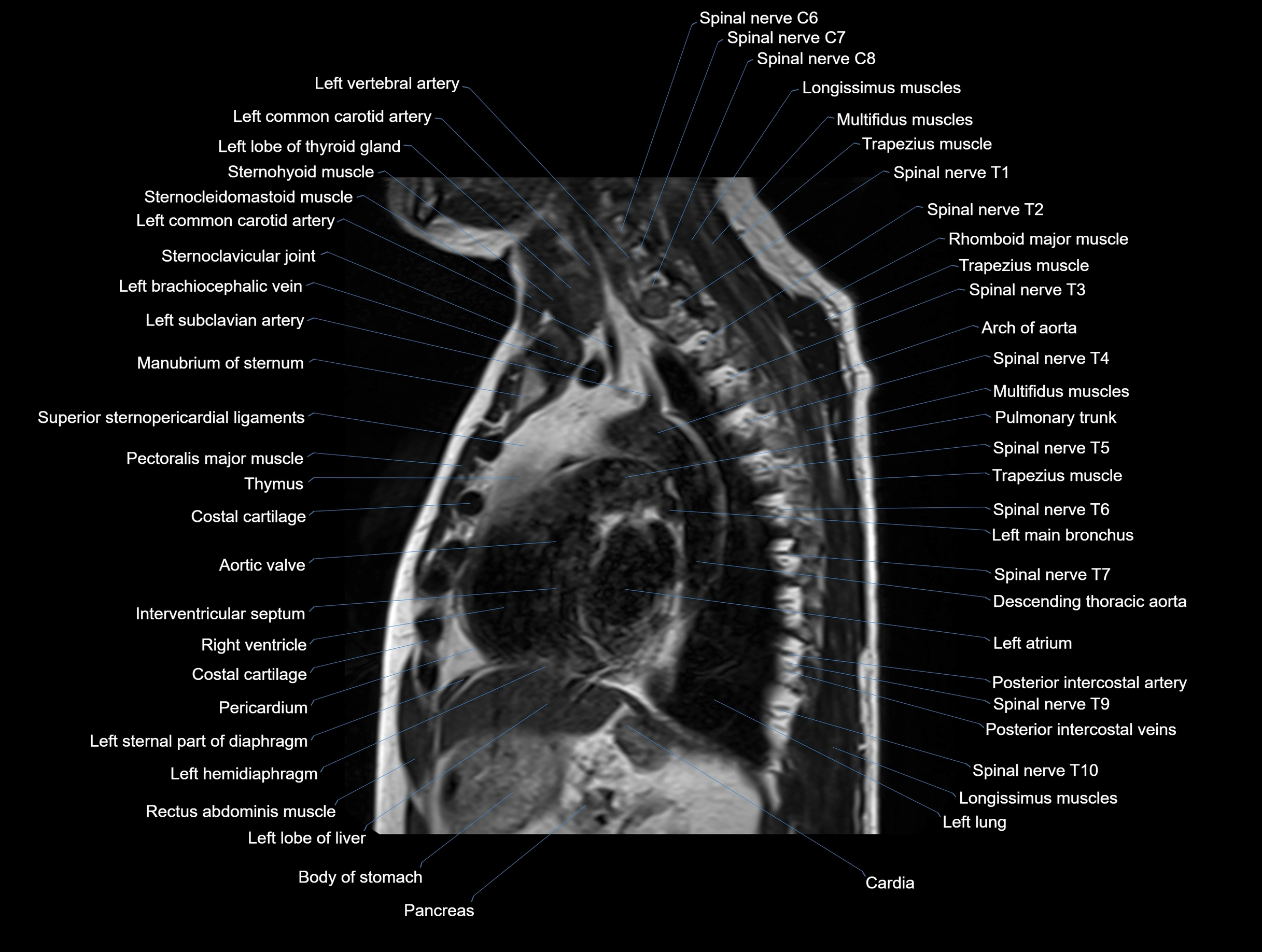
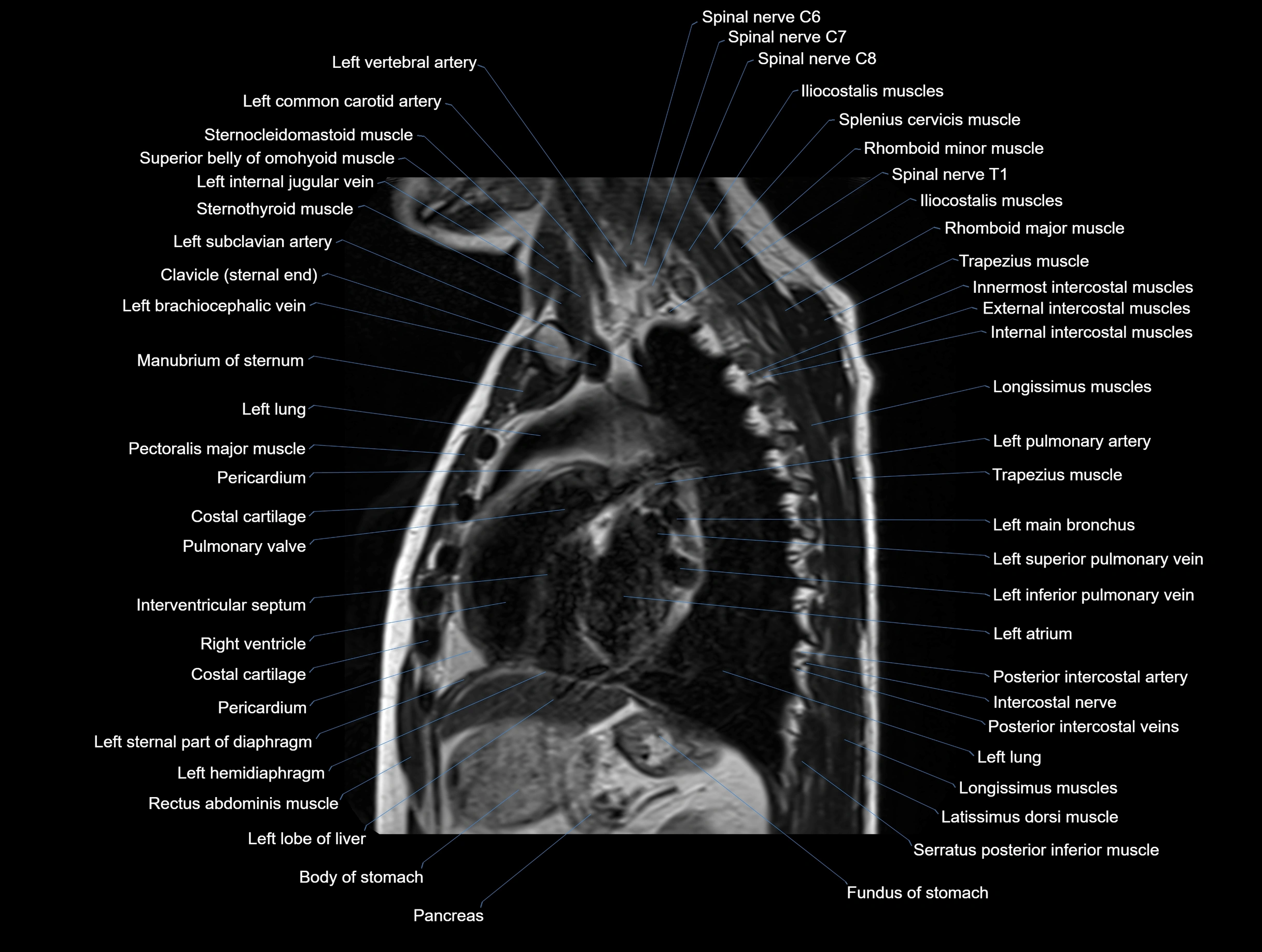
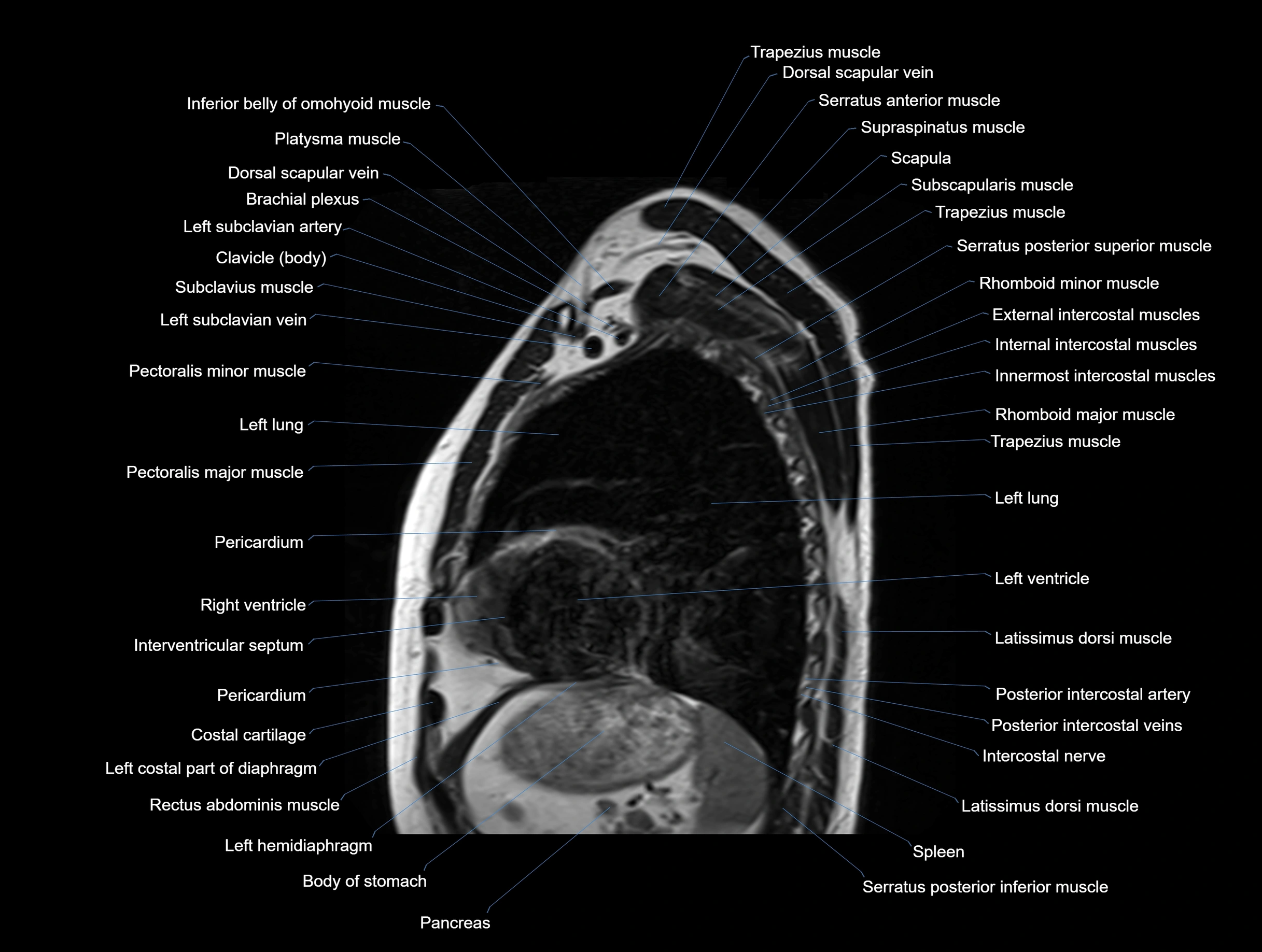
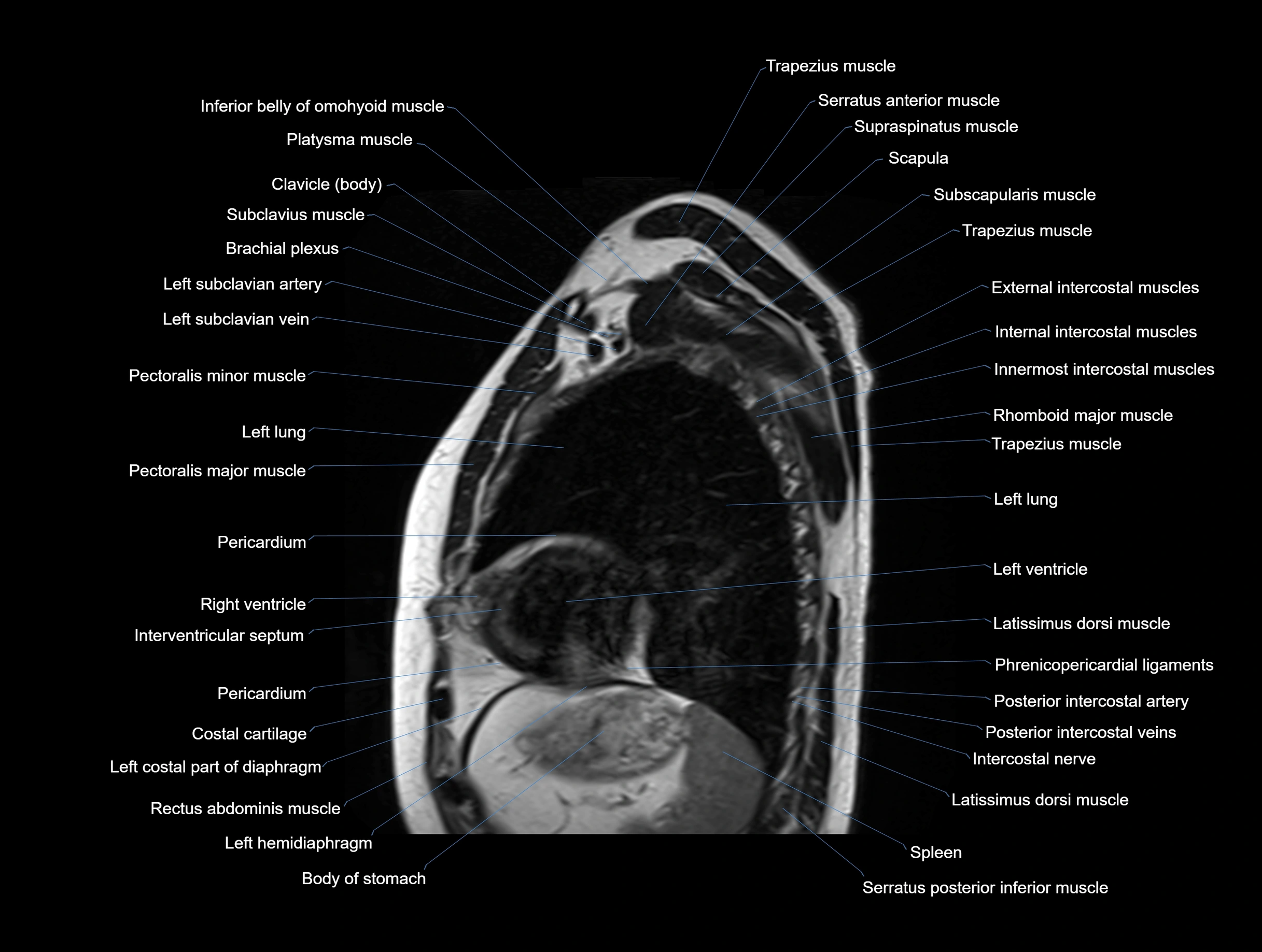
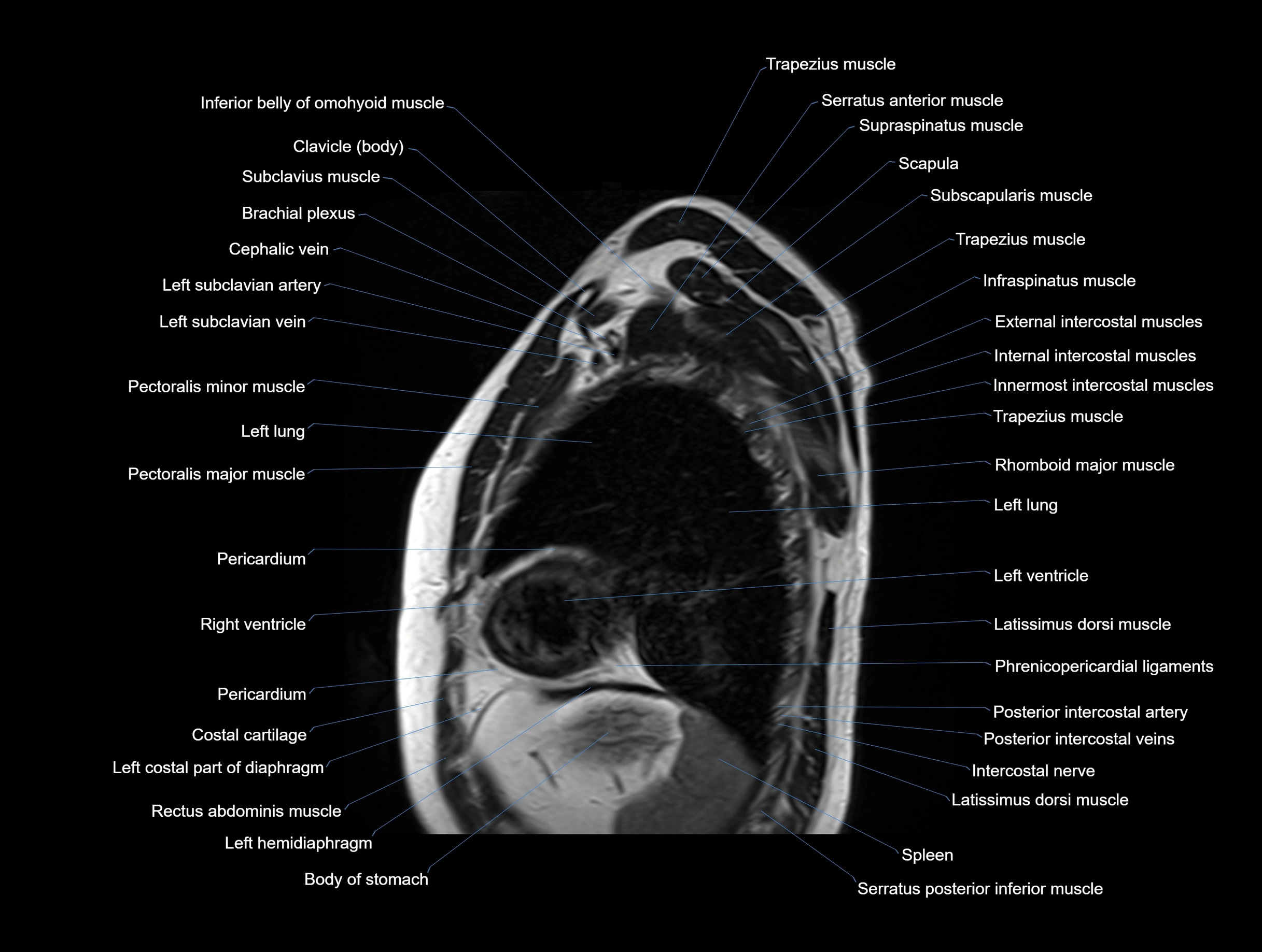
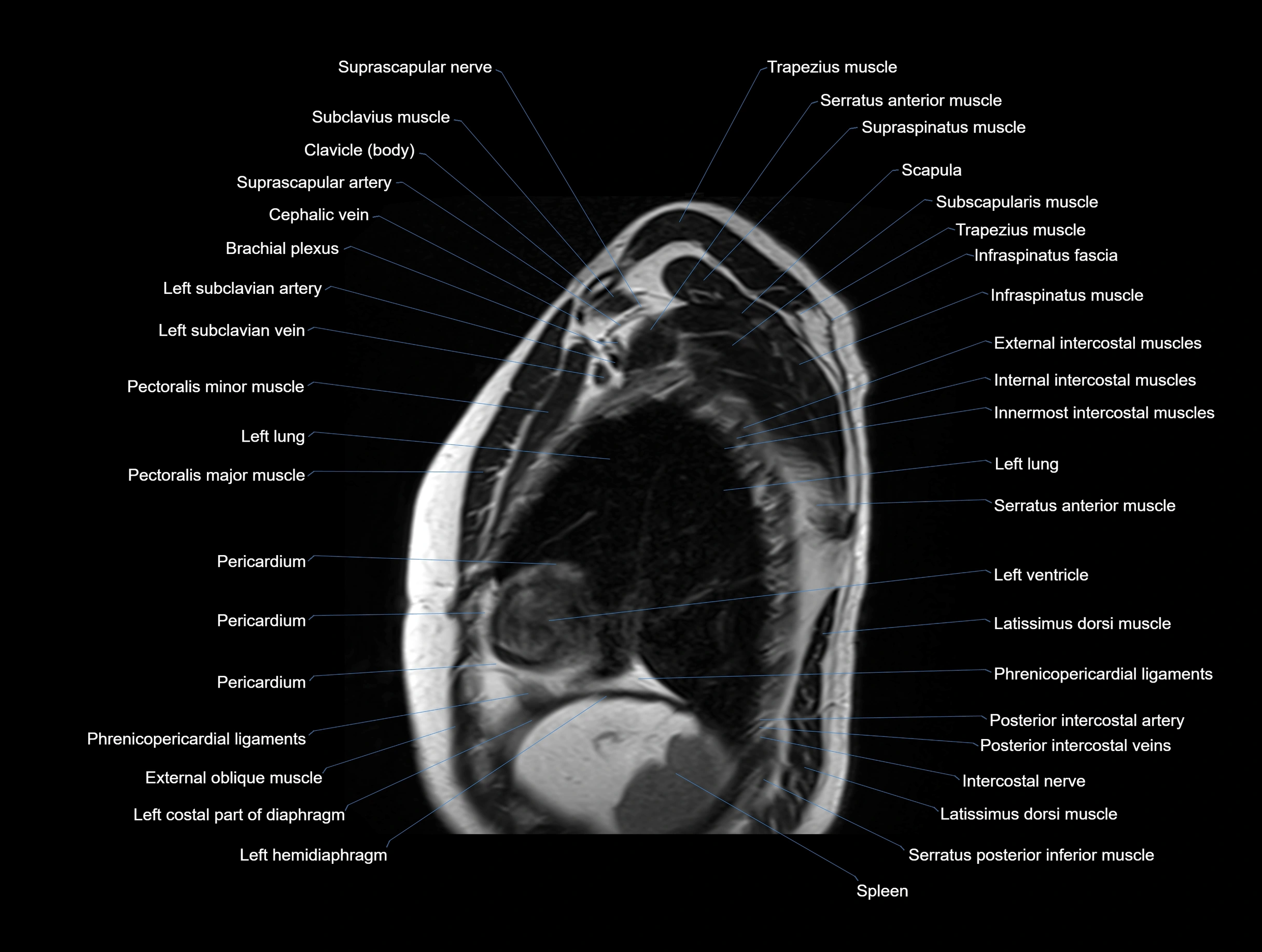
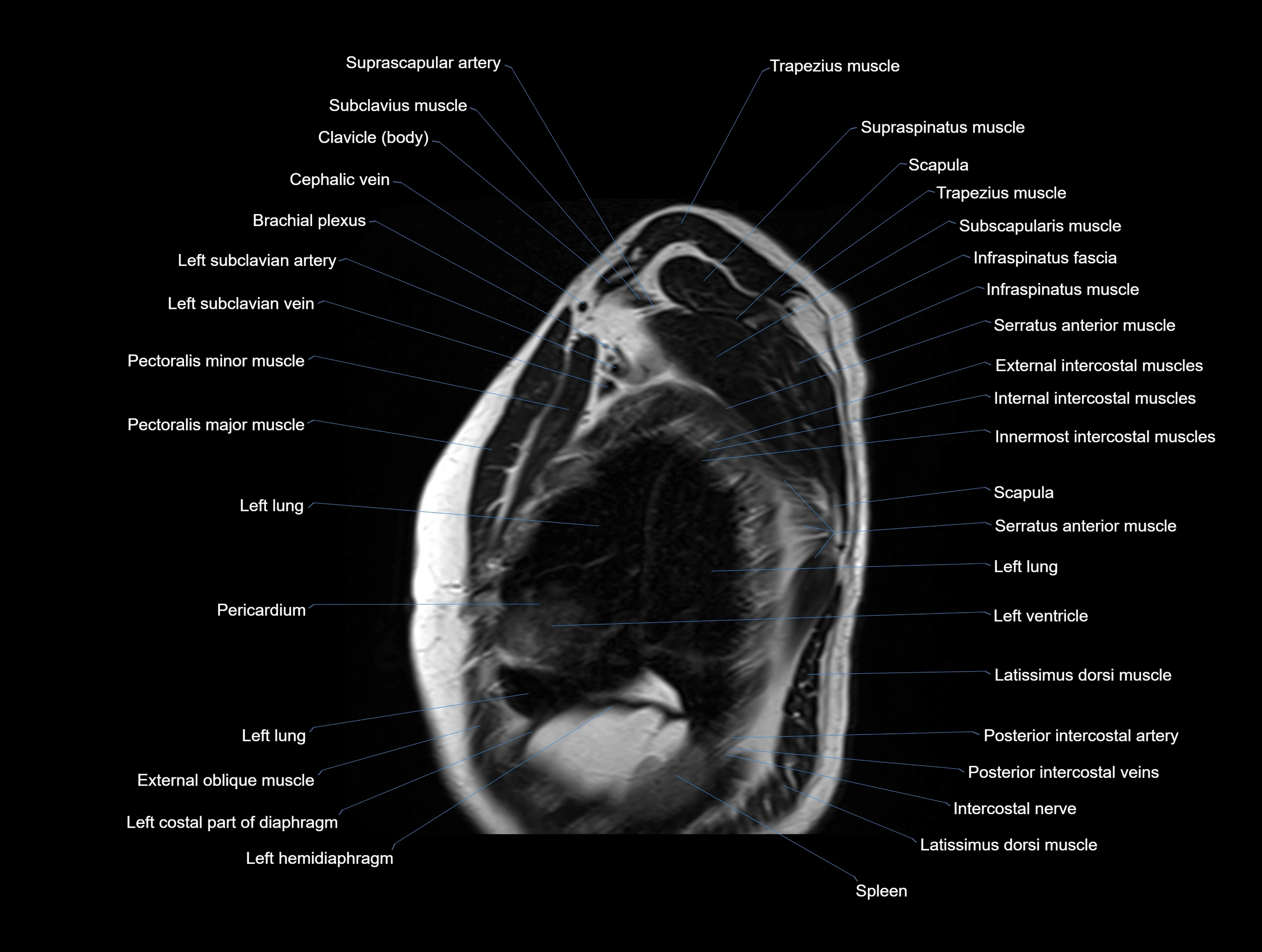
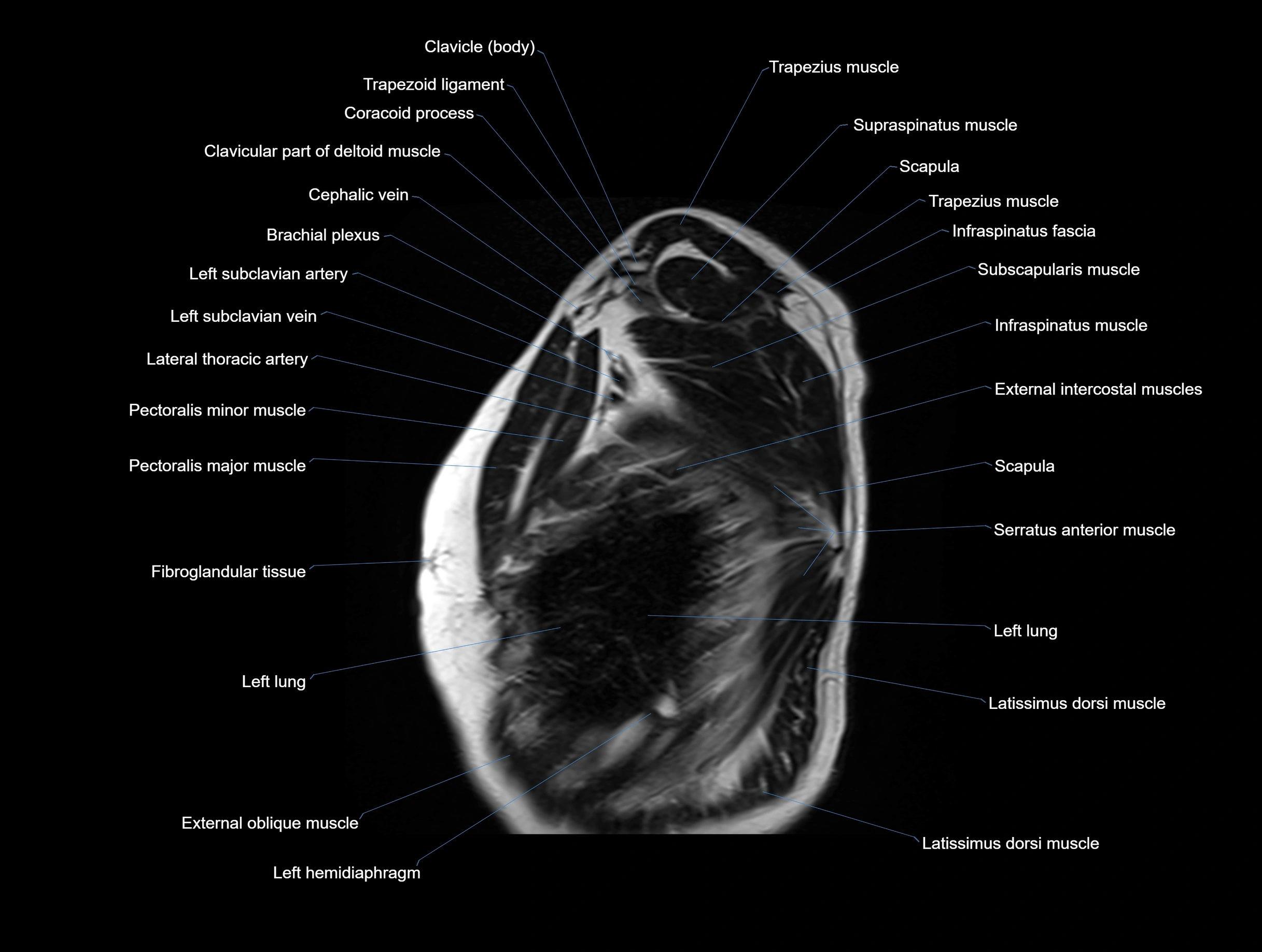
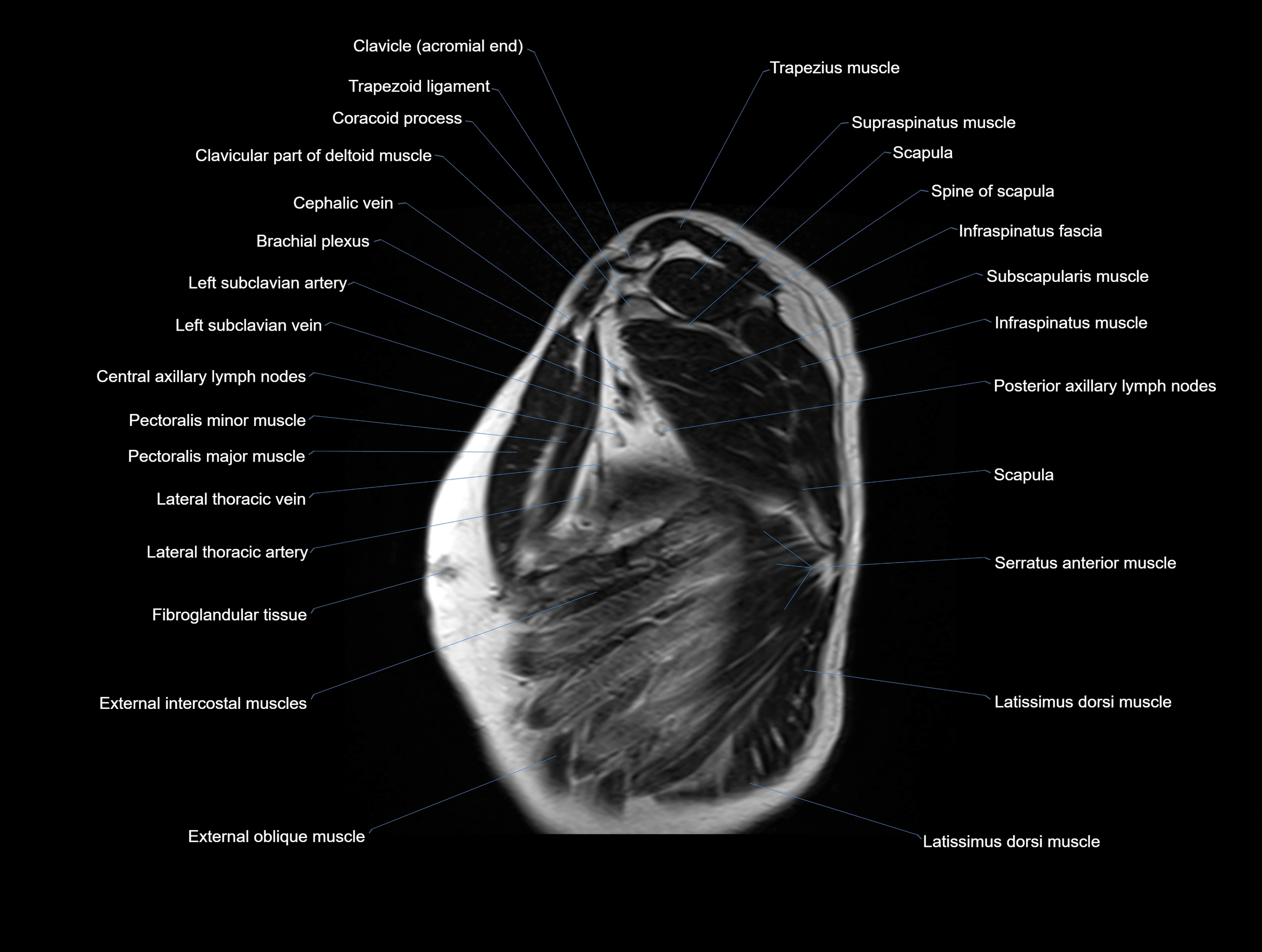
MRI images

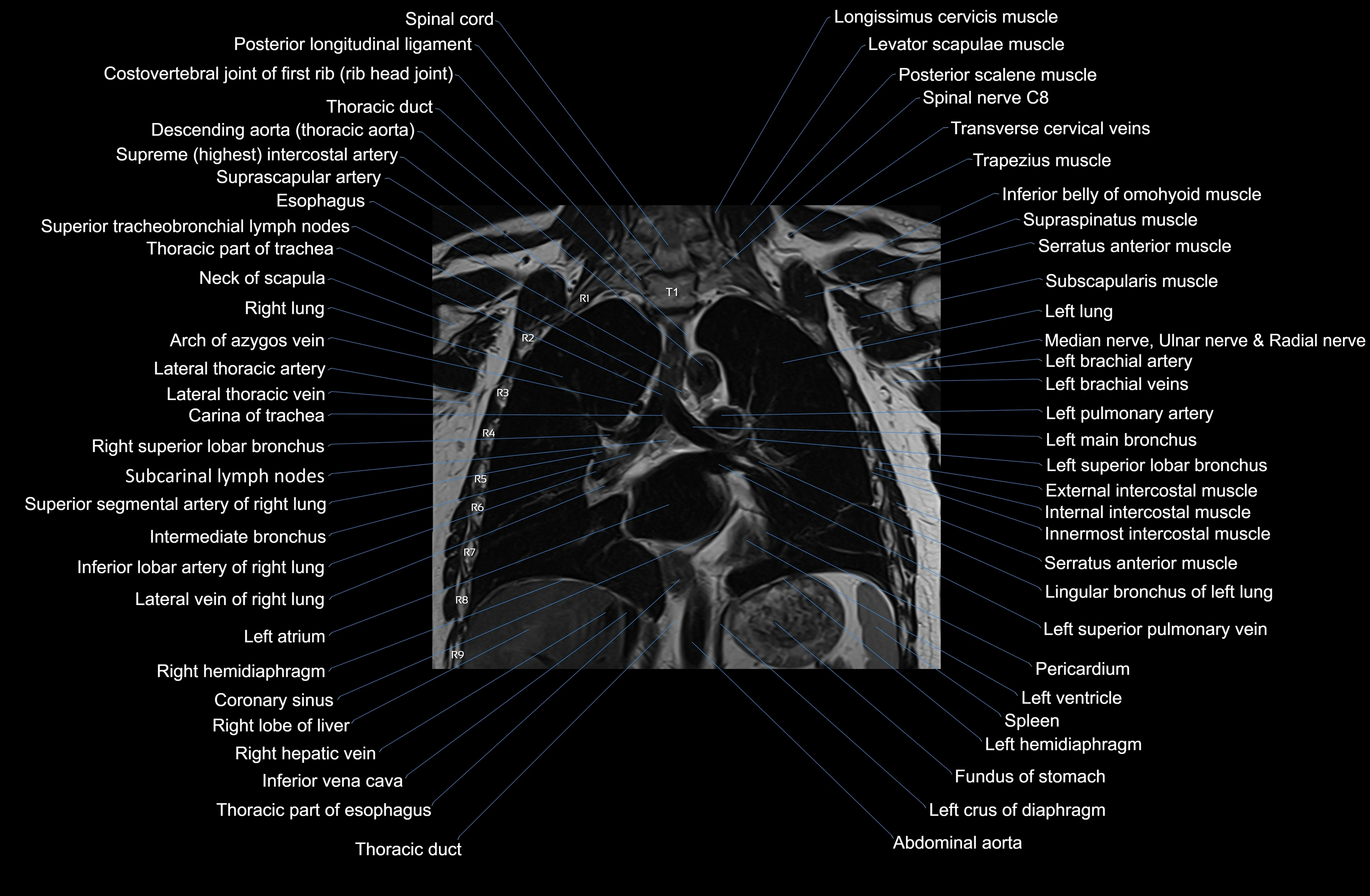
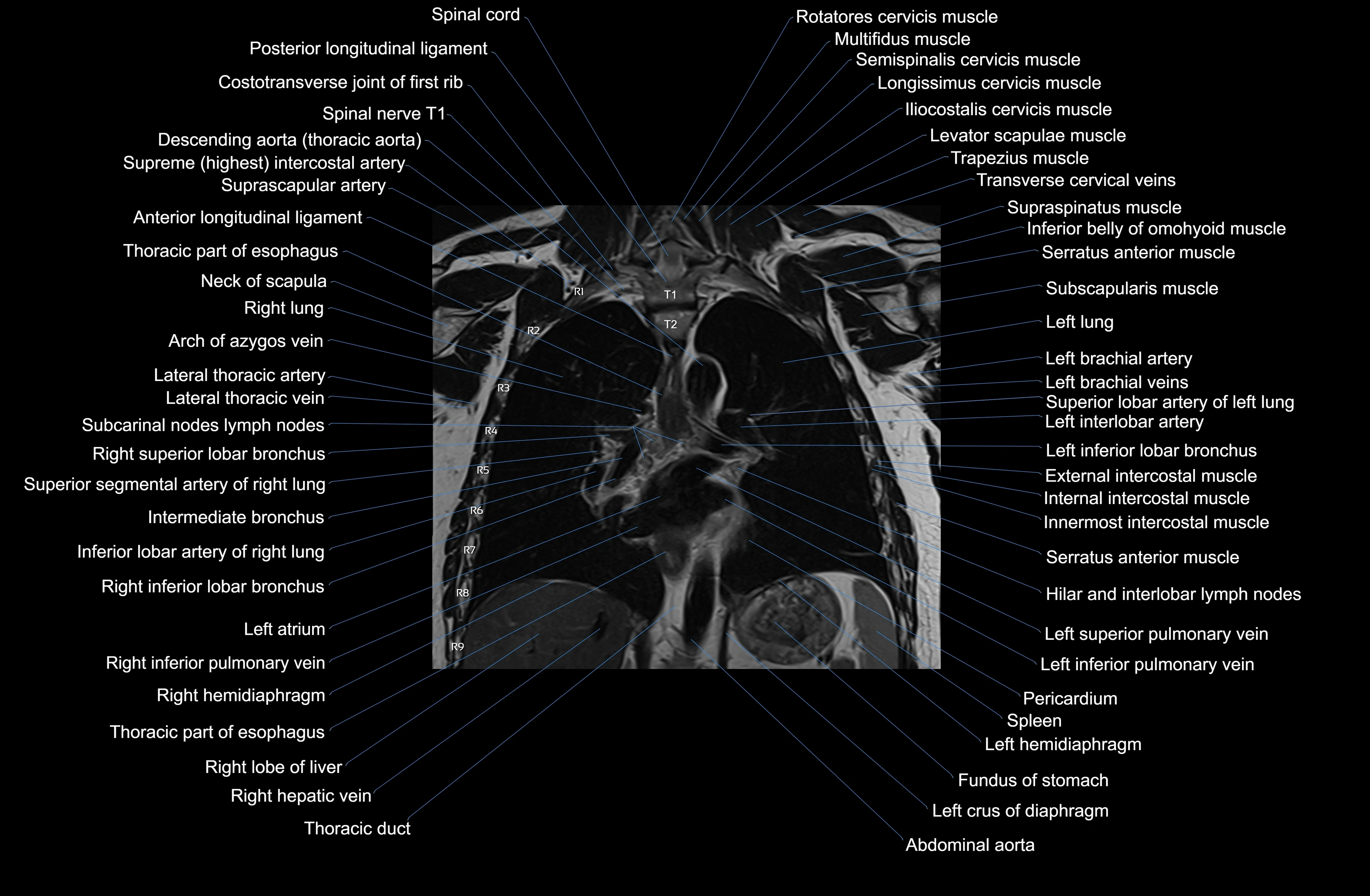
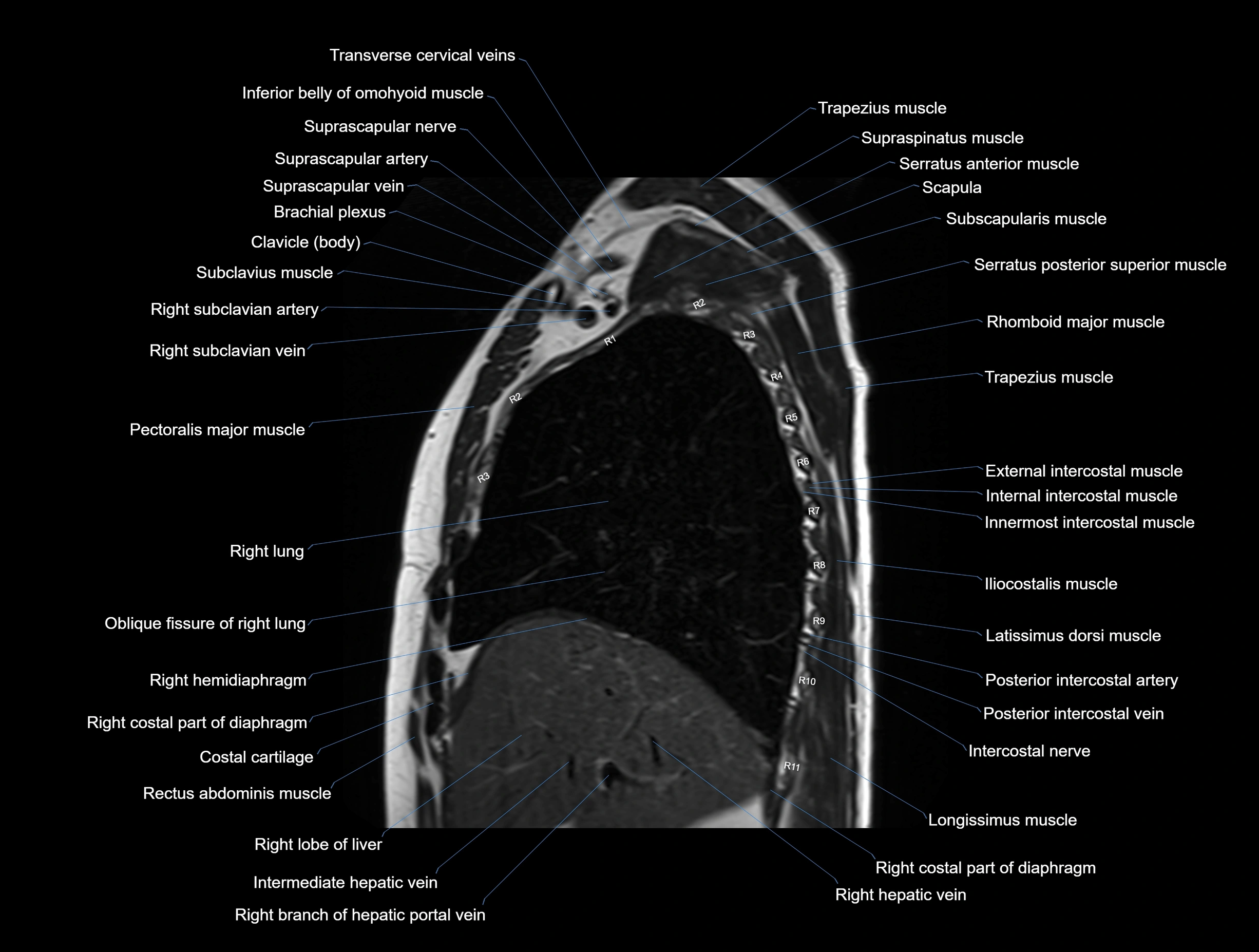
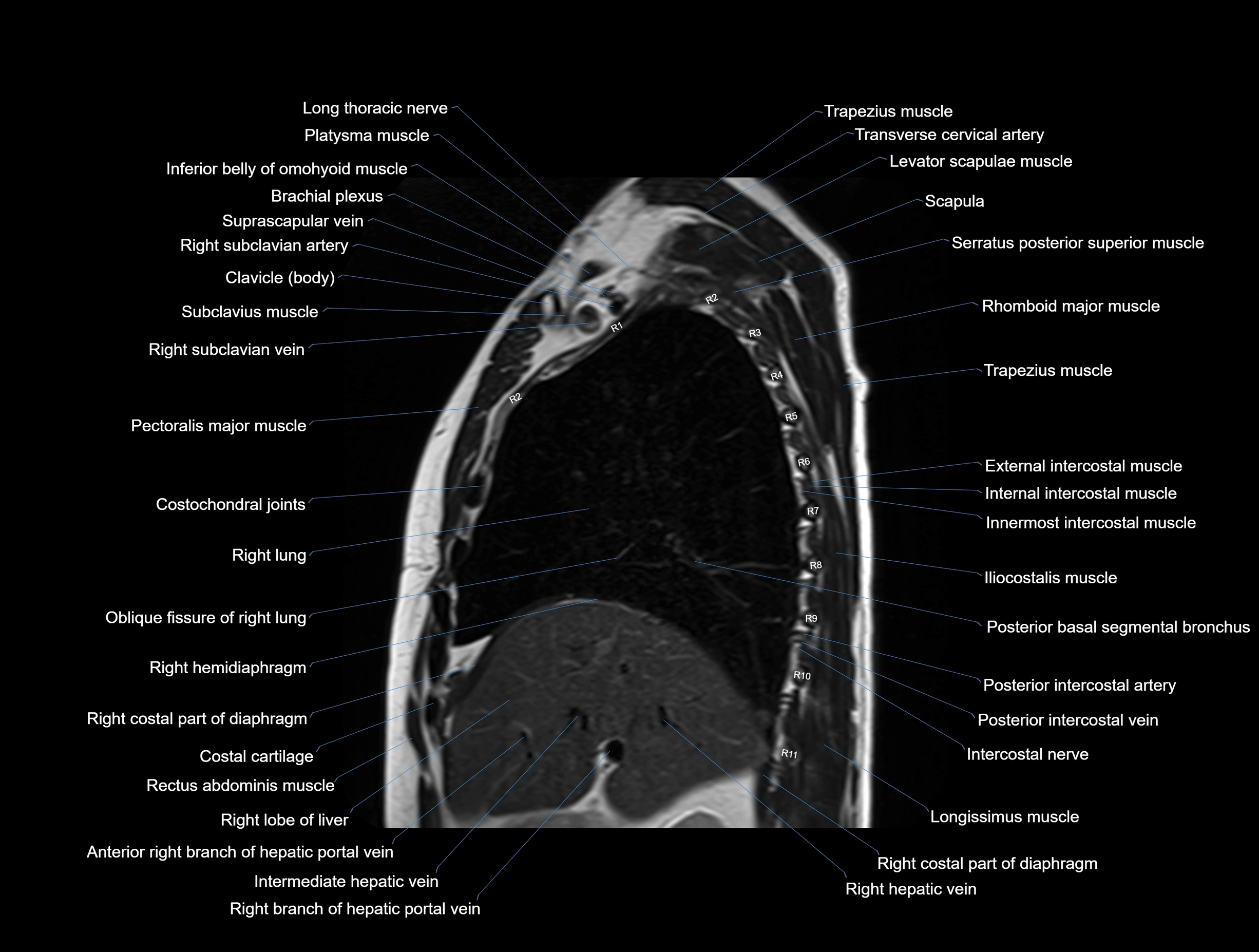
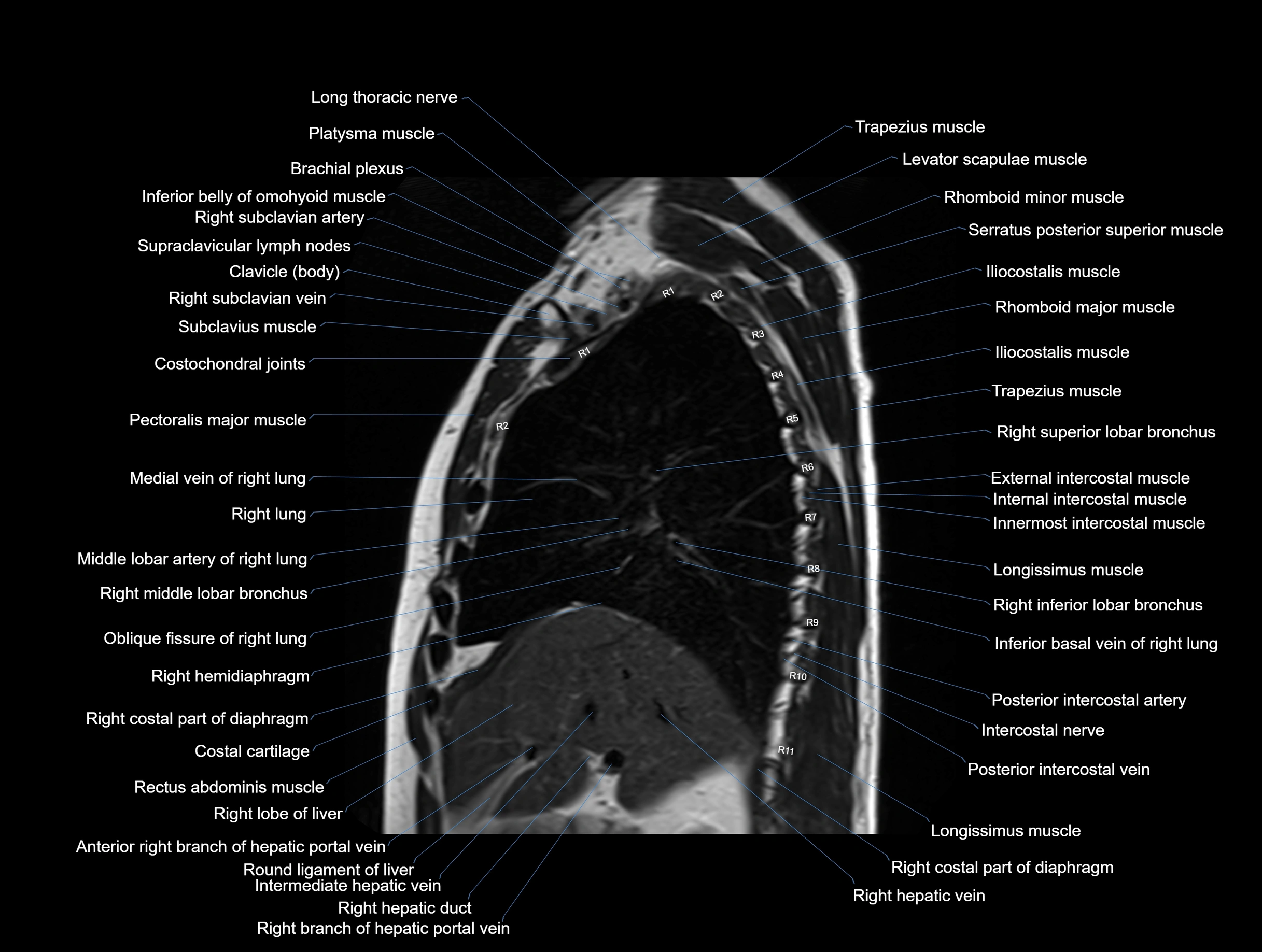
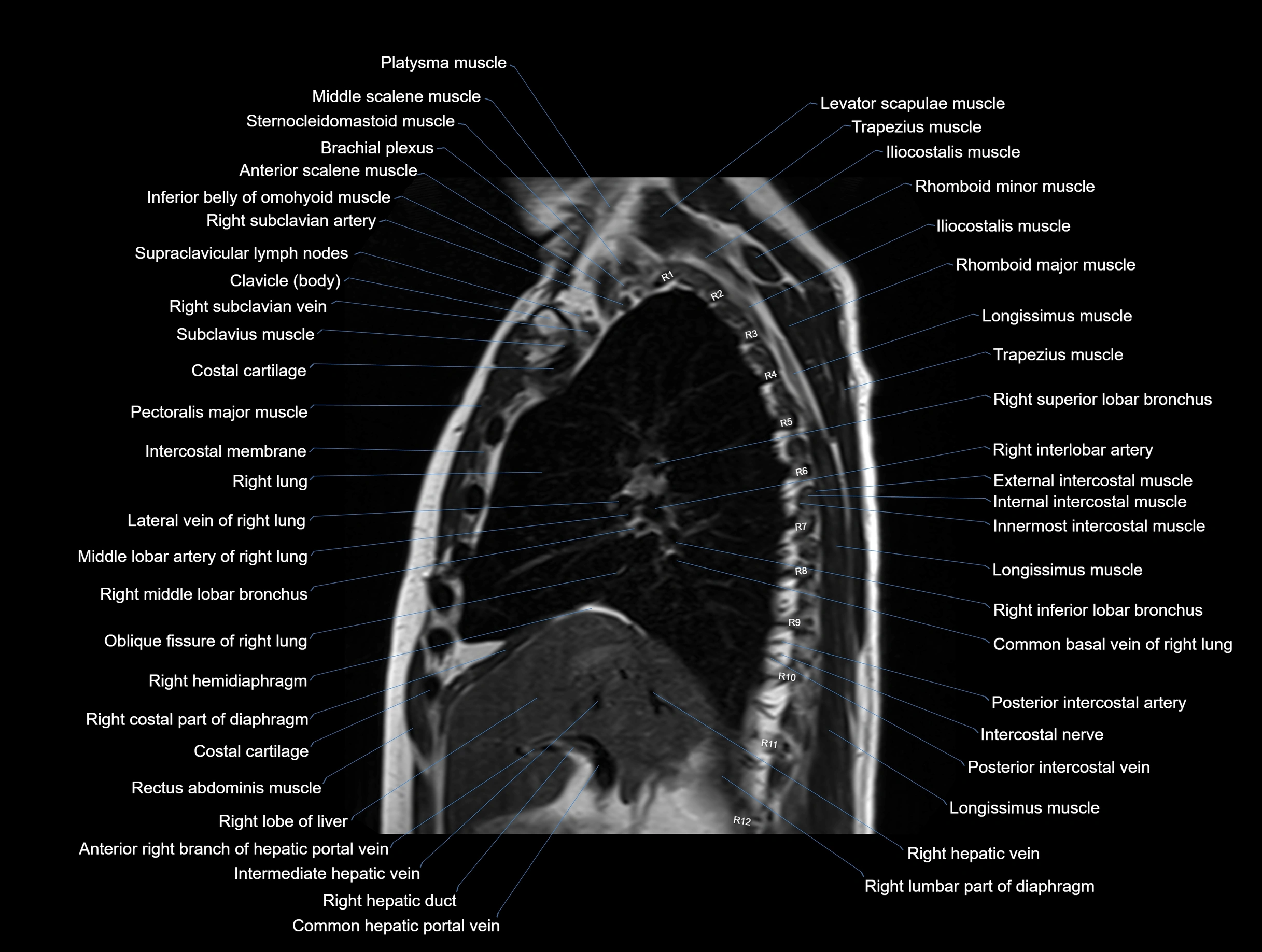
MRI images

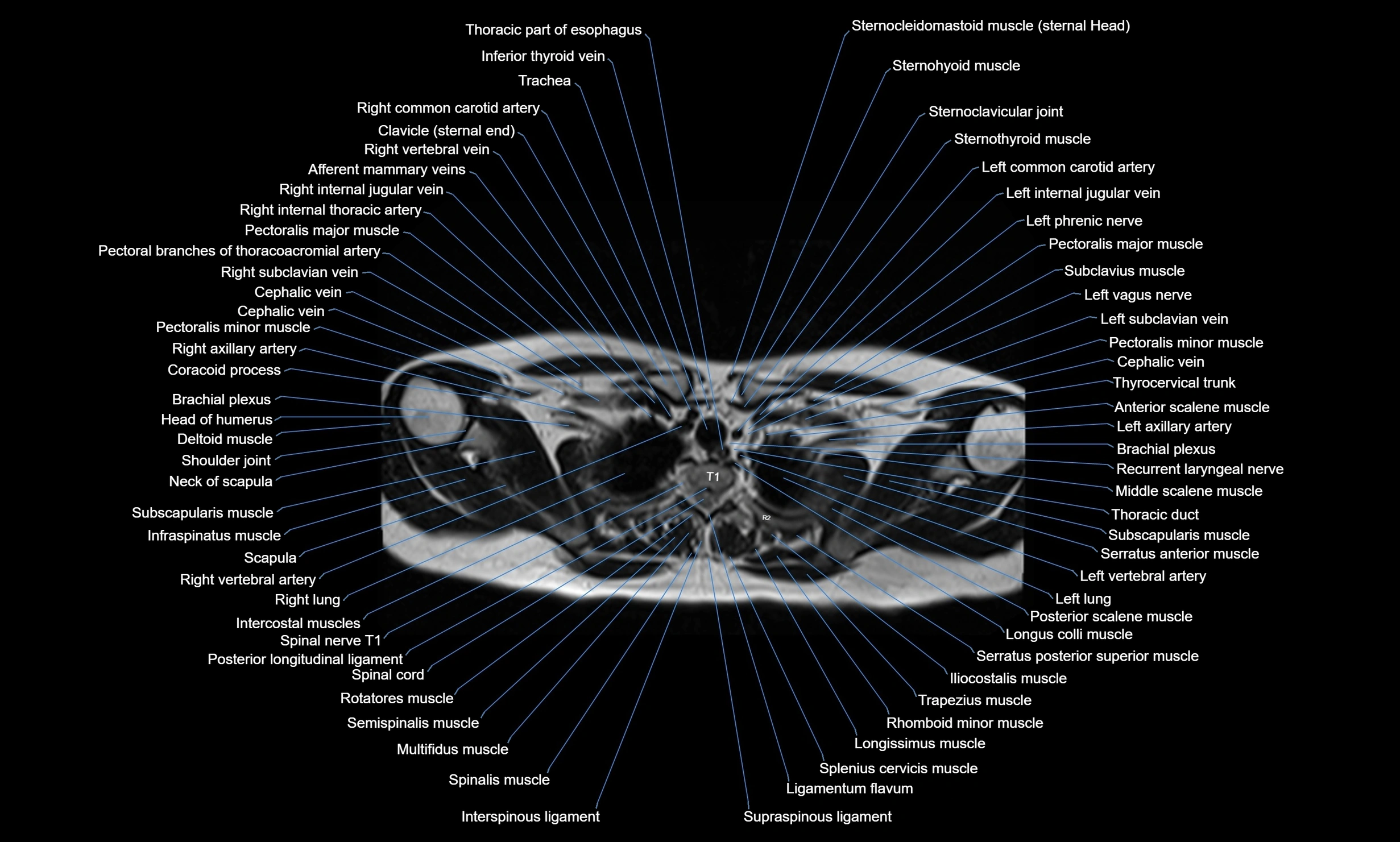
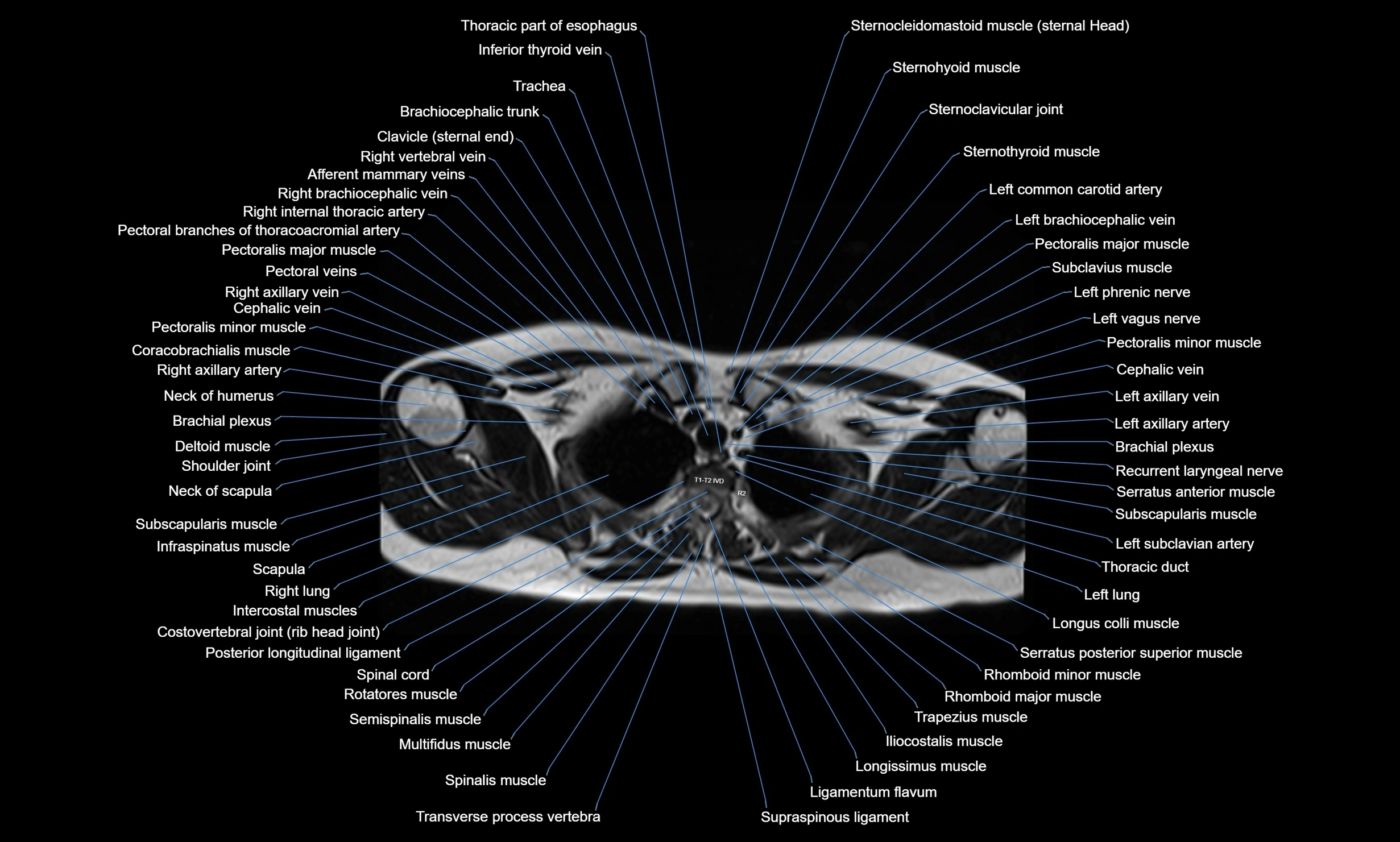
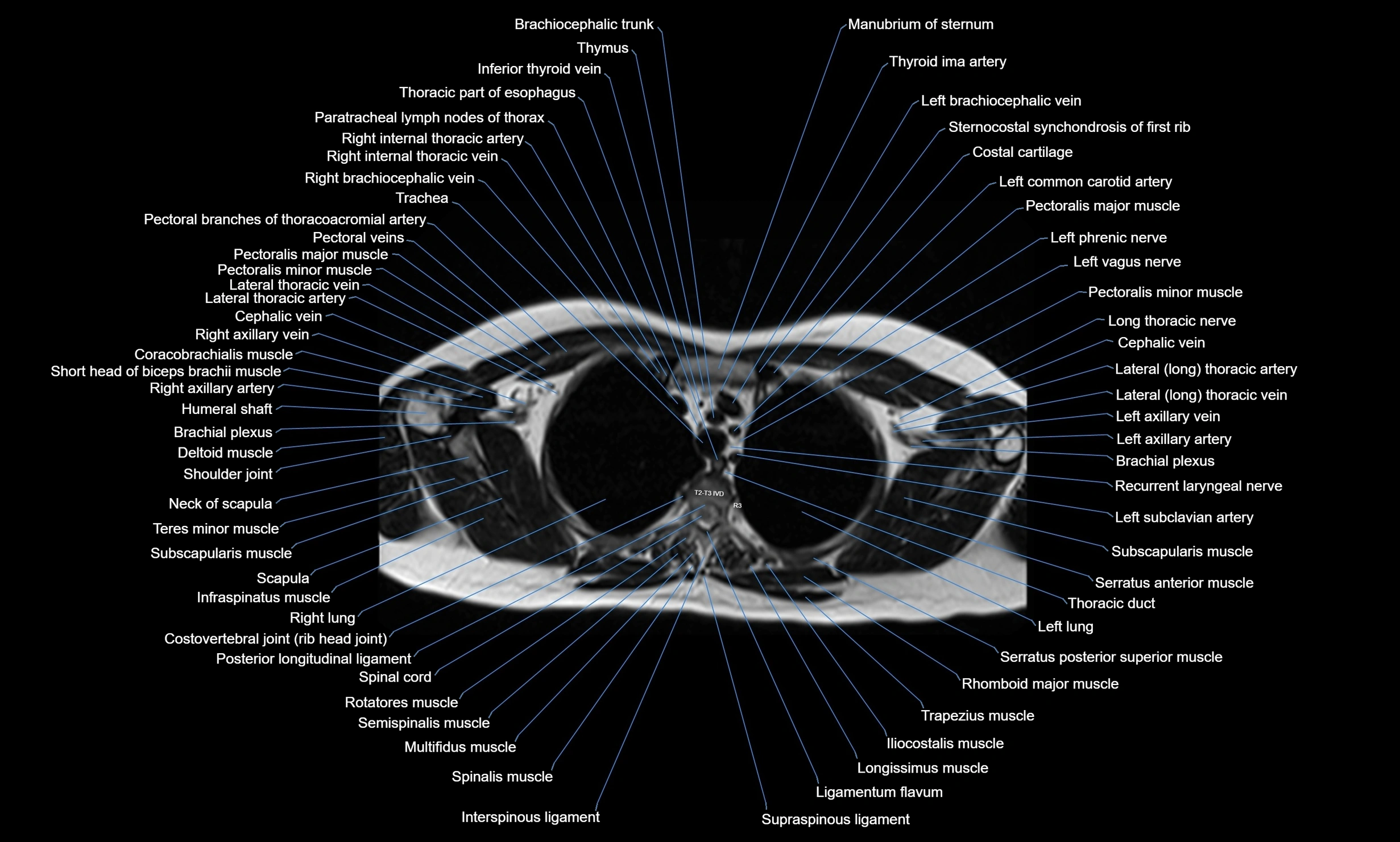
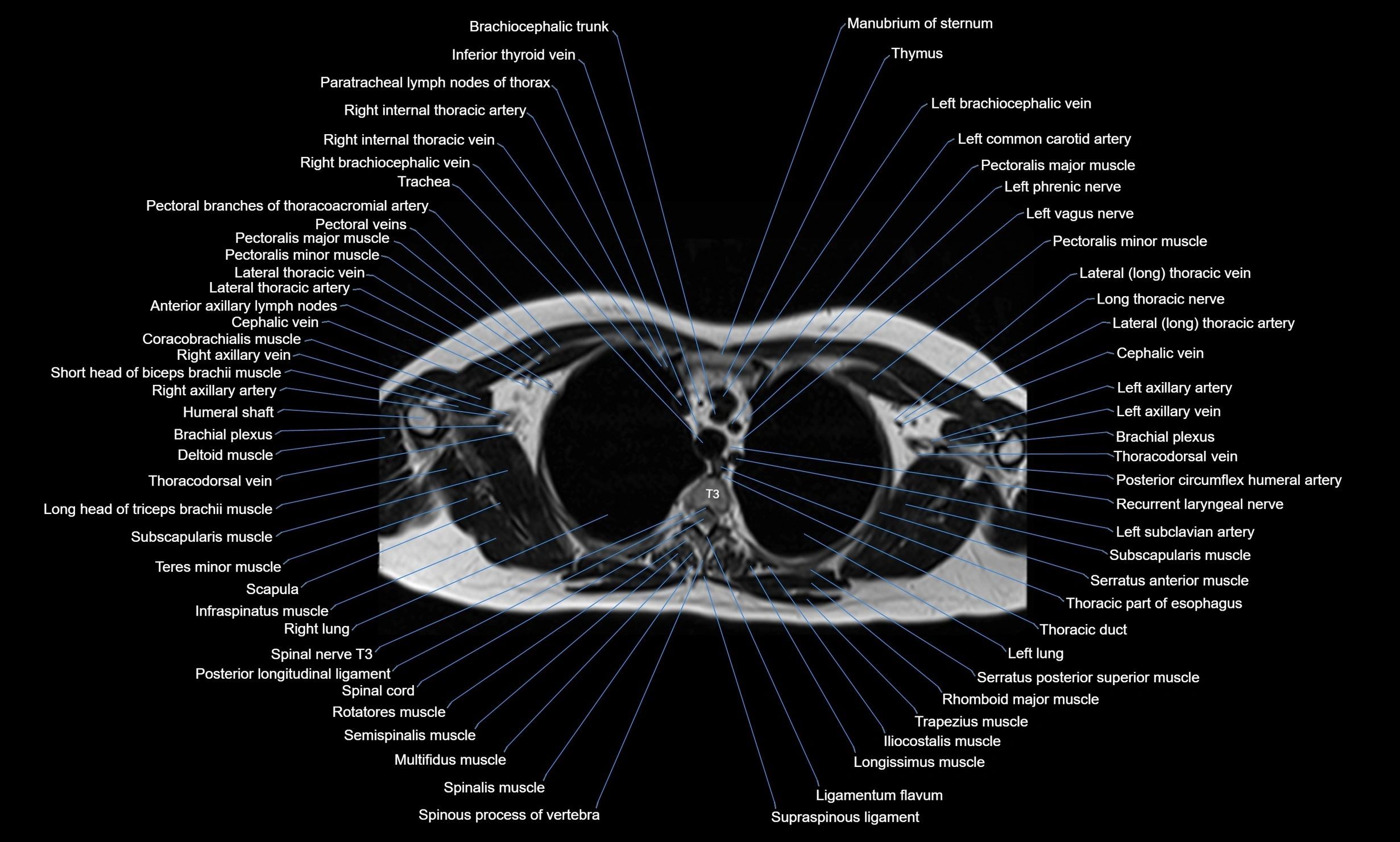
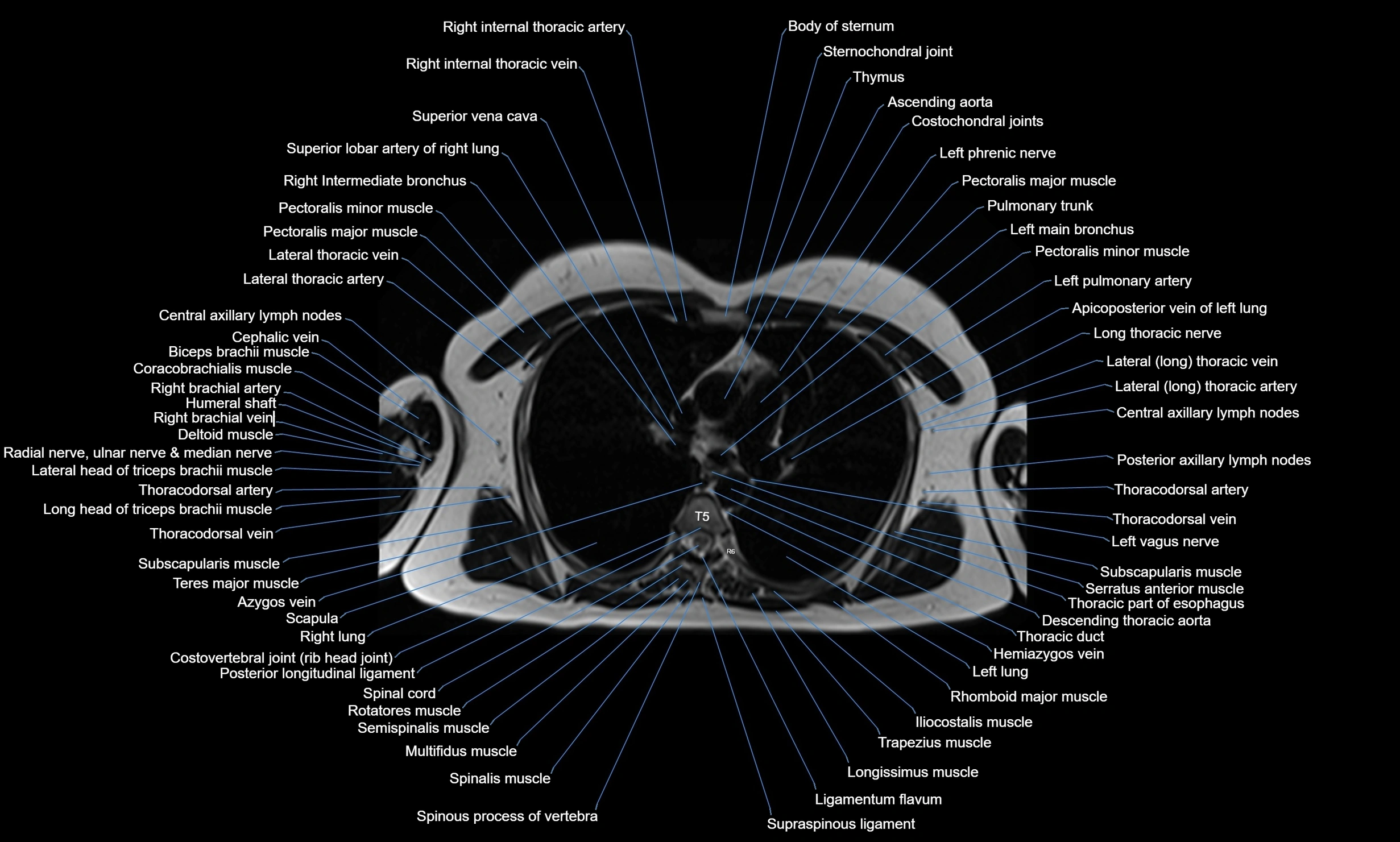
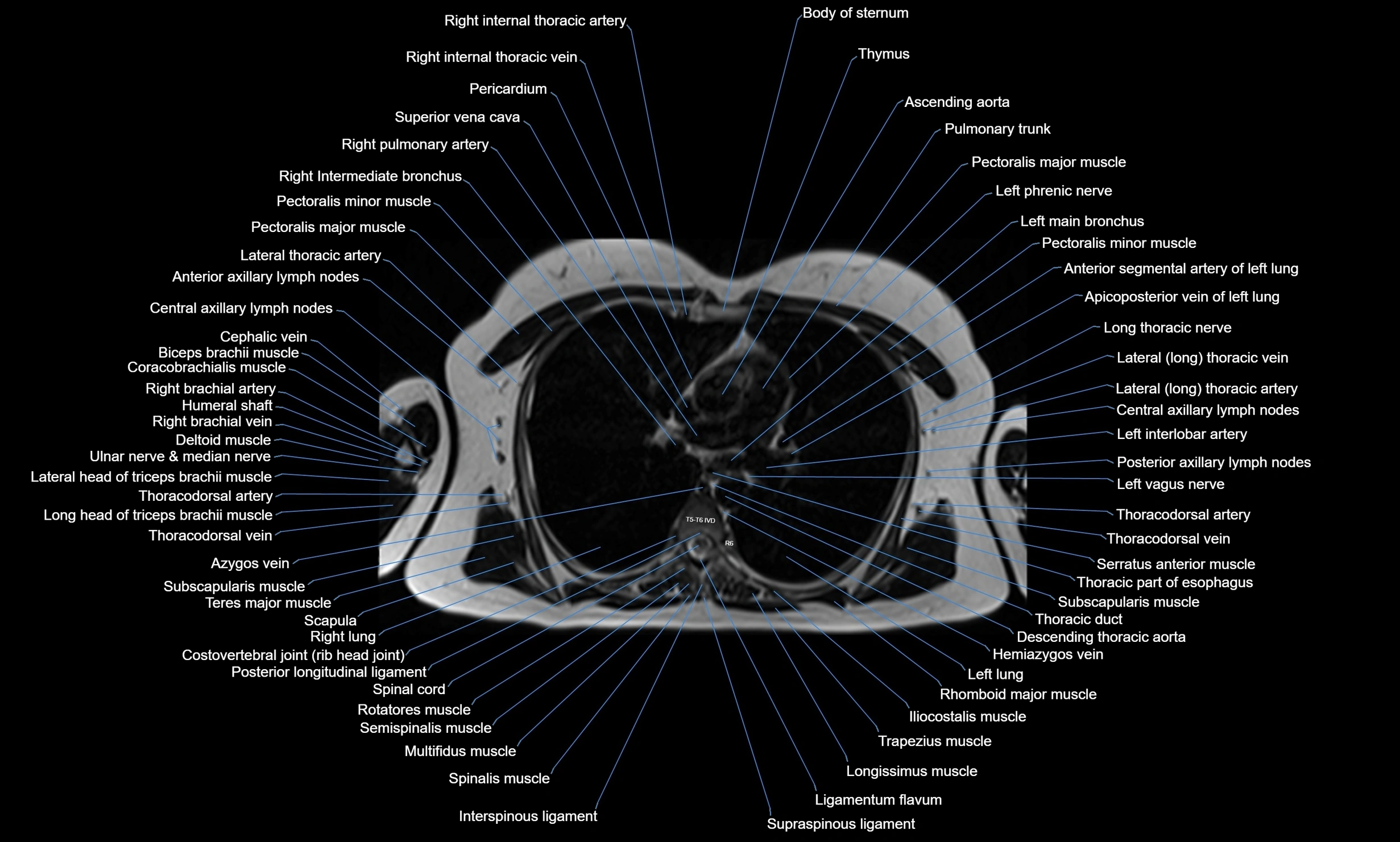
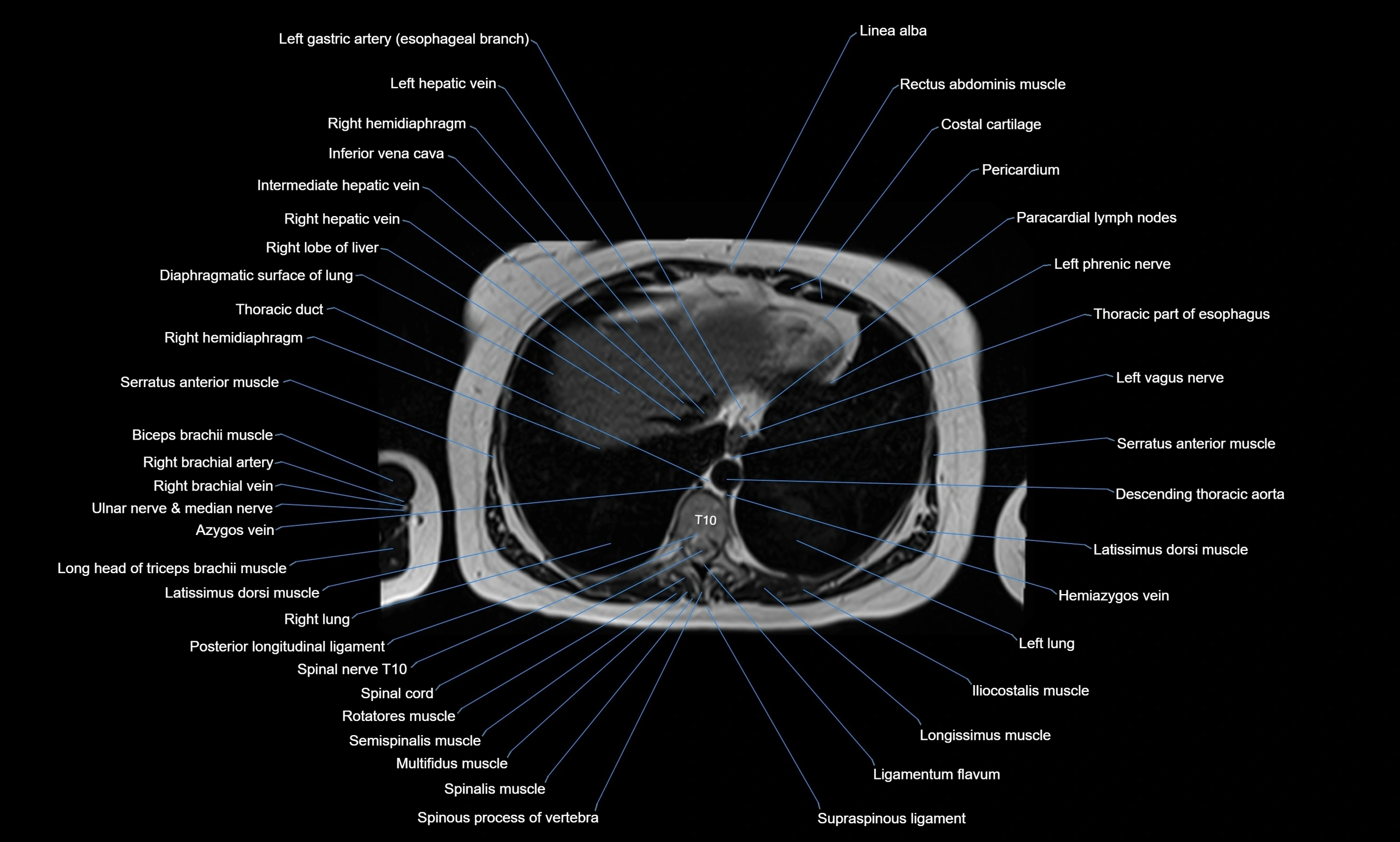
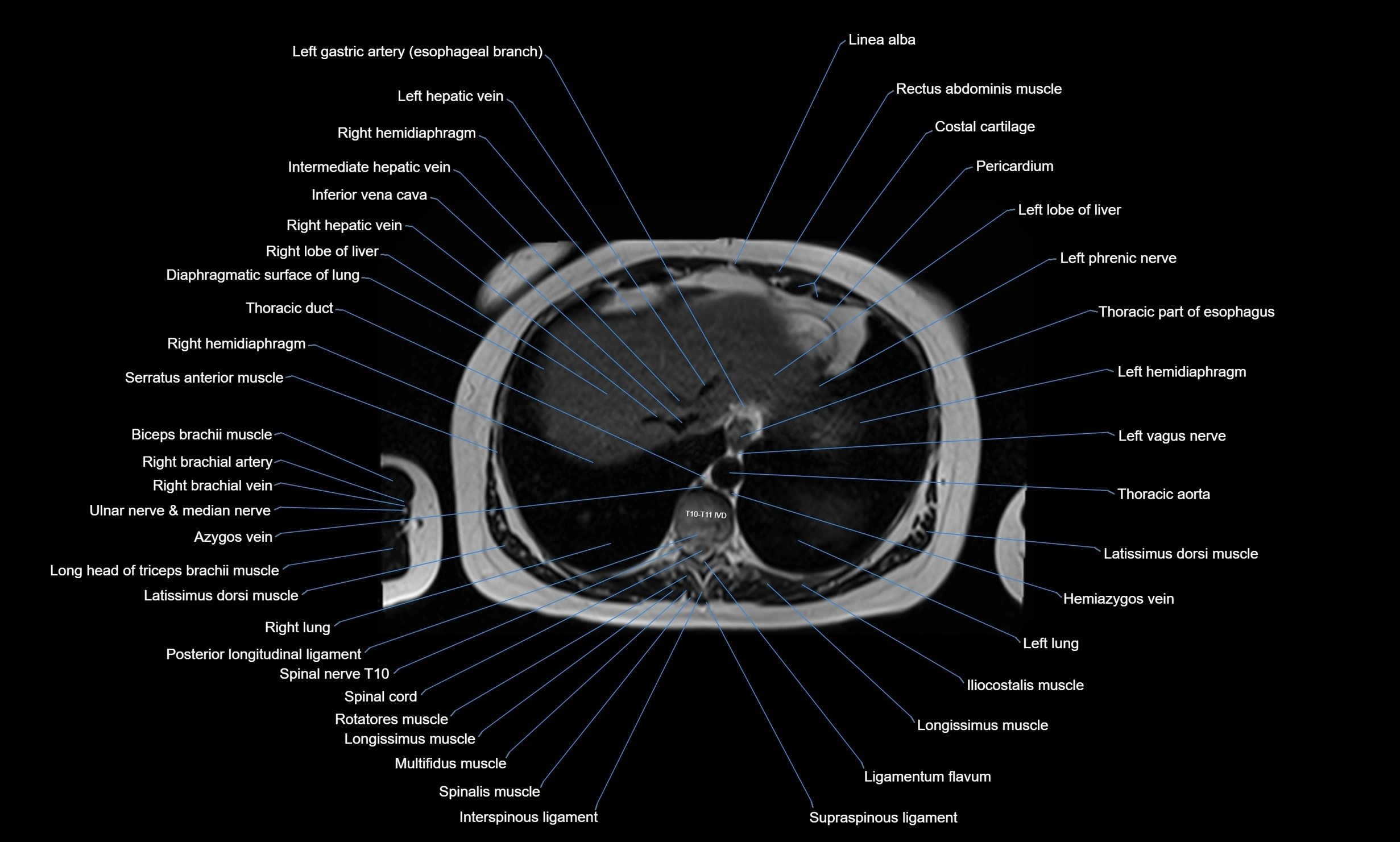
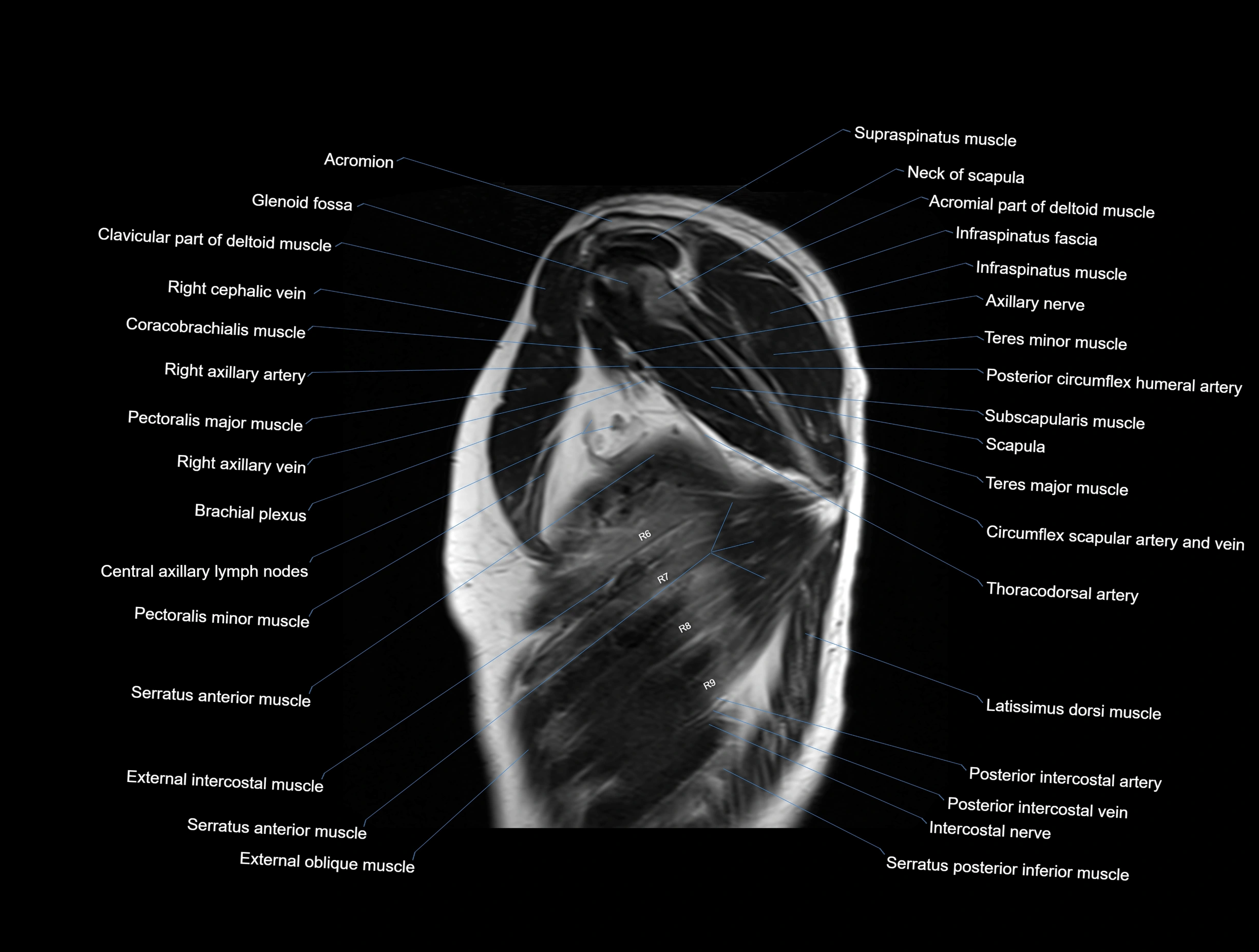
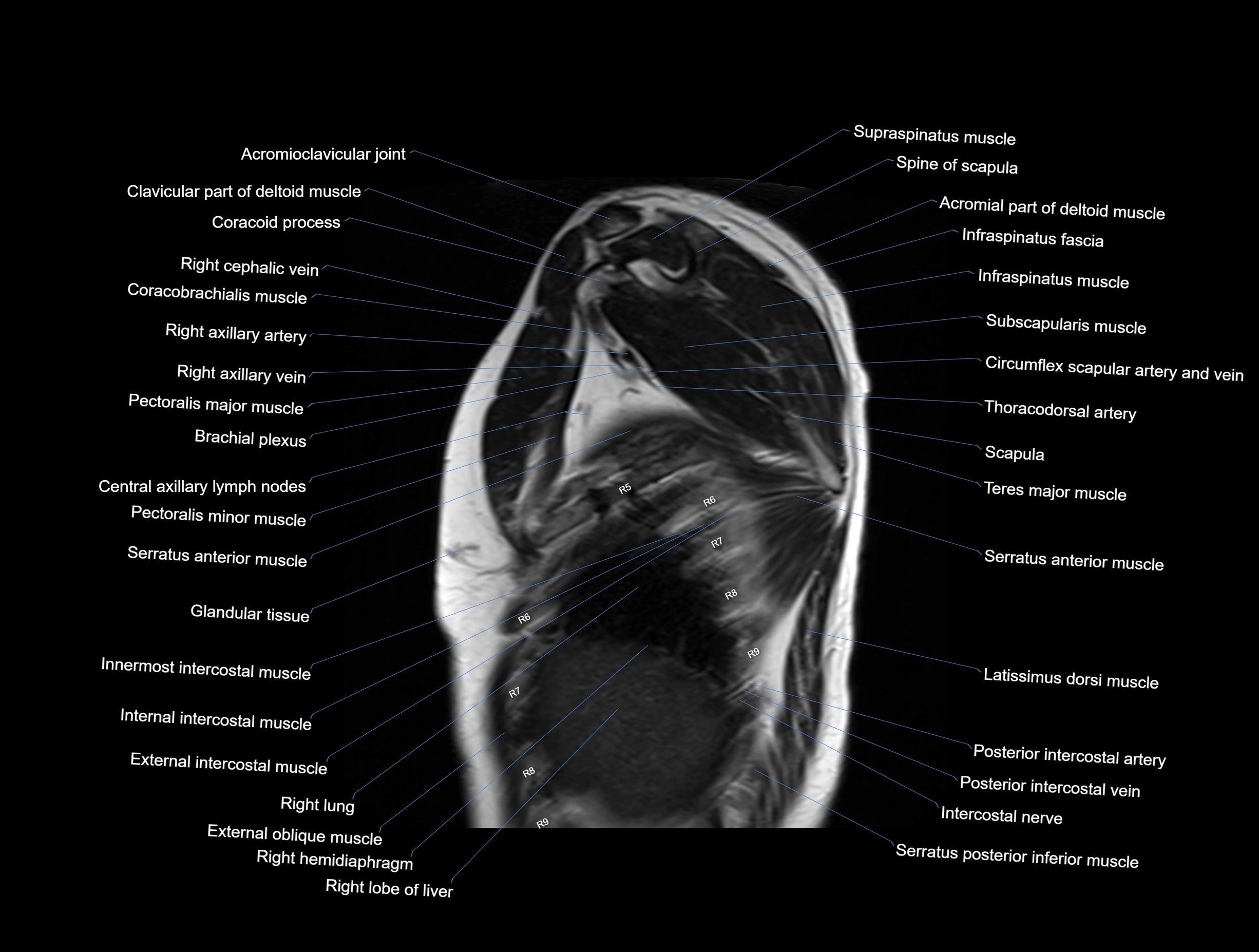
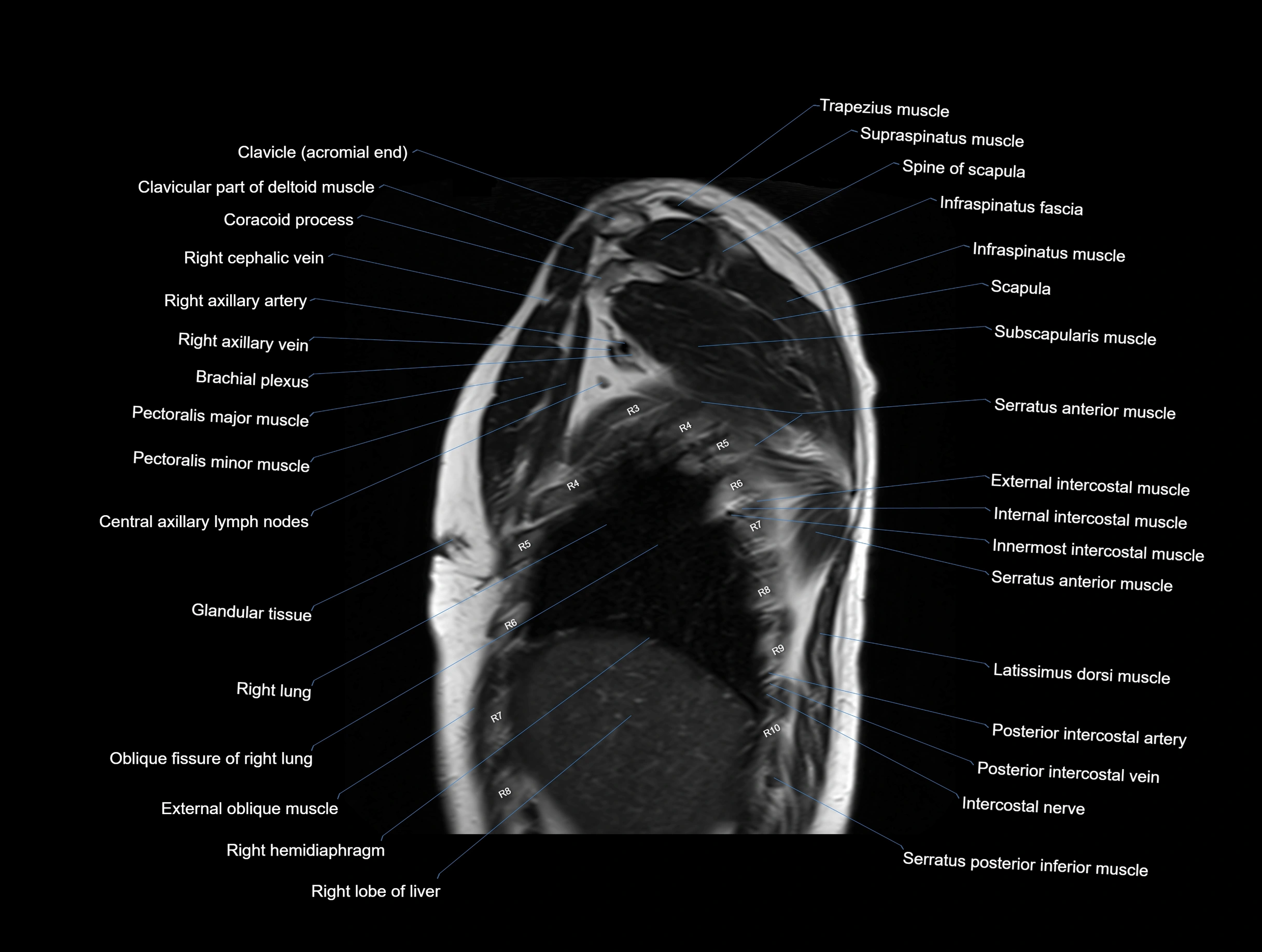
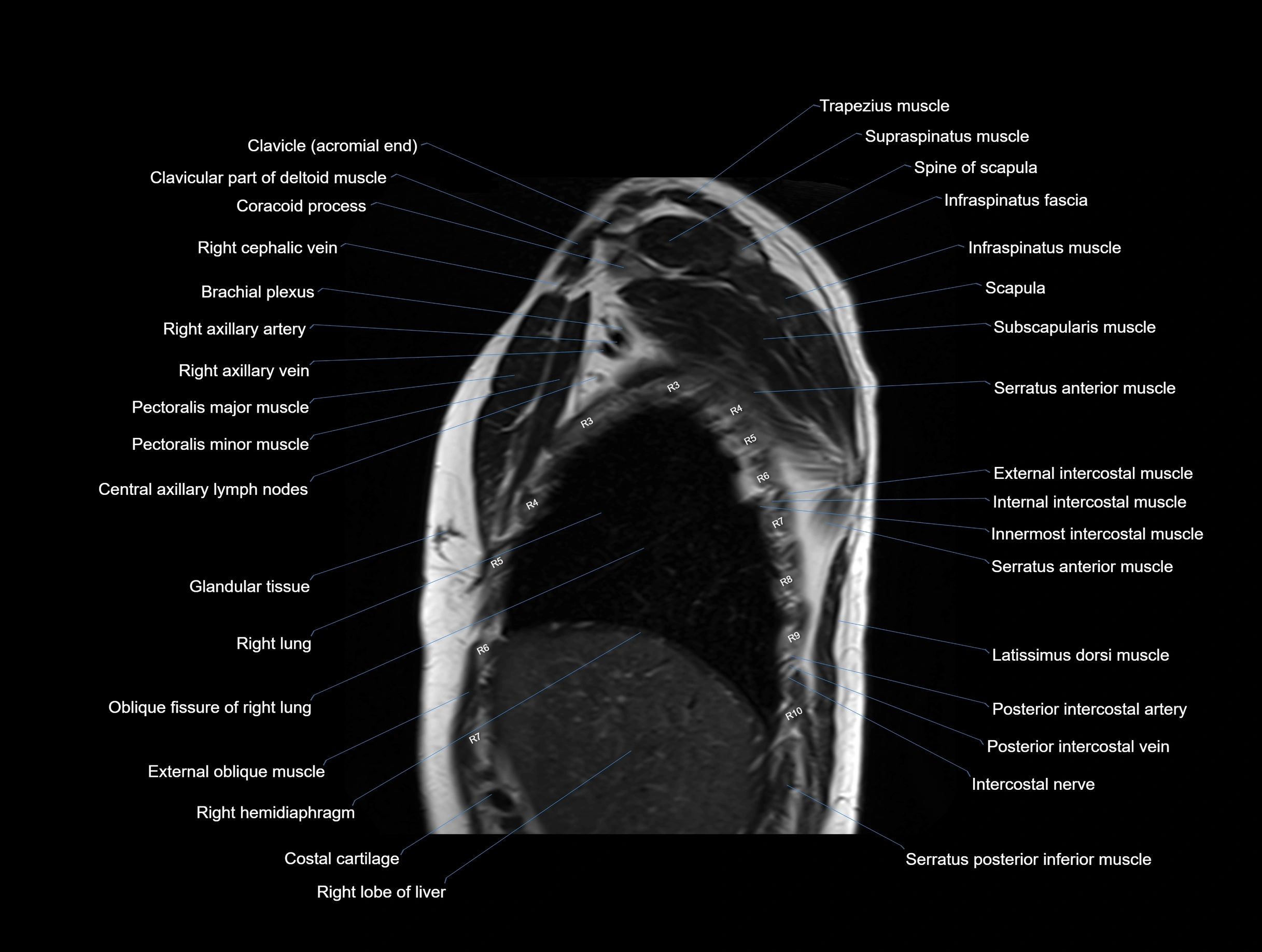
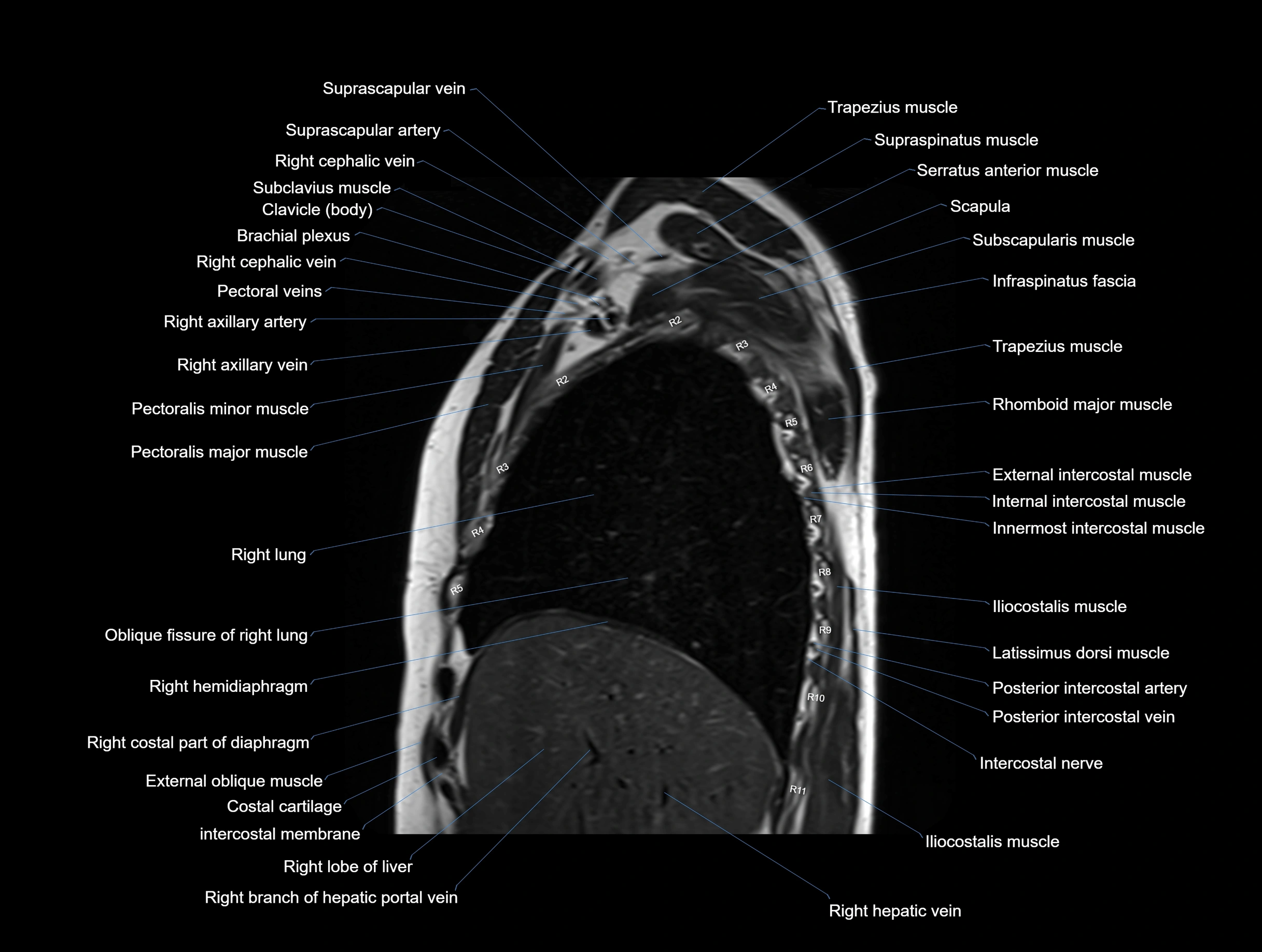
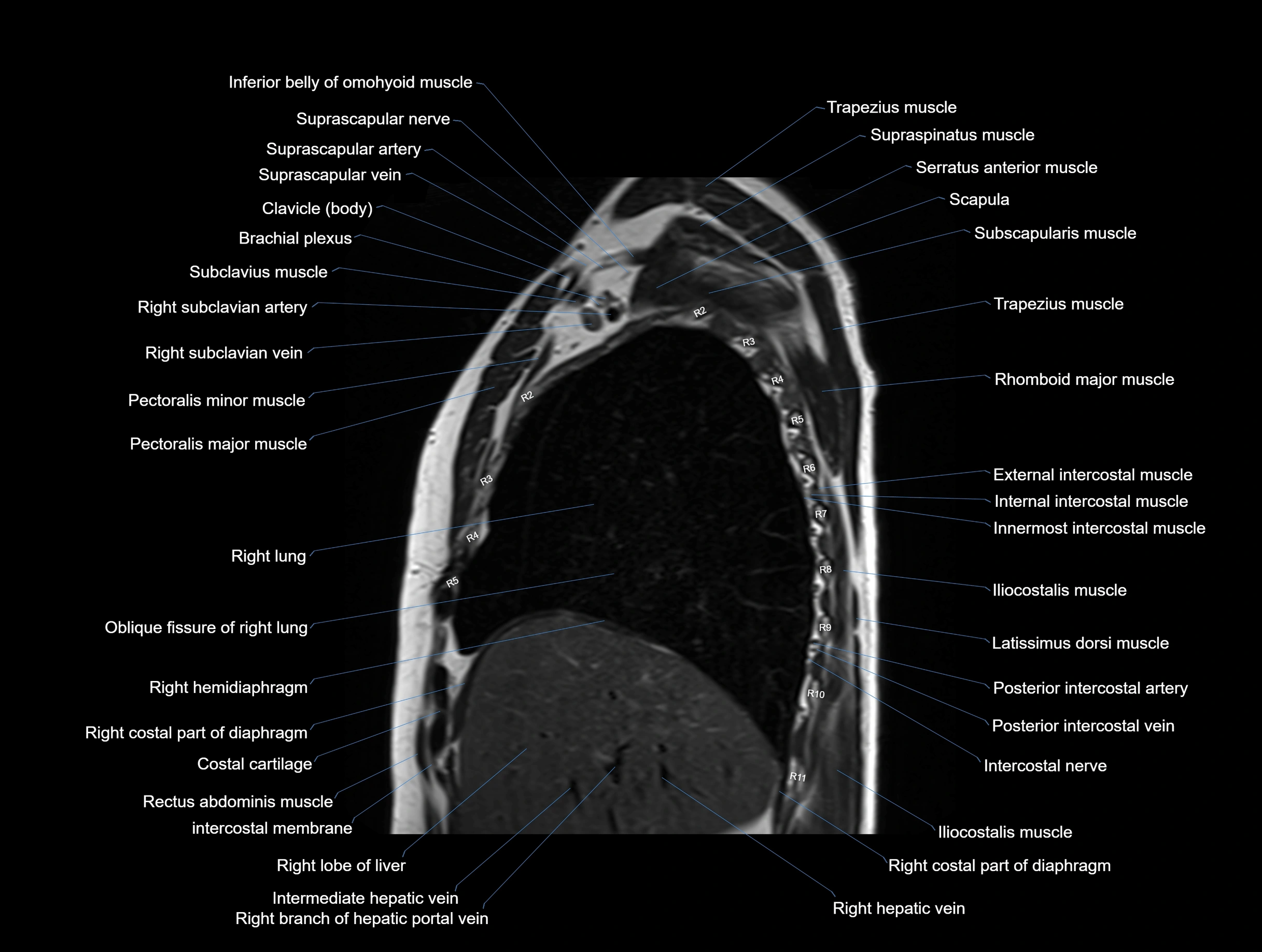
CT images

CT images