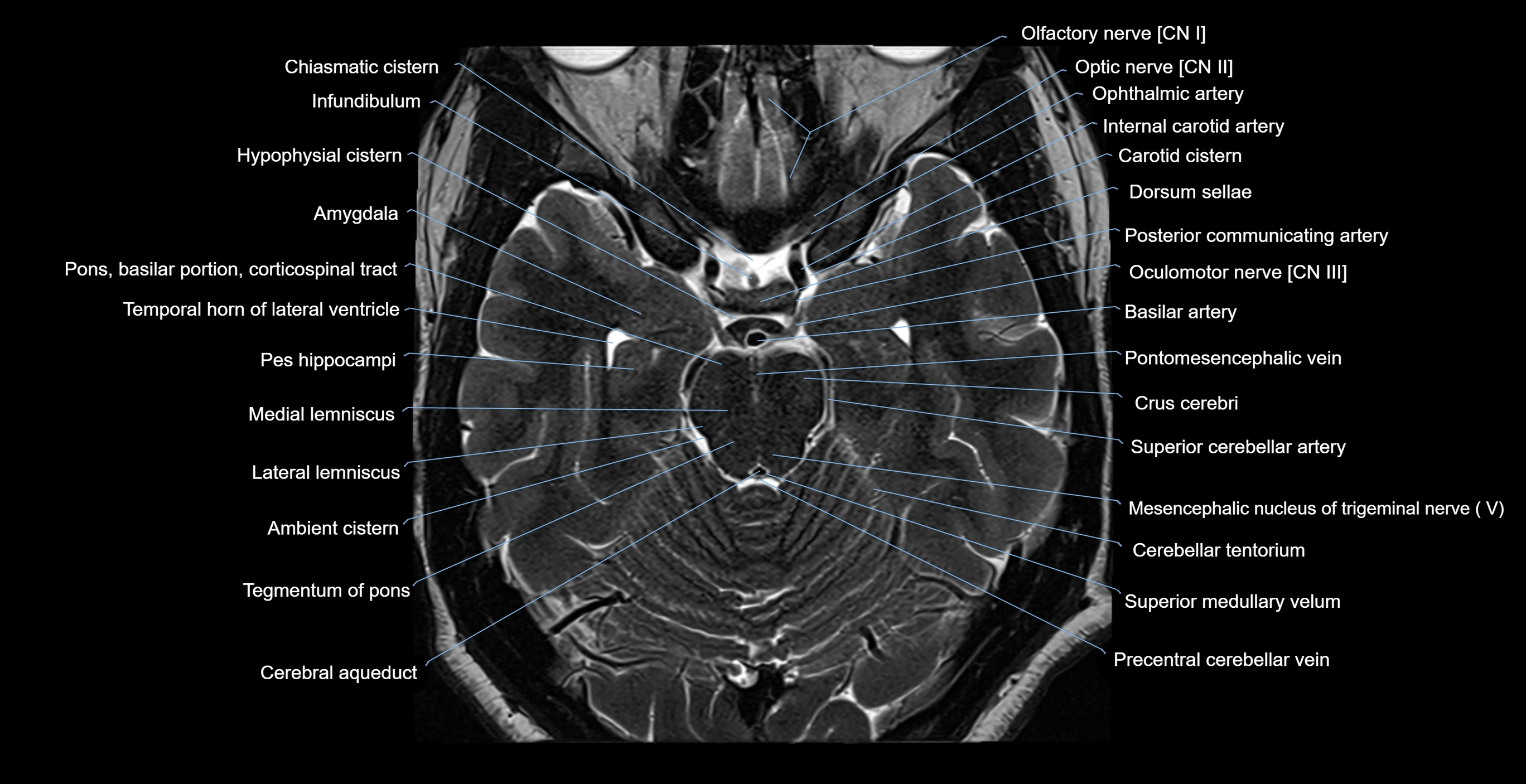
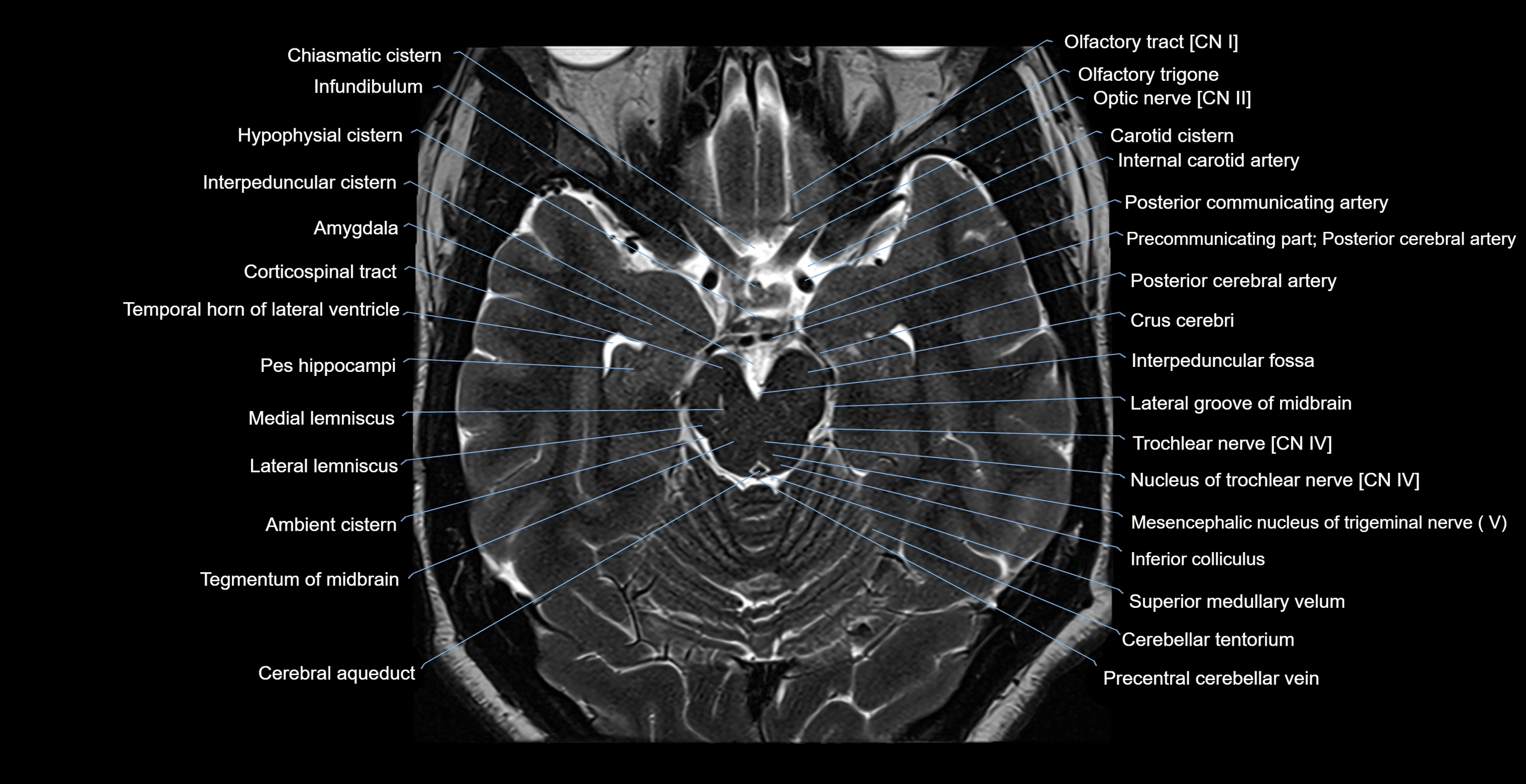
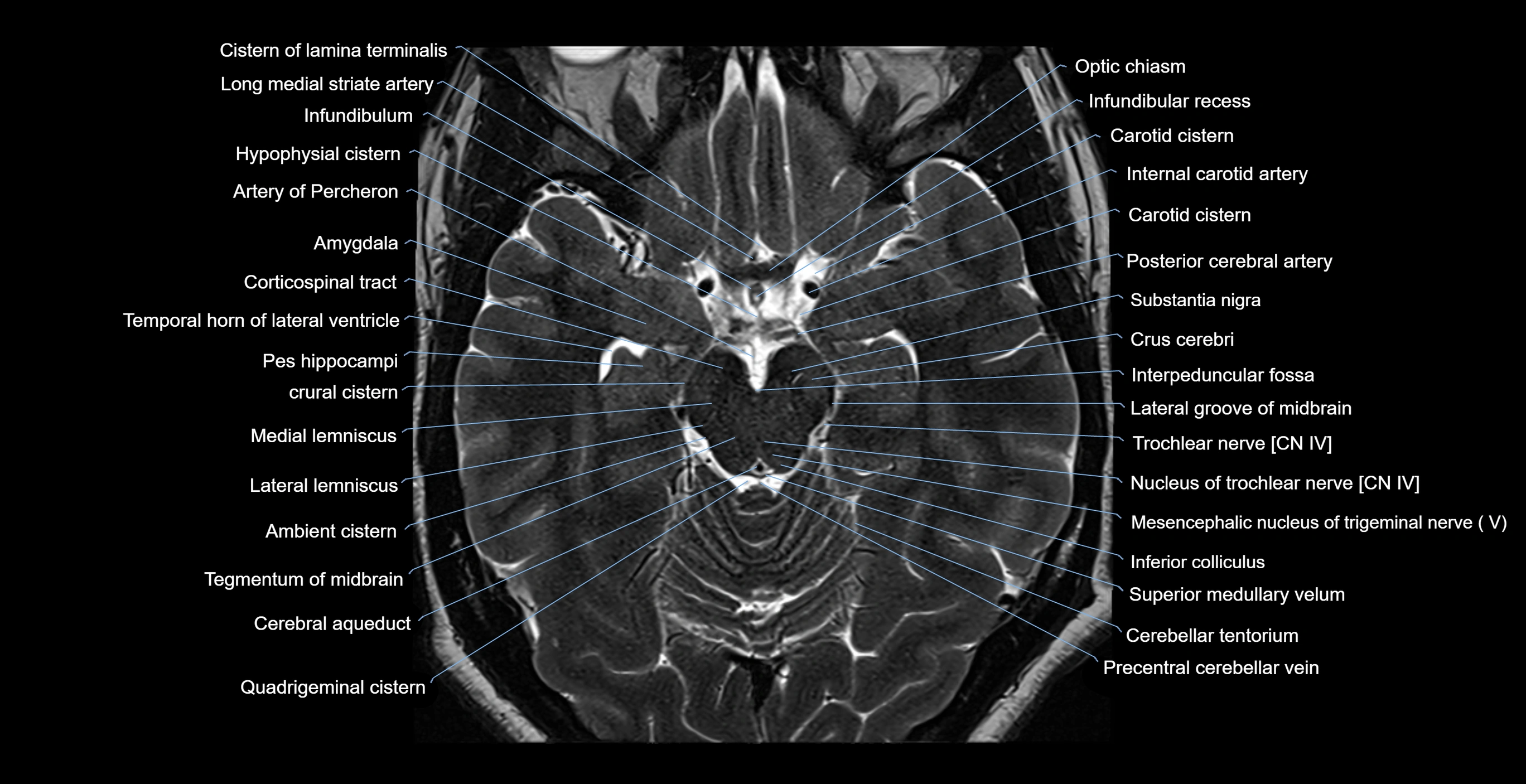
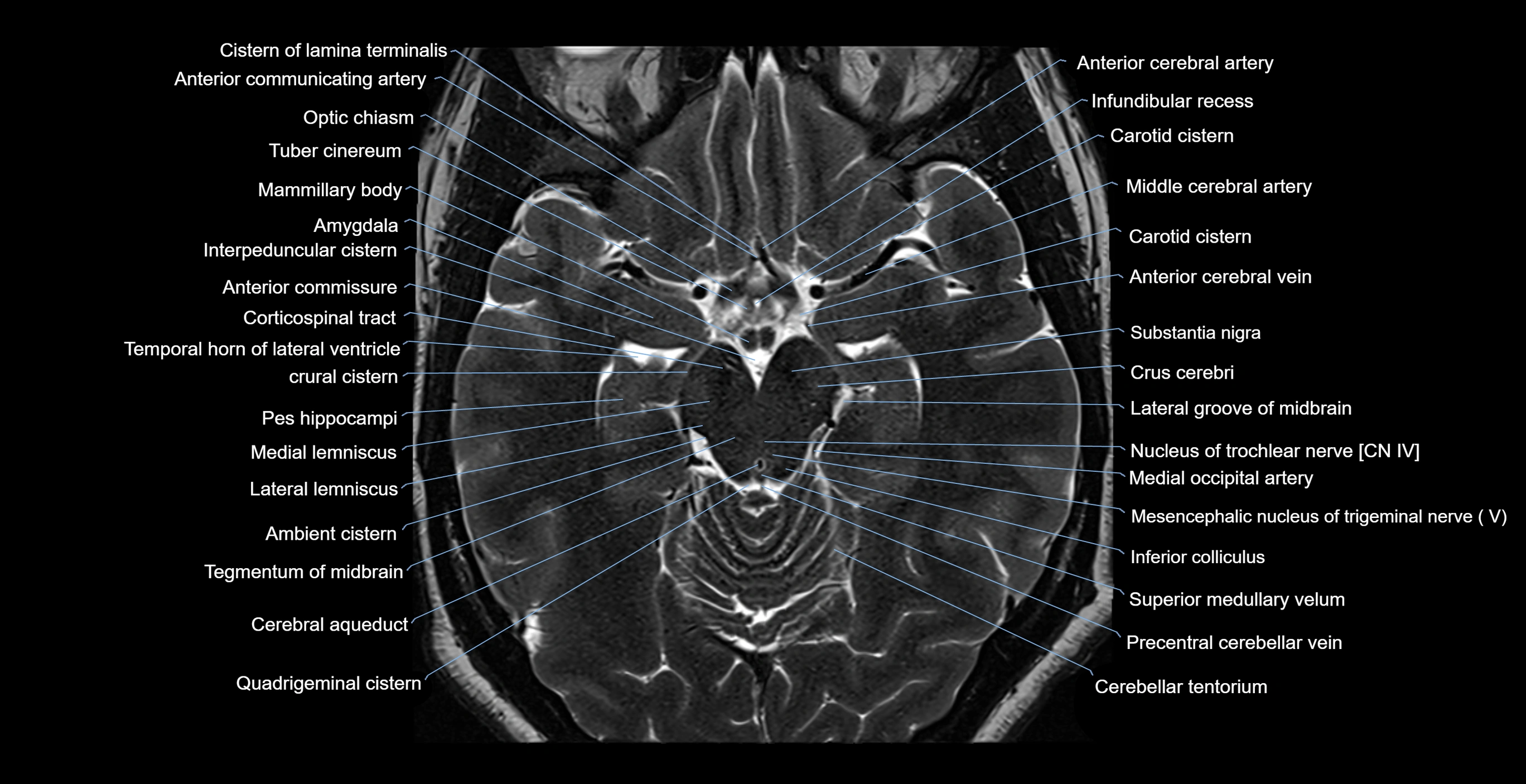
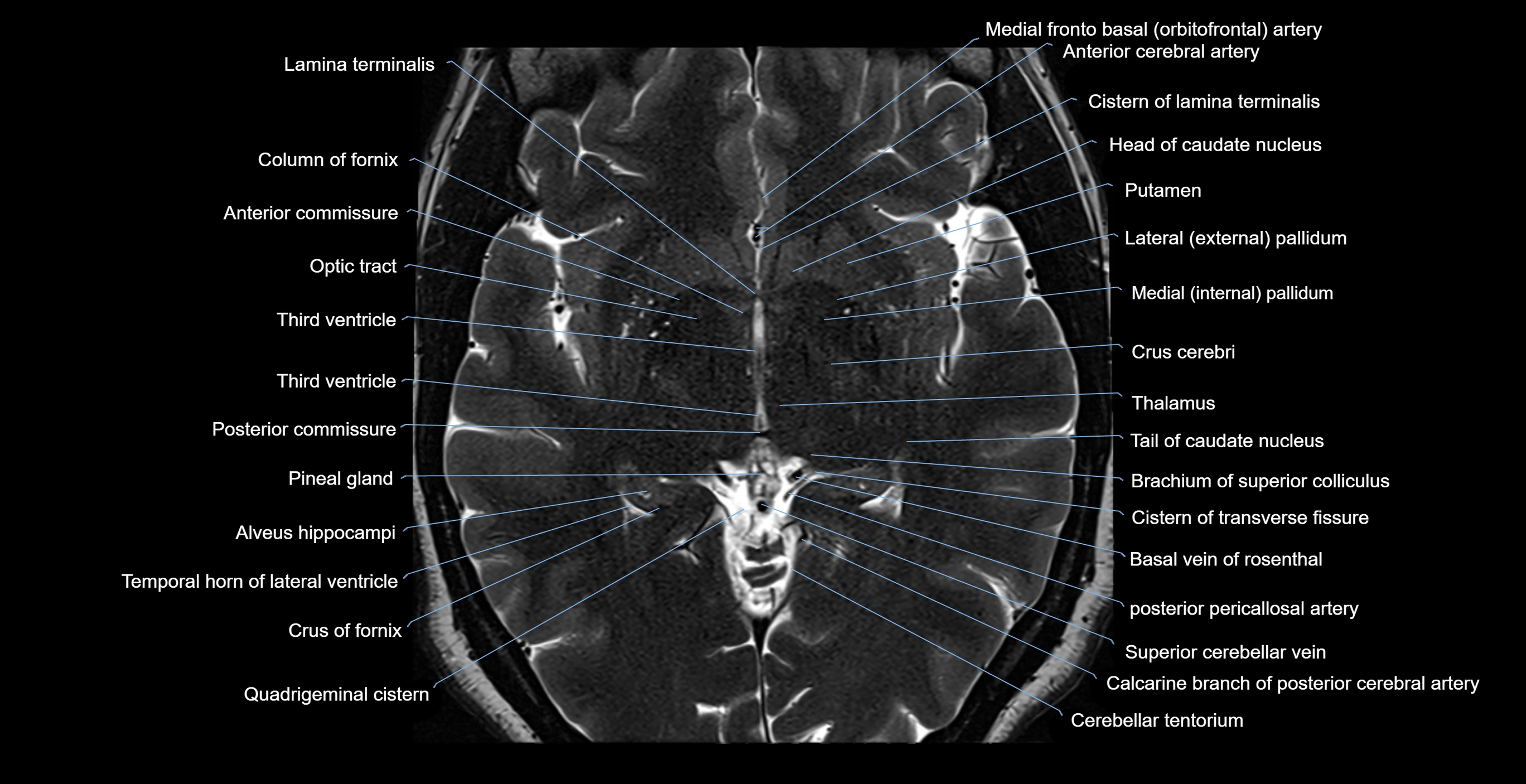
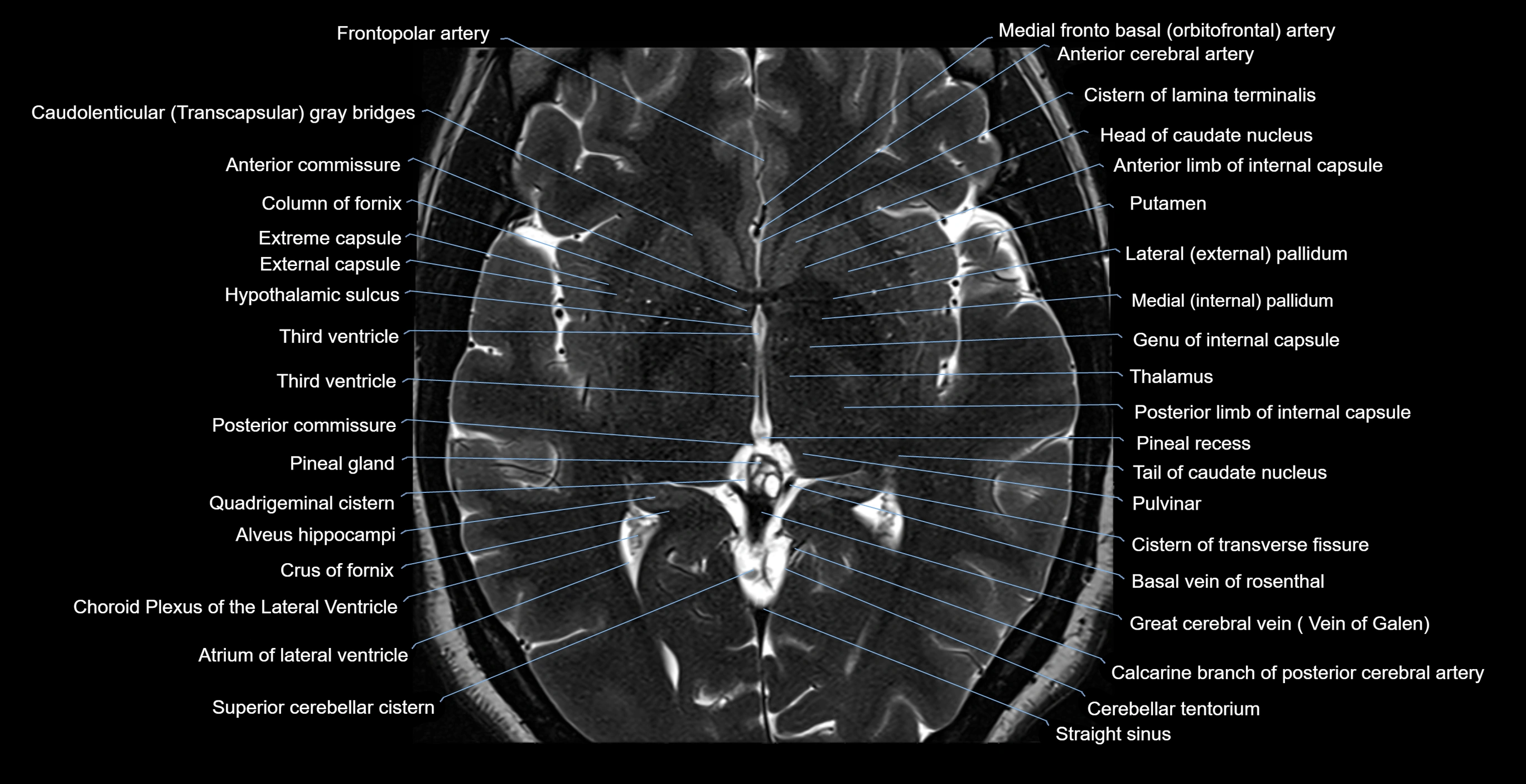
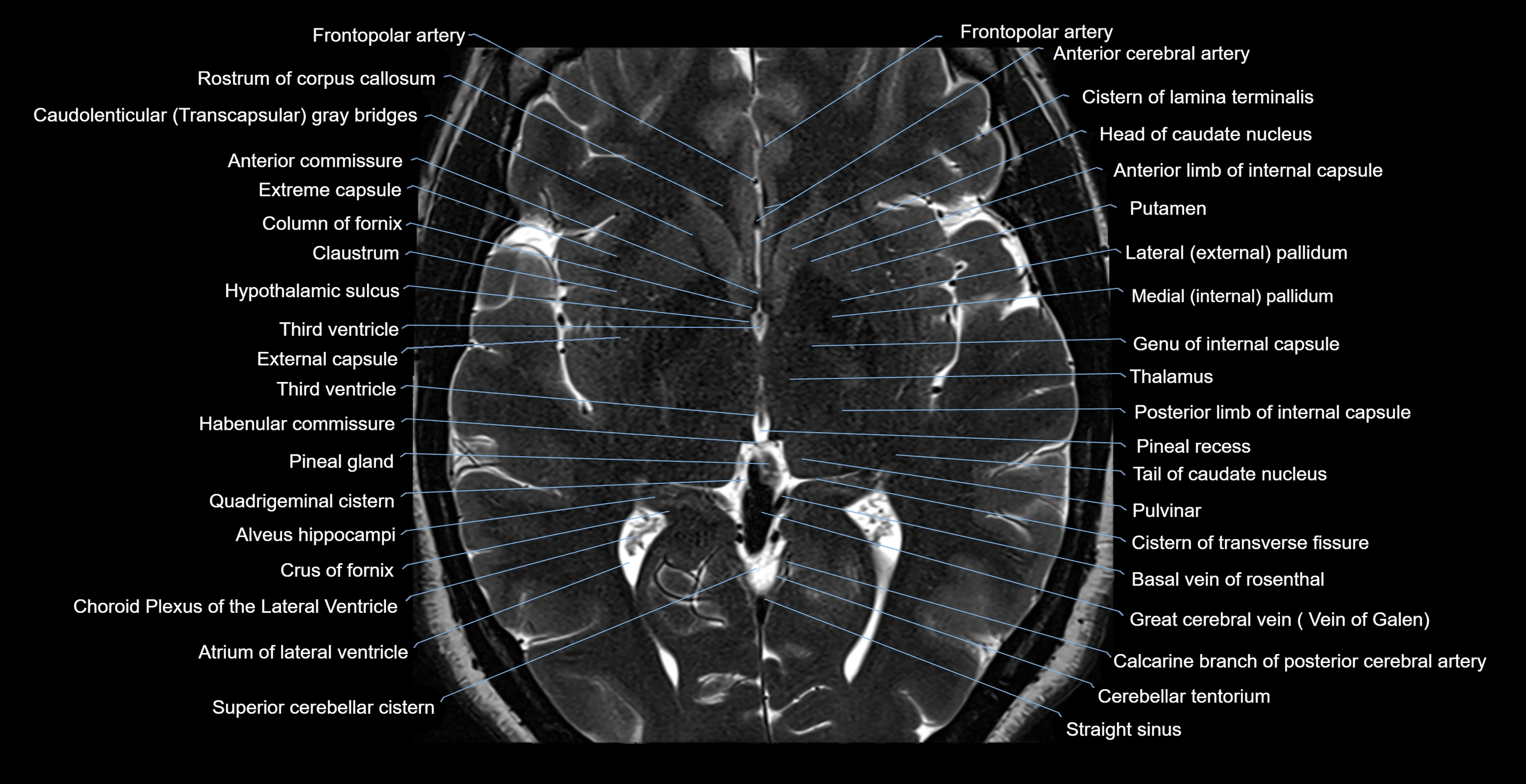
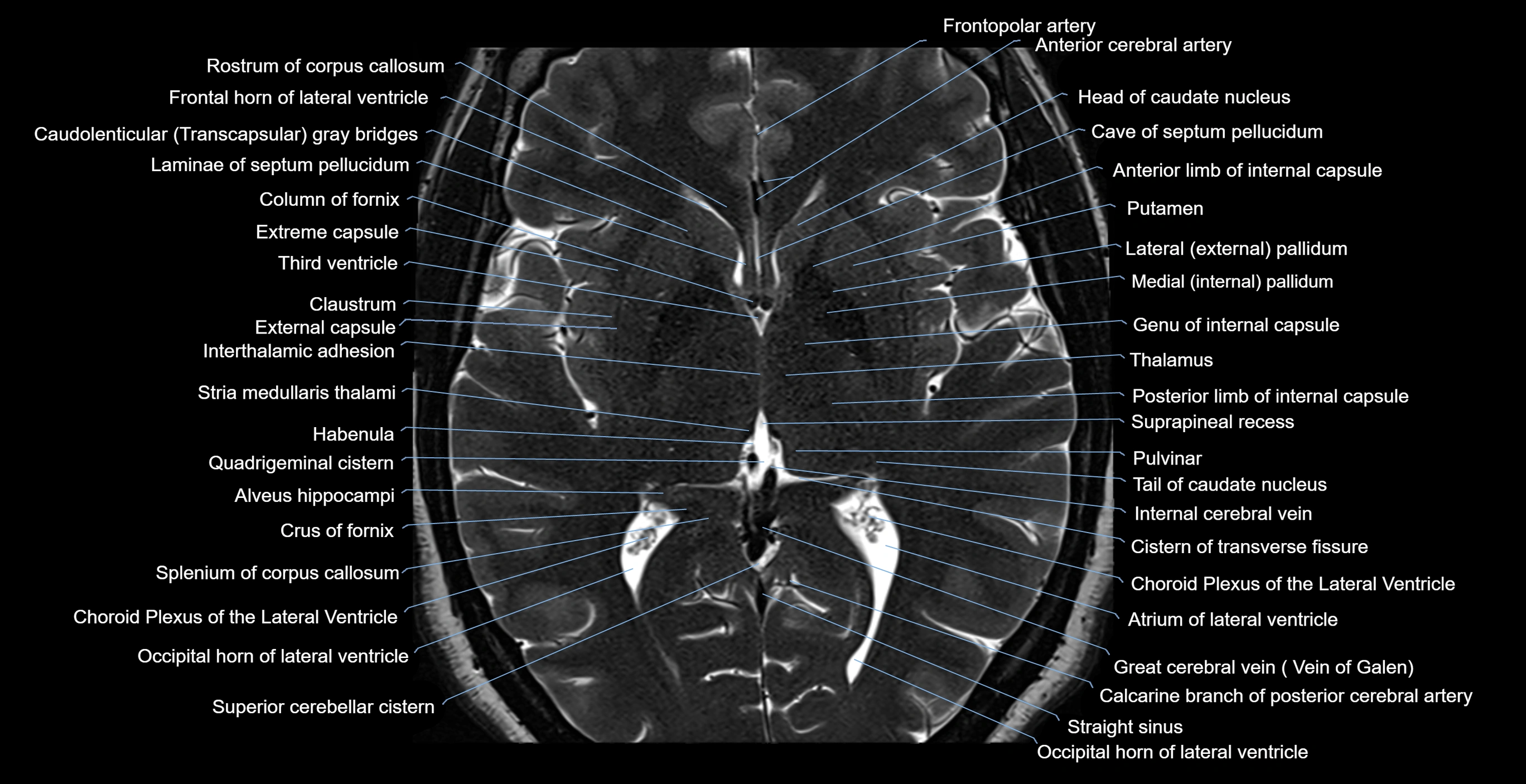
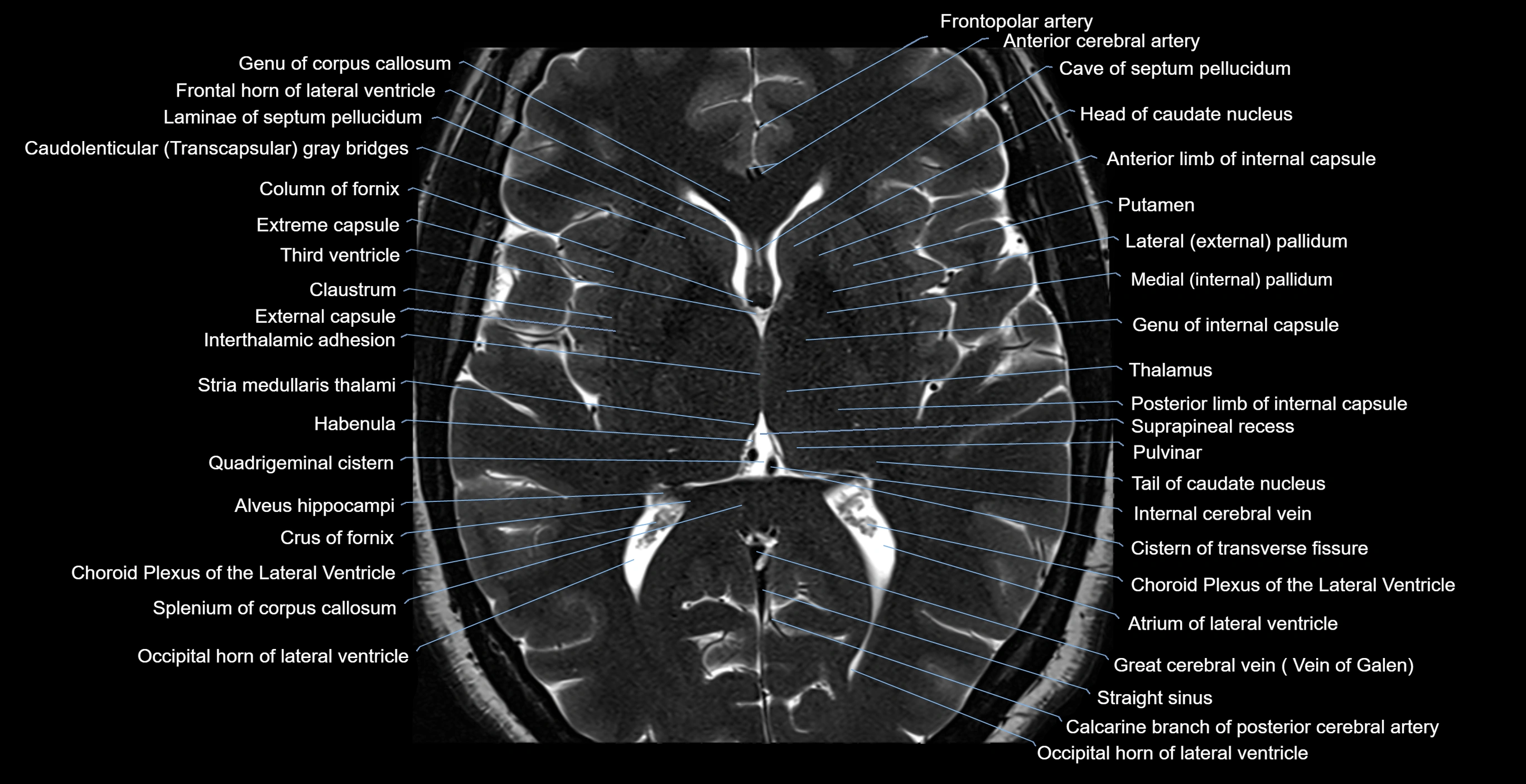
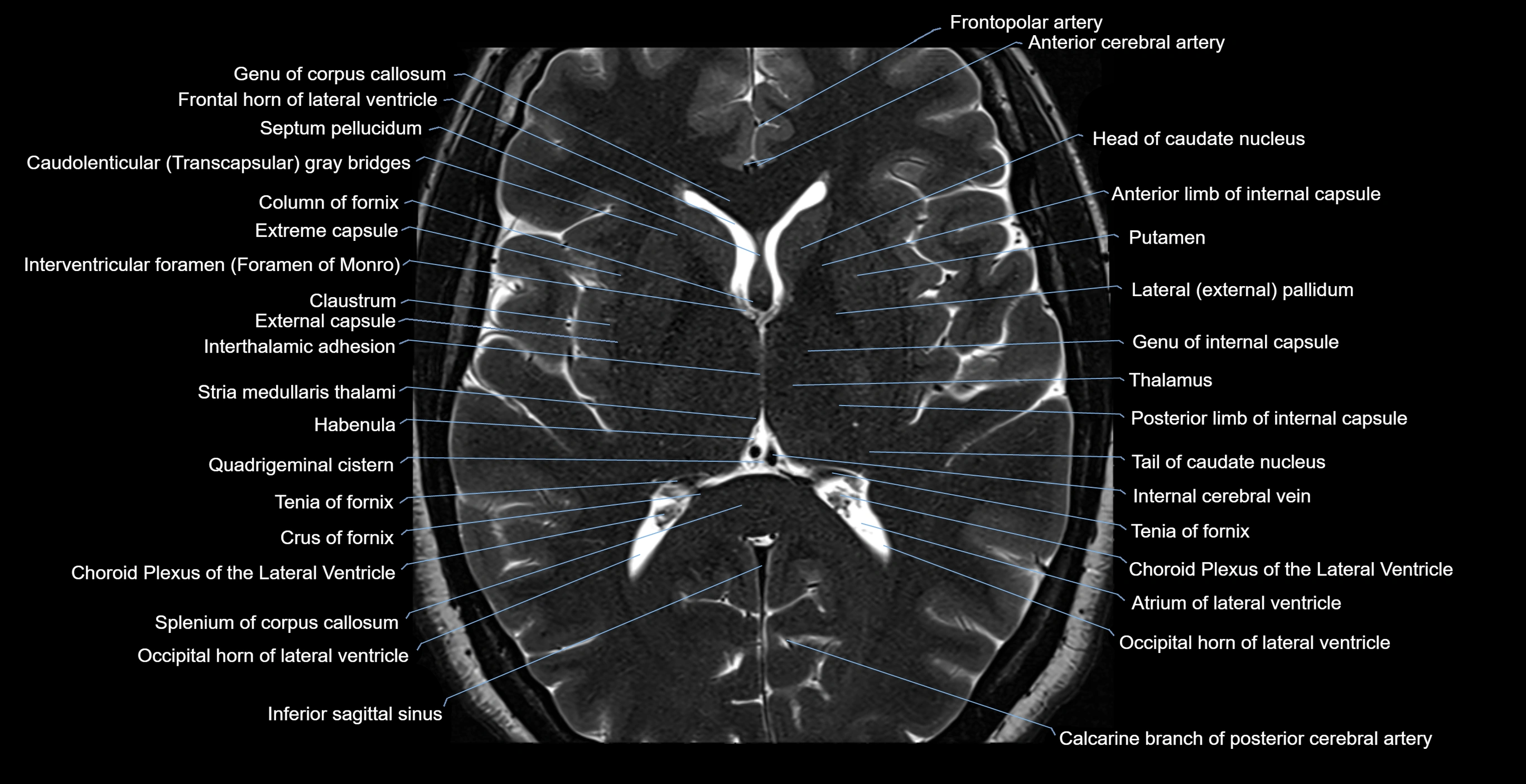
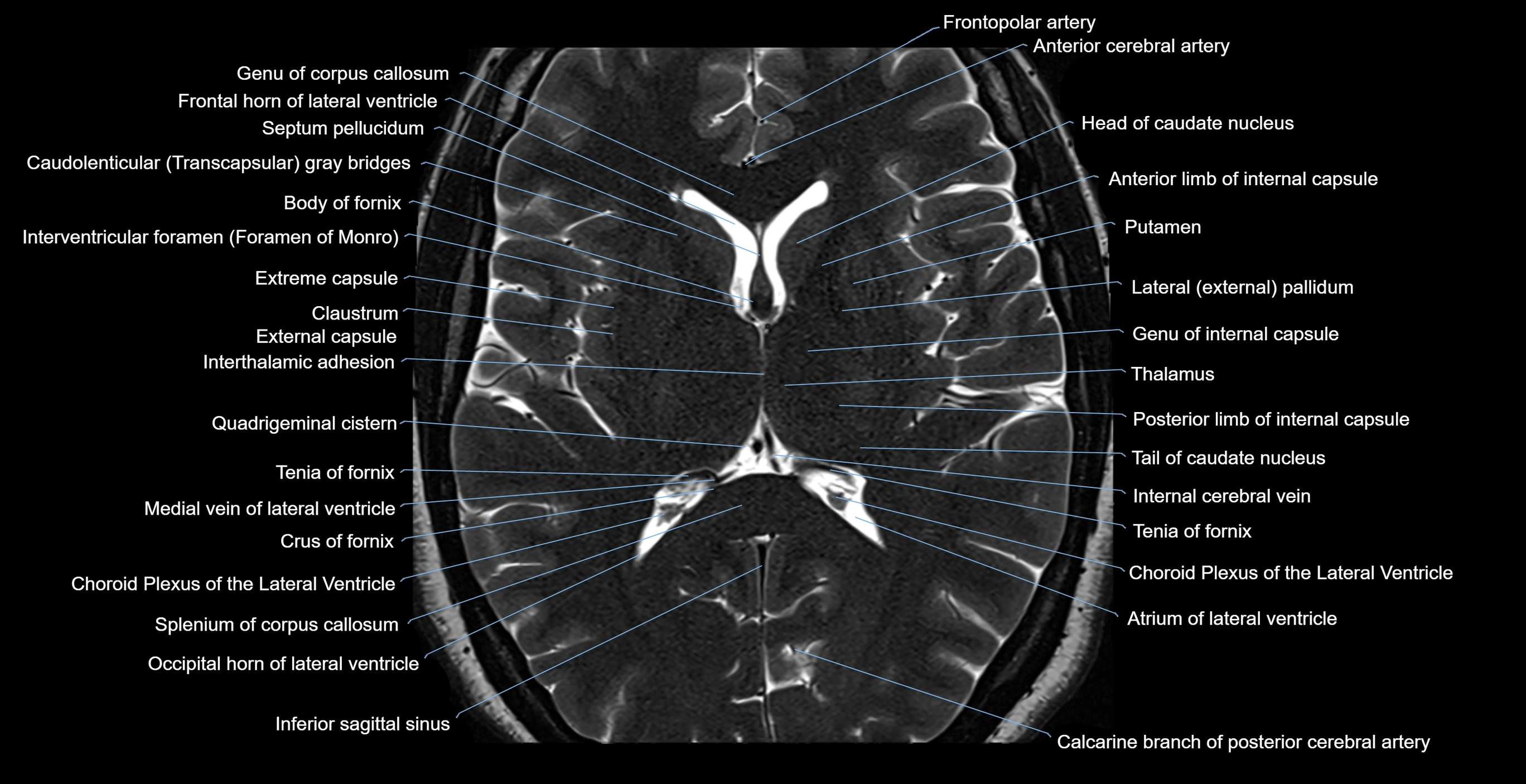
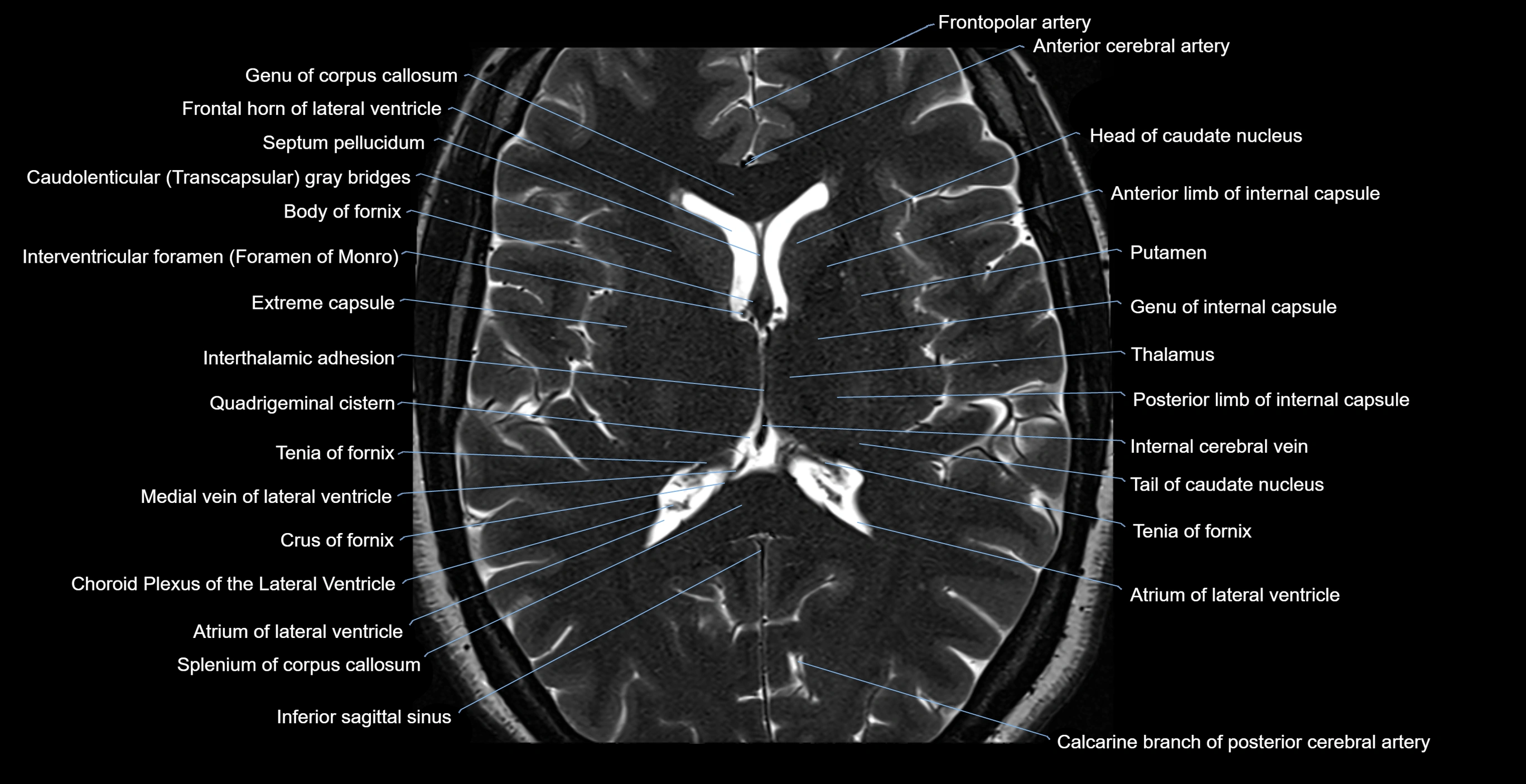
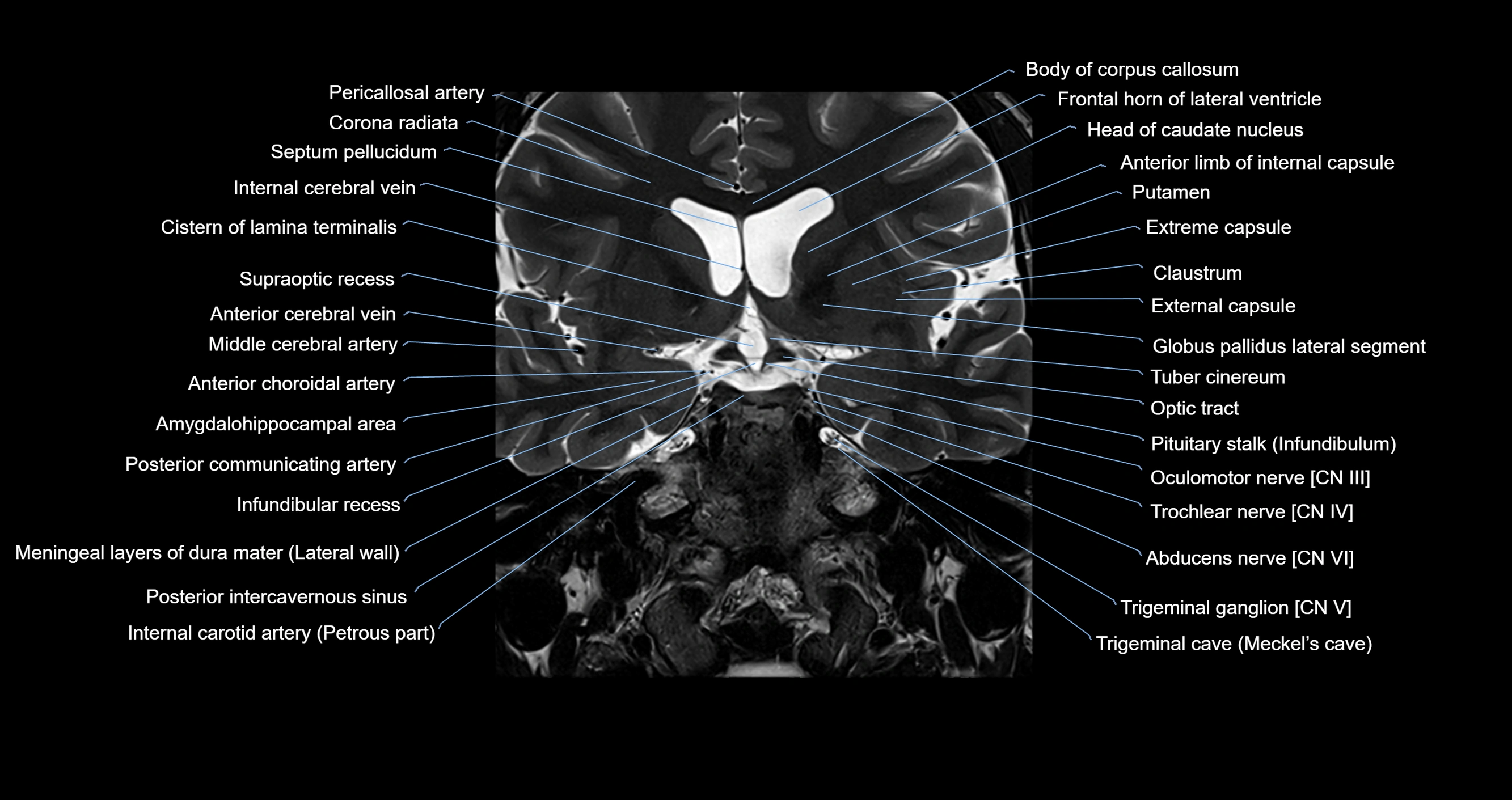
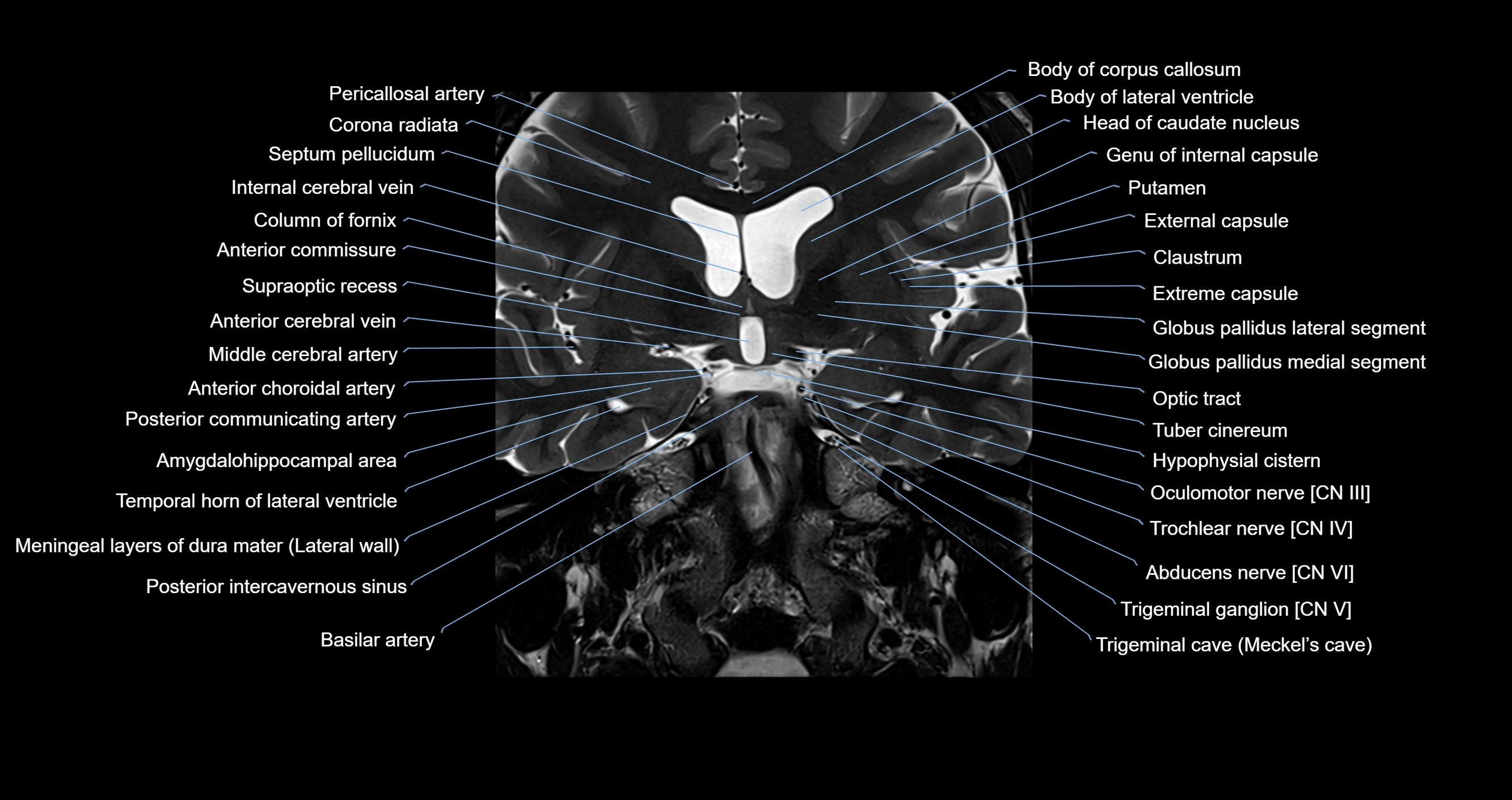
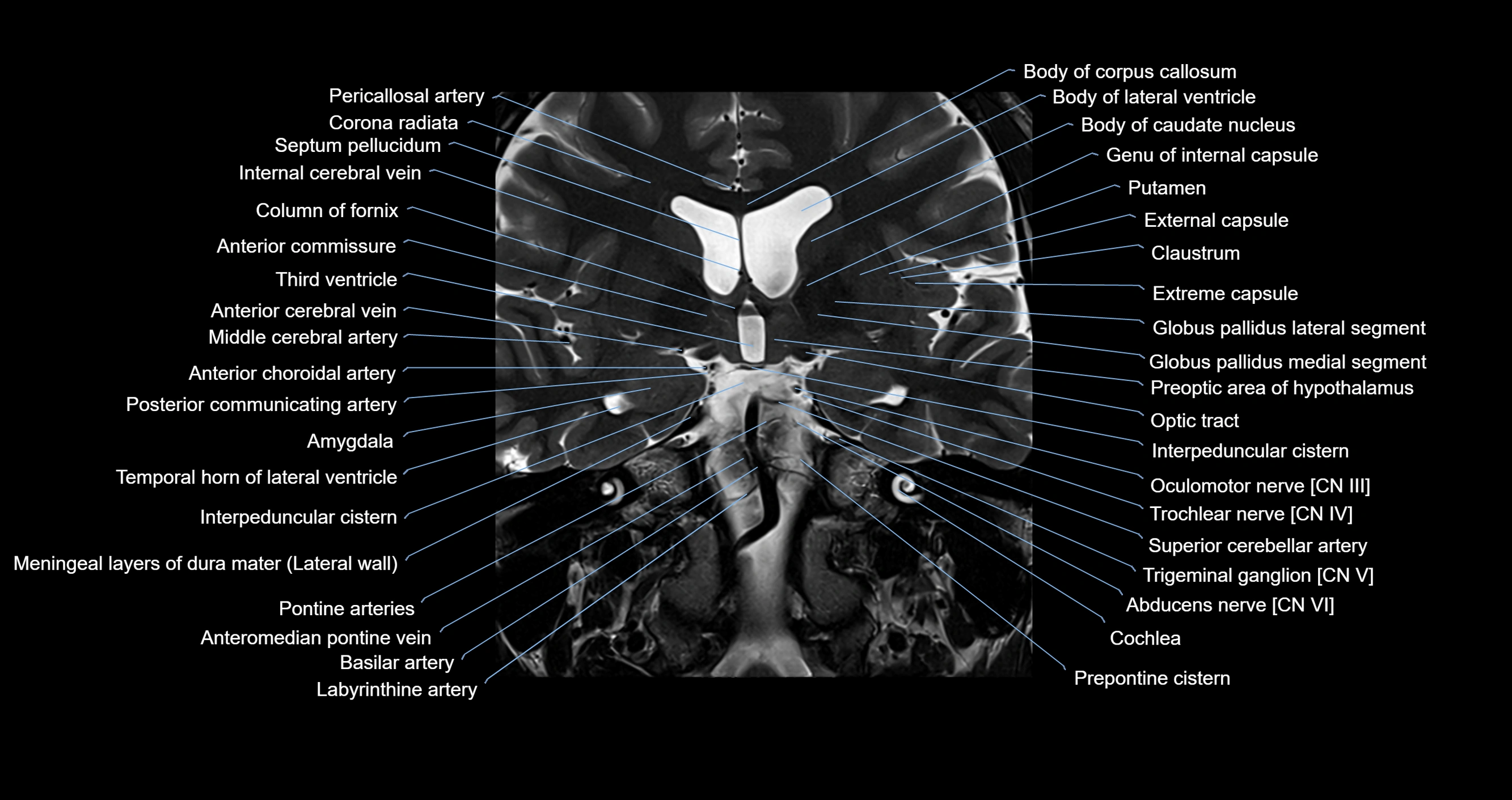
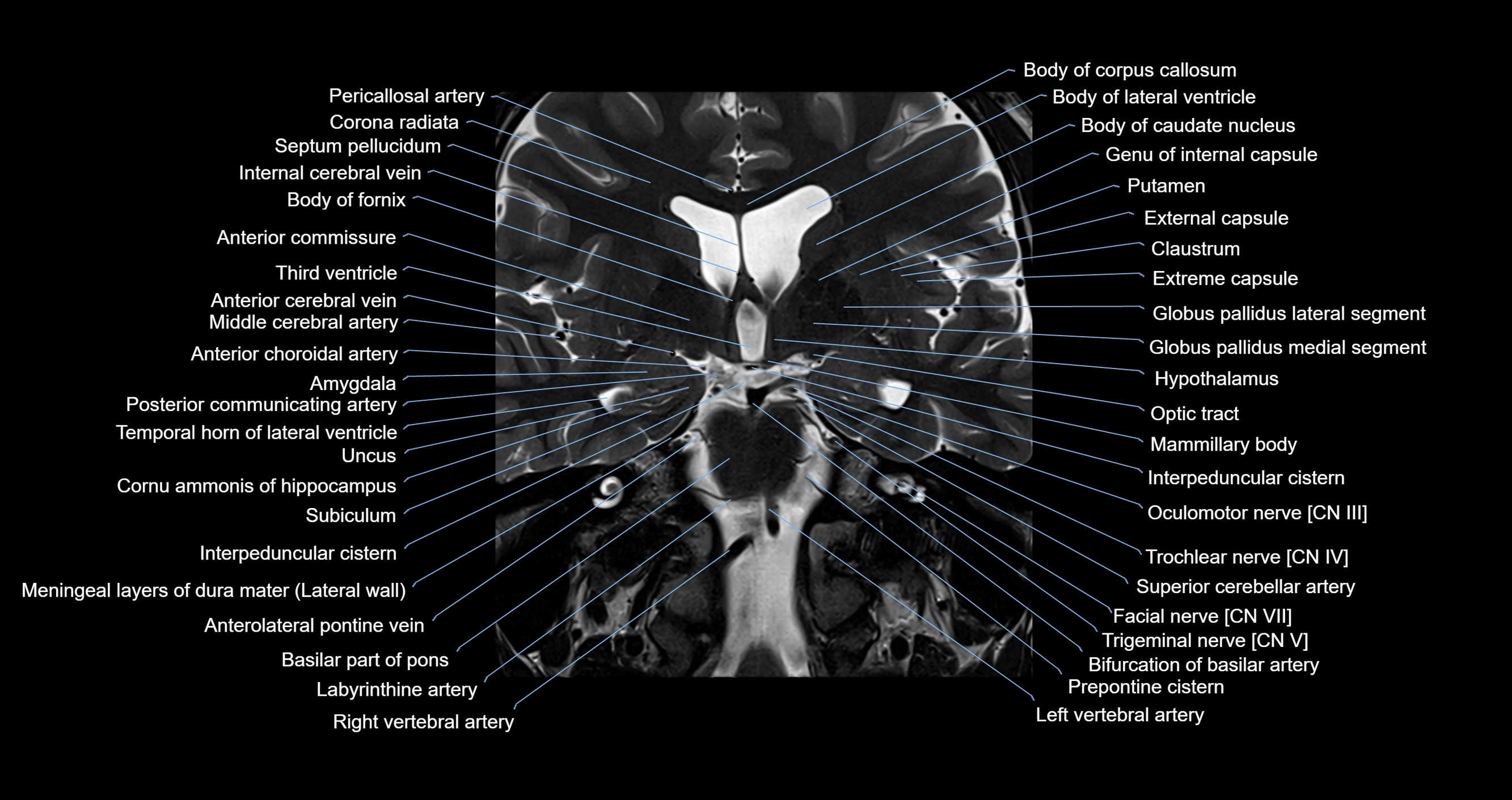
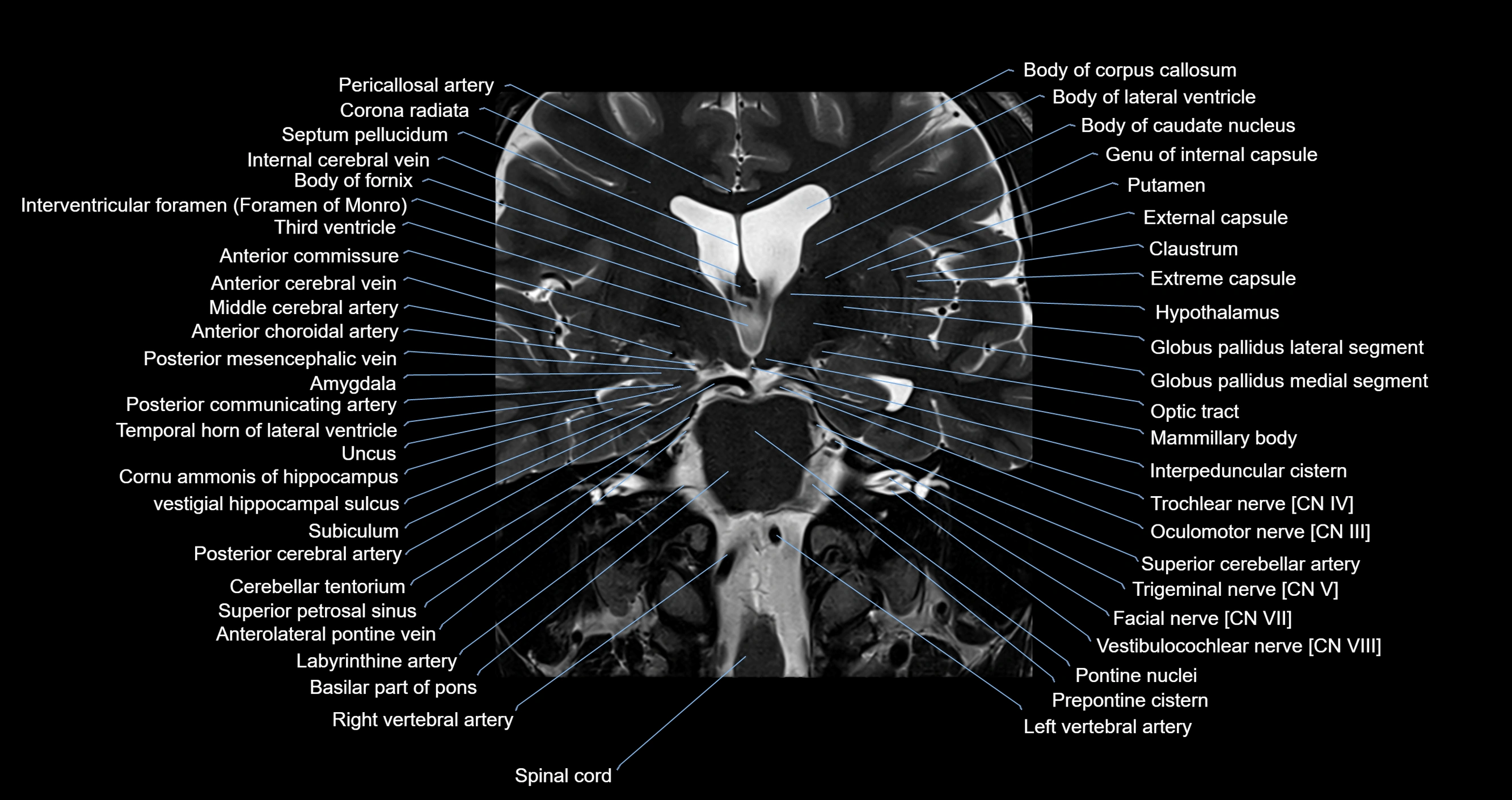
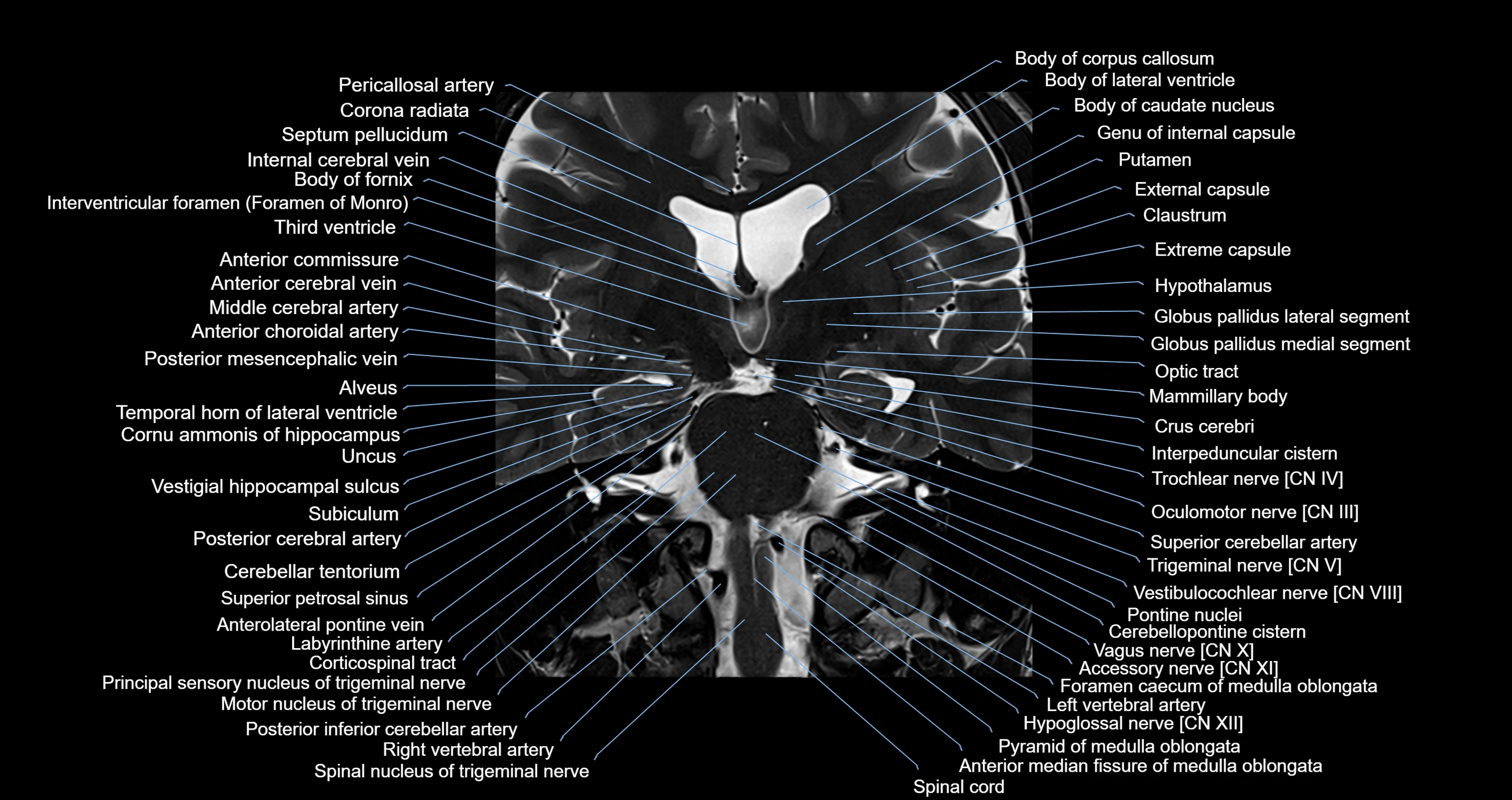
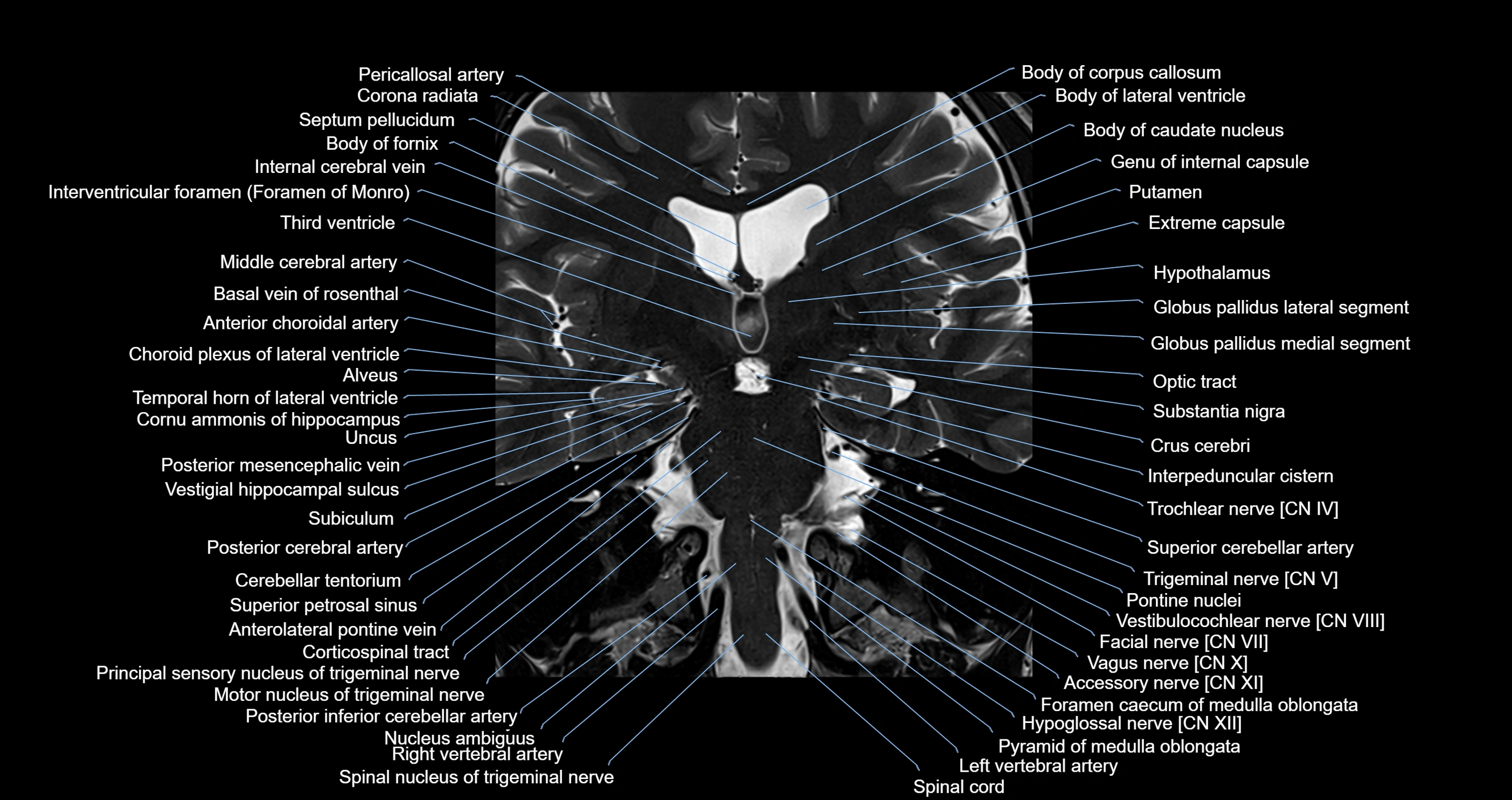
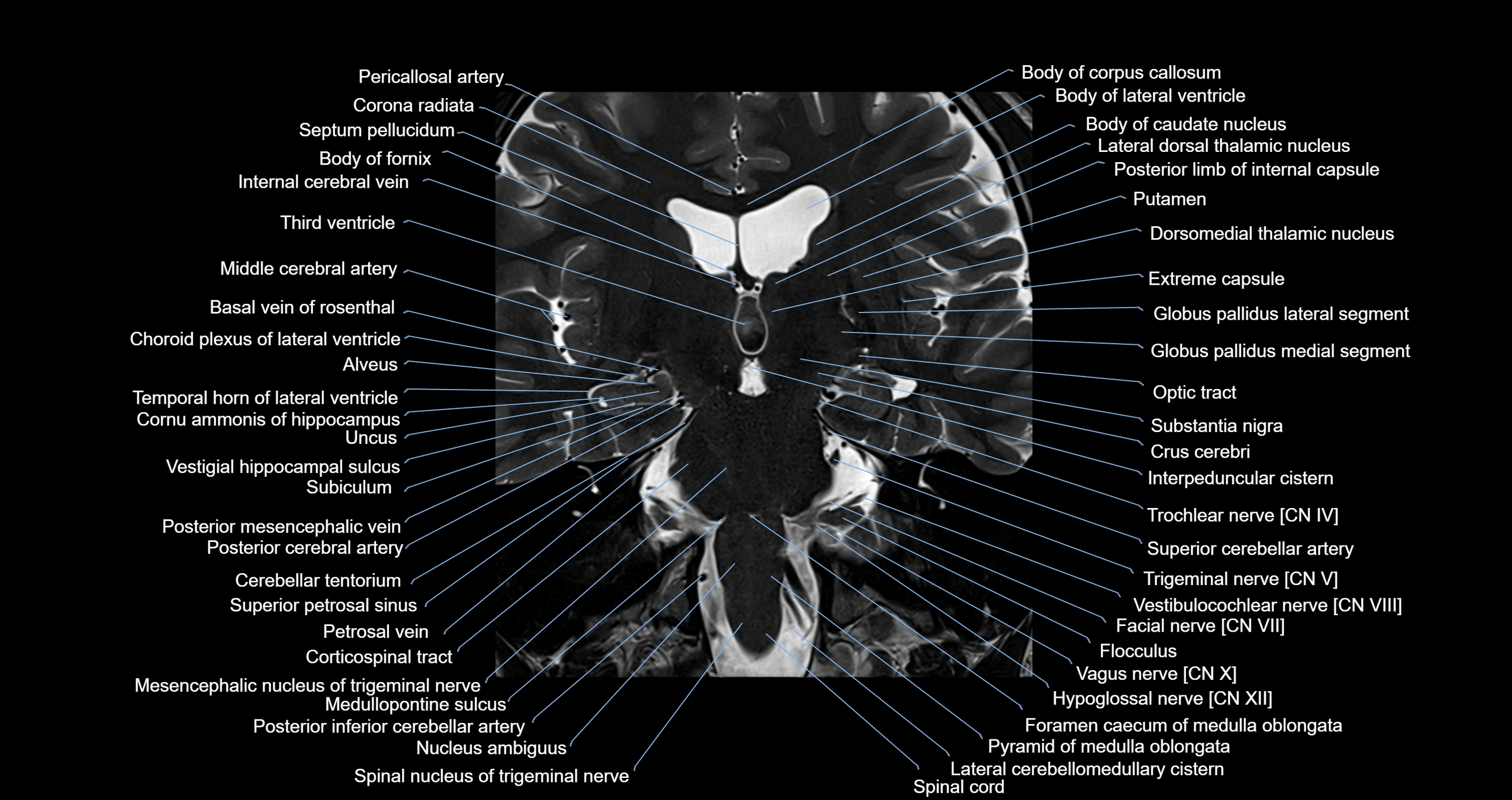
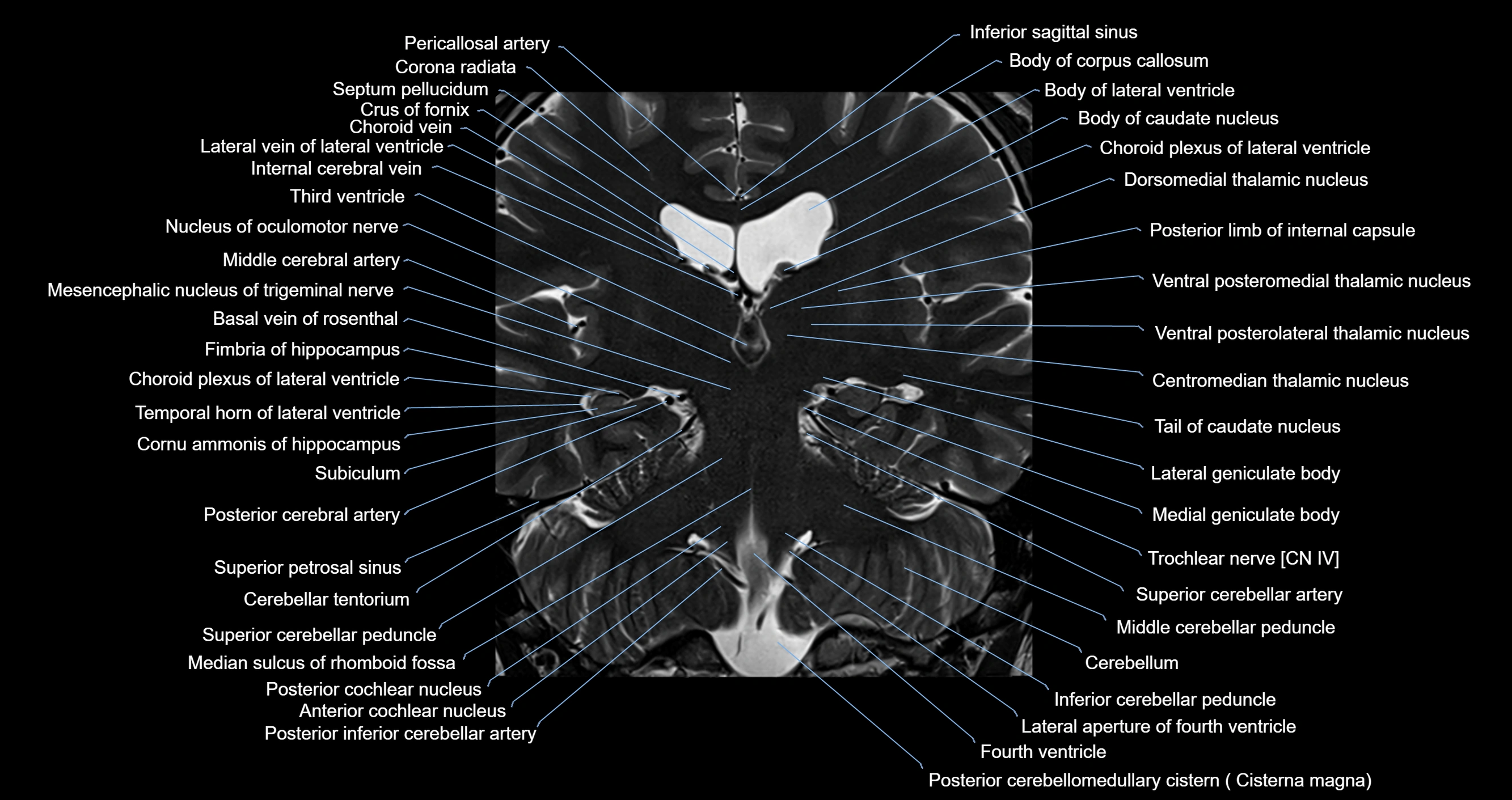
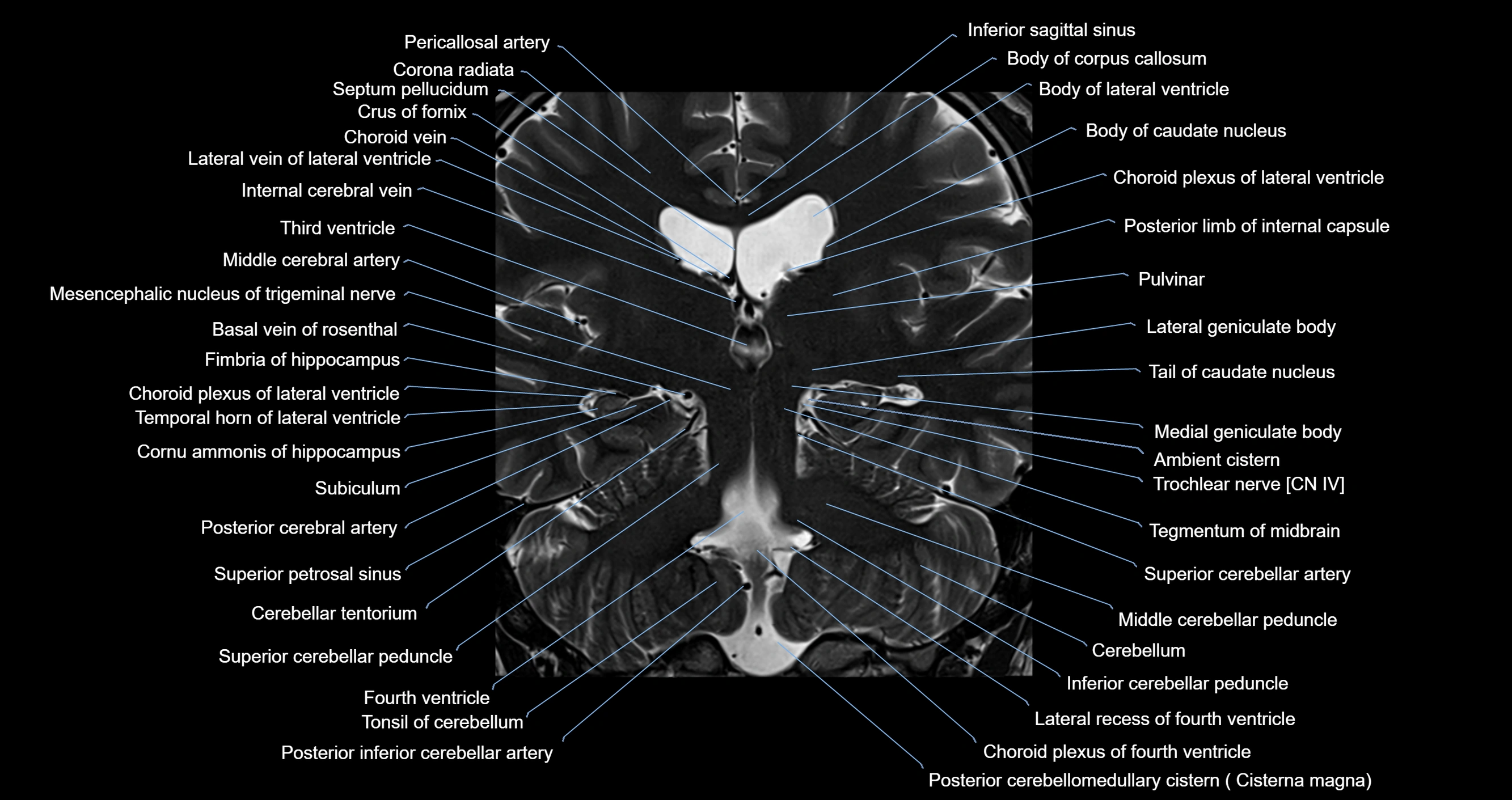
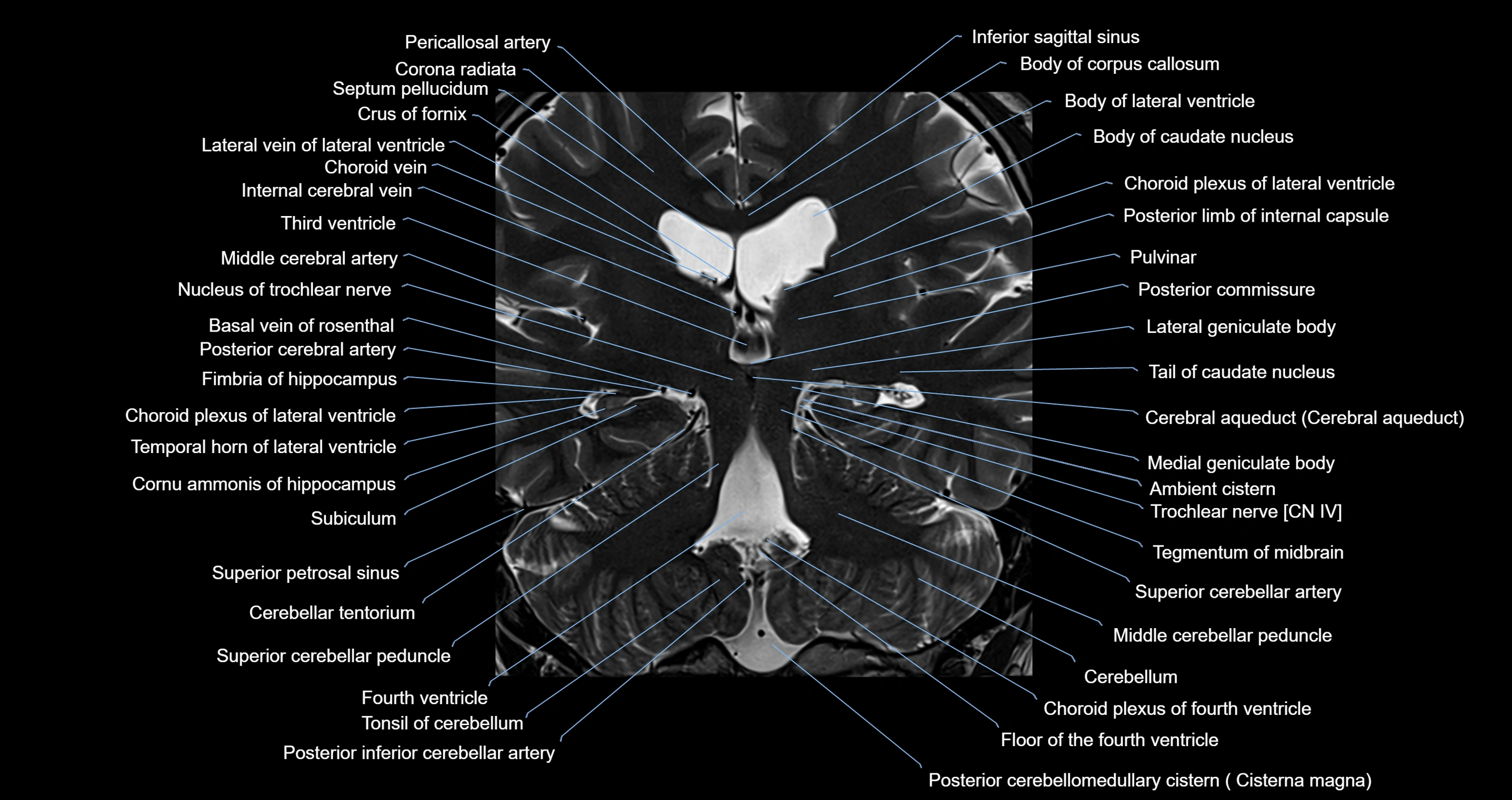
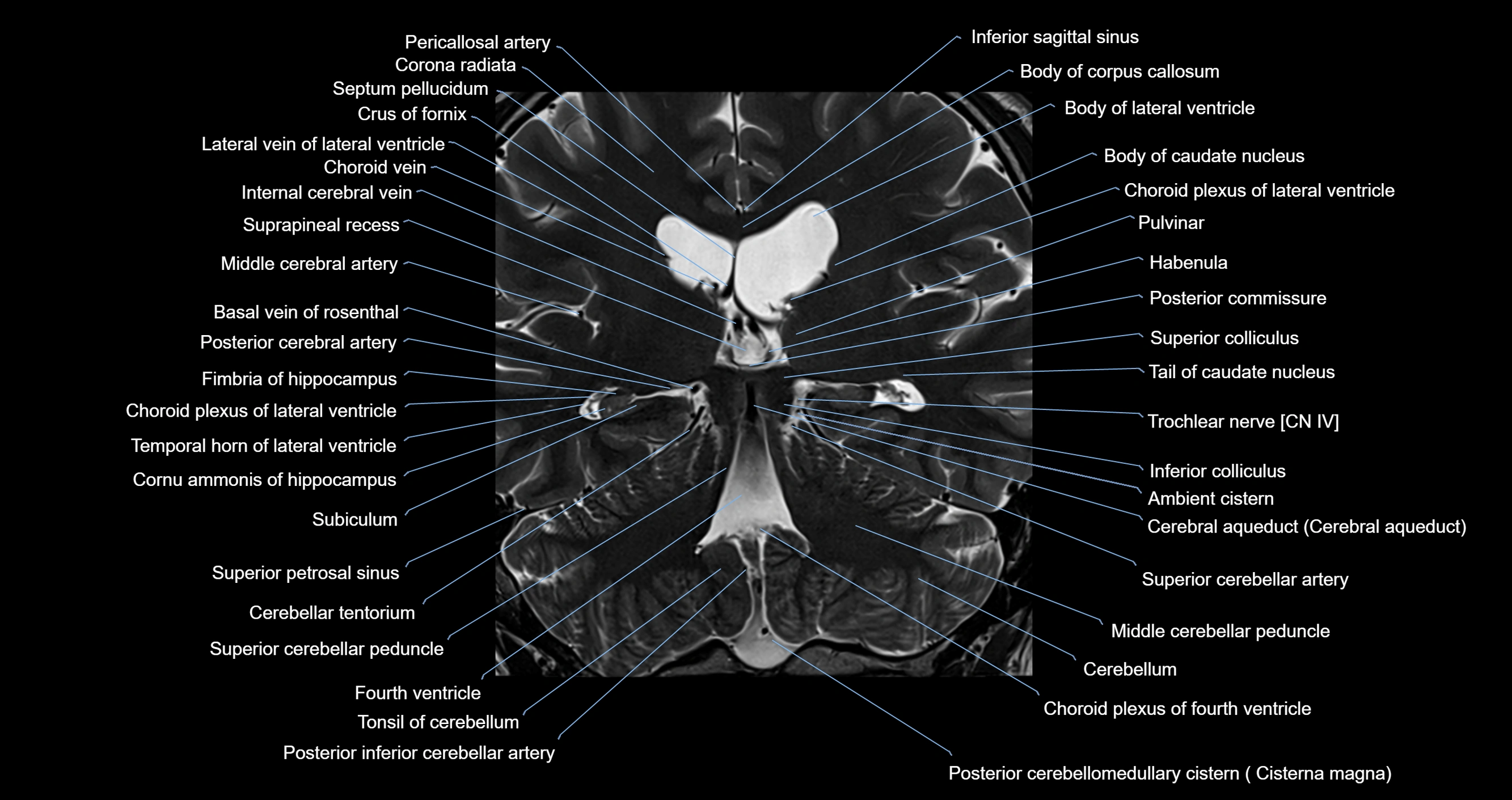
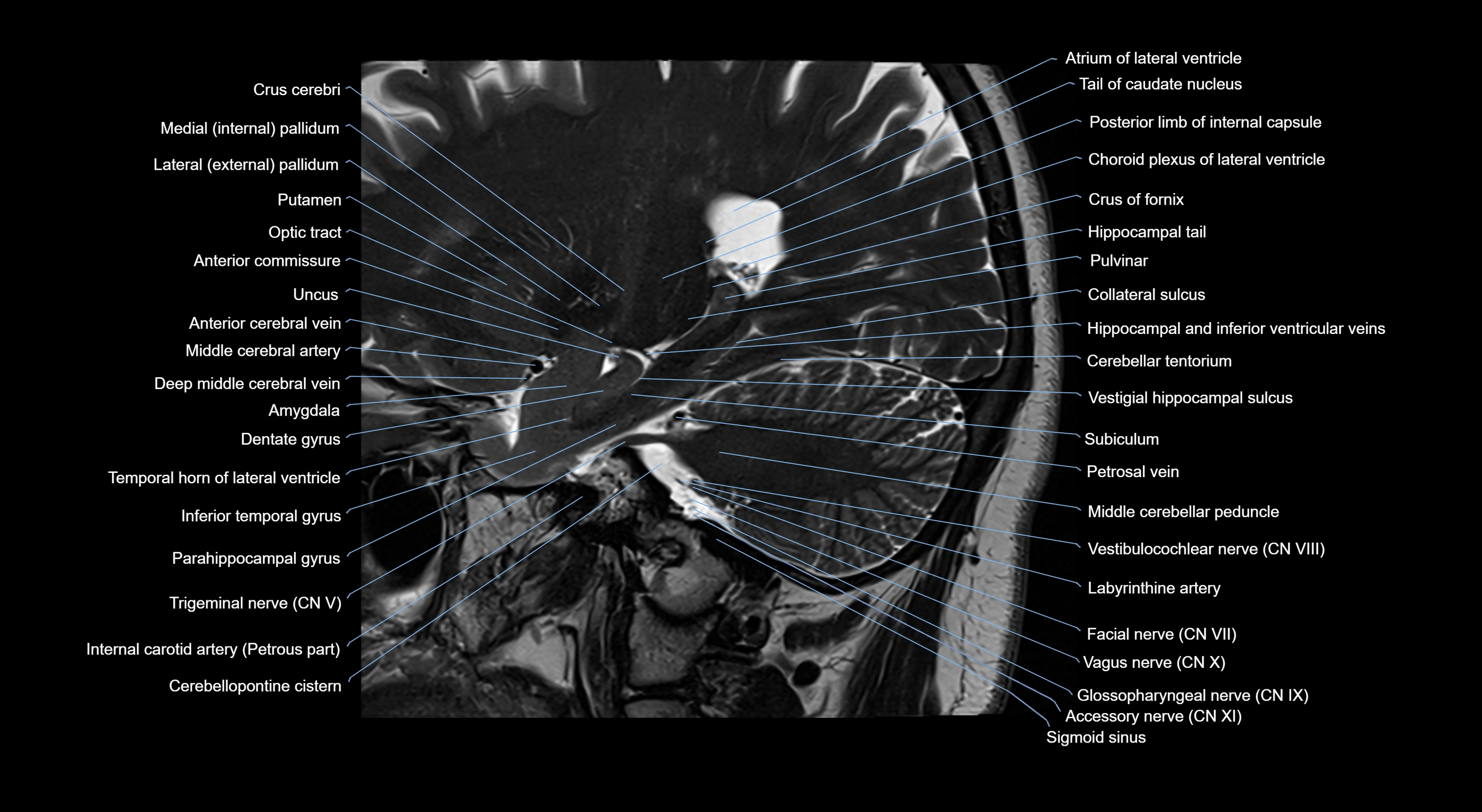
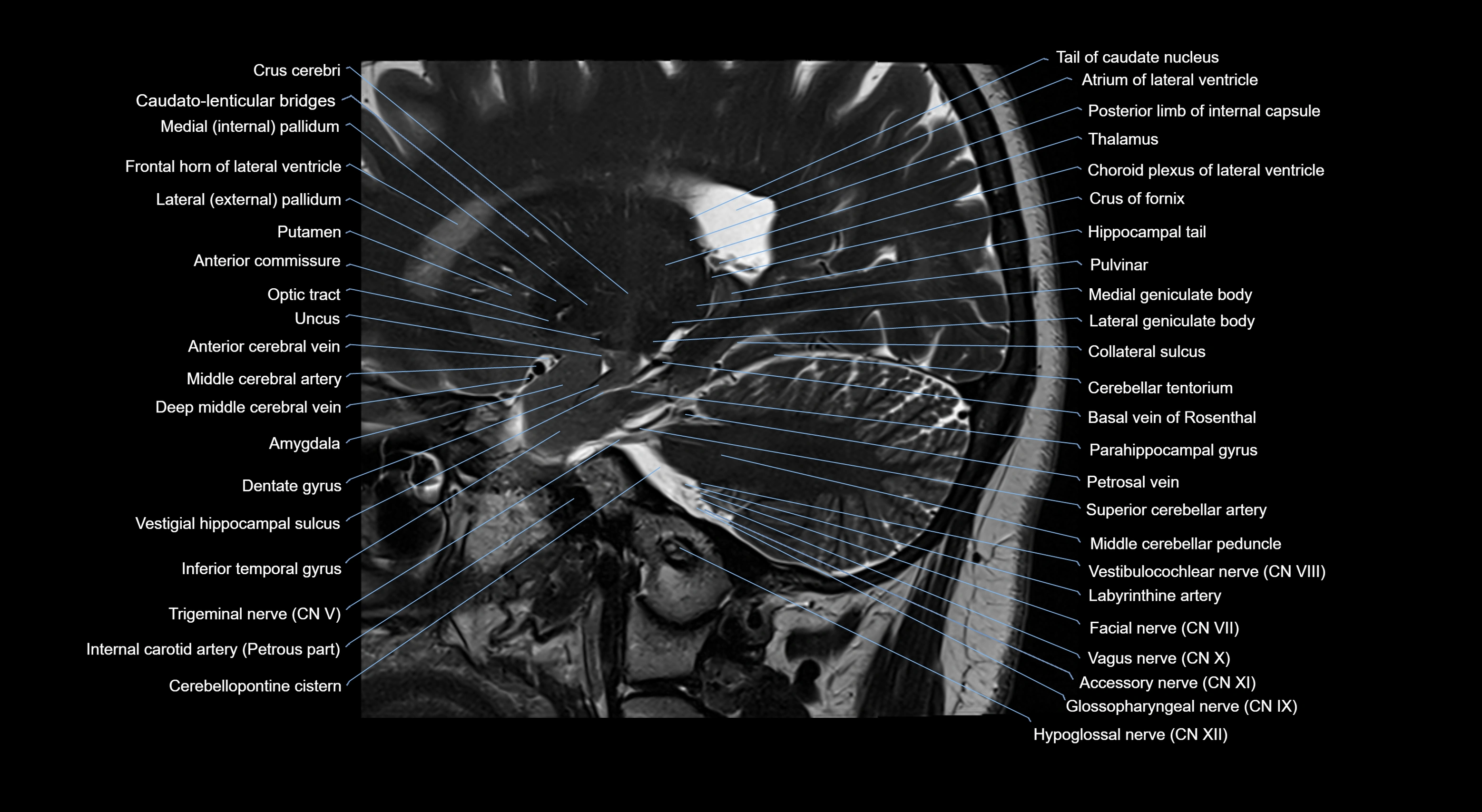
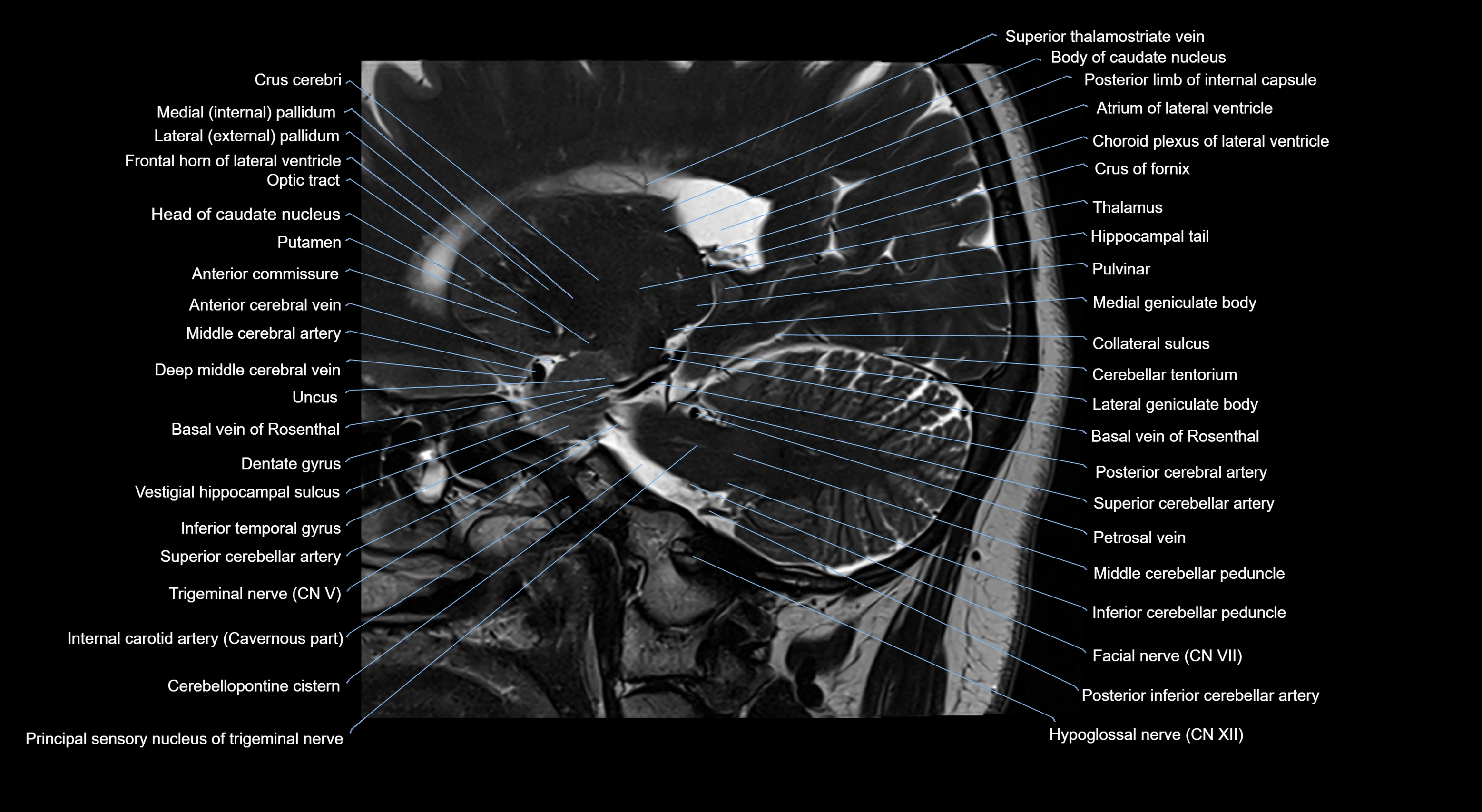
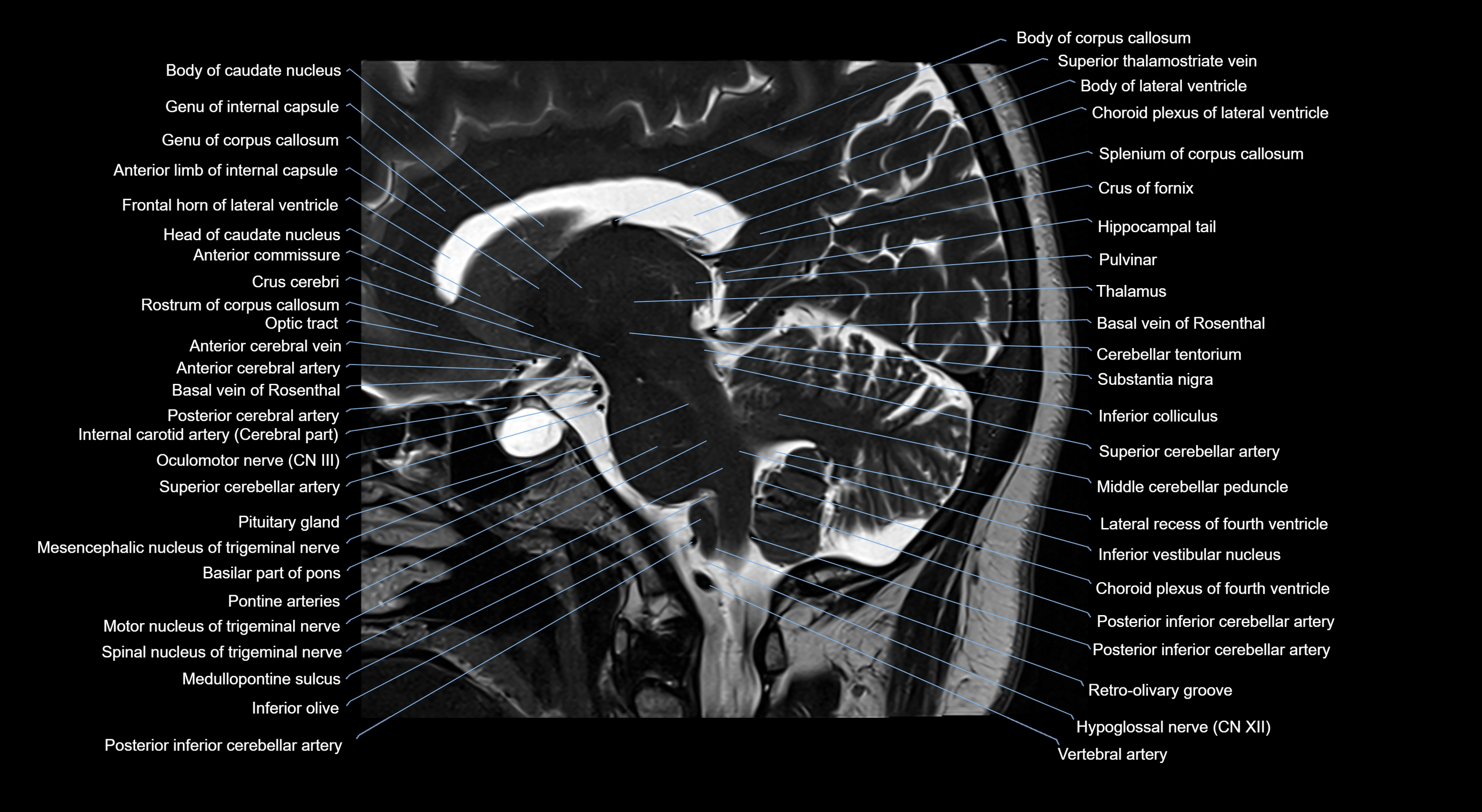
Topic
- Abducens nerve (Cranial nerve VI)
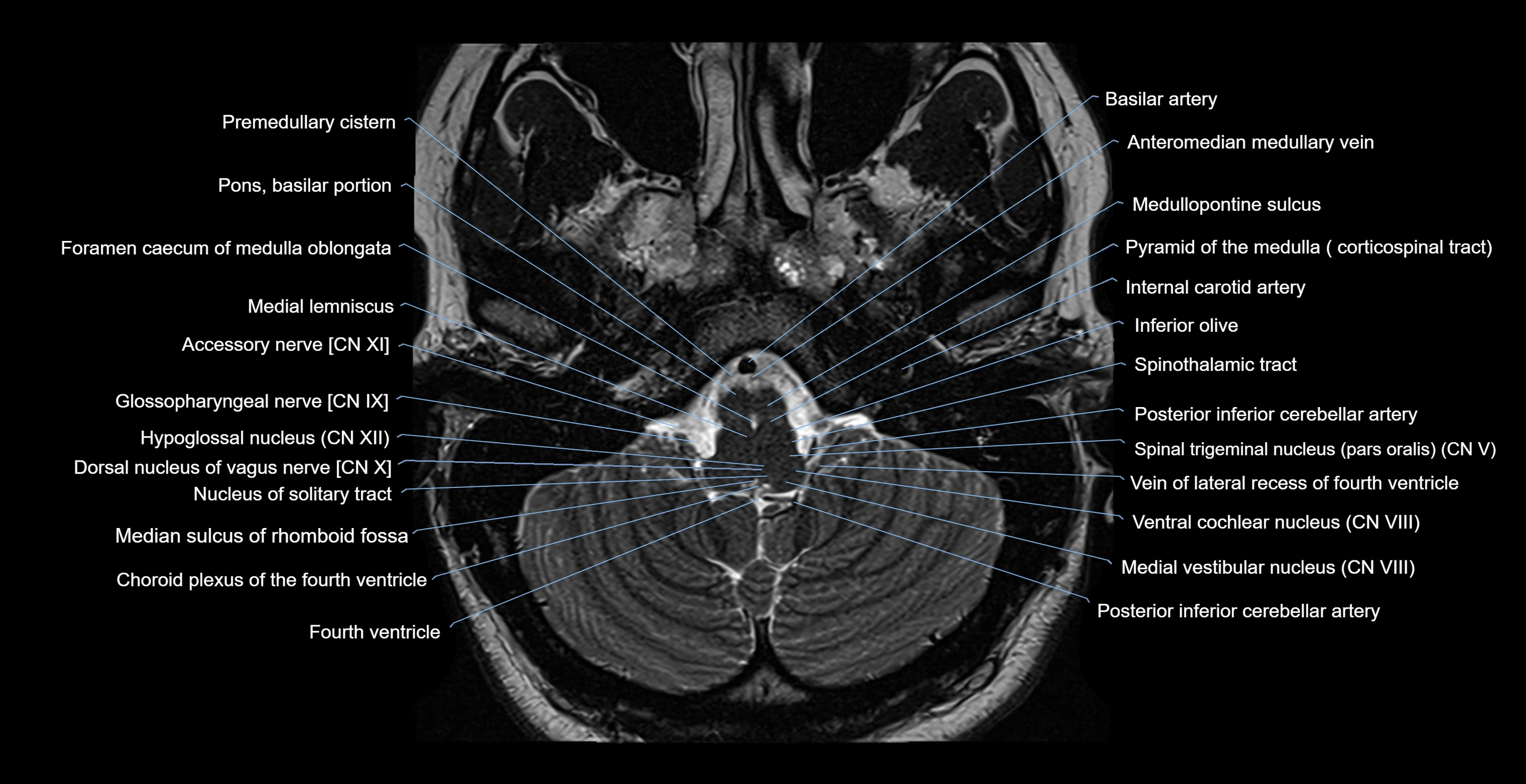
- Accessory Nerve (Cranial nerve XI)
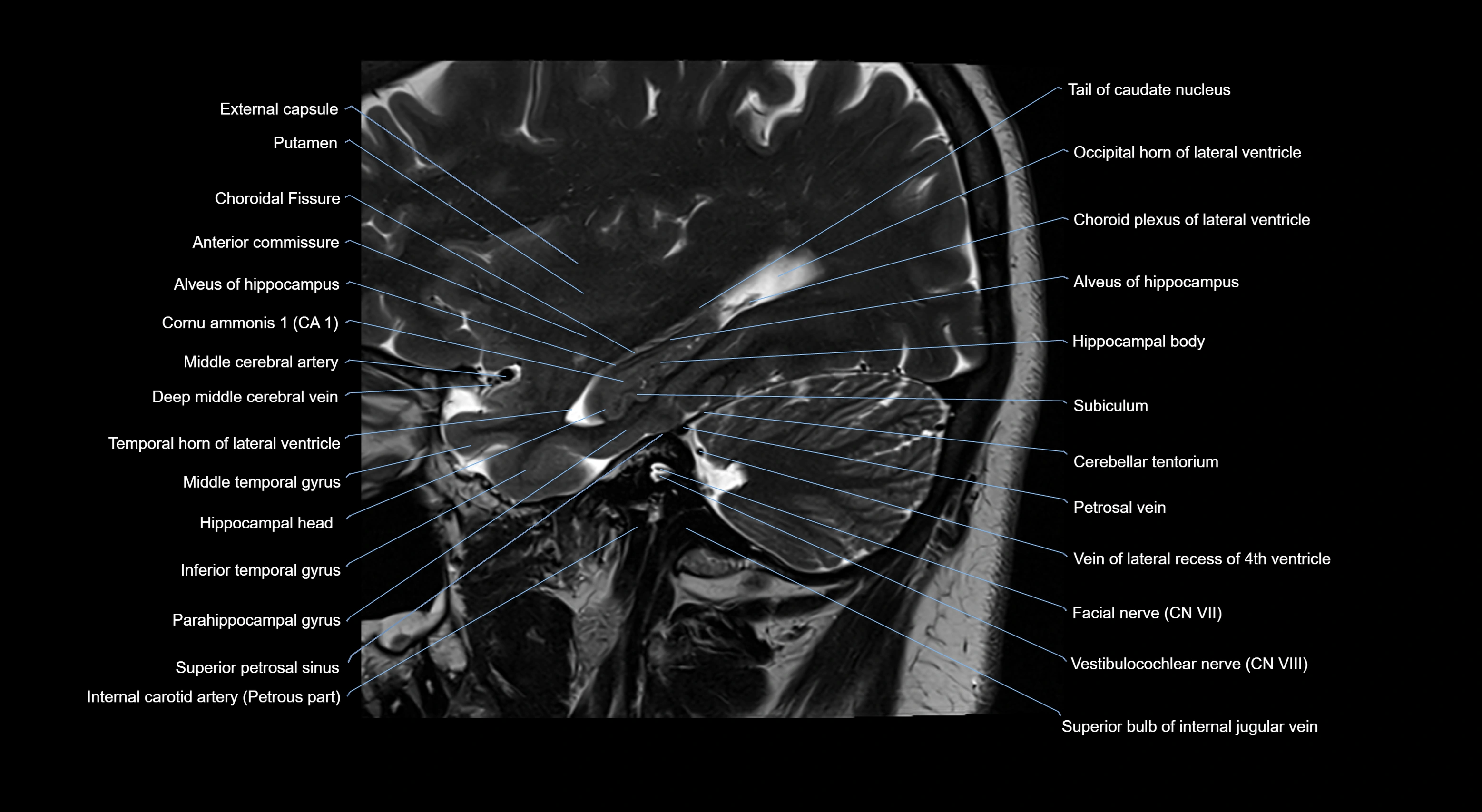
- Alveus
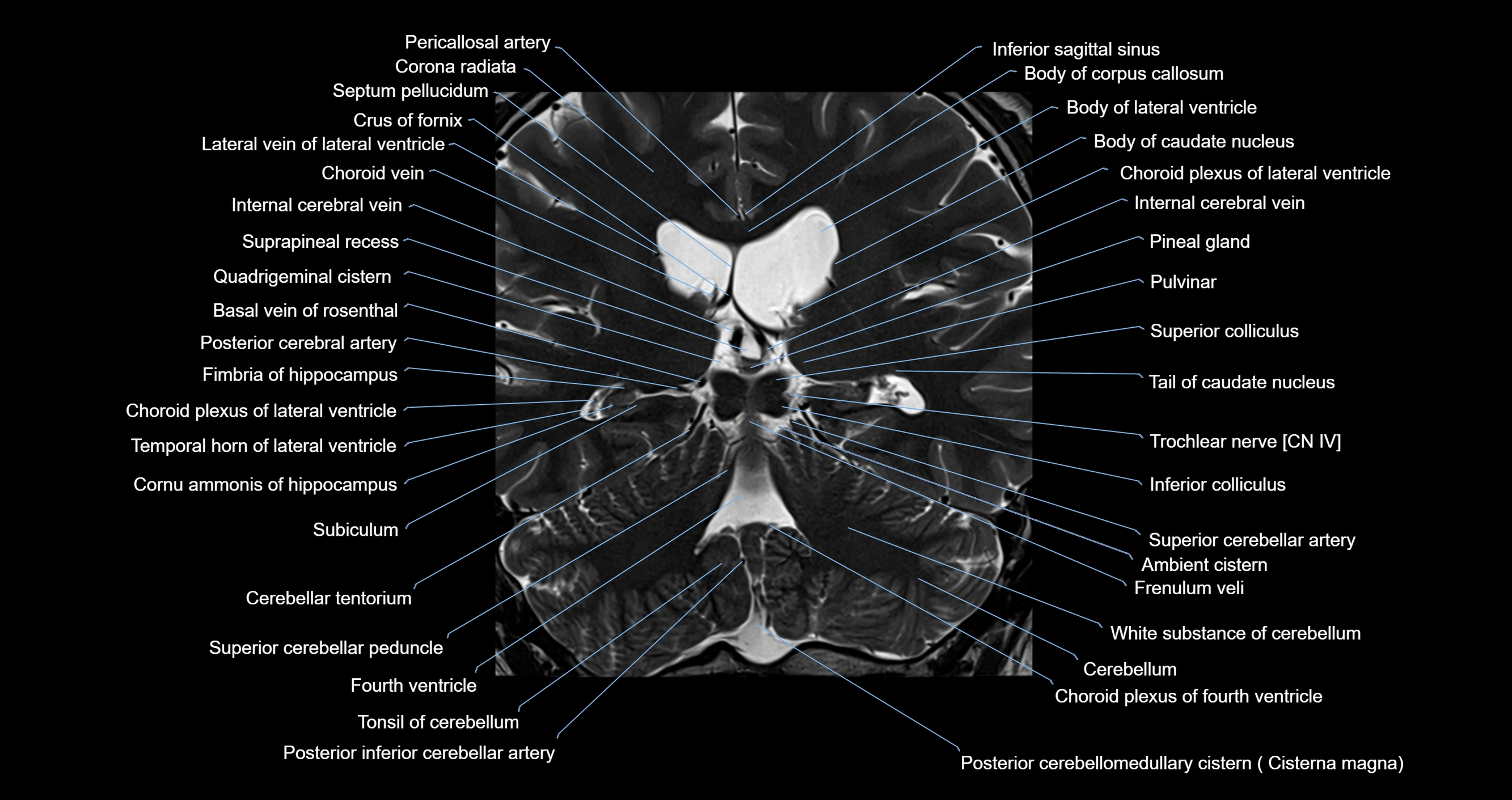
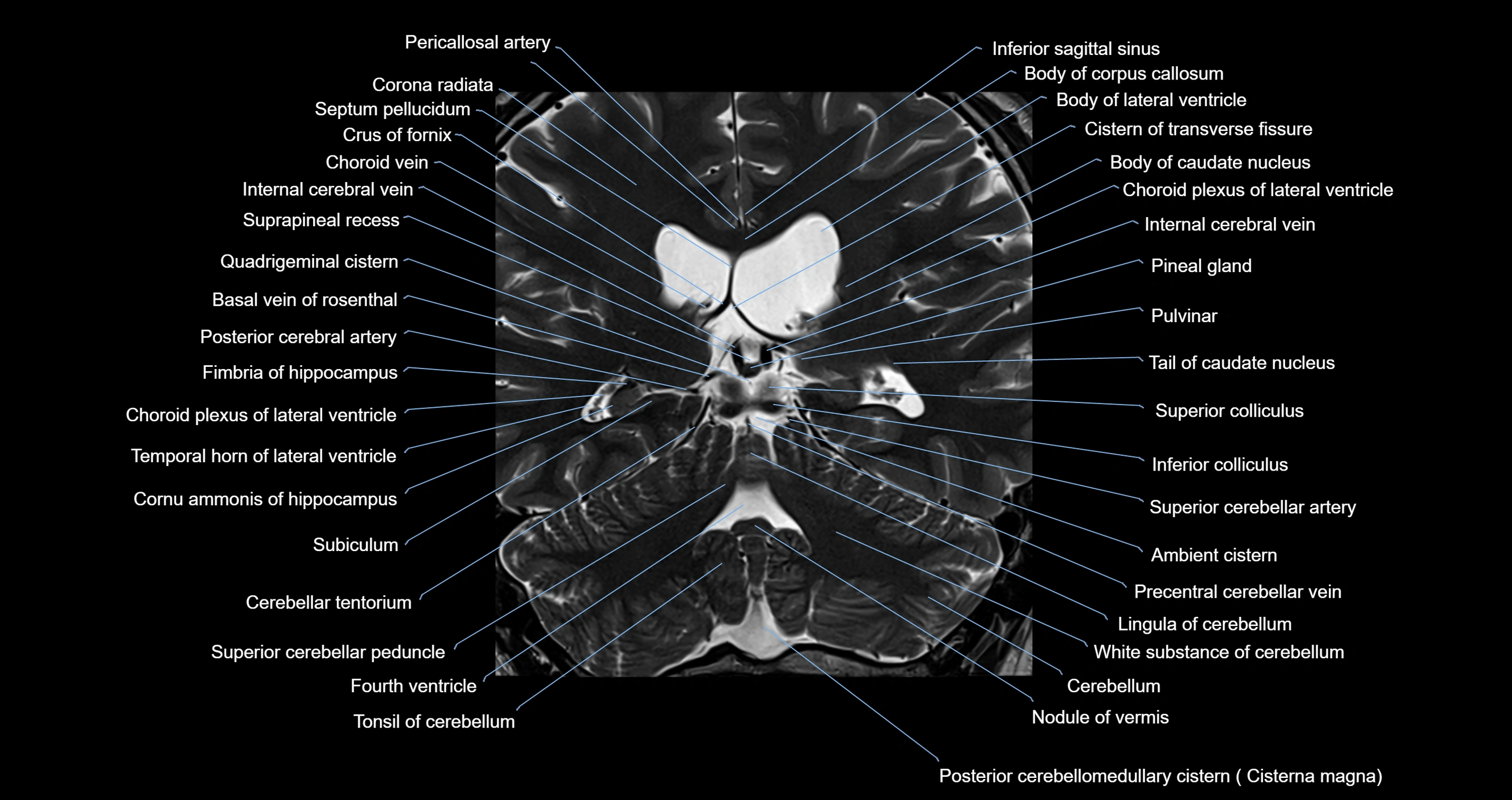
- Ambient cistern
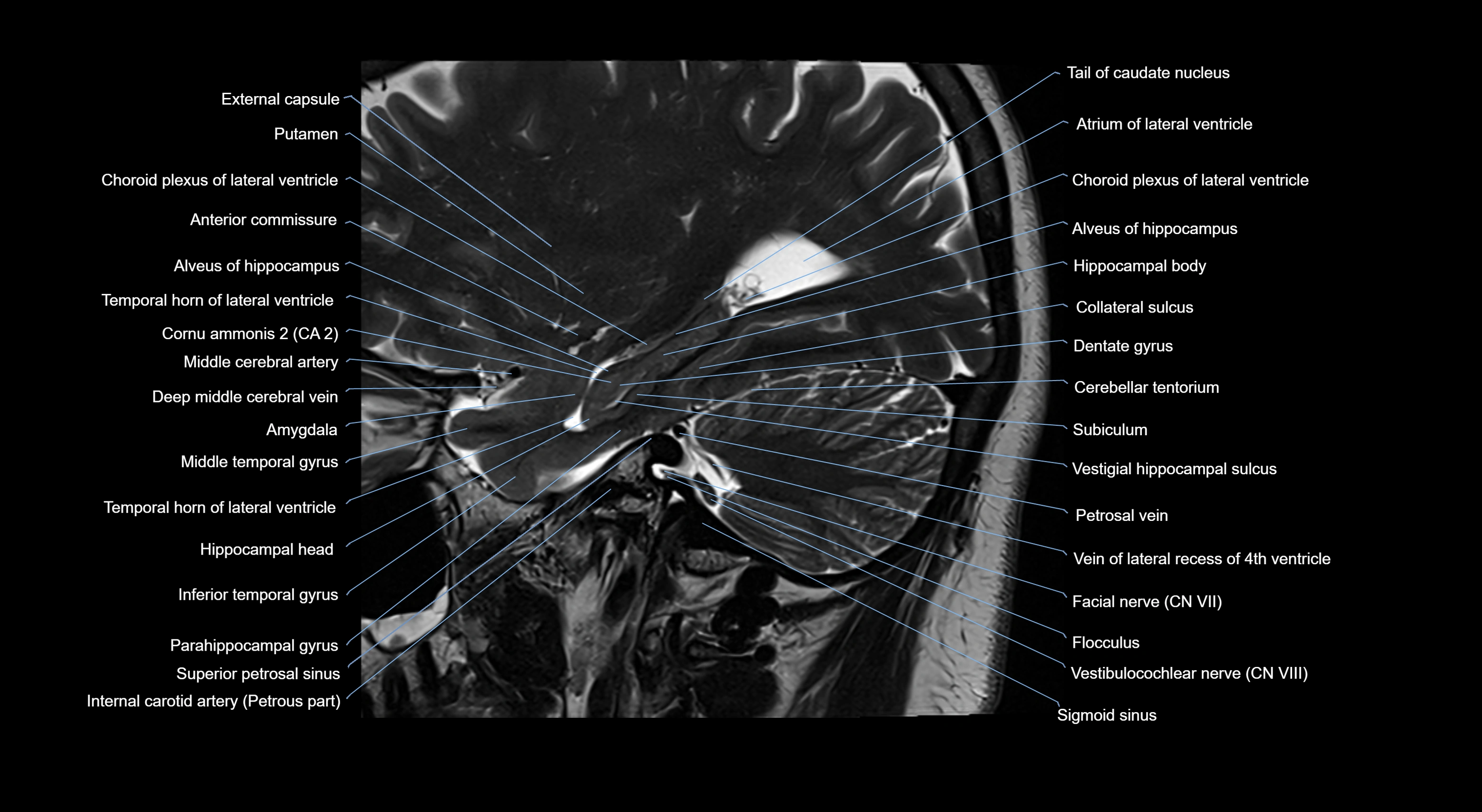
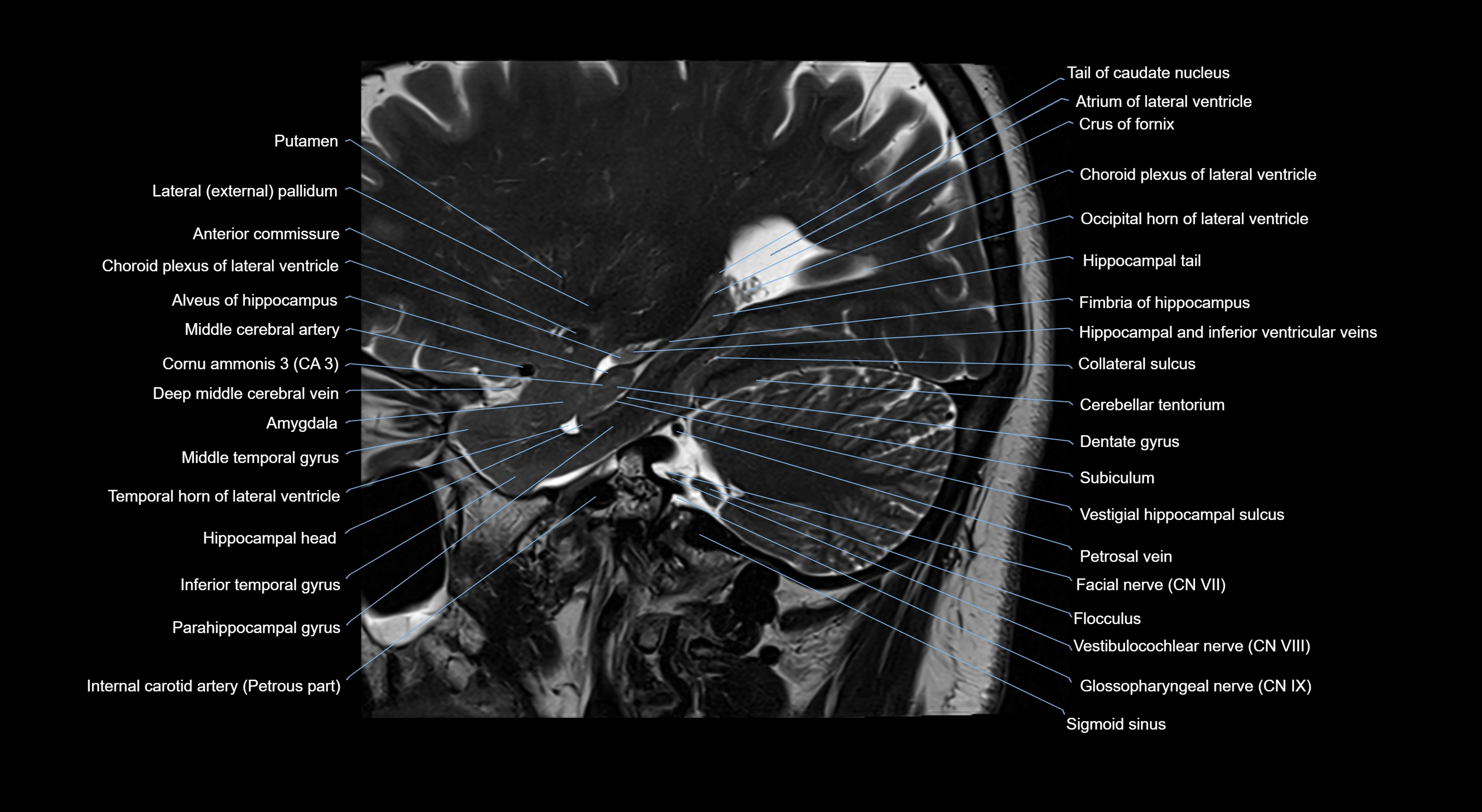
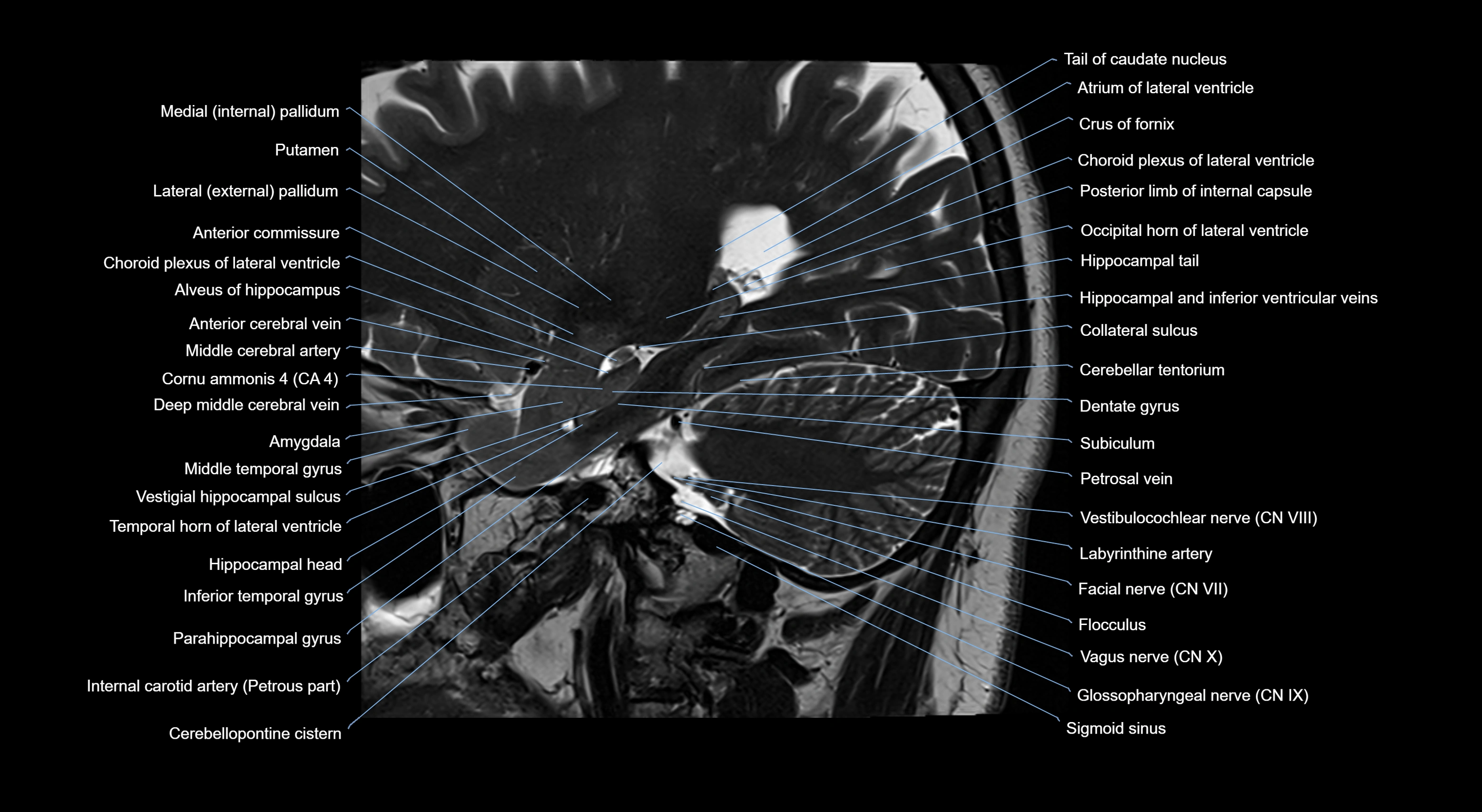
- Amygdala
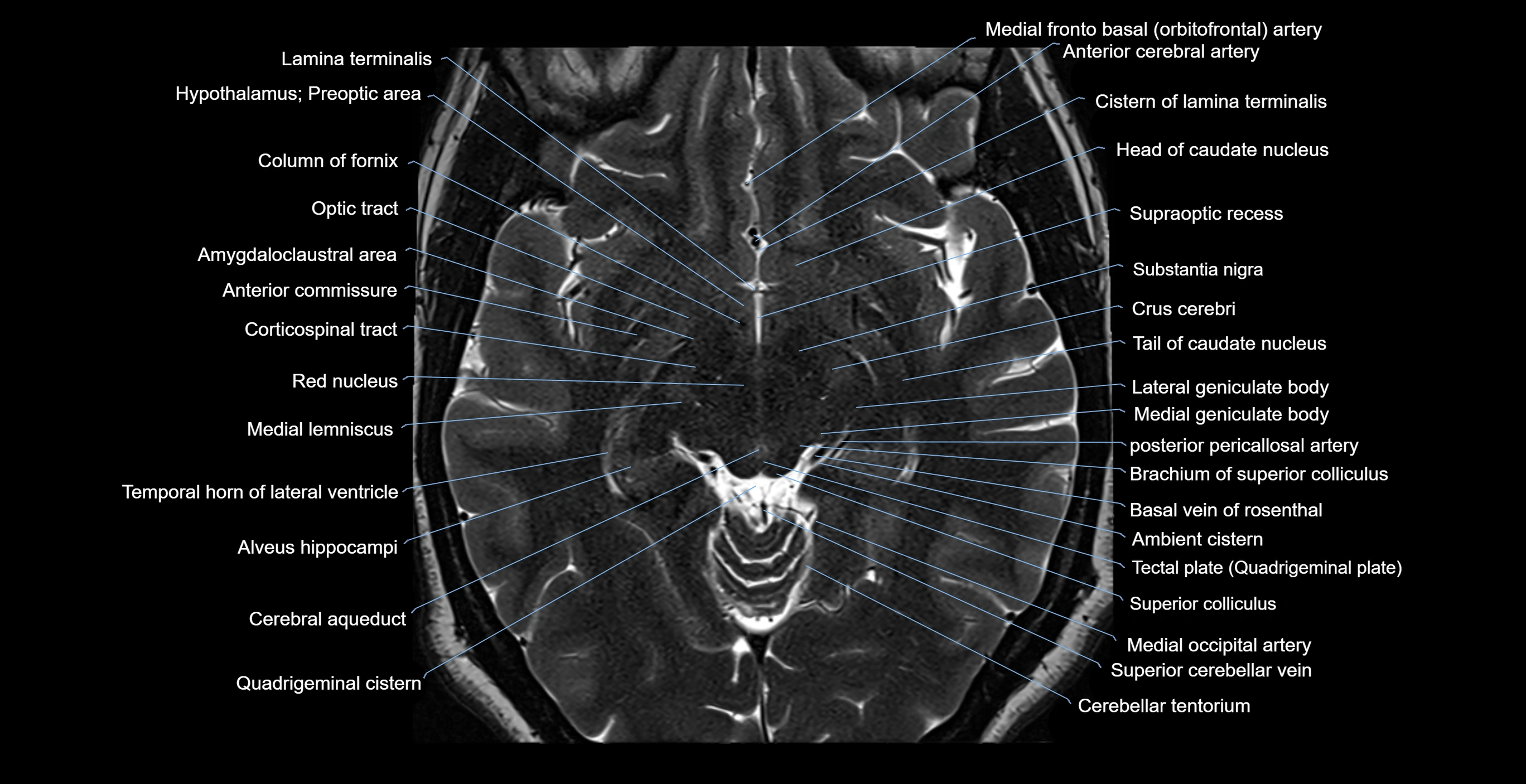
- Amygdaloclaustral area
- Amygdalohippocampal area
- Anterior Choroidal Artery
- Anterior Communicating Artery
- Anterior calcarine sulcus
- Anterior cerebral artery
- Anterior cerebral artery (A1 Segment)
- Anterior cerebral artery (A2 Segment)
- Anterior cerebral artery (A3 Segment)
- Anterior cerebral veins
- Anterior clinoid process
- Anterior cochlear nucleus
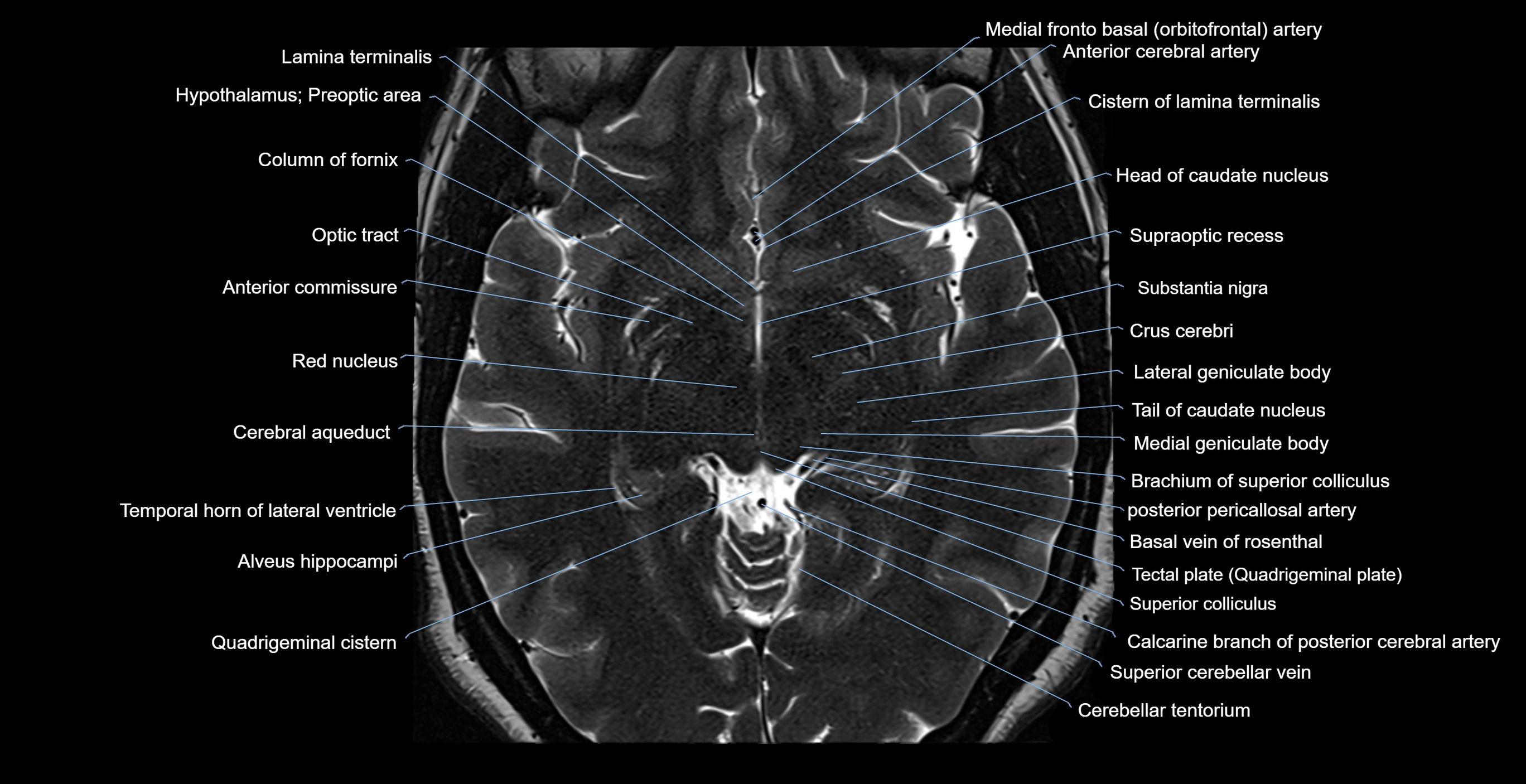
- Anterior commissure
- Anterior intercavernous sinus
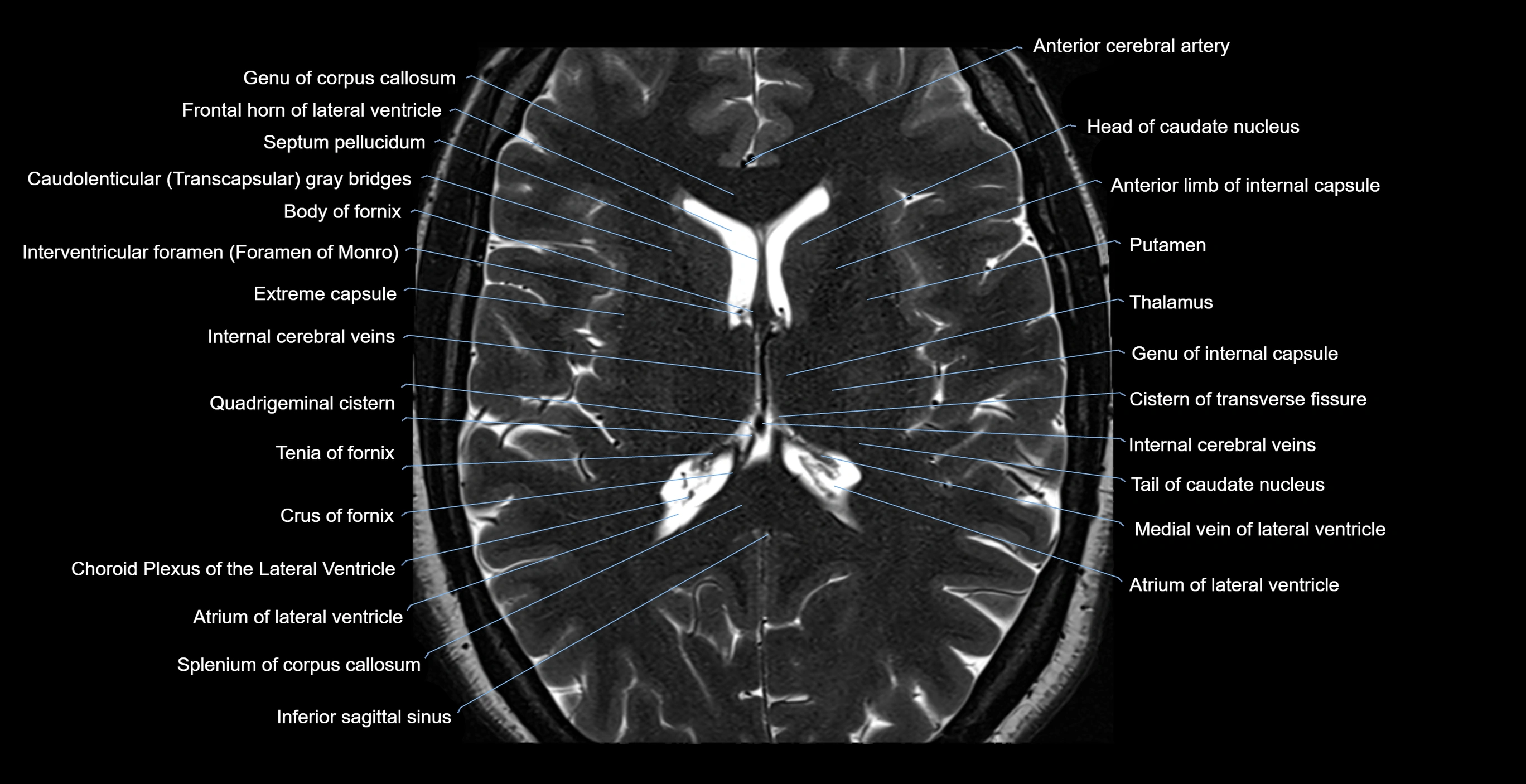
- Anterior limb of internal capsule
- Anterior lobe of cerebellum
- Anterior lobe of pituitary gland
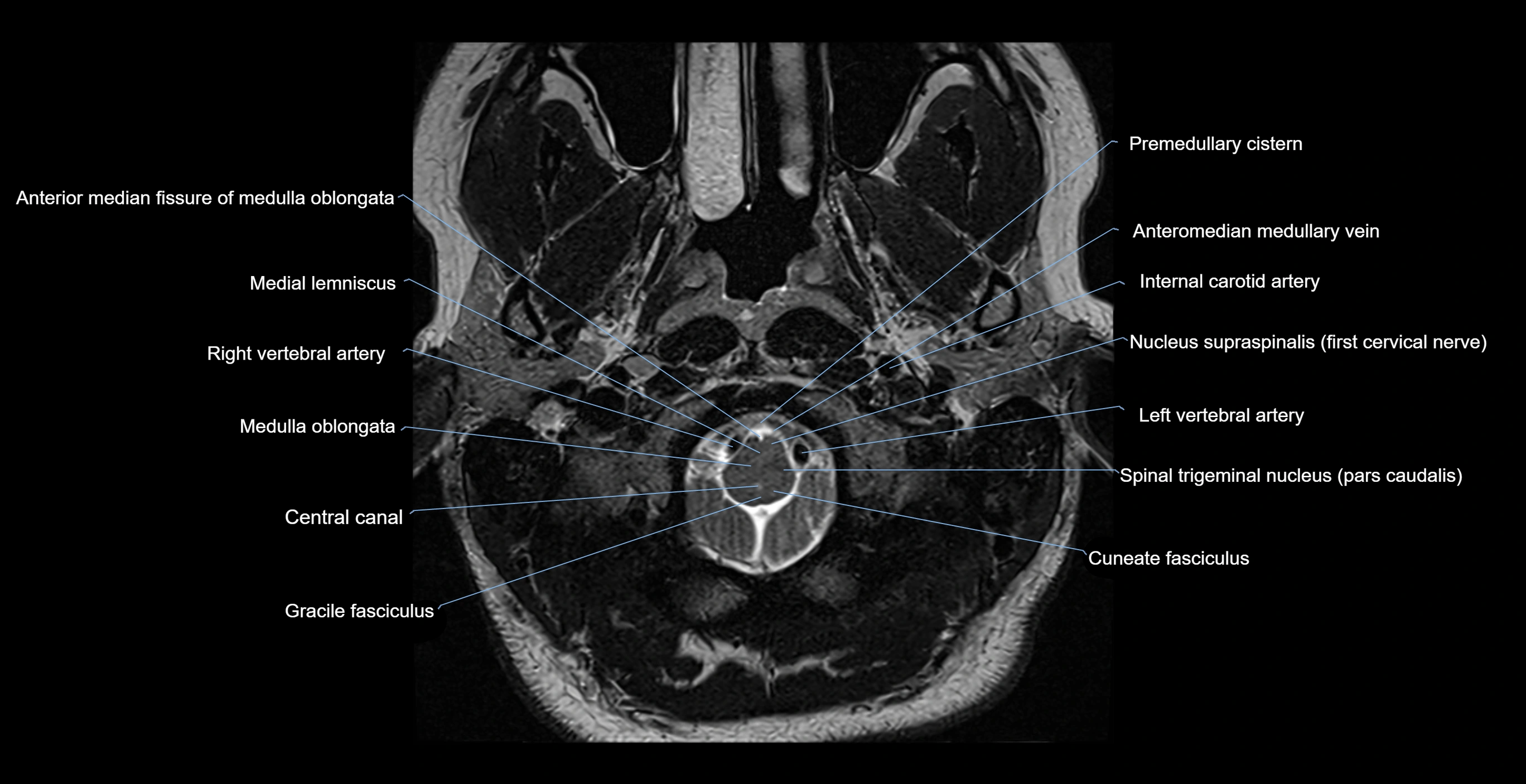
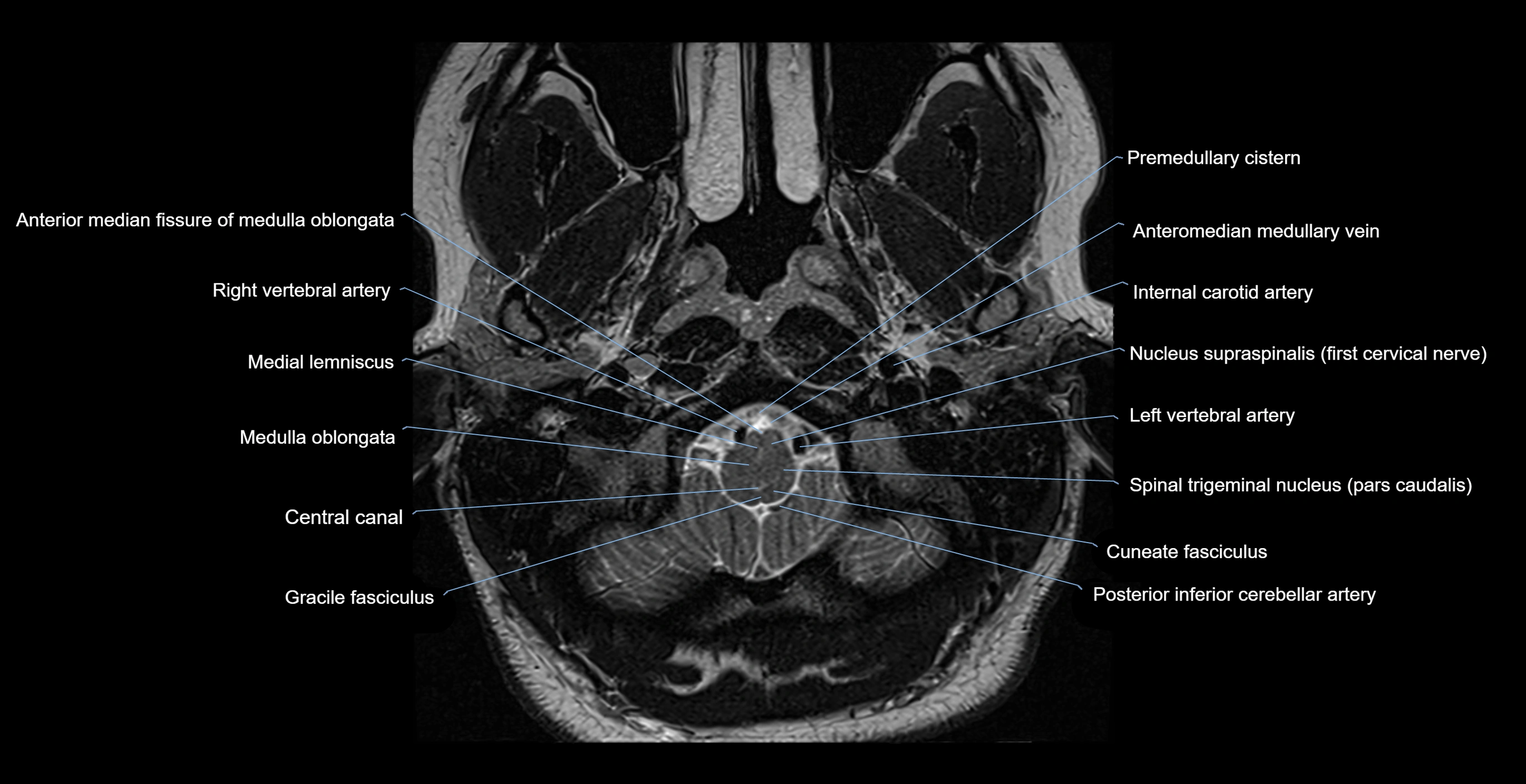
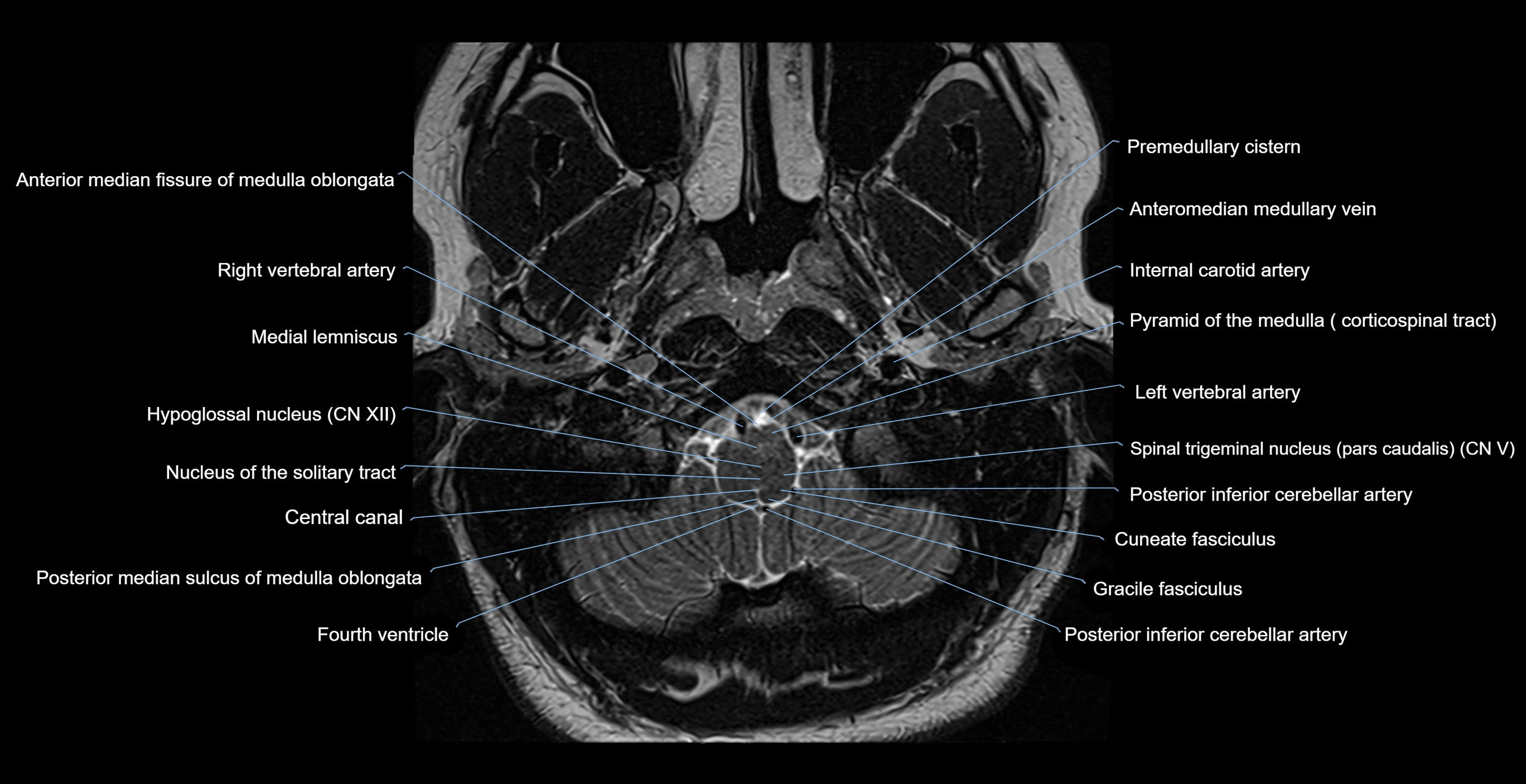
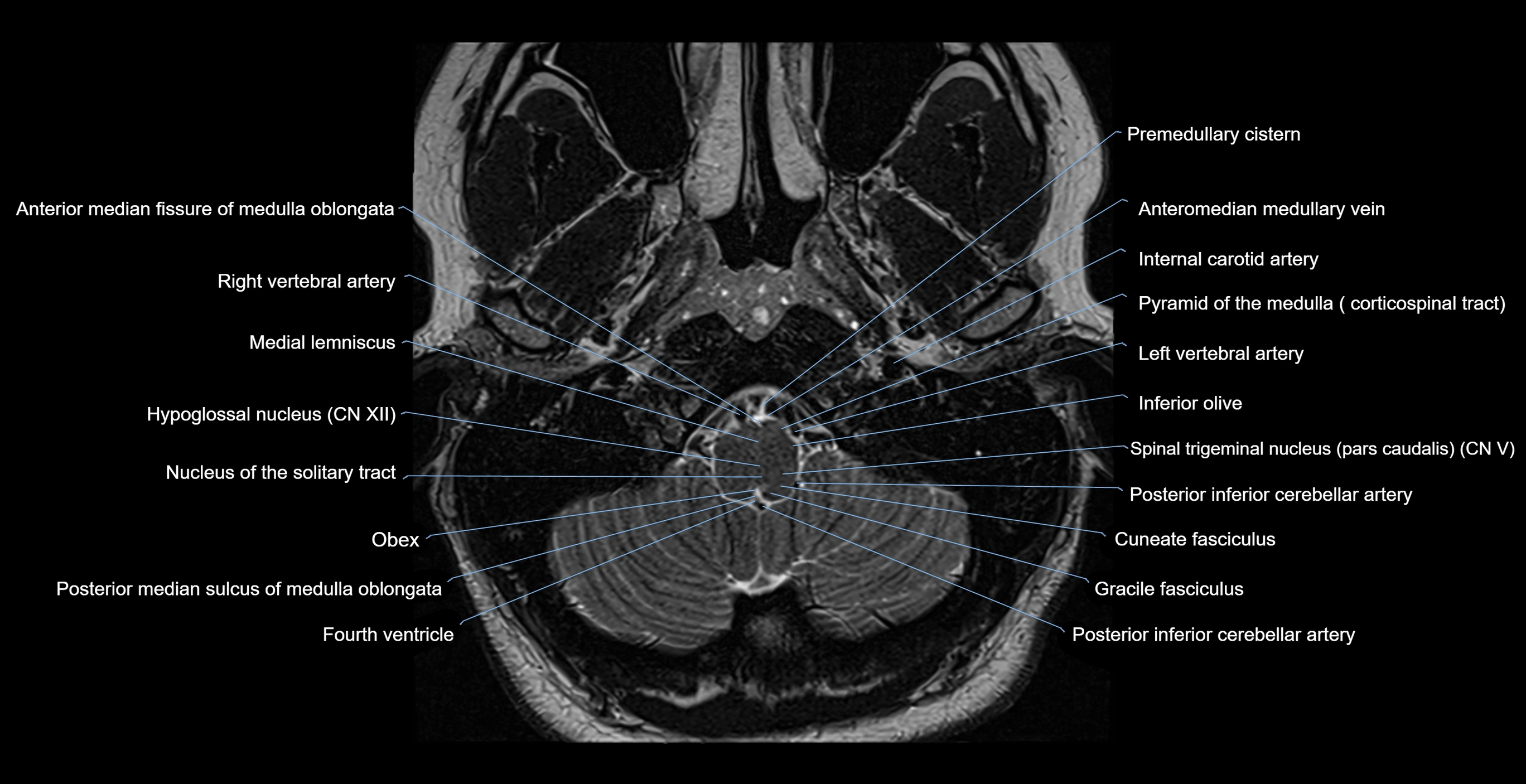
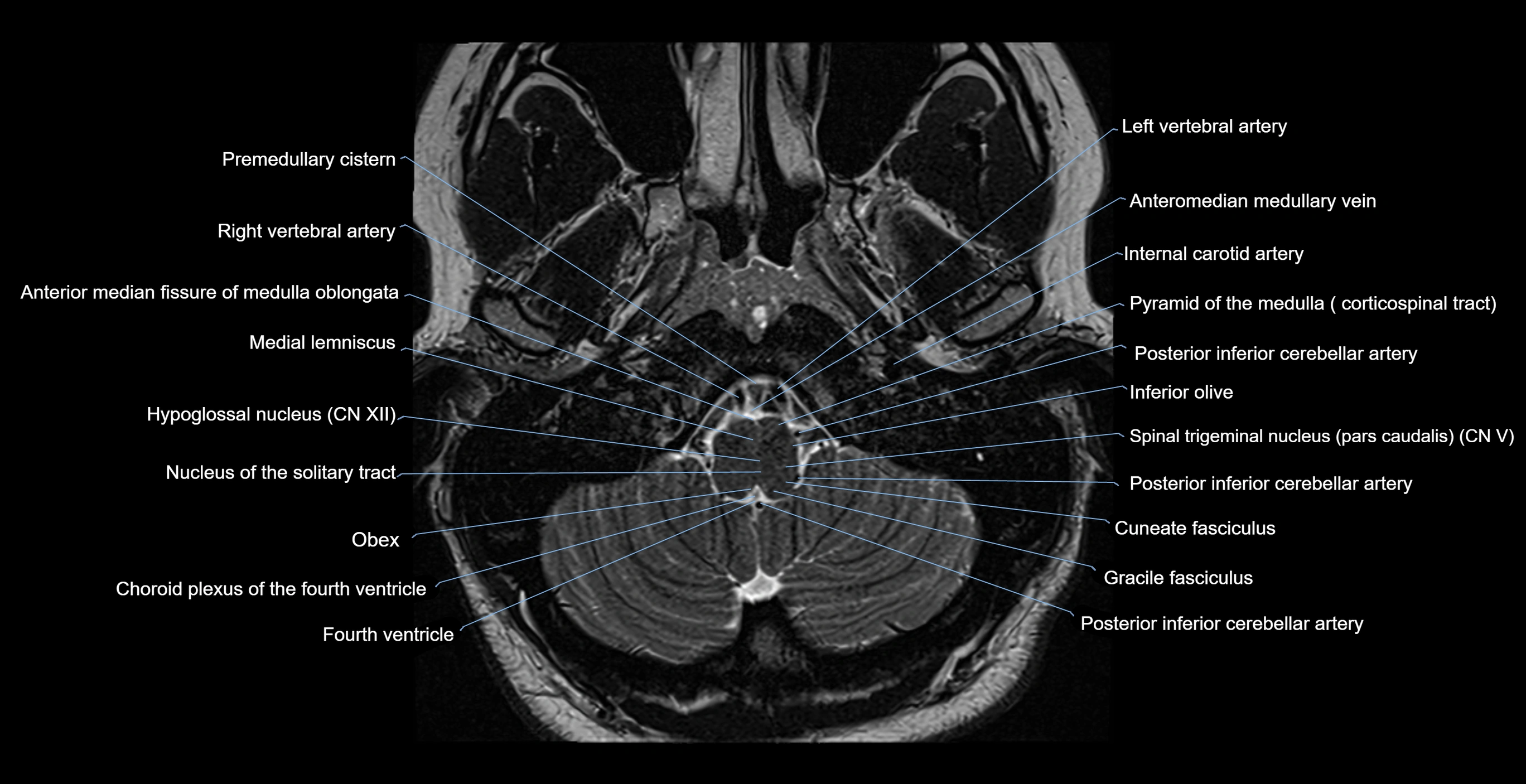
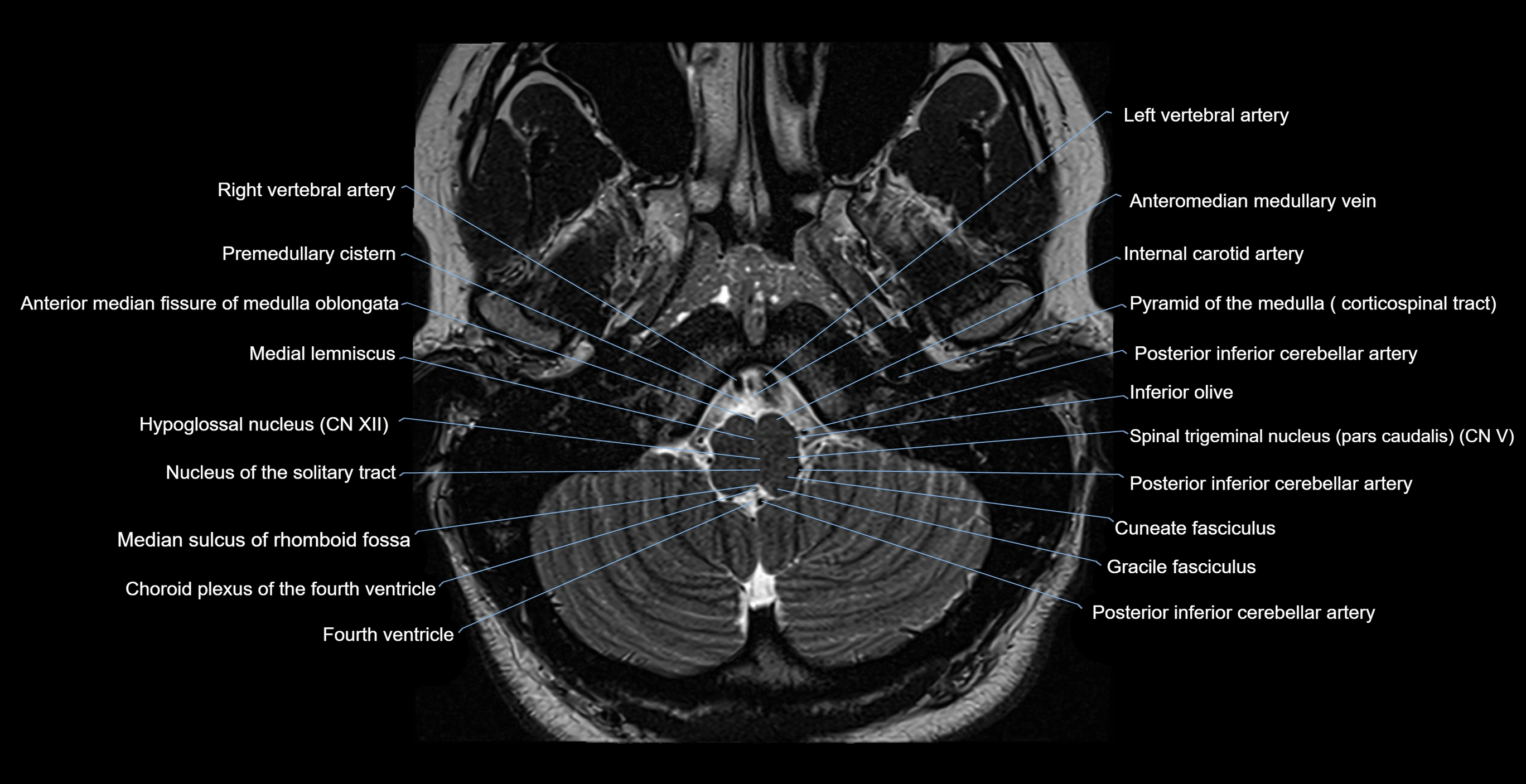
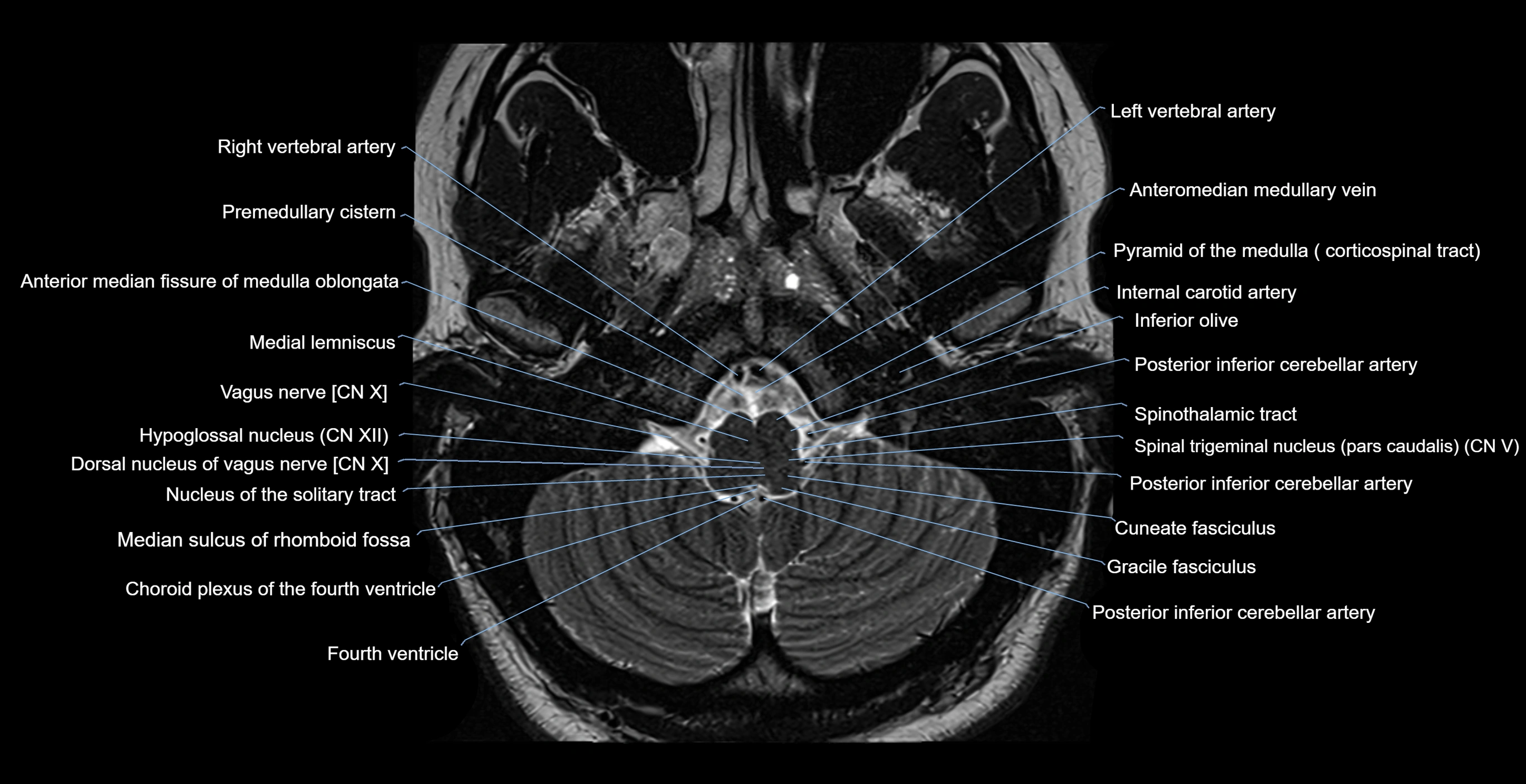
- Anterior median fissure of medulla oblongata
- Anterior parietal artery
- Anterior quadrangular lobule
- Anterior quadrangular lobule (HV) of cerebellum
- Anterior quadrangular lobule (HlV) of cerebellum
- Anterior temporal artery anatomy
- Anterior vein of caudate nucleus
- Anterolateral central (lenticulostriate) arteries anatomy
- Anterolateral medullary vein
- Anterolateral pontine vein
- Anteromedial central (perforating) arteries anatomy
- Anteromedian medullary vein
- Anteromedian pontine vein
- Apex of insula
- Aqueduct of midbrain (Sylvian Aqueduct)
- Arbor Vitae (Cerebellar White Matter)
- Artery of central sulcus
- Artery of postcentral sulcus
- Artery of precentral sulcus
- Artery to angular gyrus anatomy
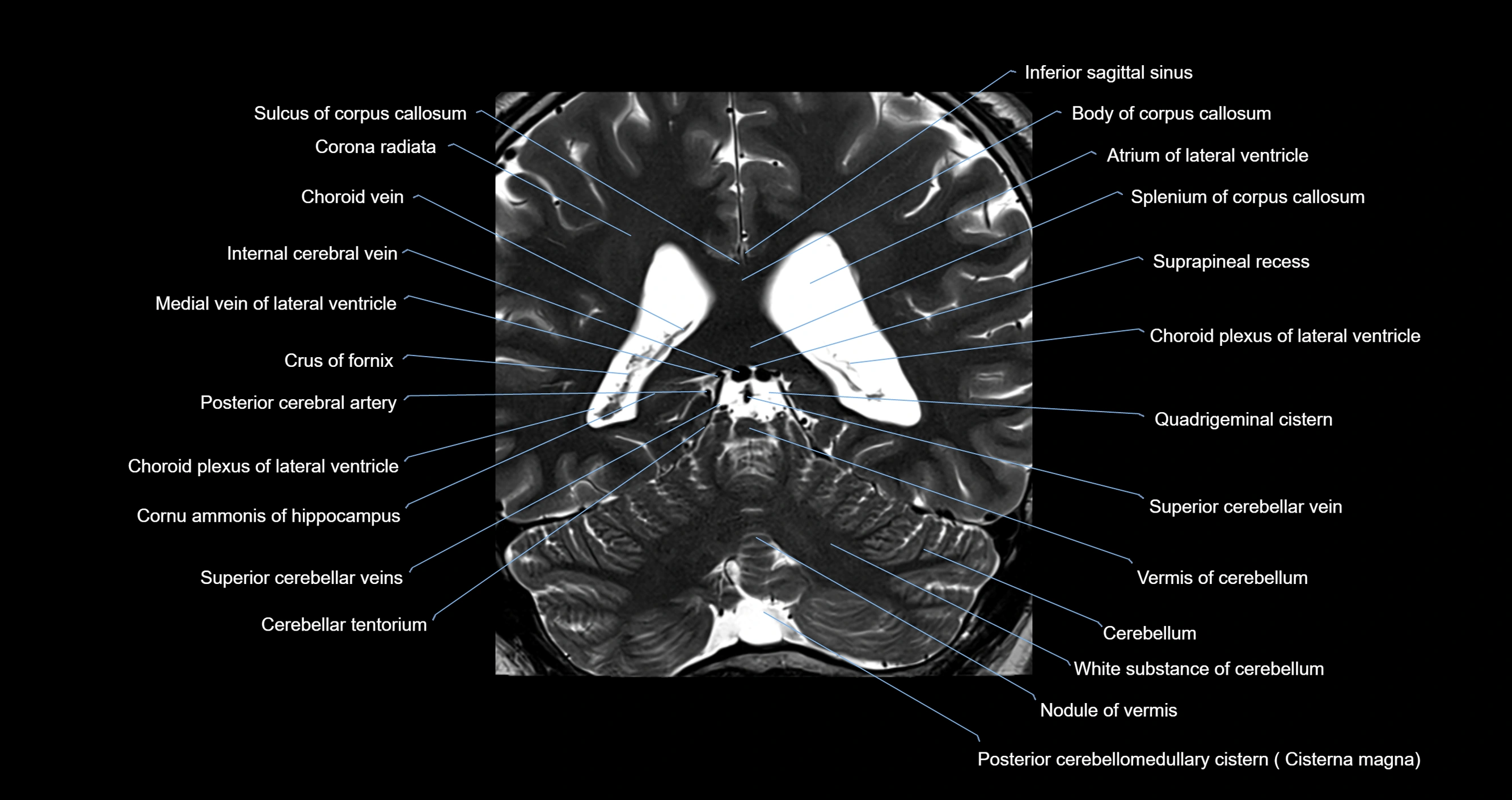
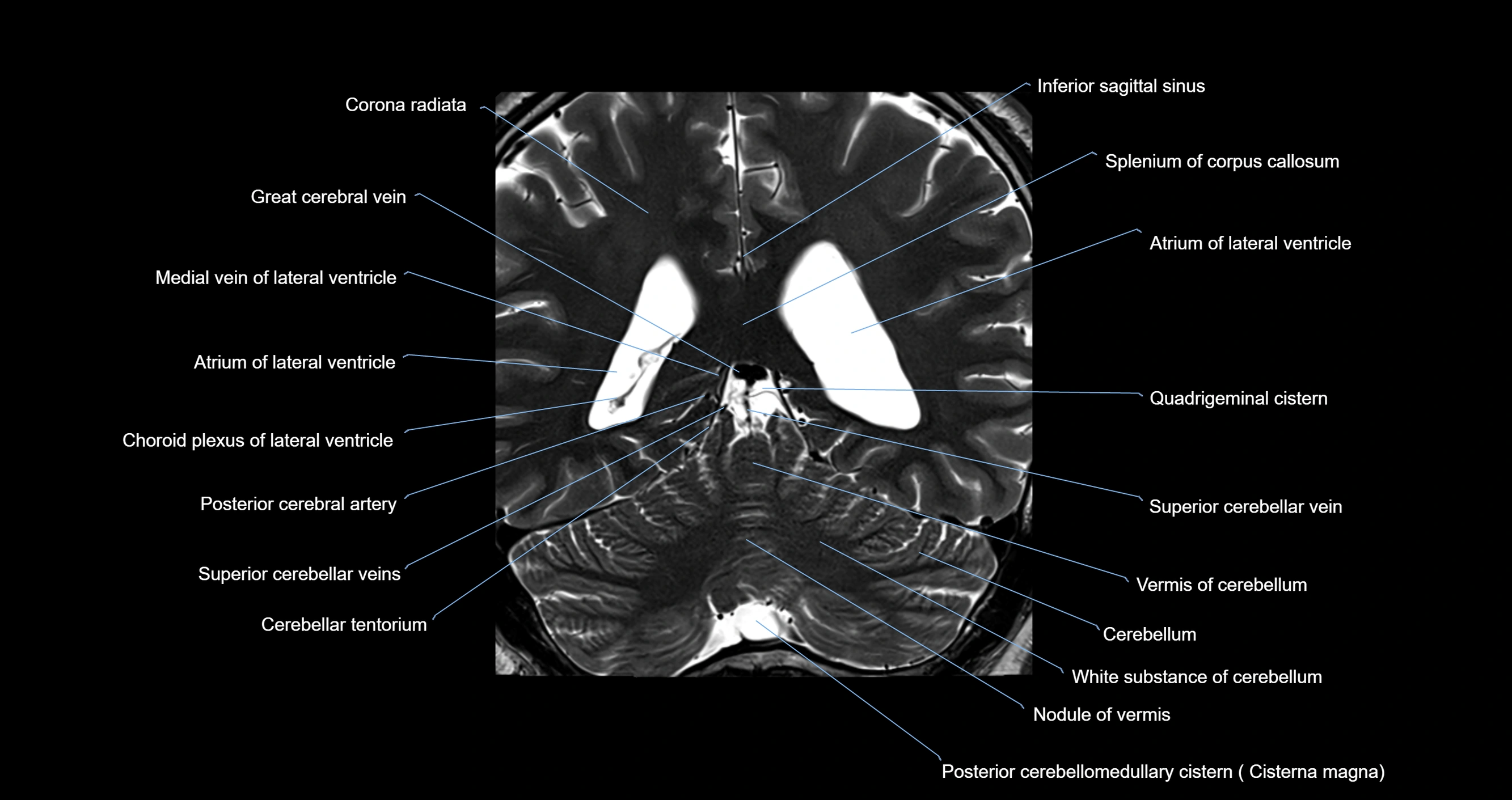
- Atrium of lateral ventricle
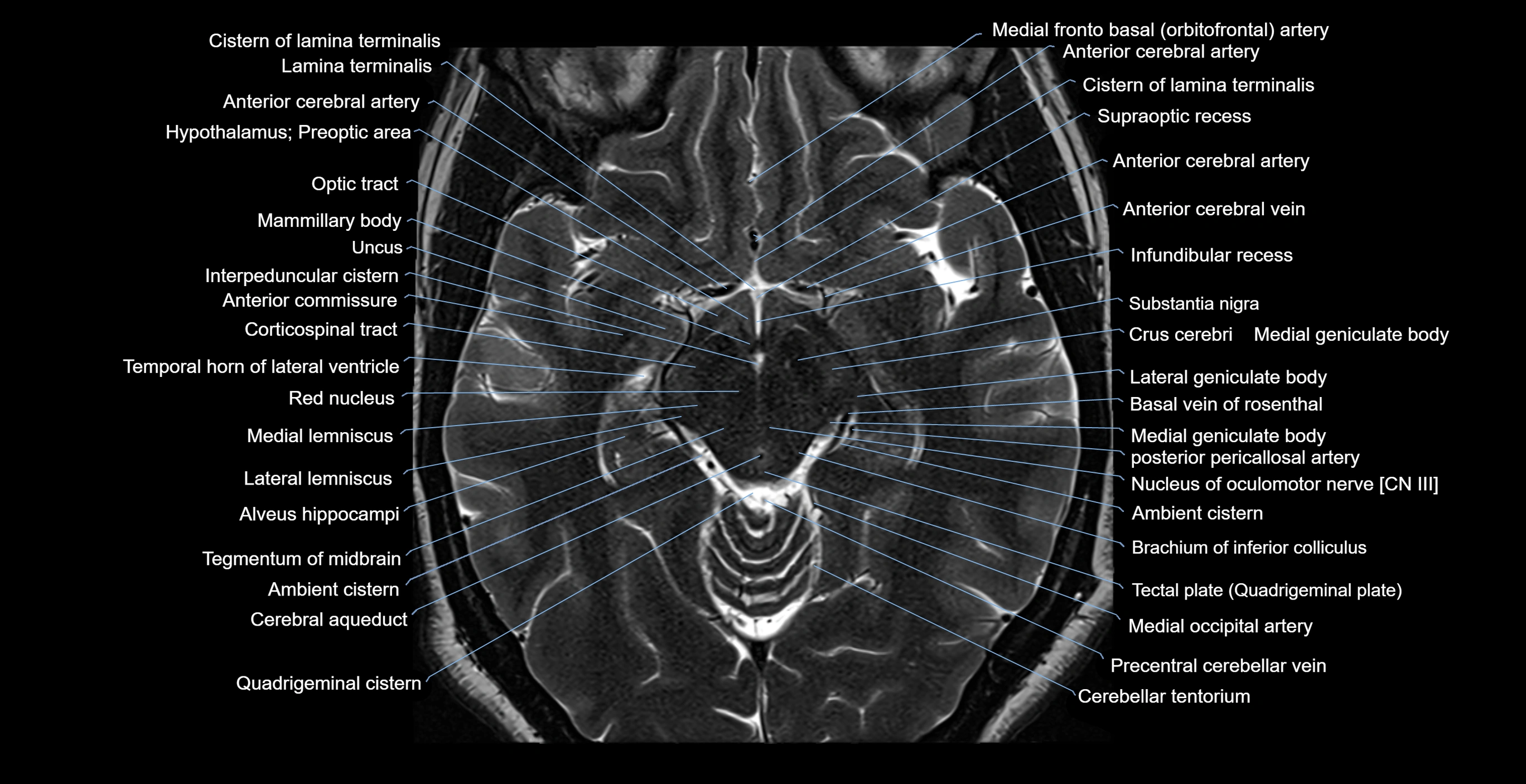
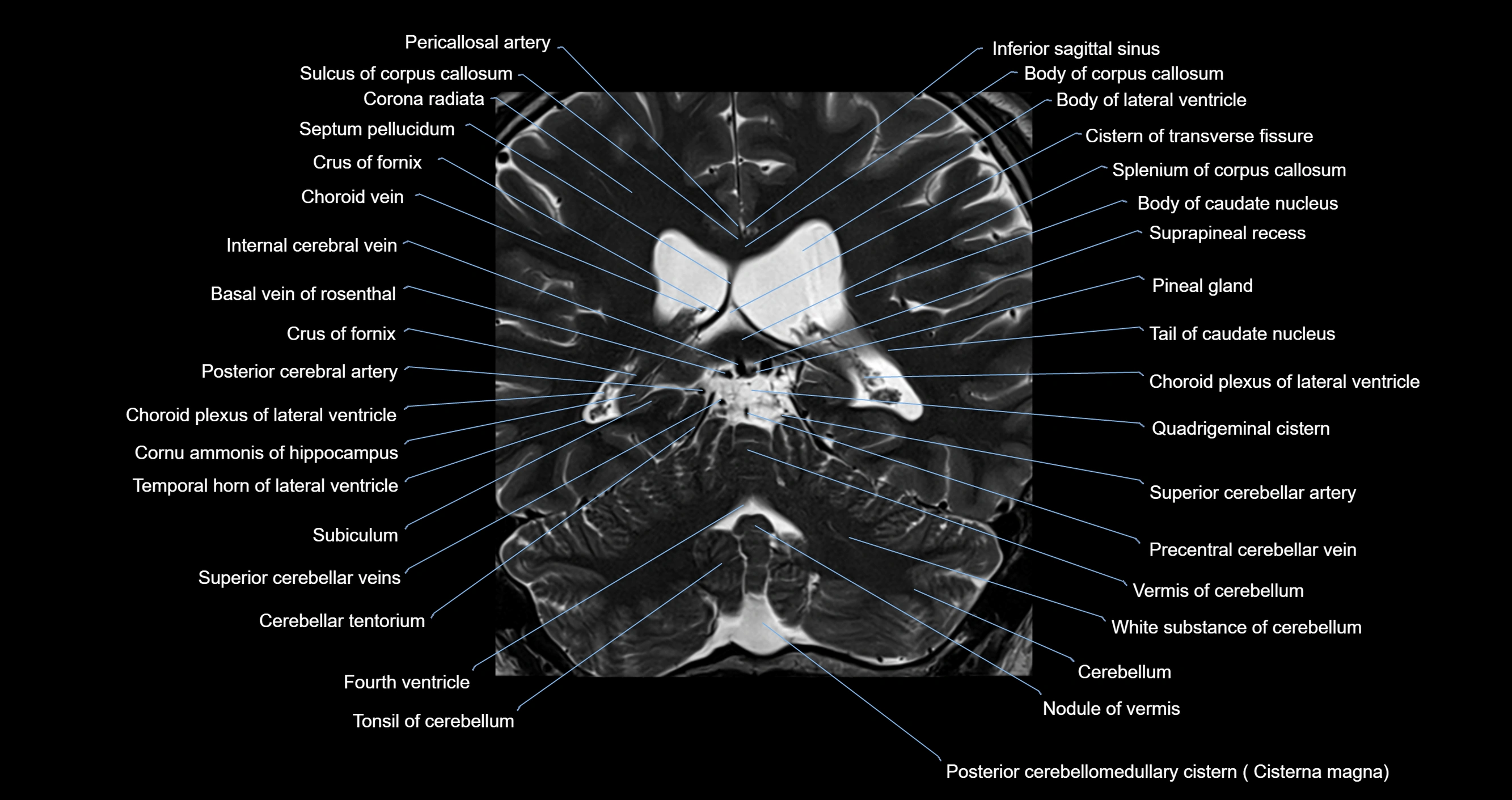
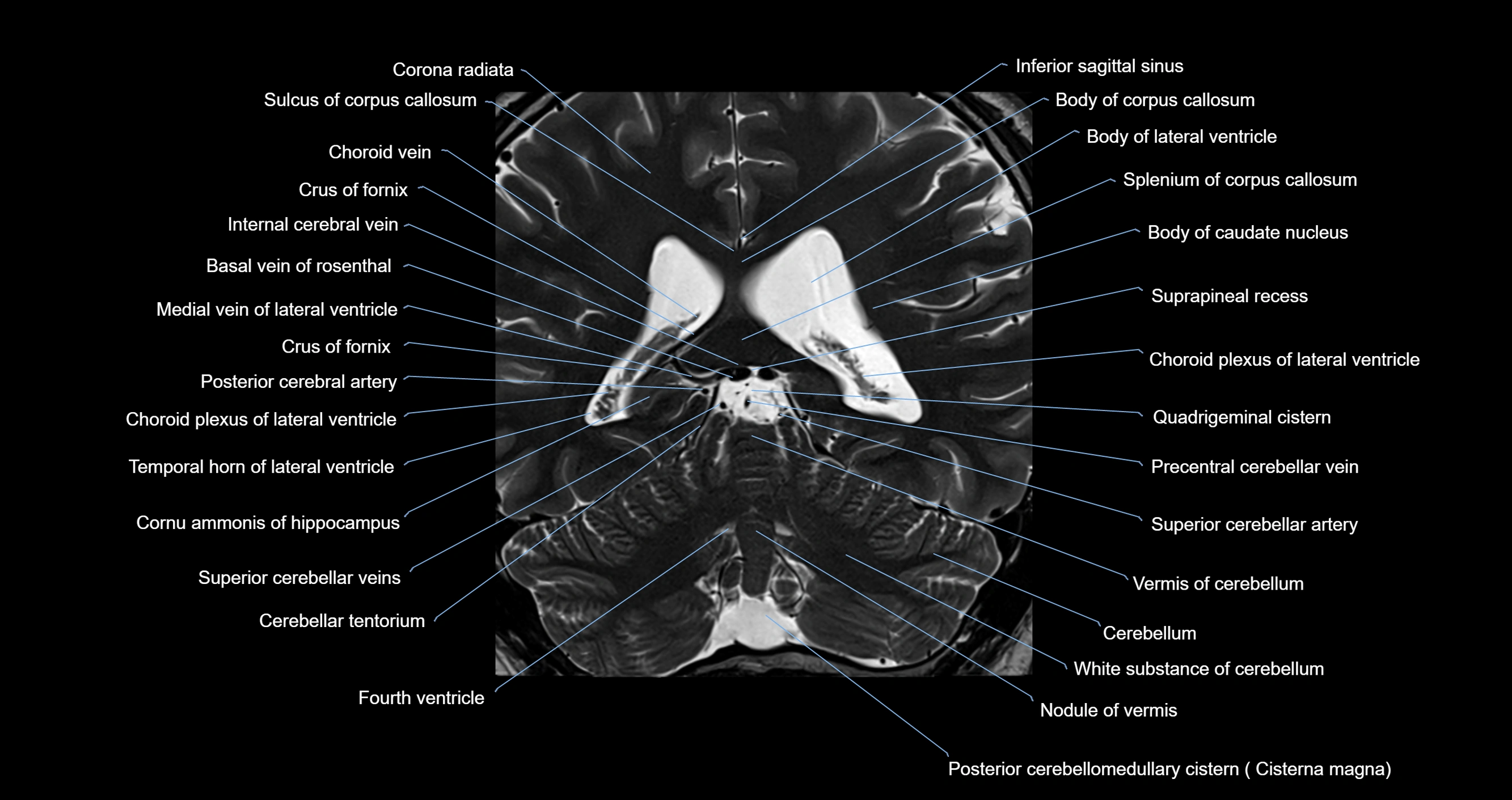
- Basal vein of rosenthal
- Basilar artery
- Basilar part of pons
- Basilar plexus
- Basilar venous plexus
- Biventral lobule (HVIII) of cerebellum
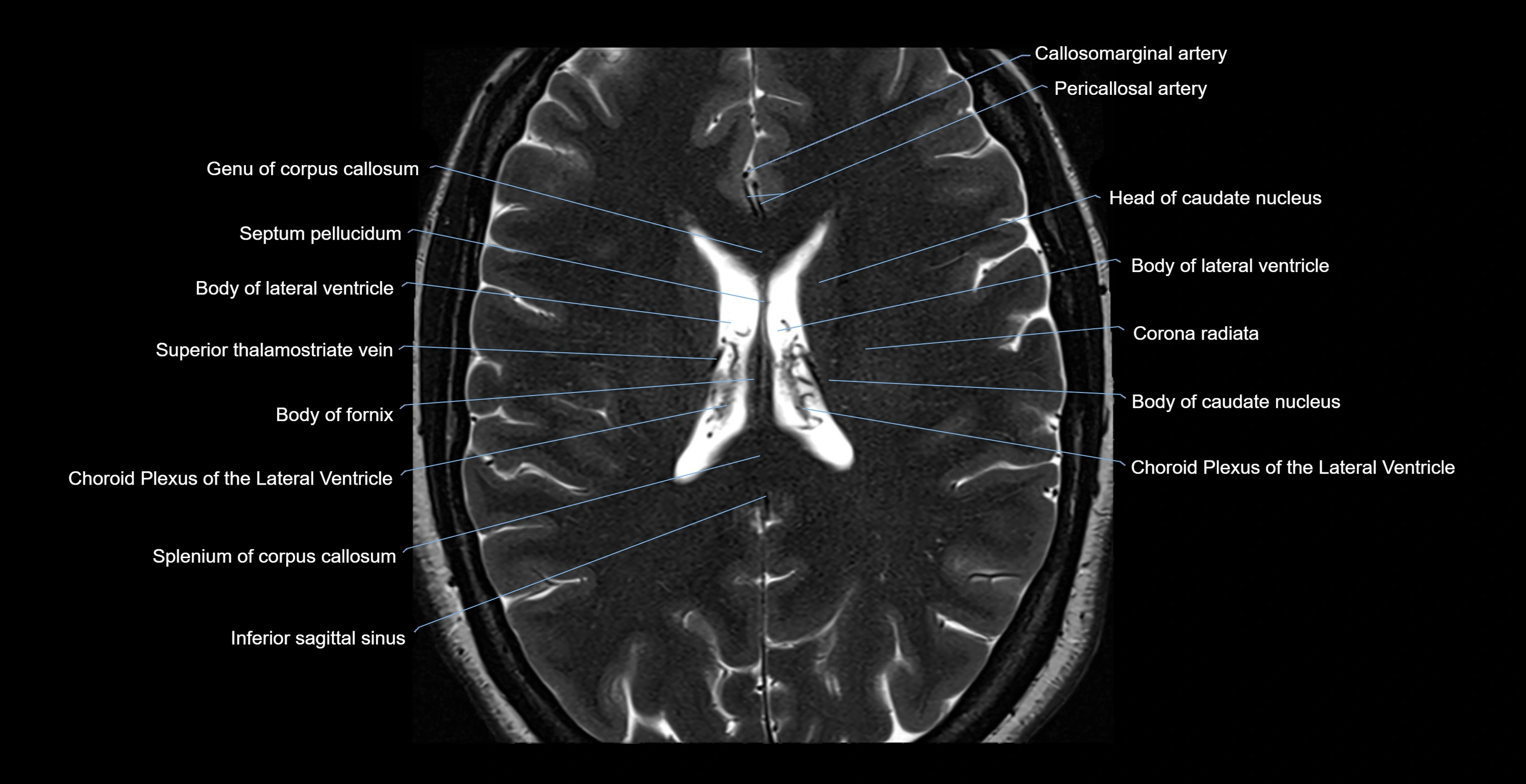
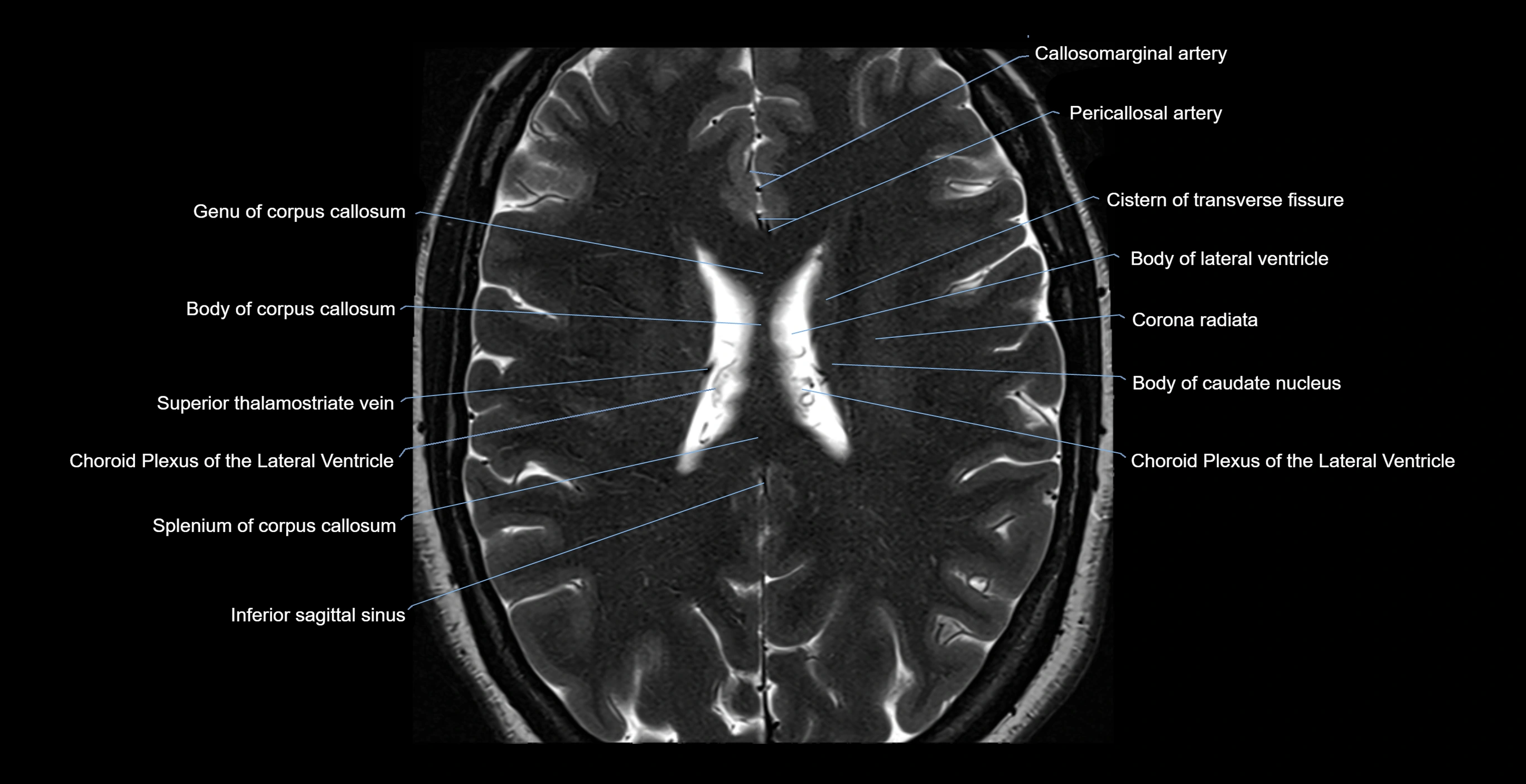
- Body of caudate nucleus
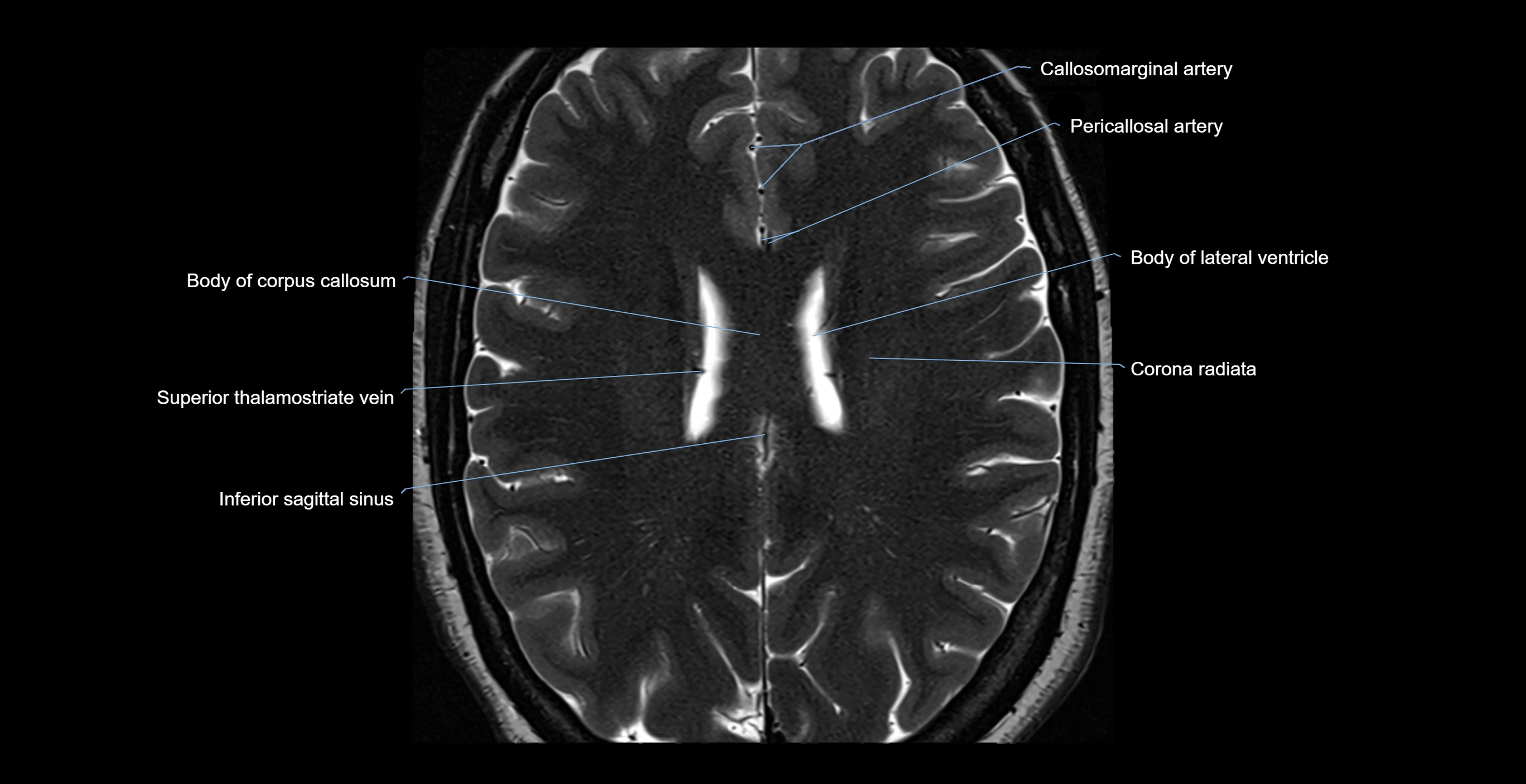
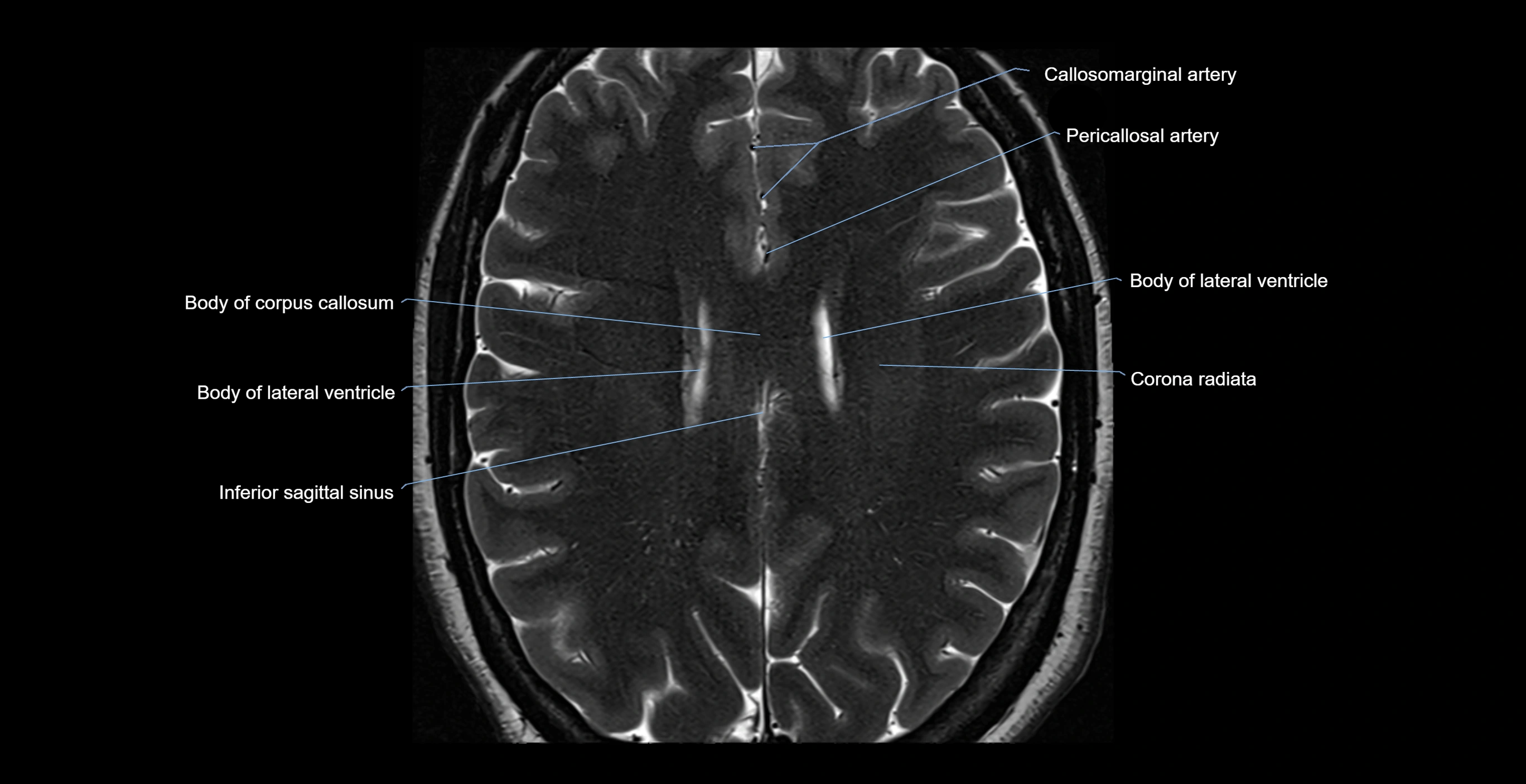
- Body of corpus callosum
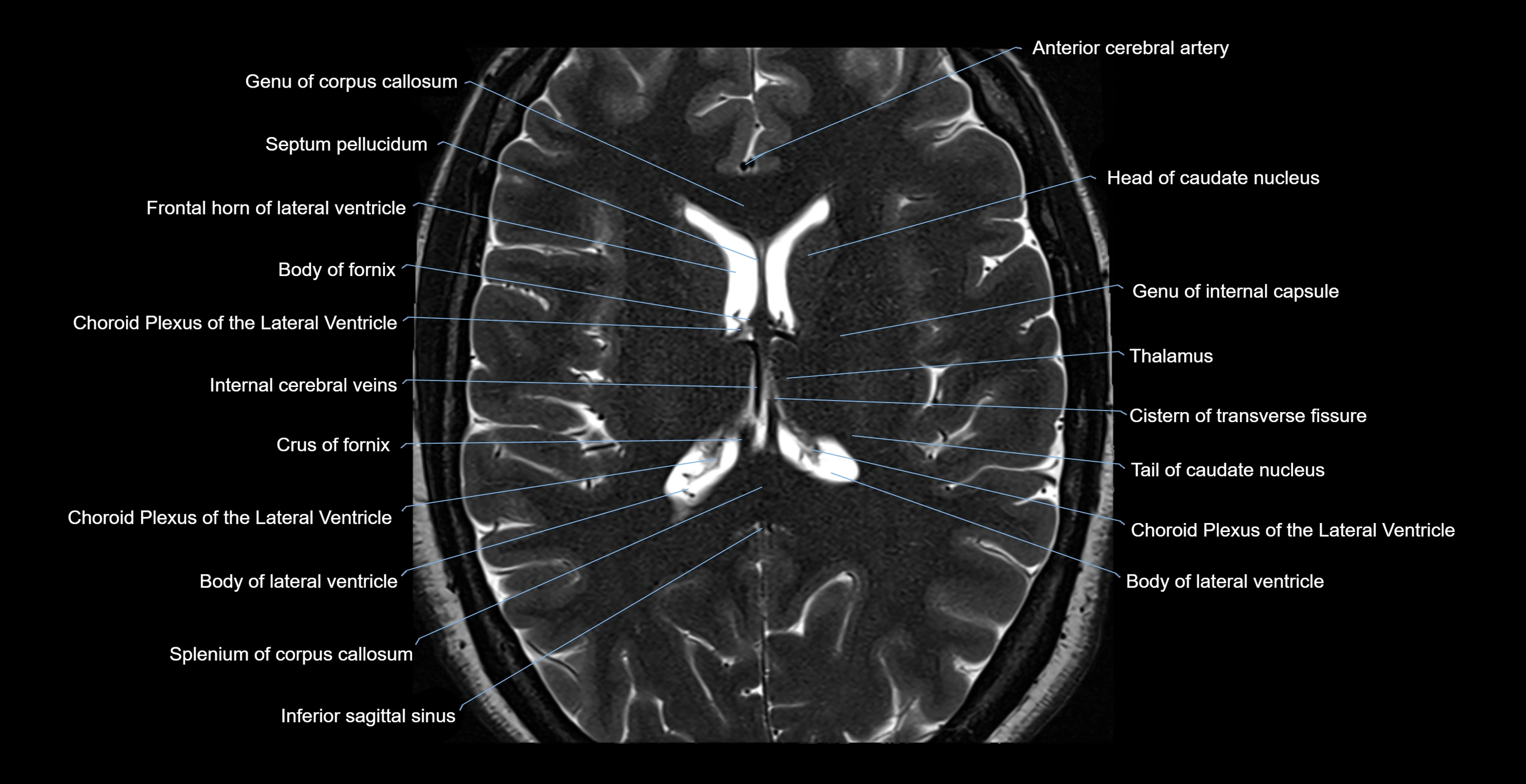
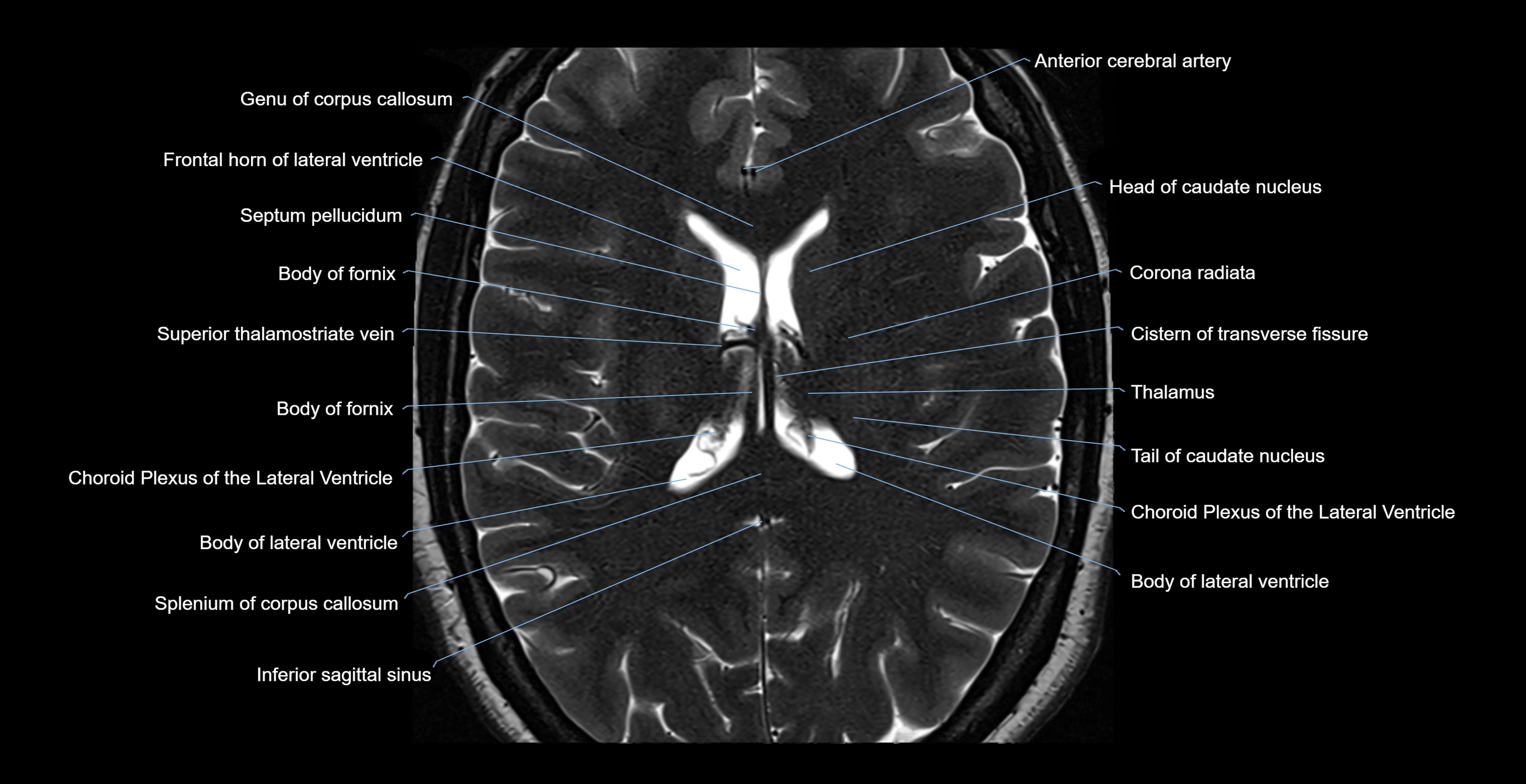
- Body of fornix
- Body of lateral ventricle
- Brachium of inferior colliculus
- Brachium of superior colliculus
- Calcarine artery
- Calcarine branch of posterior cerebral artery
- Calcarine spur
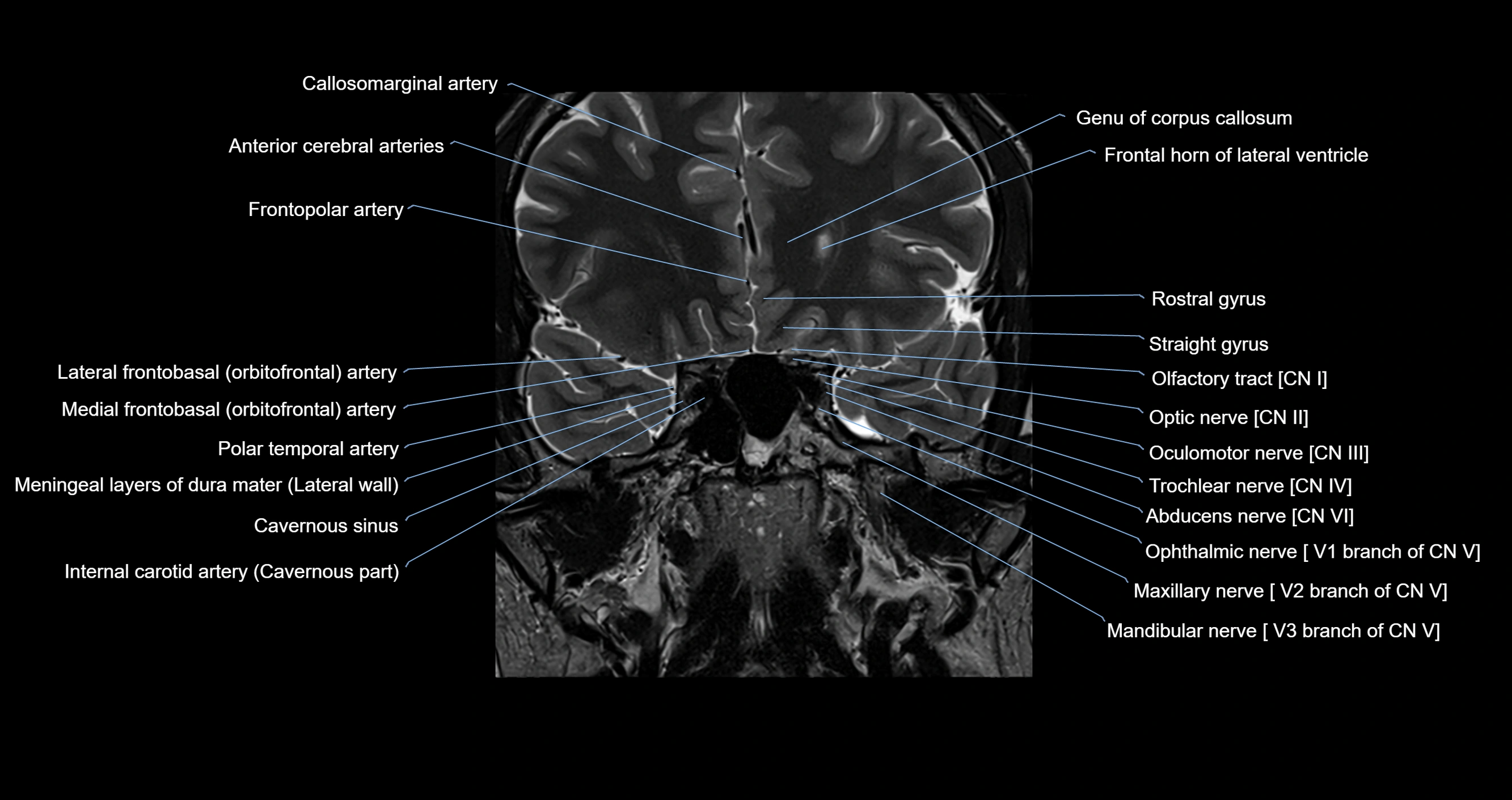
- Callosomarginal artery
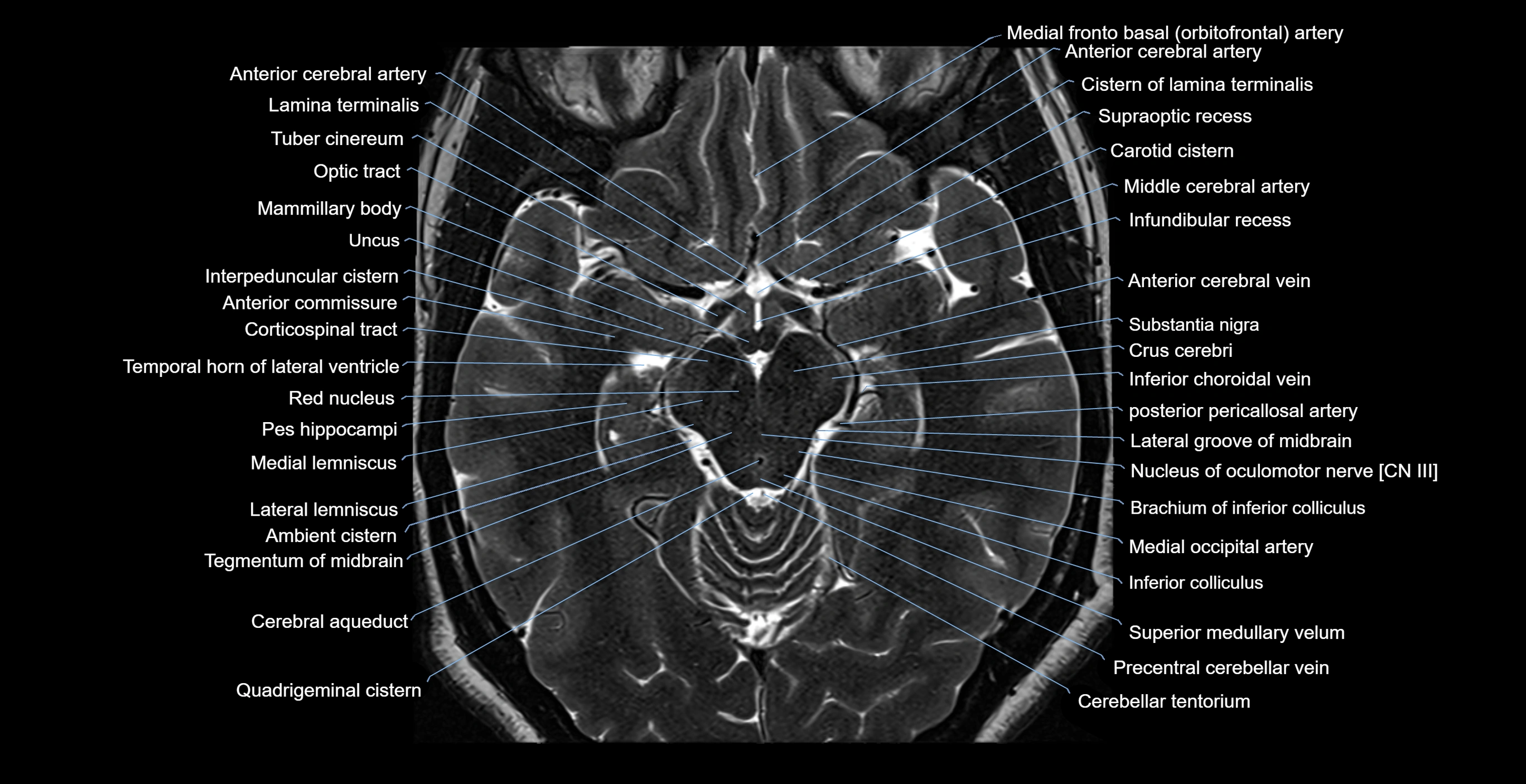
- Carotid cistern
- Carotid siphon
- Caudato-lenticular bridges
- Caudatolenticular gray bridges
- Cave of septum pellucidum
- Central canal
- Central lobule
- Central lobule (II & III) of Cerebellum
- Central part of lateral ventricle
- Cerebellar commissure
- Cerebellar falx
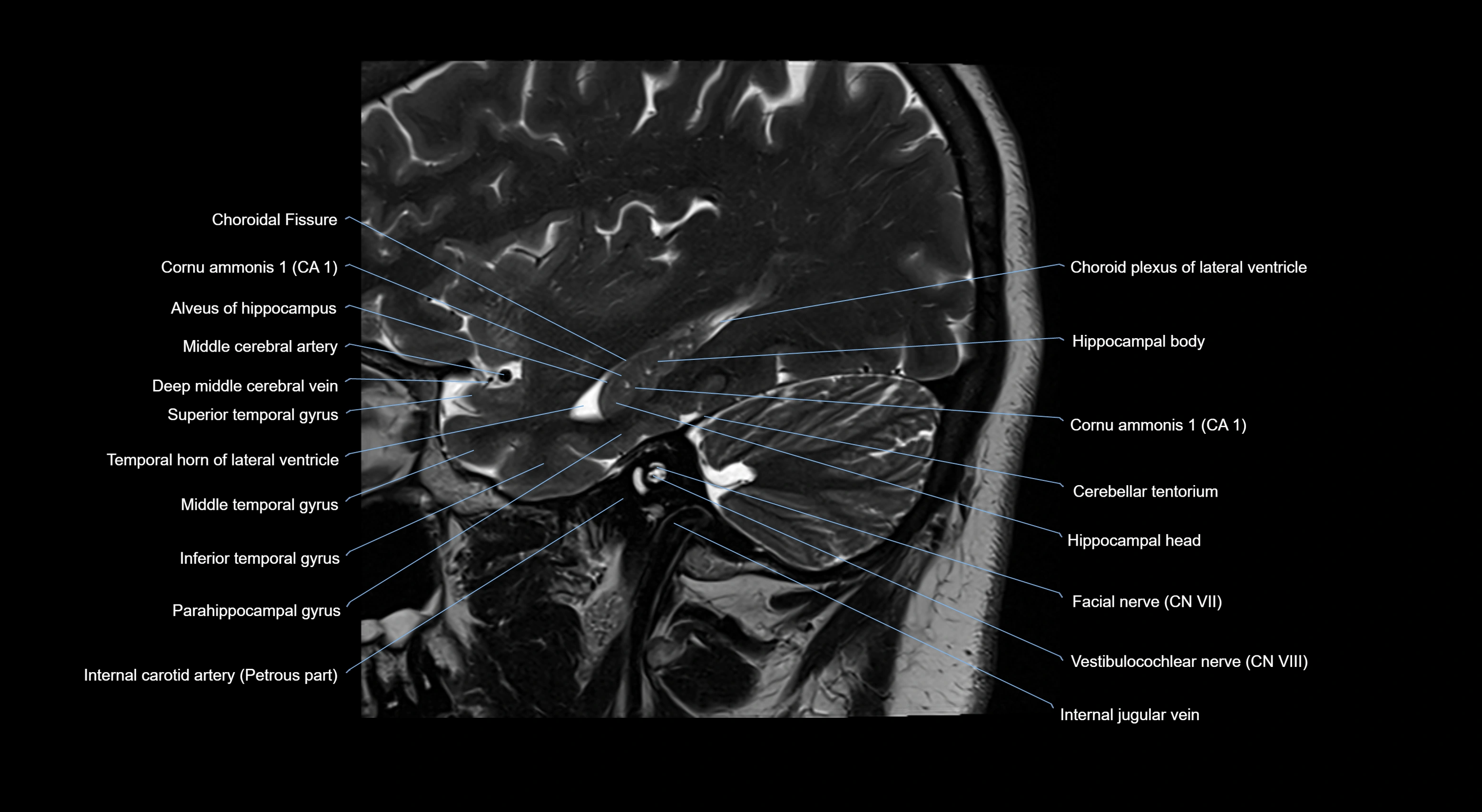
- Cerebellar tentorium
- Cerebellar tonsil (H IX)
- Cerebellopontine angle
- Cerebellopontine cistern
- Cerebellum
- Cerebral aqueduct
- Cerebral crus
- Cerebral falx
- Chiasmatic cistern
- Choroid fissure
- Choroid plexus
- Choroid plexus of fourth ventricle
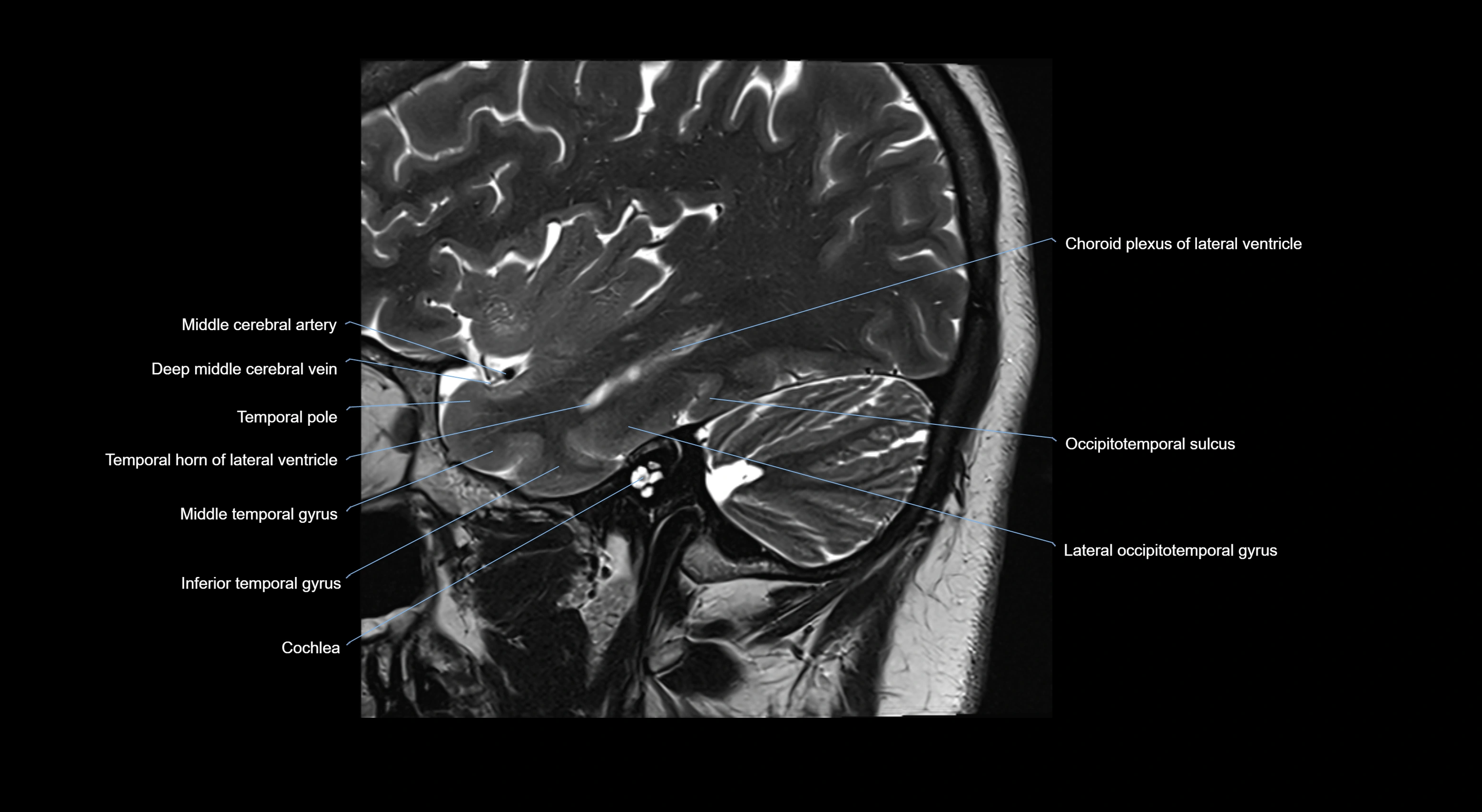
- Choroid plexus of the lateral ventricle
- Cistern of central sulcus
- Cistern of lamina terminalis
- Cistern of lateral cerebral fossa
- Cistern of transverse fissure
- Cisterna magna
- Claustrum
- Cochlea
- Cochlear nerve (Cranial nerve VIII)
- Collateral trigone
- Column of fornix
- Confluence of sinuses
- Corona radiata
- Corticospinal tract
- Crista galli
- Crural cistern
- Crus I of ansiform lobule of cerebellum
- Crus II of ansiform lobule of cerebellum
- Crus cerebri
- Crus of fornix
- Culmen
- Culmen (IV, V) of Cerebellum
- Cuneate fasciculus
- Cuneus
- Declive
- Declive (VI) of Cerebellum
- Decussation of the superior cerebellar peduncles
- Deep mddle cerebral veins
- Dentate nucleus
- Dorsal cochlear nucleus
- Dorsal nucleus of vagus nerve
- Dorsal vein of corpus callosum
- External capsule
- Extreme capsule
- Facial Nerve (Cranial nerve VII)
- Fibers of trigeminal nerve
- Flocculonodular lobe
- Flocculus
- Folium (VII) of Cerebellum
- Folium of Vermis
- Foramen caecum of medulla oblongata
- Fourth ventricle
- Frenulum veli
- Frontal bone
- Frontal horn of lateral ventricle
- Frontobasal artery
- Frontopolar artery
- Genu of corpus callosum
- Globus pallidus external segment
- Globus pallidus internal segment
- Glossopharyngeal nerve (Cranial nerve IX)
- Gracile fasciculus
- Great cerebral vein
- Habenula
- Habenular commissure
- Head of caudate nucleus
- Horizontal fissure (cerebellum)
- Hypoglossal Nerve (Cranial nerve XII)
- Hypoglossal nucleus
- Hypophysial cistern
- Hypothalamic sulcus
- Hypothalamus
- Inferior branch vestibular nerve
- Inferior cerebellar peduncle
- Inferior cerebellar veins
- Inferior colliculus
- Inferior hemispheric cerebellar veins
- Inferior hypophyseal artery anatomy
- Inferior olive
- Inferior opening of cerebral aqueduct
- Inferior parietal lobule
- Inferior petrosal sinus
- Inferior sagittal sinus
- Inferior salivatory nucleus
- Inferior semilunar lobule
- Inferior vein of vermis
- Inferior vestibular nucleus
- Infundibular recess
- Infundibulum
- Insular lobe
- Insular threshold
- Internal carotid artery
- Internal cerebral vein
- Internal jugular vein
- Internal medullary lamina
- Interpeduncular Cistern
- Interpeduncular fossa
- Interthalamic adhesion
- Interventricular foramen
- Intrabiventral Fissure of Biventral Lobule
- Intraculminate fissure
- Isthmus of cingulate gyrus
- Jugular tubercle
- Labyrinthine artery
- Lacrimal nucleus
- Lamina terminalis
- Lateral aperture of fourth ventricle (foramen of Luschka)
- Lateral aperture of the fourth ventricle
- Lateral cerebellomedullary cistern
- Lateral frontobasal artery
- Lateral geniculate body
- Lateral groove of midbrain
- Lateral lemniscus
- Lateral longitudinal fasciculus
- Lateral mesencephalic vein
- Lateral occipital artery
- Lateral orbitofrontal artery
- Lateral pallidum
- Lateral part of biventeral lobule
- Lateral pontine vein
- Lateral recess fourth ventricle
- Lateral vestibular nucleus
- Left Vertebral Artery (Intracranial Part)
- Left vertebral artery
- Limbic lobe
- Lingual gyrus
- Lingula of cerebellum
- Lingula of cerebellum (I)
- Locus ceruleus
- Long medial striate artery
- Lunogracle fissure
- Lunogranicile fissure of cerebellum
- Mammillary body
- Mandibular nerve
- Marginal branch of cingulate sulcus
- Marginal sinus
- Mastoid emissary vein
- Maxillary nerve
- Medial frontobasal artery
- Medial geniculate body
- Medial lemniscus
- Medial longitudinal fasciculus
- Medial occipital artery
- Medial orbitofrontal artery
- Medial pallidum
- Medial part of biventeral lobule
- Medial vein of lateral ventricle
- Medial vestibular nucleus
- Median aperture of fourth ventricle (foramen of Magendie)
- Median aperture of the fourth ventricle
- Median sulcus of rhomboid fossa
- Median sulcus of the 4th ventricle
- Medulla oblongata
- Medullopontine sulcus
- Meninges
- Mesencephalic nucleus of trigeminal nerve
- Middle cerebellar peduncle
- Middle cerebral artery
- Middle cerebral artery cortical segment (M4)
- Middle cerebral artery horizontal segment (M1)
- Middle cerebral artery insular segment (M2)
- Middle cerebral artery opercular segment (M3)
- Middle meningeal artery
- Middle temporal artery
- Motor nucleus of facial nerve
- Motor nucleus of trigeminal nerve
- Nodule of vermis
- Nodule of vermis (X)
- Nucleus of abducens nerve
- Nucleus of hypoglossal nerve
- Nucleus of oculomotor nerve
- Nucleus of solitary tract
- Nucleus of the solitary tract
- Nucleus of trochlear nerve
- Nucleus reticularis tegmenti pontis
- Nucleus supraspinalis
- Obex
- Occipital emissary vein
- Occipital horn of lateral ventricle
- Occipital sinus
- Oculomotor Nerve (Cranial Nerve III)
- Oculomotor cistern
- Olfactory Nerve (Cranial Nerve I)
- Olfactory bulb
- Olfactory cistern
- Olfactory tract
- Olfactory trigone
- Olfactory tubercle
- Ophthalmic artery
- Ophthalmic nerve
- Optic Nerve (Cranial Nerve II)
- Optic chiasm
- Optic tract
- Orbital Sulci
- Orbital gyri
- Parabrachial recess
- Paracentral artery
- Paracentral gyrus
- Paracentral lobule
- Paramedian lobule
- Paramedian lobule (HVII) of cerebellum
- Paraolfactory sulci
- Parieto-occipital artery
- Peduncle of flocculus
- Pericallosal artery
- Pericallosal cistern
- Perivascular spaces
- Pes hippocampi
- Petrosal vein
- Pineal gland
- Pineal recess
- Pituitary gland
- Pituitary stalk
- Polar frontal artery
- Polar temporal artery
- Pons
- Pons (basilar portion)
- Pontine arteries
- Pontine artery
- Pontine nucleus
- Pontocerebellar cistern
- Pontocerebellar fibers
- Pontomedullary junction
- Pontomedullary sulcus
- Posterior cerebellomedullary cistern (cisterna magna)
- Posterior cerebral artery
- Posterior cerebral artery (P1 Segment)
- Posterior cerebral artery (P2 Segment)
- Posterior cerebral artery (P3 Segment)
- Posterior cerebral artery (P4 Segment)
- Posterior cochlear nucleus
- Posterior commissure
- Posterior communicating artery
- Posterior hippocampal artery
- Posterior inferior cerebellar artery
- Posterior intercavernous sinus
- Posterior lateral choroidal artery
- Posterior limb of internal capsule
- Posterior lobe of cerebellum
- Posterior lobe pituitary gland
- Posterior median sulcus of medulla oblongata
- Posterior mesencephalic vein
- Posterior orbital sulcus
- Posterior parietal artery
- Posterior quadrangular lobule
- Posterior superior fissure
- Posterior vein of caudate nucleus
- Posterior veins of septum pellucidum
- Posterolateral fissure
- Posteromedial central (perforating) arteries
- Posteromedian medullary vein
- Pre-Rolandic artery
- Prebiventral fissure
- Precentral cerebellar vein
- Precentral fissure
- Precommunicating part of posterior cerebral artery
- Preculminate fissure
- Precuneal artery
- Premedullary cistern
- Preolivary groove
- Preoptic area
- Prepontine cistern
- Primary fissure
- Principal sensory nucleus of the trigeminal nerve
- Principal sensory nucleus of trigeminal nerve
- Pulvinar
- Putamen
- Pyramid of medulla oblongata
- Pyramid of vermis (VIII)
- Pyramids of the medulla oblongata
- Pyramis of vermis
- Quadrigeminal cistern
- Raphe of pons
- Red nucleus
- Retroolivary groove
- Right Vertebral Artery (Intracranial Part)
- Right vertebral artery
- Rolandiс artery
- Rostral gyrus
- Rostral sulcus
- Rostrum of corpus callosum
- Secondary fissure
- Semicircular Canals
- Septum pellucidum
- Sigmoid sinus
- Simple lobule
- Simple lobule (HVI) of cerebellum
- Sphenoparietal sinus
- Spinal cord
- Spinal lemniscus
- Spinal nucleus of trigeminal nerve
- Spinal trigeminal nucleus
- Spinal trigeminal nucleus (pars caudalis)
- Spinal trigeminal nucleus (pars oralis)
- Spinothalamic tract
- Splenium of corpus callosum
- Straight sinus
- Stria medullaris thalami
- Styloid process
- Substantia nigra
- Superficial cerebral veins
- Superficial middle cerebral vein
- Superior anastomotic vein
- Superior branch of vestibular nerve
- Superior cerebellar artery
- Superior cerebellar cistern
- Superior cerebellar peduncle
- Superior cerebellar vein
- Superior colliculus
- Superior hemispheric cerebellar veins
- Superior hemispheric veins of the cerebellum
- Superior hypophyseal artery
- Superior medullary velum
- Superior opening of cerebral aqueduct
- Superior opening of the cerebral aqueduct
- Superior ophthalmic vein
- Superior petrosal sinus
- Superior sagittal sinus
- Superior salivatory nucleus
- Superior semilunar lobule of cerebellum
- Superior thalamic veins
- Superior thalamostriate vein
- Superior vein of vermis
- Superior vestibular nucleus
- Supraoptic recess
- Suprapineal recess
- Sylvian cistern
- Tail of caudate nucleus
- Tectal plate
- Tegmentum of midbrain
- Tegmentum of pons
- Tela choroidea of third ventricle
- Temporal horn of lateral ventricle
- Temporal lobe
- Temporopolar artery
- Tenia of fornix
- Thalamus
- Third ventricle
- Tonsil of cerebellum
- Transverse occipital sulcus
- Transverse pontine fiber
- Transverse pontine vein
- Transverse sinus
- Transverse temporal sulcus
- Transverse veins of caudate nucleus
- Trigeminal cave
- Trigeminal ganglion
- Trigeminal nerve (Cranial nerve V)
- Trochlear nerve (Cranial nerve IV)
- Tuber cinereum
- Tuber of vermis
- Tuber of vermis (VII)
- Uncus
- Upper cervical spinal cord
- Uvula of vermis
- Uvula of vermis (IX)
- Vagus nerve (Cranial nerve X)
- Vein of lateral recess of fourth ventricle
- Vein of septum pellucidum
- Ventral cochlear nucleus
- Ventrolateral sulcus of medulla oblongata
- Vermis of cerebellum
- Vestibular ganglion
- Vestibule
- Vestibulocochlear nerve (Cranial nerve VIII)
- White matter of cerebellum (Arbor vitae)
- White substance of cerebellum
- Wing of central lobule
- cavernous sinus
- foramen of Monro
- genu of internal capsule
- interpeduncular veins
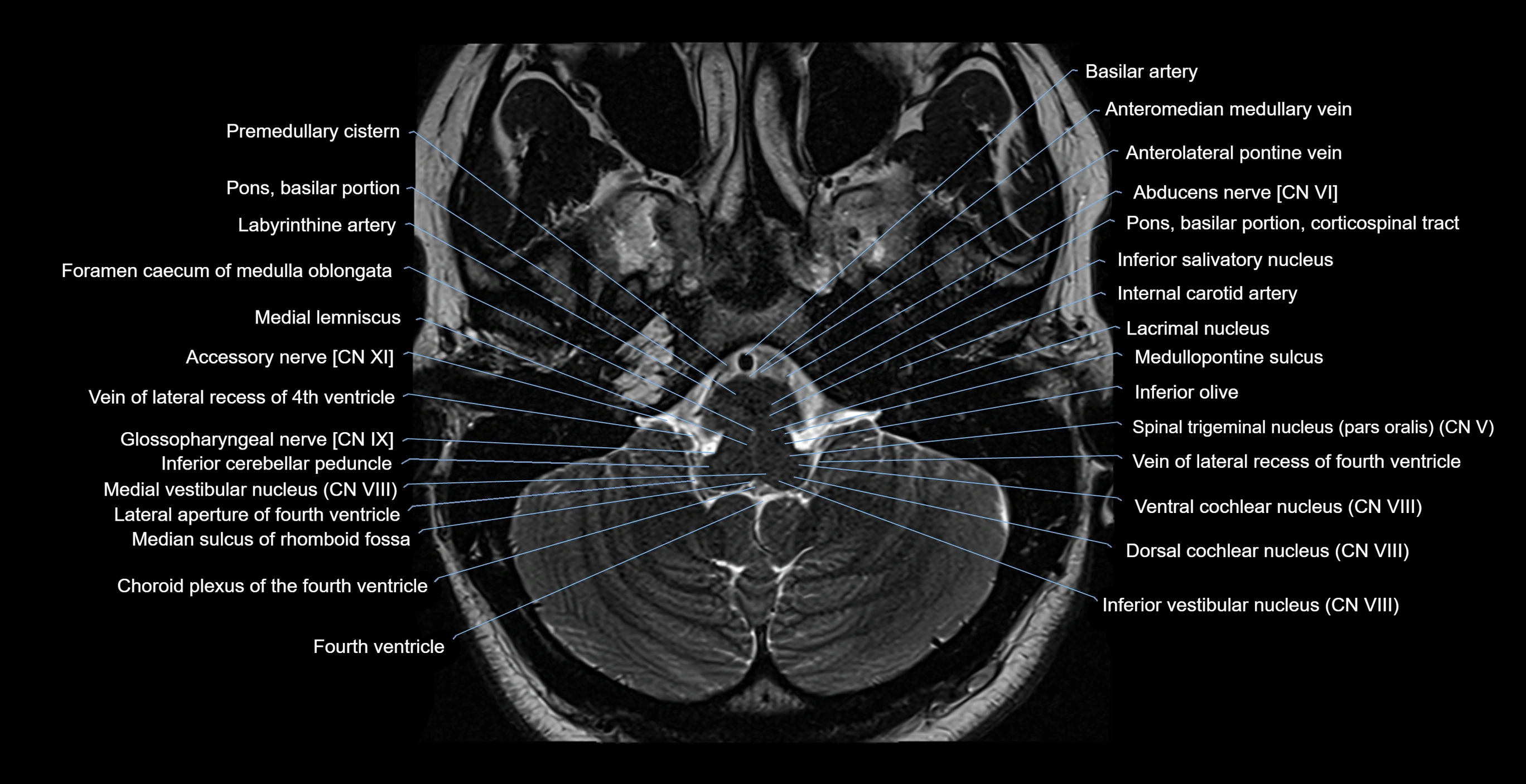
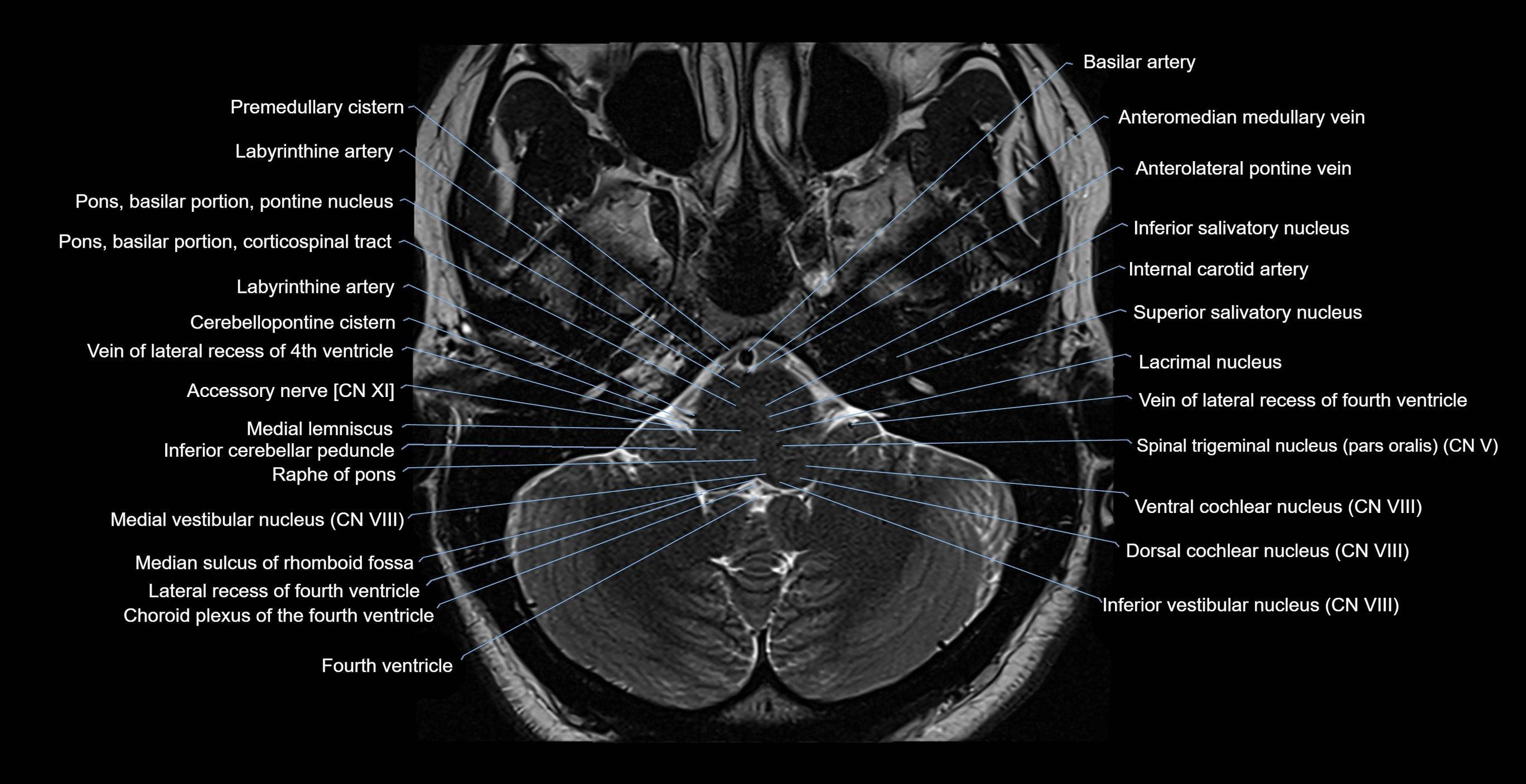
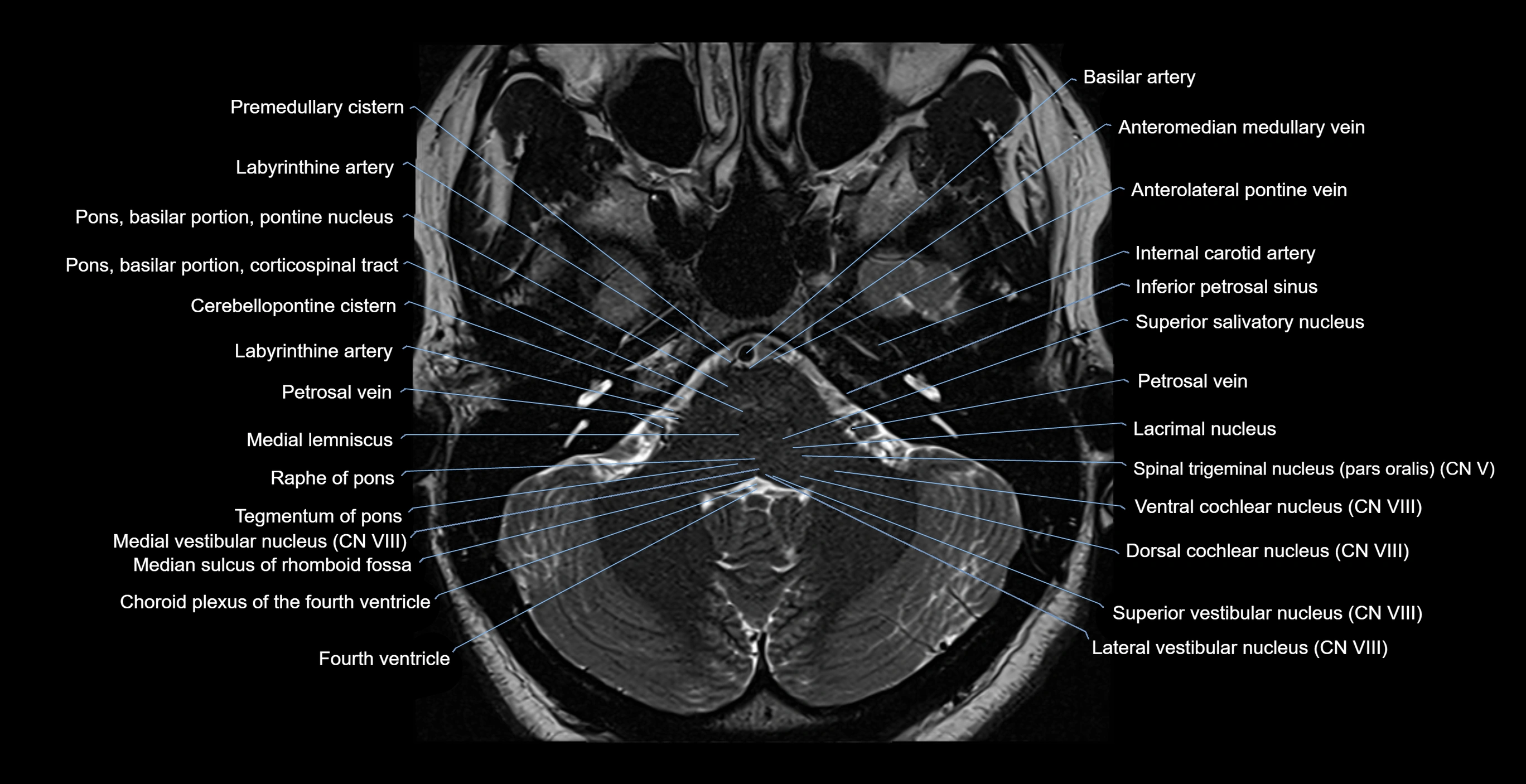
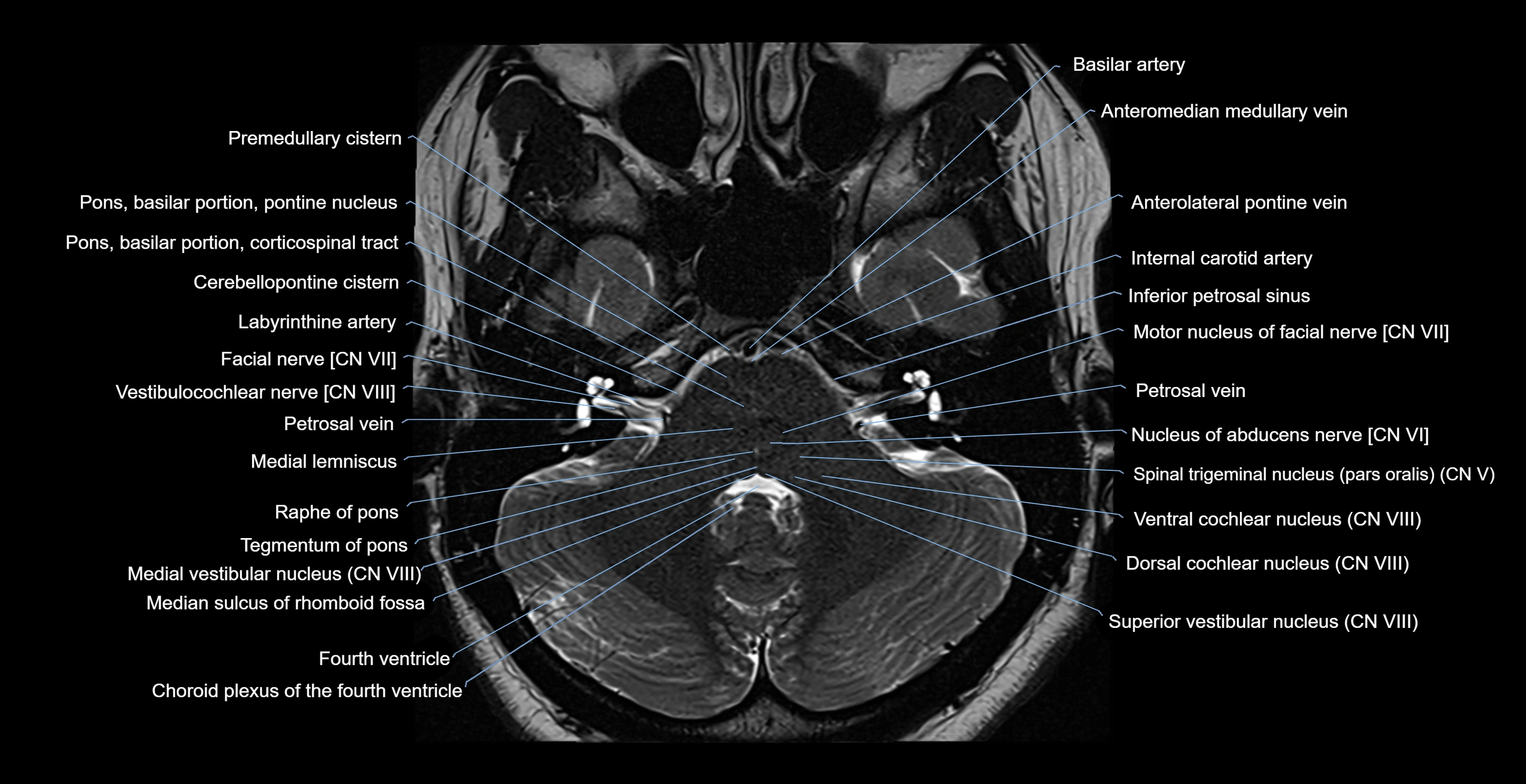
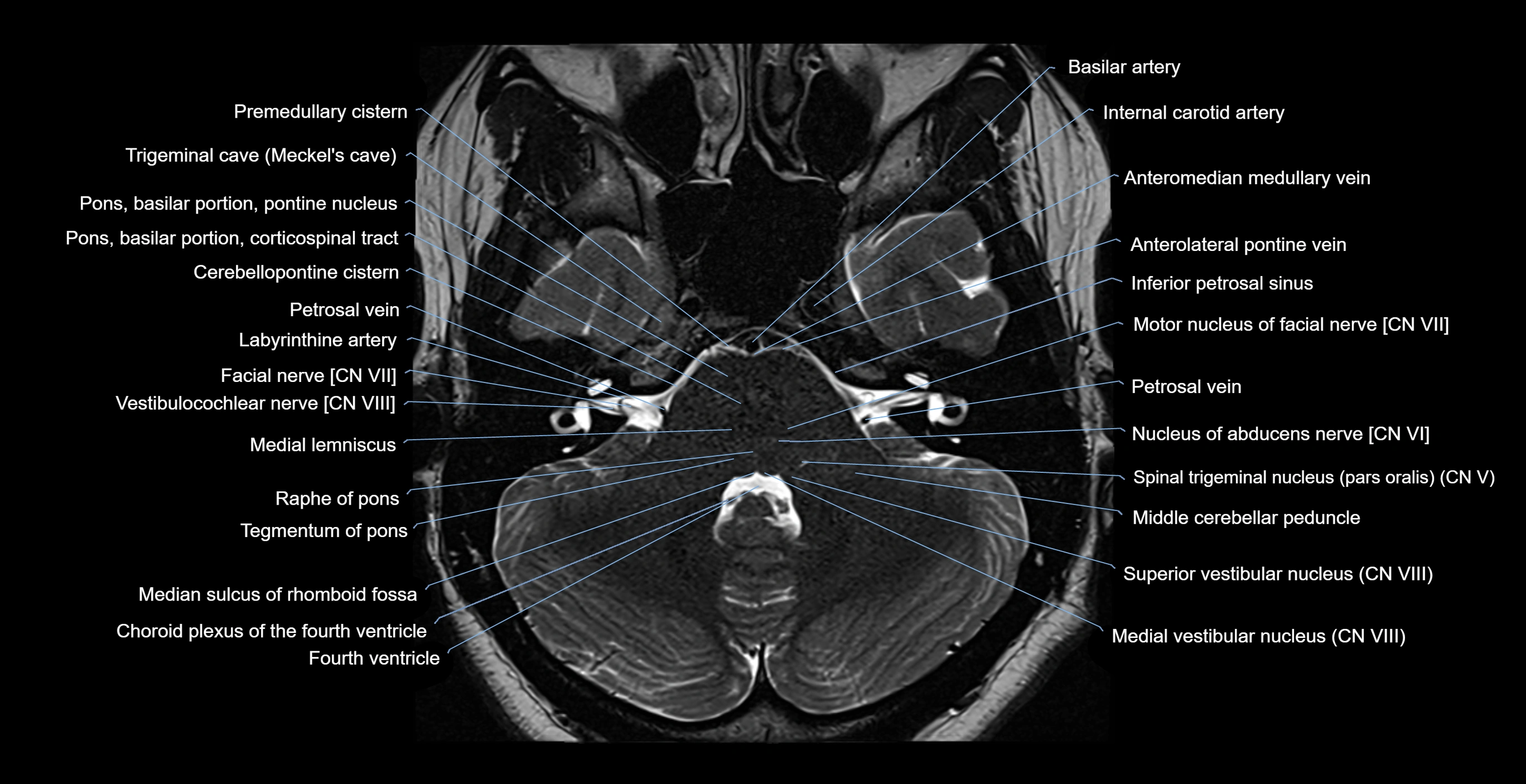
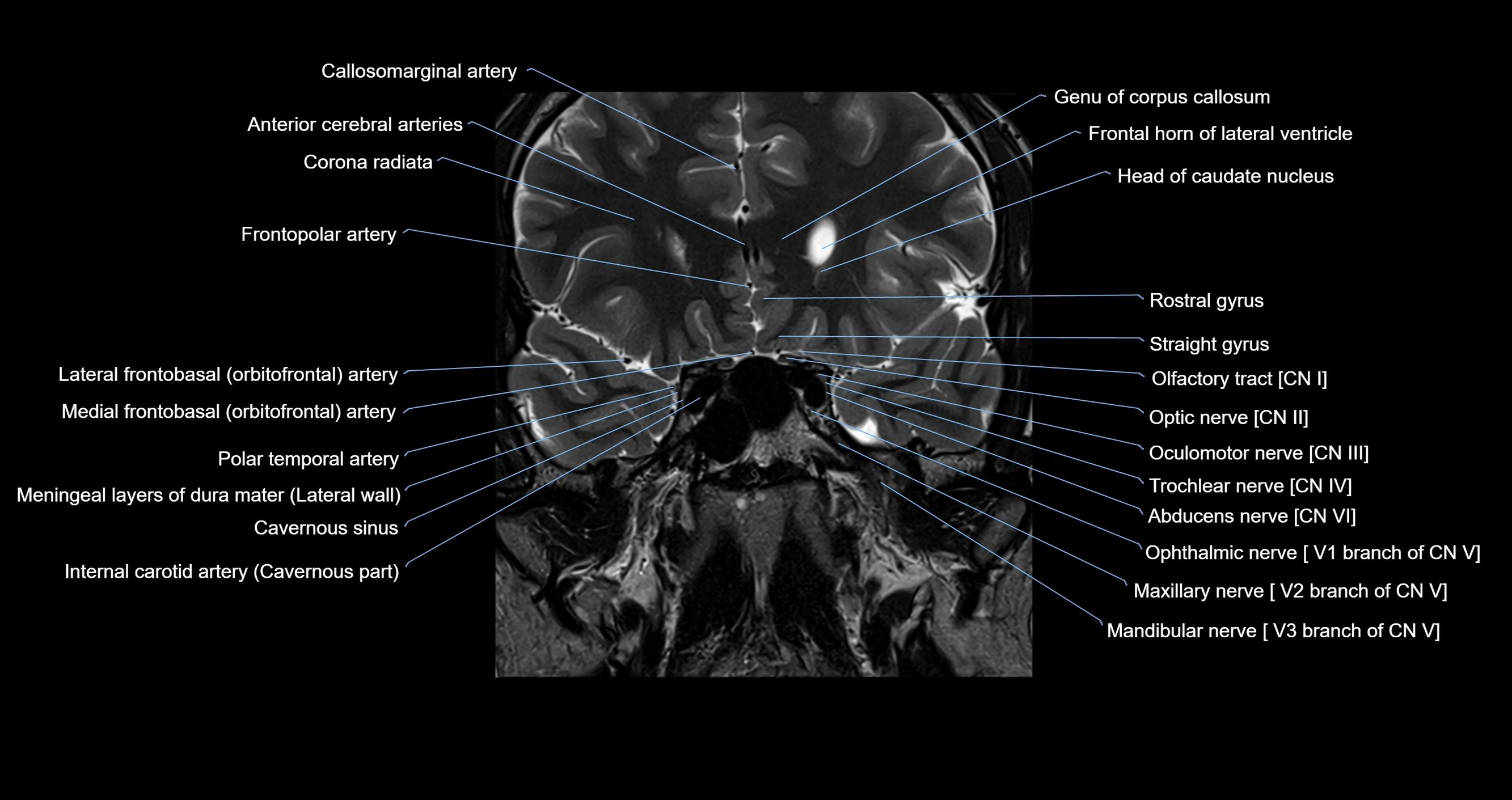
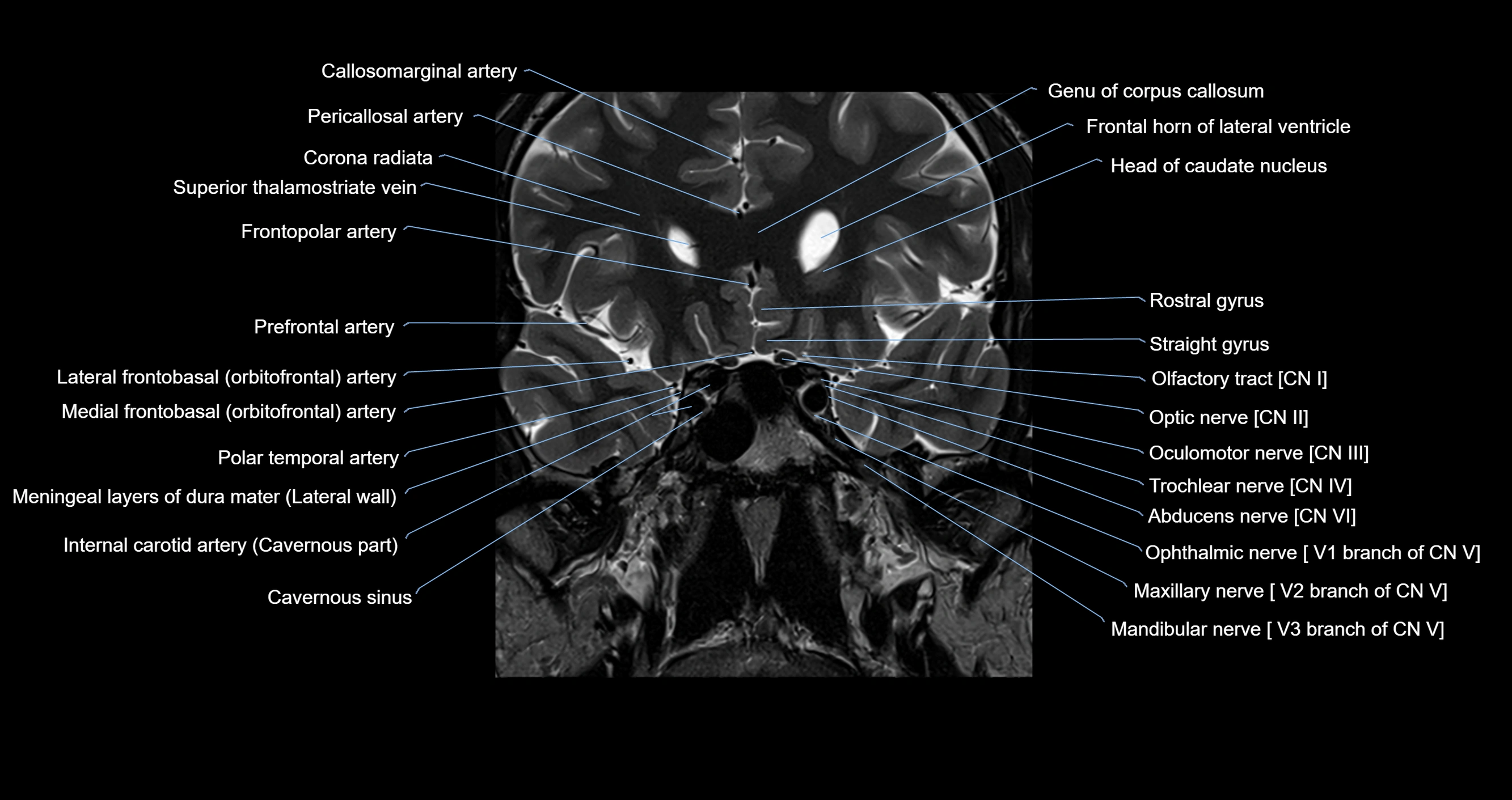
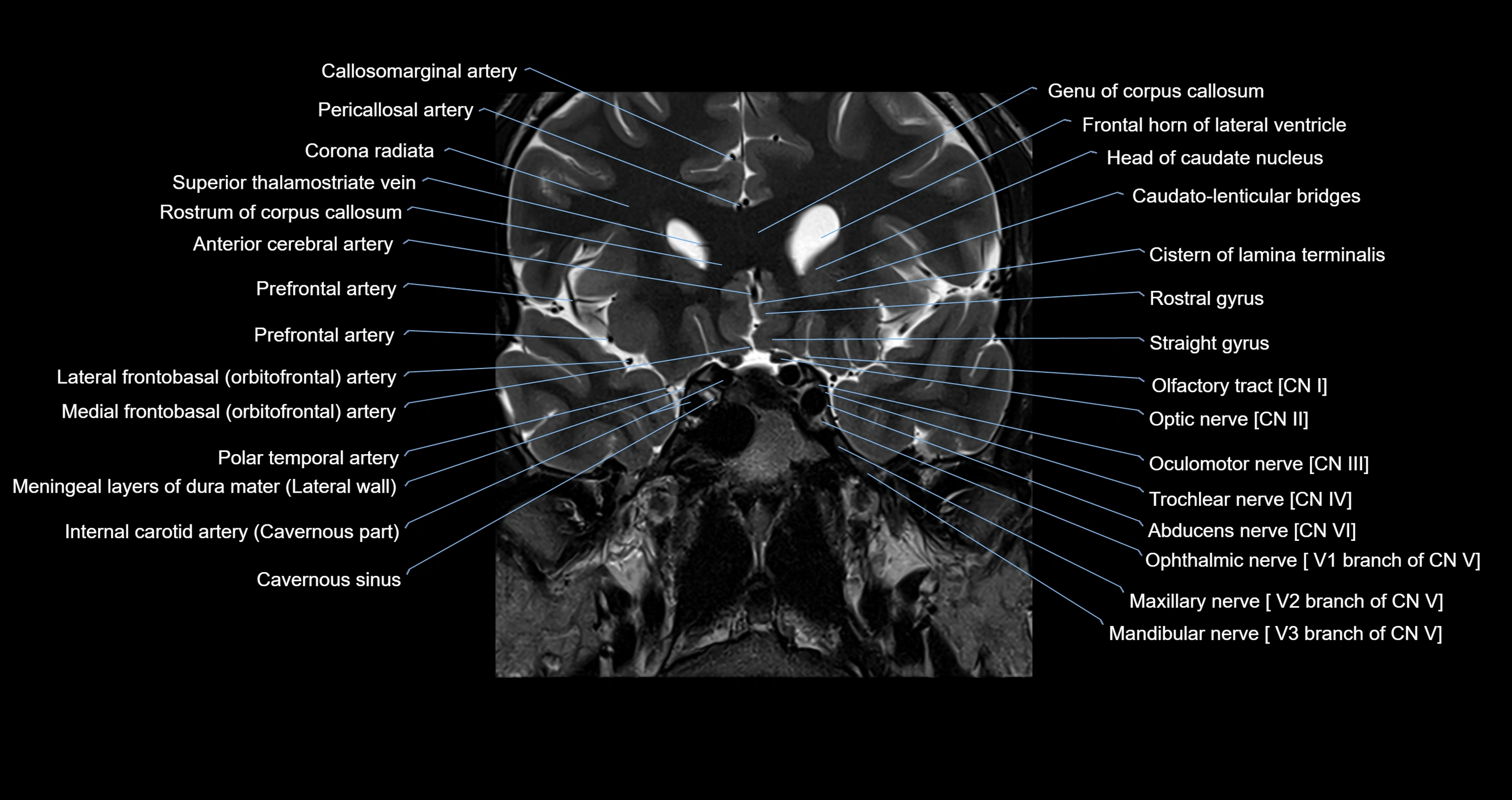
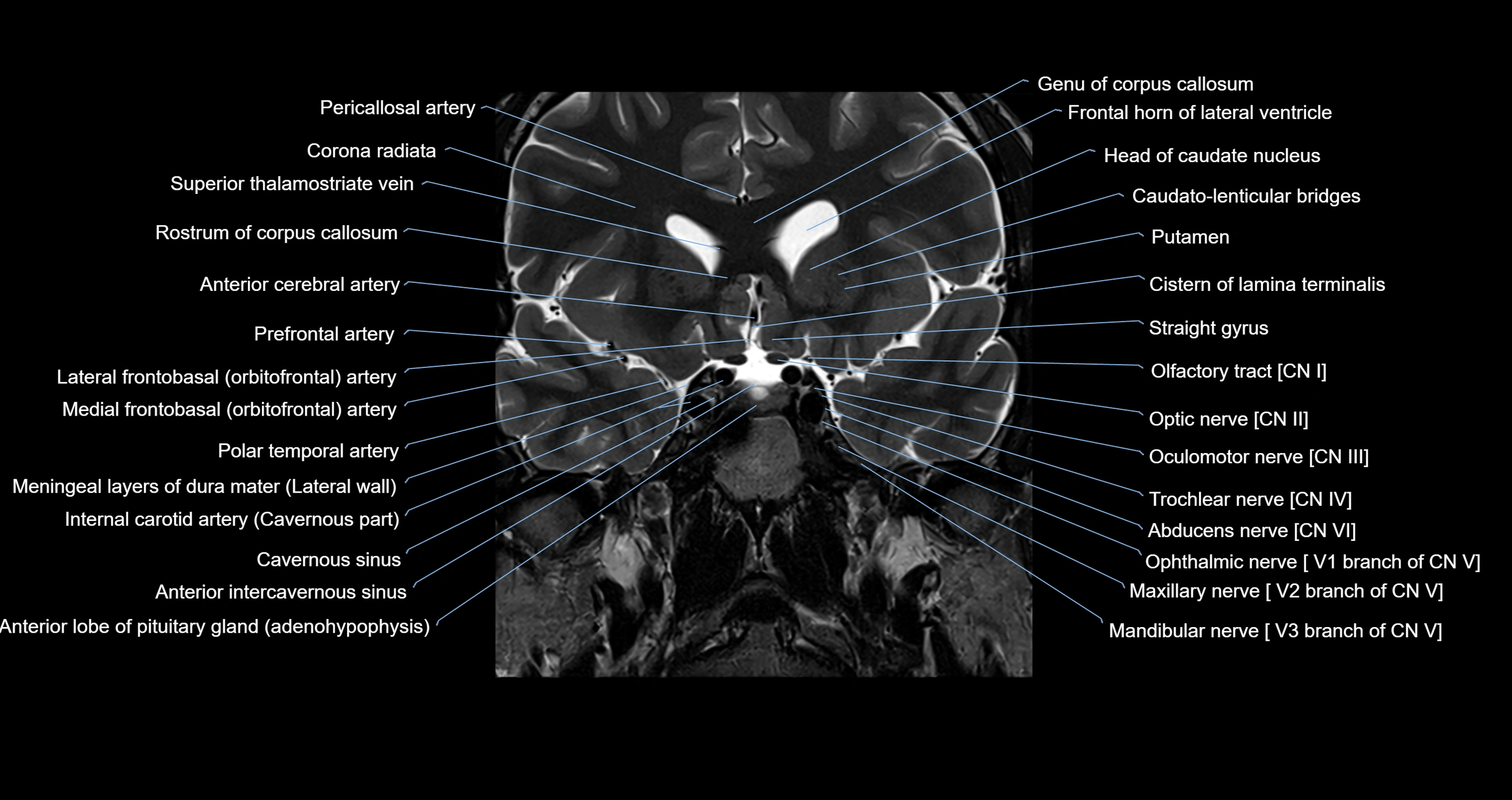
The Abducens nerve (Cranial nerve VI) is a purely motor cranial nerve responsible for innervating the lateral rectus muscle of the eye, which is crucial for lateral movement (abduction) of the eyeball. It arises from the abducens nucleus in the dorsal pons, emerges at the pontomedullary junction, and travels a long intracranial course before entering the orbit via the superior orbital fissure. Because of its long path and proximity to the clivus, it is particularly susceptible to injury from increased intracranial pressure or trauma.
Synonyms
-
Sixth cranial nerve
-
CN VI
-
N. abducens (Latin)
-
Nervus abducens
Function
-
Innervates the lateral rectus muscle of the eye
-
Responsible for abduction of the eyeball (moving the eye outward, away from the midline)
-
Is a purely motor nerve (no sensory or autonomic fibers)
-
Lesion results in inability to abduct the affected eye, leading to horizontal diplopia (double vision)
MRI Appearance
-
The abducens nerve is a small, thin, linear structure
-
Best visualized on high-resolution T2-weighted 3D MRI sequences (e.g., FIESTA or CISS)
-
Seen as a hypointense (dark) line running from the brainstem at the pontomedullary junction, traversing the prepontine cistern, and entering Dorello’s canal under the petrosphenoidal ligament, then into the cavernous sinus, and finally the orbit
-
May be challenging to visualize in standard MRI due to its small size
-
Pathology may be inferred by absence, displacement, or enhancement of the nerve
CT Appearance
-
The nerve itself is not directly visualized on conventional CT due to its small size and soft tissue density
-
Indirect signs: assessment of the bony course, such as the Dorello’s canal, superior orbital fissure, or adjacent pathologies (fractures, masses, or inflammation) that could impinge the nerve
-
CT is mainly used to exclude structural lesions or fractures that might affect the course of CN VI
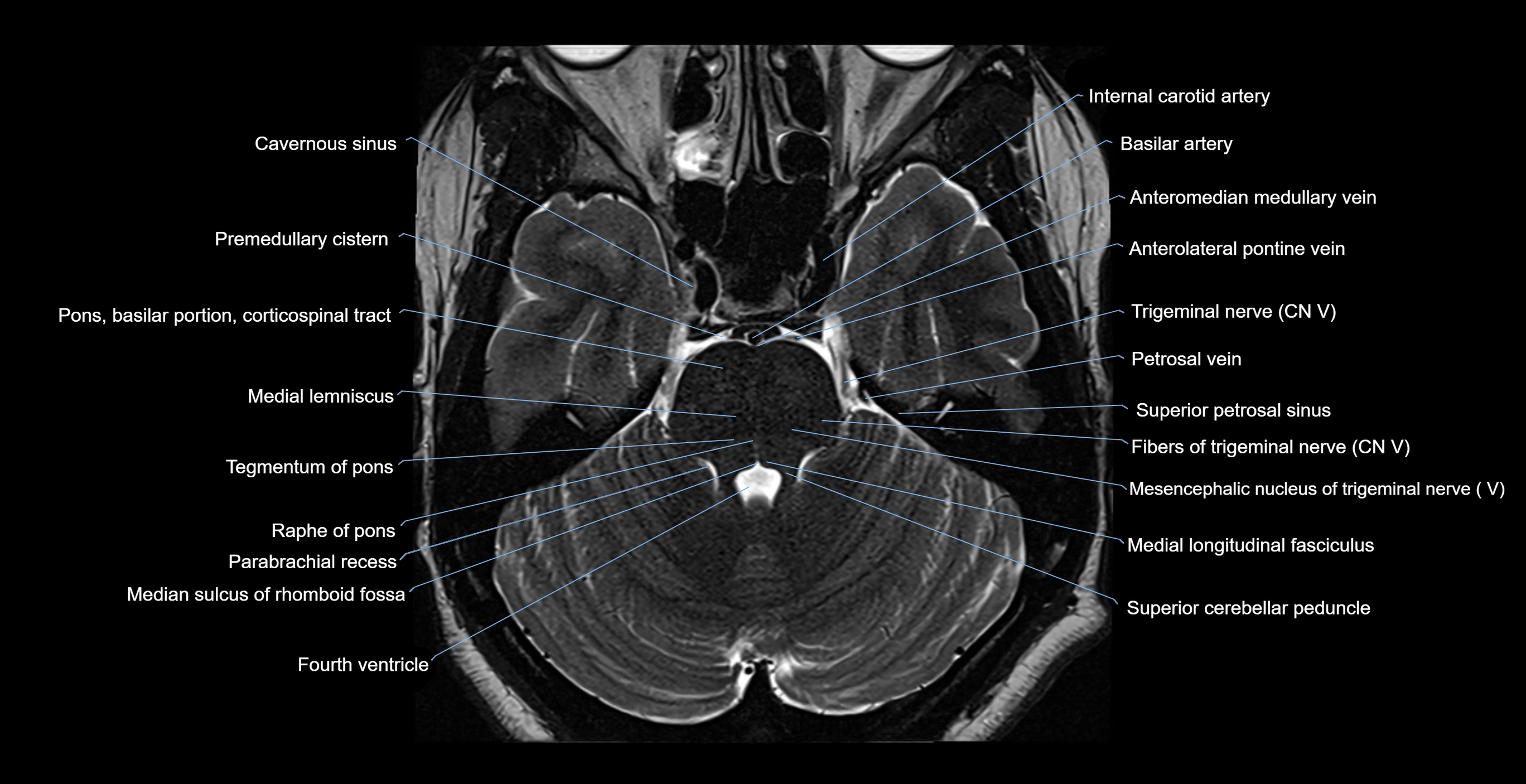
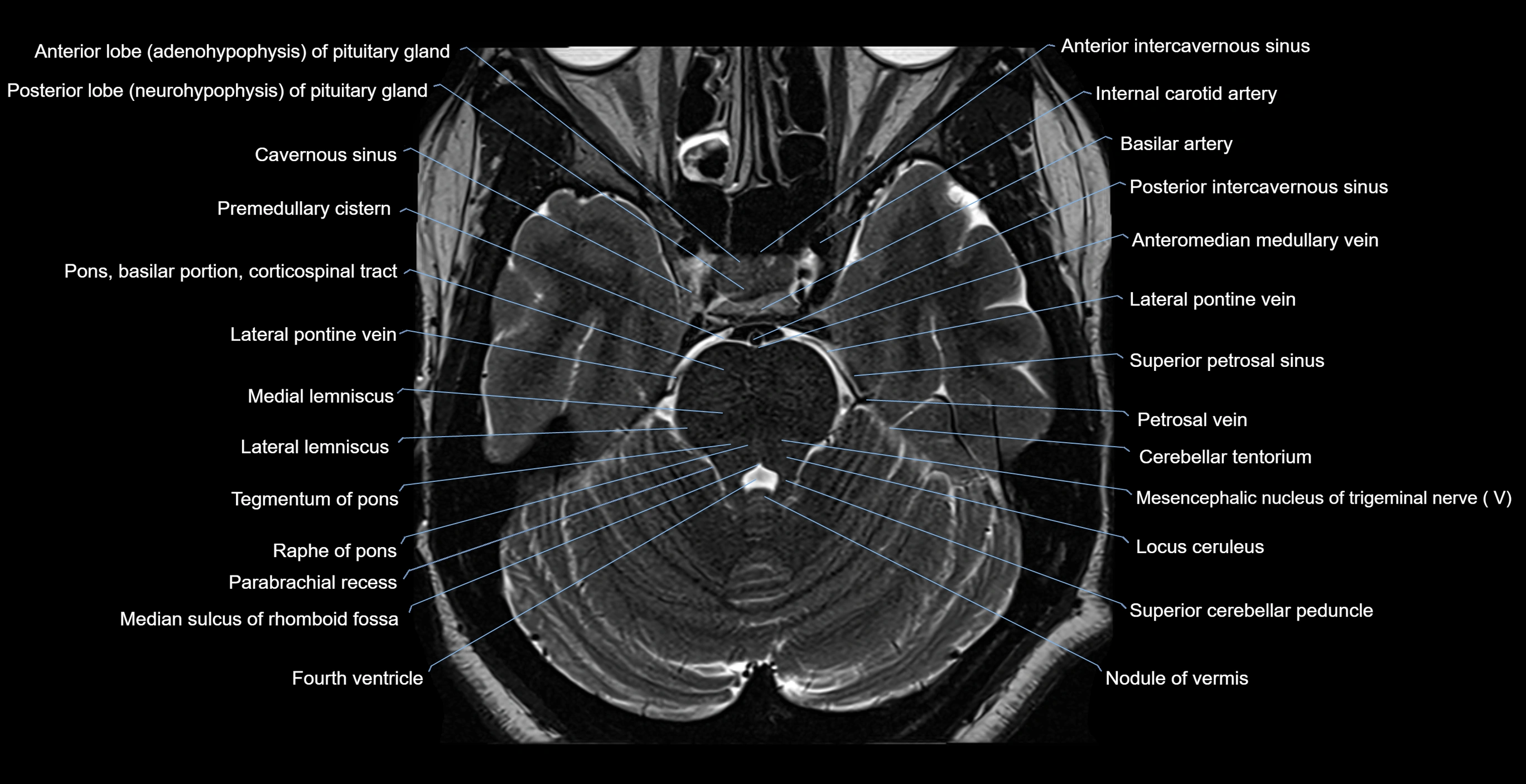
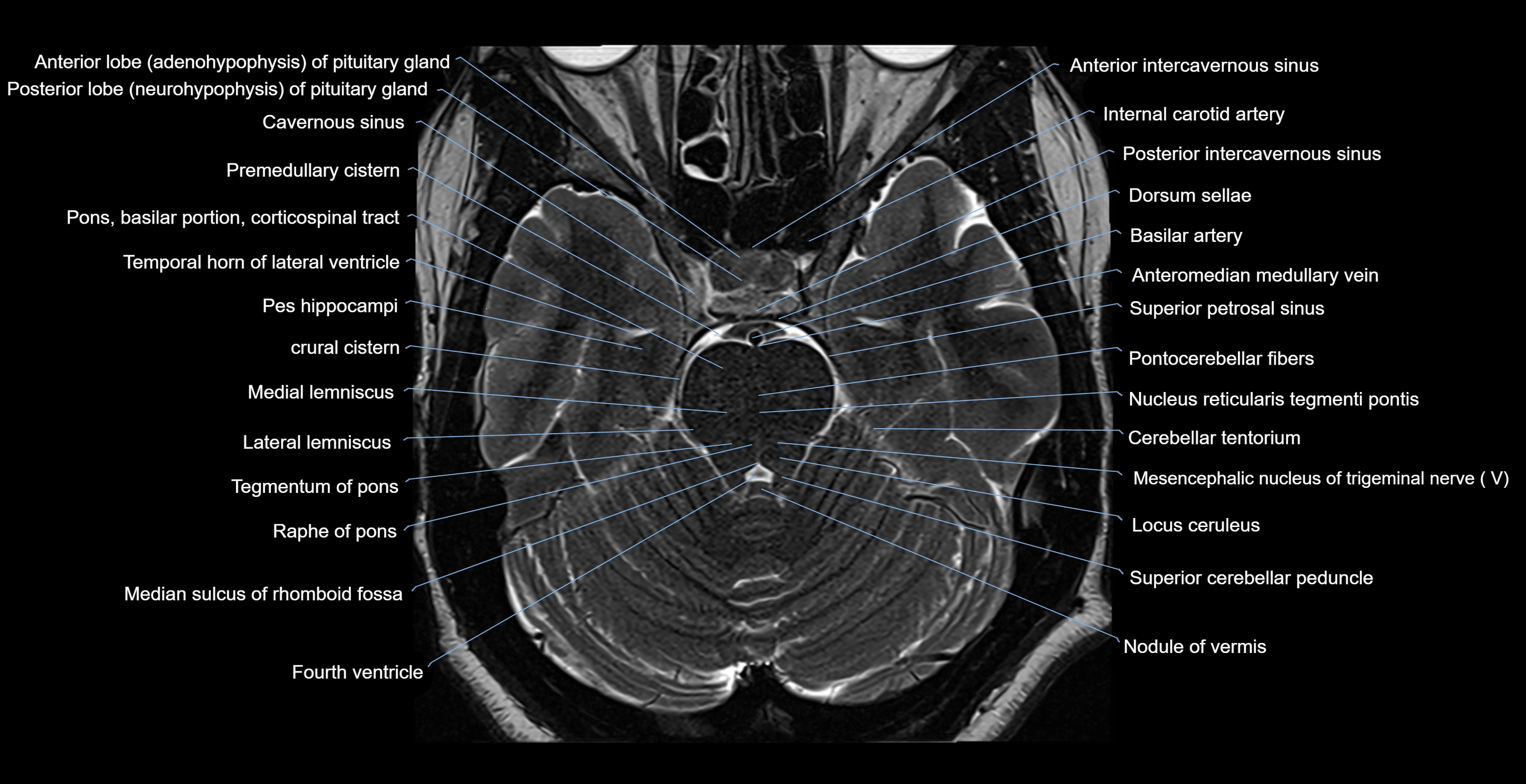
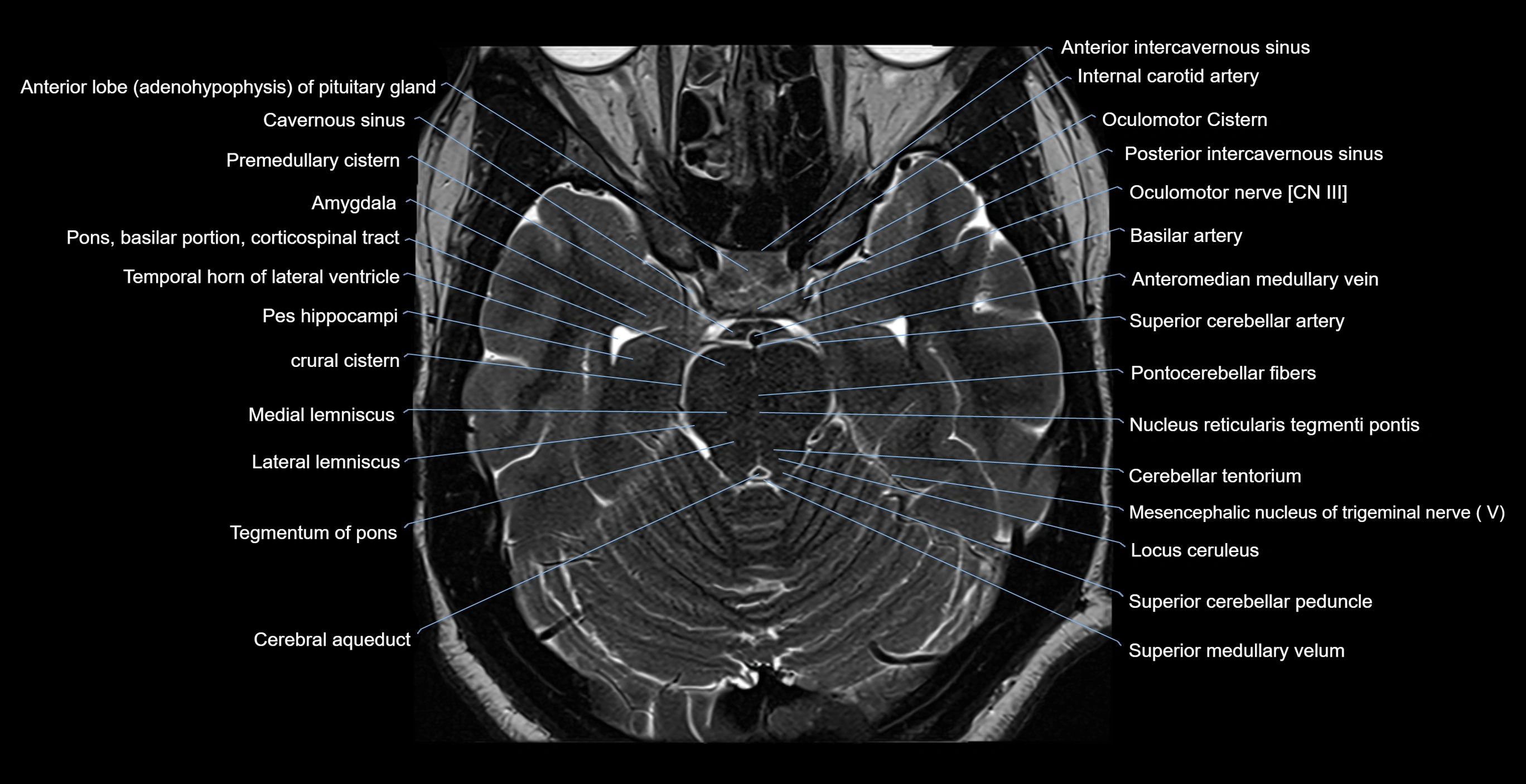
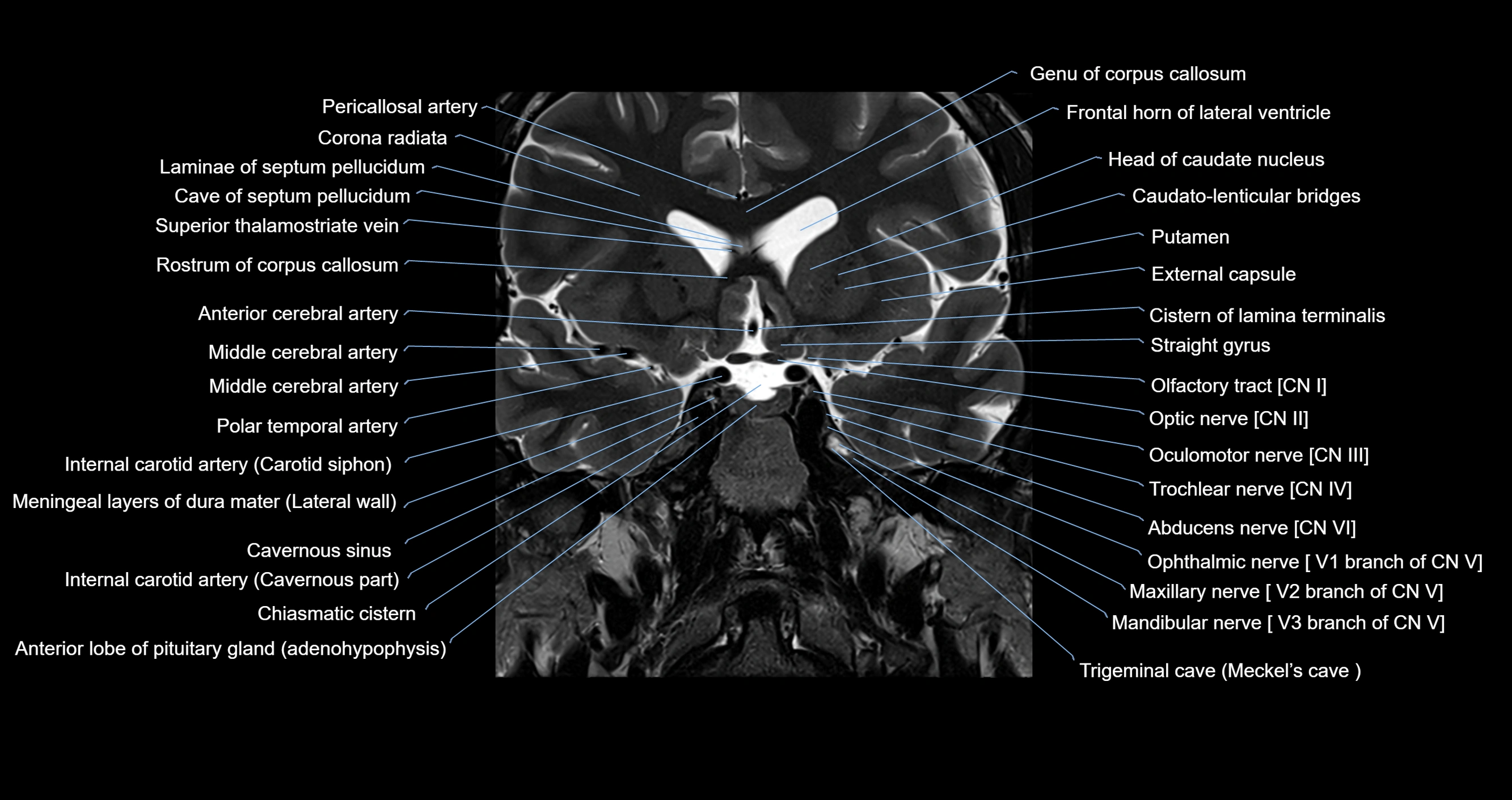
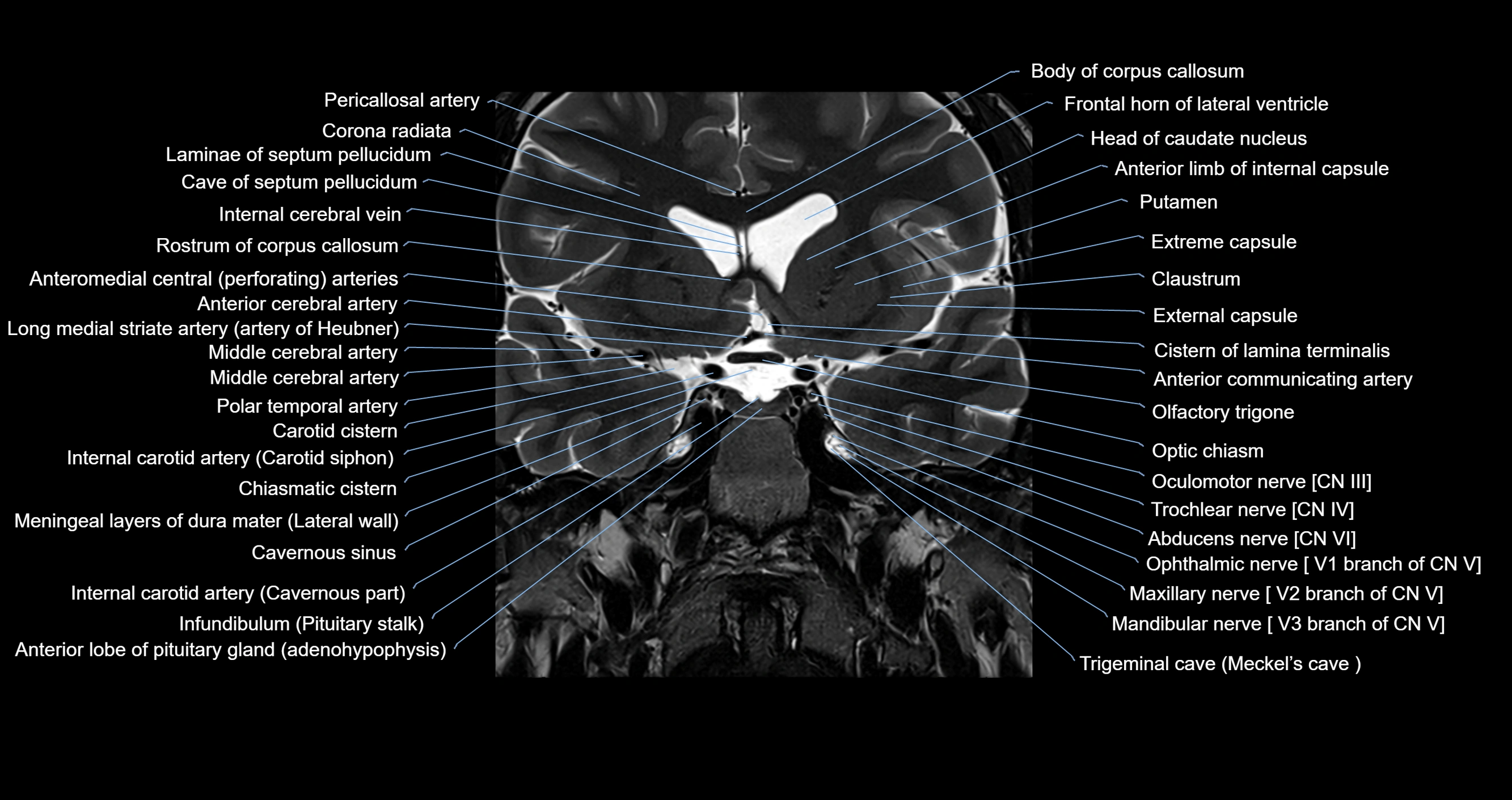
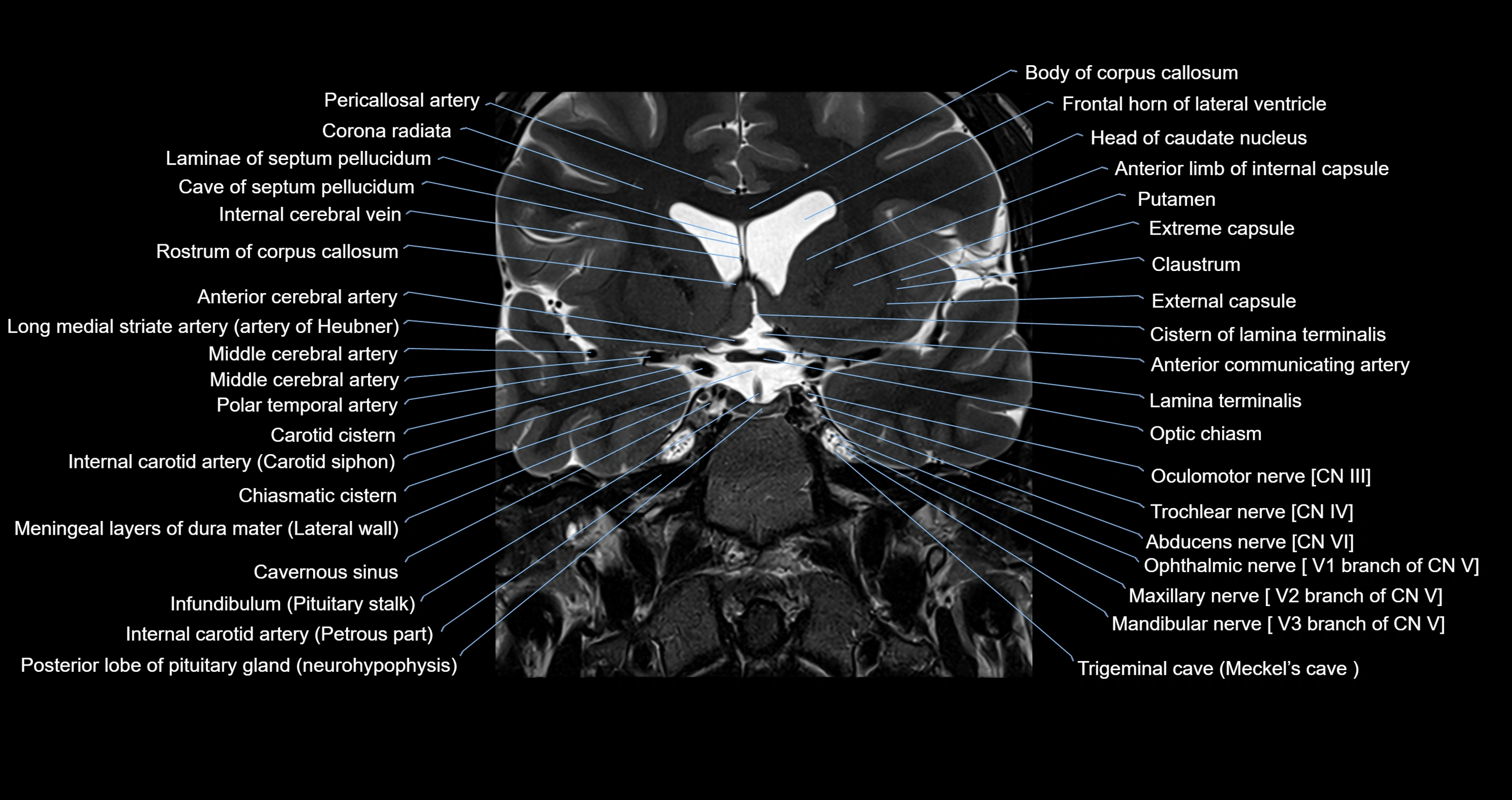
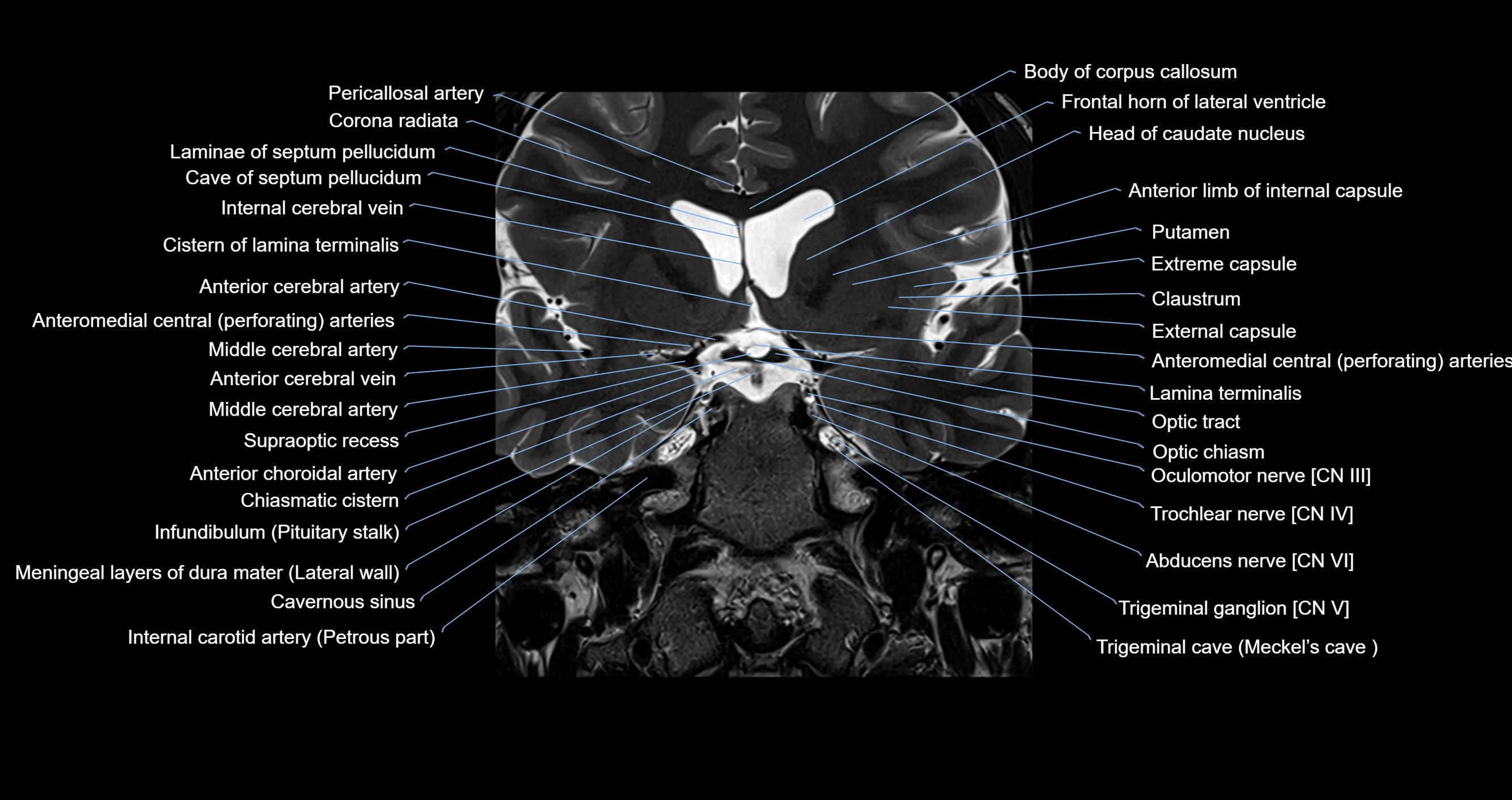
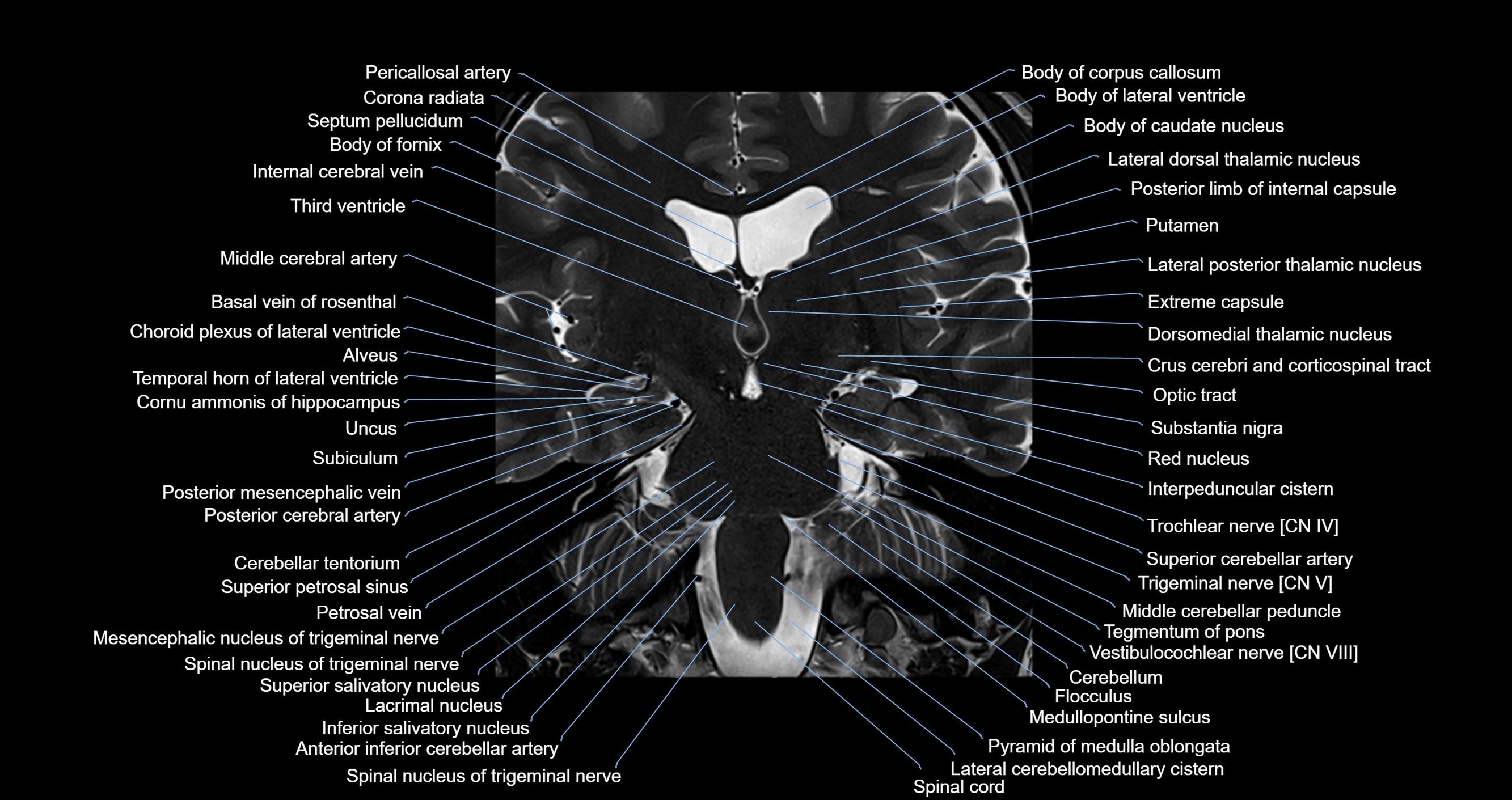
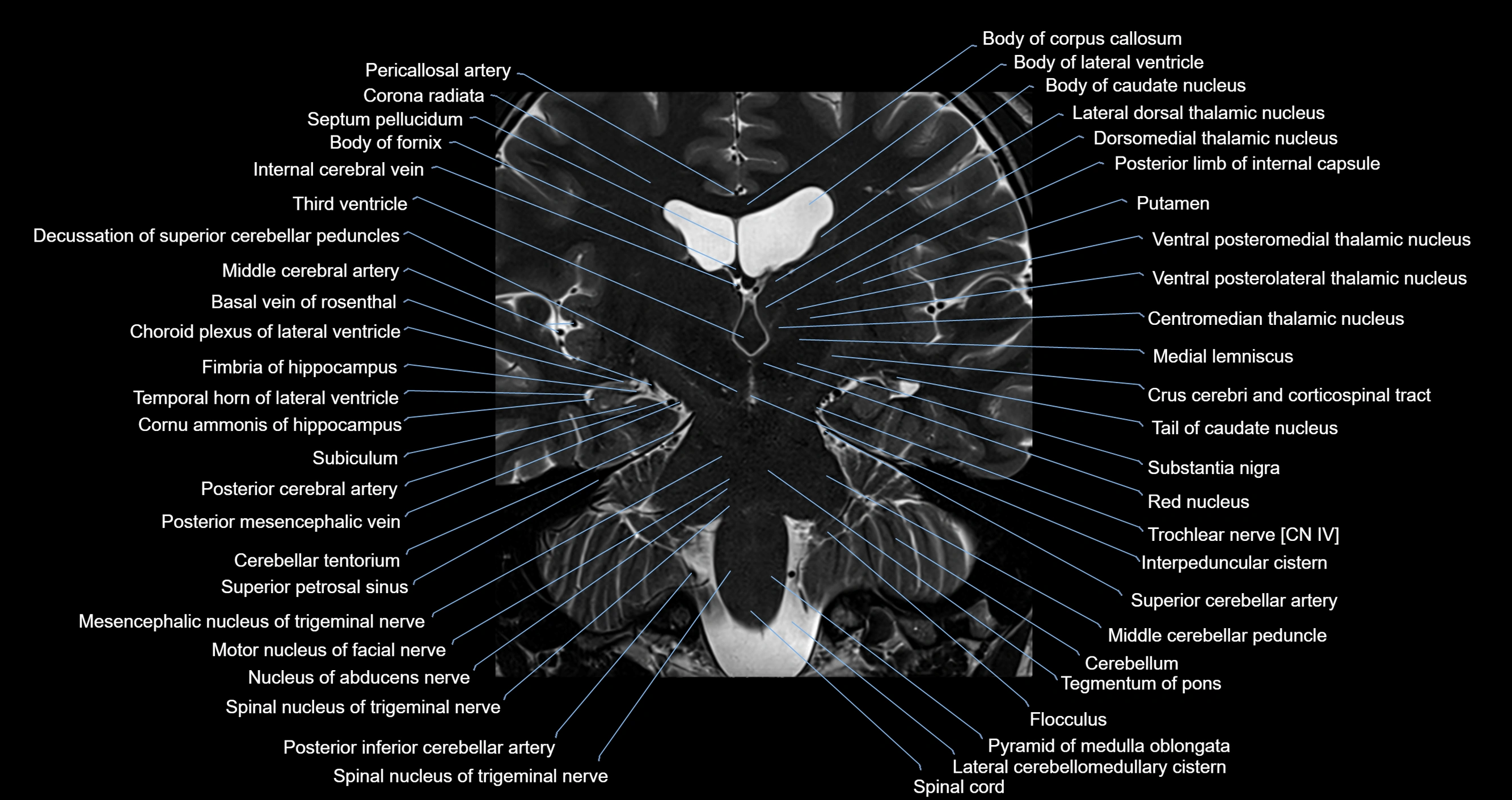
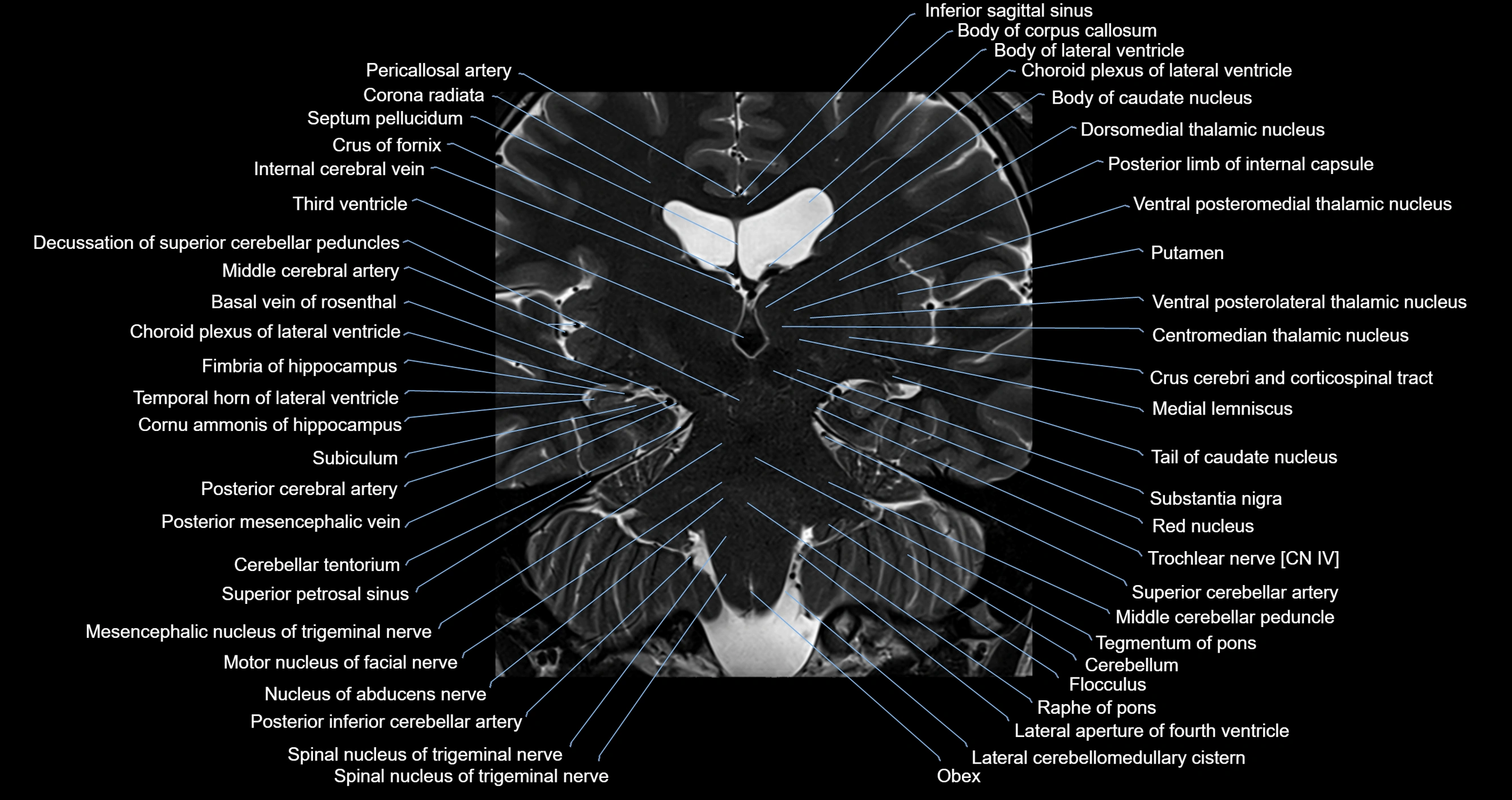
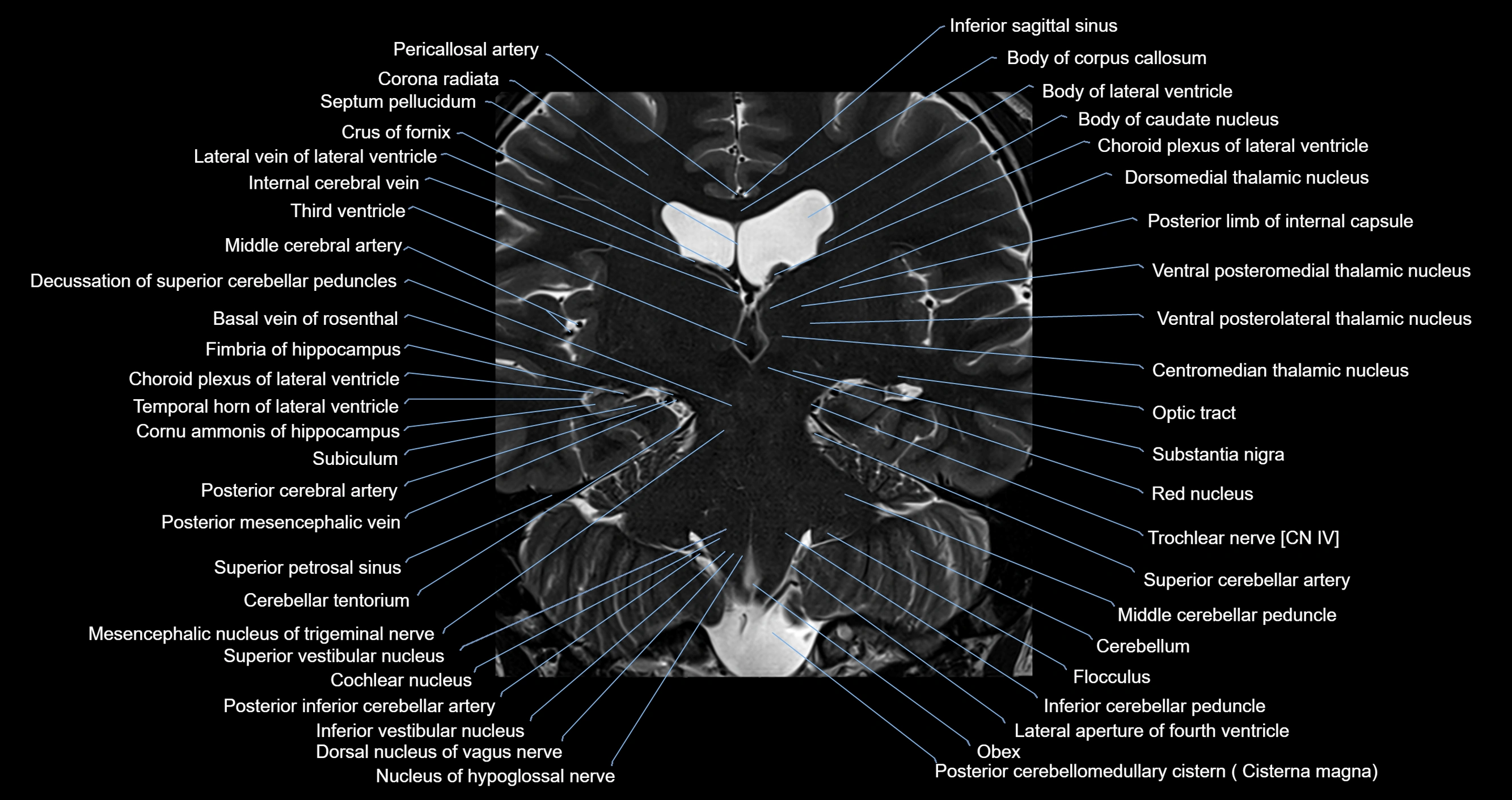
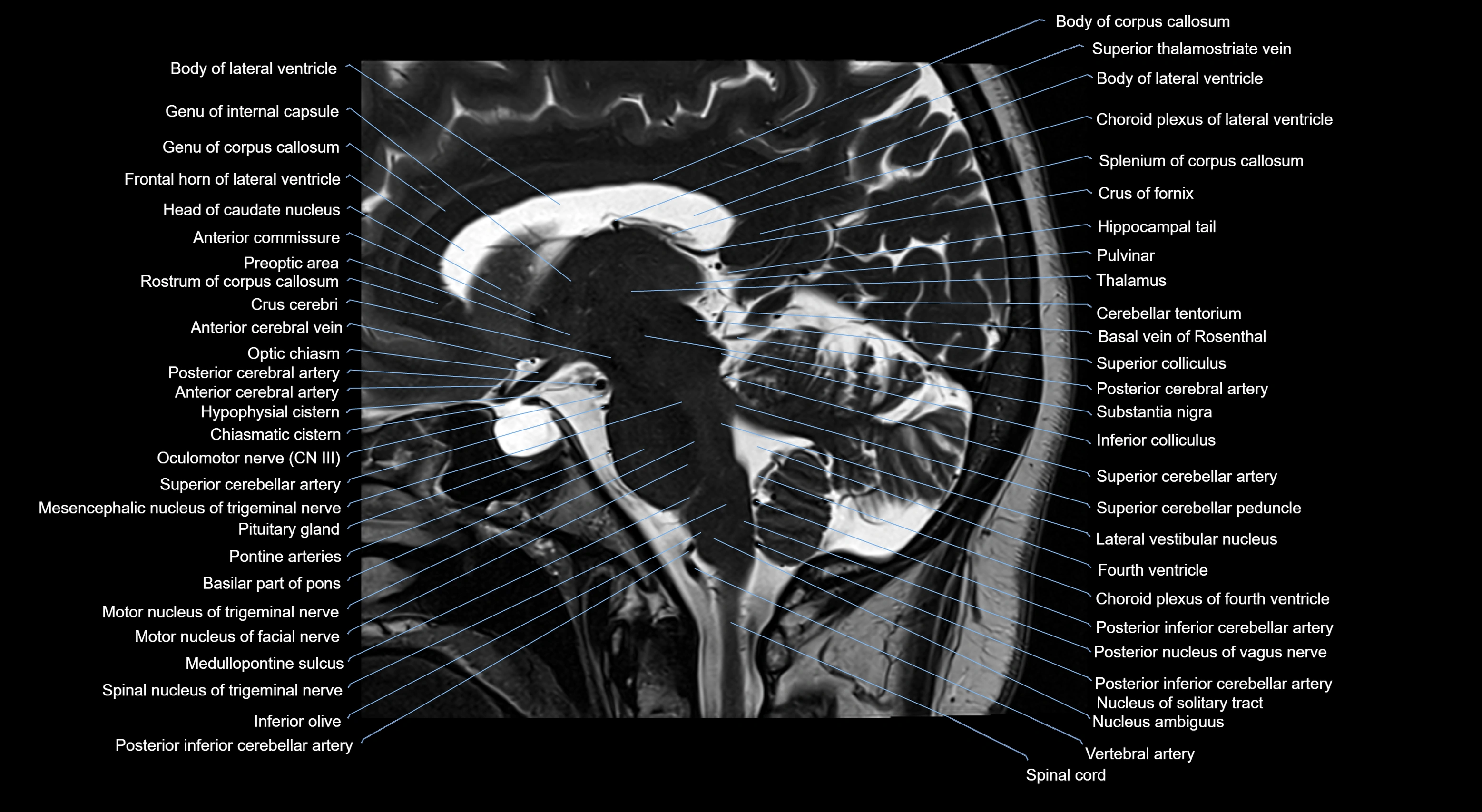
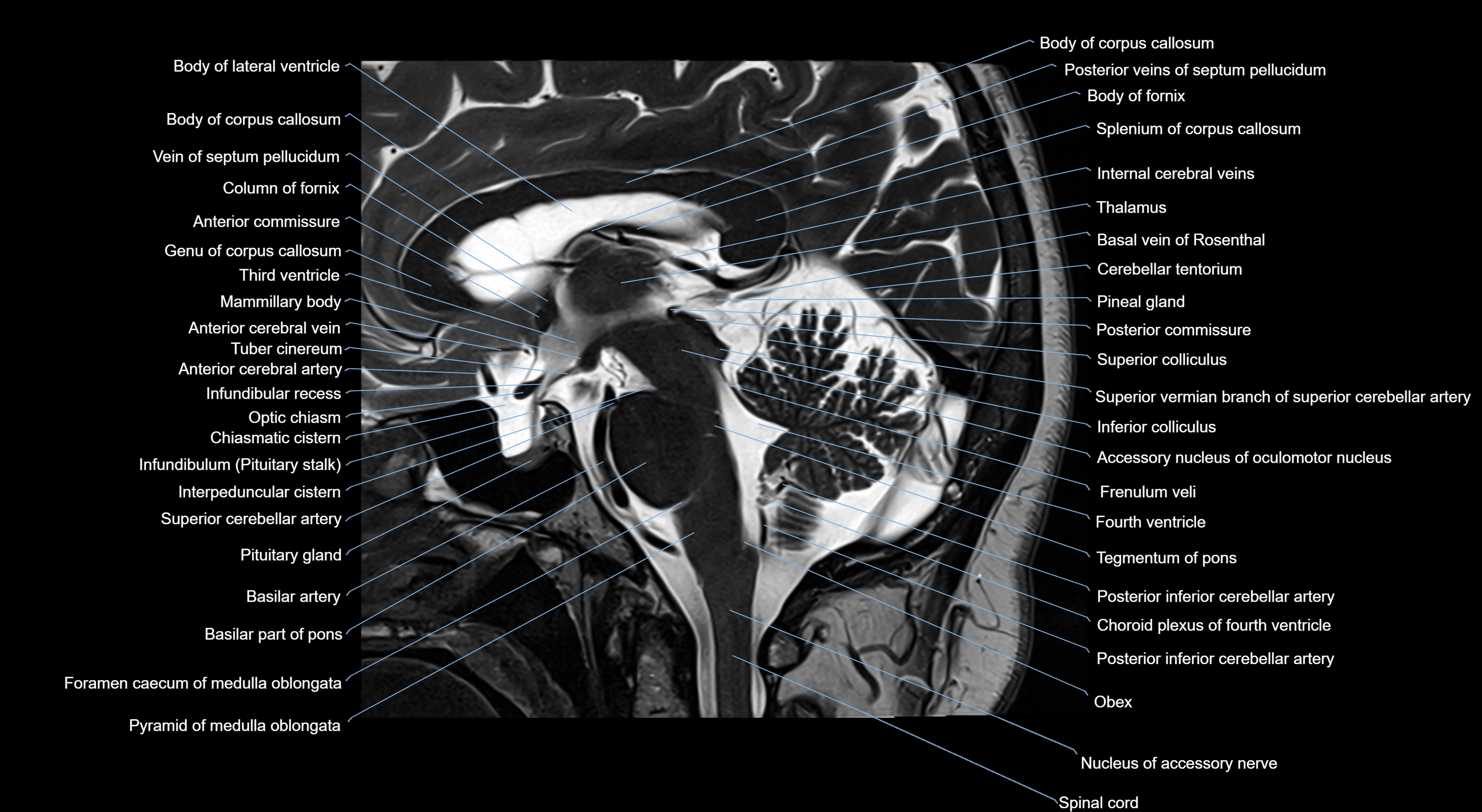
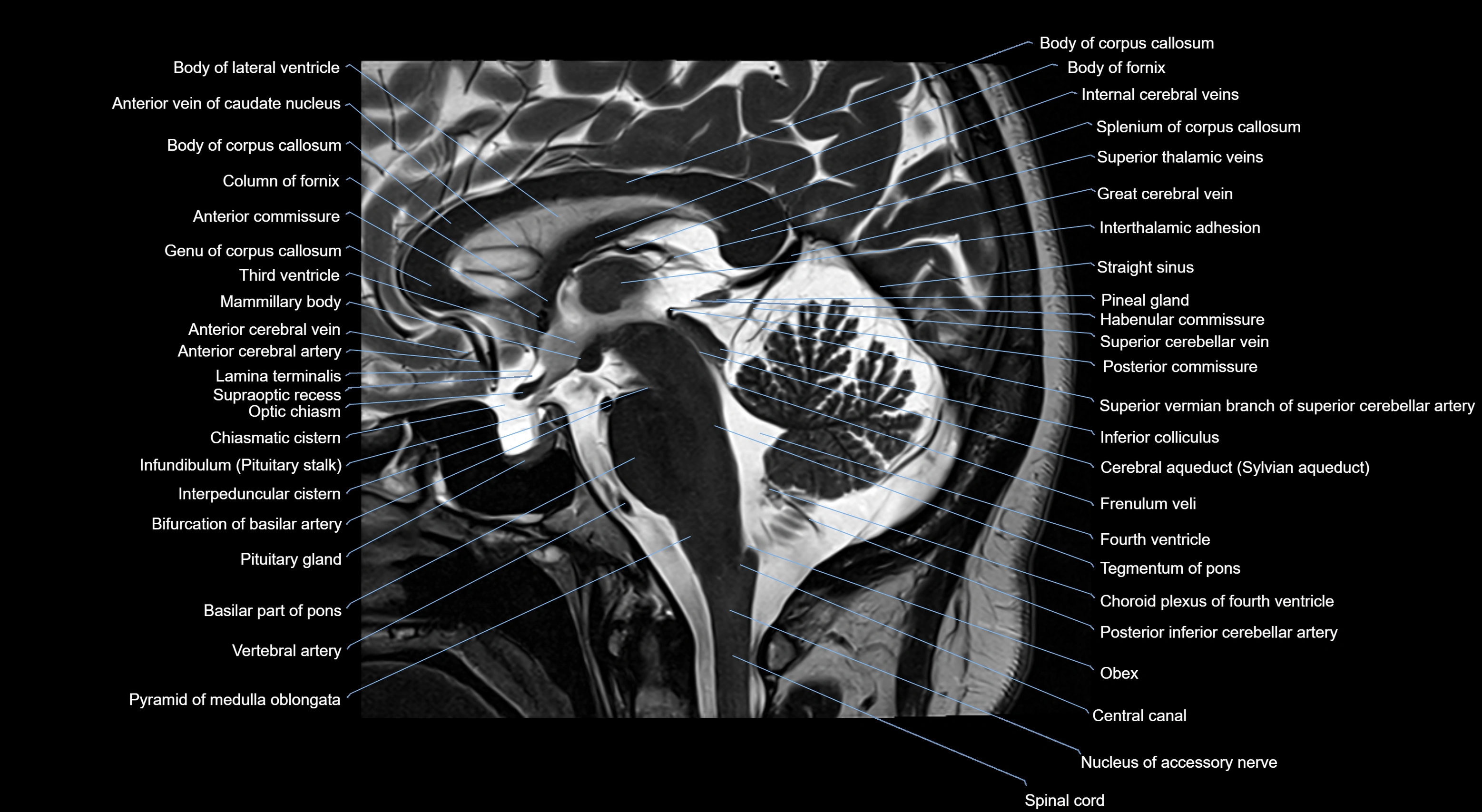
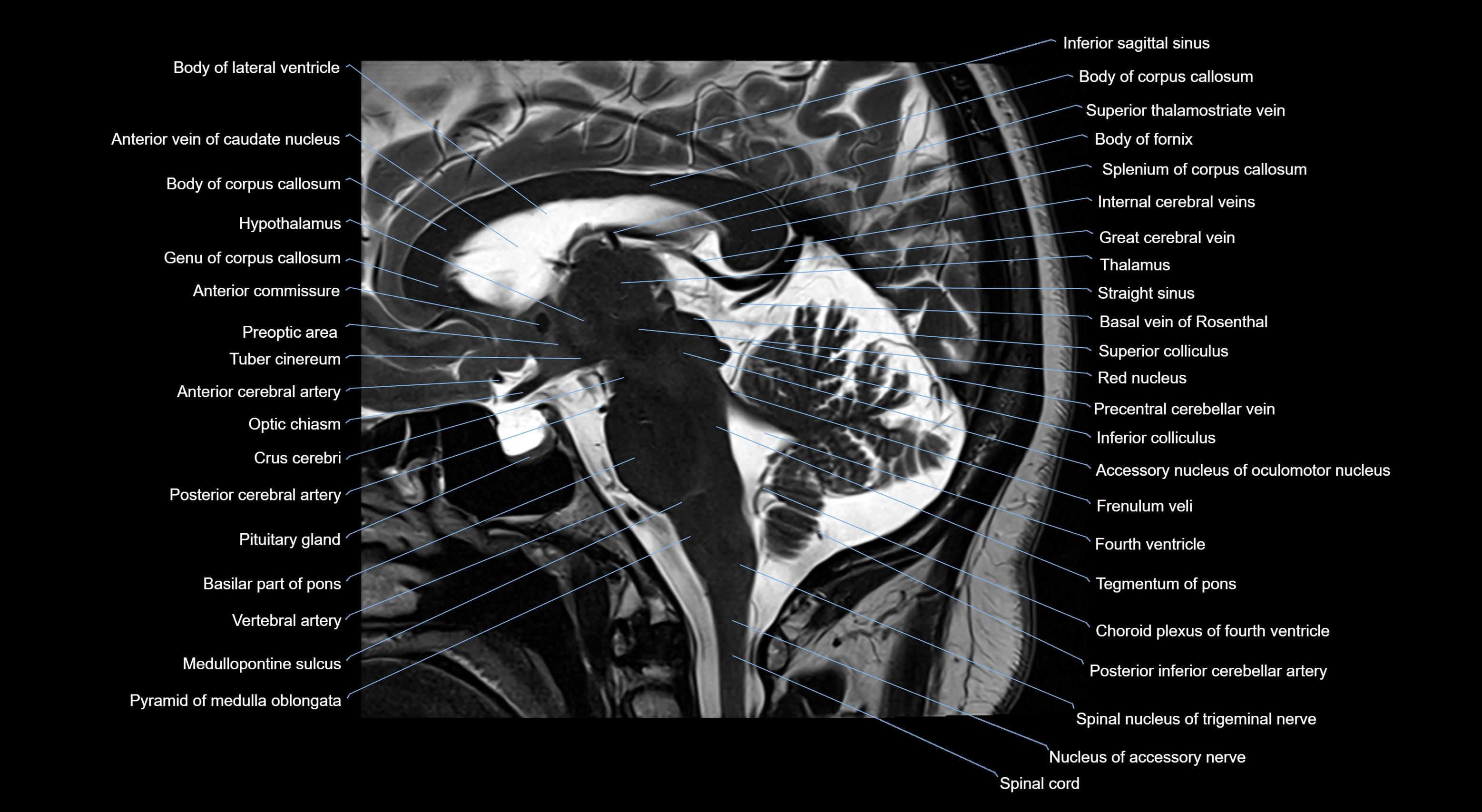
MRI images

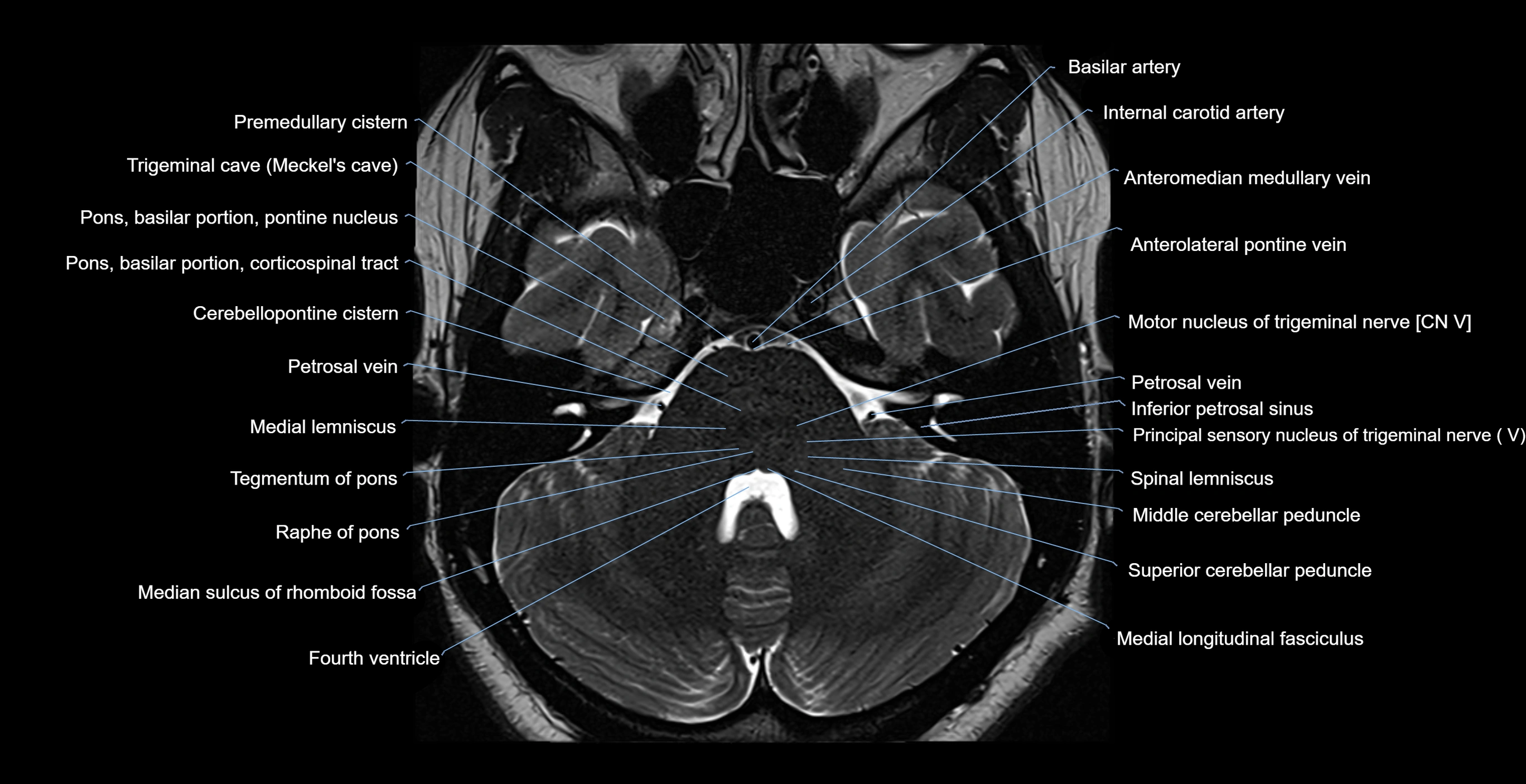
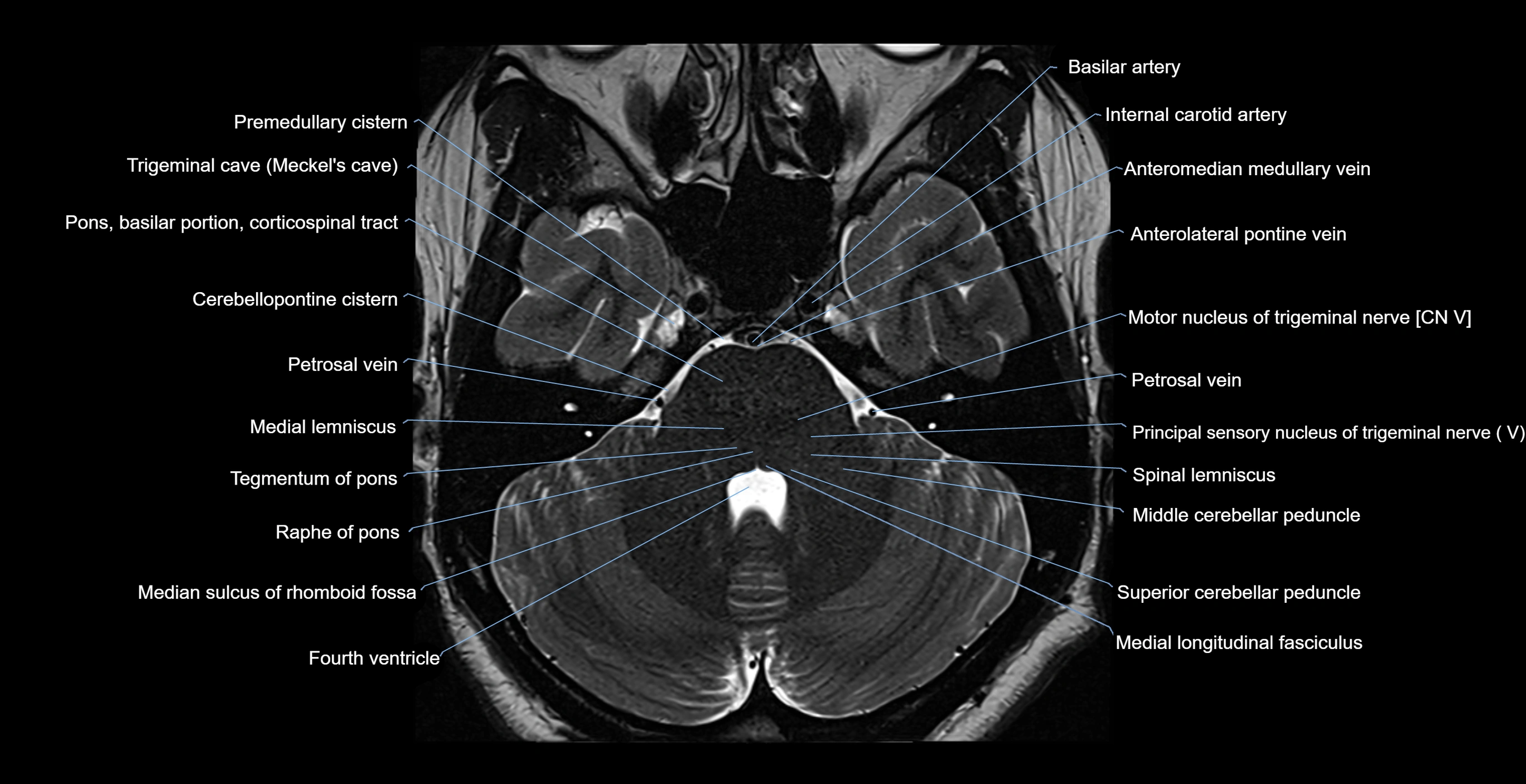
MRI images

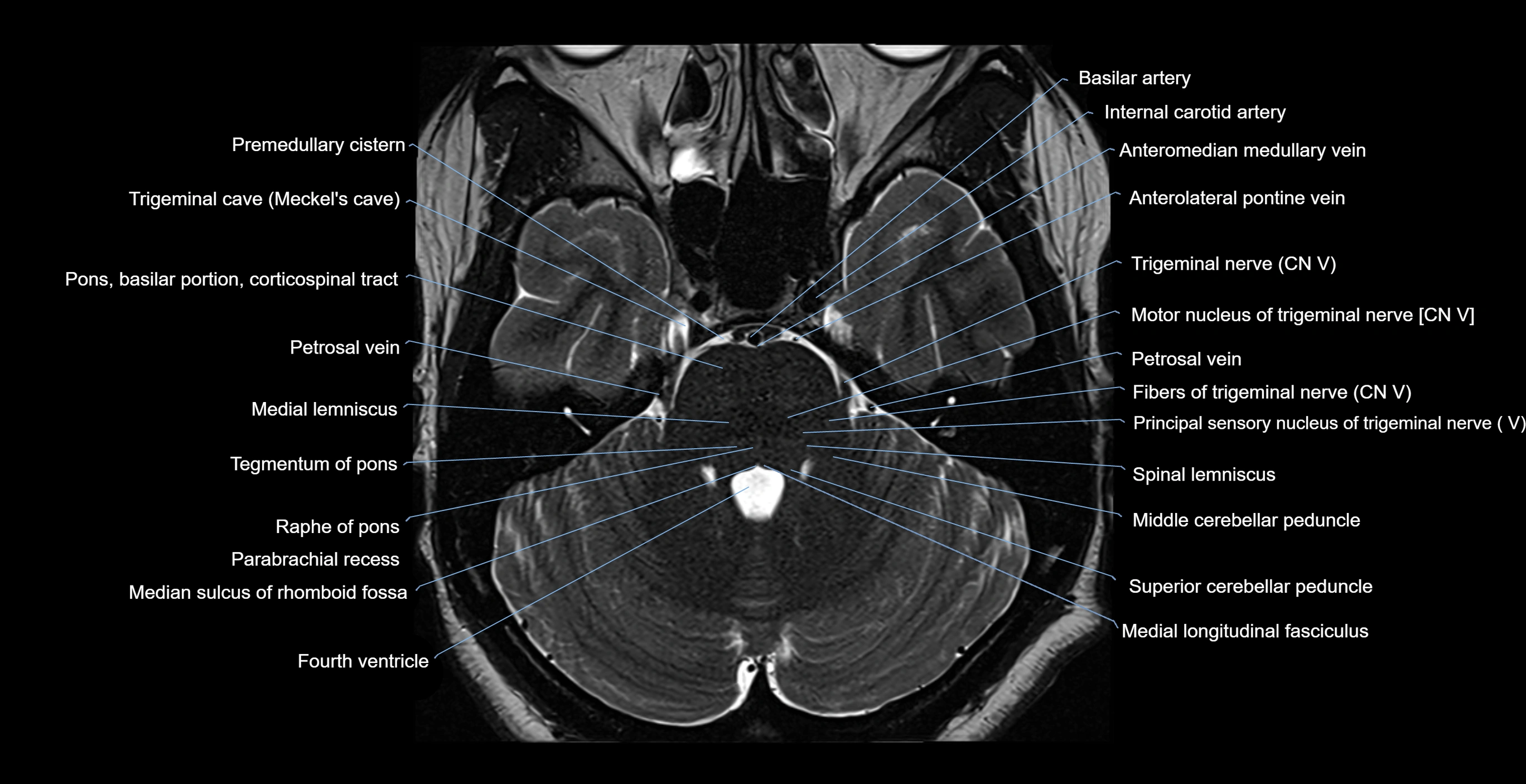
MRI images